An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Am J Pharm Educ
- v.74(8); 2010 Oct 11

Presenting and Evaluating Qualitative Research
The purpose of this paper is to help authors to think about ways to present qualitative research papers in the American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education . It also discusses methods for reviewers to assess the rigour, quality, and usefulness of qualitative research. Examples of different ways to present data from interviews, observations, and focus groups are included. The paper concludes with guidance for publishing qualitative research and a checklist for authors and reviewers.
INTRODUCTION
Policy and practice decisions, including those in education, increasingly are informed by findings from qualitative as well as quantitative research. Qualitative research is useful to policymakers because it often describes the settings in which policies will be implemented. Qualitative research is also useful to both pharmacy practitioners and pharmacy academics who are involved in researching educational issues in both universities and practice and in developing teaching and learning.
Qualitative research involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data that are not easily reduced to numbers. These data relate to the social world and the concepts and behaviors of people within it. Qualitative research can be found in all social sciences and in the applied fields that derive from them, for example, research in health services, nursing, and pharmacy. 1 It looks at X in terms of how X varies in different circumstances rather than how big is X or how many Xs are there? 2 Textbooks often subdivide research into qualitative and quantitative approaches, furthering the common assumption that there are fundamental differences between the 2 approaches. With pharmacy educators who have been trained in the natural and clinical sciences, there is often a tendency to embrace quantitative research, perhaps due to familiarity. A growing consensus is emerging that sees both qualitative and quantitative approaches as useful to answering research questions and understanding the world. Increasingly mixed methods research is being carried out where the researcher explicitly combines the quantitative and qualitative aspects of the study. 3 , 4
Like healthcare, education involves complex human interactions that can rarely be studied or explained in simple terms. Complex educational situations demand complex understanding; thus, the scope of educational research can be extended by the use of qualitative methods. Qualitative research can sometimes provide a better understanding of the nature of educational problems and thus add to insights into teaching and learning in a number of contexts. For example, at the University of Nottingham, we conducted in-depth interviews with pharmacists to determine their perceptions of continuing professional development and who had influenced their learning. We also have used a case study approach using observation of practice and in-depth interviews to explore physiotherapists' views of influences on their leaning in practice. We have conducted in-depth interviews with a variety of stakeholders in Malawi, Africa, to explore the issues surrounding pharmacy academic capacity building. A colleague has interviewed and conducted focus groups with students to explore cultural issues as part of a joint Nottingham-Malaysia pharmacy degree program. Another colleague has interviewed pharmacists and patients regarding their expectations before and after clinic appointments and then observed pharmacist-patient communication in clinics and assessed it using the Calgary Cambridge model in order to develop recommendations for communication skills training. 5 We have also performed documentary analysis on curriculum data to compare pharmacist and nurse supplementary prescribing courses in the United Kingdom.
It is important to choose the most appropriate methods for what is being investigated. Qualitative research is not appropriate to answer every research question and researchers need to think carefully about their objectives. Do they wish to study a particular phenomenon in depth (eg, students' perceptions of studying in a different culture)? Or are they more interested in making standardized comparisons and accounting for variance (eg, examining differences in examination grades after changing the way the content of a module is taught). Clearly a quantitative approach would be more appropriate in the last example. As with any research project, a clear research objective has to be identified to know which methods should be applied.
Types of qualitative data include:
- Audio recordings and transcripts from in-depth or semi-structured interviews
- Structured interview questionnaires containing substantial open comments including a substantial number of responses to open comment items.
- Audio recordings and transcripts from focus group sessions.
- Field notes (notes taken by the researcher while in the field [setting] being studied)
- Video recordings (eg, lecture delivery, class assignments, laboratory performance)
- Case study notes
- Documents (reports, meeting minutes, e-mails)
- Diaries, video diaries
- Observation notes
- Press clippings
- Photographs
RIGOUR IN QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
Qualitative research is often criticized as biased, small scale, anecdotal, and/or lacking rigor; however, when it is carried out properly it is unbiased, in depth, valid, reliable, credible and rigorous. In qualitative research, there needs to be a way of assessing the “extent to which claims are supported by convincing evidence.” 1 Although the terms reliability and validity traditionally have been associated with quantitative research, increasingly they are being seen as important concepts in qualitative research as well. Examining the data for reliability and validity assesses both the objectivity and credibility of the research. Validity relates to the honesty and genuineness of the research data, while reliability relates to the reproducibility and stability of the data.
The validity of research findings refers to the extent to which the findings are an accurate representation of the phenomena they are intended to represent. The reliability of a study refers to the reproducibility of the findings. Validity can be substantiated by a number of techniques including triangulation use of contradictory evidence, respondent validation, and constant comparison. Triangulation is using 2 or more methods to study the same phenomenon. Contradictory evidence, often known as deviant cases, must be sought out, examined, and accounted for in the analysis to ensure that researcher bias does not interfere with or alter their perception of the data and any insights offered. Respondent validation, which is allowing participants to read through the data and analyses and provide feedback on the researchers' interpretations of their responses, provides researchers with a method of checking for inconsistencies, challenges the researchers' assumptions, and provides them with an opportunity to re-analyze their data. The use of constant comparison means that one piece of data (for example, an interview) is compared with previous data and not considered on its own, enabling researchers to treat the data as a whole rather than fragmenting it. Constant comparison also enables the researcher to identify emerging/unanticipated themes within the research project.
STRENGTHS AND LIMITATIONS OF QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
Qualitative researchers have been criticized for overusing interviews and focus groups at the expense of other methods such as ethnography, observation, documentary analysis, case studies, and conversational analysis. Qualitative research has numerous strengths when properly conducted.
Strengths of Qualitative Research
- Issues can be examined in detail and in depth.
- Interviews are not restricted to specific questions and can be guided/redirected by the researcher in real time.
- The research framework and direction can be quickly revised as new information emerges.
- The data based on human experience that is obtained is powerful and sometimes more compelling than quantitative data.
- Subtleties and complexities about the research subjects and/or topic are discovered that are often missed by more positivistic enquiries.
- Data usually are collected from a few cases or individuals so findings cannot be generalized to a larger population. Findings can however be transferable to another setting.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
- Research quality is heavily dependent on the individual skills of the researcher and more easily influenced by the researcher's personal biases and idiosyncrasies.
- Rigor is more difficult to maintain, assess, and demonstrate.
- The volume of data makes analysis and interpretation time consuming.
- It is sometimes not as well understood and accepted as quantitative research within the scientific community
- The researcher's presence during data gathering, which is often unavoidable in qualitative research, can affect the subjects' responses.
- Issues of anonymity and confidentiality can present problems when presenting findings
- Findings can be more difficult and time consuming to characterize in a visual way.
PRESENTATION OF QUALITATIVE RESEARCH FINDINGS
The following extracts are examples of how qualitative data might be presented:
Data From an Interview.
The following is an example of how to present and discuss a quote from an interview.
The researcher should select quotes that are poignant and/or most representative of the research findings. Including large portions of an interview in a research paper is not necessary and often tedious for the reader. The setting and speakers should be established in the text at the end of the quote.
The student describes how he had used deep learning in a dispensing module. He was able to draw on learning from a previous module, “I found that while using the e learning programme I was able to apply the knowledge and skills that I had gained in last year's diseases and goals of treatment module.” (interviewee 22, male)
This is an excerpt from an article on curriculum reform that used interviews 5 :
The first question was, “Without the accreditation mandate, how much of this curriculum reform would have been attempted?” According to respondents, accreditation played a significant role in prompting the broad-based curricular change, and their comments revealed a nuanced view. Most indicated that the change would likely have occurred even without the mandate from the accreditation process: “It reflects where the profession wants to be … training a professional who wants to take on more responsibility.” However, they also commented that “if it were not mandated, it could have been a very difficult road.” Or it “would have happened, but much later.” The change would more likely have been incremental, “evolutionary,” or far more limited in its scope. “Accreditation tipped the balance” was the way one person phrased it. “Nobody got serious until the accrediting body said it would no longer accredit programs that did not change.”
Data From Observations
The following example is some data taken from observation of pharmacist patient consultations using the Calgary Cambridge guide. 6 , 7 The data are first presented and a discussion follows:
Pharmacist: We will soon be starting a stop smoking clinic. Patient: Is the interview over now? Pharmacist: No this is part of it. (Laughs) You can't tell me to bog off (sic) yet. (pause) We will be starting a stop smoking service here, Patient: Yes. Pharmacist: with one-to-one and we will be able to help you or try to help you. If you want it. In this example, the pharmacist has picked up from the patient's reaction to the stop smoking clinic that she is not receptive to advice about giving up smoking at this time; in fact she would rather end the consultation. The pharmacist draws on his prior relationship with the patient and makes use of a joke to lighten the tone. He feels his message is important enough to persevere but he presents the information in a succinct and non-pressurised way. His final comment of “If you want it” is important as this makes it clear that he is not putting any pressure on the patient to take up this offer. This extract shows that some patient cues were picked up, and appropriately dealt with, but this was not the case in all examples.
Data From Focus Groups
This excerpt from a study involving 11 focus groups illustrates how findings are presented using representative quotes from focus group participants. 8
Those pharmacists who were initially familiar with CPD endorsed the model for their peers, and suggested it had made a meaningful difference in the way they viewed their own practice. In virtually all focus groups sessions, pharmacists familiar with and supportive of the CPD paradigm had worked in collaborative practice environments such as hospital pharmacy practice. For these pharmacists, the major advantage of CPD was the linking of workplace learning with continuous education. One pharmacist stated, “It's amazing how much I have to learn every day, when I work as a pharmacist. With [the learning portfolio] it helps to show how much learning we all do, every day. It's kind of satisfying to look it over and see how much you accomplish.” Within many of the learning portfolio-sharing sessions, debates emerged regarding the true value of traditional continuing education and its outcome in changing an individual's practice. While participants appreciated the opportunity for social and professional networking inherent in some forms of traditional CE, most eventually conceded that the academic value of most CE programming was limited by the lack of a systematic process for following-up and implementing new learning in the workplace. “Well it's nice to go to these [continuing education] events, but really, I don't know how useful they are. You go, you sit, you listen, but then, well I at least forget.”
The following is an extract from a focus group (conducted by the author) with first-year pharmacy students about community placements. It illustrates how focus groups provide a chance for participants to discuss issues on which they might disagree.
Interviewer: So you are saying that you would prefer health related placements? Student 1: Not exactly so long as I could be developing my communication skill. Student 2: Yes but I still think the more health related the placement is the more I'll gain from it. Student 3: I disagree because other people related skills are useful and you may learn those from taking part in a community project like building a garden. Interviewer: So would you prefer a mixture of health and non health related community placements?
GUIDANCE FOR PUBLISHING QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
Qualitative research is becoming increasingly accepted and published in pharmacy and medical journals. Some journals and publishers have guidelines for presenting qualitative research, for example, the British Medical Journal 9 and Biomedcentral . 10 Medical Education published a useful series of articles on qualitative research. 11 Some of the important issues that should be considered by authors, reviewers and editors when publishing qualitative research are discussed below.
Introduction.
A good introduction provides a brief overview of the manuscript, including the research question and a statement justifying the research question and the reasons for using qualitative research methods. This section also should provide background information, including relevant literature from pharmacy, medicine, and other health professions, as well as literature from the field of education that addresses similar issues. Any specific educational or research terminology used in the manuscript should be defined in the introduction.
The methods section should clearly state and justify why the particular method, for example, face to face semistructured interviews, was chosen. The method should be outlined and illustrated with examples such as the interview questions, focusing exercises, observation criteria, etc. The criteria for selecting the study participants should then be explained and justified. The way in which the participants were recruited and by whom also must be stated. A brief explanation/description should be included of those who were invited to participate but chose not to. It is important to consider “fair dealing,” ie, whether the research design explicitly incorporates a wide range of different perspectives so that the viewpoint of 1 group is never presented as if it represents the sole truth about any situation. The process by which ethical and or research/institutional governance approval was obtained should be described and cited.
The study sample and the research setting should be described. Sampling differs between qualitative and quantitative studies. In quantitative survey studies, it is important to select probability samples so that statistics can be used to provide generalizations to the population from which the sample was drawn. Qualitative research necessitates having a small sample because of the detailed and intensive work required for the study. So sample sizes are not calculated using mathematical rules and probability statistics are not applied. Instead qualitative researchers should describe their sample in terms of characteristics and relevance to the wider population. Purposive sampling is common in qualitative research. Particular individuals are chosen with characteristics relevant to the study who are thought will be most informative. Purposive sampling also may be used to produce maximum variation within a sample. Participants being chosen based for example, on year of study, gender, place of work, etc. Representative samples also may be used, for example, 20 students from each of 6 schools of pharmacy. Convenience samples involve the researcher choosing those who are either most accessible or most willing to take part. This may be fine for exploratory studies; however, this form of sampling may be biased and unrepresentative of the population in question. Theoretical sampling uses insights gained from previous research to inform sample selection for a new study. The method for gaining informed consent from the participants should be described, as well as how anonymity and confidentiality of subjects were guaranteed. The method of recording, eg, audio or video recording, should be noted, along with procedures used for transcribing the data.
Data Analysis.
A description of how the data were analyzed also should be included. Was computer-aided qualitative data analysis software such as NVivo (QSR International, Cambridge, MA) used? Arrival at “data saturation” or the end of data collection should then be described and justified. A good rule when considering how much information to include is that readers should have been given enough information to be able to carry out similar research themselves.
One of the strengths of qualitative research is the recognition that data must always be understood in relation to the context of their production. 1 The analytical approach taken should be described in detail and theoretically justified in light of the research question. If the analysis was repeated by more than 1 researcher to ensure reliability or trustworthiness, this should be stated and methods of resolving any disagreements clearly described. Some researchers ask participants to check the data. If this was done, it should be fully discussed in the paper.
An adequate account of how the findings were produced should be included A description of how the themes and concepts were derived from the data also should be included. Was an inductive or deductive process used? The analysis should not be limited to just those issues that the researcher thinks are important, anticipated themes, but also consider issues that participants raised, ie, emergent themes. Qualitative researchers must be open regarding the data analysis and provide evidence of their thinking, for example, were alternative explanations for the data considered and dismissed, and if so, why were they dismissed? It also is important to present outlying or negative/deviant cases that did not fit with the central interpretation.
The interpretation should usually be grounded in interviewees or respondents' contributions and may be semi-quantified, if this is possible or appropriate, for example, “Half of the respondents said …” “The majority said …” “Three said…” Readers should be presented with data that enable them to “see what the researcher is talking about.” 1 Sufficient data should be presented to allow the reader to clearly see the relationship between the data and the interpretation of the data. Qualitative data conventionally are presented by using illustrative quotes. Quotes are “raw data” and should be compiled and analyzed, not just listed. There should be an explanation of how the quotes were chosen and how they are labeled. For example, have pseudonyms been given to each respondent or are the respondents identified using codes, and if so, how? It is important for the reader to be able to see that a range of participants have contributed to the data and that not all the quotes are drawn from 1 or 2 individuals. There is a tendency for authors to overuse quotes and for papers to be dominated by a series of long quotes with little analysis or discussion. This should be avoided.
Participants do not always state the truth and may say what they think the interviewer wishes to hear. A good qualitative researcher should not only examine what people say but also consider how they structured their responses and how they talked about the subject being discussed, for example, the person's emotions, tone, nonverbal communication, etc. If the research was triangulated with other qualitative or quantitative data, this should be discussed.
Discussion.
The findings should be presented in the context of any similar previous research and or theories. A discussion of the existing literature and how this present research contributes to the area should be included. A consideration must also be made about how transferrable the research would be to other settings. Any particular strengths and limitations of the research also should be discussed. It is common practice to include some discussion within the results section of qualitative research and follow with a concluding discussion.
The author also should reflect on their own influence on the data, including a consideration of how the researcher(s) may have introduced bias to the results. The researcher should critically examine their own influence on the design and development of the research, as well as on data collection and interpretation of the data, eg, were they an experienced teacher who researched teaching methods? If so, they should discuss how this might have influenced their interpretation of the results.
Conclusion.
The conclusion should summarize the main findings from the study and emphasize what the study adds to knowledge in the area being studied. Mays and Pope suggest the researcher ask the following 3 questions to determine whether the conclusions of a qualitative study are valid 12 : How well does this analysis explain why people behave in the way they do? How comprehensible would this explanation be to a thoughtful participant in the setting? How well does the explanation cohere with what we already know?
CHECKLIST FOR QUALITATIVE PAPERS
This paper establishes criteria for judging the quality of qualitative research. It provides guidance for authors and reviewers to prepare and review qualitative research papers for the American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education . A checklist is provided in Appendix 1 to assist both authors and reviewers of qualitative data.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thank you to the 3 reviewers whose ideas helped me to shape this paper.
Appendix 1. Checklist for authors and reviewers of qualitative research.
Introduction
- □ Research question is clearly stated.
- □ Research question is justified and related to the existing knowledge base (empirical research, theory, policy).
- □ Any specific research or educational terminology used later in manuscript is defined.
- □ The process by which ethical and or research/institutional governance approval was obtained is described and cited.
- □ Reason for choosing particular research method is stated.
- □ Criteria for selecting study participants are explained and justified.
- □ Recruitment methods are explicitly stated.
- □ Details of who chose not to participate and why are given.
- □ Study sample and research setting used are described.
- □ Method for gaining informed consent from the participants is described.
- □ Maintenance/Preservation of subject anonymity and confidentiality is described.
- □ Method of recording data (eg, audio or video recording) and procedures for transcribing data are described.
- □ Methods are outlined and examples given (eg, interview guide).
- □ Decision to stop data collection is described and justified.
- □ Data analysis and verification are described, including by whom they were performed.
- □ Methods for identifying/extrapolating themes and concepts from the data are discussed.
- □ Sufficient data are presented to allow a reader to assess whether or not the interpretation is supported by the data.
- □ Outlying or negative/deviant cases that do not fit with the central interpretation are presented.
- □ Transferability of research findings to other settings is discussed.
- □ Findings are presented in the context of any similar previous research and social theories.
- □ Discussion often is incorporated into the results in qualitative papers.
- □ A discussion of the existing literature and how this present research contributes to the area is included.
- □ Any particular strengths and limitations of the research are discussed.
- □ Reflection of the influence of the researcher(s) on the data, including a consideration of how the researcher(s) may have introduced bias to the results is included.
Conclusions
- □ The conclusion states the main finings of the study and emphasizes what the study adds to knowledge in the subject area.

