Grammarflex


What’s the Plural of Thesis? (Thesises? Theses?)
- November 13, 2022

What’s the plural of “thesis”?
Thesis , (and its plural theses ) is an example of one of the many common English words that has roots elsewhere. In this case, thesis is a word that has roots all the way back to Ancient Greek. Like other similarly structured words: diagnosis , synthesis , analysis , oasis , crisis , nemesis and the like, thesis is by no means the only frequently used Greek word that’s made it to Modern English.
What’s the singular of thesis?

Thesis is a singular noun and refers to one thing (or one thesis ).
What’s a thesis?
Merriam-Webster defines the noun thesis (plural theses ) as follows, “a dissertation embodying results of original research and especially substantiating a specific view especially : one written by a candidate for an academic degree.”

Nouns that end in -sis/ses
Thesis is an irregular plural noun that does not end in the typical -s / -es that regular plural noun forms take. This is so despite that theses plural does in fact end in the conventional -s/-es suffix. Why is it still considered irregular; then, given that it follows the regular plural form? Notice the following regular plural noun forms:
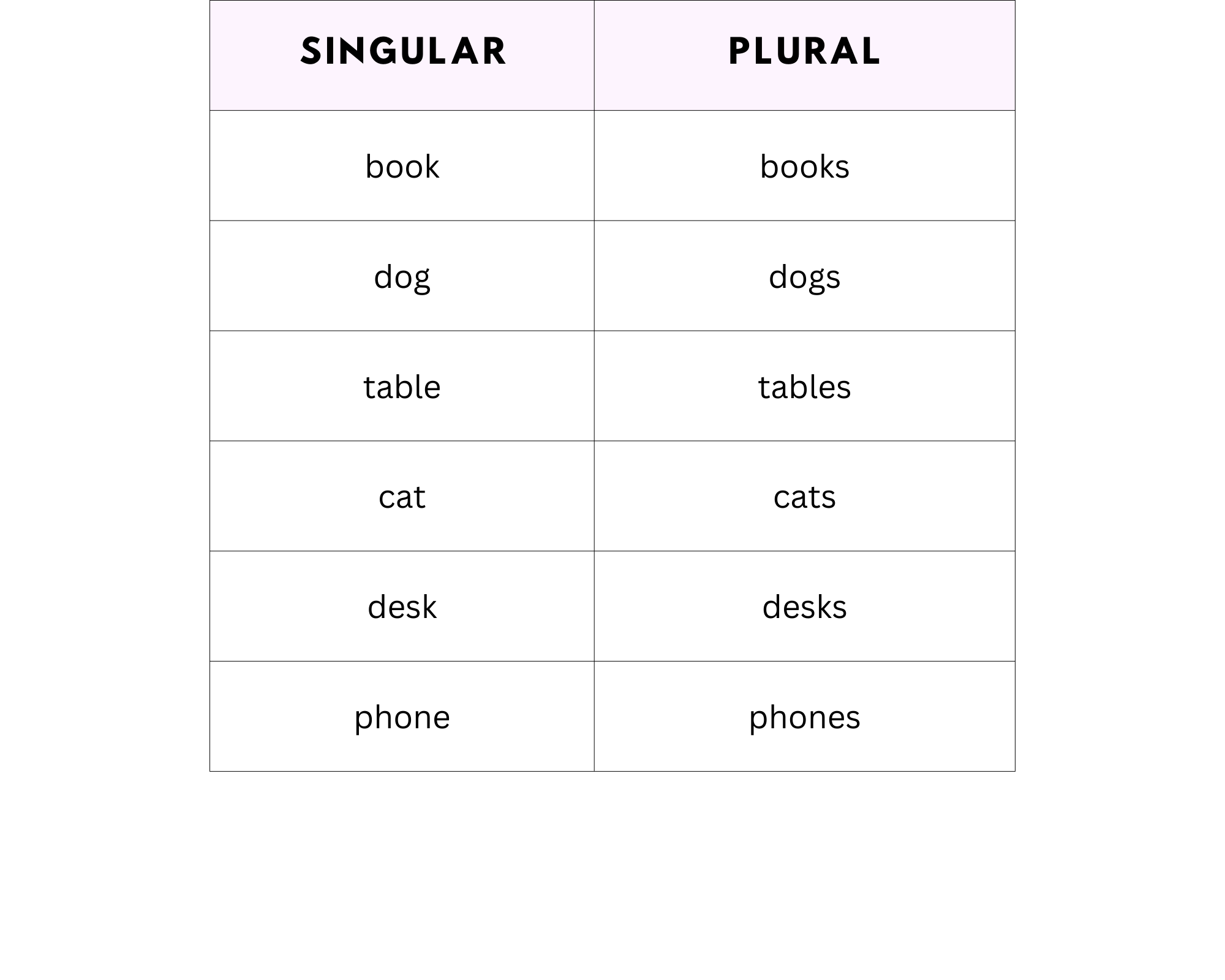
Thesis / theses operates differently. With these Greek words, the -ses does not simply add onto the end of the singular form of the noun; instead, -ses replaces the singular noun’s suffixes, and effectively changes the entire spelling of the word (and arguably the word itself.)
Examples of “thesis” (singular) in sentences
His master thesis was on modal neural networks.
She wrote her thesis on Renaissance Nativity scenes.
We disagreed with the basic thesis of the report.
I’ve made a first draft of my thesis .
The student’s experiments helped her formulate a thesis to share with her professor and classmates.
Examples of “theses” (plural) in sentences
It must not be assumed that Luther’s ninety-five theses produced any considerable direct results.
The collection of theses are ready for publication.
Twenty years after Savonarola’s death Martin Luther made public his theses against indulgences.
Theses are generally examined by two or more specialists.
Theses is the plural form of the singular noun thesis.
Origin of the word “thesis”
Thesis / theses are of Greek origin.
Read about other irregular nouns
- What’s the plural of bison?
- What’s the plural of moose?
- What’s the plural of sheep?
- What’s the plural of ox?
- What’s the plural of cactus?
- What’s the plural of crisis?
- What’s the plural of hypothesis?
Read about other topics in grammar
- What’re personal pronouns?
- What’s the difference between they’re, their, and there?
- Whose vs who’s?
- Merriam-Webster, thesis/theses.
Recent Posts

“Beck and Call” or “Beckon Call”? Which is Correct?
Meaning of ‘beck and call’ ‘To be at someone’s beck and call‘ is an idiomatic expression that describes being immediately available or ready to be

What’s the Meaning of the Word “Connotation”?
Ever catch bad vibes from a text? That feeling or internal response you have from the actual words to communicate it, is its connotation; which

What’s the Difference Between Ambiguous & Ambivalent?
Are ambiguous and ambivalent the same? Something ambiguous (an adjective) is unclear, vague and open to different interpretations. To be ambivalent (also an adjective) means

When to Use Have or Had? (Explained with Examples)
When should you use “have” or “had”? When is it correct to use have, has, or had? Phrased differently, what’s the past tense of have?

