Argumentative Essay Guide
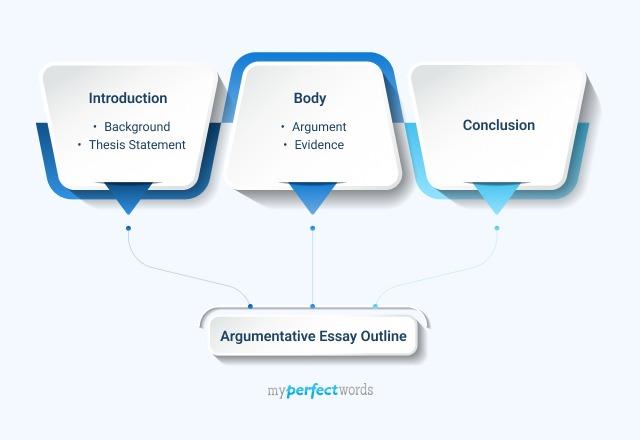
Argumentative Essay Outline

Argumentative Essay Outline: How to Structure Your Argumentative Essay
11 min read
People also read
The Ultimate Guide to Argumentative Essay Writing
250+ Argumentative Essay Topic Ideas To Help You Out
Argumentative Essay Examples: Samples & Tips
Learn the 3 Different Types of Argument and Multiple Argument Claims
Preparing to write an argumentative essay but don’t know where to start?
Making an outline is an important step in prewriting. Having a defined outline makes the essay writing process much simpler. It helps you logically present your ideas and saves you from getting stuck with writer’s block.
In this blog, we are going to teach you about how to write an outline for your essay. You’ll also get examples and templates to help you out.
So continue reading!
- 1. How To Write An Argumentative Essay Outline?
- 2. Types of Arguments and Argumentative Essay Outlines
- 3. Argumentative Essay Outline Examples
How To Write An Argumentative Essay Outline?
A simple argumentative essay outline follows the same structure as any other type of essay. The difference lies in the content of the body paragraphs. Unlike a persuasive essay, where the focus is on convincing the reader through emotional appeals, the argumentative essay presents the argument.
Some paragraphs introduce your own argument, while others state the opposing arguments and their refutations.
Here is an argumentative essay outline template you could follow for writing your essay:
The most common structure to craft an argumentative essay is as follows:
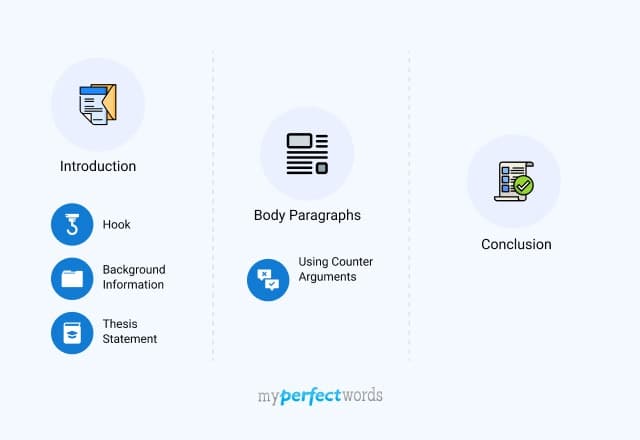
1. Argumentative Essay Introduction
The introductory paragraph introduces the main argument and provides a brief background of the argumentative essay topic you chose. Essay introductions act as a roadmap for the entire essay. For an argumentative essay, this is where you lay the foundation for your argument. An introduction comprises the following essential components:
- Hook Statement
A hook statement is written to grab the attention of your reader immediately. It should intrigue the reader and make them read the complete essay. For example, if you are writing an argumentative essay on animal testing, your hook statement could be:
- Background Information
Provide brief background information about your argument and the main claim of your essay. It will make it easier for the reader to understand the argument you will make in your essay. For example:
- Thesis Statement
An argumentative essay thesis statement should highlight your perspective, stance, and reason for your position. A thesis statement must be clearly defined, arguable, and defendable. It should express the importance of your argument and a reason why the reader should read your essay. For Example:
In case you're looking for some inspiration for your topic, check out our argumentative essay topics blog!
2. Argumentative Essay Supporting Paragraphs
In the body paragraph, you present your point of view and provide evidence that supports your argument. The goal here is to explain how valid your claim is by providing evidence that strengthens your argument.
For Example:
Here are four basic things that a body paragraph should state.
a. The purpose: Why are you making an argument about a particular issue?
b. Topic sentence: This is a fact or an example that helps the reader better understand your argument. The topic sentence of a paragraph should focus on just one point.
c. Provide evidence: State facts with examples and statistics that support your thesis statement and the topic sentence. Make sure that you have collected authentic evidence from credible sources.
d. Concluding sentence: The concluding sentence should reassert how the topic sentence helps the reader better understand the claim.
3. Argumentative Essay Counter Arguments Paragraph
The counter-argument is the other side of the issue that you will prove wrong by stating the specific reasons. In this paragraph, you mention the opposing views that the reader might pose against your argument and refute them. Conclude this paragraph by reasserting the thought provoking central idea of your essay.
4. Argumentative Essay Conclusion
A good argumentative essay conclusion summarizes the entire discussion of the essay and provides a call to action. It holds the same significance as the introduction paragraph. Here, you restate your thesis statement to remind the reader of your essay’s overall argument. Tell the reader that you have critically analyzed both sides of the argument. And based on the evidence, you have proved your side of the argument right. Explain the importance of your argument and bring your discussion to a logical end. You can propose a solution if your claim has specified a problem or make future predictions about the claim. Tell your reader the consequences if your argument is not believed and what good will happen if it's believed.
Here is an example:
Use the following argumentative essay outline graphic organizer to structure your essay efficiently.
Argumentative Essay Outline Graphic Organizer
Here’s a video demonstrating how you can prepare an argumentative essay outline:

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Types of Arguments and Argumentative Essay Outlines
Your argumentative essay structure is affected by the type of argument you are using. There are three argumentative writing models: Classical, Rogerian, and Toulmin.
Let's take a look at each one:
Classical Argument
The classical argument is the oldest and most used argument model. It is based on the principles of rhetoric, which is the art of persuasion. This type of argument has a clear structure with distinct steps, making it an ideal choice for an essay or paper.
Here is the classical argumentative writing structure.
Classical Argumentative Essay Outline Template
Rogerian argument.
The Rogerian model allows both sides of an issue to be discussed to reach a common ground.
Unlike the classical approach, the Rogerian argument seeks to understand both sides of an issue before moving forward. This style of argumentation does not look for a single ‘right’ answer but seeks to create a dialogue between all parties.
Rhetorical Rogerian Argumentative Essay Outline Template
Toulmin argument.
The Toulmin argument is a model that breaks down an issue into its component parts to analyze it more thoroughly. The Toulmin argument is composed of six parts: a claim, grounds, warrant, backing, qualifier, and rebuttal.
The first part lays out the main point being argued (the “claim”) . This is followed by the evidence that supports it (the “grounds”) . It is then connected to an underlying assumption or principle (the “warrant”) .
The warrant is then supported by additional evidence (the “backing”) , which may be followed by qualifications (the “qualifier”) . Finally, the argument may anticipate and address possible counterarguments (the “rebuttal”) .
Toulmin Argumentative Essay Outline Template
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Argumentative Essay Outline Examples
Argumentative Essay Outline Example PDF
Argumentative Essay Outline Worksheet
5 Paragraph Argumentative Essay Outline
MLA Argumentative Essay Outline
Conclusion Argumentative Essay Outline
Argumentative Essay Outline AP Lang
Vaccine Argumentative Essay Outline
Social Media Argumentative Essay Outline
Abortion Argumentative Essay Outline
Gun Control Argumentative Essay Outline
Need more sample essays to get a better idea? Give our argumentative essay examples a read!
The Bottom Line! We've covered all the essential elements of structuring your argumentative essay. With this guide, you're now well-prepared to craft a compelling essay that effectively presents your viewpoint and supports your argument with evidence.
Remember the key components: the introduction that hooks your reader, a clear thesis statement, well-organized body paragraphs, counterarguments, and a strong conclusion. Don't forget to cite your sources properly to give credibility to your work.
If you are unable to craft a perfect outline, you can always seek the help of an expert and professional essay writer at MyPerfectWords.com.
Our affordable argumentative essay writing service can help you write a top-notch argumentative paper. Our skilled writers conduct research to find facts and evidence to support your claim and write an original essay according to your needs.
So buy custom essay online from our expertts today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
- Library Catalogue
Templates for structuring argumentative essays with practice exercises and solutions
On this page, thesis statement, referring to others’ work.
- Using impersonal language
Agreeing with what you’ve reviewed in the “They say” section
Disagreeing with what you’ve reviewed in the “they say” section.
- Agreeing and disagreeing simultaneously
My critics say
This page introduces a framework for writing argumentative/analytical essays, following a structure dubbed “They Say, I Say, My Critics Say, I Respond.” [1]
This page also includes a number of templates [2] or examples that you may find helpful for writing argumentative/analytical essays. Keep in mind that it is possible to change the sequence of the framework sections. Also, the templates can be used interchangeably.
A principal element of an argumentative/analytical essay is the thesis statement.
A thesis statement is one or two sentences (maybe more in longer essays) typically occurring near the end of an essay introduction; it shows your position regarding the topic you are investigating or your answer(s) to the question(s) that you are responding to.
Here are some templates that may help you write an effective thesis statement:
- In this paper, I argue that .......... because ..........
- In the pages that follow, I will argue that .......... because ..........
- Although/Even though .......... this essay argues that/I will argue that .......... because ..........
- This paper attempts to show that ..........
- This paper contests the claim that ..........
- This paper argues that ..........
- The central thesis of this paper is ..........
- In this essay, I attempt to defend the view that ..........
Thesis statement exercise and solutions
Imagine that you have been asked to write an argumentative essay about physical education in the Canadian high school system. Use one of the templates suggested to write a thesis statement about this topic.
- In the pages that follow, I will argue that physical education in the Canadian high school system has been largely ineffective because it has remained limited in its range of exercises and has failed to connect with students’ actual interests, such a dance and martial arts.
- This paper attempts to show that physical education is a crucial aspect of the Canadian high school system because many teenagers do not experience encouragement to do physical activity outside of school and contemporary life is increasingly sedentary for people of all ages.
The body of an essay usually begins by providing a background of the topic or a summary of the resources that you have reviewed (this is sometimes called a literature review). Here, you bring other people’s views into the paper. You want to show your readers what other scholars say (“they say”) about the topic, using techniques like paraphrasing, summarizing, and direct quotation.
You can start this section using one the following templates or examples to delve into the topic.
They say exercise and solutions
Imagine that you are now trying to incorporate some sources into your academic paper about physical education in the Canadian high school system. Try using a couple of templates from the “They Say” section of the handout.
Bonus exercise: See if you can identify the “template” structure that each of the sentences below is using (hint, they are different from the templates provided above).
- Brown (2018) rejects the idea that the levels of climate change we are currently seeing can be considered “natural” or “cyclical” (p. 108).
- According to Marshall (2017), we can see evidence of both code-switching and code-meshing in students’ reflective essay writing (p. 88).
- Previous studies of physical education have revealed that teenagers experience a significant degree of dissatisfaction with their gym classes (Wilson, 2010; Vowel et al, 1999; Mossman, 1986).
- A number of studies conducted prior to the 1990s have demonstrated that teenagers used to experience more encouragement to engage in physical activities outside of school hours (Sohal, 1954; Silverman, 1965; Lu, 1970; Mossman, 1986).
- Jones’ (2017) investigations of sedentariness among young people have shown significant increases in illness among teenagers who do not engage in regular physical activity.
After the background section (e.g., summary or literature review), you need to include your own position on the topic (“I say”). Tell your reader if, for instance, you agree, disagree, or even both agree and disagree with the work you have reviewed.
You can use one of the following templates or samples to bring your voice in:
- It could be argued that ..........
- It is evident/clear/obvious that the role of modern arts is ..........
- Clearly/Evidently, the role of education is ..........
- There is no little doubt that ..........
- I agree (that) ..........
- I support the view that ...........
- I concur with the view that ..........
- I disagree (that) ..........
- I disagree with the view that ..........
- I challenge/contest the view that ..........
- I oppose/am opposed to ..........
- I disagree with X’s view that .......... because, as recent research has shown, ..........
- X contradicts herself/can’t have it both ways. On the one hand, she argues ........... On the other hand, she also says ..........
- By focusing on .........., X overlooks the deeper problem of ..........
- Although I agree with X up to a point, I cannot accept his overriding assumption that ..........
- Although I disagree with much that X says, I fully endorse his final conclusion that ..........
- Though I concede that .........., I still insist that ..........
- X is right that .........., but she seems on more dubious ground that when she claims that ..........
- While X is probably wrong when she claims tha ..........., she is right that ..........
- Whereas X provides ample evidence that .........., Y and Z’s research on .......... and .......... convinces me that .......... instead.
- I’m of two minds about X’s claim that ........... On the one hand, I agree that .......... On the other hand, I’m not sure if ..........
- My feelings on the issue are mixed. I do support X’s position that .........., but I find Y’s argument about .......... and Z’s research on .......... to be equally persuasive.
I say exercises and solutions
Try using a template from each of the sections below to bring your own position into your writing:
- Agreeing with what you’ve reviewed
- Disagreeing with that you’ve reviewed
Using impersonal language There is little doubt that the teenage years are important for establishing life-long habits.
Agreeing with what you’ve reviewed in the “They say” section I support the view, presented by Vowel et al (1999) that effective physical education needs to consider the heightened self-consciousness that many teenagers experience and, in particular, needs to be sensitive to the body image issues that can be pervasive among young people.
Disagreeing with what you’ve reviewed in the “They say” section By focusing on school physical education programs and their shortcomings, Wilson (2010) overlooks the deeper problem that young people are experiencing a lack of motivation to incorporate healthy exercise into their daily lives.
Agreeing and Disagreeing simultaneously Though I concede that school physical education programs are valuable, I still insist that they cannot be the sole or even the primary way that we promote an active lifestyle among young people.
In a good argumentative essay, in addition to expressing your position and argument, you should consider possible opposing views to your argument: refer to what your opponents say (“my critics say”) and why they may disagree with your argument.
Including the ideas of those who may disagree with you makes up the counterargument section of your paper. You can refer to actual people, including other research scholars who may disagree with you, or try and imagine what those who disagree with you might say.
Remember, a thesis should be debatable, so you should be able to imagine someone disagreeing you’re your position. Here are some templates that may help you in writing counterargument:
My critics say exercise and solutions
Using one of the templates, try imagining a counterargument for the thesis you drafted earlier.
Sociocultural theorists used to believe that adolescence was a time of “natural defiance” (Fung, 1995) and therefore discounted the role of educational programs aimed at supporting teenagers to form healthy habits. Much of the focus of schooling therefore became about teaching specific content and skills.
Critics may call into question my assumption that effective physical education can help establish life-long healthy living habits.
After explaining what your opponents say, you have to refute them. This is sometimes called the rebuttal. Here, you can show your readers that your opponents either fail to provide enough evidence to support their argument or their evidence lacks credibility and/or is flawed.
Alternatively, you may argue that your opponents’ argument is valid, but not persuasive enough to be used in your study, or that their argument could be valid in a different context.
Don’t forget that for each part of your argument, you must provide enough evidence for the claims that you make. This means that if you include one of these templates in your essays, you have to explain the evidence it presents in a way that is clear and convincing for your reader.
I respond exercise and solutions
Using one of the templates, craft a rebuttal to the counterargument you just created.
Sociocultural theorists used to believe that adolescence was a time of “natural defiance” (Fung, 1995) and therefore discounted the role of educational programs aimed at supporting teenagers to form healthy habits. Much of the focus of schooling therefore became about teaching specific content and skills. However, this argument fails to demonstrate that the defiance observed during adolescence was “natural” or inherent and not a product of a specific cultural environment. It therefore does not convince me that education during the adolescent years needs to remain rigidly focused on content and skills.
Critics may call into question my assumption that effective physical education can help establish life-long healthy living habits. While it is true that we cannot assume that physical education will automatically lead to the establishment of healthy habits, I maintain that the creation of such habits, rather than simply teaching specific physical education content or skills, should be the central goal of an effective physical education program.
Graff, G., & Birkenstein, C. (2017). They say / I say: The moves that matter in academic writing, with readings (3rd ed.). New York: Norton W. W. Company.
Marshall, S. (2017). Advance in academic writing: Integrating research, critical thinking, academic reading and writing. Toronto, Canada: Pearson Education ESL.
Morley, J. (2014). Academic phrasebank. Retrieved from http://www.phrasebank.manchester.ac.uk/
[1] Adapted from Graff and Birkenstein (2016).
[2] The templates used in this handout are adapted from Morley (2014), Marshall (2017), and Graff and Birkenstein (2016).
Argumentative Essay Examples to Inspire You (+ Free Formula)
.webp)
Table of contents

