Cardiovascular System
- It is know as the “transportation” system of the body
Structures Include:
-Blood Vessels
Layers of the Heart
- Endocardium
- Smooth layer
- Lines the interior
- Valves are made from this layer
- Muscle layer
- Thickest layer
- Thin, outermost layer
- Joins with serous lining outside the heart to form the Pe ricardium
- Separates the left and right heart
- Interatrial – top part of the septum
- Interventricular – bottom part of the septum
The Four Chambers
- Right Atrium
- Right Ventricle
- Left Atrium
- Left Ventricle
- Right Atrium – receives blood from the superior and inferior vena cava
- Right Ventricle – pumps blood to the lungs
- Left Atrium – receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
- Left Ventricle – pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body, strongest chamber
- Valves are important to control the flow of blood from one chamber of the heart to another .
- Valves allow blood to flow in only one direction
Heart Valves
Tricuspid valve – opening between right atria and right ventricle
Pulmonary semilunar valve – opening between right ventricle and pulmonary artery
Mitral valve (also called bicuspid) – opening between left atrium and left ventricle
Aortic semilunar valve – located between left ventricle and aorta
- Chordae tendineae – threads, keep valve flaps from flipping up into the atria
- Right Atrioventricular (tricuspid valve) – between the right atrium and right ventricle, has 3 flaps, prevents blood from flowing back into the right atrium
- Pulmonic (semilunar valve) – between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, prevents blood from flowing back into the right ventricle
- Left Atrioventricular (bicuspid valve) – between the left atrium and left ventricle, prevents blood from flowing back into the left atrium, has 2 flaps (mitral valve)
- Aortic Valve – between the left ventricle and the aorta, prevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle
Home Anatomy of the Human Heart PowerPoint Shapes Anatomy of Human Heart PowerPoint Presentation

Anatomy of Human Heart PowerPoint Presentation
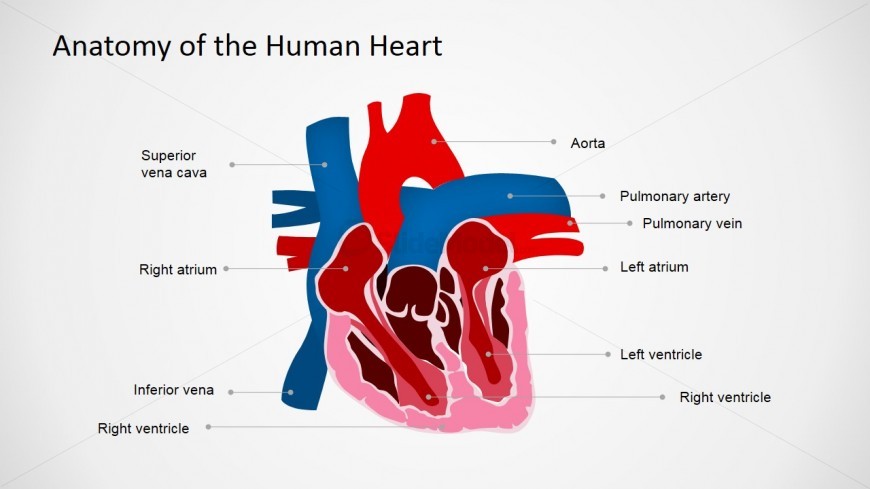
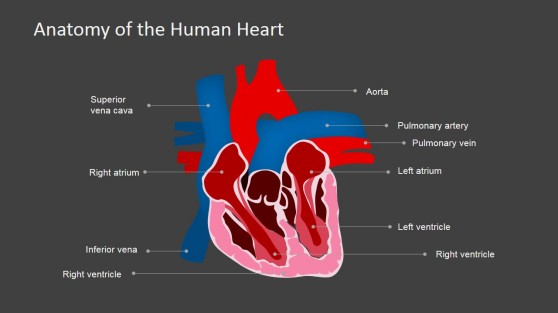
Located in the slide design is an Anatomy of Human Heart PowerPoint Presentation , which may be used as a visual aid to illustrate the parts of a heart, which is ideal for a presentation of proposals for new medical developments.
This PowerPoint slide shows a cross-section illustration of the human heart. This illustration shows the parts of the heart such as the veins, arteries and its chambers. It also shows each part labelled with its medical names. The heart’s walls and muscles are also very visible in this illustration. Another notable feature of the illustration is the clearly depicted borders and divisions of each chambers and veins. In this design, the part muscle part is clearly identified by its pink color and white borders around it. The PowerPoint objects are 100% editable to suit the presenter’s needs and preferences.
Return to Anatomy of the Human Heart PowerPoint Shapes .
Download unlimited PowerPoint templates, charts and graphics for your presentations with our annual plan.
Slide Tags:
Template tags:, related slides.
Heart Chambers PowerPoint Presentation
Circulatory System PowerPoint Design
Human Organ PowerPoint Template
Download unlimited content, our annual unlimited plan let you download unlimited content from slidemodel. save hours of manual work and use awesome slide designs in your next presentation..

