

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the 31 literary devices you must know.
General Education

Need to analyze The Scarlet Letter or To Kill a Mockingbird for English class, but fumbling for the right vocabulary and concepts for literary devices? You've come to the right place. To successfully interpret and analyze literary texts, you'll first need to have a solid foundation in literary terms and their definitions.
In this article, we'll help you get familiar with most commonly used literary devices in prose and poetry. We'll give you a clear definition of each of the terms we discuss along with examples of literary elements and the context in which they most often appear (comedic writing, drama, or other).
Before we get to the list of literary devices, however, we have a quick refresher on what literary devices are and how understanding them will help you analyze works of literature.
What Are Literary Devices and Why Should You Know Them?
Literary devices are techniques that writers use to create a special and pointed effect in their writing, to convey information, or to help readers understand their writing on a deeper level.
Often, literary devices are used in writing for emphasis or clarity. Authors will also use literary devices to get readers to connect more strongly with either a story as a whole or specific characters or themes.
So why is it important to know different literary devices and terms? Aside from helping you get good grades on your literary analysis homework, there are several benefits to knowing the techniques authors commonly use.
Being able to identify when different literary techniques are being used helps you understand the motivation behind the author's choices. For example, being able to identify symbols in a story can help you figure out why the author might have chosen to insert these focal points and what these might suggest in regard to her attitude toward certain characters, plot points, and events.
In addition, being able to identify literary devices can make a written work's overall meaning or purpose clearer to you. For instance, let's say you're planning to read (or re-read) The Lion, the Witch, and the Wardrobe by C.S. Lewis. By knowing that this particular book is a religious allegory with references to Christ (represented by the character Aslan) and Judas (represented by Edmund), it will be clearer to you why Lewis uses certain language to describe certain characters and why certain events happen the way they do.
Finally, literary techniques are important to know because they make texts more interesting and more fun to read. If you were to read a novel without knowing any literary devices, chances are you wouldn't be able to detect many of the layers of meaning interwoven into the story via different techniques.
Now that we've gone over why you should spend some time learning literary devices, let's take a look at some of the most important literary elements to know.
List of Literary Devices: 31 Literary Terms You Should Know
Below is a list of literary devices, most of which you'll often come across in both prose and poetry. We explain what each literary term is and give you an example of how it's used. This literary elements list is arranged in alphabetical order.
An allegory is a story that is used to represent a more general message about real-life (historical) issues and/or events. It is typically an entire book, novel, play, etc.
Example: George Orwell's dystopian book Animal Farm is an allegory for the events preceding the Russian Revolution and the Stalinist era in early 20th century Russia. In the story, animals on a farm practice animalism, which is essentially communism. Many characters correspond to actual historical figures: Old Major represents both the founder of communism Karl Marx and the Russian communist leader Vladimir Lenin; the farmer, Mr. Jones, is the Russian Czar; the boar Napoleon stands for Joseph Stalin; and the pig Snowball represents Leon Trotsky.
Alliteration
Alliteration is a series of words or phrases that all (or almost all) start with the same sound. These sounds are typically consonants to give more stress to that syllable. You'll often come across alliteration in poetry, titles of books and poems ( Jane Austen is a fan of this device, for example—just look at Pride and Prejudice and Sense and Sensibility ), and tongue twisters.
Example: "Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers." In this tongue twister, the "p" sound is repeated at the beginning of all major words.
Allusion is when an author makes an indirect reference to a figure, place, event, or idea originating from outside the text. Many allusions make reference to previous works of literature or art.
Example: "Stop acting so smart—it's not like you're Einstein or something." This is an allusion to the famous real-life theoretical physicist Albert Einstein.
Anachronism
An anachronism occurs when there is an (intentional) error in the chronology or timeline of a text. This could be a character who appears in a different time period than when he actually lived, or a technology that appears before it was invented. Anachronisms are often used for comedic effect.
Example: A Renaissance king who says, "That's dope, dude!" would be an anachronism, since this type of language is very modern and not actually from the Renaissance period.
Anaphora is when a word or phrase is repeated at the beginning of multiple sentences throughout a piece of writing. It's used to emphasize the repeated phrase and evoke strong feelings in the audience.
Example: A famous example of anaphora is Winston Churchill's "We Shall Fight on the Beaches" speech. Throughout this speech, he repeats the phrase "we shall fight" while listing numerous places where the British army will continue battling during WWII. He did this to rally both troops and the British people and to give them confidence that they would still win the war.
Anthropomorphism
An anthropomorphism occurs when something nonhuman, such as an animal, place, or inanimate object, behaves in a human-like way.
Example: Children's cartoons have many examples of anthropomorphism. For example, Mickey and Minnie Mouse can speak, wear clothes, sing, dance, drive cars, etc. Real mice can't do any of these things, but the two mouse characters behave much more like humans than mice.
Asyndeton is when the writer leaves out conjunctions (such as "and," "or," "but," and "for") in a group of words or phrases so that the meaning of the phrase or sentence is emphasized. It is often used for speeches since sentences containing asyndeton can have a powerful, memorable rhythm.
Example: Abraham Lincoln ends the Gettysburg Address with the phrase "...and that government of the people, by the people, for the people shall not perish from the Earth." By leaving out certain conjunctions, he ends the speech on a more powerful, melodic note.
Colloquialism
Colloquialism is the use of informal language and slang. It's often used by authors to lend a sense of realism to their characters and dialogue. Forms of colloquialism include words, phrases, and contractions that aren't real words (such as "gonna" and "ain't").
Example: "Hey, what's up, man?" This piece of dialogue is an example of a colloquialism, since it uses common everyday words and phrases, namely "what's up" and "man."
An epigraph is when an author inserts a famous quotation, poem, song, or other short passage or text at the beginning of a larger text (e.g., a book, chapter, etc.). An epigraph is typically written by a different writer (with credit given) and used as a way to introduce overarching themes or messages in the work. Some pieces of literature, such as Herman Melville's 1851 novel Moby-Dick , incorporate multiple epigraphs throughout.
Example: At the beginning of Ernest Hemingway's book The Sun Also Rises is an epigraph that consists of a quotation from poet Gertrude Stein, which reads, "You are all a lost generation," and a passage from the Bible.
Epistrophe is similar to anaphora, but in this case, the repeated word or phrase appears at the end of successive statements. Like anaphora, it is used to evoke an emotional response from the audience.
Example: In Lyndon B. Johnson's speech, "The American Promise," he repeats the word "problem" in a use of epistrophe: "There is no Negro problem. There is no Southern problem. There is no Northern problem. There is only an American problem."

A euphemism is when a more mild or indirect word or expression is used in place of another word or phrase that is considered harsh, blunt, vulgar, or unpleasant.
Example: "I'm so sorry, but he didn't make it." The phrase "didn't make it" is a more polite and less blunt way of saying that someone has died.
A flashback is an interruption in a narrative that depicts events that have already occurred, either before the present time or before the time at which the narration takes place. This device is often used to give the reader more background information and details about specific characters, events, plot points, and so on.
Example: Most of the novel Wuthering Heights by Emily Brontë is a flashback from the point of view of the housekeeper, Nelly Dean, as she engages in a conversation with a visitor named Lockwood. In this story, Nelly narrates Catherine Earnshaw's and Heathcliff's childhoods, the pair's budding romance, and their tragic demise.
Foreshadowing
Foreshadowing is when an author indirectly hints at—through things such as dialogue, description, or characters' actions—what's to come later on in the story. This device is often used to introduce tension to a narrative.
Example: Say you're reading a fictionalized account of Amelia Earhart. Before she embarks on her (what we know to be unfortunate) plane ride, a friend says to her, "Be safe. Wouldn't want you getting lost—or worse." This line would be an example of foreshadowing because it implies that something bad ("or worse") will happen to Earhart.
Hyperbole is an exaggerated statement that's not meant to be taken literally by the reader. It is often used for comedic effect and/or emphasis.
Example: "I'm so hungry I could eat a horse." The speaker will not literally eat an entire horse (and most likely couldn't ), but this hyperbole emphasizes how starved the speaker feels.
Imagery is when an author describes a scene, thing, or idea so that it appeals to our senses (taste, smell, sight, touch, or hearing). This device is often used to help the reader clearly visualize parts of the story by creating a strong mental picture.
Example: Here's an example of imagery taken from William Wordsworth's famous poem "I Wandered Lonely as a Cloud":
When all at once I saw a crowd, A host of golden Daffodils; Beside the Lake, beneath the trees, Fluttering and dancing in the breeze.
Irony is when a statement is used to express an opposite meaning than the one literally expressed by it. There are three types of irony in literature:
- Verbal irony: When someone says something but means the opposite (similar to sarcasm).
- Situational irony: When something happens that's the opposite of what was expected or intended to happen.
- Dramatic irony: When the audience is aware of the true intentions or outcomes, while the characters are not . As a result, certain actions and/or events take on different meanings for the audience than they do for the characters involved.
- Verbal irony: One example of this type of irony can be found in Edgar Allan Poe's "The Cask of Amontillado." In this short story, a man named Montresor plans to get revenge on another man named Fortunato. As they toast, Montresor says, "And I, Fortunato—I drink to your long life." This statement is ironic because we the readers already know by this point that Montresor plans to kill Fortunato.
- Situational irony: A girl wakes up late for school and quickly rushes to get there. As soon as she arrives, though, she realizes that it's Saturday and there is no school.
- Dramatic irony: In William Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet , Romeo commits suicide in order to be with Juliet; however, the audience (unlike poor Romeo) knows that Juliet is not actually dead—just asleep.

Juxtaposition
Juxtaposition is the comparing and contrasting of two or more different (usually opposite) ideas, characters, objects, etc. This literary device is often used to help create a clearer picture of the characteristics of one object or idea by comparing it with those of another.
Example: One of the most famous literary examples of juxtaposition is the opening passage from Charles Dickens' novel A Tale of Two Cities :
"It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair …"
Malapropism
Malapropism happens when an incorrect word is used in place of a word that has a similar sound. This misuse of the word typically results in a statement that is both nonsensical and humorous; as a result, this device is commonly used in comedic writing.
Example: "I just can't wait to dance the flamingo!" Here, a character has accidentally called the flamenco (a type of dance) the flamingo (an animal).
Metaphor/Simile
Metaphors are when ideas, actions, or objects are described in non-literal terms. In short, it's when an author compares one thing to another. The two things being described usually share something in common but are unalike in all other respects.
A simile is a type of metaphor in which an object, idea, character, action, etc., is compared to another thing using the words "as" or "like."
Both metaphors and similes are often used in writing for clarity or emphasis.
"What light through yonder window breaks? It is the east, and Juliet is the sun." In this line from Romeo and Juliet , Romeo compares Juliet to the sun. However, because Romeo doesn't use the words "as" or "like," it is not a simile—just a metaphor.
"She is as vicious as a lion." Since this statement uses the word "as" to make a comparison between "she" and "a lion," it is a simile.
A metonym is when a related word or phrase is substituted for the actual thing to which it's referring. This device is usually used for poetic or rhetorical effect .
Example: "The pen is mightier than the sword." This statement, which was coined by Edward Bulwer-Lytton in 1839, contains two examples of metonymy: "the pen" refers to "the written word," and "the sword" refers to "military force/violence."
Mood is the general feeling the writer wants the audience to have. The writer can achieve this through description, setting, dialogue, and word choice .
Example: Here's a passage from J.R.R. Tolkien's The Hobbit: "It had a perfectly round door like a porthole, painted green, with a shiny yellow brass knob in the exact middle. The door opened on to a tube-shaped hall like a tunnel: a very comfortable tunnel without smoke, with panelled walls, and floors tiled and carpeted, provided with polished chairs, and lots and lots of pegs for hats and coats -- the hobbit was fond of visitors." In this passage, Tolkien uses detailed description to set create a cozy, comforting mood. From the writing, you can see that the hobbit's home is well-cared for and designed to provide comfort.
Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia is a word (or group of words) that represents a sound and actually resembles or imitates the sound it stands for. It is often used for dramatic, realistic, or poetic effect.
Examples: Buzz, boom, chirp, creak, sizzle, zoom, etc.
An oxymoron is a combination of two words that, together, express a contradictory meaning. This device is often used for emphasis, for humor, to create tension, or to illustrate a paradox (see next entry for more information on paradoxes).
Examples: Deafening silence, organized chaos, cruelly kind, insanely logical, etc.
A paradox is a statement that appears illogical or self-contradictory but, upon investigation, might actually be true or plausible.
Note that a paradox is different from an oxymoron: a paradox is an entire phrase or sentence, whereas an oxymoron is a combination of just two words.
Example: Here's a famous paradoxical sentence: "This statement is false." If the statement is true, then it isn't actually false (as it suggests). But if it's false, then the statement is true! Thus, this statement is a paradox because it is both true and false at the same time.
Personification
Personification is when a nonhuman figure or other abstract concept or element is described as having human-like qualities or characteristics. (Unlike anthropomorphism where non-human figures become human-like characters, with personification, the object/figure is simply described as being human-like.) Personification is used to help the reader create a clearer mental picture of the scene or object being described.
Example: "The wind moaned, beckoning me to come outside." In this example, the wind—a nonhuman element—is being described as if it is human (it "moans" and "beckons").
Repetition is when a word or phrase is written multiple times, usually for the purpose of emphasis. It is often used in poetry (for purposes of rhythm as well).
Example: When Lin-Manuel Miranda, who wrote the score for the hit musical Hamilton, gave his speech at the 2016 Tony's, he recited a poem he'd written that included the following line:
And love is love is love is love is love is love is love is love cannot be killed or swept aside.
Satire is genre of writing that criticizes something , such as a person, behavior, belief, government, or society. Satire often employs irony, humor, and hyperbole to make its point.
Example: The Onion is a satirical newspaper and digital media company. It uses satire to parody common news features such as opinion columns, editorial cartoons, and click bait headlines.
A type of monologue that's often used in dramas, a soliloquy is when a character speaks aloud to himself (and to the audience), thereby revealing his inner thoughts and feelings.
Example: In Romeo and Juliet , Juliet's speech on the balcony that begins with, "O Romeo, Romeo! Wherefore art thou Romeo?" is a soliloquy, as she is speaking aloud to herself (remember that she doesn't realize Romeo's there listening!).
Symbolism refers to the use of an object, figure, event, situation, or other idea in a written work to represent something else— typically a broader message or deeper meaning that differs from its literal meaning.
The things used for symbolism are called "symbols," and they'll often appear multiple times throughout a text, sometimes changing in meaning as the plot progresses.
Example: In F. Scott Fitzgerald's 1925 novel The Great Gatsby , the green light that sits across from Gatsby's mansion symbolizes Gatsby's hopes and dreams .
A synecdoche is a literary device in which part of something is used to represent the whole, or vice versa. It's similar to a metonym (see above); however, a metonym doesn't have to represent the whole—just something associated with the word used.
Example: "Help me out, I need some hands!" In this case, "hands" is being used to refer to people (the whole human, essentially).
While mood is what the audience is supposed to feel, tone is the writer or narrator's attitude towards a subject . A good writer will always want the audience to feel the mood they're trying to evoke, but the audience may not always agree with the narrator's tone, especially if the narrator is an unsympathetic character or has viewpoints that differ from those of the reader.
Example: In an essay disdaining Americans and some of the sites they visit as tourists, Rudyard Kipling begins with the line, "Today I am in the Yellowstone Park, and I wish I were dead." If you enjoy Yellowstone and/or national parks, you may not agree with the author's tone in this piece.

How to Identify and Analyze Literary Devices: 4 Tips
In order to fully interpret pieces of literature, you have to understand a lot about literary devices in the texts you read. Here are our top tips for identifying and analyzing different literary techniques:
Tip 1: Read Closely and Carefully
First off, you'll need to make sure that you're reading very carefully. Resist the temptation to skim or skip any sections of the text. If you do this, you might miss some literary devices being used and, as a result, will be unable to accurately interpret the text.
If there are any passages in the work that make you feel especially emotional, curious, intrigued, or just plain interested, check that area again for any literary devices at play.
It's also a good idea to reread any parts you thought were confusing or that you didn't totally understand on a first read-through. Doing this ensures that you have a solid grasp of the passage (and text as a whole) and will be able to analyze it appropriately.
Tip 2: Memorize Common Literary Terms
You won't be able to identify literary elements in texts if you don't know what they are or how they're used, so spend some time memorizing the literary elements list above. Knowing these (and how they look in writing) will allow you to more easily pinpoint these techniques in various types of written works.
Tip 3: Know the Author's Intended Audience
Knowing what kind of audience an author intended her work to have can help you figure out what types of literary devices might be at play.
For example, if you were trying to analyze a children's book, you'd want to be on the lookout for child-appropriate devices, such as repetition and alliteration.
Tip 4: Take Notes and Bookmark Key Passages and Pages
This is one of the most important tips to know, especially if you're reading and analyzing works for English class. As you read, take notes on the work in a notebook or on a computer. Write down any passages, paragraphs, conversations, descriptions, etc., that jump out at you or that contain a literary device you were able to identify.
You can also take notes directly in the book, if possible (but don't do this if you're borrowing a book from the library!). I recommend circling keywords and important phrases, as well as starring interesting or particularly effective passages and paragraphs.
Lastly, use sticky notes or post-its to bookmark pages that are interesting to you or that have some kind of notable literary device. This will help you go back to them later should you need to revisit some of what you've found for a paper you plan to write.
What's Next?
Looking for more in-depth explorations and examples of literary devices? Join us as we delve into imagery , personification , rhetorical devices , tone words and mood , and different points of view in literature, as well as some more poetry-specific terms like assonance and iambic pentameter .
Reading The Great Gatsby for class or even just for fun? Then you'll definitely want to check out our expert guides on the biggest themes in this classic book, from love and relationships to money and materialism .
Got questions about Arthur Miller's The Crucible ? Read our in-depth articles to learn about the most important themes in this play and get a complete rundown of all the characters .
For more information on your favorite works of literature, take a look at our collection of high-quality book guides and our guide to the 9 literary elements that appear in every story !
Want to improve your SAT score by 160 points or your ACT score by 4 points? We've written a guide for each test about the top 5 strategies you must be using to have a shot at improving your score. Download it for free now:

These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Hannah received her MA in Japanese Studies from the University of Michigan and holds a bachelor's degree from the University of Southern California. From 2013 to 2015, she taught English in Japan via the JET Program. She is passionate about education, writing, and travel.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Blog • Perfecting your Craft , Book Design
Last updated on Aug 18, 2023
60 Literary Devices and Techniques Every Writer Must Know
A literary device is a writing technique that writers use to express ideas, convey meaning, and highlight important themes in a piece of text. A metaphor, for instance, is a famous example of a literary device.
These devices serve a wide range of purposes in literature. Some might work on an intellectual level, while others have a more emotional effect. They may also work subtly to improve the flow and pacing of your writing. No matter what, if you're looking to inject something special into your prose, literary devices are a great place to start.

Sentence-level devices
1. alliteration.
Alliteration describes a series of words in quick succession that all start with the same letter or sound. It lends a pleasing cadence to prose and Hamlet and the dollar as currency in Macbeth .
Example: “ One short sleepe past, wee wake eternally,
And death shall be no more; death, thou shalt die.” — “Death, Be Not Proud” by John Donne
Exercise: Pick a letter and write a sentence where every word starts with that letter or one that sounds similar.
2. Anaphora
Anaphora is the repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of a series of clauses or sentences. It’s often seen in poetry and speeches, intended to provoke an emotional response in its audience.
Example: Martin Luther King’s 1963 “I Have A Dream” speech.
“I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed.
"… and I have a dream that one day on the red hills of Georgia the sons of former slaves and the sons of former slave owners will be able to sit together at the table of brotherhood.
"… I have a dream that little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin, but by the content of their character.”
Exercise: Pick a famous phrase and write a paragraph elaborating on an idea, beginning each sentence with that phrase.
Similar term: repetition
3. Anastrophe
Anastrophe is a figure of speech wherein the traditional sentence structure is reversed. So a typical verb-subject-adjective sentence such as “Are you ready?” becomes a Yoda-esque adjective-verb-subject question: “Ready, are you?” Or a standard adjective-noun pairing like “tall mountain” becomes “mountain tall.”
Example: “Deep into that darkness peering, long I stood there wondering, fearing.” — “The Raven” by Edgar Allan Poe
Exercise: Write a standard verb-subject-adjective sentence or adjective-noun pairing then flip the order to create an anastrophe. How does it change the meaning or feeling of the sentence?
4. Chiasmus
Chiasmus is when two or more parallel clauses are inverted. “Why would I do that?” you may be wondering. Well, a chiasmus might sound confusing and unnecessary in theory, but it's much more convincing in practice — and in fact, you've likely already come across it before.
Example: “Ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country.” — John F. Kennedy
5. Congeries
Congeries is a fancy literary term for creating a list. The items in your list can be words, ideas, or phrases, and by displaying them this way helps prove or emphasize a point — or even create a sense of irony. Occasionally, it’s also called piling as the words are “piling up.”
Example: "Apart from better sanitation and medicine and education and irrigation and public health and roads and a freshwater system and baths and public order, what have the Romans done for us?" — Monty Python’s Life of Brian
6. Cumulative sentence
A cumulative sentence (or “loose sentence”) is one that starts with an independent clause, but then has additional or modifying clauses. They’re often used for contextual or clarifying details. This may sound complex, but even, “I ran to the store to buy milk, bread, and toilet paper” is a cumulative sentence, because the first clause, “I ran to the store,” is a complete sentence, while the rest tells us extra information about your run to the store.
Example: “It was a large bottle of gin Albert Cousins had brought to the party, yes, but it was in no way large enough to fill all the cups, and in certain cases to fill them many times over, for the more than one hundred guests, some of whom were dancing not four feet in front of him.” – Commonwealth by Ann Patchett
Example: Write three sentences that are related to each other. Can you combine the information into a cumulative sentence?

FREE RESOURCE
Literary Devices Cheatsheet
Master these 40+ devices to level up your writing skills.
7. Epistrophe
Epistrophe is the opposite of anaphora, with this time a word or phrase being repeated at the end of a sentence. Though its placement in a sentence is different it serves the same purpose—creating emphasis—as an anaphora does.
Example: “I’ll be ever’where – wherever you look. Wherever they’s a fight so hungry people can eat, I’ll be there. Wherever they’s a cop beatin’ up a guy, I’ll be there . If Casy knowed, why, I’ll be in the way guys yell when they’re mad an’ – I’ll be in the way kids laugh when they’re hungry an’ they know supper’s ready. An’ when our folks eat the stuff they raise an’ live in the houses they build, why, I’ll be there .” — The Grapes of Wrath by John Steinbeck
Similar terms: repetition, anaphora
Exercise: Write a paragraph where a phrase or a word is repeated at the end of every sentence, emphasizing the point you’re trying to make.
8. Erotesis
Erotesis is a close cousin of the rhetorical question. Rather than a question asked without expectation of an answer, this is when the question (and the asker) confidently expects a response that is either negative or affirmative.
Example: “ Do you then really think that you have committed your follies in order to spare your son them?” — Siddhartha by Herman Hesse
Similar term: rhetorical question
9. Hyperbaton
Hyperbaton is the inversion of words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence that differs from how they would normally be arranged. It comes from the Greek hyperbatos, which means “transposed” or “inverted.” While it is similar to anastrophe, it doesn’t have the same specific structure and allows you to rearrange your sentences in whatever order you want.
Example: “Object there was none. Passion there was none. I loved the old man. He had never wronged me. He had never given me insult. For his gold I had no desire.” — “The Tell-Tale Heart” by Edgar Allan Poe
Similar terms: anastrophe, epistrophe
10. Isocolon
If you’re a neat freak who likes things just so , isocolon is the literary device for you. This is when two or more phrases or clauses have similar structure, rhythm, and even length — such that, when stacked up on top of each other, they would line up perfectly. Isocolon often crops up in brand slogans and famous sayings; the quick, balanced rhythm makes the phrase catchier and more memorable.
Example: Veni, vidi, vici (“I came, I saw, I conquered”)
11. Litotes
Litotes (pronounced lie-toe-teez ) is the signature literary device of the double negative. Writers use litotes to express certain sentiments through their opposites, by saying that that opposite is not the case. Don’t worry, it makes more sense with the examples. 😉
Examples: “You won’t be sorry” (meaning you’ll be happy); “you’re not wrong” (meaning you’re right); “I didn’t not like it” (meaning I did)
12. Malapropism
If Shakespeare is the king of metaphors, Michael Scott is the king of malapropisms . A malapropism is when similar-sounding words replace their appropriate counterparts, typically to comic effect — one of the most commonly cited is “dance a flamingo,” rather than a “flamenco.” Malapropisms are often employed in dialogue when a character flubs up their speech.
Example: “I am not to be truffled with.”
Exercise: Choose a famous or common phrase and see if you can replace a word with a similar sounding one that changes the meaning.

13. Onomatopoeia
Amusingly, onomatopoeia (itself a difficult-to-pronounce word) refers to words that sound like the thing they’re referring to. Well-known instances of onomatopoeia include whiz, buzz, snap, grunt, etc.
Example: The excellent children's book Click, Clack, Moo: Cows That Type . “Farmer Brown has a problem. His cows like to type. All day long he hears: Click, clack, moo. Click, clack, moo. Clickety, clack, moo. ”
Exercise: Take some time to listen to the sounds around you and write down what you hear. Now try to use those sounds in a short paragraph or story.
14. Oxymoron
An oxymoron comes from two contradictory words that describe one thing. While juxtaposition contrasts two story elements, oxymorons are about the actual words you are using.
Example: "Parting is such sweet sorrow.” — Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare. (Find 100 more examples of oxymorons here .)
Similar terms: juxtaposition, paradox
Exercise: Choose two words with opposite meanings and see if you can use them in a sentence to create a coherent oxymoron.

15. Parallelism
Parallelism is all about your sentence structure. It’s when similar ideas, sounds, phrases, or words are arranged in a way that is harmonious or creates a parallel, hence the name. It can add rhythm and meter to any piece of writing and can often be found in poetry.
Example: “ That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.” — Neil Armstrong
Which famous author do you write like?
Find out which literary luminary is your stylistic soulmate. Takes one minute!
16. Polysyndeton
Instead of using a single conjunction in lengthy statements, polysyndeton uses several in succession for a dramatic effect. This one is definitely for authors looking to add a bit of artistic flair to their writing, or who are hoping to portray a particular (usually naïve) sort of voice.
Example: “Luster came away from the flower tree and we went along the fence and they stopped and we stopped and I looked through the fence while Luster was hunting in the grass.” — The Sound and the Fury by William Faulkner
Exercise: Write three or four independent sentences. Try combining them using conjunctions. What kind of effect does this have on the overall meaning and tone of the piece?
17. Portmanteau
A portmanteau is when two words are combined to form a new word which refers to a single concept that retains the meanings of both the original words. Modern language is full of portmanteaus. In fact, the portmanteau is itself a portmanteau. It’s a combination of the French porter (to carry) and manteau (cloak).
Example: Brunch (breakfast and lunch); cosplay (costume and roleplay); listicle (list and article); romcom (romance and comedy)
Exercise: Pick two words that are often used together to describe a single concept. See if there’s a way to combine them and create a single word that encompasses the meaning of both.
18. Repetition
Repetition , repetition, repetition… where would we be without it? Though too much repetition is rarely a good thing, occasional repetition can be used quite effectively to drill home a point, or to create a certain atmosphere. For example, horror writers often use repetition to make the reader feel trapped and scared.
Example: In The Shining , Jack Torrance types over and over again on his pages, “All work and no play makes Jack a dull boy.” In this case, obsessive repetition demonstrates the character’s unraveling mind.
Similar term: anaphora
Exercise: Repetition can be used to call attention to an idea or phrase. Pick an idea you want to emphasize and write a few sentences about it. Are there any places where you can add repetition to make it more impactful?

19. Tautology
A tautology is when a sentence or short paragraph repeats a word or phrase, expressing the same idea twice. Often, this is a sign that you should trim your work to remove the redundancy (such as “frozen ice”) but can also be used for poetic emphasis.
Example: "But the fact is I was napping, and so gently you came rapping, And so faintly you came tapping, tapping at my chamber door" – “The Raven” by Edgar Allan Poe
20. Tmesis
Tmesis is when a word or phrase is broken up by an interjecting word, such as abso-freaking-lutely. It’s used to draw out and emphasize the idea, often with a humorous or sarcastic slant.
Example: "This is not Romeo, he's some-other-where." – Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare
Narrative devices
21. allegory.
An allegory is a type of narrative that uses characters and plot to depict abstract ideas and themes . In an allegorical story, things represent more than they appear to on the surface. Many children's fables, such as The Tortoise and the Hare , are simple allegories about morality — but allegories can also be dark, complex, and controversial.
Example: Animal Farm by George Orwell. This dystopian novella is one of modern literature’s best-known allegories. A commentary on the events leading up to Stalin's rise and the formation of the Soviet Union, the pigs at the heart of the novel represent figures such as Stalin, Trotsky, and Molotov.
Exercise: Pick a major trend or problem in the world and consider what defines it. Try and create a story where that trend plays out on a smaller scale.
22. Anecdote
An anecdote is like a short story within a story. Sometimes, they are incredibly short—only a line or two—and their purpose is to add a character’s perspective, knowledge, or experience to a situation. They can be inspirational, humorous, or be used to inspire actions in others. Since anecdotes are so short, don’t expect them to be part of a main story. They’re usually told by a character and part of the dialogue.
Example: Marcel Proust’s Swann’s Way , part of his series of novels, In Search of Lost Time, deals with the themes of remembrance and memory. In one section of this book, to illustrate these ideas, the main character recalls an important memory of eating a madeleine cookie. “Many years had elapsed during which nothing of Combray, save what was comprised in the theatre and the drama of my going to bed there, had any existence for me, when one day in winter, as I came home, my mother, seeing that I was cold, offered me some tea, a thing I did not ordinarily take. I declined at first, and then, for no particular reason, changed my mind. She sent out for one of those short, plump little cakes called ‘petites madeleines,’ which look as though they had been moulded in the fluted scallop of a pilgrim’s shell.”
23. Deus Ex Machina
Literally meaning “god in the machine” in Greek, deus ex machina is a plot device where an impossible situation is solved by the appearance of an unexpected or unheard of character, action, object, or event. This brings about a quick and usually happy resolution for a story and can be used to surprise an audience, provide comic relief, or provide a fix for a complicated plot. However, deus ex machinas aren’t always looked upon favorably and can sometimes be seen as lazy writing, so they should be used sparingly and with great thought.
Example: William Golding’s famous novel of a group of British boys marooned on a desert island is resolved with a deus ex machina. At the climax of The Lord of the Flies, just as Ralph is about to be killed by Jack, a naval officer arrives to rescue the boys and bring them back to civilization. It’s an altogether unexpected and bloodless ending for a story about the boys’ descent into savagery.
Exercise: Consider the ending of your favorite book or movie and then write an alternate ending that uses a deus ex machina to resolve the main conflict. How does this affect the overall story in terms of theme and tone?
If you struggle to write consistently, sign up for our How to Write a Novel course to finish a novel in just 3 months.

NEW REEDSY COURSE
How to Write a Novel
Enroll in our course and become an author in three months.
24. Dramatic irony
Dramatic irony is when the readers know more about the situation going on than at least one of the characters involved. This creates a difference between the ways the audience and the characters perceive unfolding events. For instance, if we know that one character is having an affair, when that character speaks to their spouse, we will pick up on the lies and double-meanings of their words, while the spouse may take them at face value.
Example: In Titanic , the audience knows from the beginning of the movie that the boat will sink. This creates wry humor when characters remark on the safety of the ship.
25. Exposition
Exposition is when the narrative provides background information in order to help the reader understand what’s going on. When used in conjunction with description and dialogue, this literary device provides a richer understanding of the characters, setting, and events. Be careful, though — too much exposition will quickly become boring, thus undercutting the emotional impact of your work.
Example: “The Dursley’s had everything they wanted, but they also had a secret, and their greatest fear was that somebody would discover it.” – Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone by J.K. Rowling
Exercise: Pick your favorite story and write a short paragraph introducing it to someone who knows nothing about it.
26. Flashback
Flashbacks to previous events split up present-day scenes in a story, usually to build suspense toward a big reveal. Flashbacks are also an interesting way to present exposition for your story, gradually revealing to the reader what happened in the past.
Example: Every other chapter in the first part of Gone Girl is a flashback, with Amy’s old diary entries describing her relationship with her husband before she disappeared.
Similar term: foreshadowing
27. Foreshadowing
Foreshadowing is when the author hints at events yet to come in a story. Similar to flashbacks (and often used in conjunction with them), this technique is also used to create tension or suspense — giving readers just enough breadcrumbs to keep them hungry for more.
Example: One popular method of foreshadowing is through partial reveals — the narrator leaves out key facts to prompt readers’ curiosity. Jeffrey Eugenides does this in The Virgin Suicides : “On the morning the last Lisbon daughter took her turn at suicide — it was Mary this time, and sleeping pills, like Therese, the two paramedics arrived at the house knowing exactly where the knife drawer was, and the gas oven, and the beam in the basement from which it was possible to tie a rope.”
Similar term: flashback
Exercise: Go back to your favorite book or movie. Can you identify any instances of foreshadowing in the early portions of the story for events that happen in the future?
28. Frame story
A frame story is any part of the story that "frames" another part of it, such as one character telling another about their past, or someone uncovering a diary or a series of news articles that then tell the readers what happened. Since the frame story supports the rest of the plot, it is mainly used at the beginning and the end of the narrative, or in small interludes between chapters or short stories.
Example: In The Name of the Wind by Patrick Rothfuss, Kvothe is telling Chronicler the story of his life over the span of three days. Most of the novel is the story he is telling, while the frame is any part that takes place in the inn.
29. In Medias Res
In medias res is a Latin term that means "in the midst of things" and is a way of starting a narrative without exposition or contextual information. It launches straight into a scene or action that is already unfolding.
Example: “Many years later, as he faced the firing squad, Colonel Aureliano Buendía was to remember that distant afternoon when his father took him to discover ice.” — The opening line of One Hundred Years of Solitude by Gabriel García Márquez
Exercise: Pick a story you enjoy and rewrite the opening scene so that it starts in the middle of the story.
30. Point of view
Point of view is, of course, the mode of narration in a story. There are many POVs an author can choose, and each one will have a different impact on the reading experience.
Example: Second person POV is uncommon because it directly addresses the reader — not an easy narrative style to pull off. One popular novel that manages to employ this perspective successfully is Bright Lights, Big City by Jay McInerney: “You are not the kind of guy who would be at a place like this at this time of the morning. But here you are, and you cannot say that the terrain is entirely unfamiliar, although the details are fuzzy.”
Exercise: Write a short passage in either first, second, or third person. Then rewrite that passage in the other two points of view, only changing the pronouns. How does the change in POV affect the tone and feel of the story?

FREE COURSE
Understanding Point of View
Learn to master different POVs and choose the best for your story.
31. Soliloquy
Soliloquy involves a character speaking their thoughts aloud, usually at length (and often in a Shakespeare play). The character in question may be alone or in the company of others, but they’re not speaking for the benefit of other people; the purpose of a soliloquy is for a character to reflect independently.
Example: Hamlet’s “to be or not to be” speech, in which he ruminates on the nature of life and death, is a classic dramatic soliloquy.
Exercise: Pick a character from your favorite book or movie and write a soliloquy from their point of view where they consider their thoughts and feelings on an important part of their story or character arc.
Which writing app is right for you?
Find out here! Takes 30 seconds
Tone refers to the overall mood and message of your book. It’s established through a variety of means, including voice, characterization, symbolism, and themes. Tone sets the feelings you want your readers to take away from the story.
Example: No matter how serious things get in The Good Place , there is always a chance for a character to redeem themselves by improving their behavior. The tone remains hopeful for the future of humanity in the face of overwhelming odds.
Exercise: Write a short paragraph in an upbeat tone. Now using the same situation you came up with, rewrite that passage in a darker or sadder tone.
33. Tragicomedy
Tragicomedy is just what it sounds like: a blend of tragedy and comedy. Tragicomedy helps an audience process darker themes by allowing them to laugh at the situation even when circumstances are bleak.
Example: Lemony Snicket’s A Series of Unfortunate Events uses wordplay, absurd situations, and over-the-top characters to provide humor in an otherwise tragic story.
Conceptual devices
34. allusion.
An allusion is a reference to a person, place, thing, concept, or other literary work that a reader is likely to recognize. A lot of meaning can be packed into an allusion and it’s often used to add depth to a story. Many works of classic Western literature will use allusions to the Bible to expand on or criticize the morals of their time.
Example: “The two knitting women increase his anxiety by gazing at him and all the other sailors with knowing unconcern. Their eerie looks suggest that they know what will happen (the men dying), yet don’t care.” The two women knitting in this passage from Joseph Conrad’s Heart of Darkness are a reference to the Fates from Greek mythology, who decide the fate of humanity by spinning and cutting the threads of life.
Exercise: In a relatively simple piece of writing, see how many times you can use allusions. Go completely crazy. Once you’re finished, try to cut it down to a more reasonable amount and watch for how it creates deeper meaning in your piece.
35. Analogy
An analogy connects two seemingly unrelated concepts to show their similarities and expand on a thought or idea. They are similar to metaphors and similes, but usually take the comparison much further than either of these literary devices as they are used to support a claim rather than provide imagery.
Example: “ It has been well said that an author who expects results from a first novel is in a position similar to that of a man who drops a rose petal down the Grand Canyon of Arizona and listens for the echo.” — P.G. Wodehouse
Exercise: Pick two seemingly unrelated nouns and try to connect them with a verb to create an analogy.
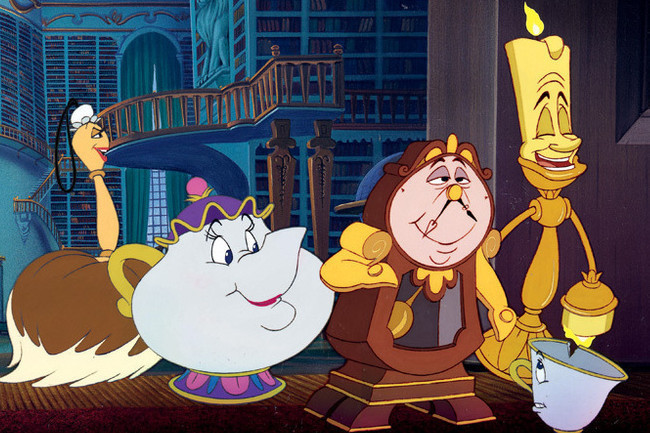
36. Anthropomorphism
To anthropomorphize is to apply human traits or qualities to a non-human thing such as objects, animals, or the weather. But unlike personification, in which this is done through figurative description, anthropomorphism is literal: a sun with a smiling face, for example, or talking dogs in a cartoon.
Examples: In Disney’s Beauty and the Beast , Mrs. Potts the teapot, Cogsworth the clock, and Lumière the candlestick are all household objects that act and behave like humans (which, of course, they were when they weren’t under a spell).
Similar term: personification
Exercise: Pick a non-human object and describe it as if it was human, literally ascribing human thoughts, feelings, and senses to it.

