How to write the structure and ownership section of your business plan?

Business planning is vital to the success of any entrepreneur because it helps them secure funding and find competent business partners. The document itself contains a variety of key sections, including the presentation of the legal structure and ownership of the business.
This section details the legal structure of your business and helps interested parties such as lenders and investors understand who they will be doing business with if they decide to go ahead and finance your company.
In this guide, we’ll look at the objective of the structure and ownership section, deepdive into the information you should include, and cover the ideal length. We’ll also assess the tools that can help you write your business plan.
Ready? Let’s get started!
In this guide:

What is the objective of the structure and ownership section of your business plan?
What information should i include when presenting the legal structure and ownership of my company in my business plan.
- How long should the structure and ownership section of your business plan be?
- Example of structure and ownership in a business plan
What tools should I use to write my business plan?
The objective of this section is to provide potential investors, lenders, and strategic partners with a clear and transparent view of your business's legal form, ownership distribution, and registration details.
It aims to build credibility and trust by showcasing your commitment to openness and compliance with regulations. Let's take a look at some of the key objectives:
Communicate the legal form and registration details
- You should explicitly state your business's legal form. For example, your business might be corporation, sole proprietorship, or limited liability company (LLC).
- Clearly explaining your chosen legal form helps stakeholders understand your entity's liability, taxation, and management implications.
- It is also essential to disclose where your company is registered. This information is vital as it provides clarity on the jurisdiction under which your business operates.
- It also helps investors and lenders assess any legal and regulatory implications specific to the location of registration.
Identify shareholders
- Potential investors and lenders need to know who owns the company and the percentage of ownership each party holds.
- By providing this information, you instill confidence in your business and help identify what needs to be verified as part of Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (ALM) checks down the line.
Transparency is the cornerstone of credibility for businesses. By openly presenting the legal structure and ownership, you signal to potential investors that your business operates with integrity and adherence to regulations.
Notably, anti-money laundering regulations require investors to verify the identity of all shareholders before committing funds. By providing a clear picture of the parties involved, you can facilitate this process and build trust with investors.
Venture capitalists (VC) firms and angel investors in particular, may have specific criteria such as location and ownership mandates governing the companies they can finance. Being transparent about your company's structure and ownership enables potential investors to assess whether your business aligns with their investment preferences and requirements.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

The structure and ownership subsection arrives quite early in your business plan as it is the first part of the company section which is the second section of the document (after the executive summary) if you are following a standard business plan outline .
At this stage, the reader is still in the process of getting familiar with your business, and this section serves as a crucial foundation for potential investors and partners and helps them understand the core aspects of your business’s structure.
Here's what you should include:
Company registration details and registered office address
Provide information about when and where your company was registered and its registration number. This enables readers to understand the jurisdiction under which your business is operating and helps verify its legal existence.
Also, mention the registration date to showcase the company's longevity or recent establishment.
Include the registered office address of your company. This is the official address where the company can be contacted, and legal notices can be served. Providing this address demonstrates your commitment to compliance and transparency.
The information above needs to repeated for each subsidiary or joint venture owned by your business in order to provide a clear map of the coporate structure.
Overview of ownership
Offer a concise overview of the ownership structure of the company. Identify the shareholders, and specify their ownership percentages or shares.
If there are numerous shareholders, list individuals or entities owning 5% or more, and highlight those with a controlling interest in the company or on the board.
If the business is controlled by another business, such as a holding company for example, it is also useful to explain who controls that business as well.
Roles and responsibilities of shareholders
In case of multiple shareholders, explain their respective roles and responsibilities within the organization.
Differentiate between passive investors, board members, and executive or non-executive directors.
Shareholders' agreement (if applicable)
If the business plan is presented for investment purposes, it is useful to clarify if a shareholders' agreement is in place between the existing investors.
This agreement outlines the rights and obligations of shareholders and adds an extra layer of legal protection for investors and shareholders.
Expertise of co-shareholders
Highlight any shareholders who contribute more than just financial capital to the company.
If, for instance, a shareholder is an industry expert and brings valuable advice, contacts, and credibility, emphasize this aspect.
Doing so demonstrates the added value these shareholders bring to the business.
Group or franchise structure
If your company operates as part of a group or franchise, provide this information for each individual company receiving funds.
Clarify the relationship between the main company and the individual entities within the group and their respective legal structures.
Addressing geographical restrictions
If some investors have geographical restrictions on their investments, clearly indicate whether your company meets their eligibility criteria.
This helps investors quickly assess whether your business aligns with their investment mandates or not.

How long should the structure and ownership section of your business plan be?
The length of your business plan's structure and ownership section requires a delicate balance.
While a general rule of thumb suggests that it should be about 2 to 3 paragraphs, the actual length depends on several factors, including the complexity of your corporate structure and the number of shareholders involved.
The complexity of your corporate structure
- A concise presentation may be sufficient if your company's legal structure is relatively straightforward, with a single owner or a small number of co-founders.
- In such cases, aim to provide the necessary information without overwhelming the reader with unnecessary details. A paragraph or two may convey the key points effectively, ensuring clarity and brevity.
- However, if you have a complex business structure, aim to provide details about members who play a key role in business continuity and profitability.
The number of shareholders involved
- If your business involves multiple shareholders, each with significant ownership percentages or unique roles, you may need to dedicate more space to this section.
- Do this by providing a comprehensive breakdown of ownership distribution and outlining each shareholder's contributions.
- This may take up more space as you need to add additional information. However, if you have a pretty straightforward ownership structure, a paragraph or two will be sufficient enough.
Regardless of the complexity, striking the right balance between providing sufficient detail and avoiding excessive technical jargon is crucial. The structure and ownership section should be reader-friendly, allowing potential investors and stakeholders to understand the core aspects of your company without feeling overwhelmed by intricate legalities.
Repetition can dilute the impact of your message and unnecessarily lengthen the section. Ensure that you don't reiterate information that has already been covered in other parts of the business plan. Instead, focus on providing unique insights and details that enhance the reader's understanding of your corporate structure and ownership.
When crafting this section, prioritize the most critical points that investors or partners need to know about your company's structure and ownership.
Focus on aspects that directly impact decision-making, such as the majority shareholder's influence, board composition, different classes of shares in issue, or any unique arrangements that set your business apart.
Need inspiration for your business plan?
The Business Plan Shop has dozens of business plan templates that you can use to get a clear idea of what a complete business plan looks like.

Example of structure and ownership section in a business plan
Below is an example of what the structure and ownership section of your business plan might look like. As you can see, it is part of the overall company section and precedes the location and management team subsections.
The structure and ownership section of a business plan provides a detailed overview of how your company is organized and who holds ownership stakes in the business.

This example was taken from one of our business plan templates .
In this section, we will review three solutions for creating a business plan for your business: using Word and Excel, hiring a consultant to write the business plan, and utilizing an online business plan software.
Create your business plan using Word and Excel
This is the old-fashioned way of creating a business plan (1990s style) and using Word and Excel has both pros and cons.
On the one hand, using either of these two programs is cheap and they are widely available.
However, creating an error-free financial forecast with Excel is only possible if you have expertise in accounting and financial modeling.
Because of that investors and lenders might not trust the accuracy of your forecast unless you have a degree in finance or accounting.
Also, writing a business plan using Word means starting from scratch and formatting the document yourself once written - a process that can be quite tedious - especially when the numbers change and you need to manually update all the tables and text.
Ultimately, it's up to the business owner to decide which program is right for them and whether they have the expertise or resources needed to make Excel work.
Hire a consultant to write your business plan
Outsourcing your business plan to a consultant can be a viable option, but it also presents certain drawbacks.
On the plus side, consultants are experienced in writing business plans and adept at creating financial forecasts without errors. Furthermore, hiring a consultant can save you time and allow you to focus on the day-to-day operations of your business.
However, hiring consultants is expensive: budget at least £1.5k ($2.0k) for a complete business plan, more if you need to make changes after the initial version (which happens frequently after the first meetings with lenders).
For these reasons, outsourcing the plan to a consultant or accountant should be considered carefully, weighing both the advantages and disadvantages of hiring outside help.
Ultimately, it may be the right decision for some businesses, while others may find it beneficial to write their own business plan using an online software.
Use an online business plan software for your business plan
Another alternative is to use online business plan software .
There are several advantages to using specialized software:
- You are guided through the writing process by detailed instructions and examples for each part of the plan
- You can be inspired by already written business plan templates
- You can easily make your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the financial calculations for you without errors
- You get a professional document, formatted and ready to be sent to your bank
- The software will enable you to easily track your actual financial performance against your forecast and update your forecast as time goes by
If you're interested in using this type of solution, you can try our software for free by signing up here .
To sum it up, a well-written structure and ownership subsection is key to ensuring that the reader is clear on who controls the business, and whether or not it fits their investment criterias.
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- How to do a market analysis for a business plan
- How to present your management team in your business plan?
- Where to write the conclusion of your business plan?
Know someone who needs help writing-up their business plan? Share this article with them and help them out!

Founder & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster is a seasoned entrepreneur and financier.
Guillaume has been an entrepreneur for more than a decade and has first-hand experience of starting, running, and growing a successful business.
Prior to being a business owner, Guillaume worked in investment banking and private equity, where he spent most of his time creating complex financial forecasts, writing business plans, and analysing financial statements to make financing and investment decisions.
Guillaume holds a Master's Degree in Finance from ESCP Business School and a Bachelor of Science in Business & Management from Paris Dauphine University.
Create a convincing business plan
Assess the profitability of your business idea and create a persuasive business plan to pitch to investors
500,000+ entrepreneurs have already tried our solution - why not join them?
Not ready to try our on-line tool ? Learn more about our solution here
Need some inspiration for your business plan?
Subscribe to The Business Plan Shop and gain access to our business plan template library.

Need a professional business plan? Discover our solution
Write your business plan with ease!

