

Get step-by-step solutions to your math problems

Try Math Solver

Get step-by-step explanations
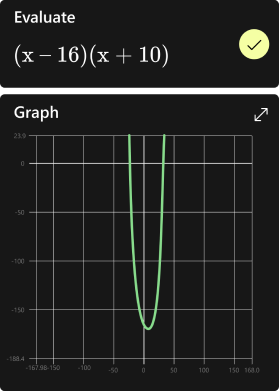
Graph your math problems
Practice, practice, practice

Get math help in your language
- Solve equations and inequalities
- Simplify expressions
- Factor polynomials
- Graph equations and inequalities
- Advanced solvers
- All solvers
- Arithmetics
- Determinant
- Percentages
- Scientific Notation
- Inequalities
What can QuickMath do?
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students.
- The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and cancelling common factors within a fraction.
- The equations section lets you solve an equation or system of equations. You can usually find the exact answer or, if necessary, a numerical answer to almost any accuracy you require.
- The inequalities section lets you solve an inequality or a system of inequalities for a single variable. You can also plot inequalities in two variables.
- The calculus section will carry out differentiation as well as definite and indefinite integration.
- The matrices section contains commands for the arithmetic manipulation of matrices.
- The graphs section contains commands for plotting equations and inequalities.
- The numbers section has a percentages command for explaining the most common types of percentage problems and a section for dealing with scientific notation.
Math Topics
More solvers.
- Add Fractions
- Simplify Fractions
Math Solver
Geogebra math solver.
Get accurate solutions and step-by-step explanations for algebra and other math problems, while enhancing your problem-solving skills!

Learn by doing
Guided interactive problem solving that’s effective and fun. master concepts in 15 minutes a day., data analysis, computer science, programming & ai, science & engineering, join over 10 million people learning on brilliant, over 50,000 5-star reviews on ios app store and google play.

Master concepts in 15 minutes a day
Whether you’re a complete beginner or ready to dive into machine learning and beyond, Brilliant makes it easy to level up fast with fun, bite-sized lessons.
Effective, hands-on learning
Visual, interactive lessons make concepts feel intuitive — so even complex ideas just click. Our real-time feedback and simple explanations make learning efficient.
Learn at your level
Students and professionals alike can hone dormant skills or learn new ones. Progress through lessons and challenges tailored to your level. Designed for ages 13 to 113.
Guided bite-sized lessons
We make it easy to stay on track, see your progress, and build your problem solving skills one concept at a time.
Stay motivated
Form a real learning habit with fun content that’s always well-paced, game-like progress tracking, and friendly reminders.
Guided courses for every journey
All of our courses are crafted by award-winning teachers, researchers, and professionals from MIT, Caltech, Duke, Microsoft, Google, and more.
- Foundational Math
- Software Development
- Foundational Logic
- Data Science
- High School Math
- Engineering
- Statistics and Finance
Courses in Foundational Math
- Solving Equations
- Measurement
- Mathematical Fundamentals
- Reasoning with Algebra
- Functions and Quadratics

