Business Plan Example and Template
Learn how to create a business plan

What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing .

A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all the important business plan elements. Typically, it should present whatever information an investor or financial institution expects to see before providing financing to a business.
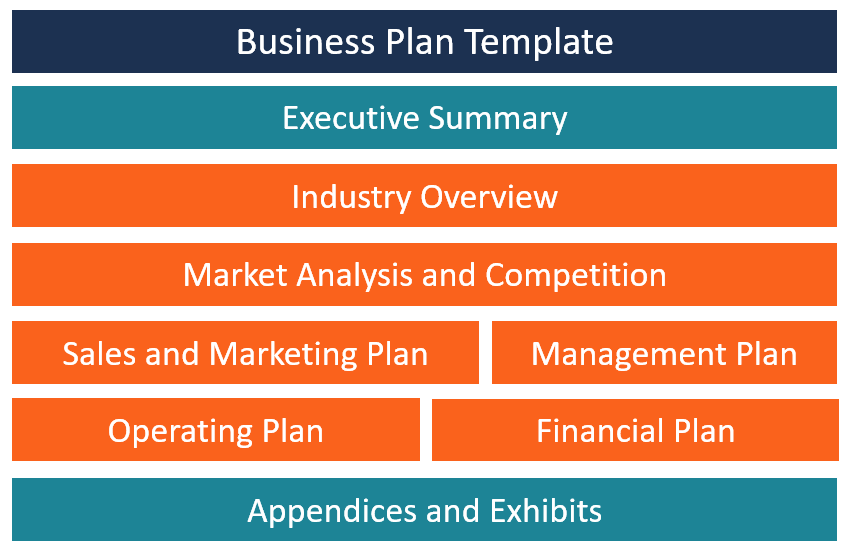
Contents of a Business Plan
A business plan should be structured in a way that it contains all the important information that investors are looking for. Here are the main sections of a business plan:
1. Title Page
The title page captures the legal information of the business, which includes the registered business name, physical address, phone number, email address, date, and the company logo.
2. Executive Summary
The executive summary is the most important section because it is the first section that investors and bankers see when they open the business plan. It provides a summary of the entire business plan. It should be written last to ensure that you don’t leave any details out. It must be short and to the point, and it should capture the reader’s attention. The executive summary should not exceed two pages.
3. Industry Overview
The industry overview section provides information about the specific industry that the business operates in. Some of the information provided in this section includes major competitors, industry trends, and estimated revenues. It also shows the company’s position in the industry and how it will compete in the market against other major players.
4. Market Analysis and Competition
The market analysis section details the target market for the company’s product offerings. This section confirms that the company understands the market and that it has already analyzed the existing market to determine that there is adequate demand to support its proposed business model.
Market analysis includes information about the target market’s demographics , geographical location, consumer behavior, and market needs. The company can present numbers and sources to give an overview of the target market size.
A business can choose to consolidate the market analysis and competition analysis into one section or present them as two separate sections.
5. Sales and Marketing Plan
The sales and marketing plan details how the company plans to sell its products to the target market. It attempts to present the business’s unique selling proposition and the channels it will use to sell its goods and services. It details the company’s advertising and promotion activities, pricing strategy, sales and distribution methods, and after-sales support.
6. Management Plan
The management plan provides an outline of the company’s legal structure, its management team, and internal and external human resource requirements. It should list the number of employees that will be needed and the remuneration to be paid to each of the employees.
Any external professionals, such as lawyers, valuers, architects, and consultants, that the company will need should also be included. If the company intends to use the business plan to source funding from investors, it should list the members of the executive team, as well as the members of the advisory board.
7. Operating Plan
The operating plan provides an overview of the company’s physical requirements, such as office space, machinery, labor, supplies, and inventory . For a business that requires custom warehouses and specialized equipment, the operating plan will be more detailed, as compared to, say, a home-based consulting business. If the business plan is for a manufacturing company, it will include information on raw material requirements and the supply chain.
8. Financial Plan
The financial plan is an important section that will often determine whether the business will obtain required financing from financial institutions, investors, or venture capitalists. It should demonstrate that the proposed business is viable and will return enough revenues to be able to meet its financial obligations. Some of the information contained in the financial plan includes a projected income statement , balance sheet, and cash flow.
9. Appendices and Exhibits
The appendices and exhibits part is the last section of a business plan. It includes any additional information that banks and investors may be interested in or that adds credibility to the business. Some of the information that may be included in the appendices section includes office/building plans, detailed market research , products/services offering information, marketing brochures, and credit histories of the promoters.
Business Plan Template
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan:
Section 1: Executive Summary
- Present the company’s mission.
- Describe the company’s product and/or service offerings.
- Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
- Summarize the industry competition and how the company will capture a share of the available market.
- Give a summary of the operational plan, such as inventory, office and labor, and equipment requirements.
Section 2: Industry Overview
- Describe the company’s position in the industry.
- Describe the existing competition and the major players in the industry.
- Provide information about the industry that the business will operate in, estimated revenues, industry trends, government influences, as well as the demographics of the target market.
Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
- Define your target market, their needs, and their geographical location.
- Describe the size of the market, the units of the company’s products that potential customers may buy, and the market changes that may occur due to overall economic changes.
- Give an overview of the estimated sales volume vis-à-vis what competitors sell.
- Give a plan on how the company plans to combat the existing competition to gain and retain market share.
Section 4: Sales and Marketing Plan
- Describe the products that the company will offer for sale and its unique selling proposition.
- List the different advertising platforms that the business will use to get its message to customers.
- Describe how the business plans to price its products in a way that allows it to make a profit.
- Give details on how the company’s products will be distributed to the target market and the shipping method.
Section 5: Management Plan
- Describe the organizational structure of the company.
- List the owners of the company and their ownership percentages.
- List the key executives, their roles, and remuneration.
- List any internal and external professionals that the company plans to hire, and how they will be compensated.
- Include a list of the members of the advisory board, if available.
Section 6: Operating Plan
- Describe the location of the business, including office and warehouse requirements.
- Describe the labor requirement of the company. Outline the number of staff that the company needs, their roles, skills training needed, and employee tenures (full-time or part-time).
- Describe the manufacturing process, and the time it will take to produce one unit of a product.
- Describe the equipment and machinery requirements, and if the company will lease or purchase equipment and machinery, and the related costs that the company estimates it will incur.
- Provide a list of raw material requirements, how they will be sourced, and the main suppliers that will supply the required inputs.
Section 7: Financial Plan
- Describe the financial projections of the company, by including the projected income statement, projected cash flow statement, and the balance sheet projection.
Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
- Quotes of building and machinery leases
- Proposed office and warehouse plan
- Market research and a summary of the target market
- Credit information of the owners
- List of product and/or services
Related Readings
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Business Plans. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following CFI resources will be helpful:
- Corporate Structure
- Three Financial Statements
- Business Model Canvas Examples
- See all management & strategy resources
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
How To Write A Business Plan (2024 Guide)

Updated: Apr 17, 2024, 11:59am

Table of Contents
Brainstorm an executive summary, create a company description, brainstorm your business goals, describe your services or products, conduct market research, create financial plans, bottom line, frequently asked questions.
Every business starts with a vision, which is distilled and communicated through a business plan. In addition to your high-level hopes and dreams, a strong business plan outlines short-term and long-term goals, budget and whatever else you might need to get started. In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to write a business plan that you can stick to and help guide your operations as you get started.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
Drafting the Summary
An executive summary is an extremely important first step in your business. You have to be able to put the basic facts of your business in an elevator pitch-style sentence to grab investors’ attention and keep their interest. This should communicate your business’s name, what the products or services you’re selling are and what marketplace you’re entering.
Ask for Help
When drafting the executive summary, you should have a few different options. Enlist a few thought partners to review your executive summary possibilities to determine which one is best.
After you have the executive summary in place, you can work on the company description, which contains more specific information. In the description, you’ll need to include your business’s registered name , your business address and any key employees involved in the business.
The business description should also include the structure of your business, such as sole proprietorship , limited liability company (LLC) , partnership or corporation. This is the time to specify how much of an ownership stake everyone has in the company. Finally, include a section that outlines the history of the company and how it has evolved over time.
Wherever you are on the business journey, you return to your goals and assess where you are in meeting your in-progress targets and setting new goals to work toward.
Numbers-based Goals
Goals can cover a variety of sections of your business. Financial and profit goals are a given for when you’re establishing your business, but there are other goals to take into account as well with regard to brand awareness and growth. For example, you might want to hit a certain number of followers across social channels or raise your engagement rates.
Another goal could be to attract new investors or find grants if you’re a nonprofit business. If you’re looking to grow, you’ll want to set revenue targets to make that happen as well.
Intangible Goals
Goals unrelated to traceable numbers are important as well. These can include seeing your business’s advertisement reach the general public or receiving a terrific client review. These goals are important for the direction you take your business and the direction you want it to go in the future.
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you’re offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are providing something necessary or entirely new. If you have any patents or trademarks, this is where you can include those too.
If you have any visual aids, they should be included here as well. This would also be a good place to include pricing strategy and explain your materials.
This is the part of the business plan where you can explain your expertise and different approach in greater depth. Show how what you’re offering is vital to the market and fills an important gap.
You can also situate your business in your industry and compare it to other ones and how you have a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Other than financial goals, you want to have a budget and set your planned weekly, monthly and annual spending. There are several different costs to consider, such as operational costs.
Business Operations Costs
Rent for your business is the first big cost to factor into your budget. If your business is remote, the cost that replaces rent will be the software that maintains your virtual operations.
Marketing and sales costs should be next on your list. Devoting money to making sure people know about your business is as important as making sure it functions.
Other Costs
Although you can’t anticipate disasters, there are likely to be unanticipated costs that come up at some point in your business’s existence. It’s important to factor these possible costs into your financial plans so you’re not caught totally unaware.
Business plans are important for businesses of all sizes so that you can define where your business is and where you want it to go. Growing your business requires a vision, and giving yourself a roadmap in the form of a business plan will set you up for success.
How do I write a simple business plan?
When you’re working on a business plan, make sure you have as much information as possible so that you can simplify it to the most relevant information. A simple business plan still needs all of the parts included in this article, but you can be very clear and direct.
What are some common mistakes in a business plan?
The most common mistakes in a business plan are common writing issues like grammar errors or misspellings. It’s important to be clear in your sentence structure and proofread your business plan before sending it to any investors or partners.
What basic items should be included in a business plan?
When writing out a business plan, you want to make sure that you cover everything related to your concept for the business, an analysis of the industry―including potential customers and an overview of the market for your goods or services―how you plan to execute your vision for the business, how you plan to grow the business if it becomes successful and all financial data around the business, including current cash on hand, potential investors and budget plans for the next few years.
- Best VPN Services
- Best Project Management Software
- Best Web Hosting Services
- Best Antivirus Software
- Best LLC Services
- Best POS Systems
- Best Business VOIP Services
- Best Credit Card Processing Companies
- Best CRM Software for Small Business
- Best Fleet Management Software
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Best Business Loans
- Best Business Software
- Best Business Apps
- Best Free Software For Business
- How to Start a Business
- How To Make A Small Business Website
- How To Trademark A Name
- What Is An LLC?
- How To Set Up An LLC In 7 Steps
- What is Project Management?

How To Start A Print On Demand Business In 2024
HR For Small Businesses: The Ultimate Guide
How One Company Is Using AI To Transform Manufacturing
Not-For-Profit Vs. Nonprofit: What’s The Difference?
How To Develop an SEO Strategy in 2024
How To Make Money On Social Media in 2024
Julia is a writer in New York and started covering tech and business during the pandemic. She also covers books and the publishing industry.
Kelly Main is a Marketing Editor and Writer specializing in digital marketing, online advertising and web design and development. Before joining the team, she was a Content Producer at Fit Small Business where she served as an editor and strategist covering small business marketing content. She is a former Google Tech Entrepreneur and she holds an MSc in International Marketing from Edinburgh Napier University. Additionally, she is a Columnist at Inc. Magazine.
Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
This guide has been designed to help you create a winning plan that stands out in the ever-evolving marketplace. U sing real-world examples and a free downloadable template, it will walk you through each step of the process.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Executive summary.
The Executive Summary serves as the gateway to your business plan, offering a snapshot of your venture’s core aspects. This section should captivate and inform, succinctly summarizing the essence of your plan.
Example: EcoTech is a technology company specializing in eco-friendly and sustainable products designed to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. Our mission is to create innovative solutions that contribute to a cleaner, greener environment.
Overview and Business Objectives
This part of the plan demonstrates to investors and stakeholders your vision for growth and the practical steps you’ll take to get there.
Company Description
Include information about the company’s founders, their expertise, and why they are suited to lead the business to success. This section should paint a vivid picture of your business, its values, and its place in the industry.
Define Your Target Market
Example: Our target market comprises environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking for innovative solutions to reduce their carbon footprint. Our ideal customers are those who prioritize sustainability and are willing to invest in eco-friendly products.
Market Analysis
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis
Competitive analysis.
In this section, you’ll analyze your competitors in-depth, examining their products, services, market positioning, and pricing strategies. Understanding your competition allows you to identify gaps in the market and tailor your offerings to outperform them.
Organization and Management Team
Example: EcoTech’s organizational structure comprises the following key roles: CEO, CTO, CFO, Sales Director, Marketing Director, and R&D Manager. Our management team has extensive experience in technology, sustainability, and business development, ensuring that we are well-equipped to execute our business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered
Marketing and sales strategy.
Describe the nature of your advertising campaigns and promotional activities, explaining how they will capture the attention of your target audience and convey the value of your products or services. Outline your sales strategy, including your sales process, team structure, and sales targets.
Logistics and Operations Plan
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
Financial Projections Plan
In the Financial Projections Plan, lay out a clear and realistic financial future for your business. This should include detailed projections for revenue, costs, and profitability over the next three to five years.
Income Statement
The income statement , also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a summary of your company’s revenues and expenses over a specified period. It helps you track your business’s financial performance and identify trends, ensuring you stay on track to achieve your financial goals.
Cash Flow Statement
| Section | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Summary | Brief overview of the business plan | Overview of EcoTech and its mission |
| Overview & Objectives | Outline of company's goals and strategies | Market leadership in sustainable technology |
| Company Description | Detailed explanation of the company and its unique selling proposition | EcoTech's history, mission, and vision |
| Target Market | Description of ideal customers and their needs | Environmentally conscious consumers and businesses |
| Market Analysis | Examination of industry trends, customer needs, and competitors | Trends in eco-friendly technology market |
| SWOT Analysis | Evaluation of Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats | Strengths and weaknesses of EcoTech |
| Competitive Analysis | In-depth analysis of competitors and their strategies | Analysis of GreenTech and EarthSolutions |
| Organization & Management | Overview of the company's structure and management team | Key roles and team members at EcoTech |
| Products & Services | Description of offerings and their unique features | Energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers |
| Marketing & Sales | Outline of marketing channels and sales strategies | Digital advertising, content marketing, influencer partnerships |
| Logistics & Operations | Details about daily operations, supply chain, inventory, and quality control | Partnerships with manufacturers, quality control |
| Financial Projections | Forecast of revenue, expenses, and profit for the next 3-5 years | Projected growth in revenue and net profit |
| Income Statement | Summary of company's revenues and expenses over a specified period | Revenue, Cost of Goods Sold, Gross Profit, Net Income |
| Cash Flow Statement | Overview of cash inflows and outflows within the business | Net Cash from Operating Activities, Investing Activities, Financing Activities |
Tips on Writing a Business Plan
3. Set realistic goals: Your business plan should outline achievable objectives that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Setting realistic goals demonstrates your understanding of the market and increases the likelihood of success.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
What is a Business Plan?
Why you should write a business plan, what are the different types of business plans.
In today’s fast-paced business world, having a well-structured roadmap is more important than ever. A traditional business plan provides a comprehensive overview of your company’s goals and strategies, helping you make informed decisions and achieve long-term success. There are various types of business plans, each designed to suit different needs and purposes. Let’s explore the main types:
| Type of Business Plan | Purpose | Key Components | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Startup Business Plan | Outlines the company's mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. | Mission Statement, Company Description, Market Analysis, Competitive Analysis, Organizational Structure, Marketing and Sales Strategy, Financial Projections. | Entrepreneurs, Investors |
| Internal Business Plan | Serves as a management tool for guiding the company's growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. | Strategies, Milestones, Deadlines, Resource Allocation. | Internal Team Members |
| Strategic Business Plan | Outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them. | SWOT Analysis, Market Research, Competitive Analysis, Long-Term Goals. | Executives, Managers, Investors |
| Feasibility Business Plan | Assesses the viability of a business idea. | Market Demand, Competition, Financial Projections, Potential Obstacles. | Entrepreneurs, Investors |
| Growth Business Plan | Focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. | Market Analysis, New Product/Service Offerings, Financial Projections. | Business Owners, Investors |
| Operational Business Plan | Outlines the company's day-to-day operations. | Processes, Procedures, Organizational Structure. | Managers, Employees |
| Lean Business Plan | A simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements. | Value Proposition, Customer Segments, Revenue Streams, Cost Structure. | Entrepreneurs, Startups |
| One-Page Business Plan | A concise summary of your company's key objectives, strategies, and milestones. | Key Objectives, Strategies, Milestones. | Entrepreneurs, Investors, Partners |
| Nonprofit Business Plan | Outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation for nonprofit organizations. | Mission Statement, Goals, Target Audience, Fundraising Strategies, Budget. | Nonprofit Leaders, Board Members, Donors |
| Franchise Business Plan | Focuses on the franchisor's requirements, as well as the franchisee's goals, strategies, and financial projections. | Franchise Agreement, Brand Standards, Marketing Efforts, Operational Procedures, Financial Projections. | Franchisors, Franchisees, Investors |
Using Business Plan Software
Enloop is a robust business plan software that automatically generates a tailored plan based on your inputs. It provides industry-specific templates, financial forecasting, and a unique performance score that updates as you make changes to your plan. Enloop also offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget.
| Software | Key Features | User Interface | Additional Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| LivePlan | Over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, progress tracking against KPIs | User-friendly, visually appealing | Allows creation of professional-looking business plans |
| Upmetrics | Customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, collaboration capabilities | Simple and intuitive | Provides a resource library for business planning |
| Bizplan | Drag-and-drop builder, modular sections, financial forecasting tools, progress tracking | Simple, visually engaging | Designed to simplify the business planning process |
| Enloop | Industry-specific templates, financial forecasting tools, automatic business plan generation, unique performance score | Robust, user-friendly | Offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget |
| Tarkenton GoSmallBiz | Guided business plan builder, customizable templates, financial projection tools | User-friendly | Offers CRM tools, legal document templates, and additional resources for small businesses |
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan, what are the 3 main purposes of a business plan, can i write a business plan by myself.
We also have examples for specific industries, including a using food truck business plan , salon business plan , farm business plan , daycare business plan , and restaurant business plan .
Is it possible to create a one-page business plan?
How long should a business plan be, what is a business plan outline, what are the 5 most common business plan mistakes, what questions should be asked in a business plan.
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
How is business planning for a nonprofit different.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)
May 24, 2021

Have you ever wondered how to write a business plan step by step? Mike Andes, told us:
This guide will help you write a business plan to impress investors.
Throughout this process, we’ll get information from Mike Andes, who started Augusta Lawn Care Services when he was 12 and turned it into a franchise with over 90 locations. He has gone on to help others learn how to write business plans and start businesses. He knows a thing or two about writing business plans!
We’ll start by discussing the definition of a business plan. Then we’ll discuss how to come up with the idea, how to do the market research, and then the important elements in the business plan format. Keep reading to start your journey!
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is simply a road map of what you are trying to achieve with your business and how you will go about achieving it. It should cover all elements of your business including:
- Finding customers
- Plans for developing a team
- Competition
- Legal structures
- Key milestones you are pursuing
If you aren’t quite ready to create a business plan, consider starting by reading our business startup guide .
Get a Business Idea
Before you can write a business plan, you have to have a business idea. You may see a problem that needs to be solved and have an idea how to solve it, or you might start by evaluating your interests and skills.
Mike told us, “The three things I suggest asking yourself when thinking about starting a business are:
- What am I good at?
- What would I enjoy doing?
- What can I get paid for?”

If all three of these questions don’t lead to at least one common answer, it will probably be a much harder road to success. Either there is not much market for it, you won’t be good at it, or you won’t enjoy doing it.
As Mike told us, “There’s enough stress starting and running a business that if you don’t like it or aren’t good at it, it’s hard to succeed.”
If you’d like to hear more about Mike’s approach to starting a business, check out our YouTube video
Conduct Market Analysis
Market analysis is focused on establishing if there is a target market for your products and services, how large the target market is, and identifying the demographics of people or businesses that would be interested in the product or service. The goal here is to establish how much money your business concept can make.
Product and Service Demand

A search engine is your best friend when trying to figure out if there is demand for your products and services. Personally, I love using presearch.org because it lets you directly search on a ton of different platforms including Google, Youtube, Twitter, and more. Check out the screenshot for the full list of search options.
With quick web searches, you can find out how many competitors you have, look through their reviews, and see if there are common complaints about the competitors. Bad reviews are a great place to find opportunities to offer better products or services.
If there are no similar products or services, you may have stumbled upon something new, or there may just be no demand for it. To find out, go talk to your most honest friend about the idea and see what they think. If they tell you it’s dumb or stare at you vacantly, there’s probably no market for it.
You can also conduct a survey through social media to get public opinion on your idea. Using Facebook Business Manager , you could get a feel for who would be interested in your product or service.
I ran a quick test of how many people between 18-65 you could reach in the U.S. during a week. It returned an estimated 700-2,000 for the total number of leads, which is enough to do a fairly accurate statistical analysis.
Identify Demographics of Target Market
Depending on what type of business you want to run, your target market will be different. The narrower the demographic, the fewer potential customers you’ll have. If you did a survey, you’ll be able to use that data to help define your target audience. Some considerations you’ll want to consider are:
- Other Interests
- Marital Status
- Do they have kids?
Once you have this information, it can help you narrow down your options for location and help define your marketing further. One resource that Mike recommended using is the Census Bureau’s Quick Facts Map . He told us,
“It helps you quickly evaluate what the best areas are for your business to be located.”
How to Write a Business Plan

Now that you’ve developed your idea a little and established there is a market for it, you can begin writing a business plan. Getting started is easier with the business plan template we created for you to download. I strongly recommend using it as it is updated to make it easier to create an action plan.
Each of the following should be a section of your business plan:
- Business Plan Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Description of Products and Services
SWOT Analysis
- Competitor Data
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Expenses Strategy
Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Channel Assessment
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organizational Strategy
- Financial Statements and/or Financial Projections
We’ll look into each of these. Don’t forget to download our free business plan template (mentioned just above) so you can follow along as we go.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page
The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions.
A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
- Professionally designed logo
- Company name
- Mission or Vision Statement
- Contact Info
Basically, think of a cover page for your business plan like a giant business card. It is meant to capture people’s attention but be quickly processed.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 2. Create a Table of Contents
Most people are busy enough that they don’t have a lot of time. Providing a table of contents makes it easy for them to find the pages of your plan that are meaningful to them.
A table of contents will be immediately after the cover page, but you can include it after the executive summary. Including the table of contents immediately after the executive summary will help investors know what section of your business plan they want to review more thoroughly.
Check out Canva’s article about creating a table of contents . It has a ton of great information about creating easy access to each section of your business plan. Just remember that you’ll want to use different strategies for digital and hard copy business plans.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 3. Write an Executive Summary

An executive summary is where your business plan should catch the readers interest. It doesn’t need to be long, but should be quick and easy to read.
Mike told us,
How long should an executive summary bein an informal business plan?
For casual use, an executive summary should be similar to an elevator pitch, no more than 150-160 words, just enough to get them interested and wanting more. Indeed has a great article on elevator pitches . This can also be used for the content of emails to get readers’ attention.
It consists of three basic parts:
- An introduction to you and your business.
- What your business is about.
- A call to action
Example of an informal executive summary
One of the best elevator pitches I’ve used is:
So far that pitch has achieved a 100% success rate in getting partnerships for the business.
What should I include in an executive summary for investors?
Investors are going to need a more detailed executive summary if you want to secure financing or sell equity. The executive summary should be a brief overview of your entire business plan and include:
- Introduction of yourself and company.
- An origin story (Recognition of a problem and how you came to solution)
- An introduction to your products or services.
- Your unique value proposition. Make sure to include intellectual property.
- Where you are in the business life cycle
- Request and why you need it.
Successful business plan examples
The owner of Urbanity told us he spent 2 months writing a 75-page business plan and received a $250,000 loan from the bank when he was 23. Make your business plan as detailed as possible when looking for financing. We’ve provided a template to help you prepare the portions of a business plan that banks expect.
Here’s the interview with the owner of Urbanity:
When to write an executive summary?
Even though the summary is near the beginning of a business plan, you should write it after you complete the rest of a business plan. You can’t talk about revenue, profits, and expected expenditures if you haven’t done the market research and created a financial plan.
What mistakes do people make when writing an executive summary?
Business owners commonly go into too much detail about the following items in an executive summary:
- Marketing and sales processes
- Financial statements
- Organizational structure
- Market analysis
These are things that people will want to know later, but they don’t hook the reader. They won’t spark interest in your small business, but they’ll close the deal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 4. Company Description
Every business plan should include a company description. A great business plan will include the following elements while describing the company:
- Mission statement
- Philosophy and vision
- Company goals
Target market
- Legal structure
Let’s take a look at what each section includes in a good business plan.
Mission Statement
A mission statement is a brief explanation of why you started the company and what the company’s main focus is. It should be no more than one or two sentences. Check out HubSpot’s article 27 Inspiring Mission Statement for a great read on informative and inspiring mission and vision statements.
Company Philosophy and Vision

The company philosophy is what drives your company. You’ll normally hear them called core values. These are the building blocks that make your company different. You want to communicate your values to customers, business owners, and investors as often as possible to build a company culture, but make sure to back them up.
What makes your company different?
Each company is different. Your new business should rise above the standard company lines of honesty, integrity, fun, innovation, and community when communicating your business values. The standard answers are corporate jargon and lack authenticity.
Examples of core values
One of my clients decided to add a core values page to their website. As a tech company they emphasized the values:
- Prioritize communication.
- Never stop learning.
- Be transparent.
- Start small and grow incrementally.
These values communicate how the owner and the rest of the company operate. They also show a value proposition and competitive advantage because they specifically focus on delivering business value from the start. These values also genuinely show what the company is about and customers recognize the sincerity. Indeed has a great blog about how to identify your core values .
What is a vision statement?
A vision statement communicate the long lasting change a business pursues. The vision helps investors and customers understand what your company is trying to accomplish. The vision statement goes beyond a mission statement to provide something meaningful to the community, customer’s lives, or even the world.
Example vision statements
The Alzheimer’s Association is a great example of a vision statement:
A world without Alzheimer’s Disease and other dementia.
It clearly tells how they want to change the world. A world without Alzheimers might be unachievable, but that means they always have room for improvement.
Business Goals
You have to measure success against goals for a business plan to be meaningful. A business plan helps guide a company similar to how your GPS provides a road map to your favorite travel destination. A goal to make as much money as possible is not inspirational and sounds greedy.
Sure, business owners want to increase their profits and improve customer service, but they need to present an overview of what they consider success. The goals should help everyone prioritize their work.
How far in advance should a business plan?
Business planning should be done at least one year in advance, but many banks and investors prefer three to five year business plans. Longer plans show investors that the management team understands the market and knows the business is operating in a constantly shifting market. In addition, a plan helps businesses to adjust to changes because they have already considered how to handle them.
Example of great business goals
My all time-favorite long-term company goals are included in Tesla’s Master Plan, Part Deux . These goals were written in 2016 and drive the company’s decisions through 2026. They are the reason that investors are so forgiving when Elon Musk continually fails to meet his quarterly and annual goals.
If the progress aligns with the business plan investors are likely to continue to believe in the company. Just make sure the goals are reasonable or you’ll be discredited (unless you’re Elon Musk).

