
An official website of the Department of Health & Human Services
- Search All AHRQ Sites
- Email Updates

1. Use quotes to search for an exact match of a phrase.
2. Put a minus sign just before words you don't want.
3. Enter any important keywords in any order to find entries where all these terms appear.
- The PSNet Collection
- All Content
- Perspectives
- Current Weekly Issue
- Past Weekly Issues
- Curated Libraries
- Clinical Areas
- Patient Safety 101
- The Fundamentals
- Training and Education
- Continuing Education
- WebM&M: Case Studies
- Training Catalog
- Submit a Case
- Improvement Resources
- Innovations
- Submit an Innovation
- About PSNet
- Editorial Team
- Technical Expert Panel

Developing critical thinking skills for delivering optimal care
Scott IA, Hubbard RE, Crock C, et al. Developing critical thinking skills for delivering optimal care. Intern Med J. 2021;51(4):488-493. doi: 10.1111/imj.15272
Sound critical thinking skills can help clinicians avoid cognitive biases and diagnostic errors. This article describes three critical thinking skills essential to effective clinical care – clinical reasoning, evidence-informed decision-making, and systems thinking – and approaches to develop these skills during clinician training.
Medication use and cognitive impairment among residents of aged care facilities. June 23, 2021
COVID-19 pandemic and the tension between the need to act and the need to know. October 14, 2020
Countering cognitive biases in minimising low value care. June 7, 2017
Scoping review of studies evaluating frailty and its association with medication harm. June 22, 2022
Choosing wisely in clinical practice: embracing critical thinking, striving for safer care. April 6, 2022
An act of performance: exploring residents' decision-making processes to seek help. April 14, 2021
'More than words' - interpersonal communication, cognitive bias and diagnostic errors. August 11, 2021
Decreased incidence of cesarean surgical site infection rate with hospital-wide perioperative bundle. September 29, 2021
Patient harm from cardiovascular medications. August 25, 2021
Analysis of lawsuits related to diagnostic errors from point-of-care ultrasound in internal medicine, paediatrics, family medicine and critical care in the USA. June 24, 2020
Pharmacists reducing medication risk in medical outpatient clinics: a retrospective study of 18 clinics. March 8, 2023
Estimating the economic cost of nurse sensitive adverse events amongst patients in medical and surgical settings. June 16, 2021
Changes in unprofessional behaviour, teamwork, and co-operation among hospital staff during the COVID-19 pandemic. September 28, 2022
Nursing surveillance: a concept analysis May 18, 2022
Delays in diagnosis, treatment, and surgery: root causes, actions taken, and recommendations for healthcare improvement. June 1, 2022
Nurse's Achilles Heel: using big data to determine workload factors that impact near misses. April 14, 2021
Multiple meanings of resilience: health professionals' experiences of a dual element training intervention designed to help them prepare for coping with error. March 31, 2021
Exploring the impact of employee engagement and patient safety. September 14, 2022
Differential diagnosis checklists reduce diagnostic error differentially: a randomised experiment. January 26, 2022
Think twice: effects on diagnostic accuracy of returning to the case to reflect upon the initial diagnosis. September 23, 2020
Associations between healthcare environment design and adverse events in intensive care unit. May 26, 2021
Barriers to accessing nighttime supervisors: a national survey of internal medicine residents. March 17, 2021
Predicting avoidable hospital events in Maryland. December 1, 2021
Pediatric transport safety collaborative: adverse events with parental presence during pediatric critical care transport. November 10, 2021
An observational study of postoperative handoff standardization failures. June 23, 2021
A partially structured postoperative handoff protocol improves communication in 2 mixed surgical intensive care units: findings from the Handoffs and Transitions in Critical Care (HATRICC) prospective cohort study. February 6, 2019
Effect of the surgical safety checklist on provider and patient outcomes: a systematic review. April 27, 2022
Toward the development of the perfect medical team: critical components for adaptation. March 17, 2021
The gaps in specialists' diagnoses. April 11, 2018
Doctors charged with manslaughter in the course of medical practice, 1795-2005: a literature review. July 19, 2006
Transforming the medication regimen review process using telemedicine to prevent adverse events. December 16, 2020
Evaluating the relationship between health information technology and safer-prescribing in the long-term care setting: a systematic review. March 17, 2021
Strategies to prevent missed nursing care: an international qualitative study based upon a positive deviance approach. May 12, 2021
Filling a gap in safety metrics: development of a patient-centred framework to identify and categorise patient-reported breakdowns related to the diagnostic process in ambulatory care. October 27, 2021
The association between nurse staffing and omissions in nursing care: a systematic review. July 11, 2018
Developing a patient safety culture in primary dental care. June 16, 2021
Impact of unacceptable behaviour between healthcare workers on clinical performance and patient outcomes: a systematic review. February 16, 2022
Standardized assessment of medication reconciliation in post-acute care. April 27, 2022
Cognitive biases in surgery: systematic review. March 1, 2023
Diagnostic errors in hospitalized adults who died or were transferred to intensive care. January 17, 2024
Reducing failure to rescue rates in a paediatric in-patient setting: a 9-year quality improvement study. November 24, 2021
Interprofessional and intraprofessional communication about older people's medications across transitions of care. May 26, 2021
Missed nursing care during the COVID-19 pandemic: a comparative observational study. July 21, 2021
Impact of interoperability of smart infusion pumps and an electronic medical record in critical care. September 23, 2020
Evaluation of a second victim peer support program on perceptions of second victim experiences and supportive resources in pediatric clinical specialties using the second victim experience and support tool (SVEST). November 3, 2021
Association between limiting the number of open records in a tele-critical care setting and retract-reorder errors. July 21, 2021
Understanding the second victim experience among multidisciplinary providers in obstetrics and gynecology. May 19, 2021
Care coordination strategies and barriers during medication safety incidents: a qualitative, cognitive task analysis. March 10, 2021
Optimising the delivery of remediation programmes for doctors: a realist review. June 2, 2021
Safety competency: exploring the impact of environmental and personal factors on the nurse's ability to deliver safe care. October 19, 2022
Risk assessment of the acute stroke diagnostic process using failure modes, effects, and criticality analysis. March 1, 2023
Encouraging patients to speak up about problems in cancer care. January 12, 2022
Treatment patterns and clinical outcomes after the introduction of the Medicare Sepsis Performance Measure (SEP-1). May 5, 2021
Patient perceptions of safety in primary care: a qualitative study to inform care. October 13, 2021
Staffing, teamwork and scope of practice: analysis of the association with patient safety in the context of rehabilitation. December 15, 2021
Use of heuristics during the clinical decision process from family care physicians in real conditions. October 6, 2021
Clinical and economic impacts of explicit tools detecting prescribing errors: a systematic review. May 26, 2021
Diagnostic errors in pediatric critical care: a systematic review. April 28, 2021
Emergency departments are higher-risk locations for wrong blood in tube errors. September 29, 2021
TRIAD IX: can a patient testimonial safely help ensure prehospital appropriate critical versus end-of-life care? September 15, 2021
Survey of nurses' experiences applying The Joint Commission's medication management titration standards. November 3, 2021
Clinical predictors for unsafe direct discharge home patients from intensive care units. October 21, 2020
A diagnostic time-out to improve differential diagnosis in pediatric abdominal pain. July 14, 2021
How providers can optimize effective and safe scribe use: a qualitative study. February 1, 2023
Estimation of breast cancer overdiagnosis in a U.S. breast screening cohort. March 16, 2022
Second victim experiences of nurses in obstetrics and gynaecology: a Second Victim Experience and Support Tool Survey December 23, 2020
Improving patient safety in intensive care units in Michigan. June 25, 2008
Perceived patient safety culture in a critical care transport program. July 31, 2013
The impact of health information management professionals on patient safety: a systematic review. December 22, 2021
Developing and aligning a safety event taxonomy for inpatient psychiatry. July 13, 2022
Opioids and falls risk in older adults: a narrative review. May 25, 2022
COVID-19: patient safety and quality improvement skills to deploy during the surge. June 24, 2020
Scoping review of patients' attitudes about their role and behaviours to ensure safe care at the direct care level. August 26, 2020
Mitigating imperfect data validity in administrative data PSIs: a method for estimating true adverse event rates. March 3, 2021
Can patients contribute to enhancing the safety and effectiveness of test-result follow-up? Qualitative outcomes from a health consumer workshop. June 2, 2021
Specificity of computerized physician order entry has a significant effect on the efficiency of workflow for critically ill patients. April 21, 2005
Improving patient care. The cognitive psychology of missed diagnoses. April 21, 2005
Quality of life after maternal near miss: a systematic review. June 2, 2021
Missed nursing care in the critical care unit, before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a comparative cross-sectional study. June 22, 2022
Accuracy of practitioner estimates of probability of diagnosis before and after testing. May 5, 2021
The July Effect in podiatric medicine and surgery residency. July 14, 2021
Medication reconciliation at hospital discharge: a qualitative exploration of acute care nurses' perceptions of their roles and responsibilities. March 23, 2022
"Good catch, Kiddo"--enhancing patient safety in the pediatric emergency department through simulation. December 9, 2020
How can never event data be used to reflect or improve hospital safety performance? May 19, 2021
Healthcare professionals' encounters with ethnic minority patients: the critical incident approach. June 16, 2021
Medication errors' causes analysis in home care setting: a systematic review. February 9, 2022
Development of a core drug list towards improving prescribing education and reducing errors in the UK. March 2, 2011
What does safety in mental healthcare transitions mean for service users and other stakeholder groups: an open-ended questionnaire study. March 3, 2021
'Doing the best we can': Registered nurses' experiences and perceptions of patient safety in intensive care during COVID-19. September 7, 2022
The critical role of health information technology in the safe integration of behavioral health and primary care to improve patient care. November 10, 2021
The influence of COVID-19 visitation restrictions on patient experience and safety outcomes: a critical role for subjective advocates. July 14, 2021
Development of a multicomponent intervention to decrease racial bias among healthcare staff. July 27, 2022
Prescribing decision making by medical residents on night shifts: a qualitative study. November 9, 2022
Pharmacist-led program to improve transitions from acute care to skilled nursing facility care. July 8, 2020
Perceptions of providing safe care for frail older people at home: a qualitative study based on focus group interviews with home care staff. November 10, 2021
Peer support by interprofessional health care providers in aftermath of patient safety incidents: a cross-sectional study. June 9, 2021
The safety of inpatient health care. January 25, 2023
Provider-patient communication and hospital ratings: perceived gaps and forward thinking about the effects of COVID-19. December 16, 2020
Characteristics of critical incident reporting systems in primary care: an international survey. January 19, 2022
The MedSafer study-electronic decision support for deprescribing in hospitalized older adults: a cluster randomized clinical trial. February 2, 2022
All in Her Head. The Truth and Lies Early Medicine Taught Us About Women's Bodies and Why It Matters Today. March 20, 2024
The racial disparities in maternal mortality and impact of structural racism and implicit racial bias on pregnant Black women: a review of the literature. December 6, 2023
A scoping review exploring the confidence of healthcare professionals in assessing all skin tones. October 4, 2023
Patient safety in palliative care at the end of life from the perspective of complex thinking. August 16, 2023
Only 1 in 5 people with opioid addiction get the medications to treat it, study finds. August 16, 2023
Factors influencing in-hospital prescribing errors: a systematic review. July 19, 2023
Introducing second-year medical students to diagnostic reasoning concepts and skills via a virtual curriculum. June 28, 2023
Context matters: toward a multilevel perspective on context in clinical reasoning and error. June 21, 2023
The good, the bad, and the ugly: operative staff perspectives of surgeon coping with intraoperative errors. June 14, 2023
Explicitly addressing implicit bias on inpatient rounds: student and faculty reflections. June 7, 2023
The time is now: addressing implicit bias in obstetrics and gynecology education. May 17, 2023
Listen to the whispers before they become screams: addressing Black maternal morbidity and mortality in the United States. May 3, 2023
Annual Perspective
Formalizing the hidden curriculum of performance enhancing errors. March 22, 2023
Implicit racial bias, health care provider attitudes, and perceptions of health care quality among African American college students in Georgia, USA. January 18, 2023
Structural racism and impact on sickle cell disease: sickle cell lives matter. January 11, 2023
The REPAIR Project: a prospectus for change toward racial justice in medical education and health sciences research: REPAIR project steering committee. January 11, 2023
Using the Assessment of Reasoning Tool to facilitate feedback about diagnostic reasoning. January 11, 2023
Exploring the intersection of structural racism and ageism in healthcare. December 7, 2022
Calibrate Dx: A Resource to Improve Diagnostic Decisions. October 19, 2022
Improved Diagnostic Accuracy Through Probability-Based Diagnosis. September 28, 2022
Medical malpractice lawsuits involving trainees in obstetrics and gynecology in the USA. September 21, 2022
Skin cancer is a risk no matter the skin tone. But it may be overlooked in people with dark skin. August 17, 2022
Narrowing the mindware gap in medicine. July 20, 2022
From principles to practice: embedding clinical reasoning as a longitudinal curriculum theme in a medical school programme. June 15, 2022
A call to action: next steps to advance diagnosis education in the health professions. June 8, 2022
Does a suggested diagnosis in a general practitioners' referral question impact diagnostic reasoning: an experimental study. April 27, 2022
WebM&M Cases
Analysis of the interprofessional clinical learning environment for quality improvement and patient safety from perspectives of interprofessional teams. March 16, 2022

Connect With Us
Sign up for Email Updates
To sign up for updates or to access your subscriber preferences, please enter your email address below.
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
5600 Fishers Lane Rockville, MD 20857 Telephone: (301) 427-1364
- Accessibility
- Disclaimers
- Electronic Policies
- HHS Digital Strategy
- HHS Nondiscrimination Notice
- Inspector General
- Plain Writing Act
- Privacy Policy
- Viewers & Players
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services
- The White House
- Don't have an account? Sign up to PSNet
Submit Your Innovations
Please select your preferred way to submit an innovation.
Continue as a Guest
Track and save your innovation
in My Innovations
Edit your innovation as a draft
Continue Logged In
Please select your preferred way to submit an innovation. Note that even if you have an account, you can still choose to submit an innovation as a guest.
Continue logged in
New users to the psnet site.
Access to quizzes and start earning
CME, CEU, or Trainee Certification.
Get email alerts when new content
matching your topics of interest
in My Innovations.
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- News & Views
- Critical thinking in...
Knowing and thinking about critical thinking. Re: Critical thinking in healthcare and education
Rapid response to:
Critical thinking in healthcare and education
- Related content
- Article metrics
- Rapid responses
Rapid Response:
Dear Editor,
Nice article on critical thinking in health care and education.
Medical students master an enormous body of knowledge, but lack systematic problem solving ability and effective clinical decision making. High profile reports have called for reforms in medical education to create a better generation of doctors who can cope with the system based problems they would encounter in an interdisciplinary and collaborative environment and make better reasoned decisions for quality patient care.
To achieve this critical thinking is at the very heart of development of new medical knowledge. Critical thinking can be defined as the ability to identify and analyse problems as well as seek and evaluate relevant information in order to reach an appropriate conclusion. Medical academics and practitioners have raised concerns about the low levels of critical thinking and stress the need for fostering critical thinking among medical practitioners. In recent times, there has been increasing recognition that medical education must focus more on the higher order thinking processes which is required to encounter the emerging challenges in medical education. Higher order thinking has become one of the essential characteristic of future health care professionals and an essential attribute of medical professionalism. Hence, knowing and thinking about critical thinking and exploring the avenues for its application in medical education through appropriate means have become the need of the hour.
Competing interests: No competing interests
You are using an outdated browser
Unfortunately Ausmed.com does not support your browser. Please upgrade your browser to continue.
Cultivating Critical Thinking in Healthcare
Published: 06 January 2019

Critical thinking skills have been linked to improved patient outcomes, better quality patient care and improved safety outcomes in healthcare (Jacob et al. 2017).
Given this, it's necessary for educators in healthcare to stimulate and lead further dialogue about how these skills are taught , assessed and integrated into the design and development of staff and nurse education and training programs (Papp et al. 2014).
So, what exactly is critical thinking and how can healthcare educators cultivate it amongst their staff?
What is Critical Thinking?
In general terms, ‘ critical thinking ’ is often used, and perhaps confused, with problem-solving and clinical decision-making skills .
In practice, however, problem-solving tends to focus on the identification and resolution of a problem, whilst critical thinking goes beyond this to incorporate asking skilled questions and critiquing solutions .
Several formal definitions of critical thinking can be found in literature, but in the view of Kahlke and Eva (2018), most of these definitions have limitations. That said, Papp et al. (2014) offer a useful starting point, suggesting that critical thinking is:
‘The ability to apply higher order cognitive skills and the disposition to be deliberate about thinking that leads to action that is logical and appropriate.’
The Foundation for Critical Thinking (2017) expands on this and suggests that:
‘Critical thinking is that mode of thinking, about any subject, content, or problem, in which the thinker improves the quality of his or her thinking by skillfully analysing, assessing, and reconstructing it.’
They go on to suggest that critical thinking is:
- Self-directed
- Self-disciplined
- Self-monitored
- Self-corrective.