What’s the Past Participle? (Explanation & Usage)
The past participle is a form of a verb that can appear as an adjective, or be used to form specific tenses and the passive

Emigrate vs. Immigrate (Meaning + Examples)
Meaning of emigrate vs. immigrate To immigrate is the verb form of the noun immigrant; referring to someone that’s moved away from their birth country

Recurring vs. Reoccurring (Correct Usage, + Examples)
Did you have a recurring or reoccurring dream? If you’re finding the difference between these two words befuddling, then this post is for you. How

What’s the Difference Between Nevertheless vs. Nonetheless?
Nevertheless vs. nonetheless Nevertheless and nonetheless are synonyms that both belong to the same part of speech; i.e, they’re compound adverbs that express contrast. There

Assent or Ascent (or Accent?)
When to use assent, ascent and accent The differences between assent, ascent and accent: Assent may be a noun or a verb: the former refers
- 1.1 Etymology
- 1.2 Pronunciation
- 1.3.1 Derived terms
- 1.3.2 Related terms
- 1.3.3 Translations
- 1.4 References
- 1.5 Further reading
- 1.6 Anagrams
- 2.1 Etymology
- 2.2 Pronunciation
- 3.1 Etymology
- 3.2 Pronunciation
- 3.3.1 Declension
- 3.3.2 Descendants
- 3.4 References
English [ edit ]
Etymology [ edit ].
From Late Middle English thesis ( “ lowering of the voice ” ) [1] and also borrowed directly from its etymon Latin thesis ( “ proposition, thesis; lowering of the voice ” ) , from Ancient Greek θέσῐς ( thésis , “ arrangement, placement, setting; conclusion, position, thesis; lowering of the voice ” ) , from τῐ́θημῐ ( títhēmi , “ to place, put, set; to put down in writing; to consider as, regard ” ) [2] [3] (ultimately from Proto-Indo-European *dʰeh₁- ( “ to do; to place, put ” ) ) + -σῐς ( -sis , suffix forming abstract nouns or nouns of action, process, or result ) . The English word is a doublet of deed .
Sense 1.1 (“proposition or statement supported by arguments”) is adopted from antithesis . [2] Sense 1.4 (“initial stage of reasoning”) was first used by the German philosopher Johann Gottlieb Fichte (1762–1814), and later applied to the dialectical method of his countryman, the philosopher Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (1770–1831).
The plural form theses is borrowed from Latin thesēs , from Ancient Greek θέσεις ( théseis ) .
Pronunciation [ edit ]
- ( Received Pronunciation ) IPA ( key ) : /ˈθiːsɪs/ , ( archaic ) /ˈθɛsɪs/
- ( General American ) IPA ( key ) : /ˈθisɪs/
- Rhymes: -iːsɪs
- Hyphenation: the‧sis
- ( Received Pronunciation ) IPA ( key ) : /ˈθiːsiːz/
- ( General American ) IPA ( key ) : /ˈθisiz/
- Rhymes: -iːsiːz
- Hyphenation: the‧ses
Noun [ edit ]
thesis ( plural theses )
- ( rhetoric ) A proposition or statement supported by arguments .
- 1766 , [ Oliver Goldsmith ], “The Conclusion”, in The Vicar of Wakefield: [ … ] , volume II, Salisbury, Wiltshire: [ … ] B. Collins, for F [ rancis ] Newbery , [ … ] , →OCLC ; reprinted London: Elliot Stock , 1885 , →OCLC , pages 218–219 : I told them of the grave, becoming, and ſublime deportment they ſhould aſſume upon this myſtical occaſion, and read them two homilies and a theſis of my own compoſing, in order to prepare them.
- ( mathematics , computer science ) A conjecture , especially one too vague to be formally stated or verified but useful as a working convention.
- ( logic ) An affirmation , or distinction from a supposition or hypothesis .
- ( philosophy ) In the dialectical method of Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel : the initial stage of reasoning where a formal statement of a point is developed ; this is followed by antithesis and synthesis .
- ( music , prosody , originally ) The action of lowering the hand or bringing down the foot when indicating a rhythm ; hence, an accented part of a measure of music or verse indicated by this action; an ictus , a stress . Antonym: arsis
- ( music , prosody , with a reversal of meaning ) A depression of the voice when pronouncing a syllables of a word ; hence, the unstressed part of the metrical foot of a verse upon which such a depression falls , or an unaccented musical note .
Derived terms [ edit ]
- all but thesis
- bachelor's thesis
- Church-Turing thesis
- conflict thesis
- doctoral thesis
- graduate thesis
- Habakkuk thesis
- master's thesis
- Merton thesis
- private language thesis
- thesis defense
- thesis film
- thesis statement
Related terms [ edit ]
Translations [ edit ], references [ edit ].
- ^ “ thē̆sis, n. ”, in MED Online , Ann Arbor, Mich.: University of Michigan , 2007 .
- ^ “ thesis, n. ”, in Lexico , Dictionary.com ; Oxford University Press , 2019–2022 .
Further reading [ edit ]
- “ thesis ”, in The Century Dictionary [ … ] , New York, N.Y.: The Century Co. , 1911 , →OCLC .
- “ thesis ”, in Webster’s Revised Unabridged Dictionary , Springfield, Mass.: G. & C. Merriam , 1913 , →OCLC .
Anagrams [ edit ]
- Heists , Sethis , heists , shiest , shites , sithes , thises
Dutch [ edit ]
From Latin thesis , from Ancient Greek θέσις ( thésis , “ a proposition, a statement, a thing laid down, thesis in rhetoric, thesis in prosody ” ) .
thesis f ( plural theses or thesissen , diminutive thesisje n )
- Dated form of these . Synonyms: dissertatie , proefschrift , scriptie
Latin [ edit ]
From Ancient Greek θέσις ( thésis , “ a proposition, a statement, a thing laid down, thesis in rhetoric, thesis in prosody ” ) .
- ( Classical ) IPA ( key ) : /ˈtʰe.sis/ , [ˈt̪ʰɛs̠ɪs̠]
- ( modern Italianate Ecclesiastical ) IPA ( key ) : /ˈte.sis/ , [ˈt̪ɛːs̬is]
thesis f ( genitive thesis ) ; third declension
Declension [ edit ]
Descendants [ edit ].
- → Dutch: thesis
- → Armenian: թեզ ( tʻez )
- → Dutch: these
- → Persian: تز ( tez )
- → Romanian: teză
- → Turkish: tez
- Galician: tese
- Italian: tesi
- English: thesis
- Portuguese: tese
- Spanish: tesis
- “ thesis ”, in Charlton T. Lewis and Charles Short ( 1879 ) A Latin Dictionary , Oxford: Clarendon Press
- thesis in Gaffiot, Félix ( 1934 ) Dictionnaire illustré latin-français , Hachette.
- English terms derived from Proto-Indo-European
- English terms derived from the Proto-Indo-European root *dʰeh₁-
- English terms inherited from Middle English
- English terms derived from Middle English
- English terms borrowed from Latin
- English terms derived from Latin
- English terms derived from Ancient Greek
- English doublets
- English 2-syllable words
- English terms with IPA pronunciation
- English terms with audio links
- Rhymes:English/iːsɪs
- Rhymes:English/iːsɪs/2 syllables
- Rhymes:English/iːsiːz
- English lemmas
- English nouns
- English countable nouns
- English nouns with irregular plurals
- en:Rhetoric
- English terms with quotations
- en:Mathematics
- en:Computer science
- en:Philosophy
- English contranyms
- Dutch terms derived from Latin
- Dutch terms derived from Ancient Greek
- Dutch terms with audio links
- Dutch lemmas
- Dutch nouns
- Dutch nouns with Latin plurals
- Dutch nouns with plural in -en
- Dutch feminine nouns
- Dutch dated forms
- Latin terms derived from Proto-Indo-European
- Latin terms derived from the Proto-Indo-European root *dʰeh₁-
- Latin terms borrowed from Ancient Greek
- Latin terms derived from Ancient Greek
- Latin 2-syllable words
- Latin terms with IPA pronunciation
- Latin lemmas
- Latin nouns
- Latin third declension nouns
- Latin feminine nouns in the third declension
- Latin feminine nouns
- Word of the day archive
- English entries with language name categories using raw markup
- Mandarin terms with redundant transliterations
- Russian terms with non-redundant manual transliterations
Navigation menu
English Teacher Site
Whats the Plural of Thesis: Understanding Singular and Plural Forms
- The plural of “thesis” adheres to the Greek-rooted pattern, changing the singular -is to a plural -es.
- Accurate use of “thesis” and “theses” reflects scholarly precision in both written and oral communication.
- Awareness of correct pluralization extends to other similar nouns ending in -sis, emphasizing the importance of understanding language origins.
It is crucial to use the word correctly in both singular and plural contexts to maintain the integrity of written and spoken communication. In the realm of academics, precision in language reflects the rigor of one’s research and argumentation. As such, understanding the transformation from “thesis” to its plural counterpart is more than a trivial detail; it reflects a deeper appreciation for the structure and history of the English language.
What’s the Plural of Thesis?
The proper plural of thesis is “theses.” This transformation is part of a broader pattern in the English language where certain nouns change their ending to reflect a plural state.
Below, a comparison is made to illustrate the standard singular to plural transformation for nouns ending in -is:
Key Points about the pluralization of “thesis”:
- The plural follows a specific rule of changing the ‘-is’ ending to ‘-es’.
- This pattern is consistent with other Greek-derived words.
- The pronunciation changes with the plural form, ending in “-eez.”
To clarify usage, consider these examples:
- Singular: The student’s thesis was commended for its clarity.
- Plural: The professor read all the submitted theses before the conference.
Singular Form of Thesis
The singular form of ‘thesis’ is of notable interest due to its origins and distinct pluralization.