- Upload Ppt Presentation
- Upload Pdf Presentation
- Upload Infographics
- User Presentation
- Related Presentations

APLASTIC ANEMIA
By: drdwayn Views: 2351

Teenage Sexuality and STDs
By: drdwayn Views: 1214

The PNPs Guide to Primary Immunodeficiencies
By: drdwayn Views: 1123

Anaphylaxis
By: drdwayn Views: 2135

Heart Failure in infants and neonates
By: drdwayn Views: 1271

Congenital Heart Disease: Outcome in Patients with Single Ventricle
By: drdwayn Views: 822

Congestive Heart Failure Case Study
By: JenniferDwayne Views: 2878

Antianginal Drugs
By: Mawaddah Views: 510

ECG grammar part 2. section A ."Understanding the genesis of ECG changes in acute myocardial ischemi
By: asadkundi Views: 1175

Antiarrhythmic Drugs
By: KhushbuSG Views: 292

- About : I am Dr. Dwayne Faulk
- Occupation : Medical Professional
- Specialty : Other Health Professionals
- Country : United States of America
HEALTH A TO Z
- Eye Disease
- Heart Attack
- Medications
Acute myocarditis: an overview of pathogenesis, diagnosis and management
Affiliations.
- 1 King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK.
- 2 University Hospitals Dorset NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK.
- 3 King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK - [email protected].
- PMID: 38536007
- DOI: 10.23736/S0031-0808.24.05042-0
Acute myocarditis encompasses a diverse presentation of inflammatory cardiomyopathies with infectious and non-infectious triggers. The clinical presentation is heterogeneous, from subtle symptoms like mild chest pain to life-threatening fulminant heart failure requiring urgent advanced hemodynamic support. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge regarding the pathogenesis, diagnostic approach, management strategies, and directions for future research in acute myocarditis. The pathogenesis of myocarditis involves interplay between the inciting factors and the subsequent host immune response. Infectious causes, especially cardiotropic viruses, are the most frequently identified precipitants. However, autoimmune processes independent of microbial triggers, as well as toxic myocardial injury from drugs, chemicals or metabolic derangements also contribute to the development of myocarditis through diverse mechanisms. Furthermore, medications like immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies are increasingly recognized as causes of myocarditis. Elucidating the nuances of viral, autoimmune, hypersensitivity, and toxic subtypes of myocarditis is key to guiding appropriate therapy. The heterogeneous clinical presentation coupled with non-specific symptoms creates diagnostic challenges. A multifaceted approach is required, incorporating clinical evaluation, electrocardiography, biomarkers, imaging studies, and endomyocardial biopsy. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging has become pivotal for non-invasive assessment of myocardial inflammation and fibrosis. However, biopsy remains the gold standard for histological classification and definitively establishing the underlying etiology. Management relies on supportive care, while disease-specific therapies are limited. Although some patients recover well with conservative measures, severe or fulminant myocarditis necessitates aggressive interventions such as mechanical circulatory support devices and transplantation. While immunosuppression is beneficial in certain histological subtypes, clear evidence supporting antiviral or immunomodulatory therapies for the majority of acute viral myocarditis cases remains insufficient. Substantial knowledge gaps persist regarding validated diagnostic biomarkers, optimal imaging surveillance strategies, evidence-based medical therapies, and risk stratification schema. A deeper understanding of the immunopathological mechanisms, rigorous clinical trials of targeted therapies, and longitudinal outcome studies are imperative to advance management and improve the prognosis across the myocarditis spectrum.
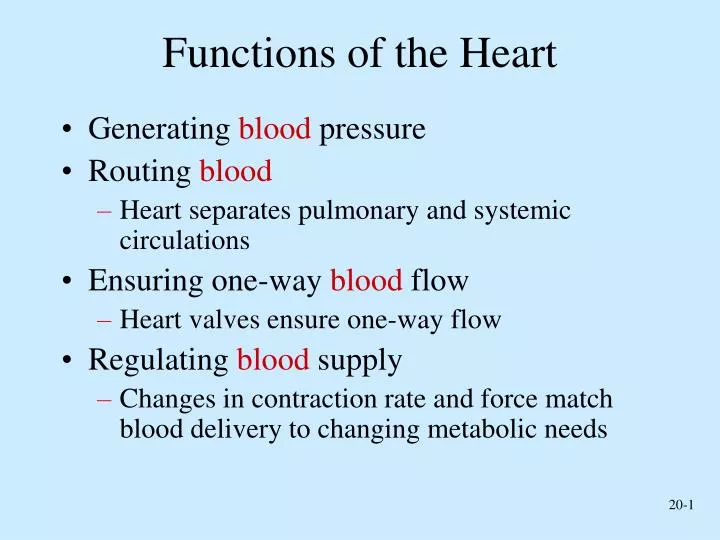
Functions of the Heart
Sep 11, 2014
410 likes | 2.98k Views
Functions of the Heart. Generating blood pressure Routing blood Heart separates pulmonary and systemic circulations Ensuring one-way blood flow Heart valves ensure one-way flow Regulating blood supply
Share Presentation
- blood pressure
- cardiac muscle
- body temperature
- heart rate decreases
- force match blood delivery