You did target market research before creating a business plan. Now it’s time to add it to the plan so others understand what your ideal customer looks like. As a new business owner, you may not be considered an expert in your field yet, so document everything. Make sure the references you use are from respectable sources.
Use information from the specific lender when you are applying for lending. Most lenders provide industry research reports and using their data can strengthen the position of your business plan.
A small business plan should include a section on the external environment. Understanding the industry is crucial because we don’t plan a business in a vacuum. Make sure to research the industry trends, competitors, and forecasts. I personally prefer IBIS World for my business research. Make sure to answer questions like:
- What is the industry outlook long-term and short-term?
- How will your business take advantage of projected industry changes and trends?
- What might happen to your competitors and how will your business successfully compete?
Industry resources
Some helpful resources to help you establish more about your industry are:
- Trade Associations
- Federal Reserve
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
Legal Structure
There are five basic types of legal structures that most people will utilize:
- Sole proprietorships
- Limited Liability Companies (LLC)
Partnerships
Corporations.
- Franchises.
Each business structure has their pros and cons. An LLC is the most common legal structure due to its protection of personal assets and ease of setting up. Make sure to specify how ownership is divided and what roles each owner plays when you have more than one business owner.
You’ll have to decide which structure is best for you, but we’ve gathered information on each to make it easier.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the easiest legal structure to set up but doesn’t protect the owner’s personal assets from legal issues. That means if something goes wrong, you could lose both your company and your home.
To start a sole proprietorship, fill out a special tax form called a Schedule C . Sole proprietors can also join the American Independent Business Alliance .
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common business structure used in the United States because an LLC protects the owner’s personal assets. It’s similar to partnerships and corporations, but can be a single-member LLC in most states. An LLC requires a document called an operating agreement.
Each state has different requirements. Here’s a link to find your state’s requirements . Delaware and Nevada are common states to file an LLC because they are really business-friendly. Here’s a blog on the top 10 states to get an LLC.
Partnerships are typically for legal firms. If you choose to use a partnership choose a Limited Liability Partnership. Alternatively, you can just use an LLC.
Corporations are typically for massive organizations. Corporations have taxes on both corporate and income tax so unless you plan on selling stock, you are better off considering an LLC with S-Corp status . Investopedia has good information corporations here .

There are several opportunities to purchase successful franchises. TopFranchise.com has a list of companies in a variety of industries that offer franchise opportunities. This makes it where an entrepreneur can benefit from the reputation of an established business that has already worked out many of the kinks of starting from scratch.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 5. Products and Services
This section of the business plan should focus on what you sell, how you source it, and how you sell it. You should include:
- Unique features that differentiate your business products from competitors
- Intellectual property
- Your supply chain
- Cost and pricing structure
Questions to answer about your products and services
Mike gave us a list of the most important questions to answer about your product and services:
- How will you be selling the product? (in person, ecommerce, wholesale, direct to consumer)?
- How do you let them know they need a product?
- How do you communicate the message?
- How will you do transactions?
- How much will you be selling it for?
- How many do you think you’ll sell and why?
Make sure to use the worksheet on our business plan template .
How to Write a Business Plan Step 6. Sales and Marketing Plan
The marketing and sales plan is focused on the strategy to bring awareness to your company and guides how you will get the product to the consumer. It should contain the following sections:
SWOT Analysis stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Not only do you want to identify them, but you also want to document how the business plans to deal with them.
Business owners need to do a thorough job documenting how their service or product stacks up against the competition.
If proper research isn’t done, investors will be able to tell that the owner hasn’t researched the competition and is less likely to believe that the team can protect its service from threats by the more well-established competition. This is one of the most common parts of a presentation that trips up business owners presenting on Shark Tank .
SWOT Examples

Examples of strengths and weaknesses could be things like the lack of cash flow, intellectual property ownership, high costs of suppliers, and customers’ expectations on shipping times.
Opportunities could be ways to capitalize on your strengths or improve your weaknesses, but may also be gaps in the industry. This includes:
- Adding offerings that fit with your current small business
- Increase sales to current customers
- Reducing costs through bulk ordering
- Finding ways to reduce inventory
- And other areas you can improve
Threats will normally come from outside of the company but could also be things like losing a key member of the team. Threats normally come from competition, regulations, taxes, and unforeseen events.
The management team should use the SWOT analysis to guide other areas of business planning, but it absolutely has to be done before a business owner starts marketing.
Include Competitor Data in Your Business Plan
When you plan a business, taking into consideration the strengths and weaknesses of the competition is key to navigating the field. Providing an overview of your competition and where they are headed shows that you are invested in understanding the industry.
For smaller businesses, you’ll want to search both the company and the owners names to see what they are working on. For publicly held corporations, you can find their quarterly and annual reports on the SEC website .
What another business plans to do can impact your business. Make sure to include things that might make it attractive for bigger companies to outsource to a small business.
Marketing Strategy
The marketing and sales part of business plans should be focused on how you are going to make potential customers aware of your business and then sell to them.
If you haven’t already included it, Mike recommends:
“They’ll want to know about Demographics, ages, and wealth of your target market.”
Make sure to include the Total addressable market . The term refers to the value if you captured 100% of the market.
Advertising Strategy
You’ll explain what formats of advertising you’ll be using. Some possibilities are:
- Online: Facebook and Google are the big names to work with here.
- Print : Print can be used to reach broad groups or targeted markets. Check out this for tips .
- Radio : iHeartMedia is one of the best ways to advertise on the radio
- Cable television : High priced, hard to measure ROI, but here’s an explanation of the process
- Billboards: Attracting customers with billboards can be beneficial in high traffic areas.
You’ll want to define how you’ll be using each including frequency, duration, and cost. If you have the materials already created, including pictures or links to the marketing to show creative assets.
Mike told us “Most businesses are marketing digitally now due to Covid, but that’s not always the right answer.”
Make sure the marketing strategy will help team members or external marketing agencies stay within the brand guidelines .

This section of a business plan should be focused on pricing. There are a ton of pricing strategies that may work for different business plans. Which one will work for you depends on what kind of a business you run.
Some common pricing strategies are:
- Value-based pricing – Commonly used with home buying and selling or other products that are status symbols.
- Skimming pricing – Commonly seen in video game consoles, price starts off high to recoup expenses quickly, then reduces over time.
- Competition-based pricing – Pricing based on competitors’ pricing is commonly seen at gas stations.
- Freemium services – Commonly used for software, where there is a free plan, then purchase options for more functionality.
HubSpot has a great calculator and blog on pricing strategies.
Beyond explaining what strategy your business plans to use, you should include references for how you came to this pricing strategy and how it will impact your cash flow.
Distribution Plan
This part of a business plan is focused on how the product or service is going to go through the supply chain. These may include multiple divisions or multiple companies. Make sure to include any parts of the workflow that are automated so investors can see where cost savings are expected and when.
Supply Chain Examples
For instance, lawn care companies would need to cover aspects such as:
- Suppliers for lawn care equipment and tools
- Any chemicals or treatments needed
- Repair parts for sprinkler systems
- Vehicles to transport equipment and employees
- Insurance to protect the company vehicles and people.
Examples of Supply Chains
These are fairly flat supply chains compared to something like a clothing designer where the clothes would go through multiple vendors. A clothing company might have the following supply chain:
- Raw materials
- Shipping of raw materials
- Converting of raw materials to thread
- Shipping thread to produce garments
- Garment producer
- Shipping to company
- Company storage
- Shipping to retail stores
There have been advances such as print on demand that eliminate many of these steps. If you are designing completely custom clothing, all of this would need to be planned to keep from having business disruptions.
The main thing to include in the business plan is the list of suppliers, the path the supply chain follows, the time from order to the customer’s home, and the costs associated with each step of the process.
According to BizPlanReview , a business plan without this information is likely to get rejected because they have failed to research the key elements necessary to make sales to the customer.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 7. Company Organization and Operational Plan
This part of the business plan is focused on how the business model will function while serving customers. The business plan should provide an overview of how the team will manage the following aspects:
Quality Control
- Legal environment
Let’s look at each for some insight.
Production has already been discussed in previous sections so I won’t go into it much. When writing a business plan for investors, try to avoid repetition as it creates a more simple business plan.
If the organizational plan will be used by the team as an overview of how to perform the best services for the customer, then redundancy makes more sense as it communicates what is important to the business.

Quality control policies help to keep the team focused on how to verify that the company adheres to the business plan and meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Quality control can be anything from a standard that says “all labels on shirts can be no more than 1/16″ off center” to a defined checklist of steps that should be performed and filled out for every customer.
There are a variety of organizations that help define quality control including:
- International Organization for Standardization – Quality standards for energy, technology, food, production environments, and cybersecurity
- AICPA – Standard defined for accounting.
- The Joint Commission – Healthcare
- ASHRAE – HVAC best practices
You can find lists of the organizations that contribute most to the government regulation of industries on Open Secrets . Research what the leaders in your field are doing. Follow their example and implement it in your quality control plan.
For location, you should use information from the market research to establish where the location will be. Make sure to include the following in the location documentation.
- The size of your location
- The type of building (retail, industrial, commercial, etc.)
- Zoning restrictions – Urban Wire has a good map on how zoning works in each state
- Accessibility – Does it meet ADA requirements?
- Costs including rent, maintenance, utilities, insurance and any buildout or remodeling costs
- Utilities – b.e.f. has a good energy calculator .
Legal Environment
The legal requirement section is focused on defining how to meet the legal requirements for your industry. A good business plan should include all of the following:
- Any licenses and/or permits that are needed and whether you’ve obtained them
- Any trademarks, copyrights, or patents that you have or are in the process of applying for
- The insurance coverage your business requires and how much it costs
- Any environmental, health, or workplace regulations affecting your business
- Any special regulations affecting your industry
- Bonding requirements, if applicable
Your local SBA office can help you establish requirements in your area. I strongly recommend using them. They are a great resource.
Your business plan should include a plan for company organization and hiring. While you may be the only person with the company right now, down the road you’ll need more people. Make sure to consider and document the answers to the following questions:
- What is the current leadership structure and what will it look like in the future?
- What types of employees will you have? Are there any licensing or educational requirements?
- How many employees will you need?
- Will you ever hire freelancers or independent contractors?
- What is each position’s job description?
- What is the pay structure (hourly, salaried, base plus commission, etc.)?
- How do you plan to find qualified employees and contractors?
One of the most crucial parts of a business plan is the organizational chart. This simply shows the positions the company will need, who is in charge of them and the relationship of each of them. It will look similar to this:

Our small business plan template has a much more in-depth organizational chart you can edit to include when you include the organizational chart in your business plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements
No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let’s dig deeper into each.
Provide All Financial Income from an Existing Business
An existing business should use their past financial documents including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to find trends to estimate the next 3-5 years.
You can create easy trendlines in excel to predict future revenue, profit and loss, cash flow, and other changes in year-over-year performance. This will show your expected performance assuming business continues as normal.
If you are seeking an investment, then the business is probably not going to continue as normal. Depending on the financial plan and the purpose of getting financing, adjustments may be needed to the following:
- Higher Revenue if expanding business
- Lower Cost of Goods Sold if purchasing inventory with bulk discounts
- Adding interest if utilizing financing (not equity deal)
- Changes in expenses
- Addition of financing information to the cash flow statement
- Changes in Earnings per Share on the balance sheet
Financial modeling is a challenging subject, but there are plenty of low-cost courses on the subject. If you need help planning your business financial documentation take some time to watch some of them.
Make it a point to document how you calculated all the changes to the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in your business plan so that key team members or investors can verify your research.
Financial Projections For A Startup Business Plan
Unlike an existing business, a startup doesn’t have previous success to model its future performance. In this scenario, you need to focus on how to make a business plan realistic through the use of industry research and averages.
Mike gave the following advice in his interview:
Financial Forecasting Mistakes
One of the things a lot of inexperienced people use is the argument, “If I get one percent of the market, it is worth $100 million.” If you use this, investors are likely to file the document under bad business plan examples.
Let’s use custom t-shirts as an example.
Credence Research estimated in 2018 there were 11,334,800,000 custom t-shirts sold for a total of $206.12 Billion, with a 6% compound annual growth rate.
With that data, you can calculate that the industry will grow to $270 Billion in 2023 and that the average shirt sold creates $18.18 in revenue.
Combine that with an IBIS World estimate of 11,094 custom screen printers and that means even if you become an average seller, you’ll get .009% of the market.
Here’s a table for easier viewing of that information.

The point here is to make sure your business proposal examples make sense.
You’ll need to know industry averages such as cost of customer acquisition, revenue per customer, the average cost of goods sold, and admin costs to be able to create accurate estimates.
Our simple business plan templates walk you through most of these processes. If you follow them you’ll have a good idea of how to write a business proposal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 9. Business Plan Example of Funding Requests
What is a business plan without a plan on how to obtain funding?
The Small Business Administration has an example for a pizza restaurant that theoretically needed nearly $20k to make it through their first month.
In our video, How to Start a $500K/Year T-Shirt Business (Pt. 1 ), Sanford Booth told us he needed about $200,000 to start his franchise and broke even after 4 months.
Freshbooks estimates it takes on average 2-3 years for a business to be profitable, which means the fictitious pizza company from the SBA could need up to $330k to make it through that time and still pay their bills for their home and pizza shop.
Not every business needs that much to start, but realistically it’s a good idea to assume that you need a fairly large cushion.
Ways to get funding for a small business
There are a variety of ways to cover this. the most common are:
- Bootstrapping – Using your savings without external funding.
- Taking out debt – loans, credit cards
- Equity, Seed Funding – Ownership of a percentage of the company in exchange for current funds
- Crowdsourcing – Promising a good for funding to create the product
Keep reading for more tips on how to write a business plan.
How funding will be used
When asking for business financing make sure to include:
- How much to get started?
- What is the minimum viable product and how soon can you make money?
- How will the money be spent?
Mike emphasized two aspects that should be included in every plan,
How to Write a Business Plan Resources
Here are some links to a business plan sample and business plan outline.
- Sample plan
It’s also helpful to follow some of the leading influencers in the business plan writing community. Here’s a list:
- Wise Plans – Shares a lot of information on starting businesses and is a business plan writing company.
- Optimus Business Plans – Another business plan writing company.
- Venture Capital – A venture capital thread that can help give you ideas.
How to Write a Business Plan: What’s Next?
We hope this guide about how to write a simple business plan step by step has been helpful. We’ve covered:
- The definition of a business plan
- Coming up with a business idea
- Performing market research
- The critical components of a business plan
- An example business plan
In addition, we provided you with a simple business plan template to assist you in the process of writing your startup business plan. The startup business plan template also includes a business model template that will be the key to your success.
Don’t forget to check out the rest of our business hub .
Have you written a business plan before? How did it impact your ability to achieve your goals?
80% of businesses fail... Learn how not to.
Learn from business failures and successes in 5 min or less. The stories, frameworks, and tactics that will make you a 10x better founder.
Brandon Boushy
Related articles

The 15 Best HR Outsourcing Companies (2024)
Which HR Tasks Can Be Outsourced?
- HR Consulting
- Benefits Administration
- Time Tracking
- Insurance Services
- Performance Management
- Payroll Administration
- Bookkeeping
- Client Management
- Policy Compliance Management
- Unemployment Claims
- Policy Development
- Staff Training and Coaching
- Labor Law Compliance
- Employee Termination
- Audit and Wage-Claim Assistance
- Talent Management
SaaS Providers
Business process outsourcing, single source outsourcing, shared services, professional employer organizations.
- BambooHR - Primarily concerned with hiring, compensation, and analyzing performance. Includes payroll as an additional service.
- Deputy - Scheduling, time tracking, and labor law compliance. Has a free edition.
- Gusto - Gusto was PC Mag's 2021 Best HR software payroll selection, but they have software to help with other processes as well.

What are the benefits of HR Outsourcing For Small Businesses?
- Better compliance with federal, state, and local regulations.
Increased growth of the business
- Potentially reduced cost of administrative services
- Ability to offer better benefits.
Outsourced HR helps small businesses comply with regulations
Outsourced hr reduces the cost of administrative services.

- Hire internal HR staff
- Outsourced human resources
Ability to offer better benefits

The cons of HR outsourcing
Hr services do things their way, you might pay for hr tasks you don't need..
- Outsourcing staff gives you less control of the hiring process
HR companies have consistently poor communication reviews
Questions to ask when talking to hr service companies.

- Does your payroll service include time tracking apps to help collect employees' hours and reimbursable expenses?
- Does your HR technology easily integrate with my current HR systems?
- Is workers' compensation included in your full-service HR package?
- What will I need to do to make sure your HR systems and HR department can handle my payroll in the future without me being actively involved?
- If I have HR-related compliance requests, what process do we have to go through?
Outsourcing HR staff gives you less control of the hiring process
Reviewing hr outsourcing services.
- Gathered a list of the 16 companies that have been reviewed by top-ranking blogs.
- Reviewed each company's website and compared it to the 15 services typically offered by HR outsourcing companies (If they offer the service, they get a 100. If unsure, or no, they get a 0).
- Compared the number of plans they offered with a maximum of 10, then multiplied by 10 get scores ranging from 10-100.
- As long as the website did not have a major issue, they got an extra 100 points for their website. CPE HR (given a zero for broken links) and G&A Partners (80 because there wasn't additional information where I wanted it) were the only ones penalized.
- Then I compared reviews on Capterra and Trust Pilot and took whichever had more reviews. I used the calculation, (# of reviews* stars given)/100=Score from 0-100. This step is for purpose of giving extra weight to ones with more reviews.
- Multiplied average stars by 20 to get a score from zero to 100. This step was to reward the strength of reviews.
- Added all scores up and divided by 19 to create a score that will range between 0 and 100.
The Best Small Business HR Outsourcing Companies & Services

ADP is the top-ranked company
Hr tasks adp offers:, what makes adp the best hr outsourcing organization:, what is adp the best at.

ADP Features, Pricing, and Reviews:
Paychex comes in at number 2, hr tasks paychex offers:, what makes paychex one of the best hr outsourcing organizations, what is paychex the best at.

Paychex Features, Pricing, and Reviews:
The third best hr outsourcing service is gusto, hr tasks gusto offers:, what makes gusto one of the best hr outsourcing organizations:, what is gusto the best at.

Gusto Features, Pricing, and Reviews:
Insperity takes 4th place, hr services insperity offers:, what is insperity the best at.

Insperity Features, Pricing, and Reviews:
Zenefits rounds out the top 5 hr service businesses, hr services zenefits offers:, what is zenefits the best at.

Zenefit Features, Pricing, and Reviews:
- Essentials: $10/mo/employee
- Growth: $18/mo/employee
- Zen: $27/mo/employee
The rest of the list
- G&A Partners - With a score of 88.4, G&A Partners offers all the services as a PEO or mix and match. Lack of reviews on common review sites harmed their rating. If you work in construction or other safety fields they might be best. They also carry the liability for HR decisions, which is great for risk management.
- CoAdvantage PEO - With a score of 88.4, CoAdvantage is another PEO that appears to offer all the services, but some were hinted at more than specifically covered. They also didn't have any ratings, but a nice referral program.
- TriNet - TriNet Scored an 85 due to an average of 2.7 stars on 97 ratings, poor disclosure of whether they offer services separately, and only offering some types of insurance. One of the things I liked about TriNet is they claim that when the SSI cap is reached, you pay less. They don't charge more when wages go up though.
- Oasis Advantage - At a score of 84.7, Oasis Advantage has the 8th best outsourcing services. They are a subsidiary of Paychex so I would just go with Paychex. Once again, ratings were missing and you have to request a quote.-
- Engage PEO - At a score of 84.7, Engage is another PEO without ratings on common sites. They were middle of the pack when it comes to their options as they primarily offer PEO services with 6 optional benefit plans.
- Workday - Workday scored an 80.3 with demerits due to lack of insurance, lack of clarity on whether they consult, and numerous reviews saying that people will not work for companies that use Workday. They came in 9th cause their overall ratings are a 4.5, but you have to take care of your employees. Trust Pilot Capterra
- BambooHR - Bamboo is primarily focused on the hiring process and payments. That's why it received a score of 73.5. It has great reviews though.
- Bambee - Bambee is a consultant to make sure you follow legal procedures. At $99/mo it is a reasonable price and has great reviews, but you can get this included in other packages. Best if you just want someone to consult with you so you can expand your skills. Their total score was 73.2
- CPEhr - I honestly don't even want to give you their link because they annoyed me. They have no reviews, they have broken links, and places where there isn't a link that there should be. They scored a 68.4
- Accenture HR - I feel like Accenture HR scored way lower than it should (36.1), but that's because it is specialized in analytics. If you want better data to manage your HR, use them. You'll need your team or another service though.
Upwork Freelancers

HR tasks they will take:
What makes hr freelancers great:, what are hr freelancers the best at, features, pricing, and reviews:.