It's easy to create a professional business plan with The Business Plan Shop
Want to find out more before you try? Learn more about our solution here
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How To Write the Company Background Part of a Business Plan
Tell the story of your company's background
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/RyanRobinsonHeadshot1-2016NewCropped1000px-5693e5055f9b58eba49350a8.jpg)
What To Include
Be creative, company background examples.
A crucial part of any business plan is spelling out your company history and telling your origin story to show potential teammates and investors how you landed on your business idea and why you are uniquely qualified to pursue it.
Sharing your business background goes far beyond simply telling a clever story of how you triumphed over adversity to launch your new business. What investors will care about is how your personal history, work experience, skills, strengths, and education will help you succeed in the business.
The background portion shows what you've already done to start executing and bringing your idea to life. Potential investors want to know you'll be able to return their investment with dividends in the years to come, and the background section can help.
Key Takeaways
- Company backgrounds share a bit about the market opportunity you are pursuing (and why you're pursuing it).
- Company backgrounds can be brief for new companies, while established corporations will have more developed backgrounds.
- Company backgrounds can be more creative than other parts of your business plan that need to include industry jargon or marketing buzzwords.
The company background should include a brief history of the company. Your company background could be very brief at the beginning stages of starting up, but you can still detail what you want your company to be about and the origin of your idea. Focus instead on your personal history and the journey that led you to start your business in the first place.
In a traditional business plan, your company background (also called the "company description") follows the executive summary.
Sharing the origin of the idea is valuable because it shows how you think and how you were able to take an idea, craft it into something more detailed, and ultimately build a business out of it. Detailing your progress to date, including any relevant key milestones, is an important part of this, as is listing the problems you’ve faced so far (and how you've overcome them).
Describe the market opportunity you're pursuing and why. A business plan to open a pizza parlor is not particularly creative or original, but if your idea is built around a specific market that is not being tapped, you need to emphasize this and discuss your short-term plans for growth and for reaching that market.
Key topics to include are:
- Any existing experience or relationships with customers
- The market you plan to cater to
- Your educational background
- Other companies you’ve worked for and the roles you've held in those businesses
- Previous businesses you’ve started and their outcomes/current status
- Your technical skills
- Your areas of expertise in your industry segment
- Your areas of weakness or inexperience and how you plan to compensate for them
- Any relevant professional clubs or associations you belong to
Company backgrounds don't need to include technical details about your business structure, finances, or other information along those lines. That information will go elsewhere in the business plan.
Tell your story in a way that's more engaging than just another page that leans on industry jargon, buzzwords, and trite platitudes.
To illustrate your company's history, use images that show how you started. For example, you could highlight charts and graphs to draw attention to key milestones or incorporate customer testimonials or excerpts from news stories that featured you or your business. Take it a step further toward building connections with the people reading your company history by showing vulnerability and sharing some of your past failures (and the lessons you learned from them).
Remember to be concise and stick to just one or two creative approaches that best highlight your particular approach to business and your specific history. This section should be brief.
Here are some company background examples from familiar names.
The Coca-Cola Company
The Coca-Cola Company (NYSE: KO) is a total beverage company with products sold in more than 200 countries and territories.
Our company's purpose is to refresh the world and make a difference. Our portfolio of brands includes Coca-Cola, Sprite, Fanta, and other sparkling soft drinks. Our hydration, sports, coffee, and tea brands include Dasani, smartwater, vitaminwater, Topo Chico, Powerade, Costa, Georgia, Gold Peak, Ayataka, and BodyArmor. Our nutrition, juice, dairy, and plant-based beverage brands include Minute Maid, Simply, innocent, Del Valle, fairlife, and AdeS.
We're constantly transforming our portfolio, from reducing sugar in our drinks to bringing innovative new products to market. We seek to positively impact people's lives, communities, and the planet through water replenishment, packaging recycling, sustainable sourcing practices, and carbon emissions reductions across our value chain. Together with our bottling partners, we employ more than 700,000 people, helping bring economic opportunity to local communities worldwide.
The Home Depot
When The Home Depot was founded in 1978, Bernie Marcus ad Arthur Blank had no idea how revolutionary this new "hardware store" would be for home improvement and the retail industry. Today, we're proud to be the world's largest home improvement retailer. In 2,300 stores across North America, we aspire to excel in service—to our customers, associates, communities, and shareholders. That's what leadership means to us. That's The Home Depot difference.
Want to read more content like this? Sign up for The Balance’s newsletter for daily insights, analysis, and financial tips, all delivered straight to your inbox every morning!
Nussbaum Center for Entrepreneurship. " Business Plan Outline ."
Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
The Coca-Cola Company. " About the Coca-Cola Company: Overview ."
The Home Depot. " Our Story ."
How to Write an Effective Business Plan for Becoming a Partner
Share this article
Print/Download PDF
Want to continue reading?
Become a free bcg attorney search subscriber..
Once you become a subscriber you will have unlimited access to all of BCG’s articles.
There is absolutely no cost!
By James Fant
Rate this article
96 Reviews Average: 4.7 out of 5
Discuss Partners on Top Law Schools
- Calling all 0Lovers! (Spouses/Partners of c/o 2021 Applicants)
- What's with Kirkland poaching all these top-tier partners from other firms lately?
- Will this hiring partner inform my boss of my application?
- Kirkland non-equity partner salary and trajectory
How to Utilize Partner Business Plans

Article Categories
- Legal Recruiter ➝
- Attorney Career Advice ➝
- Advice for Partners ➝
- Business Plans
AGREE/DISAGREE? SHARE COMMENTS ANONYMOUSLY! We Want to Hear Your Thoughts! Tell Us What You Think!!
Find Similar Articles:
- law Firm Management
- business Planning
- business Strategy
- Partner Business Plans
- attorney Networking
- strategic Partnerships
- business Expansion
- mergers And Acquisitions
- professional Development
- professional Growth
- partnership Opportunities
- client Acquisition
- business Growth Strategies
- revenue Generation
- management Consulting
Active Interview Jobs
Featured jobs.
Location: Florida - West Palm Beach
Location: New Jersey - Moorestown
Location: Colorado - Denver
Most Viewed Jobs
Location: Missouri - Kansas City
Location: California - Costa Mesa
Location: Illinois - Chicago
Upload Your Resume
Upload your resume to receive matching jobs at top law firms in your inbox.
Additional Resources
- Harrison's Perspectives
- Specific Practice Areas
- The Winning Mindset
BCG Reviews
This was my first time working with a recruiter and my legal placement professional was more than I could have hoped for.... Read more >
Jacob Speckhard
Sandra Day O'Connor College of Law Arizona State University, Class Of 2015
I liked that you had updates as to application views, whether you were under consideration and stuff like that. I liked .... Read more >
West Virginia University College of Law, Class Of 2014
I have cleared conflicts and am going to move forward at Downey Brand. I will inform Murphy Austin. You can let the othe.... Read more >
I liked the ease of the process! I appreciated that I got the updates for the positions and that I could just click on t.... Read more >
Jared Foley
Columbia University School of Law, Class Of 2008
I liked that BCG assigned me a personal recruiter who I had a conversation with. That was really nice and I liked the di.... Read more >
University of California School of Law, Class Of 2016
She was very communicative and bottom line got the job so whatever she did, it worked! You had resources that I wasn't f.... Read more >
Thomas Eastmond
USC Gould School of Law, Class Of 2000
Popular Articles by Harrison Barnes
- What is Bar Reciprocity and Which States Allow You to Waive Into the Bar?
- What Do Law Firm Titles Mean: Of Counsel, Non-Equity Partner, Equity Partner Explained
- Top 6 Things Attorneys and Law Students Need to Remove from Their Resumes ASAP
- Why Going In-house Is Often the Worst Decision a Good Attorney Can Ever Make
- Top 9 Ways For Any Attorney To Generate a Huge Book of Business
Helpful Links
- The BCG Attorney Search Guide to Basic Law Firm Economics and the Billable Hour: What Every Attorney Needs to Understand to Get Ahead
- Quick Reference Guide to Practice Areas
- Refer BCG Attorney Search to a Friend
- BCG Attorney Search Core Values
- Recent BCG Attorney Search Placements
- What Makes a World Class Legal Recruiter
- What Makes BCG Attorney Search The Greatest Recruiting Firm in the World
- Top 10 Characteristics of Superstar Associates Who Make Partner
- Off-the-Record Interview Tips From Law Firm Interviewers
- Relocating Overseas
- Writing Samples: Top-12 Frequently Asked Questions
- The 'Dark Side' of Going In-house
- "Waive" Goodbye To Taking Another Bar Exam: Typical Requirements and Tips to Effectively Manage the Waive-in Process
- Changing Your Practice Area
- Moving Your Career to Another City
- A Comprehensive Guide to Working with a Legal Recruiter
- A Comprehensive Guide to Bar Reciprocity: What States Have Reciprocity for Lawyers and Allow You to Waive into The Bar
Related Articles

What if a Law Firm Associate Discovers Evidence of Fraud on ....

Navigating the Challenges of Transitioning to a New Law Firm ....

Telling Your Story

Newly Minted Lawyer Unsure About Non-associate Position Bein ....
Related Video
- What are the Benefits of Being a Partner�
Related Podcast
- What to Do if You Are a Law Firm Partner Without Business�
When you use BCG Attorney Search you will get an unfair advantage because you will use the best legal placement company in the world for finding permanent law firm positions.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated March 18, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information you need to cover in a business plan sometimes isn’t quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
If you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template to get you started, download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

6 Min. Read
How to Get and Show Initial Traction for Your Business
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template

8 Min. Read
How to Forecast Personnel Costs in 3 Steps

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Partner Business Plans in 2024: Why are They so Important?

