Explore your training options in 10 minutes Get Started
- Graduate Stories
- Partner Spotlights
- Bootcamp Prep
- Bootcamp Admissions
- University Bootcamps
- Coding Tools
- Software Engineering
- Web Development
- Data Science
- Tech Guides
- Tech Resources
- Career Advice
- Online Learning
- Internships
- Apprenticeships
- Tech Salaries
- Associate Degree
- Bachelor's Degree
- Master's Degree
- University Admissions
- Best Schools
- Certifications
- Bootcamp Financing
- Higher Ed Financing
- Scholarships
- Financial Aid
- Best Coding Bootcamps
- Best Online Bootcamps
- Best Web Design Bootcamps
- Best Data Science Bootcamps
- Best Technology Sales Bootcamps
- Best Data Analytics Bootcamps
- Best Cybersecurity Bootcamps
- Best Digital Marketing Bootcamps
- Los Angeles
- San Francisco
- Browse All Locations
- Digital Marketing
- Machine Learning
- See All Subjects
- Bootcamps 101
- Full-Stack Development
- Career Changes
- View all Career Discussions
- Mobile App Development
- Cybersecurity
- Product Management
- UX/UI Design
- What is a Coding Bootcamp?
- Are Coding Bootcamps Worth It?
- How to Choose a Coding Bootcamp
- Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses
- Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Community College
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Self-Learning
- Bootcamps vs. Certifications: Compared
- What Is a Coding Bootcamp Job Guarantee?
- How to Pay for Coding Bootcamp
- Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans
- Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants
- Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps
- Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your Employer
- GI Bill and Coding Bootcamps
- Tech Intevriews
- Our Enterprise Solution
- Connect With Us
- Publication
- Reskill America
- Partner With Us
- Resource Center
- Bachelor’s Degree
- Master’s Degree

Top Video Editing Projects to Sharpen Your Skills and Build Your Video Editing Portfolio
Video editing is a task that requires editing software skills and basic knowledge of camera equipment. Once you’ve acquired the relevant knowledge and skills, you need to practice on real-life projects. In this article, you’ll learn about some of the best video editing projects that will allow you to practice your skills and help you build your professional portfolio.
Whether you’re editing together a collection of historical person interviews about a moment in history for a classroom video, creating a university promotion video, or creating a book trailer to promote fellow artists, working on video editing projects is a great way to build mastery.
Find your bootcamp match
5 skills that video editing projects can help you practice.
Listed below are five of the primary skills you’ll practice through video editing projects. Developing these skills will allow you to master the art of video editing and equip you with the necessary tools to produce work that is portfolio-worthy.
- Video Editing Tools. There is an extensive amount of video editing tools available in various video editing software. While you don’t need to learn or use all of them, there are certain tools that you’ll need to master the use of for clean and smooth results.
- Graphic Design. Despite their obvious differences, graphic design and video editing share many similarities. Having graphic design skills allows for easier use of typography, color editing, and combining of different media files throughout the video editing process.
- Audio Editing. Nearly half of the video editing process is audio editing. Within video editing, you’ll need to sync, edit, and adjust sound effects, music, speech, and many other sound elements.
- Video Camera Knowledge. As a video editor, you need to have a working understanding of how video cameras work. You need to know how to handle the camera, connect it to your computer, and download the footage. In addition, you’ll need to be aware of camera settings as they affect the editing process.
- Audio and Visual Effects. Depending on the nature of your project, you might be required to add or edit audio and visual effects. You can practice using software such as Adobe After Effects, Apple Motion, or Blackmagic Fusion in some of your video projects if you’re aiming for high-quality results.
Best Video Editing Project Ideas for Beginners
Listed below are some of the best video editing projects for beginners. These projects will allow you to become familiar with the editing process, develop the relevant skills, and build your portfolio. Mastering the skills involved in these video project ideas are key steps toward becoming a professional editor.
A Ghost Effect
- Video Editing Skills Practiced: Video editing tools, audio and visual effects
In this project, your goal is to add visual and audio ghost effects to a video. You can choose or shoot a short clip to work with. It should be long enough to appreciate the effect, but realistically under 30 seconds. You’ll need to use the trim, translucent overlay, and audio tools in your software. Make sure the timing of the audio effect aligns with the visual effect.
Mixed Footage
- Video Editing Skills Practiced: Video editing tools, video camera knowledge
This project requires you to work with mixed footage. Mixed footage is a combination of raw materials that have different formats and resolutions. You’ll combine them in a sequence, which means you need to adjust the frame rates, sizes, and resolution of clips that don’t match your master sequence.
Video Transitions
- Video Editing Skills Practiced: Visual effects
In this project, you’ll be adding transitions in between video clips. Most video editing software will easily be able to do this. However, you can download DaVinci Resolve for free if your current software doesn’t offer this tool. You’ll need to time your transition so that you don’t cut the end of the transitioning clip or the beginning of the clip you’re transitioning to.
Split-Screen Video Clips
- Video Editing Skills Practiced: Video editing tools
In this project, you’ll need to use a split-screen technique on movie clips. The split-screen technique allows you to simultaneously play two clips in one frame. You’ll need to remove the audio from both clips, as editing simultaneous audio is slightly more advanced.
Music in Video
- Video Editing Skills Practiced: Video editing techniques, audio effects, audio editing
For this project, you’ll need to add music to a video clip. You’ll start by uploading the video clip you want to use. You should be able to easily upload an mp3 audio file and apply it to your video. Your goal is to adjust the mp3 volume and video audio so that they complement one another. Remember, your background music shouldn’t overpower the audio in your original video file.
Best Intermediate Video Editing Project Ideas
Once you’ve mastered the beginner projects, you’re ready for more intermediate projects. The video editing projects below cover creative techniques that will further develop your editing style and abilities. They’re also excellent pieces to add to your professional portfolio and video resume.
Video Transitions
- Video Editing Skills Practiced: Visual effects, video editing tools
In this project, you’ll be creating your own transitions in between video clips. You’ll need to upload at least four video clips to create three transitions. Depending on the number of transitions you want to create, you can upload more or fewer clips. Some popular transition styles include zooming in, panning, fading, blurring, cutting, and dissolving.
Cinemagraph
In this project, you’ll be creating a cinemagraph. First, you’ll need to upload a video clip showing continuous action. You might want to start with a waterfall or fountain clip. You’ll then create a copy of the clip and add it to the timeline. Once they’re layered, you’ll use a mask and erase the layer where you want the video to appear.
Motion Titles
- Video Editing Skills Practiced: Visual effects, graphic design
Motion titles are a layered transition technique video engineers use that will improve the current version of your video project. In Adobe After Effects or Photoshop, when you upload two video clips, there will be a quick moment of transition between the clips that can look quite choppy.
Using the motion tiles tool, you can add a transition layer, typically starting from one second before the first clip ends and ending one second after the second clip begins. The result will be a more fluid finished project.
Animated Overlays
- Video Editing Skills Practiced: Video editing tools
Animated overlays are a layer of moving parts in a still frame or video clip and can make for some fun videos. You’ll begin by downloading the overlay that you want to use. You’ll then upload the content that you want to add an animated overlay to.
Finally, you’ll upload your animated overlay and drag the overlay file onto your media file to overlap the two. Fellow editors often use this technique with clay animation footage and other story-telling videos to make the viewing experience more entertaining, as no one likes to look at a blank screen background.
Blend Mode Technique
- Video Editing Skills Practiced: Video editing tools, graphic design
Blend modes alter a set of clips’ interactions. You take two video clips and blend them together so that aspects of one clip act as the background, while aspects of the other become the foreground.
You’ll need to use a cross-dissolving tool in blend mode so that the foreground continues once the cross-dissolve ends. You can easily practice this basic video editing technique using archival footage or junk footage found on the Internet if you want to hone your skills.
Advanced Video Editing Project Ideas
Once you’ve mastered a wide range of video editing skills, you’re reading to take on more challenging projects. The advanced projects listed below will help you further develop your skills and provide you with excellent portfolio pieces.
Ultra HD Background
- Video Editing Skills Practiced: Graphic design
Ultra HD backgrounds allow you to customize your videos and make them look professionally done. This project is best paired with Corel Videostudio X7 for editing the raw footage and Paintshop Pro for resizing the HD image. You’ll need to resample and resize each image before turning it into an Ultra HD background.
Keyframing For Better Editing Control
In this project, you’ll use keyframes to have greater control over your video elements using Pinnacle Studio. You will need to set precise parameters on moving objects while sizing and positioning them. Lastly, you’ll add visual effects by manipulating opacity, borders, corner curves, and dissolve effects.
Advanced Title Effects
- Video Editing Skills Practiced: Video editing tools, visual effects
This project requires you to create unique, customized, and advanced video titles using Pinnacle Studio. You’ll work with text layering, shapes, special effects, animated overlays, and creative transitions. Title effects are often used in YouTube videos, TV shows, and a variety of other video media.
Creating a Video Cinematic
- Video Editing Skills Practiced: Video effects
This project involves designing and developing a cinematic effect using Shotcut video editing software. You’ll experiment with the saturation, highlights, shadows, contrast, and hues until you attain your desired look and a final version ready for people to see. Editors often use cinematic effects to add a dramatic edge, which is often seen in movies, professional travel vlogs, and wedding videos.
Editing a Music Video
- Video Editing Skills Practiced: Audio and visual effects, video editing tools, audio editing
In this project, you’ll be editing an amatuer music video. You’ll need to upload the video clips and audio that you want to use. You’ll create a multi-cam sequence and make cuts in that sequence. You’ll also edit all of the fundamental elements, including color, transitions, overlays, and beat alignment. The most time-consuming part will be to align every video aspect with the music.
Video Editing Starter Project Templates
One of the best ways to gain video editing experience, especially as a beginner, is to use video editing templates. These templates contain pre-altered settings and effects so that all you have to do is add your project files and modify the existing settings according to your preferences. Listed below are some of the templates you can use to get started.
- After Effects Template . This template can be used to implement blur and fade transitions. It’s also conducive to a collaborative environment.
- Video Outro Template . This template is especially useful for YouTube content creators. It’s an outro clip of a beach that is fully customizable.
- Canva Video Editing Template . This template is ideal for editing a business promotional video, which can be an arduous process. It includes a huge variety of royalty-free footage and is fully customizable.
- Instagram Stories Pack . This template pack has been developed for Instagram video stories so that even casual users can have professional-looking content. You can edit text, music, images, and other basic elements.
- Animated Shapes and Symbols . This template pack comes with 45 free animated shapes and symbols that can be added to your video editing projects.
Next Steps: Start Organizing Your Video Editing Portfolio

For skills-based jobs like video editing, having an impressive portfolio is crucial to landing a job, attracting clients, or getting hired by employers. The best way to showcase your skills is by creating a video editing portfolio. You can use the tips listed below to optimize the organization of your portfolio.
Incorporate Every Software You Use
Your portfolio should include video projects that have been edited using every software that you’re proficient in. This allows employers to see that you’re capable of working with a wide range of software, which is especially important if they have a specific software they want you to use, such as Adobe Premiere or Final Cut Pro.

"Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!"
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
Highlight Your Best Work
Rather than including every project you’ve worked on, only include your best work in your professional portfolio. You’ll want to create a high-quality video portfolio, highlighting the extent of your capabilities. Your video portfolio should also allow employers and clients to see multiple dimensions of your work.
Showcase Your Unique Style
Video editing is an art, and every artist has their own unique style. Similarly, you likely have a style that’s unique to your professional preferences. You should include projects that allow employers and clients to get an idea of who you are and what your style is. Make sure you also include projects that are neutral so that they know you aren’t confined to your style.
Video Editing Projects FAQ
Yes, video editing can be profitable and has an excellent job outlook. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the average annual salary of a video editor is $61,900 . Additionally, BLS projects a 29 percent job growth between 2020 and 2030.
You can practice video editing by working on projects. It’s helpful to watch video tutorials and follow along with the experts. This is also a great way to learn new techniques, tools, and editing terminology.
According to tech review sites, the best video editing software includes Adobe Premiere Pro, Powerlink PowerDirector, Apple iMovie, Apple Final Cut Pro, Lightworks, Final Cut Pro , and Corel VideoStudio Ultimate.
A 5-minute video can take anywhere between 30 minutes to 2 weeks to edit. The editing time depends on a wide range of factors such as footage quality, audio, style, and most importantly, the project requirements or goals. Your level of experience and the quality of the software you’re using also affect the editing time.
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication .
What's Next?
Get matched with top bootcamps
Ask a question to our community, take our careers quiz.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- By use case
- AI assisted videos
- Advertising video
- Animated video
- Animated logo video
- Animated text video
- Animation video
- Cartoon video
- Commercial video
- Business video
- Explainer video
- Infographic video
- Intro video
- Movie maker
- Photo to video
- Presentation video
- Short videos
- Trailer video
- Book trailer video
- YouTube video
- Diverse Workplace Scenes
- Leadership Skills Tips
- A Reason to Celebrate
- Frank Character Explainer
- Superpowers Girl
- Robot Character Explainer
- Team Birthdays
- Birthday Cake
- Birthday Calendar
- Birthday Greetings
- Funny Birthday
- Staff Birthday
- Workplace Announcement
- Business Explainer
- Employee Onboarding
- Business Ad
- Hybrid Work Policy
- Workplace Wellness Tips
- Explainer Script
- How to Change Your Password
- Snappy Explainer
- Mental Health for Employees
- Product Explainer
- E-Learning App Ad
- Infographics
- Industry Trend Update
- Real Estate Infographic
- Marketing Infographic
- Animated Infographics
- Infographic Explainer
- Infographic
- Introductions
- New Teammate
- New Employee Introduction
- Welcome New Team Member
- Warm Welcome
- New Team Members
- Meet the Team
- We're Hiring Manager
- Recruiting Ad
- We're Hiring IT Support
- Video Resume
- Now Hiring Product Engineer
- Job Offer Congratulations
- Dancing People Ad
- Eager Dog Ad
- Winter Sale
- Funky Sloth Ad
- Product Promo
- Book Trailer
- Thanks Group
- You Rock Employee
- Great Job Team
- You Rock Team
- Great Job Employee
- Great Job Group
- Weekly Update
- Company Update
- Product Launch
- Monthly Update
- News Update
- Year in Review
Ready to get started?
- Video Trimmer
- Remove audio from video
- Add music to video
- Add text to video
- Video merger
- Video resizer
- Convert image to video
- Montage maker
- Add image to video
- Watermark maker
- Add frame to video
- Video analytics
- Add button to video
- Image Resizer
- Convert video to GIF
- Convert GIF to MP4
- Extract audio from video
- Quick start guide
- Education , Inspiration
15 creative video project ideas for students (and their teachers)

Fall is here. The leaves are starting to change color and teachers everywhere are asking the same question: How do I come up with video project ideas for my students?
Video has been a staple learning tool for decades. But having students create, design, and edit video projects themselves is becoming a much more common classroom activity. Video projects are a great way to help students of all ages actively engage with subject matter and learn from one another.
Online apps like Biteable make it easy for students to turn video ideas for school into a reality. Templates and easy-to-use editing tools keep the process simple and offer plenty of inspiration for student video projects.
To help teachers and students alike leverage video as an educational tool , we’ve gathered our favorite creative video project ideas for students. Each idea comes with a ready-to-edit video template so you and your students can get started right away.
Create videos that drive action
Activate your audience with impactful, on-brand videos. Create them simply and collaboratively with Biteable.
Elementary student video project ideas
It can be tricky to keep young students interested and engaged all day long. Creating videos gives elementary students a fun, creative way to learn about anything. And student-created videos are an amazing classroom learning supplement. If a video is produced by their peers, interest will skyrocket.
1. Create a book trailer
Instead of a traditional book report, have students design a movie-style trailer that drums up excitement about a novel or a non-fiction book. Creating a book trailer gives students the opportunity to think creatively, share a story with their classmates, and reinforce their learning in a new way.
2. Give a video tour
To supplement social studies curriculum, students can create a video showing off a significant location or their favorite part of the school. If you have a field trip planned, ask students to share their experience by recording videos throughout the day and adding voice over narration.
A video tour of the school is also a great way to share the campus with new students and visitors. As a way to pass the torch before they leave for middle school, how about asking your fifth graders to collaborate on an orientation video for incoming kindergarteners?
3. Celebrate the holidays
There’s always something to celebrate, no matter what time of year it is. Have students film letters to Santa, make video Valentines for parents or grandparents, or make short educational videos about lesser known holidays. Students can even create simple, digital thank-you notes for classroom visitors or parent volunteers.
4. Recreate a moment in history
Learning about historical people and events? Have your students research and recreate major moments in history, like the story of Rosa Parks or the Oregon Trail.
Videos help students visualize and remember these important moments. It also gives students the opportunity to experiment with digital storytelling. And students will be challenged to bring each scene to life accurately.
5. Try stop-motion video
Video learning isn’t limited to literary or historical topics. Encourage students to use stop-motion or create their own slides to explain science experiments or other STEM projects. With the right footage, like Biteable’s extensive collection of clay animation footage, students won’t even need to build stop motion models. They can just focus on the presentation and storytelling in their video.
Video project ideas for middle and high school students
Video projects for high schoolers can be a little more advanced, as students should be practicing editing and narrative skills in addition to learning about new topics.
6. Create a news channel
To supplement learning in a current events class, have your students film a news broadcast covering both local and international events.
Ask students to take on certain roles in the newsroom: anchor, sports reporter, weather reporter, or entertainment correspondent. Doing a news segment helps everyone get involved and promotes teamwork.
7. Start a portfolio
Many high school students are thinking about college applications. Give them the chance to jumpstart their applications with a portfolio video project and showcase what makes them unique.
Art students can show off their best work and design skills. Students applying to traditional schools can answer an application question or create a video showcasing their community service and extracurriculars.
8. Promote a good cause
Rather than writing a traditional essay or report, have students create a video advocating for a cause that’s important to them. This helps students build their identity and develop persuasive skills. And students can share their promotional video with everyone, not just their teacher and classmates.
9. Questions for your future self
Think ahead with a video full of inspiring questions. This project is great for incoming freshmen. At the beginning of the year, have students create videos with questions for their future self or with goals for their life and career. At graduation, send the videos back to them. It’s a fun, positive way to celebrate their success throughout high school.
Higher ed video project ideas
Higher education might not seem like the place for student-made videos. But in the real world, businesses use video for all sorts of things. Video projects build plenty of resume-worthy skills that college students can take with them to the workforce.
10. Create a university promotion video
It’s easy to forget that colleges and universities are businesses, too. And they need help with promotion. A solid college or university promotion video could open opportunities for internships or college employment. Promoting something that they’re already familiar with is a great way for students to build video persuasion skills.
11. Record and edit interviews
Being able to conduct a good interview and edit it in a way that’s appropriate for the purpose of the interview is a valuable skill in multiple industries. And interviewing experts in the field is appropriate for just about any class.
12. Make a video self-assessment
Grades are important. But being able to self-assess is also an incredibly valuable way for students to incrementally improve at any skill.
Making video self-assessments gives students a more active role in the grading process and offers them a creative way to highlight the work they’ve put into a course. It also gives them a chance to make an argument for the grade they feel they deserve — a skill that easily correlates to performance reviews in their future workplace.
13. Film a job interview guide
For most people, the interview is the most nerve-wracking part of getting a job. Practicing interview questions is a great way to prepare. But most students don’t know how to prepare for a job interview.
Creating a job interview how-to guide is a perfect way for students to learn how to prepare for a job interview and help other students prepare at the same time.
14. Create a video presentation based on a written assignment
Written assignments are the backbone of a university education (in most disciplines, at least). However, the audience for most written assignments is limited to the professor and assistants. Creating presentation videos for their assignments gives students the opportunity to share their hard work with their fellow students, while also learning valuable video editing skills.
15. Build a video resume
For most students, the job search starts even before graduation. A video resume helps students highlight the skills they acquired and the experience they gained during college. And, given the global workforce, a video resume is a great supplement to a paper resume, especially when applying for remote or distant positions where an in-person interview may not be an option.
Take your video project from idea to reality with Biteable
Ready to get started making an education video project ?
Biteable has a huge library of video templates that help students get going fast rather than struggling to start from a blank screen. Drag-and-drop editing and easy to use tools let students focus on what’s important: the project assignment and delivering a thoughtful message.
Make stunning videos with ease.
Take the struggle out of team communication.
Try Biteable now.
- No credit card required
- No complicated design decisions
- No experience necessary
- TV Matters Podcast
How to Teach Video Editing: A Step-by-Step Guide

