Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


Review of the waste management system in the Philippines

Like other developing countries, waste management has become a major problem in the Philippines in the past decades. This paper provides an overview of the waste management and recycling in the Philippines and the responses of the government to address various problems brought about the improper waste management. It reviews the policies related to waste management from 1938 to 2001, including the latest and perhaps the most comprehensive solid waste management policy in the country, the Philippine Republic Act 9003 (RA 9003). It presents the issues on the implementation of these policies, the status of the compliance by the local government, and the recent initiatives and activities to promote proper waste management and recycling. Using the experiences of some selected case studies, it illustrates the potential and benefits of recycling both in addressing the waste management problems and in alleviating poverty. This paper concludes that the application of good governance through participation of various stakeholders, strong awareness campaign, and promotion and replication of innovative and appropriate technologies that are necessary to achieve sound waste management and sustainable recycling industry. "Atienza, 2008"
Related Papers
Rochelle Salayon
Angela Jabalde
joyce barafon
This paper explores the participation or the lack of it by the local actors in the Solid Waste Management sector in the City of Tagbilaran, Bohol, Philippines. It endeavours to understand the rationale behind a case of ‘disconnect’ in ‘participatory roles’ amidst the background of democratization, decentralization and participatory governance leading to the notions of state and community failure. The paper takes advantage of governance theories in conceptualizing the main argument that is in an episode of what may be categorized as a situation of ‘failure’ on the part of the actors in the ‘governance triangle1’, the bureaucracy still stands as the most significant driver to revolutionize solutions to development issues by virtue of its ‘responsibility to its citizenry’ or more formally its nature institutionally, legally and organizationally. It is not the people in the community, the private firms and non-government organizations nor funding donors who have the inherent role to ind...
The paper explores the participation or the lack of it by the local actors in the Solid Waste Management sector in the City of Tagbilaran, Bohol, Philippines. It endeavours to understand the rationale behind a case of ‘disconnect’ in ‘participatory roles’ amidst the background of democratization, decentralization and participatory governance leading to the notions of state and community failure. The paper takes advantage of governance theories in conceptualizing the main argument that is in an episode of what may be categorized as a situation of ‘failure’ on the part of the actors in the ‘governance triangle1’, the bureaucracy still stands as the most significant driver to revolutionize solutions to development issues by virtue of its ‘responsibility to its citizenry’ or more formally its nature institutionally, legally and organizationally. It is not the people in the community, the private firms and non-government organizations nor funding donors who have the inherent role to indu...
Joyledesma Domingo
The study aimed to determine the status and extent of Ecological Solid Waste Management in Baggao National High School. This qualitative study is a descriptive research which attempts to describe the current status and extent of ecological solid waste management implementation in Baggao National High School. Descriptive method is useful to determine the extent of ESWM implementation, volume of waste and kinds of waste generated when respondents are grouped by grade level. A total of 291 Junior and Senior High School respondents were selected through random sampling. Slovin’s formula with the marginal error of 5(five) percent was also employed to come up with such number. Also Purposive and Quota sampling were utilized to determine the 28 number of class-respondents in each grade level. Categories and coding were used as qualitative data analysis as well as simple frequency counts, mean percentage, and descriptive analysis. Based on the findings, the grade 8 has the highest number of YES-O violations while grade 12 has the lowest number of violations. It was also found out that the extent of ecological solid waste management implementation in Baggao National High School is high. Also, he total number of trash bins of waste generated in the school is 540 ¾ in a period of one month with Grade 11 having the highest number of trash bins of waste generated with a total of 149 ½ and Grade 8 has the least. Residual is mostly the type of waste generated by the respondents with a total of 182 ¼ trash bins and plastic wrapper is frequently generated. These findings suggest that ESWM implementation is very evident in the school but there are still problems encountered along the process of its implementation such as occurrence of YES-O violations. This study therefore recommends that the basic content of the RA 9003 should be inculcated in the curriculum for the effective promotion of the preservation of the school’s environment.