Introduction
Business plans serve as a foundational framework that aligns the operational strategy of your partner firms with the overarching goals and expectations of your company. Tailored for each partner, these business plans outline specific sales, marketing, and training objectives that are designed to be in perfect sync with your organization's aspirations. These plans are indispensable tools for effectively overseeing your network, enabling you to evaluate and measure performance continually and, as needed, take strategic actions to bolster your partners on their path to success.
By collaboratively constructing business plans in conjunction with each partner, you foster a sense of cohesion within your indirect sales ecosystem. This shared roadmap ensures that all partners are working in synergy, collectively pursuing the identified actions necessary for accomplishing mutual success, further strengthening the strategic alignment between your firm and its partner network.
Develop Partner Bussiness Plan: Two Key Steps to Consider
1. know your partners well.
A thorough understanding of your partner network is a fundamental prerequisite for the successful development of partner business planning. Within your indirect sales ecosystem, business providers, integrators, value-added resellers (VARs), IT service companies, and resellers each operate within distinct logic and economic models. Acquiring deep insights into the nuances of each partner type is crucial for crafting business plans that align with both your partner's strategic objectives and your company's overarching goals.
Isabelle Castellanet, the founder of IXC, a firm specializing in Partners and Growth, emphasizes the importance of recognizing the diverse expectations and requirements of partners based on their typology. She notes, "Depending on the typology of its network, it is important to see that the partners do not expect the same information. A wholesaler, for example, does not require the same information and tools as a VAR, an integrator, or even a third-party publisher who prescribes or resells for you."
Recognizing these key elements in partner business planning ensures that your efforts are tailored to cater to the specific needs and expectations of each partner category, ultimately fostering a more productive and mutually beneficial collaboration.
2. Have a Well-Defined Global Business Objective
Creating a robust business plan in collaboration with your partner necessitates a well-defined and quantifiable overarching business objective. This objective must be crystal clear and expressed in measurable terms. For instance, it could be aimed at achieving specific milestones, such as:
- Capturing more than 20% of the market share in France for your product;
- Reaching an annual turnover target of "X" amount or;
- Expanding your operations to attain 5% of the turnover in a new country.
This overarching business objective serves as the cornerstone upon which you will construct the business plans tailored for each of your partners. The core concept is to apportion individual objectives to your partners that harmonize with your global strategy. Consequently, each partner's unique business plan becomes an instrumental component contributing to the fulfillment of your company's overarching business objective. This strategic alignment ensures that the combined efforts of your partner network work in unison to advance your business toward its ultimate goals.
.png)
Establishing a Partner Business Plan: The Objectives
Setting objectives within your partner's business plan is essential, engaging, and decisive for the success of the partnership. Aligned with the main objective of your business, these objectives, whether quantitative or qualitative, must be measurable and, therefore, quantified.
Set Quantitative Targets
Based on a careful analysis of historical sales performance, specific criteria such as outcomes, geographical location, and seniority within the partner network, distinct objectives will be strategically allocated to each partner. These objectives encompass a variety of key areas that guide their contributions to the partnership:
- Business Objectives on Sales Volume and Turnover: Partners will be tasked with well-defined business goals related to sales volume and revenue generation. These objectives may be tailored to the partner's track record, the market potential in their location, and their historical sales figures. This approach ensures that targets are realistic and achievable, motivating partners to excel in their specific market segments.
- Marketing Objectives through Event and Webinar Organization: In addition to sales targets, partners will also be entrusted with marketing objectives, which often involve organizing events and webinars. These events serve as crucial touchpoints for engaging potential customers and driving brand awareness. The specific objectives may vary depending on the partner's strengths and past performance, encouraging them to leverage their marketing expertise to enhance the partnership's overall success.
By customizing these objectives based on partner history and characteristics, the partnership becomes more adaptable and efficient, with each partner playing a unique role in contributing to the collective success of the collaboration. This tailored approach maximizes the potential for growth and achievement within the network.
Set Qualitative Objectives
Incorporating qualitative objectives into your business plan imparts a heightened level of professionalism to your partner network. This is especially pivotal when embarking on new indirect sales partnerships. Training sessions play a central role in this process, serving as a crucial avenue for partners to equip their sales teams with comprehensive knowledge about your brand. These sessions not only elevate your partners' understanding of your products but also empower them to embrace and disseminate your vision over the short, medium, and long-term horizons. This alignment ensures that they are seamlessly integrated into your strategic framework. As an illustrative example, you may set a target, such as achieving a certification for a specific number of "X" sales, within your business plan.
To ensure the optimal monitoring of your business plan and to gauge the progress of your partners, it is imperative to implement KPIs. These quantifiable benchmarks enable you to assess the attainment of objectives, offering valuable insights into areas where potential refinements or additional support may be necessary. By embracing KPIs, you introduce a structured, data-driven approach that ensures the partnership remains on a well-tracked trajectory toward realizing the objectives outlined in your business plan.
Have Regular Monitoring
In pursuit of ongoing refinement and shared operational efficiency, it's essential that these objectives are periodically defined and subject to regular monitoring. Constructing a business plan without a system for ongoing objective assessment is a critical oversight, as it can become too late to take corrective action should your partner deviate from their established objectives. To ensure the long-term success of your collaborative efforts, it's highly advisable to assess and potentially adjust objectives on a monthly basis, accounting for variances such as weaker performance in a specific month, such as August.
KPIs play a pivotal role in facilitating the monitoring and analysis of your partners, allowing you to identify both their strengths and areas that may require improvement. With a monthly review and a systematic reporting mechanism, you gain the capability to:
- Set Realistic Objectives : By closely aligning objectives with the current conditions on the ground, you ensure that they remain practical and attainable in the context of evolving market dynamics.
- Monitor Implementation and Achievement : Regular tracking using KPIs enables you to gauge how well partners are executing planned actions and progressing towards the predefined objectives, offering insights into areas that might need attention.
- Provide Support : Armed with this detailed data, you are better equipped to initiate timely and targeted actions that can help partners overcome challenges and, in turn, assist them in reaching their objectives. This proactive approach ensures that your partnership remains adaptive and robust, fostering sustained success in a dynamic business landscape.
The Essential Tool to Build a Business Plan and Manage it
In the endeavor to establish a comprehensive business plan and ensure its effective management with full transparency into your partner's activities, a PRM, or Partner Relationship Management system, emerges as the quintessential tool. Going beyond the capabilities of conventional management software, a PRM empowers you to systematically structure your indirect sales processes and engage with your partner ecosystem in real time, irrespective of the hour or location.
When crafting business plans for your partners within a proficient PRM platform, you can expect to benefit in several key ways:
- Tailored Business Plans : A robust PRM system should facilitate the seamless definition of unique business plans for each partner, accommodating their specific objectives, strengths, and market dynamics. This tailored approach ensures that each partner's plan is finely tuned to optimize success.
- Real-Time Progress Tracking : The PRM offers the invaluable advantage of real-time progress tracking for the objectives set within these business plans. It allows you to stay updated on your partner's performance, offering insights into their achievements and areas that might require attention or support.
- KPI Integration : Effective PRM systems seamlessly integrate KPIs into the platform, providing you with a set of critical metrics that pinpoint what is vital for the success of your partner's business plan. These KPIs offer the ability to focus on the most significant aspects of your partnership, enabling data-driven decision-making and strategic adjustments as needed.
By leveraging a PRM , your business can optimize its partnership management, ensuring that business plans are not only efficiently established but also actively tracked and adjusted as necessary, fostering the mutual success of both your company and your partner network.
Build your partnership program and strengthen partner engagement.
Looking for inspiration to never stop learning.

Partner Program Tiers: The Set Up Process A-Z

The Top 9 Skills to Look For in a Partnership Manager
Your right to know, why are partner business plans important, what elements should be included in a partner business plan, how do you write a business plan for a partner, what are the 3 types of partners in a business set up, what is an example of a strategic partnership plan, still have questions.
11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.

Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
More From Forbes
Eight essential qualities of a successful business partner.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
You have a great business idea that you're passionate about, and you're excited to get started, but before you do, you need to choose a business partner. This person can help you make complex decisions and guide your team through projects. They can be your best ally.
However, if your partner doesn't have values and goals that align with yours or adds more stress to situations, they may be detrimental to your business. To make sure you don't end up in the wrong partnership, look for these eight essential qualities of a business partner from members of Young Entrepreneur Council .
YEC members share their expert insights.
Looking for a business partner who can help take your company to the next level is crucial for the success of any business. Ideally, I look for someone who is just as passionate about the business as I am. This includes finding a partner who has a shared vision for the organization and strives to move the business forward toward the same long-term goals. Equally, it's important to share similar values, entrepreneurial spirit, working styles and compatibility. Why is this so important? A great business idea can easily be damaged by a negative business relationship. It's your responsibility as an entrepreneur to do your due diligence in finding and selecting the right partner for you and your business. - Neel Kawale , Haüskey
2. Openness
A good business partner is direct. I often use a saying in business, with my family and with my friends, and this saying is, "No one can read your mind." You have to tell people what's on your mind in a direct, straightforward manner. Nothing is truer in business. Sometimes you'll have good ideas, and sometimes they will be downright terrible. A business partner that is direct can bring honest feedback to any situation. You don't have to guess if they said what's on their mind or how they feel about it. They tell you. Every business is better when partners are direct with one another. - JT Allen , myFootpath LLC
3. Industry Knowledge
I suggest looking for potential business partners that have a firm understanding of the industry. If you've already started your company, you likely don't have time to teach a new partner the basics. Look for people with experience, education, references and, preferably, a personal brand website. When you connect with someone with these traits, you'll have more time to focus on improving the business from within. As an added bonus, partnering with another expert in the industry can boost brand awareness. - John Turner , SeedProd LLC
Best Travel Insurance Companies
Best covid-19 travel insurance plans.
4. Strong Work Ethic
Having the same work ethic was a key ingredient to finding a successful partnership in my experience. It is hard to notice this trait unless the partners were former co-workers or had worked together previously. Most of the time, people are enthusiastic when it comes to starting a business, but then they realize how much work is involved day-to-day and fade out or slow down. This could frustrate the other partners or start various conflicts. By having the same work ethics, partners would easily agree on priorities on almost everything, which makes running a business smoother. In other words, the partner should be efficient. This efficiency would lead to a successful business. - Meeky Hwang , Ndevr, Inc
You can be intellectually connected with a person, you can have complementary skills, have a different or the same background and so many more connectors that traditionally speak for a good business partnership. The one thing that you cannot buy and is not easy to find is stamina. Stamina comes into play when things get tough, which are usually the moments when you need your business partner the most. In these moments, there will always be a pull and push relationship between two business partners. This is healthy and helps to get through tough times. However, if that determination, strength and resourcefulness to get through tough times is not balanced, then it's hard for the partnership to survive that. Stamina is one of the trickiest qualities to test upfront in a business partner, but it's a "make or break" quality. - Fabi Hubschmid , Markaaz
6. Diversified Business Skills
Diversified business skills are critical when selecting a business partner. The partner should have the ability to take on different tasks within their separate skill sets and cover the core competencies of the business. You will need to dig a bit deeper and truly understand that all parties must have the same set of business and personal values. Aligning your values is mission-critical because your business will inevitably send you countless challenges, and you’ll need to lean on your core values as a team to fight your way through. If one person doesn’t have the same set of values, the partnership will break. Your core values should be discussed early on and understood, so when rough waters arrive, you’ll have the confidence in your partner to adjust the sails and persevere! - Tom Finn , LeggUP Inc.
7. Previous Successful Experience
The most important thing to look for in a business partner is a complementary skill set, not an identical or similar one to what you already possess. The key to knowing what to look for is having an accurate and impartial understanding of your own strengths and weaknesses. If you’re a big picture person but could use a hand when it comes to the mechanics of operating a successful business, look for a partner with a proven track record managing similar companies. If outside funding is going to be a requirement for growing your business, the team you’ve assembled will be the first thing that venture capitalists (VCs) and other investors evaluate. Experience speaks volumes, so if you’re a first-time founder, look to partner with someone with previous success. - Mark Stallings , Casely, Inc
8. Dedication To Growth
You really want to align yourself with someone who has a long-term vision in mind. If you partner with someone who is in it for quick success, they will be less likely to stick around when things don’t go as planned. You need someone who is reliable. Someone who is looking five years down the road. Someone who is determined to find solutions to the many challenges and obstacles that can and will pop up along the way. Someone who is dedicated to your vision and purpose. Someone who is invested in “seeing it through.” For your business venture to be successful long-term, your partner needs to have the same level of dedication as you as well as a growth mindset. - Blair Thomas , eMerchantBroker