Teaching video editing can be a rewarding and valuable experience for both educators and students. In today’s digital age, video editing skills are highly sought after in various fields, including media, marketing, and entertainment. By providing a step-by-step guide to teaching video editing, you can equip your students with the necessary knowledge and skills to excel in this rapidly growing industry. This article will walk you through the essential aspects of teaching video editing, from understanding the basics to developing a comprehensive curriculum and encouraging student engagement. Let’s dive in!
Understanding the Basics of Video Editing
Before delving into the intricacies of video editing, it is crucial to emphasize the importance of this skill. In today’s visually driven world, video content has become an integral part of communication and storytelling. From YouTube tutorials to blockbuster movies, video editing plays a pivotal role in shaping the way we consume media. By teaching video editing, you are empowering your students to express their creativity, enhance their storytelling abilities, and gain a competitive edge in the job market.
When introducing the basics of video editing, it is essential to cover key concepts that form the foundation of this craft. These include understanding the timeline, working with various video file formats, and mastering the techniques for enhancing visual and audio elements. By providing a solid grasp of these concepts, you will pave the way for your students to explore more advanced techniques with confidence.
Let’s start by exploring the concept of the timeline. The timeline is the backbone of video editing, where all the visual and audio elements come together to create a cohesive story. It allows editors to arrange clips, add transitions, and manipulate the timing of each element. Understanding how to navigate and manipulate the timeline is crucial for any aspiring video editor.
Another important aspect of video editing is working with different video file formats. There are various video file formats available, each with its own specifications and requirements. By familiarizing your students with the most commonly used video file formats, such as MP4, AVI, and MOV, you will equip them with the knowledge to handle different types of footage and ensure compatibility across different platforms.
In addition to video file formats, mastering the techniques for enhancing visual and audio elements is essential for creating engaging videos. This includes adjusting brightness, contrast, and color saturation to achieve the desired visual aesthetic. It also involves manipulating audio levels, adding background music, and incorporating sound effects to enhance the overall viewing experience.
Furthermore, video editing is not just about technical skills; it also requires a creative mindset. Encourage your students to think outside the box and experiment with different editing styles and techniques. By fostering their creativity, you will enable them to develop their unique editing style and stand out in the competitive field of video production.
Lastly, it is important to highlight the practical applications of video editing skills in today’s job market. Video editing is in high demand across various industries, including film and television production, advertising, social media marketing, and e-learning. By acquiring video editing skills, your students will open doors to a wide range of career opportunities and increase their chances of success in the digital age.
Preparing Your Teaching Materials
To ensure a successful video editing course, it is imperative to prepare the right teaching materials. One of the first steps is selecting the appropriate video editing software for your classroom. Consider the needs and skill levels of your students, as well as the available resources. Popular video editing software options include Adobe Premiere Pro, Final Cut Pro, and DaVinci Resolve, each with its own strengths and learning curves.
Additionally, gather a collection of sample videos that cover different genres and styles. These videos will serve as practical examples for your students to analyze and learn from. Encourage them to deconstruct and reassemble these videos to understand the editing techniques used, allowing them to develop their own unique style.
For more teacher resources read: EditMentor Shares Free Teacher Resources .
Developing Your Video Editing Curriculum
Structuring your video editing curriculum is essential for a well-rounded learning experience. Start by creating a syllabus that outlines the goals, learning outcomes, and schedule of your course. Make sure to cover both theory and practice, striking a balance between conceptual understanding and hands-on experience.
Divide your lessons into manageable units, focusing on specific aspects of video editing. For example, you could dedicate one unit to video capturing techniques, another to advanced effects and transitions, and yet another to color grading and audio editing. By breaking down the curriculum into digestible modules, you will facilitate better comprehension and skill development.
Teaching Video Editing Techniques
Now that you have laid the groundwork, it’s time to dive into the heart of video editing techniques. Start by introducing your students to basic editing techniques, such as cutting, trimming, and rearranging clips. Show them how to create seamless transitions and overlay visuals to enhance storytelling. Encourage experimentation and exploration, allowing them to unleash their creativity.
As your students gain confidence, venture into more advanced techniques such as keyframe animation, advanced color grading, and audio synchronization. Use project-based assignments that challenge them to apply these techniques in real-world scenarios. By incorporating practical projects, you will not only reinforce their understanding but also cultivate their problem-solving skills and ability to work under deadlines.
Encouraging Student Engagement
Engaging your students is vital for a successful video editing course. One effective way to do this is by creating interactive lessons that involve hands-on activities, discussions, and peer collaborations. Incorporate group projects where students can exchange ideas, provide feedback, and learn from one another’s strengths.
Furthermore, provide constructive feedback throughout the course to help your students improve their skills. Give them opportunities to share their work and receive feedback from both their peers and industry professionals. This will not only boost their confidence but also expose them to different perspectives and industry standards.
Teaching video editing requires patience, dedication, and a passion for the craft. By following this step-by-step guide, you can equip your students with the necessary skills and knowledge to excel in video editing. Remember to celebrate their achievements and foster a supportive learning environment that inspires creativity and innovation. Together, you can unleash their potential and pave the way for successful careers in the exciting world of video editing.
The Best Video Editing Software for Students
As technology continues to advance, video editing has become an essential skill for students in various fields. From creating multimedia presentations to editing academic projects,...
Decoding the Language of Filmmaking: A Guide to Common Abbreviations
In the intricate world of filmmaking, every detail matters, and efficiency is paramount. One way production crews streamline their communication is through the use of...
The Art of the Interview: Crafting Compelling Documentaries
Documentaries have become an increasingly popular form of storytelling, allowing filmmakers to delve deep into real-life subjects and present them in a powerful and engaging...
Never miss a new article!
Subscribe to get the latest news and tips.
An educator’s guide to teaching with video

Using educational video content in your courses can help better engage students and illustrate important concepts. This can work especially well for remote and distance learning, but is also helpful for hybrid and in-person classes. “ Blended learning ” is a relatively new term in education that allows students to learn in part through online learning and to have some control over where, when, and how they work. One effective way to incorporate blended learning is to use videos to teach specific ideas and then use valuable class time for in-depth discussions or conduct enrichment activities on the same topic.
Blended learning is a proven way to increase the effectiveness of your teaching. In a study conducted by the University of Iowa, 95 percent of students enrolled in blended learning courses earned a grade of C-minus or higher , compared to 82 percent of students in traditional lectures, and 81 percent of online-only students. Blended learning methods work well in K-12 classrooms, as well as higher education.
Aside from using video for blended learning, they can also enhance your traditional classroom environment. Multimedia adds variety to instruction and can also be a way to engage learners in projects to illustrate what they are learning.
Shift eLearning reports 40 percent of learners respond better to visual information than text alone . This is because images are easily digestible, interactive, and more engaging. Using videos for educational purposes can also help students develop media and digital literacy, which is an important skill , for any consumer of online media, but also in higher education and professional development.
Creating video content for students
The video content you create and feature in your courses will largely depend on the grade you’re teaching, as well as the type of classroom you have. For example, video content for a second-grade science class will be vastly different from a college-level psychology course.
There are several different ways you can create educational videos, including through classic filmmaking techniques and the use of editing software . Before you start creating videos for your classroom, you should consider the following:
- The concepts you want to communicate.
- The best way to connect to your students.
- The type of video that will meet your goals without exceeding your resources and abilities.
Once you know this information, you are ready to get started on your video creations.
Synchronous vs. asynchronous videos
Synchronous videos are two-way communications with no delay. For example, a zoom conference would be a synchronous video, because both the teacher and the students can respond to information in real time. The benefits of using synchronous videos include:
- Real-time collaboration
- Quicker response times
- Build trust and social bonds
- Higher material engagement
Asynchronous videos are one-way communications. A pre-recorded lecture would be an example of an asynchronous video. These types of videos are often most associated with blended learning. The benefits of asynchronous videos include:
- Deep focus during study
- Increased retention due to repeatability
- Flexibility and accessibility
- Cover more material due to fewer distractions
Synchronous and asynchronous videos are both great tools for creating a blended classroom. Synchronous videos are often more suited for remote learners who may not have other set times to interact with their teachers, while asynchronous videos provide learners with flexibility for when, where, and how often they will access the video. Whether you use either or both will depend on your classroom type and student needs.
Video creation tools and applications
Recording video is the first step in creating a video for your class. It’s relatively easy and inexpensive and there are several tools available that work for bothsynchronous and asynchronous video creation. These tools are free or low cost and usually have special offers for teachers and students. Some of these tools include:
- Google Classroom : Google Classroom partners with Google Drive to host the things your classroom needs, including student profiles, assignments, and grading, as well as instructional tools including videos. With Google classroom, you can make asynchronous videos, as well as host synchronous conferences with the Google Meet integration.
- Blackboard : Blackboard is an education portal for students and teachers. Similar to Google Classroom, you can create and share files, videos, and grades, while students can submit assignments and check grades. However, Blackboard does not have a synchronous video hosting integration, meaning any live videos will have to be hosted on another platform.
- Adobe Connect : Adobe Connect allows you and your students to access many of the same resources as Blackboard and Google Classroom, including both synchronous and asynchronous video hosting. However, Adobe Connect also offers advanced tracking tools for engagement during class. The tracking data can help you better tailor lessons to your students’ needs. Additionally, Adobe Connect has specific resources for students with accessibility needs .
- Zoom : Zoom is one of the most popular synchronous video hosting platforms. While you can use the standard platform to host virtual class meetings for free for up to 40 minutes, Zoom also has an education plan specifically for teachers. This allows for longer meetings and meeting recordings. Recorded video can be made available for asynchronous learning.
- YouTube : Owned by Google, YouTube is the largest video-sharing platform in the world. It allows you to record and store asynchronous videos for a later date, as well as host live videos. However, when hosting live video, YouTube only allows participants to interact via comments. This is sufficient for some synchronous video, such as demonstrations or lectures where audience participation is not sought.
For some of these tools, like Blackboard, you will need to have educator credentials to create an account. Other tools, like YouTube, are free and open to the public. If you require a paid account to unlock premium features, check to see what type of educational discounts are available.
Video editing software
Once you have created a video, you’ll want to edit and upload it. Editing a video can mean many things — cutting out mistakes, resizing your video for different platforms, and even adding closed-captioning, as well as inserting things like transitions and other effects.
It’s important to have at least basic editing software on your work/school device. Some tools allow you to edit video from your mobile device, however, most people find it easier to edit on a larger screen, such as a desktop monitor.
Some video editing software to help you create high-quality education materials includes:
- Adobe Premiere Rush : Adobe Premiere Rush is a simplified tool to easily make quality video and sound edits.
- Adobe Premiere Pro : Adobe Premiere Pro is a great tool for general to more-advanced editing. You can incorporate audio, text, and video clips to capture the attention of students with varying learning styles.
- Adobe Animate : Adobe Animate is a fantastic tool for adding animated elements to your videos. It’s most useful for character and flash animation, in tandem with a more general editor like Premiere.
- Adobe After Effects : Adobe After Effects is a superb software for motion graphics and general special effects. If you’re looking to use your videos outside of your classroom, or post them publicly, After Effects is a great way to improve the quality of your work.
Each of these programs offers different resources for teachers with different experience levels, from beginner to advanced. The type of editing and video production software you’ll need will depend largely on what you’re trying to do with your videos. For example, Adobe Animate is perfect for creating animated characters and elements, but wouldn’t be the best general video editor, like Premiere Rush or Premiere Pro.
Teaching strategies for video
Learning different video creation techniques, for both asynchronous and synchronous videos, is a good way to keep your content engaging, unique, and effective. Teaching to a camera can be very different from teaching to a classroom, particularly if you aren’t used to it. The following techniques can help you:
- Teach to the camera : This is the first, and one of the most important techniques you can use. When it comes to video learning, the camera is your student. It’s important to keep the camera’s eyeline at the forefront of all you’re doing so that the student can have the best view. You may be tempted to look at yourself, or other students, particularly if you’re conferencing live. However, according to Speaker Dynamics, keeping solid eye contact with your webcam can increase feelings of connectivity, which can improve retention and engagement.
- Speak clearly : This is another crucial part of creating educational videos. When you speak, you should speak clearly, and as directly into the microphone as possible. It doesn’t matter if you are sharing the world’s best content if none of your students can understand you. Investing in a lavalier mic is a great way to improve the sound quality of your videos.
- Create a “set” : As Kelly Warfield wrote for the Character Exchange teachers’ network, environment is an important part of education , even when you’re creating virtual education tools. Creating a set can not only get you in the right headspace but using the same set can also signal to students that what they’re seeing is part of their learning experience. This should help you put them in the right headspace. You’ll want to make sure that the set you create is minimally distracting, as it’s meant to be a backdrop, not a focus. This includes limiting colors, items, and even choosing softer lighting.
- Use the same tools you would use in the classroom : If you would use aids, such as a whiteboard, while teaching in the classroom, it’s important to still use those while teaching on video. This can be something like a physical whiteboard you set up on the screen, or a digital whiteboard that you can screen share. This is also important for retention and engagement for students. Some students are visual learners and rely on visual aids to fully understand something, while other students are audial learners, and can understand lessons through lectures.
- Have a clear point or goal : Anytime you sit down to make an educational video or host a conference, you need to have a clear goal in mind. This will help you make better, more-focused content that students can easily retain. For example, if you’re creating a video about a reading assignment, then you should have a theme, event, or scholarly argument in mind to contextualize the assignment. While you may open up for further discussion, having this goal creates a starting point for both you and the students to operate from.
Other aids included in your videos during editing, like transcripts and closed captioning, can make your videos more accessible to students with hearing impairments, as well as easier to produce. If you’re following a script, you’re less likely to forget what you need to say, which will make for clearer content.
Types of educational videos
Different types of educational videos can also increase engagement in blended classes. Different types of videos include:
- Animated videos
- Whiteboard videos
- Explainer videos
Creating a video type that serves your main goal can increase retention and clarity of your objective. For example, if you’re teaching a math formula, then a simple whiteboard video is a great tool. It gives a step-by-step visual that puts the focus on the formula, making it easier for students to tune out distractions.
Using non-educational videos in the classroom
When using other videos besides your own in the classroom, be selective and purposeful. The clips you show should emphasize points in the lesson objectives, rather than be a distraction. Additionally, it’s crucial to make sure the media is age-appropriate and accurate by viewing it ahead of time. This gives you time to fact-check if the media isn’t from an accredited or authoritative source.
There are several online video libraries from authoritative sources for you to choose from when creating a lesson. For example, TEDTalk offers a video library of past speeches given by experts. Adobe also offers an educational video library , which is a great classroom resource. The Library of Congress video collection is another free resource educators can use — it’s full of authoritative content.
If you’re going to use content from a non-authoritative source, make sure it still informs the lesson. For example, using a viral video from Twitter as an example of propaganda and how it works in today’s age can be a great, engaging lesson. It’s important that when you do this, you disclaim the video and explain it’s from a non-expert source before viewing. Applying digital literacy best practices to how you select video content will be a good example to your students as they choose media sources on their own.
Ways to assign videos for learning objectives and assignments
As an educator, you can also assign video projects to students. This will help them learn skills such as editing, public speaking, creative planning, and more. Some examples of video assignments could include:
- Multimedia projects
- Video presentations
- Video essays
- Skits and short films
Using video creation as a part of an assignment is a great way for you to make an average assignment — for example, a book report — more engaging. Through this, students have a higher chance of absorbing more of the material and retaining it longer because they are interacting with it in more than one way.
Ways to share your videos with others outside the classroom
If you’re interested in posting your educational videos publicly, for other students or educators to use, there are several ways you can do that. Some hosting platforms that will give those outside your classroom access to your videos include:
- Public video hosting sites : Sites like YouTube and Vimeo are perhaps the easiest way to share your content with a wider audience. Before you post, consider using tools like SafeShare , which is compatible with Google Classroom, and gives you more control over your privacy settings.
- Cloud services : Cloud-based services are ideal for easy, but “private” sharing. Services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive help you generate shareable links or files that you can give out at your leisure, as well as make public.
- Social media : Social media, like public video hosting sites, is another way that you can share your videos with a wider audience. When posting to social media, you may have less privacy control over who sees and shares your videos, so you want to be cognizant of that before posting.
- Hosting or embedding on personal websites : Sharing your videos to your personal website is a great way to have the most control over video quality and sharing, as well as be a great way to start a portfolio of your original educational materials. You can also password-protect pages and other assets on your website, making it easy for students to have more, or different, access than the general public.
In some cases, you can even earn money for the videos you share publicly, depending on the platform you use as well as the size of your audience. But in every case of a video that includes students, be sure to have a signed media release from the student, or their parent if they are a minor, before making it publicly available.
Further reading
For more reading about blended classrooms and the use of video as educational materials, check the resources below:
- ERIC : The Educational Resources Information Center (ERIC) is a federal government-sponsored site that hosts educational resources for students and teachers. It’s an article directory filled with research on different educational happenings, including blended learning .
- Next Generation Learning Challenges (NGLC) : NGLC is an organization dedicated to student-first learning. It has several resources on current events in education, as well as tools for educators, including community forums, programs, and services.
- Adobe e-Learning Archives : The Adobe e-learning archives houses several resources for e-learning, including video learning. These archives include educational and informative blog posts.
Blended and online learning continues to grow in popularity because of its proven benefits and accessibility. Applying these techniques in your classroom — such as with educational videos — is a great way to keep your students engaged and stay on top of new and exciting education trends.
https://blog.adobe.com/en/publish/2021/11/01/how-to-be-an-effective-school-leader
https://blog.adobe.com/en/publish/2021/10/18/adobe-max-bringing-creativity-heart-education
https://blog.adobe.com/en/publish/2021/10/04/ferpa-and-student-data-privacy
10 top video editing tips and tricks every beginner needs to know
Up your game with these essential video editing tips and tricks, from smoother cuts to colour grading.