10k+ Ratings

60k+ Ratings
We use cookies to improve your experience on Brilliant. Learn more about our cookie policy and settings .
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu
Khan Academy Blog
Free Math Worksheets — Over 100k free practice problems on Khan Academy
Looking for free math worksheets.
You’ve found something even better!
That’s because Khan Academy has over 100,000 free practice questions. And they’re even better than traditional math worksheets – more instantaneous, more interactive, and more fun!
Just choose your grade level or topic to get access to 100% free practice questions:
Kindergarten, basic geometry, pre-algebra, algebra basics, high school geometry.
- Trigonometry
Statistics and probability
High school statistics, ap®︎/college statistics, precalculus, differential calculus, integral calculus, ap®︎/college calculus ab, ap®︎/college calculus bc, multivariable calculus, differential equations, linear algebra.
- Addition and subtraction
- Place value (tens and hundreds)
- Addition and subtraction within 20
- Addition and subtraction within 100
- Addition and subtraction within 1000
- Measurement and data
- Counting and place value
- Measurement and geometry
- Place value
- Measurement, data, and geometry
- Add and subtract within 20
- Add and subtract within 100
- Add and subtract within 1,000
- Money and time
- Measurement
- Intro to multiplication
- 1-digit multiplication
- Addition, subtraction, and estimation
- Intro to division
- Understand fractions
- Equivalent fractions and comparing fractions
- More with multiplication and division
- Arithmetic patterns and problem solving
- Quadrilaterals
- Represent and interpret data
- Multiply by 1-digit numbers
- Multiply by 2-digit numbers
- Factors, multiples and patterns
- Add and subtract fractions
- Multiply fractions
- Understand decimals
- Plane figures
- Measuring angles
- Area and perimeter
- Units of measurement
- Decimal place value
- Add decimals
- Subtract decimals
- Multi-digit multiplication and division
- Divide fractions
- Multiply decimals
- Divide decimals
- Powers of ten
- Coordinate plane
- Algebraic thinking
- Converting units of measure
- Properties of shapes
- Ratios, rates, & percentages
- Arithmetic operations
- Negative numbers
- Properties of numbers
- Variables & expressions
- Equations & inequalities introduction
- Data and statistics
- Negative numbers: addition and subtraction
- Negative numbers: multiplication and division
- Fractions, decimals, & percentages
- Rates & proportional relationships
- Expressions, equations, & inequalities
- Numbers and operations
- Solving equations with one unknown
- Linear equations and functions
- Systems of equations
- Geometric transformations
- Data and modeling
- Volume and surface area
- Pythagorean theorem
- Transformations, congruence, and similarity
- Arithmetic properties
- Factors and multiples
- Reading and interpreting data
- Negative numbers and coordinate plane
- Ratios, rates, proportions
- Equations, expressions, and inequalities
- Exponents, radicals, and scientific notation
- Foundations
- Algebraic expressions
- Linear equations and inequalities
- Graphing lines and slope
- Expressions with exponents
- Quadratics and polynomials
- Equations and geometry
- Algebra foundations
- Solving equations & inequalities
- Working with units
- Linear equations & graphs
- Forms of linear equations
- Inequalities (systems & graphs)
- Absolute value & piecewise functions
- Exponents & radicals
- Exponential growth & decay
- Quadratics: Multiplying & factoring
- Quadratic functions & equations
- Irrational numbers
- Performing transformations
- Transformation properties and proofs
- Right triangles & trigonometry
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry (Advanced)
- Analytic geometry
- Conic sections
- Solid geometry
- Polynomial arithmetic
- Complex numbers
- Polynomial factorization
- Polynomial division
- Polynomial graphs
- Rational exponents and radicals
- Exponential models
- Transformations of functions
- Rational functions
- Trigonometric functions
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry
- Trigonometric equations and identities
- Analyzing categorical data
- Displaying and comparing quantitative data
- Summarizing quantitative data
- Modeling data distributions
- Exploring bivariate numerical data
- Study design
- Probability
- Counting, permutations, and combinations
- Random variables
- Sampling distributions
- Confidence intervals
- Significance tests (hypothesis testing)
- Two-sample inference for the difference between groups
- Inference for categorical data (chi-square tests)
- Advanced regression (inference and transforming)
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
- Scatterplots
- Data distributions
- Two-way tables
- Binomial probability
- Normal distributions
- Displaying and describing quantitative data
- Inference comparing two groups or populations
- Chi-square tests for categorical data
- More on regression
- Prepare for the 2020 AP®︎ Statistics Exam
- AP®︎ Statistics Standards mappings
- Polynomials
- Composite functions
- Probability and combinatorics
- Limits and continuity
- Derivatives: definition and basic rules
- Derivatives: chain rule and other advanced topics
- Applications of derivatives
- Analyzing functions
- Parametric equations, polar coordinates, and vector-valued functions
- Applications of integrals
- Differentiation: definition and basic derivative rules
- Differentiation: composite, implicit, and inverse functions
- Contextual applications of differentiation
- Applying derivatives to analyze functions
- Integration and accumulation of change
- Applications of integration
- AP Calculus AB solved free response questions from past exams
- AP®︎ Calculus AB Standards mappings
- Infinite sequences and series
- AP Calculus BC solved exams
- AP®︎ Calculus BC Standards mappings
- Integrals review
- Integration techniques
- Thinking about multivariable functions
- Derivatives of multivariable functions
- Applications of multivariable derivatives
- Integrating multivariable functions
- Green’s, Stokes’, and the divergence theorems
- First order differential equations
- Second order linear equations
- Laplace transform
- Vectors and spaces
- Matrix transformations
- Alternate coordinate systems (bases)
Frequently Asked Questions about Khan Academy and Math Worksheets
Why is khan academy even better than traditional math worksheets.
Khan Academy’s 100,000+ free practice questions give instant feedback, don’t need to be graded, and don’t require a printer.
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets look like?
Here’s an example:
What are teachers saying about Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets?
“My students love Khan Academy because they can immediately learn from their mistakes, unlike traditional worksheets.”
Is Khan Academy free?
Khan Academy’s practice questions are 100% free—with no ads or subscriptions.
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets cover?
Our 100,000+ practice questions cover every math topic from arithmetic to calculus, as well as ELA, Science, Social Studies, and more.
Is Khan Academy a company?
Khan Academy is a nonprofit with a mission to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere.
Want to get even more out of Khan Academy?
Then be sure to check out our teacher tools . They’ll help you assign the perfect practice for each student from our full math curriculum and track your students’ progress across the year. Plus, they’re also 100% free — with no subscriptions and no ads.
Get Khanmigo
The best way to learn and teach with AI is here. Ace the school year with our AI-powered guide, Khanmigo.
For learners For teachers For parents
Problem Solving in Mathematics
- Math Tutorials
- Pre Algebra & Algebra
- Exponential Decay
- Worksheets By Grade
The main reason for learning about math is to become a better problem solver in all aspects of life. Many problems are multistep and require some type of systematic approach. There are a couple of things you need to do when solving problems. Ask yourself exactly what type of information is being asked for: Is it one of addition, subtraction, multiplication , or division? Then determine all the information that is being given to you in the question.
Mathematician George Pólya’s book, “ How to Solve It: A New Aspect of Mathematical Method ,” written in 1957, is a great guide to have on hand. The ideas below, which provide you with general steps or strategies to solve math problems, are similar to those expressed in Pólya’s book and should help you untangle even the most complicated math problem.
Use Established Procedures
Learning how to solve problems in mathematics is knowing what to look for. Math problems often require established procedures and knowing what procedure to apply. To create procedures, you have to be familiar with the problem situation and be able to collect the appropriate information, identify a strategy or strategies, and use the strategy appropriately.
Problem-solving requires practice. When deciding on methods or procedures to use to solve problems, the first thing you will do is look for clues, which is one of the most important skills in solving problems in mathematics. If you begin to solve problems by looking for clue words, you will find that these words often indicate an operation.
Look for Clue Words
Think of yourself as a math detective. The first thing to do when you encounter a math problem is to look for clue words. This is one of the most important skills you can develop. If you begin to solve problems by looking for clue words, you will find that those words often indicate an operation.
Common clue words for addition problems:
Common clue words for subtraction problems:
- How much more
Common clue words for multiplication problems:
Common clue words for division problems:
Although clue words will vary a bit from problem to problem, you'll soon learn to recognize which words mean what in order to perform the correct operation.
Read the Problem Carefully
This, of course, means looking for clue words as outlined in the previous section. Once you’ve identified your clue words, highlight or underline them. This will let you know what kind of problem you’re dealing with. Then do the following:
- Ask yourself if you've seen a problem similar to this one. If so, what is similar about it?
- What did you need to do in that instance?
- What facts are you given about this problem?
- What facts do you still need to find out about this problem?
Develop a Plan and Review Your Work
Based on what you discovered by reading the problem carefully and identifying similar problems you’ve encountered before, you can then:
- Define your problem-solving strategy or strategies. This might mean identifying patterns, using known formulas, using sketches, and even guessing and checking.
- If your strategy doesn't work, it may lead you to an ah-ha moment and to a strategy that does work.
If it seems like you’ve solved the problem, ask yourself the following:
- Does your solution seem probable?
- Does it answer the initial question?
- Did you answer using the language in the question?
- Did you answer using the same units?
If you feel confident that the answer is “yes” to all questions, consider your problem solved.
Tips and Hints
Some key questions to consider as you approach the problem may be:
- What are the keywords in the problem?
- Do I need a data visual, such as a diagram, list, table, chart, or graph?
- Is there a formula or equation that I'll need? If so, which one?
- Will I need to use a calculator? Is there a pattern I can use or follow?
Read the problem carefully, and decide on a method to solve the problem. Once you've finished working the problem, check your work and ensure that your answer makes sense and that you've used the same terms and or units in your answer.
- 2nd Grade Math Word Problems
- The Horse Problem: A Math Challenge
- 2020-21 Common Application Essay Option 4—Solving a Problem
- How to Use Math Journals in Class
- The Frayer Model for Math
- Algorithms in Mathematics and Beyond
- "Grandpa's Rubik's Cube"—Sample Common Application Essay, Option #4
- Math Stumper: Use Two Squares to Make Separate Pens for Nine Pigs
- Critical Thinking Definition, Skills, and Examples
- College Interview Tips: "Tell Me About a Challenge You Overcame"
- Graphic Organizers in Math
- Christmas Word Problem Worksheets
- Solving Problems Involving Distance, Rate, and Time
- Innovative Ways to Teach Math
- Study Tips for Math Homework and Math Tests
- How to Do Algebra Word Problems

Game Central
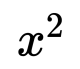
100% FREE TO USE
Usable Math
(formerly 4mality), a digital playground for math learning through problem solving and design.
Usable Math provides interactive problem solving practice for 3rd through 6th grade students learning mathematical reasoning and computation through creative writing, NoCode slideshow design, and human-AI collaboration.
- MATH MODULES

Math Friends
Featuring four coaches Estella Explainer, Chef Math Bear, How-to Hound, and Visual Vicuna who offer reading, computation, strategy, and visual strategies for solving math problems.

Estella Explainer
"I help children understand the language and meaning of questions using kid-friendly vocabulary."

Chef Math Bear
"I provide computational strategies (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) for solving problems."

How-to-Hound
" I present strategic thinking clues (rounding, estimation, elimination of wrong answers). "

Visual Vicuna
" I offer ways to see problems and their solutions using animations, pictures, charts and graphs. "
The coaches annotate hints and provide feedback to help students with various levels of knowledge solve mathematical word problems using a wide range of strategies.
Math and ISTE Standards Based
Usable Math aims to teach mathematics concepts and problem solving skills based on the Massachusetts Mathematics Curriculum Framework and the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics. Usable Math supports ISTE Standards for Students : Empowered Learner (1.1), Knowledge Constructor (1.3), and Computational Thinker (1.5).