Bijan Maskey
With rapid increase in population and economic growth, the Republic of the Philippines is facing a major challenge for effective management of its growing municipal waste. The government has enacted the Republic Act 9003, which is also called the Ecological Solid Waste Management Act of 2000, to overcome the challenges of waste management. This study was conducted in barangay Pansol of Quezon City in the Metro Manila to assess the impact of this act on households' waste generation and management practices at barangay level. A sample of 117 households surveyed in the barangay is used for the analysis. Factors that significantly impact waste generation are age of household head, employment status, household size, annual income, recycle and awareness about waste segregation policy. Thus, households with these characteristics should be focused to minimize households' waste generation and improve current waste management practices. Awareness on various aspects of waste and accessibility of Material Recovery Facility can also help lessen waste generation and improve waste management processes. It was discovered that not all households have government provided services of waste collection and street sweeping. Therefore, there should be wider geographical coverage of door-to-door collection and street sweeping services.
Chelsea Bless Nabing
Solid waste management is one of the environmental problems that the world is facing. It has already existed since the time when human beings started to create or invent, and longed for development. As human population increases over time, the need and use of solid materials has been accumulated. This study will give an overview on the Philippines‟ long-time problem on solid waste management (SWM). It includes the efforts of the local government in implementing the Solid Waste Management Act of 2000 or simply known as Republic Act 9003, in the urban areas such as in Manila. In addition, it will also include a brief history of how national government came up with such policy and how it is executed until today. This study aims to determine the success and struggles of the local government units in executing the R.A 9003 in managing the solid wastes. Furthermore, this study will also aim the role of other international laws that encouraged the creation of the R.A 9003 if there is any. ...
Pertanika journal of social science and humanities
Maria Francesca Tan
Academia Letters
Wilfredo Dalugdog
Junelyn Pagunsan
RELATED PAPERS
Meljun Cortes
Johannes Paul
Paul Johannes
Asia Pacific Journal of Multidisciplinary Research
Research and Statistics Center
Edith Castillo
Jenette Firme
International Journal of ADVANCED AND APPLIED SCIENCES
Van Ryan Kristopher Galarpe
Policarpio Malonda
Grace Sapuay
Maria Mercedes "Ched" E . Arzadon
hazel aceberos
in Southeast Asian Cities
Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Fernan Tupas
Ronald Orale , Mark Christian Paclian
carmela secuya
Arch Lalamonan
Annrou Ramos , Severino Salmo III
Jessa Blaza
Procedia Environmental Sciences
Emelita Aguinaldo , Voltaire Acosta , Johannes Paul , Crispian Lao
JOAN LAZARO
Klaus Hanuschke
Paul Johannes , Arthur Batomalaque , Klaus Hanuschke
Marilyn Alcanices
Geraldin Pamisaran - Cabang
Jerwyn Oracion
Paul Johannes , Voltaire Acosta
Hazel Ivy Jeremias
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- {{subColumn.name}}
AIMS Environmental Science
- {{newsColumn.name}}
- Share facebook twitter google linkedin

Preliminary assessment of solid waste in Philippine Fabrication Laboratories
- Lemuel Clark Velasco 1 , , ,
- Mary Jane Burden 1 ,
- Marie Joy Satiniaman 1 ,
- Rachelle Bea Uy 1 ,
- Luchin Valrian Pueblos 1 ,
- Reynald Gimena 2
- 1. Mindanao State University-Iligan Institute of Technology, Philippines
- 2. Mindanao State University-Marawi, Philippines
- Received: 08 March 2021 Accepted: 10 June 2021 Published: 30 June 2021
- Full Text(HTML)
- Download PDF
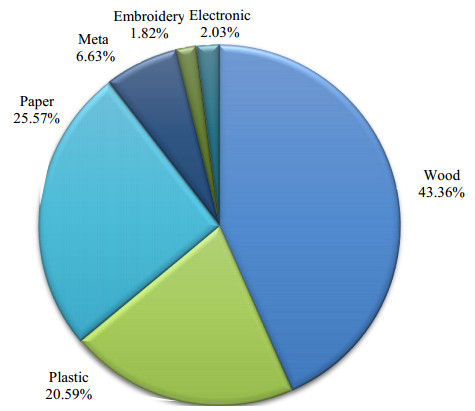