With the best video editing tips and tricks, beginners can make a big leap in their video editing skills and processes. Video editing is essential to get right, but it can be a time-consuming and painstaking process. Initially, you might also be at a loss for how to get the kind of edit you want. There's so much software out there and so many ways of working that it can feel overwhelming at first, but in this guide we suggest ten video editing tips and tricks that can make a real difference for beginner video editors.
The tips below cover everything from choosing the right video editing software to considerations such as where to cut scenes and how to make sure the music you use works alongside images. You can apply these video editing tips to all kinds of videos, so they'll be relevant whether you're working on films, a personal vlog, a documentary or creative shorts and should help you raise the standard of your video content.
In our tips, we mention the importance of video editing software, and you'll find quick links to our top three recommended tools below. Just scroll down further for our ten video editing tips and tricks. You might also want to see our guide to the best laptops for video editing .
Video editing tips and tricks: the best software

<a href="https://www.prf.hn/click/camref:1101lr4vm/pubref:hawk-custom-tracking/destination:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.adobe.com%2Fuk%2Fproducts%2Fpremiere.html" data-link-merchant="adobe.com"" target="_blank" rel="nofollow"> Premiere Pro: the best video editing software Aimed at professional editors, Adobe's Premiere Pro is our pick of video editing software. This industry standard tool works on both PC and Mac, and offers everything you need.

<a href="https://apple.sjv.io/c/221109/473657/7613?subId1=hawk-custom-tracking&u=https%3A%2F%2Fapps.apple.com%2Fgb%2Fapp%2Ffinal-cut-pro%2Fid424389933" data-link-merchant="apple.sjv.io"" target="_blank" rel="nofollow"> Final Cut Pro X: the best choice for Mac users Optimised for macOS, Final Cut Pro has a great reputation within the industry and is the best option for Apple users who want to make movies easily.

Our top 10 video editing tips and tricks
01. get the right software.
First up on our list of video editing tips and tricks, is getting the right tools. With a plethora of editing software on the market, it’s not always easy to know which to use. In fact, there are so many programmes now, that it can be almost impossible to compare them all. However, if you considering working in video editing, it can be a wise move to make sure you're familiar with the industry standards. These are Adobe's Premiere Pro , Final Cut Pro (for Apple only) and DaVinci Resolve .
However, these are complex programmes with steep learning curves. If you feel that you're not ready for that, then Adobe and Apple do offer simplified versions of their professional software in the form of Premiere Elements and iMovie , respectively. Just bear in mind that these have significant limitations when compared to fully fledged editing software. There are plenty of other options suitable for newcomers too, including Filmora and Pinnacle Studio. Fortunately, many of these tools offer a free trial, which allows you to try each of them out to see which is right for you. See our full guide to the best video editing software for more options.
02. Keep it short
There’s a reason that TikTok and Instagram Reels have become so popular. People have busier lives and more sources of media content than ever, and as a result attention spans aren’t what they used to be. The most common criticism received today by amateur films, and many professional ones too, is that they’re too long.
That doesn’t mean you should cut your half-hour masterpiece down to 30 seconds, but you can certainly improve it by removing anything extraneous. In video editing like in any kind of editing, it serves to really be brutal with your own work – if a line or a shot doesn’t add anything not stated elsewhere, try taking it out and see if the video flows better without it.
Get the Creative Bloq Newsletter
Daily design news, reviews, how-tos and more, as picked by the editors.
03. Cut on action

A cut from one angle on a scene to another can sometimes be jarring. This often happens when you’re using different takes, but it can even be a problem when you have two cameras on the same take. One little video editing tip that can help make edits look smoother is to cut midway through an action, rather than when things are static.
For example, in a scene where a person walks across a room and sits down, start on a wide and cut to a close-up as the person is sitting, not once they've sat down. This looks smoother and helps cover up slight continuity errors, as the viewer’s eye will be distracted by the movement.
04. Cut away from speakers

