Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources

How to Find Sources | Scholarly Articles, Books, Etc.
Published on June 13, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on May 31, 2023.
It’s important to know how to find relevant sources when writing a research paper , literature review , or systematic review .
The types of sources you need will depend on the stage you are at in the research process , but all sources that you use should be credible , up to date, and relevant to your research topic.
There are three main places to look for sources to use in your research:
Research databases
- Your institution’s library
- Other online resources
Table of contents
Library resources, other online sources, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about finding sources.
You can search for scholarly sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar . These provide a range of search functions that can help you to find the most relevant sources.
If you are searching for a specific article or book, include the title or the author’s name. Alternatively, if you’re just looking for sources related to your research problem , you can search using keywords. In this case, it’s important to have a clear understanding of the scope of your project and of the most relevant keywords.
Databases can be general (interdisciplinary) or subject-specific.
- You can use subject-specific databases to ensure that the results are relevant to your field.
- When using a general database or search engine, you can still filter results by selecting specific subjects or disciplines.
Example: JSTOR discipline search filter

Check the table below to find a database that’s relevant to your research.
Google Scholar
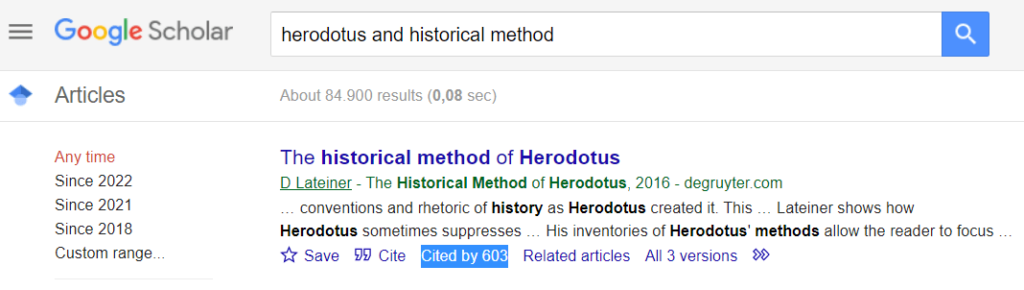
To get started, you might also try Google Scholar , an academic search engine that can help you find relevant books and articles. Its “Cited by” function lets you see the number of times a source has been cited. This can tell you something about a source’s credibility and importance to the field.
Example: Google Scholar “Cited by” function
Boolean operators
Boolean operators can also help to narrow or expand your search.
Boolean operators are words and symbols like AND , OR , and NOT that you can use to include or exclude keywords to refine your results. For example, a search for “Nietzsche NOT nihilism” will provide results that include the word “Nietzsche” but exclude results that contain the word “nihilism.”
Many databases and search engines have an advanced search function that allows you to refine results in a similar way without typing the Boolean operators manually.
Example: Project Muse advanced search

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
You can find helpful print sources in your institution’s library. These include:
- Journal articles
- Encyclopedias
- Newspapers and magazines
Make sure that the sources you consult are appropriate to your research.
You can find these sources using your institution’s library database. This will allow you to explore the library’s catalog and to search relevant keywords. You can refine your results using Boolean operators .
Once you have found a relevant print source in the library:
- Consider what books are beside it. This can be a great way to find related sources, especially when you’ve found a secondary or tertiary source instead of a primary source .
- Consult the index and bibliography to find the bibliographic information of other relevant sources.
You can consult popular online sources to learn more about your topic. These include:
- Crowdsourced encyclopedias like Wikipedia
You can find these sources using search engines. To refine your search, use Boolean operators in combination with relevant keywords.
However, exercise caution when using online sources. Consider what kinds of sources are appropriate for your research and make sure the sites are credible .
Look for sites with trusted domain extensions:
- URLs that end with .edu are educational resources.
- URLs that end with .gov are government-related resources.
- DOIs often indicate that an article is published in a peer-reviewed , scientific article.
Other sites can still be used, but you should evaluate them carefully and consider alternatives.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

You can find sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar . Use Boolean operators or advanced search functions to narrow or expand your search.
For print sources, you can use your institution’s library database. This will allow you to explore the library’s catalog and to search relevant keywords.
It is important to find credible sources and use those that you can be sure are sufficiently scholarly .
- Consult your institute’s library to find out what books, journals, research databases, and other types of sources they provide access to.
- Look for books published by respected academic publishing houses and university presses, as these are typically considered trustworthy sources.
- Look for journals that use a peer review process. This means that experts in the field assess the quality and credibility of an article before it is published.
When searching for sources in databases, think of specific keywords that are relevant to your topic , and consider variations on them or synonyms that might be relevant.
Once you have a clear idea of your research parameters and key terms, choose a database that is relevant to your research (e.g., Medline, JSTOR, Project MUSE).
Find out if the database has a “subject search” option. This can help to refine your search. Use Boolean operators to combine your keywords, exclude specific search terms, and search exact phrases to find the most relevant sources.
There are many types of sources commonly used in research. These include:
You’ll likely use a variety of these sources throughout the research process , and the kinds of sources you use will depend on your research topic and goals.
Scholarly sources are written by experts in their field and are typically subjected to peer review . They are intended for a scholarly audience, include a full bibliography, and use scholarly or technical language. For these reasons, they are typically considered credible sources .
Popular sources like magazines and news articles are typically written by journalists. These types of sources usually don’t include a bibliography and are written for a popular, rather than academic, audience. They are not always reliable and may be written from a biased or uninformed perspective, but they can still be cited in some contexts.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, May 31). How to Find Sources | Scholarly Articles, Books, Etc.. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/finding-sources/
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, types of sources explained | examples & tips, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, boolean operators | quick guide, examples & tips, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Our Program Divisions
- Our Three Academies
- Government Affairs
- Statement on Diversity and Inclusion
- Our Study Process
- Conflict of Interest Policies and Procedures
- Project Comments and Information
- Read Our Expert Reports and Published Proceedings
- Explore PNAS, the Official Scientific Journal of NAS
- Access Transportation Research Board Publications
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Economic Recovery
- Fellowships and Grants
- Publications by Division
- Division of Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education
- Division on Earth and Life Studies
- Division on Engineering and Physical Sciences
- Gulf Research Program
- Health and Medicine Division
- Policy and Global Affairs Division
- Transportation Research Board
- National Academy of Sciences
- National Academy of Engineering
- National Academy of Medicine
- Publications by Topic
- Agriculture
- Behavioral and Social Sciences
- Biography and Autobiography
- Biology and Life Sciences
- Computers and Information Technology
- Conflict and Security Issues
- Earth Sciences
- Energy and Energy Conservation
- Engineering and Technology
- Environment and Environmental Studies
- Food and Nutrition
- Health and Medicine
- Industry and Labor
- Math, Chemistry, and Physics
- Policy for Science and Technology
- Space and Aeronautics
- Surveys and Statistics
- Transportation and Infrastructure
- Searchable Collections
- New Releases
REFERENCE FINDER
Find relevant information like your own rough draft from among the 12,876 reports available for free at NAP.edu. Copy and paste up to 8 pages of content from some other source: an outside article, a rough draft of your own, etc., then select "Find Relevant Reports".
Find Relevant Reports
Click here to search reports published from the National Academy of Sciences, the Institute of Medicine, the National Academy of Engineering, and the National Research Council.
Build Web Searches
Click here to view key search phrases derived from your content for searching on Google, Yahoo, Bing, and NAP.edu.
The Reference Finder is provided exclusively as a research tool. No information will be retained regarding use of this resource beyond normal server logs. That is, entered text is not retained, and the staff of the National Academies will make no correlations between server logs, IP addresses, and submitted content.
What is the Reference Finder?

Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more.
Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
- Part of The Streets are Talking: Public Forms of Creative Expression from Around the World
- Part of The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter 2020)
- Part of Cato Institute (Aug. 3, 2021)
- Part of University of California Press
- Part of Open: Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012)
- Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020)
- Part of Leuven University Press
- Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016)
- Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
- Part of Leveraging Lives: Serbia and Illegal Tunisian Migration to Europe, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (Mar. 1, 2023)
- Part of UCL Press
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR.
Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars.
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Strategies to Find Sources
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Strategies to Find Sources
- Getting Started
- Introduction
- How to Pick a Topic
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
The Research Process
![i can't find sources for my research paper Interative Litearture Review Research Process image (Planning, Searching, Organizing, Analyzing and Writing [repeat at necessary]](https://libapps.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/64450/images/ResearchProcess.jpg)
Planning : Before searching for articles or books, brainstorm to develop keywords that better describe your research question.
Searching : While searching, take note of what other keywords are used to describe your topic, and use them to conduct additional searches
♠ Most articles include a keyword section
♠ Key concepts may change names throughout time so make sure to check for variations
Organizing : Start organizing your results by categories/key concepts or any organizing principle that make sense for you . This will help you later when you are ready to analyze your findings
Analyzing : While reading, start making notes of key concepts and commonalities and disagreement among the research articles you find.
♠ Create a spreadsheet to record what articles you are finding useful and why.
♠ Create fields to write summaries of articles or quotes for future citing and paraphrasing .
Writing : Synthesize your findings. Use your own voice to explain to your readers what you learned about the literature on your topic. What are its weaknesses and strengths? What is missing or ignored?
Repeat : At any given time of the process, you can go back to a previous step as necessary.
Advanced Searching
All databases have Help pages that explain the best way to search their product. When doing literature reviews, you will want to take advantage of these features since they can facilitate not only finding the articles that you really need but also controlling the number of results and how relevant they are for your search. The most common features available in the advanced search option of databases and library online catalogs are:
- Boolean Searching (AND, OR, NOT): Allows you to connect search terms in a way that can either limit or expand your search results
- Proximity Searching (N/# or W/#): Allows you to search for two or more words that occur within a specified number of words (or fewer) of each other in the database
- Limiters/Filters : These are options that let you control what type of document you want to search: article type, date, language, publication, etc.
- Question mark (?) or a pound sign (#) for wildcard: Used for retrieving alternate spellings of a word: colo?r will retrieve both the American spelling "color" as well as the British spelling "colour."
- Asterisk (*) for truncation: Used for retrieving multiple forms of a word: comput* retrieves computer, computers, computing, etc.
Want to keep track of updates to your searches? Create an account in the database to receive an alert when a new article is published that meets your search parameters!
- EBSCOhost Advanced Search Tutorial Tips for searching a platform that hosts many library databases
- Library's General Search Tips Check the Search tips to better used our library catalog and articles search system
- ProQuest Database Search Tips Tips for searching another platform that hosts library databases
There is no magic number regarding how many sources you are going to need for your literature review; it all depends on the topic and what type of the literature review you are doing:
► Are you working on an emerging topic? You are not likely to find many sources, which is good because you are trying to prove that this is a topic that needs more research. But, it is not enough to say that you found few or no articles on your topic in your field. You need to look broadly to other disciplines (also known as triangulation ) to see if your research topic has been studied from other perspectives as a way to validate the uniqueness of your research question.
► Are you working on something that has been studied extensively? Then you are going to find many sources and you will want to limit how far back you want to look. Use limiters to eliminate research that may be dated and opt to search for resources published within the last 5-10 years.
- << Previous: How to Pick a Topic
- Next: Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
Research Paper Guide
How To Find Sources For A Research Paper
Finding Sources For a Research Paper: A Complete Guide
14 min read