37. Aphorism
An aphorism is a universally accepted truth stated in a concise, to-the-point way. Aphorisms are typically witty and memorable, often becoming adages or proverbs as people repeat them over and over.
Example: “To err is human, to forgive divine.” — Alexander Pope
38. Archetype
An archetype is a “universal symbol” that brings familiarity and context to a story. It can be a character, a setting, a theme, or an action. Archetypes represent feelings and situations that are shared across cultures and time periods, and are therefore instantly recognizable to any audience — for instance, the innocent child character, or the theme of the inevitability of death.
Example: Superman is a heroic archetype: noble, self-sacrificing, and drawn to righting injustice whenever he sees it.
Exercise: Pick an archetype — either a character or a theme — and use it to write a short piece centered around that idea.
A cliché is a saying or idea that is used so often it becomes seen as unoriginal. These phrases might become so universal that, despite their once intriguing nature, they're now looked down upon as uninteresting and overused.
Examples: Some common cliches you might have encountered are phrases like “easy as pie” and “light as a feather.” Some lines from famous books and movies have become so popular that they are now in and of themselves cliches such as Darth Vader’s stunning revelation from The Empire Strikes Back, “Luke, I am your father.” Also, many classic lines of Shakespeare are now considered cliches like, “All that glitters is not gold” from The Merchant of Venice.
Exercise: Write a short passage using as many cliches as possible. Now try to cut them out and replace them with more original phrasing. See how the two passages compare.
40. Colloquialism
Colloquialism is the use of casual and informal language in writing, which can also include slang. Writers use colloquialisms to provide context to settings and characters, and to make their writing sound more authentic. Imagine reading a YA novel that takes place in modern America, and the characters speak to each other like this:
“Good morning, Sue. I hope that you slept well and are prepared for this morning’s science exam.”
It’s not realistic. Colloquialisms help create believable dialogue :
“Hey Sue, what’d you get up to last night? This science test is gonna suck.”
Example: Trainspotting by Irvine Welsh takes place in Scotland, a fact made undeniably obvious by the dialect: “Thing is, as ye git aulder, this character-deficiency gig becomes mair sapping. Thir wis a time ah used tae say tae aw the teachers, bosses, dole punters, poll-tax guys, magistrates, when they telt me ah was deficient: ’Hi, cool it, gadge, ah’m jist me, jist intae a different sort ay gig fae youse but, ken?’”
Exercise: Write a dialogue between two characters as formally as possible. Now take that conversation and make it more colloquial. Imagine that you’re having this conversation with a friend. Mimic your own speech patterns as you write.
41. Euphemism
A euphemism is an indirect, “polite” way of describing something too inappropriate or awkward to address directly. However, most people will still understand the truth about what's happening.
Example: When an elderly person is forced to retire, some might say they’re being “put out to pasture.”
Exercise: Write a paragraph where you say things very directly. Now rewrite that paragraph using only euphemisms.
42. Hyperbole
Hyperbole is an exaggerated statement that emphasizes the significance of the statement’s actual meaning. When a friend says, "Oh my god, I haven't seen you in a million years," that's hyperbole.
Example: “At that time Bogotá was a remote, lugubrious city where an insomniac rain had been falling since the beginning of the 16th century.” — Living to Tell the Tale by Gabriel García Márquez
Exercise: Tall tales often make use of hyperbole to tell an exaggerated story. Use hyperbole to relate a completely mundane event or experience to turn it into a tall tale.
43. Hypophora
Hypophora is much like a rhetorical question, wherein someone asks a question that doesn't require an answer. However, in hypophora, the person raises a question and answers it immediately themselves (hence the prefix hypo, meaning 'under' or 'before'). It’s often used when characters are reasoning something aloud.
Example: “Do you always watch for the longest day of the year and then miss it? I always watch for the longest day in the year and then miss it.” — Daisy in The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald

An idiom is a saying that uses figurative language whose meaning differs from what it literally says. These phrases originate from common cultural experiences, even if that experience has long ago been forgotten. Without cultural context, idioms don’t often make sense and can be the toughest part for non-native speakers to understand.
Example: In everyday use, idioms are fairly common. We say things like, “It’s raining cats and dogs” to say that it’s downpouring.
Exercise: Idioms are often used in dialogue. Write a conversation between two people where idioms are used to express their main points.
45. Imagery
Imagery appeals to readers’ senses through highly descriptive language. It’s crucial for any writer hoping to follow the rule of "show, don’t tell," as strong imagery truly paints a picture of the scene at hand.
Example: “In the hard-packed dirt of the midway, after the glaring lights are out and the people have gone to bed, you will find a veritable treasure of popcorn fragments, frozen custard dribblings, candied apples abandoned by tired children, sugar fluff crystals, salted almonds, popsicles, partially gnawed ice cream cones and wooden sticks of lollipops.” — Charlotte's Web by E.B. White
Exercise: Choose an object, image, or idea and use the five senses to describe it.

Show, Don't Tell
Master the golden rule of writing in 10 five-minute lessons.
Irony creates a contrast between how things seem and how they really are. There are three types of literary irony : dramatic (when readers know what will happen before characters do), situational (when readers expect a certain outcome, only to be surprised by a turn of events), and verbal (when the intended meaning of a statement is the opposite of what was said).
Example: This opening scene from Orson Welles’ A Touch of Evil is a great example of how dramatic irony can create tension.
47. Juxtaposition
Juxtaposition places two or more dissimilar characters, themes, concepts, etc. side by side, and the profound contrast highlights their differences. Why is juxtaposition such an effective literary device? Well, because sometimes the best way for us to understand something is by understanding what it’s not .
Example: In the opening lines of A Tale of Two Cities , Charles Dickens uses juxtaposition to emphasize the societal disparity that led to the French Revolution: “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness…”
Similar terms: oxymoron, paradox
Exercise: Pick two ideas, objects, places, or people that seem like complete opposites. Introduce them side by side in the beginning of your piece and highlight their similarities and differences throughout.
48. Metaphor
A metaphor compares two similar things by saying that one of them is the other. As you'd likely expect, when it comes to literary devices, this one is a heavy hitter. And if a standard metaphor doesn't do the trick, a writer can always try an extended metaphor : a metaphor that expands on the initial comparison through more elaborate parallels.
Example: Metaphors are literature’s bread and butter (metaphor intended) — good luck finding a novel that is free of them. Here’s one from Frances Hardinge’s A Face Like Glass : “Wishes are thorns, he told himself sharply. They do us no good, just stick into our skin and hurt us.”
Similar term: simile
Exercise: Write two lists: one with tangible objects and the other concepts. Mixing and matching, try to create metaphors where you describe the concepts using physical objects.
One metaphor example not enough? Check out this post , which has 97 of ‘em!
49. Metonymy
Metonymy is like symbolism, but even more so. A metonym doesn’t just symbolize something else, it comes to serve as a synonym for that thing or things — typically, a single object embodies an entire institution.
Examples: “The crown” representing the monarchy, “Washington” representing the U.S. government.
Similar term: synecdoche
Exercise: Create a list of ten common metonymies you might encounter in everyday life and speech.
Whatever form a motif takes, it recurs throughout the novel and helps develop the theme of the narrative. This might be a symbol, concept, or image.
Example: In Anna Karenina by Leo Tolstoy, trains are an omnipresent motif that symbolize transition, derailment, and ultimately violent death and destruction.
Similar term: symbol
Exercise: Pick a famous book or movie and see if you can identify any common motifs within it.
51. Non sequitur
Non sequiturs are statements that don't logically follow what precedes them. They’ll often be quite absurd and can lend humor to a story. But they’re just not good for making jokes. They can highlight missing information or a miscommunication between characters and even be used for dramatic effect.
Example: “It was a spring day, the sort that gives people hope: all soft winds and delicate smells of warm earth. Suicide weather.” — Girl, Interrupted by Susanna Kaysen
Exercise: Write a conversation that gets entirely derailed by seemingly unrelated non sequiturs.
52. Paradox
Paradox derives from the Greek word paradoxon , which means “beyond belief.” It’s a statement that asks people to think outside the box by providing seemingly illogical — and yet actually true — premises.
Example: In George Orwell’s 1984 , the slogan of the totalitarian government is built on paradoxes: “War is Peace, Freedom is Slavery, Ignorance is Strength.” While we might read these statements as obviously contradictory, in the context of Orwell’s novel, these blatantly corrupt sentiments have become an accepted truth.
Similar terms: oxymoron, juxtaposition
Exercise: Try writing your own paradox. First, think of two opposing ideas that can be juxtaposed against each other. Then, create a situation where these contradictions coexist with each other. What can you gather from this unique perspective?
53. Personification
Personification uses human traits to describe non-human things. Again, while the aforementioned anthropomorphism actually applies these traits to non-human things, personification means the behavior of the thing does not actually change. It's personhood in figurative language only.
Example: “Just before it was dark, as they passed a great island of Sargasso weed that heaved and swung in the light sea as though the ocean were making love with something under a yellow blanket, his small line was taken by a dolphin.” — The Old Man and the Sea by Ernest Hemingway
Similar term: anthropomorphism
Exercise: Pick a non-human object and describe it using human traits, this time using similes and metaphors rather than directly ascribing human traits to it.
54. Rhetorical question
A rhetorical question is asked to create an effect rather than to solicit an answer from the listener or reader. Often it has an obvious answer and the point of asking is to create emphasis. It’s a great way to get an audience to consider the topic at hand and make a statement.
Example: “If you prick us, do we not bleed? If you tickle us, do we not laugh? If you poison us, do we not die? And if you wrong us, shall we not revenge?” — The Merchant of Venice by William Shakespeare
Writers use satire to make fun of some aspect of human nature or society — usually through exaggeration, ridicule, or irony. There are countless ways to satirize something; most of the time, you know it when you read it.
Example: The famous adventure novel Gulliver’s Travels by Jonathan Swift is a classic example of satire, poking fun at “travelers' tales,” the government, and indeed human nature itself.
A simile draws resemblance between two things by saying “Thing A is like Thing B,” or “Thing A is as [adjective] as Thing B.” Unlike a metaphor, a similar does not posit that these things are the same, only that they are alike. As a result, it is probably the most common literary device in writing — you can almost always recognize a simile through the use of “like” or “as.”
Example: There are two similes in this description from Circe by Madeline Miller: “The ships were golden and huge as leviathans, their rails carved from ivory and horn. They were towed by grinning dolphins or else crewed by fifty black-haired nereids, faces silver as moonlight.”
Similar term: metaphor
57. Symbolism
Authors turn to tangible symbols to represent abstract concepts and ideas in their stories Symbols typically derive from objects or non-humans — for instance, a dove might represent peace, or a raven might represent death.
Example: In The Great Gatsby , Fitzgerald uses the eyes of Doctor T.J. Eckleburg (actually a faded optometrist's billboard) to represent God and his judgment of the Jazz Age.
Similar term: motif
Exercise: Choose an object that you want to represent something — like an idea or concept. Now, write a poem or short story centered around that symbol.
58. Synecdoche
Synecdoche is the usage of a part to represent the whole. That is, rather than an object or title that’s merely associated with the larger concept (as in metonymy), synecdoche must actually be attached in some way: either to the name, or to the larger whole itself.
Examples: “Stanford won the game” ( Stanford referring to the full title of the Stanford football team) or “Nice wheels you got there” ( wheels referring to the entire car)
Similar term: metonymy
Zeugma is when one word is used to ascribe two separate meanings to two other words. This literary device is great for adding humor and figurative flair as it tends to surprise the reader. And it’s just a fun type of wordplay.
Example: “ Yet time and her aunt moved slowly — and her patience and her ideas were nearly worn out before the tete-a-tete was over.” — Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen
60. Zoomorphism
Zoomorphism is when you take animal traits and assign them to anything that’s not an animal. It’s the opposite of anthropomorphism and personification, and can be either a physical manifestation, such as a god appearing as an animal, or a comparison, like calling someone a busy bee .
Example: When vampires turn into bats, their bat form is an instance of zoomorphism.
Exercise: Describe a human or object by using traits that are usually associated with animals.
Similar terms: anthropomorphism, personification
Readers and writers alike can get a lot out of understanding literary devices and how they're used. Readers can use them to gain insight into the author’s intended meaning behind their work, while writers can use literary devices to better connect with readers. But whatever your motivation for learning them, you certainly won't be sorry you did! (Not least because you'll recognize the device I just used in that sentence. 😏)
6 responses
Ron B. Saunders says:
16/01/2019 – 19:26
Paraprosdokians are also delightful literary devices for creating surprise or intrigue. They cause a reader to rethink a concept or traditional expectation. (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraprosdokian)
ManhattanMinx says:
17/01/2019 – 02:07
That's pore, not pour. Shame.....
↪️ Coline Harmon replied:
14/06/2019 – 19:06
It was a Malapropism
↪️ JC JC replied:
23/10/2019 – 00:02
Yeah ManhattanMinx. It's a Malepropism!
↪️ jesus replied:
07/11/2019 – 13:24
Susan McGrath says:
10/03/2020 – 10:56
"But whatever your motivation for learning them, you certainly won't be sorry you did! (Not least because you'll recognize the device I just used in that sentence. 😏)" Litote
Comments are currently closed.
Continue reading
Recommended posts from the Reedsy Blog

Man vs Nature: The Most Compelling Conflict in Writing
What is man vs nature? Learn all about this timeless conflict with examples of man vs nature in books, television, and film.

The Redemption Arc: Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
Learn what it takes to redeem a character with these examples and writing tips.

How Many Sentences Are in a Paragraph?
From fiction to nonfiction works, the length of a paragraph varies depending on its purpose. Here's everything you need to know.
Narrative Structure: Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
What's the difference between story structure and narrative structure? And how do you choose the right narrative structure for you novel?

What is the Proust Questionnaire? 22 Questions to Write Better Characters
Inspired by Marcel Proust, check out the questionnaire that will help your characters remember things past.

What is Pathos? Definition and Examples in Literature
Pathos is a literary device that uses language to evoke an emotional response, typically to connect readers with the characters in a story.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.

We made a writing app for you
Yes, you! Write. Format. Export for ebook and print. 100% free, always.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:

Literary Devices & Terms
An acrostic is a piece of writing in which a particular set of letters—typically the first letter of each line, word, or paragraph—spells out a word or phrase with special significance to the text. Acrostics... (read full acrostic explanation with examples) An acrostic is a piece of writing in which a particular set of letters—typically the first letter of each line,... (read more)
An allegory is a work that conveys a hidden meaning—usually moral, spiritual, or political—through the use of symbolic characters and events. The story of "The Tortoise and The Hare" is a well-known allegory with a... (read full allegory explanation with examples) An allegory is a work that conveys a hidden meaning—usually moral, spiritual, or political—through the use of symbolic characters and... (read more)
Alliteration is a figure of speech in which the same sound repeats in a group of words, such as the “b” sound in: “Bob brought the box of bricks to the basement.” The repeating sound... (read full alliteration explanation with examples) Alliteration is a figure of speech in which the same sound repeats in a group of words, such as the... (read more)
In literature, an allusion is an unexplained reference to someone or something outside of the text. Writers commonly allude to other literary works, famous individuals, historical events, or philosophical ideas, and they do so in... (read full allusion explanation with examples) In literature, an allusion is an unexplained reference to someone or something outside of the text. Writers commonly allude to... (read more)
An anachronism is a person or a thing placed in the wrong time period. For instance, if a novel set in Medieval England featured a trip to a movie-theater, that would be an anachronism. Although... (read full anachronism explanation with examples) An anachronism is a person or a thing placed in the wrong time period. For instance, if a novel set... (read more)
Anadiplosis is a figure of speech in which a word or group of words located at the end of one clause or sentence is repeated at or near the beginning of the following clause or... (read full anadiplosis explanation with examples) Anadiplosis is a figure of speech in which a word or group of words located at the end of one... (read more)
An analogy is a comparison that aims to explain a thing or idea by likening it to something else. For example, a career coach might say, "Being the successful boss or CEO of a company... (read full analogy explanation with examples) An analogy is a comparison that aims to explain a thing or idea by likening it to something else. For... (read more)
An anapest is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which two unstressed syllables are followed by a stressed syllable. The word "understand" is an anapest, with the unstressed syllables of "un" and "der" followed... (read full anapest explanation with examples) An anapest is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which two unstressed syllables are followed by a stressed syllable.... (read more)
Anaphora is a figure of speech in which words repeat at the beginning of successive clauses, phrases, or sentences. For example, Martin Luther King's famous "I Have a Dream" speech contains anaphora: "So let freedom... (read full anaphora explanation with examples) Anaphora is a figure of speech in which words repeat at the beginning of successive clauses, phrases, or sentences. For... (read more)
An antagonist is usually a character who opposes the protagonist (or main character) of a story, but the antagonist can also be a group of characters, institution, or force against which the protagonist must contend.... (read full antagonist explanation with examples) An antagonist is usually a character who opposes the protagonist (or main character) of a story, but the antagonist can... (read more)
Antanaclasis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated within a sentence, but the word or phrase means something different each time it appears. A famous example of antanaclasis is... (read full antanaclasis explanation with examples) Antanaclasis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated within a sentence, but the word... (read more)
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human characteristics, emotions, and behaviors to animals or other non-human things (including objects, plants, and supernatural beings). Some famous examples of anthropomorphism include Winnie the Pooh, the Little Engine that Could, and Simba from... (read full anthropomorphism explanation with examples) Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human characteristics, emotions, and behaviors to animals or other non-human things (including objects, plants, and supernatural beings). Some famous... (read more)
Antimetabole is a figure of speech in which a phrase is repeated, but with the order of words reversed. John F. Kennedy's words, "Ask not what your country can do for you, ask what you... (read full antimetabole explanation with examples) Antimetabole is a figure of speech in which a phrase is repeated, but with the order of words reversed. John... (read more)
Antithesis is a figure of speech that juxtaposes two contrasting or opposing ideas, usually within parallel grammatical structures. For instance, Neil Armstrong used antithesis when he stepped onto the surface of the moon in 1969... (read full antithesis explanation with examples) Antithesis is a figure of speech that juxtaposes two contrasting or opposing ideas, usually within parallel grammatical structures. For instance,... (read more)
An aphorism is a saying that concisely expresses a moral principle or an observation about the world, presenting it as a general or universal truth. The Rolling Stones are responsible for penning one of the... (read full aphorism explanation with examples) An aphorism is a saying that concisely expresses a moral principle or an observation about the world, presenting it as... (read more)
Aphorismus is a type of figure of speech that calls into question the way a word is used. Aphorismus is used not to question the meaning of a word, but whether it is actually appropriate... (read full aphorismus explanation with examples) Aphorismus is a type of figure of speech that calls into question the way a word is used. Aphorismus is... (read more)
Aporia is a rhetorical device in which a speaker expresses uncertainty or doubt—often pretended uncertainty or doubt—about something, usually as a way of proving a point. An example of aporia is the famous Elizabeth Barrett... (read full aporia explanation with examples) Aporia is a rhetorical device in which a speaker expresses uncertainty or doubt—often pretended uncertainty or doubt—about something, usually as... (read more)
Apostrophe is a figure of speech in which a speaker directly addresses someone (or something) that is not present or cannot respond in reality. The entity being addressed can be an absent, dead, or imaginary... (read full apostrophe explanation with examples) Apostrophe is a figure of speech in which a speaker directly addresses someone (or something) that is not present or... (read more)
Assonance is a figure of speech in which the same vowel sound repeats within a group of words. An example of assonance is: "Who gave Newt and Scooter the blue tuna? It was too soon!" (read full assonance explanation with examples) Assonance is a figure of speech in which the same vowel sound repeats within a group of words. An example... (read more)
An asyndeton (sometimes called asyndetism) is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and", "or", and "but" that join other words or clauses in a sentence into relationships of equal importance—are omitted.... (read full asyndeton explanation with examples) An asyndeton (sometimes called asyndetism) is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and", "or", and "but"... (read more)
A ballad is a type of poem that tells a story and was traditionally set to music. English language ballads are typically composed of four-line stanzas that follow an ABCB rhyme scheme. (read full ballad explanation with examples) A ballad is a type of poem that tells a story and was traditionally set to music. English language ballads... (read more)
A ballade is a form of lyric poetry that originated in medieval France. Ballades follow a strict rhyme scheme ("ababbcbc"), and typically have three eight-line stanzas followed by a shorter four-line stanza called an envoi.... (read full ballade explanation with examples) A ballade is a form of lyric poetry that originated in medieval France. Ballades follow a strict rhyme scheme ("ababbcbc"),... (read more)
Bildungsroman is a genre of novel that shows a young protagonist's journey from childhood to adulthood (or immaturity to maturity), with a focus on the trials and misfortunes that affect the character's growth. (read full bildungsroman explanation with examples) Bildungsroman is a genre of novel that shows a young protagonist's journey from childhood to adulthood (or immaturity to maturity),... (read more)
Blank verse is the name given to poetry that lacks rhymes but does follow a specific meter—a meter that is almost always iambic pentameter. Blank verse was particularly popular in English poetry written between the... (read full blank verse explanation with examples) Blank verse is the name given to poetry that lacks rhymes but does follow a specific meter—a meter that is... (read more)
A cacophony is a combination of words that sound harsh or unpleasant together, usually because they pack a lot of percussive or "explosive" consonants (like T, P, or K) into relatively little space. For instance, the... (read full cacophony explanation with examples) A cacophony is a combination of words that sound harsh or unpleasant together, usually because they pack a lot of... (read more)
A caesura is a pause that occurs within a line of poetry, usually marked by some form of punctuation such as a period, comma, ellipsis, or dash. A caesura doesn't have to be placed in... (read full caesura explanation with examples) A caesura is a pause that occurs within a line of poetry, usually marked by some form of punctuation such... (read more)
Catharsis is the process of releasing strong or pent-up emotions through art. Aristotle coined the term catharsis—which comes from the Greek kathairein meaning "to cleanse or purge"—to describe the release of emotional tension that he... (read full catharsis explanation with examples) Catharsis is the process of releasing strong or pent-up emotions through art. Aristotle coined the term catharsis—which comes from the... (read more)
Characterization is the representation of the traits, motives, and psychology of a character in a narrative. Characterization may occur through direct description, in which the character's qualities are described by a narrator, another character, or... (read full characterization explanation with examples) Characterization is the representation of the traits, motives, and psychology of a character in a narrative. Characterization may occur through... (read more)
Chiasmus is a figure of speech in which the grammar of one phrase is inverted in the following phrase, such that two key concepts from the original phrase reappear in the second phrase in inverted... (read full chiasmus explanation with examples) Chiasmus is a figure of speech in which the grammar of one phrase is inverted in the following phrase, such... (read more)
The word cinquain can refer to two different things. Historically, it referred to any stanza of five lines written in any type of verse. More recently, cinquain has come to refer to particular types of... (read full cinquain explanation with examples) The word cinquain can refer to two different things. Historically, it referred to any stanza of five lines written in... (read more)
A cliché is a phrase that, due to overuse, is seen as lacking in substance or originality. For example, telling a heartbroken friend that there are "Plenty of fish in the sea" is such a... (read full cliché explanation with examples) A cliché is a phrase that, due to overuse, is seen as lacking in substance or originality. For example, telling... (read more)
Climax is a figure of speech in which successive words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are arranged in ascending order of importance, as in "Look! Up in the sky! It's a bird! It's a plane! It's... (read full climax (figure of speech) explanation with examples) Climax is a figure of speech in which successive words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are arranged in ascending order of... (read more)
The climax of a plot is the story's central turning point—the moment of peak tension or conflict—which all the preceding plot developments have been leading up to. In a traditional "good vs. evil" story (like many superhero movies)... (read full climax (plot) explanation with examples) The climax of a plot is the story's central turning point—the moment of peak tension or conflict—which all the preceding plot... (read more)
Colloquialism is the use of informal words or phrases in writing or speech. Colloquialisms are usually defined in geographical terms, meaning that they are often defined by their use within a dialect, a regionally-defined variant... (read full colloquialism explanation with examples) Colloquialism is the use of informal words or phrases in writing or speech. Colloquialisms are usually defined in geographical terms,... (read more)
Common meter is a specific type of meter that is often used in lyric poetry. Common meter has two key traits: it alternates between lines of eight syllables and lines of six syllables, and it... (read full common meter explanation with examples) Common meter is a specific type of meter that is often used in lyric poetry. Common meter has two key... (read more)
A conceit is a fanciful metaphor, especially a highly elaborate or extended metaphor in which an unlikely, far-fetched, or strained comparison is made between two things. A famous example comes from John Donne's poem, "A... (read full conceit explanation with examples) A conceit is a fanciful metaphor, especially a highly elaborate or extended metaphor in which an unlikely, far-fetched, or strained... (read more)
Connotation is the array of emotions and ideas suggested by a word in addition to its dictionary definition. Most words carry meanings, impressions, or associations apart from or beyond their literal meaning. For example, the... (read full connotation explanation with examples) Connotation is the array of emotions and ideas suggested by a word in addition to its dictionary definition. Most words... (read more)
Consonance is a figure of speech in which the same consonant sound repeats within a group of words. An example of consonance is: "Traffic figures, on July Fourth, to be tough." (read full consonance explanation with examples) Consonance is a figure of speech in which the same consonant sound repeats within a group of words. An example... (read more)
A couplet is a unit of two lines of poetry, especially lines that use the same or similar meter, form a rhyme, or are separated from other lines by a double line break. (read full couplet explanation with examples) A couplet is a unit of two lines of poetry, especially lines that use the same or similar meter, form... (read more)
A dactyl is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by two unstressed syllables. The word “poetry” itself is a great example of a dactyl, with the stressed syllable... (read full dactyl explanation with examples) A dactyl is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by two unstressed syllables.... (read more)
Denotation is the literal meaning, or "dictionary definition," of a word. Denotation is defined in contrast to connotation, which is the array of emotions and ideas suggested by a word in addition to its dictionary... (read full denotation explanation with examples) Denotation is the literal meaning, or "dictionary definition," of a word. Denotation is defined in contrast to connotation, which is... (read more)
The dénouement is the final section of a story's plot, in which loose ends are tied up, lingering questions are answered, and a sense of resolution is achieved. The shortest and most well known dénouement, it could be... (read full dénouement explanation with examples) The dénouement is the final section of a story's plot, in which loose ends are tied up, lingering questions are answered, and... (read more)
A deus ex machina is a plot device whereby an unsolvable conflict or point of tension is suddenly resolved by the unexpected appearance of an implausible character, object, action, ability, or event. For example, if... (read full deus ex machina explanation with examples) A deus ex machina is a plot device whereby an unsolvable conflict or point of tension is suddenly resolved by... (read more)
Diacope is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated with a small number of intervening words. The first line of Anna Karenina by Leo Tolstoy, "Happy families are all alike;... (read full diacope explanation with examples) Diacope is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated with a small number of intervening... (read more)
Dialogue is the exchange of spoken words between two or more characters in a book, play, or other written work. In prose writing, lines of dialogue are typically identified by the use of quotation marks... (read full dialogue explanation with examples) Dialogue is the exchange of spoken words between two or more characters in a book, play, or other written work.... (read more)
Diction is a writer's unique style of expression, especially his or her choice and arrangement of words. A writer's vocabulary, use of language to produce a specific tone or atmosphere, and ability to communicate clearly... (read full diction explanation with examples) Diction is a writer's unique style of expression, especially his or her choice and arrangement of words. A writer's vocabulary,... (read more)
Dramatic irony is a plot device often used in theater, literature, film, and television to highlight the difference between a character's understanding of a given situation, and that of the audience. More specifically, in dramatic... (read full dramatic irony explanation with examples) Dramatic irony is a plot device often used in theater, literature, film, and television to highlight the difference between a... (read more)
A dynamic character undergoes substantial internal changes as a result of one or more plot developments. The dynamic character's change can be extreme or subtle, as long as his or her development is important to... (read full dynamic character explanation with examples) A dynamic character undergoes substantial internal changes as a result of one or more plot developments. The dynamic character's change... (read more)
An elegy is a poem of serious reflection, especially one mourning the loss of someone who died. Elegies are defined by their subject matter, and don't have to follow any specific form in terms of... (read full elegy explanation with examples) An elegy is a poem of serious reflection, especially one mourning the loss of someone who died. Elegies are defined... (read more)
End rhyme refers to rhymes that occur in the final words of lines of poetry. For instance, these lines from Dorothy Parker's poem "Interview" use end rhyme: "The ladies men admire, I’ve heard, / Would shudder... (read full end rhyme explanation with examples) End rhyme refers to rhymes that occur in the final words of lines of poetry. For instance, these lines from... (read more)
An end-stopped line is a line of poetry in which a sentence or phrase comes to a conclusion at the end of the line. For example, the poet C.P. Cavafy uses end-stopped lines in his... (read full end-stopped line explanation with examples) An end-stopped line is a line of poetry in which a sentence or phrase comes to a conclusion at the... (read more)
Enjambment is the continuation of a sentence or clause across a line break. For example, the poet John Donne uses enjambment in his poem "The Good-Morrow" when he continues the opening sentence across the line... (read full enjambment explanation with examples) Enjambment is the continuation of a sentence or clause across a line break. For example, the poet John Donne uses... (read more)
An envoi is a brief concluding stanza at the end of a poem that can either summarize the preceding poem or serve as its dedication. The envoi tends to follow the same meter and rhyme... (read full envoi explanation with examples) An envoi is a brief concluding stanza at the end of a poem that can either summarize the preceding poem... (read more)
Epanalepsis is a figure of speech in which the beginning of a clause or sentence is repeated at the end of that same clause or sentence, with words intervening. The sentence "The king is dead,... (read full epanalepsis explanation with examples) Epanalepsis is a figure of speech in which the beginning of a clause or sentence is repeated at the end... (read more)
An epigram is a short and witty statement, usually written in verse, that conveys a single thought or observation. Epigrams typically end with a punchline or a satirical twist. (read full epigram explanation with examples) An epigram is a short and witty statement, usually written in verse, that conveys a single thought or observation. Epigrams... (read more)
An epigraph is a short quotation, phrase, or poem that is placed at the beginning of another piece of writing to encapsulate that work's main themes and to set the tone. For instance, the epigraph of Mary... (read full epigraph explanation with examples) An epigraph is a short quotation, phrase, or poem that is placed at the beginning of another piece of writing to... (read more)
Epistrophe is a figure of speech in which one or more words repeat at the end of successive phrases, clauses, or sentences. In his Gettysburg Address, Abraham Lincoln urged the American people to ensure that,... (read full epistrophe explanation with examples) Epistrophe is a figure of speech in which one or more words repeat at the end of successive phrases, clauses,... (read more)
Epizeuxis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated in immediate succession, with no intervening words. In the play Hamlet, when Hamlet responds to a question about what he's reading... (read full epizeuxis explanation with examples) Epizeuxis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated in immediate succession, with no intervening... (read more)
Ethos, along with logos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Ethos is an argument that appeals to the audience by emphasizing the... (read full ethos explanation with examples) Ethos, along with logos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective... (read more)
Euphony is the combining of words that sound pleasant together or are easy to pronounce, usually because they contain lots of consonants with soft or muffled sounds (like L, M, N, and R) instead of consonants with harsh, percussive sounds (like... (read full euphony explanation with examples) Euphony is the combining of words that sound pleasant together or are easy to pronounce, usually because they contain lots of consonants with soft... (read more)
Exposition is the description or explanation of background information within a work of literature. Exposition can cover characters and their relationship to one another, the setting or time and place of events, as well as... (read full exposition explanation with examples) Exposition is the description or explanation of background information within a work of literature. Exposition can cover characters and their... (read more)
An extended metaphor is a metaphor that unfolds across multiple lines or even paragraphs of a text, making use of multiple interrelated metaphors within an overarching one. So while "life is a highway" is a... (read full extended metaphor explanation with examples) An extended metaphor is a metaphor that unfolds across multiple lines or even paragraphs of a text, making use of... (read more)
An external conflict is a problem, antagonism, or struggle that takes place between a character and an outside force. External conflict drives the action of a plot forward. (read full external conflict explanation with examples) An external conflict is a problem, antagonism, or struggle that takes place between a character and an outside force. External conflict... (read more)
The falling action of a story is the section of the plot following the climax, in which the tension stemming from the story's central conflict decreases and the story moves toward its conclusion. For instance, the traditional "good... (read full falling action explanation with examples) The falling action of a story is the section of the plot following the climax, in which the tension stemming from... (read more)
Figurative language is language that contains or uses figures of speech. When people use the term "figurative language," however, they often do so in a slightly narrower way. In this narrower definition, figurative language refers... (read full figurative language explanation with examples) Figurative language is language that contains or uses figures of speech. When people use the term "figurative language," however, they... (read more)
A figure of speech is a literary device in which language is used in an unusual—or "figured"—way in order to produce a stylistic effect. Figures of speech can be broken into two main groups: figures... (read full figure of speech explanation with examples) A figure of speech is a literary device in which language is used in an unusual—or "figured"—way in order to... (read more)
A character is said to be "flat" if it is one-dimensional or lacking in complexity. Typically, flat characters can be easily and accurately described using a single word (like "bully") or one short sentence (like "A naive... (read full flat character explanation with examples) A character is said to be "flat" if it is one-dimensional or lacking in complexity. Typically, flat characters can be easily... (read more)
Foreshadowing is a literary device in which authors hint at plot developments that don't actually occur until later in the story. Foreshadowing can be achieved directly or indirectly, by making explicit statements or leaving subtle... (read full foreshadowing explanation with examples) Foreshadowing is a literary device in which authors hint at plot developments that don't actually occur until later in the... (read more)
Formal verse is the name given to rhymed poetry that uses a strict meter (a regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables). This two-line poem by Emily Dickinson is formal verse because it rhymes and... (read full formal verse explanation with examples) Formal verse is the name given to rhymed poetry that uses a strict meter (a regular pattern of stressed and... (read more)
Free verse is the name given to poetry that doesn’t use any strict meter or rhyme scheme. Because it has no set meter, poems written in free verse can have lines of any length, from... (read full free verse explanation with examples) Free verse is the name given to poetry that doesn’t use any strict meter or rhyme scheme. Because it has... (read more)
Hamartia is a literary term that refers to a tragic flaw or error that leads to a character's downfall. In the novel Frankenstein, Victor Frankenstein's arrogant conviction that he can usurp the roles of God... (read full hamartia explanation with examples) Hamartia is a literary term that refers to a tragic flaw or error that leads to a character's downfall. In... (read more)
Hubris refers to excessive pride or overconfidence, which drives a person to overstep limits in a way that leads to their downfall. In Greek mythology, the legend of Icarus involves an iconic case of hubris:... (read full hubris explanation with examples) Hubris refers to excessive pride or overconfidence, which drives a person to overstep limits in a way that leads to... (read more)
Hyperbole is a figure of speech in which a writer or speaker exaggerates for the sake of emphasis. Hyperbolic statements are usually quite obvious exaggerations intended to emphasize a point, rather than be taken literally.... (read full hyperbole explanation with examples) Hyperbole is a figure of speech in which a writer or speaker exaggerates for the sake of emphasis. Hyperbolic statements... (read more)
An iamb is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which one unstressed syllable is followed by a stressed syllable. The word "define" is an iamb, with the unstressed syllable of "de" followed by the... (read full iamb explanation with examples) An iamb is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which one unstressed syllable is followed by a stressed syllable.... (read more)
An idiom is a phrase that conveys a figurative meaning that is difficult or impossible to understand based solely on a literal interpretation of the words in the phrase. For example, saying that something is... (read full idiom explanation with examples) An idiom is a phrase that conveys a figurative meaning that is difficult or impossible to understand based solely on... (read more)
Imagery, in any sort of writing, refers to descriptive language that engages the human senses. For instance, the following lines from Robert Frost's poem "After Apple-Picking" contain imagery that engages the senses of touch, movement,... (read full imagery explanation with examples) Imagery, in any sort of writing, refers to descriptive language that engages the human senses. For instance, the following lines... (read more)
Internal rhyme is rhyme that occurs in the middle of lines of poetry, instead of at the ends of lines. A single line of poetry can contain internal rhyme (with multiple words in the same... (read full internal rhyme explanation with examples) Internal rhyme is rhyme that occurs in the middle of lines of poetry, instead of at the ends of lines.... (read more)
Irony is a literary device or event in which how things seem to be is in fact very different from how they actually are. If this seems like a loose definition, don't worry—it is. Irony is a... (read full irony explanation with examples) Irony is a literary device or event in which how things seem to be is in fact very different from how... (read more)
Juxtaposition occurs when an author places two things side by side as a way of highlighting their differences. Ideas, images, characters, and actions are all things that can be juxtaposed with one another. For example,... (read full juxtaposition explanation with examples) Juxtaposition occurs when an author places two things side by side as a way of highlighting their differences. Ideas, images,... (read more)
A kenning is a figure of speech in which two words are combined in order to form a poetic expression that refers to a person or a thing. For example, "whale-road" is a kenning for... (read full kenning explanation with examples) A kenning is a figure of speech in which two words are combined in order to form a poetic expression... (read more)
A line break is the termination of one line of poetry, and the beginning of a new line. (read full line break explanation with examples) A line break is the termination of one line of poetry, and the beginning of a new line. (read more)
Litotes is a figure of speech and a form of understatement in which a sentiment is expressed ironically by negating its contrary. For example, saying "It's not the best weather today" during a hurricane would... (read full litotes explanation with examples) Litotes is a figure of speech and a form of understatement in which a sentiment is expressed ironically by negating... (read more)
Logos, along with ethos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Logos is an argument that appeals to an audience's sense of logic... (read full logos explanation with examples) Logos, along with ethos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective... (read more)
A metaphor is a figure of speech that compares two different things by saying that one thing is the other. The comparison in a metaphor can be stated explicitly, as in the sentence "Love is... (read full metaphor explanation with examples) A metaphor is a figure of speech that compares two different things by saying that one thing is the other.... (read more)
Meter is a regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables that defines the rhythm of some poetry. These stress patterns are defined in groupings, called feet, of two or three syllables. A pattern of unstressed-stressed,... (read full meter explanation with examples) Meter is a regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables that defines the rhythm of some poetry. These stress patterns... (read more)
Metonymy is a type of figurative language in which an object or concept is referred to not by its own name, but instead by the name of something closely associated with it. For example, in... (read full metonymy explanation with examples) Metonymy is a type of figurative language in which an object or concept is referred to not by its own... (read more)
The mood of a piece of writing is its general atmosphere or emotional complexion—in short, the array of feelings the work evokes in the reader. Every aspect of a piece of writing can influence its mood, from the... (read full mood explanation with examples) The mood of a piece of writing is its general atmosphere or emotional complexion—in short, the array of feelings the work evokes... (read more)
A motif is an element or idea that recurs throughout a work of literature. Motifs, which are often collections of related symbols, help develop the central themes of a book or play. For example, one... (read full motif explanation with examples) A motif is an element or idea that recurs throughout a work of literature. Motifs, which are often collections of... (read more)
A narrative is an account of connected events. Two writers describing the same set of events might craft very different narratives, depending on how they use different narrative elements, such as tone or point of view. For... (read full narrative explanation with examples) A narrative is an account of connected events. Two writers describing the same set of events might craft very different narratives,... (read more)
Onomatopoeia is a figure of speech in which words evoke the actual sound of the thing they refer to or describe. The “boom” of a firework exploding, the “tick tock” of a clock, and the... (read full onomatopoeia explanation with examples) Onomatopoeia is a figure of speech in which words evoke the actual sound of the thing they refer to or... (read more)
An oxymoron is a figure of speech in which two contradictory terms or ideas are intentionally paired in order to make a point—particularly to reveal a deeper or hidden truth. The most recognizable oxymorons are... (read full oxymoron explanation with examples) An oxymoron is a figure of speech in which two contradictory terms or ideas are intentionally paired in order to... (read more)
A paradox is a figure of speech that seems to contradict itself, but which, upon further examination, contains some kernel of truth or reason. Oscar Wilde's famous declaration that "Life is much too important to be... (read full paradox explanation with examples) A paradox is a figure of speech that seems to contradict itself, but which, upon further examination, contains some kernel... (read more)
Parallelism is a figure of speech in which two or more elements of a sentence (or series of sentences) have the same grammatical structure. These "parallel" elements can be used to intensify the rhythm of... (read full parallelism explanation with examples) Parallelism is a figure of speech in which two or more elements of a sentence (or series of sentences) have... (read more)
Parataxis is a figure of speech in which words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are set next to each other so that each element is equally important. Parataxis usually involves simple sentences or phrases whose relationships... (read full parataxis explanation with examples) Parataxis is a figure of speech in which words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are set next to each other so... (read more)
A parody is a work that mimics the style of another work, artist, or genre in an exaggerated way, usually for comic effect. Parodies can take many forms, including fiction, poetry, film, visual art, and... (read full parody explanation with examples) A parody is a work that mimics the style of another work, artist, or genre in an exaggerated way, usually... (read more)
Pathetic fallacy occurs when a writer attributes human emotions to things that aren't human, such as objects, weather, or animals. It is often used to make the environment reflect the inner experience of a narrator... (read full pathetic fallacy explanation with examples) Pathetic fallacy occurs when a writer attributes human emotions to things that aren't human, such as objects, weather, or animals.... (read more)
Pathos, along with logos and ethos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Pathos is an argument that appeals to an audience's emotions. When a... (read full pathos explanation with examples) Pathos, along with logos and ethos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective... (read more)
Personification is a type of figurative language in which non-human things are described as having human attributes, as in the sentence, "The rain poured down on the wedding guests, indifferent to their plans." Describing the... (read full personification explanation with examples) Personification is a type of figurative language in which non-human things are described as having human attributes, as in the... (read more)
Plot is the sequence of interconnected events within the story of a play, novel, film, epic, or other narrative literary work. More than simply an account of what happened, plot reveals the cause-and-effect relationships between... (read full plot explanation with examples) Plot is the sequence of interconnected events within the story of a play, novel, film, epic, or other narrative literary... (read more)
Point of view refers to the perspective that the narrator holds in relation to the events of the story. The three primary points of view are first person, in which the narrator tells a story from... (read full point of view explanation with examples) Point of view refers to the perspective that the narrator holds in relation to the events of the story. The... (read more)
Polyptoton is a figure of speech that involves the repetition of words derived from the same root (such as "blood" and "bleed"). For instance, the question, "Who shall watch the watchmen?" is an example of... (read full polyptoton explanation with examples) Polyptoton is a figure of speech that involves the repetition of words derived from the same root (such as "blood"... (read more)
Polysyndeton is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and," "or," and "but" that join other words or clauses in a sentence into relationships of equal importance—are used several times in close... (read full polysyndeton explanation with examples) Polysyndeton is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and," "or," and "but" that join other words... (read more)
The protagonist of a story is its main character, who has the sympathy and support of the audience. This character tends to be involved in or affected by most of the choices or conflicts that... (read full protagonist explanation with examples) The protagonist of a story is its main character, who has the sympathy and support of the audience. This character... (read more)
A pun is a figure of speech that plays with words that have multiple meanings, or that plays with words that sound similar but mean different things. The comic novelist Douglas Adams uses both types... (read full pun explanation with examples) A pun is a figure of speech that plays with words that have multiple meanings, or that plays with words... (read more)
A quatrain is a four-line stanza of poetry. It can be a single four-line stanza, meaning that it is a stand-alone poem of four lines, or it can be a four-line stanza that makes up... (read full quatrain explanation with examples) A quatrain is a four-line stanza of poetry. It can be a single four-line stanza, meaning that it is a... (read more)
A red herring is a piece of information in a story that distracts readers from an important truth, or leads them to mistakenly expect a particular outcome. Most often, the term red herring is used to refer... (read full red herring explanation with examples) A red herring is a piece of information in a story that distracts readers from an important truth, or leads them... (read more)
In a poem or song, a refrain is a line or group of lines that regularly repeat, usually at the end of a stanza in a poem or at the end of a verse in... (read full refrain explanation with examples) In a poem or song, a refrain is a line or group of lines that regularly repeat, usually at the... (read more)
Repetition is a literary device in which a word or phrase is repeated two or more times. Repetition occurs in so many different forms that it is usually not thought of as a single figure... (read full repetition explanation with examples) Repetition is a literary device in which a word or phrase is repeated two or more times. Repetition occurs in... (read more)
A rhetorical question is a figure of speech in which a question is asked for a reason other than to get an answer—most commonly, it's asked to make a persuasive point. For example, if a... (read full rhetorical question explanation with examples) A rhetorical question is a figure of speech in which a question is asked for a reason other than to... (read more)
A rhyme is a repetition of similar sounds in two or more words. Rhyming is particularly common in many types of poetry, especially at the ends of lines, and is a requirement in formal verse.... (read full rhyme explanation with examples) A rhyme is a repetition of similar sounds in two or more words. Rhyming is particularly common in many types... (read more)
A rhyme scheme is the pattern according to which end rhymes (rhymes located at the end of lines) are repeated in works poetry. Rhyme schemes are described using letters of the alphabet, such that all... (read full rhyme scheme explanation with examples) A rhyme scheme is the pattern according to which end rhymes (rhymes located at the end of lines) are repeated... (read more)
The rising action of a story is the section of the plot leading up to the climax, in which the tension stemming from the story's central conflict grows through successive plot developments. For example, in the story of "Little... (read full rising action explanation with examples) The rising action of a story is the section of the plot leading up to the climax, in which the tension stemming... (read more)
A character is said to be "round" if they are lifelike or complex. Round characters typically have fully fleshed-out and multi-faceted personalities, backgrounds, desires, and motivations. Jay Gatsby in F. Scott Fitzgerald's The Great Gatsby... (read full round character explanation with examples) A character is said to be "round" if they are lifelike or complex. Round characters typically have fully fleshed-out and... (read more)
Satire is the use of humor, irony, sarcasm, or ridicule to criticize something or someone. Public figures, such as politicians, are often the subject of satire, but satirists can take aim at other targets as... (read full satire explanation with examples) Satire is the use of humor, irony, sarcasm, or ridicule to criticize something or someone. Public figures, such as politicians,... (read more)
A sestet is a six-line stanza of poetry. It can be any six-line stanza—one that is, itself, a whole poem, or one that makes up a part of a longer poem. Most commonly, the term... (read full sestet explanation with examples) A sestet is a six-line stanza of poetry. It can be any six-line stanza—one that is, itself, a whole poem,... (read more)
Setting is where and when a story or scene takes place. The where can be a real place like the city of New York, or it can be an imagined location, like Middle Earth in... (read full setting explanation with examples) Setting is where and when a story or scene takes place. The where can be a real place like the... (read more)
Sibilance is a figure of speech in which a hissing sound is created within a group of words through the repetition of "s" sounds. An example of sibilance is: "Sadly, Sam sold seven venomous serpents to Sally and... (read full sibilance explanation with examples) Sibilance is a figure of speech in which a hissing sound is created within a group of words through the repetition... (read more)
A simile is a figure of speech that directly compares two unlike things. To make the comparison, similes most often use the connecting words "like" or "as," but can also use other words that indicate... (read full simile explanation with examples) A simile is a figure of speech that directly compares two unlike things. To make the comparison, similes most often... (read more)
Traditionally, slant rhyme referred to a type of rhyme in which two words located at the end of a line of poetry themselves end in similar—but not identical—consonant sounds. For instance, the words "pact" and... (read full slant rhyme explanation with examples) Traditionally, slant rhyme referred to a type of rhyme in which two words located at the end of a line... (read more)
A soliloquy is a literary device, most often found in dramas, in which a character speaks to him or herself, relating his or her innermost thoughts and feelings as if thinking aloud. In some cases,... (read full soliloquy explanation with examples) A soliloquy is a literary device, most often found in dramas, in which a character speaks to him or herself,... (read more)
A sonnet is a type of fourteen-line poem. Traditionally, the fourteen lines of a sonnet consist of an octave (or two quatrains making up a stanza of 8 lines) and a sestet (a stanza of... (read full sonnet explanation with examples) A sonnet is a type of fourteen-line poem. Traditionally, the fourteen lines of a sonnet consist of an octave (or... (read more)
A spondee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which both syllables are stressed. The word "downtown" is a spondee, with the stressed syllable of "down" followed by another stressed syllable, “town”: Down-town. (read full spondee explanation with examples) A spondee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which both syllables are stressed. The word "downtown" is a... (read more)
A stanza is a group of lines form a smaller unit within a poem. A single stanza is usually set apart from other lines or stanza within a poem by a double line break or... (read full stanza explanation with examples) A stanza is a group of lines form a smaller unit within a poem. A single stanza is usually set... (read more)
A character is said to be "static" if they do not undergo any substantial internal changes as a result of the story's major plot developments. Antagonists are often static characters, but any character in a... (read full static character explanation with examples) A character is said to be "static" if they do not undergo any substantial internal changes as a result of... (read more)
Stream of consciousness is a style or technique of writing that tries to capture the natural flow of a character's extended thought process, often by incorporating sensory impressions, incomplete ideas, unusual syntax, and rough grammar. (read full stream of consciousness explanation with examples) Stream of consciousness is a style or technique of writing that tries to capture the natural flow of a character's... (read more)
A syllogism is a three-part logical argument, based on deductive reasoning, in which two premises are combined to arrive at a conclusion. So long as the premises of the syllogism are true and the syllogism... (read full syllogism explanation with examples) A syllogism is a three-part logical argument, based on deductive reasoning, in which two premises are combined to arrive at... (read more)
Symbolism is a literary device in which a writer uses one thing—usually a physical object or phenomenon—to represent something more abstract. A strong symbol usually shares a set of key characteristics with whatever it is... (read full symbolism explanation with examples) Symbolism is a literary device in which a writer uses one thing—usually a physical object or phenomenon—to represent something more... (read more)
Synecdoche is a figure of speech in which, most often, a part of something is used to refer to its whole. For example, "The captain commands one hundred sails" is a synecdoche that uses "sails"... (read full synecdoche explanation with examples) Synecdoche is a figure of speech in which, most often, a part of something is used to refer to its... (read more)
A theme is a universal idea, lesson, or message explored throughout a work of literature. One key characteristic of literary themes is their universality, which is to say that themes are ideas that not only... (read full theme explanation with examples) A theme is a universal idea, lesson, or message explored throughout a work of literature. One key characteristic of literary... (read more)
The tone of a piece of writing is its general character or attitude, which might be cheerful or depressive, sarcastic or sincere, comical or mournful, praising or critical, and so on. For instance, an editorial in a newspaper... (read full tone explanation with examples) The tone of a piece of writing is its general character or attitude, which might be cheerful or depressive, sarcastic or sincere, comical... (read more)
A tragic hero is a type of character in a tragedy, and is usually the protagonist. Tragic heroes typically have heroic traits that earn them the sympathy of the audience, but also have flaws or... (read full tragic hero explanation with examples) A tragic hero is a type of character in a tragedy, and is usually the protagonist. Tragic heroes typically have... (read more)
A trochee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by an unstressed syllable. The word "poet" is a trochee, with the stressed syllable of "po" followed by the... (read full trochee explanation with examples) A trochee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by an unstressed syllable.... (read more)
Understatement is a figure of speech in which something is expressed less strongly than would be expected, or in which something is presented as being smaller, worse, or lesser than it really is. Typically, understatement is... (read full understatement explanation with examples) Understatement is a figure of speech in which something is expressed less strongly than would be expected, or in which something... (read more)
Verbal irony occurs when the literal meaning of what someone says is different from—and often opposite to—what they actually mean. When there's a hurricane raging outside and someone remarks "what lovely weather we're having," this... (read full verbal irony explanation with examples) Verbal irony occurs when the literal meaning of what someone says is different from—and often opposite to—what they actually mean.... (read more)
A villanelle is a poem of nineteen lines, and which follows a strict form that consists of five tercets (three-line stanzas) followed by one quatrain (four-line stanza). Villanelles use a specific rhyme scheme of ABA... (read full villanelle explanation with examples) A villanelle is a poem of nineteen lines, and which follows a strict form that consists of five tercets (three-line... (read more)
A zeugma is a figure of speech in which one "governing" word or phrase modifies two distinct parts of a sentence. Often, the governing word will mean something different when applied to each part, as... (read full zeugma explanation with examples) A zeugma is a figure of speech in which one "governing" word or phrase modifies two distinct parts of a... (read more)