Presentation Transcript
Functions of the Heart • Generating blood pressure • Routing blood • Heart separates pulmonary and systemic circulations • Ensuring one-way blood flow • Heart valves ensure one-way flow • Regulating blood supply • Changes in contraction rate and force match blood delivery to changing metabolic needs
Size, Shape, Location of the Heart • Size of a closed fist • Shape • Apex: Blunt rounded point of cone • Base: Flat part at opposite of end of cone • Located in thoracic cavity in mediastinum
Pericardium
Heart Wall • Three layers of tissue • Epicardium: This serous membrane of smooth outer surface of heart • Myocardium: Middle layer composed of cardiac muscle cell and responsibility for heart contracting • Endocardium: Smooth inner surface of heart chambers
External Anatomy • Four chambers • 2 atria • 2 ventricles Major veins • Superior vena cava • Pulmonary veins • Major arteries • Aorta • Pulmonary trunk
Heart Valves • Atrioventricular • Tricuspid • Bicuspid or mitral • Semilunar • Aortic • Pulmonary • Prevent blood from flowing back
Function of the Heart Valves
Blood Flow Through Heart
Systemic and PulmonaryCirculation
Heart Skeleton • Consists of plate of fibrous connective tissue between atria and ventricles • Fibrous rings around valves to support • Serves as electrical insulation between atria and ventricles • Provides site for muscle attachment
Cardiac Muscle • Elongated, branching cells containing 1-2 centrally located nuclei • Contains actin and myosin myofilaments • Intercalated disks: Specialized cell-cell contacts • Desmosomes hold cells together and gap junctions allow action potentials • Electrically, cardiac muscle behaves as single unit
Conducting System of Heart
Cardiac Arrhythmias • Tachycardia: Heart rate in excess of 100bpm • Bradycardia: Heart rate less than 60 bpm • Sinus arrhythmia: Heart rate varies 5% during respiratory cycle and up to 30% during deep respiration • Premature atrial contractions: Occasional shortened intervals between one contraction and succeeding, frequently occurs in healthy people
Cardiac Cycle • Heart is two pumps that work together, right and left half • Repetitive contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) of heart chambers • Blood moves through circulatory system from areas of higher to lower pressure. • Contraction of heart produces the pressure
Heart Sounds • First heart sound or “lubb” • Atrioventricular valves and surrounding fluid vibrations as valves close at beginning of ventricular systole • Second heart sound or “dupp” • Results from closure of aortic and pulmonary semilunar valves at beginning of ventricular diastole, lasts longer • Third heart sound (occasional) • Caused by turbulent blood flow into ventricles and detected near end of first one-third of diastole
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) • Average blood pressure in aorta • MAP=CO x PR • CO is amount of blood pumped by heart per minute • CO=SV x HR • SV: Stroke volume of blood pumped during each heart beat • HR: Heart rate or number of times heart beats per minute • Cardiac reserve: Difference between CO at rest and maximum CO • PR is total resistance against which blood must be pumped
Regulation of the Heart • Intrinsic regulation: Results from normal functional characteristics, not on neural or hormonal regulation • Starling’s law of the heart • Extrinsic regulation: Involves neural and hormonal control • Parasympathetic stimulation • Supplied by vagus nerve, decreases heart rate, acetylcholine secreted • Sympathetic stimulation • Supplied by cardiac nerves, increases heart rate and force of contraction, epinephrine and norepinephrine released
Heart Homeostasis • Effect of blood pressure • Baroreceptors monitor blood pressure • Effect of pH, carbon dioxide, oxygen • Chemoreceptors monitor • Effect of extracellular ion concentration • Increase or decrease in extracellular K+ decreases heart rate • Effect of body temperature • Heart rate increases when body temperature increases, heart rate decreases when body temperature decreases
- More by User