People also read
Research Paper Writing - A Step by Step Guide
Research Paper Examples - Free Sample Papers for Different Formats!
Guide to Creating Effective Research Paper Outline
Interesting Research Paper Topics for 2024
Research Proposal Writing - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Start a Research Paper - 7 Easy Steps
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper - A Step by Step Guide
Writing a Literature Review For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Qualitative Research - Methods, Types, and Examples
8 Types of Qualitative Research - Overview & Examples
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research - Learning the Basics
200+ Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Students in 2024
Learn How to Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper: Examples and Tips!
20+ Types of Research With Examples - A Detailed Guide
Understanding Quantitative Research - Types & Data Collection Techniques
230+ Sociology Research Topics & Ideas for Students
How to Cite a Research Paper - A Complete Guide
Excellent History Research Paper Topics- 300+ Ideas
A Guide on Writing the Method Section of a Research Paper - Examples & Tips
How To Write an Introduction Paragraph For a Research Paper: Learn with Examples
Crafting a Winning Research Paper Title: A Complete Guide
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion - Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a Thesis For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
How To Write A Discussion For A Research Paper | Examples & Tips
How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Writing a Problem Statement for a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
A Guide on How to Edit a Research Paper
200+ Ethical Research Paper Topics to Begin With (2024)
300+ Controversial Research Paper Topics & Ideas - 2024 Edition
150+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics For You - 2024
How to Write a Research Methodology for a Research Paper
Research paper writing can be tough and overwhelming. It's not just about your ideas but also about finding the right information. With so much stuff online, it's easy to feel lost and not know which sources are trustworthy.
Many researchers face the challenge of figuring out what's good and what's not when it comes to finding sources for their papers.
Don't worry!
In this blog, we’ll show you simple and effective ways to find good sources for your research paper. You'll learn where to look and how to tell if a source is worth using.
By the end, you'll be able to gather great information for your research paper and make it stronger and more convincing.
Let’s get started!
- 1. Different Types of Sources
- 2. How to Find Sources for a Research Paper?
- 3. What Makes a Source Credible?
- 4. List of Sources to Avoid
- 5. Tips for Effective Source Selection in Your Research Paper
Different Types of Sources
When you start a research paper , it's important to know the different kinds of sources. These sources give your paper a strong base. Each one brings different viewpoints and info, making your paper better and more trustworthy.
Here are the main types of sources:
Primary Sources
Primary sources are firsthand accounts or original materials that provide direct evidence of an event, subject, or phenomenon. This includes:
- Historical Documents
- Original Research Studies.
Secondary Sources
Secondary sources analyze, interpret, or comment on primary sources. These are works that are one step removed from the original event or information. This includes
- review articles
- Documentaries
Tertiary Sources
Tertiary sources are like the summary of the summary. They compile and summarize information from primary and secondary sources. These sources include:
- Encyclopedias
- Dictionaries
- Directories
How to Find Sources for a Research Paper?
When tasked with a research paper, the process of finding reliable sources is a critical step in building a strong foundation for your work.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to effectively find sources that will enhance the quality and credibility of your research:
Use Online Databases
Exploring academic databases is a crucial step in finding reliable sources for your research paper.
These databases, often accessible through online libraries, offer a vast repository of scholarly articles, journals, and research papers.
Here are examples of research databases for specific subjects:
Medical Sciences
- ScienceDirect
- PsychArticles
- Psychology and Behavioral Sciences Collection
Computer Science
- IEEE Xplore
- ACM Digital Library
- SpringerLink
Literature and Humanities
- Project MUSE
- MLA International Bibliography
Social Sciences
- Social Sciences Citation Index
- Sociology Database
- ProQuest Social Sciences
Here's a detailed guide on how to make the most of online libraries and various academic databases:
Utilize Library Resources
Visiting your local library database is a valuable step in the research process, offering access to a variety of resources and the expertise of librarians.
Here's how you can make the most of library resources for your research:
Library Catalog
Begin by searching the library catalog to find books, journals, and other materials related to your research topic. Use relevant keywords or titles to narrow down your search.
Once you've identified relevant books and book chapters, head to the book stacks. Libraries organize books according to a systematic classification system, making it easier to find materials on the same subject.
Reference Section
Check the reference section for encyclopedias, dictionaries, and other reference materials. These resources provide concise overviews and can be a great starting point for understanding your topic.
Periodicals Section
Visit the periodicals section to access current and past issues of journal articles and magazines. This is especially useful for finding recent research articles.
Interlibrary Loan Services
If your library doesn't have a specific book or article, take advantage of interlibrary loan services. Librarians can request materials from other libraries, broadening your access to resources.
Digital Libraries and Resources
Many libraries offer digital libraries and online databases. Check if your library provides access to platforms such as ProQuest , EBSCOhost , or other specialized resources.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Google Smartly
Google is a powerful tool for finding information, but conducting strategic searches is key to efficiently and effectively uncovering relevant sources. Here's how you can smartly use Google Scholar for your research:
- Use of Keywords: Google operates on keywords, so choose your search terms wisely. Identify key concepts from your research topic to form the basis of your search.
- Boolean Operators : Utilize Boolean operators such as AND, OR, and NOT to refine your search. For example, using "climate change AND impacts" narrows down results to pages containing both terms.
- Exact Phrase Search: When looking for an exact phrase, enclose it in quotation marks. This ensures that Google searches for the specific words in the exact order you provide.
- Use "site:" Operator : To search within a specific website or domain, use the "site:" operator. For example, "site:nytimes.com climate change" will retrieve results only from The New York Times website.
- Specify File Types : If you're looking for specific document types, use the "filetype:" operator. For instance, "filetype:pdf renewable energy" will retrieve only PDF documents related to renewable energy.
- Access Scholarly Articles : Google Scholar is a specialized search engine for scholarly articles. Use it to find academic papers, conference papers, and patents.
Check Institutional Repositories
Exploring institutional repositories is a valuable strategy to discover research conducted within universities and institutions.
These repositories often contain a wealth of scholarly work, including papers, theses, and dissertations. Here's how you can check institutional repositories for relevant materials:
Repository Search Tools
Some universities provide search tools specifically designed for their repositories. Use these tools to perform targeted searches based on your research topic or keywords.
Open Access Platforms
Some institutional repositories are accessible to the public. Platforms like DSpace and EPrints host a multitude of repositories worldwide. Check these platforms for relevant research beyond your own institution.
Theses and Dissertations
Institutional repositories often house a collection of theses and dissertations. Browse this section to find in-depth research on various topics.
Advanced Search Options
If available, use advanced search features in institutional repositories. These may include filters for publication types, publication years, or specific departments.
Full-Text Availability
Some repositories provide full-text access to papers and theses. Ensure to check the availability of full-text versions for comprehensive access to research content.
Explore Government and Organization Websites
Government web sites and reputable organizations serve as reliable repositories of valuable research reports, statistics, and authoritative information.
When conducting research, tapping into these official sources can add depth and credibility to your paper.
Government Websites
Visit official government websites relevant to your research topic. Examples include:
- USA.gov (United States)
- Gov.uk (United Kingdom)
- Europa.eu (European Union)
Organization Websites
Look for reputable organizations associated with your research area. Examples include:
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- United Nations (UN)
- Pew Research Center
Search for Research Reports
Government agencies and organizations often have dedicated sections for research reports or publications. Explore these sections to find in-depth reports on various topics.
- Accessing Government Data: Many government websites have dedicated sections for data and statistics. Explore these sections to access official figures, charts, and datasets.
- Government Data Portals : Some governments provide centralized data portals. Examples include Data.gov in the United States and data.gov.uk in the United Kingdom.
- Public Health Agencies: For health-related research, explore the websites of public health agencies like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or the World Health Organization (WHO).
- International Organizations : Access International Organizations: For global perspectives, consider websites of international organizations such as the United Nations (UN) or the World Bank.
What Makes a Source Credible?
Now that you know where to find information for your research, it's important to learn how to check if the sources are trustworthy.
Credible sources ensure that your paper is based on reliable and trustworthy information. Here are key factors to consider when evaluating the credibility of a source:
1. Who Wrote The Information?
Authors with expertise or experience in the subject matter are more likely to provide reliable information. Look for their qualifications and affiliations.
2. Where Was The Information Published?
Consider where the information is published. Academic journals, reputable websites, and well-known publishers are generally more trustworthy.
3. Did The Source Undergo A Peer-Review Process?
If the source is from an academic journal, it likely went through a peer-review process. This means experts in the field reviewed the content for accuracy and quality, adding to its credibility.
4. When Was The Information Published Or Last Updated?
For some fields, recent information is crucial, while for others, historical context may be important. Ensure your source is timely and relevant to your research.
5. Does The Source Provide References Or Citations?
Credible sources often cite their information from other reliable sources. Check for a bibliography or references list. This shows that the author has done their homework and supports their claims with evidence.
6. Is The Information Presented Objectively, Or Does It Seem Biased?
Evaluate the objectivity of the source. Look for a balanced presentation of information to avoid bias.
7. Who Is The Intended Audience Of The Source?
Some sources are written for a general audience, while others are meant for experts in a particular field. Choose sources that match the level of depth and expertise required for your research.
8. What Is The Reputation Of The Publisher Or Website?
Well-established publishers and reputable websites are more likely to produce credible content. Check the reputation of the publisher or website to ensure the information meets academic standards.
Employing CRAAP Test
When evaluating the credibility of a source, applying the CRAAP Test can serve as a systematic and comprehensive method.
The CRAAP Test assesses a source based on five key criteria: Currency, Relevance, Authority, Accuracy, and Purpose.
Here's how to employ the CRAAP Test to ensure the credibility of your sources:
- Currency : Assess how recent the information is. Depending on your research topic, you may need the most up-to-date information.
- Relevance : Evaluate whether the information is directly related to your research topic. Consider the scope and focus of the source to ensure its relevance to your paper.
- Authority : Examine the credentials and expertise of the author or organization providing the information.
- Accuracy : Verify the accuracy of the information by cross-referencing with other reliable sources.
- Purpose : Examine the purpose of the source. Consider whether it aims to inform, persuade, entertain, or sell a product.
List of Sources to Avoid
In the digital age, with an abundance of information available, it's essential to discern between credible and unreliable sources.
Avoiding certain types of sources is crucial for maintaining the integrity and academic rigor of your research. Here's a list of sources to be cautious about or avoid altogether:
While Wikipedia can provide a general overview, it's not considered a reliable academic source. Avoid citing it directly in research papers. Instead, use it as a starting point to gather background information and identify primary sources.
- Personal Blogs and Websites
Blogs or personal websites may lack peer review or editorial oversight, making the information subjective or unreliable. Use these sources cautiously and verify information from more reputable outlets.
- Social Media
Information shared on social media platforms may lack verification. Avoid relying solely on tweets, posts, or memes as sources. Instead, look for information from original and verified sources.
- Self-Published Books
Books without traditional publishers might lack rigorous peer review and editorial processes. Exercise caution and verify the credentials of self-published authors.
- Commercially-Driven Websites
Be wary of websites that exist primarily for commercial purposes. Information on these sites might be biased or skewed to promote products or services.
- Extreme Biased Websites
Websites with extreme bias may present information in a skewed manner. Aim for balanced viewpoints from sources that consider multiple perspectives.
- Outdated Sources
Information, especially in rapidly evolving fields, becomes outdated quickly. Avoid relying on sources that are not current or don't provide the latest information.
- Predatory Journals
Some journals, known as predatory, exploit the open-access model without maintaining academic standards. Check the credibility of journals before citing them.
- Non-Academic Encyclopedias
Encyclopedias geared toward a general audience may lack the depth and academic rigor needed for research papers. Prefer academic encyclopedias or peer-reviewed reference materials.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Tips for Effective Source Selection in Your Research Paper
When delving into the vast sea of information for your research paper, strategic source selection is crucial. Consider these tips to ensure you find the most relevant and reliable sources:
- Diversify Your Search Strategy
Don't limit yourself to a single database or search engine. Explore a variety of platforms, both academic and mainstream, to gather a comprehensive range of sources.
- Tap into Subject-Specific Databases
Seek out databases specific to your subject area. Subject-focused databases often provide in-depth and specialized content tailored to your research needs.
- Verify Author Credibility
Assess the qualifications and expertise of the authors. Look for authors with academic affiliations, relevant degrees, or substantial experience in the field.
- Check for Peer Review
Prioritize articles and papers that have undergone a peer-review process. Peer-reviewed sources undergo scrutiny by experts in the field, ensuring high-quality and reliable content.
- Evaluate Source Currency
While historical context is valuable, prioritize recent information for evolving topics. Check for the publication date or the last update of the source to ensure relevance.
- Consider the Source’s Purpose
Consider the purpose of the source. Identify any potential biases or intentions, and ensure that the source aligns with your research objectives.
- Use Citation Trails
When you find a relevant source, explore its bibliographic information or list of references. This can lead you to additional valuable sources that contribute to your research.
To sum it up, when you're working on your research paper, it's important to explore different places to find good information. Always check if the sources are trustworthy and have been reviewed by experts.
Remember, it's not just about finishing your paper; it's about enjoying the journey of discovering new things!
Ready to take your research paper to the next level? Get expert help at MyPerfectWords.com.Our skilled team is here to make sure your work meets top-notch academic standards. Don't miss out on the chance to improve your research paper. Hire our essay writing service today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
- Corrections
Search Help
Get the most out of Google Scholar with some helpful tips on searches, email alerts, citation export, and more.
Finding recent papers
Your search results are normally sorted by relevance, not by date. To find newer articles, try the following options in the left sidebar:
- click "Since Year" to show only recently published papers, sorted by relevance;
- click "Sort by date" to show just the new additions, sorted by date;
- click the envelope icon to have new results periodically delivered by email.
Locating the full text of an article
Abstracts are freely available for most of the articles. Alas, reading the entire article may require a subscription. Here're a few things to try:
- click a library link, e.g., "FindIt@Harvard", to the right of the search result;
- click a link labeled [PDF] to the right of the search result;
- click "All versions" under the search result and check out the alternative sources;
- click "Related articles" or "Cited by" under the search result to explore similar articles.
If you're affiliated with a university, but don't see links such as "FindIt@Harvard", please check with your local library about the best way to access their online subscriptions. You may need to do search from a computer on campus, or to configure your browser to use a library proxy.
Getting better answers
If you're new to the subject, it may be helpful to pick up the terminology from secondary sources. E.g., a Wikipedia article for "overweight" might suggest a Scholar search for "pediatric hyperalimentation".
If the search results are too specific for your needs, check out what they're citing in their "References" sections. Referenced works are often more general in nature.
Similarly, if the search results are too basic for you, click "Cited by" to see newer papers that referenced them. These newer papers will often be more specific.
Explore! There's rarely a single answer to a research question. Click "Related articles" or "Cited by" to see closely related work, or search for author's name and see what else they have written.
Searching Google Scholar
Use the "author:" operator, e.g., author:"d knuth" or author:"donald e knuth".
Put the paper's title in quotations: "A History of the China Sea".
You'll often get better results if you search only recent articles, but still sort them by relevance, not by date. E.g., click "Since 2018" in the left sidebar of the search results page.
To see the absolutely newest articles first, click "Sort by date" in the sidebar. If you use this feature a lot, you may also find it useful to setup email alerts to have new results automatically sent to you.
Note: On smaller screens that don't show the sidebar, these options are available in the dropdown menu labelled "Year" right below the search button.
Select the "Case law" option on the homepage or in the side drawer on the search results page.
It finds documents similar to the given search result.
It's in the side drawer. The advanced search window lets you search in the author, title, and publication fields, as well as limit your search results by date.
Select the "Case law" option and do a keyword search over all jurisdictions. Then, click the "Select courts" link in the left sidebar on the search results page.
Tip: To quickly search a frequently used selection of courts, bookmark a search results page with the desired selection.
Access to articles
For each Scholar search result, we try to find a version of the article that you can read. These access links are labelled [PDF] or [HTML] and appear to the right of the search result. For example:
A paper that you need to read
Access links cover a wide variety of ways in which articles may be available to you - articles that your library subscribes to, open access articles, free-to-read articles from publishers, preprints, articles in repositories, etc.
When you are on a campus network, access links automatically include your library subscriptions and direct you to subscribed versions of articles. On-campus access links cover subscriptions from primary publishers as well as aggregators.
Off-campus access
Off-campus access links let you take your library subscriptions with you when you are at home or traveling. You can read subscribed articles when you are off-campus just as easily as when you are on-campus. Off-campus access links work by recording your subscriptions when you visit Scholar while on-campus, and looking up the recorded subscriptions later when you are off-campus.
We use the recorded subscriptions to provide you with the same subscribed access links as you see on campus. We also indicate your subscription access to participating publishers so that they can allow you to read the full-text of these articles without logging in or using a proxy. The recorded subscription information expires after 30 days and is automatically deleted.
In addition to Google Scholar search results, off-campus access links can also appear on articles from publishers participating in the off-campus subscription access program. Look for links labeled [PDF] or [HTML] on the right hand side of article pages.
Anne Author , John Doe , Jane Smith , Someone Else
In this fascinating paper, we investigate various topics that would be of interest to you. We also describe new methods relevant to your project, and attempt to address several questions which you would also like to know the answer to. Lastly, we analyze …
You can disable off-campus access links on the Scholar settings page . Disabling off-campus access links will turn off recording of your library subscriptions. It will also turn off indicating subscription access to participating publishers. Once off-campus access links are disabled, you may need to identify and configure an alternate mechanism (e.g., an institutional proxy or VPN) to access your library subscriptions while off-campus.
Email Alerts
Do a search for the topic of interest, e.g., "M Theory"; click the envelope icon in the sidebar of the search results page; enter your email address, and click "Create alert". We'll then periodically email you newly published papers that match your search criteria.
No, you can enter any email address of your choice. If the email address isn't a Google account or doesn't match your Google account, then we'll email you a verification link, which you'll need to click to start receiving alerts.
This works best if you create a public profile , which is free and quick to do. Once you get to the homepage with your photo, click "Follow" next to your name, select "New citations to my articles", and click "Done". We will then email you when we find new articles that cite yours.
Search for the title of your paper, e.g., "Anti de Sitter space and holography"; click on the "Cited by" link at the bottom of the search result; and then click on the envelope icon in the left sidebar of the search results page.
First, do a search for your colleague's name, and see if they have a Scholar profile. If they do, click on it, click the "Follow" button next to their name, select "New articles by this author", and click "Done".
If they don't have a profile, do a search by author, e.g., [author:s-hawking], and click on the mighty envelope in the left sidebar of the search results page. If you find that several different people share the same name, you may need to add co-author names or topical keywords to limit results to the author you wish to follow.
We send the alerts right after we add new papers to Google Scholar. This usually happens several times a week, except that our search robots meticulously observe holidays.
There's a link to cancel the alert at the bottom of every notification email.
If you created alerts using a Google account, you can manage them all here . If you're not using a Google account, you'll need to unsubscribe from the individual alerts and subscribe to the new ones.
Google Scholar library
Google Scholar library is your personal collection of articles. You can save articles right off the search page, organize them by adding labels, and use the power of Scholar search to quickly find just the one you want - at any time and from anywhere. You decide what goes into your library, and we’ll keep the links up to date.
You get all the goodies that come with Scholar search results - links to PDF and to your university's subscriptions, formatted citations, citing articles, and more!
Library help
Find the article you want to add in Google Scholar and click the “Save” button under the search result.
Click “My library” at the top of the page or in the side drawer to view all articles in your library. To search the full text of these articles, enter your query as usual in the search box.
Find the article you want to remove, and then click the “Delete” button under it.
- To add a label to an article, find the article in your library, click the “Label” button under it, select the label you want to apply, and click “Done”.
- To view all the articles with a specific label, click the label name in the left sidebar of your library page.
- To remove a label from an article, click the “Label” button under it, deselect the label you want to remove, and click “Done”.
- To add, edit, or delete labels, click “Manage labels” in the left column of your library page.
Only you can see the articles in your library. If you create a Scholar profile and make it public, then the articles in your public profile (and only those articles) will be visible to everyone.
Your profile contains all the articles you have written yourself. It’s a way to present your work to others, as well as to keep track of citations to it. Your library is a way to organize the articles that you’d like to read or cite, not necessarily the ones you’ve written.
Citation Export
Click the "Cite" button under the search result and then select your bibliography manager at the bottom of the popup. We currently support BibTeX, EndNote, RefMan, and RefWorks.
Err, no, please respect our robots.txt when you access Google Scholar using automated software. As the wearers of crawler's shoes and webmaster's hat, we cannot recommend adherence to web standards highly enough.
Sorry, we're unable to provide bulk access. You'll need to make an arrangement directly with the source of the data you're interested in. Keep in mind that a lot of the records in Google Scholar come from commercial subscription services.
Sorry, we can only show up to 1,000 results for any particular search query. Try a different query to get more results.
Content Coverage
Google Scholar includes journal and conference papers, theses and dissertations, academic books, pre-prints, abstracts, technical reports and other scholarly literature from all broad areas of research. You'll find works from a wide variety of academic publishers, professional societies and university repositories, as well as scholarly articles available anywhere across the web. Google Scholar also includes court opinions and patents.
We index research articles and abstracts from most major academic publishers and repositories worldwide, including both free and subscription sources. To check current coverage of a specific source in Google Scholar, search for a sample of their article titles in quotes.
While we try to be comprehensive, it isn't possible to guarantee uninterrupted coverage of any particular source. We index articles from sources all over the web and link to these websites in our search results. If one of these websites becomes unavailable to our search robots or to a large number of web users, we have to remove it from Google Scholar until it becomes available again.
Our meticulous search robots generally try to index every paper from every website they visit, including most major sources and also many lesser known ones.
That said, Google Scholar is primarily a search of academic papers. Shorter articles, such as book reviews, news sections, editorials, announcements and letters, may or may not be included. Untitled documents and documents without authors are usually not included. Website URLs that aren't available to our search robots or to the majority of web users are, obviously, not included either. Nor do we include websites that require you to sign up for an account, install a browser plugin, watch four colorful ads, and turn around three times and say coo-coo before you can read the listing of titles scanned at 10 DPI... You get the idea, we cover academic papers from sensible websites.
That's usually because we index many of these papers from other websites, such as the websites of their primary publishers. The "site:" operator currently only searches the primary version of each paper.
It could also be that the papers are located on examplejournals.gov, not on example.gov. Please make sure you're searching for the "right" website.
That said, the best way to check coverage of a specific source is to search for a sample of their papers using the title of the paper.
Ahem, we index papers, not journals. You should also ask about our coverage of universities, research groups, proteins, seminal breakthroughs, and other dimensions that are of interest to users. All such questions are best answered by searching for a statistical sample of papers that has the property of interest - journal, author, protein, etc. Many coverage comparisons are available if you search for [allintitle:"google scholar"], but some of them are more statistically valid than others.
Currently, Google Scholar allows you to search and read published opinions of US state appellate and supreme court cases since 1950, US federal district, appellate, tax and bankruptcy courts since 1923 and US Supreme Court cases since 1791. In addition, it includes citations for cases cited by indexed opinions or journal articles which allows you to find influential cases (usually older or international) which are not yet online or publicly available.
Legal opinions in Google Scholar are provided for informational purposes only and should not be relied on as a substitute for legal advice from a licensed lawyer. Google does not warrant that the information is complete or accurate.
We normally add new papers several times a week. However, updates to existing records take 6-9 months to a year or longer, because in order to update our records, we need to first recrawl them from the source website. For many larger websites, the speed at which we can update their records is limited by the crawl rate that they allow.
Inclusion and Corrections
We apologize, and we assure you the error was unintentional. Automated extraction of information from articles in diverse fields can be tricky, so an error sometimes sneaks through.
Please write to the owner of the website where the erroneous search result is coming from, and encourage them to provide correct bibliographic data to us, as described in the technical guidelines . Once the data is corrected on their website, it usually takes 6-9 months to a year or longer for it to be updated in Google Scholar. We appreciate your help and your patience.
If you can't find your papers when you search for them by title and by author, please refer your publisher to our technical guidelines .
You can also deposit your papers into your institutional repository or put their PDF versions on your personal website, but please follow your publisher's requirements when you do so. See our technical guidelines for more details on the inclusion process.
We normally add new papers several times a week; however, it might take us some time to crawl larger websites, and corrections to already included papers can take 6-9 months to a year or longer.
Google Scholar generally reflects the state of the web as it is currently visible to our search robots and to the majority of users. When you're searching for relevant papers to read, you wouldn't want it any other way!
If your citation counts have gone down, chances are that either your paper or papers that cite it have either disappeared from the web entirely, or have become unavailable to our search robots, or, perhaps, have been reformatted in a way that made it difficult for our automated software to identify their bibliographic data and references. If you wish to correct this, you'll need to identify the specific documents with indexing problems and ask your publisher to fix them. Please refer to the technical guidelines .
Please do let us know . Please include the URL for the opinion, the corrected information and a source where we can verify the correction.
We're only able to make corrections to court opinions that are hosted on our own website. For corrections to academic papers, books, dissertations and other third-party material, click on the search result in question and contact the owner of the website where the document came from. For corrections to books from Google Book Search, click on the book's title and locate the link to provide feedback at the bottom of the book's page.
General Questions
These are articles which other scholarly articles have referred to, but which we haven't found online. To exclude them from your search results, uncheck the "include citations" box on the left sidebar.
First, click on links labeled [PDF] or [HTML] to the right of the search result's title. Also, check out the "All versions" link at the bottom of the search result.
Second, if you're affiliated with a university, using a computer on campus will often let you access your library's online subscriptions. Look for links labeled with your library's name to the right of the search result's title. Also, see if there's a link to the full text on the publisher's page with the abstract.
Keep in mind that final published versions are often only available to subscribers, and that some articles are not available online at all. Good luck!
Technically, your web browser remembers your settings in a "cookie" on your computer's disk, and sends this cookie to our website along with every search. Check that your browser isn't configured to discard our cookies. Also, check if disabling various proxies or overly helpful privacy settings does the trick. Either way, your settings are stored on your computer, not on our servers, so a long hard look at your browser's preferences or internet options should help cure the machine's forgetfulness.
Not even close. That phrase is our acknowledgement that much of scholarly research involves building on what others have already discovered. It's taken from Sir Isaac Newton's famous quote, "If I have seen further, it is by standing on the shoulders of giants."
- Privacy & Terms
- louisville.edu
- PeopleSoft HR
- PeopleSoft Campus Solutions
- PeopleSoft Financials
- Business Ops
- Cardinal Careers