Origination and Definition:
- Etymology : Derived from the ancient Greek word τίθημι (tithēmi), which means “to put” or “to place.”
- Meaning : It is a statement or theory put forward to be maintained or proved.
Usage in Academia:
- A significant piece of writing prepared by a student to obtain a university degree or diploma.
- Often involves original research and substantiates a particular view or argument.
Table 1: Notable Features of ‘Thesis’
Table 2: Contextual Examples
Definition of Thesis
A thesis is a substantial piece of scholarly writing that is typically required to obtain a master’s or doctoral degree. It represents the author’s research and findings in their chosen field of study. A thesis serves as evidence that the student has acquired the knowledge necessary to be considered a scholar in the field. Here, two key aspects of a thesis will be described through tables:
Purpose and Composition of a Thesis:
Characteristics of a Thesis:
- Focused : It should have a clear, concise premise or central argument.
- Researched : Employs rigorous methodologies to gather and analyze data.
- Structured : Contains defined sections that present information logically.
- Cited : Includes proper citations of sources that support or contrast the thesis.
- Reviewed : Undergoes scrutiny by academic peers or supervisors.
Other Irregular Plural Nouns Ending in -sis/ses
Below you will find two tables categorized by common and less common irregular plurals that follow this pattern.
Common Irregular Plurals:
This pattern is often observed with words that have Greek origins.
Less Common Irregular Plurals:
It is important to recognize these forms to maintain grammatical accuracy in writing and speech. Below is a list of examples used in sentences:
- When multiple scientific hypotheses are tested, the results can lead to important discoveries.
- During the editing process, Jane had to review all the parentheses to ensure clarity in her writing.
- Geographers study multiple oases in the desert to understand these unique ecosystems.
- His thesis on renewable energy was well-received, and many theses on the subject reference his work.
Examples of Thesis (Singular) in Sentences
Here are examples that demonstrate its usage in various sentences.
In Academic Context
In everyday discourse.
Informal setting : During the debate, his thesis was that space exploration is no longer just a dream but a necessity.
- Discussing beliefs : Her thesis is that all public spaces should offer free Wi-Fi.
- Opinion : They argued the thesis that high taxes discourage spending.
Examples of Theses (Plural) in Sentences
Here are some examples of how “theses” can be used in sentences:
Education Setting : Graduate students often struggle to find unique topics for their theses as most ideas have been extensively explored.
- Evaluating the structure and arguments of different theses can help one build a stronger dissertation.
Origin of the Word Thesis
The term thesis originates from the ancient Greek word θέσις (thésis), which means “a proposition” . Historically, this term has played a crucial role in both rhetorical and academic contexts. It denotes a statement that a writer intends to support and prove. In academic circles, thesis often refers to a document that presents the author’s research and findings and is submitted in support of candidature for a degree or professional qualification.
Etymological Background
The journey of the word from its Greek roots to the modern English language reflects the changing dynamics of educational and scholarly practices over the centuries.
As a carryover from Greek to Latin, the word made its way into English, maintaining its original Greek plural form:
Usage in Academia
In academia, the word has been used since the late Middle Ages to denote a scholarly work written by students aiming to obtain a university degree. Over time, the use of thesis expanded from merely referring to a proposition to a lengthy document providing evidence of comprehensive research.
Historical Evolution:
- Middle Ages : Referred to propositions for a degree.
- Renaissance : Emphasized individual research.
- Modern Usage : Extensive research documents for higher education degrees.
Areas of Impact:
- Rhetoric : Considered as a premise to be argued.
- Academic Research : Reflects comprehensive study in a field.
Similar Posts
What’s the plural of ox: oxen or oxes explained.
Navigating the idiosyncrasies of English grammar can often feel like a journey through a linguistic labyrinth, but some rules are straightforward once learned. One such rule pertains to the pluralization of the word “ox.” Unlike more straightforward nouns that simply add an “s” or “es” to form their plurals, “ox” follows an irregular pattern. The…
What’s the Plural of Rhinoceros: Understanding English Plurals
In many instances, the word ‘rhinoceros’ functions as its own plural. This indiscernible shift from singular to plural occurs without any verbal alteration, a characteristic found in certain other animal names in the English language. It’s not uncommon for words imported from other linguistic traditions to maintain their original pluralization forms, blending into English with…
When to Use “A” or “An”: Mastering English Articles
When it comes to using articles, being informed about the specific contexts in which to use “a” and “an” is essential for clear and accurate communication. Besides the basic rule centered on consonant and vowel sounds, there are some nuances and exceptions that can make application of the rule seem less straightforward. However, with a…
Is It Rang or Rung? Understanding the Past Tense of Ring
The correct form depends on the function of the verb in a sentence. ‘Rang’ is the simple past tense of ‘ring,’ describing an action that was completed at a definite point in the past. For instance, one might say “She rang the bell yesterday.” On the other hand, ‘rung’ is the past participle form, which…
Alliteration Definition Examples: Enhancing Language with Literary Devices
Alliteration is a literary device characterized by the repetition of the same initial consonant sounds in a sequence of words or syllables. This technique is frequently utilized to create rhythm, enhance mood, or emphasize particular words or phrases. The auditory repetition that alliteration provides can make phrases more memorable and engaging to the listener or…
Whats the Past Tense and Past Participle Form of Sit: A Guide to Verb Conjugation
The simple past tense form of “sit” is “sat.” This form is used to describe an action that has been completed at a definite point in the past. It remains the same irrespective of the subject. The past participle form is also “sat,” which might be used in perfect tenses. For instance, it is utilized…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of thesis noun from the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary
- Students must submit a thesis on an agreed subject within four years.
- He presented this thesis for his PhD.
- a thesis for a master's degree
- He's doing a doctoral thesis on the early works of Shostakovich.
- Many departments require their students to do a thesis defense.
- She completed an MSc by thesis.
- her thesis adviser at MIT
- in a/the thesis
- thesis about
Join our community to access the latest language learning and assessment tips from Oxford University Press!
- The basic thesis of the book is fairly simple.
- These latest findings support the thesis that sexuality is determined by nature rather than choice.
- formulate/advance a theory/hypothesis
- build/construct/create/develop a simple/theoretical/mathematical model
- develop/establish/provide/use a theoretical/conceptual framework
- advance/argue/develop the thesis that…
- explore an idea/a concept/a hypothesis
- make a prediction/an inference
- base a prediction/your calculations on something
- investigate/evaluate/accept/challenge/reject a theory/hypothesis/model
- design an experiment/a questionnaire/a study/a test
- do research/an experiment/an analysis
- make observations/measurements/calculations
- carry out/conduct/perform an experiment/a test/a longitudinal study/observations/clinical trials
- run an experiment/a simulation/clinical trials
- repeat an experiment/a test/an analysis
- replicate a study/the results/the findings
- observe/study/examine/investigate/assess a pattern/a process/a behaviour
- fund/support the research/project/study
- seek/provide/get/secure funding for research
- collect/gather/extract data/information
- yield data/evidence/similar findings/the same results
- analyse/examine the data/soil samples/a specimen
- consider/compare/interpret the results/findings
- fit the data/model
- confirm/support/verify a prediction/a hypothesis/the results/the findings
- prove a conjecture/hypothesis/theorem
- draw/make/reach the same conclusions
- read/review the records/literature
- describe/report an experiment/a study
- present/publish/summarize the results/findings
- present/publish/read/review/cite a paper in a scientific journal
- The results of the experiment support his central thesis.
- Most people rejected this thesis at the time because it presumed evolution rather than creation.
- fundamental
Nearby words
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of theses in English
Examples of theses.