The 77 Best Businesses to Start with $10K (or Less)
Do you want to start your own business but don’t know where to begin? People often wait to start a business because they don’t have the initial investment for their business idea, but you should never wait to invest in your future. We’ll provide businesses to start with $10K or less.
We’ve prepared a list of 70 businesses you can start for under $10K to help you on your path to entrepreneurship. We’ll provide you with ideas, an estimate of the startup costs, and the profit and revenue you can expect to make.
We’ll even share links to new business resources and stories from startup businesses that have done exactly what we’re suggesting. By the end of this blog, you’ll have dozens of affordable startup ideas and know what steps to take to get going.
[su_note note_color="#dbeafc"]
Read it all or click on any of the links to jump to the section that most interests you.
Need help finding your own business ideas?
- Best online business ideas 2024
Small and local businesses you can start with $10,000
Creative and crafty business ventures to start with $10k.
- What business can I start with $10K that serves food ?
- Closing [/su_note]
Keep reading for some of the best businesses to start with $10K.
We’ve created this list of businesses to start based on the ease of getting into each industry. They fall into three main categories:
- Online businesses
- No-education-needed businesses
- Low-cost-education-needed businesses
If your business idea isn’t on the list, that doesn’t mean you can’t achieve it with less than $10,000. Just keep in mind that every great business idea will need:
- A business license
- A computer (If you don’t have one, check Amazon’s open-box deals .)
- Social media
Best online business ideas 202 4
#1 dropshipping: the easiest business idea to start.
• Average Annual Revenue: $36K-$50K • Average Profit Margins: 5% • Startup Cost: $150-$500 • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 25% • Best For: Those who want flexibility and passive income, people with strong digital marketing and social media skills
Dropshipping is the easiest type of business under $10K to start! Just
- Set up a Shopify account .
- Connect Printful and social media accounts.
- Create a few designs.
- License the business.
- Start marketing your products for less than $1,000 upfront.
#2 Print-on-demand services
• Average Annual Revenue: $1.6M • Average Profit Margins: 4.3% • Startup Cost: $500-$250K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: -5.6% • Best For: Visual artists, graphic designers, marketing pros, people who want passive income potential
A print-on-demand online store is a great business idea if you want to sell products with a low initial investment. You don’t need to worry about buying or managing inventory—just create the designs and find customers.
POD selling also has the potential to be a very lucrative business. Heather Johnson started her print-on-demand store with about $30 as a side hustle, and today its revenue is over $15,000 in an average month.
Hear Heather’s advice on getting started in this interview:
#3 eCommerce reselling
• Average Annual Revenue: $60K-$120K • Average Profit Margins: 5-15% • Startup Cost: $100-$1K • Time to Revenue: 30-90 days • Annual Market Growth Rate: -9.3% • Best For: Thrifters, shopaholics, and antiquers with a sharp eye for value
You don’t need to come up with your own products to start an online store. Platforms like eBay make it easy to start a new business as a reseller.
eCommerce reselling is definitely a business you can start with $10,000 or less. All you really need is the initial inventory, and if you’re strapped for cash, you can even start selling things you already own.
That’s what Mike Watson did when he started Golden State Picker. Now, he has a very successful business selling on eBay and earns around $30,000 a month. Hear his story in this interview:
#4 Online business manager
• Average Annual Revenue: $363K+ • Average Profit Margins: 10.3% • Startup Cost: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.8% • Best For: Organized people with management and leadership experience
We included virtual business management on this list because it utilizes skills many people already have. You just need:
- Management experience
- An internet connection
If you want badges to prove your skills, check out Zippia.com’s list of certifications .
Help busy CEOs run their companies remotely and make a great living doing it!
Keep reading for more small business ideas.
#5 YouTube content creator
• Average Annual Revenue: $60K-$160K • Average Profit Margins: 8% • Startup Cost: $100-$2K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 10.5% • Best For: People with a compelling on-camera presence, digital marketing, and social media skills
Create original YouTube content, get enough views, and become a YouTube Channel Partner. You can earn revenue from:
- Paid ads - $0.10-$0.30 for each view of a paid ad during your videos
- Super Chats and Super Stickers - 70% of revenue from both
- Selling your own merchandise
- Premium channel memberships
- Partnering with companies using YouTube BrandConnect to earn money through sponsorships
- Creating 60-second videos and getting your share of the $100 million YouTube Shorts fund
HubSpot shares the number of subscribers you need to get in the top 100 in different YouTube categories.
Find out how Reyes the Entrepreneur makes $210K a year:
#6 Start a podcast
• Average Annual Revenue: $4M+ • Average Profit Margins: 27.1% • Startup Cost: $0-$5K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 6.4% • Best For: Bloggers and content creators, people with niche expertise in popular subjects
If you like the idea of a content channel but don’t want to be on camera, you could start a podcast instead.
Podcasts can be monetized much like a YouTube channel. Revenue streams include:
- Selling ad space and episode sponsorships
- Selling related merchandise or services
- Selling online courses
- Including affiliate marketing links in your podcast description
- Offering a paid membership
You can find out how Entrepreneurs on Fire makes $150,000 a month in podcast-related revenue in this interview:
#7 Search engine optimization
• Average Annual Revenue: $415K+ • Average Profit Margins: 7.3% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 4.6% • Best For: Writers, web designers, online advertising experts, systems- and data-driven entrepreneurs
You can start doing SEO with free tools to save money and build as you grow.
And there’s plenty of room for growth—top-rated SEO experts make up to $150 an hour .
Search engine optimization is focused on improving website results in search engines through:
- Keyword research
- Improving site speed
- Content marketing
- Google My Business
If small businesses don’t show up on the first page of a search engine, they need help because they aren’t getting much traffic. Once they get to the first page, their traffic skyrockets. Consider this breakdown:
- Ads: 1.2-2.1% of traffic
- 1st place organically: 39.6% of traffic
- 2nd place organically: 18.4% of traffic
- 3rd place organically: 10.1% of traffic
- 5th place organically: 5.1% of traffic
- 10th place organically: 2.1% of traffic
Master getting a page to #1, and you’ve helped a business capture 20x more traffic…and hopefully 20x more revenue.
#8 Digital marketing consultant
• Average Annual Revenue: $817K • Average Profit Margins: 6.9% • Startup Cost: $100-$10K • Time to Revenue: 1-6 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.3% • Best For: Social media marketing and online marketing pros with strong communication skills
Digital marketing consultants help businesses get more attention on social media platforms and rank higher with search engines.
There are no formal education requirements, and lots of free education is available. Check out:
- Grow with Google
- Facebook Blueprint
- Hubspot Academy
Check out our interview with Jason Yormark, founder and Chief Social Officer of Socialistics, below.
We still have more businesses to start with $10K. Keep reading!
#9 Social media management
• Average Annual Revenue: $817K • Average Profit Margins: 6.9% • Startup Cost: $100-$10K • Time to Revenue: 1-6 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.3% • Best For: Experts in social media platforms, writers and creators who are strong collaborators
Many business owners either don’t like social media or don’t know how to get the most out of it.
With a social media management business, you’ll help other small business owners connect with potential clients through platforms like Facebook, Twitter, TikTok, and Instagram.
This often means creating marketing materials and content in collaboration with the owner of the account you’re managing.
If you can do that effectively, social media management can be a very successful business to start with $10K or less.
#10 Virtual assistant
• Average Annual Revenue: $35K-$50K • Average Profit Margins: 10.5% • Startup Cost: $100-$200 • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.9% • Best For: Organized and system-driven entrepreneurs
Social media isn’t the only thing most business owners don’t have time for. There are tons of small tasks that go into running a business, and that’s where a virtual assistant comes into the picture.
A virtual assistant works remotely, usually handling administrative tasks like data entry or answering emails. Most set their own schedules, too, so it’s very flexible work.
This is one of the rare businesses you can start completely for free. All you need is a way to connect with potential clients, which you can do online through platforms including:
- 24/7 Virtual Assistant
- Freelancer.com
#11 Affiliate marketing business
• Average Annual Revenue: $60K-$160K • Average Profit Margins: 8% • Startup Cost: $100-$2K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 10.5% • Best For: Advertising and marketing professionals, content creators
Affiliate marketing is a form of online advertising where you promote products and services from other businesses. If someone buys through your site, you get a commission.
This business model is location-independent and gives you complete flexibility when it comes to your schedule. It’s also a good business to make passive income once you have content and traffic on your site.
Getting that traffic is often the hard part when it comes to starting an affiliate marketing business. Read our complete guide to affiliate marketing or hear how David Thomas Tao did it with BarBend in this interview:
#12 Domain-flipping business
• Average Annual Revenue: $239K • Average Profit Margins: 5.30% • Startup Cost: $100-$1K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.40% • Best For: Web designers and developers, people with strong sales and marketing skills
This is the best business to start with $10K if you have expertise in coding and web design.
Flipping domains is like the online version of flipping houses. You buy a website or eCommerce store, make improvements to increase its value, then sell it for a profit.
Ron Stefanski has grown a $30,000-a-month business selling websites. Hear how he got started in this interview:
#13 Sell online courses
• Average Annual Revenue: $30K-$50K • Average Profit Margins: 13.10% • Startup Cost: $100-$1K • Time to Revenue: 1-6 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 8.5% • Best For: Educators and teachers, people with niche or in-demand skills and knowledge
Online education is a $218 billion industry , and it’s expected to grow at a CAGR of 9% through 2030. Online courses are an affordable way to start a successful business in this niche.
The initial investment to start an online course business is minimal from a financial standpoint. It can take a lot of time and effort, though, and that’s the main impediment most face getting started.
Find out how Jacques Hopkins overcame that challenge to grow Piano in 21 Days into a $480K-a-year business in this interview:
#14 Transcription business
• Average Annual Revenue: $25K • Average Profit Margins: 20.50% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 4.4% • Best For: Fast typers who are excellent listeners and have strong time management skills
If you can type faster than most, you can use that skill to start a business with $10K or less as a transcriptionist.
In fact, it will probably cost much less. All you really need to get started is a computer, internet connection, and an account on a freelance platform like Fiverr , TranscribeMe , or GoTranscript .
#15 Translation business
• Average Annual Revenue: $75K-$200K • Average Profit Margins: 12.4% • Startup Cost: $100-$200 • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.2% • Best For: People who speak multiple languages
From advertising to entertainment to technical documents, there are lots of things that people need to have translated, and multilingual entrepreneurs can turn that demand into a lucrative business idea.
According to Indeed , the most profitable languages for translation are:
If you speak one or more of the above languages as well as English, then you can likely make good money in translation.
If you’re still wondering what business to start, keep reading for more affordable ways to open your own business!
#16 Vending business
• Average Annual Revenue: $182K+ • Average Profit Margins: 4.3% • Startup Cost: $2K-$10K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.5% • Best For: People who like to drive, system-driven entrepreneurs with strong sales skills
The initial investment to start a vending business varies depending on how many machines you want. That said, you can easily get started with just a few thousand dollars.
Best of all, it’s one of the most flexible low-investment business ideas and you can make a great living working just a couple of days a week.
Adam Hill makes nearly $60K a month with his vending business and teaches others to follow in his footsteps in his Vending Bootcamp . You can also hear insights from Adam in this YouTube interview:
#17 Janitorial cleaning services
• Average Annual Revenue: $74K+ • Average Profit Margins: 6.7% • Startup Cost: $1K-$30K • Time to Revenue: 1-6 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.2% • Best For: Detail-oriented entrepreneurs with strong customer service skills
Keeping an office space or workplace clean is a bigger concern than ever in the post-pandemic world. That means lots of opportunities to start a cleaning services business.
There are lots of ways to scale this business, too. Spruse Clean grew to more than $10M yearly revenue in just three years by expanding into their own product line. Hear how they did it in this YouTube video:
We’ve got more business ideas in the cleaning niche below!
#18 Airbnb cleaning service
• Average Annual Revenue: $61K+ • Average Profit Margins: 10.8% • Startup Cost: $300-$5K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 2.4% • Best For: System and detail-oriented business owners skilled in customer service
Airbnb hosting is a popular business venture in its own right—but that can take a big investment if you don’t already own property.
With Airbnb cleaning services, you help other local business owners serve their customers, and this niche offers a lot of opportunities for business growth.
Queen Bee Cleaning Services makes a lot of its revenue from Airbnb customers. Hear how founder Chris Mondragon built the business in this interview:
You can learn more in Chris’s 7-Figure Cleaning Business Blueprint , where he explains how to write a business plan, choose business insurance, find potential clients, and all the other steps required to start a successful cleaning business.
#19 Window blind cleaning business
• Average Annual Revenue: $64K • Average Profit Margins: 8.8% • Startup Cost: $200-$5K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.9% • Best For: Detail-oriented entrepreneurs with strong customer service skills
An often missed aspect of cleaning is people’s blinds. Using this business model can offer a nice spin on traditional housekeeping services.
Potential clients will be ones who value a higher level of service in the cleaning industry and are likely to pay more.
A blind cleaning service is also a great way to niche down and become known as the leading expert for a service in your area.
Keep reading even more businesses to start with $10K or less.
#20 Tutoring services
• Average Annual Revenue: $18K+ • Average Profit Margins: 13.10% • Startup Cost: $100-$1K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 8.5% • Best For: Teachers and educators, people who are strong communicators and motivators
Start tutoring for under $1,000, assuming you have:
- A vehicle (if you’ll be meeting clients in person)
Students consistently need help mastering subjects like math, science, history, and English. Whether you choose to do test prep or general tutoring, there is plenty of demand for local businesses offering to tutor.
You can even do it online using platforms like Upwork and TutorAround . Certifications from the Association for the Coaching and Tutoring Profession and National Tutoring Association can help you show proof of your tutoring skills.
#21 Lawn care or landscaping business
• Average Annual Revenue: $272K+ • Average Profit Margins: 8.7% • Startup Cost: $2K-$10K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 8.1% • Best For: People who like hands-on work and working outside
The low barrier to entry is one thing that draws small business owners to the lawn care industry. You don’t need any special skills to start, and the costs are minimal.
Trevor Kokenge started his landscaping business out of his apartment with just $300 and grew it to more than $22K a month in revenue. Hear how in this interview:
#22 Start a backyard nursery
• Average Annual Revenue: $262K+ • Average Profit Margins: 5.4% • Startup Cost: $100-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 2.8% • Best For: Gardeners, lovers of the outdoors, skilled planners and system-implementers
A nursery is a great business idea for people who have a green thumb. You can sell your plants and seeds directly to customers or to local stores like restaurants or flower shops.
While you will need some land to grow on, it takes less than you might think, especially if you grow things like herbs and flowers that don’t take up too much space.
#23 Real estate agents
• Average Annual Revenue: $298K+ • Average Profit Margins: 44.6% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: -0.3% • Best For: Outgoing and friendly people who are skilled communicators and salespeople
If you are looking for businesses you can start with less than $10,000, then you may want to consider working as a real estate agent.
Real estate agents make a great living and they set their own schedules, so it’s a smart choice if wanting flexibility is one of your reasons for starting a business.
Being a real estate agent requires mostly certifications and licensing as startup costs. You can find your state’s requirements on the Association of Real Estate License Law Officials website.
Check out our interview with Paul Balzotti to hear his tips for new real estate agents:
Keep reading for more businesses to start with $10K (or less).
#24 Property management
• Average Annual Revenue: $372K+ • Average Profit Margins: 10.1% • Startup Cost: $100-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.3% • Best For: Organized entrepreneurs with strong time management, communication, and customer service skills
Another way to save money and start a real estate business is to manage properties that other people own.
As with cleaning, Airbnb properties are a big opportunity to start a new business as a property manager. NICASA makes $3M a year as an Airbnb business, and a lot of that revenue is from managing other people’s properties. Find out more in this interview:
#25 Start a moving company
• Average Annual Revenue: $1.2M+ • Average Profit Margins: 9.91% • Startup Cost: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 3.7% • Best For: People who like physical work, outgoing and customer service-focused entrepreneurs
Moving is stressful and strenuous—and a lot of people would rather hire someone to do it for them than handle it themselves.
The main expense to start a moving company is the truck. If you don’t already have one, you can save money on startup costs by renting a truck at first then investing your profits into buying your own vehicle.
#26 Junk removal business
• Average Annual Revenue: $5.7M+ • Average Profit Margins: 2.9% • Startup Cost: $100-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.9% • Best For: People with high stamina who like physical work, construction and recycling pros
Speaking of hauling heavy things, junk removal is an in-demand business venture. You can make $15-$50 an hour doing it, plus what you can make selling junk to scrap yards.
If you have a truck, van, or another vehicle that can pull a trailer, help people get rid of their unwanted junk and make money doing it.
You’ll need to know:
- Your local dumps’ policies and billing rates
- Your cost per mile
- What recycling yards will purchase
- Whether you’ll charge by the pound or by the job
Kyle Landwehr is a junk removal business owner who made more than $2 million in three years. Hear his advice for starting in this interview:
#27 Tour guides
• Average Annual Revenue: $995K+ • Average Profit Margins: 6.6% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 3.5% • Best For: Actors and performers, extroverted entrepreneurs with good presentation and communication skills
If your location gets tourism, you could start your own business as a tour guide. Share your knowledge and help people explore:
- Favorite hiking locations
- Local restaurants
- Historical buildings and monuments
- Haunted locations
- Pub and nightclub crawls
- The business ideas are unlimited to your creativity
Keep reading for more business ideas you can start for under $10K.
#28 Green business consultant
• Average Annual Revenue: $364K • Average Profit Margins: 6.4% • Startup Cost: $1K-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 2.2% • Best For: Experts in sustainability and green business practices
If you’re passionate about sustainability, think about starting a green business consulting firm. Green business consultants need to have a firm understanding of:
- Conservation methods
- Technology available
- Calculating return on investment
- Quality, green-minded contractors for installations
Consider getting certifications from:
- Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)
- U.S. Green Building Council
- Energy Star (only for licensed PEs and Architects)
Next, we’ll look at a business venture that helps other small business owners succeed.
#29 Leadership consultant
• Average Annual Revenue: $363K+ • Average Profit Margins: 10.3% • Startup Cost: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.8% • Best For: People with management and leadership experience, business experts
You don’t need to lead a giant company to profit from your skills in leadership. Instead, you can help other people run a more successful business as a leadership consultant.
Leadership expert Libby Gill turned her experience as Head of Communications for Sony into a consultant business. Hear her insights here:
#30 Life coaching
• Average Annual Revenue: $63K+ • Average Profit Margins: 10.5% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.5% • Best For: People with high empathy and emotional IQ who are great communicators, problem-solvers, and motivators
Business owners aren’t the only ones who sometimes need advice and guidance. Everyday people do, too, and you can provide that as a life coach.
While you don’t need a license to be a life coach, getting a certification can help build trust with potential clients, which can grow your business faster. You can get these credentials from places like:
- The Life Coach School
- Coach Training Alliance
- The Transformation Academy
#31 Personal trainer
• Average Annual Revenue: $16K+ • Average Profit Margins : 10.9% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 1-6 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.6% • Best For: Health, fitness, and exercise experts who are great communicators and motivators
If you are fitness-minded, personal training might be a good business to start with $10K or less. Personal trainers help people achieve their health goals and improve their lives. You’ll need:
- Business licenses if required in your location
- AED and CPR certifications (Check with the Red Cross for where to get certified near you.)
- National Association of Sports Medicine
- American Council on Exercise
Pro Tip: Read about other certifications at FitnessTrainer.com
After working as a fireman and personal trainer, Jake Brog took his offerings even further and opened a gym for less than $10K. Watch him explain how he started Lab Athletics:
Keep reading for more business ideas under $10K.
#32 Local delivery services
• Average Annual Revenue: $131K • Average Profit Margins: 3.6% • Startup Cost: $100-$9.5K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 6.7% • Best For: Organized and system-driven entrepreneurs with strong marketing skills
If you’re looking for business ideas and have a car, starting a local delivery service can be a great way to earn some extra money.
You can sign up to work with companies like Uber , GrubHub, and DoorDash, or you can create your own.
If you want to start your own service, you’ll need to:
- Create an app.
- Recruit restaurants.
- Recruit drivers.
- Hire a customer support center to handle complaints.
Find out how Trellus same-day delivery service got started in this interview:
Business growth for food delivery is the highest in the food business. If you are looking for small businesses to start, this is low-hanging fruit.
Keep reading for more small businesses to start with less than $10K.
#33 Be a personal shopper
• Average Annual Revenue: $131K • Average Profit Margins: 3.6% • Startup Cost: $100-$9.5K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 6.7% • Best For: People who love shopping who are excellent listeners and great at customer service
Personal shoppers connect people with the products that they need—even if they don’t know exactly what those are before they start.
If you’re starting this kind of venture, your business plan should focus on how you’ll connect with clients, which is the most difficult part of starting a personal shopper business.
#34 Equipment rental service
• Average Annual Revenue: $444K+ • Average Profit Margins: 35-40% • Startup Cost: $100-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: -0.8% • Best For: People who own rentable assets, collectors of cars, boats, or other equipment
Equipment rental services are common in a variety of fields, including:
- Construction tool rentals
- Home medical equipment rentals
- Cars , boats, and other rentals
Open Door has a great article on how to improve profits on equipment and ForConstructionPros.com has a great formula to calculate the price of a rental .
Check out how Demitri started offering charter boat rentals:
Pro Tip: Make sure to carry business insurance to recover the monetary value if you have high equipment costs because accidents, theft, and injuries can occur.
Still haven’t decided which businesses to start with $10K? Read on for more to choose from!
#35 Event planning business
• Average Annual Revenue: $34K+ • Average Profit Margins: 12.2% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1% • Best For: Organized and outgoing entrepreneurs with strong communication and time management skills
If you love planning parties, you can turn that passion into a very lucrative business as an event planner.
Event planners can be generalists or focus on a specific niche. The most profitable niches for event planners include:
- Luxury wedding planners
- Destination wedding planners
- Corporate event planners
- Virtual event planning
- Festival and concert planners
The truth is, though, whatever type of event you have the passion and experience to plan, you can earn money doing it by starting a new business in this industry.
#36 Mobile locksmith services
• Average Annual Revenue: $105K+ • Average Profit Margins: 10.29% • Startup Cost: $500-$250K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 6.2% • Best For: Repair professionals, auto experts, people with strong mechanical and math skills
People lock themselves out of their cars all the time. If you offer emergency lock-out assistance, you can contract with insurance companies like AAA or attract clients independently.
#37 Telephone answering service
• Average Annual Revenue: $905K+ • Average Profit Margins: 20.50% • Startup Cost: $100-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.9% • Best For: Friendly and outgoing people with strong customer service skills
There are a ton of companies that pay independent contractors or other businesses to handle phone and web support. To get started, apply for jobs on Indeed or freelancing sites like Upwork . If you like this idea:
- Make sure you have a computer and headset.
- Start pursuing commercial clients.
- Hire other people.
- Get office space (optional).
#38 Mobile Pet Grooming Business
• Average Annual Revenue: $72K+ • Average Profit Margins: 11.5% • Startup Cost: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.1% • Best For: Animal lovers and pet experts who are patient, empathetic, and great communicators
To start a mobile pet grooming business, you’ll need:
- A van or RV
- A grooming kit
- A grooming hammock
- Sink and water supply
- Shampoo and conditioner
- A vacuum that won’t get clogged
For other business ideas involving pets, check out our blog about the number one Etsy seller in pet products.
#39 Pet sitting business
• Average Annual Revenue: $34K+ • Average Profit Margins: 16% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.7% • Best For: Pet owners and animal lovers with strong time management and communication skills
Pet sitting is another great business idea for animal lovers to start with $10K or less. Like mobile grooming, you can start easily from your home and won’t need an office space or commercial storefront.
The easiest way to get started is to join an online community for pet sitters, like Rover or Pet Sitters International . Rover even lets you book pet sits and communicate with clients right through the app.
#40 Dog walking business
• Average Annual Revenue: $34K+ • Average Profit Margins: 16% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.7% • Best For: Dog owners, lovers, and experts, fit entrepreneurs with high physical stamina who like working outdoors
Similar to other pet care sectors like pet grooming services or vet care, the demand for dog walkers has increased dramatically since 2020.
Nearly one in five Americans adopted a pet in 2020 and early 2021, so any business that helps people care for those new family members can be a great way for entrepreneurs to earn money. The typical cost for these services has increased with demand, and many dog walkers in urban areas charge $500-$600 a month or more per dog.
#41 Childcare services
• Average Annual Revenue: $143K+ • Average Profit Margins: 0.9% • Startup Cost: $0-$1K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 51.7% • Best For: Parents, teachers, people who are patient, empathetic, and strong problem-solvers
For those who have experience caring for children, opening a nanny agency can be the most profitable business to start with $10K or less.
Just look at Twinkle Toes Nanny Agency, which has grown to $11.2 million a year in revenue since it was founded in 2011. You can hear how founder Kristy Bickmeyer built the business in this interview:
#42 Security company
• Average Annual Revenue: $4.3M+ • Average Profit Margins: 9.89% • Startup Cost: $100-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.9% • Best For: Entrepreneurs with law enforcement experience or strong observation, systemization, and problem-solving skills
There are two types of security companies you can start:
- Installation of alarms, security cameras, and key card access systems
- Security guards for events, locations, and people
Note that both require special licensing as most jurisdictions want to make sure security company offerings are actually protecting people from criminals. Check out this guide to security guard requirements by state.
Whichever you choose, a security company is one of the best businesses to start with $10K. You’ll only need:
- Licensing costs before your first sale
- Up to $150 an hour for security and bodyguard services ($1.314M per client for 24/7 year-round)
- Up to $1,600 per four-camera system
#43 Pressure washing business
• Average Annual Revenue: $64K • Average Profit Margins: 8.8% • Cost: $200-$5K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.9% • Best For: Detail-focused entrepreneurs who like physical work, outdoor work, and customer service
A pressure washing business is mobile by design because you go to customers’ homes for jobs. This keeps the initial investment low—all you need to get started are a power washer, a vehicle, and some initial cleaning chemicals.
Chase Lille invested around $3,000 to start Wizard Wash as a teenager and was making about $12,000 a month in revenue by the time he finished high school. Hear his advice in this interview:
Pro Tip: You can also get step-by-step guidance on how to start your own pressure washing business with UpFlip’s new 7-Figure Pressure Washing Blueprint course.
#44 Mobile car wash
• Average Annual Revenue: $73K+ • Average Profit Margins: 16.1% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.0% • Best For: Car lovers, cleaning experts, people who like physical and outdoor work
If you like being outside and washing cars, a mobile detailing business might be right for you. You’ll need:
- A water tank
- A washing kit
- A mobile 3-in-1 vacuum
- A mobile waxing tool
Customers pay more for bigger cars and more services. You can choose to go for volume or big jobs.
- Corporate offices
- Car dealerships
- Car rental companies
Higher paying jobs:
- Market to high-end neighborhoods.
- Invest in car wraps.
- Use digital marketing.
- Offer detailing services at up to $400 per car.
Offer weekly or monthly deals for either category to maximize income. Check out how Bigs Mobile started their car detailing business:
#45 Mobile car wrapping
• Average Annual Revenue: $241K+ • Average Profit Margins: 16.1% • Startup Cost: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 1-6 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.8% • Best For: Graphic designers, detail-oriented and system-driven entrepreneurs
Many business owners use car wraps as marketing materials to turn their vehicles into moving billboards. People with luxury cars, meanwhile, may get them wrapped to protect the paint and extend their life.
Having multiple potential customer groups is one thing that makes mobile car wrapping a good business idea. Find out how WrapCo makes $70K a month (after starting with just a hundred bucks) in this interview:
#46 Handyman business
• Average Annual Revenue: $204K+ • Average Profit Margins: 5.4% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.7% • Best For: Repair and construction pros, makers, fixers, and people who like working with their hands
Becoming a handyman is consistently among the best local businesses to start with $10K or less. All you need are basic tools and a way to get to your customers.
Unlike other forms of construction, you don’t need to be a licensed contractor to work as a handyman. That said, getting your General Contractor License expands the types of jobs you can take and can prompt faster business growth.
Caleb Ingraham makes about $1,000 a day with his handyman business. Find out how he built it here:
#47 Painting business
• Average Annual Revenue: $76K+ • Average Profit Margins: 7.2% • Startup Cost: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: -2% • Best For: Artists and designers, people with contractor or construction experience
House painting is another excellent business idea for people who enjoy physical work. While having construction experience can help you build a client list, you definitely don’t need this background to get started.
This is also one of the most scalable businesses you can start with $10K. Doug Caris bought Arizona Painting Company in 2014 and has grown it to five locations with $2 million a year in revenue. Hear his advice in this interview:
#48 Research services
• Average Annual Revenue: $10M+ • Average Profit Margins: 26.88% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 2.2% • Best For: Data-driven entrepreneurs with strong organization, time management, and communication skills
Business leaders often need research for information on:
- Product features
- Market share
- Competitors
- Consumer opinions
Before they spend thousands on new market research, they will often pay people or other companies to review existing available materials. If that doesn’t work, they’ll hire market research firms to get the information for them.
While the average research services company makes $10M+ annually, the average market researcher only makes $68K per year, which means you’d need at least 50 people on your team to bring in the revenue of an average research company.
That said, all you need to start offering these services is access to the internet and a reliable computer. You can grow from there.
#49 Cell phone and electronics repair
• Average Annual Revenue: $560K+ • Average Profit Margins: 5.7% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.4% • Best For: Technology and repair pros, detail-focused and system-driven entrepreneurs
The average U.S. household had 22 connected devices in 2022. If you establish yourself as the go-to person to fix them, that’s a lot of repeat business you can secure from your customer base.
You don’t need to be an engineer to offer repair services, either. Joe of Joe’s Electronics Repair learned how to fix things by tinkering with broken items. Now, he runs a seven-figure repair shop:
#50 Dent removal service
• Average Annual Revenue: $268K+ • Average Profit Margins: 6.1% • Startup Cost: $100-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 2% • Best For: People who like working with their hands and talking to customers
Many dents can be removed with no more than a suction cup. All you have to do is:
- Watch some YouTube videos
- Print flyers
- Put the flyers on cars with small dings
#51 Tax preparation service
• Average Annual Revenue: $1.57M • Average Profit Margins: 18% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months (not including time training as a CPA) • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.7% • Best For: Certified accountants and tax professionals, people who are good with math, numbers, and finances
Everyone needs to file taxes—and almost nobody likes doing it. That makes tax prep an excellent new business for folks who are mathematically inclined.
You don’t need a special license to file simple personal returns. However, you do need to be an Enrolled Agent or CPA to file business taxes or offer other, more complex services.
That exam, along with a quality accounting software program, are the main expenses of starting a tax preparation service.
#52 Job search services
• Average Annual Revenue: $2.5M+ • Average Profit Margins: 26.88% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 3.6% • Best For: Recruiting and HR professionals, strong networkers and communicators
Something else just about everyone needs is employment, and most people dislike looking for a job even more than they dislike filing their taxes.
Some common business ideas related to job search services include:
- Resume and cover letter writing
- Interview preparation and practice
- Career coaching
- Personal recruiter
- Recruiting or staffing agency
Note that these companies must have multiple employees to be able to reach the average annual revenue listed above.
#53 Professional organizer
• Average Annual Revenue: $168K+ • Average Profit Margins: 10.6% • Startup Cost: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.2% • Best For: Neat freaks, people with strong empathy, communication, motivation, and organization skills
Being an organizer isn’t just about decluttering. These professionals also function as a kind of therapist, helping clients bring order to their thoughts and lives along with their spaces. If you have strengths in both areas, you can excel as a professional organizer.
#54 Personal stylist
• Average Annual Revenue: $114K+ • Average Profit Margins: 10.3% • Startup Cost: $500-$250K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 2% • Best For: Fashionable entrepreneurs with strong customer service skills
If you’re the type of person who always dresses for the latest trends, you can grow your own business helping others to do the same.
Social media marketing skills can be very helpful for building this kind of business. Build a reputation by offering fashion advice online to establish yourself as an expert and grow your client list.
#55 Makeup artist
• Average Annual Revenue: $51K+ • Average Profit Margins: 5% • Startup Cost: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.9% • Best For: Beauticians and visual artists who are excellent listeners and problem-solvers
Professional makeup artists aren’t just for celebrities. They also help people get ready for photo shoots or milestones like prom or weddings.
One thing to keep in mind: You may need to obtain a license as an esthetician or cosmetologist depending on where you live and the type of makeup you plan to do.
#56 Hair cutting or styling