- Undergraduate
- International
- Online Learning
University of Louisville Writing Center
- University Writing Center FAQs
- Virtual Writing Center FAQs
- HSC Writing Center FAQs
- Writing FAQs
- Handouts and Videos
- Graduate Student Writing
- Spring Dissertation Writing Retreat
- Graduate Student Writing Workshops
- Faculty and Graduate Student Writing Group
- Creative Writing Group
- Accessibility and Accommodations
- LGBTQ+ Writing Group
- The University Writing Center and Your Students
- Request a Presentation about the University Writing Center
- Resources for Teaching Writing
- The Writing Center and Your Writing
- University Writing Center Mission Statement
- Meet Our Staff
- Statement on Diversity, Inclusion, and Equity
- Research at the University Writing Center
- How I Write Blog Posts
- Our Community Writing Values and Approaches
- Community Writing Internships and Volunteering
- Family Scholar House
- Western Branch Library
- How can I make myself a stronger writer?
- What makes college writing different than the writing I’ve done up to this point?
- How are the papers I'm asked to write in my major different from those in English 101, 102, and 105 courses?
- What can I do if I don’t completely understand the writing assignment?
- I want to get started writing early, but how do I begin?
- How do I get started writing a personal statement?
- I have a lot to say, but how can I organize my thoughts?
- How can I learn how to write in a new genre (for example, personal statement, resume, or literature review)?
- How do I expand a rough draft to make it meet the assignment’s length requirement?
- How can I find good sources for my research paper?
- What are some strategies for working sources into my research paper?
- What is the difference between quotation, paraphrase, and summary?
- How can I revise my draft if it doesn’t seem to “flow”?
- What does my teacher mean by “substantial revision?”
- How do I write an essay that makes an “argument”?
- How can I avoid plagiarizing?
- What are some strategies for improving my grammar and punctuation?
- How can I format my document properly in Word, PowerPoint or Excel?
- How should I approach writing a literature review at the graduate level?
- / Resources for Students
- / Writing FAQs
- / How can I find good sources for my research paper?
Collecting sources for a research paper can sometimes be a daunting task. When beginning your research, it’s often a good idea to begin with common search engines, like Google, and general descriptions like you can find on Wikipedia. Often though these are not the sources you ultimately want in your paper. Some tips for getting from this beginning research to finding “good” sources include the following.
- Make a list of research terms you can use when searching in the library or even online. Start with your core list, but also add other keywords and phrases that you notice as you research. Also, when you find a good source, look to see if it has “tags.” You can add these phrases to your list search terms. Sometimes the tags are also links that you can follow which will take you to lists of similar sources.
- Think about the kind of sources required by the assignment and also the kind of sources that are “good” for your question or topic. Many library search engines and databases have the option to return only “peer-reviewed” or “scholarly” sources—which are sources that have been read by other scholars before being published. Also, the UofL library offers a list of Research Guides which can help you find useful databases for finding sources. When considering what counts as a “good” source, it’s smart to consider what question you’re asking. If you’re making an argument about how a term is commonly understood, then using dictionaries or Wikipedia would be a good source. If you’re making an argument about developing research in Psychology, then you’ll want to focus on those peer-review or scholarly sources.
- Review the works cited or bibliography section of sources that have already been helpful. The sources they are using will probably be helpful to you also. Some search engines, like Google Scholar, include a link under a source that says “Cited by”—which brings back a list of other sources that have used the source you’re looking at. Google Scholar provides varying quality in their results, depending on the subject area and other things, but it’s a great place to start.
- The reference librarians in Ekstrom library (right next door to the University Writing Center) are available to help you with your research. You can make appointments to meet with them here. During these appointments, they can help you find the most helpful databases, decide what sources might be most helpful, and more.
What can the Writing Center do to help?
Writing Center consultants can meet with you to help you get started and find a good direction when working on a research project. This includes but certainly isn’t limited to brainstorming lists of research terms, deciding which kinds of sources will best help you answer your research question(s), looking at some preliminary helpful sources, and more. Talking about these topics can help you figure out how to approach searching for and finding good sources. We also know how and when to refer you for a follow-up appointment with the Reference Assistance and Instruction department.
Creating Art: A Painter’s Journey Into the World of Writing Mar 25, 2024
Getting Comfortable with Directive Practices in the Writing Center Mar 08, 2024
International Mother Language Day 2024 Mar 04, 2024
University and High School Writing Centers Feb 26, 2024
How Time Affects a Writing Center Session Feb 16, 2024
ESL Instruction in the University of Louisville Writing Center Feb 09, 2024
UofL Writing Center Blog - More…
University Writing Center
Ekstrom Library 132
Kornhauser Library 221
University of Louisville
Louisville, Kentucky 40292
Spring 2024
Ekstrom Library
M -Th 9 am - 5 pm
F 9 am - 4 pm
Kornhauser Library
T & Th 9 am - 12 pm
Closed on student breaks and holidays
(502) 852-2173
Social Media