- PDF downloads of each of the 136 Lit Terms we cover
- PDF downloads of 1912 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,280 quotes across 1912 Lit Guides
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play


Common literary devices, such as metaphors and similes, are the building blocks of literature, and what make literature so enchanting. Language evolves through the literary devices in poetry and prose; the different types of figurative language make literature spark in different ways.
Consider this your crash course in common literary devices. Whether you’re studying for the AP Lit exam or looking to improve your creative writing, this article is crammed with literary devices, examples, and analysis.
What are Literary Devices?
- Personification
- Juxtaposition
- Onomatopoeia
- Common Literary Devices in Poetry
- Common Literary Devices in Prose
- Repetition Literary Devices
- Dialogue Literary Devices
- Word Play Literary Devices
- Parallelism Literary Devices
- Rhetorical Devices
Let’s start with the basics. What are literary devices?
Literary devices take writing beyond its literal meaning. They help guide the reader in how to read the piece.
Literary devices are ways of taking writing beyond its straightforward, literal meaning. In that sense, they are techniques for helping guide the reader in how to read the piece.
Central to all literary devices is a quality of connection : by establishing or examining relationships between things, literary devices encourage the reader to perceive and interpret the world in new ways.
One common form of connection in literary devices is comparison. Metaphors and similes are the most obvious examples of comparison. A metaphor is a direct comparison of two things—“the tree is a giant,” for example. A simile is an in direct comparison—“the tree is like a giant.” In both instances, the tree is compared to—and thus connected with—something (a giant) beyond what it literally is (a tree).
Other literary devices forge connections in different ways. For example, imagery, vivid description, connects writing richly to the worlds of the senses. Alliteration uses the sound of words itself to forge new literary connections (“alligators and apples”).
By enabling new connections that go beyond straightforward details and meanings, literary devices give literature its power.
What all these literary devices have in common is that they create new connections: rich layers of sound, sense, emotion, narrative, and ultimately meaning that surpass the literal details being recounted. They are what sets literature apart, and what makes it uniquely powerful.
Read on for an in-depth look and analysis at 112 common literary devices.
Check Out Our Online Writing Courses!

Tiny and True: Creating Flash Essays with Mindfulness
with Susan Barr-Toman
April 17th, 2024
How do you tell the full truth in under 1,000 words? Learn the art of flash essays and write nuggets of wisdom in this tiny essay class.

A Poet’s Calling Card: Writing and Composing a Chapbook
with Caitlin Scarano
The poetry chapbook gives poets the chance to make a small, artful collection around a poetic obsession. Learn how to craft yours in this 8 week chapbook intensive.

Plot Your Novel
with Jack Smith
Over eight weeks, you'll develop a solid basis in the fictional elements—protagonist, setting, secondary characters, point of view, plot, and theme—while you develop the outline of your novel. You'll receive feedback at all stages from your fellow writers and your instructor.

From the Source: Journaling for Self-Knowledge and Creativity
with Amy Bonnaffons
April 24th, 2024
Journal to discover yourself, find a wellspring of creativity, and produce publication-ready pieces.