Meredith Sell
Have you ever been asked to explain your opinion on a controversial issue?
- Maybe your family got into a discussion about chemical pesticides
- Someone at work argues against investing resources into your project
- Your partner thinks intermittent fasting is the best way to lose weight and you disagree
Proving your point in an argumentative essay can be challenging, unless you are using a proven formula.
Argumentative essay formula & example
In the image below, you can see a recommended structure for argumentative essays. It starts with the topic sentence, which establishes the main idea of the essay. Next, this hypothesis is developed in the development stage. Then, the rebuttal, or the refutal of the main counter argument or arguments. Then, again, development of the rebuttal. This is followed by an example, and ends with a summary. This is a very basic structure, but it gives you a bird-eye-view of how a proper argumentative essay can be built.

Writing an argumentative essay (for a class, a news outlet, or just for fun) can help you improve your understanding of an issue and sharpen your thinking on the matter. Using researched facts and data, you can explain why you or others think the way you do, even while other reasonable people disagree.
Free AI argumentative essay generator > Free AI argumentative essay generator >
What Is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is an explanatory essay that takes a side.
Instead of appealing to emotion and personal experience to change the reader’s mind, an argumentative essay uses logic and well-researched factual information to explain why the thesis in question is the most reasonable opinion on the matter.
Over several paragraphs or pages, the author systematically walks through:
- The opposition (and supporting evidence)
- The chosen thesis (and its supporting evidence)
At the end, the author leaves the decision up to the reader, trusting that the case they’ve made will do the work of changing the reader’s mind. Even if the reader’s opinion doesn’t change, they come away from the essay with a greater understanding of the perspective presented — and perhaps a better understanding of their original opinion.
All of that might make it seem like writing an argumentative essay is way harder than an emotionally-driven persuasive essay — but if you’re like me and much more comfortable spouting facts and figures than making impassioned pleas, you may find that an argumentative essay is easier to write.
Plus, the process of researching an argumentative essay means you can check your assumptions and develop an opinion that’s more based in reality than what you originally thought. I know for sure that my opinions need to be fact checked — don’t yours?
So how exactly do we write the argumentative essay?
How do you start an argumentative essay
First, gain a clear understanding of what exactly an argumentative essay is. To formulate a proper topic sentence, you have to be clear on your topic, and to explore it through research.
Students have difficulty starting an essay because the whole task seems intimidating, and they are afraid of spending too much time on the topic sentence. Experienced writers, however, know that there is no set time to spend on figuring out your topic. It's a real exploration that is based to a large extent on intuition.
6 Steps to Write an Argumentative Essay (Persuasion Formula)
Use this checklist to tackle your essay one step at a time:

1. Research an issue with an arguable question
To start, you need to identify an issue that well-informed people have varying opinions on. Here, it’s helpful to think of one core topic and how it intersects with another (or several other) issues. That intersection is where hot takes and reasonable (or unreasonable) opinions abound.
I find it helpful to stage the issue as a question.
For example:
Is it better to legislate the minimum size of chicken enclosures or to outlaw the sale of eggs from chickens who don’t have enough space?
Should snow removal policies focus more on effectively keeping roads clear for traffic or the environmental impacts of snow removal methods?
Once you have your arguable question ready, start researching the basic facts and specific opinions and arguments on the issue. Do your best to stay focused on gathering information that is directly relevant to your topic. Depending on what your essay is for, you may reference academic studies, government reports, or newspaper articles.
Research your opposition and the facts that support their viewpoint as much as you research your own position . You’ll need to address your opposition in your essay, so you’ll want to know their argument from the inside out.
2. Choose a side based on your research
You likely started with an inclination toward one side or the other, but your research should ultimately shape your perspective. So once you’ve completed the research, nail down your opinion and start articulating the what and why of your take.
What: I think it’s better to outlaw selling eggs from chickens whose enclosures are too small.
Why: Because if you regulate the enclosure size directly, egg producers outside of the government’s jurisdiction could ship eggs into your territory and put nearby egg producers out of business by offering better prices because they don’t have the added cost of larger enclosures.
This is an early form of your thesis and the basic logic of your argument. You’ll want to iterate on this a few times and develop a one-sentence statement that sums up the thesis of your essay.
Thesis: Outlawing the sale of eggs from chickens with cramped living spaces is better for business than regulating the size of chicken enclosures.
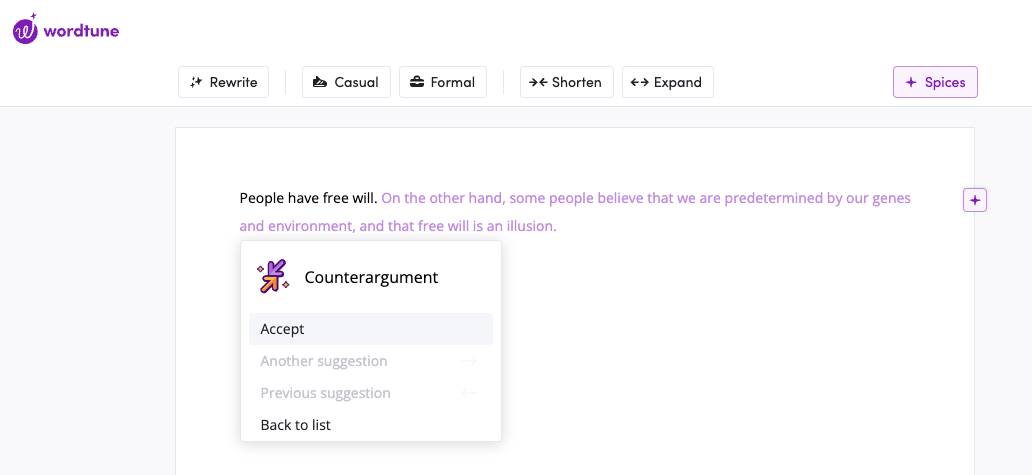
Now that you’ve articulated your thesis , spell out the counterargument(s) as well. Putting your opposition’s take into words will help you throughout the rest of the essay-writing process. (You can start by choosing the counter argument option with Wordtune Spices .)

Counterargument: Outlawing the sale of eggs from chickens with too small enclosures will immediately drive up egg prices for consumers, making the low-cost protein source harder to afford — especially for low-income consumers.
There may be one main counterargument to articulate, or several. Write them all out and start thinking about how you’ll use evidence to address each of them or show why your argument is still the best option.
3. Organize the evidence — for your side and the opposition
You did all of that research for a reason. Now’s the time to use it.
Hopefully, you kept detailed notes in a document, complete with links and titles of all your source material. Go through your research document and copy the evidence for your argument and your opposition’s into another document.
List the main points of your argument. Then, below each point, paste the evidence that backs them up.
If you’re writing about chicken enclosures, maybe you found evidence that shows the spread of disease among birds kept in close quarters is worse than among birds who have more space. Or maybe you found information that says eggs from free-range chickens are more flavorful or nutritious. Put that information next to the appropriate part of your argument.
Repeat the process with your opposition’s argument: What information did you find that supports your opposition? Paste it beside your opposition’s argument.
You could also put information here that refutes your opposition, but organize it in a way that clearly tells you — at a glance — that the information disproves their point.
Counterargument: Outlawing the sale of eggs from chickens with too small enclosures will immediately drive up egg prices for consumers.
BUT: Sicknesses like avian flu spread more easily through small enclosures and could cause a shortage that would drive up egg prices naturally, so ensuring larger enclosures is still a better policy for consumers over the long term.
As you organize your research and see the evidence all together, start thinking through the best way to order your points.
Will it be better to present your argument all at once or to break it up with opposition claims you can quickly refute? Would some points set up other points well? Does a more complicated point require that the reader understands a simpler point first?
Play around and rearrange your notes to see how your essay might flow one way or another.
4. Freewrite or outline to think through your argument
Is your brain buzzing yet? At this point in the process, it can be helpful to take out a notebook or open a fresh document and dump whatever you’re thinking on the page.
Where should your essay start? What ground-level information do you need to provide your readers before you can dive into the issue?
Use your organized evidence document from step 3 to think through your argument from beginning to end, and determine the structure of your essay.
There are three typical structures for argumentative essays:
- Make your argument and tackle opposition claims one by one, as they come up in relation to the points of your argument - In this approach, the whole essay — from beginning to end — focuses on your argument, but as you make each point, you address the relevant opposition claims individually. This approach works well if your opposition’s views can be quickly explained and refuted and if they directly relate to specific points in your argument.
- Make the bulk of your argument, and then address the opposition all at once in a paragraph (or a few) - This approach puts the opposition in its own section, separate from your main argument. After you’ve made your case, with ample evidence to convince your readers, you write about the opposition, explaining their viewpoint and supporting evidence — and showing readers why the opposition’s argument is unconvincing. Once you’ve addressed the opposition, you write a conclusion that sums up why your argument is the better one.
- Open your essay by talking about the opposition and where it falls short. Build your entire argument to show how it is superior to that opposition - With this structure, you’re showing your readers “a better way” to address the issue. After opening your piece by showing how your opposition’s approaches fail, you launch into your argument, providing readers with ample evidence that backs you up.
As you think through your argument and examine your evidence document, consider which structure will serve your argument best. Sketch out an outline to give yourself a map to follow in the writing process. You could also rearrange your evidence document again to match your outline, so it will be easy to find what you need when you start writing.
5. Write your first draft
You have an outline and an organized document with all your points and evidence lined up and ready. Now you just have to write your essay.
In your first draft, focus on getting your ideas on the page. Your wording may not be perfect (whose is?), but you know what you’re trying to say — so even if you’re overly wordy and taking too much space to say what you need to say, put those words on the page.
Follow your outline, and draw from that evidence document to flesh out each point of your argument. Explain what the evidence means for your argument and your opposition. Connect the dots for your readers so they can follow you, point by point, and understand what you’re trying to say.
As you write, be sure to include:
1. Any background information your reader needs in order to understand the issue in question.
2. Evidence for both your argument and the counterargument(s). This shows that you’ve done your homework and builds trust with your reader, while also setting you up to make a more convincing argument. (If you find gaps in your research while you’re writing, Wordtune Spices can source statistics or historical facts on the fly!)

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
3. A conclusion that sums up your overall argument and evidence — and leaves the reader with an understanding of the issue and its significance. This sort of conclusion brings your essay to a strong ending that doesn’t waste readers’ time, but actually adds value to your case.
6. Revise (with Wordtune)
The hard work is done: you have a first draft. Now, let’s fine tune your writing.
I like to step away from what I’ve written for a day (or at least a night of sleep) before attempting to revise. It helps me approach clunky phrases and rough transitions with fresh eyes. If you don’t have that luxury, just get away from your computer for a few minutes — use the bathroom, do some jumping jacks, eat an apple — and then come back and read through your piece.
As you revise, make sure you …
- Get the facts right. An argument with false evidence falls apart pretty quickly, so check your facts to make yours rock solid.
- Don’t misrepresent the opposition or their evidence. If someone who holds the opposing view reads your essay, they should affirm how you explain their side — even if they disagree with your rebuttal.
- Present a case that builds over the course of your essay, makes sense, and ends on a strong note. One point should naturally lead to the next. Your readers shouldn’t feel like you’re constantly changing subjects. You’re making a variety of points, but your argument should feel like a cohesive whole.
- Paraphrase sources and cite them appropriately. Did you skip citations when writing your first draft? No worries — you can add them now. And check that you don’t overly rely on quotations. (Need help paraphrasing? Wordtune can help. Simply highlight the sentence or phrase you want to adjust and sort through Wordtune’s suggestions.)
- Tighten up overly wordy explanations and sharpen any convoluted ideas. Wordtune makes a great sidekick for this too 😉

Words to start an argumentative essay
The best way to introduce a convincing argument is to provide a strong thesis statement . These are the words I usually use to start an argumentative essay:
- It is indisputable that the world today is facing a multitude of issues
- With the rise of ____, the potential to make a positive difference has never been more accessible
- It is essential that we take action now and tackle these issues head-on
- it is critical to understand the underlying causes of the problems standing before us
- Opponents of this idea claim
- Those who are against these ideas may say
- Some people may disagree with this idea
- Some people may say that ____, however
When refuting an opposing concept, use:
- These researchers have a point in thinking
- To a certain extent they are right
- After seeing this evidence, there is no way one can agree with this idea
- This argument is irrelevant to the topic
Are you convinced by your own argument yet? Ready to brave the next get-together where everyone’s talking like they know something about intermittent fasting , chicken enclosures , or snow removal policies?
Now if someone asks you to explain your evidence-based but controversial opinion, you can hand them your essay and ask them to report back after they’ve read it.
Share This Article:

What’s a Semicolon? + When to Use It (With Examples)