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
What If You Can’t Find Sources For Your Topic?
As a college librarian, Patricia Knapp worked with many students who were new to academic research and writing. She observed that beginning students often “have a basic misconception of the function” of research: “they look for and expect to find ‘the answer to the question’ instead of evidence to be examined” (as quoted in Kuhlthau, 10).
Don’t worry if you’ve ever harboured the mistaken belief that research is all about finding the perfect source, a book or article that completely answers your research question. Experienced researchers fall into that way of thinking, too! But they’re also able to step back and rethink their approach to a research question–they’re able to “divide and conquer.” Here’s an example:
Our research question is: How can virtual teams be implemented at Pixar Animation Studios?
You might want to dive right into a library database to find “the answer” to the question, with a search like this:
“virtual teams” AND Pixar
And you might think that such a search will find a ready-made answer to the research question, as represented in this Venn diagram:
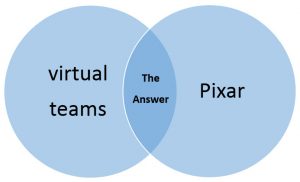
But the facts are: a) probably no one has ever published an article about virtual teams at Pixar, so the search would yield zero results, and b) research isn’t about finding “the answer”–it’s about finding ideas and facts you can use to create your own answer.
You should divide the question into two parts, in order to conquer it:
- First research virtual teams (their challenges, best practices, etc.).
- Next research Pixar (its mission, corporate culture, etc.).
Accordingly, your two separate database searches might look like this:
- “virtual teams” AND (challenges OR “best practices”)
- Pixar AND “corporate culture”
A journal article that you might choose from the first search is by Soo Jeoung Han et al., “How Virtual Team Leaders Cope with Creativity Challenges,” in which the authors study ways that creativity can be fostered in virtual teams. From your second search, you might use an article from Harvard Business Review by Pixar cofounder Ed Catmull, “How Pixar Fosters Collective Creativity.”
By putting these two texts—Han et al. and Catmull—into conversation, you can begin to develop your own argument about how virtual teams could be implemented at Pixar. You might begin with the observation that, according to Han et al., the qualities of an effective creative team are the same, whether it is a virtual or an in-person team. Because, as Catmull notes, Pixar already has such a strong team culture, the company would be well positioned to implement virtual teams: they have formed close relationships, strive to create a space where it’s safe to bring up new ideas or critique others’ ideas, and group members at all levels of the company support one another and take on leadership roles. You could lay out some of the promising parallels between Han et al.’s key findings and the vibrant group culture at Pixar.
Once you’ve started putting the two texts into dialogue, you would probably see more connections. For instance, one of Han et al.’s most interesting claims is that using state-of-the-art technology to communicate can be a motivating factor in itself. Catmull tells us that, at Pixar, “Technology inspires art, and art challenges the technology” (71). Given the fascination with technology at Pixar, members of virtual teams would be motivated to participate because of the opportunity to experiment with the newest forms of digital communication.
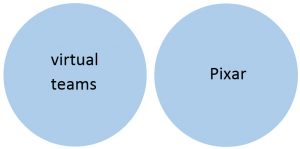
By orchestrating an interplay between your two sources, putting them in dialogue with each other and with your own ideas, you can offer an original analysis. “Conquering” your paper means offering this analysis—your thinking, visible on the page. This is what professors—and all genuinely interested readers—want to see.
Speaking again in Venn, the process of creating your own answer to the research question looks like this:
The rhetorician Kenneth Burke famously described academic writing as a conversation that has been taking place among various authors, across time, on a given topic; it’s your job as an academic writer to add something new to this conversation. You may think of academic writing and creative writing as completely separate, especially if you’ve been taught to exclude your own voice and opinions from school papers. But when you “divide and conquer,” looking for evidence that can help you to contribute an original idea, academic writing is creative.
Business Writing For Everyone Copyright © 2021 by Arley Cruthers is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Eight Ways (and More) To Find and Access Research Papers
This blog is part of our Research Smarter series. You’ll discover the various search engines, databases and data repositories to help you along the way. Click on any of the following links for in an in-depth look at how to find relevant research papers, journals , and authors for your next project using the Web of Science™. You can also check out our ultimate guides here , which include tips to speed up the writing process.
If you’re in the early stages of your research career, you’re likely struggling to learn all you can about your chosen field and evaluate your options. You also need an easy and convenient way to find the right research papers upon which to build your own work and keep you on the proper path toward your goals.
Fortunately, most institutions have access to thousands of journals, so your first step should be to be to check with library staff and find out what is available via your institutional subscriptions.
For those who may be unfamiliar with other means of access, this blog post – the first in a series devoted to helping you “research smarter” – will provide a sampling of established data sources for scientific research. These include search engines, databases, and data repositories.
Search Engines and Databases
You may have already discovered that the process of searching for research papers offers many choices and scenarios. Some search engines, for example, can be accessed free of charge. Others require a subscription. The latter group generally includes services that index the contents of thousands of published journals, allowing for detailed searches on data fields such as author name, institution, title or keyword, and even funding sources. Because many journals operate on a subscription model too, the process of obtaining full-text versions of papers can be complicated.
On the other hand, a growing number of publishers follow the practice of Open Access (OA) , making their journal content freely available. Similarly, some authors publish their results in the form of preprints, posting them to preprint servers for immediate and free access. These repositories, like indexing services, differ in that some concentrate in a given discipline or broad subject area, while others cover the full range of research.
Search Engines
Following is a brief selection of reputable search engines by which to locate articles relevant to your research.
Google Scholar is a free search engine that provides access to research in multiple disciplines. The sources include academic publishers, universities, online repositories, books, and even judicial opinions from court cases. Based on its indexing, Google Scholar provides citation counts to allow authors and others to track the impact of their work.
The Directory of Open Access Journals ( DOAJ ) allows users to search and retrieve the article contents of nearly 10,000 OA journals in science, technology, medicine, social sciences, and humanities. All journals must adhere to quality-control standards, including peer review.
PubMed , maintained by the US National Library of Medicine, is a free search engine covering the biomedical and life sciences. Its coverage derives primarily from the MEDLINE database, covering materials as far back as 1951.
JSTOR affords access to more than 12 million journal articles in upwards of 75 disciplines, providing full-text searches of more than 2,000 journals, and access to more than 5,000 OA books.
Selected Databases
The following selection samples a range of resources, including databases which, as discussed above, index the contents of journals either in a given specialty area or the full spectrum of research. Others listed below offer consolidated coverage of multiple databases. Your institution is likely subscribed to a range of research databases, speak to your librarian to see which databases you have access to, and how to go about your search.
Web of Science includes The Web of Science Core Collection, which covers more than 20,000 carefully selected journals, along with books, conference proceedings, and other sources. The indexing also captures citation data, permitting users to follow the thread of an idea or development over time, as well as to track a wide range of research-performance metrics. The Web of Science also features EndNote™ Click , a free browser plugin that offers one-click access to the best available legal and legitimate full-text versions of papers. See here for our ultimate guide to finding relevant research papers on the Web of Science .
Science.gov covers the vast territory of United States federal science, including more than 60 databases and 2,200-plus websites. The many allied agencies whose research is reflected include NASA, the US Department of Agriculture, and the US Environmental Protection Agency.
CiteSeerx is devoted primarily to information and computer science. The database includes a feature called Autonomous Citation Indexing, designed to extract citations and create a citation index for literature searching and evaluation.
Preprint and Data Repositories
An early form of OA literature involved authors, as noted above, making electronic, preprint versions of their papers freely available. This practice has expanded widely today. You can find archives devoted to a single main specialty area, as well as general repositories connected with universities and other institutions.
The specialty archive is perhaps best exemplified by arXiv (conveniently pronounced “archive,” and one of the earliest examples of a preprint repository). Begun in 1991 as a physics repository, ArXiv has expanded to embrace mathematics, astronomy, statistics, economics, and other disciplines. The success of ArXiv spurred the development of, for example, bioArXiv devoted to an array of topics within biology, and for chemistry, ChemRxiv .
Meanwhile, thousands of institutional repositories hold a variety of useful materials. In addition to research papers, these archives store raw datasets, graphics, notes, and other by-products of investigation. Currently, the Registry of Open Access Repositories lists more than 4,700 entries.
Reach Out Yourself?
If the resources above don’t happen to result in a free and full-text copy of the research you seek, you can also try reaching out to the authors yourself.
To find who authored a paper, you can search indexing platforms like the Web of Science , or research profiling systems like Publons™ , or ResearchGate , then look to reach out to the authors directly.
So, although the sheer volume of research can pose a challenge to identifying and securing needed papers, plenty of options are available.
Related posts
Unlocking u.k. research excellence: key insights from the research professional news live summit.