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Partnership Plan Templates with Examples and Samples

DivyanshuKumar Rai
When partners enter a business at the outset, they are motivated and excited to embark on this exciting new adventure together. Initially, they agree on almost everything. These new entrepreneurs think they will be in business together for the rest of their lives or until they sell the company for untold millions of dollars.
They believe that nothing can or will go wrong. They are so sure of each other that they never bother to get a written partnership plan. What could possibly go wrong in this scenario? The short answer is, "A LOT!"
The reality is that, despite dreams of longevity and unwavering trust, business owners' desires and expectations change over time. A written partnership plan can manage these expectations and give each partner confidence in the business's future. A written plan can serve as a safeguard that protects both the business venture and the investment of each partner.
Now, you might be thinking, “How to get an effective partnership plan in place?” The quick answer: Partnership Plan Templates .
Every business requires a partnership plan. Small businesses seek out partnerships more to achieve their goals and objectives. Building a strategic partnership is more complicated than creating a partnership document, but it is the first step toward action. SlideTeam’s partnership plan templates maneuver your ship to the shore.
Let’s explore these!
Template 1: Vendor Strategic Partnership Engagement Plan
Get this Strategic Partnership Plan PPT Template and deliver an impactful presentation to your audience. Its layout is divided into four sections, each describing a critical aspect: Plan, Analyze, Identify, and Act. There’s a specified section for review to ensure you have that extra cushion to make amendments, wherever necessary. Get this template now.
Download this template
Template 2: Strategic Partnerships Event Planning Service Company Profile PPT Template
This PowerPoint Template works wonders when you want to explain the role of strategic partnerships within an organization. It has ample space to highlight points you want to deliver in your presentation. You can use its standard layout to emphasize key details, including partner location, services they monitor, objectives, and more. Download it now.

Template 3: Internal Communication Plan For Partnership Firm
The importance of proper communication in the successful accomplishment of business objectives can’t be overstated. With SlideTeam’s handpicked internal communication plan template, you can enjoy the convenience of an uninterrupted flow of information across departments in your company. This plan layout describes:
- Reasons for communication
- Communication activity
- Communication channel
- Individual responsible
Download now.

Template 4: Marketing Campaign Initiated by Partnership Timeline
Build a weekly timeline for your marketing campaign using this fantastic PPT Template. Till the campaign goes live, you can include and track KPIs to ensure your effort is successful. Here, there are some predefined parameters that you can use: Target mapping exercises, Prepare brands and categories, Assign partner roles, risk register update, Negotiation and recruitment, and Activation and management. Download it now.
Template 5: Global Partnership Management for Planning and Communication
Global partnership management is a painstaking task that can be made easy with our exemplary template. It has a unique framework that explains key insights encompassing the five stages, namely: Prepare, Share Knowledge, Plan, Execute, and Achieve Results. Being 100% editable, you can tweak the design and include points in this template to serve your purpose. Download it now.
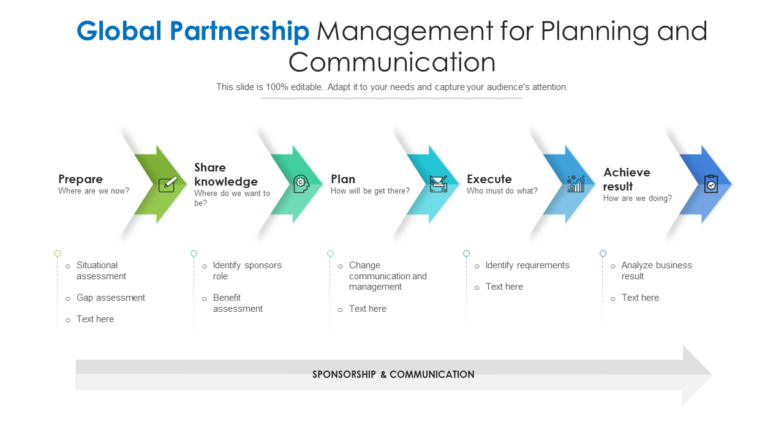
Template 6: Six Months Teamwork Partnership Strategy Roadmap
Teamwork is the key to success! We know you would have heard this phrase at least a million times, but it doesn’t take away even a slight bit of truth. Build a six-month teamwork partnership framework using our exceptional PowerPoint Template. It highlights the team member and phases spread across a month-wise timeline. The phases include:
- Develop partnership strategy
- How the partnership will operate
- Ensure stakeholder support
- Resource allocation
- Review the partnership development process
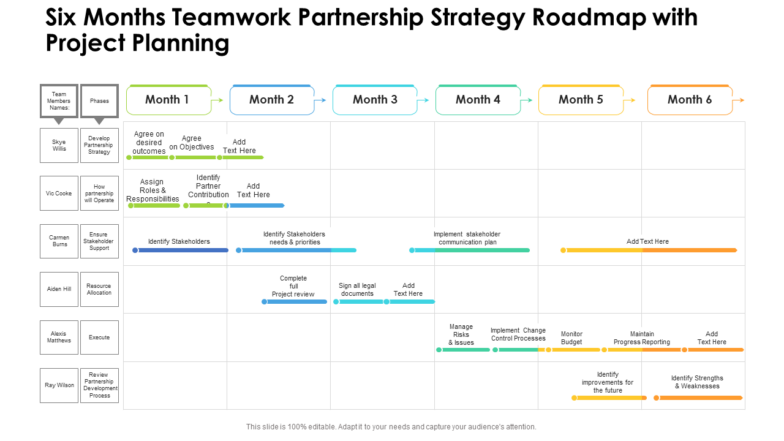
Template 7: Five-yearly Teamwork Partnership Strategy Roadmap
With a similar design to the previous template, this template accelerates the process of building a five-year teamwork partnership strategy roadmap. It has some predefined phases which you can change to suit your business requirements. You can present it to higher management to get their approval on the partnership roadmap you are long working on. Get it now.
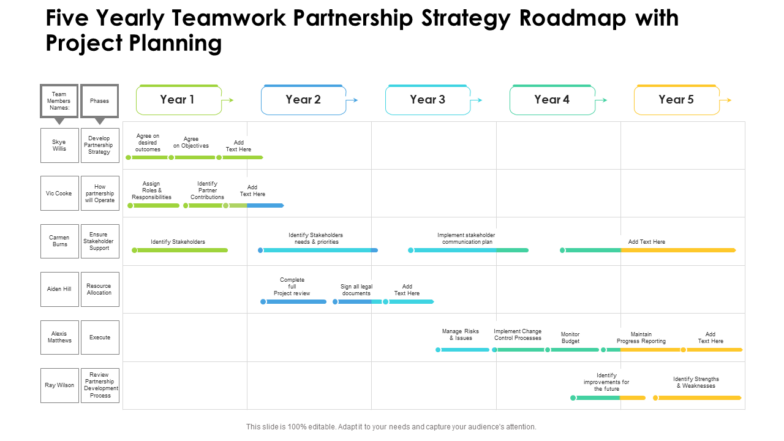
Template 8: Planned Partnership Strategy PPT Template
If you need a pre-built framework for drafting a planned partnership strategy, this is the perfect piece for you. Its layout is designed into five stages that you can use to explain critical insights that underline your strategy. You can also use it to highlight KPIs as well. Get it now.
Template 9: Strategic Partnership Showing Teamwork
‘Strategic partnership’ is a complex subject that commands resources to spark clarity in your audience. Lucky for you, SlideTeam has prepared this template that touches every essential parameter that encompasses it. This template highlights the points of collaboration, teamwork, strategy, plan, performance, and success. It is a roadmap with checkpoints you need to surpass to foster better partnerships within your organization. Download it now.
Template 10: Partnership Action Plan PPT Presentation
A partnership action plan boiled down into three stages! Hard to believe, isn’t it? SlideTeam presents a PPT Template that displays a layout that does just that. It has three levels: Action, Planning, and Partnership. The idea behind these stages is, you have to define relevant actions to ensure your organizational plans aren’t affected. Doing so will ensure there’s a more inclusive partnership forging in your company across departments. Get it now.