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 3: Presenting Qualitative Data

- Introduction
How do you present qualitative data?
Data visualization.
- Research paper writing
- Transparency and rigor in research
- How to publish a research paper
Table of contents
- Transparency and rigor
Navigate to other guide parts:
Part 1: The Basics or Part 2: Handling Qualitative Data
- Presenting qualitative data
In the end, presenting qualitative research findings is just as important a skill as mastery of qualitative research methods for the data collection and data analysis process . Simply uncovering insights is insufficient to the research process; presenting a qualitative analysis holds the challenge of persuading your audience of the value of your research. As a result, it's worth spending some time considering how best to report your research to facilitate its contribution to scientific knowledge.

When it comes to research, presenting data in a meaningful and accessible way is as important as gathering it. This is particularly true for qualitative research , where the richness and complexity of the data demand careful and thoughtful presentation. Poorly written research is taken less seriously and left undiscussed by the greater scholarly community; quality research reporting that persuades its audience stands a greater chance of being incorporated in discussions of scientific knowledge.
Qualitative data presentation differs fundamentally from that found in quantitative research. While quantitative data tend to be numerical and easily lend themselves to statistical analysis and graphical representation, qualitative data are often textual and unstructured, requiring an interpretive approach to bring out their inherent meanings. Regardless of the methodological approach , the ultimate goal of data presentation is to communicate research findings effectively to an audience so they can incorporate the generated knowledge into their research inquiry.
As the section on research rigor will suggest, an effective presentation of your research depends on a thorough scientific process that organizes raw data into a structure that allows for a thorough analysis for scientific understanding.
Preparing the data
The first step in presenting qualitative data is preparing the data. This preparation process often begins with cleaning and organizing the data. Cleaning involves checking the data for accuracy and completeness, removing any irrelevant information, and making corrections as needed. Organizing the data often entails arranging the data into categories or groups that make sense for your research framework.
Coding the data
Once the data are cleaned and organized, the next step is coding , a crucial part of qualitative data analysis. Coding involves assigning labels to segments of the data to summarize or categorize them. This process helps to identify patterns and themes in the data, laying the groundwork for subsequent data interpretation and presentation. Qualitative research often involves multiple iterations of coding, creating new and meaningful codes while discarding unnecessary ones , to generate a rich structure through which data analysis can occur.
Uncovering insights
As you navigate through these initial steps, keep in mind the broader aim of qualitative research, which is to provide rich, detailed, and nuanced understandings of people's experiences, behaviors, and social realities. These guiding principles will help to ensure that your data presentation is not only accurate and comprehensive but also meaningful and impactful.
While this process might seem intimidating at first, it's an essential part of any qualitative research project. It's also a skill that can be learned and refined over time, so don't be discouraged if you find it challenging at first. Remember, the goal of presenting qualitative data is to make your research findings accessible and understandable to others. This requires careful preparation, a clear understanding of your data, and a commitment to presenting your findings in a way that respects and honors the complexity of the phenomena you're studying.
In the following sections, we'll delve deeper into how to create a comprehensive narrative from your data, the visualization of qualitative data , and the writing and publication processes . Let's briefly excerpt some of the content in the articles in this part of the guide.
ATLAS.ti helps you make sense of your data
Find out how with a free trial of our powerful data analysis interface.
How often do you read a research article and skip straight to the tables and figures? That's because data visualizations representing qualitative and quantitative data have the power to make large and complex research projects with thousands of data points comprehensible when authors present data to research audiences. Researchers create visual representations to help summarize the data generated from their study and make clear the pathways for actionable insights.
In everyday situations, a picture is always worth a thousand words. Illustrations, figures, and charts convey messages that words alone cannot. In research, data visualization can help explain scientific knowledge, evidence for data insights, and key performance indicators in an orderly manner based on data that is otherwise unstructured.
For all of the various data formats available to researchers, a significant portion of qualitative and social science research is still text-based. Essays, reports, and research articles still rely on writing practices aimed at repackaging research in prose form. This can create the impression that simply writing more will persuade research audiences. Instead, framing research in terms that are easy for your target readers to understand makes it easier for your research to become published in peer-reviewed scholarly journals or find engagement at scholarly conferences. Even in market or professional settings, data visualization is an essential concept when you need to convince others about the insights of your research and the recommendations you make based on the data.
Importance of data visualization
Data visualization is important because it makes it easy for your research audience to understand your data sets and your findings. Also, data visualization helps you organize your data more efficiently. As the explanation of ATLAS.ti's tools will illustrate in this section, data visualization might point you to research inquiries that you might not even be aware of, helping you get the most out of your data. Strictly speaking, the primary role of data visualization is to make the analysis of your data , if not the data itself, clear. Especially in social science research, data visualization makes it easy to see how data scientists collect and analyze data.
Prerequisites for generating data visualizations
Data visualization is effective in explaining research to others only if the researcher or data scientist can make sense of the data in front of them. Traditional research with unstructured data usually calls for coding the data with short, descriptive codes that can be analyzed later, whether statistically or thematically. These codes form the basic data points of a meaningful qualitative analysis. They represent the structure of qualitative data sets, without which a scientific visualization with research rigor would be extremely difficult to achieve. In most respects, data visualization of a qualitative research project requires coding the entire data set so that the codes adequately represent the collected data.
A successfully crafted research study culminates in the writing of the research paper . While a pilot study or preliminary research might guide the research design , a full research study leads to discussion that highlights avenues for further research. As such, the importance of the research paper cannot be overestimated in the overall generation of scientific knowledge.
The physical and natural sciences tend to have a clinical structure for a research paper that mirrors the scientific method: outline the background research, explain the materials and methods of the study, outline the research findings generated from data analysis, and discuss the implications. Qualitative research tends to preserve much of this structure, but there are notable and numerous variations from a traditional research paper that it's worth emphasizing the flexibility in the social sciences with respect to the writing process.
Requirements for research writing
While there aren't any hard and fast rules regarding what belongs in a qualitative research paper , readers expect to find a number of pieces of relevant information in a rigorously-written report. The best way to know what belongs in a full research paper is to look at articles in your target journal or articles that share a particular topic similar to yours and examine how successfully published papers are written.
It's important to emphasize the more mundane but equally important concerns of proofreading and formatting guidelines commonly found when you write a research paper. Research publication shouldn't strictly be a test of one's writing skills, but acknowledging the importance of convincing peer reviewers of the credibility of your research means accepting the responsibility of preparing your research manuscript to commonly accepted standards in research.
As a result, seemingly insignificant things such as spelling mistakes, page numbers, and proper grammar can make a difference with a particularly strict reviewer. Even when you expect to develop a paper through reviewer comments and peer feedback, your manuscript should be as close to a polished final draft as you can make it prior to submission.
Qualitative researchers face particular challenges in convincing their target audience of the value and credibility of their subsequent analysis. Numbers and quantifiable concepts in quantitative studies are relatively easier to understand than their counterparts associated with qualitative methods . Think about how easy it is to make conclusions about the value of items at a store based on their prices, then imagine trying to compare those items based on their design, function, and effectiveness.
Qualitative research involves and requires these sorts of discussions. The goal of qualitative data analysis is to allow a qualitative researcher and their audience to make such determinations, but before the audience can accept these determinations, the process of conducting research that produces the qualitative analysis must first be seen as trustworthy. As a result, it is on the researcher to persuade their audience that their data collection process and subsequent analysis is rigorous.
Qualitative rigor refers to the meticulousness, consistency, and transparency of the research. It is the application of systematic, disciplined, and stringent methods to ensure the credibility, dependability, confirmability, and transferability of research findings. In qualitative inquiry, these attributes ensure the research accurately reflects the phenomenon it is intended to represent, that its findings can be understood or used by others, and that its processes and results are open to scrutiny and validation.
Transparency
It is easier to believe the information presented to you if there is a rigorous analysis process behind that information, and if that process is explicitly detailed. The same is true for qualitative research results, making transparency a key element in qualitative research methodologies. Transparency is a fundamental aspect of rigor in qualitative research. It involves the clear, detailed, and explicit documentation of all stages of the research process. This allows other researchers to understand, evaluate, replicate, and build upon the study. Transparency in qualitative research is essential for maintaining rigor, trustworthiness, and ethical integrity. By being transparent, researchers allow their work to be scrutinized, critiqued, and improved upon, contributing to the ongoing development and refinement of knowledge in their field.
Research papers are only as useful as their audience in the scientific community is wide. To reach that audience, a paper needs to pass the peer review process of an academic journal. However, the idea of having research published in peer-reviewed journals may seem daunting to newer researchers, so it's important to provide a guide on how an academic journal looks at your research paper as well as how to determine what is the right journal for your research.
In simple terms, a research article is good if it is accepted as credible and rigorous by the scientific community. A study that isn't seen as a valid contribution to scientific knowledge shouldn't be published; ultimately, it is up to peers within the field in which the study is being considered to determine the study's value. In established academic research, this determination is manifest in the peer review process. Journal editors at a peer-reviewed journal assign papers to reviewers who will determine the credibility of the research. A peer-reviewed article that completed this process and is published in a reputable journal can be seen as credible with novel research that can make a profound contribution to scientific knowledge.
The process of research publication
The process has been codified and standardized within the scholarly community to include three main stages. These stages include the initial submission stage where the editor reviews the relevance of the paper, the review stage where experts in your field offer feedback, and, if reviewers approve your paper, the copyediting stage where you work with the journal to prepare the paper for inclusion in their journal.
Publishing a research paper may seem like an opaque process where those involved with academic journals make arbitrary decisions about the worthiness of research manuscripts. In reality, reputable publications assign a rubric or a set of guidelines that reviewers need to keep in mind when they review a submission. These guidelines will most likely differ depending on the journal, but they fall into a number of typical categories that are applicable regardless of the research area or the type of methods employed in a research study, including the strength of the literature review , rigor in research methodology , and novelty of findings.
Choosing the right journal isn't simply a matter of which journal is the most famous or has the broadest reach. Many universities keep lists of prominent journals where graduate students and faculty members should publish a research paper , but oftentimes this list is determined by a journal's impact factor and their inclusion in major academic databases.

Guide your research to publication with ATLAS.ti
Turn insights into visualizations with our easy-to-use interface. Download a free trial today.
This section is part of an entire guide. Use this table of contents to jump to any page in the guide.
Part 1: The Basics
- What is qualitative data?
- 10 examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- What is mixed methods research?
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
- Research questions
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Case studies
- Survey research
- What is ethnographic research?
- Confidentiality and privacy in research
- Bias in research
- Power dynamics in research
- Reflexivity
Part 2: Handling Qualitative Data
- Research transcripts
- Field notes in research
- Research memos
- Survey data
- Images, audio, and video in qualitative research
- Coding qualitative data
- Coding frame
- Auto-coding and smart coding
- Organizing codes
- Content analysis
- Thematic analysis
- Thematic analysis vs. content analysis
- Narrative research
- Phenomenological research
- Discourse analysis
- Grounded theory
- Deductive reasoning
- What is inductive reasoning?
- Inductive vs. deductive reasoning
- What is data interpretation?
- Qualitative analysis software
Part 3: Presenting Qualitative Data
- Data visualization - What is it and why is it important?