The 12 Longest Words in English Defined and Explained
.webp)
Finding the OG Writing Assistant – Wordtune vs. QuillBot
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to write an a+ argumentative essay.
Miscellaneous

You'll no doubt have to write a number of argumentative essays in both high school and college, but what, exactly, is an argumentative essay and how do you write the best one possible? Let's take a look.
A great argumentative essay always combines the same basic elements: approaching an argument from a rational perspective, researching sources, supporting your claims using facts rather than opinion, and articulating your reasoning into the most cogent and reasoned points. Argumentative essays are great building blocks for all sorts of research and rhetoric, so your teachers will expect you to master the technique before long.
But if this sounds daunting, never fear! We'll show how an argumentative essay differs from other kinds of papers, how to research and write them, how to pick an argumentative essay topic, and where to find example essays. So let's get started.
What Is an Argumentative Essay? How Is it Different from Other Kinds of Essays?
There are two basic requirements for any and all essays: to state a claim (a thesis statement) and to support that claim with evidence.
Though every essay is founded on these two ideas, there are several different types of essays, differentiated by the style of the writing, how the writer presents the thesis, and the types of evidence used to support the thesis statement.
Essays can be roughly divided into four different types:
#1: Argumentative #2: Persuasive #3: Expository #4: Analytical
So let's look at each type and what the differences are between them before we focus the rest of our time to argumentative essays.
Argumentative Essay
Argumentative essays are what this article is all about, so let's talk about them first.
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance.
An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the factually and logically correct one. This means that an argumentative essay must use only evidence-based support to back up a claim , rather than emotional or philosophical reasoning (which is often allowed in other types of essays). Thus, an argumentative essay has a burden of substantiated proof and sources , whereas some other types of essays (namely persuasive essays) do not.
You can write an argumentative essay on any topic, so long as there's room for argument. Generally, you can use the same topics for both a persuasive essay or an argumentative one, so long as you support the argumentative essay with hard evidence.
Example topics of an argumentative essay:
- "Should farmers be allowed to shoot wolves if those wolves injure or kill farm animals?"
- "Should the drinking age be lowered in the United States?"
- "Are alternatives to democracy effective and/or feasible to implement?"
The next three types of essays are not argumentative essays, but you may have written them in school. We're going to cover them so you know what not to do for your argumentative essay.
Persuasive Essay
Persuasive essays are similar to argumentative essays, so it can be easy to get them confused. But knowing what makes an argumentative essay different than a persuasive essay can often mean the difference between an excellent grade and an average one.
Persuasive essays seek to persuade a reader to agree with the point of view of the writer, whether that point of view is based on factual evidence or not. The writer has much more flexibility in the evidence they can use, with the ability to use moral, cultural, or opinion-based reasoning as well as factual reasoning to persuade the reader to agree the writer's side of a given issue.
Instead of being forced to use "pure" reason as one would in an argumentative essay, the writer of a persuasive essay can manipulate or appeal to the reader's emotions. So long as the writer attempts to steer the readers into agreeing with the thesis statement, the writer doesn't necessarily need hard evidence in favor of the argument.
Often, you can use the same topics for both a persuasive essay or an argumentative one—the difference is all in the approach and the evidence you present.
Example topics of a persuasive essay:
- "Should children be responsible for their parents' debts?"
- "Should cheating on a test be automatic grounds for expulsion?"
- "How much should sports leagues be held accountable for player injuries and the long-term consequences of those injuries?"
Expository Essay
An expository essay is typically a short essay in which the writer explains an idea, issue, or theme , or discusses the history of a person, place, or idea.
This is typically a fact-forward essay with little argument or opinion one way or the other.
Example topics of an expository essay:
- "The History of the Philadelphia Liberty Bell"
- "The Reasons I Always Wanted to be a Doctor"
- "The Meaning Behind the Colloquialism ‘People in Glass Houses Shouldn't Throw Stones'"
Analytical Essay
An analytical essay seeks to delve into the deeper meaning of a text or work of art, or unpack a complicated idea . These kinds of essays closely interpret a source and look into its meaning by analyzing it at both a macro and micro level.
This type of analysis can be augmented by historical context or other expert or widely-regarded opinions on the subject, but is mainly supported directly through the original source (the piece or art or text being analyzed) .
Example topics of an analytical essay:
- "Victory Gin in Place of Water: The Symbolism Behind Gin as the Only Potable Substance in George Orwell's 1984"
- "Amarna Period Art: The Meaning Behind the Shift from Rigid to Fluid Poses"
- "Adultery During WWII, as Told Through a Series of Letters to and from Soldiers"

There are many different types of essay and, over time, you'll be able to master them all.
A Typical Argumentative Essay Assignment
The average argumentative essay is between three to five pages, and will require at least three or four separate sources with which to back your claims . As for the essay topic , you'll most often be asked to write an argumentative essay in an English class on a "general" topic of your choice, ranging the gamut from science, to history, to literature.
But while the topics of an argumentative essay can span several different fields, the structure of an argumentative essay is always the same: you must support a claim—a claim that can reasonably have multiple sides—using multiple sources and using a standard essay format (which we'll talk about later on).
This is why many argumentative essay topics begin with the word "should," as in:
- "Should all students be required to learn chemistry in high school?"
- "Should children be required to learn a second language?"
- "Should schools or governments be allowed to ban books?"
These topics all have at least two sides of the argument: Yes or no. And you must support the side you choose with evidence as to why your side is the correct one.
But there are also plenty of other ways to frame an argumentative essay as well:
- "Does using social media do more to benefit or harm people?"
- "Does the legal status of artwork or its creators—graffiti and vandalism, pirated media, a creator who's in jail—have an impact on the art itself?"
- "Is or should anyone ever be ‘above the law?'"
Though these are worded differently than the first three, you're still essentially forced to pick between two sides of an issue: yes or no, for or against, benefit or detriment. Though your argument might not fall entirely into one side of the divide or another—for instance, you could claim that social media has positively impacted some aspects of modern life while being a detriment to others—your essay should still support one side of the argument above all. Your final stance would be that overall , social media is beneficial or overall , social media is harmful.
If your argument is one that is mostly text-based or backed by a single source (e.g., "How does Salinger show that Holden Caulfield is an unreliable narrator?" or "Does Gatsby personify the American Dream?"), then it's an analytical essay, rather than an argumentative essay. An argumentative essay will always be focused on more general topics so that you can use multiple sources to back up your claims.
Good Argumentative Essay Topics
So you know the basic idea behind an argumentative essay, but what topic should you write about?
Again, almost always, you'll be asked to write an argumentative essay on a free topic of your choice, or you'll be asked to select between a few given topics . If you're given complete free reign of topics, then it'll be up to you to find an essay topic that no only appeals to you, but that you can turn into an A+ argumentative essay.
What makes a "good" argumentative essay topic depends on both the subject matter and your personal interest —it can be hard to give your best effort on something that bores you to tears! But it can also be near impossible to write an argumentative essay on a topic that has no room for debate.
As we said earlier, a good argumentative essay topic will be one that has the potential to reasonably go in at least two directions—for or against, yes or no, and why . For example, it's pretty hard to write an argumentative essay on whether or not people should be allowed to murder one another—not a whole lot of debate there for most people!—but writing an essay for or against the death penalty has a lot more wiggle room for evidence and argument.
A good topic is also one that can be substantiated through hard evidence and relevant sources . So be sure to pick a topic that other people have studied (or at least studied elements of) so that you can use their data in your argument. For example, if you're arguing that it should be mandatory for all middle school children to play a sport, you might have to apply smaller scientific data points to the larger picture you're trying to justify. There are probably several studies you could cite on the benefits of physical activity and the positive effect structure and teamwork has on young minds, but there's probably no study you could use where a group of scientists put all middle-schoolers in one jurisdiction into a mandatory sports program (since that's probably never happened). So long as your evidence is relevant to your point and you can extrapolate from it to form a larger whole, you can use it as a part of your resource material.
And if you need ideas on where to get started, or just want to see sample argumentative essay topics, then check out these links for hundreds of potential argumentative essay topics.
101 Persuasive (or Argumentative) Essay and Speech Topics
301 Prompts for Argumentative Writing
Top 50 Ideas for Argumentative/Persuasive Essay Writing
[Note: some of these say "persuasive essay topics," but just remember that the same topic can often be used for both a persuasive essay and an argumentative essay; the difference is in your writing style and the evidence you use to support your claims.]

KO! Find that one argumentative essay topic you can absolutely conquer.
Argumentative Essay Format
Argumentative Essays are composed of four main elements:
- A position (your argument)
- Your reasons
- Supporting evidence for those reasons (from reliable sources)
- Counterargument(s) (possible opposing arguments and reasons why those arguments are incorrect)
If you're familiar with essay writing in general, then you're also probably familiar with the five paragraph essay structure . This structure is a simple tool to show how one outlines an essay and breaks it down into its component parts, although it can be expanded into as many paragraphs as you want beyond the core five.
The standard argumentative essay is often 3-5 pages, which will usually mean a lot more than five paragraphs, but your overall structure will look the same as a much shorter essay.
An argumentative essay at its simplest structure will look like:
Paragraph 1: Intro
- Set up the story/problem/issue
- Thesis/claim
Paragraph 2: Support
- Reason #1 claim is correct
- Supporting evidence with sources
Paragraph 3: Support
- Reason #2 claim is correct
Paragraph 4: Counterargument
- Explanation of argument for the other side
- Refutation of opposing argument with supporting evidence
Paragraph 5: Conclusion
- Re-state claim
- Sum up reasons and support of claim from the essay to prove claim is correct
Now let's unpack each of these paragraph types to see how they work (with examples!), what goes into them, and why.
Paragraph 1—Set Up and Claim
Your first task is to introduce the reader to the topic at hand so they'll be prepared for your claim. Give a little background information, set the scene, and give the reader some stakes so that they care about the issue you're going to discuss.
Next, you absolutely must have a position on an argument and make that position clear to the readers. It's not an argumentative essay unless you're arguing for a specific claim, and this claim will be your thesis statement.
Your thesis CANNOT be a mere statement of fact (e.g., "Washington DC is the capital of the United States"). Your thesis must instead be an opinion which can be backed up with evidence and has the potential to be argued against (e.g., "New York should be the capital of the United States").
Paragraphs 2 and 3—Your Evidence
These are your body paragraphs in which you give the reasons why your argument is the best one and back up this reasoning with concrete evidence .
The argument supporting the thesis of an argumentative essay should be one that can be supported by facts and evidence, rather than personal opinion or cultural or religious mores.
For example, if you're arguing that New York should be the new capital of the US, you would have to back up that fact by discussing the factual contrasts between New York and DC in terms of location, population, revenue, and laws. You would then have to talk about the precedents for what makes for a good capital city and why New York fits the bill more than DC does.
Your argument can't simply be that a lot of people think New York is the best city ever and that you agree.
In addition to using concrete evidence, you always want to keep the tone of your essay passionate, but impersonal . Even though you're writing your argument from a single opinion, don't use first person language—"I think," "I feel," "I believe,"—to present your claims. Doing so is repetitive, since by writing the essay you're already telling the audience what you feel, and using first person language weakens your writing voice.
For example,
"I think that Washington DC is no longer suited to be the capital city of the United States."
"Washington DC is no longer suited to be the capital city of the United States."
The second statement sounds far stronger and more analytical.
Paragraph 4—Argument for the Other Side and Refutation
Even without a counter argument, you can make a pretty persuasive claim, but a counterargument will round out your essay into one that is much more persuasive and substantial.
By anticipating an argument against your claim and taking the initiative to counter it, you're allowing yourself to get ahead of the game. This way, you show that you've given great thought to all sides of the issue before choosing your position, and you demonstrate in multiple ways how yours is the more reasoned and supported side.
Paragraph 5—Conclusion
This paragraph is where you re-state your argument and summarize why it's the best claim.
Briefly touch on your supporting evidence and voila! A finished argumentative essay.
Your essay should have just as awesome a skeleton as this plesiosaur does. (In other words: a ridiculously awesome skeleton)
Argumentative Essay Example: 5-Paragraph Style
It always helps to have an example to learn from. I've written a full 5-paragraph argumentative essay here. Look at how I state my thesis in paragraph 1, give supporting evidence in paragraphs 2 and 3, address a counterargument in paragraph 4, and conclude in paragraph 5.
Topic: Is it possible to maintain conflicting loyalties?
Paragraph 1
It is almost impossible to go through life without encountering a situation where your loyalties to different people or causes come into conflict with each other. Maybe you have a loving relationship with your sister, but she disagrees with your decision to join the army, or you find yourself torn between your cultural beliefs and your scientific ones. These conflicting loyalties can often be maintained for a time, but as examples from both history and psychological theory illustrate, sooner or later, people have to make a choice between competing loyalties, as no one can maintain a conflicting loyalty or belief system forever.
The first two sentences set the scene and give some hypothetical examples and stakes for the reader to care about.
The third sentence finishes off the intro with the thesis statement, making very clear how the author stands on the issue ("people have to make a choice between competing loyalties, as no one can maintain a conflicting loyalty or belief system forever." )
Paragraphs 2 and 3
Psychological theory states that human beings are not equipped to maintain conflicting loyalties indefinitely and that attempting to do so leads to a state called "cognitive dissonance." Cognitive dissonance theory is the psychological idea that people undergo tremendous mental stress or anxiety when holding contradictory beliefs, values, or loyalties (Festinger, 1957). Even if human beings initially hold a conflicting loyalty, they will do their best to find a mental equilibrium by making a choice between those loyalties—stay stalwart to a belief system or change their beliefs. One of the earliest formal examples of cognitive dissonance theory comes from Leon Festinger's When Prophesy Fails . Members of an apocalyptic cult are told that the end of the world will occur on a specific date and that they alone will be spared the Earth's destruction. When that day comes and goes with no apocalypse, the cult members face a cognitive dissonance between what they see and what they've been led to believe (Festinger, 1956). Some choose to believe that the cult's beliefs are still correct, but that the Earth was simply spared from destruction by mercy, while others choose to believe that they were lied to and that the cult was fraudulent all along. Both beliefs cannot be correct at the same time, and so the cult members are forced to make their choice.
But even when conflicting loyalties can lead to potentially physical, rather than just mental, consequences, people will always make a choice to fall on one side or other of a dividing line. Take, for instance, Nicolaus Copernicus, a man born and raised in Catholic Poland (and educated in Catholic Italy). Though the Catholic church dictated specific scientific teachings, Copernicus' loyalty to his own observations and scientific evidence won out over his loyalty to his country's government and belief system. When he published his heliocentric model of the solar system--in opposition to the geocentric model that had been widely accepted for hundreds of years (Hannam, 2011)-- Copernicus was making a choice between his loyalties. In an attempt t o maintain his fealty both to the established system and to what he believed, h e sat on his findings for a number of years (Fantoli, 1994). But, ultimately, Copernicus made the choice to side with his beliefs and observations above all and published his work for the world to see (even though, in doing so, he risked both his reputation and personal freedoms).
These two paragraphs provide the reasons why the author supports the main argument and uses substantiated sources to back those reasons.
The paragraph on cognitive dissonance theory gives both broad supporting evidence and more narrow, detailed supporting evidence to show why the thesis statement is correct not just anecdotally but also scientifically and psychologically. First, we see why people in general have a difficult time accepting conflicting loyalties and desires and then how this applies to individuals through the example of the cult members from the Dr. Festinger's research.
The next paragraph continues to use more detailed examples from history to provide further evidence of why the thesis that people cannot indefinitely maintain conflicting loyalties is true.
Paragraph 4
Some will claim that it is possible to maintain conflicting beliefs or loyalties permanently, but this is often more a matter of people deluding themselves and still making a choice for one side or the other, rather than truly maintaining loyalty to both sides equally. For example, Lancelot du Lac typifies a person who claims to maintain a balanced loyalty between to two parties, but his attempt to do so fails (as all attempts to permanently maintain conflicting loyalties must). Lancelot tells himself and others that he is equally devoted to both King Arthur and his court and to being Queen Guinevere's knight (Malory, 2008). But he can neither be in two places at once to protect both the king and queen, nor can he help but let his romantic feelings for the queen to interfere with his duties to the king and the kingdom. Ultimately, he and Queen Guinevere give into their feelings for one another and Lancelot—though he denies it—chooses his loyalty to her over his loyalty to Arthur. This decision plunges the kingdom into a civil war, ages Lancelot prematurely, and ultimately leads to Camelot's ruin (Raabe, 1987). Though Lancelot claimed to have been loyal to both the king and the queen, this loyalty was ultimately in conflict, and he could not maintain it.
Here we have the acknowledgement of a potential counter-argument and the evidence as to why it isn't true.
The argument is that some people (or literary characters) have asserted that they give equal weight to their conflicting loyalties. The refutation is that, though some may claim to be able to maintain conflicting loyalties, they're either lying to others or deceiving themselves. The paragraph shows why this is true by providing an example of this in action.
Paragraph 5
Whether it be through literature or history, time and time again, people demonstrate the challenges of trying to manage conflicting loyalties and the inevitable consequences of doing so. Though belief systems are malleable and will often change over time, it is not possible to maintain two mutually exclusive loyalties or beliefs at once. In the end, people always make a choice, and loyalty for one party or one side of an issue will always trump loyalty to the other.
The concluding paragraph summarizes the essay, touches on the evidence presented, and re-states the thesis statement.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 8 Steps
Writing the best argumentative essay is all about the preparation, so let's talk steps:
#1: Preliminary Research
If you have the option to pick your own argumentative essay topic (which you most likely will), then choose one or two topics you find the most intriguing or that you have a vested interest in and do some preliminary research on both sides of the debate.
Do an open internet search just to see what the general chatter is on the topic and what the research trends are.
Did your preliminary reading influence you to pick a side or change your side? Without diving into all the scholarly articles at length, do you believe there's enough evidence to support your claim? Have there been scientific studies? Experiments? Does a noted scholar in the field agree with you? If not, you may need to pick another topic or side of the argument to support.
#2: Pick Your Side and Form Your Thesis
Now's the time to pick the side of the argument you feel you can support the best and summarize your main point into your thesis statement.
Your thesis will be the basis of your entire essay, so make sure you know which side you're on, that you've stated it clearly, and that you stick by your argument throughout the entire essay .
#3: Heavy-Duty Research Time
You've taken a gander at what the internet at large has to say on your argument, but now's the time to actually read those sources and take notes.
Check scholarly journals online at Google Scholar , the Directory of Open Access Journals , or JStor . You can also search individual university or school libraries and websites to see what kinds of academic articles you can access for free. Keep track of your important quotes and page numbers and put them somewhere that's easy to find later.
And don't forget to check your school or local libraries as well!
#4: Outline
Follow the five-paragraph outline structure from the previous section.
Fill in your topic, your reasons, and your supporting evidence into each of the categories.
Before you begin to flesh out the essay, take a look at what you've got. Is your thesis statement in the first paragraph? Is it clear? Is your argument logical? Does your supporting evidence support your reasoning?
By outlining your essay, you streamline your process and take care of any logic gaps before you dive headfirst into the writing. This will save you a lot of grief later on if you need to change your sources or your structure, so don't get too trigger-happy and skip this step.
Now that you've laid out exactly what you'll need for your essay and where, it's time to fill in all the gaps by writing it out.
Take it one step at a time and expand your ideas into complete sentences and substantiated claims. It may feel daunting to turn an outline into a complete draft, but just remember that you've already laid out all the groundwork; now you're just filling in the gaps.
If you have the time before deadline, give yourself a day or two (or even just an hour!) away from your essay . Looking it over with fresh eyes will allow you to see errors, both minor and major, that you likely would have missed had you tried to edit when it was still raw.
Take a first pass over the entire essay and try your best to ignore any minor spelling or grammar mistakes—you're just looking at the big picture right now. Does it make sense as a whole? Did the essay succeed in making an argument and backing that argument up logically? (Do you feel persuaded?)
If not, go back and make notes so that you can fix it for your final draft.
Once you've made your revisions to the overall structure, mark all your small errors and grammar problems so you can fix them in the next draft.
#7: Final Draft
Use the notes you made on the rough draft and go in and hack and smooth away until you're satisfied with the final result.
A checklist for your final draft:
- Formatting is correct according to your teacher's standards
- No errors in spelling, grammar, and punctuation
- Essay is the right length and size for the assignment
- The argument is present, consistent, and concise
- Each reason is supported by relevant evidence
- The essay makes sense overall
#8: Celebrate!
Once you've brought that final draft to a perfect polish and turned in your assignment, you're done! Go you!