Partnerships are critical to the success of any business. Merchants and traders have used the principles of strategic partnership to conduct their businesses since the genesis of trade and commerce; the trend continues today.
A partnership can take many forms, from business owners working together to invest in a project to firms sharing technical knowledge and ideas. Whatever a company does, finding the right partnership plan template that benefits both parties is critical. (And that’s why SlideTeam has put together this list of top 10 partnership plan templates!)
FAQs on Partnership Plan
What is a partnership plan.
A partnership plan is a way two or more parties in a business agree on conducting the venture together. Each party takes different functions to perform, helping the business run more efficiently. This plan is documented in the form of an agreement. This document lays down the ground rules on how the partners will handle business responsibilities, ownership and investments, profits and losses, and company management.
While "partners" usually refers to two people, there is no limit to how many partners can form a business partnership in this context.
How do you create a partnership plan?
When forming a business partnership, it is critical to draft a partnership plan contract that outlines all of the terms and conditions of the professional relationship. Your business partnership plan should include a list of all partners and should address the following issues:
- Name of the partnership
- Partnership goals
- Partnership duration
- Contribution amounts of each partner (cash, property, services, future contributions)
- Each partner ownership interest (assets)
- Management roles and terms of authority of each partner
- Accounting obligations
- Distribution of profits and losses between the partners
- Salaries, work hours, sick leaves, and vacation times of each partner
- Permissions and restrictions on any outside business activity
- Buyout options of partners
- Process for adding new partners or removing original partners
- Terms and conditions of termination of the partnership
What are the stages of partnership?
Here are the five stages of partnership:
Stage I. The Singles Stage (Non-Partnering)
Stage II. The Searching Stage (Pre-Partnering)
Stage III. The Courtship Stage (Active Partnering)
Stage IV. The Bonding Stage (Consolidated Partnering)
Stage V. The Commitment Stage (Going to Scale)
What are the 5 principles of partnership?
There are five basic tenets that work together to form a framework for establishing a solid foundation for effective business relationships.
- Shared knowledge
- Agreed Goals
- Balance of return
While some of these are easier to quantify than others, each has a significant impact on the partnership's strength.
Related posts:
- How to Design the Perfect Service Launch Presentation [Custom Launch Deck Included]
- Quarterly Business Review Presentation: All the Essential Slides You Need in Your Deck
- [Updated 2023] How to Design The Perfect Product Launch Presentation [Best Templates Included]
- 99% of the Pitches Fail! Find Out What Makes Any Startup a Success
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Partnership Agreement Templates for Harmonious Synchronization

Top 10 Strategic Partnership Proposal Templates To Form Successful Alliances (Free PDF Attached)
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format


with Garrison & Sisson
Business Plans for Lateral Partners – Good vs. Great
Most effective business plans, if not done correctly, are relatively useless. Why? Because many partners end up borrowing a template from a friend at another firm, and they just fill in the sections.
There is not that much thought about why certain information is included, and how it fits with the LPQ and the overall business case for joining the new firm. Effective business plans often read like a rehash of a partner’s website biography and contain duplicative information that will be included in other documents as part of the due diligence process.
But effective business plans don’t have to be superfluous, and here are recommendations.
There are three main questions partners have regarding effective business plans:
- “Should I have a effective business plan?”
- “If so, when should it be presented to the firm?”
- “What should the business plan include?”
Main Purpose of Business Plan
Before I answer the above three questions about effective business plans and it’s important to explain that the purpose of a effective business plan is to show your future vision for your practice at a particular firm.
Effective Business plans are used in conjunction with a Lateral Partner Questionnaire (LPQ), which is a detailed questionnaire that focuses on various aspects of your practice and includes questions about the historical, current, and projected financial aspects and economics of your practice. Taken together, these provide firms with the most comprehensive 360 degree view of your practice and how it will potentially fit in to the new firm.
In short : The LPQ looks at your past and present practice, and also encompasses projections for the future. Business plans supplement the LPQ by putting more “meat on the bones” about your current practice, where you want to go, and how you plan to get there. The business plan is also, at times, a stand-alone document that can be used at the new firm to present to the executive/hiring committee to explain why you should be hired.
Now let’s address each of the above three questions.
- “Should I have a business plan?” Answer: it depends.
If you have an immediately portable practice that is at least self-sustaining (meaning you can keep yourself busy with your own work), or the new firm has enough work to keep you busy based on your unique skillset, a business plan may not be needed. The information that you include in the LPQ will likely be sufficient.
If it’s unclear as to whether you may have enough business to keep yourself busy, a business plan is important to help explain your vision and plan for your practice. It’s a piece of the puzzle that helps the new firm answer, “What’s the likelihood this partner will be successful at our firm?”
- “When should it be presented to a firm?”
Do not present a business plan before you are interviewing (the exception is if you are coming from the government).
The business plan must be tailored to each specific firm you are considering, and you will learn important information during the interview process that you will use to help build your case as to why you and your practice is a good fit for the new firm. A big mistake is presenting a generic business plan. I remember attending a seminar a few years ago on lateral partner business plans, and the speakers (hiring partners at law firms) basically said, “We don’t like generic business plans and think they are sort of useless. If we actually want a business plan, it should be focused on our firm specifically.”
Your business plan ideally connects these dots: (1) what the firm wants to accomplish, (2) what you want to accomplish, and (3) how coming together could help you both accomplish these mutual goals. You are (obviously) unable to connect the dots if you have a generic business plan that is presented at the outset. As a result, presenting it after a round or two of discussions will enable you to connect the dots much better.
- “What information should it contain?”
The level of detail included in your business plan will depend upon your particular circumstances, where you are in the process, and what you wish to highlight. Below are the most relevant sections that can be presented. Think of this as a general lateral partner business plan template, which should be modified and tailored based on your specific situation.
DETAILS TO INCLUDE IN THE BUSINESS PLAN
- Practice Description . Briefly describe nature of your practice, including areas of expertise or specialization; ideal to provide breakdowns (e.g., example 30% M&A, 25% private equity, etc.).
- Practice Development to Date : What you have done to develop your practice to date. Although the LPQ will cover your business development track record, it doesn’t hurt to reiterate your main clients, origination track record over the past few years, and your billing rate.
- Highlights/Accomplishments : Any highlights about your practice (e.g., particular high-profile deals or cases) and/or industry recognition.
- Firm Citizenship: Leadership roles, etc.
- Key Strengths : What are your unique strengths as a partner? Where do you see yourself adding the most value to a new firm/practice?
- Future Goals : Where you want your practice to be in the next 3-5 years. For example, do you want to expand your practice area or enhance a particular industry focus? Are there additional clients you want to pursue, but you are limited at your current firm due to conflicts, rates, or geography?
- Industry Trends : What industries do you focus on? What is happening in your particular industries that could create more opportunity at the new firm? What are the untapped opportunities and how are you positioned to capitalize on them?
- Limitations or Challenges with Current Firm (this is optional, depending on the particular circumstances of your situation) : Why are your future goals difficult to accomplish at your current firm? Note: the challenges can also be “softer” factors such as the manner in which client credit is shared is not consistent with the type of culture in which you enjoy practicing, etc. Be careful, however, not to come across as venting your frustrations. The more this is focused on business and limitations to your practice, the better.
- Your understanding of the new firm’s goals/strategic needs as it pertains to your practice (based on your discussions).
- How your background/experience could fit into the firm’s goals/strategic needs.
- How the new firm could help you (1) more easily accomplish your goals and/or (2) reduce some of the challenges with your current firm. In short, how could both sides come together in a way that meets everyone’s needs.
- Your Network of Contacts : Include a list or chart of people you would plan to continue receiving business from, and who would you expect to approach to develop new business. The ideal format for the headers is the name, company, title, and the nature of your relationship, including how long your have represented the client (if they are a current client). This can include the new firm’s clients to the extent it has been discussed already. If you do mention the new firm’s clients, be sure to take a collaborative tone that includes pitching together as a group and not as a lone wolf. Note : Some partners are understandably reluctant to “share their rolodex” too early in the process. If you are uncomfortable, it’s ok to hold off on providing too much detail regarding your network if it’s still early in the process and you are unsure if the firm is a fit. If the firm presses you for information on your network and future prospects, you can equalize the process by asking the firm to share information on their main clients/contacts as well, so it’s more of a “mutual brainstorming.”
- Specific Business Development/External-Facing Activities : Many business plans have generic sections such as “Writing: I plan to write articles” or “Speaking: I plan to speak at industry conferences to help get my and the firm’s name out there.” There is nothing wrong with this, but it often comes across as very generic. To make more of an impact, provide specific examples of what you have done to date, and what you plan to continue doing. For example, are you on the Board of any high-profile publications or do you often participate at certain industry conferences?
The business plan is not a one-size-fits all approach, but the above provides more clarity on the key issues these documents involve and how to best approach this part of the lateral hiring process.
Subscribe for Updates
Your information will be kept confidential.

Author: Dan Binstock
Dan co-owns Garrison & Sisson, where he focuses on lateral partner and practice group placements. He has consistently been recognized as one of the Top 100 Global Legal Strategists and Consultants by LawDragon, and authored "The Attorney's Guide to Using (or Not Using) Legal Recruiters." Dan is the Immediate Past President of the National Association of Legal Search Consultants (NALSC), where he also served as Chair of the Ethics Committee. Visit here to learn more about Dan, or contact him confidentially with any questions at (202) 559-0492 or [email protected].
Home / The Guide / Entering the Market / Business Plans for Lateral Partners – Good vs. Great
Related Articles
The waiting period and lateral partner interviews.