Open Education Resource
Usable Math is an open education resource project developed in the College of Education, University of Massachusetts Amherst. Usable Math received a 2023 classroom grant from MassCUE (Massachusetts Computer Using Educators) . An initial version called 4mality was developed with funding support from the Verizon Foundation and a grant from the US Department of Education, Institute of Education (IES).
BROWSE MATH MODULES
Storywriting, history, and science modules, a jenny-the-fisher math and citizen scientist adventure, math & science, a tai-the-math historian time travel adventure, math & history, ai-enhanced, a sofia-the-forester adventure, math & storywriting, math problem-solving and design modules, area and perimeter, total problems: 6.

Total problems: 8

Multiplication and Division
Algebraic Thinking

Total problems: 7

Measurement
Total problems: 10.

Geometry: Lines and Lines of Symmetry
Geometry: Maps + Grids + Ordered Pairs

Charts & Graphs

Geometry: Figures, Shapes and Angles

Total problems: 11

Add & Take Away

Place Value
Total problems: 14.


Total problems: 9
Total problems: 5
More coming soon, welcome to usable math. in this interactive website, you will find learning modules designed to develop mathematical problem solving skills among young learners in grades 3 to 6..
Our Modules explore standards-based math concepts including Fractions, Measurement, Geometry, Decimals, Money, and more. Usable Math is free to access using a computer, smartphone, or iPad.

What do we mean by Usable Math?
The word Usable can read as follows:
U Able meaning you can do math problem solving.
Us Able meaning together all of us can do math problem solving.
Usable meaning anyone is able to learn math problem solving - with practice, effort, and support.
What are the Usable Math Learning Modules?
Each learning module in Usable Math consists of a group of math word problems related to a specific mathematical concept. The problems are based on the Massachusetts Mathematics Curriculum Framework↗ as well as Common Core Standards↗ .
Each problem within a module consists of a question, three to four possible answer choices, and problem solving ideas and strategies provided by our four coaches: Estella Explainer, Chef Math Bear, How-to-Hound, and Visual Vicuna.
How are the Modules Displayed online?
Each module has been developed using Google Slides.
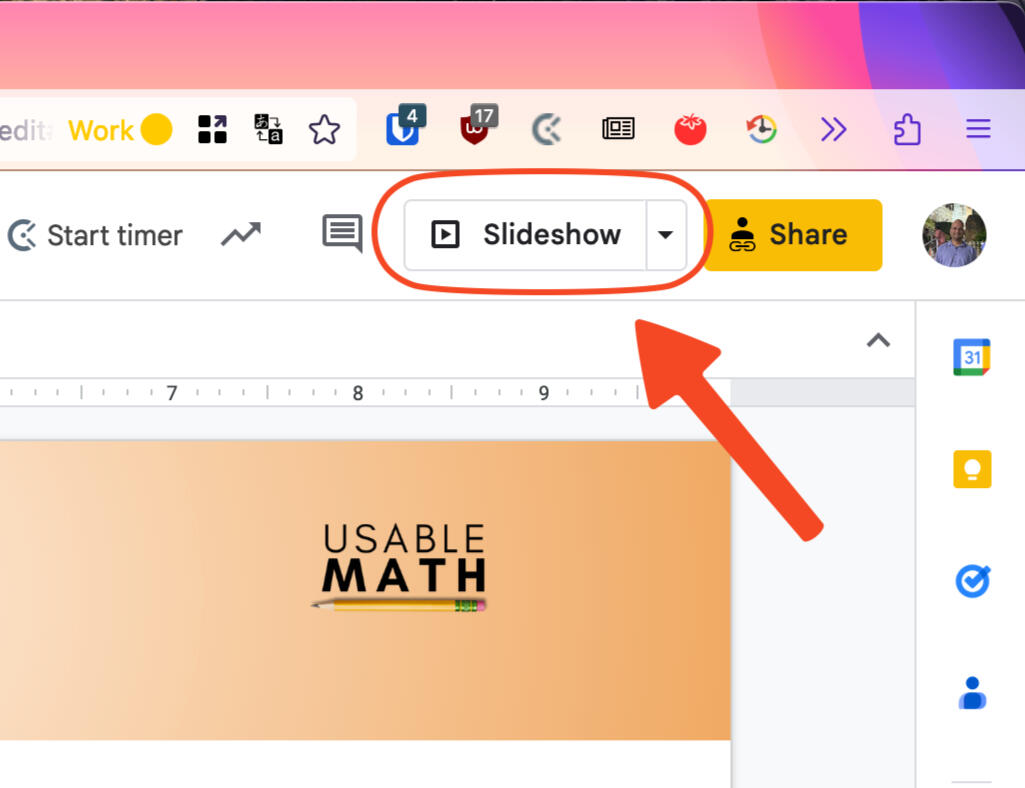
Click. Pause. Solve.
View each module in Slideshow.
How do teachers, students and families use each module?
We strive to make every module on Usable Math kid friendly . Clicking on a module from the selections on the Modules Homepage , each user controls what happens during the learning experience by clicking to open strategies and spending time thinking about them before answering the question. The goal is for students, by themselves, in small groups, or with a teacher, or a family member, to analyze and understand what the problem is asking them to solve before providing an answer.
A question appears without its answer choices or any problem solving strategies.
Click one time and Estella offers a problem solving strategy.
Click again and the Bear offers a different strategy.
Click again and the Hound presents a strategy.
Click again and the Vicuna has an additional strategy approach.
The next click gives the four answer choices, but not yet the correct answer.
The final click highlights the correct answer from among the answer choices.
Before going to the next problem, a motivational statement and gif appears offering encouragement to the users.
What is the purpose of the Motivational Statements between Problems?
Each motivational statement is intended to provide feedback and encouragement to students using the system. Following the insights of researchers into the use of praise and the development of growth mindsets in young learners, these motivational statements are designed to reward students’ effort, hard work, persistence, and belief in one’s self as a learner. We want youngsters to realize that they can learn anything with the right tools, the right beliefs, the right coaches, and their own work and practice.
Need more help? Or have a question?
Reach out to us and we will do our best to get back to you within 12 hours.
RESEARCH AND RESOURCES
We believe that every child deserves a strong foundation in mathematics. our platform is designed to provide engaging and effective math instruction to elementary school students, and we are proud to say that there is science behind the way we deliver this instruction..
UsableMath was formerly known as 4MALITY. As a result of our commitment to providing the best possible math instruction to elementary school students, we have rebranded our platform as UsableMath.com to better reflect our mission and approach to teaching mathematics.
Our platform is designed to provide engaging and effective math instruction to students in grades K-5, using a unique approach that emphasizes hands-on, problem-solving activities. We use interactive, multimedia elements such as videos, games, and simulations to help students understand key mathematical concepts and build a strong foundation of knowledge.
Math Coaches
The use of virtual coaches that provides students with personalized support and feedback, has become increasingly popular in the field of math education. Research has shown that learning companions can be effective in improving student engagement and motivation, as well as helping students to better understand mathematical concepts and build a stronger foundation of knowledge. UsableMath employs the concept of learning companions to help students succeed in mathematics. Our virtual math coaches serve as personal guides, providing students with individualized support and feedback as they work through mathematical concepts and problems. These coaches, or learning companions, are designed to be like friends or mentors, helping students to build their confidence, overcome challenges, and achieve their full potential.
How are we using Generative AI to enhance Usable Math Modules?
As developers of Usable Math, we are aware of both the educational potentials and complexities of Generative AI technologies. In our system, ChatGPT is used to support teachers and other adults to expand and enhance how math can be understood and taught in schools and homes. When you click on the AI icon, you are linked to a blog where we have recorded how AI proposes to solve selected math word problems found in Usable Math modules in a side-by-side view next to the hints we have authored from the perspectives of our four math coaches: Estella Explainer, Chef Math Bear, How-to-Hound, and Visual Vicuna. Our hope is that our strategies along with the AI-developed strategies will give adults more ways to inspire math learning among students.
Look for this icon for AI-enhanced guides.
Prompts for ChatGPT, BingAI and Other Generative AI Tools