Be prepared and ♪ you'll never go hungry again ♪, *cough*, or struggle with your argumentative essay-writing again. (Walt Disney Studios)
Good Examples of Argumentative Essays Online
Theory is all well and good, but examples are key. Just to get you started on what a fully-fleshed out argumentative essay looks like, let's see some examples in action.
Check out these two argumentative essay examples on the use of landmines and freons (and note the excellent use of concrete sources to back up their arguments!).
The Use of Landmines
A Shattered Sky
The Take-Aways: Keys to Writing an Argumentative Essay
At first, writing an argumentative essay may seem like a monstrous hurdle to overcome, but with the proper preparation and understanding, you'll be able to knock yours out of the park.
Remember the differences between a persuasive essay and an argumentative one, make sure your thesis is clear, and double-check that your supporting evidence is both relevant to your point and well-sourced . Pick your topic, do your research, make your outline, and fill in the gaps. Before you know it, you'll have yourself an A+ argumentative essay there, my friend.
What's Next?
Now you know the ins and outs of an argumentative essay, but how comfortable are you writing in other styles? Learn more about the four writing styles and when it makes sense to use each .
Understand how to make an argument, but still having trouble organizing your thoughts? Check out our guide to three popular essay formats and choose which one is right for you.
Ready to make your case, but not sure what to write about? We've created a list of 50 potential argumentative essay topics to spark your imagination.
Courtney scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT in high school and went on to graduate from Stanford University with a degree in Cultural and Social Anthropology. She is passionate about bringing education and the tools to succeed to students from all backgrounds and walks of life, as she believes open education is one of the great societal equalizers. She has years of tutoring experience and writes creative works in her free time.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Essay Guides
- Main Academic Essays
- Argumentative Essay Outline: Writing Steps & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
Argumentative Essay Outline: Writing Steps & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
An argumentative essay outline is a roadmap for the writer to organize their thoughts, research, and arguments in a clear and logical way. It helps to stay focused on the topic and effectively present arguments. Creating an outline before writing an argumentative essay allows students to identify the key points and evidence that should back up ideas.
Struggling with an argumentative essay outline? Stuck at the beginning or not sure which format to take? It’s okay, you’ll find some explanations and pieces of advice here, as well as an argument outline template you could use. We’ve collected everything you need to know before composing an outline for your top-notch argumentative paper. This page contains information about:
- The notion of outline and why it is important
- Specifics of sketching an essay where you defend your position
- Argument essay layout
- Several useful tips and examples.
Ready to receive some help with your work? Let’s get you prepared to write an excellent essay!
What Is an Argumentative Essay Outline?
Before starting to work on an argumentative paper outline, it is important to understand its definition and purpose. So, what is the outline for an argumentative essay? Outline for an argumentative essay involves defending one’s position on a certain topic by using logic and factual evidence. It requires doing preliminary research and presenting your findings in sketch form. An argumentative essay outline forms the essay’s basic structure and contains its main elements, briefly described and connected together using logical transitions. Once you finish and review this short version, it will be much easier to spot mistakes and logical gaps. After correcting them, you’ll be one step away from writing a high-quality essay.
Argumentative Essay Outline Format
Setting a correct format for argumentative essay outline is important, as it ensures that the entire composition will be properly organized. This is where you create the logical structure, which can be checked for gaps and mistakes before writing the complete text. A simple argumentative essay outline should be composed like this:
- Introduction This part contains your main topic description and your thesis statement. The latter should be provided fully, while the other descriptions can be sketchy at this stage. Try using some kind of a ‘hook’ to engage your readers.
- Body paragraphs It is where you briefly introduce your arguments, as well as counterarguments you aim to refute. Mention your evidence and include your sources, but don’t be too wordy, as this is just a sketch for now.
- Conclusion It should briefly summarize the argumentation and how it supports your thesis.
More examples of an argumentative essay structure outline are available in our downloadable materials.
Learn more: How to Write an Argumentative Essay Introduction
Types of an Argumentative Essay Outline
Before learning how to write an outline for an argumentative essay, you must figure out which type is best for your specific topic. This information might be specified in your assignment, otherwise, it is up to you. The layout of an argumentative essay you’re writing depends on the persuasive approach you’ve chosen. There are three main types:
- Classical, also known as Aristotelian
Now let's talk about each argument essay outline type in detail. We’ll show you what the differences between them are and when it is better to choose one or another.
Classical Argumentative Essay Outline
Let’s start with the classical argument outline. It is also named Aristotelian, honoring the memory of the ancient Greek philosopher who perfected the logical method of presenting argumentation. The general structure should follow a 5 paragraph essay format . Here is how you should compose your outline of an argumentative essay when using this structure type:
- Explain your thesis, making it clear
- Mention the opposing thesis if there is one
- List your arguments, referring to evidence you have collected
- Mention counterarguments, providing evidence that contradicts them
- Summarize it, showing that your thesis has been proven by your arguments.
This type is used for direct discussions and straightforward topics.
Rogerian Argumentative Essay Outline
In a Rogerian outline for an argumentative essay, you are expected to pay more attention to the opposing viewpoints, considering the strong and weak sides of both. In this case, the paper focuses not on refuting antagonistic argumentation but rather on finding some middle ground. This argumentative essay layout can be used when you’re aiming to help two opposing sides reach a mutual agreement at a certain point. Another situation when you should consider such an approach is when addressing an audience hostile to your viewpoint – for example, when arguing against the rules or habits of a specific group.
Toulmin Argumentative Essay Outline
When your topic needs some complicated analysis on different levels, use the Toulmin outline of an argumentative essay. This model is based on six main elements:
- Claim – your central statement
- Grounds – evidence backing the claim
- Warrant – logical connection between the grounds and the claim
- Backings – additional arguments strengthening the warrant
- Qualifier – the measure of certainty in the claim
- Rebuttal – refutes possible counterarguments to the claim.
This format of argumentative essay outline should be used for refuting existing argumentation against your own claim. If you are struggling with outlining your argumentative essay, re-check its main points. Correcting mistakes early on saves hundreds of working hours. To save even more, consider to buy college essays from professional academic writers.
Argumentative Essay Outline Template
Have you picked your paper format? If yes, you should be ready to proceed. Need an argumentative outline template? If you still hesitate and search for extra hints, it's fine – there are plenty of them on this page! We’ve prepared a comprehensive argument essay outline template for each of the main types described in the previous section. You can find them below.
Classical Argumentative Essay Outline Template
If your task is to simply present your point of view on a certain subject and back it up with solid facts, you need a classical argument essay outline. This is the most common and straightforward type of structuring your argumentation, so it can be freely used unless your situation requires a different approach. Here is our outline for argumentative essay example:
- Intriguing description or some wordplay to ‘hook’ your audience
- Brief context of the problem
- Your full thesis statement together with an extra explanation if necessary
- Data set #1
- Data set #2, etc.
- Your argument #2: Formatted the same way as the previous one
- Point out its logical flaws or provide the evidence that refutes it (or refutatio).
- Briefly mention how this analysis results in reinforcing your own position.
- Counterargument #2: This and further ones should be formatted in exactly the same way
- Summarize your argumentation without repeating it and show how it supports your thesis (this part is also known as peroratio).
- Add some final notes or a call to action to engage your audience.
Rogerian Argumentative Essay Outline Template
When attempting to counter a formidable position, you need to pay great attention to opposing claims. You might want to find some common ground and reach an agreement with the opposing side, and that is what the Rogerian type is meant for. Follow this argument essay template for conducting an extra analysis of conflicting viewpoints:
- Describe the problem and add brief context if necessary.
- Explain your own viewpoint on it as well as opposing stances. You might pick the most well-known of them or the one which shares enough common ground with your position if that helps. Highlight this common ground.
- Give your thesis statement in a full sentence.
- Explore the evidence which supports it.
- Analyze the strength of this position, given the quality of evidence. See if it can be refuted.
- Mention other positions, if any. Follow the same format as used for the first one.
- Explain that you understand the opposing position and the reasons behind it.
- Highlight specific details or areas where you have common ground with the opponent.
- Your argument #1: explain how it is related to your thesis and provide the supporting evidence.
- Your argument #1: present it in the same format as the 1st one. The same goes for all other arguments.
- Point out the elements of both positions which you and your opponent could agree upon.
- Develop a compromising solution that would encompass these agreeable elements from both sides.
- Summarize the compromise and the arguments from both sides which back it.
- Explain how both sides could benefit from agreeing upon this common ground position.
Check below for more argumentative essay outline examples.
Toulmin Argumentative Essay Outline Template
This argument template for an essay will be useful in case of facing complicated argumentation, which should be properly analyzed. The Toulmin format outline argumentative essay example is here:
- Come up with something interesting to ‘hook’ your audience.
- Provide a brief context of the problem.
- Give your full thesis statement.
- Evidence #1, including the logical connection between it and your claim
- Evidence #2, formatted in the same way, etc.
- Briefly show how it supports your thesis.
- Show which of your evidence elements backs this warrant.
- Provide qualifiers for your argumentation: be open and show its weak sides.
- Your warrant #2, formatted in the same way, etc.
- Analyze their claim, evaluating its warrants and qualifiers.
- Provide your rebuttal.
- Opposing viewpoint #2, formatted in the same way, etc.
- Briefly summarize your warrants.
- Summarize the opposing viewpoints, mentioning how you have refuted them.
- Show that your thesis is supported better.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay Outline Step-By-Step
Let’s put together all the tips on how to write an argumentative essay outline . This section contains a quick guide that could serve as your argumentative essay planning sheet. Make sure to follow this recommended course when composing an academic paper:
- Think it through Making an argumentative writing outline efficient and persuasive requires good knowledge of the selected topic. So, choose one you are familiar with. You must be able to explain your position well and defend it successfully. And don’t pick an easy one. It should be interesting enough for your audience to get engaged.
- Do your research Gather key information about your problem before writing an argumentative essay outline. Check if you have enough evidence to back your claim and refute possible counterarguments. Verify that it clearly shows what you actually need and doesn’t prove an opposing position.
- Pick a format Given the specifics of the chosen problem, find out which approach will suit you best: Classical, Rogerian, or Toulmin. If you start creating your argumentative essay outline in one format and then realize that you need to switch to another, you might lose a lot of time. Too risky for those who have tight deadlines!
- Structure it properly Follow the recommended templates and put every argument outline into a separate paragraph. The same applies to introductory sections. Remember that proper formatting increases your essay’s readability and thus serves your cause.
- Keep it concise Make it brief but understandable, ensuring that all key points and data are mentioned. Remember that you just need to outline an argumentative essay, not write the full text. Besides, writing briefly saves you some precious time.
- Review and correct Spend some time going through your argumentative research essay outline and check carefully for errors or gaps. Read it to yourself or ask someone else to give it as much critique as possible. If you miss something important now, it will be more difficult to find and correct this mistake later.
These tips should be enough for creating an argumentative essay outline for high school and college. You can check how to write an argumentative essay in one of our guides. But also check the samples we've collected for you – maybe you’ll get some extra ideas for your own work.
Argumentative Essay Outline Examples
Searching for a real argumentative outline example? We’ve collected several outlines for essays addressing popular questions. Check them out, and hopefully, you’ll draw some inspiration from them, which will help you with your own work. Just don’t copy any of that content, as it would mean plagiarism. Don’t forget about the downloadable argumentative essay outline sample. Scroll down, and you’ll find it. Death Penalty Argument Outline Example