How to Craft a Poem
with Zining Mok
A poem can tell a story, communicate our innermost thoughts, and reveal what moves us most deeply. Craft poems that do all of this and more in this guided poetry workshop.
Literary Devices List: 14 Common Literary Devices
In this article, we focus on literary devices that can be found in both poetry and prose.
There are a lot of literary devices to cover, each of which require their own examples and analysis. As such, we will start by focusing on common literary devices for this article: literary devices that can be found in both poetry and prose. With each device, we’ve included examples in literature and exercises you can use in your own creative writing.
Afterwards, we’ve listed other common literary devices you might see in poetry, prose, dialogue, and rhetoric.
Let’s get started!
1. Metaphor
Metaphors, also known as direct comparisons, are one of the most common literary devices. A metaphor is a statement in which two objects, often unrelated, are compared to each other.
Example of metaphor: This tree is the god of the forest.
Obviously, the tree is not a god—it is, in fact, a tree. However, by stating that the tree is the god, the reader is given the image of something strong, large, and immovable. Additionally, using “god” to describe the tree, rather than a word like “giant” or “gargantuan,” makes the tree feel like a spiritual center of the forest.
Metaphors allow the writer to pack multiple descriptions and images into one short sentence. The metaphor has much more weight and value than a direct description. If the writer chose to describe the tree as “the large, spiritual center of the forest,” the reader won’t understand the full importance of the tree’s size and scope.
Similes, also known as indirect comparisons, are similar in construction to metaphors, but they imply a different meaning. Like metaphors, two unrelated objects are being compared to each other. Unlike a metaphor, the comparison relies on the words “like” or “as.”
Example of simile: This tree is like the god of the forest. OR: This tree acts as the god of the forest.
What is the difference between a simile and a metaphor?
The obvious difference between these two common literary devices is that a simile uses “like” or “as,” whereas a metaphor never uses these comparison words.
Additionally, in reference to the above examples, the insertion of “like” or “as” creates a degree of separation between both elements of the device. In a simile, the reader understands that, although the tree is certainly large, it isn’t large enough to be a god; the tree’s “godhood” is simply a description, not a relevant piece of information to the poem or story.
Simply put, metaphors are better to use as a central device within the poem/story, encompassing the core of what you are trying to say. Similes are better as a supporting device.
Does that mean metaphors are better than similes? Absolutely not. Consider Louise Gluck’s poem “ The Past. ” Gluck uses both a simile and a metaphor to describe the sound of the wind: it is like shadows moving, but is her mother’s voice. Both devices are equally haunting, and ending the poem on the mother’s voice tells us the central emotion of the poem.
Learn more about the difference between similes and metaphors here:
Simile vs. Metaphor vs. Analogy: Definitions and Examples
Simile and Metaphor Writing Exercise: Tenors and Vehicles
Most metaphors and similes have two parts: the tenor and the vehicle. The tenor refers to the subject being described, and the vehicle refers to the image that describes the tenor.
So, in the metaphor “the tree is a god of the forest,” the tenor is the tree and the vehicle is “god of the forest.”
To practice writing metaphors and similes, let’s create some literary device lists. grab a sheet of paper and write down two lists. In the first list, write down “concept words”—words that cannot be physically touched. Love, hate, peace, war, happiness, and anger are all concepts because they can all be described but are not physical objects in themselves.
In the second list, write down only concrete objects—trees, clouds, the moon, Jupiter, New York brownstones, uncut sapphires, etc.
Your concepts are your tenors, and your concrete objects are your vehicles. Now, randomly draw a one between each tenor and each vehicle, then write an explanation for your metaphor/simile. You might write, say:
Have fun, write interesting literary devices, and try to incorporate them into a future poem or story!
An analogy is an argumentative comparison: it compares two unalike things to advance an argument. Specifically, it argues that two things have equal weight, whether that weight be emotional, philosophical, or even literal. Because analogical literary devices operate on comparison, it can be considered a form of metaphor.
For example:
Making pasta is as easy as one, two, three.
This analogy argues that making pasta and counting upwards are equally easy things. This format, “A is as B” or “A is to B”, is a common analogy structure.
Another common structure for analogy literary devices is “A is to B as C is to D.” For example:
Gordon Ramsay is to cooking as Meryl Streep is to acting.
The above constructions work best in argumentative works. Lawyers and essayists will often use analogies. In other forms of creative writing, analogies aren’t as formulaic, but can still prove to be powerful literary devices. In fact, you probably know this one:
“That which we call a rose / By any other name would smell as sweet” — Romeo & Juliet by William Shakespeare
To put this into the modern language of an analogy, Shakespeare is saying “a rose with no name smells as a rose with a name does.” The name “rose” does not affect whether or not the flower smells good.
Analogy Writing Exercise
Analogies are some of the most common literary devices, alongside similes and metaphors. Here’s an exercise for writing one yourself.
On a blank sheet of paper: write down the first four nouns that come to mind. Try to use concrete, visual nouns. Then, write down a verb. If you struggle to come up with any of these, any old word generator on the internet will help.
The only requirement is that two of your four nouns should be able to perform the verb. A dog can swim, for example, but it can’t fly an airplane.
Your list might look like this:
Verb: Fall Nouns: Rain, dirt, pavement, shadow
An analogy you create from this list might be: “his shadow falls on the pavement how rain falls on the dirt in May.
Your analogy might end up being silly or poetic, strange or evocative. But, by forcing yourself to make connections between seemingly disparate items, you’re using these literary devices to hone the skills of effective, interesting writing.
Is imagery a literary device? Absolutely! Imagery can be both literal and figurative, and it relies on the interplay of language and sensation to create a sharper image in your brain.
Imagery is what it sounds like—the use of figurative language to describe something.
Imagery is what it sounds like—the use of figurative language to describe something. In fact, we’ve already seen imagery in action through the previous literary devices: by describing the tree as a “god”, the tree looks large and sturdy in the reader’s mind.
However, imagery doesn’t just involve visual descriptions; the best writers use imagery to appeal to all five senses. By appealing to the reader’s sense of sight, sound, touch, taste, and smell, your writing will create a vibrant world for readers to live and breathe in.
The best writers use imagery to appeal to all five senses.
Let’s use imagery to describe that same tree. (I promise I can write about more than just trees, but it’s a very convenient image for these common literary devices, don’t you think?)
Notice how these literary device examples also used metaphors and similes? Literary devices often pile on top of each other, which is why so many great works of literature can be analyzed endlessly. Because imagery depends on the object’s likeness to other objects, imagery upholds the idea that a literary device is synonymous with comparison.
Imagery Writing Exercise
Want to try your hand at imagery? You can practice this concept by describing an object in the same way that this article describes a tree! Choose something to write about—any object, image, or idea—and describe it using the five senses. (“This biscuit has the tidy roundness of a lady’s antique hat.” “The biscuit tastes of brand-new cardboard.” and so on!)
Then, once you’ve written five (or more) lines of imagery, try combining these images until your object is sharp and clear in the reader’s head.
Imagery is one of the most essential common literary devices. To learn more about imagery, or to find more imagery writing exercises, take a look at our article Imagery Definition: 5+ Types of Imagery in Literature .
5. Symbolism
Symbolism combines a lot of the ideas presented in metaphor and imagery. Essentially, a symbol is the use of an object to represent a concept—it’s kind of like a metaphor, except more concise!
Symbols are everywhere in the English language, and we often use these common literary devices in speech and design without realizing it. The following are very common examples of symbolism:
A few very commonly used symbols include:
- “Peace” represented by a white dove
- “Love” represented by a red rose
- “Conformity” represented by sheep
- “Idea” represented by a light bulb switching on
The symbols above are so widely used that they would likely show up as clichés in your own writing. (Would you read a poem, written today, that started with “Let’s release the white dove of peace”?) In that sense, they do their job “too well”—they’re such a good symbol for what they symbolize that they’ve become ubiquitous, and you’ll have to add something new in your own writing.
Symbols are often contextually specific as well. For example, a common practice in Welsh marriage is to give your significant other a lovespoon , which the man has designed and carved to signify the relationship’s unique, everlasting bond. In many Western cultures, this same bond is represented by a diamond ring—which can also be unique and everlasting!
Symbolism makes the core ideas of your writing concrete.
Finally, notice how each of these examples are a concept represented by a concrete object. Symbolism makes the core ideas of your writing concrete, and also allows you to manipulate your ideas. If a rose represents love, what does a wilted rose or a rose on fire represent?
Symbolism Writing Exercise
Often, symbols are commonly understood images—but not always. You can invent your own symbols to capture the reader’s imagination, too!
Try your hand at symbolism by writing a poem or story centered around a symbol. Choose a random object, and make that object represent something. For example, you could try to make a blanket represent the idea of loneliness.
When you’ve paired an object and a concept, write your piece with that symbol at the center:
The down blanket lay crumpled, unused, on the empty side of our bed.
The goal is to make it clear that you’re associating the object with the concept. Make the reader feel the same way about your symbol as you do!
6. Personification
Personification, giving human attributes to nonhuman objects, is a powerful way to foster empathy in your readers.
Personification is exactly what it sounds like: giving human attributes to nonhuman objects. Also known as anthropomorphism, personification is a powerful way to foster empathy in your readers.
Think about personification as if it’s a specific type of imagery. You can describe a nonhuman object through the five senses, and do so by giving it human descriptions. You can even impute thoughts and emotions—mental events—to a nonhuman or even nonliving thing. This time, we’ll give human attributes to a car—see our personification examples below!
Personification (using sight): The car ran a marathon down the highway.
Personification (using sound): The car coughed, hacked, and spluttered.
Personification (using touch): The car was smooth as a baby’s bottom.
Personification (using taste): The car tasted the bitter asphalt.
Personification (using smell): The car needed a cold shower.
Personification (using mental events): The car remembered its first owner fondly.
Notice how we don’t directly say the car is like a human—we merely describe it using human behaviors. Personification exists at a unique intersection of imagery and metaphor, making it a powerful literary device that fosters empathy and generates unique descriptions.
Personification Writing Exercise
Try writing personification yourself! In the above example, we chose a random object and personified it through the five senses. It’s your turn to do the same thing: find a concrete noun and describe it like it’s a human.
Here are two examples:
The ancient, threadbare rug was clearly tired of being stepped on.
My phone issued notifications with the grimly efficient extroversion of a sorority chapter president.
Now start writing your own! Your descriptions can be active or passive, but the goal is to foster empathy in the reader’s mind by giving the object human traits.
7. Hyperbole
You know that one friend who describes things very dramatically? They’re probably speaking in hyperboles. Hyperbole is just a dramatic word for being over-dramatic—which sounds a little hyperbolic, don’t you think?
Basically, hyperbole refers to any sort of exaggerated description or statement. We use hyperbole all the time in the English language, and you’ve probably heard someone say things like:
- I’ve been waiting a billion years for this
- I’m so hungry I could eat a horse
- I feel like a million bucks
- You are the king of the kitchen
None of these examples should be interpreted literally: there are no kings in the kitchen, and I doubt anyone can eat an entire horse in one sitting. This common literary device allows us to compare our emotions to something extreme, giving the reader a sense of how intensely we feel something in the moment.
This is what makes hyperbole so fun! Coming up with crazy, exaggerated statements that convey the intensity of the speaker’s emotions can add a personable element to your writing. After all, we all feel our emotions to a certain intensity, and hyperbole allows us to experience that intensity to its fullest.
Hyperbole Writing Exercise
To master the art of the hyperbole, try expressing your own emotions as extremely as possible. For example, if you’re feeling thirsty, don’t just write that you’re thirsty, write that you could drink the entire ocean. Or, if you’re feeling homesick, don’t write that you’re yearning for home, write that your homeland feels as far as Jupiter.
As a specific exercise, you can try writing a poem or short piece about something mundane, using more and more hyperbolic language with each line or sentence. Here’s an example:
A well-written hyperbole helps focus the reader’s attention on your emotions and allows you to play with new images, making it a fun, chaos-inducing literary device.
Is irony a literary device? Yes—but it’s often used incorrectly. People often describe something as being ironic, when really it’s just a moment of dark humor. So, the colloquial use of the word irony is a bit off from its official definition as a literary device.
Irony is when the writer describes something by using opposite language. As a real-life example, if someone is having a bad day, they might say they’re doing “ greaaaaaat ”, clearly implying that they’re actually doing quite un-greatly. Or a story’s narrator might write:
Like most bureaucrats, she felt a boundless love for her job, and was eager to share that good feeling with others.
In other words, irony highlights the difference between “what seems to be” and “what is.” In literature, irony can describe dialogue, but it also describes ironic situations : situations that proceed in ways that are elaborately contrary to what one would expect. A clear example of this is in The Wizard of Oz . All of the characters already have what they are looking for, so when they go to the wizard and discover that they all have brains, hearts, etc., their petition—making a long, dangerous journey to beg for what they already have—is deeply ironic.
Irony Writing Exercise
For verbal irony, try writing a sentence that gives something the exact opposite qualities that it actually has:
The triple bacon cheeseburger glistened with health and good choices.
For situational irony, try writing an imagined plot for a sitcom, starting with “Ben lost his car keys and can’t find them anywhere.” What would be the most ironic way for that situation to be resolved? (Are they sitting in plain view on Ben’s desk… at the detective agency he runs?) Have fun with it!
9. Juxtaposition
Juxtaposition refers to the placement of contrasting ideas next to each other, often to produce an ironic or thought-provoking effect. Writers use juxtaposition in both poetry and prose, though this common literary device looks slightly different within each realm of literature.
In poetry, juxtaposition is used to build tension or highlight an important contrast. Consider the poem “ A Juxtaposition ” by Kenneth Burke, which juxtaposes nation & individual, treble & bass, and loudness & silence. The result is a poem that, although short, condemns the paradox of a citizen trapped in their own nation.
Just a note: these juxtapositions are also examples of antithesis , which is when the writer juxtaposes two completely opposite ideas. Juxtaposition doesn’t have to be completely contrarian, but in this poem, it is.
Juxtaposition accomplishes something similar in prose. A famous example comes from the opening A Tale of Two Cities by Charles Dickens: “It was the best of times, it was the worst of time.” Dickens opens his novel by situating his characters into a world of contrasts, which is apt for the extreme wealth disparities pre-French Revolution.
Juxtaposition Writing Exercise
One great thing about juxtaposition is that it can dismantle something that appears to be a binary. For example, black and white are often assumed to be polar opposites, but when you put them next to each other, you’ll probably get some gray in the middle.
To really master the art of juxtaposition, try finding two things that you think are polar opposites. They can be concepts, such as good & evil, or they can be people, places, objects, etc. Juxtapose your two selected items by starting your writing with both of them—for example:
Across the town from her wedding, the bank robbers were tying up the hostages.
I put the box of chocolates on the coffee table, next to the gas mask.
Then write a poem or short story that explores a “gray area,” relationship, commonality, or resonance between these two objects or events—without stating as much directly. If you can accomplish what Dickens or Burke accomplishes with their juxtapositions, then you, too, are a master!
10. Paradox
A paradox is a juxtaposition of contrasting ideas that, while seemingly impossible, actually reveals a deeper truth. One of the trickier literary devices, paradoxes are powerful tools for deconstructing binaries and challenging the reader’s beliefs.
A simple paradox example comes to us from Ancient Rome.
Catullus 85 ( translated from Latin)
I hate and I love. Why I do this, perhaps you ask. I know not, but I feel it happening and I am tortured.
Often, “hate” and “love” are assumed to be opposing forces. How is it possible for the speaker to both hate and love the object of his affection? The poem doesn’t answer this, merely telling us that the speaker is “tortured,” but the fact that these binary forces coexist in the speaker is a powerful paradox. Catullus 85 asks the reader to consider the absoluteness of feelings like hate and love, since both seem to torment the speaker equally.
Another paradox example comes from Oscar Wilde’s The Importance of Being Earnest.
“To be natural is such a very difficult pose to keep up.”
Here, “natural” and “pose” are conflicting ideas. Someone who poses assumes an unnatural state of being, whereas a natural poise seems effortless and innate. Despite these contrasting ideas, Wilde is exposing a deeper truth: to seem natural is often to keep up appearances, and seeming natural often requires the same work as assuming any other pose.
Note: paradox should not be confused with oxymoron. An oxymoron is also a statement with contrasting ideas, but a paradox is assumed to be true, whereas an oxymoron is merely a play on words (like the phrase “same difference”).
Paradox Writing Exercise
Paradox operates very similarly to literary devices like juxtaposition and irony. To write a paradox, juxtapose two binary ideas. Try to think outside of the box here: “hate and love” are an easy binary to conjure, so think about something more situational. Wilde’s paradox “natural and pose” is a great one; another idea could be the binaries “awkward and graceful” or “red-handed and innocent.”
Now, situate those binaries into a certain situation, and make it so that they can coexist. Imagine a scenario in which both elements of your binary are true at the same time. How can this be, and what can we learn from this surprising juxtaposition?
11. Allusion
If you haven’t noticed, literary devices are often just fancy words for simple concepts. A metaphor is literally a comparison and hyperbole is just an over-exaggeration. In this same style, allusion is just a fancy word for a literary reference; when a writer alludes to something, they are either directly or indirectly referring to another, commonly-known piece of art or literature.
The most frequently-alluded to work is probably the Bible. Many colloquial phrases and ideas stem from it, since many themes and images from the Bible present themselves in popular works, as well as throughout Western culture. Any of the following ideas, for example, are Biblical allusions:
- Referring to a kind stranger as a Good Samaritan
- Describing an ideal place as Edenic, or the Garden of Eden
- Saying someone “turned the other cheek” when they were passive in the face of adversity
- When something is described as lasting “40 days and 40 nights,” in reference to the flood of Noah’s Ark
Of course, allusion literary devices aren’t just Biblical. You might describe a woman as being as beautiful as the Mona Lisa, or you might call a man as stoic as Hemingway.
Why write allusions? Allusions appeal to common experiences: they are metaphors in their own right, as we understand what it means to describe an ideal place as Edenic.
Like the other common literary devices, allusions are often metaphors, images, and/or hyperboles. And, like other literary devices, allusions also have their own sub-categories.
Allusion Writing Exercise
See how densely you can allude to other works and experiences in writing about something simple. Go completely outside of good taste and name-drop like crazy:
Allusions (way too much version): I wanted Nikes, not Adidas, because I want to be like Mike. But still, “a rose by any other name”—they’re just shoes, and “if the shoe fits, wear it.”
From this frenetic style of writing, trim back to something more tasteful:
Allusions (more tasteful version): I had wanted Nikes, not Adidas—but “if the shoe fits, wear it.”
12. Allegory
An allegory is a story whose sole purpose is to represent an abstract concept or idea. As such, allegories are sometimes extended allusions, but the two common literary devices have their differences.
For example, George Orwell’s Animal Farm is an allegory for the deterioration of Communism during the early establishment of the U.S.S.R. The farm was founded on a shared goal of overthrowing the farming elite and establishing an equitable society, but this society soon declines. Animal Farm mirrors the Bolshevik Revolution, the overthrow of the Russian aristocracy, Lenin’s death, Stalin’s execution of Trotsky, and the nation’s dissolution into an amoral, authoritarian police state. Thus, Animal Farm is an allegory/allusion to the U.S.S.R.:
Allusion (excerpt from Animal Farm ):
“There were times when it seemed to the animals that they worked longer hours and fed no better than they had done in [Farmer] Jones’s day.”
However, allegories are not always allusions. Consider Plato’s “ Allegory of the Cave ,” which represents the idea of enlightenment. By representing a complex idea, this allegory could actually be closer to an extended symbol rather than an extended allusion.
Allegory Writing Exercise
Pick a major trend going on in the world. In this example, let’s pick the growing reach of social media as our “major trend.”
Next, what are the primary properties of that major trend? Try to list them out:
- More connectedness
- A loss of privacy
- People carefully massaging their image and sharing that image widely
Next, is there something happening at—or that could happen at—a much smaller scale that has some or all of those primary properties? This is where your creativity comes into play.
Well… what if elementary school children not only started sharing their private diaries, but were now expected to share their diaries? Let’s try writing from inside that reality:
I know Jennifer McMahon made up her diary entry about how much she misses her grandma. The tear smudges were way too neat and perfect. Anyway, everyone loved it. They photocopied it all over the bulletin boards and they even read it over the PA, and Jennifer got two extra brownies at lunch.
Try your own! You may find that you’ve just written your own Black Mirror episode.
13. Ekphrasis
Ekphrasis refers to a poem or story that is directly inspired by another piece of art. Ekphrastic literature often describes another piece of art, such as the classic “ Ode on a Grecian Urn ”:
O Attic shape! Fair attitude! with brede Of marble men and maidens overwrought, With forest branches and the trodden weed; Thou, silent form, dost tease us out of thought As doth eternity: Cold Pastoral! When old age shall this generation waste, Thou shalt remain, in midst of other woe Than ours, a friend to man, to whom thou say’st, “Beauty is truth, truth beauty,—that is all Ye know on earth, and all ye need to know.”
Ekphrasis can be considered a direct allusion because it borrows language and images from other artwork. For a great example of ekphrasis—as well as a submission opportunity for writers!—check out the monthly ekphrastic challenge that Rattle Poetry runs.
Ekphrasis writing exercise
Try your hand at ekphrasis by picking a piece of art you really enjoy and writing a poem or story based off of it. For example, you could write a story about Mona Lisa having a really bad day, or you could write a black-out poem created from the lyrics of your favorite song.
Or, try Rattle ‘s monthly ekphrastic challenge ! All art inspires other art, and by letting ekphrasis guide your next poem or story, you’re directly participating in a greater artistic and literary conversation.
14. Onomatopoeia
Flash! Bang! Wham! An onomatopoeia is a word that sounds like the noise it describes. Conveying both a playfulness of language and a serious representation of everyday sounds, onomatopoeias draw the reader into the sensations of the story itself.
Onomatopoeia words are most often used in poetry and in comic books, though they certainly show up in works of prose as well. Some onomatopoeias can be found in the dictionary, such as “murmur,” “gargle,” and “rumble,” “click,” and “vroom.” However, writers make up onomatopoeia words all the time, so while the word “ptoo” definitely sounds like a person spitting, you won’t find it in Merriam Webster’s.
Here’s an onomatopoeia example, from the poem “Honky Tonk in Cleveland, Ohio” by Carl Sandburg .
The onomatopoeias have been highlighted in bold. These common literary devices help make your writing fresh, interesting, and vivid, creating a sonic setting that the reader can fall into.
Learn more about onomatopoeias here!
Onomatopoeia Writing Exercise
Onomatopoeias are fun literary devices to use in your work, so have fun experimenting with them. In this exercise, take a moment to listen to the noises around you. Pay close attention to the whir of electronics, the fzzzzzzz of the heater, the rumbling of cars on the street, or the tintintintintin of rain on the roof.
Whatever you hear, convert those sounds into onomatopoeias. Make a list of those sounds. Try to use a mix of real words and made up ones: the way you represent noise in language can have a huge impact on your writing style .
Do this for 5 to 10 minutes, and when you have a comprehensive list of the sounds you hear, write a poem or short story that uses every single word you’ve written down.
If you built your political campaign off of wordplay, would you be punning for president?
A pun is a literary device that plays with the sounds and meanings of words to produce new, often humorous ideas. For example, let’s say you used too much butter in your recipe, and it ruined the dish. You might joke that you were “outside the margarine of error,” which is a play on the words “margin of error.”
Puns have a rich literary history, and famous writers like Shakespeare and Charles Dickens, as well as famous texts like The Bible, have used puns to add depth and gravity to their words.
Pun Writing Exercise
Jot down a word or phrase that you commonly use. If you’re not sure of what to write down, take a look at this list of English idioms . For example, I might borrow the phrase “blow off steam,” which means to let out your anger.
Take any saying, and play around with the sounds and meanings of the words in that saying. Then, incorporate the new phrase you’ve created into a sentence that allows for the double meaning of the phrase. Here’s two examples:
If I play with the sound of the words, I might come up with “blowing off stream.” Then, I would put that into a sentence that plays with the original meaning of the phrase. Like: “Did you hear about the river boat that got angry and went off course? It was blowing off stream.”
Or, I might play with the meanings of words. For example, I might take the word “blowing” literally, and write the following: “someone who cools down their tea when they’re angry is blowing off steam.”
Searching for ways to add double meanings and challenge the sounds of language will help you build fresh, exciting puns. Learn more about these common literary devices in our article on puns in literature .
16–27. Common Literary Devices in Poetry
The following 12 devices apply to both poetry and prose writers, but they appear most often in verse. Learn more about:
- Metonymy/Synecdoche
- Alliteration
- Consonance/Assonance
- Euphony/Cacophony
12 Literary Devices in Poetry: Identifying Poetic Devices
28–37. Common Literary Devices in Prose
The following 10 devices show up in verse, but are far more prevalent in prose. Learn more about:
- Parallel Plot
- Foreshadowing
- In Media Res
- Dramatic Irony
10 Important Literary Devices in Prose: Examples & Analysis
38–48. Repetition Literary Devices
Though they have uncommon names, these common literary devices are all forms of repetition.
- Anadiplosis
- Anaphora (prose)
- Antanaclasis
- Antimetabole
- Antistrophe
- Epanalepsis
Repetition Definition: Types of Repetition in Poetry and Prose
49–57. Dialogue Literary Devices
While these literary elements pertain primarily to dialogue, writers use euphemisms, idioms, and neologisms all the time in their work.
- Colloquialism
How to Write Dialogue in a Story
58–67. Word Play Literary Devices
The following literary devices push language to the limits. Have fun with these!
- Double Entendre
- Malapropism
- Paraprosdokian
- Portmanteau
Word Play: Examples of a Play on Words
68–72. Parallelism Literary Devices
Parallelism is a stylistic device where a sentence is composed of equally weighted items. In essence, parallel structure allows form to echo content. Learn all about this essential stylistic literary device below.
- Grammatical parallelism
- Rhetorical parallelism
- Synthetic parallelism
- Antithetical parallelism
- Synonymous parallelism
Parallelism Definition: Writing With Parallel Structure
73–112. Rhetorical Devices
Rhetorical devices are literary devices intended to persuade the reader of something. You might have heard of ethos, pathos, and logos, but do you know your aposiopesis from your hyperbaton?
Many literary devices can also be considered rhetorical devices. After all, a metaphor can convince you of something just as well as a syllogism. Nonetheless, the following 40 rhetorical/literary devices will sharpen your style, argumentation, and writing abilities.
- Anacoluthon
- Polysyndeton
- Procatalepsis
- Reductio ad Absurdum
- Amplification
- Antiphrasis
- Overstatement
- Adnomination
- Aposiopesis
- Circumlocution
Common Rhetorical Devices List: The Art of Argument
Master These Common Literary Devices With Writers.com!
The instructors at Writers.com are masters of literary devices. Through masterful instruction and personal expertise, our instructors can help you add, refine, and improve your literary devices, helping you craft great works of literature. Check out our upcoming courses , and join our writing community on Facebook !
Sean Glatch
91 comments.
Very nice the litrery divices
Brilliant litery devices
I love this literary term it help a lot
thank you this was life-changing
Broaden the vucablry it does
Very effectively and simply elaborated
enjoyed this (and learned some new things, too). HB
Wow, very educating and nice! Quite helpful
It is very nice visiting this site.
This was put together profoundly; thank you! As a writer, you can never learn enough. I will begin incorporating these into my stories. Words can’t express how helpful this was, and it was very efficiently put together as well, so kudos to that!
I’m so happy this article helped you, Jalen! Happy writing!
Thank you for this article! It really helped a lot! hands up to the good samaritan of understanding literature :D.
But I would have one last question: Would any sort of intertextuality be considered an Allusion? (Also when you refer to the author for example?)
Great questions! That’s a great way to think about allusion–any sort of intertextuality is indeed allusive. In fact, your use of “Good Samaritan” is an allusion to the Bible, even if you didn’t mean it to be!
And yes, because an allusion is anything referential, then a reference to another author also counts as an allusion. Of course, it can’t be directly stated: “She’s reading Shakespeare” doesn’t count, but “She worships the Immortal Bard” would be an allusion. (It’s also an allusion to the story of the same name by Isaac Asimov).
I’m glad to hear our article was helpful. Happy reading!
This will help! Thanks!
There is also Onomatopoeia, you can make the list 45
This article really helped me, the techniques are amazing, and the detail is incredible. Thank you for taking your time to write this!
I’m so glad this was helpful, Gwen! Happy writing!
this was useful 🙂 thanks
I love personification; you can do so much with it.
Hi, I’m really sorry but I am still confused with juxtaposition.
Hi Nate! Juxtaposition simply describes when contrasting ideas are placed next to each other. The effect of juxtaposition depends on the ideas that are being juxtaposed, but the point is to surprise or provoke the reader.
Take, for example, the opening line of Anna Karenina by Leo Tolstoy: “Happy families are all alike; every unhappy family is unhappy in its own way.”
Here, happy and unhappy families are being juxtaposed, and the contrast between the two is meant to provoke the reader and highlight the differences between those families. This juxtaposition sets up the novel as a whole, which often discusses themes of family and happiness (among many other themes).
I hope this helps!
very nice indeed
[…] 33 Common Literary Devices: Definitions, Examples, and Exercises […]
[…] 44 Common Literary Devices: Definitions, Examples, and Exercises […]
Thanks a lot for this it was really nice, good and fun to read it and it was really helpful for me as a student👔so please keep up with the good work 😉🌹💖😚😍💝💞💐
VERY GOOD READ I LOVED IT SO MUCH YAY QUEEEEEEEENNNNNN
Really helping. It’s a wonderful article
O mother Ghana, teach your children to change their negative attitudes towards you and what you have Please which literary device is this?
The device employed here is called apostrophe, which is when the writer addresses something not actually present for literary effect. Read more about it at this link .
This was very effective towards my writing and my family really enoyed seeing how much I had learnt. Thanks a lot.
so irony is literally sarcasm then
Sometimes! Sarcasm is a form of verbal irony.
Verbal irony occurs when a person intentionally says the opposite of what they mean. For example, you might say “I’m having the best day ever” after getting hit by a car.
Sarcasm is the use of verbal irony with the intent of mocking someone or something. You might say “Good going, genius” to someone who made a silly mistake, implying they’re not a genius at all.
Hope that makes sense!
Love this article! I used to struggle in my literature class, but after reading though this article, I certainly improved! Thanks! However, I have one question I really need your help with- Can I assume that a phrase which is the slightest bit plausible, a hyperbole? For example, a young elementary student who is exceptionally talented in basketball, to such an extent that he was quite famous nation-wide, said that he would be the next Lebron James although he was still very young. Would this be considered as a hyperbole? It would be great if you can help me with this.
That’s a great question! Although that claim is certainly exaggerated, it probably wouldn’t be hyperbole, because the child believes it to be true. A hyperbole occurs when the writer makes an exaggerated statement that they know to be false–e.g. “I’ve been waiting a billion years for this.”
Of course, if the child is self-aware and knows they’re just being cheeky, then it would be hyperbole, but I get the sense that the child genuinely believes they’re the next Lebron. 🙂
I’m glad this article has helped you in your literature class!
That makes a lot of sense, thanks for your reply!
Sorry, I have another question related to hyperbole. This is an extract from Animal Farm:
“Squealer was sent to make the necessary explanation to the others. ‘Comrades!’ he cried. ‘You do not imagine, I hope, that we pigs are doing this in a spirit of selfishness and privilege? Many of us actually dislike milk and apples. I dislike them myself. Our sole object in taking these things is to preserve our health. Milk and apples (this has been proved by Science, comrades) contain substances absolutely necessary to the well being of a pig. We pigs are brain-workers. The whole management and organisation of this farm depend on us. Day and night we are watching over your welfare. It is for your sake that we drink that milk and eat those apples. Do you know what would happen if we pigs failed in our duty? Jones would come back! Yes, Jones would come back! Surely, comrades,’ cried Squealer almost pleadingly, skipping from side to side and whisking his tail, ‘surely there is no one among you who wants to see Jones come back?’ Now if there was one thing that the animals were completely certain of, it was that they did not want Jones back. When it was put to them in this light, they had no more to say. The importance of keeping the pigs in good health was all too obvious.”
May I know if the speech made by Squealer in this extract is a hyperbole, gaslight (I’m not sure if this is a literary device), or some other device(s)? I know this is very wordy so you can take your time, no rush.
(I am doing a chapter analysis of chapter 3 in Animal Farm)
By the way, if you have written any other articles, please let me know! I would like to read them, thanks!
Take a look at writers.com/writing-tips for our archive on the craft of writing!
It wouldn’t be hyperbole, as a hyperbole is usually a word or phrase, not an entire passage of text. It’s better to analyze this passage in terms of its rhetorical strategies: Squealer is appealing to nebulous ideas like Science and the return of Jones–appeals to logos and pathos, despite there being a lack of evidence.
These strategies are logical fallacies: arguments that are easily disproven through reasoning, but which often resonate when people don’t employ critical thinking. Some of the fallacies here are “appeal to fear” and the “false dilemma” that Jones will return if the pigs don’t eat apples and milk (this is also a “red herring”).
I can’t provide much more help than this, as I don’t want to write your assignment for you, but I’m happy to point you in this direction, because understanding how logical fallacies are abused is essential to being an informed reader and citizen. 🙂
Ok, thanks for your reply!
Thank you! I am studying for an English final and this was a life saver!
My pleasure, Isla, good luck on your final!
I have a literature exam coming up,so this was much needed.Thank you!
Indeed this has been of great help to me.
I am so greatful of this website it really helps me a lot about myself and my family
This is awesome
This website is very useful to understand litery devices…
thanks it was helpful
Hi what is the name of the literary device where you name a character after their personality eg. Mr Knighley, Miss honey or Miss Trunchball? Thank you
That’s called an “aptronym”!
Mind blowing indeed. I had no idea there were so many names for patterns I hear people use with words. This lis is great as is. I am using it to probe further into what they are. I would only suggest that if the time ever allowed for someone to provide a brief detail or definition to each it would save a lot of time for many like me. None the less, I am grateful for the work provided. Thank you.
It awesome and amazing
It is personification as well as apostrophe, as Sean suggested. Ghana (the nation, I am assuming) is personified as a mother who is able to teach her citizens (children) to change their negative attitudes towards her.
Helped alot😊
This has truly helped me alot. Definitely great
Thanks so much, I never knew the list to this was as tall as everest, way back in school I didn’t take lit lessons serious and forgot everything til it came to mind to revise these devices And here google landed me, and thanks again so much.
This is awesome,it truly help me alot
It was great fun I had an amazing time doing the literary exercises and they helped so much. They really expanded my knowledge of the entire topic it was a wonderful thing to read, it will definitely help me with any English essay I have in the future.
It was very helpful. I must say that I have a better understanding of these literary devices. It was wonderful reading them.
I am overjoyed in knowing that we have different types of literary devices in literature. Thank you for this interesting article.
This is excellent and amazing.
This information was very useful Appreciated 🤗🙏
Thank you so much, I was literarily dying because of my English final!! I needed all these literal devices.
This article has really elevated me in the world of Literature.Thanks sir
This information is very important to me in my education . Thank you very much.
The articles are well written and the concepts well explained to the understanding of a beginner. The simplified way the author explained every term makes the article not only an interesting read but also a good note for teaching.
The litrarery device is the best way to get a knowledge in education
I liked it and the English is understandable
Can Dystopia be considered a kind of literary device?
Thank you so much for this! It helped me get ready for my English exam.
Best of luck on your exam, Olive!
Thank you so much! I learned so much that I can use in my upcoming assignments for writing.
Thank you so much . I learned so much understanding of my semester exams
Exactly this was really really helpful to everyone including me
[…] https://writers.com/common-literary-devices […]
Great definition and examples
I love this so much
[…] 112 Common Literary Devices: Definitions, Examples, and Exercises […]
This was Uber helpful! BUT, I do wish that we got more examples, and I can see why you made it shorter. If you put examples for all of them, then this would be really long.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Improve your writing in one of the largest and most successful writing groups online
Join our writing group!
Literary Devices List: 33 Main Literary Devices with Examples

by Fija Callaghan
If “literary devices” sounds like a throwback to something you slept through in your English Lit 101 class, you’re not alone. Maybe breaking down the finer points of metaphor, perspective, and juxtaposition sounds like a fast track to sucking all the fun out of actually enjoying creative writing.
On the other hand, it might surprise you to learn that these literary devices are present in all stories, from epic poetry to Saturday morning cartoons to those guilty-pleasure paperbacks you pick up at the airport and then “accidentally” leave behind on the plane.
If you’re reading, watching, or listening to a story and find yourself engaged for even a moment… that’s literary devices at work. They’re tools that the writer uses to engage with the reader on a visceral level, to make them look at the story—and the world around them through the story—in a completely different way.
Here we’ll show you multiple literary devices and rhetorical devices, with examples, that you can use to create powerful stories.
What are literary devices?
Literary devices are tools and techniques that a writer can use to elevate their story beyond the literal meaning of the words on the page. These techniques work on an unconscious level to enhance characterization, heighten tension, and help your story’s theme create a more powerful impact on the reader.
There are many types of literary devices that writers can use to create different effects in their work. The skilled writer uses them to create a powerful, lasting work of art; without them, a story would be much more basic, less enjoyable, and less memorable.
In other words, literary devices are the techniques that turn a literal, step-by-step retelling of events into a rich, engaging, and memorable piece of literature.

What’s the difference between literary devices and literary elements?
You’ll sometimes hear these terms being used interchangeably, but they’re not quite the same thing. We’ve looked at how literary elements are the structural skeleton of our story ; you can think of them as the blank canvas, the first washes of colour, the rough outlines that help us understand the shapes we’re seeing and what they have the potential to become.
Literary devices are everything that gives these outlines life and form. In a painting, these devices would be the play of light, shadow, and perspective; the use of contrasting and complimentary colour theory; the cool stuff you do with your sparkly gel pens at the very end that makes the finished piece really jump out. They’re tools that the writer uses—sometimes bold, masterful turns and sometimes nothing more than small nudges—to guide and engage the reader.
Or, consider a house. Literary elements are the house’s structure: They’re the foundation, the beams, the drywall, the roof. Without these elements there’s no physical house. Literary devices are what you do to a a building to turn it from a house into a home: the wallpaper you select, the style of furniture, the books on the shelf, the comfy couch, the good smells in the kitchen.
You probably won’t use all of the literary devices we’re going to show you here in your own work. Most writers will come back to the same ones again and again, mastering them as they keep using them. This is what becomes their distinctive storytelling style, or voice.
Having a basic understanding of the ideas on this literary devices list, however, will help you see why other storytellers make the choices they do so that you can begin developing a storytelling voice of your own.
33 literary devices (with examples!) you can use to strengthen your writing
Once you’ve formed the bones of your story, you can use these literary devices to add shape and style to your work. It’s worth exploring all of these literary devices in your practice, though you’ll likely find a handful of them that become your writer’s toolkit—devices that you come back to again and again.
As you grow in your skill, these literary devices will become a part of your storytelling voice.
1. Allegory
Allegory is kind of like a cross between metaphor (which we’ll talk about a little further on) and theme. It’s the practice of telling a real, true, relevant story through the filter of fiction.
Often these stories stand in place for something the author can’t say, due to political or cultural barriers; other times it’s simply a way to get the reader or viewer to consider an issue in a different light.
This doesn’t mean that the story is being told as a direct comparison to a central idea; it means the story on the surface is composed of a complex web of metaphors that tell a second story with a deeper meaning underneath.
An classic example of allegory is Dante’s Divine Comedy , where Dante uses his fictional journey through Hell, Purgatory, and Heaven as an allegory for the journey of a person’s soul to God.
2. Allusion
Allusion is a common literary device that indirectly references a real life person, place, or event.
It invites the reader to meet you, the author, in the middle, piecing together a cultural clue that you’ve left for them. Sometimes this is done because the idea is too sensitive to lay out overtly. Other times allusions can be used for light, comedic effect.
For example, in Eoin Colfer’s The Wish List, several repeated references are made to “the rockstar with the hair.” For a while the author lets the reader hypothesize as to whom he might be referring to, before dropping in a detail where a character begins humming “Blue Suede Shoes.” We talk about the value of repetition a little farther on.
3. Anachronism
Anachronism is a conflict of time within a single work —for example, describing a character as “zipping up her dress” if the story is set at a time before the invention of zippers, or causing national outrage by leaving a plastic water bottle on a 1920s film set .
Generally, anachronism is a negative thing that will cause your readers and viewers to delight in calling you out for it. This is why it’s so important, when writing historical pieces, to thoroughly research all the minute details of your story. However, anachronism as a literary device can sometimes be used quite effectively for comedic effect or to create a sense of displacement.

4. Archetypes
In literature, a character archetype is a standardized pattern that we instantly recognize from generations upon generations of storytelling.
Contrary to stereotypes , which are oversimplifications of an archetype’s most extreme personality traits, archetypes work because they speak to a universal truth. All character archetypes exist and, on some level, exist in us .
Examples of archetypes are the warrior, the mentor, the damsel, the lost child, and, of course, the villain. These archetypes can take on many different faces and sometimes a character can embody more than one archetype at the same time.
In Robert Munsch’s groundbreaking feminist page turner The Paper Bag Princess , the typical damsel-and-dragon story is turned on its head as none of the three central characters fit into the roles they’re expected to. This is an example of using archetypes in an unexpected way, inverting them to delight the reader.
5. Cliffhanger
A cliffhanger is a literary device in which the author ends a segment of the story on a dramatic question. This segment might be smaller, like a chapter, or larger, like the first novel in a continuing series. It holds the reader’s attention and makes them wonder what happens next.
You may recognize cliffhangers from your favourite TV series—they’re one of the most common literary devices in TV storytelling because they’re what gets the show pilot picked up by the network and then, once the show is running, they’re what keeps the viewers engaged and coming back again and again.
An example of a cliffhanger in literature is where the literary device got it’s name: In Thomas Hardy’s A Pair of Blue Eyes , a chapter ends with the main character hanging from a cliff by his fingers. The reader has to start the next chapter to discover the protagonist’s fate.
Cliffhangers are one of the many literary devices that are beloved by filmmakers and creative writers alike.
Dialect is a fantastic literary device to use when crafting strong, distinctive, believable characters. It’s essentially the sound of someone’s voice—not an easy feat to achieve when all you have to work with is paper and ink. It’s their regional accent, but also their upbringing, their level of education, their mood, the sort of people they’ve been exposed to.
When done well, and done sparingly, individual dialects can give your characters more life and lend a wonderful richness to their world.
D. H. Lawrence was famous for his use of dialect in his novels, which preserve the unique vocabulary and pronunciation of Victorian-era coal miners in the north of England.
Diction is related to dialect in that it’s a reflection of the sound of the story’s voice—which, again, you as the writer need to accomplish with nothing more than twenty-six letters. The difference between dialect and diction is that while dialect is a part of characterization, diction is the voice of the narrator.
The author makes choices about how to convey their voice in a story based on the mood and the world they’re trying to create. Very formal language creates distance between the author and the story; more colloquial word choices and regional slang make the story more intimate and immediate.
8. Euphemism
Euphemism is a word or phrase that uses figurative language to reference something that would otherwise be indelicate. “Passed away” is a common euphemism for dying; being “let go” or “made redundant” is a nicer way of saying you’ve been fired. “Cognitively challenged” refers to a stupid person, and “in the family way” is a sensitive way of saying that a woman is pregnant.
These all use informal language to convey something with a different meaning.
Although euphemisms were more commonly used in the eras of banned books, church censorship, and general societal timidity than they are today, they’re still a great way to show characterisation (as an important aspect of dialect, as we discussed above) and the time and place in which your story is happening.

9. Exposition
Exposition is the act of working relevant information into the events of your story —whether that’s through dialogue, observation, narrative detail, or flashbacks .
Exposition can be a tricky literary device to master, but it’s important in helping your readers understand your world, your characters, and what drives your characters to make the choices they do. Too much of this can bog down the reader and take them away from the present action, but just enough will give them a fuller understanding of the world you’re trying to create.
10. Flashback
Flashbacks are interruptions in the narrative that bring the reader to a past point in time in order to create tension and arm them with important information.
You may recognize flashbacks in TV series like crime shows or sitcoms, accompanied by subtitles like “earlier that day,” “three days ago,” etc. This is a way to communicate with the viewer that they’re being taken out of the present moment and redirected to another time.
Sometimes flashbacks are used as dramatic devices, like when the opening shows something horrible or unexpected, and then the flashback shows us what brought our characters to that moment.
11. Foreshadowing
Foreshadowing is a wonderful literary device that gives the reader hints of what is to come later in the story , either through subtle clues based on narrative events or by simply using thematic elements like symbolism and tone. It can help build suspense and keep the reader engaged by making them guess what’s going to happen.
You might foreshadow a turn of events in your story by placing symbolic images and colours through your story. For example, in her fairytale retelling The Bloody Chamber , Angela Carter uses a ruby choker to suggest a cut throat and give hints of what might come later on.
Don’t confuse foreshadowing with the rule of Chekhov’s Gun ; the two are very different concepts! But you can use both literary techniques to give depth to your story.
12. Hyperbole
Hyperbole is an exaggerated statement used for emphatic effect. It’s different than simply overstating something, where the context teeters on the edge of being a lie. Hyperbole isn’t meant to be taken literally.
For example, a child waiting for a parent too long after school might say, “I was waiting for fifty years!” Obviously, no one in this context actually believes they were waiting for fifty years—the child hasn’t even been alive that long. It’s using figurative language to emphatically say, “I’ve been kept waiting for too long and I am less than pleased about it.”
13. Imagery
Imagery is the art of making a moment come alive for the reader. We see this literary device in both fiction and poetry. To create an image that’s vivid and engaging, use a range of senses to create your world such as sight, sound, smell, touch, and taste (this is called visual, auditory, olfactory, tactile, and gustatory imagery, respectively).
In addition to making the world more real for the reader, the details that you focus on can influence the mood of the story. Well-placed images can also support foreshadowing in the story , as we saw previously.

14. In Medias Res
In media res is a Latin term you might hear in literary analysis that means “in the midst of things.” This means placing the reader in the middle of an exciting event, without any previous backstory or buildup. In other words, this can mean showing the middle of your story first, and then later revealing the events leading up to that moment.
For example, Sara Gruen’s novel Water for Elephants opens with an action-packed scene that takes place towards the end of the novel; then she doubles back to the beginning and shows the reader the events that took place to arrive there.
Other times it simply means dropping your reader in the middle of things that are happening, rather than starting with a lot of flowery description and exposition. Any information the reader needs can be slowly released throughout the scene, and the following scenes.
This immerses your reader in your story’s world right from the beginning. It makes them ask questions about who the people are in the scene and what’s causing the events to unfold—things they’ll learn as they read on through the entire book to the end.
There are different types of irony in literature , but all of them come down to an inversion of belief. The three types of irony you see most often in stories are dramatic irony, where the audience knows some essential piece of information that the characters don’t; situational irony, where the events of the story contradict what we would normally expect; and verbal irony, the contrast of speech and intention.
Verbal irony might be something like sarcasm, where someone says the opposite of what they mean.
Dramatic irony happens when the story reveals information but keeps it hidden from the characters—for example, the dramatic irony of watching someone open a door in a horror film when you know the monster’s waiting behind it.
Situational irony happens when two elements contradict to create a surprising result: for example, a policeman vowing to uphold the law and then giving in to corruption.
16. Juxtaposition
Juxtaposition is a useful literary device that deals in contrast —in other words, putting two characters, images, or ideas side by side to draw attention to their differences.
You see this often in central and supporting characters, such as Batman and Robin—Batman’s dark, silent moodiness contrasts Robin’s bright, youthful energy. You can see this in their personalities as well as their costumes, with Batman all in black and Robin in positive primary colours. It’s this juxtaposition between the two that makes them such an engaging team.
Juxtaposition can also be used in sensory imagery, such as placing a happy event underneath a dark and stormy sky or using a tactile sensation that seems out of place in its environment.
17. Language
If you’re reading this article, you’re probably intending to write your stories in English. But using language as a literary device by adding in glimmers of other languages can add depth to your characters and your world.
A great example is J. R. R. Tolkien, who creates richness in the world of his English-language work by inventing entirely new languages and referencing them just enough to make them seem real.
Cara Black, in her Parisian mystery series, writes in English but uses the occasional French word or phrase here and there to more fully immerse the reader in her Francophone world.
Language can also be useful literary device for characterisation; for example, an elderly family member who struggles with English might have dialogue almost entirely in another language, or a bilingual character might revert to their native language in times of overwhelming stress.

18. Metaphor
As a writing technique, metaphor is quite close to simile . Both are common literary devices used to draw comparisons between two seemingly unrelated ideas. But unlike a simile, which draws a comparison between two things, a metaphor goes a step further and uses one image to literally serve in place of another.
One of the most famous metaphors of all time is Shakespeare’s “All the world’s a stage,” which uses a literal theatrical performance as a comparison to illustrate the tragedies and comedies of everyday life.

19. Misdirection
Also called the “red herring,” misdirection is one of the most satisfying literary devices in storytelling of all kinds. It involves laying out clues as the story progresses, and nudging the reader towards the wrong deductions instead of the right ones.
The very important key to making this literary device work is to ensure the reader doesn’t feel cheated at the end—they should be able to look back at the path you’ve laid out and see that the true answer does make sense after all. This might mean working backwards after your first draft and sneaking in hints of what’s to come amidst other worldbuilding details.
Understanding the principle of Chekhov’s Gun can help avoid unwanted red herrings in your story . The risk of creating an unsatisfying red herring makes misdirection one of the trickiest literary devices to use.
A motif is a literary device in which recurring symbols, story elements, or ideas support the overall theme.
This could be something small and concrete, like apples popping up here and there throughout the story to symbolize a theme of battling temptation, or it could be something broader, like showing characters eating grander or sparser meals depending on the stage of their character arc.
You can use motifs to connect with readers on a subconscious, cultural level and help them immerse themselves even deeper in the story world.
A myth is a story that explains why things are how they are in the world—for instance, the creation myth of the Bible, or the story of how Raven stole the moon and stars in Indigenous mythology. Myths and legends are a fantastic archive of character archetypes and big, thematic ideas.
Unlike myths, legends are stories of something that may or may not have happened at some point in history, like the legends of Robin Hood or King Arthur’s knights. More importantly, both myths and legends are stories that stay with us for the long game because they represent values, needs, and desires that transcend generational divides.
Many stories—if not all stories—have their roots somewhere in this collective library of imagination. When composing your own work, try using old myths and legends to ground your story as you retell them from a new perspective. You could retell of a familiar story, or you could simply use myths and legends as inspiration for the sort of values, strengths, and weaknesses you want to explore in your own characters.
22. Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia is a way of communicating sounds in a way that relates to what they actually sound like. “Buzz” for the sound of a bee, “ruff” for the bark of a dog, and “plop” for the sound of a drop of water are all words that sound like the action they’re describing. “Slam,” “pop,” and “pow” are other common words you see in superhero comics.
Onomatopoeia is a literary device used most often in children’s literature and in the comic book medium, though we find it in just about everything including our everyday dialect. It’s best approached sparingly in literature, but the right word choices can add a lot of depth to your sensory environment: describing a stream as “burbling” or a wind as “shrieking” (notice the harsh “ee” vowel followed by the hard “k”) makes the scene clearer and more vibrant to the reader.
23. Oxymoron
An oxymoron is a literary device closely related to a paradox , in that they both present two seemingly contradictory ideas. Unlike a paradox, an oxymoron is a figure of speech that having to do with two words one after the other: a “deafening silence” is an oxymoron, because it combines two words that contradict each other. A “friendly argument,” “act natural,” and “openly deceptive” are some oxymorons.
Although they would appear to be impossible contradictions, many of us have experienced these ideas in our own lives and know that there is a deeper meaning lying behind them.
As a figure of speech, oxymorons can be used in humour and to convey an aspect of a character’s personality—sometimes at the same time.

24. Paradox
A paradox is quite similar to an oxymoron , but it presents two contrasting ideas instead of two contrasting words.
Oscar Wilde’s famous on-brand quote, “I can resist anything except temptation,” is an example of a paradox. By its very nature it can’t be true, and yet one feels that there is some resonant truth hidden somewhere within it.
Others examples are the sayings “the only constant is change” and “the louder you shout, the less they hear.” Both of these examples are composed of ideas that appear to be in conflict with each other, and yet both can be true statements.
The first tells us the only thing that never truly changes is the fact that things are always changing, and the second shows us that causing a scene isn’t always the way to get your voice across.
Paradoxes are useful literary devices that help readers see ideas from a new perspective.
25. Personification
Personification is a literary device that uses figurative language to give recognizable human-like qualities to inanimate or non-human entities.
The most extreme example of this is anthropomorphism, which is giving human traits to an animal or other non-human character. This is a very popular literary device in children’s literature, as it tends to make the ideas and lessons in these stories feel more accessible (this is the same device used to give life to a French candelabra in Beauty and the Beast ).
However, personification can be done on a smaller scale in order to make sensory images more vivid and easier for the reader to understand. A “weeping willow” is an example of attaching a human action to a non-human thing, and to say the weeping willow’s boughs were “lazily sweeping the dust from the road” is another.
26. Perspective
Perspective is the view from which the story is being told .
For instance, if you were to set your story in an old country manor house, you could tell a story following the same events in several different ways.
The matriarch of the house would be one perspective; a small, privileged child another. What would the housemaid see that no one else would? What about the cook or the gardener? What secrets, prejudices, or knowledge would they give to the story?
Not only would all of these people contribute different worldviews, cultural upbringings, and dialects, but they might genuinely believe in different series of events.
27. Repetition
In fiction writing and story structure, repetition is a literary device used to emphasize central themes and to create a subtle kind of rhythm.
The most famous example of repetition is in the “three wishes” often found in faerie tales, as well as three quests, three trials, three paths to choose from. This is because three is the number in which our brains start to recognize patterns. In your own writing, you can use this kind of repetition to support your story’s theme and character arcs.
You can also use targeted repetition of a word or phrase to emphasise an idea or create rhythm (which we’ll look at next!)
In prose writing, rhythm is all about the pacing of your story . Slow, languid writing can feel like being wrapped up in a snuggly blanket. Too much of this, however, becomes suffocating.
Short sentences are more like quick footsteps against a sidewalk. Readers like them because they make us feel like we’re going somewhere, but too many of them for too long and it starts to get hard to keep up.
It’s your job as a writer to use sentences of varying lengths to keep the reader engaged. Longer sentences will slow down the pace, so they’re best used for quiet, reflective moments. Short sentences will kick up the pace, so lean into them for action scenes.
While all good writers use both longer and shorter sentences to some degree, you’ll find that some tend to rely more on one than the other. This is part of what forms their signature voice . Experimenting with sentences of all rhythms will help you find yours.