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Qualitative Data Analysis
23 Presenting the Results of Qualitative Analysis
Mikaila Mariel Lemonik Arthur
Qualitative research is not finished just because you have determined the main findings or conclusions of your study. Indeed, disseminating the results is an essential part of the research process. By sharing your results with others, whether in written form as scholarly paper or an applied report or in some alternative format like an oral presentation, an infographic, or a video, you ensure that your findings become part of the ongoing conversation of scholarship in your field, forming part of the foundation for future researchers. This chapter provides an introduction to writing about qualitative research findings. It will outline how writing continues to contribute to the analysis process, what concerns researchers should keep in mind as they draft their presentations of findings, and how best to organize qualitative research writing
As you move through the research process, it is essential to keep yourself organized. Organizing your data, memos, and notes aids both the analytical and the writing processes. Whether you use electronic or physical, real-world filing and organizational systems, these systems help make sense of the mountains of data you have and assure you focus your attention on the themes and ideas you have determined are important (Warren and Karner 2015). Be sure that you have kept detailed notes on all of the decisions you have made and procedures you have followed in carrying out research design, data collection, and analysis, as these will guide your ultimate write-up.
First and foremost, researchers should keep in mind that writing is in fact a form of thinking. Writing is an excellent way to discover ideas and arguments and to further develop an analysis. As you write, more ideas will occur to you, things that were previously confusing will start to make sense, and arguments will take a clear shape rather than being amorphous and poorly-organized. However, writing-as-thinking cannot be the final version that you share with others. Good-quality writing does not display the workings of your thought process. It is reorganized and revised (more on that later) to present the data and arguments important in a particular piece. And revision is totally normal! No one expects the first draft of a piece of writing to be ready for prime time. So write rough drafts and memos and notes to yourself and use them to think, and then revise them until the piece is the way you want it to be for sharing.
Bergin (2018) lays out a set of key concerns for appropriate writing about research. First, present your results accurately, without exaggerating or misrepresenting. It is very easy to overstate your findings by accident if you are enthusiastic about what you have found, so it is important to take care and use appropriate cautions about the limitations of the research. You also need to work to ensure that you communicate your findings in a way people can understand, using clear and appropriate language that is adjusted to the level of those you are communicating with. And you must be clear and transparent about the methodological strategies employed in the research. Remember, the goal is, as much as possible, to describe your research in a way that would permit others to replicate the study. There are a variety of other concerns and decision points that qualitative researchers must keep in mind, including the extent to which to include quantification in their presentation of results, ethics, considerations of audience and voice, and how to bring the richness of qualitative data to life.
Quantification, as you have learned, refers to the process of turning data into numbers. It can indeed be very useful to count and tabulate quantitative data drawn from qualitative research. For instance, if you were doing a study of dual-earner households and wanted to know how many had an equal division of household labor and how many did not, you might want to count those numbers up and include them as part of the final write-up. However, researchers need to take care when they are writing about quantified qualitative data. Qualitative data is not as generalizable as quantitative data, so quantification can be very misleading. Thus, qualitative researchers should strive to use raw numbers instead of the percentages that are more appropriate for quantitative research. Writing, for instance, “15 of the 20 people I interviewed prefer pancakes to waffles” is a simple description of the data; writing “75% of people prefer pancakes” suggests a generalizable claim that is not likely supported by the data. Note that mixing numbers with qualitative data is really a type of mixed-methods approach. Mixed-methods approaches are good, but sometimes they seduce researchers into focusing on the persuasive power of numbers and tables rather than capitalizing on the inherent richness of their qualitative data.
A variety of issues of scholarly ethics and research integrity are raised by the writing process. Some of these are unique to qualitative research, while others are more universal concerns for all academic and professional writing. For example, it is essential to avoid plagiarism and misuse of sources. All quotations that appear in a text must be properly cited, whether with in-text and bibliographic citations to the source or with an attribution to the research participant (or the participant’s pseudonym or description in order to protect confidentiality) who said those words. Where writers will paraphrase a text or a participant’s words, they need to make sure that the paraphrase they develop accurately reflects the meaning of the original words. Thus, some scholars suggest that participants should have the opportunity to read (or to have read to them, if they cannot read the text themselves) all sections of the text in which they, their words, or their ideas are presented to ensure accuracy and enable participants to maintain control over their lives.
Audience and Voice
When writing, researchers must consider their audience(s) and the effects they want their writing to have on these audiences. The designated audience will dictate the voice used in the writing, or the individual style and personality of a piece of text. Keep in mind that the potential audience for qualitative research is often much more diverse than that for quantitative research because of the accessibility of the data and the extent to which the writing can be accessible and interesting. Yet individual pieces of writing are typically pitched to a more specific subset of the audience.
Let us consider one potential research study, an ethnography involving participant-observation of the same children both when they are at daycare facility and when they are at home with their families to try to understand how daycare might impact behavior and social development. The findings of this study might be of interest to a wide variety of potential audiences: academic peers, whether at your own academic institution, in your broader discipline, or multidisciplinary; people responsible for creating laws and policies; practitioners who run or teach at day care centers; and the general public, including both people who are interested in child development more generally and those who are themselves parents making decisions about child care for their own children. And the way you write for each of these audiences will be somewhat different. Take a moment and think through what some of these differences might look like.
If you are writing to academic audiences, using specialized academic language and working within the typical constraints of scholarly genres, as will be discussed below, can be an important part of convincing others that your work is legitimate and should be taken seriously. Your writing will be formal. Even if you are writing for students and faculty you already know—your classmates, for instance—you are often asked to imitate the style of academic writing that is used in publications, as this is part of learning to become part of the scholarly conversation. When speaking to academic audiences outside your discipline, you may need to be more careful about jargon and specialized language, as disciplines do not always share the same key terms. For instance, in sociology, scholars use the term diffusion to refer to the way new ideas or practices spread from organization to organization. In the field of international relations, scholars often used the term cascade to refer to the way ideas or practices spread from nation to nation. These terms are describing what is fundamentally the same concept, but they are different terms—and a scholar from one field might have no idea what a scholar from a different field is talking about! Therefore, while the formality and academic structure of the text would stay the same, a writer with a multidisciplinary audience might need to pay more attention to defining their terms in the body of the text.
It is not only other academic scholars who expect to see formal writing. Policymakers tend to expect formality when ideas are presented to them, as well. However, the content and style of the writing will be different. Much less academic jargon should be used, and the most important findings and policy implications should be emphasized right from the start rather than initially focusing on prior literature and theoretical models as you might for an academic audience. Long discussions of research methods should also be minimized. Similarly, when you write for practitioners, the findings and implications for practice should be highlighted. The reading level of the text will vary depending on the typical background of the practitioners to whom you are writing—you can make very different assumptions about the general knowledge and reading abilities of a group of hospital medical directors with MDs than you can about a group of case workers who have a post-high-school certificate. Consider the primary language of your audience as well. The fact that someone can get by in spoken English does not mean they have the vocabulary or English reading skills to digest a complex report. But the fact that someone’s vocabulary is limited says little about their intellectual abilities, so try your best to convey the important complexity of the ideas and findings from your research without dumbing them down—even if you must limit your vocabulary usage.
When writing for the general public, you will want to move even further towards emphasizing key findings and policy implications, but you also want to draw on the most interesting aspects of your data. General readers will read sociological texts that are rich with ethnographic or other kinds of detail—it is almost like reality television on a page! And this is a contrast to busy policymakers and practitioners, who probably want to learn the main findings as quickly as possible so they can go about their busy lives. But also keep in mind that there is a wide variation in reading levels. Journalists at publications pegged to the general public are often advised to write at about a tenth-grade reading level, which would leave most of the specialized terminology we develop in our research fields out of reach. If you want to be accessible to even more people, your vocabulary must be even more limited. The excellent exercise of trying to write using the 1,000 most common English words, available at the Up-Goer Five website ( https://www.splasho.com/upgoer5/ ) does a good job of illustrating this challenge (Sanderson n.d.).
Another element of voice is whether to write in the first person. While many students are instructed to avoid the use of the first person in academic writing, this advice needs to be taken with a grain of salt. There are indeed many contexts in which the first person is best avoided, at least as long as writers can find ways to build strong, comprehensible sentences without its use, including most quantitative research writing. However, if the alternative to using the first person is crafting a sentence like “it is proposed that the researcher will conduct interviews,” it is preferable to write “I propose to conduct interviews.” In qualitative research, in fact, the use of the first person is far more common. This is because the researcher is central to the research project. Qualitative researchers can themselves be understood as research instruments, and thus eliminating the use of the first person in writing is in a sense eliminating information about the conduct of the researchers themselves.
But the question really extends beyond the issue of first-person or third-person. Qualitative researchers have choices about how and whether to foreground themselves in their writing, not just in terms of using the first person, but also in terms of whether to emphasize their own subjectivity and reflexivity, their impressions and ideas, and their role in the setting. In contrast, conventional quantitative research in the positivist tradition really tries to eliminate the author from the study—which indeed is exactly why typical quantitative research avoids the use of the first person. Keep in mind that emphasizing researchers’ roles and reflexivity and using the first person does not mean crafting articles that provide overwhelming detail about the author’s thoughts and practices. Readers do not need to hear, and should not be told, which database you used to search for journal articles, how many hours you spent transcribing, or whether the research process was stressful—save these things for the memos you write to yourself. Rather, readers need to hear how you interacted with research participants, how your standpoint may have shaped the findings, and what analytical procedures you carried out.
Making Data Come Alive
One of the most important parts of writing about qualitative research is presenting the data in a way that makes its richness and value accessible to readers. As the discussion of analysis in the prior chapter suggests, there are a variety of ways to do this. Researchers may select key quotes or images to illustrate points, write up specific case studies that exemplify their argument, or develop vignettes (little stories) that illustrate ideas and themes, all drawing directly on the research data. Researchers can also write more lengthy summaries, narratives, and thick descriptions.
Nearly all qualitative work includes quotes from research participants or documents to some extent, though ethnographic work may focus more on thick description than on relaying participants’ own words. When quotes are presented, they must be explained and interpreted—they cannot stand on their own. This is one of the ways in which qualitative research can be distinguished from journalism. Journalism presents what happened, but social science needs to present the “why,” and the why is best explained by the researcher.
So how do authors go about integrating quotes into their written work? Julie Posselt (2017), a sociologist who studies graduate education, provides a set of instructions. First of all, authors need to remain focused on the core questions of their research, and avoid getting distracted by quotes that are interesting or attention-grabbing but not so relevant to the research question. Selecting the right quotes, those that illustrate the ideas and arguments of the paper, is an important part of the writing process. Second, not all quotes should be the same length (just like not all sentences or paragraphs in a paper should be the same length). Include some quotes that are just phrases, others that are a sentence or so, and others that are longer. We call longer quotes, generally those more than about three lines long, block quotes , and they are typically indented on both sides to set them off from the surrounding text. For all quotes, be sure to summarize what the quote should be telling or showing the reader, connect this quote to other quotes that are similar or different, and provide transitions in the discussion to move from quote to quote and from topic to topic. Especially for longer quotes, it is helpful to do some of this writing before the quote to preview what is coming and other writing after the quote to make clear what readers should have come to understand. Remember, it is always the author’s job to interpret the data. Presenting excerpts of the data, like quotes, in a form the reader can access does not minimize the importance of this job. Be sure that you are explaining the meaning of the data you present.
A few more notes about writing with quotes: avoid patchwriting, whether in your literature review or the section of your paper in which quotes from respondents are presented. Patchwriting is a writing practice wherein the author lightly paraphrases original texts but stays so close to those texts that there is little the author has added. Sometimes, this even takes the form of presenting a series of quotes, properly documented, with nothing much in the way of text generated by the author. A patchwriting approach does not build the scholarly conversation forward, as it does not represent any kind of new contribution on the part of the author. It is of course fine to paraphrase quotes, as long as the meaning is not changed. But if you use direct quotes, do not edit the text of the quotes unless how you edit them does not change the meaning and you have made clear through the use of ellipses (…) and brackets ([])what kinds of edits have been made. For example, consider this exchange from Matthew Desmond’s (2012:1317) research on evictions:
The thing was, I wasn’t never gonna let Crystal come and stay with me from the get go. I just told her that to throw her off. And she wasn’t fittin’ to come stay with me with no money…No. Nope. You might as well stay in that shelter.
A paraphrase of this exchange might read “She said that she was going to let Crystal stay with her if Crystal did not have any money.” Paraphrases like that are fine. What is not fine is rewording the statement but treating it like a quote, for instance writing:
The thing was, I was not going to let Crystal come and stay with me from beginning. I just told her that to throw her off. And it was not proper for her to come stay with me without any money…No. Nope. You might as well stay in that shelter.
But as you can see, the change in language and style removes some of the distinct meaning of the original quote. Instead, writers should leave as much of the original language as possible. If some text in the middle of the quote needs to be removed, as in this example, ellipses are used to show that this has occurred. And if a word needs to be added to clarify, it is placed in square brackets to show that it was not part of the original quote.
Data can also be presented through the use of data displays like tables, charts, graphs, diagrams, and infographics created for publication or presentation, as well as through the use of visual material collected during the research process. Note that if visuals are used, the author must have the legal right to use them. Photographs or diagrams created by the author themselves—or by research participants who have signed consent forms for their work to be used, are fine. But photographs, and sometimes even excerpts from archival documents, may be owned by others from whom researchers must get permission in order to use them.
A large percentage of qualitative research does not include any data displays or visualizations. Therefore, researchers should carefully consider whether the use of data displays will help the reader understand the data. One of the most common types of data displays used by qualitative researchers are simple tables. These might include tables summarizing key data about cases included in the study; tables laying out the characteristics of different taxonomic elements or types developed as part of the analysis; tables counting the incidence of various elements; and 2×2 tables (two columns and two rows) illuminating a theory. Basic network or process diagrams are also commonly included. If data displays are used, it is essential that researchers include context and analysis alongside data displays rather than letting them stand by themselves, and it is preferable to continue to present excerpts and examples from the data rather than just relying on summaries in the tables.
If you will be using graphs, infographics, or other data visualizations, it is important that you attend to making them useful and accurate (Bergin 2018). Think about the viewer or user as your audience and ensure the data visualizations will be comprehensible. You may need to include more detail or labels than you might think. Ensure that data visualizations are laid out and labeled clearly and that you make visual choices that enhance viewers’ ability to understand the points you intend to communicate using the visual in question. Finally, given the ease with which it is possible to design visuals that are deceptive or misleading, it is essential to make ethical and responsible choices in the construction of visualization so that viewers will interpret them in accurate ways.
The Genre of Research Writing
As discussed above, the style and format in which results are presented depends on the audience they are intended for. These differences in styles and format are part of the genre of writing. Genre is a term referring to the rules of a specific form of creative or productive work. Thus, the academic journal article—and student papers based on this form—is one genre. A report or policy paper is another. The discussion below will focus on the academic journal article, but note that reports and policy papers follow somewhat different formats. They might begin with an executive summary of one or a few pages, include minimal background, focus on key findings, and conclude with policy implications, shifting methods and details about the data to an appendix. But both academic journal articles and policy papers share some things in common, for instance the necessity for clear writing, a well-organized structure, and the use of headings.
So what factors make up the genre of the academic journal article in sociology? While there is some flexibility, particularly for ethnographic work, academic journal articles tend to follow a fairly standard format. They begin with a “title page” that includes the article title (often witty and involving scholarly inside jokes, but more importantly clearly describing the content of the article); the authors’ names and institutional affiliations, an abstract , and sometimes keywords designed to help others find the article in databases. An abstract is a short summary of the article that appears both at the very beginning of the article and in search databases. Abstracts are designed to aid readers by giving them the opportunity to learn enough about an article that they can determine whether it is worth their time to read the complete text. They are written about the article, and thus not in the first person, and clearly summarize the research question, methodological approach, main findings, and often the implications of the research.
After the abstract comes an “introduction” of a page or two that details the research question, why it matters, and what approach the paper will take. This is followed by a literature review of about a quarter to a third the length of the entire paper. The literature review is often divided, with headings, into topical subsections, and is designed to provide a clear, thorough overview of the prior research literature on which a paper has built—including prior literature the new paper contradicts. At the end of the literature review it should be made clear what researchers know about the research topic and question, what they do not know, and what this new paper aims to do to address what is not known.
The next major section of the paper is the section that describes research design, data collection, and data analysis, often referred to as “research methods” or “methodology.” This section is an essential part of any written or oral presentation of your research. Here, you tell your readers or listeners “how you collected and interpreted your data” (Taylor, Bogdan, and DeVault 2016:215). Taylor, Bogdan, and DeVault suggest that the discussion of your research methods include the following:
- The particular approach to data collection used in the study;
- Any theoretical perspective(s) that shaped your data collection and analytical approach;
- When the study occurred, over how long, and where (concealing identifiable details as needed);
- A description of the setting and participants, including sampling and selection criteria (if an interview-based study, the number of participants should be clearly stated);
- The researcher’s perspective in carrying out the study, including relevant elements of their identity and standpoint, as well as their role (if any) in research settings; and
- The approach to analyzing the data.
After the methods section comes a section, variously titled but often called “data,” that takes readers through the analysis. This section is where the thick description narrative; the quotes, broken up by theme or topic, with their interpretation; the discussions of case studies; most data displays (other than perhaps those outlining a theoretical model or summarizing descriptive data about cases); and other similar material appears. The idea of the data section is to give readers the ability to see the data for themselves and to understand how this data supports the ultimate conclusions. Note that all tables and figures included in formal publications should be titled and numbered.
At the end of the paper come one or two summary sections, often called “discussion” and/or “conclusion.” If there is a separate discussion section, it will focus on exploring the overall themes and findings of the paper. The conclusion clearly and succinctly summarizes the findings and conclusions of the paper, the limitations of the research and analysis, any suggestions for future research building on the paper or addressing these limitations, and implications, be they for scholarship and theory or policy and practice.
After the end of the textual material in the paper comes the bibliography, typically called “works cited” or “references.” The references should appear in a consistent citation style—in sociology, we often use the American Sociological Association format (American Sociological Association 2019), but other formats may be used depending on where the piece will eventually be published. Care should be taken to ensure that in-text citations also reflect the chosen citation style. In some papers, there may be an appendix containing supplemental information such as a list of interview questions or an additional data visualization.
Note that when researchers give presentations to scholarly audiences, the presentations typically follow a format similar to that of scholarly papers, though given time limitations they are compressed. Abstracts and works cited are often not part of the presentation, though in-text citations are still used. The literature review presented will be shortened to only focus on the most important aspects of the prior literature, and only key examples from the discussion of data will be included. For long or complex papers, sometimes only one of several findings is the focus of the presentation. Of course, presentations for other audiences may be constructed differently, with greater attention to interesting elements of the data and findings as well as implications and less to the literature review and methods.
Concluding Your Work
After you have written a complete draft of the paper, be sure you take the time to revise and edit your work. There are several important strategies for revision. First, put your work away for a little while. Even waiting a day to revise is better than nothing, but it is best, if possible, to take much more time away from the text. This helps you forget what your writing looks like and makes it easier to find errors, mistakes, and omissions. Second, show your work to others. Ask them to read your work and critique it, pointing out places where the argument is weak, where you may have overlooked alternative explanations, where the writing could be improved, and what else you need to work on. Finally, read your work out loud to yourself (or, if you really need an audience, try reading to some stuffed animals). Reading out loud helps you catch wrong words, tricky sentences, and many other issues. But as important as revision is, try to avoid perfectionism in writing (Warren and Karner 2015). Writing can always be improved, no matter how much time you spend on it. Those improvements, however, have diminishing returns, and at some point the writing process needs to conclude so the writing can be shared with the world.
Of course, the main goal of writing up the results of a research project is to share with others. Thus, researchers should be considering how they intend to disseminate their results. What conferences might be appropriate? Where can the paper be submitted? Note that if you are an undergraduate student, there are a wide variety of journals that accept and publish research conducted by undergraduates. Some publish across disciplines, while others are specific to disciplines. Other work, such as reports, may be best disseminated by publication online on relevant organizational websites.
After a project is completed, be sure to take some time to organize your research materials and archive them for longer-term storage. Some Institutional Review Board (IRB) protocols require that original data, such as interview recordings, transcripts, and field notes, be preserved for a specific number of years in a protected (locked for paper or password-protected for digital) form and then destroyed, so be sure that your plans adhere to the IRB requirements. Be sure you keep any materials that might be relevant for future related research or for answering questions people may ask later about your project.
And then what? Well, then it is time to move on to your next research project. Research is a long-term endeavor, not a one-time-only activity. We build our skills and our expertise as we continue to pursue research. So keep at it.
- Find a short article that uses qualitative methods. The sociological magazine Contexts is a good place to find such pieces. Write an abstract of the article.
- Choose a sociological journal article on a topic you are interested in that uses some form of qualitative methods and is at least 20 pages long. Rewrite the article as a five-page research summary accessible to non-scholarly audiences.
- Choose a concept or idea you have learned in this course and write an explanation of it using the Up-Goer Five Text Editor ( https://www.splasho.com/upgoer5/ ), a website that restricts your writing to the 1,000 most common English words. What was this experience like? What did it teach you about communicating with people who have a more limited English-language vocabulary—and what did it teach you about the utility of having access to complex academic language?
- Select five or more sociological journal articles that all use the same basic type of qualitative methods (interviewing, ethnography, documents, or visual sociology). Using what you have learned about coding, code the methods sections of each article, and use your coding to figure out what is common in how such articles discuss their research design, data collection, and analysis methods.
- Return to an exercise you completed earlier in this course and revise your work. What did you change? How did revising impact the final product?
- Find a quote from the transcript of an interview, a social media post, or elsewhere that has not yet been interpreted or explained. Write a paragraph that includes the quote along with an explanation of its sociological meaning or significance.
The style or personality of a piece of writing, including such elements as tone, word choice, syntax, and rhythm.
A quotation, usually one of some length, which is set off from the main text by being indented on both sides rather than being placed in quotation marks.
A classification of written or artistic work based on form, content, and style.
A short summary of a text written from the perspective of a reader rather than from the perspective of an author.
Social Data Analysis Copyright © 2021 by Mikaila Mariel Lemonik Arthur is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on June 19, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analyzing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, history, etc.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organization?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography , action research , phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasize different aims and perspectives.
Note that qualitative research is at risk for certain research biases including the Hawthorne effect , observer bias , recall bias , and social desirability bias . While not always totally avoidable, awareness of potential biases as you collect and analyze your data can prevent them from impacting your work too much.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves “instruments” in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analyzing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organize your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorize your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analyzing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasize different concepts.
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analyzing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analyzing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalizability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalizable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labor-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square goodness of fit test
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organization to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organize your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, June 22). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, how to do thematic analysis | step-by-step guide & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