Sample Outline for Argumentative Essay on Abortion

Argument Essay Outline Example on Human Trafficking

Sample of Argumentative Essay Outline on Gender Equality

Argumentative Essay Outline Example on Bullying

Browse StudyCrumb’s Blog to find complete argumentative essay examples formatted accordingly.
Argumentative Paper Outline Checklist
Here’s also a brief list of what should be written in an outline for an argument:
Bottom Line on Argumentative Essay Outline
We have shown in detail how to outline an argumentative essay and what are main structure types you could use for it, namely:
We have also listed what should an outline for an argumentative essay include, particularly:
- Introduction with context and a ‘hook’
- Thesis statement
- Arguments with supporting evidence
- Counterarguments with their rebuttal
- Conclusion.
An argumentative writing template has also been provided. We believe that this information will help you complete an excellent paper on any argumentative essay topic . If you are still unsure about your writing skills, StudyCrumb got you covered. Remember this phrase — " write an argumentative essay for me ." It's a secret pass to tell our Support reps. Say it, and the magic will happen.
Our professional writing service will help you with any kind of essay. Just contact us and get any paper written properly.
FAQ About Argumentative Essay Outline
1. why is it important to create an argumentative essay outline.
Writing an argument essay outline helps to form its layout and properly place the main elements: thesis, background, arguments, evidence, and conclusion. It serves as an argumentative essay plan with logical transitions between the key elements. Now you can read this draft version again and spot any inconsistencies before composing the full-text version. That is a much easier task.

3. What should be included in the outline for an argument?
Your argument outline needs to include the following:
- Analysis of certain aspects of the problem which you could use to clearly maintain your point
- Logic and reasoning to defend your position using your debate skills
- Solid evidence retrieved from credible sources to back your claim
- Visible connection to your thesis and your other arguments, otherwise, your audience might have an issue with understanding your essay.
2. What should include a strong outline for an argumentative essay?
A strong outline for an argumentative essay should include:
- Strong thesis, preferably about an interesting and controversial problem
- Proper arguments backed by logic and solid evidence
- Credible sources you can obtain the evidence from
- Proper rebuttal for counterarguments, pointing at their weak sides
- Logical connection between all parts of your outline
- Conclusion, which summarizes all arguments and rebuttals, showing that your thesis is maintained.

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

- checkbox My thesis statement is full and clear.
- checkbox I provided the necessary context of the selected problem.
- checkbox I considered the ‘hook’ in order to engage your audience.
- checkbox Main arguments that support the thesis are logically connected to each other.
- checkbox I selected solid evidence backing the arguments.
- checkbox I planned the main counterarguments , together with their rebuttal based on facts and logic.
- checkbox My conclusion is going to summarize the strength of my position compared to opposing ones.
- checkbox My argument writing template includes a strong call to action and gives some food for thought.
Argumentative Essay – Outline, Form, and Examples

What is an argumentative essay?
An argumentative essay requires the writer to investigate a specific topic by collecting and evaluating evidence to establish a position on the subject matter.
When preparing to compose a good argumentative essay, utilize the following steps:
Step 1: Select a topic.
Step 2: Identify a position.
Step 3: Locate appropriate resources.
Step 4: Identify evidence supporting the position. ( NOTE: If there is little evidence in support of the claim, consider re-examining the main argument.)

When gathering evidence, use credible sources . To determine the credibility of the source, consider authority, currency, accuracy, and objectivity:
Who is the author ? Are they an expert in the field? Has a reputable publisher published the work?
How current is the information in the source? Does the currency of the source matter? Does the age of the source impact the content? Is there newer information that disproves the source’s information?
Can other sources verify the accuracy of the information? Does the information contradict that found in other commonly accepted sources?
Is there any evidence of bias, or is the source objective ? Is the research sponsored by an organization that may skew the information?
The following are typically recognized as providing appropriate, credible research material:
Peer-reviewed journals/research papers
Government agencies
Professional organizations
Library databases
Reference books

Writers should avoid using the following sources:
Social media posts
Out-of-date materials
Step 5: Utilize the research to determine a thesis statement that identifies the topic, position, and support(s).
Step 6: Use the evidence to construct an outline, detailing the main supports and relevant evidence.

Argumentative essay outline
After gathering all of the necessary research, the next step in composing an argumentative essay focuses on organizing the information through the use of an outline:
Introduction
Attention Grabber/Hook
Background Information: Include any background information pertinent to the topic that the reader needs to know to understand the argument.
Thesis: State the position in connection to the main topic and identify the supports that will help prove the argument.
Topic sentence
Identify evidence in support of the claim in the topic sentence
Explain how the evidence supports the argument
Evidence 3 (Continue as needed)
Support 2 (Continue as needed)
Restate thesis
Review main supports
Concluding statement
Invite the audience to take a specific action.
Identify the overall importance of the topic and position.

How to write an argumentative essay
Regardless of the writer’s topic or point of view, an argumentative essay should include an introductory paragraph, body paragraphs, a conclusion, and works cited.
Background information
Body Paragraphs
Analysis of evidence
Rephrased thesis
Review of main ideas
Call to action
Works Cited

Argumentative essay introduction
The introduction sets the tone for the entire paper and introduces the argument. In general, the first paragraph(s) should attract the reader’s attention, provide relevant context, and conclude with a thesis statement.
To attract the reader's attention , start with an introductory device. There are several attention-grabbing techniques, the most common of which consist of the following:
The writer can emphasize the topic’s importance by explaining the current interest in the topic or indicating that the subject is influential.
Pertinent statistics give the paper an air of authority.
There are many reasons for a stimulating statement to surprise a reader. Sometimes it is joyful; sometimes it is shocking; sometimes it is surprising because of who said it.
An interesting incident or anecdote can act as a teaser to lure the reader into the remainder of the essay. Be sure that the device is appropriate for the subject and focus of what follows.
Provide the reader with relevant context and background information necessary to understand the topic.
Conclude with a thesis statement that identifies the overall purpose of the essay (topic and position). Writers can also include their support directly in the thesis, which outlines the structure of the essay for the reader.
Avoid the following when writing the introduction to argumentative writing:
Starting with dictionary definitions is too overdone and unappealing.
Do not make an announcement of the topic like “In this paper I will…” or “The purpose of this essay is to….”
Evidence supporting or developing the thesis should be in the body paragraphs, not the introduction.
Beginning the essay with general or absolute statements such as “throughout history...” or “as human beings we always...” or similar statements suggest the writer knows all of history or that all people behave or think in the same way.
Argumentative essay thesis
The thesis statement is the single, specific claim the writer sets out to prove and is typically positioned as the last sentence of the introduction . It is the controlling idea of the entire argument that identifies the topic, position, and reasoning.
When constructing a thesis for an argumentative paper, make sure it contains a side of the argument, not simply a topic. An argumentative thesis identifies the writer’s position on a given topic. If a position cannot be taken, then it is not argumentative thesis:
Topic: Capital punishment is practiced in many states.
Thesis: Capital punishment should be illegal.
While not always required, the thesis statement can include the supports the writer will use to prove the main claim. Therefore, a thesis statement can be structured as follows:
TOPIC + POSITION (+ SUPPORTS)
No Supports: College athletes (TOPIC) should be financially compensated (POSITION).
Supports: College athletes (TOPIC) should be financially compensated (POSITION) because they sacrifice their minds and bodies (SUPPORT 1), cannot hold
Argumentative essay body paragraphs
Body paragraphs can be of varying lengths, but they must present a coherent argument unified under a single topic. They are rarely ever longer than one page, double-spaced; usually they are much shorter.
Lengthy paragraphs indicate a lack of structure. Identify the main ideas of a lengthy paragraph to determine if they make more sense as separate topics in separate paragraphs.
Shorter paragraphs usually indicate a lack of substance; there is not enough evidence or analysis to prove the argument. Develop the ideas more or integrate the information into another paragraph.
The structure of an argumentative paragraph should include a topic sentence, evidence, and a transition.
The topic sentence is the thesis of the paragraph that identifies the arguable point in support of the main argument. The reader should know exactly what the writer is trying to prove within the paragraph by reading the first sentence.
The supporting evidence and analysis provide information to support the claim. There should be a balance between the evidence (facts, quotations, summary of events/plot, etc.) and analysis (interpretation of evidence). If the paragraph is evidence-heavy, there is not much of an argument; if it is analysis-heavy, there is not enough evidence in support of the claim.
The transition can be at the beginning or the end of a paragraph. However, it is much easier to combine the transition with the concluding observation to help the paragraphs flow into one another. Transitions in academic writing should tell the reader where you were, where you are going, and relate to the thesis.
Some essays may benefit from the inclusion of rebuttals to potential counterarguments of the writer’s position.
Argumentative essay conclusion
The conclusion should make readers glad they read the paper. It can suggest broader implications that will not only interest readers but also enrich their understanding in some way. There are three aspects to follow when constructing the conclusion: rephrase the thesis, synthesize information, and call the reader to action.
Rephrased the thesis in the first sentence of the conclusion. It must be in different words; do not simply write it verbatim.
Synthesize the argument by showing how the paper's main points support the argument.
Propose a course of action or a solution to an issue. This can redirect the reader's thought process to apply the ideas to their life or to see the broader implications of the topic.
Avoid the following when constructing the conclusion:
Beginning with an unnecessary, overused phrase such as "in conclusion," "in summary," or "in closing;" although these phrases can work in speeches, they come across as trite in writing
Introducing a new idea or subtopic in the conclusion
Making sentimental, emotional appeals that are out of character with the rest of the paper
Including evidence (quotations, statistics, etc.) that should be in the body of the paper
Argumentative essay examples
Examples of argumentative essays vary depending upon the type:
Academic essays differ based upon the topic and position. These essays follow a more traditional structure and are typically assigned in high school or college. Examples of academic argumentative essay topics include the following:
Advantages or disadvantages of social media
Animal testing
Art education
Benefit or detriment of homework
Capital punishment
Class warfare
Immigration
School uniforms
Universal healthcare
Violence in video games
Argumentative literary essays are typically more informal and do not follow the same structure as an academic essay. The following are popular examples of argumentative literary essays:
“Letter from Birmingham Jail” by Martin Luther King, Jr.
“Death of the Moth” by Virginia Woolf
“Shooting an Elephant” by George Orwell
“Thoughts for the Times on War and Death” by Sigmund Freud
“Does the Truth Matter? Science, Pseudoscience, and Civilization” by Carl Sagan
“Self-Reliance” by Ralph Waldo Emerson

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

9.3: The Argumentative Essay
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 58378
- Lumen Learning
Learning Objectives
- Examine types of argumentative essays
Argumentative Essays
You may have heard it said that all writing is an argument of some kind. Even if you’re writing an informative essay, you still have the job of trying to convince your audience that the information is important. However, there are times you’ll be asked to write an essay that is specifically an argumentative piece.
An argumentative essay is one that makes a clear assertion or argument about some topic or issue. When you’re writing an argumentative essay, it’s important to remember that an academic argument is quite different from a regular, emotional argument. Note that sometimes students forget the academic aspect of an argumentative essay and write essays that are much too emotional for an academic audience. It’s important for you to choose a topic you feel passionately about (if you’re allowed to pick your topic), but you have to be sure you aren’t too emotionally attached to a topic. In an academic argument, you’ll have a lot more constraints you have to consider, and you’ll focus much more on logic and reasoning than emotions.