Estella Explainer Prompt:
Take the personality of a math coach who provides strategies for understanding language and meaning of questions using kid-friendly vocabulary. The coach’s motto is "My job is to explain the math questions clearly so you know what you are supposed to do to solve the problem. Sometimes there are unfamiliar or confusing terms in the question. I will help you understand what they mean. The first math problem is {replace math word problem here}

Chef Math Bear Prompt:
Take the personality of a math coach who provides computational strategies (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) for solving problems. The coach’s motto is “I am here to make sure that you know how to do the math needed to answer these questions. Sometimes you need to do addition, subtraction, multiplication or division. Some questions ask you to use fractions, decimals, large numbers, and probability. When you need ideas for what to do, I am ready.

How-to-Hound Prompt:
Take the personality of a math coach who uses strategic thinking clues (rounding, estimation, elimination of wrong answers) to solve math problems. The coach’s motto is “Answering math questions means you need a plan and my role is to help you figure out different strategies for solving problems. Sometimes you can get the correct answer by crossing out the wrong answers; other times you can round numbers up or down to make figuring a problem easier. I know other strategies as well.

Visual Vicuna Prompt:
Take the personality of a math coach who offers ways to see problems and their solutions using animations, pictures, charts and graphs. The coach’s motto is “I find math is a lot clearer when I take the numbers and words and put them into pictures and drawings or move objects around so I can see how to answer a question. When you find yourself unsure about a question, see if one of my ideas will explain what to do.
Growth Mindset Statements
As education researchers, we understand the important role that a positive attitude and motivation play in learner success. That's why we’ve integrated the use of growth mindset and motivational cues in Usable Math. After every math challenge, students receive messages that encourage them to adopt a growth mindset, reinforcing the idea that with effort and persistence, they can improve their math skills and achieve success.

A sample motivational cue from the Fractions module.
Collaborative Problem Solving
We believe in the power of collaboration and teamwork when it comes to learning mathematics. Our platform creates a learning climate that promotes collaborative problem solving, providing students with opportunities to work together and explore mathematical concepts in a supportive and inclusive environment. Whether you are a student, teacher, or parent, we invite you to explore our platform and experience the science behind the way we deliver math instruction to elementary school students. Read more about our work on the Journal of STEM Education↗
Papers, Presentations and Blogs
UsableMath GenAI Prompts: Learn Math with Our Tailor-Made Prompts for ChatGPT, Claude, and other GenAI tools. Usable Math Blog. https://blog.usablemath.org/usablemath-genai-prompts .
Maloy, R. W. & Gattupalli, S. (2024). Prompt Literacy. EdTechnica: The Open Encyclopedia of Educational Technology . https://edtechbooks.org/encyclopedia/prompt_literacy
Gattupalli, S., & Maloy, R. W. (2024). On Human-Centered AI in Education. https://doi.org/10.7275/KXAP-FN13
Gattupalli, S., Edwards, S.A, Maloy, R. W., & Rancourt, M. (2023, October). Designing for Learning: Key Decisions for an Open Online Math Tutor for Elementary Students. Digital Experiences in Mathematics Education . https://doi.org/10.1007/s40751-023-00128-3 .
Gattupalli, S., Maloy, R.W., Edwards, S.A. & Gearty, A. (2023, August 23). Prompt Literacy for STEM Educators: Enhance Your Teaching and Learning with Generative AI. Berkshire Resources for Learning and Innovation (BRLI) Teaching with Technology Conference, Pittsfield, MA. ScholarWorks@UMass.
Blending Gardens and Geometry: Socio-cultural Approaches in Math Ed. Usable Math Blog. https://blog.usablemath.org/blending-gardens-and-geometry-socio-cultural-approaches-in-math-education .
Maloy, R. W., Gattupalli, S., & Edwards, S. A. (2023). Developing Usable Math Online Tutor for Elementary Math Learners with NoCode Tools . Scholarworks@UMass.
Gattupalli, S., Maloy, R. W., & Edwards, S. A. (2023). Prompt Literacy: A Pivotal Educational Skill in the Age of AI . Scholarworks@UMass.
Gattupalli, S., Maloy, R. W., & Edwards, S. (2023). Comparing Teacher-Written and AI-Generated Math Problem Solving Strategies for Elementary School Students: Implications for Classroom Learning . https://doi.org/10.7275/8sgx-xj08
Making Math Usable for Young Learners . Guest post on Rachelle Dené Poth's EdTech blog Learning as I go: Experiences, Reflections, Lessons Learned . January, 2023.
Math Learning Digital Choice Board (2020) . ScholarWorks, University of Massachusetts Amherst.
Maloy, R.W., Razzaq, L., & Edwards, S.A. (2014). Learning by Choosing: Fourth Graders Use of an Online Multimedia Tutoring System for Math Problem Solving . Journal of Interactive Learning Research , 25(1), 51-64.
Razzaq, L., Maloy, R. W., Edwards, S. A., Arroyo, I., & Woolf, B.P. (2011). “4MALITY: Coaching Students with Different Problem Solving Strategies Using an Online Tutoring System” (p. 359-364). In J. A. Konstan, Ricardo Conejo, Jose L, Marzo & Nuria Oliver, User Modeling, Adaptation and Personalization: 19th International Conference, UMAP 2011, Girona, Spain, July 11-15 Proceedings . Berlin: Springer Verlag.
Maloy, R.W., Edwards,S. A. & Anderson G. (2010, January-June). “Teaching Math Problem Solving Using a Web-based Tutoring System, Learning Games, and Students’ Writing .” Journal of STEM Education: Innovations and Research, 11 (1&2).
Edwards, S. A., Maloy, R.W., & Anderson G. (2010, February). “Classroom Characters Coach Students to Success.” Teaching Children Mathematics, 16 (6), 342-349.
Edwards, S. A., Maloy, R. W., & Anderson G. (2009, Summer). “Reading Coaching of Math Word Problems.” Literacy Coaching Clearinghouse . http://www.literacycoachingonline.org/briefs.html .
MEET OUR TEAM

Sharon Edwards , Ph.D.
Teacher Education & Curriculum Studies
College of Education, University of Massachusetts Amherst
Sharon (she/her) is a clinical faculty in the Department of Teacher Education and Curriculum Studies in the College of Education at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. Sharon is the big brains behind the development of Usable Math online math tutor.
Email : sae at umass dot edu

Robert Maloy , Ph.D.
Elementary Math and History
Bob (he/him) is a history and math senior lecturer in the Department of Teacher Education and Curriculum Studies in the College of Education at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. Bob is the creative math content creator and storytelling artist behind Usable Math.
Email : rwm at umass dot edu

Sai Gattupalli
Math, Science & Learning Technologies (MSLT)
Sai (he/him) is a PhD candidate at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, where he researches education technology to make STEM teaching and learning and more effective. Sai is passionate about understanding learner culture to create effective learning experiences. Email : sgattupalli at umass dot edu Website : gattupalli.com

Marguerite Rancourt
Lead Teacher, Discovery School at Four Corners
Greenfield, Massachusetts
Marguerite (she/her) teaches fourth grade at the Discovery School in addition to serving as Lead Teacher for the school. She has created and taught professional development workshop for other elementary school teachers. In 2018, she received the Pioneer Valley Excellence in Teaching Award. Students in her class have been contributing to the design of system throughout the 2022-2023 school year.