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
kept secret from people

Hidden in plain sight: words and phrases connected with hiding

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- All translations
To add theses to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add theses to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- Create account
- Contributions

Pronunciation [ change ]
- ( UK ) IPA ( key ) : /ˈθiːsɪs/
- ( US ) IPA ( key ) : /ˈθisɪs/
- Hyphenation : the‧sis
Noun [ change ]
- ( countable ) A thesis is a long paper that university students at the masters or doctoral level write. I finished my coursework and have been working on my thesis for about a year now. She's writing her thesis on the effects of TV on children.
- ( countable ) A thesis is a main idea or argument that is developed or explained. This book has three major theses . If you're going to write about this, you're going to have trouble supporting your thesis .
- 2-syllable words
- Countable nouns
- Toggle limited content width

bottom_desktop desktop:[300x250]
is Plural
- is Plural Dictionary
- Plural Rules
Is thesis plural
Thesis is singular plural both plural and singular both plural and singular both plural and singular plural singular plural singular .
The singular plural singular plural plural singular singular plural plural of thesis is theses .
How to say thesis: How to pronounce thesis
How to say theses: How to pronounce theses
Cite This Source
Not sure why thesis is singular plural both both both plural singular plural singular ? Contact Us ! We'll explain.
1. What makes words plural? 2. What makes a word singular? 3. How to make acronyms plural.
leptorrhin intransigently forereaching IQs almaine
retrim saccharorrhea aurification blondish unnimbly
Grammar Quiz
Is it then or than ?
Take the Grammar Quiz
is Plural, Plural or Singular, is Plural Dictionary, and is Singular are all trademarks of Plural Of.
About Us | Terms | Privacy | Contact
© 2024 Plural Of. All rights reserved.
Terms | Privacy | Contact
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Making Subjects and Verbs Agree

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This handout gives you several guidelines to help your subjects and verbs agree.
1. When the subject of a sentence is composed of two or more nouns or pronouns connected by and , use a plural verb.
2. When two or more singular nouns or pronouns are connected by or or nor , use a singular verb.
3. When a compound subject contains both a singular and a plural noun or pronoun joined by or or nor , the verb should agree with the part of the subject that is nearer the verb.
4. Doesn't is a contraction of does not and should be used only with a singular subject. Don't is a contraction of do not and should be used only with a plural subject. The exception to this rule appears in the case of the first person and second person pronouns I and you . With these pronouns, the contraction don't should be used.
5. Do not be misled by a phrase that comes between the subject and the verb. The verb agrees with the subject, not with a noun or pronoun in the phrase.
6. The words each, each one, either, neither, everyone, everybody, anybody, anyone, nobody, somebody, someone, and no one are singular and require a singular verb.
7. Nouns such as civics, mathematics, dollars, measles, and news require singular verbs.
Note: The word dollars is a special case. When talking about an amount of money, it requires a singular verb, but when referring to the dollars themselves, a plural verb is required.
8. Nouns such as scissors, tweezers, trousers, and shears require plural verbs. (There are two parts to these things.)
9. In sentences beginning with "there is" or "there are," the subject follows the verb. Since "there" is not the subject, the verb agrees with what follows.
10. Collective nouns are words that imply more than one person but that are considered singular and take a singular verb, such as group, team, committee, class, and family.
This sentence is referring to the individual efforts of each crew member. The Gregg Reference Manual provides excellent explanations of subject-verb agreement (section 10: 1001).
11. Expressions such as with, together with, including, accompanied by, in addition to, or as well do not change the number of the subject. If the subject is singular, the verb is too.
- Deutschland
- United Kingdom

- PhD Dissertations
- Master’s Dissertations
- Bachelor’s Dissertations
- Scientific Dissertations
- Medical Dissertations
- Bioscience Dissertations
- Social Sciences Dissertations
- Psychology Dissertations
- Humanities Dissertations
- Engineering Dissertations
- Economics Dissertations
- Service Overview
- Revisión en inglés
- Relecture en anglais
- Revisão em inglês
Manuscript Editing
- Research Paper Editing
- Lektorat Doktorarbeit
- Dissertation Proofreading
- Englisches Lektorat
- Journal Manuscript Editing
- Scientific Manuscript Editing Services
- Book Manuscript Editing
- PhD Thesis Proofreading Services
- Wissenschaftslektorat
- Korektura anglického textu
- Akademisches Lektorat
- Journal Article Editing
- Manuscript Editing Services
PhD Thesis Editing
- Medical Editing Sciences
- Proofreading Rates UK
- Medical Proofreading
- PhD Proofreading
- Academic Proofreading
- PhD Proofreaders
- Best Dissertation Proofreaders
- Masters Dissertation Proofreading
- Proofreading PhD Thesis Price
- PhD Dissertation Editing
- Lektorat Englisch Preise
- Lektorieren Englisch
- Wissenschaftliches Lektorat
- Thesis Proofreading Services
- PhD Thesis Proofreading
- Proofreading Thesis Cost
- Proofreading Thesis
- Thesis Editing Services
- Professional Thesis Editing
- PhD Thesis Editing Services
- Thesis Editing Cost
- Dissertation Proofreading Services
- Proofreading Dissertation
PhD Dissertation Proofreading
- Dissertation Proofreading Cost
- Dissertation Proofreader
- Correção de Artigos Científicos
- Correção de Trabalhos Academicos
- Serviços de Correção de Inglês
- Correção de Dissertação
- Correção de Textos Precos
- Revision en Ingles
- Revision de Textos en Ingles
- Revision de Tesis
- Revision Medica en Ingles
- Revision de Tesis Precio
- Revisão de Artigos Científicos
- Revisão de Trabalhos Academicos
- Serviços de Revisão de Inglês
- Revisão de Dissertação
- Revisão de Textos Precos
- Corrección de Textos en Ingles
- Corrección de Tesis
- Corrección de Tesis Precio
- Corrección Medica en Ingles
- Corrector ingles
- Choosing the right Journal
- Journal Editor’s Feedback
- Dealing with Rejection
- Quantitative Research Examples
- Number of scientific papers published per year
- Acknowledgements Example
- ISO, ANSI, CFR & Other
- Types of Peer Review
- Withdrawing a Paper
- What is a good h-index
- Appendix paper
- Cover Letter Templates
- Writing an Article
- How To Write the Findings
- Abbreviations: ‘Ibid.’ & ‘Id.’
- Sample letter to editor for publication
- Tables and figures in research paper
- Journal Metrics
- Revision Process of Journal Publishing
- JOURNAL GUIDELINES
Select Page
PhD Theses Grammar – Nouns & Words Both, Either, Neither, Nor & Only
Posted by Rene Tetzner | Oct 30, 2021 | PhD Success | 0 |