Key Qualities and Characteristics of a Critical Thinker
Given that critical thinking is a process that encompasses conceptualisation , application , analysis , synthesis , evaluation and reflection , what qualities should be expected from a critical thinker?
In answering this question, Fortepiani (2018) suggests that critical thinkers should be able to:
- Formulate clear and precise questions
- Gather, assess and interpret relevant information
- Reach relevant well-reasoned conclusions and solutions
- Think open-mindedly, recognising their own assumptions
- Communicate effectively with others on solutions to complex problems.
All of these qualities are important, however, good communication skills are generally considered to be the bedrock of critical thinking. Why? Because they help to create a dialogue that invites questions, reflections and an open-minded approach, as well as generating a positive learning environment needed to support all forms of communication.
Lippincott Solutions (2018) outlines a broad spectrum of characteristics attributed to strong critical thinkers. They include:
- Inquisitiveness with regard to a wide range of issues
- A concern to become and remain well-informed
- Alertness to opportunities to use critical thinking
- Self-confidence in one’s own abilities to reason
- Open mindedness regarding divergent world views
- Flexibility in considering alternatives and opinions
- Understanding the opinions of other people
- Fair-mindedness in appraising reasoning
- Honesty in facing one’s own biases, prejudices, stereotypes or egocentric tendencies
- A willingness to reconsider and revise views where honest reflection suggests that change is warranted.
Papp et al. (2014) also helpfully suggest that the following five milestones can be used as a guide to help develop competency in critical thinking:
Stage 1: Unreflective Thinker
At this stage, the unreflective thinker can’t examine their own actions and cognitive processes and is unaware of different approaches to thinking.
Stage 2: Beginning Critical Thinker
Here, the learner begins to think critically and starts to recognise cognitive differences in other people. However, external motivation is needed to sustain reflection on the learners’ own thought processes.
Stage 3: Practicing Critical Thinker
By now, the learner is familiar with their own thinking processes and makes a conscious effort to practice critical thinking.
Stage 4: Advanced Critical Thinker
As an advanced critical thinker, the learner is able to identify different cognitive processes and consciously uses critical thinking skills.
Stage 5: Accomplished Critical Thinker
At this stage, the skilled critical thinker can take charge of their thinking and habitually monitors, revises and rethinks approaches for continual improvement of their cognitive strategies.
Facilitating Critical Thinking in Healthcare
A common challenge for many educators and facilitators in healthcare is encouraging students to move away from passive learning towards active learning situations that require critical thinking skills.
Just as there are similarities among the definitions of critical thinking across subject areas and levels, there are also several generally recognised hallmarks of teaching for critical thinking . These include:
- Promoting interaction among students as they learn
- Asking open ended questions that do not assume one right answer
- Allowing sufficient time to reflect on the questions asked or problems posed
- Teaching for transfer - helping learners to see how a newly acquired skill can apply to other situations and experiences.
(Lippincott Solutions 2018)
Snyder and Snyder (2008) also make the point that it’s helpful for educators and facilitators to be aware of any initial resistance that learners may have and try to guide them through the process. They should aim to create a learning environment where learners can feel comfortable thinking through an answer rather than simply having an answer given to them.
Examples include using peer coaching techniques , mentoring or preceptorship to engage students in active learning and critical thinking skills, or integrating project-based learning activities that require students to apply their knowledge in a realistic healthcare environment.
Carvalhoa et al. (2017) also advocate problem-based learning as a widely used and successful way of stimulating critical thinking skills in the learner. This view is echoed by Tsui-Mei (2015), who notes that critical thinking, systematic analysis and curiosity significantly improve after practice-based learning .
Integrating Critical Thinking Skills Into Curriculum Design
Most educators agree that critical thinking can’t easily be developed if the program curriculum is not designed to support it. This means that a deep understanding of the nature and value of critical thinking skills needs to be present from the outset of the curriculum design process , and not just bolted on as an afterthought.
In the view of Fortepiani (2018), critical thinking skills can be summarised by the statement that 'thinking is driven by questions', which means that teaching materials need to be designed in such a way as to encourage students to expand their learning by asking questions that generate further questions and stimulate the thinking process. Ideal questions are those that:
- Embrace complexity
- Challenge assumptions and points of view
- Question the source of information
- Explore variable interpretations and potential implications of information.
To put it another way, asking questions with limiting, thought-stopping answers inhibits the development of critical thinking. This means that educators must ideally be critical thinkers themselves .
Drawing these threads together, The Foundation for Critical Thinking (2017) offers us a simple reminder that even though it’s human nature to be ‘thinking’ most of the time, most thoughts, if not guided and structured, tend to be biased, distorted, partial, uninformed or even prejudiced.
They also note that the quality of work depends precisely on the quality of the practitioners’ thought processes. Given that practitioners are being asked to meet the challenge of ever more complex care, the importance of cultivating critical thinking skills, alongside advanced problem-solving skills , seems to be taking on new importance.
Additional Resources
- The Emotionally Intelligent Nurse | Ausmed Article
- Refining Competency-Based Assessment | Ausmed Article
- Socratic Questioning in Healthcare | Ausmed Article
- Carvalhoa, D P S R P et al. 2017, 'Strategies Used for the Promotion of Critical Thinking in Nursing Undergraduate Education: A Systematic Review', Nurse Education Today , vol. 57, pp. 103-10, viewed 7 December 2018, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0260691717301715
- Fortepiani, L A 2017, 'Critical Thinking or Traditional Teaching For Health Professionals', PECOP Blog , 16 January, viewed 7 December 2018, https://blog.lifescitrc.org/pecop/2017/01/16/critical-thinking-or-traditional-teaching-for-health-professions/
- Jacob, E, Duffield, C & Jacob, D 2017, 'A Protocol For the Development of a Critical Thinking Assessment Tool for Nurses Using a Delphi Technique', Journal of Advanced Nursing, vol. 73, no. 8, pp. 1982-1988, viewed 7 December 2018, https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jan.13306
- Kahlke, R & Eva, K 2018, 'Constructing Critical Thinking in Health Professional Education', Perspectives on Medical Education , vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 156-165, viewed 7 December 2018, https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40037-018-0415-z
- Lippincott Solutions 2018, 'Turning New Nurses Into Critical Thinkers', Lippincott Solutions , viewed 10 December 2018, https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/expert-insights/turning-new-nurses-into-critical-thinkers
- Papp, K K 2014, 'Milestones of Critical Thinking: A Developmental Model for Medicine and Nursing', Academic Medicine , vol. 89, no. 5, pp. 715-720, https://journals.lww.com/academicmedicine/Fulltext/2014/05000/Milestones_of_Critical_Thinking___A_Developmental.14.aspx
- Snyder, L G & Snyder, M J 2008, 'Teaching Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Skills', The Delta Pi Epsilon Journal , vol. L, no. 2, pp. 90-99, viewed 7 December 2018, https://dme.childrenshospital.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Optional-_Teaching-Critical-Thinking-and-Problem-Solving-Skills.pdf
- The Foundation for Critical Thinking 2017, Defining Critical Thinking , The Foundation for Critical Thinking, viewed 7 December 2018, https://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/our-conception-of-critical-thinking/411
- Tsui-Mei, H, Lee-Chun, H & Chen-Ju MSN, K 2015, 'How Mental Health Nurses Improve Their Critical Thinking Through Problem-Based Learning', Journal for Nurses in Professional Development , vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 170-175, viewed 7 December 2018, https://journals.lww.com/jnsdonline/Abstract/2015/05000/How_Mental_Health_Nurses_Improve_Their_Critical.8.aspx
Anne Watkins View profile
Help and feedback, publications.
Ausmed Education is a Trusted Information Partner of Healthdirect Australia. Verify here .
Medical Student Guide For Critical Thinking

Critical thinking is an essential cognitive skill for every individual but is a crucial component for healthcare professionals such as doctors, nurses and dentists. It is a skill that should be developed and trained, not just during your career as a doctor, but before that when you are still a medical student.
To be more effective in their studies, students must think their way through abstract problems, work in teams and separate high quality from low quality information. These are the same qualities that today's medical students are supposed to possess regardless of whether they graduate in the UK or study medicine in Europe .
In both well-defined and ill-defined medical emergencies, doctors are expected to make competent decisions. Critical thinking can help medical students and doctors achieve improved productivity, better clinical decision making, higher grades and much more.
This article will explain why critical thinking is a must for people in the medical field.
Definition of Critical Thinking
You can find a variety of definitions of Critical Thinking (CT). It is a term that goes back to the Ancient Greek philosopher Socrates and his teaching practice and vision. Critical thinking and its meaning have changed over the years, but at its core always will be the pursuit of proper judgment.
We can agree on one thing. Critical thinkers question every idea, assumption, and possibility rather than accepting them at once.
The most basic definition of CT is provided by Beyer (1995):
"Critical thinking means making reasoned judgements."
In other words, it is the ability to think logically about what to do and/or believe. It also includes the ability to think critically and independently. CT is the process of identifying, analysing, and then making decisions about a particular topic, advice, opinion or challenge that we are facing.
Steps to critical thinking
There is no universal standard for becoming a critical thinker. It is more like a unique journey for each individual. But as a medical student, you have already so much going on in your academic and personal life. This is why we created a list with 6 steps that will help you develop the necessary skills for critical thinking.
1. Determine the issue or question
The first step is to answer the following questions:
- What is the problem?
- Why is it important?
- Why do we need to find a solution?
- Who is involved?
By answering them, you will define the situation and acquire a deeper understanding of the problem and of any factors that may impact it.
Only after you have a clear picture of the issue and people involved can you start to dive deeper into the problem and search for a solution.
2. Research
Nowadays, we are flooded with information. We have an unlimited source of knowledge – the Internet.
Before choosing which medical schools to apply to, most applicants researched their desired schools online. Some of the areas you might have researched include:
- If the degree is recognised worldwide
- Tuition fees
- Living costs
- Entry requirements
- Competition for entry
- Number of exams
- Programme style
Having done the research, you were able to make an informed decision about your medical future based on the gathered information. Our list may be a little different to yours but that's okay. You know what factors are most important and relevant to you as a person.
The process you followed when choosing which medical school to apply to also applies to step 2 of critical thinking. As a medical student and doctor, you will face situations when you have to compare different arguments and opinions about an issue. Independent research is the key to the right clinical decisions. Medical and dentistry students have to be especially careful when learning from online sources. You shouldn't believe everything you read and take it as the absolute truth. So, here is what you need to do when facing a medical/study argument:
- Gather relevant information from all available reputable sources
- Pay attention to the salient points
- Evaluate the quality of the information and the level of evidence (is it just an opinion, or is it based upon a clinical trial?)
Once you have all the information needed, you can start the process of analysing it. It’s helpful to write down the strong and weak points of the various recommendations and identify the most evidence-based approach.
Here is an example of a comparison between two online course platforms , which shows their respective strengths and weaknesses.
When recommendations or conclusions are contradictory, you will need to make a judgement call on which point of view has the strongest level of evidence to back it up. You should leave aside your feelings and analyse the problem from every angle possible. In the end, you should aim to make your decision based on the available evidence, not assumptions or bias.
4. Be careful about confirmation bias
It is in our nature to want to confirm our existing ideas rather than challenge them. You should try your best to strive for objectivity while evaluating information.
Often, you may find yourself reading articles that support your ideas, but why not broaden your horizons by learning about the other viewpoint?
By doing so, you will have the opportunity to get closer to the truth and may even find unexpected support and evidence for your conclusion.
Curiosity will keep you on the right path. However, if you find yourself searching for information or confirmation that aligns only with your opinion, then it’s important to take a step back. Take a short break, acknowledge your bias, clear your mind and start researching all over.
5. Synthesis
As we have already mentioned a couple of times, medical students are preoccupied with their studies. Therefore, you have to learn how to synthesise information. This is where you take information from multiple sources and bring the information together. Learning how to do this effectively will save you time and help you make better decisions faster.
You will have already located and evaluated your sources in the previous steps. You now have to organise the data into a logical argument that backs up your position on the problem under consideration.
6. Make a decision
Once you have gathered and evaluated all the available evidence, your last step is to make a logical and well-reasoned conclusion.
By following this process you will ensure that whatever decision you make can be backed up if challenged
Why is critical thinking so important for medical students?
The first and most important reason for mastering critical thinking is that it will help you to avoid medical and clinical errors during your studies and future medical career.
Another good reason is that you will be able to identify better alternative options for diagnoses and treatments. You will be able to find the best solution for the patient as a whole which may be different to generic advice specific to the disease.
Furthermore, thinking critically as a medical student will boost your confidence and improve your knowledge and understanding of subjects.
In conclusion, critical thinking is a skill that can be learned and improved. It will encourage you to be the best version of yourself and teach you to take responsibility for your actions.
Critical thinking has become an essential for future health care professionals and you will find it an invaluable skill throughout your career.
We’ll keep you updated

- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …
Critical Thinking in Healthcare and Medicine: A Crucial Skill for Improved Outcomes