For better insights, assess research performance at the department level

Getting the Full Picture: Institutional unification in the Web of Science


DIY: Research Help
- I need help choosing a topic
Where to begin?
Background information, developing a research question.
- Identify the Type of Information Sources You Need
- Develop a Search Strategy
- Searching for Information Sources: Ebooks & Print Books
- Searching for Information Sources: Streaming Media
- Searching for Items in the Library's Digital Archives
- Accessing Online Items
- Accessing Physical Items Located in the Library
- Request Items Not Found in the Library
- Are my resources good for my research?
- Chicago/Turabian Style
- Citation Tools
- DIY Library Help
- Chat with a Librarian - Schedule a Research Appointment This link opens in a new window
Before you can start any research on your topic, you must have a background knowledge about your topic. Books, reference sources, and websites can provide you with that knowledge.
This is important because:
- Background sources give you the language that people are using to discuss your topic. You will use this language when you start to search databases for scholarly articles and resources on the topic.
- This "pre-research" gives you a sense if your topic is focused enough. If your initial searches bring back so many results you can't even figure out what the language people are using to discuss your topic, then you should consider narrowing your topic.
Remember , background information is always a starting point for research, not an ending point .
Wikipedia Yes, it is OK to use Wikipedia for background information, but never cite to it. And only use it as a starting point.
Library resources to use to find background information:
Identify Keywords
Before you can begin searching for information, you need to identify keywords related to your topic. Key terminology can be easily be found by scanning:
- Your research questions
- Bibliographies found at the end of books and articles
If you are still struggling:
- Use a thesaurus to identify synonyms.
- Find pictures related to your topic, then describe them.
- Brainstorm keywords with a librarian, your instructor, or a friend.
- Use a keyword generator.
- Keyword Worksheet Make a list or use the chart below to track keywords related to your topic. Keep it by your side when you start your research.
- Text alternative for "Developing a Research Question" Infographic
- << Previous: I need help choosing a topic
- Next: Identify the Type of Information Sources You Need >>
- Last Updated: Sep 27, 2023 3:29 PM
- URL: https://fitchburgstate.libguides.com/diyresearch

No products in the cart.

The Perfect Fit: 5 Steps for Finding Academic Sources without Frustration

Whenever I start a research paper, I either feel like I can’t find anything on my topic or that I'm only finding useless information. Am I doing something wrong?
Dear Lisa,
I know exactly how you feel.
My best friend’s wedding is coming up, and I need a dress. THE dress.
It can’t be too dark – I’m not going to a funeral, after all. It can’t be white – wouldn’t want to upstage my friend. It can’t be too short – I plan on dancing all night. …and also not too tight – this lady likes to eat.
For hours I’ve been sitting in front of my laptop and sifting through one online shop after another.
THE dress must be out there somewhere.
It’s no different when searching for quality sources for your research paper. You'll want the perfect fit:
- A source that covers your topic exactly and doesn’t just discuss one specialized aspect of it.
- A source that deepens your knowledge of the topics you’re already familiar with but also gives you new ideas.
- A source that’s written by a scholar in your field, has undergone peer review, and was published by an academic publishing company.
You should be exactly as picky as you would be when looking for the perfect dress.
The problem is that it can start to feel as if you're looking for a needle in a haystack. Hours fly by as you randomly search a never-ending string of online shops.
For your research paper, there's a better way:
Why not just search Google? Most academic journal articles either aren't listed online or are difficult to find among all the non-scholarly and unverified information on the internet. A good database for your subject area helps you locate high-quality peer-reviewed articles efficiently.
Find databases you have access to by visiting your university or college’s library website. Look for a “databases” or “electronic resources” section.
Don’t get frustrated if your first attempts don’t give you what you want. Usually you’ll have to try a few searches before you find the optimal combination of terms.
Let’s say you're looking at how social media platforms such as Snapchat and Instagram are currently affecting social media marketing strategies. Here's how you might search for sources in the Business Source Premier database:
Look at the keywords your database displays for some of your results and use these terms in a new search. Or go back and perform steps 1 and 2 again to find new terms.
Place multiple word terms in quotation marks. This tells the database to search for the exact phrase. For more complex searches, see Citavi's guides to using Boolean operators and wildcards .
If you feel like you’re not getting anywhere, look to others for help. Ask your peers what they did to find their sources or set up a research consultation session with a librarian.
Meet with your professor or teaching assistant and show them what you’ve found already. They will let you know if you’ve gone off track and give you some new ideas for what to try next.
Another good strategy is to take a look at the references in articles or books you already have on your topic. Do you see a particular source being referenced by many different authors? That could be your perfect fit.
What would you recommend that Lisa do? Are there any strategies you use to avoid frustration when locating sources for a research paper?
Let us know on our Facebook page !
----
Additional Resources:
- The University of Leeds offers an excellent video introduction for developing a search strategy from your initial research question: https://library.leeds.ac.uk/researcher-literature-search-strategy
- Do you struggle with identifying whether an article is scholarly enough for your papers? The following guide from the University of Wisconsin Library will help you distinguish between popular and academic sources: https://www.library.wisc.edu/help/research-tips-tricks/evaluate-sources/
About Jana Behrendt

Jana Behrendt, a librarian by training, is deeply interested in everything related to personal information management. However, she does not read as much as you would expect from a librarian. She loves hiking in the Swiss Alps – as long as she doesn’t have to look dow
Recent Articles
How to Find Valid Sources for Your Research Papers
Priyanka recently posted some advice on graduate research. If you are doing grad research now or may want to in the future, I definitely recommend Priyanka’s blog entry .
But even if you’re just an undergrad, it’s important to develop good academic research skills. Writing academic essays as an undergrad is your chance to learn the most important research skill: identifying and gathering valid, proven information. This skill is really the key to all research— whether you are doing your own experiments or just looking for good writings on your subject, universities expect you to find information that is valid . This research skill also helps you develop critical thinking skills, which are very valuable not just in grad school, but also in the workplace… and in life.
What does “valid” mean anyway?
If you just asked yourself that question, don’t feel bad—I have had many of my own university students ask me that over the years. The answer is simple: a source is valid if you can make an intelligent argument that the information in the source can be trusted.

In other words, if someone—such as a professor—doubts that a source for your essay is true, you’ll have to defend your source. So your next question probably is “ How do I defend a source if my professor criticizes it?” Read on…
Signs that a source is probably valid
Arguing to defend your choice of sources can seem scary at first. Fortunately, there are several clues that a source may be valid. If your sources have these signs of validity, it will be easy to convince people that your sources are trustworthy. And if your source has enough signs of validity, your professors probably won’t even make you defend it at all.
Here are some of the key signs:
- The source is scholarly, and peer-reviewed. Scholarly, peer reviewed sources are written by one person with an advanced degree, and then confirmed as true by a group of judges who also have similar graduate-level qualifications.There are specific search engines and websites that collect only peer reviewed scholarly writings. For example, ScienceDirect collects peer-reviewed article on STEM subjects (science, technology, engineering, and math). And other services such as JSTOR and EBSCOHost provide peer-reviewed articles in pretty much every academic subject.
- The source is professionally edited . This means that a qualified editor or group of editors is paid to review source materials and make sure everything is correct and accurate.For print resources such as magazines and books, this is pretty easy to prove, usually—most print publishers have a paid staff of editors.For online sources, this can be a little trickier. You may need to investigate a website you’re using as a source. Most informational websites have an “About Us” link or a “Careers” link. At those links, you can usually figure out if the staff has—or hires—paid professional editors.
- The source is well-qualified. Do a web search on the author of any article you want to use as a source. Figure out whether or not the author has good knowledge of the subject he or she is writing about. Does the author have a relevant degree or work experience that connects to his or her subject?
- The source cites other good sources. This is an obvious one really. Your professors will judge your paper based on how good your sources are. So when you’re reading something, you should also judge it by its sources. Where does an article get its information? If the article you want to use as a source also uses good sources, you can probably trust it as valid.
- The source is supported by other good sources. Suppose you find an article you really want to use, but the source doesn’t seem to cite any other sources. And you can’t find out anything about the author, or figure out if the article has been peer reviewed or edited. You can still check to see if the information in the source is confirmed in other writings that are peer reviewed, edited, written by well-qualified writers, etc…
Of course, none of these signs of validity are magic. A source could have some or all of the traits listed above, and your professor might still find a reason that the source isn’t valid. But the more signs of validity your source has, the easier it will be for you to defend it. And if you find a source that doesn’t have any of the features I listed above, you probably shouldn’t use it.
In my next post on this subject, we’ll look at how to identify information that is weak or not valid at all. Watch out for this post!

David is a Test Prep Expert for Magoosh TOEFL and IELTS. Additionally, he’s helped students with TOEIC, PET, FCE, BULATS, Eiken, SAT, ACT, GRE, and GMAT. David has a BS from the University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire and an MA from the University of Wisconsin-River Falls. His work at Magoosh has been cited in many scholarly articles , his Master’s Thesis is featured on the Reading with Pictures website, and he’s presented at the WITESOL (link to PDF) and NAFSA conferences. David has taught K-12 ESL in South Korea as well as undergraduate English and MBA-level business English at American universities. He has also trained English teachers in America, Italy, and Peru. Come join David and the Magoosh team on Youtube , Facebook , and Instagram , or connect with him via LinkedIn !
View all posts
More from Magoosh

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Campus Life

Writing a good college essay can be tough and time-consuming. It will cost you several trips to the library, hours of pouring over your notes, and sleepless nights scouring online databases. ⏳
And while the internet is a huge pool of information, it is crucial to identify and use credible sources . So, the big question is: How can you find the right academic references for your college essay?
Here’s a guide to finding essay sources that will impress your professor and get you that well-deserved A! 🔍
Start With Wikipedia
Yes, we all know academic researchers frown upon Wikipedia since it’s user-generated (so anyone can write anything). But it’s actually a great springboard to get an overview of your essay topic . 💻
At the bottom of each Wikipedia page, you’ll find a treasure trove of legitimate sources and citations that you can use in your essay.
Check Out Primary Sources
Primary sources are the building blocks of any research project. They must serve as the foundation of your research, whereas secondary sources should inform and supplement the primary sources.
Primary sources are first-hand accounts on a subject, often unedited, that offer a close, personal overview of a topic. They encourage students to read between the lines and approach them with a critical mindset. 🤔

When analyzing primary sources, ask yourself key questions like, “Who is the intended audience?” or “What does the source tell me about the period?”
By considering these questions, you can effectively understand the historical context and cultural perspectives and avoid potential bias or inaccuracy . This will also help you develop well-supported arguments and strengthen your essay. 💪
Get the Most Out of the Library
Students may gravitate toward online research but the good old library is still a trusted source of information . In fact, 58 percent of Americans aged 16 and older have a library card — and for good reason!
Library databases allow you to efficiently search for published information, such as magazines, journals, and newspaper articles .
These sources contain scholarly articles by notable authors, journalists, and researchers. If you hit a paywall for a journal or newspaper, verify if your library has a subscription — problem solved! ✅

But the most underutilized tool in libraries is the staff. Librarians know all about research methods, using information systems, statistics, and management.
They’re experts when it comes to finding the information you need. All you have to do is ask your university librarian for help finding top-tier resources on your essay topic. 📚
Use Academic Search Engines
Let’s get this straight: It’s hard to write a research paper without consulting the internet .
Most of us start our search with Google, but unfortunately, search engines don’t always churn out credible results . That’s why it’s crucial to explore other portals with an academic focus when searching for essay sources . ⚠️
Check out these options:
- BASE : The Bielefeld Academic Search Engine (BASE) contains 4,000 sources and provides search results from more than 100 million documents. They also offer an advanced search option that allows users to narrow down their research. The BASE advanced search lets users use filters such as author names, publication dates, and document types to find more relevant results, saving time and improving academic research efficiency.
- Refseek : A web search tool for students and researchers. You can access over a billion documents, books, newspapers, and journals without getting distracted by ads or sponsored links.
- Google Scholar : This connects you with hundreds of relevant scholarly journals. What’s more, it provides formatted citations in MLA, AP, or APA that you can export to RefWorks or BibTex.
- JSTOR : The platform provides a large collection of academic journals, books, and original sources from a variety of subjects.
- PubMed : This includes articles from scholarly journals and research institutes with a focus on biomedical and life sciences research.
- LexisNexis Academic : It focuses on researching legal and news-related subjects, including reports, legal publications, and court cases.
Opt for Digital Libraries and Databases
Digital libraries have specialized collections in all fields of study. They are easy to access and contain millions of books, audiobooks, journals, and videos that can help you further your essay research.
The best part? No more waiting for popular books to become available! Digital libraries let you read and download content instantly, anytime, anywhere, using your computer or phone . 📱
Of course, there may be some occasions where you’ll find your university doesn’t have access to a particular online database.
If you’ve found the perfect journal article but can’t get access, try emailing the professor who wrote it and ask for a PDF — most academics will be quite happy to provide you access to their work. 📧