Solid waste management is seen as a response to the increase in waste generation due to the rising number of industrial facilities. This includes digital manufacturing facilities such as Fabrication Laboratories (FAB LAB) which acts as innovation centers that generates prototypes using a common set of digital fabrication equipment. Previous studies have tackled with the environmental impacts of FAB LABs in a macro-level scale; however, there has been a lack of research specifically assessing the solid waste of laboratories, more so on Philippine FAB LABs. A baseline assessment study on FAB LABs of the Philippines could be applicable in future implementations of solid waste management systems through the crafting of institutional policies and guidelines for environmental sustainability. Using data gathered from 11 respondent FAB LABs, this study quantified percentage compositions of the waste according to waste type as well as the relative waste generated by each respondent FAB LAB. Machine availability was seen as a factor in waste generation resulting in the high generation of wood and plastic waste. Moreover, it was observed that earlier established laboratories generally had more active makers than recently established ones, hence the older FAB LABs statistically produced more waste. Approximately 53% of the overall waste produced was considered recyclable by Philippine standards but the actual recyclability of the waste was still undetermined due to the ambiguous criteria for recyclables and the lack of feedback data from recycling facilities. The initial findings suggest that an implementation of continuous waste monitoring, sufficient in-laboratory protocols, and coordination between FAB LABs and recycling facilities could improve actual waste recyclability and—by extension—the environmental sustainability of Philippine FAB LABs.
- Fabrication Laboratories ,
- environmental sustainability ,
- solid waste management ,
- digital manufacturing ,
- solid waste assessment
Citation: Lemuel Clark Velasco, Mary Jane Burden, Marie Joy Satiniaman, Rachelle Bea Uy, Luchin Valrian Pueblos, Reynald Gimena. Preliminary assessment of solid waste in Philippine Fabrication Laboratories[J]. AIMS Environmental Science, 2021, 8(3): 255-267. doi: 10.3934/environsci.2021017
Related Papers:
- This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 4.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/ -->
Supplements
Access history.
- Corresponding author: Email: [email protected] ;
Reader Comments
- © 2021 the Author(s), licensee AIMS Press. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0 )
通讯作者: 陈斌, [email protected]
沈阳化工大学材料科学与工程学院 沈阳 110142

Article views( 14475 ) PDF downloads( 447 ) Cited by( 0 )
Figures and Tables
Figures( 4 ) / Tables( 2 )

Associated material
Other articles by authors.
- Lemuel Clark Velasco
- Mary Jane Burden
- Marie Joy Satiniaman
- Rachelle Bea Uy
- Luchin Valrian Pueblos
- Reynald Gimena

Related pages
- on Google Scholar
- Email to a friend
- Order reprints
Export File

- Figure 1. Composition of waste by-products produced by Philippine FAB LABs
- Figure 2. Summary of available machines and equipment in different Philippine FAB LABs
- Figure 3. Distribution of overall solid wastes from different Philippine FAB LABs
- Figure 4. Recyclability of wastes generated by Philippine FAB LABs
“A Literature Review on Solid Waste Management: Characteristics, Techniques, Environmental Impacts and Health Effects in Aligarh City”, Uttar Pradesh, India”
- Conference paper
- First Online: 01 November 2019
- Cite this conference paper

- Harit Priyadarshi 8 ,
- Sarv Priya 9 ,
- Ashish Jain 8 &
- Shadab Khursheed 10
Part of the book series: Sustainable Civil Infrastructures ((SUCI))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Congress and Exhibition "Sustainable Civil Infrastructures”
551 Accesses
1 Citations
India is known as one of the most heavily settled countries in the world. It appears to be the second country to have the highest number of residents. With the total population of about expected data 1.37 billion in 2019. The management of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) in India has encountered problems. Each year, the population grew by 3–3.5%, as this factor arises, the rate of solid waste generation also rise up to 1.3% in Aligarh city, Uttar Pradesh a large number of ingenious factors like, rapid urbanization, rapid population density, rapid commercialization, uneven living standards and also enlargement of industrialization has created destructive consequences in terms of biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste generations which are estimated at about 415 tons per day.