Satire has been around since its inception in ancient Greece and shows no sign of slowing down. It’s a literary device that uses irony and humour as a way to draw attention to prevalent cultural and societal flaws .
Sometimes this can be done in a lighthearted way: Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland was considered a gentle satire of the upper classes of that time period. But sometimes satires are darker and more biting, such as in dystopian fiction like George Orwell’s 1984 .
Much like a metaphor , a simile is a literary device that compares two unrelated concepts to create vivid, sense-driven imagery. While a metaphor is used to stand in place for something else, a simile is used only in description: “he was as brave as a lion,” for instance, is a simile, while “he had a lion’s heart” is a metaphor.
Similes are great in descriptive passages because you have a whole world in which to draw inspiration from. Is the new girl at school like a “cascading waterfall”? A “fire hydrant”? A “broken chair”? She could be reminiscent of any one of those things, and you as the writer are going to tell us why.
A well-placed simile can give the reader a better sense of a character or place than pages and pages of telling us what it looks like.
31. Suspense
One of the most marvelous literary devices for engaging your readers is suspense —creating a darkly indulgent sort of tension between the reader and the story that keeps them turning page after page. The writer accomplishes this by posing one dramatic question after another.
Cliffhangers are one great way to make this happen. Putting time constraints on your characters is another, as well as shifting perspectives to reveal more information to the reader.
32. Symbolism
Symbolism is the act of using a person, place, or object to convey a larger, more abstract idea . When used repeatedly in a story to emphasise this idea, it’s called a motif .
In Shakespeare’s Hamlet , the skull of Yorik is a symbol of death and fate—it serves as a tangible, physical representation of these things in the context of the story.
Symbolism can also be used in setting—for instance, a rising sun to symbolize a new beginning—or in character, like a young child symbolising a parent’s lost innocence.
A writer can also use colours, animals, or icons that have made their way into our cultural consciousness in order to support the mood and theme of the story. Symbols that we see in our everyday lives include things like red roses for love, butterflies for transformation, or the the caduceus for medicine.
Tone is the way your story world feels to the reader. In film this would be a combination of lighting, cinematography, and soundtrack.
“It was a dark and stormy night” is an infamous opening line that immediately sets the tone for the story. In addition to giving us some context as to the setting of the scene, words like “dark,” “stormy,” and “night” naturally resonate with us in a particular way.
When trying to create an atmospheric tone for your story, you can try brainstorming words that you associate with the feeling you want to evoke, and then working them into your story.
In longer works, it’s a good idea to use different tones for different scenes or chapters. This helps each one stand out from the rest, and keeps them fresh and vibrant for the reader.
How to use literary devices to craft your own story
Now that you have an understanding of the literary devices available to you as a writer, you’re ready for the next part: putting it into practice in your novel, poem, or short story. The literary device examples we’ve looked at are a great starting point for thinking about how to apply them in your own writing.
Plus, we have dedicated lessons on all of these techniques waiting for you in our writing academy !

Every writer is unique, and the literary devices you see other authors using to fantastic effect might not be the ones that bring out the best in your own writing. The sort of imagery, dialect, and characterization we bring into our own work as storytellers is directly related to the way we view the world around us.
Finding your own unique style and voice is an exciting journey that can only be travelled by trying things out, finding what feels right deep in your bones, and practicing them again and again.
To get an idea of what literary devices will work best for you, take a look at the stories that you’ve written so far. Most likely, many of the things on this literary devices list will already be present in some form or another—you’ll be naturally drawn to them because of the powerful stories you’ve absorbed over your life.
Once you see where these literary devices are beginning to take shape, you can work on refining, enriching, and mastering them to create powerful stories of your own.
Get feedback on your writing today!
Scribophile is a community of hundreds of thousands of writers from all over the world. Meet beta readers, get feedback on your writing, and become a better writer!
Join now for free

Related articles

What Is Personification? Definition and Examples from Literature

What is Tone? Definition, with Examples

What Is a Cliffhanger? Definition, Examples, and How to Write Great Ones

In Medias Res: Definition, Synonyms & Examples in Writing

What is a Paradox? Definition, Types, and Examples

What is Euphemism? Examples & Definition in Literature
- SAT BootCamp
- SAT MasterClass
- SAT Private Tutoring
- SAT Proctored Practice Test
- ACT Private Tutoring
- Academic Subjects
- College Essay Workshop
- Academic Writing Workshop
- AP English FRQ BootCamp
- 1:1 College Essay Help
- Online Instruction
- Free Resources
16 Essential Literary Devices to Know
Bonus Material: Literary Devices Summary Sheet + Identification Quiz
Do you know the difference between a simile and a metaphor? Can you spot personification when it’s being used out in the wild?
If you’re a student in an English class , if you’re taking a test like the SAT or the ACT or the AP English Language or the AP English Literature exams, or if you’re writing college application essays , you’re going to need to know some literary devices!
Our students have used knowledge of these literary devices to write amazing college essays that helped get them into their dream schools.
Knowing their literary devices has also helped our students achieve great scores on the SAT, ACT, and AP tests.
However, there are a lot of literary devices out there. Literally hundreds. How do you tell which ones you actually need to know?
We’ve used our many years of experience teaching high school and college students to narrow down the list to the 16 most essential literary devices.
These are the ones that you’ll actually be expected to know on important exams or in your English classes. They’re also the most useful literary devices to make your college application essays really ✨ sparkle ✨ .
Think you know your literary devices? Try our quiz and see how many you can correctly identify in context!
Then keep reading for explanations and examples of all 16 essential literary devices. No offense to Shakespeare and Dickens, but we took all of our examples from the best books out there today for young adults, the ones you’re actually reading 😉.
Download a definition of each term with our one-page summary sheet to use as a study guide!
This post will cover:
What is a literary device?
Why you need to know these literary devices, personification, foreshadowing, rhetorical question, satire (and sarcasm), alliteration, onomatopoeia, parallel structure.
- FYI: The books we used

Download now: literary devices summary sheet + identification quiz
A literary device is any technique that an author uses to achieve their purpose.
These techniques help authors describe things in more detail, cause a more emotional reaction for readers, convey their ideas with more precision, add additional layers of meaning, and so on.
Over the centuries, we’ve developed a set of terms that help define these different techniques.
You may also hear people refer to rhetorical devices . These are largely the same thing!
People often use “literary device” to refer to terms that are more decorative and artistic, whereas “rhetorical device” is used to describe techniques that make writing more persuasive. The term “poetic device” is used to describe these techniques when talking about poetry.
In practice, though, these three terms are more or less the same!
Download literary devices summary sheet + quiz
These 16 literary devices are essential knowledge for the SAT or ACT .
They’re even more important for the AP English Literature and AP English Language tests.
And your instructors in high school and college English classes will expect you to know them and be able to use them to analyze different pieces of literature.
What’s more, knowledge of these literary devices will help you immensely as you write your college application essays , along with any other type of creative or personal writing.
Using devices like metaphors, alliteration, and parallel structure helps you to set your writing apart and raise it to the next level. This is especially important if you’re applying to a competitive school!

The 16 essential literary devices:
Probably the most famous and commonly-used literary device is the simile . A simile uses the words “like” or “as” to compare two unrelated things. Don’t confuse similes with metaphors !
(The word “simile” comes from the same root as the word “similar”—so essentially we’re saying two things are similar.)
Similes are powerful tools that allow authors to show us a new way of looking at the world.
“He gets up slowly like he is a very old toy running out of batteries .” — Kathryn Erskine, Mockingbird
“There are moments that I feel like I might suffocate, as if all my insides are tied into a tight little ball. ” — Erika L. Sánchez, I Am Not Your Perfect Mexican Daughter
“Now I was alone, leaving the smaller cities that had winked out long ago like Christmas lights on a faulty wire .” — Cherie Dimaline, The Marrow Thieves
“Her words fell in between the sheets of rain like downed planes: defeated, useless .” — Cherie Dimaline, The Marrow Thieves
“There are lemons, grapes, strawberries, and the brightest mangoes I’ve ever seen. They look like miniature suns .” — Kacen Callender, Felix Ever After
“Call me tonight, okay? If you go into the prom court kickoff meeting tomorrow without me prepping you on what to expect, it’ll be like seasoning yourself and stepping directly into a lion’s mouth .” — Leah Johnson, You Should See Me in a Crown
Think you can identify a simile? Try our 55-question literary devices quiz!

Often confused with similes , metaphors are direct comparisons. Whereas similes say that two things are similar to each other, metaphors just go for it and flat out claim that a person, place, or thing is something else. Metaphors do not use the words “like” or “as.”
Check out the difference:
Simile: The bad news was like a slap to the face.
Metaphor: The bad news was a slap to the face.
These two sentences are almost identical. But where the simile version compares the news to a slap indirectly, the metaphor version says that the news actually was a slap. The reader has to suspend their disbelief here, because of course the news didn’t actually involve any physical slapping.
“Night is a starlit blanket outside , and the cold air reaches my bones .” — Ibi Zoboi, American Street
“These, the regular injections of poison I was gifted from strangers , were definitely the worst things about wearing a headscarf. But the best thing about it was that my teachers couldn’t see me listening to music.” — Tahereh Mafi, A Very Large Expanse of Sea
“Mas has had to grow up fast these past two years. He tries to be like Dad and keep me and Shig out of trouble, especially now, except Dad was made of warm, soft pine instead of stone .” — Traci Chee, We Are Not Free
Extended metaphors take the same idea and develop it over more sentences. Sometimes an extended metaphor can last for an entire essay or entire chapter! This can be a beautiful and impactful technique when executed well.
“To call Linda and Mark Mom and Dad on purpose would mean that Joaquin’s heart would form into something much more fragile, something impossible to put back together if it broke , and he could not—would not—do that to himself again. He still hadn’t managed to pick up all the pieces after last time , and one or two holes remained in his heart, letting the cold air in .” — Robin Benway, The Far From the Tree
Practice distinguishing between similes and metaphors with our 55-question quiz on identifying literary devices .

Personification is what it sounds like—it means giving human attributes to an animal, place, or thing.
Another related term is anthropomorphism , which is when an animal or thing behaves in a human-like way.
A slight variation on this term is zoomorphism , which is when you assign traits from an animal to a person or thing.
“Manman will not go quietly. She will fight with her claws to get to me.” — Ibi Zoboi, American Street
Personification is often accomplished either with a simile or a metaphor , because you’re describing a thing as something else. It’s an effective way of creating a sense of empathy in the reader.
“The summer is made for stoop-sitting And since it’s the last week before school starts, Harlem is opening its eyes to September .” — Elizabeth Acevedo, The Poet X
“There are no mansions or big buildings here. The small houses are so close together, they might as well be holding hands .” — Ibi Zoboi, American Street
“When the animals and the wildflowers were gone from the brush field, the men of the town took their axes and hammers and mallets to the base of the water tower, until it fell like a tree. It arced toward the ground, its fall slow, as though it were leaning forward to touch its own shadow .” — Anna-Marie McLemore, When the Moon Was Ours

Imagery is a great catch-all term. Imagery means using descriptive and figurative language to paint a mental picture of something.
Similes , metaphors , and personification are all types of imagery. At times authors might combine all of these techniques at once!
“The stars began to rip through the hard skin of dark [metaphor] like the sharp points of silver needles through velvet [simile].” — Cherie Dimaline, The Marrow Thieves
Imagery can also include a particularly detailed description. Strong imagery might include multiple sensory elements: sight, sound, smell, taste, feel. Combining all of these elements creates vivid, immersive writing.
Life-hack for English class and literary analysis: if you’re not sure what to call it, or if it seems to fit multiple categories…call it imagery! It might not be the most specific term to use, but it won’t be wrong. 😉
“The words sit in my belly, and I use my nerves like a pulley to lift them out of my mouth.” — Elizabeth Acevedo, The Poet X
“Joaquin always liked early mornings best. He liked the pink sky that slowly turned yellow and then blue on clear mornings. When it wasn’t clear, he liked the fog that folded into the city like a blanket, curling itself over the hills and freeways, so thick that sometimes Joaquin could touch it.” — Robin Benway, The Far From the Tree
“Deborah Howard steps closer to me. At first she smells of her freshly ironed uniform, but then I smell the faint scent of cigarettes and oily food lingering behind her starchy presence.” — Ibi Zoboi, American Street
“It was the end of August, all volatile heat and the occasional breeze. I was surrounded by starched backpacks and stiff denim and kids who smelled like fresh plastic. They seemed happy.” — Nina LaCour, We Are Okay
“And although our names do have similar letters, mine is full of silverware-sharp sounds: E-Mah-Nee . Hers is soft, rolls off the tongue like a half-dreamed murmur.” — Elizabeth Acevedo, With the Fire on High
“They had been in the same classes together for years, but it was as if they had been figurines in an automated diorama, moving on mechanical tracks that approached each other but never intersected until now. Today they had broken free from those prescribed grooves, and Lily was acutely aware of the unprecedented nature of their new friendliness.” — Malinda Lo, Last Night at the Telegraph Club
For a one-page summary of all 16 essential literary devices, download our guide and practice quiz .

An allusion is a brief and indirect reference to literature, history, or cultural figures with which the reader would be familiar.
In the mid 2000s, the show Gilmore Girls was famous for packing every scene with countless allusions to literature, movies, history, and popular culture.
In Western literature, allusions to the Bible, Homer ( The Iliad and The Odyssey ), and Virgil ( The Aeneid ) are especially common.
“I didn’t know things could get any worse at home, but apparently they can. The apartment feels like the play The House of Bernarda Alba , but much less interesting. Just like the crazy and grieving mother , Amá keeps all the blinds and curtains drawn, which makes our cramped apartment even more stuffy and depressing.” — Erika L. Sánchez, I Am Not Your Perfect Mexican Daughter
“Suddenly I’m Eve in the Garden after she ate the fruit —it’s like I realize I’m naked. I’m by myself at a party I’m not even supposed to be at, where I barely know anybody.” — Angie Thomas, The Hate U Give
“I could scroll through Twitter until my vision blurs and then collapse on my bed like an Oscar Wilde character .” — Nina LaCour, We Are Okay
“We dressed pretty much the way we always are: even though it’s summer, Ezra wears a black T-shirt, sleeves rolled up to his shoulders to show off his Klimt tattoo of Judith I and the Head of Holofernes . He has on tight black jeans that’re cut off a few inches too high above his ankles, stained white Converses, and long socks with portraits of Andy Warhol .” — Kacen Callender, Felix Ever After
“Babygirl nods as if I just gave her the most serious Jada Pinkett Smith success speech . I hug her to my stomach, making sure not to nuzzle her too tight and fuzz up the braids I spent an hour doing.” — Elizabeth Acevedo, With the Fire on High
“With clearly practiced finesse, Rachel runs forward, leaps into his arms, and is lifted above the crowd in the cafeteria. She looks less like Baby and more like Simba looking over the Pride Lands if you ask me, but whatever.” — Leah Johnson, You Should See Me in a Crown
“ Smaug , the Irrepressibly Finicky, was our industrial-strength water boiler. I named it Smaug my first week on the job, when I got scalded three times in a single shift, but so far the name hadn’t stuck with anyone else at Tea Haven.” — Adib Khorram, Darius the Great is Not Okay
Foreshadowing refers to when the author hints at upcoming events in the narrative, either explicitly or through imagery or allusion. It can often create a sense of foreboding and suspense.
“It looks like a one-winged bird crouching in the corner of our living room. Hurt. Trying to fly every time the heat pump turns on with a click and a groan and blows cold air onto the sheet and lifts it up and it flutters for just a moment and then falls down again. Still. Dead.” — Kathryn Erskine, Mockingbird
“I would give anything to go back to the day she died and do things differently. I think of all the ways I could have kept Olga from getting on that bus.” — Erika L. Sánchez, I Am Not Your Perfect Mexican Daughter
“You asked for a story, so here it is. I’ll begin with the night the sluggers told me the world was toast, and when I’m finished, we can wait for the end together.” — Shaun David Hutchinson, We Are the Ants
Loosing track of the differences between these essential literary devices? Download our one-page summary sheet .

A rhetorical question is a question for which the speaker doesn’t actually expect an answer, usually where the answer is supposed to be obvious.
A very specific type of rhetorical question is hypophora , which refers to when someone asks a question and then immediately answers it themself.
“Would it kill you to be home before eight o’clock at night? Really? Would it? Oh, well, remind me again who wanted to redo the kitchen? Do you think that just pays for itself?” — Robin Benway, Far from the Tree
Verbal irony is when the words are the opposite of what they mean. It’s similar to sarcasm , but sarcasm is intended to be critical and negative, whereas verbal irony is much broader and can be more neutral.
One example of verbal irony would be the character Little John in the DIsney Robin Hood film—Little John isn’t “little” at all, as he’s actually larger than all the other characters!
“Ms. Fuentes looks up from the classroom window shades to see me staring at her inspirational sign. ‘Ms. Santiago, how was your summer?’ she says as she adjusts the shades so they let in more light. I shrug. ‘Good. Got a job. Yours?’ Ms. Fuentes stops mid-shade-fussing to side-eye me. ‘ You’re always so loquacious. It’s refreshing to have a student who believes in something other than monosyllables .’ But she’s smiling. She’s never said it, but I know I’m one of her favorites.” — Elizabeth Acevedo, With the Fire on High
Situational irony is when readers expect a certain outcome, but the opposite occurs. An example of situational irony would be if the firehouse burns down.
Dramatic irony is when the readers know more about what’s going on in the story than the characters do—so the readers interpret events differently than do the characters. An example of dramatic irony is at the beginning of the film Titanic, when the audience knows the ship will sink but the characters do not.
“What is it like to even love someone at all? My name is Felix Love, but I’ve never actually been in love. I don’t know.” — Kacen Callender, Felix Ever After

Like hyperbole , sarcasm is a literary device that many of us use on a daily basis: using words that clearly mean the opposite of what they say, made in order to hurt someone’s feelings, express irritation, or to criticize something in a humorous way.
“I looked around his messy room. ‘ I can see that you really like to take care of things .’ He didn’t get mad. He laughed. He handed me a book. ‘Here,’ he said. ‘You can read this while I clean my room.’ ‘Maybe I should just, you know, leave you—’ I stopped. My eyes searched the messy room. ‘It’s a little scary in here.’” — Benjamin Alire Sáenz, Aristotle and Dante Discover the Secrets of the Universe
Satire is kind of like sarcasm but on a larger scale. It’s usually used to describe a work as a whole that criticizes or makes fun of some element of human society.
The book The Marrow Thieves could be interpreted as a satire about racism and colonialism in our current world. It describes a dystopia set in a near-future North America, where indigenous people of North America are being hunted and harvested for their bone marrow, the only way that the rest of the population are able to regain something they’ve lost—the ability to dream.
Hyperbole is a literary device that many of us (at least those of us who are more dramatic!) use frequently in our everyday lives.
It’s an exaggeration or grandiose claim that’s not intended to be interpreted literally. It’s a great way to inject a little creativity or humor into your writing, especially if you avoid cliches like “I’m so hungry I could eat a horse.”
“Always is their thing. They’ll always love each other and whatever. I would conservatively estimate they have texted each other the word always four million times in the last year.” — John Green, The Fault in Our Stars
“The nice thing about having an overachieving ***hole for an older brother is that it takes the pressure off. Charlie has always been good enough for two sons. Now that he’s not so perfect after all, the pressure’s on me. Here’s a conversation I’ve had 1.3 billion (give or take) times since he’s been home: Mom: Your grades still okay? Me: Yup. Mom: Biology? Me: Yup…” — Nicola Yoon, The Sun is Also a Star
See if you can find more examples of hyperbole on our practice quiz !

Like imagery , diction is another great catch-all term. Diction refers to the author’s word choice , which can include the tone (formal, informal, humorous, sarcastic, etc.), words with specific meanings or etymologies, repetition, onomatopoeia, and so on.
Whereas imagery is a broad term for the ideas or content being conveyed, diction is a broad term for how the author is conveying them.
Use the term diction when you want to describe the author’s striking word choice more generally—if you’re not sure what narrower literary devices are being used, or if you want to refer to a mix of literary devices.
“Two and a half more years until I could get free from this panopticon they called high school, these monsters they called people I was desperate to escape the institution of idiots. I wanted to go to college, make my own life. I just had to survive until then.” — Tahereh Mafi, A Very Large Expanse of Sea
Rhyme is a literary device familiar to all of us from nursery rhymes and children’s books: words with endings that have corresponding sounds. However, rhyme has also been used in complicated ways in lots of adult literature from Shakespeare to Hamilton.
There are many specific terms used to describe different types of rhyme schemes. When working with rhyme, you might encounter words like couplet, quatrains, sonnets, and internal rhyme.
Rhyme is most common in poetic and theatrical works, but a careful reader can sometimes spot it sneaking into prose works as well!
“Josh Bell is my name . but Filthy McNasty is my claim to fame . Folks call me that ‘cause my game’s acclaimed , so downright dirty, it’ll put you to shame . My hair is long, my height’s tall . See, I’m the next Kevin Durant, LeBron, and Chris Paul .” — Kwame Alexander, The Crossover
“I didn’t know it would be this many people. Girls wear their hair colored, curled, laid , and slayed . Got me feeling basic as hell with my ponytail.” — Angie Thomas, The Hate U Give
Related to rhyme is the term meter , which refers to the rhythm of the words. Some poetic traditions are metered rather than rhyming, and some types of poetry will combine both meter and rhyme. Some terms that are associated with meter are caesura, dactyl, spondee, elision, iamb, pentameter, and hexameter .

Alliteration refers to when a series of neighboring or linked words begins with the same letter or sound. Writers are especially fond of alliteration in titles and poetry, but you’ll find it used to create emphasis in prose as well.
Assonance is a close cousin of alliteration. It’s when the internal vowel sounds of a word repeat.
So alliteration is repetition of initial consonant sounds, assonance is repetition of internal vowel sounds, and rhyme is repetition of end sounds.
“The summer is made for stoop-sitting And since it’s the last week before school starts , Harlem is opening its eyes to September .” — Elizabeth Acevedo, The Poet X
“He was funny and focused and fierce .” — Benjamin Alire Sáenz, Aristotle and Dante Discover the Secrets of the Universe
Alliteration is often the secret sauce that makes something sound good without us realizing why! See if you can spot all of the examples of alliteration on our practice quiz .
This term has a long name, but it’s quite a simple concept: onomatopoeia refers to words that sound like the noise they describe.
This literary device is especially common in children’s books and poetry. It creates vivid, fun writing with lots of drama.
Not all words used as onomatopoeia will be in the dictionary! Feel free to make up your own words to convey the sound you’re describing.
“Our color printer clicks and whirrs .” — Nina LaCour, We Are Okay
“ BOOM-BOOM-boom-BOOM . The drums.” — Sabaa Tahir, An Ember in the Ashes

When used deliberately, repetition can create powerful effects. Repetition can be of individual words, phrases, or even entire sentences. Sometimes the meaning might change with each repetition, or the repetition could be used for emphasis.
“In my white room, against my white walls, on my glistening white bookshelves, book spines provide the only color.” — Nicola Yoon, Everything, Everything
“It’s so hard to say, Shawn’s dead. Shawns’s dead. Shawn’s dead. So strange to say. So sad. But I guess not surprising, which I guess is even stranger, and even sadder.” — Jason Reynolds, Long Way Down
“I open the fridge to find bottles of soda and ketchup and hot sauce and mayonnaise and bread and eggs and too many plastic containers. In the freezer are boxes of pizza and waffles and frozen meat wrapped in plastic…I grab a slice of orange cheese wrapped in plastic.” — Ibi Zoboi, American Street
One specific type of repetition is anaphora , which is the repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of a sentence. It’s especially common in speeches (think Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream” speech).
For a one-page review of all 16 essential literary devices, download our summary sheet .
Parallel structure or parallelism is the repetition of a grammatical structure. It’s a great way to enhance clarity in your writing, but it can also be used for great dramatic effect.
We have more precise terms for specific types of parallelism. Isocolon refers to when phrases match exactly in structure, length, and rhythm. Antithesis refers to when the things placed in the parallel structure are complete opposites of each other.
Syndeton is when multiple conjunctions (words like “and” or “or”) are used in a row. Asyndeton is the opposite—when conjunctions aren’t used where you might expect them, and ideas are in separate sentences or joined by commas.
This poem is a great example of parallelism , specifically syndeton :
“I don’t know you, don’t know your last name, if you got brothers or sisters or mothers or fathers or cousins that be like brothers and sisters or aunties or uncles that be like mothers and fathers…” — Jason Reynolds, Long Way Down
“I find the blog of a woman named Josephine who explains the healing properties of gemstones and how to use them. I find images of pyrite (for protection), hematite (for grounding), jade (for serenity).” — Nina LaCour, We Are Okay

Now that you’re read these definitions of the 16 most essential literary devices, test your knowledge with our quiz .
We’ve also included a handy one-page definition sheet to use as a study guide! Make sure that you know what each of these terms means and that you can recognize it in context.
If you’re working on writing your college application essays, try and incorporate a few of these literary devices into your writing!
If you’re interested in customized one-on-one tutoring support for the SATs , ACTs , APs , or your high school and college classes , please feel free to reach out to us. Our expert tutors are Ivy-League grads and students who can help you understand these literary devices.
If you’re looking for help drafting and polishing your college essays or other writing assignments , our top-tier tutors can also help guide you through the writing process.
The books we used
We drew on our team members’ professional experience as librarians and in the publishing industry to curate a list of the best YA books of the past decade.
All of these books have won prestigious awards like the National Book Award for Young Adult Literature and are listed among “ TIME’s Best YA Books of All Time .” They’re national bestsellers that have captured the hearts of this generation. Many have also been adapted for film or for television.
If you’re looking for new books to read, check these out!

- Elizabeth Acevedo, The Poet X (2018 National Book Award for YA winner)
- Elizabeth Acevedo, With the Fire On High
- Kwame Alexander, The Crossover
- Leigh Bardugo, Six of Crows
- Robin Benway, Far From the Tree (2017 National Book Award for YA winner)
- Angeline Boulley, Firekeeper’s Daughter
- Kacen Callender, Felix Ever After
- Kacen Callender, King and the Dragonflies (2020 National Book Award for YA winner)
- Traci Chee, We Are Not Free
- Cherie Dimaline, The Marrow Thieves
- Akwaeke Emezi, Pet
- Kathryn Erskine, Mockingbird (2010 National Book Award for YA winner)
- John Green, The Fault in Our Stars
- Shaun David Hutchinson, We Are the Ants
- Adiba Jaigirdar, The Henna Wars
- Leah Johnson, You Should See Me in a Crown
- Cynthia Kadohata, The Thing About Luck (2013 National Book Award for YA winner)
- Adib Khorram, Darius the Great is Not Okay
- Nina LaCour, We Are Okay
- Malinda Lo, Last Night at the Telegraph Club (2021 National Book Award for YA winner)
- Tahereh Mafi, A Very Large Expanse of Sea
- Anna-Marie McLemore, When the Moon Was Ours
- Sandhya Menon, When Dimple Met Rishi
- Jandy Nelson, I’ll Give You the Sun
- Jason Reynolds, Long Way Down
- Benjamin Alire Sáenz, Aristotle and Dante Discover the Secrets of the Universe
- Erika L. Sánchez, I Am Not Your Perfect Mexican Daughter
- Neal Shusterman, Challenger Deep (2015 National Book Award for YA winner)
- Adam Silvera, More Happy Than Not
- Sabaa Tahir, Ember in the Ashes
- Angie Thomas, The Hate U Give
- David Yoon, Frankly in Love
- Nicola Yoon, The Sun is Also a Star
- Nicola Yoon, Everything, Everything
- Ibi Zoboi, American Street

Emily graduated summa cum laude from Princeton University and holds an MA from the University of Notre Dame. She was a National Merit Scholar and has won numerous academic prizes and fellowships. A veteran of the publishing industry, she has helped professors at Harvard, Yale, and Princeton revise their books and articles. Over the last decade, Emily has successfully mentored hundreds of students in all aspects of the college admissions process, including the SAT, ACT, and college application essay.
CHECK OUT THESE RELATED POSTS

15 Best ACT Tutoring Services for 2024 (75 Tutoring Services Reviewed)
April 18, 2024
A list of the 15 best online ACT tutoring services, reviewed and ranked. Compare prices & instructor qualifications. Best overall: PrepMaven’s SAT tutoring ($79–349/hr). Best on a budget: Wyzant ($20–600/hr). Best…

How to Transfer Colleges
April 11, 2024
The college transfer process is different from what you went through in high school to get into college. We’ll walk you through important steps in your application …

Varsity Tutors Review
Comprehensive review of Varsity Tutors: pricing, instructor qualifications, online platform, customer service, and educational quality.

15 Best PSAT Tutoring Services for 2024 (75 Tutoring Services Reviewed)
April 10, 2024
A list of the 13 best online SSAT tutoring services, reviewed and ranked. Compare prices & quality. Best overall: PrepMaven. Best self-guided: Test Innovators. Best on a budget...

16 Best Online Tutoring Services — Reviewed & Ranked by an Ivy-League Expert
April 9, 2024
A list of the 16 best online tutoring services, reviewed and ranked by an Ivy-League expert. Compare prices & tutor qualifications. Best overall: PrepMaven’s writing tutoring ($66–349/hr). Best on a budget: Wyzant ($20–600/hr). Best…

17 Best Online Math Tutoring Services — Reviewed & Ranked by an Ivy-League Educator
A list of the 17 best online math tutoring services, reviewed and ranked by an Ivy-League educator. Compare prices & tutor qualifications. Best overall: PrepMaven’s writing tutoring ($66–349/hr). Best on a budget: Wyzant ($20–600/hr). Best…

Should You Transfer Colleges?
April 4, 2024
If you’re thinking about transferring colleges, there’s a lot you should think about. Not all reasons for transferring are great ones: read on to learn about good reasons to transfer, bad reasons to transfer, and…

How to Request your High School Transcript
You may need to get a copy of your high school transcript for college applications, scholarship competitions, or just for your own records. Learn the most efficient way to receive your high school transcript and …

13 Best SSAT Tutoring Services for 2024 (36 Services Reviewed)
March 29, 2024

15 Best Online SAT Tutoring Services for 2024 (75 Tutoring Services Reviewed)
A list of the 15 best online SAT tutoring services, reviewed and ranked. Compare prices & instructor qualifications. Best overall: PrepMaven’s SAT tutoring ($79–349/hr). Best on a budget: Wyzant ($20–600/hr). Best…
Privacy Preference Center
Privacy preferences.
- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
How College Students Can Use Literary Devices to Improve their Essay Writing
Table of contents
“ If you can look into the seeds of time, and say which grain will grow and which will not, speak then to me.” — Macbeth , William Shakespeare
Mind-blowing, isn’t it?
But do you realize what made this sentence so “mind-blowing”? The strategic use of metaphor.
We have always wondered how certain writers manage to leave us in awe and inspired. You might think you can’t achieve it, but with the proper techniques and practice, it isn’t.
While many elements make up powerful writing, one of the techniques is literary devices. What are literary devices, you ask?
They are tools writers use to heighten their narrative and evoke emotions to convey their message. Instead of simply stating things for what they are, literary devices manage to bring writing to life and leave a more substantial impact on readers, especially in the case of creative writing assignments.
How You Can Use Literary Devices to Write an Essay
Being a college student, you are bound to be bombarded with several writing assignments. Whether it’s a narrative essay, book critique, or personal statement, knowing how to inject literary devices into your writing can make a huge difference.
More than getting the grades you want, it’s about embracing the art of storytelling and making efforts to ‘wow’ your instructors.
You can be lazy and churn out the same old essay.
Or you can take the use of literary devices and your writing to the next level.
The choice is yours.
Decided to go with the latter? Good. Here’s everything you need to know about using literary devices to improve your essay-writing skills.
How do Literary Devices Improve College Essay Writing?
Literary devices, if used smartly, can take your writing from ‘meh’ to ‘wow.’ Here’s how they enhance your writing and take it to the next level.
What is this ‘depth,’ you might wonder ? Well, ‘depth’ is what hooks readers and keeps them invested in your writing. It is that ‘oomph’ factor that makes your essay riveting.
When you use literary devices to put your message across, you can make people ponder about the setting you create, the characters you develop, or the situations you describe. Well-placed literary devices have the power to heighten your writing which would have otherwise been flat and dull.
Paint a Picture
You’ve heard of the age-old writing advice, “Show, Don’t Tell”, haven’t you? It encourages writers to write vividly and paint a picture in the minds of readers which is way more powerful than a thousand words.
Using literary devices can help you achieve that because you let readers visualize what you’re trying to say, leaving a more significant impact in their minds.
Want to know more about writing descriptively?
Watch this video by Darin Mount , wherein he throws more light on this subject
Evoke Emotional Response
We can all agree that the best writing connects with the reader and evokes an emotional response. Whether it’s sadness, joy, anger, or disdain - using literary devices to make readers feel what you want them to feel is always a winner.
Make it Interesting
Last but not least, literary devices make the piece more pleasurable to read.
No one likes boring essays. You must constantly innovate and think of new, creative ways to add life to your writing. Whether you want to add humor, drama, or just pace your essay - the use of the proper devices can do this for you.
10 Types of Literary Devices You Can Use in Your Essay
There is a laundry list of literary devices but let’s look at the best literary devices ones you should know about:
1. Metaphor
One of the most common literary devices, metaphors, is used across essays, books, songs, poems, and speeches. They are used to compare two completely unrelated objects. The idea is to provide a more robust description such that the reader interprets it better.
E.g., All the world’s a stage, and all the men and women are merely players.
Here, Shakespeare is comparing the world to the stage and implying that we are all actors enacting different scenes.
The problem with metaphors is that there are so many of them doing the rounds that using the common ones, such as “It is raining cats and dogs” or “Life is a rollercoaster,” among many others, don’t have the impact they should.
Hence, before inserting a metaphor, ensure it’s unique and not overused for it to be truly effective.
Similes and metaphors are not the same. Even though similes compare two different objects, they use the words ‘as’ or ‘like’, making explicit comparisons, unlike metaphors.
Using similes makes writing more interesting and descriptive. Coming up with new similes gets you to push your creative boundaries.
E.g., Fit as a fiddle, Brave as a lion, Slept like a log, etc.
3. Symbolism
As the name suggests, symbolism is when you give a different meaning to an object/subject/action to represent a more extensive concept for readers to understand it at a deeper level. Unlike metaphors and similes, symbolism is a more subtle form of comparison.
Using symbolism is almost like making your writing poetic. Instead of explicitly stating the obvious, you can use symbolism to let readers interpret it and think deeper.
E.g., The works of women are symbolic.
We sew, sew, prick our fingers, dull our sight,
Producing what? A pair of slippers, sir,
To put on when you're weary.
These lines are from Elizabeth Barret Browning’s Aurora Leigh, wherein she compares women to ‘slippers’ that one only turns to when tired, implying how undervalued women are.
4. Alliteration
Alliteration means “letter of the alphabet” and refers to using words that begin with the letters of the same sound group in quick succession. They also refer to using words that start with the same letter.
Alliterations are generally used to draw attention and make something pleasurable to read. You can also use alliteration to name a character or place.
E.g., Peter Piper Picked a Peck of Pickled Peppers.
They all begin with the letter ‘p.’
Sally ate salmon on Sunday.
Even though ‘Sally,’ ‘salmon,’ and ‘Sunday’ begin with ‘s,’ this is not considered an alliteration because none of the words have a similar sound.
“Oh, the irony!” - you must have encountered this phase several times. So, what does irony mean? It is used to highlight situations wherein something is very different from what it seems to be. Irony can be used to inject humor or to add a profound meaning.
Broadly, ironies are divided into - verbal irony, situational irony, and dramatic irony.
Verbal irony is when the speaker says something that is the opposite of what he/she actually means. “Isn’t that sarcasm?” many might wonder.
Video by Christopher Warner explaining the difference between the two
Situational irony is when the outcome of a situation is very different from what was expected. Dramatic irony is when the character’s understanding of a situation is different from the audience’s.
E.g. Brutus says he is ambitious, And Brutus is an honorable man.
These lines are said by Mark Antony in Julius Caesar wherein he seems to be praising Brutus but actually isn’t.
6. Hyperbole
Think exaggeration. Yes, that is what hyperboles are.
Hyperboles are when you use words or phrases to make something grander or give it a larger-than-life effect. Sometimes exaggerating or using hyperbole is an effective way to convey the message powerfully or lay emphasis on a particular situation. They are purely used for effect and are not meant to be taken literally.
E.g. I was helpless. I did not know what in the world to do. I was quaking from head to foot and could have hung my hat on my eyes, and they stuck out so far.
These lines are from Mark Twain’s Old Times on the Mississippi. The hyperbole here is “hung my hat on my eyes. They stuck out so far”. The writer only uses this sentence to emphasize how helpless he was - in reality, his eyes were not sticking out.
7. Personification
Personification is when you give human characteristics and feelings to inanimate objects, animals, or nature. It gives your writing a dramatic effect and lets your readers relate more easily to the situation or object. Personification is also a powerful storytelling tool to create vivid imagery in the minds of readers.
E.g., Her heart was divided between concern for her sister and resentment against all the others.
Here Jane Austen writes about how the character’s (Elizabeth) ‘heart’ was divided between concern and resentment. It is a way of signifying how Elizabeth herself was torn between these two emotions.
8. Oxymoron
An oxymoron refers to a pair of words that are contradictory or opposing. It is used to focus on the multiple meanings an object might have. It makes descriptions more effective while making the reader understand the intensity of the situation or character.
E.g., All animals are equal, but some animals are more equal than others.
George Orwell writes this line in Animal Farm to explain the prevalent hypocrisies. The fact that “some animals are more equal than others” negates the former part of the sentence, thereby demonstrating a paradoxical situation.
Words and phrases used to create a graphic, mental images are referred to as imagery in the readers' minds. You can use imagery to describe a character, weather, place, event, or emotion.
It is not just limited to the visual senses but also includes any description that appeals to all the other senses, like taste, smell, touch, and hearing.
E.g., Mr. Jaggers's room was lighted by a skylight only and was a most dismal place; the skylight, eccentrically patched like a broken head . . . there were some odd objects that I should not have expected to see--such as an old rusty pistol, a sword in a scabbard, several strange-looking boxes and packages, and two dreadful casts on a shelf, of faces peculiarly swollen, and twitchy about the nose.
This is an excerpt from Charles Dickens’s Great Expectations wherein Pip is describing Mr. Jaggers’ room and reading this. We can almost visualize and get a sense of what it would look like.
10. Onomatopoeia
Now, here’s an interesting one - onomatopoeia refers to sound words that are spelled the way their sounds sound. They let the reader hear the sound being written about, engrossing them in the situation or world created in the writing. It’s a simple yet powerful way to emphasize a sound.
Eg.: Hark, hark!
The watch-dogs bark!
Hark, hark! I hear.
These lines from Shakespeare’s The Tempest use onomatopoeia to emphasize on the dogs barking, making us visualize sounds.
Please don’t get overwhelmed by the number of literary devices and be pressured to memorize them or even use all of them in your college essays, for that matter.
While there is no rule for the number of literary devices you can use, what’s important is to maintain a healthy balance and use this tool sparingly. It would be best to use literary devices that can genuinely add value, enhance your description and engage readers .
If you need help writing an interesting essay for college or want your essay to be polished further, we at Writers Per Hour can help.
Our professional team of essay writers knows precisely where and how to use literary devices in college essays. You can receive superior-quality, 100% original, custom-written essays to meet your needs when you work with us. So, contact us today, and let us come to your rescue!
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Literary Devices ‒ How To Use Them In Your College Essay
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