IDOLS OF THE HEART
IDOLS OF THE HEART. Learning to Long for God Alone by Elyse Fitzpatrick Presented by Elder Wendie G. Trott. Chapter 4: The Heart Changer.
526 views • 22 slides

Development of the Heart
Development of the Heart . ANHB 2212 – 2006 – Week 5 Avinash Bharadwaj. Retrospect….
776 views • 27 slides

Anatomy of the Heart
Anatomy of the Heart. Part 1. Anatomy of the Heart. Heart Hollow organ Located in the middle mediastinum Surrounded by pericardium Attached to the thorax by the great vessels. Thoracic Cavity. Thoracic Cavity. Right Pleural Cavity. Mediastium. Left Pleural Cavity. Left Lung.
1.43k views • 32 slides

Doors of the Heart Chambers of the Heart The Crimson Stream
Easy: The Heart Doors of the heart Chambers of the heart The Crimson stream. Easiest. Easy. Hard. Hardest. Tour Guide. Welcome buddy , If this is too hard for you, click here If this is too easy for you, click here. Doors of the Heart Chambers of the Heart The Crimson Stream.
1.06k views • 88 slides


Pathology of the Heart
Pathology of the Heart. 4/22/09 Dr. Winokur. The Heart as a Pump. Pump parts - Cardiac equivalent Powersource - Blood supply/oxygen Motor - Myocardium Pump with valves - Cardiac valves Control circuit - Conducting system and neurohumoral control.
889 views • 60 slides
Anatomy of the Heart. The heart is located in the chest cavity, surrounded by the pericardial sac, in the anterior portion of the mediastinum. . The Pericardium. Pericardial cavity. The pericardium is a double-walled sac (pericardial sac) that encloses the heart. Parietal pericardium.
1.95k views • 31 slides

Development of the heart
Development of the heart. Dr Rania Gabr. oBJECTIVES. Describe the formation and position of the heart tube. Explain the mechanism of formation of the cardiac loop. Discuss the development of sinus venosus . Explain how cardiac septa are formed.
1.49k views • 56 slides

Anatomy of the Heart . BIOLOGY FORM 5.
232 views • 13 slides

Anatomy of the Heart. DR. SAEED VOHRA DR . SANAA AL-SHAARAWI. OBJECTIVES. At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to : Describe the shape of heart regarding : apex, base, sternocostal and diaphragmatic surfaces.
1.01k views • 27 slides

Auscultation of the heart
Auscultation of the heart. Auscultatory content. Heart rate Cardiac rhythm Cardiac sound extra cardiac sound Cardiac murmur Pericardial friction sound. Auscultatory valve. Mitral valve area (Apical ~) Pulmonary ~ Aortic ~ The second aortic ~ Tricuspid ~.
530 views • 11 slides

Functions of the Heart. Chapter 17. The Heart.
315 views • 23 slides

THE HEART OF STOICHIOMETRY
THE HEART OF STOICHIOMETRY. A BALANCED EQUATION. Proportional Relationships. Stoichiometry mass relationships between substances in a chemical reaction based on the mole ratio Mole Ratio indicated by coefficients in a balanced equation. 2 Mg + O 2 2 MgO. Ratio of eggs to cookies.
411 views • 22 slides

Physiology of the Heart
Physiology of the Heart. Review. The heart is a four-chambered muscular pump The body has two circulations; Pulmonary to the lungs and systemic to the entire body The atria receive blood from both circulations The ventricles send blood through the two circulations
1.12k views • 71 slides