No products in the cart.
Preparing the presentation of qualitative findings: considering your roles and goals

Dr. Philip Adu is a Methodology Expert at The Chicago School of Professional Psychology (TCSPP). In this post he explains the things to consider when presenting your research findings.
This post follows on from his previous blog post “Perfecting the art of qualitative coding” in which he took us through the stages of qualitative coding and, along the way, outlined the features he found most useful.
In my previous blog post, I presented on making good use of the innovative features of NVivo across the three main stages of qualitative analysis. Expounding on the third stage which is the ‘ Post-Coding stage (Presenting your findings) ’, I want to throw light on things to consider when drafting and refining your presentation. The moment you reach a milestone of successfully using NVivo 12 (Version 12.1.249; QSR International Pty Ltd, 2018) to complete the data analysis process, the reality of preparing all of this data so you can present your findings sets in (Adu, 2016). Your methodical review of the qualitative data and development of codes, categories and themes has yielded massive and interesting NVivo outputs. The outcomes include but are not limited to; codes/nodes, categories/themes, Word Clouds, Word Tree, Framework Matrices, Cluster Tree, code-case matrices, and code-attribute matrices (see Figure 1). These findings need to be carefully examined – selecting the ones that will be useful in drafting a meaningful presentation. You can watch the presentation I developed below:

Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xEyGGFtVQFw
Note, not all of this information (i.e. the outcomes) needs to be presented to your audience (see Adu, 2019 ). Other questions that may arise as you develop your presentation include; what kind of results should you present? How do you engage with your audience when presenting your findings? How would you help your audience to understand and believe your findings?
In this post, I will discuss the three pertinent components a good presentation of qualitative findings should have. They are; background information, data analysis process and main findings.

Figure 1. Presentation of findings
Presenting background information
Participants’ past and current situations influence the information they provide to you. Due to this, there is the need to provide readers a summary of who participants are and any background information which may help them to put the findings into the proper context. Also, as a researcher analyzing qualitative data, there is the likelihood of your own background impacting the data analysis process. In the same way, you need to let readers know who you are, what your background is and how you ‘bracketed’ them from not having an effect on the findings ( Adu, 2019 ).
Presenting the data analysis process
Qualitative analysis doesn’t only involve engaging in subjective development of codes and categories, but also promoting transparency in the coding and categorization process (Greckhamer & Cilesiz, 2014). Due to this, you are expected to describe the main and detailed steps you took to analyze your data to arrive at your findings and their respective outcomes. Addressing the following questions would be great:
- What coding strategy did you use?
- What kinds of codes did you assign to relevant excerpts of the data?
- What are the examples of codes you generated?
- What categorization technique did you use?
- How did you develop categories/themes out of the codes?
Your audience’s aim is not only consuming what you found but also learning more about how you came up with the results.
Presenting main findings
When it comes to the presentation of findings, there are two main structures you could choose from. You could present them based on the themes generated or based on the cases (participants or groups of participants) you have. The decision to either structure depends on the kind of research question(s) or the research purpose you have. For a detailed explanation of the types of presentation formats and how to select an appropriate structure, see Chapter 13 of the book, “ A Step-by-Step Guide to Qualitative Data Coding ”.
Considering your roles and goals
As you plan on how to communicate the above components, make sure you accomplish your goals and carry out your role as a communicator of qualitative data analysis outcomes (See Figure 1). Your roles are; to thoughtfully arrange the data analysis outcomes and to adequately address your research questions.
Liken the presentation of your findings to sharing a puzzle which has been solved. Your goal is to prevent a situation where the burden is put on the audience to piece together the puzzle of findings. In other words, you are expected to present the findings in a meaningful way that would enhance the audience’s understanding of the data analysis outcomes (Adu, 2016 & 2019). By so doing, they are more likely to trust what you found.
Let’s summarize the action items:
- Out of a pool of qualitative analysis outcomes, select the ones that would allow you to address your research questions and meaningfully communicate your findings.
- Decide on how you want to structure the presentation of the findings.
- Irrespective of the presentation format you choose, make sure you include background information, the data analysis process and main findings in your presentation.
- Make sure you are ‘narrating’ participants’ stories or what you found – making the numeric outputs include the tables and charts generated play a supporting role when presenting the main findings.
Adu, P. (2016). Presenting Qualitative Findings Using NVivo Output to Tell the Story. [PowerPoint slides]. SlideShare. Retrieved from https://www.slideshare.net/kontorphilip/presenting-qualitative-findings-using-nvivo-output-to-tell-the-story
QSR International Pty Ltd. (2018). NVivo 12. Version 12.1.249 [Computer software]. Retrieved from https://qsrinternational.com/nvivo-qualitative-data-analysis-software
Adu, P. (2019). A Step-by-Step Guide to Qualitative Data Coding . Oxford: Routledge
Greckhamer, T., & Cilesiz, S. (2014). Rigor, Transparency, Evidence, and Representation in Discourse Analysis: Challenges and Recommendations. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 13(1), 422-443. doi:10.1177/160940691401300123
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Dr. Philip Adu is a Methodology Expert at The Chicago School of Professional Psychology (TCSPP). His role is to provide support to dissertating students in TCSPP addressing their methodology related concerns. You could access some of his webinars at the ‘Methodology Related Presentations – TCSPP’ YouTube Channel. He completed his Doctoral degree in Education with a concentration in Learning, Instructional Design and Technology from West Virginia University (WVU). Dr. Adu recently authored a book titled, “A Step-by-Step Guide to Qualitative Data Coding” (available on routledge.com or amazon.com ). You could reach Dr. Adu at [email protected] and @drphilipadu on twitter.
Recent Articles