One of the best ways to make your college essay and other academic writing assignments interesting is by using literary devices. They serve as essential tools that authors employ to enrich their narratives, engage readers, and convey complex thoughts and emotions in an accessible way. This article will explore what literary devices are, why they’re important, and the most common literary devices you can use to make your academic essays more interesting.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Literary Devices ‒ In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Literary devices
- 3 Literary devices woven into the essay structure
- 4 Literary devices for storytelling
- 5 Literary devices: Imagery
- 6 Literary devices: Tone
- 7 Sentence-integrated literary devices
Literary Devices ‒ In a Nutshell
- Literary devices are tools used by writers to elevate their writing skills.
- Literary devices allow writers to communicate with their audiences from a unique angle.
- Literary devices can upgrade your essay writing skills and get you good grades.
Definition: Literary devices
Literary devices are tools or techniques writers use to make their narrations more captivating and hint at bigger meanings than what’s on paper. While some literary devices are only used on a sentence level, others transform the entire story. Most skilled writers use several literary devices to create a more powerful and memorable story.
Some common types of literary devices include:
- Figurative language – metaphors and similes create images and comparisons for better understanding.
- Sound devices – alliteration and onomatopoeia contribute to the rhythm, mood, and emphasis of the text.
- Narrative devices – foreshadowing and flashbacks affect the structure of the story and how it’s told.
- Stylistic devices – repetition and irony shape the overall voice, tone, and mood of the work.
In sum, literary devices enhance a piece of writing by making it more effective, memorable, and engaging in conveying its ideas and themes.
Literary devices woven into the essay structure
The following are some of the best literary devices for essay writing and how to use them:
This refers to using an object, person, place, or subject to represent a broader concept or idea.
- A dove can represent peace
- A sheep can mean conformity
- A black cat can represent bad luck.
Extended metaphor
A metaphor is a figure of speech that compares two, unlike things without using the words “like” or “as.”
On the other hand, an extended metaphor is a metaphor that continues the comparison across multiple sentences or paragraphs in the same piece of writing.
- Simple metaphor: “The truth is thorny.”
This metaphor compares the truth to something painful.
- Extended metaphor: “The truth is thorny, but you have to embrace it even if it hurts. Sometimes it leaves a small puncture, sometimes a huge wound, but it eventually heals.”
With this extended metaphor, you’ve spread the comparison of truth to a thorn across two sentences.
- Choose the third metaphor you think of
- Use a comprehensive comparison
- Look for extended metaphors
- Always keep it subtle
- Don’t overuse extended metaphors
- Don’t use clichés
- Don’t use distracting metaphors
- Don’t use weakening metaphors
Literary devices for storytelling
The following are some literary devices that work best with storytelling:
Into the action
“In medias res” is a Latin word that means “in the midst of things.” This writing style places the reader in the middle of the action or scene without providing any contextual information.
Beginning your story in the middle of the action helps immerse the reader into your story from the start. It makes them ask a lot of questions regarding the characters in the opening scene and what’s the reason behind the events that are unfolding.
The opening line of One Hundred Years of Solitude by Gabriel Garcia Marquez reads:
- “Many years later, as he faced the firing squad, Colonel Aureliano Buendia was to remember that distant afternoon when his father took him to discover ice.”
Writers often use dialogue to show communication between two characters in the story.
You can use dialogue in your college essay to move your story forward, show different points of view, or engage the reader with your story at an emotional level.
- Algernon : I’m afraid I’m not that. That’s why I want you to reform me. You might make that your mission if you don’t mind, cousin Cecily.
- Cecily : I’m afraid I’ve no time this afternoon.
- Algernon : Well, would you mind me reforming myself this afternoon?
- Cecily : It is rather Quixotic of you. But I think you should try.
A flashback is a sudden interruption in the story’s narration that brings the reader to an earlier event to provide context or backstory of the present event.
You can use flashbacks in your essay to arm the reader with some important information about a character’s backstory that they might not have known.
The realtor handed me the keys to my new three-bedroom house. I was overjoyed to become a homeowner before my 30th birthday. It’s hard to imagine that I was living with my brother a year ago because I couldn’t afford to pay rent for my apartment.
Using a famous quote in your college essay provides the reader with more context of the topic you’re writing about and helps strengthen your argument.
As a parent, you want to raise well-behaved children who do well in school and are never in trouble. However, you should know that what you do or say in front of your children plays a major role in shaping their character. Pierre Corneille once said, “Remember: sooner or later, your son will follow your example and not your advice.”
Literary devices: Imagery
Writers use imagery to engage the human senses or create a picture in the reader’s mind. The following are some of the literary devices used to create imagery:
Personification
This is a writing technique used to give human characteristics to non-humans. When used in essays, personification allows the reader to relate easily to the object the writer is talking about.
Similes compare two objects using the words “like” or “as.” Using similes in your college essay can help make it more interesting and descriptive.
As brave as a lion.
Five senses
This writing technique describes a particular object’s taste, smell, touch, sight, and sound. Using the five senses in your essay helps immerse the reader in your story by creating vivid images in their mind.
She wanted a taste of the sweet hot coffee.
Literary devices: Tone
The tone is the mood or atmosphere the writer’s words paint to the reader. The following are the literary devices used to portray the writer’s tone:
This is using exaggeration to add more impact to a certain statement.
I have a million things to do when I wake up.
Colloquialisms
This refers to using informal phrases in a piece of writing.
Y’all ain’t giving me time to explain.
Sentence-integrated literary devices
The following are the most commonly used sentence-integrated literary devices:
What are literary devices used for?
Literary devices are used to make pieces of writings more interesting to read.
How many literary devices can I use in my essay?
You can use as many literary devices as you want, as long as they make sense and add something to the reader’s experience.
What forms of writing can you incorporate literary devices?
There are no restrictions when it comes to using literary devices.
You can use literary devices with all forms of formal and informal writing, including college essays, book reports, research papers, emails, and even text messages.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint

The Admissions Strategist
Literary devices (so many of them): the complete & unbeatable guide.
There are a lot of terms in literature, and at times, it may seem overwhelming to learn them all.
One way to simplify learning literary terms is to learn about literary devices.
This subject area includes tons of literary terms, and learning the ins and outs will bring your writing (and reading comprehension) to a whole new level.
What is a Literary Device?
A literary device is exactly what it sounds like; it’s a tool used by writers to transform words into literature.
Some literary devices are common terms that you likely use often: theme, plot, style, etc. Others you may have never heard of: ad hominem, neologism, spondee, etc.
No matter how common or far-fetched these terms get, every literary device has its place. The more you know, the better you can write. With the help of the following information, you can be well on your way to knowing every literary vice in existence:
Literary Devices v.s. Literary Elements v.s. Literary Techniques
Before diving into a real list of literary devices, there’s two terms you’ll need to know: Literary elements and literary techniques. These are the two different categories of literary devices.
Literary elements are the “big things.” They are something that the reader is able to figure out, and they allow the reader to gain a deeper understanding of the text. They include devices such as character, tone, and genre.
Literary techniques are devices that are used specifically by the writer to make their words come to life. They include devices such as metaphors, symbolism, and rhymes.
The Most Well-Known Literary Elements:
These literary elements are terms you may already be familiar with, and they’re a great way to dip your toes into literary device learning:
Voice: Voice is simply the way in which a writer portrays their words. Voice may be professional in a research paper, and heartfelt and funny in a letter to a loved one, for example.
Voice can also be written in either active or passive form. Active Voice is written as follows “He picked up the wrapper and threw it in the trash. Passive Voice would state “The piece of trash was picked up by the man and thrown into the trash. Active Voice is clear, and it is preferred in most writing circumstances.
Point of View: Point of View is a term that shares whose voice the words on the page are coming from. Here are some examples of point of view:
- First Person : The writer is telling the story to an audience. For example, “I am riding my bike to Jan’s house.”
- Second Person : The writer is telling the story to “you,” using the term “you” throughout the piece. For example, “I am riding my bike to your house.”
- Third Person : The writer is telling the story from an outside perspective, using names as well as the terms “he” and “she.” For example, “She is riding her bike to Jan’s house.”
Theme: The theme, in regards to writing, is the big idea behind a piece. A novel, for example, could tell a story of a young couple in the 1940’s and have a historical theme.
Structure: Structure is how writing is organized. Structure can organize written work in many ways, including chronologically, by cause and effect, by offering a problem then a solution, as well as many other ways (as long as they are logical and able to be understood by the writer and the reader).
Here are some common structures:
- Novel: A novel is a longer piece of fiction that has a distinctive form. Its structure includes an exposition (important information that needs to be told before the story can begin), a rising action ( a series of events that bring about feelings of interest and suspense), a climax (the big event or turning point in the story), a falling action (the action that follows the climax), and a resolution (the way the story ends).
- Novella: This is a piece of writing that is shorter than a novel, but longer than a short story. “Of Mice and Men,” by John Steinback, is a well-known example of a novella.
- Short Story: Short Story still follows a polt, but it’s shorter than a novella. Fairy tales are often written in the form of short stories.
- Vignette: This is even shorter than a short story. It’s basically just a quick description of one happenstance. “House on Mango Street,” by Sandra Cisnreos is a popular vignette.
Style: Style is simply the way in which a writer expresses themself. There are four styles of writing, which are also literary elements:
- Expository: This is an informational writing style. Your research paper would take on this style, as would a news report.
- Narrative: This style tells a story, whether fiction or nonfiction. Examples include novels, autobiographies, and much, much more.
- Descriptive: This writing style engages the senses to draw the reader into a space that the writer creates. Many poems fall into this category.
- Persuasive: This writing style tried to persuade the reader to share the writer’s opinion. An article filled with heartfelt stories on the benefits that would come from raising the legal drinking age, for example, would be persuasive.
Audience: The audience is who you are writing to. For example, if you’re writing a young adult novel, your audience is adolescents. You’ll want to write with them in mind.
The Most Well-Known Literary Techniques:
This is another list of terms you may know, but this time they are literary techniques. These are simple, but they’ll once again transform your writing:
Simile: A simile compares one thing to another. For example, “you’re sweet like honey.”
Metaphor: A metaphor refers to one thing as something else. “You’re my knight in shining armor,” used to describe a normally dressed, non-knight boyfriend, is a commonly used example.
A metaphor can be extended , to drive in the point of the comparison. For example, “He’s the apple of my eye. He fell down from the branch in front of my eyes as I walked past the apple tree. I picked him up, and his crisp, clean look convinced me to keep him near. I only became more and more impressed to learn his beauty was more than peel-deep.” This cheesy metaphor is brought into a clearer image with descriptive language that continues throughout the following sentences.
Metaphors can also be implied , which means this object of comparison is understood, but not mentioned. For example, “She’s a good catch.” It’s clear the comparison is being made between the girl and a fish, yet fish are never actually mentioned.
Personification: Personification gives human-like tendencies to non-human or non-living objects. For example, “My running shoes stared at me from across the room, telling me it was time to wake up and get my morning jog in.”
Imagery: Imagery is a descriptive language that draws the reader in, so they’re able to feel, see, hear, and even smell what the writer is describing. An example would be “She picked a leaf from the tomato plant, hearing a soft crunch when the leaf broke off its stem and feeling the hair-like texture that covered it well.”
Alliteration: Alliteration is the repetition of the beginning sounds of words throughout a sentence. “Sally sold seashells by the seashore” is a commonly used example of this literary technique.
Sentence-Related Literary Devices:
Did you know that types of sentences are considered literary devices? It’s because these types of sentences are formed in a way that serves a specific purpose:
Imperative Sentence:
Balanced Sentence: A balanced sentence has two parts, each of which are close to equal in regards to length. For example, “I want to go to the park, but it’s cold and raining right now.”
Cumulative Sentence: This type of sentence begins with the main clause, and ends with multiple more clauses or phrases that add to or change the main clause. For example, “We went to the store often, so often, in fact, that we started to dread the trip, and it became our least favorite place to go.”
Hypothetical Question: This sentence type asks a question that is based on opinions or assumptions instead of fact. An example would be, “You’re in a boat that’s starting to fill with water; do you jump out and swim to shore or do you attempt to mend the boat?”
Simple Paragraph: The simple paragraph isn’t quite a sentence, but it’s a simple writing form nonetheless. Simple paragraphs are written with a topic sentence at the beginning, support sentences in the middle, and a concluding sentence at the end. They’re used in almost all types of writing, making them an essential technique for all writers to learn.
The description above can be viewed as a simple paragraph example. Convenient, right?
Literary Devices by Genre:
First off, it’s important to note that “genre” itself is a literary device! It’s considered a literary element, to be exact. A genre is a category of writing, and can include drama, romance, humor, poetry, and more. Each genre is also considered a literary device, and each genre has many devices that are used within it.
This may seem a little bit like opening up a matryoshka doll, but it’s simpler than it sounds. Check out these literary devices organized by genre to gain a deeper understanding:
Fiction: Fiction is all about make-believe. It’s any written work that is not based on true events.
- Science Fiction: This is a type of fiction writing that’s based on future technological or scientific advances; think robots, aliens, time travel, etc.
- Drama: Drama is a fiction narrative that is written with a more serious tone. Shakespeare’s “A Midsummer Night’s Dream” is a great example of a drama piece.
- Melodrama: To understand this genre, think drama, but exaggerated. Soap Operas can be considered melodramas.
- Tragedy: This is a form of drama that brings suffering to center stage. Romeo and Juliet is the perfect example for the tragedy genre.
- Fantasy: This is a form of fiction that’s based around myths, legends, or supernatural activity; think The Lord of the Rings and the world created within its pages.
- Romance: Romance highlights love stories and ends with optimism. Nicholas Sparks novels are all about Romance.
- Comedy: Comedy is funny, amusing, and almost always has a happy ending. Comedy is a common genre for adolescent reads, though there are comedy pieces written for all ages.
- Tragicomedy: This is just what it sounds like – a mix between comedy and tragedy. It may be that the tragic events are so overdone that they are funny, or the story may end in an uplifting and goofy way. Shakespeare’s “The Winter’s Tale” is a tragicomedy.
- Tall Tale: A Tall Tale is written as if it’s true, but the events are so far-fetched that any reader would know they’re actually fake. The tales of Paul Bunyon and Johnny Appleseed are great ways to view into this genre.
- Fable: Fables are short stories that teach a lesson. They are often written with animals as characters. One well-known fable is “The Tortoise and the Hare.”
- Fairy Tale: Fairy Tales are creative stories filled with fascinating characters. They are usually written for children. Cinderella is Fairy Tale that almost everyone knows.
- Utopia: A Utopia is a story in which the characters live in a “perfect world.” Plato’s “Republic” is a well-known Utopia.
- Dystopia: A Dystopia is just the opposite; the characters live in an awful world. “The Hunger Games,” by Suzanne Collins are Dystopian novels.
- Satire: Satire is a genre that is meant to shame a person or organization. Satire is especially common in today’s web in the area of tearing down opposing politicians.
- Thriller: Thrillers are books that are meant to keep readers on their toes. Stephen King’s books are popular thrillers.
- Suspense: A Suspense story is similar to a thriller, but it keeps the reader in a state of anxiousness, eager for additional information. Murder mystery books fit into the Suspense genre.
- Parody: A Parody piece is similar to Satire, but it simply imitates another story instead of tearing it down. An example would be “Bored of the Rings,” by Henry Beard and Douglas Kenney. It’s not meant to bring “The Lord of the Rings” down, rather it’s a read that is built for humor and entertainment.
As fiction has plenty of subtypes, it also has a long list of literary devices that are often used within its genre. These literary devices play large roles in creating make-believe writing:
- Protagonist: The protagonist is the main character in a story. Harry Potter is the protagonist in the Harry Potter series.
- Antagonist: The antagonist is actively working against the protagonist. For example, Voldemort (or should we say “he who shall not be named?” is the antagonist in the Harry Potter books.
- Hero: The hero is another name that the main character in a story may be called, especially if they accomplish something great. Hamlet is the hero in Shakespeare’s “Hamlet.”
- Anti-hero: This is a main character that just doesn;t have those hero-like characteristics. Lucifer in “Paradise Lost” is a strong example of an anti-hero in literature.
- Anti-climax: In an anti-climax, tension builds up to an event, but nothing major actually happens. For example, a woman forgets to shut the door to her home in a horror movie, causing the audience to feel suspense as they believe the evil character may sneak inside. Later on, though, the main character simply remembers to close and lock the door.
- Dialogue: This is where two or more characters talk between each other. Most novels are written with a large amount of dialogue.
- Monologue: Monologue is where only one character speaks for a fairly lengthy amount of time. King Henry V’s “St Crispin’s Day” Speech in Shakespeare’s “Henry V” is a well known example of a monologue.
- Character: A character is a person who appears in a work of fiction. Every fiction book you read is filled with characters (as well as many nonfiction books).
- Flat Character: Flat characters stay the same from the beginning of the story to the end. Usually, flat characters aren’t the main characters. They are smaller roles, such as the strict teacher or the loving mother, who do not grow or change throughout the book.
- Static Character: This is just another term that describes flat characters! See the above term for more information.
- Dynamic Character: A Dynamic Character grows and changes throughout the book. They learn from the challenges that they face throughout the pages of the book. Most main characters are dynamic.
- Round Character: This is once again the same as a dynamic character. It’s simply another term that holds the same meaning.
- Direct Character: This just means that an author explicitly explains who a character is. Their personality does not need to be found through the happenings in the book. For example, an author may state that the main character is young but wiser than their years may suggest. This characteristic would then be reinstated throughout the story.
- External Conflict: This type of conflict takes place between a character and an external force. For example, a man is in a plane crash and works to survive in the wilderness until help arrives.
- Internal Conflict: Internal conflict takes place within a character. This may be related to a decision a character has to make, or an important, internal opinion that changes throughout the book.
- Flashback: A flashback is a scene in a book that shares a glimpse into the past. For example, when a hero is fighting off a monster and they are growing weak, about to give up, they may have a flashback and remember a person they love telling them they are strong enough to accomplish anything. The strength they receive from reliving this flashback would help them to win the fight that is occuring in current time.
- Flash-Forward: A flash-forward gives the audience a glimpse of the future before it actually happens. The Scrooge visits in Chalres Dickens’ “A Christmas Carol” are a perfect example of flash-forward scenes.
- Foreshadowing: This gives the reader a hint of what is to come. An example would be when Little Red Riding Hood’s grandmother tells Little Red to “watch out for the wolf in the woods.”
- Frame Story: This is a story within a story. “Frankenstein,” by Mary Shelley has multiple frame stories.
- Narrator: This is a third-party voice that tells the story. “The Book Thief” is told from the perspective of a narrator.
- Plot: This is simply the name for the events that make up a story. Every work of fiction has a plot!
- Subplot: This is a smaller story that happens alongside the main story. A romantic relationship that occurs in an action-based book would be a subplot.
- Prologue: This is a chapter that provides an opening for a story, giving necessary background information. “The Book Thief,” by Markus Zusak has a prologue that introduces the narrator, for example.
- Epilogue: An epilogue is a chapter found at the end of a book that provides a conclusion, even though the actual story has already been finished. The Harry Potter series ends with an epilogue set nineteen years in the future, for example..
Get personalized advice!
- Setting: This is simply where the story takes place. It could be a city, a school, or within a character’s home.
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy: This is something that is believed by a character to the point that they make it come true. Macbeth’s death was due to a self-fulfilling prophecy.
- Tragic Hero: A tragic hero does something that causes their own failure. Maybe their inability to ask others for help got them into a situation they couldn’t overcome on their own.
- Tragic Flaw: This is a trait that causes the main character to fail. For example, the character’s pride could get in the way of them winning a race.
- Cliffhanger: Some people hate them, and some people love them. A Cliffhanger is a story that ends without telling the audience what exactly happened. Every Harry Potter book ends with a cliffhanger.
Non-Fiction: Nonfiction is the opposite, so it’s based on true events. The types of nonfiction writing are listed below:
- Autobiography: An Autobiography is the written story of someone’s life, written by themselves. “The Diary of a Young Girl,” by Anne Frank, is a strong example of an autobiography.
- Biography: A Biography is the written story of someone’s life, written by someone other than them. Most biographies share the life story of famous people, such as authors, presidents, musicians, actors, etc.
- Memoir: A Memoir is a type of autobiography written about specific memories or events in a person’s life. One popular memoir is “The Glass Castle,” by Jeanette Walls.”
Play: A play is a written work meant to be performed in front of an audience. It tells a story through character dialogue. One common play is “Les Miserables.” Plays, once again, have some literary devices of their own:
- Dramatic Irony: In a play, dramatic irony is where the audience understands what is happening, but the characters do not. For example, the audience may see that a teacher is leaving lunch on the desk of a child who normally goes without, while the character of the child does not know where the food is coming from until later on in the story.
- Dramatic Monologue: A dramatic monologue is a speech made by a character often in a play though they can also occur in books, where the character tells a part of the story. Shakespeare’s works are filled with examples of these.
- Comic Relief: Comic relief is a funny moment or character that gives the audience a break from a serious matter. The nurse in “Romeo and Juliet” provides comic relief through her multiple jokes.
Poem: A poem is a form of written work filled with imagery that provokes emotion. Robert Frost is a well known poet. Poems have many literary devices, which you can learn more about below:
- Anapest: This describes two short, unstressed syllables followed by a long, stressed syllable. An example is “Welcome home.”
- Blank Verse: A Blank Verse is a line of a poem that does not use a rhyme. They are often written in Iambic Pentameter (a line of ten syllables, stressed syllables following unstressed syllables). Blank Verses appear often in works of Shakespeare.
- Ballad: This is a poem that tells a story through the use of short stanzas. It can also be set to music, similar to a song. Thomas Hardy’s “During WInd and Rain” is a popular ballad.
- Caesura: This refers to a pause in the middle of a line of poetry.
“The bird flew; his wings were black as night.”
- Canto: This is the name of a section of a long poem.
- Catalogue: This is a type of poem that is filled with many images.
- Cinquain: A Cinquain is a style of poem written with fines.
- Common Meter: This poem writing style uses lines that alternate between six and eight syllables, and follows the iambic (stressed syllable followed by unstressed syllable) pattern.
- Couplet: A Couplet is two lines of a poem that work together, often with a rhyme.
- Dactyl: This is one stressed syllable, and then two unstressed syllables. “Elephant” could be a dactyl, for example.
- End Rhyme: This is just what it sounds like, rhymes that appear at the end of lines.
- End Stopped Line: This is a line in a poem that ends with punctuation, to show the end of a segment or thought.
- Epic: This is a long, narrative poem that focuses on a specific heroic or brave person, often from historical times.
- Exact Rhyme: An exact rhyme uses two words with the same stressed vowel sound and the same ending sound. For example, ”cat” and “hat” are an exact rhyme.
- Eye Rhyme: This is a rhyme in regards to the way your eyes see the word. For example, “cow” and “tow.” The words look the same, but they do not rhyme when they are said aloud.
- Feminine Rhyme: This is a set of words that rhyme in both the stressed syllable and the unstressed syllable that follows. For example, “paper” and “taper” are feminine rhymes.
- Foot: This is one stressed syllable, followed by one or more unstressed syllable(s). A dactyl is one type of foot.
- Formal Verse: This is a piece of poetry that follows a specific meter. It could follow any of the meters in Poetry, for example. It could follow Iambic Pentameter.
- Free Verse: A free verse follows no meter or structure. It is written however the author wants it to be.
- Haiku: A Haiku is a poem that has three lines. The first line has five syllables, the second line has seven, and the third line has five once again. Here’s an example of a Haiku:
“I woke up at dawn
To the sound of many birds
They were flying near.”
- An example of a half rhyme is “pun” and “fume.”
- Hyperbaton: This term refers to the inversion of words. Yoda speaks with inversion, for example.
- Hyperbole: A hyperbole is exaggerated, and not necessarily true.
“I’ll walk one thousand miles just to be with you.”
- Hypophora: This is when a question is asked, and then answered right away.
“What day is it? The most beautiful day.”
- Hypotaxis: Hypotaxis is when a clause is subordinate to another clause.
“The moon was bright, lighting up the sky.”
- Imab: This refers to a short, stressed syllable followed by a long, unstressed syllable. “Attack” is an example of an iamb.
- Internal Rhyme: Two words that rhyme because of their middle segments are internal rhymes. “Together forever” is an example of this type of rhyme.
- Innuendo: This is a slightly sneaky, often inappropriate, hint.
- Limerick: A limerick is a funny poem with five lines. One popular limerick is “Hickory Dickory Dock.”
- Line Break: This is when a line of a poem ends with punctuation.
“The sun was warming the ground
“Making the early morning dew dry up.”
- Lyric Poem: This is a style of poem that expresses emotion. Edmund Waller’s “Go, Lovely Rose” is an example of a lyric poem.
- Meter: Meter is the pattern of syllables that makes up a poem. Iambic Pentameter is a common example.
- Narrative Poem: This is a type of poem that tells a story. Geoffrey Chaucer’s “The Canterbury Tales” is a well known example.
- Onomatopoeia: An onomatopoeia is a word that describes a sound. “Click,” “Plop,” “Sizzle” are all examples of this term.
- Octave: An octave is a set of eight lines in a poem. It can make up a poem alone, or it can be a piece of a longer work.
- Ode: An ode is a lyric poem written to a person or a thing and filled with emotion. John Keats’ “Ode to a Nightingale” is a popular example.
- Poetic Justice: This describes the good characters winning and the bad characters losing. Most children’s stories, for example, have poetic justice.
- Quatrain: This is a stanza with four lines.
- Refrain: This is a line, often found at the end of stanzas, that is repeated throughout the poem.
- Rhyme: A rhyme is made up of two words that have similar sounds. For example, “ball” and “tall” are rhymes.
- Rhyme Scheme: This is the pattern in which rhymes are placed throughout a poem.
- Riddle: A riddle is a short, beautifully written question, that is asked as a type of game.
“What has to be broken before being used?”
- Sestet: A sestet is the last six lines in a type of poem called a sonnet.
- Slant Rhyme: Slant rhymes are similar, but they do not sound exactly the same. An example could be “orange” and “porridge.”
- Sonnet: A sonnet is a poem made up of fourteen lines. It can use any type of rhyme scheme. Shakespeare wrote many sonnets.
- Stanza: A Stanza is a set of lines in a poem that is grouped together.
- Tercet: This is three lines of a poem that often rhyme.
“I chased the cat
I swung the bat
I wore a hat.”
- Trochaic: This is a poetry meter that is made up of Trochees , or stressed syllables followed by unstressed syllables.
Prose: Prose is a form of writing that has no formal structure. Everyday language is technically even spoken in prose.
Proverb: Proverbs are simple statements that share truth, whether it be based on life experience or spiritual beliefs. A common proverb is “Once bitten, twice shy.”
Folklore: Folklore is a genre that encompasses fictional stories, songs, and more, specifically related to a culture and its history. Fairy tales, tall tales, myths, and legends can all be considered folklore.
Myth: A myth is a story, typically an origin tale, that often involves gods or other supernatural beings. Greek Mythology and the stories within it are strong examples.
Legend: A legend is a story that is told as if it were true. It typically takes place in the distant past, and it has a lesson or value behind it.The story of the Loch Ness Monster is an example of a legend.
Essay: An essay is a short piece of prose writing that focuses on a specific topic. School assignments are great examples of essays. Here are some literary devices that are found within essays:
- Main Idea: The main idea is the purpose behind a piece. For example, the main idea of this piece is literary devices.
- Transition: A transition smooths the movement from one topic to the next. For example, If you’re talking about the history of dogs and you need to move into speaking about dogs in current times, your transition could state “The history of dogs is rich and fascinating, but the present world of dogs has even more to offer.”
- Thesis: The thesis is the statement sentence that shares what the rest of the essay will discuss or prove. For example, a paper about the dangers of drinking and driving could state “Drinking and driving is dangerous because it puts both yourself and others at risk.” The rest of the essay would then go on to prove those two statements.
- Argument: An argument is the presentation of opposing or opinion-based views. FOr example, you may state “The death penalty should not exist.” The rest of your essay would back up why you hold the beliefs that are presented in your argument.
Critique: A Critique is a form of writing that reviews something, such as a movie, restaurant, or piece of art. When you look at the reviews for a new movie in theatres, you’re likely reading a critique.
More Literary Devices to Explore:
Knowing the most common literary devices is one thing, but knowing ones that aren’t often used can set your writing apart. Here’s a list of every other literary device for you to explore (and add to your future writing projects):
- Allegory: An allegory is a story that has a deeper meaning buried within it, often regarding real-world events. Animal Farm by George Orwen is an allegory.
- Allusion: An Allusion is a brief way to bring something up without actually saying it. For example, stating someone is acting like “Eeyore” would be an allusion toward them feeling down and depressed.
- An example could be “I saw a dog in a blue dress.” Was the dog wearing the blue dress, or were you?
- Amplification: Amplification is simply adding onto a point or sentence. For example, “Biking is great exercise” can be amplified by stating “Biking is an excellent workout for your entire body, from the cardio work that benefits your heart and lungs to the lower body movements that strengthen your muscles.
- Analogy: An analogy is a descriptive tool that compares one thing to another. “Life is like a box of chocolates; you never know what you’re gonna get” from “Forrest Gump” is a well-known analogy.
- Ad Hominem: Ad Hominem is a remark made against a person instead of an argument. It’s often found to be noncredible. An example would be stating that a person didn’t graduate high school and therefore their facts on global warming must be incorrect.
- Anachronism: An anachronism is a part of literature that is out of place or out of time when compared to the rest of the work. Anachronisms can be used to help the audience relate or to provide humor. An example would be placing cell phones in a story that occured in the nineteenth century.
- Anadiplosis: This is when a sentence endswith a specific word, and the next sentence begins with that same word. It’s often used to provide emphasis or style to a piece. For example, “Life is short. Short chunks of time are all we have to fill with memory and adventure.”
- Anagram: An anagram is a word that has the same exact letters as another word, but in a different order. An example would be “silent” and “listen.”
- Accumulation: Accumulation is when multiple similar terms or characteristics are listed to describe something. It works to provide emphasis. An example would be, “My kitten’s fur is as soft as the sky, as fuzzy as a peach, and as smooth as linen.”
- “ D irty paw prints fill the floor on muddy days. O ver all the furniture you’ll find little strands of fun. G reater than these issues, though, is the love my sweet pet gives back to me.”
- Adage: An Adage is a short saying that is regarded as truth throughout society. An example is “Many hands make light work.”
- Anacoluthon: This is a term for an interrupted sentence. These can be used as literary tools, but you may notice them more often in everyday life: “I need to stop by the store to get- Wait, did you send me the recipe we need for dinner tonight?”
- Anagnorisis: This is a term that describes the moment in a story when a character discovers truth, whether it be who they are or what is happening. It leads to the resolution of the conflict. Almost every story written today contains this moment; you just may need to search for it!
- “I’m so hungry I could eat a whole elephant.”
- “It was cold. It was dark. It was time to go home.”
- Anecdote: This is a short story that shares a point, and also often makes the audience laugh. It could be any story within a story, or relating to a topic being discussed.
- Anthimeria: This is simply trading one term for another. For example, in the phrase “Let’s hop to it,” “hop to it” means to go or get started on a task.
- Antanaclasis: This is when a term is repeated, but with a different meaning each time. It is often used in humor. “Othello” by Shakespeare has an antanaclasis that states “Put out the light, then put out the light.” The first term means blowing out a candle and the second means ending someone’s life.
- Antecedent: This is a word in a sentence that can later be replaced by a pronoun. For example, “Mary flew a kite. She thought it was a lot of fun.” In this case, “Mary” is the antecedent as the name is later replaced by the word “she.”
- Anthology: This is a collection of works that make up a single piece. For example, a book made up of poems could be referred to as an anthology.
- Anthropomorphism: This means giving human-like characteristics to nonhuman things. “The Little Engine that Could” is a great example.
- Antimetabole: This is when something is repeated, but backwards. For example, “Cats love dogs. Dogs love cats.”
- Antithesis: This is basically a fancy term for two contrasting phrases that work together. An example would be when man landed on the moon and the saying “One small step for man, one giant leap for mankind” came to be.
- “Sardines on a birthday cake– delicious.”
- “It’s time to go to school. Every child needs to go to school.”
- “The simplest questions are the hardest to answer.”
- Aporia: This is an expression of doubt. For example, “How am I supposed to do this without you?”
- Apostrophe: This is when writing turns from addressing one audience to address something else. For example, a character could turn to their green pasture and state “You look beautiful today.”
- Aposiopesis: This is when someone stops speaking mid sentence, whether it be out of passion, fear, or an unwillingness to keep talking. For example, “I’m going to take what’s mine and–” The sentence ends abruptly, and the ending is left for the audience to guess.
- “My doggy, Mr. Fluffy, is playing in the backyard.
- Archaism: This is the use of an old-fashioned word. An example would be writing with the word “Thou” in today’s time.
- Archetype: This is something, whether it be a character, action, or setting, that represents a universal pattern. There are many different archetypes, a well known one is the “Scapegoat.”
- Aside: This is when a character speaks, but their words are only heard by the audience. The other characters are not aware of them. These are often present in plays.
- Assertion: This is a statement that represents a strong belief, whether it is true or not. For example, “I will not let her go to the office” could be said by a student who believes their friend is not guilty of what the teacher accuses.
- Assonance: This is when similar, but non-rhyming vowel sounds are used. “A pot of rocks” is an example of assonance.
- Asyndeton: This is a sentence with missing words, written in a style that emphasizes the meaning. Julius Caesar’s “I came, I played, I conquered” is an example of this.
- Atmosphere: This is the feelings the writer wants the reader to experience. For example, authors of thriller books want their readers to feel suspense.
- Attitude: This is the tone a writer uses toward certain subjects. For example, a positive attitude could be expressed toward rescuing shelter dogs in a story about a rescued pet.
- Auditory image: This expresses through words something that is typically heard. For example, “The metal bowl and wooden spoon clanged together, making piercing, yet somewhat beautiful music.”
- Bandwagon: This is a tool used in persuasive writing that suggests because the greater audience believes something, the reader should believe it as well. It’s the written version of the “Everyone else is doing it” argument.
- Bathos: This term refers to deep, expressive, and emotion-filled writing. It’s commonly found in poetry.
- Bias: Bias is an undue favor (or unfavor) to a topic or group of people. It’s typically something you want to avoid when writing.
- Bildungsroman: This is another term for a coming-of-age novel, and follows the story of the main character from adolescence into adulthood. Harper Lee’s “To Kill a Mockingbird” is a popular example.
- Black humor: This is when a subject that is normally “off limits” is talked about with a bit of humor.
- Cacophony: This is when multiple loud, harsh-sounding words are used. Lewis Carroll’s “Through the Looking Glass” contains a lot of cacophony.
- Cadence: This is the rhythm or beat a piece of writing follows. It’s mostly found in poetry, though it can be used as a stylistic tool in any type of writing.
- Catastrophe: This is another word for a huge disaster. “Romeo and Juliet” is a catastrophe-based story.
- Catharsis: This is the use of large, often negative, emotions in literature to help readers deal with the same feelings in their everyday life. The tragedy genre is often considered to be catharsis.
- Chiasmus: This term describes two phrases that are similar, but reversed.
“We ate all of our dinner. It’s entirety, we consumed.”
- Circumlocution: This simply means unneeded words. For example, “Mean people who want to hurt others are not welcome.” In this sentence, the words “who want to hurt others” are unnecessary.
- Claim: This is the point the writer is trying to make. In an essay meant to persuade readers to vote, the point would be the importance of participating in elections.
- Cliche: This is a phrase that is overused, and therefore has turned a bit cheesy.
“Actions speak louder than words.”
- “Let’s go! Let’s catch up! We can win this race!”
- Coherence: This term means logical and consistent. This is an important tool to use when trying to prove a point.
- Colloquialism: These are phrases that are used in a specific area. “Y’all” is a colloquialism used in the Southern part of the United States.
- Comparatives: This is an area that looks into the differences between literature in various countries. For example, it may compare American and British literature.
- Conceit: A conceit is a comparison that is made between two very different things. For example, “Friendship is like slipping on a banana peel.”
- Concession: A concession is a sentence that admits not everyone agrees with your thesis and provides a few reasons why, but then goes on to show why they should change their minds and side with you. For example, “I know not everyone likes summer because it’s hot and humid, but the daily sunshine and the life that sprouts all around us are things no one should take for granted.”
- Connotation: This term related to the feeling a word has behind it, whether it be positive or negative. For example, a toddler digging through the kitchen cupboards could be called “mischievous” with a negative connotation, or “curious” with a positive connotation.
- Consonance: This is when consonant sounds are repeated. For example, “The b irds in the b lue sky b ounced all around.”
- Context: Context is the background or details surrounding a word that affect its meaning. For example, a word may have one meaning in a research paper and a different meaning in a romance novel. The reader uncovers what the writer means by using context.
- Contrast: This is the use of opposites in writing. It may be opposite characters, for example, that emphasize each other’s characteristics by use of contrast.
- Denotation: Words have many meanings. Denotation refers to the literal meaning. For example, blue is a color (not another term for sadness).
- Denouement: This is basically how a story ends. For example, it’s the conclusion of events that take place in a novel.
- Deus ex machina: This is when an unfixable problem in a story is solved by a very unexpected twist. “Charlie and the Chocolate Factory” is a good example, when Charlie’s financial situation is fixed by him inheriting Wonka’s factory.
- Diacope: This is a phrase that is repeated with words in between. For example, “To be or not to be.”
- Diction: This is the way words are chosen, in hopes of them fitting into a specific style. Many famous, historical novels provide excellent diction examples.
- Diatribe: This is a harsh form of writing that is meant to bring something down. Joseph COnrad’s “Heart of Darkness” is an example of diatribe.
- Dichotomy: This is when something is broken into two different parts. For example, good and evil.
- Didacticism: This is a form of writing that teaches something. “How to” articles are a great example.
- Digression: This is when a writer begins talking about something that is off-topic for an amount of time. It’s a common occurrence in storytelling.
- Dilemma: A dilemma occurs when a character needs to make a choice between two good (or bad) things. An example may be choosing to help their friend pass a class, or avoiding the act of cheating on an assignment.
- Discourse: This is a formal type of writing that often conveys important information. They are common in educational work.
- Dissonance: This is the use of harsh-sounding words in poetry. It’s similar to cacophony.
- Distortion: Distortion is when something is twisted and turned to represent something other than what it actually is. An example would be when someone exaggerates the truth to the point that it is false.
- Doppelgänger: This is a fictional character that looks extremely similar to the protagonist.
- Double entendre: This is a term or phrase that can be interpreted in two different ways. They are often used in comedy.
- Dysphemism: This is when negative terms are used instead of positive terms. For example, a dysphemism would be calling a rollercoaster a “death trap.”
- Elegy: This is a type of poem that honors a person who has died. They are commonly written for famous people or historical people who have made an impact on the writer.
- Elision: An elision is when some sounds are removed from words or phrases. “Tis” used in place of “it is” is an elision.
- Ellipsis: An ellipsis is the three dots that are used when a word or phrase is removed from a sentence. For example, “I love you because… and I will continue to love you forever.” The three dots are replacing the reasons behind the love to shorten the sentence and show the main point.
- Enjambment: This is when a thought or phrase in poetry runs from one line to the next.
“The green grass grows
And covers the entire field.”
- Enthymeme: This is an argument that is written logically, but with an implied conclusion. For example, “I had a bad sandwich at her house last week, so all of her meals must be bad.”
- Enumeration: An enumeration is a complete list within a work of literature. It could be a set of steps in a “How To” article, for example.
- Epanalepsis: This is when a word or phrase is used at the beginning and the end of a sentence.
“Cats are magnificent creatures and no creature is as great as cats.”
- Epiphany: This is a sudden idea or insight a character has. It’s the “lightbulb” moment in literature.
- Epiphora: This is when a word is repeated in nearby segments of text. For example, “I have a banana, you have a banana, and Tom has a banana.”
- Epistle: This is a long, formal letter. Epistles are common in the Bible.
- Epigram: An epigram is an idea that is stated in a quick, clever fashion.
“True friends stab you in the front.” -Oscar Wilde
- Epigraph: An epigraph is a short bit of writing (written by someone else) placed at the top of a piece. Ernest Hemingway’s “The Sun Also Rises” begins with an epigraph.
- Epistrophe: This is the repetition of words at the end of sentences. For example, “The sky’s awake. I am awake.”
- Epitaph: This is a short poem written about a friend after they die. They are sometimes engraved on tombstones.
- Epithet: This is a tool used to describe an object or a character. In Alexander the Great’s name, for example, “the Great” is an epithet.
- Eponym: An eponym is something that is named after a person (or referred to in a certain way because of that person). For example, John Hancock is another name for signature.
- Epizeuxis: This is simply another word for diacope, which is explained above.
- Eristic: When an author writes about a heated topic without actually trying to solve the issue at hand, it’s referred to as Eristis. It’s considered a form of debate.
- Ethos: This is a way to make the audience trust the writer by showing credibility and ethical behavior. For example, a persuasive essay on why it’s important to not text and drive has more meaning when it’s written by a former police officer who had to report to all of the texting and driving accidents.
- Euphemism: This is a nicer way to say something that’s hard to talk about. “He who shall not be named” is a euphemism for Voldemort in “Harry Potter.”
- Euphony: Euphony is writing that is made up of pleasant sounds. It is common in poetry.
- Evidence: Evidence is required in argumentative essays to prove the point the writer is trying to make. If the writer states that zoos should not exist, their evidence needs to show the downsides of zoos in regards to animals.
- Exaggeration: This is when something is described as more than it really was. For example, “I saw the biggest dog in the world today.”
- Exemplum: This proves the point of a story. For example, the exemplum in fables is the lesson the story brings to light.
- Expletive: An expletive is an unnecessary word (or words) that take up space in a sentence. For example, “it is” in the sentence “It is time to go to the movies.” The words aren’t needed to understand what is being said.
- Explication: This is a short write up that explains the meaning of a work. For example, an explication of a poem wouldn’t mention how the piece was written, it would only explain the meaning it holds.
- Fallacy: This is an incorrect or illogical statement that makes an argument invalid. The ad hominem is an example of a fallacy.
- Farce: This is a type of comedy that is written solely for entertainment and humor. The movie “Home Alone” is a good example.
- Figurative Language: This is language that is used in a non-literal sense. Metaphors and similes are types of figurative language.
- Figure of Speech: A figure of speech has a second meaning, beside its literal meaning. “Falling in love” is a well known example of a figure of speech.
- Foil: This is when a good character is presented as an evil character. Mercutio is a foil in Shakespeare’s “Romeo and Juliet.”
- Hamartia: This is simply another term for Tragic Flaw.
- Hubris: This is another word for pride in a literary character. It is a common tragic flaw.
- Idiom: This is a saying that does not stand for its literal meaning. For example, “Stop bugging me” has nothing to do with bugs.
- In Medias Res: This is when a story starts in the middle, because the audience already knows what happened beforehand. An example is Homer’s “The Iliad.”
- Inciting incident: This is when the action begins in a story. In fiction, it’s followed by the rising action.
- Induction: Induction is when a reader finds a fact and draws a conclusion from it. That conclusion may be right or wrong. Induction happens all the time throughout the process of reading. A writer may use this knowledge to add surprises into the text.
- Inference: This is when opinions are formed based on a set of observations. A writer can supply facts to guide the reader toward a certain inference.
- Intertextuality: Intertextuality is when one text is shaped by another. William Golding’s “Lord of the Flies” is shaped by Robert Louis Stevenson’s “Treasure Island,” for example.
- Inversion: This is when words are revered. Yoda speaks in an inverted fashion.
- Irony: Irony is an extremely unexpected occurrence or something has the opposite meaning than what would be expected. An example would be a fire station burning down.
- “I want to go to the park, because it is a beautiful day and because the sun is shining bright.”
- Jargon: Jargon is a set of words with meanings that are only understood by a specific group of people. Lawyers have a large amount of legal jargon.
- Juxtaposition: This is when two characters or phrases are placed together for comparison. For example, “When it rains, it pours.”
- Kenning: This is a metaphor that combines two words. An example would be a bookworm.
- Kinesthesia: This is imagery, typically found in poetry, that describes a bodily movement such as a heartbeat or running legs.
- Lampoon: A lampoon is basically a way to make fun of something. Satire and sarcasm are types of lampoons.
- Litotes: This means to understate something in a funny way. For example, if a person got into a car accident on their way to work, they could say “Well this is not the best morning I’ve ever had.”
- Logos: This is just another term for logic, and it’s especially important in argumentative writing. Including statistics in a report is a type of logos.
- Malapropism: This is when a word that sounds right, but is completely wrong, is used to confuse the reader (or to make them laugh).
“She went to expensive measures to keep her son safe.”
- Maxim: These are clever sayings that share truths of life. An example is “Opposites attract.”
- Meiosis: This term refers to downplaying something. An example could be calling a psychiatrist a “shrink,” and therefore diminishing the important work they do.
- Metalepsis: Metalepsis is when something is described by using a similar, yet unrelated term. An example would be calling something good by stating “It wasn’t bad.”
- Metaphysical: This is a complex and bold form of poetry that is said to be outside the realm of human understanding. It was commonly written during the seventeenth century.
- Metonymy: This is when something is referred to with a closely related term. For example, “heart” often refers to “love.”
- Mood: The mood refers to the emotions that are evoked by a piece of writing. It can be affected by setting, character, plot, and more. One mood written works can have is uplifting.
- Moral: This is the lesson that is meant to be learned by a story. For example, the moral of “The Tortoise and the Hare” is “slow and steady wins the race.”
- Motif: This is an image or idea that occurs throughout a written work that adds to the theme. For example, the spring season could represent new life.
- Motivation: This is the reason behind a character’s actions. It can be intrinsic (within the character) or extrinsic (an outside force). An example would be a student who wants to pass high school to get a better job than her parents had throughout her childhood.
- Nemesis: The nemesis is an evil character who works against the protagonist. An example would be Ursula in “The Little Mermaid.”
- Neologism: This is a term that basically means “a made up word.” “Selfie” is a neologism for a picture of yourself.
- Non Sequitur: This is a sentence or statement that does not make logical sense. It’s often used for comedic purposes.
“I saw a cat today, so I’ll likely win the lottery tomorrow.”
- Nostalgia: This is a description of the past, and can bring back either feelings of pleasure or feelings of pain. The famous beginning of Charles Dickens’ “A Tale of Two Cities” is an example of nostalgia.
- Omniscient: In literature, an omniscient view can see the thoughts of every character. Many novels are written from this point of view.
- Ordinal Number: These are number terms such as first, second, third, and so on. They can be used to organize thoughts or books in a series.
- Overstatement: An overstatement is describing something as more than it was. For example, someone who found a dollar on the ground could say “I had the best day of my life today!”
- Oxymoron: This is when two words or phrases with opposite meaning are used together. “Good pain” could be considered an oxymoron.
- Pacing: This is how a writer controls the speed of a story. It can be told quickly, or it can be more drawn out.
- Palindrome: This is a word that backward or forward, spells the same. An example is “racecar.”
- Paradox: A paradox is a sentence that cannot be true, but it also cannot be false.
“This sentence is a lie.”
- Paralipsis: This refers to the act of purposely leaving information out. It is commonly used in political speeches.
- Parallel structure: This is a sentence that is made up equally in regards to grammar.
“We went outside, rode our bikes, drew with chalk, and ate a snack.”
- Paraphrase: This is taking someone else’s writing and putting it in your own words.
“Tigers are elegant creatures with their orange and black stripes.”
“The black and orange stripes that tigers have make them beautiful.”
- Paraprosdokian: This term describes a surprise ending to a sentence. For example, “I had two pets named Fred, one was a dog and the other was my husband.”
- “The horse galloped and jumped and bucked and played.”
- Parenthesis: This is an explanatory word or phrase that’s inserted into a text (and placed inside of parenthesis). Did you spot the example right in the definition?
- Paronomasia: This is a funny play on words. They are found often throughout the work of Shakespeare.
- Parrhesia: This is another term for free speech, often expressing the opinion of the author. George Orwell’s “Animal Farm” contains plenty of this.
- Pastiche: This is a type of writing that imitates the work of someone else. An example would be trying to write in a Shakespearian style.
- Pathos: This gets the emotions of the reader involved. Bringing up how farm animals are treated by large corporations, for example, would be an effective use of pathos in an argument for supporting local farmers.
- Periphrasis: Periphrasis is just an indirect way of speaking. For example, stating “The bowl of water that belongs to the dog” instead of “The dog’s water bowl.”
- Persona: The persona is who is thought to be speaking in a written work. For example, the writer could take on an educational voice to create a fitting persona for a research paper.
- Perspective: This describes who is telling the story. Some examples include first person, second person, and third person.
- Pleonasm: Thi is when something is described with more than the amount of necessary descriptive terms. For example, “I saw it this morning at the beginning of the day.”
- Polyptoton: This is when words with the same root are repeated. For example, “My lover is looking lovely today.”
- Polysyndeton: This style of writing uses multiple conjunctions. “We went to the bank and the store and the restaurant and the mall.”
- Portmanteau: This is when two words are combined to create a new word. A popular portmanteau is “hangry.”
- “Many people believe it is okay to text and drive, but it is one of the most dangerous things you can do.”
- Propaganda: Propaganda publicly shares a specific opinion. “Animal Farm” is propaganda.
- Prosody: Prosody is the attitude that gives a phrase the correct meaning. For example, if someone says “I had a wonderful day,” prosody would determine whether that statement was true or sarcastic.
- Prosthesis: This is when a syllable is added to the beginning of a word. For example, “She went a-walkin’.”
- Pun: A pun is a funny type of word play. An example could be “Horses are stable animals.”
- Realism: This is a writing style that represents real life. As long as a book has nothing make-believe in it, it’s likely realism.
- Rebuttal: This is when a writer breaks down the opposing argument. For example, in a piece that states truancy is too harshly enforced, the writer could look at countries with less truancy punishments and show they have better attendance rates.
- Red Herring: This is when a writer avoids an argument or negative subject by bringing up something completely unrelated. It is once again common in political pieces.
- Reductio Ad Absurdum: This is another term for argumentative essays, where the writer breaks down the opposing view to the point no one could possibly believe it.
- Repetition: Repetition is repeating a word or phrase for emphasis. For example, The strong wind blew over the table, and the strong wind knocked down a tree.”
- Rhetorical Devices: Rhetoric is using literature for a variety of purposes, including bringing about emotions or proving a point. Most literary techniques can be considered rhetorical devices.
- Sarcasm: This is when something is said one way, but has the opposite meaning. Stating “It’s a beautiful day” during a giant storm is an example of sarcasm.
- Semantic: Semantic is the thought that words can be used in many ways other than to represent their literal meaning. Semantics show that “heart” can be a human organ, and it can be something that represents love.
- Sensory Language: This connects the reader to a story through the use of the five senses. It may include terms that explain sounds or feelings, for example.
- Sesquipedalian: This term refers to the use of extremely long words. It can include the use of any ridiculous words or phrases.
- Sestine: This is a type of poem with six, six-line stanzas followed by one three-line stanza. An example is Elizabeht Bishop’s “A Miracle for Breakfast.”
- Sibilance: Sibilance is the repeated use of “hissing” sounds. “Sally sold seashells by the seashore” could be a sibilance.
- Situational Irony: This is when something extremely unexpected (and often funny) happens. An example would be a teacher forgetting to do their homework.
- Slang: These are made-up words that have been accepted and are understood by society. “BAE” is a slang word that means “before anyone else,” or babe, that is often used today.”
- Snark: Snark is made up of quick, unkind comments. Saying “Nice catch” when someone drops a football would be an example of snark.
- Soliloquy: This is when a character speaks to themselves. Soliloquies are often found in plays.
- Sound Devices: These create a specific sound in writing, and specifically in poetry. Rhymes are the most common sound device.
- Spondee: A spondee is two stressed syllables. An example could be “Schoolyard.”
- Straw Man: This is when an argument goes after the most extreme point of view instead of what the other person actually thinks. An example would be arguing with someone on lowering the legal drinking age, and state they want more alcoholics in the world.
- Stream of Consciousness: This is a writing style that follows the thoughts in the author’s mind. Virginia Woolf’s works are great examples of this style.
- Subjective: Subjective means opinion-based. A subjective topic example is “What is the best color in the rainbow?”
- Superlative: Superlatives are words that add “-est” onto an adverb or adjective. “Happiest” is an example of a superlative.
- Surrealism: Surrealism is work that is almost dreamlike. It is full of descriptive imagery. Salvador Dahli’s work is a great example.
- Symbolism: Symbolism is when one object holds the meaning of something larger. A necklace given to a character by her lover could be a symbol of his commitment and love.
- Syncope: This is a term that represents a shortened word. For example, the syncope for “You all” is “Y’all.”
- Synecdoche: This is a saying in which a piece of something represents the whole thing. A good example is “All hands on deck.” WHen this phrase is used, they are not just asking for hands, they are asking for the help of the people.
- Synesis: This is a type of phrase where the technical rules of grammar are let go to allow something that still makes sense. Mark Twain’s novels use synesis.
- Synesthesia: This is when something is being described with characteristics of something else. A simile is a great example of synesthesia.
- Syntax: This term refers to how words are arranged in a sentence.
- Tautology: Tautology is when a meaning is repeated through a seemingly unnecessary word. For example, “Cold snow.” We already know that snow is cold, so using the adjective to describe it isn’t really necessary.
- Tmesis: This cuts a word or phrase into two different parts. “Fan-freaking-tastic” is a slang version of a tmesis.
- Tricolon: This means three words or phrases that are parallel.
“Eat, Pray, Love.”
- Trope: This is a broad term that describes something in a way that is not literal. A metaphor is a type of trope.
- Truism: This is a statement that is based on a fact, so it does not need to be proven. For example, “Water is wet.”
- Understatement: This is when something is downplayed. Saying “I had a decent race” when you won the state championship would be an example of an understatement.
- Undertone: This is an implied attitude that lies at the surface of a piece. For example, an argumentative essay on the why the death penalty should not exist may have a depressing undertone.
- Verbal Irony: Verbal irony is when a character says one thing but means the opposite. They could say “I wish I was at home” while on the best vacation of their life.
- Villanelle: This is a specific type of poem with nineteen lines (five tercets, one quatrain, and one couplet). “One Art” by Elizabeth Bishop is a great example.
- Verisimilitude: This is the process a writer uses to make their piece seem believable. For example, people in a certain country speak the native language, making it seem true that the characters are actually there.
- Vernacular: These are sets of words used by specific groups of people. Medical terms are vernacular for doctors and nurses.
- Volta: This is a switch in a written work. It could be a change in emotion or a switch to the other side of an argument. For example, a character may go from being happy that it’s snowing to being sad that school is cancelled for the day.
- Wit: Wit is a quick, well-thought-out, and funny way to respond to something. It is often used in comedy writing, or as comic relief.
- Zeugma: A Zeugma is a verb or an adjective that explains two different things. For example, “He threw away the assignment and his chance at passing the class.”
- Zoomorphism: This is when animal-like characteristics are given to people (or to anything that is not an animal).
“She ran with the speed of a cheetah.”
Conclusion: Literary Devices, Techniques, and Elements
The list of literary devices is long, and it’ll never be required of you to memorize them all.
The more you know, however, the more complexity and style you can add to your writing.
Take this list and work your way toward becoming the best writer you can possibly be.
Learn how we can help you with college and career guidance! Check out our YouTube channel!
Click Here to Schedule a Free Consult!