5.4.3 Nouns and Agreement
The use of most English nouns is relatively straightforward, but spelling and word choice can sometimes be an issue if English is not your native language. It is usually quite easy to deal with such problems through careful and critical proofreading, especially with the assistance of the spell-checking function of your word-processing program, which in most cases will highlight obvious errors (though it should not be trusted to discover them all). If a word is underlined or otherwise highlighted by the program, check the spelling and correct it if necessary; if spelling is not the problem, it is likely that you have chosen the wrong or an inappropriate word (perhaps you used ‘content’ for ‘context,’ for example, ‘implementation’ for ‘intervention’ and so on), in which case you will need to use a dictionary or perhaps a thesaurus to find the correct or a more appropriate word. Watch for nouns that are too vague to express your exact meaning to all readers: ‘in this context,’ ‘in our area’ and ‘in local universities’ are classic examples of instances in which you and your thesis committee will know what you are talking about, but other readers (especially those from other contexts and areas) cannot unless the context or area you are working in or the location of those universities is specified wherever necessary for absolute clarity (specific language is also best for dates: see Section 6.4.4). Conversely, your language should not be so specific to one country or region that its meaning will not be fully understood by international readers: currency and educational systems are good examples of topics for which you should provide not only specific information relevant to the original locality, but also careful enough explanations of the specifics to make them clear to readers who are not familiar with that locality and its culture.
Agreement should always be maintained between nouns and the verbs used with them, which in most cases is easily established: singular nouns should be used with the singular forms of verbs (‘the doctoral candidate investigates,’ ‘the brush untangles’ and ‘the child plays’) and plural nouns with the plural forms of verbs (‘the doctoral candidates investigate,’ ‘the brushes untangle’ and ‘the children play’). If you want your language to suggest the possibility of both singular and plural situations simultaneously, for most nouns you can enclose the ‘s’ or ‘es’ of the plural form in parentheses – ‘the methodology chapter(s)’ – in which case the verb form should be governed by the singular noun because the plural is technically parenthetical: for example, ‘the methodology chapter(s) describes the research methods used in the thesis.’ Another (and often preferable) solution is to word the text in such a way that the verb works for both the singular and plural forms of the noun: ‘the methodology chapter(s) should describe the research methods used in the thesis.’ With plural nouns formed through the addition of endings other that ‘s’ or ‘es,’ the same strategy can be used – ‘the child(ren) will be going to a party this afternoon’ – but with nouns that change their stems to form the plural (such as ‘man’ that becomes ‘men’ and ‘woman’ that becomes ‘women’), effective constructions can be complicated and confusing for readers, and are generally best avoided.

There are certain nouns in the English language that present special challenges when it comes to agreement. Plural nouns that seem like singular nouns (‘data,’ ‘media,’ ‘criteria’ etc.), for instance, should take a plural verb (‘the criteria required were,’ not ‘the criteria required was’), although ‘data’ can, alternatively, be used as a singular noun (‘the data were’ or ‘the data was’). This is to say that ‘data’ can be treated as a collective or group noun instead of as a normal plural noun, in which case the important point is to ensure that the noun is treated as a singular whenever it is used in a document. With collective nouns in general, it is essential that each noun is consistently treated as either a singular or a plural, ideally throughout a thesis and certainly within a single sentence, but this can be rather tricky because such nouns tend to be used as both singular and plural in casual conversation, so there is a tendency to be inconsistent: for example, in ‘The society was founded in 1995; since then, they have grown rapidly,’ ‘they have’ in the second part of the sentence should actually be ‘it has’ to agree with the singular ‘society’ and its verb ‘was’ in the first part. Also complicated is the fact that the decision to use a singular or plural verb with a collective noun can depend on whether the noun refers to the group as a unit (singular) or to its members as individuals (plural), and also on whether British or American English is used: in American English, when the group is considered as a unit, a singular verb is usually used (our hockey team is playing very poorly this year), but in British English, collective nouns tend to use plural verbs (our hockey team are playing very poorly this year). The collective nouns ‘couple’ and ‘pair’ are usually used as plurals when they refer to people – ‘The couple ride their bicycles to work’ – but collective nouns of quantity such as ‘number,’ ‘percentage’ and ‘proportion’ tend to take a singular verb when a definite article precedes the noun and a plural verb when an indefinite article precedes the noun (‘The proportion of customers with home phones is decreasing,’ but ‘A large proportion of customers are giving up their home phones in favour of mobile phones’).

5.4.4 Both, Either, Neither, Nor and Only
Certain other words, phrases and constructions can cause particular problems when constructing sentences, especially for authors whose native language is not English. ‘Both’ takes a plural verb (e.g., ‘both a pool and a water slide were added to the playground’), whereas ‘either’ and ‘neither’ take a singular verb (either a pool or a water slide is being added to the playground), and so does a ‘neither . . . nor’ construction (neither a pool nor a waterslide was added to the playground). Please note that ‘or’ should not be used instead of ‘nor’ in a ‘neither . . . nor’ construction.’ ‘Neither,’ ‘either’ and ‘both’ should be correctly positioned in a sentence to achieve balance and avoid repetition, so the phrasing should be ‘that affect neither him nor her,’ not ‘that neither affect him nor her,’ and ‘that affect both him and her,’ not ‘that both affect him and her.’ ‘Only’ can be placed where it sounds best in a sentence unless there is a possibility of ambiguity or confusion, in which case it should be carefully positioned to clarify the meaning: for example, ‘vegetable gardens only watered on Sundays’ could mean ‘only vegetable gardens are watered on Sundays’ or ‘vegetable gardens are watered on Sundays only’ or ‘vegetable gardens are watered, but not weeded, on Sundays’ (examples adapted from Butcher et al., 2006, p.164). It is therefore wise to consider all the placement and semantic options as you are writing such sentences and choose the one that most effectively expresses your intentions. ‘Only’ can also be problematic when used not to mean ‘exclusively,’ but to refer to a small number or percentage: ‘just 39%’ or ‘as small as 39%’ is more accurate than and preferable to ‘only 39%.’