Critical thinking is a crucial skill for individuals working in various healthcare domains, such as doctors, nurses, lab assistants, and patients. It serves as the foundation for evidence-based practice in healthcare and education and is essential for making informed decisions while evaluating research findings, which may sometimes be mixed or even conflicting [ The BMJ ].
In healthcare and medicine, critical thinking facilitates a more in-depth understanding of patients’ situations, complex clinical scenarios, and the ability to integrate various sources of information to make informed decisions. Professionals with strong critical thinking skills can better evaluate options, weigh potential risks and benefits, and ultimately choose the most appropriate course of action for their patients [ NurseJournal ].
Developing critical thinking skills in the healthcare sector is vital not only for patient safety but also for the professional development and career advancement of clinical and administrative nursing leaders. Ensuring that these skills are continuously nurtured and improved is critical for the ongoing success of the healthcare industry and for delivering the highest quality of patient care [ PubMed ].
Critical Thinking in Healthcare and Medicine
Critical thinking in healthcare and medicine involves the application of evidence-based practices and analytical skills to make informed decisions about patient care. This process often requires healthcare professionals to reflect on their knowledge, collaborate with colleagues, and evaluate the validity of various sources of information, including medical research, clinical experience, and patient preferences.
An example of critical thinking in healthcare is when a primary care doctor encounters a patient with acute, atypical chest pain. The doctor must assess the patient’s condition, review their medical history, and consider possible diagnoses while ruling out other potential causes of the pain [source] . Applying critical thinking skills enables healthcare practitioners to provide safe and effective care that is tailored to the needs of each patient.
Developing critical thinking skills is vital for healthcare professionals, as they often face complex and unique cases, where the available evidence is uncertain or conflicting. The ability to question claims, evaluate sources, and make informed decisions based on evidence contributes to improved patient outcomes and the overall quality of care [source] .
Some key components of critical thinking in healthcare and medicine include:
- Applying clinical reasoning to diagnose and treat patients
- Assessing the reliability of medical research and information sources
- Identifying gaps in knowledge and seeking additional information as needed
- Collaborating with team members and integrating their perspectives into patient care
- Reflecting on performance and implementing strategies for continuous improvement
By fostering these critical thinking skills, healthcare professionals can navigate the complexities of their field, make better clinical decisions, and ultimately provide a higher standard of patient care.
The Role of Critical Thinking in Decision-Making
Critical thinking plays a pivotal role in healthcare and medicine, affecting every aspect of the decision-making process. In clinical practice, it serves a key function in assessing patients’ symptoms, interpreting diagnostic results, and choosing appropriate interventions. This cognitive skill involves questioning, analysis, synthesis, interpretation, inference, inductive and deductive reasoning, intuition, application, and creativity to guide professional judgments and actions ( source ).
In many medical situations, such as triage, critical thinking can be crucial to ensure appropriate prioritization of patients based on their medical needs. Healthcare professionals must quickly adapt and process an influx of information to efficiently make critical decisions ( Rasmussen University ). Some practical examples of critical thinking in decision-making include:
- Evaluating multiple treatment options and selecting the best course of action for a particular patient;
- Appraising and integrating relevant evidence from research into clinical practice;
- Asking meaningful questions that lead to useful answers and promote deeper understanding of complex medical issues ( NurseJournal ); and
- Identifying personal biases and potential barriers that could impair objective decision-making.
Furthermore, fostering critical thinking in medical education empowers healthcare professionals to make informed decisions, even in ambiguous or uncertain circumstances. Cross-sector collaboration between healthcare and education sectors can nurture and enhance the development of these essential skills, creating better-prepared providers ( The BMJ ).
Developing Critical Thinking Skills in Healthcare Professionals
Enhancing critical thinking abilities in healthcare professionals is crucial for promoting effective decision making, improving patient outcomes, and maintaining quality patient care. This can be achieved through various approaches, including education and training, mentoring, and continuing professional development.
Education and Training
Formal education and specialized training programs play a vital role in developing critical thinking skills among healthcare professionals. These programs should emphasize the importance of honing these skills as an essential component of their professional growth. Incorporating interactive learning methods, such as case studies, group discussions, and problem-solving exercises, can encourage participants to engage in reflective and analytical thinking. Courses on clinical reasoning and decision making can further strengthen these abilities.
Mentoring has been shown to be an effective method for fostering critical thinking skills in healthcare professionals. Experienced mentors can support and guide their mentees in developing the habits of mind associated with critical thinking, such as open-mindedness, intellectual curiosity, and reflection. The mentor-mentee relationship offers a platform for the exchange of ideas, constructive feedback, and experiential learning. By reflecting on real-life clinical scenarios with their mentors, mentees can hone their critical thinking skills to make better informed decisions in their practice.
Continuing Professional Development
Continuing Professional Development (CPD) is an integral component of maintaining and improving critical thinking skills in the healthcare setting. By participating in relevant workshops, seminars, and courses, healthcare professionals can stay up-to-date with the latest advances in their field and strengthen their decision-making abilities. Additionally, engaging in regular self-reflection and assessment allows them to identify areas for improvement and seek targeted education to further enhance their critical thinking skills.
To summarize, developing critical thinking skills in healthcare professionals is crucial in promoting optimal patient care, decision-making, and overall professional growth. Fostering these skills through education and training, mentoring, and continuing professional development ensures that healthcare providers remain effective, well-rounded professionals.
Critical Thinking Tools and Techniques
Critical thinking in healthcare and medicine is an essential skill for professionals to make well-informed decisions and provide quality care to patients. This process combines cognitive abilities with strategic skills to achieve specific objectives. This section will explore some common tools and techniques used to promote critical thinking in healthcare professionals.
1. Interpretation : Professionals should be able to understand and explain the meaning of various types of information, such as diagnostic results or patient medical histories. They need to interpret complex data and make sense of it to provide the best possible care. This skill is important for accurate diagnosis, efficient treatment, and effective communication with patients and colleagues (APA) .
2. Analysis : Critical thinking in healthcare requires professionals to assess the quality and relevance of information, such as research findings or clinical guidelines. By breaking down information into its constituent parts and evaluating its strengths and weaknesses, professionals can make informed decisions that are based on evidence and best practices (The BMJ) .
3. Evaluation : Healthcare professionals need to appraise the credibility, accuracy, and applicability of information. Evaluating the reliability of sources, such as the reputation of journals or the robustness of research, helps ensure that only high-quality, trustworthy information is used to guide clinical decisions (Nursing Clinical Practice, Education and Research) .
4. Inference : Drawing conclusions from available information is a crucial aspect of critical thinking in healthcare. Professionals must infer the best course of action, considering all relevant variables and factors, such as patient preferences, clinical guidelines, and ethical considerations. Inference requires professionals to weigh the potential benefits and harms and use their judgment to make sound decisions (Critical Thinking in Critical Care) .
5. Self-regulation : It is essential for healthcare professionals to monitor and adjust their thinking processes by maintaining an open-minded and reflective approach. Self-regulation involves the ability to identify biases and inconsistencies in one’s thinking, question assumptions, and adapt to new information or insights as they emerge (Scoping Review of Critical Thinking) .
Using these critical thinking tools and techniques, healthcare professionals can better navigate complex situations, problem-solve effectively, and ensure that they are providing the highest quality care to their patients.
Challenges in Implementing Critical Thinking in Healthcare
One of the major challenges in implementing critical thinking in healthcare is overcoming personal biases. These biases can sometimes lead healthcare professionals to make incorrect inferences or judgments, which ultimately affects patient care. In nursing, for example, personal biases are regarded as one of the most common pitfalls to critical thinking ( NurseJournal ).
Another challenge is the risk of conflicting metrics. Healthcare professionals often need to balance various metrics and targets to provide the best possible care to patients. Sometimes, success in one area may come at the expense of another, making it difficult to find a balance conducive to critical thinking ( International Journal for Quality in Health Care ).
Moreover, healthcare professionals must also deal with disconnected metrics. Staff members may face multiple targets and metrics that appear unrelated or difficult to comprehend, making it harder for them to incorporate critical thinking into their decision-making processes ( International Journal for Quality in Health Care ).
In terms of education, there is an ongoing need to identify the most effective strategies for teaching critical thinking in healthcare. A scoping review of critical thinking literature in healthcare education highlights the broad range of methods used to teach critical thinking, as well as the variability in research methodologies ( PubMed ). This suggests a need for further research and consensus to develop the most effective critical thinking educational methods for healthcare professionals.
The Impact of Critical Thinking on Patient Outcomes
Critical thinking is essential in healthcare as it enables healthcare professionals to make well-informed decisions, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes. This higher-order thinking skill involves the application of knowledge and experience to identify patient problems and direct clinical judgments and actions that result in positive outcomes (NCBI) .
One of the ways critical thinking can positively impact patient outcomes is through accurate problem identification. This skill can help healthcare professionals correctly diagnose patients’ issues, resulting in a more efficient and effective care plan (ScienceDirect) .
Another impact of critical thinking on patient outcomes is seen through proper planning and administration of care. A healthcare professional who utilizes critical thinking skills can carefully examine all aspects of patient care and make informed decisions that minimize harm and improve outcomes (ScienceDirect) .
Furthermore, critical thinking skills can also enhance communication and collaboration among healthcare professionals. This can lead to more effective teamwork and coordinated care, ultimately benefiting the patient and improving their overall experience in the healthcare system.
In summary, incorporating critical thinking skills into healthcare practice can play a significant role in improving patient outcomes. Accurate problem identification, effective planning, and administration of care, coupled with better communication and collaboration among professionals, all contribute to enhancing the quality of care delivered to patients.
Future Perspectives
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, the importance of critical thinking skills in medical practice is becoming increasingly evident. The ability to critically evaluate evidence, diagnose complex problems, and develop effective solutions will be paramount for healthcare providers as they face new challenges and adapt to novel technologies.
One of the exciting prospects for the future of critical thinking in healthcare is cross-sector collaboration. Professionals from various disciplines, such as medicine, nursing, psychology, and education, have the opportunity to work together to gain new insights and develop innovative approaches to patient care. This collaboration could lead to significant advancements in both healthcare practice and medical education, as described in The BMJ .
Furthermore, the integration of new technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning will necessitate a greater emphasis on critical thinking. Healthcare practitioners will need to adapt and learn how to effectively use these tools while maintaining their ability to think critically about diagnoses and treatment plans.
Medical education must also evolve to reflect the shifting landscape of healthcare. Educators should prioritize the development of critical thinking skills in their curricula, alongside clinical competencies and lifelong learning. This entails incorporating teaching strategies that foster problem-solving, evidence-based decision making, and collaboration, as highlighted in The BMJ .
In summary, the future of critical thinking in healthcare and medicine holds promise for enhancing patient care and improving medical education. By fostering a culture of collaboration and embracing new technologies, healthcare professionals can leverage their critical thinking skills to navigate complex challenges and drive innovation in their field.
You may also like

Does Personality Matter When Choosing A Career?
Take a look at the different departments of a company and see if you can spot certain characteristics unique to each: The […]

Why Podcasts Are Killing Critical Thinking: Assessing the Impact on Public Discourse
The consumption of content through podcasts has soared with their rise as a convenient medium for learning and entertainment. However, this surge […]

Best Approach to Problem Solving: Efficient Strategies for Success
Problem-solving is a crucial skill in all aspects of life, from personal interactions to navigating complex work situations. It is essential for […]

5 Activities that Will Teach Children about Critical Thinking
Teaching your children to dig deeper and solve problems with a higher level of thinking can be tough. But as a parent, […]
The Value of Critical Thinking in Nursing

- How Nurses Use Critical Thinking
- How to Improve Critical Thinking
- Common Mistakes

Some experts describe a person’s ability to question belief systems, test previously held assumptions, and recognize ambiguity as evidence of critical thinking. Others identify specific skills that demonstrate critical thinking, such as the ability to identify problems and biases, infer and draw conclusions, and determine the relevance of information to a situation.
Nicholas McGowan, BSN, RN, CCRN, has been a critical care nurse for 10 years in neurological trauma nursing and cardiovascular and surgical intensive care. He defines critical thinking as “necessary for problem-solving and decision-making by healthcare providers. It is a process where people use a logical process to gather information and take purposeful action based on their evaluation.”
“This cognitive process is vital for excellent patient outcomes because it requires that nurses make clinical decisions utilizing a variety of different lenses, such as fairness, ethics, and evidence-based practice,” he says.
How Do Nurses Use Critical Thinking?
Successful nurses think beyond their assigned tasks to deliver excellent care for their patients. For example, a nurse might be tasked with changing a wound dressing, delivering medications, and monitoring vital signs during a shift. However, it requires critical thinking skills to understand how a difference in the wound may affect blood pressure and temperature and when those changes may require immediate medical intervention.
Nurses care for many patients during their shifts. Strong critical thinking skills are crucial when juggling various tasks so patient safety and care are not compromised.
Jenna Liphart Rhoads, Ph.D., RN, is a nurse educator with a clinical background in surgical-trauma adult critical care, where critical thinking and action were essential to the safety of her patients. She talks about examples of critical thinking in a healthcare environment, saying:
“Nurses must also critically think to determine which patient to see first, which medications to pass first, and the order in which to organize their day caring for patients. Patient conditions and environments are continually in flux, therefore nurses must constantly be evaluating and re-evaluating information they gather (assess) to keep their patients safe.”
The COVID-19 pandemic created hospital care situations where critical thinking was essential. It was expected of the nurses on the general floor and in intensive care units. Crystal Slaughter is an advanced practice nurse in the intensive care unit (ICU) and a nurse educator. She observed critical thinking throughout the pandemic as she watched intensive care nurses test the boundaries of previously held beliefs and master providing excellent care while preserving resources.
“Nurses are at the patient’s bedside and are often the first ones to detect issues. Then, the nurse needs to gather the appropriate subjective and objective data from the patient in order to frame a concise problem statement or question for the physician or advanced practice provider,” she explains.
Top 5 Ways Nurses Can Improve Critical Thinking Skills
We asked our experts for the top five strategies nurses can use to purposefully improve their critical thinking skills.
Case-Based Approach
Slaughter is a fan of the case-based approach to learning critical thinking skills.
In much the same way a detective would approach a mystery, she mentors her students to ask questions about the situation that help determine the information they have and the information they need. “What is going on? What information am I missing? Can I get that information? What does that information mean for the patient? How quickly do I need to act?”
Consider forming a group and working with a mentor who can guide you through case studies. This provides you with a learner-centered environment in which you can analyze data to reach conclusions and develop communication, analytical, and collaborative skills with your colleagues.
Practice Self-Reflection
Rhoads is an advocate for self-reflection. “Nurses should reflect upon what went well or did not go well in their workday and identify areas of improvement or situations in which they should have reached out for help.” Self-reflection is a form of personal analysis to observe and evaluate situations and how you responded.
This gives you the opportunity to discover mistakes you may have made and to establish new behavior patterns that may help you make better decisions. You likely already do this. For example, after a disagreement or contentious meeting, you may go over the conversation in your head and think about ways you could have responded.
It’s important to go through the decisions you made during your day and determine if you should have gotten more information before acting or if you could have asked better questions.
During self-reflection, you may try thinking about the problem in reverse. This may not give you an immediate answer, but can help you see the situation with fresh eyes and a new perspective. How would the outcome of the day be different if you planned the dressing change in reverse with the assumption you would find a wound infection? How does this information change your plan for the next dressing change?
Develop a Questioning Mind
McGowan has learned that “critical thinking is a self-driven process. It isn’t something that can simply be taught. Rather, it is something that you practice and cultivate with experience. To develop critical thinking skills, you have to be curious and inquisitive.”
To gain critical thinking skills, you must undergo a purposeful process of learning strategies and using them consistently so they become a habit. One of those strategies is developing a questioning mind. Meaningful questions lead to useful answers and are at the core of critical thinking .
However, learning to ask insightful questions is a skill you must develop. Faced with staff and nursing shortages , declining patient conditions, and a rising number of tasks to be completed, it may be difficult to do more than finish the task in front of you. Yet, questions drive active learning and train your brain to see the world differently and take nothing for granted.
It is easier to practice questioning in a non-stressful, quiet environment until it becomes a habit. Then, in the moment when your patient’s care depends on your ability to ask the right questions, you can be ready to rise to the occasion.
Practice Self-Awareness in the Moment
Critical thinking in nursing requires self-awareness and being present in the moment. During a hectic shift, it is easy to lose focus as you struggle to finish every task needed for your patients. Passing medication, changing dressings, and hanging intravenous lines all while trying to assess your patient’s mental and emotional status can affect your focus and how you manage stress as a nurse .
Staying present helps you to be proactive in your thinking and anticipate what might happen, such as bringing extra lubricant for a catheterization or extra gloves for a dressing change.
By staying present, you are also better able to practice active listening. This raises your assessment skills and gives you more information as a basis for your interventions and decisions.
Use a Process
As you are developing critical thinking skills, it can be helpful to use a process. For example:
- Ask questions.
- Gather information.
- Implement a strategy.
- Evaluate the results.
- Consider another point of view.
These are the fundamental steps of the nursing process (assess, diagnose, plan, implement, evaluate). The last step will help you overcome one of the common problems of critical thinking in nursing — personal bias.

Common Critical Thinking Pitfalls in Nursing
Your brain uses a set of processes to make inferences about what’s happening around you. In some cases, your unreliable biases can lead you down the wrong path. McGowan places personal biases at the top of his list of common pitfalls to critical thinking in nursing.
“We all form biases based on our own experiences. However, nurses have to learn to separate their own biases from each patient encounter to avoid making false assumptions that may interfere with their care,” he says. Successful critical thinkers accept they have personal biases and learn to look out for them. Awareness of your biases is the first step to understanding if your personal bias is contributing to the wrong decision.
New nurses may be overwhelmed by the transition from academics to clinical practice, leading to a task-oriented mindset and a common new nurse mistake ; this conflicts with critical thinking skills.
“Consider a patient whose blood pressure is low but who also needs to take a blood pressure medication at a scheduled time. A task-oriented nurse may provide the medication without regard for the patient’s blood pressure because medication administration is a task that must be completed,” Slaughter says. “A nurse employing critical thinking skills would address the low blood pressure, review the patient’s blood pressure history and trends, and potentially call the physician to discuss whether medication should be withheld.”
Fear and pride may also stand in the way of developing critical thinking skills. Your belief system and worldview provide comfort and guidance, but this can impede your judgment when you are faced with an individual whose belief system or cultural practices are not the same as yours. Fear or pride may prevent you from pursuing a line of questioning that would benefit the patient. Nurses with strong critical thinking skills exhibit:
- Learn from their mistakes and the mistakes of other nurses
- Look forward to integrating changes that improve patient care
- Treat each patient interaction as a part of a whole
- Evaluate new events based on past knowledge and adjust decision-making as needed
- Solve problems with their colleagues
- Are self-confident
- Acknowledge biases and seek to ensure these do not impact patient care
An Essential Skill for All Nurses
Critical thinking in nursing protects patient health and contributes to professional development and career advancement. Administrative and clinical nursing leaders are required to have strong critical thinking skills to be successful in their positions.
By using the strategies in this guide during your daily life and in your nursing role, you can intentionally improve your critical thinking abilities and be rewarded with better patient outcomes and potential career advancement.
Frequently Asked Questions About Critical Thinking in Nursing
How are critical thinking skills utilized in nursing practice.
Nursing practice utilizes critical thinking skills to provide the best care for patients. Often, the patient’s cause of pain or health issue is not immediately clear. Nursing professionals need to use their knowledge to determine what might be causing distress, collect vital information, and make quick decisions on how best to handle the situation.
How does nursing school develop critical thinking skills?
Nursing school gives students the knowledge professional nurses use to make important healthcare decisions for their patients. Students learn about diseases, anatomy, and physiology, and how to improve the patient’s overall well-being. Learners also participate in supervised clinical experiences, where they practice using their critical thinking skills to make decisions in professional settings.
Do only nurse managers use critical thinking?
Nurse managers certainly use critical thinking skills in their daily duties. But when working in a health setting, anyone giving care to patients uses their critical thinking skills. Everyone — including licensed practical nurses, registered nurses, and advanced nurse practitioners —needs to flex their critical thinking skills to make potentially life-saving decisions.
Meet Our Contributors

Crystal Slaughter, DNP, APRN, ACNS-BC, CNE
Crystal Slaughter is a core faculty member in Walden University’s RN-to-BSN program. She has worked as an advanced practice registered nurse with an intensivist/pulmonary service to provide care to hospitalized ICU patients and in inpatient palliative care. Slaughter’s clinical interests lie in nursing education and evidence-based practice initiatives to promote improving patient care.

Jenna Liphart Rhoads, Ph.D., RN
Jenna Liphart Rhoads is a nurse educator and freelance author and editor. She earned a BSN from Saint Francis Medical Center College of Nursing and an MS in nursing education from Northern Illinois University. Rhoads earned a Ph.D. in education with a concentration in nursing education from Capella University where she researched the moderation effects of emotional intelligence on the relationship of stress and GPA in military veteran nursing students. Her clinical background includes surgical-trauma adult critical care, interventional radiology procedures, and conscious sedation in adult and pediatric populations.