Endocrine functions of the Kidneys, Heart and Pineal Gland
Endocrine functions of the Kidneys, Heart and Pineal Gland. The kidneys produce 3 hormones. 1,25 DHC Renin Erythropoietin. The heart produces ANP although also produced by other tissues. Acts to increase excretion of Na by the kidneys. The pineal gland secretes melatonin. Renin.
1.14k views • 17 slides

From the heart of Westchester To the heart of the world!
From the heart of Westchester To the heart of the world!. Who We Are. Storefront learning and community services / resource center Located in central business district of Dobbs Ferry, NY 0.3 miles from St. Cabrini Nursing Home
307 views • 21 slides
What are the functions of the heart?
What are the functions of the heart?. Functions of the Heart. Did you know? At rest, 2 ounces of blood is circulated with each heart beat. It’s a PUMP. What do pumps do? How does this relate to heart function?. Heart Facts. Adult heart is about 5 inches long and 3.5 inches wide
507 views • 25 slides
Functions of the Heart. Functions of the Heart. Generate blood Pressure Routing Blood Ensuring one way blood flow Regulating blood supply. The Heart. Located in the Thorax Part of the Mediastinum ( heart, trachea and esophagus) Size of a Fist
801 views • 48 slides

Functions of the heart 1. Pump 2. Transportation
Functions of the heart 1. Pump 2. Transportation. Did you know? At rest, 2 ounces of blood is circulated with each heart beat. Systemic Circulation & Cardiopulmonary Circulation.
460 views • 31 slides

Parts of the Heart
Parts of the Heart. Can you label the parts of the heart?. Right Ventricle. Pulmonary Vein. Inferior Vena Cava. Aorta. Left Atrium. Pulmonary Artery. Superior Vena Cava. Right Atrium. Left Ventricle. Superior Vena Cava. Aorta. Pulmonary Artery. Pulmonary Vein. Right Atrium.
217 views • 5 slides

Testing The Heart: Modes Of Investigating Heart
Testing the Heart - Modes of investigating Heart: ECG (Electrocardiography) and TMT; Chest X Ray, Echocardiography, Coronary Angiography, CT Scan, MRI Scan, Nuclear Scanning etc.
96 views • 8 slides
“Heart Smarts” Anatomy of the Heart
“Heart Smarts” Anatomy of the Heart. Pumps your Blood. John Peters, EMT-LP Hereford High School. Identify the 4 chambers, the 2 sides and 4 valves of the heart Define the medical terms associated with the heart Discuss how the blood flows through the heart.
207 views • 16 slides

Matters of the Heart
Matters of the Heart. Life Issues and the Gospel. Matters of the Heart . Abortion. Crisis Pregnancy. Assisted Suicide. Post-abortion Syndrome. Euthanasia. Matters of the Heart . Abortion. Crisis Pregnancy. Hot-Button. Assisted Suicide. Post-abortion Syndrome. Political.
303 views • 29 slides
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

55 templates

8 templates

44 templates

solar eclipse
25 templates

13 templates

philippines
38 templates
Medical Center Specializing in Heart Disease
Medical center specializing in heart disease presentation, free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
Download the "Medical Center Specializing in Heart Disease" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Hospitals, private clinics, specific wards, you know where to go when in need of medical attention. Perhaps there’s a clinic specialized in treating certain issues, or a hospital in your area that is well-known for its state-of-the-art technology. How about giving a try to this editable Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template to promote the services offered by the healthcare center you work for?
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- Different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