Navigating Lateral Partner Ethical Considerations – Interview with Tina Solis (Nixon Peabody)
The lateral partner questionnaire (lpq), search lateral partners.com, table of contents.
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Business consultants
Entrepreneurs and Small Business
Accelerators and Incubators
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai pitch deck generator
Stratrgic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
Small Business Tools
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Strategic Planning
How to Write a Business Plan Cover Letter That Wins Investors

Business Plan Cover Pages
Ayush Jalan
- December 12, 2023

Writing a business plan cover letter is an important part of presenting your business plan to potential lenders and investors when seeking investment. It’s the first thing an interested investor will read, and it’s your chance to make a good first impression.
In this article, we’ll see an overview of what a business plan cover letter is, why it’s important, and how to write it. We’ll also share a template, some examples, and useful tips you can use to write a formal cover letter for your own business plan and make it stand out.
What is a business plan cover letter?
A business plan cover letter is a formal document that accompanies your business plan and serves the purpose of introducing you and your business venture to potential investors or lenders. In other words, it’s a way for you to sell your business idea and show why you believe in it.
In the same way that a job seeker presents a cover letter alongside their resume to an employer in order to get hired, you need a cover letter to go alongside your business plan in order to secure funding or a business loan.
Why is a business plan cover letter important?
Through a cover letter, you show the investor why you are a good fit, what value your business can bring to them, and why they should invest in your company instead of your competitor.
To increase your chances of getting funding, it’s wise to tailor your cover letter based on the investor reading it. This means researching the companies the investor has previously invested in, their risk tolerance, and the values they look for in a business partner.
Although your business plans already details all crucial data, the cover letter should provide a glimpse into the current financial position of your company, including its profitability, debt, projections, and more.
The idea here is to let the investor know what they are getting into and reduce uncertainties. If they like your cover letter, they will be more interested to go through the whole business plan and ask questions before investing .
How to write a business plan cover letter?
Before you start writing a cover letter, make sure you’re done preparing a business plan and that there are no errors in it. A well-written cover letter isn’t going to get you very far if the business plan itself is not properly made.
Once your business plan is ready, follow these steps to write a cover letter:
Step 1. Create a header
The header of your business plan cover letter should include your name, the name of your business, your address, and your contact information. Next, write the date. And finally, write the name of the investor, the institution they are affiliated with, and their address.
If you’re sending the document via email, there’s no need to write a header, and you can jump to addressing the recipient with a formal greeting.
Step 2. Address the recipient
Unless you don’t know the name of the recipient, don’t make the mistake of addressing them as “Dear Investor” as that may give the impression that you haven’t researched the person you’re sending your business plan to.
Addressing the name of the recipient such as “Dear Mr. Green” or “Dear Ms. Jones” sets a good tone and is preferred over a generic greeting.
Step 3. Write a strong opening
The first paragraph of your letter should immediately grab the reader’s attention. This means stating the intent of the letter, the reason you want to work with this investor, and how you will use their money to scale the business.
Explain why you think your business is a good investment opportunity, and mention details such as the type of ownership, legal formation, the structure of the business , its history, and any notable achievements.
Step 4. Support your statements
Claims made without evidence don’t mean much, so you’re going to need to provide some form of data or facts to prove that you’re worth the risk.
This is admittedly hard to do if you’re a startup since most startups fail. That’s why it’s a good idea to track these key startup metrics to assess your financial position and the overall viability of your business idea.
Step 5. Close with an acknowledgment
The last paragraph of a cover letter should emphasize three things: your interest in working with the investor, the value of this opportunity, and the timeline of how you’re expecting things to happen.
Once done, thank the reader for their time, express your eagerness to see their response, and request a meeting to discuss things further. End the letter with a formal sign-off.
Tips for writing a business plan cover letter
Here are some tips for writing a business plan cover letter:
- Keep the letter short and descriptive, no more than one or two pages.
- Use a formal, conversational tone, and avoid using slang, jargon, and contractions. The easier it is to read your letter, the better.
- Address the reader by name, and avoid using “To Whom It May Concern.”
- Mention your professional background, the competency of the management team, and how it all benefits the business.
- If you’ve acquired funding in the past, highlight the individuals, institutions, or banks that have invested in your company.
Business plan cover letter template
[Your Name] [Your Company’s Name] [Your Address] [Your Contact Information] [Date]
[Investor’s Name] [Investor’s Company Name] [Investor’s Address] Dear [Name of Investor],
I am writing to request your investment in [Your Business Name]. We are [ brief overview of your business ] and we believe that [Your Business Name] has great potential to be a valuable addition to your portfolio.
[Provide a brief description of your current financial situation and how the funds will be used]
[Mention your unique selling proposition]
Please find attached a copy of our business plan which provides more information on our company and product offerings. We would appreciate it if you could take the time to review our plan and offer your feedback. We look forward to working with you.
Thank you for your time and consideration.
Sincerely, [Your Name].
Business plan cover letter example
William Cutler Cutler and Colors Co. 132, My Street, Kingston New York 12401 [email protected] February 17, 2023
James F. Miller Miller Industries Pvt. Ltd. 1234 NW Bobcat Lane, St. Robert, Missouri Dear Mr. Miller,
Cutler and Colors is an emerging fashion retailer in New York City specializing in men’s garments, and we’re looking to expand to six more cities in the U.S. by the end of 2023. With your financial support, we project to double our production and strengthen our supply chain efficiency.
We believe Cutler and Colors will be a valuable addition to your portfolio. We currently have $220,000 of our own funds invested in the business and are looking to raise an additional $500,000. The money will be used to hire more staff, set up new stores, purchase new equipment, and advertise online.
By streamlining our supply chain, we intend to undercut our competitors and offer high-quality garments at an affordable price.
Please find attached a copy of our business plan which provides more information on our company and product offerings. We would appreciate it if you could take the time to review our plan and provide us with your feedback. We look forward to working with you.
Sincerely, William Cutler
Lure investors with a great first impression
Writing a good cover letter is key when presenting your business plan to potential lenders and investors. Your cover letter should be well-written, professional-looking, and tailored to the interests of the investor reading your business plan.
Be mindful of the length of your cover letter; it should be short enough to retain the reader’s interest and long enough to cover the subject. If you’re sending the cover letter over email, it’s a good idea to follow up after some time in case you don’t get a response.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

Frequently Asked Questions
How long should a business plan cover letter be.
Ideally, your cover letter should not exceed one page; if there’s more to add, a maximum of two pages is considered permissible. That said, it’s usually better to write a shorter cover letter than a longer one.
Can I include statistics in a business plan cover letter?
Yes, you can mention data in your cover letter to support your claims, but don’t overdo it since your business plan already highlights your financials and future projections in great detail.
Can I skip writing a business plan cover letter?
If you’re sending a physical copy of your business plan to an investor or lender, it’s absolutely crucial that you attach a cover letter with it. However, a cover letter is not that necessary if you’re sending it via email as you can simply write a note in the body of the email.
About the Author

Ayush is a writer with an academic background in business and marketing. Being a tech-enthusiast, he likes to keep a sharp eye on the latest tech gadgets and innovations. When he's not working, you can find him writing poetry, gaming, playing the ukulele, catching up with friends, and indulging in creative philosophies.
Related Articles

How to Write a Business Plan Complete Guide

How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)

How to Write an Operations Plan Section of your Business Plan
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

Find anything you save across the site in your account
What to Look for in a Business Partner
By Danine Alati

When choosing a life partner, we tend to be very particular and discerning. You might want to put just as much thought into selecting your business partner, especially if your goal is to build a long-lasting relationship with an individual who will help your company prosper. Professional expertise and aesthetic vision may be top of mind in your search, but just as important are a person’s personality traits, trustworthiness, and values. Indeed, this is someone who you may end up spending as much time with as anyone else in your life (if not more).
When it comes to finding that individual, the search may take time. Richard Gluckman, founding partner of AD100 firm Gluckman Tang Architects , advises, “Identify people within your firm who have the potential to grow into a partnership role. [Then] provide autonomy, responsibility, and support. If looking outside, look for potential partners among like-minded colleagues with complementary skill sets who may be ready for a move.”
Is it time to expand the leadership of your firm? Gluckman, Nate Berkus, Samantha Josaphat, and Ron Radziner and Leo Marmol elaborate on what makes their own business relationships successful, and what to consider when taking on a partner of your own.
Identify skills you need
“I’d suggest evaluating in what areas a prospective partner could bring value to your business—and not necessarily just provide additional man- or woman-power,” explains Samantha Josaphat, principal of Studio 397 Architecture. She knew she wanted to bring on an individual who could be involved on the technical construction side of her projects as well as advise on budget, and she thought that her fiancé Luis Medina-Carreto fit the bill with his background in finance and construction management. “We needed someone who would diversify the skills and experience in our company in order to grow as a boutique yet well-rounded firm,” says Josaphat, who brought on Medina-Carreto as a business partner earlier this year.
Gluckman seconds that notion, sharing that a design partner should be “someone who can help realize a core part of the strategic plan that would otherwise be unrealized or under-tended.” He named his longtime colleague Dana Tang a partner in 2015, after she demonstrated talent, hard work, and “uncompromising pursuit of great design” at the 25-person firm for 20 years. “A partner can be the ideal way to…help move [a company’s] goals forward,” he says.
Look for good differences
Ron Radziner , design partner at AD100 firm Marmol Radziner, points out that having different experiences from your partner is key to avoiding conflict. “Our partnership works, because we made a commitment to a shared aesthetic and level of quality in our designs and construction. However, our background and concerns are pretty different,” he says of his relationship with Leo Marmol, the managing partner at the 200-plus-person firm, which the duo co-founded in 1989. “Some overlap in background and interest is obviously good, but you want to avoid working with someone who wants to do the exact same things as you.”
In their office, each leader assumes distinct roles. “As managing partner, I field most of the day-to-day new business inquiries and track these potential projects,” Marmol explains. “This allows Ron to oversee the design progress of every project. When projects begin to take shape in the construction phase, we both visit sites to make sure things are going smoothly.” Maintaining some autonomy ultimately helps advance the firm’s goals. “We bring different perspectives, and we often differ in opinion, which ultimately broadens the depth of experience between us,” Marmol says.
Reinforce shared vision and values
While distinct points of view can contribute to the strength of a business, sharing like-minded core beliefs is vital. “It’s very important that you share the same vision and set of values—about design, about how to approach the business, and also in life in general,” says AD100 interior designer Nate Berkus , who named Lauren Buxbaum Gordon the first-ever partner of his 25-year-old eponymous design firm last year. “Lauren has worked for me for 18 years. We’ve literally grown up together,” Berkus says. “She has been a constant at the firm and helped navigate all kinds of things over the years. It felt like the right time to acknowledge that contribution and let her step into a leadership role.”
Don’t forget about personality
Flash Sale: Join AD PRO for only $20 $12 per month

“When I put someone in a leadership role, it’s because I really trust them. And I really trust Lauren’s vision and ability to help shepherd the firm forward,” Berkus says of Gordon, adding that “the ability to have hard conversations when needed” is also crucial.
Like any good relationship, working with a colleague whose personality jibes with yours and who gets you through stressful, challenging situations with poise, humor, and support will make all the difference. Gluckman emphasizes, “While you don’t need to—and probably shouldn’t—agree on everything, it is important that you and your partners have shared core beliefs, mutual respect, and bring out the best in each other.”
Berkus adds, “And you’ve also got to enjoy spending time with that person—or else what’s the point?”