5.4.5 Beginning Sentences Correctly and Avoiding Dangling Participles
The wording at the beginning of sentences should be both precise and complete in formal scholarly prose, and certain elements should not be used in that position. Numerals, for instance, should be avoided, so any number at the beginning of a sentence should be written out in words unless writing it out would be cumbersome (e.g., ‘237,482’ would be very unwieldy if written as words), in which case the sentence should be reworded to avoid using the number at its beginning (for information on formatting numbers, see Section 6.4 below). Certain abbreviations should also be avoided at the beginning of sentences, although acronyms and initialisms are usually acceptable (see Section 6.3.8 below). As a general rule, sentences should not begin with conjunctions such as ‘and,’ ‘or,’ ‘but’ and ‘so,’ although the occasional lapse in this regard, even in formal writing, is tolerated in most cases as long as the sentence does not begin a paragraph, the meaning is clear and the rhythm of the prose is effective. A sentence and especially a paragraph should not normally start with a pronoun such as ‘this,’ ‘that’ or ‘they’ even if the antecedent is clear from what has gone before, but particularly if the antecedent is at all ambiguous. Instead, the subject should be clearly stated as a noun or noun phrase to avoid confusion, but the pronoun ‘I’ (as well as ‘we’ in texts with more than one author) is acceptable at the beginning of a sentence or paragraph because there can be no doubt, if the pronoun is used only when it should be, about the meaning. Keep in mind that when a descriptive phrase is used at the beginning of a sentence, it applies to everything that follows until the subject changes or is restated: in the sentence ‘In 1879 he painted his first watercolour and began to work with oils in 1886,’ for instance, the date 1879 applies incorrectly to ‘began’ as well as correctly to ‘painted,’ so rewording is necessary: either ‘He painted his first watercolour in 1879 and began to work with oils in 1886’ or ‘In 1879 he painted his first watercolour, and in 1886 he began to work with oils’ would work.
Dangling participles are often problematic at the beginning of sentences, though they can turn up anywhere in a sentence. A dangling participle occurs when a participle or participial phrase is followed by a word other than the subject it modifies, as it is in ‘Plunging to enormous depths, we marvelled at the canyon’ and ‘Having found the right food at last, the diabetic dog was fed.’ It is clear to a thinking reader familiar with English that the ‘canyon’ plunges ‘to enormous depths’ and the person feeding the dog is the one who ‘found the right food,’ but the sentences do not actually say these things: they say that ‘we’ plunge ‘to enormous depths’ and ‘the diabetic dog’ was the one who ‘found the right food’ because those are the subjects that appear immediately after the participial phrases. Such sentences should be reworded so that their syntax reflects the realities reported: ‘We marvelled at the canyon that plunged to enormous depths’ and ‘Having found the right food at last, he fed the diabetic dog.’ Other kinds of dependent clauses that frequently appear at the beginning of sentences can present problems as well, particularly when they are mistakenly used as independent clauses or full sentences. Although a dependent clause contains a subject and a verb (as the opening clause of this sentence does), it does not express a complete thought; instead, it often begins with a dependent marker word (such as ‘after,’ ‘when,’ ‘if,’ ‘because’ and ‘although’) that leaves the reader waiting for the rest of the thought: ‘After he had drafted his thesis’ and ‘Because she is afraid of fireworks’ are good examples. For this reason, a dependent clause cannot be a complete sentence, but should be either followed by a comma and an independent clause that does complete the thought, or preceded by an independent clause and (if necessary) a comma: ‘After he had drafted his thesis, he had it checked by a professional proofreader’ or ‘We left our dog at home because she is afraid of fireworks.’
Why PhD Success?
To Graduate Successfully
This article is part of a book called "PhD Success" which focuses on the writing process of a phd thesis, with its aim being to provide sound practices and principles for reporting and formatting in text the methods, results and discussion of even the most innovative and unique research in ways that are clear, correct, professional and persuasive.

The assumption of the book is that the doctoral candidate reading it is both eager to write and more than capable of doing so, but nonetheless requires information and guidance on exactly what he or she should be writing and how best to approach the task. The basic components of a doctoral thesis are outlined and described, as are the elements of complete and accurate scholarly references, and detailed descriptions of writing practices are clarified through the use of numerous examples.

The basic components of a doctoral thesis are outlined and described, as are the elements of complete and accurate scholarly references, and detailed descriptions of writing practices are clarified through the use of numerous examples. PhD Success provides guidance for students familiar with English and the procedures of English universities, but it also acknowledges that many theses in the English language are now written by candidates whose first language is not English, so it carefully explains the scholarly styles, conventions and standards expected of a successful doctoral thesis in the English language.
Individual chapters of this book address reflective and critical writing early in the thesis process; working successfully with thesis supervisors and benefiting from commentary and criticism; drafting and revising effective thesis chapters and developing an academic or scientific argument; writing and formatting a thesis in clear and correct scholarly English; citing, quoting and documenting sources thoroughly and accurately; and preparing for and excelling in thesis meetings and examinations.

Completing a doctoral thesis successfully requires long and penetrating thought, intellectual rigour and creativity, original research and sound methods (whether established or innovative), precision in recording detail and a wide-ranging thoroughness, as much perseverance and mental toughness as insight and brilliance, and, no matter how many helpful writing guides are consulted, a great deal of hard work over a significant period of time. Writing a thesis can be an enjoyable as well as a challenging experience, however, and even if it is not always so, the personal and professional rewards of achieving such an enormous goal are considerable, as all doctoral candidates no doubt realise, and will last a great deal longer than any problems that may be encountered during the process.

Interested in Proofreading your PhD Thesis? Get in Touch with us
If you are interested in proofreading your PhD thesis or dissertation, please explore our expert dissertation proofreading services.

Rene Tetzner
Rene Tetzner's blog posts dedicated to academic writing. Although the focus is on How To Write a Doctoral Thesis, many other important aspects of research-based writing, editing and publishing are addressed in helpful detail.
Related Posts

PhD Success – How To Write a Doctoral Thesis
October 1, 2021

Table of Contents – PhD Success
October 2, 2021

The Essential – Preliminary Matter
October 3, 2021

The Main Body of the Thesis
October 4, 2021

paper-free learning
- conjunctions
- determiners
- interjections
- prepositions
- affect vs effect
- its vs it's
- your vs you're
- which vs that
- who vs whom
- who's vs whose
- averse vs adverse
- 250+ more...
- apostrophes
- quotation marks
- lots more...
- common writing errors
- FAQs by writers
- awkward plurals
- ESL vocabulary lists
- all our grammar videos
- idioms and proverbs
- Latin terms
- collective nouns for animals
- tattoo fails
- vocabulary categories
- most common verbs
- top 10 irregular verbs
- top 10 regular verbs
- top 10 spelling rules
- improve spelling
- common misspellings
- role-play scenarios
- favo(u)rite word lists
- multiple-choice test
- Tetris game
- grammar-themed memory game
- 100s more...
The Plural Forms of Words
What are the plural forms of words.

Forming the Plurals of Nouns
- 1 dog > 2 dogs
- 1 house > 2 houses
- 1 video > 2 videos
- How to form the plurals of nouns (spelling rules)
- How to form the plurals of compound nouns (e.g., mothers-in-law, Knights Templar)
- How to form the plurals of abbreviations (e.g., MOTs, L.R.S.s)
What Are the Plural Pronouns?
What is the plural form of a verb, what are plural demonstrative determiners.
Forming the Plurals of Foreign Words
- stadium > stadia or stadiums
- datum > data
- radius > radii or radiuses
- agendum > agenda
"Plural" Also Applies to Zero
- 0 dogs (plural)
- 1 dog (singular)
- 2 dogs (plural)
- 3 dogs (plural)
- There are no alligators in the lake.