This paper emphasizes the waste characteristics, techniques, adverse environmental impacts, health risks, poor waste management practices and also problems associated with the solid waste management system at the municipal level.
The findings from this study indicates failure of the existing facilities due to lack of concern, high volume of waste generation, deficient collection space, delayed sanctioning of new landfill sites and a number of open-dump sites which generate fires. The innuendos of the waste management practices in the city are discussed.
- Sources of M.S.W
- Component of M.S.W
- Health risks and sustainable approaches
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Lavee, A., Vievek, : Is municipal solid waste recycling economically efficient. Environ. Manag. 40 , 926–943 (2009)
Article Google Scholar
Asnani, P.U.: United States Asia Environmental Partnership Report, United States Agency for International Development, Centre for Environmental Planning and Technology, Ahmedabad (2004)
Google Scholar
Bhoyar, R.V., Titus, S.K., Bhide, A.D., Khanna, P.: Municipal and industrial solid waste management in India. J. IAEM 23 , 53–64 (1996)
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB): Management of Municipal Solid Waste. Ministry of Environment and Forests, New Delhi, India (2004)
Zhu, D., Asnani, P.U., Zurbrügg, C., Anapolsky, S., Mani, S.: Improving Municipal Solid Waste Management in India (2008)
Ravi, D.: Solid waste management issues and challenges in Asia, Asian Productivity Organization (2007)
Dayal, G.: Solid wastes: sources, implications and management. Indian J. Environ. Prot. 14 (9), 669–677 (1994)
Garg, S., Prasad, B.: Plastic waste generation and recycling in Chandigarh. Indian J. Environ. Prot. 23 (2), 121–125 (2003)
Gupta, S., Krishna, M., Prasad, R.K., Gupta, S., Kansal, A.: Solid waste management in India: options and opportunities. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 24 , 137–154 (1998)
Priyadarshi, H., Rao, S., Khan, S.S., Vats, D.: “Mission for the sanitary India: a case study of Aligarh City” Uttar Pradesh, India. In: Towards Sustainable Cities in Asia and the Middle East, International Congress and Exhibition “Sustainable Civil Infrastructures: Innovative Infrastructure Geotechnology”, pp. 47–62. Springer publication Book Series (2018)
Priyadarshi, H., Jain, A.: Municipal solid waste management study and strategy in Aligarh City, Uttar Pradesh India. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Invent. (IJESI) 7 (5), 29–40 (2018). Ver. III
Joseph, K.: Perspectives of solid waste management in India. In: International Symposium on the Technology and Management of the Treatment and Reuse of the Municipal Solid Waste (2002)
Khan, R.R.: Environmental management of municipal solid wastes. Indian J. Environ. Prot. 14 (1), 26–30 (1994)
Kumar, S., et al.: Assessment of the status of municipal solid waste management in metro cities, state capitals, class I cities, and class II towns in India: an insight. Waste Manage. 29 (2), 883–895 (2009)
Kumar, S., Mondal, A.N., Gaikwad, S.A., Devotta, S., Singh, R.N.: Qualitative assessment of methane emission inventory from municipal solid waste disposal sites: a case study. Atmos. Environ. 38 , 4921–4929 (2004)
NEERI: Strategy Paper on SWM in India, National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, Nagpur (1995)
Schubeler, P.: NEERI Report “Strategy Paper on Solid Waste Management in India”, pp. 1–7 (1996)
Rajput, R., Prasad, G., Chopra, A.K.: Scenario of solid waste management in present Indian context. Caspian J. Environ. Sci. 7 (1), 45–53 (2009)
Rao, K.J., Shantaram, M.V.: Physical characteristics of urban solid wastes of Hyderabad. Indian J. Environ. Prot. 13 (10), 425–721 (1993)
Rathi, S.: Alternative approaches for better municipal solid waste management in Mumbai. India J. Waste Manage. 26 (10), 1192–1200 (2006)
Sharma, S., Shah, K.W.: Generation and disposal of solid waste in Hoshangabad. In: Book of Proceedings of the Second International Congress of Chemistry and Environment, Indore, India, pp. 749–751 (2005)
Shekdar, A.V.: Municipal solid waste management – the Indian perspective. J. Indian Assoc. Environ. Manag. 26 (2), 100–108 (1999)