By Tim Nelson

By Sophie Aliece Hollis

By Alia Akkam

MODERNISH CAFE
Saturday, august 15, 2009.
- BUSINESS PLAN ( Partners Background)

Posted by modernishcafe at 4:04:00 AM
1 comments:
TINN TENS! TIPS, HABANERO HOT SAUCE - TITADOWSKI TINN TENS! TIPS, titanium bicycle HABANERO HOT SAUCE. HABANERO HOT SAUCE. $2.99. titanium wedding ring Quantity. Add To Cart. Sold Out. Add To sunscreen with titanium dioxide List. Buy. Related Searches. power supply titanium TINN TENS. titanium trim hair cutter reviews TOSTERS.
Post a Comment
Blog Archive
- BUSINESS PLAN( Introduction)
- BUSINESS PLAN ( Company Background)
- BUSINESS PLAN ( Location)
- BUSINESS PLAN ( Organization Chart)
- BUSINESS PLAN ( ManPower Planning)
- BUSINESS PLAN ( Schedule Of Tasks and Responsibili...
- BUSINESS PLAN ( SCHEDULE OF REMUNERATION)
- ► September ( 1 )
- ► October ( 6 )
My Playlist
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
Xi Jinping tells US CEOs that China’s growth prospects remain ‘bright’

- Xi Jinping tells US CEOs that China’s growth prospects remain ‘bright’ on x (opens in a new window)
- Xi Jinping tells US CEOs that China’s growth prospects remain ‘bright’ on facebook (opens in a new window)
- Xi Jinping tells US CEOs that China’s growth prospects remain ‘bright’ on linkedin (opens in a new window)
- Xi Jinping tells US CEOs that China’s growth prospects remain ‘bright’ on whatsapp (opens in a new window)
Joe Leahy in Bo’ao, China
Simply sign up to the US-China relations myFT Digest -- delivered directly to your inbox.
China’s economy has not “peaked” and its growth prospects remain “bright”, Xi Jinping told visiting US chief executives on Wednesday as Beijing sought to revive foreign investor confidence in the world’s second-largest country.
Meeting the group of about 20 US business figures, who included Chubb’s Evan Greenberg, Blackstone’s Stephen Schwarzman and Qualcomm’s Cristiano Amon in the Great Hall of the People in Beijing, Xi insisted that Beijing remained committed to reform.
“China’s reforms will not stall, and our opening up will not stop,” he said, according to state media.
The meeting, which included a group photo, comes as concern is growing among China’s trading partners that Beijing is investing heavily in manufacturing to overcome a deep property slowdown, leading to oversupply and potential dumping in international markets.
China has set a growth target of 5 per cent this year, the same as last year’s figure and the lowest in decades, but analysts believe it will be difficult to achieve without an increase in domestic demand.
“China’s development, having overcome various difficulties and challenges, has not collapsed . . . in the past, nor will it ‘peak’ now,” Xi told the executives.
The attendees, who also included Bloomberg chair Mark Carney and FedEx’s Raj Subramaniam, were in the capital this week to attend the China Development Forum , Beijing’s flagship annual business conference.

Xi had met US business leaders in November during a dinner that was organised on the sidelines of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum in San Francisco by the US-China Business Council and the National Committee on US-China Relations. The heads of both organisations, Craig Allen and Stephen Orlins, also participated in the meeting with Xi on Wednesday. Chubb’s Greenberg is chair of the NCUSCR and a director of the US-China Business Council.
Other figures present included Hock Tan, chief executive of Broadcom, Joshua Cooper Ramo, co-chief executive of Kissinger Associates, Peng Zhao, chief executive of Citadel Securities and Bill Hornbuckle of MGM China.
European chief executives who had also gone to Beijing at the weekend for the CDF were not invited to the meeting on Wednesday. The people said this was because it was organised in response to the San Francisco event.
US-China relations have partly stabilised since Xi and US President Joe Biden held bilateral talks on the sidelines of the Apec forum.
But tensions continue to flare. The US has pledged to investigate whether imported Chinese electric vehicles constitute a security threat , while Beijing has blocked the use of Apple’s iPhone and Tesla vehicles in government offices. Beijing on Tuesday filed a World Trade Organization case against US EV subsidies.
China has sought to present a more welcoming picture to international business in recent months after foreign direct investment fell last year to its lowest level in decades.
China’s foreign minister Wang Yi met Greenberg and Orlins on Tuesday, and said bilateral tensions stemmed from the US “misperception” of China as a strategic threat.
On bilateral relations, Xi said: “Promoting the recovery of the world economy and solving international and regional hot issues all need China and the US to co-ordinate co-operation.”
He added that countries could disagree but should “seek common ground while reserving differences”.
Last week, ahead of the CDF, China announced clarifications to new data laws in a move welcomed by businesses anxious about cross-border data transfers.
“The [US] companies that are here to serve the China market or to sell into China, I think they’re a little more positive than they were, say, a year out,” said Sean Stein, chair of the American Chamber of Commerce in China. “There are still deep structural issues that are holding the economy back, but the cyclical part seems to have improved, and so where they are in the business cycle is in a better place.”
Business heads have traditionally met China’s second-ranked leader, the premier, after the CDF. That did not happen this year.
Premier Li Qiang also did not hold a briefing at the conclusion of the rubber-stamp parliament’s annual meeting this month. In the past, the press conference served as a rare opportunity for domestic and international media to question the official in charge of the world’s second-biggest economy.
But there were more bilateral meetings with ministers at the CDF and conversations were more direct compared with last year, said attendees.
Denis Depoux, global managing director at consultancy Roland Berger, said there were more foreign visitors at this year’s CDF and at the Boao Forum for Asia, another international conference that opened on Tuesday on China’s Hainan island.
“It’s more like 2019,” Depoux said. “I saw a lot more CEOs at the CDF and they were a lot more vocal.”
China’s economy is showing signs of stabilising, with industrial profits up 10.2 per cent for the January-February period from a year earlier, according to official statistics released on Wednesday, although this was partially thanks to a low base in 2023.
The chief executive of one large multinational company said the rhetoric from Beijing, including from Li, who spoke at the opening of the CDF, was more “confident” than last year.
But he said it was difficult to know whether this was an attempt to shore up investor sentiment or genuinely felt by the leadership given the structural challenges in China’s economy.
“It’s very hard to call it at the moment,” he said.
Additional reporting by Wenjie Ding in Beijing
Promoted Content
Follow the topics in this article.
- Chinese politics & policy Add to myFT
- US-China trade dispute Add to myFT
- US-China relations Add to myFT
- Chinese business & finance Add to myFT
- Xi Jinping Add to myFT
International Edition
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
‘Winners and Losers’ as $20 Fast-Food Wage Nears in California
The nation’s highest state minimum wage for fast-food workers takes effect on Monday. Owners and employees are sizing up the potential impact.

By Kurtis Lee
Reporting from Lancaster, Calif.
A decade ago, Jamie Bynum poured his life savings into a barbecue restaurant now tucked between a Thai eatery and a nutrition store in a Southern California strip mall.
As a franchise owner of a Dickey’s Barbecue Pit, Mr. Bynum is pridefully particular about the details of his establishment — the size of the hickory wood pile on display near the entrance, the positioning of paper towel rolls on each table, the careful calibration it takes to keep his restaurant staffed 10 hours a day with a small crew.
The staffing, he said, has become harder in recent years, as the state’s minimum wage has steadily increased since 2017, often rising by a dollar per year. Today, it’s $16 an hour.
But on Monday, it will jump to $20 an hour for most fast-food workers in California, propelling them to the top of what minimum-wage earners make anywhere in the country. (Only Tukwila, Wash., a small city outside Seattle, sets the bar higher, with a minimum wage of $20.29 for many employees.)
The ambitious law, which supporters hope to see replicated nationwide, has been characterized by opposing sides in stark terms. To backers, it is a step toward fair compensation for low-wage workers who faced significant risk during the pandemic. To opponents, it is a cataclysmic move that will raise food prices, lead to job losses and force some franchisees to consider closing.
“People don’t understand that when wages rise, so do the prices,” Mr. Bynum said.
Mr. Bynum has, in recent years, raised prices to try to maintain profit margins — and each time, he said, he has noticed a drop in customers. That, in turn, forced painful decisions about cutting staffing and trimming hours.
The new minimum wage will add $3,000 to $4,000 to his monthly expenses, he said, and while he hopes to keep all eight of his employees, he doesn’t know if he can make the numbers add up.
One employee, Josue Reyes, has worked at the restaurant on and off over the past decade.
He works the evening shift, often taking the bus and then riding his hybrid bike the rest of the way to the restaurant. Mr. Reyes, 35, said the consistent pay raises through the years — he now makes $16 an hour — had helped him significantly. He puts much of his paycheck toward assisting his mother pay the rent at their trailer park and tries to save where he can.
While another pay increase will help him, Mr. Reyes, who has worked in fast food for much of his life, said he feared that before long, jobs would become more competitive and harder to keep.
“There can be job losses because restaurants close,” he said on a recent weekday, dressed in jeans and a T-shirt for his shift. “No one wants that, but it seems very possible.”
The potential ripple effects of the law weighed by Mr. Bynum and Mr. Reyes at this fast-food restaurant in Lancaster, a high desert city at the northern edge of Los Angeles County, mirror conversations that will play out across the state as owners and employees — and eventually consumers — adjust to the new reality.
Championed by powerful labor organizations, including the Service Employees International Union, the law will lift pay for more than half a million California employees who work for fast-food chains with 60 or more locations nationwide. It also creates a council comprising, among others, workers, franchise owners and union representatives who will oversee future increases to the minimum wage and devise workplace standards.
In an interview, Mary Kay Henry, president of the S.E.I.U., said the law was long overdue. “We are talking about a billion-dollar industry that can and should afford this raise,” she said, noting that most workers are Black and Latino. “Raising pay improves employers’ ability to hire and retain workers.”
The potential beneficiaries include Anna Velazquez-Cruz, who has worked at a Papa Johns in the East Hollywood neighborhood of Los Angeles for a year.
Ms. Velazquez-Cruz, 19, lives with relatives in an apartment a short walk from the shop, where she makes around $18 an hour. “The internet bills, the rent, it gets higher,” she said on a recent evening.
But Matt Haller, president of the International Franchise Association, said he expected the new law to significantly harm many small businesses.
“Local restaurants will face hundreds of thousands of dollars in increased operating costs,” Mr. Haller said. “Customers will face higher food prices, and restaurant owners will have to cut costs to keep their doors open.”
Economists are divided over the merits and pitfalls.
Ismael Cid-Martinez, an economist at the Economic Policy Institute, a think tank partly funded by labor unions, said the law would help lift wages for workers in other low-paying industries in the state.
“These workers are also consumers,” he said. “Any increase in earnings for them means additional resources that they use to feed their families, bolster small businesses and strengthen their state economy.”
David Neumark, a professor of economics at the University of California, Irvine, said the impact would be more nuanced. “A higher minimum wage creates winners and losers,” he said.
The winners will be workers who keep their jobs and at most have a modest reduction in hours, he said, while the losers will be those whose hours are substantially cut or who lose their jobs — along with smaller franchise owners who were already struggling to make much of a profit.
“They make more than minimum-wage workers,” he said. “But lots of them are not high-income.”
That is the case for Mr. Bynum, whose path to franchise ownership started with a career change 10 years ago.
He and his wife, Liza, who both then worked in the information technology sector, noticed a dearth of barbecue restaurants near their home in Lancaster and used all of their $150,000 in savings to open a Dickey’s Barbecue Pit.