Nicholas McGowan, BSN, RN, CCRN
Nicholas McGowan is a critical care nurse with 10 years of experience in cardiovascular, surgical intensive care, and neurological trauma nursing. McGowan also has a background in education, leadership, and public speaking. He is an online learner who builds on his foundation of critical care nursing, which he uses directly at the bedside where he still practices. In addition, McGowan hosts an online course at Critical Care Academy where he helps nurses achieve critical care (CCRN) certification.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Med Sci Monit
- v.17(1); 2011

Evidence and its uses in health care and research: The role of critical thinking
Milos jenicek.
1 Department of Clinical Epidemiology & Biostatistics, Michael G. de Groote School of Medicine, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
Pat Croskerry
2 Department of Emergency Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada
David L. Hitchcock
3 David L. Hitchcock, Department of Philosophy, Faculty of Humanities, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
Obtaining and critically appraising evidence is clearly not enough to make better decisions in clinical care. The evidence should be linked to the clinician’s expertise, the patient’s individual circumstances (including values and preferences), and clinical context and settings. We propose critical thinking and decision-making as the tools for making that link.
Critical thinking is also called for in medical research and medical writing, especially where pre-canned methodologies are not enough. It is also involved in our exchanges of ideas at floor rounds, grand rounds and case discussions; our communications with patients and lay stakeholders in health care; and our writing of research papers, grant applications and grant reviews.
Critical thinking is a learned process which benefits from teaching and guided practice like any discipline in health sciences. Training in critical thinking should be a part or a pre-requisite of the medical curriculum.
Sackett et al. originally defined evidence based medicine (EBM) as ‘… the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients’, and its integration with individual clinical expertise [ 1 ].’ In the nearly two decades that have intervened, there has been significant uptake of the idea that clinical care should be based upon sound, systematically researched evidence. There has been less emphasis on how clinical expertise itself might be improved, perhaps because the concept is more amorphous and difficult to define.
Clinical expertise is an amalgam of several things: there must be a solid knowledge base, some considerable clinical experience, and an ability to think, reason, and decide in a competent and well-calibrated fashion. Our focus here is on this last component: the faculties of thinking, reasoning and decision making. Clinicians must be able to integrate the best available critically appraised evidence with insights into their patients, the clinical context, and themselves [ 2 ]. To accomplish this integration, physicians need to develop their critical thinking skills. Yet historically this need has not received explicit attention in medical training. We believe that it should.
As an illustration of the use of critical thinking in clinical care, consider the following clinical scenario from emergency medicine : A 52-year-old male presents to the emergency department of a community centre with a complaint of constipation and is triaged with a low level acuity score to a ‘minors’ area. The department is extremely busy and several hours elapse before he is seen by the emergency physician. His principal complaint is constipation; he hasn’t had a bowel movement for 4 days. His abdomen is soft and non-tender. A large amount of firm stool is evident on rectal examination. He recalls a minor back strain a few days earlier. The physician orders a soapsuds enema and continues seeing other patients. After about 30 minutes he finds the nurse who administered the enema; she reports that it was ineffective. He orders a fleet enema which again proves ineffective. The nurse expresses her opinion that the patient is taking up too much time and suggests he be given an oral laxative and another fleet enema to take home with him. She is clearly unwilling to continue investing her effort in a patient with a trivial complaint. Nevertheless, the physician decides to administer a third enema himself. The third enema is only marginally effective and he then decides to disimpact the patient. The physician notes poor rectal tone and enquires further about the patient’s urination. He says he has been unable to urinate that day. On catheterisation he is found to have 1200cc. Neurological findings are equivocal: reflexes are present in both legs and there is some subjective diminished sensation.
A diagnosis of cauda equina syndrome is made and the emergency physician calls the neurosurgery service at a tertiary care hospital. It is now late in the evening. The neurosurgeon is reluctant to accept the working diagnosis. He suggests that the loss of sphincter tone might be due to the disimpaction, and argues that there was no significant history of back injury or convincing neurological findings. When the ED physician persists, the neurosurgeon suggests transferring the patient to the tertiary hospital ED for further evaluation and asks for a CT investigation of the patient’s lower spine before seeing him. The CT reveals only some minor abnormalities and the patient is kept overnight. An MRI is done in the morning. It shows extensive disc herniation with compression of nerve roots. The patient subsequently undergoes prolonged back surgery.
This case had a good outcome, although things might have been dramatically different. The patient might have suffered permanent neurological injury requiring lifelong catheterisation for urination.
Our scenario illustrates some key points about clinical decision making. At the outset, the patient presents with an apparently benign condition – constipation. The impression of a benign condition is incorporated at triage and results in a low-level acuity score and prolonged wait. The patient’s nurse also incorporates this diagnosis and exerts coercive pressure on the physician to discharge the patient. The neurosurgeon is dismissive of a physician’s assessment in a community centre ED, creating considerable inertia against referral. Thus the ED physician faces a variety of obstacles to ensure optimal patient care. These have little to do with EBM. He must resist and overcome a variety of cognitive, affective and systemic biases, his own as well as others’, and various contextual constraints. He must continue to think critically and persist in a course that has become increasingly challenging.
Our scenario also illustrates some key points about critical thinking. The initial impression of a benign condition of constipation is not the only diagnosis compatible with the patient’s symptoms. A health care professional reaching a preliminary diagnosis must be aware of the danger of fixing prematurely on this diagnosis and ignoring (or failing to look for) subsequent evidence that tells against it, as the nurse in our scenario was inclined to do. Observational and textual studies both indicate that the most common source of errors in reasoning is to close prematurely on a favoured conclusion and then ignore evidence that argues against that conclusion [ 3 ]. It is also important to keep in mind that a patient’s signs or symptoms may have more than one cause. Data that may confirm one of the causes does not necessarily rule out all the others. Attentive listening to the patient and careful looking in the data-gathering stage are essential to good medical practice, as Groopman has recently pointed out [ 4 ]. From a logical point of view, the physician’s diagnostic task is to gather data that will determine which one (or ones) of the possible causes is (or are) responsible for the patient’s problem. This goal will guide the selection of data and of additional tests. ‘Parallel’ or ‘lateral’ thinking [ 5 ] will help with the differential diagnosis.
Critical Thinking
Dewey’s original conceptualization [ 6 ] of what he called “reflective thinking” has spawned in the intervening century a variety of definitions of critical thinking, most notably that of Ennis as “ reasonable reflective thinking that is focused on deciding what to believe or what to do” [ 7 ] . Scriven and Paul have elaborated this definition as “… the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skilfully conceptualizing, applying, synthesizing or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication as a guide to belief or action ” [ 8 ].
The consensus of 48 specialists in critical thinking from the fields of education, philosophy and psychology was that it should be defined as ‘ purposeful self-regulatory judgment which results in interpretation, analysis, evaluation and inference, as well as explanation of the evidential, conceptual, methodological, criteriological, or contextual considerations upon which that judgement is based ’ [ 9 ]. The list of additional definitions remains impressive [ 10 , 11 ].
Even more useful than these definitions are various lists of dispositions and skills characteristic of a “critical thinker” [ 7 , 9 , 12 ]. More useful still are criteria and standards for measuring possession of those skills and dispositions [ 13 ], criteria that have been used to develop standardized tests of critical thinking skills and dispositions [ 14 – 17 ] including some with specific reference to health sciences [ 18 ].
The elements of critical thinking subsume what has variously been described as clinical judgment [ 19 ] , logic of medicine [ 20 , 21 ] , logic in medicine [ 22 ] , philosophy of medicine [ 23 ] , causal inference [ 24 ] , medical decision making [ 25 ], clinical decision making [ 26 ], clinical decision analysis [ 27 ], and clinical reasoning [ 28 ]. An increasing number of monographs on logic and critical thinking in general have appeared [ 29 – 34 ] and their content is being adapted for medicine [ 35 – 37 ].
Everyday medical practice, whether in physicians’ offices or emergency departments or hospital wards, clearly involves “ reasonable reflective thinking that is focused on deciding what to believe (meaning the understanding of the problem) and/or what to do (i.e. deciding what to do to solve the problem)” [ 7 , 38 ]. Table 1 lists specific abilities underlying critical thinking in medical practice.
Specific abilities underlying critical thinking in medical practice.
Critical thinking is also called for in medical research and medical writing. Editors of leading medical journals have called for it. Edward Huth [ 39 , 40 ], former editor of Annals of Internal Medicine, has urged that medical articles reflect better and more organized ways of reasoning. Richard Horton [ 41 , 42 ], former editor of The Lancet , has proposed the use in medical writing of a contemporary approach to argument along the lines used by the philosopher Toulmin [ 40 , 41 ]. Subsequently, two of us have developed this approach in detail for medicine [ 43 , 44 ]. Dickinson [ 45 ] has called for an argumentative approach in medical problem solving and brought it to the attention to the world of medical informatics and beyond.
Dual Process Theory
An important component of critical thinking is being aware of one’s own thinking processes. In recent years, two general modes of thinking have been described under an approach described as dual process theory. The model is universal and has been directly applied to medicine [ 46 – 48 ] and nursing [ 49 ]. One mode is fast, reflexive, autonomous, and generally referred to as intuitive or System 1 thinking. The other is slow, deliberate, rule-based, and referred to as analytical or System 2 thinking. The mechanisms that underlie System 1 thinking are based on associative learning and innate dispositions: the latter are hard-wired, as a result of the evolutionary history of our species, to respond reflexively to certain cues in the environment. We have discrete, functionally-specialized mental programs that were selected when the brain was undergoing significant development especially spanning the last 6 million years of hominid evolution [ 50 ]. Although these programs may have served us well in our ancestral past, they may not be appropriate in some aspects of modern living. Some of this System 1 substrate also underlies various heuristics and biases in our thinking – the tendency to take mental short-cuts, or demonstrate reflexive responses in certain situations, often on the basis of past experience. Not surprisingly, most error occurs in System 1 thinking.
Contemplative , or fully reflective thinking, is System 2 thinking. It suits any practice of medicine or medical research activity where there is time to utilise the best critically appraised evidence in a step-by-step process of reasoning and argument. Contemplative, fully reflective thinking is appropriate, for example, in internal medicine, psychiatry, public health, and other specialties, in etiological research and clinical trials, and in writing up the results of such research [ 35 ].
In contrast, a shortcut or heuristic approach [ 51 ] with somehow truncated thinking is often dictated by the realities of emergency medicine, surgery, obstetrics or any situation where there is incomplete information, bounded rationality, and insufficient time to be fully reflective. The extant findings and the decision maker’s experience are all that is available. The quintessential challenge for well-calibrated decision making is to optimise performance in System 1. Hogarth [ 52 ] sees this challenge as educating our intuitive processes and has delineated a variety of strategies through which this might be accomplished.
No responsible physician would engage in reflective thinking on every occasion when a decision has to be made. Such acute emergencies as sudden complications of labour and delivery, ruptured aneurysms, multiple trauma victims and other immediately life-threatening situations generally leave no time for fully reflective thinking. A shortcut or heuristic approach is required [ 51 ], involving pattern recognition, steepest ascent reasoning, or algorithmic paths [ 21 , 53 ]. There is of course a place for reflective thinking before and after such time-constrained emergency decisions. More generally, reflective thinking is called for in any aspect of medical practice where there is time and reason for it.
The distinction should be made between the involuntary autonomous nature of System 1 thinking and a deliberate decision to use a shortcut for expediency, which is System 2 thinking. There is normally an override function of System 2 over System 1 but this may be deliberately lifted under extreme conditions.
Future Direction
Critical thinking is a learned process which benefits from teaching and guided practice like any other discipline in health sciences. It was already proposed as part of an early medical curriculum [ 54 ]. If we are to train future generations of health professionals as critical thinkers, we should do so in the spirit of critical thinking as it stands today. Clinical teachers should know how to run a Socratic discourse, and in which situations it is appropriate. They should be aware of contemporary models of argument. Clinical teachers should be trained and experienced in engaging with their interns and residents in meaningful discourse while presenting and discussing morning reports, at floor and other rounds, in morbidity and mortality conferences, or at less informal ‘hallway’, ‘elevator’ or ‘coffee-maker/drinking fountain’ teaching sites for busy clinicians. Such discourse is better than so-called “pimping”, i.e. quizzing of juniors with objectives ranging from knowledge acquisition to embarrassment and humiliation [ 37 , 55 ].
Also, somebody should point out to trainees the relevance to the health context of some basics of informal logic, critical thinking and argumentation, if those basics have been acquired as the result of studying for their first undergraduate degree.
Unquestionably, the appropriate critically appraised best evidence should be used as a foundation for reasoning and argument about how to care for patients. But, if we want to link the best available evidence to a patient’s biology, the patient’s values and preferences, the clinical or community setting, and other circumstances, we should take all these factors into account in using the best available evidence to get to the beliefs and decisions that have the best possible support.
Such a reflective integration cannot be mastered by mere exposure. A learning experience is required. Trainees in medicine need to learn how to think critically [ 56 ], just as they need to learn contemporary approaches to ‘rational’ medical decision making: how to use Bayes’ theorem in the diagnostic process, how to determine the sample size in a clinical trial, how to analyze survival curves in prognosis and outcomes studies, and how to calculate odds ratios in case control research. To understand each other, the teacher and the learner should both know the fundamentals of reasoning and argument in medicine. To achieve this understanding, we can either offer separate and distinct courses on critical thinking and decision making in medicine; or spread learning, practice and experience in critical thinking and decision making across various specialties; or do both. Only the future will show which of the alternatives is better. The integrated approach seems more promising, but harder to implement. Given the limitations on the current medical undergraduate curriculum, we might be hard-pressed to persuade a curriculum committee that precious space and time should be allocated to such concepts. The overriding rationale, however, should be that the knowledge of critical and reflective thinking is declarative knowledge (knowing how) and not simply an addition of procedural knowledge (know-how) or explicit knowledge. The old adage about it being preferable to teach someone how to fish rather than giving them fish applies. Any new additions will need to be streamlined and practical. A teaching module on critical thinking might for example include attention to how we reason and make decisions, factors that may impair decision making, the concept of critical thinking, situations where critical thinking is appropriate, some basic principles of logic and some logical fallacies. However the teaching, learning and practice of critical thinking is incorporated in the medical curriculum, it will need to include not only the contemplative, fully reflective thinking on hospital floors and in clinics but also the shortcut thinking [ 57 ] in such heuristic environments as operating theatres or emergency departments [ 46 , 48 , 58 – 60 ].
Similar education is required as a basis for framing grant applications and research reports as reasoned arguments, especially in the discussion section [ 61 , 62 ]. We may see a day when most medical journals are what Paton [ 63 ] terms “reflective journals”. If an application for a research grant, a research proposal, or a group of research findings (systematically reviewed or not) presented in a medical article are all exercises in argumentation and critical thinking, their authors, readers, and editors should find a common language for all these types of scientific and professional communication.
Almost four decades ago Feinstein [ 64 ] asked what kind of basic science clinical medicine needs. At that time, he had mostly clinical biostatistics and epidemiology in mind. Recently, Redelmeier et al. [ 65 ] proposed to add cognitive psychology as one more basic science. It is time, we think, to add critical thinking to that list.
Competing interests
None declared.
Source of support: None. Departmental support to produce the manuscript is acknowledged and appreciated
- Open access
- Published: 20 March 2023
Thinking more wisely: using the Socratic method to develop critical thinking skills amongst healthcare students
- Yueh-Ren Ho 1 , 2 ,
- Bao-Yu Chen 3 &
- Chien-Ming Li 2 , 4
BMC Medical Education volume 23 , Article number: 173 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
10k Accesses
7 Citations
7 Altmetric
Metrics details
In medicine, critical thinking is required for managing and tolerating medical uncertainty, as well as solving professional problems and treating diseases. However, the core of Confucianism, teacher-centered and exam-oriented settings in middle and high school education may pose challenges to developing critical thinking in Han Chinese or Taiwanese students. Students may be adversely affected by these pedagogies since student-centered settings were more effective in stimulating their critical and reflective thinking, as well as a sense of responsibility, in the ever-changing world. Therefore, guiding students with less stable foundations of critical thinking might require a different approach. A review article highlighted the potential utility of the Socratic method as a tool for teaching critical thinking in the healthcare field. The method involves posing a series of questions to students. More importantly, medical students and residents in clinical teaching are familiar with the method. Almost all healthcare students must complete a biochemistry laboratory course as part of their basic science training. Thus, we aimed to train students to develop critical thinking in the biochemistry laboratory course by using learning sheets and teacher guidance based on the Socratic method and questioning.