Shekdar, A.V., Krshnawamy, K.N., Tikekar, V.G., Bhide, A.D.: Indian urban solid waste management systems – jaded systems in need of resource augmentation. J. Waste Manag. 12 (4), 379–387 (1992)
Siddiqui, T.Z., Siddiqui, F.Z., Khan, E.: Sustainable development through integrated municipal solid waste management (MSWM) approach – a case study of Aligarh District. In: Proceedings of National Conference of Advanced in Mechanical Engineering (AIME-2006), Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi, India, pp. 1168–1175 (2006)
Kumar, V., Pandit, R.K.: Problems of solid waste management in Indian cities. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 3 (3), 1–9 (2013)
Download references
Acknowledgement
First of all I would like to thanks Hon’ble Prime minister Narendra Damodar Das Modi to continue the dream of Mahatma Gandhi Make in India mission “Mission for sanitary India. The authors acknowledge all the persons involved in Aligarh Municipal Corporation (AMC) for providing all the pertinent information.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Civil Engineering, Mangalayatan University, Beswan, Aligarh, 202145, Uttar Pradesh, India
Harit Priyadarshi & Ashish Jain
Department of Civil Engineering, KIET, Murad Nagar, Ghaziabad, 201206, Uttar Pradesh, India
Department of Geology, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, 202002, Uttar Pradesh, India
Shadab Khursheed
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Harit Priyadarshi .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Housing and Building National Research Centre, Cairo, Egypt
Hesham Ameen
Polytechnic University of Turin, Turin, Italy
Michele Jamiolkowski
International Society for Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Turin, Italy
Mario Manassero
Soil Structure Interaction Group Egypt, Cairo, Egypt
Hany Shehata
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Priyadarshi, H., Priya, S., Jain, A., Khursheed, S. (2020). “A Literature Review on Solid Waste Management: Characteristics, Techniques, Environmental Impacts and Health Effects in Aligarh City”, Uttar Pradesh, India”. In: Ameen, H., Jamiolkowski, M., Manassero, M., Shehata, H. (eds) Recent Thoughts in Geoenvironmental Engineering. GeoMEast 2019. Sustainable Civil Infrastructures. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-34199-2_6
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-34199-2_6
Published : 01 November 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-34198-5
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-34199-2
eBook Packages : Earth and Environmental Science Earth and Environmental Science (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

IMAGES
COMMENTS
report, the current amount of waste produc ed in the. Philippine cities wi ll increase by approximately. 165% in 2025 - from abo ut 29,315 to 77, 776 tons. per day (Ng, 2012). The increasing ...
comprehensive solid waste management policy in the country, the Philippines Republic Act 9003 (RA 9003), known as the "Ecological Solid Waste Management Act of 2000." Also, this section presents the current status of compliance and the issues on its implementation. After discussing the current situation of waste management in the country and
This chapter provides a brief review of solid waste management in the Philippines (Atienza, 2019), particularly on the legal bases for promoting local collaboration in waste management, the status and types of local collaboration, and the challenges and opportunities. Section 5.2 focuses on some emerging trends on public service delivery such ...
Solid waste management is considered a pressing global issue calling for an immediate response from the government and its people. ... 10.47540/ijsei.v2i3.144 Page: 213 - 220 A Long-Standing Problem: A Review on the Solid Waste Management in the Philippines Ericson E. Coracero1, RB J. Gallego2, Kristine Joy M. Frago3, Ruel Joseph R. Gonzales4 ...
Solid waste management issues continue to pose challenges in the Philippines. The increasing generation of waste, coupled with a foreseen lack of infrastructure for disposal, inevitably leads to overflowing sanitary landfills laced with environmental and health issues. As a result, the Philippine government is placing emphasis on Waste-to-Energy (WtE) technology as an ideal and immediate ...