Aubrey Coyne
Math Content Designer and Reviewer
College of Education, Commonwealth Honors College, University of Massachusetts Amherst.
Aubrey Coyne (she/her) is a sophomore at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. She is a math tutor and is studying to be an elementary teacher. Aubrey is passionate about finding ways to make learning accessible and enjoyable for all students.

Graduate Student, Math and Digital Media Research Assistant
Sara Shea (she/her) is a graduate student at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. She is currently part of the university’s Collaborative Teacher Education Pathway program, working towards earning her master’s degree in elementary education.

Katie Allan
Math and Digital Media Research Assistant
Katie Allan (she/her) is a senior at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. She is a math major with a concentration in education and passionate about math education.
SUGGESTIONS AND FEEDBACK
We welcome ideas from teachers, students, and families about the usable math system..
Please complete our UsableMath Module Review and Feedback↗ form.
Your responses will help us to improve how the system works instructionally and technically. Let us know any additional thoughts about the problems, characters, hints, gifs, mindset statements and more.

Your message has been received. We will get back to you shortly. The average response time is approximately 6 hours.
Solver Title
Generating PDF...
- Pre Algebra Order of Operations Factors & Primes Fractions Long Arithmetic Decimals Exponents & Radicals Ratios & Proportions Percent Modulo Number Line Expanded Form Mean, Median & Mode
- Algebra Equations Inequalities System of Equations System of Inequalities Basic Operations Algebraic Properties Partial Fractions Polynomials Rational Expressions Sequences Power Sums Interval Notation Pi (Product) Notation Induction Logical Sets Word Problems
- Pre Calculus Equations Inequalities Scientific Calculator Scientific Notation Arithmetics Complex Numbers Polar/Cartesian Simultaneous Equations System of Inequalities Polynomials Rationales Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Coordinate Geometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Conic Sections Trigonometry
- Calculus Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series Fourier Transform
- Functions Line Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Conic Sections Transformation
- Linear Algebra Matrices Vectors
- Trigonometry Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify
- Statistics Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Average Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability Mid-Range Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal Distribution
- Physics Mechanics
- Chemistry Chemical Reactions Chemical Properties
- Finance Simple Interest Compound Interest Present Value Future Value
- Economics Point of Diminishing Return
- Conversions Roman Numerals Radical to Exponent Exponent to Radical To Fraction To Decimal To Mixed Number To Improper Fraction Radians to Degrees Degrees to Radians Hexadecimal Scientific Notation Distance Weight Time Volume
- Pre Algebra
- One-Step Addition
- One-Step Subtraction
- One-Step Multiplication
- One-Step Division
- One-Step Decimals
- Two-Step Integers
- Two-Step Add/Subtract
- Two-Step Multiply/Divide
- Two-Step Fractions
- Two-Step Decimals
- Multi-Step Integers
- Multi-Step with Parentheses
- Multi-Step Rational
- Multi-Step Fractions
- Multi-Step Decimals
- Solve by Factoring
- Completing the Square
- Quadratic Formula
- Biquadratic
- Logarithmic
- Exponential
- Rational Roots
- Floor/Ceiling
- Equation Given Roots
- Newton Raphson
- Substitution
- Elimination
- Cramer's Rule
- Gaussian Elimination
- System of Inequalities
- Perfect Squares
- Difference of Squares
- Difference of Cubes
- Sum of Cubes
- Polynomials
- Distributive Property
- FOIL method
- Perfect Cubes
- Binomial Expansion
- Negative Rule
- Product Rule
- Quotient Rule
- Expand Power Rule
- Fraction Exponent
- Exponent Rules
- Exponential Form
- Logarithmic Form
- Absolute Value
- Rational Number
- Powers of i
- Complex Form
- Partial Fractions
- Is Polynomial
- Leading Coefficient
- Leading Term
- Standard Form
- Complete the Square
- Synthetic Division
- Linear Factors
- Rationalize Denominator
- Rationalize Numerator
- Identify Type
- Convergence
- Interval Notation
- Pi (Product) Notation
- Boolean Algebra
- Truth Table
- Mutual Exclusive
- Cardinality
- Caretesian Product
- Age Problems
- Distance Problems
- Cost Problems
- Investment Problems
- Number Problems
- Percent Problems
- Addition/Subtraction
- Multiplication/Division
- Dice Problems
- Coin Problems
- Card Problems
- Pre Calculus
- Linear Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Conversions

Most Used Actions
Number line.
- \mathrm{Lauren's\:age\:is\:half\:of\:Joe's\:age.\:Emma\:is\:four\:years\:older\:than\:Joe.\:The\:sum\:of\:Lauren,\:Emma,\:and\:Joe's\:age\:is\:54.\:How\:old\:is\:Joe?}
- \mathrm{Kira\:went\:for\:a\:drive\:in\:her\:new\:car.\:She\:drove\:for\:142.5\:miles\:at\:a\:speed\:of\:57\:mph.\:For\:how\:many\:hours\:did\:she\:drive?}
- \mathrm{The\:sum\:of\:two\:numbers\:is\:249\:.\:Twice\:the\:larger\:number\:plus\:three\:times\:the\:smaller\:number\:is\:591\:.\:Find\:the\:numbers.}
- \mathrm{If\:2\:tacos\:and\:3\:drinks\:cost\:12\:and\:3\:tacos\:and\:2\:drinks\:cost\:13\:how\:much\:does\:a\:taco\:cost?}
- \mathrm{You\:deposit\:3000\:in\:an\:account\:earning\:2\%\:interest\:compounded\:monthly.\:How\:much\:will\:you\:have\:in\:the\:account\:in\:15\:years?}
- How do you solve word problems?
- To solve word problems start by reading the problem carefully and understanding what it's asking. Try underlining or highlighting key information, such as numbers and key words that indicate what operation is needed to perform. Translate the problem into mathematical expressions or equations, and use the information and equations generated to solve for the answer.
- How do you identify word problems in math?
- Word problems in math can be identified by the use of language that describes a situation or scenario. Word problems often use words and phrases which indicate that performing calculations is needed to find a solution. Additionally, word problems will often include specific information such as numbers, measurements, and units that needed to be used to solve the problem.
- Is there a calculator that can solve word problems?
- Symbolab is the best calculator for solving a wide range of word problems, including age problems, distance problems, cost problems, investments problems, number problems, and percent problems.
- What is an age problem?
- An age problem is a type of word problem in math that involves calculating the age of one or more people at a specific point in time. These problems often use phrases such as 'x years ago,' 'in y years,' or 'y years later,' which indicate that the problem is related to time and age.
word-problems-calculator
- High School Math Solutions – Systems of Equations Calculator, Elimination A system of equations is a collection of two or more equations with the same set of variables. In this blog post,...
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.