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
Learning Resources
more actions:
This test is printable and sendable
Help Us Improve Grammar Monster
- Do you disagree with something on this page?
- Did you spot a typo?
Find Us Quicker!
- When using a search engine (e.g., Google, Bing), you will find Grammar Monster quicker if you add #gm to your search term.
You might also like...
Share This Page

If you like Grammar Monster (or this page in particular), please link to it or share it with others. If you do, please tell us . It helps us a lot!
Create a QR Code

Use our handy widget to create a QR code for this page...or any page.
< previous lesson
next lesson >
Is thesis singular or plural
Add your answer:
Plural form of hypothesis?
it's theses: pronounced (thee-sees)
Can you give 100 examples of plural pronoun?
No, because there are not 100 plural pronouns.The plural pronouns are:weusyou (can be singular or plural)theythemthesethoseouroursyour (can be singular or plural)yours (can be singular or plural)theirtheirsourselvesyourselvesthemselvesbothfewfewermanyothersseveralall (can be singular or plural)any (can be singular or plural)more (can be singular or plural)most (can be singular or plural)none (can be singular or plural)some (can be singular or plural)such (can be singular or plural)
Is are plural or singular?
Are is plural. "Is" is singular. For example, "There is a glove on the chair". That is singular. "There are gloves on the chair". That is plural.
Is coat singular or plural?
singular Singular: plural is coats
Is who singular or plural?
Who may be singular or plural.
How do you write thesis as a singular noun?
The form thesis is the singular; the plural form is theses.
Is theses singular or plural?
The word theses is plural; the singular form is thesis. Examples:singular: I will write my thesis over the holiday.plural: The teacher had twenty two theses to grade.
What is singular of theses?
The singular form of "theses" is "thesis."
Is has singular or plural?
"Has" is singular, e.g. He has, she has. "Have" is plural, e.g. They have, we have. The exception is "I" - e.g. I have.
plural example as chlidren and singular as chlid?
singular and plural
Are the following words singular or plural practitioner sofa satellite clips dentist dollars article magazines laminator radios?
practitioner is singular (plural practitioners)sofa is singular (plural sofas)satellite is singular (plural satellites)clips is plural (singular clip)dentist is singular (plural dentists)dollars is plural (singular dollar)article is singular (plural articles)magazines is plural (singular magazine)laminator is singular (laminators is plural)radios is plural (singular radio)
Is word team singular or plural?
The word team is singular; the plural form is teams.
Is this plural or singular?
This is singular. These is the plural form.
Top Categories

The Editor’s Manual
Free learning resource on English grammar, punctuation, usage, and style.
Is Data Singular or Plural?

The word data is now generally treated as singular, much like the word information ( all the data you need is on this drive ). Its use as a plural word is now restricted mainly to academic and scientific writing ( the data are inconclusive ). When using this word, check whether you want to convey the sense of a plural noun ( the data indicate that . . . ) or a singular mass noun ( the data has been downloaded ).

Data : Singular or plural?
Data can be either singular or plural , though it is now more often used as a singular word. The word data came into English as the plural of the Latin word datum , which means “a single piece of information.” Over time, data became synonymous with “information”: it then became a singular word in its own right, no longer simply a plural.
- Singular: The data is unreliable.
- Singular: Our data indicates that dogs like ice-cream.
- Plural: The data are all from the same source.
- Plural: Our data indicate that cats like country music.
Although traditionalists prefer retaining the plural meaning of data , standard dictionaries agree that data can now be used as singular. Merriam-Webster lists data as a word that is “plural in form, but singular or plural in construction,” providing examples of both singular and plural usage. Oxford meanwhile simply lists data as a mass noun, noting that in technical fields, the word is still treated as plural. Cambridge also lists data as a noun that can be used with both singular and plural verbs.
Data as singular
Data is now generally considered singular and used to mean information . It is no longer used only as the plural of datum but stands on its own as a singular mass noun. It then agrees with singular verbs and pronouns .
- Data for this year is not available, but it is available for last year.
- Our data shows that incidents of violent crime have declined over the last decade.
When the word data is considered singular, it is used with determiners and quantifiers used with mass nouns ( this , much , little ).
- There is little data available for verification.
- Much of the data released is questionable.
Data as plural
In academic and scientific papers, data generally retains its meaning as the plural of datum . It is then used with plural verbs and pronouns.
- The data are ready to be presented in graphs and figures.
- Acme Inc.’s earnings data have just been released.
- After population data were collected, they were cross-referenced and published.
Note that when data is considered plural, it is used with plural determiners and quantifiers like these , many , and few .
- These data come from various sources.
- Only a few of the data published are as yet unverified.
Interestingly, cardinal numbers are not used before data , even when it is a plural noun.
- Incorrect: Poco has updated four data in the file. Correct: Poco has updated four points of data in the file.
- Incorrect: Four hundred data are ready to be shown in graphs and figures. Correct: Four hundred sets of data are ready to be shown in graphs and figures.
This behavior—the inability to take a number — is similar to that of mass nouns.
How to correctly use the word data
In speech and nonscientific writing, use data as singular rather than plural. In writing for a general audience, “data is” sounds more natural than “data are,” which can sound overly formal and pedantic.
- The data from his brain has been downloaded into a computer.
- When data is organized in tabular format, it can easily be analyzed.
- All the data that makes up a human life is now stored in the cloud.
Sometimes, you may want to convey the sense of a plural word. Using data as a plural noun can help suggest discreteness. This can be useful in scientific writing, where it is important to focus on the individual pieces of information that make up a data set.
- The data indicate that the fiscal measures implemented by various states are working. discrete pieces of data from different states
- Genetic data are linkable to individual participants, thus raising concerns of privacy.
- The data used in this study have been collected through various methodologies.
Data may be singular or plural ( the data is / are . . . ), but the word data s does not exist.
Chicago, AP, APA style
Many major style manuals now allow for data to be used as a singular noun. The Chicago Manual of Style considers it acceptable to use data as singular, admitting that treating the word as plural can sound pedantic. It does recommend using data as a plural word in the sciences.
The AP Stylebook also suggests using data as singular when writing for a general audience, but still recommends using it as plural in academic texts.
In contrast, the APA Publication Manual recommends restricting data to plural usage. This advice is consistent with the general recommendation to treat data as plural in academic writing, given that APA style is preferred in the social sciences.
Examples from published content
Here are some examples from published content that illustrate how data is generally considered singular.
- He says the data is likely being used for further malicious hacking campaigns. — “How your personal data is being scraped from social media,” BBC News (2021)
- Companies say the data is shared only with vetted partners. — “Twelve Million Phones, One Dataset, Zero Privacy,” New York Times (2019)
- Real-world driving data from connected cars is both a treasure trove and a mine-field for auto insurers. — “Driver Data Is a Help and a Hazard for Auto Insurers,” Wall Street Journal (2020)
- What type of data is available on Data.nasa.gov? — NASA website (Accessed August 8, 2021)
In academic writing, the word data is often treated as plural, not only because it sounds more formal but also to convey a sense of plurality: to emphasize the individual pieces of information that comprise a data set.
- Available meteorological data include wind speed and direction . . . . These data are available from the Royal Dutch Meteorological Institute. — “Genetic Data Provide Evidence for Wind-Mediated Transmission of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza,” The Journal of Infectious Diseases (2012)
- Vector data are composed of points, polylines, and polygons. — Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering (2019)
Metadata: Singular or plural?
Metadata , a word that refers to data about other data, is also used as both singular and plural, though it is most often used as a singular mass noun. Like the word data (from which metadata was derived), metadata is generally treated as plural only in formal texts, such as scientific and academic papers.
- Singular: The metadata changes whenever the data is changed.
- Singular: Metadata is often useful for accounting and forensic purposes.
- Plural: Metadata are incredibly useful for providing context to a set of data.
- Plural: Metadata provide information not provided by the data itself.
As with data , metadata is more often used as singular than plural. Check whether you want to convey the meaning of a singular entity (a single set of metadata) or a plural word (the various pieces of information that make up the metadata). Also note that using metadata as plural can sound stuffy and pedantic in everyday usage.
Here are some examples from published content that show how metadata can be used as both singular and plural.
- Singular: Metadata is implacable, unreasoning, unironic. — Devon McCann Jackson, “ When Meta Met Data ,” New York Times (2013)
- Singular: But metadata is not the only thing hidden in your photos. — Jerone Andrews, “ The Hidden Fingerprint inside Your Photos “, BBC Future (2021)
- Singular: Descriptive metadata provides information about the intellectual content of a digital object. — Allison B. Zhang and Don Gourley, “Descriptive Metadata,” Creating Digital Collections (2009)
- Plural: Metadata are included to provide context or extended information that is outside of the scope of data itself, for example, author information, or time stamps beyond those on the local file system. — Cory Altheide and Harlan Carvey, Digital Forensics with Open Source Tools (2011)
Other Latin plurals
Latin plurals generally retain their plural behavior in English: radi us / radi i , bacteri um / bacteri a , phyl um / phyl a . Two notable exceptions (other than data ) are agenda and media .
Agenda started out as the plural of the Latin agendum . Today in English, it is used as a singular word instead.
- What is / are Poco’s agenda for today’s meeting?
- Farley’s agenda is / are to make the world a better place.
Agenda even has its own English plural: agenda s .
- The NGOs all had their own agendas .
- Our methods were the same, though our agendas were different.
Media , as many know, is the plural of medium . But when used to refer to mass communication, it may be considered either singular or plural.
- The media has found its scapegoat.
- New media have significantly affected twenty-first-century politics.
Many words that come to English from other languages retain their singular and plural identities. For example, the Greek criteria is the plural of the singular criterion : one criteri on , many criteri a . Through usage, however, data , agenda , and media , now have their own singular identities.
Share this article
Data is used in both singular and plural constructions.
The word data can take either singular or plural verbs ( indicate s or indicate ).
Cardinal numbers (one, two, three . . .) are generally not used before the word data .
Data is used as a plural noun mainly in written material (academic documents in particular).