Monograph Matters
Qualitative analysis: process and examples | powerpoint – 85.2.
Authors Laura Wray-Lake and Laura Abrams describe qualitative data analysis, with illustrative examples from their SRCD monograph, Pathways to Civic Engagement Among Urban Youth of Color . This PowerPoint document includes presenter notes, making it an ideal resource for researchers learning about qualitative analysis and for instructors teaching about it in upper-level undergraduate or graduate courses.
Created by Laura Wray-Lake and Laura S. Abrams. All rights reserved.
Citation: Wray-Lake, L. & Abrams, L. S. (2020) Qualitative Analysis: Process and Examples [PowerPoint]. Retrieved from https://monographmatters.srcd.org/2020/05/12/teachingresources-qualitativeanalysis-powerpoint-85-2
Share this:
- AI Templates
- Get a demo Sign up for free Log in Log in
Buttoning up research: How to present and visualize qualitative data

15 Minute Read

There is no doubt that data visualization is an important part of the qualitative research process. Whether you're preparing a presentation or writing up a report, effective visualizations can help make your findings clear and understandable for your audience.
In this blog post, we'll discuss some tips for creating effective visualizations of qualitative data.
First, let's take a closer look at what exactly qualitative data is.
What is qualitative data?
Qualitative data is information gathered through observation, questionnaires, and interviews. It's often subjective, meaning that the researcher has to interpret it to draw meaningful conclusions from it.
The difference between qualitative data and quantitative data
When researchers use the terms qualitative and quantitative, they're referring to two different types of data. Qualitative data is subjective and descriptive, while quantitative data is objective and numerical.
Qualitative data is often used in research involving psychology or sociology. This is usually where a researcher may be trying to identify patterns or concepts related to people's behavior or attitudes. It may also be used in research involving economics or finance, where the focus is on numerical values such as price points or profit margins.
Before we delve into how best to present and visualize qualitative data, it's important that we highlight how to be gathering this data in the first place.

How best to gather qualitative data
In order to create an effective visualization of qualitative data, ensure that the right kind of information has been gathered.
Here are six ways to gather the most accurate qualitative data:
- Define your research question: What data is being set out to collect? A qualitative research question is a definite or clear statement about a condition to be improved, a project’s area of concern, a troubling question that exists, or a difficulty to be eliminated. It not only defines who the participants will be but guides the data collection methods needed to achieve the most detailed responses.
- Determine the best data collection method(s): The data collected should be appropriate to answer the research question. Some common qualitative data collection methods include interviews, focus groups, observations, or document analysis. Consider the strengths and weaknesses of each option before deciding which one is best suited to answer the research question.
- Develop a cohesive interview guide: Creating an interview guide allows researchers to ask more specific questions and encourages thoughtful responses from participants. It’s important to design questions in such a way that they are centered around the topic of discussion and elicit meaningful insight into the issue at hand. Avoid leading or biased questions that could influence participants’ answers, and be aware of cultural nuances that may affect their answers.
- Stay neutral – let participants share their stories: The goal is to obtain useful information, not to influence the participant’s answer. Allowing participants to express themselves freely will help to gather more honest and detailed responses. It’s important to maintain a neutral tone throughout interviews and avoid judgment or opinions while they are sharing their story.
- Work with at least one additional team member when conducting qualitative research: Participants should always feel comfortable while providing feedback on a topic, so it can be helpful to have an extra team member present during the interview process – particularly if this person is familiar with the topic being discussed. This will ensure that the atmosphere of the interview remains respectful and encourages participants to speak openly and honestly.
- Analyze your findings: Once all of the data has been collected, it’s important to analyze it in order to draw meaningful conclusions. Use tools such as qualitative coding or content analysis to identify patterns or themes in the data, then compare them with prior research or other data sources. This will help to draw more accurate and useful insights from the results.
By following these steps, you will be well-prepared to collect and analyze qualitative data for your research project. Next, let's focus on how best to present the qualitative data that you have gathered and analyzed.

Create your own AI-powered templates for better, faster research synthesis. Discover new customer insights from data instantly.

The top 10 things Notably shipped in 2023 and themes for 2024.
How to visually present qualitative data.
When it comes to how to present qualitative data visually, the goal is to make research findings clear and easy to understand. To do this, use visuals that are both attractive and informative.
Presenting qualitative data visually helps to bring the user’s attention to specific items and draw them into a more in-depth analysis. Visuals provide an efficient way to communicate complex information, making it easier for the audience to comprehend.
Additionally, visuals can help engage an audience by making a presentation more interesting and interactive.
Here are some tips for creating effective visuals from qualitative data:
- Choose the right type of visualization: Consider which type of visual would best convey the story that is being told through the research. For example, bar charts or line graphs might be appropriate for tracking changes over time, while pie charts or word clouds could help show patterns in categorical data.
- Include contextual information: In addition to showing the actual numbers, it's helpful to include any relevant contextual information in order to provide context for the audience. This can include details such as the sample size, any anomalies that occurred during data collection, or other environmental factors.
- Make it easy to understand: Always keep visuals simple and avoid adding too much detail or complexity. This will help ensure that viewers can quickly grasp the main points without getting overwhelmed by all of the information.
- Use color strategically: Color can be used to draw attention to certain elements in your visual and make it easier for viewers to find the most important parts of it. Just be sure not to use too many different colors, as this could create confusion instead of clarity.
- Use charts or whiteboards: Using charts or whiteboards can help to explain the data in more detail and get viewers engaged in a discussion. This type of visual tool can also be used to create storyboards that illustrate the data over time, helping to bring your research to life.

Visualizing qualitative data in Notably
Notably helps researchers visualize their data on a flexible canvas, charts, and evidence based insights. As an all-in-one research platform, Notably enables researchers to collect, analyze and present qualitative data effectively.
Notably provides an intuitive interface for analyzing data from a variety of sources, including interviews, surveys, desk research, and more. Its powerful analytics engine then helps you to quickly identify insights and trends in your data . Finally, the platform makes it easy to create beautiful visuals that will help to communicate research findings with confidence.
Research Frameworks in Analysis
The canvas in Analysis is a multi-dimensional workspace to play with your data spatially to find likeness and tension. Here, you may use a grounded theory approach to drag and drop notes into themes or patterns that emerge in your research. Utilizing the canvas tools such as shapes, lines, and images, allows researchers to build out frameworks such as journey maps, empathy maps, 2x2's, etc. to help synthesize their data.
Going one step further, you may begin to apply various lenses to this data driven canvas. For example, recoloring by sentiment shows where pain points may distributed across your customer journey. Or, recoloring by participant may reveal if one of your participants may be creating a bias towards a particular theme.

Exploring Qualitative Data through a Quantitative Lens
Once you have begun your analysis, you may visualize your qualitative data in a quantitative way through charts. You may choose between a pie chart and or a stacked bar chart to visualize your data. From here, you can segment your data to break down the ‘bar’ in your bar chart and slices in your pie chart one step further.
To segment your data, you can choose between ‘Tag group’, ‘Tag’, ‘Theme’, and ‘Participant'. Each group shows up as its own bar in the bar chart or slice in the pie chart. For example, try grouping data as ‘Participant’ to see the volume of notes assigned to each person. Or, group by ‘Tag group’ to see which of your tag groups have the most notes.
Depending on how you’ve grouped or segmented your charts will affect the options available to color your chart. Charts use colors that are a mix of sentiment, tag, theme, and default colors. Consider color as a way of assigning another layer of meaning to your data. For example, choose a red color for tags or themes that are areas of friction or pain points. Use blue for tags that represent opportunities.

AI Powered Insights and Cover Images
One of the most powerful features in Analysis is the ability to generate insights with AI. Insights combine information, inspiration, and intuition to help bridge the gap between knowledge and wisdom. Even before you have any tags or themes, you may generate an AI Insight from your entire data set. You'll be able to choose one of our AI Insight templates that are inspired by trusted design thinking frameworks to stimulate generative, and divergent thinking. With just the click of a button, you'll get an insight that captures the essence and story of your research. You may experiment with a combination of tags, themes, and different templates or, create your own custom AI template. These insights are all evidence-based, and are centered on the needs of real people. You may package these insights up to present your research by embedding videos, quotes and using AI to generate unique cover image.

You can sign up to run an end to end research project for free and receive tips on how to make the most out of your data. Want to chat about how Notably can help your team do better, faster research? Book some time here for a 1:1 demo with your whole team.