Argumentative essays are quite common in academic writing and are often an important part of writing in all disciplines. You may be asked to take a stand on a social issue in your introduction to writing course, but you could also be asked to take a stand on an issue related to health care in your nursing courses or make a case for solving a local environmental problem in your biology class. And, since argument is such a common essay assignment, it’s important to be aware of some basic elements of a good argumentative essay.
When your professor asks you to write an argumentative essay, you’ll often be given something specific to write about. For example, you may be asked to take a stand on an issue you have been discussing in class. Perhaps, in your education class, you would be asked to write about standardized testing in public schools. Or, in your literature class, you might be asked to argue the effects of protest literature on public policy in the United States.
However, there are times when you’ll be given a choice of topics. You might even be asked to write an argumentative essay on any topic related to your field of study or a topic you feel that is important personally.
Whatever the case, having some knowledge of some basic argumentative techniques or strategies will be helpful as you write. Below are some common types of arguments.
Causal Arguments
- In this type of argument, you argue that something has caused something else. For example, you might explore the causes of the decline of large mammals in the world’s ocean and make a case for your cause.
Evaluation Arguments
- In this type of argument, you make an argumentative evaluation of something as “good” or “bad,” but you need to establish the criteria for “good” or “bad.” For example, you might evaluate a children’s book for your education class, but you would need to establish clear criteria for your evaluation for your audience.
Proposal Arguments
- In this type of argument, you must propose a solution to a problem. First, you must establish a clear problem and then propose a specific solution to that problem. For example, you might argue for a proposal that would increase retention rates at your college.
Narrative Arguments
- In this type of argument, you make your case by telling a story with a clear point related to your argument. For example, you might write a narrative about your experiences with standardized testing in order to make a case for reform.
Rebuttal Arguments
- In a rebuttal argument, you build your case around refuting an idea or ideas that have come before. In other words, your starting point is to challenge the ideas of the past.
Definition Arguments
- In this type of argument, you use a definition as the starting point for making your case. For example, in a definition argument, you might argue that NCAA basketball players should be defined as professional players and, therefore, should be paid.
https://assessments.lumenlearning.co...essments/20277
Essay Examples
- Click here to read an argumentative essay on the consequences of fast fashion . Read it and look at the comments to recognize strategies and techniques the author uses to convey her ideas.
- In this example, you’ll see a sample argumentative paper from a psychology class submitted in APA format. Key parts of the argumentative structure have been noted for you in the sample.
Link to Learning
For more examples of types of argumentative essays, visit the Argumentative Purposes section of the Excelsior OWL .
Contributors and Attributions
- Argumentative Essay. Provided by : Excelsior OWL. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/rhetorical-styles/argumentative-essay/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of a man with a heart and a brain. Authored by : Mohamed Hassan. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : pixabay.com/illustrations/decision-brain-heart-mind-4083469/. License : Other . License Terms : pixabay.com/service/terms/#license

8 Effective Strategies to Write Argumentative Essays
In a bustling university town, there lived a student named Alex. Popular for creativity and wit, one challenge seemed insurmountable for Alex– the dreaded argumentative essay!
One gloomy afternoon, as the rain tapped against the window pane, Alex sat at his cluttered desk, staring at a blank document on the computer screen. The assignment loomed large: a 350-600-word argumentative essay on a topic of their choice . With a sigh, he decided to seek help of mentor, Professor Mitchell, who was known for his passion for writing.
Entering Professor Mitchell’s office was like stepping into a treasure of knowledge. Bookshelves lined every wall, faint aroma of old manuscripts in the air and sticky notes over the wall. Alex took a deep breath and knocked on his door.
“Ah, Alex,” Professor Mitchell greeted with a warm smile. “What brings you here today?”
Alex confessed his struggles with the argumentative essay. After hearing his concerns, Professor Mitchell said, “Ah, the argumentative essay! Don’t worry, Let’s take a look at it together.” As he guided Alex to the corner shelf, Alex asked,
Table of Contents
“What is an Argumentative Essay?”
The professor replied, “An argumentative essay is a type of academic writing that presents a clear argument or a firm position on a contentious issue. Unlike other forms of essays, such as descriptive or narrative essays, these essays require you to take a stance, present evidence, and convince your audience of the validity of your viewpoint with supporting evidence. A well-crafted argumentative essay relies on concrete facts and supporting evidence rather than merely expressing the author’s personal opinions . Furthermore, these essays demand comprehensive research on the chosen topic and typically follows a structured format consisting of three primary sections: an introductory paragraph, three body paragraphs, and a concluding paragraph.”
He continued, “Argumentative essays are written in a wide range of subject areas, reflecting their applicability across disciplines. They are written in different subject areas like literature and philosophy, history, science and technology, political science, psychology, economics and so on.
Alex asked,
“When is an Argumentative Essay Written?”
The professor answered, “Argumentative essays are often assigned in academic settings, but they can also be written for various other purposes, such as editorials, opinion pieces, or blog posts. Some situations to write argumentative essays include:
1. Academic assignments
In school or college, teachers may assign argumentative essays as part of coursework. It help students to develop critical thinking and persuasive writing skills .
2. Debates and discussions
Argumentative essays can serve as the basis for debates or discussions in academic or competitive settings. Moreover, they provide a structured way to present and defend your viewpoint.
3. Opinion pieces
Newspapers, magazines, and online publications often feature opinion pieces that present an argument on a current issue or topic to influence public opinion.
4. Policy proposals
In government and policy-related fields, argumentative essays are used to propose and defend specific policy changes or solutions to societal problems.
5. Persuasive speeches
Before delivering a persuasive speech, it’s common to prepare an argumentative essay as a foundation for your presentation.
Regardless of the context, an argumentative essay should present a clear thesis statement , provide evidence and reasoning to support your position, address counterarguments, and conclude with a compelling summary of your main points. The goal is to persuade readers or listeners to accept your viewpoint or at least consider it seriously.”
Handing over a book, the professor continued, “Take a look on the elements or structure of an argumentative essay.”
Elements of an Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay comprises five essential components:
Claim in argumentative writing is the central argument or viewpoint that the writer aims to establish and defend throughout the essay. A claim must assert your position on an issue and must be arguable. It can guide the entire argument.
2. Evidence
Evidence must consist of factual information, data, examples, or expert opinions that support the claim. Also, it lends credibility by strengthening the writer’s position.
3. Counterarguments
Presenting a counterclaim demonstrates fairness and awareness of alternative perspectives.
4. Rebuttal
After presenting the counterclaim, the writer refutes it by offering counterarguments or providing evidence that weakens the opposing viewpoint. It shows that the writer has considered multiple perspectives and is prepared to defend their position.
The format of an argumentative essay typically follows the structure to ensure clarity and effectiveness in presenting an argument.
How to Write An Argumentative Essay
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an argumentative essay:
1. Introduction
- Begin with a compelling sentence or question to grab the reader’s attention.
- Provide context for the issue, including relevant facts, statistics, or historical background.
- Provide a concise thesis statement to present your position on the topic.
2. Body Paragraphs (usually three or more)
- Start each paragraph with a clear and focused topic sentence that relates to your thesis statement.
- Furthermore, provide evidence and explain the facts, statistics, examples, expert opinions, and quotations from credible sources that supports your thesis.
- Use transition sentences to smoothly move from one point to the next.
3. Counterargument and Rebuttal
- Acknowledge opposing viewpoints or potential objections to your argument.
- Also, address these counterarguments with evidence and explain why they do not weaken your position.
4. Conclusion
- Restate your thesis statement and summarize the key points you’ve made in the body of the essay.
- Leave the reader with a final thought, call to action, or broader implication related to the topic.
5. Citations and References
- Properly cite all the sources you use in your essay using a consistent citation style.
- Also, include a bibliography or works cited at the end of your essay.
6. Formatting and Style
- Follow any specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or institution.
- Use a professional and academic tone in your writing and edit your essay to avoid content, spelling and grammar mistakes .
Remember that the specific requirements for formatting an argumentative essay may vary depending on your instructor’s guidelines or the citation style you’re using (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Always check the assignment instructions or style guide for any additional requirements or variations in formatting.
Did you understand what Prof. Mitchell explained Alex? Check it now!
Fill the Details to Check Your Score

Prof. Mitchell continued, “An argumentative essay can adopt various approaches when dealing with opposing perspectives. It may offer a balanced presentation of both sides, providing equal weight to each, or it may advocate more strongly for one side while still acknowledging the existence of opposing views.” As Alex listened carefully to the Professor’s thoughts, his eyes fell on a page with examples of argumentative essay.
Example of an Argumentative Essay
Alex picked the book and read the example. It helped him to understand the concept. Furthermore, he could now connect better to the elements and steps of the essay which Prof. Mitchell had mentioned earlier. Aren’t you keen to know how an argumentative essay should be like? Here is an example of a well-crafted argumentative essay , which was read by Alex. After Alex finished reading the example, the professor turned the page and continued, “Check this page to know the importance of writing an argumentative essay in developing skills of an individual.”
Importance of an Argumentative Essay
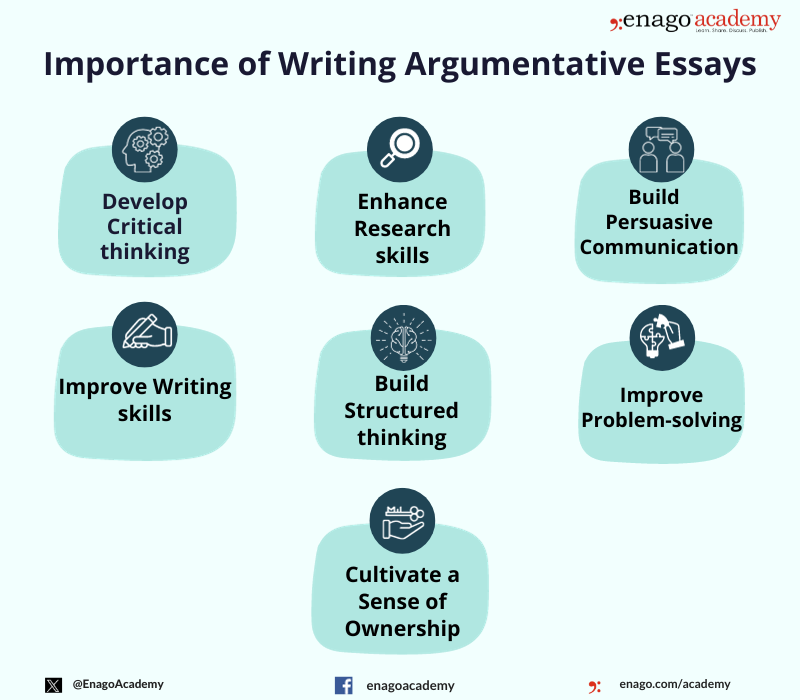
After understanding the benefits, Alex was convinced by the ability of the argumentative essays in advocating one’s beliefs and favor the author’s position. Alex asked,
“How are argumentative essays different from the other types?”
Prof. Mitchell answered, “Argumentative essays differ from other types of essays primarily in their purpose, structure, and approach in presenting information. Unlike expository essays, argumentative essays persuade the reader to adopt a particular point of view or take a specific action on a controversial issue. Furthermore, they differ from descriptive essays by not focusing vividly on describing a topic. Also, they are less engaging through storytelling as compared to the narrative essays.
Alex said, “Given the direct and persuasive nature of argumentative essays, can you suggest some strategies to write an effective argumentative essay?
Turning the pages of the book, Prof. Mitchell replied, “Sure! You can check this infographic to get some tips for writing an argumentative essay.”
Effective Strategies to Write an Argumentative Essay

As days turned into weeks, Alex diligently worked on his essay. He researched, gathered evidence, and refined his thesis. It was a long and challenging journey, filled with countless drafts and revisions.
Finally, the day arrived when Alex submitted their essay. As he clicked the “Submit” button, a sense of accomplishment washed over him. He realized that the argumentative essay, while challenging, had improved his critical thinking and transformed him into a more confident writer. Furthermore, Alex received feedback from his professor, a mix of praise and constructive criticism. It was a humbling experience, a reminder that every journey has its obstacles and opportunities for growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
An argumentative essay can be written as follows- 1. Choose a Topic 2. Research and Collect Evidences 3. Develop a Clear Thesis Statement 4. Outline Your Essay- Introduction, Body Paragraphs and Conclusion 5. Revise and Edit 6. Format and Cite Sources 7. Final Review
One must choose a clear, concise and specific statement as a claim. It must be debatable and establish your position. Avoid using ambiguous or unclear while making a claim. To strengthen your claim, address potential counterarguments or opposing viewpoints. Additionally, use persuasive language and rhetoric to make your claim more compelling
Starting an argument essay effectively is crucial to engage your readers and establish the context for your argument. Here’s how you can start an argument essay are: 1. Begin With an Engaging Hook 2. Provide Background Information 3. Present Your Thesis Statement 4. Briefly Outline Your Main 5. Establish Your Credibility
The key features of an argumentative essay are: 1. Clear and Specific Thesis Statement 2. Credible Evidence 3. Counterarguments 4. Structured Body Paragraph 5. Logical Flow 6. Use of Persuasive Techniques 7. Formal Language
An argumentative essay typically consists of the following main parts or sections: 1. Introduction 2. Body Paragraphs 3. Counterargument and Rebuttal 4. Conclusion 5. References (if applicable)
The main purpose of an argumentative essay is to persuade the reader to accept or agree with a particular viewpoint or position on a controversial or debatable topic. In other words, the primary goal of an argumentative essay is to convince the audience that the author's argument or thesis statement is valid, logical, and well-supported by evidence and reasoning.
Great article! The topic is simplified well! Keep up the good work
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
How to Effectively Cite a PDF (APA, MLA, AMA, and Chicago Style)
The pressure to “publish or perish” is a well-known reality for academics, striking fear into…

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
Using AI for Journal Selection — Simplifying your academic publishing journey in the smart way
Strategic journal selection plays a pivotal role in maximizing the impact of one’s scholarly work.…

- Career Corner
Recognizing the signs: A guide to overcoming academic burnout
As the sun set over the campus, casting long shadows through the library windows, Alex…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Reassessing the Lab Environment to Create an Equitable and Inclusive Space
The pursuit of scientific discovery has long been fueled by diverse minds and perspectives. Yet…