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Thesis becomes theses in plural form for two reasons: 1) The word thesis has a Greek root, and theses is how it is pluralized in that original language. 2) There are many English words ending with -is that take on -es endings when pluralized: e.g., crisis becomes crises. The pluralization isn't all that unique.
"Theses" is the only way to make the noun "thesis" plural. Confusion arises because some mistakenly believe that all nouns ending in "s" should form a plural that adds "es" to the end of the word. When a noun ends with "is," you need to replace the "is" with an "es" to form the plural. This is because its plural form derives from Greek.
The meaning of THESIS is a dissertation embodying results of original research and especially substantiating a specific view; especially : one written by a candidate for an academic degree. ... But a thesis may also be an idea; so in the course of the paper the student may put forth several theses (notice the plural form) and attempt to prove ...
The plural of thesis is "theses.". In English, most nouns form the plural by adding an "s" at the end. However, "thesis" is one of the few exceptions to this rule. The word "thesis" has a Greek root, and "theses" is how it is pluralized in that original language. Singular.
Thesis, which means "proposition", and derives from Greek, is a singular noun. The plural of thesis is theses. Started Grammarflex (ing) in 2022—been a word nerd and writing enthusiast ever since. (BA, MA in phil).
Noun [ edit] thesis (plural theses) ( rhetoric) A proposition or statement supported by arguments. (by extension) A lengthy essay written to establish the validity of a thesis (sense 1.1), especially one submitted in order to complete the requirements for a non- doctoral degree in the US and a doctoral degree in the UK; a dissertation .
The plural of "thesis" adheres to the Greek-rooted pattern, changing the singular -is to a plural -es. Accurate use of "thesis" and "theses" reflects scholarly precision in both written and oral communication. Awareness of correct pluralization extends to other similar nouns ending in -sis, emphasizing the importance of ...
THESES definition: 1. plural of thesis 2. plural of thesis . Learn more.
(plural theses /ˈθiːsiːz/ ... thesis (that…) a statement or an opinion that is discussed in a logical way and presented with evidence in order to prove that it is true. The basic thesis of the book is fairly simple. These latest findings support the thesis that sexuality is determined by nature rather than choice.
THESES meaning: 1. plural of thesis 2. plural of thesis . Learn more.
Noun [ change] Singular. thesis. Plural. theses. ( countable) A thesis is a long paper that university students at the masters or doctoral level write. I finished my coursework and have been working on my thesis for about a year now. She's writing her thesis on the effects of TV on children. ( countable) A thesis is a main idea or argument that ...
The plural form of thesis is theses . Find more words! They can continue classes or use the research as their master's theses and doctoral dissertations. Many scientists, including people writing doctoral theses, had access to the bones, and they were laboriously studied. Leuthner was fiercely attacked for his theses at the time by social ...
singular plural both plural and singular plural plural both plural and singular. . The. singular plural. plural. singular plural plural singular plural singular. of thesis is theses. How to say thesis: How to pronounce thesis.
Thesis is singular, theses is plural. Thesis' is singular genitive, theses' is plural genitive. As a general rule for genitives of words ending in s, you use s', the Saxon genitive. So, assuming you want to talk about the multiple goals in multiple theses, then you would use "theses' goals".
1. When the subject of a sentence is composed of two or more nouns or pronouns connected by and, use a plural verb. She and her friends are at the fair. 2. When two or more singular nouns or pronouns are connected by or or nor, use a singular verb. The book or the pen is in the drawer. 3.
A singular subject ( she, Bill, car) takes a singular verb ( is, goes, shines ), whereas a plural subject takes a plural verb. Example: The list of items is /are on the desk. If you know that list is the subject, then you will choose is for the verb. Exceptions to the Basic rule: a. The first person pronoun I takes a plural verb ( I go, I drive ...
With collective nouns in general, it is essential that each noun is consistently treated as either a singular or a plural, ideally throughout a thesis and certainly within a single sentence, but this can be rather tricky because such nouns tend to be used as both singular and plural in casual conversation, so there is a tendency to be ...
Forming the Plurals of Nouns In most cases, a noun will form its plural by adding "s" to the singular form. For example: 1 dog > 2 dogs; 1 house > 2 houses; 1 video > 2 videos; The spelling rules for forming the plurals of nouns (e.g., whether to add "s," "es," or "ies") usually depend on how the noun ends.
I need to choose a name for my masters thesis (computer science degree). My current name proposal is following: Computer Vision Application in a Driver Assistance System. What I am not sure of is whether parts of name should be in singular or plural. I consider also following: Computer Vision Application in Driver Assistance Systems
The plural of thesis is theses. The answer is: 👍. Helpful ( 0) 💡. Interesting ( 0) 😄. Funny ( 0) 🤔.
The word theses is plural; the singular form is thesis. Examples:singular: I will write my thesis over the holiday.plural: The teacher had twenty two theses to grade.
14. I am going to do an oral presentation for my thesis. Normally, when presenting a paper, as the paper is a collaboration work, I always use the pronoun "we". The thesis is written based on the papers. However, when presenting (for example, when talking about the contributions of the thesis), I feel using "we" a bit odd.
Data can be either singular or plural, though it is now more often used as a singular word. The word data came into English as the plural of the Latin word datum, which means "a single piece of information.". Over time, data became synonymous with "information": it then became a singular word in its own right, no longer simply a plural.
33 likes, 0 comments - islamicinspirations2024 on April 23, 2024: "A Hadith (Arabic plural aHadith; the word "Hadith" is used as both a singular and a collective ...