- April 13, 2024 | Earth’s Infrared Secrets: Key to Finding Life in Distant Worlds
- April 12, 2024 | Spotted Royalty: How Wild Is the Bengal Cat Genome?
- April 12, 2024 | Bath Salts Epidemic: Pentylone Use Surges by 75%, Experts Warn
- April 12, 2024 | An Unprecedented 190% Quantum Efficiency – New Material Could Drastically Increase the Efficiency of Solar Panels
- April 12, 2024 | Unlocking Tomorrow’s Water Secrets Through Sci-Fi
This Math Problem Stumped Scientists for Almost a Century – Two Mathematicians Have Finally Solved It
By University of California - San Diego April 11, 2024

Jacques Verstraete and Sam Mattheus, researchers at the University of California, San Diego, have made a significant breakthrough in Ramsey theory by solving the r(4,t) problem, a challenge that has eluded mathematicians for decades.
Mathematicians at UC San Diego have discovered the secret behind Ramsey numbers.
We’ve all been there: staring at a math test with a problem that seems impossible to solve. What if finding the solution to a problem took almost a century? For mathematicians who dabble in Ramsey theory, this is very much the case. In fact, little progress had been made in solving Ramsey problems since the 1930s.
Now, University of California San Diego researchers Jacques Verstraete and Sam Mattheus have found the answer to r(4,t), a longstanding Ramsey problem that has perplexed the math world for decades.
What was Ramsey’s problem, anyway?
In mathematical parlance, a graph is a series of points and the lines in between those points. Ramsey theory suggests that if the graph is large enough, you’re guaranteed to find some kind of order within it — either a set of points with no lines between them or a set of points with all possible lines between them (these sets are called “cliques”). This is written as r(s,t) where s are the points with lines and t are the points without lines.
To those of us who don’t deal in graph theory, the most well-known Ramsey problem, r(3,3), is sometimes called “the theorem on friends and strangers” and is explained by way of a party: in a group of six people, you will find at least three people who all know each other or three people who all don’t know each other. The answer to r(3,3) is six.
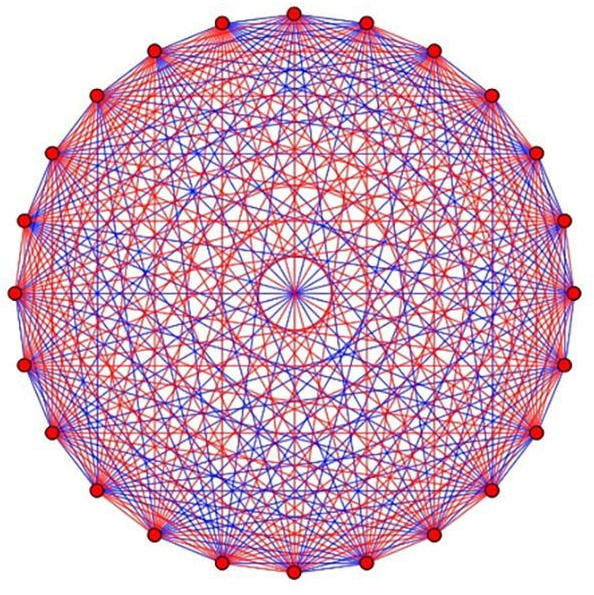
Ramsey problems, such as r(4,5) are simple to state, but as shown in this graph, the possible solutions are nearly endless, making them very difficult to solve. Credit: Jacques Verstraete
“It’s a fact of nature, an absolute truth,” Verstraete states. “It doesn’t matter what the situation is or which six people you pick — you will find three people who all know each other or three people who all don’t know each other. You may be able to find more, but you are guaranteed that there will be at least three in one clique or the other.”
What happened after mathematicians found that r(3,3) = 6? Naturally, they wanted to know r(4,4), r(5,5), and r(4,t) where the number of points that are not connected is variable. The solution to r(4,4) is 18 and is proved using a theorem created by Paul Erdös and George Szekeres in the 1930s.
Currently, r(5,5) is still unknown.
A good problem fights back
Why is something so simple to state so hard to solve? It turns out to be more complicated than it appears. Let’s say you knew the solution to r(5,5) was somewhere between 40-50. If you started with 45 points, there would be more than 10 234 graphs to consider!
“Because these numbers are so notoriously difficult to find, mathematicians look for estimations,” Verstraete explained. “This is what Sam and I have achieved in our recent work. How do we find not the exact answer, but the best estimates for what these Ramsey numbers might be?”
Math students learn about Ramsey problems early on, so r(4,t) has been on Verstraete’s radar for most of his professional career. In fact, he first saw the problem in print in Erdös on Graphs: His Legacy of Unsolved Problems, written by two UC San Diego professors, Fan Chung and the late Ron Graham. The problem is a conjecture from Erdös, who offered $250 to the first person who could solve it.
“Many people have thought about r(4,t) — it’s been an open problem for over 90 years,” Verstraete said. “But it wasn’t something that was at the forefront of my research. Everybody knows it’s hard and everyone’s tried to figure it out, so unless you have a new idea, you’re not likely to get anywhere.”
Then about four years ago, Verstraete was working on a different Ramsey problem with a mathematician at the University of Illinois-Chicago, Dhruv Mubayi. Together they discovered that pseudorandom graphs could advance the current knowledge on these old problems.
In 1937, Erdös discovered that using random graphs could give good lower bounds on Ramsey problems. What Verstraete and Mubayi discovered was that sampling from pseudo random graphs frequently gives better bounds on Ramsey numbers than random graphs. These bounds — upper and lower limits on the possible answer — tightened the range of estimations they could make. In other words, they were getting closer to the truth.
In 2019, to the delight of the math world, Verstraete and Mubayi used pseudorandom graphs to solve r(3,t). However, Verstraete struggled to build a pseudorandom graph that could help solve r(4,t).
He began pulling in different areas of math outside of combinatorics, including finite geometry, algebra, and probability. Eventually, he joined forces with Mattheus, a postdoctoral scholar in his group whose background was in finite geometry.
“It turned out that the pseudorandom graph we needed could be found in finite geometry,” Verstraete stated. “Sam was the perfect person to come along and help build what we needed.”
Once they had the pseudorandom graph in place, they still had to puzzle out several pieces of math. It took almost a year, but eventually, they realized they had a solution: r(4,t) is close to a cubic function of t . If you want a party where there will always be four people who all know each other or t people who all don’t know each other, you will need roughly t 3 people present. There is a small asterisk (actually an o) because, remember, this is an estimate, not an exact answer. But t 3 is very close to the exact answer.
The findings are currently under review with the Annals of Mathematics .
“It really did take us years to solve,” Verstraete stated. “And there were many times where we were stuck and wondered if we’d be able to solve it at all. But one should never give up, no matter how long it takes.”
Verstraete emphasizes the importance of perseverance — something he reminds his students of often. “If you find that the problem is hard and you’re stuck, that means it’s a good problem. Fan Chung said a good problem fights back. You can’t expect it just to reveal itself.”
Verstraete knows such dogged determination is well-rewarded: “I got a call from Fan saying she owes me $250.”
Reference: “The asymptotics of r(4,t)” by Sam Mattheus and Jacques Verstraete, 5 March 2024, Annals of Mathematics . DOI: 10.4007/annals.2024.199.2.8
More on SciTechDaily

Scientists Develop Stronger, Stretchier, Self-Healing Plastic

Cells May Use “Fingers” to Communicate Instructions for Wound Closure

From Big Bang to Big Picture: A Comprehensive New View of All Objects in the Universe
Modernizing planetary protection: less restrictive “bioburden” rules would make mars missions simpler.