6 Current Waste Management System The country's current waste management system is clearly defined in the existing primary law on solid waste management which is the Republic Act 9003 of 2000 (Fig. 3). The waste management system involves the formulation of guidelines and setting of targets for waste avoidance and volume reduction through source
Abstract. Solid waste management is considered a pressing global issue calling for an immediate response from the government and its people. The Philippines has a continuously rising amount of waste and is expected to further increase in the succeeding years. As reviewed, associated problems with solid waste management in the country include an ...
The only data available on waste composition are the results of the waste analysis and characterization survey (WACS) conducted by the Asian Development Bank for Metro Manila in 2003.The WACS was conducted through the technical assistance project of ADB (Asian Development Bank-Metro Manila Solid Waste Management Project, 2002-2003.) specifically for the cities of Makati, Muntinlupa, Pasig ...
Solid waste management is considered a pressing global issue calling for an immediate response from the government and its people. The Philippines has a continuously rising amount of waste and is expected to further increase in the succeeding years. As reviewed, associated problems with solid waste management in the country include an increasing amount of solid waste, weak law implementation ...
Globally, the Philippines has one of the highest rates of mismanaged plastic waste recycling, with only about 28 percent of the key resins it consumed in 2019 being recycled. Unrecycled plastics are disposed of in dumpsites and landfills, remain as litter, or accumulate in sewers, drainage systems, and rivers before being discharged into ...
The global community recognized that Solid Waste Management (SWM) is an issue that requires serious attention. The aggressive pursuit for economic growth, by developing countries like the Philippines, has resulted in the manufacture, distribution and use of products and generation of wastes that contributes to environmental degradation and global climate change. Available data showed that the ...
This paper provides an overview of the waste management and recycling in the Philippines and the responses of the government to address various problems brought about the improper waste management. It reviews the policies related to waste management from 1938 to 2001, including the latest and perhaps the most comprehensive solid waste ...
A Finnish study (Motiva 2013) shows an average gas yield from typical food waste is 150-250 m3/tonne with 65% methane content. 200 m3/tonne (including carbon dioxide) is used to calculate gas generation in this study, in which methane comprises about 60%.
This review aims to explore the availability of national as well as local regulation related to HHW management in Southeast Asian developing countries and to analyze the correlation between GNI level and the government concern on HHW issues. ... Pile of solid waste in the collecting or dumping sites produce methane gas that threaten earths ...
Allesch A, Brunner PH (2014) Assessment methods for solid waste management: A literature review. Waste Manag Res 32: 461-473. doi: 10.1177/0734242X14535653 ... Atienza V (2011) Review of the Waste Management System in the Philippines: Initiatives to Promote Waste Segregation and Recycling through Good Governance, Chiba, Japan, Institute of ...
Like other developing countries, waste management has become a major problem in the Philippines for the past decades. This paper provides an overview of the waste management and recycling in the Philippines and the responses of the government to address various problems brought about by improper waste management. It reviews the policies related to waste management from 1938 to 2001, including ...
Over the past three decades, research on the established linkages between solid waste management and psychological models has progressed rapidly. This informs statutory bodies that wish to design an effective solid waste management system. To further address this crucial task, this paper examined the existing literature on behavioral approaches ...
Managing municipal solid waste is one of the most significant environmental challenges of the 21st century. Municipalities have been facing difficulties in managing their solid waste (SW) due to, among other reasons, lack of information. Generating data on SW generation (SWG) is difficult because sampling, weighing, and classifying SW require time and resources, which can often be scarce.
solid waste management in Cagayan de Oro City, contributing to environmental protection and the promotion of a smart city. 2. Literature Review Garbage management is a pressing problem for society and the planet's future. This is almost inevitable as a result of human actions. Not only has the human population exploded
This review shows better adequacy of public policies for solid waste management and more significant inspection of irregular conduct harmful to the environment. ... through a literature review, the present study aimed to elucidate the environmental issues brought by the use of plastic materials and their waste, as well as to provide an overview ...
India is known as one of the most heavily settled countries in the world. It appears to be the second country to have the highest number of residents. With the total population of about expected data 1.37 billion in 2019. The management of Municipal Solid Waste...