Knowing when to cut when people are speaking is another vital video editing tip. If you linger on one person speaking, your video can look really static. To improve pace, it's usually better to cut away to other visuals as speech continues. For example, when editing a vlog in which you speak to the camera, consider adding B-roll illustrating what you’re talking about.
In scenes with two or more people, it’s often more valuable to see the person who isn’t speaking than the person who is. So, at some point while Person A is speaking, try cutting to Person B. If they give an interesting non-verbal reaction, this can add an extra element, such as enhancing drama or comedy.
05. Learn to use colour
There are two colour editing processes in video editing: colour correction and colour grading. Colour correction involves adjusting your clips for basic consistency. Shots from two different cameras or ones taken in different lighting conditions can look jarringly different when placed one after another in an edit, and this can often be fixed by adjusting brightness, contrast, and white balance.
Colour grading, on the other hand, is a global process that gives a scene a particular “look.” If you’re serious about this, certain high-end editing applications have detailed grading interfaces, but many also make it easy for newcomers to achieve using LUTs, which apply a preset colour style. This can really change the feel of a video. Consider how the tone of your video changes if you give it a colder or warmer look, for example.
06. Cut to music
Our next recommendation in this list of video editing tips and tricks is about music, which is vital for almost all video editing. Setting your video to the right music can really boost its energy – and often help its performance if you're editing for social media. But where amateur editors often go wrong is that they don’t synchronise the editing with the beat of the music, which results in jarring cuts.
Try playing the track and tapping your fingers along to the music – on your desk or on the keyboard shortcut to add markers, if your software has one. The points where you tap are the ideal points for the video to cut. You can also look at the audio waveform to help you identify the peaks that you should cut on.
07. Balance your audio
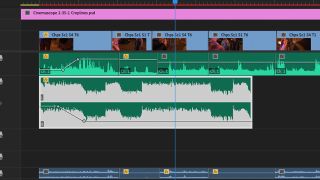
Sticking with music, another video editing tip is to make sure your audio is balanced. If the level of your music makes it difficult to hear speech, it’s doing more harm than good. Another common mistake is putting together different clips with speech at noticeably different volumes. You need to carefully balance your audio to avoid these imbalances grating on the viewer, and possibly even making your video unviewable.
Balance speech first. To do that mute any other audio, and go through your video adjusting the volume of speech clips so they’re as close as possible to each other. Then, adjust other audio elements around the speech. If your software has audio keyframing or ducking, you can use this to lower music volume when someone is speaking and to raise it elsewhere.
08. Check your rights
Another common mistake in using music in video editing is to use songs without having the appropriate rights. Sites like YouTube and Facebook have become a lot more strict in taking down videos that contain copyrighted music, so abandon any hope of being able to use your favourite hit.
Today, there are lots of websites and services that offer royalty-free music – some free and some at a cost – so it’s not difficult to find alternative tracks that suit your video. Read the terms properly, though, to be sure you’re permitted to use the music in the way you want to. Some licences only apply to specific platforms or use cases. Alternatively, if you have contacts with musicians, they may be willing to reach an arrangement to give you permission to use their tracks.
09. Always put the story first
When deciding what shot to use or where to cut when you're editing video – and in fact, with any decision you make in the editing process – always ask yourself how your choice will impact the story. That doesn’t just apply to fiction; all videos tell a story of some sort, even advertising.
If you’re adding an effect just because it looks flashy or choosing clips that look the nicest, know that this perhaps isn’t the best approach. In fact, these choices can often distract from the main point, which is to tell your story. Think about the message that you want the viewers to take from the video, what they should be thinking at each point, and what the best images and sounds to enhance that message would be.
10. Back up your work!
Finally, this is probably the most important thing we can recommend in our video editing tips and tricks. All your time and effort can go to waste if you lose your work. Many editing applications make regular automated backups, which is useful – especially for going back to previous versions if you want to backtrack, but this isn't enough. These backups are usually made to the same drive that your main project is saved on, so if that drive crashes, they won’t save you.
Ideally, you should be backing up to two additional locations, one of which shouldn't be stored at the same location. For the best peace of mind, we recommend copying your files to both an external hard drive and to a cloud server at the end of each session. This ensures that your files are safe from the many things that could go wrong (hard drives fail for various reasons, and even cloud storage isn't completely infallible – and plenty of video editors have had the experience of accidentally deleting their own work. See our pick of the best cloud storage and the best external hard drives for options.
Video editing can seem a daunting task at first, but keep these video editing tips and tricks in mind as you go, and you’ll soon be editing like a pro. You’ll also find it’s an incredibly satisfying process, especially when you watch your finished masterpiece.
- The best video editing apps : edit video on the go
- The best online video editing courses : Learn online
- Instagram Reels tutorial: A beginner's guide
Thank you for reading 5 articles this month* Join now for unlimited access
Enjoy your first month for just £1 / $1 / €1
*Read 5 free articles per month without a subscription
Join now for unlimited access
Try first month for just £1 / $1 / €1

Kieron Moore is a freelance writer based in Manchester, England. He contributes to Future sites including TechRadar and Creative Bloq, focusing on subjects including creative software, video editing, and streaming services. This work draws on his experience as an independent filmmaker and an independent TV watcher. He can be found on Twitter at @KieronMoore, usually when he’s meant to be writing.
- Joseph Foley
Related articles