Transparent Solar Panels for Windows Hit New Efficiency Record – Could Help Enable Skyscrapers to Serve As Power Sources

Redefining Physics: Plasma Jets With Unexpected X-Ray Emissions
Flexible Robot Designed to “Grow” Like a Plant Snakes Through Tight Spaces, Lifts Heavy Loads [Video]

NASA’s Perseverance Rover Discovers Possible Organic Compounds in Mars Crater Rocks
Be the first to comment on "this math problem stumped scientists for almost a century – two mathematicians have finally solved it", leave a comment cancel reply.
Email address is optional. If provided, your email will not be published or shared.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&

- edWebinar Calendar
- edWebinar Recordings
- AI in Education
- Power of Purposeful Reading Practice Week 2024
- Elementary Writing Week 2024
- Science of Reading Week 2024
- Structured Literacy and Language Diversity Week
- Emergent Bilingual Week
- Mental Health & Wellness Week
- Earn Free CE Certificates
- edWeb K-12 State Approvals
- Early Childhood Approvals
- Professional Association Approvals
- Communities
- Create a PLC on edWeb for Your Teachers and Staff
- Best Practices Guide & Framework
- Case Studies: Virtual Professional Learning
- School District Members
- edWeb 2024 Professional Learning Survey
- About edWeb
- Advisory Board
- Press Releases
- Awards & Recognition
- Partners and Sponsors
- Testimonials
- Sponsorship Opportunities
- edWeb Tutorials
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Accessibility Information
- Member Login
News & Views from edWeb

Solving Math Problems and Negative Feelings About Math

Watch the Recording Listen to the Podcast
As students progress through the upper elementary grades and into middle school, many are becoming caught in a negative feedback loop, with their limited understanding of math facts and underlying concepts resulting in poor grades and a lack of engagement, making successful math learning even less likely to occur.
Ways to teach math effectively and engage students in math learning were discussed during the edLeader Panel “ Differentiate Elementary Math Instruction to Increase Engagement and Flexibility: Build Your Toolbox .”
Alexa Poulin, Customer Marketing Manager at Unruly Studios and panel moderator, shared poll results about key challenges educators face when teaching math, and the data showed more than half of the educators found their students did not have the number sense and foundational knowledge needed for high-level thinking about math. Many educators also felt that math classes were not engaging and that many students were performing at levels that were multiple grades below their state standards.
Developing Math Knowledge and Positive Attitudes
The panelists agreed that students struggling with math need a fundamental understanding of how numbers work and relate to each other. Building a solid foundation of knowledge about base 10 and place value is crucial, as students can then apply that knowledge when solving math problems and thereby gain confidence and further engage in math learning.
Emma Simmons, Principal of Roxbury Prep Charter School (MA), discussed the importance of developing a culture of confidence and error acceptance in math classes so that a fear of failure does not lead to a lack of engagement and learning. This can be accomplished by encouraging discussions about how errors were found and what can be done to correct them. This way, errors are perceived as a routine part of the learning process, and any gaps in students’ understanding can be identified and remedied.
Another key part of the process is showing students that there is often more than one way to solve a math problem, and encouraging a willingness to try different approaches even if the students are not sure their answers will be correct. Students also need to be taught to “think holistically” about math problems, by considering what the problem is asking, what needs to be solved, and which steps need to be taken to arrive at a correct answer.
Strategies to Increase Learning and Engagement
To engage students in learning and flexible thinking, Elijah Ortiz, Fifth-Grade Educator and Teacher Leader at Concourse Village Elementary School (NY), explained three different strategies, all of which use a three-part approach. A “3-act task” can start with a brief video that students then discuss, after which additional information and a question are presented and prompt students to discuss how they should proceed and why. The third part of the process is revealing the answer and exploring different ways the answer can be found.
A “3-read protocol” is an approach to word problems that starts with reading a word problem like a story in order to determine what is happening and improve students’ comprehension of the problem. The second step is a choral reading that is followed by consideration of potential problem-solving strategies. The third step is another choral reading that includes the ending question to ensure understanding of the content.
The third approach is known as a “CRA frame,” in which students progress from a Concrete experience to a Representational one and then an Abstract one. This can start with the use of manipulatives, then proceed to students doing a drawing, and finally to the students performing a written math function or solving an equation.
Emily Semrad, Elementary Educator at Academy Adventures Midtown Charter School (AZ), pointed out that math vocabulary can be a crucial obstacle for students, creating confusion when the students encounter and try to differentiate between words such as “numerator” and “denominator.” To develop math vocabulary, she recommends starting with a brief video that students can just listen to and watch. Next, there can be a class discussion about what they saw and heard, including any familiar or unfamiliar terms. Students can then be encouraged to define key terms, write notes about them, and discuss them in relation to the math processes they are learning.
Semrad also has found that teamwork and competition can be effective ways to engage students in math learning and practice. One technique is a “relay race” in which students are divided into groups, and each member of a group is responsible for performing one part of a math function or providing one part of a solution to a word problem. There can also be a competition to see which group can come up with the most ways to solve a problem, thereby reinforcing the creative thinking that can lead to math solutions.
Through these and other techniques, educators can engage students in continuing to increase their knowledge and conceptual understanding of math, as well as becoming more engaged in the learning process.
Learn more about this edWeb broadcast, Differentiate Elementary Math Instruction to Increase Engagement and Flexibility: Build Your Toolbox , sponsored by Unruly Studios
Join the Community
Building Understanding in Mathematics is a free professional learning community that provides a platform, advice and support in helping educators learn methods that help students build understanding in mathematics.

Unruly Studios combines high-quality STEM learning with active recess-style play for K-8 schools and districts. Our award-winning Unruly Splats platform introduces students to computer science through the creation of physically active games in our block-based coding app. Unruly Math is a supplemental K-5 math program that reinforces foundational math skills through active, experiential group play using the Unruly Splats platform. Unruly Math infuses kinesthetic learning and peer-to-peer collaboration into your school’s existing math curriculum with a scope and sequence of 80 standards-aligned activities. The Unruly Splats platform can be utilized for various subject areas from STEAM, to math, to ELA, making it the perfect tool to create engaging summer programs for students and teachers. Splats are made to be stomped on and are iPad and Chromebook compatible.