We recruited second-year students from a medical school, of whom 32 had medical science and biotechnology majors (MSB), 27 had pharmaceutical science majors (PS), and 85 were medical undergraduate (MU) students. An exercise in critical thinking was conducted during a biochemistry laboratory course, which consisted of five different biochemical experiments, along with learning sheets that contained three or four critical thinking questions. Then, the teacher evaluated the students’ ability to think critically based on nine intellectual dimensions (clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance, depth, breadth, logic, fairness, and significance) based on the universal intellectual standards developed by Prof. Linda Elder and Richard Paul. In the following analysis, regression models and multivariate analysis were used to determine how students improved over time, and trajectory analysis were carried out in order to observe the trends in students’ critical thinking skills construction.
Clarity and logic dimensions were identified as the key elements to facilitate the development of critical thinking skills through learning sheets and teacher guidance in students across all three different healthcare majors. The results showed that metacognitive monitoring via Socratic questioning learning sheets have demonstrated potential encourage students to develop critical thinking skills in all dimensions. Another unique contribution of current study was present the heterogeneous learning patterns and progress trajectories of clarity and logic dimensions within classes.
Using the Socratic learning model could effectively develop students’ critical thinking skills so they can more effectively care for their patients.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Emerging trends in information technology requires that the new generation of medical students become critical thinkers [ 1 ]. The General Medical Council (GMC) of the United Kingdom encourages teachers to facilitate the acquisition of critical thinking skills by students in the medical and health professions [ 2 ]. Decades of research have proven that critical thinkers can present dispositions like flexibility, persistence, and willingness when faced with a range of tasks; they display meta-cognitive monitoring and a willingness to self-correct to seek long-term consensus[ 3 ]. Although, critical thinking is constructed from childhood in most Western countries and are valued by higher education as a necessary skill for coping with society [ 4 ]. However, critical thinking constructing and teaching has attracted little attention in Eastern education systems until recently [ 5 , 6 ].
Aside from the development of critical thinking skills is a key component of educational systems, recent educational philosophy also emphasizes both thinking processes as well as metacognitive integration skills [ 7 ]. Metacognitive monitoring includes making ease-of-learning judgments (i.e., processing fluency and beliefs), judgments of learning, feeling-of-knowing judgments (i.e., assessing the familiarity of the cue and the question itself or the domain of the question), and having confidence in the retrieved answers [ 8 , 9 ]. It is an adaptive skill of personal insight that health-profession students need to succeed in the rapidly changing and challenging healthcare industry [ 2 , 10 ]. Despite this, higher education curriculum does not emphasize on teaching these skills [ 7 ]. Additionally, any attempts to change the standards in higher education are generally met with resistance and challenges since they are require to encourage teachers to create new curriculum and change the current teaching content by researchers in current study who have more than 40 years’ teaching experience observaions. Healthcare curriculum, in general, remains conservative; Taiwan is not an exception.
Critical thinking is a fundamental component of innovative thinking and has thus become the fundamental skill for cultivating innovative talents in Western education [ 11 ]. Western scholars have asserted that teaching critical thinking should start at an early age and that its foundations should be laid in elementary and secondary schools. There are many ways to define critical thinking. A leading educational expert, Prof. Dewey, defined critical thinking as inclusive of reflective thinking and argued that the thinking process should also be taken as one of the objectives of education [ 12 ]. There are a few general dispositions that an ideal critical thinker would present according to Prof. Ennis’ observation of the constitutive abilities, such as (1) provide a clear statement of the conclusion or question; (2) provide clear reasons and be specific about their relationships with each other; (3) try to be well informed; (4) always seek and use credible sources, observations and mention them frequently; (5) consider the entire situation; (6) be mindful of the context’s primary concern; (7) be aware of alternative options; (8) be open-minded toward other points of view and refrain from making a judgment when there are insufficient evidence and reasons; (9) be willing to change your position when sufficient evidence and reasons support it; (10) seek as much precision as the nature of the subject admits; (11) whenever possible, seek the truth, and more broadly, strive to “get it right”; and (12) utilize their critical thinking abilities and dispositions [ 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 ]. In the eyes of Profs. Dewey and Ennis, critical thinking is a process of careful thought and reflection before a decision is made [ 17 ].
Nevertheless, the measurement or evaluation of critical thinking skills and abilities does not seem easy. Based on another perspective on critical thinking, intellectual standards are evolving [ 18 ]. According to Profs. Elder and Paul, critical thinking is the ability to use the most appropriate reasoning in any situation [ 18 ]. To evaluate these abilities, they established nine dimensions of critical thinking to represent different aspects of critical thinking: clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance, depth, breadth, logic, significance, and fairness [ 18 ]. As Profs. Elder and Paul concluded, those who possess discipline and critical thinking skills would make use of intellectual standards every day; thus, people should target these standards when they ask questions during the thinking process [ 18 , 19 ]. As a result of teachers’ regular introduction of the tools of critical thinking in their classrooms, the Socratic questioning and discussions become more productive and disciplined, thereby enabling students to realize the significance of questioning during the learning process [ 20 , 21 , 22 ].
According to a review article, teaching critical thinking to healthcare students (primarily medical and pharmacy students) through Socratic methods is more effective in developing critical thinking for a number of reasons [ 23 ]. In particular, Socratic questioning provides students with the opportunity to justify their own preconceived beliefs and thoughts after a series of specific, targeted inquiries [ 24 ]. Using Socratic questioning can also assist healthcare students, interns, or residents in thinking critically by understanding the “deep structure” of the question, i.e., deconstructing the question and understanding its true meaning [ 23 ]. The effectiveness of Socratic questioning lies in ascertaining the current knowledge of the students [ 25 ] and establishing a foundation for teaching at their level [ 26 ]. The teacher can accomplish this probing by asking progressively more challenging questions until the limits of the students’ knowledge are discovered [ 25 , 27 , 28 ], as well as by allowing students to express their existing knowledge, which in turn will allow them to synthesize new knowledge [ 26 ], and the dialogue represents the Socratic method [ 29 ]. Alternatively, a critical thinker is more likely to engage in certain established metacognitive strategies under the Socratic paradigm and/or channel the intellectual dimensions of critical thinking [ 17 ].
Unfortunately, Han Chinese students have struggled with learning critical thinking, which is thought to be part of their characterological profile [ 30 ]. This struggle has been faced by students studying abroad [ 11 ] and in students enrolled in the Han Chinese education system, which mainly cultivates Confucianism [ 31 ]. There are at least two types of problems with developing critical thinking in Han Chinese or Taiwanese education. The first involves the core of Confucianism, where foreign teachers have tried to promote critical thinking in elementary and high schools but sensed ethical concerns from the students who refused to participate. This is likely because if they chose to participate, they would have felt obligated to express disagreement and negative feelings to the instructor. The Han Chinese culture values harmony and “not losing face,” emphasizing a holistic perspective and collective good. Thus, students would feel uncomfortable because disagreeing with someone’s opinion in public is consciously or often avoided [ 30 ]. Therefore, encouraging the student to participate in healthy discussions and respectfully challenge their teachers is the starting point for promoting critical thinking in students enrolled in the Han Chinese educational system.
Second, in the Western education approach, learners take an active role in and are responsible for their learning process. On the contrary, the Han Chinese and Taiwan education systems are teacher-centered and exam-oriented; students are expected to follow their teachers’ instructions and perform well in class. More importantly, the textbook or teacher-centered framework lacks half of Ennis’s twelve constitutive abilities for critical thinking [ 13 , 14 , 15 ], such as judging the credibility of a source, observing and judging observation reports, drawing explanatory conclusions (including hypotheses), making and judging value judgments, and attributing unstated assumptions. As a result, Han Chinese students may find it difficult to develop critical thinking skills and present key traits and dispositions that are indicative of an ideal critical thinker. Hence, guiding and evaluating critical thinking in students might not be implemented through the same approach in Eastern educational circumstances as in the West. By understanding the difficulties that Han Chinese students face in developing critical thinking, the current study aims to design a set of critical thinking models that are suitable for Han Chinese students as a starting point for reform teaching.
Research questions, hypotheses and objectives
Research has shown that the laboratory class is not just limited to a step-wise approach to experimentation. It also allows students to develop their critical thinking skills by repeatedly engaging a simple learning framework [ 32 ]. To explore this further, the current study’s primary purpose is to use Socratic questioning in a biochemistry laboratory course with specifically designed learning sheets and feedback from teacher to guide students to improve their critical thinking skills. The learning sheets were evaluated following the universal intellectual standards for critical thinking developed by Prof. Elder and Paul [ 19 , 33 ]. For this study, we hypothesized that students with different healthcare majors might present different improvement trajectories in their intellectual dimensions according to the years of teaching observations in the three healthcare majors. Based on the research and rationale described above, the intervention effect of Socratic questioning in a biochemistry laboratory course was hypothesized as follows (see Fig. 1 ):
Pre-intervention critical thinking abilities are different amongst students of different healthcare majors, especially in each intellectual dimension (H1a). Post-intervention critical thinking abilities would develop in students from each healthcare major after using the Socratic method (H1b).
Critical thinking abilities differs significantly between pre- and post-assessments of the intellectual dimensions of students with the three different healthcare majors (H2).
After clarifying the relation of Socratic method interventions in the class, we aim to scrutinize the trajectories of students between majors further to understand the learning style in class (Aim 1). Furthermore, we also aim to identify the key intellectual dimensions that could lead to an overall improvement in the critical thinking of students in each major (Aim 2). Additionally, we observed improvement trajectories of specific intellectual dimensions within major (Aim 3).
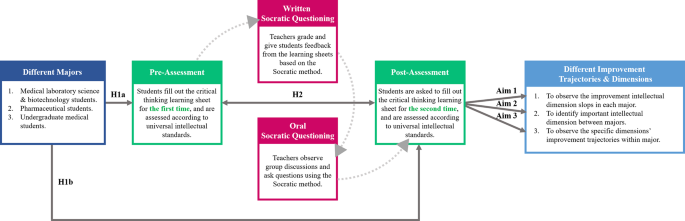
Socratic method framework and structure of the research hypotheses behind the biochemistry laboratory course
Literature review
Critical thinking engagement in the eastern and western medical education.
Over the last decade, medical education has been undergoing a variety of approaches for effectiveness teaching and transformation [ 34 ]. Many paradigms of active teaching/learning methodologies have been adopted in both Eastern and Western medical education systems, some of which are used partially (actual or conceptual similar) Socratic questioning to challenge students’ critical thinking. In this regard, the primary philosophy of case-based learning (CBL) established in the 1920s by Harvard Medical School is to guide students to apply their acquired knowledge base via critical thinking to make clinical decisions to solve the problems that they may encounter in the healthcare environment [ 35 ]. A meta-analysis study of China’s dental education reported that the CBL was a practical pedagogical method across the Chinese dental education system [ 36 ]. The results showed that the CBL method significantly increased knowledge scores, skill scores, comprehensive ability scores, and teaching satisfaction compared with the traditional lecture-based learning (LBL) mode in 2,356 dental students. Hence, there is an urgent need to change the traditional didactic lecture or teacher-centered classroom setting in which students are passive listeners instead of active participants.
Healthcare professionals are also required to solve complex problems and efficiently integrate didactic preclinical knowledge into actual clinical application in patient care [ 35 ]. On the other hand, the design thinking process may enhance both creativity and innovation so that healthcare professionals can respond to clinical problems effectively [ 37 , 38 ]. Problem-based learning (PBL) is a pedagogical approach widely accepted in medical education. It promotes active learning and results in better outcomes [ 39 , 40 , 41 ]. PBL focuses on active lifelong learning by triggering problems, directing student focus, and facilitating tutor involvement [ 39 , 42 , 43 , 44 ]. However, it is noteworthy that some hybrid PBL models have become less effective over time, as well as less aligned with the intended philosophy of student-centered learning [ 45 ]. Another alternative blended learning approach of PBL is team-based learning (TBL), which allows medical educators to provide students with pre-class work, in-class initial tests with immediate feedback, and real clinical problem-solving activities [ 46 ]. In the year-one studies of the Sydney Medical Program, a greater level of engagement in learning, a deeper understanding of concepts, and a sense of responsibility were shown among the medical students working in a TBL setting than among those in a PBL setting [ 47 , 48 ].
Medical educators face another significant challenge with the millennial generation, which has ubiquitous information technology access throughout its education. Thus, it is extremely important to improve students’ motivation to learn through hands-on instruction or teacher–student interaction and then stimulate students’ thinking and learning. In recent years, gamification has been successfully integrated into medical and scientific endeavors, enhancing motivation, participation, and time commitment across a variety of settings [ 49 , 50 , 51 ]. Another healthcare curriculum reform to stimulate active learning is flipped classroom (FC), which assigns learners didactic material, creating opportunities of longitudinal and interprofessional learning experiences for students during class participation [ 52 ] to encourage extracurricular learning, such as critical thinking. As part of the FC model, medical educators also develop formative and diagnostic assessments to identify learning gaps. According to these teaching modules, encouraging students to participate, emphasizing their learning, and observing their development trajectory are the core ideas in recent educational designs [ 53 ].
Although most of above-mentioned studies have been performed in the Eastern and Western education systems, however, without mentioning the differences between cultures and learning styles. Most importantly, the cultivation and foundations of critical thinking neglect the fact that Eastern and Western education systems emerged from very different learning and thinking patterns. Moreover, clinical reasoning and decision achievements depend on established critical thinking skills, therefore, it becomes more important to construct critical thinking early and comprehensively [ 54 ]. While Han Chinese students are not familiar with the core of critical thinking, the most effective approach to teaching critical thinking is still a highly debated topic in medical schools. Taken Taiwan medical education as an example, most clinical courses focuses on professional skills, problem solving, and disease treatment rather than construct critical mindset and metacognitive skills. Education strategies often emphasize the outcome while neglecting the process. Nevertheless, medical educators should also emphasize the process of forming students’ critical thinking when instructing and guiding them in this regard. Consequently, using metacognitive monitoring to enhance critical thinking in healthcare education would be appropriate, especially for Han Chinese systems with a Confucianist outlook. Thus, critical thinking via metacognitive monitoring is important in healthcare education, especially in Han Chinese systems with a Confucianist background.
Proficiency in the art of socratic questioning to enhance students’ critical thinking
Socratic questioning is a disciplined method of engaging in content-driven discourse that can be applied for various purposes: analyzing concepts, finding out the truth, examining assumptions, uncovering assumptions, understanding concepts, distinguishing knowledge from ignorance, and following the logical implications of thought. The scholars who established the intellectual standards of critical thinking have consistently indicated that “The key to distinguishing it from other types of questioning is that the Socratic questioning is systemic, disciplined, and deep and usually focus on foundational concepts, principles, theories, issues, or problems [ 20 , 21 , 22 ].” In short, the Socratic method is a questioning method that stimulates personal understanding. More importantly, the core principle of learning from the unknown fits best within healthcare environments.
Numerous studies have consistently urged teachers to develop Socratic dialogue in their classrooms, regardless of their learning stages and situations [ 55 , 56 , 57 ]. Using enhancement exercises in an elementary school, a study introduced a Socratic questioning strategy to provide guidance and hints to students so that they could think more deeply about an issue or problem before sharing their thoughts [ 55 ]. The lecturer of a speech course in higher education demonstrated how Socratic questioning could help students learn when confronted with a series of questions [ 56 ]. The process improves students’ ability to ask and answer questions and helps them overcome some obstacles related to their lack of self-confidence. In the book Socratic circles: Fostering critical and creative thinking in middle and high school , Dr. Matt Copeland stated that, in middle and high schools, teachers must facilitate discussions by asking questions [ 58 ]. Furthermore, this method could be applied not only to elementary school, middle school, high school but also to higher education classes [ 59 ]. During the Covid-19 pandemic, synchronous discussions in online learning demonstrated that the Socratic questioning strategy successfully improves students’ critical thinking skills [ 57 ].
The incorporation of Socratic questioning in healthcare education curriculum is under development, including for general medical education [ 60 ], medical [ 61 ], pharmacy [ 54 , 62 ], and nursing students [ 63 ]. A review article of revisiting the Socratic method as a tool for teaching critical thinking in healthcare professions revels few advantages of Socratic questioning [ 23 ]. Three type of Socratic questions were mention and could commonly used in different clinical situations [ 23 ], such as procedure question would use in those with correct answers (e.g., Which of the following medications has antithrombotic function? ); preference question can apply in those with no correct answers (e.g., What type of consultation is most suitable for this patient? ); judgment question would be the most challenge critical thinking within a Socratic paradigm by integrating different domain knowledge and skills (e.g., Does this patient require antibiotic treatment? ). It is necessary to apply and analyze information in a logical manner as well as self-regulate and use critical thinking in order to achieve the best outcome for patients. For medical doctors, pharmacists or clinical laboratory technicians to provide high quality health care across all disciplines, critical thinking is inherently required.