Ten Engaging Video Assignments to Get Your Students Talking

- Post to Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
- Send via Email
In the classroom, video means instant engagement, and making video is an increasingly important skill for youngsters to develop. We’ve put together ten exciting assignment ideas that will help elementary and middle school teachers get their students making great video! Parents, feel free to steal these ideas for rainy weekends, too.
Make Video Really Easy For All Students
Not all students will be able to access their own camera equipment. This could be due to their families’ budgets, their age, parental permissions, or some may be a little too shy to be on camera.
Remove obstacles by creating groups to work on each project, and consider setting up a couple different “studios” in the classroom. Then, come up with fun and quiet assignments that groups not actively filming can tackle, like script writing or prop-making, while others get their turn in front of the camera.
An in-class studio could be as simple as a backdrop with a tripod, or more complex depending on your school’s resources and the space you have to work with. If you are able to setup a couple different studios, more than one group could be creating videos at the same time, and, no one will be left out if they can’t get the right equipment.
Basic video equipment is really inexpensive in this day and age, especially for this type of kid-friendly production. A low-cost video camcorder from Amazon would likely suffice, and simple tripods are usually under $50. If you aren’t in a position to purchase equipment, you can always use a smartphone or tablet with a mini-tripod or similar stand, or a laptop with a built-in camera.
Editing the final video together might not be required for all of these project ideas, but it makes sense to check on the availability of video editing programs on school computers to see if it might be possible. iMovie or Windows Movie Maker are both free and easy to use. That way, any particularly inspired students can take their project to the next level if they’d like.
Video Assignments for Elementary School Students
1. task: make a short video reviewing your favorite book..
Objective: Students should record themselves giving a synopsis of the book and sharing what they enjoy about it. Using age-appropriate props, younger children can shoot a scene from the book; older children can direct a scene featuring their friends.
In addition to putting thoughts together coherently, and learning how to write for film (for older students), this task will enable children to be comfortable in front of and behind the camera, and encourage collaborative group work.
2. Task: Make a commercial.
Objective: Take an everyday object – an apple, pen, table, lunchbox – and ask students to make a commercial trying to sell it. They should put together a script, create a jingle, and design a brand logo as well as filming the advert.
Depending on the age of your students, they could work together. Ask each member of the group to take responsibility for a different element of the video. This is an effective task at showing students the power of persuasive writing, and how to work effectively in a team, as well as the objective behind advertising.
3. Task: Create a video tour of the school for new students.
Objective: Pupils can share their school experience with new students by recording and narrating it. They should interview teachers and other students, as well as showing their classmates using the school’s facilities (outdoor play area, pool, computer room). In addition to learning filming and editing skills, this task enables students to hone interviewing and communication skills.
4. Task: Exchange video messages with other schools.
Objective: Students from a partnering elementary school exchange short videos with your class that explain what life is like at their school, or another agreed-upon topic. The idea would be to generate interest in another culture, or to introduce students from a far-flung part of the USA. Not only would this type of exchange expand their horizons, but it would help develop their story-telling abilities, too.
5. Task: Explain how to make your favorite food.
Objective: Have students make a short video about their favorite food, or a special family recipe. Use creativity for those who aren’t able to do any filming at home. For instance, have them bring in some of their favorite food to share, or use animated pictures instead of actual footage.
As an alternative, assign students to different meal groups, like breakfast, lunch, and dinner. Then, have them work on the assignment in teams. This assignment will help students get to know and appreciate other food cultures, while also having a really fun time.
Video Assignments for Middle School Students
6. task: create vocabulary vines..
Objective: Show a word on paper (perhaps a student could be filmed writing it), then record a visual representation of the term. Each short video should be shared with the whole class so students can easily access them. This is also a great exercise for foreign language classes.
Although Vine may no longer exist as a platform, short videos are still a great way to promote learning.
7. Task: Make a two-minute video assignment about your hobby.
Objective: The student will learn to operate a video camera (or the video function on their smartphone or tablet), grab copyright free clips from the web, and edit footage.
Part of the challenge will be to adhere to the two-minute time limit. Older students can be taught how to use industry-standard editing software. Whatever level they are at, students will respond positively to being given free rein to get creative and produce original content about a topic that interests them.
8. Task: Create a video dialogue with a famous historical character.
Objective: Using the split screen effect, the student should record themselves in conversation with someone the class has been studying in history. They will enjoy dressing up and getting into character for this task!
This video assignment challenges the student to demonstrate a deep understanding of the psyche and motivations of an historical personage. Note: this assignment also works well as a conversation between the student and a character from the book the class are studying.
9. Task: Film your science lab project.
Objective: Film a project from start to end, hypothesis to conclusion. Students should show footage of the experiment being set up, carried out, and concluded. They should add a voiceover explaining what’s happening and why in each shot.
This assignment is two-fold. In addition to demonstrating their understanding of the relevant scientific principles, students will hone their filming and editing skills.
10. Task: Give your own TED Talk.
Objective: Show students an age-appropriate TED Talk that’s relevant to a topic they’re studying in your class. They should use it as a basis to put together their own presentation on that subject area. Encourage them to use visual aids and to adapt an engaging mode of presenting, just like the TED speakers. A cameo from friends, family members, or even pets makes for a great video!
For demonstrating to students that a ‘talk’ is more than just talking, we recommend showing them the following TED videos: The Shared Experience of Absurdity, The New Bionics that Let Us Run, Climb and Dance, and Einstein the Parrot.
Secure Sharing
For sharing the video, it’s important to be sensitive to the privacy of the children participating. Consider sharing the video with a password or with login protection to make sure only the participants, or their parents, can view it.
Make sure you can track viewers at a very granular level. For instance, video engagement metrics enable you to check that only approved viewers are accessing your content.
If you need a website for sharing your students’ videos, we even have that covered. Each SproutVideo account comes with a customizable video website that you can configure to your specifications.
With SproutVideo, you’ll get the best live and on-demand video hosting platform for business. Start your free 30-day trial today and get unlimited access to all our features.
Start Your Free Trial
Don't miss a post — get them by email! Learn how to:
- Leverage video for marketing and business
- Produce higher quality online video
- Take advantage of the latest video trends
We will use your email address to send you new blog posts, and for any other uses outlined in our Privacy Policy . You can opt out of these messages at any time.
Thanks for subscribing to our weekly newsletter!
Sample Video Editing Project with Multiple Stages
Follow along with this sample project to see how a fully edited video comes together.
This article is adapted from one part of a "Get Started in Video Editing" seminar by Noble Desktop. Follow along with the demo by going to the Degrees chapter in the seminar.
So what does an actual editor do on a project? Let's look at an example: making a skating video in Premiere Pro.
Let's say you are given a job to create a skating promo video, and the client has an idea or a concept of what they want. You'd meet with them to discuss that concept. You’d take notes, of course, because that's how we do it. You would come up with an idea of what you want to show.
Maybe this client already has some music or audio in mind, or maybe they give you an audio file for the background. You'll have to ensure they have the legal rights to use that audio, but that's a different issue. We'll assume that, in this case, they have. Maybe they're also giving you some video they’ve created, or maybe the video is from a stock website. For this example, let's assume you have a legal right to use the video.
Assuming that you're not about to shoot more video: even if you get video from a client, you may have to supplement that with stock footage, depending on the story you're trying to make.
So let's say you have a folder on your desktop called “promo skateboarding,” and in that folder, you have another folder called “media.” In the media folder, you have a video, text, and audio folder. We're going to open a video of two skateboarders. You've got two audio files because you may need to make some adjustments, and then some text. The text is a quote by Tony Hawk that you can work in at the beginning. Instead of just using text on screen, you can animate that in After Effects.
Audio Editing
For something like this, you're given the original audio file. You'd listen to and open it up in Audition, because the first thing to check with the audio is how loud it is. This is a waveform, which is a representation of volume over time. If you're recording your audio, normally you're told to record audio somewhere between -10 and -20 decibels. This is a lot higher. This is a song, so it's easily recorded, and it's really loud. Red, for the record, is loud. When it comes to volume, green is good. Red is bad, very, very bad.
When making a video for broadcast television, you would need the audio somewhere around -12 decibels. Because you're doing this one for output on the Internet, there's no standard, so you could probably go somewhere around -3 to -5 decibels for that. You would adjust this and alter and tweak it if needed. Once that is completed, you'll end up with the normalized file that you can work with in Audition. Taking care of any audio that needs to be adjusted is a good place to start your video editing project.
You can use Audition’s tools to check the audio volume, see what it was at, and then adjust it, pulling it down to a television level of -12. So if you listen to this music and it is blowing-out-your-eardrums loud, you should adjust that.
Premiere Pro
After that, you may want to bring all this stuff into the video editing program to see what you’ve got. The first thing in Premiere you need to do is make a project, and then you're going to bring the footage to the project to look at it. You're going to review it, see what you have, and see if it makes any sense visually, because sometimes you get stuff from clients and it's not necessarily the best footage that we could use.
You're going to make a new project called“Skateboard Promo.” Choose where to save it by selecting browse . Then, you can put it back in that Promo Skateboarding folder. By default, it wants to save it into the documents folder, but to keep everything together, you’ll want to save everything on your desktop to that skateboarding promo folder. That way, you can use that as the location to save your project. Premiere Pro makes you save a project first. The reason it does this is that it needs to actually make files of its own.
As of March 2022, anyone using Premiere Pro should know the interface is going to change soon. Right now in the beta format, they're trying out a different layout with the rationale that since you don't change these menus very often, they don’t need to be in front of your face when you make a new project.
Eventually, this dialog box is going to look different. It will have the name and location and then something different in the middle. The name and location are the important things here; everything else you can change later.
Select OK , and then go to the project we just made. Premiere Pro has what's called a workspace. This is its interface. When you first start the program, you're in the Learning space. Usually people start off in Editing , which is the default editing workspace. If you’re not the biggest fan of the default editing workspace, you can make your own process called My Editing that you can work with. Just like any other Adobe program, you can completely change the interface by just pulling these windows around, reconfiguring them, and just going into Window > Workspace . Once there, you can Save as New Workspace . The more you use the program, the more you’ll realize that you want your own custom workspaces.
Importing Assets
When you start a new project, this is where you're working. You’ve got a panel called Program . This is where you’re going to see the live timeline content. After making your project, the next step is importing what you want to work with. We call that media, footage, or assets. So you're going to import it, and it says Important Media to Start . You can file import, use the keyboard shortcut command + I or control + I , right click > Import , or simply double click in the project to open the import dialog box. If you're on a Mac device, you can import multiple folders by highlighting several at a time. If you’re on a Windows device, it will not let you select more than one folder, but you can grab the parent folder. So if you highlight the Media folder with the three video, text, and audio folders inside, it will import all the subfolders and all their content.
In your promo skateboarding folder where you save your project, you will highlight the Media folder and click Import . This dialog box will tell you there’s an unrecognized file in here. This PKF file was made by Audition, and it's a preview file. This didn't interfere with your import. It just stopped that one file from importing.
In your preview of the project, you're going to switch to your list view because it gives you a list of the folders and open the folder up. The audio was imported, and the two audio files that were there came in. The video came in. You're going to make this column a little wider so you can see the full name. All those video files that were there came in.
The one thing that didn't come in exactly the same is the text folder. This is a weird glitch in the program: any folder you try to import that has a single file inside will only come in as a single file. For some reason, it will not bring in everything. You're going to click on the New Bin icon, make a new bin, click on the name and rename it “Text,” and then grab that text file and drag it in.
Text files are a little strange. Technically, they get imported, but they're not actually media. They're not editable inside of the program. If you double click on that text file, it opens your text editor so you can just copy and paste from it. Premiere Pro lets you import them, but technically it doesn't let you edit them. If you click on video and right click on that, you get a lot more options, including the new bin from sequence selection option that you were looking for. That's why we said that technically the text files do import, but Premiere Pro doesn't treat them the same way that it treats all the other files.
If you don't actually want your Media bin, you can drag the other bins out of it by clicking on them and dragging them through space. Once the Media bin is empty, so you can delete it. Just click backspace on the keyboard to delete.
If you like numbering stuff, you can number the folder. Let’s make this 01-video, click on the audio and call it 02, and text let’s call 05 so that if you make any other bins, it will be the last one.
Previewing Assets
Let's see our audio. This is the original file, the one that was too loud, and it is the one that you made in Audition, the normalized one. This is a lot lower. If you double click on that, you can preview it. If you double click on the first one, it's much taller. Height equals volume. This normalized one that you made earlier is the one you want to work with. If you play that, you can hear it.
After that, you may need to make some more stuff. Let’s say you know that you want to use this music, but you would also like to see what your video is. You can't really see which video this is; you can just see the names. That's not helpful, so you'll switch your view to icon view , which gives a visual preview. If you hover your cursor and move it left and right over the little thumbnail previews, you can scrub and preview them so you can get an idea of what this looks like visually. You cannot hear the audio when you scrub this, but if you need to hear audio, you can click on the preview and tap the spacebar on your keyboard to play it as audio. All of these have the audio stripped.
Now you can see what these videos look like. It's not bad, but they're a little small. Adjust that by using the little slider here to make them bigger, or you double click on the window to make it larger.
Ordering Assets
Let’s say you want to start your video project with the clip showing a nice overview of the city. First, you'll track back to the beginning as they're skating over the rooftops. It's a nice drone shot. Then, let’s go to the underground shot. Maybe this clip of the kids doing trick shots in the skatepark is a good clip to go next. But then you figure out this shot of him lacing up his skates is a better choice of your first opening shot, so you'll drag that to the beginning.
This is called a storyboard edit, and it allows you to organize how you want your footage displayed so that you can organize your story. You want to vary your shot distance, so this is a nice mid-shot. You're thinking a close-up of someone doing tricks might be cool. You don't want to end up on this shot of them from behind, so you'll make that your second-to-last shot and your last one.
Okay, that's kind of cool. Some of these you want to use more than once. This nice aerial shot is pretty cool. You might want to have this as an establishing shot of the area and then show the bridge flying out over it. You might want these at the end as well. With this, you can organize it into a nice little visual layout called a storyboard edit.
You have an idea of how you want to use these things, but you don't have any place to put them. If you double click on a clip, you can preview it in source, which lets you see it, listen to it, and trim it to shorten or pull out parts of it. If you want to assemble these, you need someplace to do that, and that's called a sequence.
A sequence allows you to lay out your content. A sequence displays on the timeline where it says currently no sequences. So you made your project, you imported your files, you previewed your files, but now you need a place to put them. If you hover over these clips, you can see what size they are.
These all look like different sizes if you hover over them. If you look at the second line, this one is 3840 by 2160, and that one is as well. These are 4K files. Some of these 4096 ones are extra widescreen. There are several different sizes that go into your project.
You can have high def footage, maybe 920 by 1080, or 1287 by 1080. These are all pixels. You can have 4K footage. You can have footage that is ultra widescreen, that's maybe 6K or 8K.
There are a lot of different sizes that this video can be made in. You have to make your sequence in one of them, and it’s easiest to make it in whatever the majority of the footage is, which in this case is 4K.
Here’s the clip you want to be the first one you want to use, but do you want to use all of it? Let’s say you only want to use a little bit where he's tying his shoes. So, you're going to trim this clip. You don't want the beginning (before 19 frames), and you can move your playhead to where you want to trim the clip. This dark gray area will not be included when you add this clip to your timeline. That gives you a three-second clip. You'll mark this out out, so now that’s a two-second clip that you'll use.
Grab it and drag it to your timeline, and it’s going to make your sequence for you. Here is your sequence right there. The program took the name of the file, “Man tying his shoes,” and used that to make the sequence height and framerate.
If you don't want that name, so you're going to rename this one “Promo Skateboarding Main.” That's your sequence, and you can start adding stuff to it.
Next, you’ll start with your audio. Let’s listen to it. This is 29 seconds. That’ll work, so you'll drag that into your timeline. You can't really see this, so you're going to use a keyboard shortcut, shift + plus , which makes them taller. You don't want to start with this loud music in the beginning, so you're going to right click on that audio clip and Apply Default Transition , which will give you a nice fade.
There are parts in the music that are higher and lower, the beat of the music. When you're cutting a promo or a music video, you want to cut so that each clip ends to match the beat. When you made this clip, you just made an arbitrary length, but you want to have it match the beat. As you play it, listen to it, and zoom in, which is plus on the keyboard, you can see changes in the music where it's higher. you'll take your selection tool and drag that clip to make it longer so it lines up. Now, your next clip will be right as the music changes, which will hide those edits better.
Minus on your keyboard zooms out of your timeline; plus on your keyboard zooms in. Backslash on your keyboard fits everything in your timeline. Then you would go grab your next clip, figure out where you want it to start and stop, add that to your timeline, and so on until you get a nice rough layout of your clips. That'll be your rough cut. You would then use the editing tools in the program to refine that rough cut and keep working on it to make it more refined.
That's the basic editing process. Yes, it’s simplified. In general, the music for a promo like this or a music video or something with the voiceover, it's audio-driven. So audio's the first thing on your timeline. You don't want to do anything to screw up the music, so you would use one of the common features in video editing programs to lock the timeline. Once that's been locked, nothing you do can interact with it. You can then freely add the rest of your clips, adjust them, trim them, shorten them, or delete them.
One last note is that for the timeline itself, you can use shift + plus to make it taller and shift + minus to make it shorter. The video tracks in the timeline work like layers in other programs, if you’re familiar with those, where you can stack content one on top of the other.
Video Editing Software
Premiere Pro, Final Cut Pro, Avid, and all major video editing programs have features for creating basic graphics, basic animation, and basic text. They all have compositing features, but for serious animation, you'd want to use After Effects, or Motion if you’re using Final Cut Pro.
That's a general overview of the video editing process with Adobe Premiere Pro. You could have done the same thing with Avid, Final Cut Pro, DaVinci Resolve, or any other video editing program. Certain aspects of the editing process are global, like how to cut. The principles of editing will work no matter what software you use. That's the cool part.
Everyone has their own preferences, and you could use any of the options above to complete the project we just did. There's a program called iMovie that you get almost for free when you buy a new Mac, and there was a film at South by Southwest about ten years ago edited in iMovie. Some things are global and will always work no matter what you do, and other things you'll find are better with professional-level programs. The only real reason to learn professional editing software is if you plan to work in certain industries where that software is prevalent. If you want to work in editing in New York City, you have to match what they want you to use.
How to Learn Video Editing
Master video editing with hands-on training. Video editing is the process of arranging and modifying clips of film to create a cohesive narrative, whether for a ten-second commercial or a feature-length film.
- Video Editing Certificate at Noble Desktop : live, instructor-led course available in NYC or live online
- Find Video Editing Classes Near You : Search & compare dozens of available courses in-person
- Attend a video editing class live online (remote/virtual training) from anywhere
- Find & compare the best online video editing classes (on-demand) from the top providers and platforms
- Train your staff with corporate and onsite video editing training
51 Creative Video Project Ideas for Students (With Templates)
- video project ideas
It’s always a challenge to keep students engaged during classes, especially virtual classes. One of the ways to do this are video projects. Video projects not only make for fun viewing, they also supplement learning. While creating videos with fellow students is a fun activity, it’s not always easy to come up with video project ideas.
So here we bring you some of our favorite creative video project ideas for students. We also share ready-to-use free video templates that you can plug into and start using. Stay tuned till the end and find a bonus section for students on how to make a good video project! Let’s dive in!
A. Video project ideas for elementary students B. Video project ideas for high school students C. Video project ideas for higher education students D. How to make a good video project
Bring your video project ideas to life in minutes
With 3000+ ready-to-use project video templates