• Average Annual Revenue: $51K+ • Average Profit Margins: 5% • Startup Cost: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.9% • Best For: Stylists and beauticians, detail-oriented people with strong communication and customer service skills
The great thing about cutting or styling hair is that it comes with built-in repeat business if you make your customers happy.
The biggest expense for most is the physical salon space. You can save money on startup costs by offering mobile services or renting a chair from existing businesses while you save up for your own space.
Learn how Bernard Franklin grew Busy B’s Barbershop to $130K a year in this interview:
#57 Massage therapy
• Average Annual Revenue: $78K+ • Average Profit Margins: 4.35% • Startup Cost: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 2.3% • Best For: Empathetic people with excellent communication skills and knowledge of physiology
You need a license in all 50 states to become a massage therapist.
Along with the $200-$300 for that education, you’ll need to budget around $2,000-$2,500 for a massage table and other equipment, but those are the only startup costs if you start out of your home or as a mobile business that meets clients where they are.
#58 Tailoring and clothing alterations
• Average Annual Revenue: $27K+ • Average Profit Margins: 8.3% • Startup Cost: $500-$250K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.6% • Best For: Detail-focused entrepreneurs, fashion and clothing experts who excel at listening and communication
Clothes are expensive, especially formal and professional attire. Tailors help people make the most of that expense by adjusting or repairing clothes to achieve a perfect fit.
The main things you’ll need to get started are:
- A sewing machine
- Work tables
- Measuring tools
- Fabric, thread, and other accessories
All told, you can get everything you need for around $1,500-$5,000.
#59 Valet parking services
• Average Annual Revenue: $1M+ • Average Profit Margins: 9.91% • Startup Cost: $100-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 7.2% • Best For: Excellent drivers with strong customer service skills
Valet services can be a very lucrative venture for people who live in urban areas or near event venues and tourist destinations where parking is at a premium.
Best of all, the startup costs are next to nothing. If you have a driver’s license, you can connect with local business owners to offer their customers valet service.
#60 Fashion designer
• Average Annual Revenue: $114K+ • Average Profit Margins: 10.3% • Startup Cost: $500-$250K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 2% • Best For: Tailors and sewing experts, fashionable and creative entrepreneurs
If you love fashion, you can start designing your own clothes and wearing them as free marketing. The sky’s the limit when it comes to earnings—the world’s richest fashion designer is worth over $10 billion!
You’ll need:
- Sewing machine
- Fabric – Find fabric at your local craft store or order from Amazon clearance rolls for savings .
- Fabric scissors – Our recommended scissors come with additional accessories including a measuring tape.
- Measuring tape
It helps to understand pattern-making. Many seamstresses offer skills classes to help people learn the basics or hone specific skills. Connect with a local seamstress if you need help gaining experience.
Afshan Abbas, the founder of Fuchsia Shoes, makes $60K a month designing sustainably made shoes. Check out our interview with her below.
Keep reading for more businesses to start with less than $10K.
#61 Freelance writer
• Average Annual Revenue: $712K • Average Profit Margins: 14.6% • Startup Cost: $100-$200 • Time to Revenue: 1 month to 3 years • Annual Market Growth Rate: -1.5% • Best For: Writers, editors, and other language experts
If you love writing, a copywriting service is one of the best online businesses to start. There’s plenty of work for a small business owner. Copywriting service is focused on:
- Writing content for businesses
- Reviewing content for grammatical errors and SEO for businesses
- Translation services if you are bilingual (or a ninja at Google Translate)
Use SurferSEO to optimize your writing for the web.
#62 Freelance editing and proofreading
• Average Annual Revenue: $25K+ • Average Profit Margins: 9% • Startup Cost: $100-$1K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.9% • Best For: Writers and language experts with a strong eye for detail
Another way to make money from your language skills is to edit things that other people write. If you’re an expert in grammar rules and have a sharp eye for spotting small errors, then editing can be a good business option.
#63 Web design business
• Average Annual Revenue: $239K+ • Average Profit Margins: 5.3% • Startup Cost: $100-$1K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.4% • Best For: Programmers, coders, and designers with strong time and task management skills
A website is a necessity for small businesses today—but most business owners aren’t web design experts.
If you are, you can build a successful online business offering web design services. You’ll be in especially high demand if you have skills like SEO-focused design, eCommerce design, or other niche expertise that can help drive more traffic to websites.
#64 Woodworking and furniture making
• Average Annual Revenue: $6.4M+ • Average Profit Margins: 8.53% • Startup Cost: $100-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.9% • Best For: Artistic entrepreneurs who like working with their hands
The woodworking industry in the U.S. is expected to surpass $291 billion in 2024, so there’s definitely a lot of profit potential for local business owners in this niche.
Woodworking equipment costs less than you might expect, too. You can get everything you need to start a business for around $3,500-$5,000.
The UpFlip blog post on how to start a woodworking business has more info on how to get started. Or you can watch this interview with Daniel Westbrook to find out how he started a $30K-a-month woodworking business:
Note that you’d need around 33 employees to meet the average revenue value listed above.
#65 Candle maker
• Average Annual Revenue: $60K-$120K • Average Profit Margins: 5-15% • Startup Cost: $100-$10K • Time to Revenue: 30-90 days • Annual Market Growth Rate: -9.3% • Best For: Creative people with strong sales, marketing, and customer service skills
Candle-making is super easy to start; you just need:
- 10 pounds of wax
- Pouring pitcher
- A pot to put the pitcher in to create a double boiler
- Thermometer
- Containers to hold the candles
- Scented fragrances
Check out how the owner of Blk Sunflower made $300K in 18 months by making and selling candles:
#66 Jewelry maker
• Average Annual Revenue: $114K+ • Average Profit Margins: 10.3% • Startup Cost: $500-$250K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 2.0% • Best For: People who are dextrous, creative, and have strong sales skills
Six of the top 10 Etsy sellers in 2022 were jewelry makers.
That’s both good news and bad news: There’s definitely a market, but you’ll also be up against a lot of competition from existing businesses.
Finding a unique niche or target audience is one way to stand out. Some popular types of jewelry that are affordable to make include:
- Morse code bracelets
- Upcycled jewelry made from found objects
- Stone pendants and necklaces
- Beaded necklaces
- Personalized charms or pendants
#67 Decorating services
• Average Annual Revenue: $168K+ • Average Profit Margins: 10.6% • Startup Cost: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.2% • Best For: Artists, designers, and other creative entrepreneurs
Interior designers, Christmas light hanging companies, and prop designers are all decorating services that you can make a great living offering. These types of jobs are great for creatives.
#68 Graphic design business
• Average Annual Revenue: $123K+ • Average Profit Margins: 13.5% • Startup Cost: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 2% • Best For: Tech-savvy visual artists
Graphic designers make images for websites, social media platforms, and marketing materials—and there’s a lot of demand for these services.
This is among the best businesses to start for creative people who want flexibility. You can build a graphic design business by:
- Creating custom images for clients based on their specifications
- Selling your graphics through a marketplace like Pixabay or Creative Market
- Selling items with your designs in a print-on-demand store
Whichever way you go, the startup costs are low.
#69 Photography business
• Average Annual Revenue: $50K • Average Profit Margins: 7.3% • Startup Cost: $1K-$10K • Time to Revenue: 1-6 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.3% • Best For: Visual artists, creative people with strong interpersonal skills
Most of the initial investment to start a photography business is buying professional cameras and camera equipment.
If you’re a hobbyist photographer and already have quality gear, you can get started for much less.
There are tons of niches in the photography industry, from portraits and art prints to ad copy photos. Choosing the right one for your skill set is the best way to set yourself up for success.
That’s how Mile High Productions built a $35K-a-month business doing drone photography for local real estate agents. See how they got started in this interview:
#70 Teach music lessons
• Average Annual Revenue: $18K+ • Average Profit Margins: 13.10% • Startup Cost: $100-$1K • to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 8.5% • Best For: Singers and musicians who are good communicators and motivators
If you know how to sing or play an instrument, you can start a business sharing that knowledge.
Most music lesson instructors charge $25-$50 for a half-hour lesson, so you can make a very good living as a music teacher if you can keep a full student list.
What business can I start with $10K that serves food?
A brick-and-mortar restaurant might be rather involved and costly, but there are other food business models that can be started for under $10K in most places. Major cities will normally have more stringent requirements that might include:
- A food handler card – Check for requirements in your area . Note that “Highly recommended” means not required.
- Health district inspections
- Additional insurance requirements
Let’s look at some attainable food businesses to start for under $10K.
#71 Start a food truck
• Average Annual Revenue: $41K+ • Average Profit Margins: 6.4% • Startup Cost: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.2% • est For: Cooks and food service pros with excellent customer service skills
A food truck is one of the most popular food business models because:
- Food trucks are less expensive than buying a restaurant.
- You don’t have to clean the dining room
- You don’t have to hire servers or hosts/hostesses
- You can go where your customers are
To keep it under $10K , you’ll need to start it with a used rig and limited menu, but it can be done.
Vet Chef started with more upfront but still has some great tips for you:
#72 Become the ice cream man
• Average Annual Revenue: $279K+ • Average Profit Margins: 3.7% • Startup Cost: $100-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.7% • Best For: Customer service pros who like driving
Almost everyone recognizes the sound of the ice cream man coming around the corner. Kids run out to it in droves and parents know they are about to spend money when they hear the familiar tune.
These trucks differ from food trucks because:
- The target market is kids,
- There are more seasonal fluctuations.
- You just need a freezer on wheels.
Keep reading for more food startup businesses to start with $10K.
#73 Meal prep company
• Average Annual Revenue: $21M+ • Average Profit Margins: 2.24% • Startup Cost: $500-$250K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 18.8% • Best For: System-driven chefs, cooks, and foodies
Hard-working families are often too busy to prepare their own home-cooked food. If you love cooking and want to make a great living, then start offering meal prep services.
- Create a menu.
- Market your meals.
- Buy in bulk.
- Offer pickup or delivery.
Check out Food Business Pros for information on how they make money running a food prep company .
You’ll need around 16 employees to make the average annual revenue listed above, as the revenue per employee across the industry is around $1.4 million.
Keep reading for another food idea that doesn’t cost more than $10K.
#74 Mobile food carts
• Average Annual Revenue: $41K+ • Average Profit Margins: 6.4% • Startup Cost: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.2% • Best For: Extroverted food pros with strong multitasking and sales skills
I’ve seen people in Las Vegas buy a rolling cooler, a bag of ice, and a 32-pack of water and then go sell it in parks, on the Strip, or on busy corners. They make their money back on the first 32-pack and then make $28 a case.
That’s the super cheap route, but you can go a more professional route by buying:
- A hot or cold mobile cart like the one pictured below
- A vehicle to transport the cart
- The food to serve
- Disposable serving utensils
Keep reading for more businesses to start with $10K!
#75 Catering

• Average Annual Revenue: $124K+ • Average Profit Margins: 5.5% • Startup Cost: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.0% • Best For: Cooks and chefs who are organized with strong project and time management skills
The catering industry is expected to reach $378.39 billion in 2026 with a CAGR of 8.2%.
People hire caterers for weddings, business meetings, and other events. You can get everything you need on Amazon and (depending on your area’s food-service rules and regulations) cook the food at home.
Make sure to have a great presentation because people paying for premium services expect the presentation to be exquisite.
#76 Be a baker
• Average Annual Revenue: $1.52M • Average Profit Margins: 5.4% • Startup Cost: $100-$3M • Time to Revenue: 1-6 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.1% • Best For: Food industry professionals who are creative, good with customers, and have strong math skills
Opening a brick-and-mortar bakery costs more than $10,000, but there are ways to get started with less.
Mignon Francois spent about $5 to start baking cupcakes. She used the profits from that first batch to make more, and grew a name doing cupcake catering until she saved up enough to open a storefront. Hear her advice in this interview:
#77 Make and sell artisanal foods
• Average Annual Revenue: $278K+ • Average Profit Margins: 16.33% • Startup Cost: $500-$250K • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: -0.8% • Best For: Creative foodies who are good at planning and marketing
You don’t need to open a restaurant to sell food you make to customers. Another option is to make things like candy, pickles, sauces, or other homemade foods.
The startup costs for this are lower if you don’t open a storefront right away. Instead, you can start an online store or sell in person at farmers markets and other pop-up events.
We’ve provided you with a list of 77 businesses that cost less than $10K to start.
If you want to jump in where someone else left off, look for liquidated inventory sales and going-out-of-business offers with existing businesses for sale under $10K.
We’re always looking for business owners to profile in our blogs and YouTube videos . What are some businesses you’ve seen started for under $10K?

How to Start a $100K/Year Massage Business (Step-By-Step Guide)
1. Make a Plan

How Do I Start a Massage Business?
Start-up costs.
- Training and Education
- Massage Room Décor
- Deposit (if you're opening an office)
- Equipment and Supplies (table, oils, stools, and sheets)
- Accountant or Accounting Software (QuickBooks)
- Marketing Materials
Ongoing costs
- Lease (if renting an office)
- Laundry and Cleaning
- Website, Phone, Internet
2. Purchase Equipment

What Equipment and Supplies Do I Need?
Choose safety, protect your body.
- Massage Table
- Massage Chair
- Linens and Towels (Have enough to change between each client)
- Oils, lotions (You may get a discount from a supplier if you purchase in bulk)
- Candles and Music
- Laundry and Cleaning Equipment
- Carrying Equipment
3. Licensing and Certification

License or Certification?
Defining license or certification, 4. training and education.
- National Holistic Institute
- National University of Health Sciences
- Myotherapy College of Utah
- Cortiva Institute Schools of Massage Therapy
Board Certification Training and Specialization

- Sports Massage
- Military Veteran Massage
- Oncology Massage
- Clinical Rehabilitative Massage
5. Location: Home or Office?

How do I Start a Massage Business from Home?
You need a big room, don't forget the other tasks, save money and be free.

How do I Start a Massage Business at an Office?
Rent a room, purchase later, where do i rent a massage therapy space.
- American Massage Therapy Association (AMTA)
- Associated Bodywork & Massage Professionals (ABMP)
6. Business Registration

What Type of Business is a Massage Business?
Local registration, 7. insurance, personal health insurance, 8. write a business plan.

- Market Analysis
- Marketing Plan
Personal Funds and Business Loans
Zero-interest credit card, 10. marketing.

- Squarespace
Scheduling Applications
- Hubspot Meetings Tool
Social Media

11. Customer Service
Create a stress-free environment., keep your hygiene in check., be personable, but don't be pushy, give clients self-care tips., 12. financial goals and massage business profits.

Cancellation Policy
Can you make good money as a massage therapist, 13. take care of your body.
nice work https://binarychemist.com/
My Name is PRETTY NGOMANE. A south African female. Aspiring to do farming. And finding a home away from home for the differently abled persons in their daily needs.
Become a business owner in less than 90 days
Start your 10-day free trial of the UpFlip Academy and learn how to start your own business from scratch.
Get business advice straight to your Inbox
START YOUR ECOMMERCE BUSINESS FOR JUST $1
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
A magazine for young entrepreneurs
The best advice in entrepreneurship
Subscribe for exclusive access, how to write a business plan (tips, templates, examples).

Written by Jesse Sumrak | May 14, 2023
Comments -->

Get real-time frameworks, tools, and inspiration to start and build your business. Subscribe here
Business plans might seem like an old-school stiff-collared practice, but they deserve a place in the startup realm, too. It’s probably not going to be the frame-worthy document you hang in the office—yet, it may one day be deserving of the privilege.
Whether you’re looking to win the heart of an angel investor or convince a bank to lend you money, you’ll need a business plan. And not just any ol’ notes and scribble on the back of a pizza box or napkin—you’ll need a professional, standardized report.
Bah. Sounds like homework, right?
Yes. Yes, it does.
However, just like bookkeeping, loan applications, and 404 redirects, business plans are an essential step in cementing your business foundation.
Don’t worry. We’ll show you how to write a business plan without boring you to tears. We’ve jam-packed this article with all the business plan examples, templates, and tips you need to take your non-existent proposal from concept to completion.
Table of Contents
What Is a Business Plan?
Tips to Make Your Small Business Plan Ironclad
How to Write a Business Plan in 6 Steps
Startup Business Plan Template
Business Plan Examples
Work on Making Your Business Plan
How to Write a Business Plan FAQs
What is a business plan why do you desperately need one.
A business plan is a roadmap that outlines:
- Who your business is, what it does, and who it serves
- Where your business is now
- Where you want it to go
- How you’re going to make it happen
- What might stop you from taking your business from Point A to Point B
- How you’ll overcome the predicted obstacles
While it’s not required when starting a business, having a business plan is helpful for a few reasons:
- Secure a Bank Loan: Before approving you for a business loan, banks will want to see that your business is legitimate and can repay the loan. They want to know how you’re going to use the loan and how you’ll make monthly payments on your debt. Lenders want to see a sound business strategy that doesn’t end in loan default.
- Win Over Investors: Like lenders, investors want to know they’re going to make a return on their investment. They need to see your business plan to have the confidence to hand you money.
- Stay Focused: It’s easy to get lost chasing the next big thing. Your business plan keeps you on track and focused on the big picture. Your business plan can prevent you from wasting time and resources on something that isn’t aligned with your business goals.
Beyond the reasoning, let’s look at what the data says:
- Simply writing a business plan can boost your average annual growth by 30%
- Entrepreneurs who create a formal business plan are 16% more likely to succeed than those who don’t
- A study looking at 65 fast-growth companies found that 71% had small business plans
- The process and output of creating a business plan have shown to improve business performance
Convinced yet? If those numbers and reasons don’t have you scrambling for pen and paper, who knows what will.
Don’t Skip: Business Startup Costs Checklist
Before we get into the nitty-gritty steps of how to write a business plan, let’s look at some high-level tips to get you started in the right direction:
Be Professional and Legit
You might be tempted to get cutesy or revolutionary with your business plan—resist the urge. While you should let your brand and creativity shine with everything you produce, business plans fall more into the realm of professional documents.
Think of your business plan the same way as your terms and conditions, employee contracts, or financial statements. You want your plan to be as uniform as possible so investors, lenders, partners, and prospective employees can find the information they need to make important decisions.
If you want to create a fun summary business plan for internal consumption, then, by all means, go right ahead. However, for the purpose of writing this external-facing document, keep it legit.
Know Your Audience
Your official business plan document is for lenders, investors, partners, and big-time prospective employees. Keep these names and faces in your mind as you draft your plan.
Think about what they might be interested in seeing, what questions they’ll ask, and what might convince (or scare) them. Cut the jargon and tailor your language so these individuals can understand.
Remember, these are busy people. They’re likely looking at hundreds of applicants and startup investments every month. Keep your business plan succinct and to the point. Include the most pertinent information and omit the sections that won’t impact their decision-making.
Invest Time Researching
You might not have answers to all the sections you should include in your business plan. Don’t skip over these!
Your audience will want:
- Detailed information about your customers
- Numbers and solid math to back up your financial claims and estimates
- Deep insights about your competitors and potential threats
- Data to support market opportunities and strategy
Your answers can’t be hypothetical or opinionated. You need research to back up your claims. If you don’t have that data yet, then invest time and money in collecting it. That information isn’t just critical for your business plan—it’s essential for owning, operating, and growing your company.
Stay Realistic
Your business may be ambitious, but reign in the enthusiasm just a teeny-tiny bit. The last thing you want to do is have an angel investor call BS and say “I’m out” before even giving you a chance.
The folks looking at your business and evaluating your plan have been around the block—they know a thing or two about fact and fiction. Your plan should be a blueprint for success. It should be the step-by-step roadmap for how you’re going from Point A to Point B.

How to Write a Business Plan—6 Essential Elements
Not every business plan looks the same, but most share a few common elements. Here’s what they typically include:
- Executive Summary
- Business Overview
- Products and Services
- Market Analysis
- Competitive Analysis
- Financial Strategy
Below, we’ll break down each of these sections in more detail.
1. Executive Summary
While your executive summary is the first page of your business plan, it’s the section you’ll write last. That’s because it summarizes your entire business plan into a succinct one-pager.
Begin with an executive summary that introduces the reader to your business and gives them an overview of what’s inside the business plan.
Your executive summary highlights key points of your plan. Consider this your elevator pitch. You want to put all your juiciest strengths and opportunities strategically in this section.
2. Business Overview
In this section, you can dive deeper into the elements of your business, including answering:
- What’s your business structure? Sole proprietorship, LLC, corporation, etc.
- Where is it located?
- Who owns the business? Does it have employees?
- What problem does it solve, and how?
- What’s your mission statement? Your mission statement briefly describes why you are in business. To write a proper mission statement, brainstorm your business’s core values and who you serve.
Don’t overlook your mission statement. This powerful sentence or paragraph could be the inspiration that drives an investor to take an interest in your business. Here are a few examples of powerful mission statements that just might give you the goosebumps:
- Patagonia: Build the best product, cause no unnecessary harm, use business to inspire and implement solutions to the environmental crisis.
- Tesla: To accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.
- InvisionApp : Question Assumptions. Think Deeply. Iterate as a Lifestyle. Details, Details. Design is Everywhere. Integrity.
- TED : Spread ideas.
- Warby Parker : To offer designer eyewear at a revolutionary price while leading the way for socially conscious businesses.
3. Products and Services
As the owner, you know your business and the industry inside and out. However, whoever’s reading your document might not. You’re going to need to break down your products and services in minute detail.
For example, if you own a SaaS business, you’re going to need to explain how this business model works and what you’re selling.
You’ll need to include:
- What services you sell: Describe the services you provide and how these will help your target audience.
- What products you sell: Describe your products (and types if applicable) and how they will solve a need for your target and provide value.
- How much you charge: If you’re selling services, will you charge hourly, per project, retainer, or a mixture of all of these? If you’re selling products, what are the price ranges?
4. Market Analysis
Your market analysis essentially explains how your products and services address customer concerns and pain points. This section will include research and data on the state and direction of your industry and target market.
This research should reveal lucrative opportunities and how your business is uniquely positioned to seize the advantage. You’ll also want to touch on your marketing strategy and how it will (or does) work for your audience.
Include a detailed analysis of your target customers. This describes the people you serve and sell your product to. Be careful not to go too broad here—you don’t want to fall into the common entrepreneurial trap of trying to sell to everyone and thereby not differentiating yourself enough to survive the competition.
The market analysis section will include your unique value proposition. Your unique value proposition (UVP) is the thing that makes you stand out from your competitors. This is your key to success.
If you don’t have a UVP, you don’t have a way to take on competitors who are already in this space. Here’s an example of an ecommerce internet business plan outlining their competitive edge:
FireStarters’ competitive advantage is offering product lines that make a statement but won’t leave you broke. The major brands are expensive and not distinctive enough to satisfy the changing taste of our target customers. FireStarters offers products that are just ahead of the curve and so affordable that our customers will return to the website often to check out what’s new.
5. Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis examines the strengths and weaknesses of competing businesses in your market or industry. This will include direct and indirect competitors. It can also include threats and opportunities, like economic concerns or legal restraints.
The best way to sum up this section is with a classic SWOT analysis. This will explain your company’s position in relation to your competitors.
6. Financial Strategy
Your financial strategy will sum up your revenue, expenses, profit (or loss), and financial plan for the future. It’ll explain how you make money, where your cash flow goes, and how you’ll become profitable or stay profitable.
This is one of the most important sections for lenders and investors. Have you ever watched Shark Tank? They always ask about the company’s financial situation. How has it performed in the past? What’s the ongoing outlook moving forward? How does the business plan to make it happen?
Answer all of these questions in your financial strategy so that your audience doesn’t have to ask. Go ahead and include forecasts and graphs in your plan, too:
- Balance sheet: This includes your assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Profit & Loss (P&L) statement: This details your income and expenses over a given period.
- Cash flow statement: Similar to the P&L, this one will show all cash flowing into and out of the business each month.
It takes cash to change the world—lenders and investors get it. If you’re short on funding, explain how much money you’ll need and how you’ll use the capital. Where are you looking for financing? Are you looking to take out a business loan, or would you rather trade equity for capital instead?
Read More: 16 Financial Concepts Every Entrepreneur Needs to Know
Startup Business Plan Template (Copy/Paste Outline)
Ready to write your own business plan? Copy/paste the startup business plan template below and fill in the blanks.
Executive Summary Remember, do this last. Summarize who you are and your business plan in one page.
Business Overview Describe your business. What’s it do? Who owns it? How’s it structured? What’s the mission statement?
Products and Services Detail the products and services you offer. How do they work? What do you charge?
Market Analysis Write about the state of the market and opportunities. Use date. Describe your customers. Include your UVP.
Competitive Analysis Outline the competitors in your market and industry. Include threats and opportunities. Add a SWOT analysis of your business.
Financial Strategy Sum up your revenue, expenses, profit (or loss), and financial plan for the future. If you’re applying for a loan, include how you’ll use the funding to progress the business.

5 Frame-Worthy Business Plan Examples
Want to explore other templates and examples? We got you covered. Check out these 5 business plan examples you can use as inspiration when writing your plan:
- SBA Wooden Grain Toy Company
- SBA We Can Do It Consulting
- OrcaSmart Business Plan Sample
- Plum Business Plan Template
- PandaDoc Free Business Plan Templates
Get to Work on Making Your Business Plan
If you find you’re getting stuck on perfecting your document, opt for a simple one-page business plan —and then get to work. You can always polish up your official plan later as you learn more about your business and the industry.
Remember, business plans are not a requirement for starting a business—they’re only truly essential if a bank or investor is asking for it.
Ask others to review your business plan. Get feedback from other startups and successful business owners. They’ll likely be able to see holes in your planning or undetected opportunities—just make sure these individuals aren’t your competitors (or potential competitors).
Your business plan isn’t a one-and-done report—it’s a living, breathing document. You’ll make changes to it as you grow and evolve. When the market or your customers change, your plan will need to change to adapt.
That means when you’re finished with this exercise, it’s not time to print your plan out and stuff it in a file cabinet somewhere. No, it should sit on your desk as a day-to-day reference. Use it (and update it) as you make decisions about your product, customers, and financial plan.
Review your business plan frequently, update it routinely, and follow the path you’ve developed to the future you’re building.
Keep Learning: New Product Development Process in 8 Easy Steps
What financial information should be included in a business plan?
Be as detailed as you can without assuming too much. For example, include your expected revenue, expenses, profit, and growth for the future.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when writing a business plan?
The most common mistake is turning your business plan into a textbook. A business plan is an internal guide and an external pitching tool. Cut the fat and only include the most relevant information to start and run your business.
Who should review my business plan before I submit it?
Co-founders, investors, or a board of advisors. Otherwise, reach out to a trusted mentor, your local chamber of commerce, or someone you know that runs a business.
Ready to Write Your Business Plan?
Don’t let creating a business plan hold you back from starting your business. Writing documents might not be your thing—that doesn’t mean your business is a bad idea.
Let us help you get started.
Join our free training to learn how to start an online side hustle in 30 days or less. We’ll provide you with a proven roadmap for how to find, validate, and pursue a profitable business idea (even if you have zero entrepreneurial experience).
Stuck on the ideas part? No problem. When you attend the masterclass, we’ll send you a free ebook with 100 of the hottest side hustle trends right now. It’s chock full of brilliant business ideas to get you up and running in the right direction.

About Jesse Sumrak
Jesse Sumrak is a writing zealot focused on creating killer content. He’s spent almost a decade writing about startup, marketing, and entrepreneurship topics, having built and sold his own post-apocalyptic fitness bootstrapped business. A writer by day and a peak bagger by night (and early early morning), you can usually find Jesse preparing for the apocalypse on a precipitous peak somewhere in the Rocky Mountains of Colorado.
Related Posts

What’s the Most Profitable Business to Start in 2024?

9 Best Businesses You Can Start with No Money

Is Selling On Amazon Worth it? Get Your Questions Answered

8 Businesses That Make Money Right Away (In 1-3 Months or Less)

How Much To Unapologetically Charge For Public Speaking

Write the Perfect Consulting Proposal: Tools, Examples, and a Template

How to Create an Online Course That Sells in 2024

I Used this Product Launch Checklist to Start 5 Ecom Brands

How to Get Sponsored: From 0 to $50,000 in 4 Weeks

How Shay Mitchell Is Disrupting a $17B Industry

MaryRuth Ghiyam: From $700K in Debt to $100M in Revenue

His Ecommerce Funnel Generated $70M Last Year

How Do You Launch a Product?

Why Erin Deering Sold Swimwear Sensation Triangl

How Suneera Madhani’s Rejected Pitch Led to a Billion-Dollar Startup
FREE TRAINING FROM LEGIT FOUNDERS
Actionable Strategies for Starting & Growing Any Business.
Don't Miss Out! Get Instant Access to foundr+ for Just $1!
1000+ lessons. customized learning. 30,000+ strong community..

Home > Business > Business Startup
How To Write a Business Plan

We are committed to sharing unbiased reviews. Some of the links on our site are from our partners who compensate us. Read our editorial guidelines and advertising disclosure .

Starting a business is a wild ride, and a solid business plan can be the key to keeping you on track. A business plan is essentially a roadmap for your business — outlining your goals, strategies, market analysis and financial projections. Not only will it guide your decision-making, a business plan can help you secure funding with a loan or from investors .
Writing a business plan can seem like a huge task, but taking it one step at a time can break the plan down into manageable milestones. Here is our step-by-step guide on how to write a business plan.
Table of contents
- Write your executive summary
- Do your market research homework
- Set your business goals and objectives
- Plan your business strategy
- Describe your product or service
- Crunch the numbers
- Finalize your business plan

By signing up I agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Step 1: Write your executive summary
Though this will be the first page of your business plan , we recommend you actually write the executive summary last. That’s because an executive summary highlights what’s to come in the business plan but in a more condensed fashion.
An executive summary gives stakeholders who are reading your business plan the key points quickly without having to comb through pages and pages. Be sure to cover each successive point in a concise manner, and include as much data as necessary to support your claims.
You’ll cover other things too, but answer these basic questions in your executive summary:
- Idea: What’s your business concept? What problem does your business solve? What are your business goals?
- Product: What’s your product/service and how is it different?
- Market: Who’s your audience? How will you reach customers?
- Finance: How much will your idea cost? And if you’re seeking funding, how much money do you need? How much do you expect to earn? If you’ve already started, where is your revenue at now?
Step 2: Do your market research homework
The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research . This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to gather this information. Your method may be formal or more casual, just make sure that you’re getting good data back.
This research will help you to understand the needs of your target market and the potential demand for your product or service—essential aspects of starting and growing a successful business.
Step 3: Set your business goals and objectives
Once you’ve completed your market research, you can begin to define your business goals and objectives. What is the problem you want to solve? What’s your vision for the future? Where do you want to be in a year from now?
Use this step to decide what you want to achieve with your business, both in the short and long term. Try to set SMART goals—specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound benchmarks—that will help you to stay focused and motivated as you build your business.
Step 4: Plan your business strategy
Your business strategy is how you plan to reach your goals and objectives. This includes details on positioning your product or service, marketing and sales strategies, operational plans, and the organizational structure of your small business.
Make sure to include key roles and responsibilities for each team member if you’re in a business entity with multiple people.
Step 5: Describe your product or service
In this section, get into the nitty-gritty of your product or service. Go into depth regarding the features, benefits, target market, and any patents or proprietary tech you have. Make sure to paint a clear picture of what sets your product apart from the competition—and don’t forget to highlight any customer benefits.
Step 6: Crunch the numbers
Financial analysis is an essential part of your business plan. If you’re already in business that includes your profit and loss statement , cash flow statement and balance sheet .
These financial projections will give investors and lenders an understanding of the financial health of your business and the potential return on investment.
You may want to work with a financial professional to ensure your financial projections are realistic and accurate.
Step 7: Finalize your business plan
Once you’ve completed everything, it's time to finalize your business plan. This involves reviewing and editing your plan to ensure that it is clear, concise, and easy to understand.
You should also have someone else review your plan to get a fresh perspective and identify any areas that may need improvement. You could even work with a free SCORE mentor on your business plan or use a SCORE business plan template for more detailed guidance.
Compare the Top Small-Business Banks
$0.00 | ||||||
$0.00 | ||||||
$0.00 | ||||||
$10.00 (waivable) | ||||||
$0.00 |
Data effective 1/10/23. At publishing time, rates, fees, and requirements are current but are subject to change. Offers may not be available in all areas.
The takeaway
Writing a business plan is an essential process for any forward-thinking entrepreneur or business owner. A business plan requires a lot of up-front research, planning, and attention to detail, but it’s worthwhile. Creating a comprehensive business plan can help you achieve your business goals and secure the funding you need.
Related content
- 5 Best Business Plan Software and Tools in 2023 for Your Small Business
- How to Get a Business License: What You Need to Know
- What Is a Cash Flow Statement?
Best Small Business Loans

5202 W Douglas Corrigan Way Salt Lake City, UT 84116
Accounting & Payroll
Point of Sale
Payment Processing
Inventory Management
Human Resources
Other Services
Best Inventory Management Software
Best Small Business Accounting Software
Best Payroll Software
Best Mobile Credit Card Readers
Best POS Systems
Best Tax Software
Stay updated on the latest products and services anytime anywhere.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Disclaimer: The information featured in this article is based on our best estimates of pricing, package details, contract stipulations, and service available at the time of writing. All information is subject to change. Pricing will vary based on various factors, including, but not limited to, the customer’s location, package chosen, added features and equipment, the purchaser’s credit score, etc. For the most accurate information, please ask your customer service representative. Clarify all fees and contract details before signing a contract or finalizing your purchase.
Our mission is to help consumers make informed purchase decisions. While we strive to keep our reviews as unbiased as possible, we do receive affiliate compensation through some of our links. This can affect which services appear on our site and where we rank them. Our affiliate compensation allows us to maintain an ad-free website and provide a free service to our readers. For more information, please see our Privacy Policy Page . |
© Business.org 2024 All Rights Reserved.
- Design for Business
- Most Recent
- Presentations
- Infographics
- Data Visualizations
- Forms and Surveys
- Video & Animation
- Case Studies
- Digital Marketing
- Design Inspiration
- Visual Thinking
- Product Updates
- Visme Webinars
- Artificial Intelligence

How to Write a Business Plan: Beginner’s Guide (& Templates)

Written by: Chloe West

Thinking about starting a business? One of the first steps you’ll need to take is to write a business plan. A business plan can help guide you through your financial planning, marketing strategy, unique selling point and more.
Making sure you start your new business off on the right foot is key, and we’re here to help. We’ve put together this guide to help you write your first business plan. Or, you can skip the guide and dive right into a business plan template .
Ready to get started?
Here’s a short selection of 8 easy-to-edit business plan templates you can edit, share and download with Visme. View more templates below:

8-Step Process for Writing a Business Plan
What is a business plan, why is a business plan important, step #1: write your executive summary, step #2: put together your company description, step #3: conduct your market analysis, step #4: research your competition, step #5: outline your products or services, step #6: summarize your financial plan, step #7: determine your marketing strategy, step #8: showcase your organizational chart, 14 business plan templates to help you get started.
A business plan is a document that helps potential new business owners flesh out their business idea and put together a bird’s eye view of their business. Writing a business plan is an essential step in any startup’s ideation process.
Business plans help determine demographics, market analysis, competitive analysis, financial projections, new products or services, and so much more.
Each of these bits of information are important to have on hand when you’re trying to start a business or pitching investors for funds.
Here’s an example of a business plan that you can customize to incorporate your own business information.