In medical school, the emphasis is laid on training learners in meta-capabilities, such as self-driven pattern recognition, ideally as part of an apprenticeship under the supervision of an expert diagnostician [ 61 ]. An in-depth study of the current trends in developing critical thinking amongst medical students demonstrated the use of dialogue for proper questioning and how it directs the learner’s thinking [ 64 ]. Moreover, another study confirmed that critical thinking occurs only when students are motivated and challenged to engage in higher-level thought processes [ 65 ]. In the pharmacy classroom, educators can play a significant role in influencing their students’ mindsets. Growth mindsets can be cultivated through the creation of an environment that encourages it. [ 62 ]. The Socratic questioning method can facilitate critical thinking in nursing education. One study showed that problem solving using critical thinking skills can be facilitated in both educational and practice settings by using Socratic inquiry [ 63 ].
The Socratic method has been adapted in different ways to different domains, but it has become closely associated with many areas, such as basic scientific thinking training, legal dialectical guidance, and clinical teaching. Some adaptations are helpful, some are not. The adaptations can be looked at through reasoning-focused lenses with varying degrees of magnification —a high-magnification adaptation rigorously and precisely tracks or guides the path of reasoning. Thus, how to use the Socratic method to direct students onto the path of critical thinking with appropriate guidance, but not revealing answers becomes an art that tests instructors’ teaching experience and proficiency in questioning.
Critical thinking and reflection exercises in the laboratory course
Medical schools have increasingly encouraged students to become life-long, self-directed learners because of the continual changes in the evidence-based healthcare environment. Science is often applied in everyday life, including translating knowledge from scholarly fields [ 66 ]. However, there is a vast gap between what is taught in medical schools and what is actually required in practice has increasingly widened in this information era. The majority of healthcare professionals are not considered to be real scientists. [ 2 ]. Nevertheless, they need to know how to apply scientific knowledge to their practice. Therefore, a science curriculum in medical school, such as a biochemistry laboratory course, should provide an opportunity to learn scientific methods and conceptual frameworks. It should also promote critical reasoning, providing healthcare students with problem-solving skills.
Medical educators need to accept that critical thinking is important for healthcare students and know how to teach it effectively [ 67 ]. Medical educators are now faced with a dilemma: should they develop a new course or adapt old course to develop critical thinking skills? An effective learning model should promote and stimulate students’ development of such skills [ 67 ]. One of the most common compulsory courses for healthcare students is the biochemistry laboratory course [ 68 , 69 ]. These courses are specifically designed to introduce students to prescribed experiments, requiring them to complete stepwise protocols by themselves [ 68 , 70 ]. The students are expected to understand the concepts behind the methods, procedures, and assays. However, this type of curriculum construction often fails to provide students with adequate opportunities to monitor their critical thinking and thus reduces the chances of developing problem-solving skills [ 70 ]. In order to provide students with more opportunities to think critically, previous studies have also adapted laboratory, basic science, and science fusion courses to help students develop critical thinking skills [ 67 , 68 , 71 , 72 , 73 ].
Several studies have demonstrated that students need critical thinking skills to interpret data and formulate arguments. Thus, science education, particularly in the laboratory setting, is designed to teach quantitative critical thinking (i.e. interpretation and critical evaluation of statistical reports), but the evidence has suggested that this is seldom, if ever, achieved [ 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 , 79 ]. By providing multiple opportunities for students to participate in critical thinking in the physics laboratory classes at Stanford University, scholars engaged the students to improve the experiment and modify the model repeatedly [ 32 ]. Additionally, a simple learning framework using decision-making cycles and demonstrating experts’ critical thinking significantly improved students’ critical thinking. We thus argue that students should engage in critical thinking exercises with repeated comparisons, decisions, and teacher guidance that are meant to construct their critical thinking in each of their disciplines.
Participants
This research was conducted during the 2017–2018 academic year. The participants were second-year students in the College of Medicine at the National Cheng Kung University (NCKU) of Taiwan. A total of 144 students participated in this study, of whom 32 had medical science and biotechnology majors (hereafter, MSB), 27 had pharmaceutical science majors (hereafter, PS), and 85 were medical undergraduate (hereafter, MU) students. The biochemistry laboratory course was compulsory for these three majors.
For each biochemistry laboratory class, the teacher assembled five to six groups of four to five students each. The course contained five different biochemical experiments: (1) Plasmid DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) extraction and purification; (2) restriction enzyme digestion and electrophoresis of plasmid DNA; (3) polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of plasmid DNA; (4) recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli ; and (5) quantification of recombinant protein. The experimental learning sheets included three or four critical thinking questions (Table S1 ), encouraging students to explore experimental principles and alternative explanations further. To facilitate discussion, students were organized into small groups of four to five students seated around a single table, discussing and answering the questions. At this time, the students would pen down their first answers to the critical thinking questions, and the teacher would grade them based on the universal intellectual standards (learning sheets, first evaluation).
Furthermore, according to the students’ answers, the teacher offered a response by asking more questions according to the Socratic method to encourage students to think deeper rather than provide the correct answers. At the following week’s class, the teacher returned the learning sheet and supervised the ongoing activity, clarifying any questions raised by students and encouraging them to re-discuss and re-answer the critical thinking questions according to the teacher’s suggestions. The objective was to create a highly interactive environment to engage students in learning the relevant principles of each laboratory, including troubleshooting experiments and formulating critical concepts and skills. After the discussion, the teacher reexamined the students’ responses and assessed them based on the universal intellectual standards for subsequent grading (learning sheets, second evaluation).
The biochemistry laboratory courses and the Socratic method in current study are performed and taught by a senior biochemistry teacher (PhD in Institute of Basic Medical Science, NCKU) who has 40 years teaching experience. The teacher has long focused on teaching critical thinking skills to students, and also offers four senior clinical case related courses by practicing the Socratic method, such as clinical concept, critical thinking in medicine, clinical reasoning and special topics in clinical reasoning with more than 20 years of experience. Therefore, in the course, teacher will often ask a series of questions for students to think about the relevance of biochemical science and clinical practice.
Assessment development
The research team designed the learning sheets to guide discussion on the key issues concerning five biochemical experiments. The learning sheets were assessed according to the universal intellectual standards for critical thinking [ 33 ]. However, the assessment was adapted to include nine intellectual dimensions to assess student reasoning [ 19 , 33 ]: clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance, depth, breadth, logic, fairness, and significance (Table S2 ). Each dimension was evaluated using a binary score (0 = does not present the skill; 1 = presents the skill) for each question in the learning sheets for both the first and second evaluations. The students received the teacher’s guidance following the first evaluation, providing them with the opportunity to reconsider their reasoning and revise their answers. Our goal was to improve our students’ learning by stimulating the teaching process; at the same time, we were committed to allowing students to speak freely so that we could more effectively facilitate prospective discussions. Thus, the critical thinking scoring system based on nine intellectual dimensions was only for the purpose of the research, without consequences on students’ study progress. In this regard, students were not able to know their intellectual scores. As a result, their course grades were not determined by the learning sheets; rather, they were determined by the general operation, experiment report, and the learning attitude demonstrated during the experiments.
Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics and variable tests.
We calculated the differences between the performance means for the first and second evaluations using paired t -tests. The mean differences between the students from the three majors were analyzed using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). For the improvement slope for each universal intellectual dimension, we used the second evaluation scores of each experiment as the point with which to construct a quadratic equation curve in one variable (dimension) and then access the slope to represent the students’ improvement. The higher the slope score, the greater the students’ progress on that dimension.
Multivariate analysis
We used traditional analytical methods to observe and analyze the students’ improvement in the five experiments. Data from the second evaluation scores of each experiment served as the multi-time point measurement data. The Cox regression model for multivariate analysis was used to investigate the effect of several variables upon the time during which a specified outcome happened [ 80 ]. For each dimension, the model’s outcome determined that a student’s improvement slope was defined as minor progress if it was lower than the improvement slopes of their peers in the same major overall. However, if the student’s improvement slope was higher than the overall progress intercept of their peers, then it was defined as greater progress. The Cox regression models’ outcomes for each dimension were divided into two groups: minor and more progress. For this model’s outcome, (1) we calculated all dimensions’ slopes mean from each major (MSB: 0.369; PS: 0.405; MU: 0.401); (2) then compared the mean slope of the individual students with the mean slope of major; (3) if the student’s individual improvement slope was lower than mean slope of major, then defined as minor progress; if the student’s individual improvement slope was higher than mean slope of major, then defined as greater progress. From the analysis at this point, we understood that teacher could help students from different majors develop the different dimensions of critical thinking with the use of Socratic methods and simple repeated thinking framework practice. Additionally, we wanted to represent the improvement of intellectual dimensions between the students of different majors and their heterogeneity in critical thinking.
Dimension identification and comparison
To understand which intellectual dimensions were most representative of student improvement across majors, the analysis was divided into three sections: (1) to identify the progress percentage of all nine intellectual dimensions; (2) to identify the progress percentage of statistically significant intellectual dimensions; (3) to compare the differences among all nine dimensions, the significant dimensions, and the reciprocal dimensions. This analysis offered a better understanding of what dimensions represented the overall improvement of students’ critical thinking. Our first step was to calculate the percentage of improvement for each experiment by determining the results of the first and second evaluations for each intellectual dimension. Second, we took average percentage of improvements for each dimension. Finally, we used Student’s t -test to compare the differences among the average of all nine dimensions, the significant dimensions, and the reciprocal dimensions.
Trajectory analysis
In this study, we also hypothesized that each student’s learning and progress trajectories were heterogeneous across different majors. Depending on the major, there may also be differences between students in the same class. To focus our observations on the students’ use of the clarity and logic dimensions, we used a trajectory-tracking analysis [ 81 , 82 ] and categorized the students into two groups based on the participants’ improvement levels within the same major.
Descriptive data
We recruited 144 second-year students from three majors in the College of Medicine, among which 32 were MSB, 27 were PS, and 85 were MU students. All participants’ first and second evaluations were compared in all five biochemistry experiments. The statistically significant between-group differences in the mean initial evaluation results for each dimension are presented in Table 1 .
Overall improvement from the initial to second evaluations throughout the five experiments (H1, H2, and Aim 1)
Table 1 presents the mean results of the first and second evaluations; the five experiments exhibited statistically significant differences ( p < 0.05) across all study groups and dimensions. More detailed analyses revealed significant differences in performance in the second evaluation between the groups after all five biochemistry experiments in the clarity ( p = 0.0019), depth ( p = 0.0097), breadth ( p < 0.0001), logic ( p = 0.0371), and significance ( p = 0.0037) dimensions. However, for some of the dimensions (clarity, accuracy, precision, logic, and fairness), the initial evaluation results differ significantly between the MU and the MSB students, but this was not the case for the secondary evaluation results. The MSB students exhibited the best progress (2nd mean score minus 1st mean score) in the clarity dimension across all experiments. The PS students exhibited the best performance in the logic dimension ( p < 0.05) in the second evaluation after the five experiments.
The results of the MSB students improved steeply in most dimensions in the five experiments, especially depth (slope: 0.472), logic (0.455), and clarity (0.410) (Table 2 ). Time had a stronger effect on several of the dimensions in the multivariate analysis, specifically clarity ( p = 0.0012), relevance ( p = 0.0007), and logic ( p < 0.0001). By contrast, the PS students showed a significant overall improvement in the clarity (slope: 0.212, p < 0.0001), accuracy (0.539, p = 0.0063), precision (0.381, p = 0.0085), relevance (0.216, p < 0.0001), breadth (0.426, p = 0.0045), and logic (0.515, p = 0.0027) dimensions over the observation period (Table 3 ). Finally, the MU students showed a significant overall improvement in six dimensions: clarity (slope: 0.277, p < 0.0001), accuracy (0.520, p = 0.0003), depth (0.459, p = 0.0092), breadth (0.356, p = 0.0100), logic (0.544, p = 0.0190), and significance (0.327, p = 0.0225) (Table 4 ).
Trajectory tracking of the overall, significant, and reciprocal dimensions (Aim 2 and Aim 3)
Figure 2 a illustrates the overall improvement of students across the three majors in all nine dimensions, as assessed via trajectory analysis. The trajectory-tracking algorithm revealed that the significant dimensions for each group were as follows: MSB students—clarity, relevance, and logic; PS students—clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance, breadth, and logic; and MU students—clarity, accuracy, depth, breadth, logic, and significance (Tables 2 , 3 and 4 ; Fig. 2 b). The comparison of each group’s average percentage of improvement between the nine dimensions, the significant dimensions, and the reciprocal dimensions (clarity and logic) is summarized in Fig. 2 c. Figure 2 d–i depicts the students’ improvement in clarity and logic within the different majors using group-based trajectory modeling.
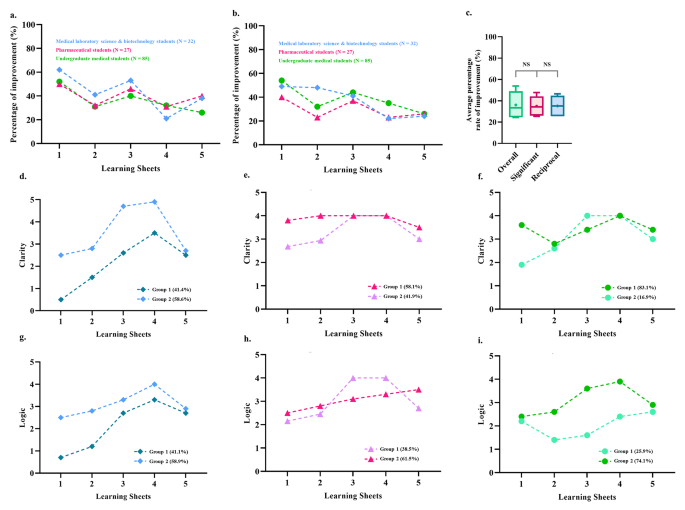
Overall improvement comparison between the students of three majors using a trajectory-tracking analysis approach . ( a ) The mean evaluation scores from the second evaluation minus those from the first evaluation for the nine dimensions were considered an improvement. They were converted to percentages to compare them to the performance in the first evaluation. ( b ) The mean evaluation scores from the second evaluation minus those from the first evaluation for the significant dimensions (within the students of each major, Tables 2 – 4 ) were considered to represent improvement and were converted to percentages to compare them to the performance in the first evaluation. ( c ) Comparison of the average percentage improvement among all nine dimensions, the significant dimensions, and the reciprocal dimensions (i.e., clarity and logic). ( d ) Trajectory analysis to assess the progress of the two subgroups of medical laboratory science and biotechnology students in the clarity dimension. ( e ) Trajectory analysis to assess the progress of the two subgroups of pharmaceutical students in the clarity dimension. ( f ) Trajectory analysis to assess the progress of the two subgroups of undergraduate medical students in the clarity dimension. ( g ) Trajectory analysis to identify the progress of the two subgroups of medical laboratory science and biotechnology students in the logic dimension. ( h ) Trajectory analysis to assess the progress of the two subgroups of pharmaceutical students in the logic dimension. ( i ) Trajectory analysis to assess the progress of the two subgroups of undergraduate medical students in the logic dimension
Empirical contributions
The Han Chinese educational system relies on the passive transmission of knowledge, as evidenced by the years of preparation by students’ through paper-based exams. By adopting this approach during teaching and learning, students do not develop a critical thinking mindset. Our experience has shown that when we encounter first-year students who have just graduated from high school, their previous education failed to develop critical thinking skills. Many foreign and Western teachers have the same experience when they encounter Asian students studying abroad for the first time. Thus, this research aims to provide clinical teachers with guidance on reducing the blind spots that students face when introduced to critical thinking. Moreover, this research aims to provide teachers with a simple teaching model and structure to guide students with less stable foundations in critical thinking. For the teaching structure and process, please refer to the procedure paragraph in the methods section and the teaching flow chart in Fig. 1 . Furthermore, the scoring system shown in the assessment development paragraph in the methods, as well as the scoring rubric is presented in Table S1 .
To our knowledge, this is the first study that uses the Socratic method and the universal intellectual standards to assess and improve critical thinking skills in biochemistry laboratory courses across different healthcare majors. We also used a novel design for teaching critical thinking, with multi-timepoint assessments and trajectory-tracking analysis to observe the students’ process and the improvement intheir critical thinking. This Socratic method, combined with critical thinking-based learning sheets, significantly improved the students’ critical thinking in all nine dimensions of the universal intellectual standards, according to the first and second evaluations conducted in each of the five sessions. Another unique contribution of this study is that it analyzed the progression results at multiple time points in the critical thinking performance of students across different majors. According to the results of comparing the average percentage improvement between all nine dimensions, the significant and reciprocal dimensions (i.e., clarity and logic) do not significantly differ from each other statistically speaking. By reducing the nine intellectual dimensions scoring system, medical educators can focus more on establishing clarity and logic skills in students. In sum, our most important finding was the identification of the clarity and logic dimensions as key elements that facilitate the development of critical thinking skills via the Socratic method in students across three different healthcare majors.
The trajectories of outcomes for students of medical science and biotechnology majors
Understanding what we learn has been identified as the starting point in the professional-development journey [ 2 ]. In principle, if thinking and decision making can be taught, educational intervention is possible. Nevertheless, for a science class like biochemistry, abductive reasoning requires a deep understanding of knowledge, and thinking must be inspired through stimulation.