Stay on track and ease your anxiety with our second-to-none college application assistance.

- Ethics & Honesty
- Privacy Policy
- Join Our Team
(732) 339-3835
Literary Devices and Terms
literary devices refers to the typical structures used by writers in their works to convey his or her messages in a simple manner to the readers. When employed properly, the different literary devices help readers to appreciate, interpret and analyze a literary work. Below is a list of literary devices with detailed definition and examples.
- Accumulation
- Active Voice
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anacoluthon
- Anadiplosis
- Anagnorisis
- Analytical Essay
- Antanaclasis
- Anthropomorphism
- Anti-Climax
- Antimetabole
- Antiphrasis
- Antistrophe
- Antonomasia
- Aposiopesis
- Argumentative Essay
- Auditory Imagery
- Autobiography
- Balanced Sentence
- Bildungsroman
- Black Humor
- Blank Verse
- Catachresis
- Catastrophe
- Cause and Effect Essay
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Colloquialism
- Comic Relief
- Comparatives
- Comparison and Contrast Essay
- Connotation
- Critical Essay
- Cumulative Sentence
- Deductive Reasoning
- Deus Ex Machina
- Deuteragonist
- Didacticism
- Direct Characterization
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic Irony
- Dramatic Monologue
- Dynamic Character
- End-Stopped Line
- Enumeration
- Equivocation
- Exact Rhyme
- Exaggeration
- Existentialism
- Explication
- Explicatory Essay
- Expository Essay
- Extended Metaphor
- External Conflict
- Falling Action
- Feminine Rhyme
- Figurative Language
- Figure of Speech
- Flash-Forward
- Flat Character
- Foreshadowing
- Frame Story
- Gustatory Imagery
- Hypothetical Question
- Iambic Pentameter
- Imperative Sentence
- Implied Metaphor
- In Medias Res
- Inciting Incident
- Internal Rhyme
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Kinesthesia
- Kinesthetic Imagery
- Malapropism
- Metaphysical
- Narrative Poem
- Non Sequitur
- Olfactory Imagery
- Onomatopoeia
- Ordinal Number
- Overstatement
- Parallel Structure
- Parallelism
- Paraprosdokian
- Parenthesis
- Paronomasia
- Passive Voice
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Periphrasis
- Personification
- Perspective
- Persuasive Essay
- Poetic Justice
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Portmanteau
- Procatalepsis
- Process Essay
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Reductio ad Absurdum
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Rhyme Scheme
- Rising Action
- Romanticism
- Round Character
- Run-On Sentence
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Sensory Language
- Sesquipedalian
- Short Story
- Simple Paragraph
- Situational Irony
- Sound Devices
- Static Character
- Stream of Consciousness
- Superlative
- Supporting Sentence
- Synesthesia
- Tactile Imagery
- Tragic Flaw
- Tragic Hero
- Tragicomedy
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verbal Irony
- Verisimilitude
- Visual Imagery
- Zoomorphism
- Literary Terms
When and How to Use Literary Devices
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Use Literary Devices
How to Use Literary Devices
- Write Naturally. Whenever you write, you’re using literary/ rhetorical devices – even if you don’t know it! That’s because some of these techniques are such a natural part of everyday speech that they slip into our writing as well.
- Read Carefully. All your favorite authors use literary devices , and if you pay close attention, you can keep track of them as you read. As you get good at recognizing literary devices, try to see how the author uses many different devices to contribute to the overall effect of the story or poem.
- Learn individual techniques . Each literary device has its own tricks and benefits, and no one is perfect at all of them. But the only way to improve is through patient practice. Try to learn a new technique every week or so and incorporate it into your own everyday writing.
When to Use Literary Devices
By definition, literary devices occur in literature rather than essays . So, strictly speaking, they belong to creative writing. Rhetorical devices would be the ones used in an essay. Again, though, literary devices are basically the same as rhetorical devices, so this distinction doesn’t matter too much. Literary/ rhetorical devices are appropriate for every form of writing – even emails and text messages! If you pay attention, you’ll probably catch yourself using devices like rhetorical questions , analogies , and puns as you write.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
beginner's guide to literary analysis
Understanding literature & how to write literary analysis.
Literary analysis is the foundation of every college and high school English class. Once you can comprehend written work and respond to it, the next step is to learn how to think critically and complexly about a work of literature in order to analyze its elements and establish ideas about its meaning.
If that sounds daunting, it shouldn’t. Literary analysis is really just a way of thinking creatively about what you read. The practice takes you beyond the storyline and into the motives behind it.
While an author might have had a specific intention when they wrote their book, there’s still no right or wrong way to analyze a literary text—just your way. You can use literary theories, which act as “lenses” through which you can view a text. Or you can use your own creativity and critical thinking to identify a literary device or pattern in a text and weave that insight into your own argument about the text’s underlying meaning.
Now, if that sounds fun, it should , because it is. Here, we’ll lay the groundwork for performing literary analysis, including when writing analytical essays, to help you read books like a critic.
What Is Literary Analysis?
As the name suggests, literary analysis is an analysis of a work, whether that’s a novel, play, short story, or poem. Any analysis requires breaking the content into its component parts and then examining how those parts operate independently and as a whole. In literary analysis, those parts can be different devices and elements—such as plot, setting, themes, symbols, etcetera—as well as elements of style, like point of view or tone.
When performing analysis, you consider some of these different elements of the text and then form an argument for why the author chose to use them. You can do so while reading and during class discussion, but it’s particularly important when writing essays.
Literary analysis is notably distinct from summary. When you write a summary , you efficiently describe the work’s main ideas or plot points in order to establish an overview of the work. While you might use elements of summary when writing analysis, you should do so minimally. You can reference a plot line to make a point, but it should be done so quickly so you can focus on why that plot line matters . In summary (see what we did there?), a summary focuses on the “ what ” of a text, while analysis turns attention to the “ how ” and “ why .”
While literary analysis can be broad, covering themes across an entire work, it can also be very specific, and sometimes the best analysis is just that. Literary critics have written thousands of words about the meaning of an author’s single word choice; while you might not want to be quite that particular, there’s a lot to be said for digging deep in literary analysis, rather than wide.
Although you’re forming your own argument about the work, it’s not your opinion . You should avoid passing judgment on the piece and instead objectively consider what the author intended, how they went about executing it, and whether or not they were successful in doing so. Literary criticism is similar to literary analysis, but it is different in that it does pass judgement on the work. Criticism can also consider literature more broadly, without focusing on a singular work.
Once you understand what constitutes (and doesn’t constitute) literary analysis, it’s easy to identify it. Here are some examples of literary analysis and its oft-confused counterparts:
Summary: In “The Fall of the House of Usher,” the narrator visits his friend Roderick Usher and witnesses his sister escape a horrible fate.
Opinion: In “The Fall of the House of Usher,” Poe uses his great Gothic writing to establish a sense of spookiness that is enjoyable to read.
Literary Analysis: “Throughout ‘The Fall of the House of Usher,’ Poe foreshadows the fate of Madeline by creating a sense of claustrophobia for the reader through symbols, such as in the narrator’s inability to leave and the labyrinthine nature of the house.
In summary, literary analysis is:
- Breaking a work into its components
- Identifying what those components are and how they work in the text
- Developing an understanding of how they work together to achieve a goal
- Not an opinion, but subjective
- Not a summary, though summary can be used in passing
- Best when it deeply, rather than broadly, analyzes a literary element
Literary Analysis and Other Works
As discussed above, literary analysis is often performed upon a single work—but it doesn’t have to be. It can also be performed across works to consider the interplay of two or more texts. Regardless of whether or not the works were written about the same thing, or even within the same time period, they can have an influence on one another or a connection that’s worth exploring. And reading two or more texts side by side can help you to develop insights through comparison and contrast.
For example, Paradise Lost is an epic poem written in the 17th century, based largely on biblical narratives written some 700 years before and which later influenced 19th century poet John Keats. The interplay of works can be obvious, as here, or entirely the inspiration of the analyst. As an example of the latter, you could compare and contrast the writing styles of Ralph Waldo Emerson and Edgar Allan Poe who, while contemporaries in terms of time, were vastly different in their content.
Additionally, literary analysis can be performed between a work and its context. Authors are often speaking to the larger context of their times, be that social, political, religious, economic, or artistic. A valid and interesting form is to compare the author’s context to the work, which is done by identifying and analyzing elements that are used to make an argument about the writer’s time or experience.
For example, you could write an essay about how Hemingway’s struggles with mental health and paranoia influenced his later work, or how his involvement in the Spanish Civil War influenced his early work. One approach focuses more on his personal experience, while the other turns to the context of his times—both are valid.
Why Does Literary Analysis Matter?
Sometimes an author wrote a work of literature strictly for entertainment’s sake, but more often than not, they meant something more. Whether that was a missive on world peace, commentary about femininity, or an allusion to their experience as an only child, the author probably wrote their work for a reason, and understanding that reason—or the many reasons—can actually make reading a lot more meaningful.
Performing literary analysis as a form of study unquestionably makes you a better reader. It’s also likely that it will improve other skills, too, like critical thinking, creativity, debate, and reasoning.
At its grandest and most idealistic, literary analysis even has the ability to make the world a better place. By reading and analyzing works of literature, you are able to more fully comprehend the perspectives of others. Cumulatively, you’ll broaden your own perspectives and contribute more effectively to the things that matter to you.
Literary Terms to Know for Literary Analysis
There are hundreds of literary devices you could consider during your literary analysis, but there are some key tools most writers utilize to achieve their purpose—and therefore you need to know in order to understand that purpose. These common devices include:
- Characters: The people (or entities) who play roles in the work. The protagonist is the main character in the work.
- Conflict: The conflict is the driving force behind the plot, the event that causes action in the narrative, usually on the part of the protagonist
- Context : The broader circumstances surrounding the work political and social climate in which it was written or the experience of the author. It can also refer to internal context, and the details presented by the narrator
- Diction : The word choice used by the narrator or characters
- Genre: A category of literature characterized by agreed upon similarities in the works, such as subject matter and tone
- Imagery : The descriptive or figurative language used to paint a picture in the reader’s mind so they can picture the story’s plot, characters, and setting
- Metaphor: A figure of speech that uses comparison between two unlike objects for dramatic or poetic effect
- Narrator: The person who tells the story. Sometimes they are a character within the story, but sometimes they are omniscient and removed from the plot.
- Plot : The storyline of the work
- Point of view: The perspective taken by the narrator, which skews the perspective of the reader
- Setting : The time and place in which the story takes place. This can include elements like the time period, weather, time of year or day, and social or economic conditions
- Symbol : An object, person, or place that represents an abstract idea that is greater than its literal meaning
- Syntax : The structure of a sentence, either narration or dialogue, and the tone it implies
- Theme : A recurring subject or message within the work, often commentary on larger societal or cultural ideas
- Tone : The feeling, attitude, or mood the text presents
How to Perform Literary Analysis
Step 1: read the text thoroughly.
Literary analysis begins with the literature itself, which means performing a close reading of the text. As you read, you should focus on the work. That means putting away distractions (sorry, smartphone) and dedicating a period of time to the task at hand.
It’s also important that you don’t skim or speed read. While those are helpful skills, they don’t apply to literary analysis—or at least not this stage.
Step 2: Take Notes as You Read
As you read the work, take notes about different literary elements and devices that stand out to you. Whether you highlight or underline in text, use sticky note tabs to mark pages and passages, or handwrite your thoughts in a notebook, you should capture your thoughts and the parts of the text to which they correspond. This—the act of noticing things about a literary work—is literary analysis.
Step 3: Notice Patterns
As you read the work, you’ll begin to notice patterns in the way the author deploys language, themes, and symbols to build their plot and characters. As you read and these patterns take shape, begin to consider what they could mean and how they might fit together.
As you identify these patterns, as well as other elements that catch your interest, be sure to record them in your notes or text. Some examples include:
- Circle or underline words or terms that you notice the author uses frequently, whether those are nouns (like “eyes” or “road”) or adjectives (like “yellow” or “lush”).
- Highlight phrases that give you the same kind of feeling. For example, if the narrator describes an “overcast sky,” a “dreary morning,” and a “dark, quiet room,” the words aren’t the same, but the feeling they impart and setting they develop are similar.
- Underline quotes or prose that define a character’s personality or their role in the text.
- Use sticky tabs to color code different elements of the text, such as specific settings or a shift in the point of view.
By noting these patterns, comprehensive symbols, metaphors, and ideas will begin to come into focus.
Step 4: Consider the Work as a Whole, and Ask Questions
This is a step that you can do either as you read, or after you finish the text. The point is to begin to identify the aspects of the work that most interest you, and you could therefore analyze in writing or discussion.
Questions you could ask yourself include:
- What aspects of the text do I not understand?
- What parts of the narrative or writing struck me most?
- What patterns did I notice?
- What did the author accomplish really well?
- What did I find lacking?
- Did I notice any contradictions or anything that felt out of place?
- What was the purpose of the minor characters?
- What tone did the author choose, and why?
The answers to these and more questions will lead you to your arguments about the text.
Step 5: Return to Your Notes and the Text for Evidence
As you identify the argument you want to make (especially if you’re preparing for an essay), return to your notes to see if you already have supporting evidence for your argument. That’s why it’s so important to take notes or mark passages as you read—you’ll thank yourself later!
If you’re preparing to write an essay, you’ll use these passages and ideas to bolster your argument—aka, your thesis. There will likely be multiple different passages you can use to strengthen multiple different aspects of your argument. Just be sure to cite the text correctly!
If you’re preparing for class, your notes will also be invaluable. When your teacher or professor leads the conversation in the direction of your ideas or arguments, you’ll be able to not only proffer that idea but back it up with textual evidence. That’s an A+ in class participation.
Step 6: Connect These Ideas Across the Narrative
Whether you’re in class or writing an essay, literary analysis isn’t complete until you’ve considered the way these ideas interact and contribute to the work as a whole. You can find and present evidence, but you still have to explain how those elements work together and make up your argument.
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay
When conducting literary analysis while reading a text or discussing it in class, you can pivot easily from one argument to another (or even switch sides if a classmate or teacher makes a compelling enough argument).
But when writing literary analysis, your objective is to propose a specific, arguable thesis and convincingly defend it. In order to do so, you need to fortify your argument with evidence from the text (and perhaps secondary sources) and an authoritative tone.
A successful literary analysis essay depends equally on a thoughtful thesis, supportive analysis, and presenting these elements masterfully. We’ll review how to accomplish these objectives below.
Step 1: Read the Text. Maybe Read It Again.
Constructing an astute analytical essay requires a thorough knowledge of the text. As you read, be sure to note any passages, quotes, or ideas that stand out. These could serve as the future foundation of your thesis statement. Noting these sections now will help you when you need to gather evidence.
The more familiar you become with the text, the better (and easier!) your essay will be. Familiarity with the text allows you to speak (or in this case, write) to it confidently. If you only skim the book, your lack of rich understanding will be evident in your essay. Alternatively, if you read the text closely—especially if you read it more than once, or at least carefully revisit important passages—your own writing will be filled with insight that goes beyond a basic understanding of the storyline.
Step 2: Brainstorm Potential Topics
Because you took detailed notes while reading the text, you should have a list of potential topics at the ready. Take time to review your notes, highlighting any ideas or questions you had that feel interesting. You should also return to the text and look for any passages that stand out to you.
When considering potential topics, you should prioritize ideas that you find interesting. It won’t only make the whole process of writing an essay more fun, your enthusiasm for the topic will probably improve the quality of your argument, and maybe even your writing. Just like it’s obvious when a topic interests you in a conversation, it’s obvious when a topic interests the writer of an essay (and even more obvious when it doesn’t).
Your topic ideas should also be specific, unique, and arguable. A good way to think of topics is that they’re the answer to fairly specific questions. As you begin to brainstorm, first think of questions you have about the text. Questions might focus on the plot, such as: Why did the author choose to deviate from the projected storyline? Or why did a character’s role in the narrative shift? Questions might also consider the use of a literary device, such as: Why does the narrator frequently repeat a phrase or comment on a symbol? Or why did the author choose to switch points of view each chapter?
Once you have a thesis question , you can begin brainstorming answers—aka, potential thesis statements . At this point, your answers can be fairly broad. Once you land on a question-statement combination that feels right, you’ll then look for evidence in the text that supports your answer (and helps you define and narrow your thesis statement).
For example, after reading “ The Fall of the House of Usher ,” you might be wondering, Why are Roderick and Madeline twins?, Or even: Why does their relationship feel so creepy?” Maybe you noticed (and noted) that the narrator was surprised to find out they were twins, or perhaps you found that the narrator’s tone tended to shift and become more anxious when discussing the interactions of the twins.
Once you come up with your thesis question, you can identify a broad answer, which will become the basis for your thesis statement. In response to the questions above, your answer might be, “Poe emphasizes the close relationship of Roderick and Madeline to foreshadow that their deaths will be close, too.”
Step 3: Gather Evidence
Once you have your topic (or you’ve narrowed it down to two or three), return to the text (yes, again) to see what evidence you can find to support it. If you’re thinking of writing about the relationship between Roderick and Madeline in “The Fall of the House of Usher,” look for instances where they engaged in the text.
This is when your knowledge of literary devices comes in clutch. Carefully study the language around each event in the text that might be relevant to your topic. How does Poe’s diction or syntax change during the interactions of the siblings? How does the setting reflect or contribute to their relationship? What imagery or symbols appear when Roderick and Madeline are together?
By finding and studying evidence within the text, you’ll strengthen your topic argument—or, just as valuably, discount the topics that aren’t strong enough for analysis.
Step 4: Consider Secondary Sources
In addition to returning to the literary work you’re studying for evidence, you can also consider secondary sources that reference or speak to the work. These can be articles from journals you find on JSTOR, books that consider the work or its context, or articles your teacher shared in class.
While you can use these secondary sources to further support your idea, you should not overuse them. Make sure your topic remains entirely differentiated from that presented in the source.
Step 5: Write a Working Thesis Statement
Once you’ve gathered evidence and narrowed down your topic, you’re ready to refine that topic into a thesis statement. As you continue to outline and write your paper, this thesis statement will likely change slightly, but this initial draft will serve as the foundation of your essay. It’s like your north star: Everything you write in your essay is leading you back to your thesis.
Writing a great thesis statement requires some real finesse. A successful thesis statement is:
- Debatable : You shouldn’t simply summarize or make an obvious statement about the work. Instead, your thesis statement should take a stand on an issue or make a claim that is open to argument. You’ll spend your essay debating—and proving—your argument.
- Demonstrable : You need to be able to prove, through evidence, that your thesis statement is true. That means you have to have passages from the text and correlative analysis ready to convince the reader that you’re right.
- Specific : In most cases, successfully addressing a theme that encompasses a work in its entirety would require a book-length essay. Instead, identify a thesis statement that addresses specific elements of the work, such as a relationship between characters, a repeating symbol, a key setting, or even something really specific like the speaking style of a character.
Example: By depicting the relationship between Roderick and Madeline to be stifling and almost otherworldly in its closeness, Poe foreshadows both Madeline’s fate and Roderick’s inability to choose a different fate for himself.
Step 6: Write an Outline
You have your thesis, you have your evidence—but how do you put them together? A great thesis statement (and therefore a great essay) will have multiple arguments supporting it, presenting different kinds of evidence that all contribute to the singular, main idea presented in your thesis.
Review your evidence and identify these different arguments, then organize the evidence into categories based on the argument they support. These ideas and evidence will become the body paragraphs of your essay.
For example, if you were writing about Roderick and Madeline as in the example above, you would pull evidence from the text, such as the narrator’s realization of their relationship as twins; examples where the narrator’s tone of voice shifts when discussing their relationship; imagery, like the sounds Roderick hears as Madeline tries to escape; and Poe’s tendency to use doubles and twins in his other writings to create the same spooky effect. All of these are separate strains of the same argument, and can be clearly organized into sections of an outline.
Step 7: Write Your Introduction
Your introduction serves a few very important purposes that essentially set the scene for the reader:
- Establish context. Sure, your reader has probably read the work. But you still want to remind them of the scene, characters, or elements you’ll be discussing.
- Present your thesis statement. Your thesis statement is the backbone of your analytical paper. You need to present it clearly at the outset so that the reader understands what every argument you make is aimed at.
- Offer a mini-outline. While you don’t want to show all your cards just yet, you do want to preview some of the evidence you’ll be using to support your thesis so that the reader has a roadmap of where they’re going.
Step 8: Write Your Body Paragraphs
Thanks to steps one through seven, you’ve already set yourself up for success. You have clearly outlined arguments and evidence to support them. Now it’s time to translate those into authoritative and confident prose.
When presenting each idea, begin with a topic sentence that encapsulates the argument you’re about to make (sort of like a mini-thesis statement). Then present your evidence and explanations of that evidence that contribute to that argument. Present enough material to prove your point, but don’t feel like you necessarily have to point out every single instance in the text where this element takes place. For example, if you’re highlighting a symbol that repeats throughout the narrative, choose two or three passages where it is used most effectively, rather than trying to squeeze in all ten times it appears.
While you should have clearly defined arguments, the essay should still move logically and fluidly from one argument to the next. Try to avoid choppy paragraphs that feel disjointed; every idea and argument should feel connected to the last, and, as a group, connected to your thesis. A great way to connect the ideas from one paragraph to the next is with transition words and phrases, such as:
- Furthermore
- In addition
- On the other hand
- Conversely
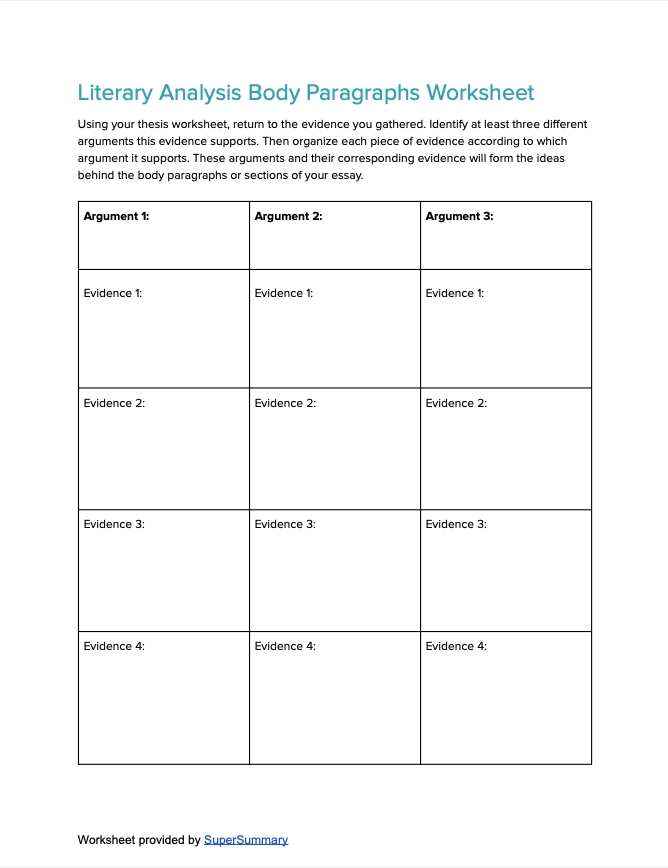
Step 9: Write Your Conclusion
Your conclusion is more than a summary of your essay's parts, but it’s also not a place to present brand new ideas not already discussed in your essay. Instead, your conclusion should return to your thesis (without repeating it verbatim) and point to why this all matters. If writing about the siblings in “The Fall of the House of Usher,” for example, you could point out that the utilization of twins and doubles is a common literary element of Poe’s work that contributes to the definitive eeriness of Gothic literature.
While you might speak to larger ideas in your conclusion, be wary of getting too macro. Your conclusion should still be supported by all of the ideas that preceded it.
Step 10: Revise, Revise, Revise
Of course you should proofread your literary analysis essay before you turn it in. But you should also edit the content to make sure every piece of evidence and every explanation directly supports your thesis as effectively and efficiently as possible.
Sometimes, this might mean actually adapting your thesis a bit to the rest of your essay. At other times, it means removing redundant examples or paraphrasing quotations. Make sure every sentence is valuable, and remove those that aren’t.
Other Resources for Literary Analysis
With these skills and suggestions, you’re well on your way to practicing and writing literary analysis. But if you don’t have a firm grasp on the concepts discussed above—such as literary devices or even the content of the text you’re analyzing—it will still feel difficult to produce insightful analysis.
If you’d like to sharpen the tools in your literature toolbox, there are plenty of other resources to help you do so:
- Check out our expansive library of Literary Devices . These could provide you with a deeper understanding of the basic devices discussed above or introduce you to new concepts sure to impress your professors ( anagnorisis , anyone?).
- This Academic Citation Resource Guide ensures you properly cite any work you reference in your analytical essay.
- Our English Homework Help Guide will point you to dozens of resources that can help you perform analysis, from critical reading strategies to poetry helpers.
- This Grammar Education Resource Guide will direct you to plenty of resources to refine your grammar and writing (definitely important for getting an A+ on that paper).
Of course, you should know the text inside and out before you begin writing your analysis. In order to develop a true understanding of the work, read through its corresponding SuperSummary study guide . Doing so will help you truly comprehend the plot, as well as provide some inspirational ideas for your analysis.