Introducing Notably + Miro Integration: 3 Tips to Analyze Miro Boards with AI in Notably

5 Steps to turn data into insights with Notably
Give your research synthesis superpowers..
Try Teams for 7 days
Free for 1 project


How to Use Creative Data Visualization Techniques for Easy Comprehension of Qualitative Research
“A picture is worth a thousand words!”—an adage used so often stands true even whilst reporting your research data. Research studies with overwhelming data can perhaps be difficult to comprehend by some readers or can even be time-consuming. While presenting quantitative research data becomes easier with the help of graphs, pie charts, etc. researchers face an undeniable challenge whilst presenting qualitative research data. In this article, we will elaborate on effectively presenting qualitative research using data visualization techniques .
Table of Contents
What is Data Visualization?
Data visualization is the process of converting textual information into graphical and illustrative representations. It is imperative to think beyond numbers to get a holistic and comprehensive understanding of research data. Hence, this technique is adopted to help presenters communicate relevant research data in a way that’s easy for the viewer to interpret and draw conclusions.
What Is the Importance of Data Visualization in Qualitative Research?
According to the form in which the data is collected and expressed, it is broadly divided into qualitative data and quantitative data. Quantitative data expresses the size or quantity of data in a countable integer. Unlike quantitative data, qualitative data cannot be expressed in continuous integer values; it refers to data values described in the non-numeric form related to subjects, places, things, events, activities, or concepts.
What Are the Advantages of Good Data Visualization Techniques?
Excellent data visualization techniques have several benefits:
- Human eyes are often drawn to patterns and colors. Moreover, in this age of Big Data , visualization can be considered an asset to quickly and easily comprehend large amounts of data generated in a research study.
- Enables viewers to recognize emerging trends and accelerate their response time on the basis of what is seen and assimilated.
- Illustrations make it easier to identify correlated parameters.
- Allows the presenter to narrate a story whilst helping the viewer understand the data and draw conclusions from it.
- As humans can process visual images better than texts, data visualization techniques enable viewers to remember them for a longer time.
Different Types of Data Visualization Techniques in Qualitative Research
Here are several data visualization techniques for presenting qualitative data for better comprehension of research data.
1. Word Clouds

- Word Clouds is a type of data visualization technique which helps in visualizing one-word descriptions.
- It is a single image composing multiple words associated with a particular text or subject.
- The size of each word indicates its importance or frequency in the data.
- Wordle and Tagxedo are two majorly used tools to create word clouds.
2. Graphic Timelines
- Graphic timelines are created to present regular text-based timelines with pictorial illustrations or diagrams, photos, and other images.
- It visually displays a series of events in chronological order on a timescale.
- Furthermore, showcasing timelines in a graphical manner makes it easier to understand critical milestones in a study.
3. Icons Beside Descriptions
- Rather than writing long descriptive paragraphs, including resembling icons beside brief and concise points enable quick and easy comprehension.
4. Heat Map
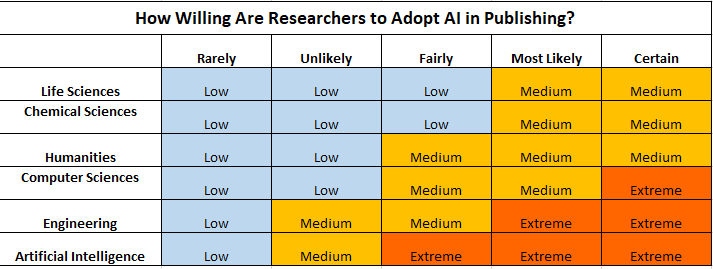
- Using a heat map as a data visualization technique better displays differences in data with color variations.
- The intensity and frequency of data is well addressed with the help of these color codes.
- However, a clear legend must be mentioned alongside the heat map to correctly interpret a heat map.
- Additionally, it also helps identify trends in data.
5. Mind Map
- A mind map helps explain concepts and ideas linked to a central idea.
- Allows visual structuring of ideas without overwhelming the viewer with large amounts of text.
- These can be used to present graphical abstracts
Do’s and Don’ts of Data Visualization Techniques
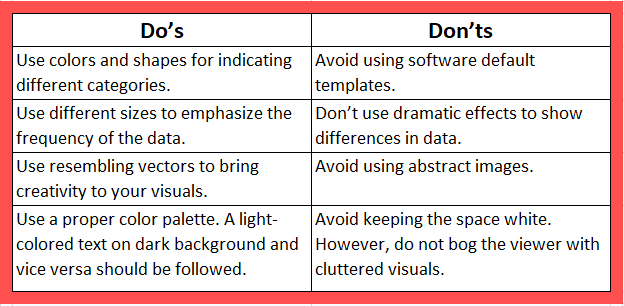
It perhaps is not easy to visualize qualitative data and make it recognizable and comprehensible to viewers at a glance. However, well-visualized qualitative data can be very useful in order to clearly convey the key points to readers and listeners in presentations.
Are you struggling with ways to display your qualitative data? Which data visualization techniques have you used before? Let us know about your experience in the comments section below!
nicely explained
None. And I want to use it from now.
Would it be ideal or suggested to use these techniques to display qualitative data in a thesis perhaps?
Using data visualization techniques in a qualitative research thesis can help convey your findings in a more engaging and comprehensible manner. Here’s a brief overview of how to incorporate data visualization in such a thesis:
Select Relevant Visualizations: Identify the types of data you have (e.g., textual, audio, visual) and the appropriate visualization techniques that can represent your qualitative data effectively. Common options include word clouds, charts, graphs, timelines, and thematic maps.
Data Preparation: Ensure your qualitative data is well-organized and coded appropriately. This might involve using qualitative analysis software like NVivo or Atlas.ti to tag and categorize data.
Create Visualizations: Generate visualizations that illustrate key themes, patterns, or trends within your qualitative data. For example: Word clouds can highlight frequently occurring terms or concepts. Bar charts or histograms can show the distribution of specific themes or categories. Timeline visualizations can help display chronological trends. Concept maps can illustrate the relationships between different concepts or ideas.
Integrate Visualizations into Your Thesis: Incorporate these visualizations within your thesis to complement your narrative. Place them strategically to support your arguments or findings. Include clear and concise captions and labels for each visualization, providing context and explaining their significance.
Interpretation: In the text of your thesis, interpret the visualizations. Explain what patterns or insights they reveal about your qualitative data. Offer meaningful insights and connections between the visuals and your research questions or hypotheses.
Maintain Consistency: Maintain a consistent style and formatting for your visualizations throughout the thesis. This ensures clarity and professionalism.
Ethical Considerations: If your qualitative research involves sensitive or personal data, consider ethical guidelines and privacy concerns when presenting visualizations. Anonymize or protect sensitive information as needed.
Review and Refinement: Before finalizing your thesis, review the visualizations for accuracy and clarity. Seek feedback from peers or advisors to ensure they effectively convey your qualitative findings.
Appendices: If you have a large number of visualizations or detailed data, consider placing some in appendices. This keeps the main body of your thesis uncluttered while providing interested readers with supplementary information.
Cite Sources: If you use specific software or tools to create your visualizations, acknowledge and cite them appropriately in your thesis.
Hope you find this helpful. Happy Learning!
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Research Interviews: An effective and insightful way of data collection
Research interviews play a pivotal role in collecting data for various academic, scientific, and professional…

Planning Your Data Collection: Designing methods for effective research
Planning your research is very important to obtain desirable results. In research, the relevance of…

- Manuscript Preparation
- Publishing Research
Qualitative Vs. Quantitative Research — A step-wise guide to conduct research
A research study includes the collection and analysis of data. In quantitative research, the data…

Explanatory & Response Variable in Statistics — A quick guide for early career researchers!
Often researchers have a difficult time choosing the parameters and variables (like explanatory and response…

6 Steps to Evaluate the Effectiveness of Statistical Hypothesis Testing
You know what is tragic? Having the potential to complete the research study but not…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?

[Guide] How to Present Qualitative Research Findings in PowerPoint?
By: Author Shrot Katewa
![what is data presentation in qualitative research [Guide] How to Present Qualitative Research Findings in PowerPoint?](https://artofpresentations.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/Featured-Image-Present-qualitative-findings-using-Powerpoint.jpg)
As a researcher, it is quite pointless to do the research if we are unable to share the findings with our audience appropriately! Using PowerPoint is one of the best ways to present research outcomes. But, how does one present qualitative research findings using PowerPoint?
In order to present the qualitative research findings using PowerPoint, you need to create a robust structure for your presentation, make it engaging and visually appealing, present the patterns with explanations for it and highlight the conclusion of your research findings.
In this article, we will help you understand the structure of your presentation. Plus, we’ll share some handy tips that will make your qualitative research presentation really effective!
How to Create a Structure for your Qualitative Research Presentation?
Creating the right structure for your presentation is key to ensuring that it is correctly understood by your audience.
The structure of your Research Presentation not only makes it easier for you to create the document, it also makes it simple for the audience to understand what all will be covered in the presentation at the time of presenting it to your audience.
Furthermore, having a robust structure is a great way to ensure that you don’t miss out on any of the points while working on creating the presentation.
But, what structure should one follow?
Creating a good structure can be tricky for some. Thus, I’m sharing what has worked well for me during my previous research projects.
NOTE – It is important to note that although the following structure is highly effective for most research findings presentation, it has been generalized in order to serve a wide range of research projects. You may want to take a look at points that are very specific to the nature of your research project and include them at your discretion.
Here’s my recommended structure to create your Research Findings presentation –
1. Objective of the Research
A great way to start your presentation is to highlight the objective of your research project.
It is important to remember that merely sharing the objective may sometimes not be enough. A short backstory along with the purpose of your research project can pack a powerful punch ! It not only validates the reasoning for your project but also subtly establishes trust with your audience.
However, do make sure that you’re not reading the backstory from the slide. Let it flow naturally when you are delivering the presentation. Keep the presentation as minimalistic as possible.
2. Key Parameters Considered for Measurement
Once you’ve established the objective, the next thing that you may want to do is perhaps share the key parameters considered for the success of your project.
Every research project, including qualitative research, needs to have a few key parameters to measure against the objective of the research.
For example – If the goal of your project is to gather the sentiments of a certain group of people for a particular product, you may need to measure their feelings. Are they happy or unhappy using the product? How do they perceive the branding of the product? Is it affordable?
Make sure that you list down all such key parameters that were considered while conducting the qualitative research.
In general, laying these out before sharing the outcome can help your audience think from your perspective and look at the findings from the correct lens.
3. Research Methodology Adopted
The next thing that you may want to include in your presentation is the methodology that you adopted for conducting the research.
By knowing your approach, the audience can be better prepared for the outcome of your project. Ensure that you provide sound reasoning for the chosen methodology.
This section of your presentation can also showcase some pictures of the research being conducted. If you have captured a video, include that. Doing this provides further validation of your project.
4. Research Outcomes (Presenting Descriptive Analysis)

This is the section that will constitute the bulk of the your presentation.
Use the slides in this section to describe the observations, and the resulting outcomes on each of the key parameters that were considered for the research project.
It is usually a good idea to dedicate at least 1 or more slides for each parameter . Make sure that you present data wherever possible. However, ensure that the data presented can be easily comprehended.
Provide key learnings from the data, highlight any outliers, and possible reasoning for it. Try not to go too in-depth with the stats as this can overwhelm the audience. Remember, a presentation is most helpful when it is used to provide key highlights of the research !
Apart from using the data, make sure that you also include a few quotes from the participants.
5. Summary and Learnings from the Research
Once you’ve taken the audience through the core part of your research findings, it is a good practice to summarize the key learnings from each of the section of your project.
Make sure your touch upon some of the key learnings covered in the research outcome of your presentation.
Furthermore, include any additional observations and key points that you may have had which were previously not covered.
The summary slide also often acts as “Key Takeaways” from the research for your audience. Thus, make sure that you maintain brevity and highlight only the points that you want your audience to remember even after the presentation.
6. Inclusions and Exclusions (if any)
While this can be an optional section for some of the researchers.
However, dedicating a section on inclusions and exclusions in your presentation can be a great value add! This section helps your audience understand the key factors that were excluded (or included) on purpose!
Moreover, it creates a sense of thoroughness in the minds of your audience.
7. Conclusion of the Research
The purpose of the conclusion slide of your research findings presentation is to revisit the objective, and present a conclusion.
A conclusion may simply validate or nullify the objective. It may sometimes do neither. Nevertheless, having a conclusion slide makes your presentation come a full circle. It creates this sense of completion in the minds of your audience.
8. Questions
Finally, since your audience did not spend as much time as you did on the research project, people are bound to have a few questions.
Thus, the last part of your presentation structure should be dedicated to allowing your audience to ask questions.
Tips for Effectively Presenting Qualitative Research Findings using PowerPoint
For a presentation to be effective, it is important that the presentation is not only well structured but also that it is well created and nicely delivered!
While we have already covered the structure, let me share with you some tips that you can help you create and deliver the presentation effectively.
Tip 1 – Use Visuals