Article by Robert Low , based on this edLeader Panel
Related Posts
Comments are closed.
Upcoming edWebinars
Redefining pd: strategies that amplify math & literacy achievement, early warning systems and mtss: how to flag and prevent student failure, building foundational reading skills through application and continual review, closing the reading gap for el learners: your multilingual learners are here, empowering wellness through music: explore teachrock’s harmony student wellness program.
Solve Math Problems 4+
Geometry solver pic answer, hhh technologies llc, ipad용으로 디자인됨.
- 4.9 • 13개의 평가
Introducing "AI Math Solver" - your ultimate academic sidekick! Say goodbye to math headaches and hello to instant solutions at your fingertips. Why Choose AI Math Solver? - Instant Math Magic: Snap a pic of any math problem, and watch our AI work its magic with lightning-fast solutions! - All-Subject AI Chat: Stuck on science or tangled up in literature? No worries! Our AI chat is here to give you personalized guidance whenever you need it. - Learning, Simplified: We're not just about answers; we're all about making complex concepts easy to understand! - Super Easy to Use: Our app is designed to be super intuitive and fun for learners of all ages! Key Features: - Snap & Solve: Snap a pic of any problem, and our AI will crack it in seconds! - Live Chat Help: Get instant explanations and study tips through interactive chat! - Covers Everything: From math mysteries to literary puzzles, we've got every subject covered! Your Ultimate Study Buddy: - Always Improving: We're constantly updating with the latest AI advancements and feedback from users like you! - Perfect for Everyone: Whether you're a student, teacher, or just curious, our app is tailor-made for all learners! Don't let homework stress you out any longer. With "AI Math Solver" by your side, acing assignments has never been easier! Download now and unleash your academic superpowers! Privacy Policy: https://www.hhhtechnologies.com/privacy-policy Terms of Use: https://www.hhhtechnologies.com/terms-and-conditions
This update fixes bugs and makes your experience smoother and faster.
앱이 수집하는 개인정보
HHH Technologies LLC 개발자가 아래 설명된 데이터 처리 방식이 앱의 개인정보 처리방침에 포함되어 있을 수 있다고 표시했습니다. 자세한 내용은 개발자의 개인정보 처리방침 을 참조하십시오.
데이터가 수집되지 않음
개발자가 이 앱에서 데이터를 수집하지 않습니다.
개인정보 처리방침은 사용하는 기능이나 사용자의 나이 등에 따라 달라질 수 있습니다. 더 알아보기
- Lifetime Access ₩0
- Weekly Access ₩9,900
- Yearly Access ₩55,000
이 개발자의 앱 더 보기
QR Scanner & Generator Pro
좋아할 만한 다른 항목
Pi - Math AI Solver
Edu AI - AI Homework Helper
AI Math Solver Homework Help
Math Solver: Homework AI Tutor
The Math Solver App: AI Helper
Solver.AI - Homework Helper

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Solve math problems with step-by-step explanations, graphs, and videos. Type a math problem or use the sketch, calculator, or matrix features to get instant feedback and learn from your mistakes.
Quickmath Solvers is a web-based tool that helps you solve various types of math problems, such as equations, inequalities, systems, fractions, matrices and graphs. You can enter your problem and get detailed explanations, steps and graphs for free.
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations.
Symbolab helps you solve math problems with detailed steps and explanations. You can also practice math skills, graph functions, and explore calculators for various topics.
To solve math problems step-by-step start by reading the problem carefully and understand what you are being asked to find. Next, identify the relevant information, define the variables, and plan a strategy for solving the problem. Show more; en. Related Symbolab blog posts.
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with step-by-step solutions. Our math solver supports basic math, pre-algebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more.
Download our apps here: English / English (United States) Get accurate solutions and step-by-step explanations for algebra and other math problems with the free GeoGebra Math Solver. Enhance your problem-solving skills while learning how to solve equations on your own. Try it now!
Cymath | Math Problem Solver with Steps | Math Solving App ... \\"Solve
Brilliant - Build quantitative skills in math, science, and computer science with hands-on, interactive lessons.
Art of Problem Solving offers two other multifaceted programs. Beast Academy is our comic-based online math curriculum for students ages 6-13. And AoPS Academy brings our methodology to students grades 2-12 through small, in-person classes at local campuses. Through our three programs, AoPS offers the most comprehensive honors math pathway ...
Module 6: Problem solving with the coordinate plane: 5th grade (Eureka Math/EngageNY) 6th grade (Eureka Math/EngageNY) Learn sixth grade math aligned to the Eureka Math/EngageNY curriculum—ratios, exponents, long division, negative numbers, geometry, statistics, and more.
Algebra (all content) 20 units · 412 skills. Unit 1 Introduction to algebra. Unit 2 Solving basic equations & inequalities (one variable, linear) Unit 3 Linear equations, functions, & graphs. Unit 4 Sequences. Unit 5 System of equations. Unit 6 Two-variable inequalities. Unit 7 Functions. Unit 8 Absolute value equations, functions, & inequalities.
The Algebra 1 course, often taught in the 9th grade, covers Linear equations, inequalities, functions, and graphs; Systems of equations and inequalities; Extension of the concept of a function; Exponential models; and Quadratic equations, functions, and graphs. Khan Academy's Algebra 1 course is built to deliver a comprehensive, illuminating, engaging, and Common Core aligned experience!
Understand the how and why See how to tackle your equations and why to use a particular method to solve it — making it easier for you to learn.; Learn from detailed step-by-step explanations Get walked through each step of the solution to know exactly what path gets you to the right answer.; Dig deeper into specific steps Our solver does what a calculator won't: breaking down key steps ...
Algebra Calculator - get free step-by-step solutions for your algebra math problems
Khan Academy offers over 100,000 free practice questions for various math topics and grade levels. You can choose your topic and grade level to access interactive and fun worksheets that help you improve your math skills.
Mathematician George Pólya's book, "How to Solve It: A New Aspect of Mathematical Method," written in 1957, is a great guide to have on hand.The ideas below, which provide you with general steps or strategies to solve math problems, are similar to those expressed in Pólya's book and should help you untangle even the most complicated math problem.
Algebra. Combine Like Terms Solve for a Variable Factor Expand Evaluate Fractions Linear Equations Quadratic Equations Inequalities Systems of Equations Matrices. Learn about algebra using our free math solver with step-by-step solutions.
A digital playground for math learning through problem solving and design. Usable Math provides interactive problem solving practice for 3rd through 6th grade students learning mathematical reasoning and computation through creative writing, NoCode slideshow design, and human-AI collaboration. MATH MODULES.
Free, online math games and more at MathPlayground.com! Problem solving, logic games and number puzzles kids love to play.
MathGPT can solve word problems, write explanations, and provide quick responses. Drag & drop an image file here, or click to select an image. MathGPT is an AI-powered math problem solver, integral calculator, derivative cacluator, polynomial calculator, and more! Try it out now and solve your math homework!
An age problem is a type of word problem in math that involves calculating the age of one or more people at a specific point in time. These problems often use phrases such as 'x years ago,' 'in y years,' or 'y years later,' which indicate that the problem is related to time and age.
In 2019, to the delight of the math world, Verstraete and Mubayi used pseudorandom graphs to solve r(3,t). However, Verstraete struggled to build a pseudorandom graph that could help solve r(4,t). He began pulling in different areas of math outside of combinatorics, including finite geometry, algebra, and probability.
Free math problem solver answers your calculus homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. get Go. Calculus. Basic Math. Pre-Algebra. Algebra. Trigonometry. Precalculus.
Solving Math Problems and Negative Feelings About Math. April 12, 2024. Watch the Recording Listen to the Podcast. As students progress through the upper elementary grades and into middle school, many are becoming caught in a negative feedback loop, with their limited understanding of math facts and underlying concepts resulting in poor grades ...
Key Features: - Snap & Solve: Snap a pic of any problem, and our AI will crack it in seconds! - Live Chat Help: Get instant explanations and study tips through interactive chat! - Covers Everything: From math mysteries to literary puzzles, we've got every subject covered! Your Ultimate Study Buddy: - Always Improving: We're constantly updating ...