Simplifying the Literature Review Journey — A comparative analysis of 6 AI summarization tools
Imagine having to skim through and read mountains of research papers and books, only to…
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
How to Improve Lab Report Writing: Best practices to follow with and without…
Digital Citations: A comprehensive guide to citing of websites in APA, MLA, and CMOS…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
Argumentative Essay Examples & Analysis
July 20, 2023
Writing successful argumentative or persuasive essays is a sort of academic rite of passage: every student, at some point in their academic career, will have to do it. And not without reason—writing a good argumentative essay requires the ability to organize one’s thoughts, reason logically, and present evidence in support of claims. They even require empathy, as authors are forced to inhabit and then respond to viewpoints that run counter to their own. Here, we’ll look at some argumentative essay examples and analyze their strengths and weaknesses.
What is an argumentative essay?
Before we turn to those argumentative essay examples, let’s get precise about what an argumentative essay is. An argumentative essay is an essay that advances a central point, thesis, or claim using evidence and facts. In other words, argumentative essays are essays that argue on behalf of a particular viewpoint. The goal of an argumentative essay is to convince the reader that the essay’s core idea is correct.
Good argumentative essays rely on facts and evidence. Personal anecdotes, appeals to emotion , and opinions that aren’t grounded in evidence just won’t fly. Let’s say I wanted to write an essay arguing that cats are the best pets. It wouldn’t be enough to say that I love having a cat as a pet. That’s just my opinion. Nor would it be enough to cite my downstairs neighbor Claudia, who also has a cat and who also prefers cats to dogs. That’s just an anecdote.
For the essay to have a chance at succeeding, I’d have to use evidence to support my argument. Maybe there are studies that compare the cost of cat ownership to dog ownership and conclude that cat ownership is less expensive. Perhaps there’s medical data that shows that more people are allergic to dogs than they are to cats. And maybe there are surveys that show that cat owners are more satisfied with their pets than are dog owners. I have no idea if any of that is true. The point is that successful argumentative essays use evidence from credible sources to back up their points.
Argumentative essay structure
Important to note before we examine a few argumentative essay examples: most argumentative essays will follow a standard 5-paragraph format. This format entails an introductory paragraph that lays out the essay’s central claim. Next, there are three body paragraphs that each advance sub-claims and evidence to support the central claim. Lastly, there is a conclusion that summarizes the points made. That’s not to say that every good argumentative essay will adhere strictly to the 5-paragraph format. And there is plenty of room for flexibility and creativity within the 5-paragraph format. For example, a good argumentative essay that follows the 5-paragraph template will also generally include counterarguments and rebuttals.
Introduction Example
Now let’s move on to those argumentative essay examples, and examine in particular a couple of introductions. The first takes on a common argumentative essay topic —capital punishment.
The death penalty has long been a divisive issue in the United States. 24 states allow the death penalty, while the other 26 have either banned the death penalty outright or issued moratoriums halting the practice. Proponents of the death penalty argue that it’s an effective deterrent against crime. Time and time again, however, this argument has been shown to be false. Capital punishment does not deter crime. But not only that—the death penalty is irreversible, which allows our imperfect justice system no room for error. Finally, the application of the death penalty is racially biased—the population of death row is over 41% Black , despite Black Americans making up just 13% of the U.S. population. For all these reasons, the death penalty should be outlawed across the board in the United States.
Why this introduction works: First, it’s clear. It lays out the essay’s thesis: that the death penalty should be outlawed in the United States. It also names the sub-arguments the author is going to use to support the thesis: (1), capital punishment does not deter crime, (2), it’s irreversible, and (3), it’s a racially biased practice. In laying out these three points, the author is also laying out the structure of the essay to follow. Each of the body paragraphs will take on one of the three sub-arguments presented in the introduction.
Argumentative Essay Examples (Continued)
Something else I like about this introduction is that it acknowledges and then refutes a common counterargument—the idea that the death penalty is a crime deterrent. Notice also the flow of the first two sentences. The first flags the essay’s topic. But it also makes a claim—that the issue of capital punishment is politically divisive. The following sentence backs this claim up. Essentially half of the country allows the practice; the other half has banned it. This is a feature not just of solid introductions but of good argumentative essays in general—all the essay’s claims will be backed up with evidence.
How it could be improved: Okay, I know I just got through singing the praises of the first pair of sentences, but if I were really nitpicking, I might take issue with them. Why? The first sentence is a bit of a placeholder. It’s a platitude, a way for the author to get a foothold in the piece. The essay isn’t about how divisive the death penalty is; it’s about why it ought to be abolished. When it comes to writing an argumentative essay, I always like to err on the side of blunt. There’s nothing wrong with starting an argumentative essay with the main idea: Capital punishment is an immoral and ineffective form of punishment, and the practice should be abolished .
Let’s move on to another argumentative essay example. Here’s an introduction that deals with the effects of technology on the brain:
Much of the critical discussion around technology today revolves around social media. Critics argue that social media has cut us off from our fellow citizens, trapping us in “information silos” and contributing to political polarization. Social media also promotes unrealistic and unhealthy beauty standards, which can lead to anxiety and depression. What’s more, the social media apps themselves are designed to addict their users. These are all legitimate critiques of social media, and they ought to be taken seriously. But the problem of technology today goes deeper than social media. The internet itself is the problem. Whether it’s on our phones or our laptops, on a social media app, or doing a Google search, the internet promotes distracted thinking and superficial learning. The internet is, quite literally, rewiring our brains.
Why this introduction works: This introduction hooks the reader by tying a topical debate about social media to the essay’s main subject—the problem of the internet itself. The introduction makes it clear what the essay is going to be about; the sentence, “But the problem of technology…” signals to the reader that the main idea is coming. I like the clarity with which the main idea is stated, and, as in the previous introduction, the main idea sets up the essay to follow.
How it could be improved: I like how direct this introduction is, but it might be improved by being a little more specific. Without getting too technical, the introduction might tell the reader what it means to “promote distracted thinking and superficial learning.” It might also hint as to why these are good arguments. For example, are there neurological or psychological studies that back this claim up? A simple fix might be: Whether it’s on our phones or our laptops, on a social media app, or doing a Google search, countless studies have shown that the internet promotes distracted thinking and superficial learning . The body paragraphs would then elaborate on those points. And the last sentence, while catchy, is a bit vague.
Body Paragraph Example
Let’s stick with our essay on capital punishment and continue on to the first body paragraph.
Proponents of the death penalty have long claimed that the practice is an effective deterrent to crime. It might not be pretty, they say, but its deterrent effects prevent further crime. Therefore, its continued use is justified. The problem is that this is just not borne out in the data. There is simply no evidence that the death penalty deters crime more than other forms of punishment, like long prison sentences. States, where the death penalty is still carried out, do not have lower crime rates than states where the practice has been abolished. States that have abandoned the death penalty likewise show no increase in crime or murder rates.
Body Paragraph (Continued)
For example, the state of Louisiana, where the death penalty is legal, has a murder rate of 21.3 per 100,000 residents. In Iowa, where the death penalty was abolished in 1965, the murder rate is 3.2 per 100,000. In Kentucky the death penalty is legal and the murder rate is 9.6; in Michigan where it’s illegal, the murder rate is 8.7. The death penalty simply has no bearing on murder rates. If it did, we’d see markedly lower murder rates in states that maintain the practice. But that’s not the case. Capital punishment does not deter crime. Therefore, it should be abolished.
Why this paragraph works: This body paragraph is successful because it coheres with the main idea set out in the introduction. It supports the essay’s first sub-argument—that capital punishment does not deter crime—and in so doing, it supports the essay’s main idea—that capital punishment should be abolished. How does it do that? By appealing to the data. A nice feature of this paragraph is that it simultaneously debunks a common counterargument and advances the essay’s thesis. It also supplies a few direct examples (murder rates in states like Kentucky, Michigan, etc.) without getting too technical. Importantly, the last few sentences tie the data back to the main idea of the essay. It’s not enough to pepper your essay with statistics. A good argumentative essay will unpack the statistics, tell the reader why the statistics matter, and how they support or confirm the essay’s main idea.
How it could be improved: The author is missing one logical connection at the end of the paragraph. The author shows that capital punishment doesn’t deter crime, but then just jumps to their conclusion. They needed to establish a logical bridge to get from the sub-argument to the conclusion. That bridge might be: if the deterrent effect is being used as a justification to maintain the practice, but the deterrent effect doesn’t really exist, then , in the absence of some other justification, the death penalty should be abolished. The author almost got there, but just needed to make that one final logical connection.
Conclusion Example
Once we’ve supported each of our sub-arguments with a corresponding body paragraph, it’s time to move on to the conclusion.
It might be nice to think that executing murderers prevents future murders from happening, that our justice system is infallible and no one is ever wrongly put to death, and that the application of the death penalty is free of bias. But as we have seen, each of those thoughts are just comforting fictions. The death penalty does not prevent future crime—if it did, we’d see higher crime rates in states that’ve done away with capital punishment. The death penalty is an irreversible punishment meted out by an imperfect justice system—as a result, wrongful executions are unavoidable. And the death penalty disproportionately affects people of color. The death penalty is an unjustifiable practice—both practically and morally. Therefore, the United States should do away with the practice and join the more than 85 world nations that have already done so.
Why this conclusion works: It concisely summarizes the points made throughout the essay. But notice that it’s not identical to the introduction. The conclusion makes it clear that our understanding of the issue has changed with the essay. It not only revisits the sub-arguments, it expounds upon them. And to put a bow on everything, it restates the thesis—this time, though, with a little more emotional oomph.
How it could be improved: I’d love to see a little more specificity with regard to the sub-arguments. Instead of just rehashing the second sub-argument—that wrongful executions are unavoidable—the author could’ve included a quick statistic to give the argument more weight. For example: The death penalty is an irreversible punishment meted out by an imperfect justice system—as a result, wrongful executions are unavoidable. Since 1973, at least 190 people have been put to death who were later found to be innocent.
An argumentative essay is a powerful way to convey one’s ideas. As an academic exercise, mastering the art of the argumentative essay requires students to hone their skills of critical thinking, rhetoric, and logical reasoning. The best argumentative essays communicate their ideas clearly and back up their claims with evidence.
- College Success
- High School Success
Dane Gebauer
Dane Gebauer is a writer and teacher living in Miami, FL. He received his MFA in fiction from Columbia University, and his writing has appeared in Complex Magazine and Sinking City Review .
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
Argumentative Essay Examples (3 College Samples to Use)

When writing an argumentative essay, it can be helpful to look at examples and samples that provide the structure of the outline for the essay form. Here are argumentative essay examples to use when writing your university-level essay.

What is an argumentative essay?
An argumentative essay backs up its claims with facts and evidence. Its ultimate goal is to persuade the reader to concur with the thesis. Instead of only the author’s thoughts and feelings, a strong argumentative essay will incorporate facts and evidence to back up its claims.
This article will find three different argumentative essay examples to help you understand how to frame a good argument.
Argumentative essay outline:
Argumentative essays typically follow the conventional five-paragraph pattern. However, this is not necessary. The two common frameworks for these articles are the Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
- The most popular model is the Toulmin one. It starts with an introduction, moves on to a thesis or claim, and then provides information and proof to support that argument. Rebuttals of opposing points are also included in this type of essay.
- The Rogerian paradigm examines both sides of an argument, weighs their advantages and disadvantages, and then draws a decision.
Argumentative essay examples
Below are three examples of argumentative essays.
Essay Example 1:
Some people have proposed closing public libraries and replacing them with iPads with e-reader subscriptions as online learning becomes more widespread and more resources are transformed into digital form.
The idea’s proponents claim that it will result in financial savings for nearby cities and villages because libraries are expensive. They think more people will read since they won’t have to go to the library to borrow a book. Instead, they can just click on the book they want to read and read it from wherever they are. Additionally, since libraries won’t need to purchase physical copies of books because they can simply rent as many digital ones, they’ll have access to more resources.
But using tablets to replace libraries would be a grave error. First, compared to print resources, digital books and resources are more problematic and are connected with less learning. According to research comparing tablet and book reading, tablet users read 20–30% slower, remember 20–20% less information, and comprehend 10–15% less of what they read than those who read the same material in print. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that gazing at a computer for an extended period is significantly more likely than reading print to result in several health issues. Such as blurred vision, faintness, dry eyes, headaches, and eye strain.
A higher incidence of more significant health conditions like fibromyalgia, shoulder and back discomfort, and carpal tunnel syndrome. And muscle strain is also observed in individuals who use tablets and mobile devices extensively.
Second, assuming that libraries provide book lending is limited-minded. There are many advantages to libraries, many of which can only be accessed if the library is physically there. These advantages include serving as a peaceful study area, offering a forum for neighborhood interaction, hosting classes on various subjects, creating employment opportunities, responding to client inquiries, and maintaining a sense of community. Over a third of residents in one neighborhood said they felt more connected to their community when a local library started hosting community events like play dates for young children and their parents .
Similarly, a 2015 Pew survey revealed that nearly two-thirds of American respondents believed eliminating their neighborhood library would significantly negatively impact their neighborhood.
Tablets can’t provide these advantages nearly as well as libraries do for those looking to connect with others and find answers to their queries.
Despite the numerous problems with digital screens, replacing libraries with tablets may seem straightforward, but it would inspire people to spend even more time staring at screens. Additionally, many of the advantages of libraries on which people have come to rely would no longer be accessible. A simple object in many communities could never replace libraries since they are such a vital element of the social fabric.
Essay Example 2:
Malaria is a contagious illness brought on by parasites that are spread to humans by female Anopheles mosquitoes. Over 500 million people contract malaria each year, with about 80% of those individuals residing in Sub-Saharan Africa. Every year, malaria claims the lives of close to 500,000 people, the majority of them being young children under the age of five. Malaria has a higher death rate than many other infectious disorders.
Rather than treating the illness once the person is already infected, even though there have been numerous programs created to increase access to malaria treatment.
Numerous medications are available to treat malaria; many are effective and life-saving. Nonetheless, malaria eradication projects in Sub-Saharan Africa that place an excessive emphasis on treatment and insufficient emphasis on prevention have not been successful over the long run . The WHO’s Global Malaria Eradication Programme was a significant initiative to eradicate malaria. It was founded in 1955 to eradicate malaria in Africa during the following ten years . The program largely focused on vector control and was based on earlier successful initiatives in Brazil and the US. Chloroquine was widely dispersed, while DDT was sprayed in massive quantities.
The effort to eradicate malaria cost more than one billion dollars. However, the initiative was plagued by numerous issues, and in 1969, WHO had to acknowledge that the program had failed to eradicate malaria. During the period the initiative was in place, the number of malaria cases and malaria-related deaths in Sub-Saharan Africa had increased by more than 10%.
The project’s failure was largely due to the consistent strategies and procedures it imposed. The program was not nearly as effective as it could have been since it did not consider differences in governments, geography, and infrastructure. Sub-Saharan Africa lacks the resources and infrastructure necessary to sustain such a complex program, making it impossible to carry out in an intended manner.
Most African nations lack the funds to adequately treat and immunize all of their citizens, let alone afford to clean marshes or other malaria-prone areas. Only 25% of what Brazil spent on malaria eradication was spent per person on the continent. Africa’s Sub-Saharan region cannot rely on a strategy that calls for increased funding, infrastructure, or further expertise.
The widespread use of chloroquine has also led to developing parasites that are now a problem in Sub-Saharan Africa. Because chloroquine was used frequently but ineffectively, mosquitoes became resistant, and as a result, over 95% of mosquitoes in Sub-Saharan Africa are now resistant to it. To prevent and treat malaria, newer, more expensive treatments must be utilized, which raises the price of malaria treatment for a region that can’t afford it.
Programs should concentrate on preventing infection from arising in the first place rather than creating plans to treat malaria after the infection has already occurred. This strategy is more affordable and effective and also decreases the number of days lost to missed work or school, which can further impair the region’s output.
Insecticide-treated bed nets are one of the easiest and most cost-efficient ways to prevent malaria (ITNs). These nets offer a secure perimeter around whoever is utilizing them. Bed nets treated with insecticides are far more useful than those that haven’t since they prevent mosquitoes from biting people through the netting. And help lower mosquito populations in a neighborhood, aiding those who don’t even possess bed nets. Because most mosquito bites occur when a person is asleep, bed nets can significantly lessen the number of transmissions at night. Where ITNs are widely used, malaria transmission can be decreased by as much as 90%.
Households suffering from malaria can usually only gather 40% of the yields that healthy families can. A household with malaria sufferers also spends about a fifth of its income on medical expenses, not accounting for the time lost from work due to the sickness. According to estimates, malaria causes Africa to lose 12 billion USD in revenue annually. Sub-Saharan Africa needs a strong economy made possible by a large working population.
Essay Example 3:
People are once again debating whether college athletes should be paid due to the continued popularity of college athletics and the significant financial success of the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA).
There are numerous possible payment structures. Student-athletes might receive compensation through sponsorships, autographs, and the right to use their likeness, just like professional Olympians do. These payments could take a free-market approach in which players can earn whatever the market offers.
The idea’s proponents contend that college athletes need to be paid in some way for their labor since they are the ones who practice, compete in games, along with drawing spectators. Without college athletes, the NCAA wouldn’t exist, coaches wouldn’t be paid their (sometimes very high) salaries, and companies like Nike wouldn’t be able to make money off college sports. College athletes don’t receive any of the $1 billion in annual revenue that the NCAA generates in the form of a paycheck.
People who support paying college athletes assert that doing so will encourage them to stay in school longer and delay turning pro.
The Duke basketball sensation Zion Williamson, who suffered a catastrophic knee injury during his freshman year, is cited by the idea’s proponents as evidence. Many others claimed that even he adored representing Duke, risking another injury and prematurely terminating his professional career for an organization that wasn’t paying him wasn’t worth it. Later that year, Williamson declared his eligibility for the NCAA draught, showing that he agreed with them. He might have remained at Duke for more time had he been paid.
Paying athletes might also end the NCAA’s ongoing recruitment issues. Because it was determined that coaches were utilizing sex workers to attract recruits to join the team, which was completely wrong. The NCAA stripped the University of Louisville men’s basketball team of its national championship trophy in 2018. Numerous additional recruiting scandals have occurred, in which college athletes and recruiters were bought off with anything from free automobiles to having their grades modified to outright bribery.
The NCAA might end the dishonest and unlawful methods certain schools and coaches use to recruit athletes by paying college athletes and disclosing their earnings.
Even though both sides have valid arguments, it is evident that the drawbacks of compensating collegiate athletes exceed their advantages. College athletes dedicate much time and effort to representing their institution but are rewarded with scholarships and benefits. This can result in a bidding war only for the top athletes.
In contrast, most student athletics and college athletic programs would suffer or shut down due to a lack of funding. It is possible for many people if benefits for student-athletes are maintained at the current level.
A successful argumentative essay incorporates the author’s thoughts and opinions and uses facts and evidence to support its claims. For instance, you might have wished to write an argumentative essay arguing that your friends would like to travel to New York.
The majority of individuals concur that eating fast food is unhealthy. It is arguable whether the federal government should regulate the size of sodas sold at fast-food restaurants because junk food is detrimental to your health. The statement is open to reasonable agreement or disagreement.
Start with a sentence that will grab your attention. Describe the texts in detail. Declare your position. Verify that you have rephrased the prompt. Add a topic sentence that restates your assertion and justification.
Inside this article
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy
Argumentative Essay Writing
Argumentative Essay Examples