We’re going to walk you through some of the most important parts of your business plan as well as how to write your own business plan in 8 easy steps.
If you’re in the beginning stages of starting a business , you might be wondering if it’s really worth your time to write out your business plan.
We’re here to tell you that it is.
A business plan is important for a number of reasons, but mostly because it helps to set you up for success right from the start.
Here are four reasons to prove to you why you need to start your business off on the right foot with a plan.
Reason #1: Set Realistic Goals and Milestones
Putting together a business plan helps you to set your objectives for growth and make realistic goals while you begin your business.
By laying out each of the steps you need to take in order to build a successful business, you’re able to be more reasonable about what your timeline is for achieving everything as well as what your financial projections are.
The best way to set goals is using the SMART goals guidelines, outlined below.

Reason #2: Grow Your Business Faster
Having a business plan helps you be more organized and strategic, improving the overall performance of your business as you start out. In fact, one study found that businesses with a plan grow 30% faster than businesses that don’t.
Doesn’t that sound reason enough alone to start out your business venture with a solidified plan? We thought so too, but we’ve still got two more reasons.
Reason #3: Minimize Risk
Starting a new business is uncharted territory. However, when you start with a roadmap for your journey, it makes it easier to see success and minimize the risks that come with startups.
Minimize risk and maximize profitability by documenting the most important parts of your business planning.
Reason #4: Secure Funding
And finally, our last reason that business plans are so important is that if you plan to pitch investors for funding for your new venture, they’re almost always going to want to see a detailed business plan before deciding whether or not to invest.
You can easily create your business plan and investor pitch deck right here with Visme. Just sign up for a free account below to get started.
Hey executives! Looking to cut design costs?
- Spend less time on presentations and more time strategizing
- Ensure your brand looks and feels visually consistent across all your organization's documents
- Impress clients and stakeholders with boardroom ready presentations
Sign up. It’s free.

The executive summary is a brief overview of your entire business plan, giving anyone who reads through your document a quick understanding of what they’re going to learn about your business idea.
However, you need to remember that some of the people who are going to read your business plan don’t want to or have time to read the entire thing. So your executive summary needs to incorporate all of the most important aspects of your plan.
Here’s an example of an executive summary from a business plan template you can customize and turn into your own.

Your executive summary should include:
- Key objective(s)
- Market research
- Competitor information
- Products/services
- Value proposition
- Overview of your financial plan
- How you’re going to actually start your business
One thing to note is that you should actually write your executive summary after the rest of your business plan so that you can properly summarize everything you’ve already created.
So at this point, simply leave a page blank for your executive summary so you can come back to it at the end of your business plan.

The next step is to write out a full description of your business and its core offerings. This section of your business plan should include your mission statement and objectives, along with your company history or overview.
In this section, you may also briefly describe your business formation details from a legal perspective.
Mission Statement
Don’t spend too much time trying to craft this. Your mission statement is a simple “why” you started this business. What are you trying to achieve? Or what does your business solve?
This can be anything from one single quote or a paragraph, but it doesn’t need to be much longer than that. In fact, this could be very similar to your value proposition.

What are your goals? What do you plan to achieve in the first 90 days or one year of your business? What kind of impact do you hope to make on the market?
These are all good points to include in your objectives section so anyone reading your business plan knows upfront what you hope to achieve.
History or Overview
If you’re not launching a brand new business or if you’ve previously worked on another iteration of this business, let potential investors know the history of your company.
If not, simply provide an overview of your business, sharing what it does or what it will do.

Your third step is to conduct a market analysis so you know how your business will fit into its target market. This page in your business plan is simply meant to summarize your findings. Most of your time should be spent actually doing the research.
Your market analysis needs to look at things like:
- Market size, and if it’s grown in recent years or shrinking
- The segment of the market you plan to target
- Demographics and behavior of your target audience
- The demand for your product or service
- Your competitive advantage or differentiation strategy
- The average price of your product or service
Put together a summary of your market analysis and industry research in a 1-2 page format, like we see below.

Your next step is to conduct a competitive analysis. While you likely touched on this briefly during your market analysis, now is the time to do a deep dive so that you have a good grasp on what your competitors are doing and how they are generating customers.
Start by creating a profile of all your existing competitors, or at the very least, your closest competitors – the ones who are offering very similar products or services to you, or are in a similar vicinity (if you’re opening a brick and mortar store).
Focus on their strengths and what they’re doing really well so that you can emulate their best qualities in your own way. Then, look at their weaknesses and what your business can do better.
Take note of their current marketing strategy, including the outlets you see a presence, whether it’s on social media, you hear a radio ad, you see a TV ad, etc. You won’t always find all of their marketing channels, but see what you can find online and on their website.

After this, take a minute to identify potential competitors based on markets you might try out in the future, products or services you plan to add to your offerings, and more.
Then put together a page or two in your business plan that highlights your competitive advantage and how you’ll be successful breaking into the market.
Step five is to dedicate a page to the products or services that your business plans to offer.
Put together a quick list and explanation of what each of the initial product or service offerings will be, but steer clear of industry jargon or buzzwords. This should be written in plain language so anyone reading has a full understanding of what your business will do.

You can have a simple list like we see in the sample page above, or you can dive a little deeper. Depending on your type of business, it might be a good idea to provide additional information about what each product or service entails.
The next step is to work on the financial data of your new business. What will your overhead be? How will your business make money? What are your estimated expenses and profits over the first few months to a year? The expenses should cover all the spending whether they are recurring costs or just one-time LLC filing fees .
There is so much that goes into your financial plan for a new business, so this is going to take some time to compile. Especially because this section of your business plan helps potential cofounders or investors understand if the idea is even viable.

Your financial plan should include at least five major sections:
- Sales Forecast: The first thing you want to include is a forecast or financial projection of how much you think your business can sell over the next year or so. Break this down into the different products, services or facets of your business.
- Balance Sheet: This section is essentially a statement of your company’s financial position. It includes existing assets, liabilities and equity to demonstrate the company’s overall financial health.
- Income Statement: Also known as a profit and loss statement (P&L), this covers your projected expenses and revenue, showcasing whether your business will be profitable or not.
- Operating Budget: A detailed outline of your business’s income and expenses. This should showcase that your business is bringing in more than it’s spending.
- Cash Flow Statements: This tracks how much cash your business has at any given point, regardless of whether customers or clients have paid their bills or have 30-60+ days to do so.
While these are the most common financial statements, you may discover that there are other sections that you want to include or that lenders may want to see from you.
You can automate the process of looking through your documents with an OCR API , which will collect the data from all your financial statements and invoices.
The next step is coming up with a successful marketing plan so that you can actually get the word out about your business.
Throughout your business plan, you’ve already researched your competitors and your target market, both of which are major components of a good marketing strategy. You need to know who you’re marketing to, and you want to do it better than your competition.

On this page or throughout this section of your business plan, you need to focus on your chosen marketing channels and the types of marketing content you plan to create.
Start by taking a look at the channels that your competitors are on and make sure you have a good understanding of the demographics of each channel as well. You don’t want to waste time on a marketing channel that your target audience doesn’t use.
Then, create a list of each of your planned marketing avenues. It might look something like:
- Social media ( Facebook, Instagram, Pinterest)
- Email newsletter
- Digital ads
Depending on the type of business you’re starting, this list could change quite a bit — and that’s okay. There is no one-size-fits-all marketing strategy, and you need to find the one that brings in the highest number of potential customers.
Your last section will be all about your leadership and management team members. Showcasing that you have a solid team right from the start can make potential investors feel better about funding your venture.
You can easily put together an organizational chart like the one below, with the founder/CEO at the top and each of your team leaders underneath alongside the department they’re in charge of.

Simply add an organizational chart like this as a page into your overall business plan and make sure it matches the rest of your design to create a cohesive document.
If you want to create a good business plan that sets your new business up for success and attracts new investors, it’s a good idea to start with a template.
We’ve got 14 options below from a variety of different industries for you to choose from. You can customize every aspect of each template to fit your business branding and design preferences.
Template #1: Photography Business Plan Template

This feminine and minimalistic business plan template is perfect for getting started with any kind of creative business. Utilize this template to help outline the step-by-step process of getting your new business idea up and running.
Template #2: Real Estate Business Plan Template

Looking for a more modern business plan design? This template is perfect for plainly laying out each of your business plans in an easy-to-understand format. Adjust the red accents with your business’s colors to personalize this template.
Template #3: Nonprofit Business Plan Template

Creating a business and marketing plan for your nonprofit is still an essential step when you’re just starting out. You need to get the word out to increase donations and awareness for your cause.
Template #4: Restaurant Business Plan Template

If your business plan needs to rely heavily on showcasing photos of your products (like food), this template is perfect for you. Get potential investors salivating at the sight of your business plan, and they’re sure to provide the capital you need.
Template #5: Fashion Business Plan Template

Serifs are in. Utilize this template with stunning serif as all the headers to create a contemporary and trendy business plan design that fits your business. Adjust the colors to match your brand and easily input your own content.
Template #6: Daycare Business Plan Template

Creating a more kid-friendly or playful business? This business plan template has bold colors and design elements that will perfectly represent your business and its mission.
Use the pages you need, and remove any that you don’t. You can also duplicate pages and move the elements around to add even more content to your business plan.
Template #7: Consulting Business Plan Template

This classic business plan template is perfect for a consulting business that wants to use a stunning visual design to talk about its services.
Template #8: Coffee Shop Business Plan Template

Customize this coffee shop business plan template to match your own business idea. Adjust the colors to fit your brand or industry, replace photos with your own photography or stock photos that represent your business, and insert your own logo, fonts and colors throughout.
Template #9: SaaS Business Plan Template

A SaaS or service-based company also needs a solid business plan that lays out its financials, list of services, target market and more. This template is the perfect starting point.
Template #10: Small Business Plan Template

Every startup or small business needs to start out with a strong business plan in order to start off on the right foot and set yourself up for success. This template is an excellent starting point for any small business.
Template #11: Ecommerce Business Plan Template

An ecommerce business plan is ideal for planning out your pricing strategy of all of your online products, as well as the site you plan to use for setting up your store, whether WordPress, Shopify, Wix or something else.
Template #12: Startup Business Plan Template

Customize this template and make it your own! Edit and Download
This is another generic business plan template for any type of startup to customize. Switch out the content, fonts and colors to match your startup branding and increase brand equity.
Template #13: One-Page Business Plan Template

Want just a quick business plan to get your idea going before you bite the bullet and map out your entire plan? This one-page template is perfect for those just starting to flesh out a new business idea.
Template #14: Salon Business Plan Template

This salon business plan template is easy on the design and utilizes a light color scheme to put more focus on the actual content. You can use the design as is or keep it as a basis for your own design elements.
Create Your Own Business Plan Today
Ready to write your business plan? Once you’ve created all of the most important sections, get started with a business plan template to really wow your investors and organize your startup plan.
Design beautiful visual content you can be proud of.

Trusted by leading brands
Recommended content for you:

Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
About the Author
Chloe West is the content marketing manager at Visme. Her experience in digital marketing includes everything from social media, blogging, email marketing to graphic design, strategy creation and implementation, and more. During her spare time, she enjoys exploring her home city of Charleston with her son.
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
| Function | Audience | Type of Business Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Serve as a loose guide of objectives and timeline | Internal | Lean |
| Serve as a detailed, brass-tacks blueprint of business goals and timeline | Internal | Traditional |
| Serve as a strategic document with a narrative focus on organization-wide goals, priorities, and vision | Internal | Strategic |
| Earn a company loan or grant | External | Traditional (with focus on financial documents) |
| Attract investors or partners | External | Traditional/strategic (with focus on financials, as well as support departments, such as marketing, sales, product, etc.) |
| To test a business or startup idea | Internal | Lean |
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
What is a Business Plan? Definition and Resources

9 min. read
Updated May 10, 2024
If you’ve ever jotted down a business idea on a napkin with a few tasks you need to accomplish, you’ve written a business plan — or at least the very basic components of one.
The origin of formal business plans is murky. But they certainly go back centuries. And when you consider that 20% of new businesses fail in year 1 , and half fail within 5 years, the importance of thorough planning and research should be clear.
But just what is a business plan? And what’s required to move from a series of ideas to a formal plan? Here we’ll answer that question and explain why you need one to be a successful business owner.
- What is a business plan?

A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business.
Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research , analyze their competitors , validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition .
The business plan captures that opportunity you see for your company: it describes your product or service and business model , and the target market you’ll serve.
It also includes details on how you’ll execute your plan: how you’ll price and market your solution and your financial projections .
Reasons for writing a business plan
If you’re asking yourself, ‘Do I really need to write a business plan?’ consider this fact:
Companies that commit to planning grow 30% faster than those that don’t.
Creating a business plan is crucial for businesses of any size or stage. It helps you develop a working business and avoid consequences that could stop you before you ever start.
If you plan to raise funds for your business through a traditional bank loan or SBA loan , none of them will want to move forward without seeing your business plan. Venture capital firms may or may not ask for one, but you’ll still need to do thorough planning to create a pitch that makes them want to invest.
But it’s more than just a means of getting your business funded . The plan is also your roadmap to identify and address potential risks.
It’s not a one-time document. Your business plan is a living guide to ensure your business stays on course.
Related: 14 of the top reasons why you need a business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
What research shows about business plans
Numerous studies have established that planning improves business performance:
- 71% of fast-growing companies have business plans that include budgets, sales goals, and marketing and sales strategies.
- Companies that clearly define their value proposition are more successful than those that can’t.
- Companies or startups with a business plan are more likely to get funding than those without one.
- Starting the business planning process before investing in marketing reduces the likelihood of business failure.
The planning process significantly impacts business growth for existing companies and startups alike.
Read More: Research-backed reasons why writing a business plan matters
When should you write a business plan?
No two business plans are alike.
Yet there are similar questions for anyone considering writing a plan to answer. One basic but important question is when to start writing it.
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business.
But the reality can be more nuanced – it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written.
Ideal times to write a business plan include:
- When you have an idea for a business
- When you’re starting a business
- When you’re preparing to buy (or sell)
- When you’re trying to get funding
- When business conditions change
- When you’re growing or scaling your business
Read More: The best times to write or update your business plan
How often should you update your business plan?
As is often the case, how often a business plan should be updated depends on your circumstances.
A business plan isn’t a homework assignment to complete and forget about. At the same time, no one wants to get so bogged down in the details that they lose sight of day-to-day goals.
But it should cover new opportunities and threats that a business owner surfaces, and incorporate feedback they get from customers. So it can’t be a static document.
Related Reading: 5 fundamental principles of business planning
For an entrepreneur at the ideation stage, writing and checking back on their business plan will help them determine if they can turn that idea into a profitable business .
And for owners of up-and-running businesses, updating the plan (or rewriting it) will help them respond to market shifts they wouldn’t be prepared for otherwise.
It also lets them compare their forecasts and budgets to actual financial results. This invaluable process surfaces where a business might be out-performing expectations and where weak performance may require a prompt strategy change.
The planning process is what uncovers those insights.
Related Reading: 10 prompts to help you write a business plan with AI
- How long should your business plan be?
Thinking about a business plan strictly in terms of page length can risk overlooking more important factors, like the level of detail or clarity in the plan.
Not all of the plan consists of writing – there are also financial tables, graphs, and product illustrations to include.
But there are a few general rules to consider about a plan’s length:
- Your business plan shouldn’t take more than 15 minutes to skim.
- Business plans for internal use (not for a bank loan or outside investment) can be as short as 5 to 10 pages.
A good practice is to write your business plan to match the expectations of your audience.
If you’re walking into a bank looking for a loan, your plan should match the formal, professional style that a loan officer would expect . But if you’re writing it for stakeholders on your own team—shorter and less formal (even just a few pages) could be the better way to go.
The length of your plan may also depend on the stage your business is in.
For instance, a startup plan won’t have nearly as much financial information to include as a plan written for an established company will.
Read More: How long should your business plan be?
What information is included in a business plan?
The contents of a plan business plan will vary depending on the industry the business is in.
After all, someone opening a new restaurant will have different customers, inventory needs, and marketing tactics to consider than someone bringing a new medical device to the market.
But there are some common elements that most business plans include:
- Executive summary: An overview of the business operation, strategy, and goals. The executive summary should be written last, despite being the first thing anyone will read.
- Products and services: A description of the solution that a business is bringing to the market, emphasizing how it solves the problem customers are facing.
- Market analysis: An examination of the demographic and psychographic attributes of likely customers, resulting in the profile of an ideal customer for the business.
- Competitive analysis: Documenting the competitors a business will face in the market, and their strengths and weaknesses relative to those competitors.
- Marketing and sales plan: Summarizing a business’s tactics to position their product or service favorably in the market, attract customers, and generate revenue.
- Operational plan: Detailing the requirements to run the business day-to-day, including staffing, equipment, inventory, and facility needs.
- Organization and management structure: A listing of the departments and position breakdown of the business, as well as descriptions of the backgrounds and qualifications of the leadership team.
- Key milestones: Laying out the key dates that a business is projected to reach certain milestones , such as revenue, break-even, or customer acquisition goals.
- Financial plan: Balance sheets, cash flow forecast , and sales and expense forecasts with forward-looking financial projections, listing assumptions and potential risks that could affect the accuracy of the plan.
- Appendix: All of the supporting information that doesn’t fit into specific sections of the business plan, such as data and charts.
Read More: Use this business plan outline to organize your plan
- Different types of business plans
A business plan isn’t a one-size-fits-all document. There are numerous ways to create an effective business plan that fits entrepreneurs’ or established business owners’ needs.
Here are a few of the most common types of business plans for small businesses:
- One-page plan : Outlining all of the most important information about a business into an adaptable one-page plan.
- Growth plan : An ongoing business management plan that ensures business tactics and strategies are aligned as a business scales up.
- Internal plan : A shorter version of a full business plan to be shared with internal stakeholders – ideal for established companies considering strategic shifts.
Business plan vs. operational plan vs. strategic plan
- What questions are you trying to answer?
- Are you trying to lay out a plan for the actual running of your business?
- Is your focus on how you will meet short or long-term goals?
Since your objective will ultimately inform your plan, you need to know what you’re trying to accomplish before you start writing.
While a business plan provides the foundation for a business, other types of plans support this guiding document.
An operational plan sets short-term goals for the business by laying out where it plans to focus energy and investments and when it plans to hit key milestones.
Then there is the strategic plan , which examines longer-range opportunities for the business, and how to meet those larger goals over time.
Read More: How to use a business plan for strategic development and operations
- Business plan vs. business model
If a business plan describes the tactics an entrepreneur will use to succeed in the market, then the business model represents how they will make money.
The difference may seem subtle, but it’s important.
Think of a business plan as the roadmap for how to exploit market opportunities and reach a state of sustainable growth. By contrast, the business model lays out how a business will operate and what it will look like once it has reached that growth phase.
Learn More: The differences between a business model and business plan
- Moving from idea to business plan
Now that you understand what a business plan is, the next step is to start writing your business plan .
The best way to start is by reviewing examples and downloading a business plan template. These resources will provide you with guidance and inspiration to help you write a plan.
We recommend starting with a simple one-page plan ; it streamlines the planning process and helps you organize your ideas. However, if one page doesn’t fit your needs, there are plenty of other great templates available that will put you well on your way to writing a useful business plan.
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- Reasons to write a business plan
- Business planning research
- When to write a business plan
- When to update a business plan
- Information to include
- Business vs. operational vs. strategic plans
Related Articles

6 Min. Read
How to Write an Ice Cream Shop Business Plan + Free Sample Plan PDF

5 Min. Read
Business Plan Vs Strategic Plan Vs Operational Plan—Differences Explained

4 Min. Read
10 Business Plan Myths That Hurt Your Business

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

Free Business Plan Template for Small Businesses (2024)
Use this free business plan template to write your business plan quickly and efficiently.
A good business plan is essential to successfully starting your business — and the easiest way to simplify the work of writing a business plan is to start with a business plan template.
You’re already investing time and energy in refining your business model and planning your launch—there’s no need to reinvent the wheel when it comes to writing a business plan. Instead, to help build a complete and effective plan, lean on time-tested structures created by other entrepreneurs and startups.
Ahead, learn what it takes to create a solid business plan and download Shopify's free business plan template to get started on your dream today.
What this free business plan template includes
- Executive summary
- Company overview
- Products or services offered
- Market analysis
- Marketing plan
- Logistics and operations plan
- Financial plan
This business plan outline is designed to ensure you’re thinking through all of the important facets of starting a new business. It’s intended to help new business owners and entrepreneurs consider the full scope of running a business and identify functional areas they may not have considered or where they may need to level up their skills as they grow.
That said, it may not include the specific details or structure preferred by a potential investor or lender. If your goal with a business plan is to secure funding , check with your target organizations—typically banks or investors—to see if they have business plan templates you can follow to maximize your chances of success.
Our free business plan template includes seven key elements typically found in the traditional business plan format:
1. Executive summary
This is a one-page summary of your whole plan, typically written after the rest of the plan is completed. The description section of your executive summary will also cover your management team, business objectives and strategy, and other background information about the brand.
2. Company overview
This section of your business plan will answer two fundamental questions: “Who are you?” and “What do you plan to do?” Answering these questions clarifies why your company exists, what sets it apart from others, and why it’s a good investment opportunity. This section will detail the reasons for your business’s existence, its goals, and its guiding principles.
3. Products or services offered
What you sell and the most important features of your products or services. It also includes any plans for intellectual property, like patent filings or copyright. If you do market research for new product lines, it will show up in this section of your business plan.
4. Market analysis
This section includes everything from estimated market size to your target markets and competitive advantage. It’ll include a competitive analysis of your industry to address competitors’ strengths and weaknesses. Market research is an important part of ensuring you have a viable idea.
5. Marketing plan
How you intend to get the word out about your business, and what strategic decisions you’ve made about things like your pricing strategy. It also covers potential customers’ demographics, your sales plan, and your metrics and milestones for success.
6. Logistics and operations plan
Everything that needs to happen to turn your raw materials into products and get them into the hands of your customers.
7. Financial plan
It’s important to include a look at your financial projections, including both revenue and expense projections. This section includes templates for three key financial statements: an income statement, a balance sheet, and a cash-flow statement . You can also include whether or not you need a business loan and how much you’ll need.
Business plan examples
What do financial projections look like on paper? How do you write an executive summary? What should your company description include? Business plan examples can help answer some of these questions and transform your business idea into an actionable plan.
Professional business plan example
Inside our template, we’ve filled out a sample business plan featuring a fictional ecommerce business .
The sample is set up to help you get a sense of each section and understand how they apply to the planning and evaluation stages of a business plan. If you’re looking for funding, this example won’t be a complete or formal look at business plans, but it will give you a great place to start and notes about where to expand.

Lean business plan example
A lean business plan format is a shortened version of your more detailed business plan. It’s helpful when modifying your plan for a specific audience, like investors or new hires.
Also known as a one-page business plan, it includes only the most important, need-to-know information, such as:
- Company description
- Key members of your team
- Customer segments
💡 Tip: For a step-by-step guide to creating a lean business plan (including a sample business plan), read our guide on how to create a lean business plan .