Using visuals in your presentation is a great way to keep the presentations engaging!
Visual aids not only help make the presentation less boring, but it also helps your audience in retaining the information better!
So, use images and videos of the actual research wherever possible. If these do not suffice or do not give a professional feel, there are a number of resources online from where you can source royalty-free images.
My recommendation for high-quality royalty-free images would be either Unsplash or Pexels . Both are really good. The only downside is that they often do not provide the perfect image that can be used. That said, it can get the job done for at least half the time.
If you are unable to find the perfect free image, I recommend checking out Dreamstime . They have a huge library of images and are much cheaper than most of the other image banks. I personally use Dreamstime for my presentation projects!
Tip 2 – Tell a Story (Don’t Show Just Data!)
I cannot stress enough on how important it is to give your presentation a human touch. Delivering a presentation in the form of a story does just that! Furthermore, storytelling is also a great tool for visualization .
Data can be hard-hitting, whereas a touching story can tickle the emotions of your audience on various levels!
One of the best ways to present a story with your research project is to start with the backstory of the objective. We’ve already talked about this in the earlier part of this article.
Start with why is this research project is so important. Follow a story arc that provides an exciting experience of the beginning, the middle, and a progression towards a climax; much like a plot of a soap opera.
Tip 3 – Include Quotes of the Participants
Including quotes of the participants in your research findings presentation not only provides evidence but also demonstrates authenticity!
Quotes function as a platform to include the voice of the target group and provide a peek into the mindset of the target audience.
When using quotes, keep these things in mind –
1. Use Quotes in their Unedited Form
When using quotes in your presentation, make sure that you use them in their raw unedited form.
The need to edit quotes should be only restricted to aid comprehension and sometimes coherence.
Furthermore, when editing the quotes, make sure that you use brackets to insert clarifying words. The standard format for using the brackets is to use square brackets for clarifying words and normal brackets for adding a missing explanation.
2. How to Decide which Quotes to Consider?
It is important to know which quotes to include in your presentation. I use the following 3 criteria when selecting the quote –
- Relevance – Consider the quotes that are relevant, and trying to convey the point that you want to establish.
- Length – an ideal quote should be not more than 1-2 sentences long.
- Choose quotes that are well-expressed and striking in nature.
3. Preserve Identity of the Participant
It is important to preserve and protect the identity of the participant. This can be done by maintaining confidentiality and anonymity.
Thus, refrain from using the name of the participant. An alternative could be using codes, using pseudonyms (made up names) or simply using other general non-identifiable parameters.
Do note, when using pseudonyms, remember to highlight it in the presentation.
If, however, you do need to use the name of the respondent, make sure that the participant is okay with it and you have adequate permissions to use their name.
Tip 4 – Make your Presentation Visually Appealing and Engaging
It is quite obvious for most of us that we need to create a visually appealing presentation. But, making it pleasing to the eye can be a bit challenging.
Fortunately, we wrote a detailed blog post with tips on how to make your presentation attractive. It provides you with easy and effective tips that you can use even as a beginner! Make sure you check that article.
7 EASY tips that ALWAYS make your PPT presentation attractive (even for beginners)
In addition to the tips mentioned in the article, let me share a few things that you can do which are specific to research outcome presentations.
4.1 Use a Simple Color Scheme
Using the right colors are key to make a presentation look good.
One of the most common mistakes that people make is use too many colors in their presentation!
My recommendation would be to go with a monochromatic color scheme in PowerPoint .
4.2 Make the Data Tables Simple and Visually Appealing
When making a presentation on research outcomes, you are bound to present some data.
But, when data is not presented in a proper manner, it can easily and quickly make your presentation look displeasing! The video below can be a good starting point.
Using neat looking tables can simply transform the way your presentation looks. So don’t just dump the data from excel on your PowerPoint presentation. Spend a few minutes on fixing it!
4.3 Use Graphs and Charts (wherever necessary)
When presenting data, my recommendation would be that graphs and charts should be your first preference.
Using graphs or charts make it easier to read the data, takes less time for the audience to comprehend, and it also helps to identify a trend.
However, make sure that the correct chart type is used when representing the data. The last thing that you want is to poorly represent a key piece of information.
4.4 Use Icons instead of Bullet Points
Consider the following example –
This slide could have been created just as easily using bullet points. However, using icons and representing the information in a different format makes the slide pleasing on the eye.
Thus, always try to use icons wherever possible instead of bullet points.
Tip 5 – Include the Outliers
Many times, as a research project manager, we tend to focus on the trends extracted from a data set.
While it is important to identify patterns in the data and provide an adequate explanation for the pattern, it is equally important sometimes to highlight the outliers prominently.
It is easy to forget that there may be hidden learnings even in the outliers. At times, the data trend may be re-iterating the common wisdom. However, upon analyzing the outlier data points, you may get insight into how a few participants are doing things successfully despite not following the common knowledge.
That said, not every outlier will reveal hidden information. So, do verify what to include and what to exclude.
Tip 6 – Take Inspiration from other Presentations
I admit, making any presentation can be a tough ask let alone making a presentation for showcasing qualitative research findings. This is especially hard when we don’t have the necessary skills for creating a presentation.
One quick way to overcome this challenge could be take inspiration from other similar presentations that we may have liked.
There is no shame in being inspired from others. If you don’t have any handy references, you can surely Google it to find a few examples.
One trick that almost always works for me is using Pinterest .
But, don’t just directly search for a research presentation. You will have little to no success with it. The key is to look for specific examples for inspiration. For eg. search for Title Slide examples, or Image Layout Examples in Presentation.
Tip 7 – Ask Others to Critic your Presentation
The last tip that I would want to provide is to make sure that you share the presentation with supportive colleagues or mentors to attain feedback.
This step can be critical to iron out the chinks in the armor. As research project manager, it is common for you to get a bit too involved with the project. This can lead to possibilities wherein you miss out on things.
A good way to overcome this challenge is to get a fresh perspective on your project and the presentation once it has been prepared.
Taking critical feedback before your final presentation can also prepare you to handle tough questions in an adept manner.
Final Thoughts
It is quite important to ensure that we get it right when working on a presentation that showcases the findings of our research project. After all, we don’t want to be in a situation wherein we put in all the hard-work in the project, but we fail to deliver the outcome appropriately.
I hope you will find the aforementioned tips and structure useful, and if you do, make sure that you bookmark this page and spread the word. Wishing you all the very best for your project!

VIDEO
COMMENTS
The purpose of this paper is to help authors to think about ways to present qualitative research papers in the American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education. It also discusses methods for reviewers to assess the rigour, quality, and usefulness of qualitative research. Examples of different ways to present data from interviews, observations, and ...
Findings from qualitative research are inextricably tied up with the way those findings are presented. These presentations do not always need to be in writing, but they need to happen. Think of ethnographies, for example, and their thick descriptions of a particular culture. Witnessing a culture, taking fieldnotes, talking to people—none of ...
Qualitative data presentation differs fundamentally from that found in quantitative research. While quantitative data tend to be numerical and easily lend themselves to statistical analysis and graphical representation, qualitative data are often textual and unstructured, requiring an interpretive approach to bring out their inherent meanings.
In fact, qualitative data can and should, be presented , a number of in interesting and attractive ways. _____ Quotation Banks . Creating a transcript of any interviews that are taken or oral histories that are recorded should provide the researcher with a number of relevant quotations, each of which can be used as a piece of data.
From Paul Mihas, Assistant Director of Education and Qualitative Research at the Odum Institute for Research in Social Science at UNC: Qualitative Data Analysis: A Methods Sourcebook (4th ed.) by Miles, Huberman, and Saldana has a section on Displaying the Data (and a chapter on Designing Matrix, Network, and Graphic Displays) that can help students consider numerous options for visually ...
One of the most important parts of writing about qualitative research is presenting the data in a way that makes its richness and value accessible to readers. As the discussion of analysis in the prior chapter suggests, there are a variety of ways to do this. ... This section is an essential part of any written or oral presentation of your ...
For many researchers unfamiliar with qualitative research, determining how to conduct qualitative analyses is often quite challenging. Part of this challenge is due to the seemingly limitless approaches that a qualitative researcher might leverage, as well as simply learning to think like a qualitative researcher when analyzing data. From framework analysis (Ritchie & Spencer, 1994) to content ...
Visual displays help in the presentation of inferences and conclusions and represent ways of organizing, summarizing, simplifying, or transforming data. Data displays such as matrices and networks are often utilized to enhance data analysis and are more commonly seen in quantitative than in qualitative studies.
The qualitative research findings presentation, as a distinct genre, conventionally shares particular facets of genre entwined and contextualized in method and scholarly discourse. Despite the commonality and centrality of these presentations, little is known of the quality of current presentations of qualitative research findings.
The data presentation is one of the segments of the methodology in every research depending on the approach. The methodology, therefore, refers to the design and the theory that underpins the ...
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Key Points. Analysing and presenting qualitative data is one of the most confusing aspects of qualitative research. This paper provides a pragmatic approach using a form of thematic content ...
Preparing the presentation of qualitative findings: considering your roles and goals. Dr. Philip Adu is a Methodology Expert at The Chicago School of Professional Psychology (TCSPP). In this post he explains the things to consider when presenting your research findings. This post follows on from his previous blog post "Perfecting the art of ...
By Monograph Matters May 12, 2020 Teaching and Research Resources. Authors Laura Wray-Lake and Laura Abrams describe qualitative data analysis, with illustrative examples from their SRCD monograph, Pathways to Civic Engagement Among Urban Youth of Color. This PowerPoint document includes presenter notes, making it an ideal resource for ...
Qualitative data is often used in research involving psychology or sociology. This is usually where a researcher may be trying to identify patterns or concepts related to people's behavior or attitudes. It may also be used in research involving economics or finance, where the focus is on numerical values such as price points or profit margins ...
Here are several data visualization techniques for presenting qualitative data for better comprehension of research data. 1. Word Clouds. Word Clouds is a type of data visualization technique which helps in visualizing one-word descriptions. It is a single image composing multiple words associated with a particular text or subject.
2. Generating research hypotheses that can be tested using more quant.tat.ve approaches. 3. Stimulating new .deas and creative concepts. 4. Diagnosing the potential for prob ems with a new program, service, or product. 5. Generating impressions of products, programs, services, institutions, or other objects of interest.
Abstract. Visual displays help in the presentation of inferences and conclusions and represent ways of organizing, summarizing, simplifying, or transforming data. Data displays such as matrices and networks are often utilized to enhance data analysis and are more commonly seen in quantitative than in qualitative studies.
construction in their qualitative research presentations. When I talk about this point, I usually paraphrase the anthropologist Gregory Bateson (Harries-Jones, 1995) and say that it takes two studies to present one in qualitative research. One study is the "official" research project and the other study is the study about that study. In a well-done
DATA PRESENTATION, ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION. 4.0 Introduction. This chapter is concerned with data pres entation, of the findings obtained through the study. The. findings are presented in ...
In order to present the qualitative research findings using PowerPoint, you need to create a robust structure for your presentation, make it engaging and visually appealing, present the patterns with explanations for it and highlight the conclusion of your research findings. In this article, we will help you understand the structure of your ...