Best Argumentative Essay Examples for Your Help
Published on: Mar 10, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 30, 2024

People also read
Argumentative Essay - A Complete Writing Guide
Learn How to Write an Argumentative Essay Outline
Basic Types of Argument and How to Use Them?
Take Your Pick – 200+ Argumentative Essay Topics
Essential Tips and Examples for Writing an Engaging Argumentative Essay about Abortion
Crafting a Winning Argumentative Essay on Social Media
Craft a Winning Argumentative Essay about Mental Health
Strategies for Writing a Winning Argumentative Essay about Technology
Crafting an Unbeatable Argumentative Essay About Gun Control
Win the Debate - Writing An Effective Argumentative Essay About Sports
Make Your Case: A Guide to Writing an Argumentative Essay on Climate Change
Ready, Set, Argue: Craft a Convincing Argumentative Essay About Wearing Mask
Crafting a Powerful Argumentative Essay about Global Warming: A Step-by-Step Guide
Share this article
Argumentative essays are one of the most common types of essay writing. Students are assigned to write such essays very frequently.
Despite being assigned so frequently, students still find it hard to write a good argumentative essay .
There are certain things that one needs to follow to write a good argumentative essay. The first thing is to choose an effective and interesting topic. Use all possible sources to dig out the best topic.
Afterward, the student should choose the model that they would follow to write this type of essay. Follow the steps of the chosen model and start writing the essay.
The models for writing an argumentative essay are the classical model, the Rogerian model, and the Toulmin model.
To make sure that you write a good argumentative essay, read the different types of examples mentioned in this blog.
On This Page On This Page -->
Good Argumentative Essay Examples
Argumentative essays are an inevitable part of academic life. To write a good argumentative essay, you need to see a few good examples of this type of essay.
To analyze whether the example is good to take help from or not. You need to look for a few things in it.
Make sure it follows one specific model and has an introductory paragraph, organized body paragraphs, and a formal conclusion.

Get More Examples From Our AI Essay Writer
How to Start an Argumentative Essay Example
Learning how to start an argumentative essay example is a tricky thing for beginners. It is quite simple but can be challenging for newbies. To start an argumentative essay example, you need to write a brief and attractive introduction. It is written to convince the reader and make them understand your point of view .
Add body paragraphs after the introduction to support your thesis statement. Also, use body paragraphs to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of your side of the argument.
Write a formal conclusion for your essay and summarize all the key elements of your essay. Look at the example mentioned below to understand the concept more clearly.
Check out this video for more information!
Argumentative Essay Example (PDF)
Argumentative Essay Example
Argumentative essays are assigned to university students more often than the students of schools and colleges.
It involves arguments over vast and sometimes bold topics as well.
For university students, usually, argumentative essay topics are not provided. They are required to search for the topic themselves and write accordingly.
The following examples will give an idea of how university students write argumentative essays.
Argumentative Essay Example for University (PDF)
Argumentative Essay Examples for College
For the college level, it is recommended to use simple language and avoid the use of complex words in essays.
Make sure that using simple language and valid evidence, you support your claim well and make it as convincing as possible
If you are a college student and want to write an argumentative essay, read the examples provided below. Focus on the formatting and the vocabulary used.
Argumentative Essay Example for College (PDF)
College Argumentative Essay Sample (PDF)
Argumentative Essay Examples for Middle School
Being a middle school student, you must be wondering how we write an argumentative essay. And how can you support your argument?
Go through the following examples and hopefully, you will be able to write an effective argumentative essay very easily.
Argumentative Essay Example for Middle School(PDF)
Middle School Argumentative Essay Sample (PDF)
Argumentative Essay Examples for High School
High school students are not very aware of all the skills that are needed to write research papers and essays.
Especially, when it comes to argumentative essays, it becomes quite a challenge for high schools to defend their argument
In this scenario, the best option is to look into some good examples. Here we have summed up two best examples of argumentative essays for high school students specifically.
Argumentative Essay Example for High School (PDF)
High School Argumentative Essay Sample (PDF)
Argumentative Essay Examples for O Level
The course outline for O levels is quite tough. O levels students need to have a good command of the English language and amazing writing skills.
If you are an O-level student, the following examples will guide you on how to write an argumentative essay.
Argumentative Essay Example for O Level (PDF)
Argumentative Essay for O Level Students (PDF)
5-Paragraph Argumentative Essay Examples
A 5-paragraph essay is basically a formatting style for essay writing. It has the following five parts:
- Introduction
In the introduction, the writer introduces the topic and provides a glance at the collected data to support the main argument.
- Body paragraph 1
The first body paragraph discusses the first and most important point related to the argument. It starts with a topic sentence and has all the factual data to make the argument convincing.
- Body paragraph 2
The second body paragraph mentions the second most important element of the argument. A topic sentence is used to start these paragraphs. It gives the idea of the point that will discuss in the following paragraph.
- Body paragraph 3
The third paragraph discusses all the miscellaneous points. Also, it uses a transitional sentence at the end to show a relation to the conclusion.
The conclusion of a five-paragraph essay reiterates all the major elements of an argumentative essay. It also restates the thesis statement using a more convincing choice of words.
Look at the example below to see how a well-written five-paragraph essay looks like
5 Paragraph Argumentative Essay Example (PDF)
Argumentative Essay Examples for 6th Grade
Students in 6th grade are at a point where they are learning new things every day.
Writing an argumentative essay is an interesting activity for them as they like to convince people of their point of view.
Argumentative essays written at such levels are very simple but well convincing.
The following example will give you more detail on how a 6th-grade student should write an argumentative essay.
6th Grade Argumentative Essay Example (PDF)
Argumentative Essay Examples for 7th Grade
There is not much difference between a 6th-grade and a 7th-grade student. Both of them are enhancing their writing and academic skills.
Here is another example to help you with writing an effective argumentative essay.
7th Grade Argumentative Essay Example (PDF)
Tough Essay Due? Hire a Writer!

Short Argumentative Essay Examples
For an argumentative essay, there is no specific limit for the word count. It only has to convince the readers and pass on the knowledge of the writer to the intended audience.
It can be short or detailed. It would be considered valid as far as it has an argument involved in it.
Following is an example of a short argumentative essay example
Short Argumentative Essay Example (PDF)
Immigration Argumentative Essay Examples
Immigration is a hot topic for a very long time now. People have different opinions regarding this issue.
Where there is more than one opinion, an argumentative essay can be written on that topic. The following are examples of argumentative essays on immigration.
Read them and try to understand how an effective argumentative essay is written on such a topic.
Argumentative Essay Example on Immigration (PDF)
Argumentative Essay Sample on Immigration (PDF)
Writing essays is usually a tiring and time-consuming assignment to do. Students already have a bunch of assignments for other subjects to complete. In this situation, asking for help from professional writers is the best choice.
If you are still in need of assistance, our essay writer AI can help you create a compelling essay that presents your argument clearly and effectively.
With our argumentative essay writing service, you will enjoy perks like expert guidance, unlimited revisions, and helpful customer support. Let our essay writer help you make an impact with your essay on global warming today!
Place your order with our college essay writing service today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 7 types of arguments.
The seven types of arguments are as follows:
- Statistical
What is the structure of an argument?
The structure of an argument consists of a main point (thesis statement) that is supported by evidence.
This evidence can include facts, statistics, examples, and other forms of data that help to prove or disprove the thesis statement.
After providing the evidence, arguments also often include a conclusion that summarizes the main points made throughout the argument.
Cathy A. (Literature, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
Some paragraphs introduce your own argument, while others state the opposing arguments and their refutations. Here is an argumentative essay outline template you could follow for writing your essay: The most common structure to craft an argumentative essay is as follows: 1. Argumentative Essay Introduction.
In this essay, I attempt to defend the view that ..... Thesis statement exercise and solutions. Imagine that you have been asked to write an argumentative essay about physical education in the Canadian high school system. Use one of the templates suggested to write a thesis statement about this topic. view solutions
Argumentative essay formula & example. In the image below, you can see a recommended structure for argumentative essays. It starts with the topic sentence, which establishes the main idea of the essay. Next, this hypothesis is developed in the development stage. Then, the rebuttal, or the refutal of the main counter argument or arguments.
When you're writing a persuasive essay, you need more than just an opinion to make your voice heard. Even the strongest stance won't be compelling if it's not structured properly and reinforced with solid reasoning and evidence. Learn what elements every argumentative essay should include and how to structure it depending on your audience in this easy step-by-step guide.
Remember the differences between a persuasive essay and an argumentative one, make sure your thesis is clear, and double-check that your supporting evidence is both relevant to your point and well-sourced. Pick your topic, do your research, make your outline, and fill in the gaps. Before you know it, you'll have yourself an A+ argumentative ...
An argumentative essay outline is a roadmap for the writer to organize their thoughts, research, and arguments in a clear and logical way. It helps to stay focused on the topic and effectively present arguments. Creating an outline before writing an argumentative essay allows students to identify the key points and evidence that should back up ideas.
An argumentative essay is a good tool of persuasion because you show the reader: 1) You have considered both sides of the argument before choosing your position 2) You are able to anticipate and refute any opposing arguments. ... This outline is designed to help students understand argumentative essay outlines in more detail. ...
When preparing to compose a good argumentative essay, utilize the following steps: Step 1: Select a topic. Step 2: Identify a position. Step 3: Locate appropriate resources. Step 4: Identify evidence supporting the position.(NOTE: If there is little evidence in support of the claim, consider re-examining the main argument.)Steps to write an argumentative essay
In an academic argument, you'll have a lot more constraints you have to consider, and you'll focus much more on logic and reasoning than emotions. Figure 1. When writing an argumentative essay, students must be able to separate emotion based arguments from logic based arguments in order to appeal to an academic audience.
An argumentative essay comprises five essential components: 1. Claim. Claim in argumentative writing is the central argument or viewpoint that the writer aims to establish and defend throughout the essay. A claim must assert your position on an issue and must be arguable. It can guide the entire argument.
When writing an argumentative essay outline, it's important to have all your facts straight. More than any other type of essay, you need to have solid and verifiable sources. Read on to learn more!
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
For example, a good argumentative essay that follows the 5-paragraph template will also generally include counterarguments and rebuttals. Introduction Example. ... Argumentative Essay Examples (Continued) Why this conclusion works: It concisely summarizes the points made throughout the essay. But notice that it's not identical to the ...
Offer some more specific background information (as needed). 3. Provide the title of the piece and the author's name if the essay is about a specific book/poem/article/passage. C. Thesis Statement 1. State your topic and position. Remember that a thesis = claim + reasons. 2. Outline your main points and ideas.
Argumentative essay outline: Argumentative essays typically follow the conventional five-paragraph pattern. However, this is not necessary. The two common frameworks for these articles are the Toulmin model and the Rogerian model. The most popular model is the Toulmin one.
Argumentative Essay Outline (Claim) Directions: Use this outline as a "road map" to write your essay. If you need more examples or sentence starters, use page 2 to help you! 1) Introduction/Claim (One paragraph) • Start with a hook or attention getting sentence.
Essay outlines can be used for any college essay, research papers, a contrast essay, speech writing, or an expository essay. There are a range of essay outline templates to use, and they vary depending on the style of essay you are writing. These include: Argumentative essay outline. Narrative essay outline. Contrast essay outline.
MLA Sample Argumentative Papers (Note: these sample papers are in MLA 7th ed. format). For sample papers in MLA 8th or 9th ed., please ask a librarian or check the Documenting Sources in MLA Style: 2016 Update: A Bedford/St. Martin's Supplement pp. 30-41, at Skyline College Library's Ready Reference shelf.
Jul 22, 2020 - Explore the art of persuasion with our collection of argumentative essays. Engage in debates on a wide array of topics, from social issues to technology. Each essay is meticulously crafted to present compelling arguments, supported by evidence and analysis, challenging readers to consider different perspectives. Perfect for those looking to refine their argumentative skills or ...
The models for writing an argumentative essay are the classical model, the Rogerian model, and the Toulmin model. To make sure that you write a good argumentative essay, read the different types of examples mentioned in this blog. 1. Good Argumentative Essay Examples.