A. Video project ideas for elementary students
Video projects for elementary students are mostly a way for the teachers to ensure comprehension and interest in the classroom. These can also be a good tool to make students think about different topics. Let’s check out some video project ideas for this age group:
1. Summarise a lesson
Get your students to summarise history or literature lessons on video. Have students research major figures and events in history and make videos around these concepts. This gives students the chance to learn digital storytelling as well as thoroughly research important historical figures! For example, check out this video sharing the history of television!
Use This Template
2. Share a talent video
Have students share a video performing a talent! They can share singing, dancing, painting, art, baking, playing an instrument or various such videos. This can be a fun activity where students learn more about their peers. For example, check out this music artist launch promotion video that can be used by students to promote their own music videos .
3. Create a book report video
Instead of traditional book reports, get students to create book reports or trailers for various literature projects. These can be a good way to get students curious about concepts you will be teaching them too! Check out this video book report.
4. Celebrate a holiday
Get students to create videos on their traditional or religious holidays. This is a great way to cultivate curiosity, awareness and tolerance for different ethnicities and cultures. Check out this Christmas facts video as an example.
Use This template
5. Create science experiment videos
Encourage students to create their own slides to explain science experiments and their findings. This way, students start thinking of STEM disciplines in a more analytical, hands on manner. Check out the lesson plan presentation below that can be used to document the objectives and findings of such an experiment.
B. Video project ideas for high school students
Video projects for high school students can be a little more advanced as they are in the process of growing their skills and learning more about different subjects.
1. Create a video portfolio
High school is when students start thinking about college applications. This is a great time to start making a portfolio. Teachers can give students the chance to create a portfolio video and share their unique skills and interests. For example, students interested in engineering and STEM can share their coding or science related know-how. Check out this copywriter portfolio as an example.
2. Create a news show
Students need to know current events, both for their school community and for the world around them. Having a school news show is a way to communicate with the school community of students, teachers, staff, and parents. This can be a group effort that helps students learn the value of teamwork and allocation. Check out this newsreel video you can customise to create your own weekly news show.
Use This Template
3. Make a video tour of an important location
If students visit a place -- on a field trip, on vacation or any time -- they can share their learning experience with others by recording video of it and narrating as they go. (If they're at a museum or other such places, asking permission first is probably a good idea!) If they can't visit it, creating a video slideshow with InVideo is also an option. Get your students to share video projects on important locations as an assignment. These projects can be themed around festivals , cultural concepts and activities too. For example, check out their Halloween cross country tour slideshow.
4. Share practice records
Learning a language, cooking , music or sports require constant practise. To gauge the progress of each student, you can ask them to record themselves learning to play an instrument or speaking a new language. Students can make video projects of themselves learning or mastering a particular song, key phrases and more. For example, check out this violinist’s progress video.
5. Create an ad or a promotional video for school events
Get students to make an advertisement or a pitch for a school event. This could include a political ad for class president election, a video resume , or an ad for the latest games or tournaments in the school. Students will need to think about the audience they are trying to reach and the length of the advertisement. For example, check out this match poster video.
6. Promote a good cause
Get students to create a video project promoting a cause they believe in. This helps them build their opinions and develop persuasive skills. Students can share this video with everyone, not just the classroom! For example, here’s a video you can customise to debunk myths around a way of life (going vegan in this case).
C. Video project ideas for higher education students
Post high school, it may seem that video projects aren’t that important. But this is the time when students are most focused on improving skills related to their career. Video projects can thus help students showcase their understanding and interest areas, especially to future employers. So let’s check out some video project ideas for these students.
1. Interview interesting people
The people around us and around the world are living history. Their experiences, information, and advice is a treasure trove waiting to be mined. Get your students to interview individuals from their interest areas or in interesting professions. They could be in-person interviews where both parties sit next to each other or they could be virtual interviews, where someone far away records responses to questions. These interviews can act as learning aids, as well as help students connect with people in their future careers. Check out this video interview on how to approach people for their life stories.
Make your own video highlighting interesting interviews by sharing quotes , testimonials, and more. Check out this testimonial video as an example you can use and customise.
2. Teach a concept via videos
Truly understanding something is the ability to teach it to others. Students can make a video where they are recording themselves completing a task on their computer screen or they can make a demonstration video like a coding class. Teachers and professors could then use these videos to help reinforce skills in your class or even flip some of your lessons. For example, check out this video tutorial on note taking apps.
3. Create a self-assessment video
Being able to assess oneself is an extremely important skill that students need to improve themselves. Self assessment empowers students to become better learners. It also allows them to take an active role in their assessment and push for a grade they feel is unfair - a direct correlation to performance reviews at the workplace! Personalise this testimonial video to create your own self assessment video.
4. Create a video presentation for a written assignment
Written assignments are a staple when it comes to college. But only professors and classmates can view these. Instead, creating a short, promotional video on a written assignment is a great way for students to share their work with more people and learn editing skills at the same time. Check out this digital marketing trends video you can use to create your own video presentations .
5. Create a video resume
For most students, the job hunt begins in college itself. A video resume helps highlight key skills as well as share the student’s personality and attitude with employers. Especially when applying to remote or distant positions, a video resume along with a normal resume provides brownie points. Check out this video resume you can use as a blueprint to create your own.
Leverage the power of video to land your dream job!
Create a PRO video resume in minutes with InVideo

6. Create a University promotion video
Universities and colleges need as much promotion as they can get. And who better than students to share their experiences and highlights. Get students to create unique videos with their best anecdotes or areas in the university. This is also a good way to get them to research interesting aspects of college life. Check out the University promotional video and make it your own.
D. BONUS: How To Make A Good Video Project
Your school video project can earn you good grades. It is also an opportunity to showcase your creativity. But how to create the perfect video without any error? Video creation may not be your forte, but you still wish to excel in school video projects, right? No worries!
If you have a school video assignment in hand but don’t know where to begin, read below to learn how to create a video project super easy and quick, without any error and fuss. Now, let’s divide your video project into 5 easy steps.
Step 1: Video topic or idea
If you are working on a school assignment, you probably have a video topic given by your teacher or professor. If you are looking for video topic ideas though, find them here .
Step 2: Plan your video assignment
Planning is super important for your videos. This is when you decide how you want to create your video. Consider whether you want to live record your video or create it online using an app or a tool. An online tool like InVideo offers you pre-created templates that might meet your requirements. This is also a super quick and easy way to make your video from scratch. The first thing you need to do is go to InVideo and login or sign up if you wish to use this tool. Next click on the “Pre Made Templates” Option and select the video dimension you want. Finally, type phrases related to your video in the search bar.
You will now see templates related to your search as you scroll below. Simply select the template you want to use and click on the “Use This Template” button to start editing!
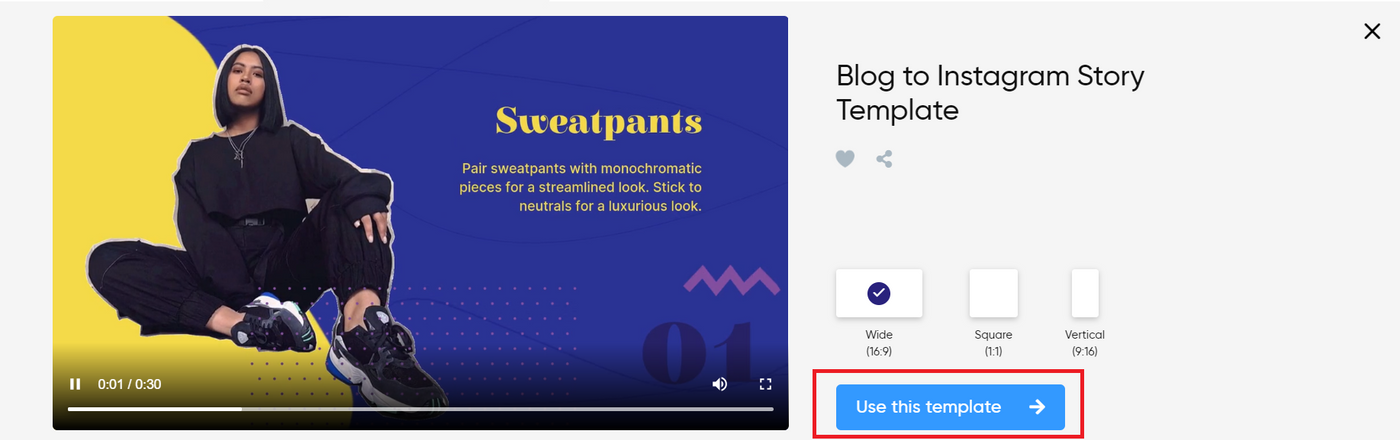
If your video idea is to record an event , but you don’t have a DSLR, camcorder or GoPro, use your own smartphone camera for the school project.
Step 3: Prepare a video script
Now that you know how you will record your video, the next step is creating a script for your video. Here’s a step-by-step guide on script writing you can refer to.
3 questions to ask yourself before you create your script:
- What is the objective of your video? - How long does your video need to be? - Who is the audience that will watch your video?
Step 4: Shoot your video + audio
Once your script is finalized, it’s time to shoot your video. You also need to make sure that you are recording audio to go with your video. Check out this list of equipment and how you can use it to record video and audio.
Step 5: Edit your video
As mentioned earlier, one of the most effortless ways you can edit your video is using the free, online InVideo editor . This is simple, easy to use, and does not need you to make any downloads. Here’s how you can edit your video on InVideo.
Step 1: Log in to InVideo . Now click on the “Blank Canvas” option and select the dimension of your video. Next, click the “Make A Video” button.
Step 2: Now click on the “Upload Media” button at the left-hand corner of your screen and upload the video you shot.
Step 3: Double click your uploaded video to add it to the timeline. You will now see a pop-up that asks if you wish to trim your video. You can Trim your video or use the full version. Simply click on the “Done” button once you are finished with your trim.
Step 4: You can now use the controls on the right side of the screen to edit your video further.
Step 5: You can apply filters, create transitions between shots for a seamless flow, add subtitles, or insert a logo to give a personal touch to your school video. Just head to the left side of your screen and select the controls you wish to use.
Step 6: Once you are done with your edits, it’s time to download your video. For this click on the “Download & Share” button on the top right. Now click the “Export” video button.
Step 7: Your video will now start to render. You can download it once it’s complete. You can also directly share the video link or share it on social media using the button provided.
Wrapping up
So these were some video project ideas for students and how you can create your own videos on InVideo. If you’ve found value in this article, and are looking for more video ideas, you also want to check out this guide where we’ve put together 200+ video ideas for businesses and brands that you can take further inspiration from.
For more quick tips and hacks on editing and creating videos, subscribe to our YouTube Channel .
This post was written by Upasna and edited by Abhilash from Team InVideo
Let’s create superb videos
FREE Video Editing Assessment Questions and Answers
What is the normal television screen aspect ratio, a harsh cut is defined as..., the following is a technique that uses black bars above and below a widescreen video image (16:9 aspect ratio) on a regular television screen:, what is a "talking head" in video directing and production, the numerical countdown (5-4-3-2-1) that appears before the start of an old movie has a unique moniker. what is its name, what does the "aspect ratio" of a video represent, the individual video pictures that comprise a moving sequence are referred to as, premium tests $49/mo free april-2024, free video editing elements questions and answers.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
Assignment Editing Services
Better Writing, Better Grades