Benefits of writing a solid business plan
It’s tempting to dive right into execution when you’re excited about a new business or side project, but taking the time to write a thorough business plan and get your thoughts on paper allows you to do a number of beneficial things:
- Test the viability of your business idea. Whether you’ve got one business idea or many, business plans can make an idea more tangible, helping you see if it’s truly viable and ensure you’ve found a target market.
- Plan for your next phase. Whether your goal is to start a new business or scale an existing business to the next level, a business plan can help you understand what needs to happen and identify gaps to address.
- Clarify marketing strategy, goals, and tactics. Writing a business plan can show you the actionable next steps to take on a big, abstract idea. It can also help you narrow your strategy and identify clear-cut tactics that will support it.
- Scope the necessary work. Without a concrete plan, cost overruns and delays are all but certain. A business plan can help you see the full scope of work to be done and adjust your investment of time and money accordingly.
- Hire and build partnerships. When you need buy-in from potential employees and business partners, especially in the early stages of your business, a clearly written business plan is one of the best tools at your disposal. A business plan provides a refined look at your goals for the business, letting partners judge for themselves whether or not they agree with your vision.
- Secure funds. Seeking financing for your business—whether from venture capital, financial institutions, or Shopify Capital —is one of the most common reasons to create a business plan.
Why you should you use a template for a business plan
A business plan can be as informal or formal as your situation calls for, but even if you’re a fan of the back-of-the-napkin approach to planning, there are some key benefits to starting your plan from an existing outline or simple business plan template.
No blank-page paralysis
A blank page can be intimidating to even the most seasoned writers. Using an established business planning process and template can help you get past the inertia of starting your business plan, and it allows you to skip the work of building an outline from scratch. You can always adjust a template to suit your needs.
Guidance on what to include in each section
If you’ve never sat through a business class, you might never have created a SWOT analysis or financial projections. Templates that offer guidance—in plain language—about how to fill in each section can help you navigate sometimes-daunting business jargon and create a complete and effective plan.
Knowing you’ve considered every section
In some cases, you may not need to complete every section of a startup business plan template, but its initial structure shows you you’re choosing to omit a section as opposed to forgetting to include it in the first place.
Tips for creating a successful business plan
There are some high-level strategic guidelines beyond the advice included in this free business plan template that can help you write an effective, complete plan while minimizing busywork.
Understand the audience for your plan
If you’re writing a business plan for yourself in order to get clarity on your ideas and your industry as a whole, you may not need to include the same level of detail or polish you would with a business plan you want to send to potential investors. Knowing who will read your plan will help you decide how much time to spend on it.
Know your goals
Understanding the goals of your plan can help you set the right scope. If your goal is to use the plan as a roadmap for growth, you may invest more time in it than if your goal is to understand the competitive landscape of a new industry.
Take it step by step
Writing a 10- to 15-page document can feel daunting, so try to tackle one section at a time. Select a couple of sections you feel most confident writing and start there—you can start on the next few sections once those are complete. Jot down bullet-point notes in each section before you start writing to organize your thoughts and streamline the writing process.
Maximize your business planning efforts
Planning is key to the financial success of any type of business , whether you’re a startup, non-profit, or corporation.
To make sure your efforts are focused on the highest-value parts of your own business planning, like clarifying your goals, setting a strategy, and understanding the target market and competitive landscape, lean on a business plan outline to handle the structure and format for you. Even if you eventually omit sections, you’ll save yourself time and energy by starting with a framework already in place.
- How to Start an Online Boutique- A Complete Playbook
- How To Source Products To Sell Online
- The Ultimate Guide To Dropshipping (2024)
- How to Start a Dropshipping Business- A Complete Playbook for 2024
- 6 Creative Ways to Start a Business With No Money in 2024
- What is Shopify and How Does it Work?
- What Is Affiliate Marketing and How to Get Started
- How to Price Your Products in 3 Simple Steps
- 10 Common Small Business Mistakes to Avoid
- How to Turn a Hobby into a Business in 8 Steps
Business plan template FAQ
What is the purpose of a business plan.
The purpose of your business plan is to describe a new business opportunity or an existing one. It clarifies the business strategy, marketing plan, financial forecasts, potential providers, and more information about the company.
How do I write a simple business plan?
- Choose a business plan format, such as a traditional or a one-page business plan.
- Find a business plan template.
- Read through a business plan sample.
- Fill in the sections of your business plan.
What is the best business plan template?
If you need help writing a business plan, Shopify’s template is one of the most beginner-friendly options you’ll find. It’s comprehensive, well-written, and helps you fill out every section.
What are the 5 essential parts of a business plan?
The five essential parts of a traditional business plan include:
- Executive summary: This is a brief overview of the business plan, summarizing the key points and highlighting the main points of the plan.
- Business description: This section outlines the business concept and how it will be executed.
- Market analysis: This section provides an in-depth look at the target market and how the business will compete in the marketplace.
- Financial plan: This section details the financial projections for the business, including sales forecasts, capital requirements, and a break-even analysis.
- Management and organization: This section describes the management team and the organizational structure of the business.
Are there any free business plan templates?
There are several free templates for business plans for small business owners available online, including Shopify’s own version. Download a copy for your business.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Jun 11, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business What is A Business Plan & How To Design It?
What is A Business Plan & How To Design It?
Written by: Midori Nediger Jul 11, 2023

A business plan outlines the goals of your business and how it plans to achieve them.
Real important – because without it, it’s like running a business in the dark. It’s like a roadmap that guides your company’s direction and helps everyone stay on track.
Gone are the days when designing a business plan from scratch was a time-consuming and challenging task. Today, business plan templates offer a convenient solution by providing pre-designed layouts that simplify the process.
In this blog, I’m going to break it down for you. I’ll share the six things you need to know to put together a compelling, engaging business plan. Ready to get started now? Venngage’s online Business Plan Maker lets anyone create a winning business plan quickly and easily.
Click to jump ahead:
- How to format your business plan
Startup business plan templates
Simple business plan templates.
- How to write your business plan
- How to design an engaging executive summary
- How to use charts and graphs to present data
- How to communicate growth strategies in your business plan
How to present financial data in your business plan
How to format your business plan.
To format your business plan:
- Start with a clear title page.
- Include an executive summary.
- Provide a company description.
- Conduct a market analysis.
- Describe your product or service offering.
- Outline your marketing and sales strategy.
- Include organizational or business structure and management information.
A typical business plan is an in-depth document and covers every facet of your business (present and future). Creating a traditional business plan makes sense when you have a clear growth plan for the next three to five years, are in need of major funding, or want to attract long-term partners.
A professional business plan typically has the following sections:
- Table of Contents
- Executive summary
- Company description
- Market analysis
- Organization and management
- Service or product line
- Marketing and sales
- Funding request
- Financial projections
- An appendix
A business plan can span a dozen or more pages because it presents the big picture, as complete as possible, to reassure others to invest in you. Investment can mean a few different things – usually financial, but also as partners or employees.
The sections that can take a lot of research and add to the bulk of your business plan are your market analysis, marketing and sales plans, and financial projections.
These are the sections that demonstrate your business acumen, your long-term vision, and your accountability. Whereas, sections like the executive summary are meant to grab attention, inspire and get people excited about your business.
Start with a business plan template
To get started on your business plan, save yourself some time and use a template.
Most business plan templates will include things like a cover page, table of contents and the main sections you need. It will also have pre-formatted pages with placeholder text and charts that you can swap out.

It takes time to do market research, present growth plans, put together financial projections, analyze your customer base, create competitor breakdowns…the list goes on.
The last thing you want to do is spend precious time formatting the resulting document.
Save time by building your business plan from an existing business plan template, and customize it with your own content.
With a clean, consistent structure and clear headings, this template is the perfect starting point:

Then you’re free to customize the template with helpful visual elements like charts, tables, and diagrams, that will make your business pitch impossible to resist.
A Venngage business plan template is designed to help you communicate visually and explain complex ideas easily. The right business plan template for you depends on the length and detail of your business plan, your brand and style, and the different sections you want to cover.
If your small business doesn’t have a dedicated design team, but you still need to learn how to write a business plan to present to investors–build off of a pre-designed business plan template:

There are just a handful of our business plan templates that can be customized in the Venngage editor. Browse more business plan templates, choose one that’s best for you and start editing right away.
Structuring your startup business plan involves organizing it into sections such as executive summary, company description, market analysis, product/service offering, marketing and sales strategy, financial projections, and operational plan.
Here are some business plan template examples:

Short Business Plan Template
Number your pages and include a table of contents
A table of contents is crucial to help readers navigate your document and quickly find specific sections that are of interest to them.
It’s a good idea to include page numbers, main section headings, and section subheadings here for easy reference.

Keeping these tips in mind will ensure that your business plan design feels clean and professional and doesn’t distract from your content. You want your information, not your formatting, to be the focus!
How to write your business plan
Here are three tips for writing your business plan to ensure it’s easy to read, appears professional and is memorable.
Use bulleted lists, bold text, and a clear type hierarchy for ‘skimmability’
Business plans need to be understandable at a glance to attract funding . Investors are looking for information that will help them understand your business quickly and without much effort.
Take a look at this snippet of the business plan template from above:

What stands out to you?
To me, the large green headers pop out first, making it easy to scan through the sections to find what I want to focus on.
This is because there’s a defined type hierarchy, giving more visual weight to the headers over the body text.

Next, the unique selling points of this business–superior quality products, unique glass carving and brass inlays, and excellent service–jump out. Because they’re presented in an indented list , they’re easier to see at a glance, which will likely make them more memorable.
Finally, I’m drawn to the bolded stats–“top 30% of the industry” and “4 out of 5 households spent money on renovation”.
Key statistics like these can go a long way towards convincing your investors that you’re worth their time and money. If you’re going to include them within larger paragraphs, make sure they stand out by increasing their font weight.
To sum up: make your report skimmable. Draw attention to important takeaways with indented lists, bolded text, and a clear type hierarchy.
Consider using a one-column or two-column grid

If your business plan contains only text, stick with a single-column layout that reinforces the linear flow of the document. If your business plan includes some supporting data in the form of charts and tables, use a two-column layout to juxtapose text with its corresponding data.
Maintain page margins that set text at a readable line length
When we read long passages of text, the ease at which we read depends on how the text flows on the page. Something called line length (the number of characters in a horizontal line of text) plays a huge role in readability, and is something you should consider when formatting your business plan.
To dictate line length, designers and typesetters play with the width of page margins (the edges of a document that don’t contain any text or images) with the aim of maximizing readability.
It’s generally accepted that the ideal line length sits somewhere between 40 and 90 characters per line. Any longer or shorter and you’ll find that something feels “off” about your document.
How do you achieve this in your business plan?
If you use a single-column layout, use nice wide margins (1 ½ to 2 inches) to limit your text to less than 90 characters per line.
With a two-column layout, you might need to use narrower margins (possibly as little as ½ an inch on either side) to make sure there’s enough space for at least 40 characters per line of text.
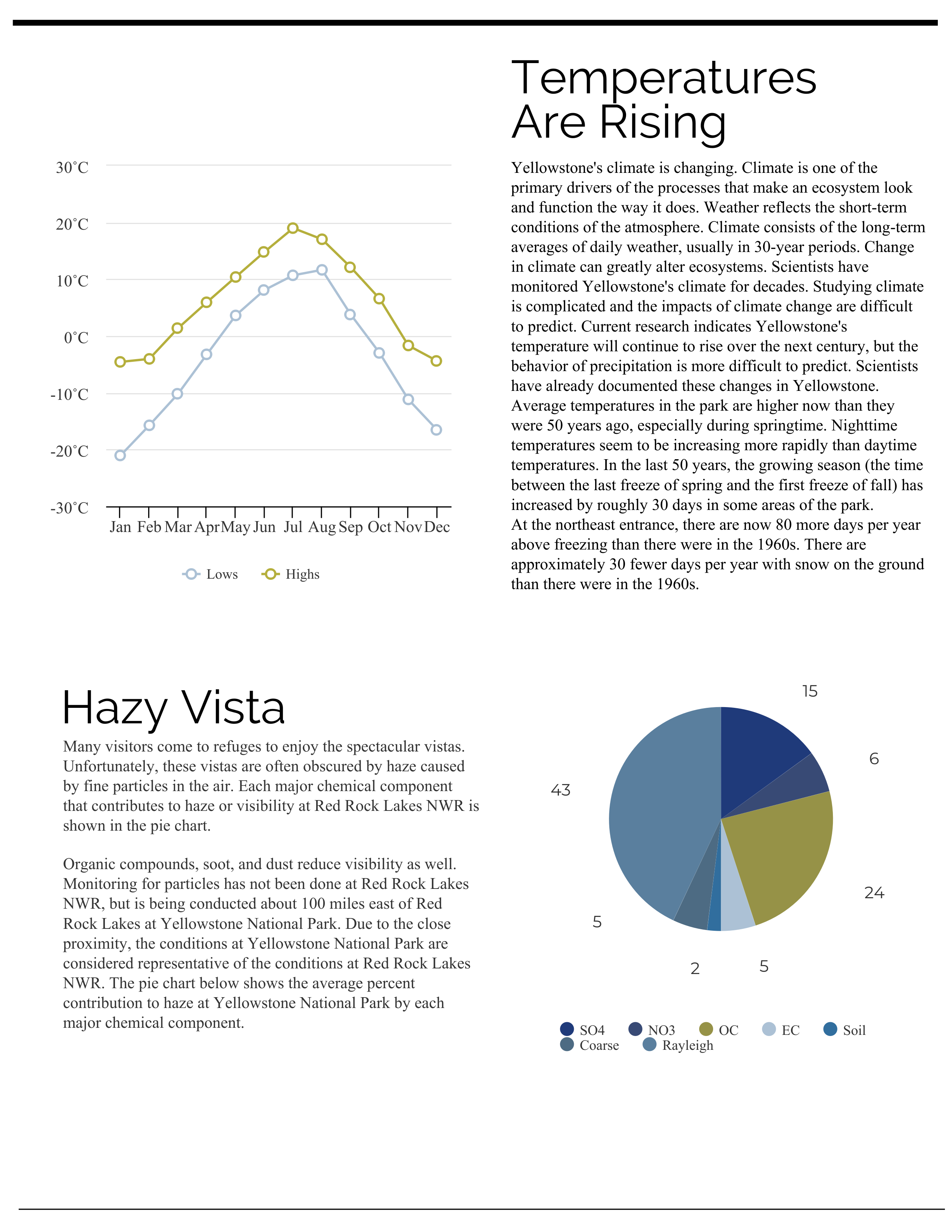
The last thing to remember about margins and line length–don’t play around with them from page to page. Use consistent margins across your whole document.
How to design an executive summary
An executive summary is a snapshot of your business plan. It should be concise and hook your readers. It should reassure stakeholders that your business plan will be a worthwhile read.
How you choose to structure your executive summary is key. You can deliver a lot of excellent information that simply gets lost in a sea of text and paragraphs. Even if someone reads through it entirely, they may have missed something.
To make key information stand out, use vibrant headings, incorporate visuals throughout, and break up the layout of your text.

Not every investor looks for the same thing. Some will care more about who you or your executive team are, while another is interested solely in the financials of the business. Identifying each section makes it easy for readers to find exactly what they’re looking for.
You can also list out the key takeaways, briefly explaining them in the executive summary. If your reader finds everything they needed to know in the executive summary, they’ll happily move onto the rest of the business plan.

Use one feature color to tie your business plan together
Color should be used with restraint in professional documents like business plans. Instead of adding color solely for aesthetic purposes, think of color selection as another tool to highlight information you want your reader to focus on and to tie the document together.
You shouldn’t need more than a single color (ideally one of your brand colors ) to achieve this in a business plan.
In business plan charts, color should be used only to clarify trends and relationships. Use color to emphasize single important data points, differentiate between real and projected values, or group related data:

In the rest of your business plan, keep color to a minimum. At most, use it to make headers stand out or to highlight key points in long-form text, diagrams, or tables.
The nice thing about keeping document colors this simple? It’s hard to mess up, and without any complex design work, it creates a sense of cohesion and unity within a document.
How to use charts and graphs to present your data
Since your business plan should be backed by solid data, you might want to include some of that data as evidence, in the form of charts, tables or diagrams . Even simple visuals can communicate better than long paragraphs of text.
I’ll touch on some specific types of charts commonly used in business plans next, but first let’s review a few general chart design tactics.
Use descriptive titles and annotations to spell out chart takeaways
Avoid generic headers whenever possible. Maximize your chart’s value and impact by providing takeaway messages right in the title.
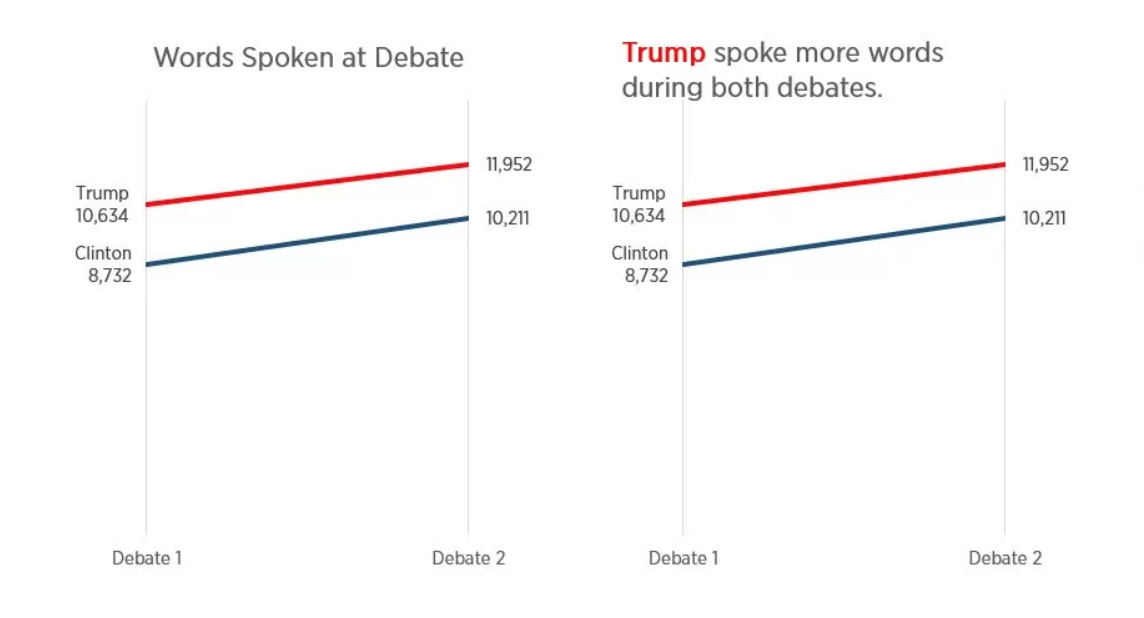
In the same vein, add direct annotations to data points or trends that support your case.

Repeating key messages within a chart, in the title, annotations, and captions, may improve viewers understanding and recall of those messages .
Aid understanding of market size and market share with area charts and pie charts
A market potential analysis is a fundamental pillar of your business plan. Market size and market share are two major components of a market potential analysis.
These numbers are typically in the millions and billions (the bigger the better, really), but most people have trouble grasping the meaning of such big numbers . At a surface level we can understand that one billion is one thousand times larger than one million, but we often struggle to comprehend what that really means.
This is the perfect opportunity to add some visual aids to your business plan.
Use bubble charts to represent market size
Bubble charts are useful for showing general proportions among numbers. Check out this one from our redesigned version of AirBnb’s first pitch deck :

Without having to think about the absolute values of these very large numbers, we can quickly see how they relate to one another.
While bubble charts are good for making quick, general comparisons, they’re less useful when it comes to precise measurements. To help readers make slightly more accurate judgements of proportion:
Use pie or donut charts to represent market share and market composition
Pie and donut charts are the industry standard for showing market share and market composition, since they’re the most widely understood method for representing part-to-whole relationships.
The way Uber breaks down their market with a simple donut chart makes their biggest segment (a key takeaway) really stand out, while the subtler differences between the smaller segments are still evident.
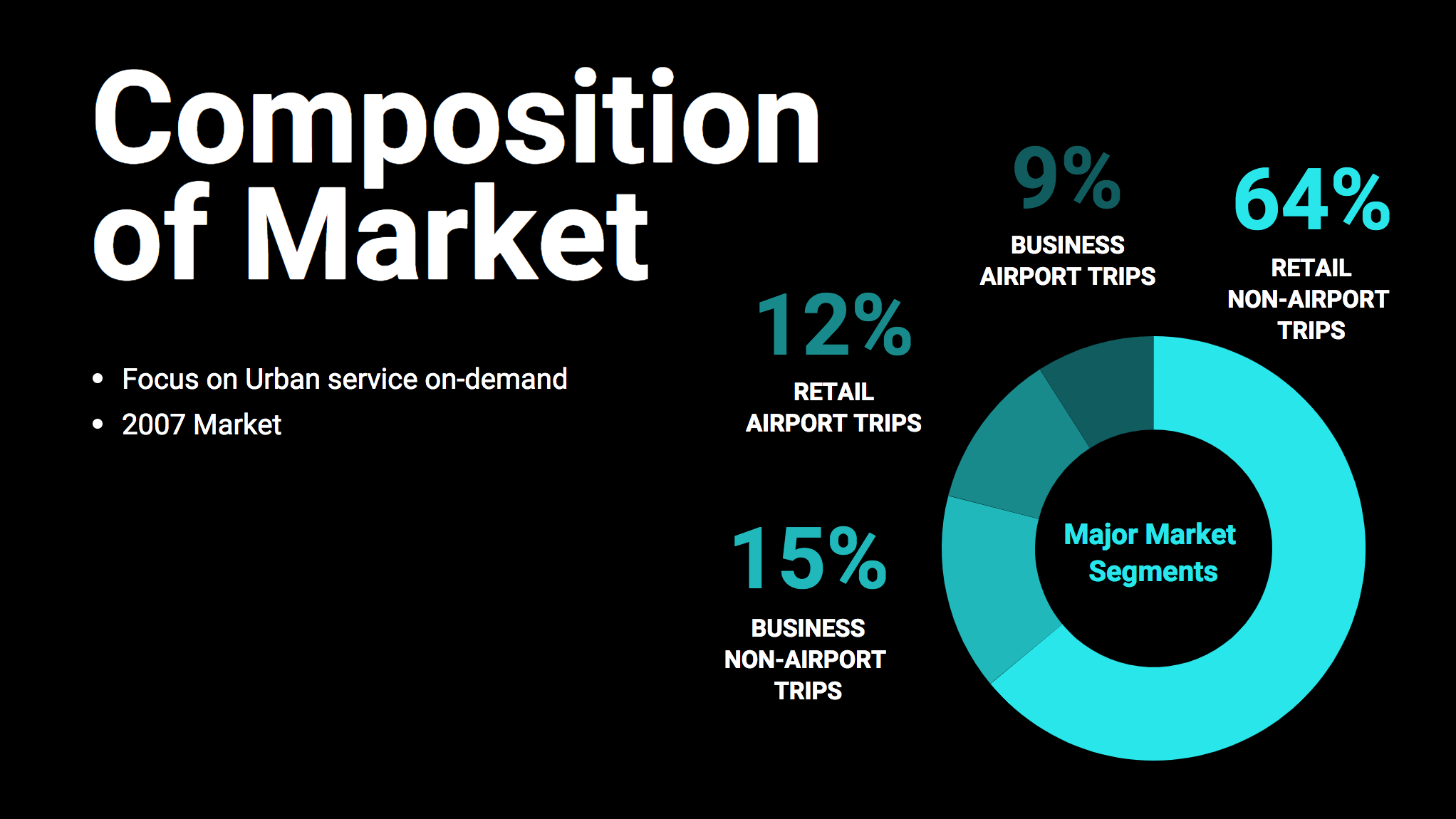
When you present a market analysis, use pie charts, donut charts, or bubble charts to aid the reader understanding proportions and part-to-whole relationships.
Use histograms and bar charts to represent demographic distributions in market segmentation summaries
Another part of analyzing market potential is about identifying and understanding target customers. This means segmenting customers by geography, interests, demographics…really anything that might affect purchasing behaviour.
Two standard metrics that most businesses include in a market segmentation summary are customer age and gender. These data are easily summarized in a histogram, with bars that represent age group distribution.
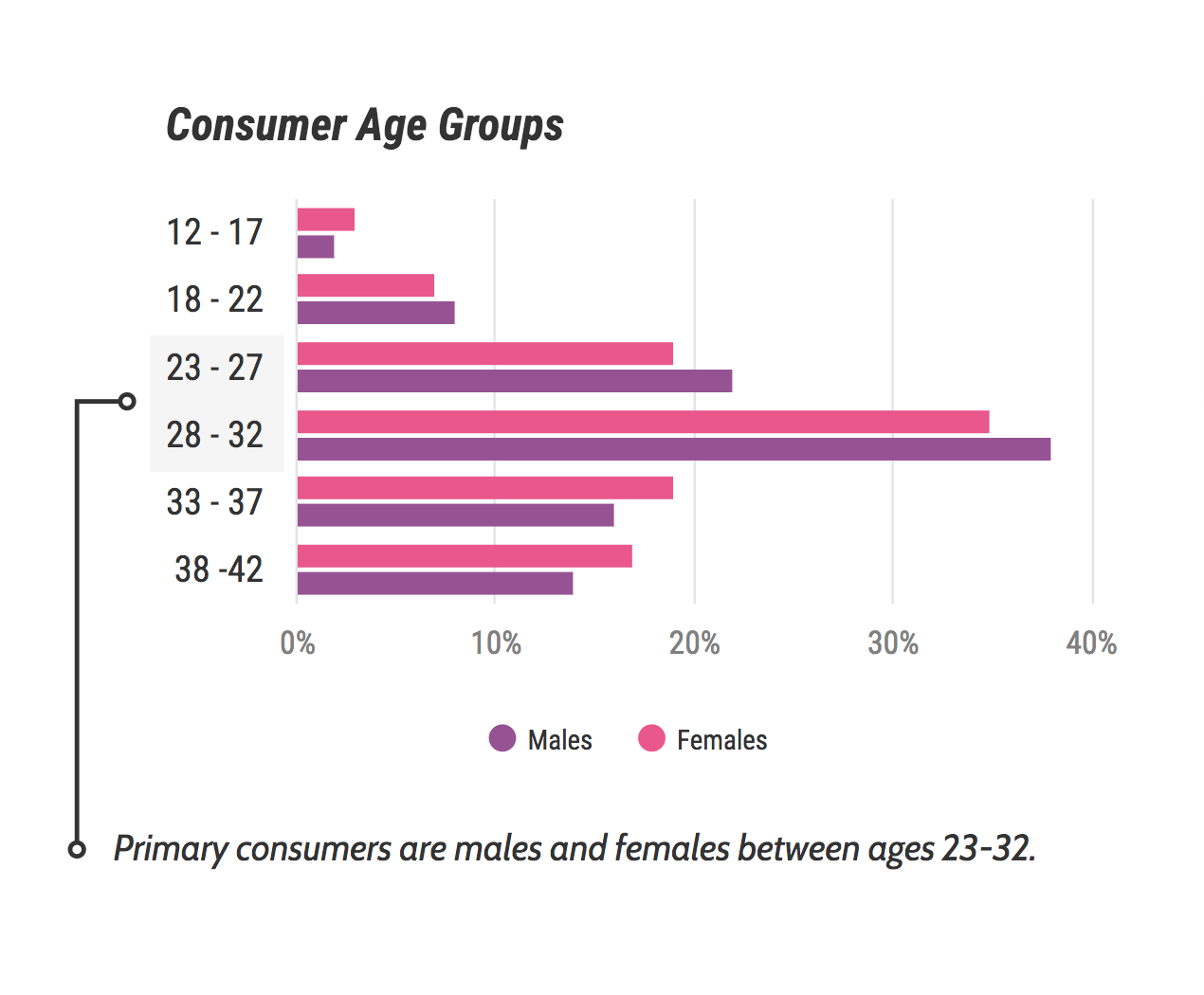
Bar charts can then be used to contrast the key behaviors and lifestyle choices of the top consumer segments.
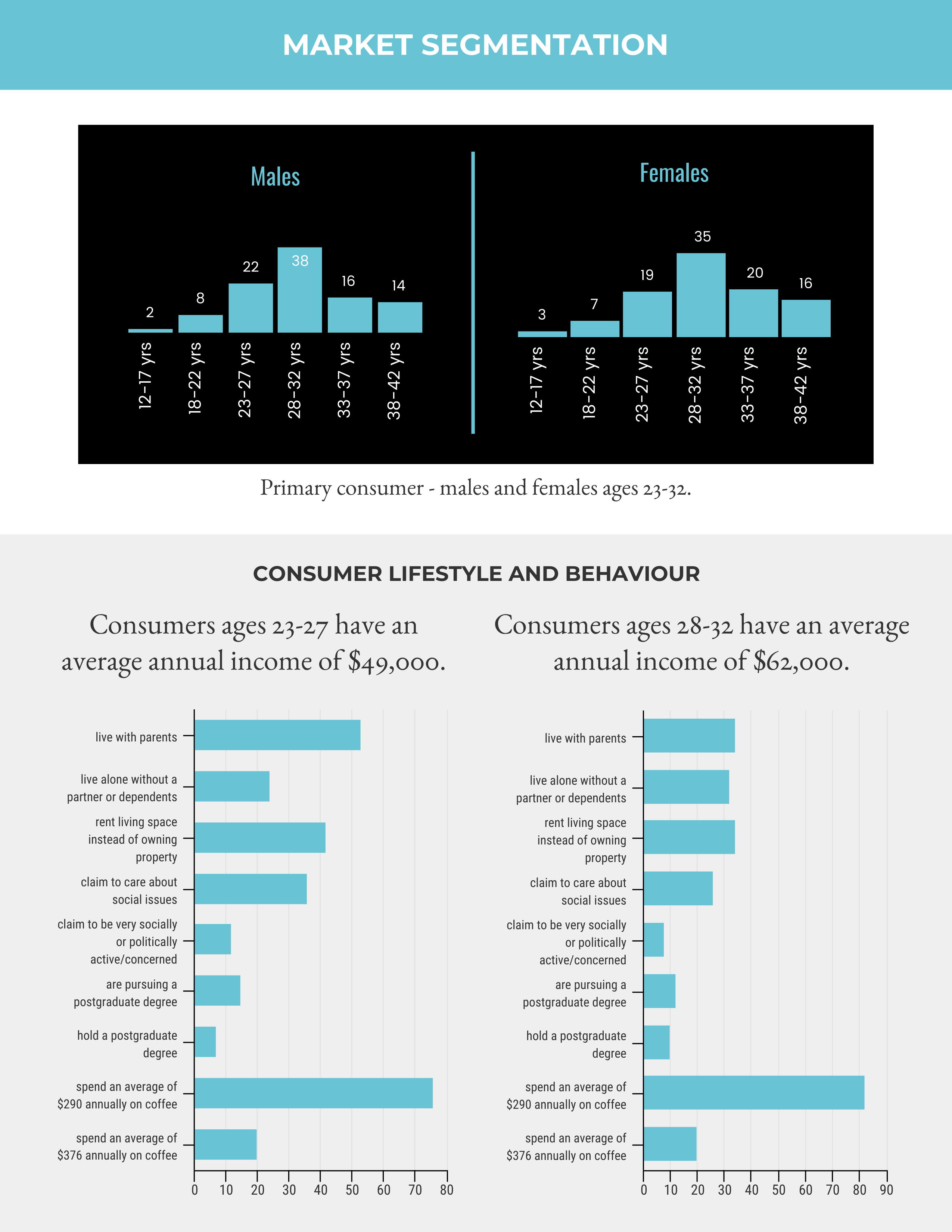
Histograms and bar charts are standard features of a market segmentation summary. Use them together to identify and present information about top customer segments.
Outline major milestones with a Gantt chart
Stakeholders will want to see that you have a concrete plan in place to help you reach your revenue goals. When formulating your goals, use the SMART principle to provide your stakeholders with a very clear vision of how you intend to achieve them.
Use a Gantt chart (a sort of modified bar chart) to outline the major milestones and phases of your business strategy. Try to include a multi-year plan, broken down by quarter and by project or department.
You can create your own Gantt chart with Venngage.
How to communicate growth strategies in your business plan
No matter how impressive your product line or services, your business won’t just magically grow. You concrete marketing and sales plans in place, and effectively communicate strategies to your stakeholders.
Start by acknowledging your target market – who are you going after? This is what your marketing and sales efforts will revolve around after all.
Demonstrate an understanding of the competitor landscape. You will always have direct or indirect competition, and showing how your planning accounts for it is key. Then you can talk about actual plans and strategies you wish to implement.
Present your target audience with persona guides
A product may great on its own. But its value is determined when there is a clear and obvious market for it. You can point out shortcomings of your competition, but you also need to show that your target audience exists and how you’re serving them.
A persona guide provides a great deal of context to readers of your business plan. It’s the best way for them to understand who cares about your product or service, how it aligns with their lifestyle and needs, and why your marketing and sales tactics will work.
A persona guide needs to be detailed, and share an intimate understanding of your target audience. The more you can divulge, the more reassuring your research and overall business plan will be.
Even if you don’t have a substantial customer base, you can still create an ideal persona guide to show who you’re pursuing.
Highlight competitors and differentiate yourself with a SWOT analysis
Every business plan should include an analysis of the competitive landscape–an assessment of the strengths and weaknesses of competitive businesses.
In terms of visuals, this competitive analysis is typically summarized in a SWOT analysis matrix .