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
Why Are Literary Devices Important?
by Antony W
September 4, 2021

Used on plots and characters, literary devices can elevate the value of a story and easily prompt reflection on life and society and give readers a clear understanding of a given subject or character.
Given the role they play in writing, the use of literary devices might just be the secret recipe to that A+ paper.
Literary devices used in writing include allegory, allusion, cliffhanger, dramatic irony, satire, personification, simile, motif, imagery, flashbacks, and symbolism.
In this guide, we’ll look at what literary devices are, learn why they’re important, and give you detailed examples that you can incorporate into your writing to make your assignment more comprehensive and interesting to read.
What Are Literary Devices?

Credit: kidsmart
A literary device is a writing technique used by professional writers and students to improve writing.
Since literary devices highlight the most significant details in a piece of writing, it makes it easy for readers to not only connect with the characters in the story but also understand the underlying themes.
Quite too often, these devices work on intellectual level, although it’s not uncommon to notice some emotional effects from the same.
There are many literary devices used in writing, from those used at the sentence to the ones that serve an entire piece of writing. Each device serves a unique purpose, and you can use multiple literary devices to communicate with your audience.
Literary devices are easy to integrate into your writing, so you should use them intentionally to add an extra something to your writing.
Given that they deal mostly with sound, meaning, repetition, and description of words and phrases, these devices can create a deeper connection between your audience and your story and elicit emotional reactions in the process.
Why are Literary Devices Important?

For a writer, literary devices allow you to communicate your message from a unique angle. With these devices, you’re able to mention the most important concept in a sentence, a paragraph, or an entire essay .
If used correctly, literary devices can make it easy for you connect theme and characters and strengthen your narrative.
Literary devices can easily grab readers’ attention and keep them reading your narrative.
Moreover, it makes it easy for them to establish a stronger connection between characters and themes in a narrative on a deeper level because they understand the message you’re trying to communicate.
Different Types of Literary Devices to Use in Your Writing
In the following, we’ll look at examples of literary devices that you can use to make your narratives more engaging.
Use this literary device to simplify large, complex concepts and thematic ideas and themes .
Sometimes, allegories are dark and controversial. But you can distant yourself from an issue, especially if it comes to criticizing sensitive social, economic, and political status.
In other words, you use characters, events, objects, and other relevant elements to describe something in a way your readers can understand.
In the case where you distant yourself from the issue(s) you’re discussing, you can even go as far as to use symbols to uncover a hidden meaning in a story.
Allusion is a powerful literary device for creating relationship to known works. It can reference just about anything provided it helps to develop characters and storylines. In other words, you take a known character from a known story and add some of your own work to it.
Although not a common case, allusions can be somewhat confusing and risky altogether, especially if your readers have no idea what character you’re referring to. That notwithstanding, it can be a powerful literary device if used right.
The key to implementing allusion in your writing is to keep things as simple as possible. Instead of referring to characters, objects, events, or places in details, just mention them. A mere mention is enough to grab your readers attention and even communicate your message in a better way than you would if you used plain words and phrases.
Anachronism
Anachronism is where an author refers to a character or object in a different time than when it existed. We refer to this as error in chronology.
Educators refer to anachronism as an error in writing. However, sometimes authors use intentionally to add humor, reference a period in history, or comment on a theme such as society and time.
Cliffhanger
Bring the kind of suspense you see in a 2-hour movie flick to writing with a cliffhanger. Besides marking the end in a section of a story, cliffhangers are great for keeping your audience engaged in a story.
Dramatic Irony
Effective in works for literature, film, and television, dramatic irony is where an audience already knows the fate of characters in a story, but the character don’t know the fate of each other.
Foreshadowing
Foreshadowing is a powerful literary device that somewhat indicates the future in an anecdote.
Like flashback, this literary device creates tension, suspense, and sometimes both at the same time.
Since foreshadowing makes your readers crave for more of what’s yet to come, it’s such a powerful literary device to use if you want to keep them glued to your story.
Hyperbole
Hyperbole is an exaggeration of a statement, which gives more significance on the meaning of that very statement. For example, telling a friend that you haven’t gone to the movies in a coon’s age is a hyperbole.
In its very form, an oxymoron is a figurative approach to language where authors use a combination of words in a non-literal sense to come up with new words or phrases with completely new meanings.
Personification
Rarely do we read a book and not see personification. It’s a powerful writing strategy that give human attributes to non-human objects, with the primary objective being to communicate an idea in a more imaginary and meaningful way.
Satire is a literary device used to make fun of things, places, society, or human nature. Writers use satirical approach through ridicule, exaggerations, or irony.
To be clear, authors don’t use satire to invoke hatred or demean.
Mostly, it’s to elicit humor and drive a social change. It’s so common today that it fits in just about any work of entertainment and art.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
Literary Devices
Literary devices, terms, and elements, definition of essay.
An essay is a short piece writing, either formal or informal, which expresses the author’s argument about a particular subject. A formal essay has a serious purpose and highly structured organization, while an informal essay may contain humor, personal recollections and anecdotes, and any sort of organization or form which the author wants. Note that while a formal essay has a more detached tone, it can also represent the author’s personal opinions and be written from the author’s point of view . Essays are shorter than a thesis or dissertation, and thus deal with the matter at hand in a limited way. Essays can deal with many different themes, such as analysis of a text, political opinions, scientific ideas, abstract concepts, fragments of autobiography, and so on.
The word essay comes from the French word essayer , which means “to try” or “to attempt.” A sixteenth-century Frenchman named Michel de Montaigne was the first to create the modern-day definition of essay when he called his writing exercises essays, meaning that he was simply “trying” to get his thoughts on paper.
Common Examples of Essay
Essays are a mainstay of many educational systems around the world. Most essays include some form of analysis and argument, and thus develop a student’s critical thinking skills. Essays require a student to understand what he or she has read or learned well enough to write about it, and thus they are a good tool for ensuring that students have internalized the material. Tests such as the SATs and GREs include a very important essay section. Essays also can be important for admission to university programs and even to be hired for certain jobs.
There are many popular magazines which feature intellectual essays as a core part of their offerings, such as The New Yorker, The Atlantic, and Harper’s Magazine .
Significance of Essay in Literature
Many famous writers and thinkers have also written numerous examples of essays. For instance, the treatises of the philosophers Plutarch, Cicero, and Seneca are all early forms of essay writing. Essay writing might seem dull to school children, but in fact the form has become extremely popular, often converging with a type of writing called “creative non-fiction.” Authors are able to explore complex concepts through anecdote , evidence , and exploration. An author may want to persuade his or her audience to accept a central idea, or simply describe what he or she has experienced. Below you will find examples of essays from famous writers.
Examples of Essay in Literature
Trust thyself: every heart vibrates to that iron string. Accept the place the divine providence has found for you, the society of your contemporaries, the connection of events. Great men have always done so, and confided themselves childlike to the genius of their age, betraying their perception that the absolutely trustworthy was seated at their heart, working through their hands, predominating in all their being. And we are now men, and must accept in the highest mind the same transcendent destiny; and not minors and invalids in a protected corner, not cowards fleeing before a revolution, but guides, redeemers, and benefactors, obeying the Almighty effort, and advancing on Chaos and the Dark.
(“Self-Reliance” by Ralph Waldo Emerson)
Ralph Waldo Emerson was an essayist and poet who was a part of the Transcendentalist movement and who believed strongly in the importance of individualism and self-reliance. The above essay example, in fact, is titled “Self-Reliance,” and encourages human beings to trust themselves and strike out on their own.
Yet, because he was so small, and so simple a form of the energy that was rolling in at the open window and driving its way through so many narrow and intricate corridors in my own brain and in those of other human beings, there was something marvelous as well as pathetic about him. It was as if someone had taken a tiny bead of pure life and decking it as lightly as possible with down and feathers, had set it dancing and zig-zagging to show us the true nature of life. Thus displayed one could not get over the strangeness of it. One is apt to forget all about life, seeing it humped and bossed and garnished and cumbered so that it has to move with the greatest circumspection and dignity. Again, the thought of all that life might have been had he been born in any other shape caused one to view his simple activities with a kind of pity.
(“The Death of the Moth” by Virginia Woolf)
Virginia Woolf’s essay “The Death of the Moth” describes the simplest of experiences—her watching a moth die. And yet, due to her great descriptive powers, Woolf makes the experience seem nontrivial.
Here was I, the white man with his gun, standing in front of the unarmed native crowd — seemingly the leading actor of the piece; but in reality I was only an absurd puppet pushed to and fro by the will of those yellow faces behind. I perceived in this moment that when the white man turns tyrant it is his own freedom that he destroys. He becomes a sort of hollow, posing dummy, the conventionalized figure of a sahib. For it is the condition of his rule that he shall spend his life in trying to impress the ‘natives’, and so in every crisis he has got to do what the ‘natives’ expect of him. He wears a mask, and his face grows to fit it. I had got to shoot the elephant. I had committed myself to doing it when I sent for the rifle. A sahib has got to act like a sahib; he has got to appear resolute, to know his own mind and do definite things. To come all that way, rifle in hand, with two thousand people marching at my heels, and then to trail feebly away, having done nothing — no, that was impossible. The crowd would laugh at me. And my whole life, every white man’s life in the East, was one long struggle not to be laughed at.
(“Shooting an Elephant” by George Orwell)
George Orwell’s marvelous essay “Shooting an Elephant” tells the story of when he was a police officer in Lower Burma and was asked to deal with an elephant wandering through a market. Orwell brilliantly extrapolates his role in shooting and killing the animal to the effects of Imperialism and the British Empire.
Not that it’s profound, but I’m struck, amid the pig’s screams and wheezes, by the fact that these agricultural pros do not see their stock as pets or friends. They are just in the agribusiness of weight and meat. They are unconnected, even at the fair’s self-consciously special occasion of connection. And why not?—even at the fair their products continue to drool and smell and scream, and the work goes on. I can imagine what they think of us, cooing at the swine: we fairgoers don’t have to deal with the business of breeding and feeding our meat; our meat simply materializes at the corn-dog stand, allowing us to separate our healthy appetites from fur and screams and rolling eyes. We tourists get to indulge our tender animal-rights feelings with our tummies full of bacon. I don’t know how keen these sullen farmers’ sense of irony is, but mine’s been honed East Coast keen, and I feel like a bit of an ass in the Swine Barn.
(“Ticket to the Fair” by David Foster Wallace)
David Foster Wallace wrote many famous essays as well as novels; he often looks at modern life with a heightened attention to detail and different perspectives. In the essay “Ticket to the Fair,” he visits a fair and describes what he sees and feels, including the excerpt above where he considers the different way he and the farmers at the fair feel about animals.
Test Your Knowledge of Essay
1. Which of the following statements is the best essay definition? A. A research project of many tens of thousands of words concerning a particular argument. B. A short piece of writing that expresses the author’s opinion or perspective on a subject. C. A strict and highly organized piece of writing that doesn’t contain the author’s own opinion.
2. Which of the following is not likely to be featured in an example of essay? A. A political opinion B. An anecdote C. A fable
3. Which of the following statements is true? A. Essays are found in many intellectual magazines. B. Essays are only used in school settings. C. Essays are always boring.

Suggestions

10 Best Literary Devices to Use in Your Essay

Different techniques, like metaphors and alliteration, take an essay from mediocre to stunning in no time. This article breaks down the best literary devices and how to use them so that your papers will get a score of 100% every time.
1. Alliteration
Alliteration is the repetition of a word’s beginning consonant. Examples include:
- Jen jumps for joy
- Three tan trucks
Many think alliteration will make an essay sound unprofessional, but this isn’t true ! This technique can emphasize specific ideas and make your writing more engaging for readers. It’s also a great tool to make essay titles sound catchy.
2. Simile and Metaphor
A simile uses the words “like” or “as” to compare two things. A metaphor works almost the same way but doesn’t contain “like” or “as.”
Similes and metaphors are incredibly useful in essays. They help to emphasize the connection between unrelated objects or ideas, provide further clarification for complex ideas, and allow the reader to relate to foreign concepts.
3. Synecdoche
Synecdoche is one of the lesser-known literary devices, but chances are you’re already using it. Synecdoche refers to using a part of something to signify its whole. Examples of this are:
- “Wheels” refers to a vehicle
- “All hands on deck,” with “hands” referring to members of the crew
- “The eyes watch me,” with “eyes” referring to people
When it comes to essays, synecdoche is especially useful when you run out of synonyms. Instead of repeating the same word, you can replace it with a part of the whole! This helps your essays sound more natural and fluid.
4. Juxtaposition
Similes and metaphors serve to compare two things, and juxtaposition does the opposite: it places two items close together to emphasize their differences.
Juxtaposition is a critical element of essay writing. Often, you’ll make distinctions between things or ideas. Juxtaposition can help emphasize those differences and help your reader understand your main point.
Next on the list of literary devices is imagery. Imagery is anything that evokes a mental image. There are many types, such as:
- Emotions and Feelings
Imagery creates vivid descriptions that keep the reader focused on your essay. It’s also great for setting the tone of a work—you can use imagery to help your writing sound more professional and eloquent.
6. Hyperbole
Hyperbole is an extreme exaggeration. While it’s not always appropriate in a formal essay, there are rare instances where a well-placed hyperbole takes writing to the next level. For example, hyperbole can be used to highlight how ridiculous something is.
A great rule of thumb for using hyperbole in academic essays is to think about how believable the phrase is. Exaggeration that reads like a fact will confuse readers, but if it’s obviously false, the effect will be completely different: readers will get a sense of the absurdity.
7. Symbolism
If you want to add layers of meaning to your essay, look no further than symbolism. Symbolism is the use of a thing, usually an object, to represent a bigger concept. For example, a dove often symbolizes peace.
Symbolism can help readers understand complex ideas in essays. It also makes your writing more fun to read!
8. Oxymoron
An oxymoron is a phrase that contradicts itself. For example:
- Deafening silence
- Cruel kindness
- Alone together
In essays, an oxymoron is excellent at communicating a paradox. Paradoxes are challenging to include in writing because you typically want to maintain clarity. An oxymoron helps by keeping your point transparent.
Idioms are phrases with a non-literal meaning. An example is “call it a day.” It doesn’t mean to literally call something “a day”—it refers to wrapping up an activity. More examples of idioms are:
- Break a leg
- When pigs fly
- Beat around the bush
Idioms create a welcoming tone for your essay. They feel less professional but are often accepted in academic writing, meaning you can use them to help your reader relax and better understand your writing.
10. Personification
Personification is giving human characteristics to nonhuman things.
It helps readers connect to ideas or assign emotion to things that would otherwise seem dull. It’s beneficial in argumentative essays that seek to convince.
With this list, you’re ready to conquer your next essay and earn the highest marks. Readers will be startled at how engaging and atmospheric your writing feels.
Next time you sit down to write an essay, try throwing in a metaphor or some alliteration. You’ll be surprised at how much more engaging your writing becomes!
Daniel Reed
Don't miss.

The Brilliance of Amy Sherman-Palladino’s Leading Ladies in Television

Spanish Rock Band Airú Sparkles On Their First U.S. Tour
The impact of listening to indigenous voices in 2024 america.

‘Star Trek’: Jake Sisko’s Coming of Age Story

Büşra Kayıkçı The Turkish Pianist Going ‘Places’
5 Important Literary Devices and How to Use Them in Your Essays

So, you are working on an essay and are trying to make it look even better than it already is. But, unfortunately, you don’t know how you can improve the write-up even more.
Now, this is a scenario and is quite common in the college student community.
When writing something, they try to use difficult words to make their essay look “good.” But, in truth, that’s not how you can make your write-up more engaging and ‘literary.’
In my opinion, using a literary device or two may be quite beneficial in this aspect. However, before we start working on that, let’s learn more about what literary devices actually are.
What is a Literary Device?
According to an essay writing service in the US , IvoryResearch, a literary device can serve a variety of purposes in essay writing. For example, some of them may help you connect the reader with a write-up emotionally, while others can be used to strike an intellectual response.
According to a popular writing service, IvoryResearch , a literary device can serve a variety of purposes in essay writing. For example, some of them may help you connect the reader with a write-up emotionally, while others can be used to strike an intellectual response.
In some cases, literary devices may also be used to improve the pacing and the flow of the essay. So if you want to inject something special into your writing, literary devices will be a key to your purpose. Move on to the next section to learn more about them.
Literary Devices to be Used in Your Essay
In this section, we will talk about five excellent literary devices and how you can use them same in your essay. It’s going to be a little informative, so sit tight and enjoy the ride.
1: Allegory.
An allegory, in essence, is a type of literary tool that employs the plot and characters to depict an abstract idea or a theme. In an allegorical essay, the basic theme would suggest much more than what has been written in a simplified manner.
Example: The story of “The Tortoise and The Hare” is all about a race between two animals. However, it actually talks about the moral code of never giving up. Some people also use the same to explain how a slow and steady person will always be better than an impulsive one.
But, in some cases, allegory can be quite dark and complex too.
Consider George Orwell’s Animal Farm as an example. It might look like a dystopian novel at first. However, it’s actually a social commentary on Stalin’s and Soviet Union’s formation. The main characters or the pigs of the novel represent people like Molotov, Trotsky, and Stalin.
2: Allusion.
An allusion, on the other hand, is more about developing the story or an essay in a linear way. It can help the writer in framing the storyline properly while ensuring that the characters have been created carefully as well. It’s mostly used in novels and short stories.
Example: “Bah Humbug” is an allusion that has been used in the popular novella of Charles Dickens’s – A Christmas Carol. The phrase in the novel has always been utilized to convey the dissatisfaction of a character with something.
However, in reality, it mostly refers to one of the worst characters of the storyline – Scrooge. It is a person who’s ill-tempered and behaves rudely with everyone.
3: Anachronism.
Anachronism is something that makes your characters different from an actual plot or setting of a story or an essay. For example, imagine watching a TV adaptation of a Jane Austen story, where everyone is texting each other instead of writing a letter. Weird, right?
Example: Anachronism is a literary device that’s used to denote an error in the chronology of a write-up. It can raise the eyebrow of a reader and make them think twice before reading any further. It’s mostly used to comment on social status or add some humor to the story.
An excellent example of anachronism is the BBC’s TV show, Sherlock. In this piece of the show, you can see Sherlock using a smartphone instead of a pen and paper. He’s sending texts to the police about a criminal or clicking the photo of the evidence.
The usage of this literary device made it easier for the audience to consider Sherlock as their own and helped them understand how a detective might work in the modern world.
4: Cliffhanger.
A cliffhanger is basically all about keeping the audience on the edge of their seat and waiting for the later edition of the story. In most cases, it is done by ending a novel in a tense and impactful situation. It can be used in the introduction to make the reader excited regarding the entire essay, especially the body section where you explain everything.
Example: An example of a cliffhanger is the Half-Blood Prince book of J.K. Rowling’s Harry Potter series. In this case, Severus Snape appears to have killed Professor Dumbledore. But, it is impossible for anyone to know or understand the reason behind it.
5: Extended Metaphor.
This is usually used to build an evocative image of a storyline and create an allegorical meaning out of it. It’s mostly used in argumentative essays. However, you can also use it in a theoretical essay to talk about a point before explaining it later on.
It, in turn, can help you engage your readers and ensure that you’re making them understand the context of your article.
So, that will be all for this article.
Hopefully, we can convey whatever information you are looking for here. But, before we finish up, here’s something you should know about – using literary devices in an essay will not be easy. However, if you know how to use it and make the most out of it, you will surely get decent grades altogether.
Anyway, if you want to know about something else, don’t forget to comment below!
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Tamara is a professional photographer, a mama of four, a Lifestyle Blogger/Social Media Influencer/Brand Ambassador, and a nearly professional cookie taster. She has been known to be all four of those things at all hours of the day and night. She is a very proud contributor to the book, The Mother Of All Meltdowns, the Stigma Fighters Anthology (volume 1), and The HerStories Project: So Glad They Told Me. She is also a proud Community Lead and a regular contributor to the SoFab Food blog, and the Target Made Me Do It blog. After two cross country moves, due to her intense Bi-Coastal Disorder, she lives with her husband, four kids, five dogs, cat, and 30 chickens in glorious western Massachusetts.
Similar Posts

Top 5 Sports to Get Rid of Writing Blocks and Improve Creativity
Do you know what it’s like to be a student?…
It’s a Flood or It’s a Drought.
I think, but I’m not positive, but I think…I nursed…

My Writing Process – The Sequel!
I know you may be wondering after my last post…

How To Choose The Best Essay Writing Services
Managing essays and modules is not that easy all the…
5 Essential Items an Ambitious Blogger Needs
The reviewer has been compensated in the form of a…

When You’re a Writer.
When I was just about Scarlet’s age, I wanted to…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Discover more from Tamara Like Camera
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Home — Essay Samples — Literature — Literary Devices
Essays on Literary Devices
Brief description of literary devices.
Literary devices are tools or techniques used by writers to convey meaning and create an impact on the reader. They add depth and richness to the text, and can include elements such as metaphor, simile, symbolism, and foreshadowing. Understanding literary devices is crucial for analyzing and interpreting literature, as they help readers uncover layers of meaning and appreciate the artistry of the writer.
Importance of Writing Essays on This Topic
Essays on literary devices are important for academic and personal exploration as they help students develop critical thinking and analytical skills. By examining how writers use literary devices to convey their ideas, students can gain a deeper understanding of the text and become more adept at expressing their own thoughts and interpretations. Writing essays on this topic also encourages creativity and fosters a love for literature.
Tips on Choosing a Good Topic
- Consider the literary work: Choose a topic that relates to a specific literary work you are passionate about.
- Analyze the impact: Look for topics that explore the significance of a particular literary device in a text and its effect on the overall meaning.
- Personal connection: Select a topic that resonates with you personally, as it will motivate you to delve deeper into the analysis.
Essay Topics
- The use of symbolism in "To Kill a Mockingbird" and its impact on the story.
- How irony is employed in "The Catcher in the Rye" to convey the protagonist's disillusionment.
- The effectiveness of foreshadowing in "Macbeth" in creating suspense and tension.
- The role of allegory in "Animal Farm" and its relevance to modern society.
- A comparison of the use of imagery in the poetry of William Wordsworth and Samuel Taylor Coleridge.
- Analyzing the differing approaches to character development in the novels of Jane Austen and Charlotte Brontë.
Concluding Thought
Exploring literary devices through essay writing offers a unique opportunity to engage with literature at a deeper level. By delving into the intricacies of how writers use these devices to convey their ideas, students can develop a richer understanding and appreciation of the art of storytelling. Happy writing!
Uncoiling Poem by Pat Mora Analysis
Situational irony: a closer look at unexpected twists in literature, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Thou Blind Mans Mark Figurative Language
Analysis of literary devices in an excerpt from romeo and juliet, literary devices to present conflict in 'the outsiders', william shakespeare’s romeo and juliet: the impact of literary devices, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Themes and Literary Techniques in Atonement by Ian Mcewan
1984 by george orwell: literary devices to portray government controlling its citizens, symbolism, satire, and other literary devices in animal farm, a novel by george orwell, literary devices used within the penal colony, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
The Use of Literary Devices in a White Heron
Analysis of literary devices in the black walnut tree, robert frost's use of literary devices in fire and ice, remarque’s use of literary devices in "all quiet on the western front", postmodernism and metafiction in slaughterhouse five: analysis of literary devices, analysis of imagery and other literary devices in dover beach, literary analysis of "frostbitten faithlessness", literary analysis of in the time of the butterflies by julia alvarez, the use similes, strong irony, and imagery in "the tell-tale heart", the reflection of war in mahabharata, use of figurative language in daffodils by william wordsworth, literary analysis of dickinson’s i felt a funeral, in my brain, moving toward the destination: an analysis of stephen vizinczey's "elephant", literary analysis of twelve angry men by reginald rose, claude mckay’s political message in if we must die, deconstructing the poem legal alien by pat mora, the use of imagery, metaphors, and similes in 'dover beach', symbolism in the flowers by alice walker, macabre imagery in 'the lowest animal' by mark twain, analysis of rab bradbury’s use of literary elements in fahrenheit 451, relevant topics.
- Marxist Criticism
- Literary Criticism
- Tragic Hero
- Coming of Age
- Fan Fiction
- Translation
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Bibliography
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tip 1: Read Closely and Carefully. First off, you'll need to make sure that you're reading very carefully. Resist the temptation to skim or skip any sections of the text. If you do this, you might miss some literary devices being used and, as a result, will be unable to accurately interpret the text.
Writers use a wide variety of literary devices across different genres. Each literary device serves a specific purpose. Understanding how to correctly wield these devices can significantly improve your own writing. 1. Allegory. Allegory is a literary device used to express large, complex ideas in an approachable manner.
A literary device is a writing technique that writers use to express ideas, convey meaning, and highlight important themes in a piece of text. A metaphor, for instance, is a famous example of a literary device. These devices serve a wide range of purposes in literature. Some might work on an intellectual level, while others have a more ...
Literary Devices & Terms. Literary devices and terms are the techniques and elements—from figures of speech to narrative devices to poetic meters—that writers use to create narrative literature, poetry, speeches, or any other form of writing. All.
Literary Devices List: 14 Common Literary Devices. In this article, we focus on literary devices that can be found in both poetry and prose. There are a lot of literary devices to cover, each of which require their own examples and analysis.As such, we will start by focusing on common literary devices for this article: literary devices that can be found in both poetry and prose.
As you grow in your skill, these literary devices will become a part of your storytelling voice. 1. Allegory. Allegory is kind of like a cross between metaphor (which we'll talk about a little further on) and theme. It's the practice of telling a real, true, relevant story through the filter of fiction.
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
Simile. Probably the most famous and commonly-used literary device is the simile. A simile uses the words "like" or "as" to compare two unrelated things. Don't confuse similes with metaphors! (The word "simile" comes from the same root as the word "similar"—so essentially we're saying two things are similar.)
Literary devices are the techniques writers use to help them communicate their ideas more colorfully, more meaningfully, and most effectively. They often involve the use of figurative language and things like metaphors, similes, symbols, exaggeration, irony, assonance, and alliteration. All great writers use literary devices, whether in poetry ...
10 Types of Literary Devices You Can Use in Your Essay. There is a laundry list of literary devices but let's look at the best literary devices ones you should know about: 1. Metaphor. One of the most common literary devices, metaphors, is used across essays, books, songs, poems, and speeches. They are used to compare two completely unrelated ...
Most skilled writers use several literary devices to create a more powerful and memorable story. Some common types of literary devices include: Figurative language - metaphors and similes create images and comparisons for better understanding. Sound devices - alliteration and onomatopoeia contribute to the rhythm, mood, and emphasis of the ...
School assignments are great examples of essays. Here are some literary devices that are found within essays: Main Idea: The main idea is the purpose behind a piece. For example, the main idea of this piece is literary devices. Transition: A transition smooths the movement from one topic to the next.
literary devices refers to the typical structures used by writers in their works to convey his or her messages in a simple manner to the readers. When employed properly, the different literary devices help readers to appreciate, interpret and analyze a literary work. Below is a list of literary devices with detailed definition and examples.
When to Use Literary Devices. By definition, literary devices occur in literature rather than essays. So, strictly speaking, they belong to creative writing. Rhetorical devices would be the ones used in an essay. Again, though, literary devices are basically the same as rhetorical devices, so this distinction doesn't matter too much.
Step 1: Read the Text Thoroughly. Literary analysis begins with the literature itself, which means performing a close reading of the text. As you read, you should focus on the work. That means putting away distractions (sorry, smartphone) and dedicating a period of time to the task at hand.
How to Write a Literary Analysis. These 4 steps will help prepare you to write an in-depth literary analysis that offers new insight to both old and modern classics. 1. Read the text and identify literary devices. As you conduct your literary analysis, you should first read through the text, keeping an eye on key elements that could serve as ...
For a writer, literary devices allow you to communicate your message from a unique angle. With these devices, you're able to mention the most important concept in a sentence, a paragraph, or an entire essay . If used correctly, literary devices can make it easy for you connect theme and characters and strengthen your narrative.
Significance of Essay in Literature. Many famous writers and thinkers have also written numerous examples of essays. For instance, the treatises of the philosophers Plutarch, Cicero, and Seneca are all early forms of essay writing. Essay writing might seem dull to school children, but in fact the form has become extremely popular, often ...
Literary analysis involves examining all the parts of a novel, play, short story, or poem—elements such as character, setting, tone, and imagery—and thinking about how the author uses those elements to create certain effects. A literary essay isn't a book review: you're not being asked whether or not you liked a book or whether you'd ...
Similes and metaphors are incredibly useful in essays. They help to emphasize the connection between unrelated objects or ideas, provide further clarification for complex ideas, and allow the reader to relate to foreign concepts. 3. Synecdoche. Synecdoche is one of the lesser-known literary devices, but chances are you're already using it.
Literary Devices to be Used in Your Essay. In this section, we will talk about five excellent literary devices and how you can use them same in your essay. It's going to be a little informative, so sit tight and enjoy the ride. 1: Allegory. An allegory, in essence, is a type of literary tool that employs the plot and characters to depict an ...
Essays on literary devices are important for academic and personal exploration as they help students develop critical thinking and analytical skills. By examining how writers use literary devices to convey their ideas, students can gain a deeper understanding of the text and become more adept at expressing their own thoughts and interpretations