In this study, the evaluation scores for MSB students did not improve significantly in almost any dimension at the beginning of the course. At first, most students felt uncomfortable with criticizing others, disagreeing with others, or challenging teacher’s knowledge and authority when they spoke their minds. Other MSB students believed that their ability to find answers and make decisions was inadequate and expected the teacher to provide the correct answers. However, preclinical medical technologists must gradually develop their critical thinking skills. Thus, the teacher provided critical thinking cues during the class and monitored the group discussions.
On the other hand, teachers must encourage these types of students, enabling them to accomplish simpler learning goals by providing them with easier-to-attempt clues. The joy of discovering answers on their own rather than the frustration of not achieving high goals should be encouraged. This coaching process improved the MSB students’ willingness to think and explore, leading to greater relevance and breadth of coverage.
The teacher used generation, conceptualization, optimization, and implementation [ 33 ] with the Socratic method to stimulate critical thinking in a four-step cycle in the five experiments. When the spontaneous discussion started in the generation phase, they tried to clarify their knowledge of the theme and identify the problem from the learning sheet. The following step was to conceptualize the problem, and the students drafted all of the possibilities and problems. Teacher frequently asked the students, ‘ What are other possible reasons? ’ Finally, the teacher provided feedback to help the MSB students reach a proper solution and implement it. The teacher would also ask the students leading questions like ‘ What relevant theories can be confirmed more precisely? ’ These guiding processes sharpened their logic and helped them better understand what they had learned. In sum, the benefits of this process included an enhanced ability to think logically, clarification of questions and knowledge gaps, and improvements in the thought process about the theme discussed.
The steady improvement of critical thinking in the students of pharmaceutical science
Currently, pharmacists are seeing their roles and responsibilities shift to becoming patient counselors and educators on the rational use of medicine. Pharmacists are trained to focus on patient-centered care and resolve current and potential drug-related problems [ 83 , 84 ]. Critical thinking, clinical reasoning, and decision-making skills are needed to solve these problems. Nowadays, pharmacists are not just responsible for carrying out doctor’s orders, while there are always alternative treatment options available for them to recommend. Teacher therefore repeatedly emphasized the link between critical thinking and pharmacist practice and encouraged students to ask questions and find out the best alternative through Socratic method in the classroom.
During class, the PS students were required to exert considerable mental effort to conduct an inquiry to solve the learning sheet questions. Instead of providing students with clues or information to help them solve the problems, the teacher guided the PS students on how to seek the information they needed for themselves. The question for the PS students was be ‘ What are the possibly executable strategies? ’ The teacher also joined the students in discussion, using the Socratic method to stimulate critical thinking and draw out ideas and underlying suppositions. In high-quality cooperative argumentative dialogue, teacher should not direct or refer learning, nor should they ask students for the correct answers as in a traditional classroom. The hints that teacher would provide were more like ‘ The narrative explanation can be more precise. ’ Thus, asking high-quality questions and providing feedback also challenges the instructors’ teaching experience.
The PS students were guided not only toward the development of critical thinking skills but also toward solving problems using evidence-based knowledge and decision-making skills. The Socratic method process meets the student where they are on the educational spectrum and encourages and helps them advance. Using this method, the PS students engaged in student-to-student interaction to build knowledge as a group and individually. The course of five experiments conducted via the learning sheets improved many aspects of the students’ critical thinking, including their clarity, relevance, breadth, and logic. In sum, the abilities that they developed in the course should help them focus more on the possible outcomes of pharmacotherapy, medication surveillance, and proper communication and therefore improve the quality of their professional future.
The advanced construction of critical thinking skills in undergraduate medical students
In medical education, “ better thinking and learning skills grounded in understanding ” are recommended for future doctors [ 2 ]. Practicing medicine requires an ability to address current and future diseases using new diagnostic and therapeutic methods [ 10 ]. Therefore, problem solving is not the only core medical skill; the ability to deal with complex, insoluble health issues is also required [ 83 ]. In this domain, critical thinking skills have proven essential in tackling difficult, complex, interdisciplinary health problems [ 10 ].
In our study, the MU students began with high-performance scores in almost all dimensions. As a result, teachers needed to create a more challenging and thought-provoking learning environment to encourage them to think more broadly and deeply. Thus, the teacher would give students advice like ‘ Searching for more relevant information can increase the breadth of knowledge ’ and ‘ If the result is true, what is the relevant theory? ’ Most MU students were faster than other majors at defining and constructing critical thinking. However, another phenomenon often observed in the classroom was that the MU students were more reluctant to express their reasoning than the students of other majors. In other words, MU students were afraid to speak openly about their reasoning and thinking, probably due to the excessive pursuit of the correct answer. In sum, the course of five experiments conducted via the learning sheets enhanced abilities of clarity, accuracy, depth, breadth, logic, and significance in MU students.
Apart from providing structure for their critical thinking, as was done with the other preclinical students, the teacher guided the MU students to use advanced critical thinking skills by regularly analyze their thinking processes, reflecting on the decision-making and thinking process [ 84 ]. Researchers have suggested that reflective practice is key to successful medical professionalism [ 85 ] and humanism [ 86 , 87 ]; but more importantly, it may help medical professionals develop better physician–patient relationships [ 88 ]. Therefore, to advance the critical thinking experience of the MU students, teacher should encourage them to gather ideas, analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information. The teacher guided them to reflect on their plan and solve the questions on the learning sheets using their thoughts and words. These reflective practices could involve various biases in the thinking process and outcome, such as the base-rate fallacy, bias blind spot, or choice-supportive bias. The Socratic debate is a common way to model a complex thinking situation and may help teachers inspire students to become critical thinkers. MU students improved their abilities in the clarity, accuracy, depth, breadth, logic, and significance dimensions in the five experiments. This kind of training in thinking should help preclinical students constantly challenge and critically appraise evidence within their context, as well as their patients’ and their own belief and value systems.
Limitations
This study provides a model for developing a specific learning environment like a biochemistry laboratory class into one that will help students develop their critical thinking skills through inquiry. Our results have shown this method to be feasible and effective. However, there were a few limitations to this study. First, although it included students from three different majors, there was no interdisciplinary collaboration that would have simulated collaborations and communication among other healthcare professionals from different fields, as occurs in clinical practice. Introducing such collaboration may have produced more exciting and comprehensive ideas for solving the problems. Training in these professions is specialized to a considerable extent, so inter-professional collaboration should improve therapeutic outcomes and optimize patient care. Second, the original scoring system was time-consuming. However, one of our study objectives was to modify and reduce the nine intellectual dimensions scoring system into the clarity and logic dimensions. Based on the analysis in the current study, the clarity and logic dimensions were sufficient for monitoring the growth of students’ critical thinking.
The present curriculum innovation aimed to teach critical thinking skills to preclinical students in various medical majors using a Socratic questioning learning model instead of a cookbook approach to learning in laboratory courses. The development of problem-solving and critical thinking skills, in addition to process-related skills, in biochemistry laboratory courses supplements traditional curriculum in a helpful way. The curriculum innovation that we described and proposed may represent an incremental step forward for the discipline; it is a novel educational approach for promoting critical thinking skills, fostering an appreciation of the affective domain, and enabling reflective practice by using small-group processing skill instruction and one-on-one Socratic questioning. The current study results are based on training critical thinking skills that should enable students to engage in the “reflection-on-action” process, which might provide an additional bridge between basic medical knowledge and clinical practice. More importantly, reconstructive mental reviews may indirectly shape preclinical students’ future actions in the challenging healthcare industry characterized by uncertainty and novel circumstances.
Data Availability
Due to conditions on participant consent and other ethical restrictions, the datasets used and analysed in the current study are not publicly available. If you have any database data requirements, please contact the corresponding author of this study.
Art-in S. Current situation and need in learning management for developing the analytical thinking of teachers in basic education of Thailand. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2015;197:1494–500.
Article Google Scholar
Maudsley G, Strivens J. Science’,‘critical thinking’and ‘competence’for tomorrow’s doctors. A review of terms and concepts. Med Educ. 2000;34:53–60.
Halpern DF. Thought and knowledge: an introduction to critical thinking. Psychology Press;2013.
Davies M, Barnett R. The Palgrave handbook of critical thinking in higher education. Springer;2015.
Sit HHW. Characteristics of Chinese students’ learning styles. Int Proc Econ Dev Res. 2013;62:36.
He Y. The roles of thinking styles in learning and achievement among Chinese university students.The University of Hong Kong Libraries.
Nordin S, Yunus K. Exploring Metacognitive Awareness among Teachers. Int J Acad Res Progress Educ Dev. 2020;9:462–72
Nelson TO, Narens L. Why investigate metacognition. Metacognition: Knowing about knowing. 1994;13:1–25.
Google Scholar
Dinsmore DL. Examining the ontological and epistemic assumptions of research on metacognition, self-regulation and self-regulated learning. Educational Psychol. 2017;37:1125–53.
Maudsley G, Strivens J. Promoting professional knowledge, experiential learning and critical thinking for medical students. Med Educ. 2000;34:535–44.
Zhong W, Cheng M. Developing critical thinking: experiences of Chinese International Students in a Post-1992 University in England. Chin Educ Soc. 2021;54:95–106.
Dewey J. How we think. In.: D C Heath; 1910.
Book Google Scholar
Ennis R. Critical thinking: a streamlined conception. Teach Philos. 1991;14:5–24.
Ennis RH. Is critical thinking culturally biased? Teach Philos. 1998;21:15–33.
Ennis R. Critical thinking: reflection and perspective part II. Inquiry: Crit Think Disciplines. 2011;26:5–19.
Ennis RH. A taxonomy of critical thinking dispositions and abilities. 1987. https://education.illinois.edu/docs/default-source/faculty-documents/robert-ennis/thenatureofcriticalthinking_51711_000.pdf
Zare P, Mukundan J. The use of socratic method as a teaching/learning tool to develop students’ critical thinking: a review of literature. Lang India. 2015;15:256–65.
Elder L, Paul R. Critical thinking: Tools for taking charge of your professional and personal life. The Foundation for Critical Thinking;2005.
Paul R, Elder L. Critical thinking: intellectual Standards essential to reasoning well within every domain of human thought, part two. J Dev Educ. 2013;37:32.
Elder L, Paul R. Critical thinking: the art of socratic questioning, part II. J Dev Educ. 2007;31:32.
Paul R, Elder L. Critical thinking: the art of socratic questioning. J Dev Educ. 2007;31:36.
Paul R, Elder L. Critical thinking: the art of socratic questioning, part III. J Dev Educ. 2008;31:34–5.
Oyler DR, Romanelli F. The Fact of Ignorance Revisiting the Socratic Method as a Tool for Teaching Critical Thinking. Am J Pharm Educ. 2014;78.
Paul R, Elder L, Bartell T. A Brief History of the Idea of Critical Thinking, The Critical Thinking Community. In.; 1997.
Tofade T, Elsner J, Haines ST. Best practice strategies for effective use of questions as a teaching tool. Am J Pharm Educ. 2013;77:1–7.
Vygotsky L. Zone of proximal development. Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes 1987;5291:157.
Rud AG Jr. The Use and Abuse of Socrates in Present Day Teaching;1990.
Oh RC. The socratic method in medicine-the labor of delivering medical truths. For the Office-based Teacher of Family Medicine. 2005;37:537–9.
Stoddard HA, O’Dell DV. Would Socrates have actually used the “Socratic Method” for clinical teaching? J Gen Intern Med. 2016;31:1092–6.
Ku KY, Ho IT. Dispositional factors predicting chinese students’ critical thinking performance. Pers Indiv Differ. 2010;48:54–8.
Liu OL, Shaw A, Gu L, Li G, Hu S, Yu N, Ma L, Xu C, Guo F, Su Q. Assessing college critical thinking: preliminary results from the chinese HEIghten ® critical thinking assessment. High Educ Res Dev. 2018;37:999–1014.
Holmes NG, Wieman CE, Bonn D. Teaching critical thinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2015, 112(36):11199–11204.
Elder L, Paul R. The aspiring thinker’s guide to critical thinking. Rowman & Littlefield; 2019.
Cooke M, Irby DM, Sullivan W, Ludmerer KM. American Medical Education 100 years after the Flexner Report. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1339–44.
Behar-Horenstein LS, Catalanotto FA, Nascimento MM. Anticipated and actual implementation of case-based learning by Dental Faculty Members during and after training. J Dent Educ. 2015;79:1049–60.
Dong H, Guo C, Zhou L, Zhao J, Wu X, Zhang X, Zhang X. Effectiveness of case-based learning in chinese dental education: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e048497–7.
Sandars J, Goh P-S. Design thinking in Medical Education: the key features and practical application. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2020;7:2382120520926518–8.
Khan S, Vandermorris A, Shepherd J, Begun JW, Lanham HJ, Uhl-Bien M, Berta W. Embracing uncertainty, managing complexity: applying complexity thinking principles to transformation efforts in healthcare systems. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18:192–2.
Preeti B, Ashish A, Shriram G. Problem based learning (PBL)-an effective approach to improve learning outcomes in medical teaching. J Clin Diagn research: JCDR. 2013;7:2896–7.
Ibrahim ME, Al-Shahrani AM, Abdalla ME, Abubaker IM, Mohamed ME. The effectiveness of problem-based learning in Acquisition of Knowledge, soft skills during basic and preclinical sciences: medical students’ points of view. Acta Informatica Medica. 2018;26:119–24.
Servant-Miklos VF. Problem solving skills versus knowledge acquisition: the historical dispute that split problem-based learning into two camps. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2019;24:619–35.
Bjork RA, Dunlosky J, Kornell N. Self-regulated learning: beliefs, techniques, and illusions. Ann Rev Psychol. 2013;64:417–44.
Colliver JA. Effectiveness of problem-based learning curricula: research and theory. Acad Med. 2000;75:259–66.
Bate E, Hommes J, Duvivier R, Taylor DC. Problem-based learning (PBL): Getting the most out of your students–Their roles and responsibilities: AMEE Guide No. 84. Medical teacher 2013.
Lim WK. Dysfunctional problem-based learning curricula: resolving the problem. BMC Med Educ. 2012;12:89–9.
Burgess AW, McGregor DM. Use of established guidelines when reporting on Interprofessional Team-Based learning in Health Professions Student Education: a systematic review. Acad Med. 2021;97:143–51.
Burgess A, Bleasel J, Haq I, Roberts C, Garsia R, Robertson T, Mellis C. Team-based learning (TBL) in the medical curriculum: better than PBL? BMC Med Educ. 2017;17:243.
Burgess A, Ayton T, Mellis C. Implementation of team-based learning in year 1 of a PBL based medical program: a pilot study. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:49–9.
Schrope M. Solving tough problems with games. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2013;110:7104–6.
Nessler M. Three Ways virtual Technologies are making a difference in HR. Employ Relations Today. 2014;40:47–52.
Nevin CR, Westfall AO, Rodriguez JM, Dempsey DM, Cherrington A, Roy B, Patel M, Willig JH. Gamification as a tool for enhancing graduate medical education. Postgrad Med J. 2014;90:685–93.
Technologies in Medical Education. In. The SAGE Encyclopedia of Educational Technology. edn.: SAGE Publications, Inc.; 2015.
Hurtubise L, Hall E, Sheridan L, Han H. The Flipped Classroom in Medical Education: Engaging Students to Build Competency. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2015;2:JMECD.S23895.
Persky AM, Medina MS, Castleberry AN. Developing critical thinking skills in pharmacy students. Am J Pharm Educ. 2019;83.
Chew SW, Lin I-H, Chen N-S. Using Socratic questioning strategy to enhance critical thinking skill of elementary school students. In: 2019 IEEE 19th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT): 2019 : IEEE; 2019;290–294.
Manurung YH, Siregar FS. Developing students’ critical thinking on speaking through socratic questioning method. Adv Social Sci Educ Humanit Res. 2018;263:212–6.
Wediyantoro PL, Lailiyah M, Yustisia KK. Synchronous discussion in online learning: investigating students’ critical thinking. En Jour Me. (English Journal of Merdeka): Culture Language and Teaching of English. 2020;5:196–203.
Copeland M. Socratic circles: fostering critical and creative thinking in middle and high school. Stenhouse Publishers; 2005.
Tweed RG, Lehman DR. Learning considered within a cultural context: confucian and socratic approaches. Am Psychol. 2002;57:89–99.
Wilberding E. Socratic methods in the classroom: encouraging critical thinking and problem solving through dialogue. Routledge; 2021.
Sanchez-Lara PA, Grand K, Haanpää MK, Curry CJ, Wang R, Ezgü F, Rose CM, D’Cunha Burkardt D, Conway RL, Relan A. Thinking outside “The Box”: Case‐based didactics for medical education and the instructional legacy of Dr John M. Graham, Jr. Am J Med Genet Part A. 2021;185:2636–45.
Cooley JH, Larson S. Promoting a growth mindset in pharmacy educators and students. Curr Pharm Teach Learn. 2018;10:675–9.
Makhene A. The use of the Socratic inquiry to facilitate critical thinking in nursing education. Health SA Gesondheid. 2019;24.
Harasym PH, Tsai T-C, Hemmati P. Current trends in developing medical students’ critical thinking abilities. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2008;24:341–55.
Roberts TG, Dyer JE. The relationship of self-efficacy, motivation, and critical thinking disposition to achievement and attitudes when an illustrated web lecture is used in an online learning environment. J agricultural Educ. 2005;46:12–23.
Chalmers AF. What is this thing called science? Hackett Publishing; 2013.
Zain AR. Effectiveness of guided inquiry based on blended learning in physics instruction to improve critical thinking skills of the senior high school student. In: Journal of Physics: Conference Series : 2018: IOP Publishing; 2018: 012015.
Goodey NM, Talgar CP. Guided inquiry in a biochemistry laboratory course improves experimental design ability. Chem Educ Res Pract. 2016;17:1127–44.
Talgar CP, Goodey NM. Views from academia and industry on skills needed for the modern research environment. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2015;43:324–32.
Handelsman J, Ebert-May D, Beichner R, Bruns P, Chang A, DeHaan R, Gentile J, Lauffer S, Stewart J, Tilghman SM. Education. Scientific teaching. Science. 2004;304:521-2.
Thaiposri P, Wannapiroon P. Enhancing students’ critical thinking skills through teaching and learning by inquiry-based learning activities using social network and cloud computing. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2015;174:2137–44.
Hirschberg CB. A course in critical thinking for PhD students in biomolecular sciences and biotechnology: classical experiments in biochemistry;2016.
Van Winkle LJ, Cornell S, Fjortoft N, Bjork BC, Chandar N, Green JM, La Salle S, Viselli SM, Burdick P, Lynch SM. Critical thinking and reflection exercises in a biochemistry course to improve prospective health professions students’ attitudes toward physician-pharmacist collaboration. Am J Pharm Educ. 2013;77.
Kanari Z, Millar R. Reasoning from data: how students collect and interpret data in science investigations. J Res Sci Teach. 2004;41:748–69.