Don’t Forget the Bibliography of Your Sources
After you have a list of credible sources, take a closer look at their citations. Seek out the primary sources these citations used for research. This will open up a new set of materials to work with for your essay. 🗒️
Plus, they often contain references to publications that make alternate viewpoints or offer diverse interpretations of the topic at hand.
TIP: Once you start your research, you may find the same sources pop up over and over again. Consult Google Scholar to see the articles in a publication that are cited the most (along with who cited them). Make a list of these and incorporate them in your essay.
Look Beyond Journals and Books
The world of research is your oyster, and with a diverse array of sources, your academic essay can shine if you dare to explore the unconventional.
Peruse through thrilling audio and video recordings that transport you to historic moments or cultural events, or explore interviews with experts who can add personal insights and real-life perspectives to your essay . 🎧

Incorporate variety in the resources you add to make your essay an interesting read. This will also show your professor that you’ve gone above and beyond to create a well-researched essay. 👌
Note: Critically assess the reliability and validity of sources outside of the conventional academic channels because their level of accuracy may vary. Always check the author’s qualifications, and the reputation of the source, and cross-reference information from various sources.
Learn to Quickly Evaluate a Source
Essays and research papers come with deadlines. In an ideal world, you would meticulously examine each potential essay source, but there’s a smarter way to do it to save time! 🗓️
Here’s a helpful approach to evaluating a source: First, read the abstract or introduction of the source to decide if it’s useful for your work .
Then, take a look at the citations and references at the end of the source . You can also check the publication date to ensure the information is current.
If it’s an online source, check out the domain name. Sites with .edu domains are associated with educational facilities, while .gov domains belong to government agencies. These sources are generally reliable due to their affiliation with reputable institutions.
Additionally, examine the author’s credentials and expertise in the field . Look for authors who have relevant academic backgrounds or professional experience related to the topic. ✍️
Lastly, consider the reputation of the publisher . Reputable publishers are known for maintaining high standards of quality and accuracy in their publications.
Don’t know where to start? Check the publisher’s website, browse through its publication list, and look for details about its editorial board and reviewers. 🧐
Putting together a top-notch essay is a Herculean task — but if you can collect the right resources you’re already halfway there! 💯
The Easy Guide to Finding Essay Sources: Frequently Asked Questions
What are academic sources .
Academic sources are dependable and trustworthy documents created by subject-matter specialists and distributed by respectable publishers or academic publications .
They go through an exhaustive screening procedure and frequently contain citations or references to other academic publications.
How do I find trustworthy sources for my academic research?
Start with reputable sources such as scholarly journals and books from respected publishers. Consider the expertise of the author and the publisher’s reputation, and look for sources that have undergone the peer review process.
Check the publication date to ensure the information is current. Be aware of potential biases in the sources and evaluate the evidence provided.
What are the best sources for essays?
The best sources for essays are those that offer accurate and up-to-date information.
Scholarly journals, expert books, government websites, academic databases, credible websites with specific domains (.gov,.edu, and .org), must-read books related to the topic, secondary readings for additional insights, scholarly sites, scientific papers, and reliable news and interviews are examples of these.
How do I include a source in an essay?
Introduce the source with an initial phrase. Then, summarize, paraphrase, or quote the material as needed and provide proper citations .
When directly quoting the source, use quotation marks and cite the author, year, and page number.
For summarizing, briefly present the main points and cite the author and year. When paraphrasing, restate the information in your own words and cite the author, year, and page number.
Include relevant details about the author, title, and genre when citing the source for the first time. Each college may have varying guidelines for sourcing, so it’s important to check with your institution what is required.
Other Readers Loved:
27 of the weirdest college team names in the us, colleges in the us with the weirdest (sometimes funny) names, 31 states with free community college to save you money.
The College Post is part of Globe Post Media, a US digital news organization publishing the world’s best targeted news sites.
Latest Posts
13 best college traditions in the us to ignite school spirit, 12 best books for college students: 2024 must-reads, these 10 us colleges offer awesome work-study programs, most popular, these are the cheapest colleges in the us, 73 top side hustles for college students to make fast cash in 2024, fast access.
© Globe Post Media | All rights reserved
Find academic sources for your next paper
Finish Your Research in Minutes. Save Your Sleep.
Paste your essay to find, summarize, and add credible sources. (That's something Google Scholar can't do!)
200m+ research papers
Precise search filters
Just paste your essay

Join 10,000+ students saving 100s of hours
See Sourcely in action 👇

Please wait. This may take a minute...
If it takes longer than a minute, try again.
Text exceeds 300 characters. Click here to upgrade to SourcelyPRO for unlimited characters
Success: Scroll Down to see results
Publications From
Minimum Citations
Include Keywords
Exclude Keywords
Results for...

Publication Year:
Publication Venue:
Edit your papers with Yomu AI
Seamless Transition from Sources to Masterpiece
Congratulations on finding the perfect sources for your academic paper! Now, take the next step towards crafting a flawless masterpiece with Yomu. Our AI writing assistant is your guide to refined, error-free writing. Edit your paper like a pro with real-time feedback and efficient writing tools. From research to writing, Yomu & Sourcely are your all-in-one solution for academic excellence.
Sources about
Discover more sources for your essay today, sources about .

Trusted By Academics From
Why trust us? Because we are trusted by the absolute best academic institutions, including Harvard, MIT, and Stanford, among others
POWERFUL FEATURES
Fed up with scrolling through pages of search results? Our source-finding tool simplifies the process so you can find your sources quickly and easily.

Paste Your Essay
Simply paste your essay or paragraph and let Sourcely do the rest!

Get Credible Summaries
Save time and effort by quickly getting a general overview/summary of a source material
.png)
Export References
Save time and ensure accuracy by exporting your sourced references in various formats, making citation and bibliography creation a breeze.
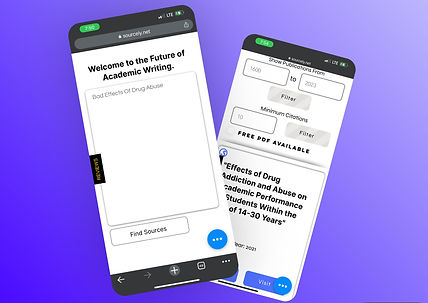_edited.jpg)
F ind Sources
Hit the button, and watch Sourcely find all suitable sources.

Free PDF Downloads
Sourcely also allows users to download free PDFs of many of the sources it lists.
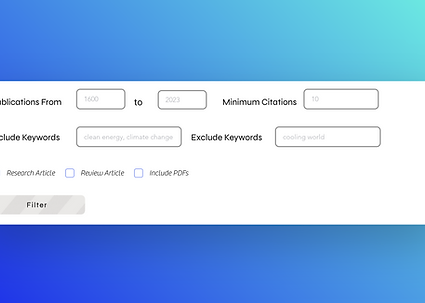.png)
Advanced Filters
Tailor your source discovery by applying advanced filters, such as publication year, authorship, relevance, and more.
PRICING & PLANS
Sourcely is an investment in your academic career, but we know that budgets can be tight. That's why we strive to keep wallet-friendly prices, with monthly plans starting at just $9 per month or yearly plans at $87 - affordable for everyone.
Pay Per Use
Sourcelyfree.
- Skip hours of Manual Research!
- Assured Credibility of Sources
- Only UP TO 300 characters :(
- Quality results for 300 characters
SourcelyPRO Monthly
- Quick and Easy Source-finding
- Ease of Pasting your Entire Essay
- Skip Tedious Manual Research!
- Generate Credible Summaries
- PDF Downloads of Sources
- Search Millions of Sources
- Filter by Year of Publication
SourcelyPRO Yearly
- All features of the Monthly plan
- Save 20% Off the Monthly Plan
- One purchase, endless benefits
- Lock it in before price increases!
- Pro Yearly users suggest features
- Equal to $7.25/month
SourcelyPRO 2000 Words
- Skip tedious Manual Research!
- Total of 2,000 words
Trusted by researchers and organizations around the world
Over 10,000 students, researchers, and industry experts use Sourcely
See what they're saying

10,000 students helped

100,000 hours saved

250,000 sources generated
- How does it work? Our AI algorithms analyze the text and identify key themes and concepts. Then, it searches through our vast data set to find relevant and reliable sources to support those themes. This makes it easy for you to find the information you need to back up your work.
- Who can use it? Our service is perfect for students, researchers, writers, and anyone else who needs to find reliable sources to support their work. It's a great tool for anyone looking to improve the credibility and quality of their writing.
- How much does it cost? We offer a variety of pricing options to fit your needs. We have a free basic plan that is very limited and for the full experience, we have paid versions. Our monthly plan is £4.99 a month, our yearly plan is £29.99/year.
- What makes this service different from others? Unlike other services that simply provide a list of sources, our AI is able to understand the context of your text and find sources that are truly relevant and reliable. Additionally, our data set is the largest in the world, giving you access to more information than any other service.
- Is it easy to use? Yes, our service is very user-friendly. Simply upload your text, and our AI will take care of the rest. You can then easily sort and filter through the sources it finds to find the information you need.
- How quickly can I expect to get the result? Our service is instant, you will get the result as soon as you upload the text.
- How accurate is the service? Our AI is constantly being trained and refined to ensure the highest level of accuracy. We are always working to improve our algorithms to provide you with the most relevant and reliable sources possible.
- Can I use it for any language? Currently, our service supports English language only.
- Is there a customer support? Yes, we have a dedicated customer support team that is available to help you with any questions or issues you may have. You can contact us via email or chat.

Elman Mansimov

Armin Hamrah

Daniel Felix
Software Developer

Welcome to Sourcely! Our AI-powered source finding tool is built by students for students, and this approach allows us to create a tool that truly understands the needs of the academic community. Our student perspective also enables us to stay up-to-date with the latest research and trends, and our collaborative approach ensures that our tool is continually improving and evolving.
Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
Are you struggling to find sources for your research paper? (Module 6)
Let me guess, it’s late at night, you procrastinated your research paper, and now you are struggling to find quality sources to cite in your paper. Let me be the first one to tell you, you are not alone. I too struggle with writing research papers because I feel as if the sources I am using are just not good enough. But once you learn a few tips and tricks of the web you will have quality sources in no time!
First I am going to let you in on a few tricks that I learned to help narrow down my search results on Google…
- The more descriptive you can be the better! Searching general terms such as “global warming” will produce millions of results that may overwhelm you, but if you search “global warming longterm effect on the atmosphere” you will return fewer results that will be more useful to your paper.
- Too many results? Use Googles ‘advanced search’ option! This option allows you to narrow down results using any detail of the web page such as the URL, description, title, etc.. This is useful if you are searching for a url containing .edu or .gov because Google will only return results containing the information you have requested.
There are many other ways you can use to narrow down Google results, but these are two tips that I find the most helpful!
Once you have narrowed some results on Google and clicked on one of the links, you then need to determine if the source will be a quality source for you to use in your research paper. Ideally you want to check the sources reliability, quality, and utility. Check things such as the author, publish date, and reviews of the website. All of this information will let you know right away if the source is something that is going to be credible and reliable for good information. Also check and see how well the paper is written. Does it cite any sources? Are there any strong details or bias? If the article is too general, it is not something that you will want to use. Also, if the article contains any bias you should avoid it because in a research paper facts are extremely important. Lastly, check and make sure the article is actually focused toward the topic you are writing about. You want to keep your information pretty narrowed, and getting too far off of your topic can hurt your paper. If the webpage meets these credentials it is most-likely a credible source to use and something that will add value to you paper!
Don’t stress too much about your sources! With some practice it will become easier to identify reliable sources!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Frequently asked questions
How can i find sources to use in my research.
You can find sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar . Use Boolean operators or advanced search functions to narrow or expand your search.
For print sources, you can use your institution’s library database. This will allow you to explore the library’s catalog and to search relevant keywords.
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Chat with us
- Email [email protected]
- Call +44 (0)20 3917 4242
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our support team is here to help you daily via chat, WhatsApp, email, or phone between 9:00 a.m. to 11:00 p.m. CET.
Our APA experts default to APA 7 for editing and formatting. For the Citation Editing Service you are able to choose between APA 6 and 7.
Yes, if your document is longer than 20,000 words, you will get a sample of approximately 2,000 words. This sample edit gives you a first impression of the editor’s editing style and a chance to ask questions and give feedback.
How does the sample edit work?
You will receive the sample edit within 24 hours after placing your order. You then have 24 hours to let us know if you’re happy with the sample or if there’s something you would like the editor to do differently.
Read more about how the sample edit works
Yes, you can upload your document in sections.
We try our best to ensure that the same editor checks all the different sections of your document. When you upload a new file, our system recognizes you as a returning customer, and we immediately contact the editor who helped you before.
However, we cannot guarantee that the same editor will be available. Your chances are higher if
- You send us your text as soon as possible and
- You can be flexible about the deadline.
Please note that the shorter your deadline is, the lower the chance that your previous editor is not available.
If your previous editor isn’t available, then we will inform you immediately and look for another qualified editor. Fear not! Every Scribbr editor follows the Scribbr Improvement Model and will deliver high-quality work.
Yes, our editors also work during the weekends and holidays.
Because we have many editors available, we can check your document 24 hours per day and 7 days per week, all year round.
If you choose a 72 hour deadline and upload your document on a Thursday evening, you’ll have your thesis back by Sunday evening!
Yes! Our editors are all native speakers, and they have lots of experience editing texts written by ESL students. They will make sure your grammar is perfect and point out any sentences that are difficult to understand. They’ll also notice your most common mistakes, and give you personal feedback to improve your writing in English.
Every Scribbr order comes with our award-winning Proofreading & Editing service , which combines two important stages of the revision process.
For a more comprehensive edit, you can add a Structure Check or Clarity Check to your order. With these building blocks, you can customize the kind of feedback you receive.
You might be familiar with a different set of editing terms. To help you understand what you can expect at Scribbr, we created this table:
View an example
When you place an order, you can specify your field of study and we’ll match you with an editor who has familiarity with this area.
However, our editors are language specialists, not academic experts in your field. Your editor’s job is not to comment on the content of your dissertation, but to improve your language and help you express your ideas as clearly and fluently as possible.
This means that your editor will understand your text well enough to give feedback on its clarity, logic and structure, but not on the accuracy or originality of its content.
Good academic writing should be understandable to a non-expert reader, and we believe that academic editing is a discipline in itself. The research, ideas and arguments are all yours – we’re here to make sure they shine!
After your document has been edited, you will receive an email with a link to download the document.
The editor has made changes to your document using ‘Track Changes’ in Word. This means that you only have to accept or ignore the changes that are made in the text one by one.
It is also possible to accept all changes at once. However, we strongly advise you not to do so for the following reasons:
- You can learn a lot by looking at the mistakes you made.
- The editors don’t only change the text – they also place comments when sentences or sometimes even entire paragraphs are unclear. You should read through these comments and take into account your editor’s tips and suggestions.
- With a final read-through, you can make sure you’re 100% happy with your text before you submit!
You choose the turnaround time when ordering. We can return your dissertation within 24 hours , 3 days or 1 week . These timescales include weekends and holidays. As soon as you’ve paid, the deadline is set, and we guarantee to meet it! We’ll notify you by text and email when your editor has completed the job.
Very large orders might not be possible to complete in 24 hours. On average, our editors can complete around 13,000 words in a day while maintaining our high quality standards. If your order is longer than this and urgent, contact us to discuss possibilities.
Always leave yourself enough time to check through the document and accept the changes before your submission deadline.
Scribbr is specialised in editing study related documents. We check:
- Graduation projects
- Dissertations
- Admissions essays
- College essays
- Application essays
- Personal statements
- Process reports
- Reflections
- Internship reports
- Academic papers
- Research proposals
- Prospectuses
Calculate the costs
The fastest turnaround time is 24 hours.
You can upload your document at any time and choose between three deadlines:
At Scribbr, we promise to make every customer 100% happy with the service we offer. Our philosophy: Your complaint is always justified – no denial, no doubts.
Our customer support team is here to find the solution that helps you the most, whether that’s a free new edit or a refund for the service.
Yes, in the order process you can indicate your preference for American, British, or Australian English .
If you don’t choose one, your editor will follow the style of English you currently use. If your editor has any questions about this, we will contact you.