You can also present the SWOT analysis as a table or a list. The layout is up to you, but you want to focus on strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats in relation to your competition.

While the SWOT analysis framework provides valuable insights, it’s not the entire reflection of your competitive landscape. For example, it doesn’t make it easy to see at a glance the qualities that differentiate your business from your competitors.
To highlight those offerings that set you apart from your competitors, a comparison matrix is more effective. Take a look at these two templates:
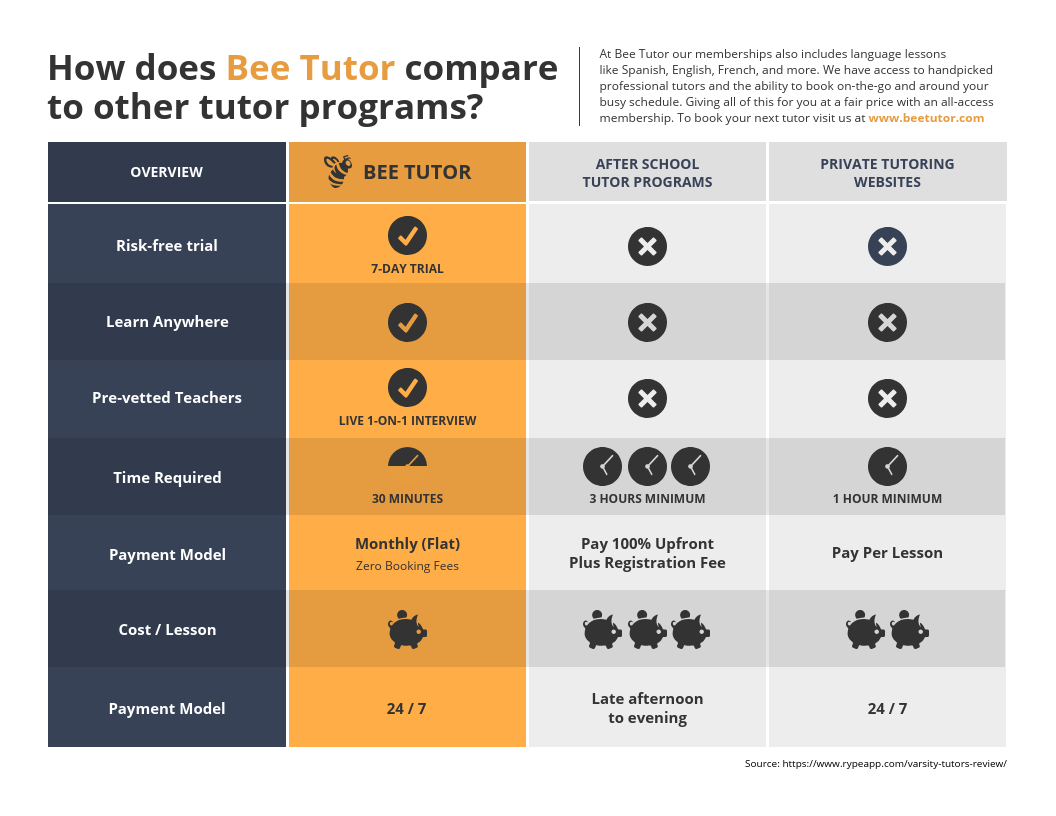
With a direct competitor comparison, it’s easy to present the key differentiators between the existing options for a product or service, and your business.
Alternatively, a “ Magic Quadrant ” can be useful when you’re focused on comparing across two main metrics ( key differentiators ):
Finally, in a competitive market, there are going to be a lot of players who compete directly or indirectly with you. A breakdown of them all may not be necessary. Instead, you can point visually to the space that you will address, that has been so far ignored up to now.
To do that, a prioritization chart can be used. By plotting competing businesses on a prioritization chart, you highlight experiences existing competitors focus on, and where your business falls.
Use roadmaps to present your marketing and sales plans
To explain any long-term marketing or sales plan, you want visuals. It’s easier to break down strategies you’ll be deploying every month or each quarter, when you can actually show what you’re talking about.
Keep in mind, those reading your business plan may not be marketers or sales executives. Being able to lay out your approach in a way that’s organized, shows how much thought you’ve given to your growth strategies.
You can design a simple roadmap that points to what you’ll be doing throughout the year. The more detailed you can get, the better.
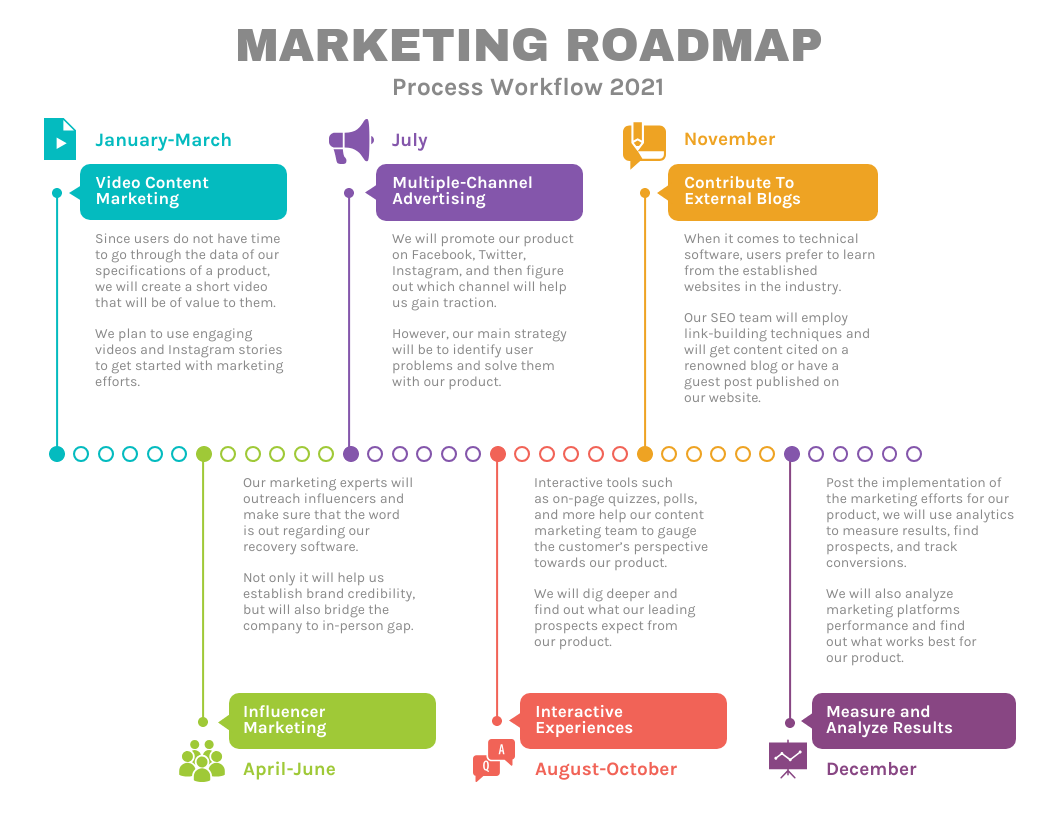
You can also present your product roadmap , with your marketing roadmap how the business will be growing overall.

You don’t need to use a traditional roadmap layout, either. Experiment with different formats as you may find one easier to work with than another. As long as the time period for different strategies is clear, your roadmap will be easy to understand.
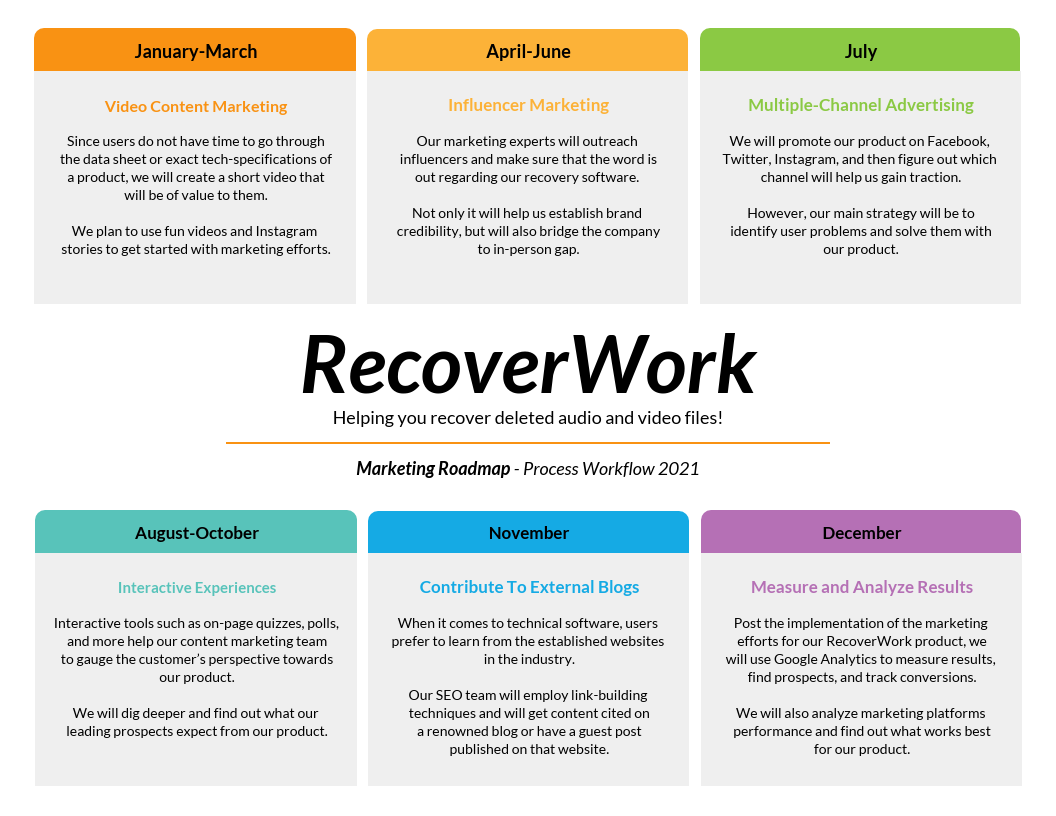
Presenting financial data isn’t easy. You have to crunch a lot of numbers before you can share projections with confidence. You’ll also need to explain how you arrived at the numbers and prepare for your answers.
Understanding how to organize your information is key to walking potential investors and other stakeholders through your projections.
Use organizational flow charts and summary tables for budget breakdowns and financial summaries
The financials section of your business plan will get a lot of attention from stakeholders. Simple bar charts and pie charts won’t suffice, as they can’t present financial data in very much detail.
If your business has already been operating for some time, stakeholders will expect a detailed report of revenues and expenses. Tables are usually the best choice for this kind of financial summary, as they provide an unbiased view of the numbers and allow stakeholders to look up specific values.

If you’re interested in highlighting a particular trend, however, you may want to include a line chart featuring a smaller snapshot of your financial data:
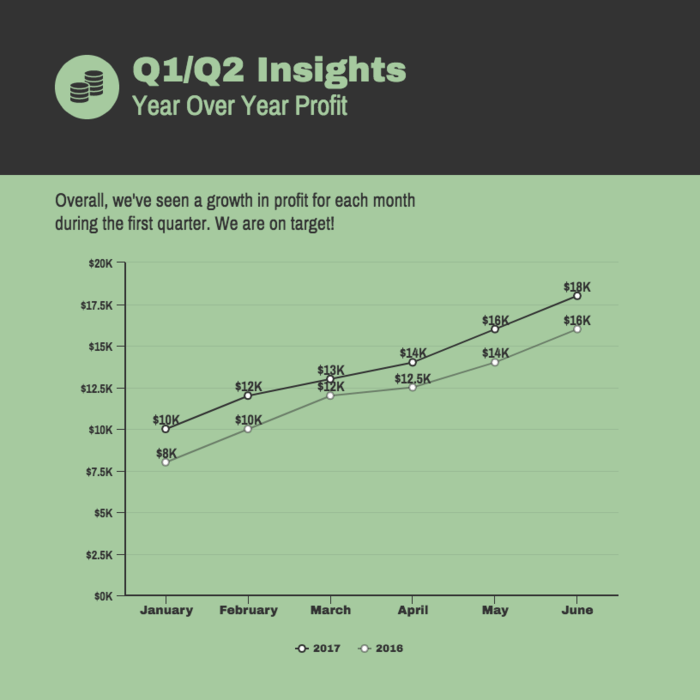
If you’re just starting your business and you don’t have any detailed revenue data, you can still provide useful information about your budget. Outline higher-level budget allocation with an organizational flow chart .
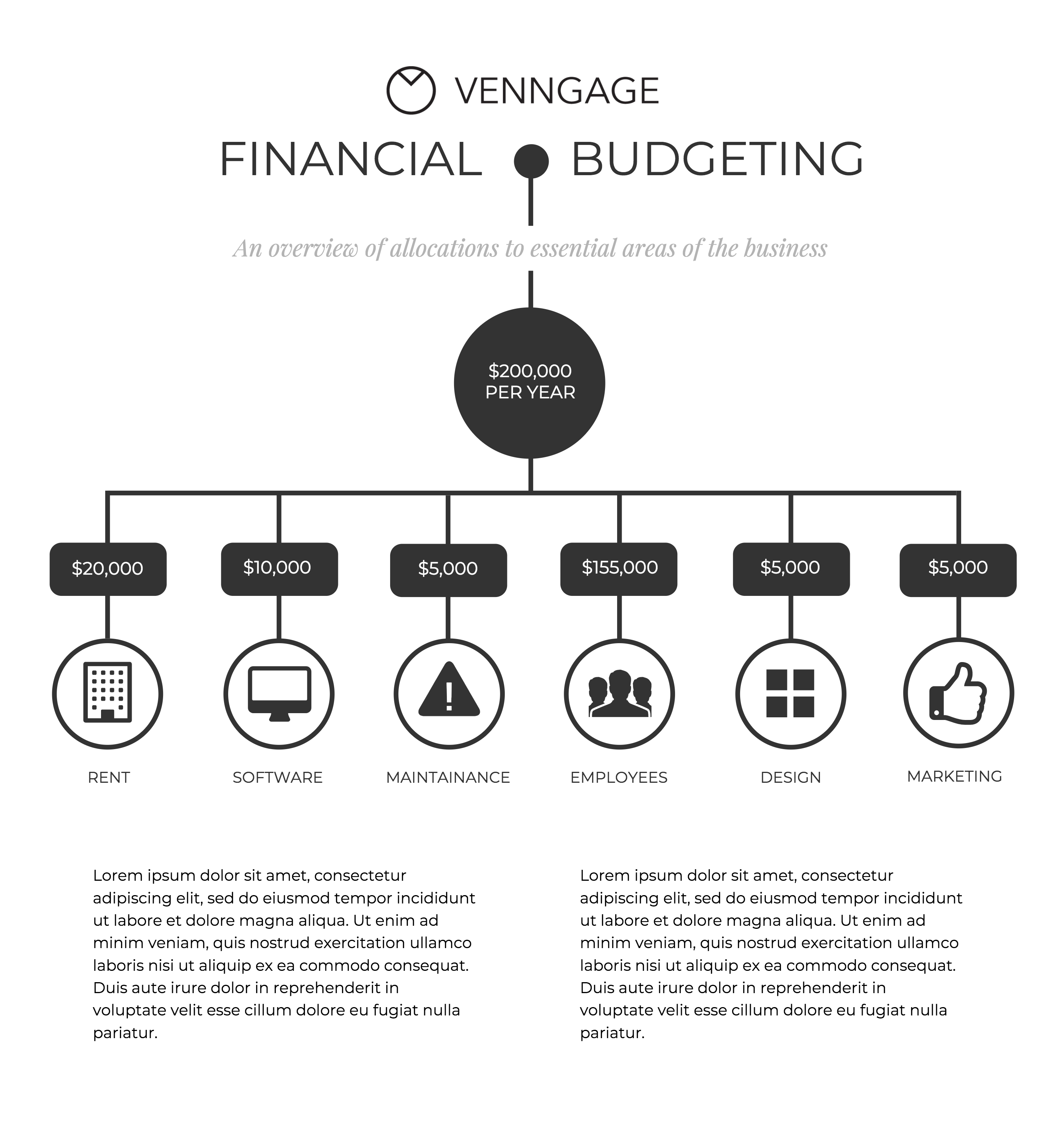
Use line or bar graphs to visualize financial trends
You can use different types of graphs to also show how your business has performed thus far.
You can share results over the course of a year with a line graph. This is effective to show an overall set of trends and growth rates.

You can also compare previous years to highlight how your business has grown.
Your audience should be able to draw conclusions from your data within seconds. If there is simply too much information, or it’s hard to find important information, they will lose interest.

Looking for a business plan software to help save time and reduce errors? Pick from one of these 7 best business plan software to get started.
A quick summary
A business plan is the one key document that every young business needs to present their vision to potential investors and other stakeholders.
The quality of a business plan can make or break a young business Here’s a quick recap of what we covered for you to keep in mind:
- Get started with a template
- Use a table of contents and numbered pages
- Use lists, bold headings and aim for skimmability
- Consider using a one-column or two-column
- Maintain page margins
- Use headings to identify the most important information
- Use one thematic color palette for your design
- Use descriptive titles and annotations
- Use area and pie charts to explain market size and market share
- Use pie/donut charts to visualize marketing share and market composition
- Use bar charts and histograms to capture demographics data
- Highlight major milestones with a gantt chart
- Identify your target audience using persona guides
- Differentiate yourself with a SWOT analysis/competitor chart
- Use roadmaps to visualize your marketing and sales plans
- Use flow charts and summary tables for financial breakdowns
- Use line or bar graphs for financial trends and projection
You can always reference this post as you work on your business plan. I’ve also included additional blog posts you can reference for specific areas of your business plan.
More Resources for business planning and growth:
- Growth Strategy Checklist: Plan Your Business Goals With These 5 Templates
- What is a Marketing Plan & How to Create One [with Examples]
- How to Communicate Strategy To Your Team Effectively
- 50+ Essential Business Report Examples with Templates
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
How to Develop a Content Strategy in 7 Steps: A Start-to-Finish Guide
Published: April 10, 2024
Whether you‘re just starting out with content marketing or you’ve been using the same approach for a while, it never hurts to revisit your content strategy plan and make sure it's innovative and engaging for your prospects and customers.

If you're having trouble planning for the upcoming year or need some fresh ideas to include in your plan, read on.

In this post, we'll dive into what content strategy is, why your business needs a content marketing plan, and what steps you need to take to create your strategy.
Plus, we'll explore some examples of effective content marketing strategies for inspiration.
Table of Contents
What is content strategy?
Why marketers need to create a content marketing strategy, elements of a content strategy plan, how to create a content strategy framework.
- Content Marketing Strategy Statistics
Questions to Ask When Creating a Content Strategy
Content strategy template, content marketing strategy example, content strategy tactics.
A content strategy is the planning, creation, publication, management, and governance of content. A great content strategy will attract and engage a target audience, meeting their needs while driving business goals.
Say your business goals include increasing brand awareness.
To achieve this, you might implement a content strategy that focuses on SEO to increase your website's visibility on the search engine results pages (SERPs) and drive traffic to your products or services.
New business owners might assume a content strategy is a nice-to-have, but not necessary early on. However, producing high-quality content can be invaluable in building trust with new audiences and succeeding in the long haul.
In essence, a good content strategy is the foundation of your Attract and Delight stages in a buyer's journey that follows the inbound marketing framework.
Along with attracting prospects to your brand, you can leverage a content strategy for sales enablement and customer satisfaction.
Plus, with 70% of marketers actively investing in content marketing , it's critical to develop a good content strategy to compete in your industry.

Content Marketing Planning Templates
Plan your content strategically with these handy templates.
- Editorial Calendar Template
- Buyer Persona Templates
- SWOT Analysis Templates
- SMART Goal Template
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A couple of years ago, I worked as a content writer for a literary company that just launched.
Despite all the meetings the team had before the launch, the founder and CEO of the company didn’t understand why it was important to create a content marketing strategy we’d adhere to when the website went live.
Three months after the launch, the CEO called another meeting and expressed their dissatisfaction with the poor performance so far.
Both the website and the company’s social media profiles were receiving crickets by way of organic traffic, and the paid ads were not converting at all.
I suggested that we create a content strategy plan for the next quarter and see what happens.
We did that, and sure enough, by the end of Q2, we recorded an increase in traffic and conversions from both the website and social media profiles.
No matter the kind of company or industry you work in, a content marketing strategy is integral for the success of your digital marketing efforts.
Here are some reasons why.

1. It aligns the team on goals and objectives.
A content marketing strategy ensures that everyone on the marketing team understands the overarching goals and specific objectives of the business.
When content creators, social media managers, writers, and other team members are aligned on goals such as brand awareness, lead generation, or customer engagement, they can produce content that consistently supports these aims.
This increases the chances of getting tangible results.
Carl Broadbent , a digital marketing expert, values content marketing strategies for the alignment they bring.
“After years of publishing blogs, ebooks, and videos, I‘ve learned that a strong content strategy acts like a guiding compass. It points you towards topics and formats aligned with business goals, so you’re not just cranking out content for content's sake,” Broadbent says.
Broadbent also notes that teams will make mistakes along the way.
He recalls, “‘I've made that mistake! Last year, we invested heavily in podcasts, thinking it would attract our target buyers. Turns out our audience preferred snappy infographics. Our podcast push fizzled out fast without the right strategy in place.”
2. It guides content creation and distribution.
Ayomide Joseph , a freelance content marketer for SaaS companies like Aura, Nextiva, and Trengo, explains the purpose of a content marketing strategy:
“The concept of ‘strategy’ in content marketing is simply to give you a roadmap that’ll guide you from where you are to where you want to be,” Joseph says.
For example, Joseph notes that if you’re looking to drive more inbound leads via content, ideally, creating bottom-of-the-funnel content is the way to go.
“A content marketing strategy answers the questions, ‘How do you go about it? What’s the keyword you’re going to target, search volume, difficulty — and what distribution approach will you utilize?’” Joseph says. “If you don’t have a content marketing strategy, you’ll be working blind.”
A content marketing strategy requires you to plan the type of content to create, such as blog posts, infographics, videos, and podcasts.
You’ll also determine the most effective channels for distribution, whether that be social media platforms, email marketing, or the company’s website.
This planning ensures that content is consistent, timely, and relevant to the audience’s interests and needs, fostering brand loyalty and advocacy.
3. It optimizes resources.
When you map out a fully-fledged content marketing strategy, you’ll be able to allocate resources more efficiently, whether those resources are time, budget, or manpower, to bring the strategy to life.
By knowing the type of content you need to produce and the platforms through which you’ll distribute it, you can direct your efforts and budget toward activities that offer the best return on investment (ROI).
4. It improves online visibility.
A well-executed content marketing strategy can alleviate this problem by improving a brand’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs).
High-quality, optimized content is favored by search engines and ranks higher in search results, which leads to increased organic traffic.
By targeting specific keywords and topics relevant to your target audience, you can attract more qualified leads to your website.
5. It builds brand authority and trust.
By consistently producing high-quality, relevant, and valuable content, you can establish your business as a thought leader in its industry.
This authority builds trust with your audience, which is crucial for long-term relationships and customer loyalty.
A content marketing strategy ensures that your content not only attracts attention but also provides value and encourages your audience to return and interact with the brand further.
Since a content strategy plan is a roadmap designed to guide the creation, publication, and governance of useful content, here are some key elements you should include when creating yours.
1. Goals and Objectives
What do you want to achieve with your content?
Do you want to increase brand awareness? Generate leads? Or maybe, improve customer engagement? Is it all three — or something else?
When you define the goals and objectives you want your content to help you achieve, you’re establishing your North Star.
So, if you’re not sure whether to include a certain type of content in your strategy, you can look to your North Star and determine if that content type will lead you in the direction you want to go.
2. Audience Persona
An audience persona (or buyer persona) is a semi-fictional representation of your ideal customer based on data and research.
It helps you understand who you’re creating content for.
To create an accurate audience persona, you’ll need to conduct research through surveys and interviews and analyze your social media engagement to gather insights.
These insights include your audience’s demographic information, interests, pain points, and content preferences, to mention a few.
Knowing this information will help you understand the content types, topics, and marketing channels that will help you reach your goals.
3. Content Audit and Analysis
Once you’ve gotten your audience persona down, review your existing content to determine what’s working and what’s not.
This way, you’ll be able to identify gaps and opportunities for content.
In the Content Audit section of your content strategy plan, explain:
- The kinds of content and topics that are already working well for you (e.g., blogs that discuss web development, micro-videos that explain coding tips and tricks, etc.)
- The kinds of content and topics that are not gaining traction (e.g., white papers about the evolution of programming)
- The content gaps and opportunities you’ve discovered
Pro tip: Use tools like Google Analytics and social media analytics to evaluate the performance of your content. Look for patterns in what types of content perform best and use this to inform future content creation.
4. Content Types and Channels
The Feedly RSS feed is a wonderful way to track trendy topics in your industry and find content ideas at the same time.
You start by telling the software what topics you're most interested in, and its AI tool will do the rest.
You won't need to scour the internet to find new content ideas anymore. Instead, you can go through your curated list, compiled from news sites, newsletters, and social media.
2. BuzzSumo
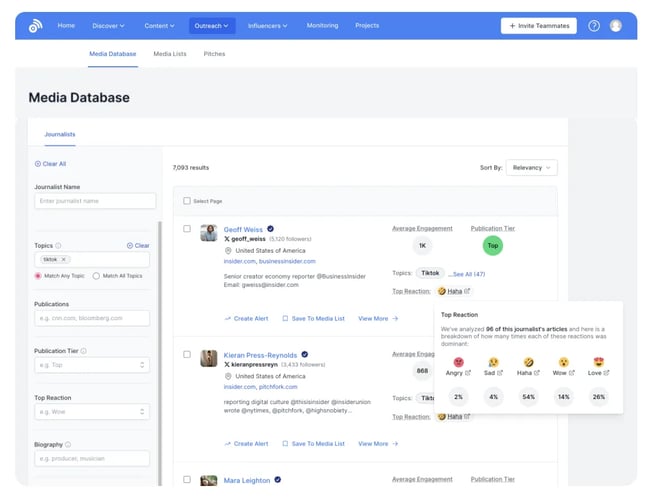
Want to discover popular content and content ideas?
This company offers several market research tools, one of which uses social media shares to figure out if a piece of content is popular and well-liked.
This information helps you see which content ideas would do well if you were to create content about them.
3. BlogAbout
Get your mind gears going with IMPACT's blog title generator.
This tool works a bit like Mad Libs, but instead of joke sentences, it shows you common headline formats with blanks where you can fill in the subject you have in mind.
This brainstorming technique helps you put general ideas in contexts that would be appealing to your target audience. Once you have a headline you like, BlogAbout lets you add it to your “Notebook” so you can save your best ideas.
4. CoSchedule Headline Analyzer
You can get blog post ideas for an entire year with HubSpot's Blog Ideas Generator .
All you need to do is enter general topics or terms you'd like to write about, and this content idea generator does all the work for you.
This tool analyzes headlines and titles and gives feedback on length, word choice, grammar, and keyword search volume.
If you have an idea in mind, run a few title options through the Headline Analyzer to see how you could make it stronger.
5. HubSpot's Website Grader
This is a great tool to use when you want to see where you're at with your website and SEO efforts.
The Website Grader grades you on vital areas of your website performance and sends you a detailed report to help you optimize.
With this tool, you can figure out how to make your website more SEO-friendly and discover areas of improvement.
Refine and rank your ideas.
The brainstorming process should be loose and unstructured.
It can be tempting to jump on an idea and start creating content right away. But instead, try to throw out your wildest ideas and see where they lead.
Then, take that list of content ideas and refine them.
To start, break ideas into groups and organize them around your goals, topics, or personas. Then, review each idea in detail and add specifics.
For example, say your topic is AI . One of your content ideas might be image generation. You can break this idea down further with content for image-generation tools, text-to-image prompts, or how to edit existing images.
Another way to refine content ideas is to conduct keyword research .
You can also define your process for refining ideas in your content workflow .
7. Publish and manage your content.
Your marketing plan should go beyond the types of content you‘ll create — it should also cover how you’ll organize your content.
Develop a content calendar.
With the help of an editorial calendar, you'll be on the right track to publishing a well-balanced and diverse content library on your website.
Then, create a social media content calendar to promote and manage your content on other sites.
Featured Tool: Free Editorial Calendar Templates

An ebook here might dive deeper into a particular problem and solution options and include templates or calculators.
[Lastly,] ebooks further down the funnel should become more personalized and offer more sales content. Comparison guides or an ebook of case studies are beneficial for prospects at this stage."
Ebooks are the next step in the inbound marketing process . After reading a blog post, visitors might want more information.
This is where calls-to-action (CTAs) come into play, directing people to a landing page where they can submit their contact information and download an ebook to learn more valuable information for their business.
In turn, the business producing the ebook has a new lead for the sales team to contact.
Featured Tool: 18 Free Ebook Templates

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

8 Steps to Launching an Online Learning Academy Your Customers Will Love

What is Content Governance? 4 Easy Steps to Create a Model in 2022

Top B2B Content Marketing Trends to Watch This Year, According to Experts

The Ultimate Round-Up of Content Marketing Tips

The Future of Content Strategy

What Is a Micro Niche ... and Do You Need One?