Register for free and start editing online

COMMENTS
Premium Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. Present the fascinating world of the heart with our comprehensive presentation on its anatomy and function. This medical template features stunning heart illustrations, tables, graphs, and infographics to help you dive deep into the subject matter. Whether you're a healthcare professional or ...
heart, organ that serves as a pump to circulate the blood.It may be a straight tube, as in spiders and annelid worms, or a somewhat more elaborate structure with one or more receiving chambers (atria) and a main pumping chamber (ventricle), as in mollusks. In fishes the heart is a folded tube, with three or four enlarged areas that correspond to the chambers in the mammalian heart.
Mycardium - middle layer. Serous membrane - epithelial membrane the secretes a thin, watery fluid (lubricant) - eases the movement of the heart. Pericardium - membrane that encloses the heart. Layers of the Heart. Endocardium. Smooth layer. Lines the interior. Valves are made from this layer. Layers of the Heart.
Heart Presentation templates We wholeheartedly want to invite you to pour all your heart into editing these amazing presentations about hearts! This is the strongest muscle in your body and it never rests, it's always working for you. Speak about it with these designs where this organ is the protagonist and edit them, your public will skip a ...
Heart anatomy. The heart has five surfaces: base (posterior), diaphragmatic (inferior), sternocostal (anterior), and left and right pulmonary surfaces. It also has several margins: right, left, superior, and inferior: The right margin is the small section of the right atrium that extends between the superior and inferior vena cava .
Do you want to learn more about the anatomy and function of the human heart? Watch this 3D medical animation that shows how the heart pumps blood throughout the body and what happens when it is ...
The heart beats around 100,000 times a day, pumping approximately 8 pints of blood throughout the body 24/7. This delivers oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood to tissues and organs and carries away ...
Located in the slide design is an Anatomy of Human Heart PowerPoint Presentation, which may be used as a visual aid to illustrate the parts of a heart, which is ideal for a presentation of proposals for new medical developments.. This PowerPoint slide shows a cross-section illustration of the human heart. This illustration shows the parts of the heart such as the veins, arteries and its chambers.
Slide 46-. Chapter 18, Cardiovascular System 46 Heart Sounds Heart sounds (lub-dup) are associated with closing of heart valves First sound occurs as AV valves close and signifies beginning of systole (contraction) Second sound occurs when SL valves close at the beginning of ventricular diastole (relaxation) Slide 47-.
Presentation Transcript. Anatomy of the Heart. The heart is located in the chest cavity, surrounded by the pericardial sac, in the anterior portion of the mediastinum. The Pericardium Pericardial cavity The pericardium is a double-walled sac (pericardial sac) that encloses the heart. Parietal pericardium Visceral pericardium (epicardium ...
The Heart. Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett, Parkland College. 20-1 Describe the anatomy of the heart, including vascular supply and pericardium structure, and trace the flow of blood through the heart, identifying the major blood vessels, chambers, and heart valves. 20-2 Explain the events of an action potential in cardiac muscle, indicate ...
The Heart- Structure and Function. Lungs Body cells Our circulatory system is a double circulatory system. This means it has two parts . the right side of the system deals with deoxygenated blood. the left side of the system deals with oxygenated blood. The Heart This is a vein. It brings blood from the body, except the lungs.
Presentation Transcript. 1. Anatomy & physiology of the heart. 4. Heart Anatomy Size, Location, and Orientation Enclosed in the mediastinum Base (posteriorsuperior portion) and Apex (inferioranterior portion) 5. Heart Anatomy Coverings Pericardium protects the heart anchors the heart to surrounding structures such as the diaphragm and the great ...
Check out the Respiratory System series, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GfR7zxwjmFQ&t=Which chamber of the heart pumps blood into the pulmonary artery?a. th...
When the heart can no longer do this, blood that. A healthy heart should be able to pump blood to all parts of the body in a few seconds. should be pumped out of the heart backs up in the lungs and other parts of the body. This results is symptoms of heart failure: shortness of breath or swelling in the hands, legs, and feet.
The clinical presentation is heterogeneous, from subtle symptoms like mild chest pain to life-threatening fulminant heart failure requiring urgent advanced hemodynamic support. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge regarding the pathogenesis, diagnostic approach, management strategies, and directions ...
Presentation Transcript. Functions of the Heart • Generating blood pressure • Routing blood • Heart separates pulmonary and systemic circulations • Ensuring one-way blood flow • Heart valves ensure one-way flow • Regulating blood supply • Changes in contraction rate and force match blood delivery to changing metabolic needs.
Pierce focused her presentation on the significant risk that women face in relation to heart disease and discussed actionable steps that women can take to mitigate these risks. She pointed out that the risk of heart disease in women begins to rise between the ages of 40 and 60 but the heart health message applies to younger women as well.
The presentation of this study using the MyoVista to the World Congress of Anesthesiologists comes on the back of a recent publication assessing the use of MyoVista for identifying heart disease ...
The relationship between emotion and attention is vital for adaptation. Trained attention to bodily sensations can heighten emotional awareness, including during "visceroception" (sensing the viscera, principally the heart, lungs and gut), which has been linked to emotion intensity and regulation. However, it is not always clear when bodily attention is adaptive, and useful to maintain, or ...
Download the "Medical Center Specializing in Heart Disease" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Hospitals, private clinics, specific wards, you know where to go when in need of medical attention. Perhaps there's a clinic specialized in treating certain issues, or a hospital in your area that is well-known for its state-of-the-art ...