- Richard G. Trefry Library
Q. I wanted to cite an article (or book) in my paper, but I've lost it! How can I find it again?

- Course-Specific
- Textbooks & Course Materials
- Tutoring & Classroom Help
- Writing & Citing
- 44 Articles & Journals
- 11 Capstone/Thesis/Dissertation Research
- 37 Databases
- 56 Information Literacy
- 9 Interlibrary Loan
- 9 Need help getting started?
- 22 Technical Help
Answered By: Priscilla Coulter Last Updated: Jul 29, 2022 Views: 9381
First, an ounce of prevention: as you're doing your research , keep careful track of the sources that you think you'll want to use in your paper . A research journal and citation management tool can be a big help.
When you've lost that perfect article or book, don't panic. Try these steps to recover it:
- If you can remember all or part of the title or an exact quote from the text , search for it in quotation marks in the database where you found it originally (or, if you can't remember where you were searching, try Google Scholar ).
- If you can remember an author or editor , try searching by author name .
- If you remember what keywords you were using when you found it, try them again (in the same database, if possible). If you can remember the author, add the name to your keywords, too (for example: time management AND Smith).
You might find the full text again when you try the steps above. But, if all you find is a complete citation , that's a good place to start. The FAQs below will show you how to track down an article or book with a citation:
- How can I find the full text of a specific article?
I'm trying to find a specific book. How can I find out if our library has it?
Still can't find it? Email the librarians with as much information as you can, and we'll see what we can dig up for you.
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 14 No 1
Related Topics
- Articles & Journals
Need personalized help? Librarians are available 365 days/nights per year! See our schedule.

Learn more about how librarians can help you succeed.

- my research
- contributions and comments
I can’t find anything written on my topic… really?
Sometimes people tell me that they can’t find any literature that is relevant to their research. They are doing something that nobody else has researched and written about and so there isn’t anything to read. What, they ask, can they do for their literature chapter.
A lack of literature is very rarely a real problem. The real problem is that the researcher with the nothing-written-on-my-topic question has drawn the boundary around their topic too tightly. They haven’t thought about the kinds of literatures that might be relevant, even if they are not written on exactly the same question.
Let me give an example. Say a researcher is doing a project on the use of whiteboards in science lectures. OK, I don’t know why, but let’s go with this for argument’s sake. Its just a hypothetical. The researcher has searched and searched through the literatures and they can only find one paper written on the use of whiteboards in science. Hooray, they say, I’ve found a gap. My research is needed. But there is nothing written on it. That’s a problem. What will go in my literature chapter?
Well, no. That’s not the case. Of course there’s something in print. Even if it’s not directly on the exact same topic, it’s related. Let’s think of some of the other literatures that might be connected and relevant to our pretend inquiry. There’s probably research about the use of whiteboards in subject areas other than science. There is some research into the lecture as a form of teaching and learning (I know this to be the case!). And there is certainly material about general teaching and learning in science. So all of these different literatures have a connection with our imaginary topic.
But wait, there’s more. There is an enormous literature about the use of digital technologies in higher education, some of which quite specifically addresses the pedagogical strategies that they do and don’t afford – this is relevant to the way in which whiteboards are used in science lectures. And there’s material about students’ experiences of lectures and their own personal use of digital technologies. And of course all of this related research is framed within a broader scholarly conversation about learning and teaching – and our mythical researcher concerned about whiteboards in science lectures is certainly going to have to establish their work within a general pedagogical conceptual framework – so there’s more reading.
So it’s not that there is no literature for the pretend researcher on their topic, it’s rather that they have to think more broadly about what they might need and use. They have to map the possible areas that are linked to their question and then sort out, by skimming and noting, what’s most relevant and related. They must then bring these selected literatures together in a way that supports the research they are going to do.
The answer to the no literature question is always, always, always – what else is pertinent. The resulting strategy is to widen the boundaries of the search to include related and framing scholarship. Take off the blinkers and look further… There is another answer of course. It’s one that always lurks behind the nothing-written-on-my-topic question. And this answer is a scary one, but its always one worth asking. Nothing in your area? Maybe there is nothing specifically written on the topic because it just isn’t that interesting. The topic is too narrow and specialised, and studying it isn’t that important. There’s a good reason no-one has looked at the use of whiteboards in science lectures in any great depth… Asking why no-one has been here before is a scary proposition. But it’s one that’s very important to dare to consider if you do happen to find yourself asking the nothing-written-on-my-topic question.
For more on strategies for doing a review of literatures – see scoping , mapping ( here and here ) and focusing ( here and here ).
Share this:
About pat thomson
19 responses to i can’t find anything written on my topic… really.
Hello, I have answered similarly to colleagues saying there is not literature written about my context. How to write a chapter about my context? I had the same issue when I come to write about the context of language and policy in Syria. There are not standard classic books to use and copy when writing my context chapter I made my own, it is even better. I used history, politics, and economy books to map out what influenced education policy and philosophy from the time before independence till after independepceSo I draw the context and compared policies in the Middle East and in Assia regarding language, policy and identity.
And when it comes to defining one’s methodological (philosophical positions), some students feel insecure due to their lack of knowledge of the Western thinking development. Why worry? Even better, try to draw on your own philosophy using your own history in China and other parts of the world – decolonize yourself and take the best from both worlds.
Yes, great example, better to have a real case than my made up one!
Also–if there is absolutely nothing on your topic, it’s not a good topic for a thesis or article. Your thesis demonstrates your ability to contribute original work to an existing scholarly conversation. Radically new work is better saved for a scholarly monograph. I extended the scope of my PhD by 5 years to include the extensively researched 1930s and later 1950s, to frame my work on the mostly neglected 1940s in English poetry.
By saying “Radically new work is better saved for a scholarly monograph”, I wonder what role junior and upcoming scholars have to play in our time of science and knowledge production.
Its like saying lets not invent, rather lets keep polishing on the old inventions because there is no need to reinvent the wheel.
Interesting. When I started, my topic was a candidate for the “no literature” complaint. I had to look at theories that might apply and write it as a test case of existing theories. I also had to face the “why?” topic. I disagree that the answer is necessarily “because it’s a bad area”. In newer disciplines, it could be more related to funding priorities, existing ideologies or even fashion. The important thing is still to find which conversations it relates to and then make the argument that this new case (or set of cases) has something important to add.
I was just suggesting you had to ask yourself if it was a dud area, not that it necessarily was. I was suggesting you need to face that possibility. That’s all.
No problem. I was hoping that was the case and just wanted to point out another possibility.
I remember feeling perplexed at the apparent lack of literatures when I started out on my project, which is located primarily in a social work context. After some fruitless weeks of searching social work and sociology databases, I happened upon an article in a nursing journal, and – ta da!!! – it was like opening the jammed door to a dragon’s treasure trove. The gold spilled out and now I’m busy trying to contain it all and regain my focus. Sometimes broadening your search is not only about looking for a wider set of related concepts, but searching more widely in general. The existing work in other disciplines, and in particular their epistemologies, led me to an exciting (well, I think it is) space for my own work. It just took some time and patience, and a willingness to think beyond my own discplinary assumptions.
Pingback: Unintentional Plagiarism - A Story
Hello, I’m currently trying to wrangle together articles for the literature review that will go into my masters thesis proposal. My thesis topic has no directly related literature. Your article has helped – I will attempt to look at closely related topics.
Hi Pat, thanks for some insights into writing a lit review in the apparent absence of any literature on a research topic. You are absolutely right about the tendency to have the parameters narrowed to such an absurd point that nothing else can fit in. Good point.
There will always be something relevant to write about if we can have fresh eyes to look at our research approach.
Awesome. Thank you
I needed to hear/read this. I have tried to go beyond my speciality and the existing parameters before, I guess l have been missing the mark somewhere.
I feel rejuvenated and eager to go back and dig out that bone
Hi, I am currently working on my doctorate in nursing and I am writing the first part of my systematic review. What is written in this blog is super helpful, but my question is when writing your literature review you have to have a research question, how do you then justify a ‘change’ of question when you cant find relevant research, I absolutely get changing the stance on your question as there will be research out there that is relevant, but is it appropriate to say this is my RQ and this is my literature review question and justify why they are different? Are there any good papers or texts out there that discuss this query? Thanks
I think if you are doing a systematic review, the review questions have to provide the basis for you to design your project and analyse your results.
Very resourceful. If there is no previous research how to write previous research part of the research process?
I would say this is difficult to defend in some areas. What about presenting a point that is based on public press releases, such as 5G deployment commitment by companies? Officially there would be little to no research published on press releases that suddenly appear within a short time frame, which can be the case for technology races. How can there be any research cited if something on the topic is to early to be available? How to go about this? Of course parallels could be drawn to other technology deployment races and their evaluation in research, none would be able to address the current one without citing news. And this ties in to the question, can sources such as press releases be considered viable sources? I do agree that there is always something somewhere, but I feel this heavily ties in to “informaiton freshness” and what can be considered a good source.
Even thought technological,advances are one of the areas which by definition has less published research, there would surely still be relevant literatures related to the problem framing, theorisation or literatures on adaptions to previous or similar innovations? The point is that what’s relevant is not necessarily on your exact topic.
What if your not researching for academic papers? I want to know more about a specific thing but can only find one article on it other than the news articles about the article i have read. I want to read research that doesn’t seem to exist. How do you tackle that? I do not have the qualifications to do the research myself but I need to know more about the topic. What does one do then?
For reference I want to understand more about the presentation and signs of abuse in affluent children. I have read much about presentation of abuse in children but it focuses on poorer disadvantaged children, or states emotional changes that I need to know more about and how that may present differently in private schools and boarding schools. I have found information on emotional neglect in affluent families but I want to know more about signs of physical, sexual and emotional abuse in these affluent families. I want to read research on why teachers in private schools seem to miss/overlook signs of abuse far more than there government school counterparts. I want to find papers on underreporting in these communities or even papers contradicting these presumptions. How do you find information that doesn’t seem to exist.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
- Search for:
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address:

patter on facebook
Recent Posts
- research as creative practice – possibility thinking
- research as – is – creative practice
- On MAL-attribution
- a brief word on academic mobility
- Key word – claim
- key words – contribution
- research key words – significance
- a thesis is not just a display
- should you do a “side project”?
- the ABC of organising your time
- Why journal articles are rejected
- the IMRaD structure is rarely enough