Kumassah E, Ampiah J, Adjei E. An investigation into senior high school (shs3) physics students understanding of data processing of length and time of scientific measurement in the Volta region of Ghana. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2014;37–61.
Kung RL, Linder C. University students’ ideas about data processing and data comparison in a physics laboratory course. Nordic Stud Sci Educ. 2006;2:40–53.
Ryder J, Leach J. Interpreting experimental data: the views of upper secondary school and university science students. Int J Sci Educ. 2000;22:1069–84.
Ryder J. Data interpretation activities and students’ views of the epistemology of science during a university earth sciences field study course. Teaching and Learning in the Science Laboratory.edn. Springer;2002. p.151–162.
Séré MG, Journeaux R, Larcher C. Learning the statistical analysis of measurement errors. Int J Sci Educ. 1993;15:427–38.
Lunn M, McNeil D. Applying Cox regression to competing risks. Biometrics. 1995;524–532.
Haviland A, Nagin DS, Rosenbaum PR. Combining propensity score matching and group-based trajectory analysis in an observational study. Psychol Methods. 2007;12:247–67.
Helland-Hansen W, Hampson G. Trajectory analysis: concepts and applications. Basin Res. 2009;21:454–83.
Barrows HS, Tamblyn RM. Problem-based learning: an approach to medical education. Volume 1. Springer;1980.
Jensen G, Denton B. Teaching physical therapy students to reflect: a suggestion for clinical education. J Phys Therapy Educ. 1991;5:33–8.
Stern DT, Papadakis M. The developing physician—becoming a professional. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1794–9.
Gracey CF, Haidet P, Branch WT, Weissmann P, Kern DE, Mitchell G, Frankel R, Inui T. Precepting humanism: strategies for fostering the human dimensions of care in ambulatory settings. Acad Med. 2005;80:21–8.
Branch WT Jr, Kern D, Haidet P, Weissmann P, Gracey CF, Mitchell G, Inui T. Teaching the human dimensions of care in clinical settings. JAMA. 2001;286:1067–74.
Wald HS, Davis SW, Reis SP, Monroe AD, Borkan JM. Reflecting on reflections: enhancement of medical education curriculum with structured field notes and guided feedback. Acad Med. 2009;84:830–7.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Chi-Her Lin, MD for their encouragement and support in the writing of this manuscript, and Prof. Woei-Jer Chuang, Hung-Chi Cheng, Chang-Shi Chen, Po-Hsin J. Huang, Chien-hung Yu, and Wen-Tsan Chang for their help with the experimental design. Special thanks to Tanvi Gupta for her help with the improving reading fluency.
This work was supported by the Teaching Practice Research Program, Ministry of Education, Taiwan (Grant No: PMN1110350, PMN1100853, PMN1090364, PMN108075, PMN107018).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, College of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University, University Road No.1, East District 701, Tainan City, Taiwan (R.O.C.)
Yueh-Ren Ho
School of Medicine, College of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University, University Road No.1, East District 701, Tainan City, Taiwan (R.O.C.)
Yueh-Ren Ho & Chien-Ming Li
Institute of Clinical Medicine, College of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University, University Road No.1, East District 701, Tainan City, Taiwan (R.O.C.)
Bao-Yu Chen
Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Chi Mei Medical Center, Zhonghua Raod No.901, Yongkang District 710, Tainan City, Taiwan (R.O.C.)
Chien-Ming Li
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Yueh-Ren Ho: substantially contributed to the conception, data curation, interpretation, drafting and critical revision of the paper. She has given final approval to the manuscript and agrees to be accountable for the work. Bao-Yu Chen: substantially contributed to the conception, formal analysis, methodology, visualization, and writing and editing the manuscript. Chien-Ming Li: substantially contributed to the conception, data curation, review and editing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yueh-Ren Ho .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Students participating in this course will be informed before the class begins that their results will be used for educational academic research, and their written informed consent were obtained. The methodology of the study including the content analysis of literature on data curation activities were approved and funded by Teaching Practice Research Program, Ministry of Education, Taiwan. Throughout the study, all methods followed the approved methodology and adhered to the relevant guidelines and regulations. According to Human Subjects Research Act, Chap. 2, article 5: The Ministry of Education review current study nature and announced the principal investigator shall not submit the research protocol for review and approval by the Institutional Review Board. Please refer to the source of law in the website of Laws & Regulations Database of The Republic of China (Taiwan) ( https://law.moj.gov.tw/ENG/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?pcode=L0020176 ).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors have declared that there are no conflicts of interest in relation to the subject of this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Ho, YR., Chen, BY. & Li, CM. Thinking more wisely: using the Socratic method to develop critical thinking skills amongst healthcare students. BMC Med Educ 23 , 173 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-023-04134-2
Download citation
Received : 20 September 2022
Accepted : 02 March 2023
Published : 20 March 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-023-04134-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Biochemistry experiment
- Critical thinking
- Socratic method
- Medical education
- Metacognition
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Palgrave Encyclopedia of the Health Humanities pp 1–7 Cite as
Reflective Practice in Medical Education
- Rachel Conrad Bracken 3
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 23 November 2021
95 Accesses
Critical reflection ; Reflection ; Reflective writing
“Practice” refers both to the repeated exercise of a skill or activity in order to achieve proficiency and the application of a method, skill, or belief. Accordingly, “reflective practice” refers to the ways in which reflection, as a skill and a habit of mind, is first acquired and then utilized by professionals. Within the fields of medicine and medical education, reflective practice encompasses both a praxis – to do the work of healing patients guided by ongoing reflective thought – and the curricular interventions through which medical trainees hone their reflective capacity. As it pertains to reflective practice, “reflection” is “the process of analyzing, questioning, and reframing an experience in order to make an assessment of it for the purposes of learning (reflective learning) and/or to improve practice (reflective practice)” (Aronson, 2011 : 200–201). The capacity for reflection as “an epistemology of...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Aronson, L. (2011). Twelve tips for teaching reflection at all levels of medical education. Medical Teacher, 33 (3), 200–205. https://doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2010.507714
Article Google Scholar
Belling, C. (2010). Sharper instruments: On defending the humanities in undergraduate medical education. Academic Medicine, 85 (6), 938–940.
Bolton, G. (1999). Stories at work: Reflective writing for practitioners. Lancet, 354 , 243–245.
Charon, R. (2006). Narrative medicine: Honoring the stories of illness . Oxford University Press.
Google Scholar
Charon, R., & Hermann, N. (2012). A sense of story, or why teach reflective writing? Academic Medicine, 87 (1), 5–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACM.0b013e31823a59c7
Clandinin, D. J., & Cave, M. T. (2008). Creating pedagogical spaces for developing doctor professional identity. Medical Education, 42 , 765–770. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2923.2008.03098.x
Clará, M. (2015). What is reflection? Looking for clarity in an ambiguous notion. Journal of Teacher Education, 66 (3), 261–271.
DasGupta, S. & Charon, R. (2004). Personal illness narratives: Using reflective writing to teach empathy. Academic Medicine, 79 (4), 351–356.
de la Croix, A., & Veen, M. (2018). The reflective zombie: Problematizing the conceptual framework of reflection in medical education. Perspectives on Medical Education, 7 (6), 394–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40037-018-0479-9
Engel, J. D., Zarconi, J., Pethtel, L. L., & Missimi, S. A. (2008). Narrative in health care: Healing patients, practitioners, profession, and community . Radcliffe Publishing Ltd.
Fragkos, K. C. (2016). Reflective practice in healthcare education: An umbrella review. Education Sciences, 6 (27). https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci6030027
Hafferty, F. W. (1998). Beyond curriculum reform: Confronting medicine’s hidden curriculum. Academic Medicine, 73 (4), 403–407. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001888-199804000-00013
Jennings, M. L. (2009). Medical student burnout: Interdisciplinary exploration and analysis. Journal of Medical Humanities, 30 , 253–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10912-009-9093-5
Kumagai, A. K., & Naidu, T. (2015). Reflection, dialogue, and the possibilities of space. Academic Medicine, 90 , 283–288.
Mann, K., Gordon, J., & MacLeod, A. (2009). Reflection and reflective practice in health professions education: A systematic review. Advances in Health Sciences Education, 14 , 595–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-007-9090-2
Murphy, J. W., Franz, B. A., & Schlaerth, C. (2018). The role of reflection in narrative medicine. Journal of Medical Education and Curricular Development, 5 , 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1177/2382120518785301
Ng, S. L., Kinsella, E. A., Friesen, F., & Hodges, B. (2015). Reclaiming a theoretical orientation to reflection in medical education research: A critical narrative review. Medical Education, 49 , 461–475. https://doi.org/10.1111/medu.12680
Ng, S. L., Wright, S. R., & Kuper, A. (2019). The divergence and convergence of critical reflection and critical reflexivity: Implications for health professions education. Academic Medicine, 94 , 1122–1128.
Nguyen, Q. D., Fernandez, N., Karsenti, T., & Charlin, B. (2014). What is reflection? A conceptual analysis of major definitions and a proposal of a five-component model. Medical Education, 48 , 1176–1189. https://doi.org/10.1111/medu.12583
Platt, L. (2014). The ‘wicked problem’ of reflective practice: A critical literature review. Innovations in Practice, 9 (1), 44–53.
Rodgers, C. R. (2002). Defining reflection: Another look at John Dewey and reflective thinking. Teachers College Record, 104 (4), 842–866.
Sandars, J. (2009). The use of reflection in medical education: AMEE guide no. 44. Medical Teacher, 31 (8), 685–695. https://doi.org/10.1080/01421590903050374
Shapiro, J., Kasman, D., & Shafer, A. (2006). Words and wards: A model of reflective writing and its uses in medical education. Journal of Medical Humanities, 27 , 231–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10912-006-9020-y
Shemtob, L. (2016). Reflecting on reflection: A medical student’s perspective. Academic Medicine, 91 (9), 1190–1191.
Wald, H. S. (2015). Refining a definition of reflection for the being as well as doing the work of a physician. Medical Teacher, 37 , 696–699.
Wald, H. S., & Reis, S. P. (2010). Beyond the margins: Reflective writing and development of reflective capacity in medical education. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 25 (7), 746–749.
Wald, H. S., Davis, S. W., Reis, S. P., Monroe, A. D., & Borkan, J. M. (2009). Reflecting on reflection: Enhancement of medical education curriculum with structured field notes and guided feedback. Academic Medicine, 84 (7), 830–836.
Wald, H. S., Borkan, J. M., Taylor, J. S., Anthony, D., & Reis, S. P. (2012). Fostering and evaluating reflective capacity in medical education: Developing the REFLECT rubric for assessing reflective writing. Academic Medicine, 87 (1), 41–50.
Wass, V., & Harrison, C. (2014). Empowering the learner to reflect: Do we need another approach? Medical Education, 48 (12), 1146–1147.
Wear, D., Zarconi, J., Garden, R., & Jones, T. (2012). Reflection in/and writing: Pedagogy and practice in medical education. Academic Medicine, 87 (5), 603–609. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACM.0b013e31824d22e9
Whiting, E., Wear, D., Aultman, J. M., & Zupp, L. (2012). Teaching softly in hard environments: Meanings of small-group reflective teaching to clinical faculty. Journal for Learning through the Arts, 8 (1). https://doi.org/10.21977/D9812654
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Family and Community Medicine, Northeast Ohio Medical University, Rootstown, OH, USA
Rachel Conrad Bracken
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rachel Conrad Bracken .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
School of Health Sciences, The University of Nottingham, Derby, UK
Paul Crawford
University of Global Health Equity, Kigali, Rwanda
Paul Kadetz
Section Editor information
No affiliation provided
Paul I. Kadetz
Kira Hopkins
Jamie Crawford
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Bracken, R.C. (2021). Reflective Practice in Medical Education. In: Crawford, P., Kadetz, P. (eds) Palgrave Encyclopedia of the Health Humanities. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26825-1_203-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26825-1_203-1
Received : 19 December 2020
Accepted : 10 April 2021
Published : 23 November 2021
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-26825-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-26825-1
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Literature, Cultural and Media Studies Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Humanities
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critical thinking is connected to a broader idea of what 'good thinking'—and, by extension, the 'good professional'—looks like for each educator [ 38] within a given context or community. These observations lead one to speculate about what purpose fluidity in conceptions of critical thinking might serve.
How critical thinking can help medical students? Critical thinking helps healthcare professionals in the following ways:[15-19] Avoid medical/clinical errors Identify better alternate options for diagnosis and treatment. Increases productivity Better clinical decision making Work in resource limited settings Quality thinking and quality work output
Yet, until recently, the UK regulator the General Medical Council and similar bodies in North America did not mention "critical thinking" anywhere in their standards for licensing and accreditation,1 and critical thinking is not explicitly taught or assessed in most education programmes for health professionals.2 Moreover, although more ...
This article describes three critical thinking skills essential to effective clinical care - clinical reasoning, evidence-informed decision-making, and systems thinking - and approaches to develop these skills during clinician training. ... Toward the development of the perfect medical team: critical components for adaptation. March 17 ...
Critical thinking is an essential cognitive skill for the individuals involved in various healthcare domains such as doctors, nurses, lab assistants, patients and so on, as is emphasized by the Authors. ... Medical professionals who could thinking critically in their own discipline would have difficulty thinking critically about problems in ...
In countering these shortcomings, clinicians must be able to think critically, interpret and assimilate new knowledge, deal with uncertainty and change behaviour in response to compelling new evidence. Three critical thinking skills underpin effective care: clinical reasoning, evidence-informed decision-making and systems thinking.
Critical thinking skills are also a vital resource for the medical and health professionals who deliver our healthcare. Notwithstanding significant improvements in the standard of patient care in hospitals, it remains the case that medical errors are alarmingly common, and can result in death and significant patient harm.
Higher order thinking has become one of the essential characteristic of future health care professionals and an essential attribute of medical professionalism. Hence, knowing and thinking about critical thinking and exploring the avenues for its application in medical education through appropriate means have become the need of the hour.
Critical thinking, the capacity to be deliberate about thinking, is increasingly the focus of undergraduate medical education, but is not commonly addressed in graduate medical education. ... In light of these data and the Institute of Medicine's 2015 recommendation to "enhance health care professional education and training in the ...
Kahlke, R & Eva, K 2018, 'Constructing Critical Thinking in Health Professional Education', Perspectives on Medical Education, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 156-165, viewed 7 December 2018, ... Anne is a freelance lecturer and medical writer at Mind Body Ink. She is a former midwife and nurse teacher with over 25 years' experience working in the fields ...
Critical Thinking. Nursing education ... Critical reflection is a crucial professional skill, but it is not the only reasoning skill or logic clinicians require. The ability to think critically uses reflection, ... While some aspects of medical and nursing practice fall into the category of techne, much of nursing and medical practice falls ...
Team-based learning (TBL) is useful in encouraging individual self-assessment and peer-peer instruction, while al-so providing an opportunity for the development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills. After the Individual Readiness Assurance Test (iRAT) exam, students work to-gether to answer the Group Readiness Assurance Test (gRAT).
Medistudents team. August 18, 2021. Critical thinking is an essential cognitive skill for every individual but is a crucial component for healthcare professionals such as doctors, nurses and dentists. It is a skill that should be developed and trained, not just during your career as a doctor, but before that when you are still a medical student.
Furthermore, fostering critical thinking in medical education empowers healthcare professionals to make informed decisions, even in ambiguous or uncertain circumstances. Cross-sector collaboration between healthcare and education sectors can nurture and enhance the development of these essential skills, creating better-prepared providers ( The ...
Purpose: Critical thinking is central to the function of health care professionals.However, this topic is not explicitly taught or assessed within current programs, yet the need is greater than ever, in an era of information explosion, spiraling health care costs, and increased understanding about metacognition.
For example, a nurse might be tasked with changing a wound dressing, delivering medications, and monitoring vital signs during a shift. However, it requires critical thinking skills to understand how a difference in the wound may affect blood pressure and temperature and when those changes may require immediate medical intervention.
Teaching and Assessing Critical Thinking and Clinical Reasoning Skills in Medical Education. of teaching which dates back to 470-399 BC dur ing Socrates era (Paul, Elder, & Bartell, 1997). This ...
Critical thinking is one of the most important skills required to be possessed by any medical student for providing quality health care. With the introduction of a new competency-based medical education curriculum that focuses on the desired and observable ability of Indian medical graduates in real-life situations, inculcating critical thinking skills in the medical graduate is the need of ...
Approximately 100 years later, the Liaison Committee on Medical Education ... helping enable students develop critical thinking skills; and encouraging students to develop "expertise" in their chosen discipline. ... Kahlke R, Kevin E. Constructing critical thinking in health professional education. Perspect Med Educ. 2018;7(3):156-65.
Introduction Calls for enabling 'critical thinking' are ubiquitous in health professional education. However, there is little agreement in the literature or in practice as to what this term means and efforts to generate a universal definition have found limited traction. Moreover, the variability observed might suggest that multiplicity has value that the quest for universal definitions ...
Critical thinking is also called for in medical research and medical writing. Editors of leading medical journals have called for it. Edward Huth [39,40], former editor of Annals of Internal Medicine, has urged that medical articles reflect better and more organized ways of reasoning.Richard Horton [41,42], former editor of The Lancet, has proposed the use in medical writing of a contemporary ...
In medicine, critical thinking is required for managing and tolerating medical uncertainty, as well as solving professional problems and treating diseases. However, the core of Confucianism, teacher-centered and exam-oriented settings in middle and high school education may pose challenges to developing critical thinking in Han Chinese or Taiwanese students.
The capacity for reflection as "an epistemology of practice" and "a critical approach to inquiry" (Ng et al., 2015: 263) is considered essential for the provision of competent and compassionate healthcare. Integrating reflective practice into medical education is, therefore, critical to medical trainees' personal and professional ...