The chain, based in Dallas, operates more than 400 restaurants, and Mr. Bynum said he pays 9 percent in royalties to the headquarters. He has cut his staff by half over the past decade and trimmed hours. He has raised prices: A loaded baked potato cost $8 when he opened; now it’s almost $20 when ordering at the restaurant.
That’s a significant increase for his customers in Lancaster, a city 70 miles north of downtown Los Angeles where about 15 percent of residents live at or below the poverty line — and where higher pay and higher costs will both be keenly felt.
Most days in recent years, Mr. Bynum and his wife have run the restaurant with help from their two adult children.
“What started as a dream has slowly faded,” Mr. Bynum said.
Joe Marques is another owner wondering how to navigate the months ahead.
He became the owner of a Wienerschnitzel restaurant in San Jose, Calif., in the early 1990s and now has two other locations in the area. He employs around 45 people at the three stores combined. As an owner, he said, he is surviving week to week and has little money for capital improvements, such as repaving parking lots and painting.
“There is a lot of perception that we are a big corporation simply because of the name,” he said. “In reality, I am essentially an independent small-business owner.”
At current staffing levels — 60 percent of his employees work full time, the others part time — it will cost him an additional $4,500 to $5,000 a month per store to remain open, he said. Mr. Marques, 64, had wanted to permanently hand his businesses over to his son. That hope, he said, seems more and more fleeting these days.
“It’s not like we are getting rich on this,” he said. “We are trying to make a living.”
For Mr. Reyes, the longtime Dickey’s employee, his job has given a sense of stability that he worries may soon shatter.
He likes that the job is close to home, Mr. Reyes said, so someone in his family can pick him up and he can avoid taking a late-night bus. While welcoming the higher pay that the law will mandate, he expressed sympathy about the financial strain on Mr. Bynum.
“There has been a type of companionship,” he said. “He’s given me consistent work.”
What Mr. Bynum sees on the horizon concerns him. For months, he and his wife have thought about what they might do next — perhaps, he said, go back to I.T. — but he fears his options would be limited. At 51, he’s not sure who would hire him. He worries, too, about what would happen to Mr. Reyes and his other employees.
“We’re all in this as a team,” he said. “I care about my people and have given people a lot of opportunities over the years.”
And singling out the fast-food industry for a higher minimum wage, Mr. Bynum said, “all just seems targeted and like an attack.”
“I am a small-business owner at the end of the day,” he added, “just scraping along.”
Kurtis Lee is an economics correspondent based in Los Angeles who focuses on the lives and livelihoods of everyday Americans. He has written about income inequality for nearly a decade. More about Kurtis Lee

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Your management team plan has 3 goals: To prove to you that you have the right team to execute on the opportunity you have defined, and if not, to identify who you must hire to round out your current team. To convince lenders and investors (e.g., angel investors, venture capitalists) to fund your company (if needed)
The length of your business plan's structure and ownership section requires a delicate balance. While a general rule of thumb suggests that it should be about 2 to 3 paragraphs, the actual length depends on several factors, including the complexity of your corporate structure and the number of shareholders involved.
The key elements of a successful partner business plan include: 1. Vision and strategy. A clear vision and strategy should be outlined in the plan to provide guidance and inform decisions from a long-term perspective. This should include a description of the desired outcomes and the processes required to achieve them. 2.
The business background portion of a business plan is a section that traditionally follows the executive summary. It describes the inspiration behind your business and crucial details about the company itself, such as the location, size, purpose, and mission. Generally, it sets out the direction and focus of your brand, helping potential ...
Fact checked by. Hans Jasperson. In This Article. What To Include. Be Creative. Company Background Examples. Photo: Ezra Bailey/Taxi/Getty Images. Examples of what you should include in your business plan's company background to explain your history and why you're qualified.
That includes: Your company name: This should be the official name of your business, exactly as it is written when you registered your business with the state. Business structure: Your reader will ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
The plan should also be reviewed on a regular basis to ensure that it is still relevant and up to date. When creating a partner business plan, it is important to start with a clear vision. This should include an analysis of the market trends and the competitive landscape. It should also address the company's objectives, how it intends to reach ...
The summary emphasizes those factors that will make the business a success. It must contain sound numbers for market size, trends, company goals, spending, return on investment, capital expenditures, and funding required. For new businesses or businesses seeking funding, credibility and excitement are key elements of the executive summary.
Download Now: Free Business Plan Template. Writing a business plan doesn't have to be complicated. In this step-by-step guide, you'll learn how to write a business plan that's detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
A business plan should be structured in a way that it contains all the important information that investors are looking for. Here are the main sections of a business plan: 1. Title Page. The title page captures the legal information of the business, which includes the registered business name, physical address, phone number, email address, date ...
Steps For Planning a Business Partnership. Write a mission statement to clearly state the direction and goals the business plans to take. By writing a mission statement, the partners agree to the company's direction now and in the future. Develop a reimbursement plan for the costs and investments incurred during startup.
Develop Partner Bussiness Plan: Two Key Steps to Consider. 1. Know Your Partners Well. A thorough understanding of your partner network is a fundamental prerequisite for the successful development of partner business planning. Within your indirect sales ecosystem, business providers, integrators, value-added resellers (VARs), IT service ...
Create a Brief Business Plan. Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business.
2. Openness. A good business partner is direct. I often use a saying in business, with my family and with my friends, and this saying is, "No one can read your mind." You have to tell people what ...
The quick answer: Partnership Plan Templates. Every business requires a partnership plan. Small businesses seek out partnerships more to achieve their goals and objectives. Building a strategic partnership is more complicated than creating a partnership document, but it is the first step toward action. SlideTeam's partnership plan templates ...
If we actually want a business plan, it should be focused on our firm specifically.". Your business plan ideally connects these dots: (1) what the firm wants to accomplish, (2) what you want to accomplish, and (3) how coming together could help you both accomplish these mutual goals.
Once your business plan is ready, follow these steps to write a cover letter: Step 1. Create a header. The header of your business plan cover letter should include your name, the name of your business, your address, and your contact information. Next, write the date. And finally, write the name of the investor, the institution they are ...
While your background should be concise — half a page to a page at most — you should instill confidence in the reader that you are the person to run such a business. After writing your personal background, review it and eliminate any extraneous information. Invite a neutral party to review your background information as well.
Richard Gluckman, founding partner of AD100 firm Gluckman Tang Architects, advises, "Identify people within your firm who have the potential to grow into a partnership role. [Then] provide ...
BUSINESS PLAN ( Partners Background) PARTNERS BACKGROUND. Name :MOHD AZIZAN BIN MAT AKHIIR. Identity Card no : 730403-04-5141. Permanent address : B-3-9, Jln SM 1, Sunway Batu Caves, 68100, Selangor Darul Ehsan. Correspondence address : [email protected].
Partner Background In Business Plan. The narration in my narrative work needs to be smooth and appealing to the readers while writing my essay. Our writers enhance the elements in the writing as per the demand of such a narrative piece that interests the readers and urges them to read along with the entire writing. View Sample.
Henry. 1 (888)302-2675 1 (888)814-4206. Show More. Pay only for completed parts of your project without paying upfront. Sociology Category. Level: College, High School, University, Undergraduate, Master's. Research Paper.
Trump Media & Technology Group is poised to debut on Wall Street at a market value of around $5 billion — based on the $37 share price of its merger partner, Digital World Acquisition Corp.
Meeting the group of about 20 US business figures, who included Chubb's Evan Greenberg, Blackstone's Stephen Schwarzman and Qualcomm's Cristiano Amon in the Great Hall of the People in ...
The nation's highest state minimum wage for fast-food workers takes effect on Monday. Owners and employees are sizing up the potential impact. By Kurtis Lee Reporting from Lancaster, Calif. A ...