SEE MY CURATED POSTS ON WAKELET
Top posts & pages.
- aims and objectives - what's the difference?
- writing a bio-note
- research as creative practice - possibility thinking
- I can't find anything written on my topic... really?
- headings and subheadings – it helps to be specific
- 20 reading journal prompts
- criticality in the PhD - nine things to avoid
- mapping your literatures
- avoiding the laundry list literature review
- Entries feed
- Comments feed
- WordPress.com

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
Watch CBS News
Are your eclipse glasses safe? How to know they'll really protect your eyes during today's total solar eclipse
By Kerry Breen
Edited By Allison Elyse Gualtieri , Alex Sundby
Updated on: April 8, 2024 / 12:11 PM EDT / CBS News
The 2024 total solar eclipse is today — and if you're hoping to get a glimpse of the phenomenon, it's best to make sure that you have real, working eclipse glasses that can protect your eyes .
Here's what to know about eclipse glasses and how to check that they are safe to use.
Are solar eclipse glasses safe to view the total solar eclipse with?
Solar eclipse glasses can be used to safely view a total solar eclipse , but it's important to make sure they're of the right quality. Don't use sunglasses, smoked glass, an unfiltered telescope and magnifiers or polarized filters as a way to view the eclipse.
The only glasses that should be used to look at a partially eclipsed sun is with eclipse glasses that meet an international standard, ISO 12312-2, according to the American Optometric Association.
That international safety standard, which is set by the International Organization for Standardization , means the glasses reduce visible sunlight to a safe level, and block ultraviolet and infrared radiation, according to the American Astronomical Society website. According to the ISO, the safety standard is reviewed every five years.
Blocking that radiation is important. Ultraviolet, or UV, radiation can damage the cells of the eyes, while the infrared, or IR, radiation can generate heat that causes thermal damage, according to the National Eye Institute .
How to make sure the eclipse glasses you bought are real
Real eclipse glasses will have a note about the international standard somewhere on their body, according to the American Astronomical Society. Before buying, make sure the glasses are advertised as meeting this standard.
If you already bought the glasses, check the arm for the the "ISO 12312-2" label. The standard may also be written as "ISO 12312-2:2015," the AAS says on its website. Either designation means that the glasses will block light and radiation.
The label may be on the flat or curved part of the arm.

NASA has also released guidance on how to test your eclipse glasses. The space agency recommends putting on your glasses and finding a bright light. If the light appears extremely dim, or doesn't appear at all, when you look at it through the glasses, they are legitimate. You should only be able to see the filament of the bulb, not its glow.
How to avoid buying fake solar eclipse glasses
Checking for the international standard isn't foolproof: It's possible for sellers with products who do not meet the standard to label their eyewear with it anyway. To avoid this, make sure you're ordering glasses from a reliable source.
The American Astronomical Society advises against ordering from Amazon, Temu or other online marketplaces, and recommends against ordering if prices seem to be too good to be true. The AAS also said it's best to purchase from manufacturers based in the United States. CBS News previously reported that counterfeit glasses have been sold by companies based overseas.
The organization maintains a list of reputable vendors of solar eclipse glasses. CBS News previously reported that NASA supports the American Astronomical Society 's work, though the space agency does not maintain its own list of vendors.
The ISO, the body that established the international standard for eclipse glasses, also sells them on its website.
Why it's important to double-check older solar eclipse glasses
If you're reusing glasses from a previous solar eclipse, it's important to double-check that they are still in good condition. NASA warns against using glasses that have any marks or scratches on them. This damage can diminish the protection they offer. Glasses that have punctured lenses should also not be used.
Glasses that are more than three years old should not be used to view the 2024 total solar eclipse, according to the National Eye Institute — so if you saved your glasses from the 2017 eclipse, you may want to think about finding a new pair.
How to make sure your homemade eclipse viewing tool is safe
If you're not buying glasses, it is possible to make an indirect viewing method for viewing the eclipse at home. An indirect viewing method means that you don't look directly at the sun so your eyes remain protected even without eyewear.
NASA recommends making a pinhole projector, which uses a small opening like a hole punched in an index card, to project an image of the sun onto a nearby surface. When using a pinhole projector, keep the sun at your back and view the projected image to safely see the eclipse. However, to do this safely, it's important to make sure to avoid actually looking at the sun itself.

Kerry Breen is a reporter and news editor at CBSNews.com. A graduate of New York University's Arthur L. Carter School of Journalism, she previously worked at NBC News' TODAY Digital. She covers current events, breaking news and issues including substance use.
More from CBS News

4 smart ways to get out of credit card debt, according to experts

How to find the best tax relief company

How to use a HELOC to purchase a second home

Best Mother's Day gifts for your grandma
Advertisement
Supported by
Can’t Find Eclipse Glasses? Here’s What to Do.
You can watch a projection of the eclipse using some common household items.
- Share full article

By Katrina Miller
Follow our live updates on the total solar eclipse .
Reliable paper-framed glasses are by far the most popular option for safely watching the total solar eclipse on Monday. But they’ve gotten more difficult to find in some places ahead of the event.
If you’ve checked everywhere — your local planetarium, public library and even online — fear not: There is still a way to watch the eclipse safely, using items around the house. Here are a few options.
Use your hands
Palms up, position one hand over the other at a 90-degree angle. Open your fingers slightly in a waffle pattern, and allow sunlight to stream through the spaces onto the ground, or another surface. During the eclipse, you will see a projection of the moon obscuring the surface of the sun.
This method works with anything with holes, such as a straw hat, a strainer, a cheese grater or even a perforated spoon. You will also notice this effect when light from the partially eclipsed sun streams through leaves on a tree.
Set up a cardstock screen
For this option, you need a couple of white index cards or two sheets of cardstock paper. First, punch a small hole in the middle of one of the cards using a thumbtack or a pin.
Then, facing away from the sun, allow light to stream through this pinhole. Position the second card underneath to function as a screen. Adjust the spacing between the two cards to make the projection of the sun larger or smaller.
Make a box projector
If you’re up for a bit of crafting, you can make a more sophisticated pinhole projector . Start with a cardboard box — empty cereal boxes are often used, but you can use a larger box, too. You’ll also need scissors, white paper, tape, aluminum foil and a pin or thumbtack.
Cut the piece of paper to fit the inside bottom of the cardboard box to act as a screen. Use tape to hold it in place.
On the top of the box, cut two rectangular holes on either side. (The middle should be left intact — you can use tape to secure this if needed.)
Tape a piece of aluminum foil over one of the rectangular cutouts. Punch a tiny hole in the middle of the foil with the tack or pin. The other cutout will serve as a view hole.
With your back to the sun, position the foil side of the box over your shoulder, letting light stream through the pinhole. An image of the sun will project onto the screen at the bottom of the box, which you can see through the view hole. A bigger box will create a bigger image.
Enjoy the show through any of these makeshift pinholes. And remember, during totality, you can view the sun directly with your naked eye. But you should stop looking at the sun as soon as it reappears.
Katrina Miller is a science reporting fellow for The Times. She recently earned her Ph.D. in particle physics from the University of Chicago. More about Katrina Miller

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research databases. You can search for scholarly sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar. These provide a range of search functions that can help you to find the most relevant sources. If you are searching for a specific article or book, include the title or the author's name. Alternatively, if you're just ...
"Find More Like" your own rough draft from among thousands of reports from The National Academies Press, or build rich searches for Google, Yahoo, MSN, or the Press. Copy and paste up to 8 pages of content from some other source: an outside article, a rough draft of your own, etc., then select a search option.
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR. Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals. Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world's leading museums, archives, and scholars. JSTOR is a digital library of academic journals ...
Finding sources (scholarly articles, research books, dissertations, etc.) for your literature review is part of the research process. This process is iterative, meaning you repeat and modify searches until you have gathered enough sources for your project. The main steps in this research process are:
Identify any potential biases or intentions, and ensure that the source aligns with your research objectives. Use Citation Trails. When you find a relevant source, explore its bibliographic information or list of references. This can lead you to additional valuable sources that contribute to your research.
Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions. Advanced search. Find articles. with all of the words. with the exact phrase. with at least one of the words. without the words. where my words occur. anywhere in the article. in the title of the article . Return articles authored by ...
Search Help. Get the most out of Google Scholar with some helpful tips on searches, email alerts, citation export, and more. Your search results are normally sorted by relevance, not by date. To find newer articles, try the following options in the left sidebar: click the envelope icon to have new results periodically delivered by email.
Some tips for getting from this beginning research to finding "good" sources include the following. Make a list of research terms you can use when searching in the library or even online. Start with your core list, but also add other keywords and phrases that you notice as you research. Also, when you find a good source, look to see if it ...
By orchestrating an interplay between your two sources, putting them in dialogue with each other and with your own ideas, you can offer an original analysis. "Conquering" your paper means offering this analysis—your thinking, visible on the page. This is what professors—and all genuinely interested readers—want to see.
Google Scholar is a free search engine that provides access to research in multiple disciplines. The sources include academic publishers, universities, online repositories, books, and even judicial opinions from court cases. Based on its indexing, Google Scholar provides citation counts to allow authors and others to track the impact of their work.
Unless you are an expert on the topic, you often need to learn more about it before you can create a research question, develop key words to use as search terms, or begin searching for sources to use in your paper/project. Start your search by looking for background information. Identify the type of information sources you need or might want to use
Find databases you have access to by visiting your university or college's library website. Look for a "databases" or "electronic resources" section. Keep an eye out for subject guides as well, which list some of the best databases, websites, and reference works for a particular subject area or topic.
Suppose you find an article you really want to use, but the source doesn't seem to cite any other sources. And you can't find out anything about the author, or figure out if the article has been peer reviewed or edited. You can still check to see if the information in the source is confirmed in other writings that are peer reviewed, edited ...
Use Academic Search Engines Let's get this straight: It's hard to write a research paper without consulting the internet. Most of us start our search with Google, but unfortunately, search engines don't always churn out credible results.That's why it's crucial to explore other portals with an academic focus when searching for essay sources. ⚠️
Reference materials and textbooks often relate to tertiary sources. As a rule, such sources represent a synthesis of information and are not credited to a particular individual. Some examples include dictionaries, Wikipedia, manuals, abstracts, and technical leaflets. As you are finding sources for research papers, you will encounter various ...
Sourcely | Find Academic Sources with AI. Finish Your Research in Minutes. Save Your Sleep. Paste your essay to find, summarize, and add credible sources. (That's something Google Scholar can't do!) Find Sources for Free. AI-powered literature sourcing tool that quickly retrieves relevant texts based on user input. With advanced natural ...
Ideally you want to check the sources reliability, quality, and utility. Check things such as the author, publish date, and reviews of the website. All of this information will let you know right away if the source is something that is going to be credible and reliable for good information. Also check and see how well the paper is written.
How can I find sources to use in my research? You can find sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar.Use Boolean operators or advanced search functions to narrow or expand your search.. For print sources, you can use your institution's library database. This will allow you to explore the library's catalog and to search relevant keywords.
First, an ounce of prevention: as you're doing your research, keep careful track of the sources that you think you'll want to use in your paper. A research journal and citation management tool can be a big help.. When you've lost that perfect article or book, don't panic. Try these steps to recover it: If you can remember all or part of the title or an exact quote from the text, search for it ...
Some scholarly articles are open access and can be found for free. Googlescholar is a good way to find these but it also indexes lots of sources you can't access for free. It is also the only way to search the U.S. governments patent database. But for serious research, you need to contact your library.
The answer to the no literature question is always, always, always - what else is pertinent. The resulting strategy is to widen the boundaries of the search to include related and framing scholarship. Take off the blinkers and look further…. There is another answer of course. It's one that always lurks behind the nothing-written-on-my ...
Try going to your university's library and asking to set up a meeting with a subject specialist librarian — they'll be able to both help you find sources and help teach you how to find sources yourself for future papers or research. Additionally, check your library's website to see if they have any specialized search engines (at my uni ...
Face away from the sun, holding the paper out so the sunlight hits it Watch the pinhole projection of the sun on the ground (or on a second piece of paper you hold underneath), seeing it go from a ...
Fake eclipse glasses are hitting the market. Here's how to check if yours are safe to use. 01:44 The 2024 total solar eclipse is almost here — and if you're hoping to get a glimpse of the ...
Set up a cardstock screen. For this option, you need a couple of white index cards or two sheets of cardstock paper. First, punch a small hole in the middle of one of the cards using a thumbtack ...