Advanced Assignment Editing
Writing a great assignment is no small feat. Even after the research, you still need to present your ideas clearly and concisely to demonstrate your depth of knowledge. But our expert editing will help you communicate effectively, so try our assignment proofreading service today to get the grades you deserve.

Expert Editor

Expert Academic Proofreaders
Our team of academic proofreaders understand the importance of error-free writing. And having helped countless students with their work, our experts are the ideal choice to help you polish yours.
Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing

Assignment Proofreading And Editing
As part of our assignment proofreading service, we will:
- Fix punctuation, spelling, and grammar errors
- Ensure clear sentence structure and concision
- Highlight areas of ambiguity or inconsistencies
- Check that word choice and tone are suitably academic
- Offer feedback and suggestions regarding writing style
- Make sure references are clear and complete
In addition, we aim to provide two copies of your edited assignment:
- A ‘Clean’ copy in the original file format
- An MS Word Track Changes copy
The Track Changes copy will allow you to review and approve every edit we make. And if your chosen file format doesn’t support Track Changes, we will adapt our process to ensure you’re always in control of the final draft.
Our assignment proofreading combines traditional proofreading with light copy editing to make sure you can express yourself clearly. And we always follow academic plagiarism guidelines , so we will never make changes that could be considered cheating. If you need more assistance with any other documents, though, we do offer editing services for non-student writing.
Lightning-Fast Delivery
You’ll never miss a deadline with our speedy services: our Next-Day Guarantee means we’ll return any document up to 10,000 words long within 24 hours
And if you need a faster turnaround, simply select your desired delivery speed when you submit your document. We have three options:
We can also meet custom deadlines! Just let us know what you need.
*For documents up to 8,000 words
**For documents up to 3,000 words
How We Work With Students
You’ll never miss a deadline with our speedy services: our Next-Day Guarantee means we’ll return any document up to 8,000 words long within 24 hours.
We can also meet custom deadlines! Just let us know what you need.
* For documents up to 8,000 words
** For documents up to 3,000 words
Great Pricing
Our pricing is affordable and transparent – the cost is based on the exact length of your document. Check out our pricing calculator for an instant quote, and rest assured that you’ll receive the highest quality proofreading and editing for the best value on the market.
Referencing Expertise
Our editors are experts in various referencing styles, including but not limited to APA, Harvard, MLA, Chicago, and IEEE. No matter what style you’re using, they’ll make sure your citations and references are correct and let you know if any information is missing. Visit our referencing page to learn more.
Subject-Matter Experts
Our team includes over 750 professional editors with expertise in thousands of topics. This means we can always match you with the best proofreader for your writing, whether you need help with a dissertation in medicine or an essay on economics.
24-Hour Support
Our support team is available around the clock to address any concerns or questions you have about your order. This means you’ll never be left in the dark, no matter where you are or what time it is.
Instant Quote
You can also upload a document to get an instant quote
Drag & drop your file
or browse your computer
Browse from your device
Drop your file here!
Your file is being uploaded!

Looking For A Proofreading Partner?
Let’s talk about the support you need.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this project, you'll be editing an amatuer music video. You'll need to upload the video clips and audio that you want to use. You'll create a multi-cam sequence and make cuts in that sequence. You'll also edit all of the fundamental elements, including color, transitions, overlays, and beat alignment.
Create a promo video. 9. Questions for your future self. Think ahead with a video full of inspiring questions. This project is great for incoming freshmen. At the beginning of the year, have students create videos with questions for their future self or with goals for their life and career.
Start by creating a syllabus that outlines the goals, learning outcomes, and schedule of your course. Make sure to cover both theory and practice, striking a balance between conceptual understanding and hands-on experience. Divide your lessons into manageable units, focusing on specific aspects of video editing.
Video assignments. Video assignments comprise a wide range of possible assignment types from personal reflection videos in which students video-record themselves and upload those recordings to a shared space, such as Canvas, to assignments in which students are responsible for capturing, editing, narrating, and producing a polished product.
Video editing describes the process of manipulating a video's elements, such as its visuals and sounds, to produce a polished, finished version. 1 It can involve tasks such as reordering and trimming scenes, adjusting audio and color levels, and applying special effects. The goal of video editing is to bring the video closer to achieving a ...
Some video editing software to help you create high-quality education materials includes: ... For example, if you're creating a video about a reading assignment, then you should have a theme, event, or scholarly argument in mind to contextualize the assignment. While you may open up for further discussion, having this goal creates a starting ...
Our top 10 video editing tips and tricks. 01. Get the right software. Popular editing applications include Premiere Pro, Premiere Elements, and DaVinci Resolve (Image credit: Adobe, BlackMagic) First up on our list of video editing tips and tricks, is getting the right tools. With a plethora of editing software on the market, it's not always ...
Editing the final video together might not be required for all of these project ideas, but it makes sense to check on the availability of video editing programs on school computers to see if it might be possible. iMovie or Windows Movie Maker are both free and easy to use. ... Video Assignments for Elementary School Students 1. Task: Make a ...
Adobe Premiere Pro is a professional video editing software that lets editors create and manage projects, import and preview assets, edit audio and video, and more. The software is set to change its interface soon, which may affect how users interact with it. Editing often requires sequencing, or organizing clips in a logical order.
Managing audio elements seamlessly within the editing process. Utilizing effects like speed adjustments. Changing clip speeds to add variety and emphasis. Adding subtitles for improved accessibility and viewer experience. Creating a complete video from scratch, applying all the learned skills. Exporting the finished video for sharing or further use
Video Editing - Assignments Activity 1: Cell Shock - Shot Sequencing ... Assignment: Coffee Edit - Visual Storytelling (Compressed Time and Cutting on Action Shot Sequence Video) 1. You will be re-creating the entire video from the provided clips and media. 2. You will need to start a new project, import the footage/media content (that you ...
4. Create a video presentation for a written assignment. Written assignments are a staple when it comes to college. But only professors and classmates can view these. Instead, creating a short, promotional video on a written assignment is a great way for students to share their work with more people and learn editing skills at the same
Tips for Instructors. Here are a few things that can be helpful to keep in mind when assigning video projects: Keep it concise! Unless you're a film program approving capstone projects, it's good to keep video projects limited to around 2-5 minutes. If it's high quality, even a 5-minute video can still take 5-10 hours (or more) to produce.
However, with video assignments, you will also need to plan for where, when and how you will record and edit your video. ... If you can edit the video, you can film it in sections, allowing you to ...
Ignite student creativity with the leading collaborative video editing tool for students and teachers. Try for free in your classroom today! ... Seamlessly integrate standards-aligned lessons into your curriculum using our Assignment Ideas Library. Save time and boost instructional quality as you confidently align your lessons with ISTE ...
Teachers. Create, monitor, and measure engagement with interactive video. Challenge students to create their own content and satisfy the highest level of Bloom's taxonomy. Provide real-time feedback along the way. Explore WeVideo for Teachers.
In this assignment, you will learn how to create, edit, and produce your own original video. You will use WeVideo's online video editor to optimize your video, splice together multiple clips, add music or audio tracks, and more. Once your video is complete, you will publish the video to Youtube. Assignment Preparation
Online Video Editing Classes. Find what fascinates you as you explore these online classes. Start for Free. Related Skills. Company About Careers Press Blog Affiliates Partnerships. Community Team Plans Refer a Friend Limited Memberships Scholarships Free Classes. Teaching
Activity: Coffee Scene - Shot Sequencing
Video Editing and Digital Design Online Web Conference. Summer 2121. Tuesdays & Thursdays 6:30-9:30pm. Instructor: Allyson Sherlock. ... Assignment 1 - Continuity Edit ( h t t p s : / / c a n v a s . h a r v a r d . e d u / c o u r s e s / 8 7 5 5 2 / a s s i g n m e n ts / 4 7 6 2 8 4 )
The good news is, you don't need complicated video editing software to edit like a pro. Make full use of a free online video editor like Canva's video-making app for starters and unleash your creativity. Here are a few practical tips to get you started: 1. Turn your vision into a story with a beginning, middle, and end. 2.
FREE Video Editing Assessment Questions and Answers - Practice Test Geeks. 0%. The following is a technique that uses black bars above and below a widescreen video image (16:9 aspect ratio) on a regular television screen: Letterbox. Framing. Frame rate. Overscan.
Assignment Proofreading And Editing. As part of our assignment proofreading service, we will: Fix punctuation, spelling, and grammar errors. Ensure clear sentence structure and concision. Highlight areas of ambiguity or inconsistencies. Check that word choice and tone are suitably academic. Offer feedback and suggestions regarding writing style.