Rethinking Your Premium Content: How to Build a Guided Learning Course

What Are Website Traffic Exchange Sites? (And Why You Shouldn't Use Them)

What You Need to Know About Commercial Use

Why A Digital PR Specialist Should Always Be Involved in Content Creation
A Beginner's Guide to Applying Content Marketing to your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team
- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Online Business Certificate Courses
Business Strategy
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Business Strategy →
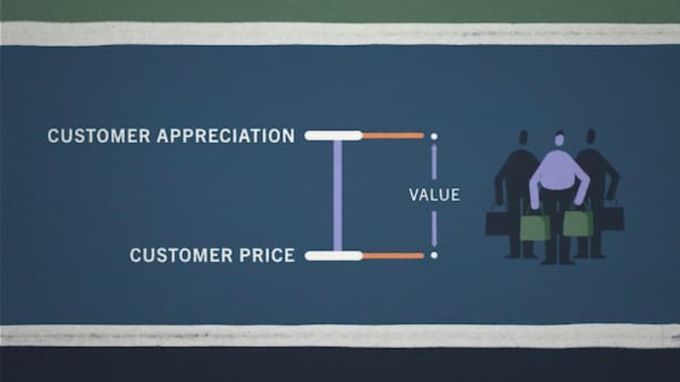
Key Concepts
Who will benefit, mid-career professionals, general managers, consultants and investors.

What You Earn

Certificate of Completion
Boost your resume with a Certificate of Completion from HBS Online
Earn by: completing this course

Certificate of Specialization
Prove your mastery of strategy
Earn by: completing any three courses within this subject area to earn a Certificate of Specialization
Creating Value for Customers

- An Introduction to Value-Based Strategy
- Sales Success and Willingness to Pay
- Near-Customers
Featured Exercises
Adding value through complements.

- Understanding Complements
- Shifting Value
- Navigating the Frenemy Relationship
- Discerning Complements from Substitutes
Competing with Network Effects

- Understanding Network Effects
- Which Markets Will Tip
- Strategies for Underdogs
- Digital Platforms and Innovation
Creating Value for Talent

- Linking Productivity and Customer Delight
- Competing on Flexibility
- Compensation Policy
Mastering Productivity

- Measuring Productivity
- Economies of Scale
- Teaching and Learning
- Good Management
Implementing Strategy

- Evolving Your Value Proposition
- Connecting Strategy, Activities, and KPIs
- Execution Challenges

How to Formulate a Successful Business Strategy
Our difference, about the professor.

Felix Oberholzer-Gee Business Strategy
Dates & eligibility.
No current course offerings for this selection.
All applicants must be at least 18 years of age, proficient in English, and committed to learning and engaging with fellow participants throughout the course.
Learn about bringing this course to your organization .
Learner Stories

Business Strategy FAQs
What are the learning requirements in order to successfully complete the course, and how are grades assigned.
Participants in Business Strategy are eligible for a Certificate of Completion from Harvard Business School Online.
Participants are expected to fully complete all coursework in a thoughtful and timely manner. This will mean meeting each week’s course module deadlines and fully answering questions posed therein. This helps ensure your cohort proceeds through the course at a similar pace and can take full advantage of social learning opportunities. In addition to module and assignment completion, we expect participation in the social learning elements of the course by offering feedback on others’ reflections and contributing to conversations on the platform. Participants who fail to complete the course requirements will not receive a certificate and will not be eligible to retake the course.
More detailed information on course requirements will be communicated at the start of the course. No grades are assigned for Business Strategy. Participants will either be evaluated as complete or not complete.
What materials will I have access to after completing Business Strategy?
You will have access to the materials in every prior module as you progress through the program. Access to course materials and the course platform ends 60 days after the final deadline in the program.
How should I list my certificate on my resume?
Once you've earned your Certificate of Completion, list it on your resume along with the date of completion:
Harvard Business School Online Certificate in Business Strategy [Cohort Start Month and Year]
List your certificate on your LinkedIn profile under "Education" with the language from the Credential Verification page:
School: Harvard Business School Online Dates Attended: [The year you participated in the program] Degree: Other; Certificate in Business Strategy Field of Study: Leave blank Grade: "Complete" Activities and Societies: Leave blank
Description: Business Strategy is a 6-week, 30-35 hour online certificate program from Harvard Business School. Business Strategy equips professionals with a simplified framework they can immediately apply to create value for customers, employees, and suppliers while maximizing returns and an organization’s competitive edge. Participants learn to evaluate trade-offs and align, prioritize, and formulate strategic initiatives for the greatest business impact.
Related Program

CLIMB enables new and experienced leaders to ignite their careers with a combination of vital and forward-looking business skills, self-reflection, and an immersive cohort-based learning experience with a diverse global network.
5 best health insurance companies for small businesses

More and more people are deciding to become entrepreneurs. Approximately 19% of working-age adults in the U.S. were in the process of starting a business or running a business less than 42 months old, according to the 2023 Global Entrepreneurship Monitor report.
As your business grows and you bring on workers, you may need to provide benefits. Businesses with fewer than 50 employees aren’t required by law to provide health insurance benefits, but health insurance is a highly-desired benefit. To attract and maintain a talented workforce, providing benefits may be essential.
We identified the leading providers based on their availability, plan options and customer satisfaction ratings (see our full methodology ):
The 5 best small business health insurance providers for 2024
Best overall: blue cross blue shield, best for added benefits: kaiser permanente.
- Best for Micro businesses: UnitedHealthcare
Best for Small to Midsize Companies: Cigna
Best for comparison shopping: small business health options program (shop).
*Last updated March 12, 2024
If you’re shopping for coverage, finding the right provider can be daunting. To help you narrow down your options, we selected the five top providers of small business health insurance:
Blue Cross Blue Shield
| Minimum number of employees: | Varies by state, but typically employers need at least one or two employees |
| Availability: | 50 states |

Our verdict
Blue Cross Blue Shield is one of the few providers that has insurance options in all 50 states, so it’s a good choice for businesses nationwide. Its independent BCBS companies typically have options for small to midsize companies. Whether you have one employee or 100, you can likely get coverage through BCBS, and you can choose a network plan that fits your budget and employee needs.
Kaiser Permanente
| Minimum number of employees: | As little as one |
| Availability: | 8 states and the District of Columbia |

Our verdict
If you live in one of the states where Kaiser Permanente operates, it can be a good choice for employers looking to offer robust coverage to their employees as a recruitment or retention tool. With its plans, you can give your employees the convenience of telehealth visits and supplemental benefits, including acupuncture, chiropractic care, and dental and vision coverage.
Best for Micro Businesses: UnitedHealthcare
Unitedhealthcare.
| Minimum number of employees: | As little as two |
| Availability: | 50 states |

UnitedHealthcare is best for micro business owners, or those who own a business with fewer than 10 employees. Its small business store is available to small business owners with two to 50 employees, and you can use the tool to get quotes and see what deductible, copay and premium amounts are common in your area. If you find coverage that suits your needs, you can purchase coverage directly through the store.

If you have a growing business, Cigna could be a useful option. Whereas some providers only offer coverage for employers with fewer than 50 employees, Cigna has options for small to midsize businesses, allowing you to get coverage for up to 499 employees. Its plans include benefits like virtual care and it offers multiple plan tiers, including high-deductible health plans.
Small Business Health Options Program (SHOP)
| Minimum number of employees: | As little as one |
| Availability: | 50 states |

SHOP is a marketplace that was created through the Affordable Care Act (ACA). Through SHOP, employers can compare plans and prices from leading providers in their area. With SHOP, you can control how much you pay toward employee premiums, and you may be eligible for valuable tax credits that are only available to employers who enroll in SHOP plans.
What to know about health insurance for small businesses
If you are a business owner with 50 or more employees, the law requires you to offer coverage to your employees.
By contrast, those with fewer than 50 employees aren’t required to provide health insurance. But even if you aren’t legally obligated to provide coverage, it can be a smart idea as a recruitment and retention tool. In fact, studies, including one conducted by Avalere Health and funded by the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, have shown that offering health insurance benefits produces a strong return on investment and increased productivity.
You may also qualify for valuable tax credits if you offer health insurance benefits. The Small Business Health Care Tax Credit is worth up to 50% of the costs of your employees’ premiums. To qualify for the tax credit, your business must meet the following criteria:
- You have fewer than 25 full-time employees
- The average annual salary of your workers is about $56,000 or less
- You cover at least 50% of your employees’ premiums
- You offer coverage through SHOP to all of your full-time employees
How to choose a small business health insurance company
When shopping for a small business health insurance provider, consider the following variables:
Employee size: Each provider has its own employee requirements. In general, you’ll need between one and 50 employees to qualify for small business health insurance.
Availability: While some providers offer coverage nationwide, others are more limited in scope, only issuing policies in certain states. Similarly, some plans allow workers to receive care in any state, but some plans have more restrictive local networks.
Customer support tools: Most insurance providers require you to work with an agent or broker to get details about cost and plan options. But some companies have online tools and platforms that allow you to get quotes and view your options on your own.
Networks: Insurance providers offer plans with different network types. Depending on the provider, you may be able to provide your workers with the following options:
- Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO): EPOs are managed care plans that only cover services if you visit healthcare providers and hospitals within the network.
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): With an HMO, you’re limited to care within the network, and you must get a referral to visit a specialist. HMOs tend to be the lowest-cost option.
- Point of Service (POS): POS plans are less expensive if you use in-network providers, but you need a referral to visit a specialist.
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): PPOs are often more expensive, but they give covered persons more flexibility. In-network providers are less expensive, but you can visit out-of-network providers, and you can see a specialist without a referral.
There’s a lot to consider when it comes to business insurance, not just health insurance for your business. Our comprehensive guide breaks down the types of insurance options — from BOP’s to general liability and others — to help you understand which policy watches your needs. We have also compiled the best insurance companies for small businesses . If you operate a jewelry retail business, you may want to consider Jewelers Mutual’s business insurance specifically designed for jewelers.
Frequently asked questions
How much does health insurance cost a small business for each of their employees.
The cost of health insurance for small business employees will vary based on a number of factors including types of plans, risk to injuries, and region in the country. According to a 2023 KFF report , the average costs per employee per month is $690.
Do I have to provide health insurance to my employees?
You only have to provide health insurance to your employees if you have 50 or more full-time workers. Those with fewer than 50 employees aren’t legally required to offer coverage, but you may be eligible for valuable tax benefits if you do.
What are the penalties for not offering health benefits?
Employers with 50 employees or more that don’t offer coverage that meets minimum value and affordability standards may incur penalties. Depending on what coverage you offer, the penalty ranges from $247.50 to $371.67 per month, per full-time employee.
What do entrepreneurs do for health insurance?
If you don’t have any employees, you won’t qualify for group plans from small business insurance providers. However, you may be eligible for an individual health insurance plan through Healthcare.gov or your state health insurance marketplace.
Our methodology
We evaluated seven leading providers and marketplaces of small business health insurance. To make our selections, we evaluated each company on the following criteria:
- Availability: Preference was given to companies operating in the majority of states.
- Employee minimums: We looked for companies with low employee minimums, offering coverage to businesses with just one or two employees.
- Product options: We focused on companies with multiple insurance plans, including multiple network options and tiers of coverage.
- Customer satisfaction: Priority was given to companies with high ratings from the National Committee for Quality Assurance Ratings.
EDITORIAL DISCLOSURE : The advice, opinions, or rankings contained in this article are solely those of the Fortune Recommends ™ editorial team. This content has not been reviewed or endorsed by any of our affiliate partners or other third parties.
Your life on an installment plan: 'Buy now, pay later' features creep into more credit tools

Why pay all at once?
It’s a question consumers are getting asked more often at checkouts, as installment plans resembling those offered by “buy now, pay later” services pop up in more places.
Popular BNPL offerings like Afterpay, Affirm, Sezzle, Klarna and others — which let borrowers break up a purchase into several equal installments with little or no interest — exploded during the pandemic, fueled by lockdown-era e-commerce, stimulus checks and savings. Adoption of the installment loans has cooled since then, but their influence over how consumers spend with borrowed money is just getting started.
It was exactly what I needed to do some fun stuff and not go into debt. Or at least not feel like I’m going into debt.
Aaron Gans, 37, New York City
Aaron Gans, a 37-year-old resident physician in New York City, got a notification in March from his American Express Platinum card offering to split his and his husband’s $1,700 charge for their flights to Taiwan and South Korea into 12 interest-free installments. He said yes.“It was exactly what I needed to do some fun stuff and not go into debt,” said Gans. “Or at least not feel like I’m going into debt.”
In an era of stubborn inflation and stretched household finances, as well as high interest rates stoking fears of credit card debt , lenders are leaning into a model that many shoppers — especially younger ones — are embracing as a way to keep spending . That BNPL-ification of consumer credit is underscoring existing socioeconomic divides, with people of different means paying off debt in installments for different reasons.
Big brands bring installment plans in-house
American Express began rolling out more features like the one Gans recently took advantage of several years ago, just as BNPL startups surged in popularity. Amex made its “Plan It” program available for travel bookings in 2021 — the same year Mastercard and Barclays unveiled their own BNPL programs — and expanded that and related offerings to more of its cards last summer.
“All your major card issuers are going to be watching the success” of BNPL services, said Ben Danner, senior analyst at Javelin, a payments-focused research firm. “They wanted some of that market share.”
Retailers have been getting in on the action, too. In April, a Walmart-backed startup began offering BNPL loans for big-ticket items at thousands of stores, effectively adding an in-house option to compete with Affirm, the retailer’s exclusive BNPL provider since 2019.
Others are finding ways to offer customers installment features without additional transaction fees. Last year, Amazon partnered with Citi to let cardholders use the brand’s Flex Pay option with any merchant using Amazon Pay.
But moves like these coincide with a slowdown in BNPL usage overall.
By March, growth in the share of Bank of America customers with an active BNPL payment was lower than 12 months earlier, researchers at the bank said last month, and adoption was down nearly fourfold since March 2021. In a survey by The Motley Fool, an investing advice company, just 35% of adults said last year that they’d used a BNPL loan at least once, down sharply from 50% in 2022 and 56% in 2021.
That’s not necessarily surprising, or unique to the BNPL market. When a new type of product sees an initial burst of popularity, intrigued customers tend to flood in all at once. As time goes on, some stick around and others drop off, while familiar habits reassert themselves and the pool of eager first-time users gets shallower.
But at least two other factors could be limiting BNPL services’ growth.
First, they’re used disproportionately by some of the riskiest borrowers — those with shaky credit and household finances — including for everyday purchases , not just the occasional large expense. That may not be helping providers win over skeptics who see them as enablers of dangerous overspending . And second, the spread of installment options across the tools already in many consumers’ wallets reduces the need to sign up for a new one.
Need to pay later vs. nice to be able to
According to a NerdWallet analysis last month, the use of BNPL loans is most common among young people and parents of small kids — groups where strained finances are comparatively widespread .
More than 1 in 3 parents of minor children have used a BNPL loan over the past year, the researchers found, versus just 1 in 5 for those without young kids. The Bank of America report found nearly half of BNPL borrowers made less than $50,000 annually. And Gen Z borrowers are leaning more heavily on credit overall than millennials did at the same age a decade ago, recent data from the credit agency TransUnion shows.
Many customers of stand-alone BNPL services use them like Benjamin Espinoza, a San Antonio-based video editor in his late 20s. He told NBC News earlier this year that he’d used Klarna to pay for an Instacart grocery order when cash was tight.
“It sucks that these are the avenues I have to go through,” said Espinoza, who estimated making less than $7,000 last year.
Consumers are generally most satisfied with the BNPL plans offered by their credit card issuers.
Miles Tullo, managing director of banking and payments, J.D. Power
By contrast, mainstream brands’ BNPL riffs are likely looking to pull in higher-income users, while hanging on to existing ones who might otherwise go elsewhere to try the approach. That could create a sorting effect, with cash-strapped borrowers relying more heavily on stand-alone apps like Klarna for essentials, and more affluent ones embracing the installment features offered by name-brand companies for occasional luxuries like travel.“Consumers are generally most satisfied with the BNPL plans offered by their credit card issuers,” Miles Tullo, managing director of banking and payments at J.D. Power, said in a report earlier this year .
But the market remains fluid. “Experiences vary quite a bit by brand and some of the newest providers are receiving the greatest increases in satisfaction scores,” he said.
Customers ranked Amex’s Plan It the top BNPL offering, the J.D. Power survey found, followed by My Chase Plan and Citi Flex Pay — all services from mainstream credit cards that typically require higher creditworthiness for borrowers to qualify. Those plans also tend to have higher purchase minimums than stand-alone BNPL services; Plan It is only available for Amex purchases over $100, for example.
Plus, as Danner pointed out, “one big factor here is you’re still able to get your rewards” when using a card’s installment feature. While some BNPL providers, including Afterpay and Sezzle, have experimented with loyalty programs, those aren’t likely to be as attractive as the ones offered by a huge Wall Street bank, Danner said.
Another upside to sticking with a credit card’s installment options: Cardholders can often use these features to circumvent interest charges. Rather than “rolling a bunch of debt into the next month at a 30% interest rate,” Danner said, “you can leverage some of these installment plans to kind of lower that total cost.”
When Gans paid for his travel on Amex, he noticed “they just sort of package it for you.” In fact, he said, there was a no-fee promotion when he first used Plan It. The service typically charges a fixed monthly rate of up to 1.33%.
Not everyone is racing to try out installment financing. Older borrowers, for example, appear to be sticking with what they know. Credit usage data that LexisNexis Risk Solutions analyzed for NBC News shows retail store cards — whose users have long skewed older — are becoming more popular among mature consumers. In 2019, borrowers ages 60 and up comprised 20% of all retail card applicants. Last year, that share hit 25%.
Experts foresee more experimentation among lenders as the U.S. consumer population ages and as high living costs continue to squeeze many households.
“These factors collectively contribute to a rise in credit demand,” said Kevin King, vice president of credit risk and marketing strategy at LexisNexis Risk Solutions. “There’s a lot of smart people at those companies who are thinking about how to evolve their products and their businesses.”
J.J. McCorvey is a business and economy reporter for NBC News.
- Employee quick setup
- Download and install apps
- Setup and use Outlook
- Move your email, calendars, and contacts
- Setup OneDrive
- Collaborate and meet with Teams
- Create an email signature
- Security features and settings
- Create a hub for your team
- Collaborate on business documents
- Share files with my team members
- Create polls to survey employees
- Let customers book appointments
- Schedule meetings with anyone
- Save and share files with clients
- Add your clients as guests
- Manage your business finances
- Track product inventory
- Plan projects and track deadlines
- Scheduling staff shifts
- Suport resources
- Welcome to Microsoft 365 for business
- Buy Microsoft 365
- Microsoft 365 Admin Center
- Add a custom domain
- Manage payment information
- Add more users
- All about passwords
- Remote work
- File sharing and storage
- Secure your business

Manage Microsoft 365 payment information and billing for your business
In the Microsoft 365 admin center, you can manage the payment information and billing for your Microsoft 365 subscription. From here you can review your invoices, add a new payment method, or check your other Microsoft billing information.
View a bill or invoice

Sign in to the Microsoft 365 admin center with your admin credentials.
Go to the Billing > Bills & payments page.
On the Invoices tab, choose the invoice that you want to view. If you don't see an invoice, use the date filter and select Past 3 months , Past 6 months , or Specify date range .
On the Invoice summary page are invoice details including a list of items, the price for each item, and the total cost for all items in the invoice.
To print or save a PDF copy of the invoice, select Download PDF .
If you want to receive a copy of your billing statement in email, see Manage billing notifications and invoice attachments .
Microsoft 365 services do not provide payment receipts. For credit card payments, use the invoice and credit card billing statement to match your payment.
Add a payment method
Go to Billing > Bills & payments > Payment methods .
Select Add a payment method .
On the Payment methods page, pick a payment method from the drop-down menu.
Enter the information for the new card, and then select Add .
For steps to add additional users and buy and assign licenses, see to Add more users and licenses .
Get expert advice, dedicated support and personalized guidance from business specialists. With Business Assist, get help making Microsoft 365 products work for you and everyone in your business. Learn More
Related topics
Microsoft 365 help for small businesses on YouTube
Business subscriptions and billing documentation
Manage payment methods for Microsoft business accounts
Small business help and learning
Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders

Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
Your current User-Agent string appears to be from an automated process, if this is incorrect, please click this link:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Learn how to create a business plan with this guide that covers the main sections, contents, and format. Download a free template to get started with your own business plan.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Tips on Writing a Business Plan. 1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively. 2.
Traditional business plans use some combination of these nine sections. Executive summary. Briefly tell your reader what your company is and why it will be successful. Include your mission statement, your product or service, and basic information about your company's leadership team, employees, and location.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page. The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions. A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
1. Executive Summary. While your executive summary is the first page of your business plan, it's the section you'll write last. That's because it summarizes your entire business plan into a succinct one-pager. Begin with an executive summary that introduces the reader to your business and gives them an overview of what's inside the ...
The Bplans Weekly. Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business. A business plan is the backbone of a successful business. Learn to write, use, and improve your business plan with exclusive guides, templates, and examples.
This is why crafting a business plan is an essential step in the entrepreneurial process. In this post, we'll walk you through the process of filling out your business plan template, like this free, editable version: Download a free, editable one-page business plan template. We know that when looking at a blank page on a laptop screen, the idea ...
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
Step 2: Do your market research homework. The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research. This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to ...
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
Learn the steps and tips to create a business plan for any stage and size of company. Find free templates, examples, and expert advice for different types of business plans.
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business. But the reality can be more nuanced - it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written. Ideal times to write a business plan include: When you have an idea for a ...
1. Investors Are Short On Time. If your chief goal is using your business plan to secure funding, then it means you intend on getting it in front of an investor. And if there's one thing investors are, it's busy. So keep this in mind throughout writing a business plan.
Step 7: Financial Analysis and Projections. It doesn't matter if you include a request for funding in your plan, you will want to include a financial analysis here. You'll want to do two things here: Paint a picture of your business's performance in the past and show it will grow in the future.
A business plan is a document that helps small business owners determine the viability of their business idea. Combining market research and financial analysis, a professional business plan helps startup CEOs and potential investors determine if the company can compete in the target market. Typically, a good business plan consists of the following:
Our free business plan template includes seven key elements typically found in the traditional business plan format: 1. Executive summary. This is a one-page summary of your whole plan, typically written after the rest of the plan is completed. The description section of your executive summary will also cover your management team, business ...
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
Jul 11, 2023. A business plan outlines the goals of your business and how it plans to achieve them. Real important - because without it, it's like running a business in the dark. It's like a roadmap that guides your company's direction and helps everyone stay on track. Gone are the days when designing a business plan from scratch was a ...
This section of your content strategy plan outlines the steps for producing content, from idea generation to publication. This process includes assigning roles and responsibilities to other team members or freelancers. Pro tip: Develop a content calendar to plan and schedule content in advance. Use collaboration tools to streamline the content ...
CLIMB enables new and experienced leaders to ignite their careers with a combination of vital and forward-looking business skills, self-reflection, and an immersive cohort-based learning experience with a diverse global network. 1 year, 5-9 hrs/week. Apply by August 21st & 28th $15,000 (four installments of $3,750) Credential.
The 5 best small business health insurance providers for 2024. Best Overall: Blue Cross Blue Shield. Best for Added Benefits: Kaiser Permanente. Best for Micro businesses: UnitedHealthcare. Best ...
Aaron Gans, 37, New York City. Aaron Gans, a 37-year-old resident physician in New York City, got a notification in March from his American Express Platinum card offering to split his and his ...
Add a payment method. Sign in to the Microsoft 365 admin center with your admin credentials. Go to Billing > Bills & payments > Payment methods. Select Add a payment method. On the Payment methods page, pick a payment method from the drop-down menu. Enter the information for the new card, and then select Add. Next steps.
Microsoft 365 E3 combines best-in-class enterprise productivity apps with core security and compliance capabilities. Improve productivity and foster a culture of collaboration with connected experiences. Transform how you manage your business and enhance customer relationships with integrated workflows. Proactively protect your employees, data ...
Publicly owned vehicles specifically designed to perform public works other than general transportation, and directly engaged in a core agency purpose, are exempt from the Congestion Relief Zone toll. Learn more and apply. Discounts and exemptions to the Congestion Relief Zone toll (Congestion Pricing) will apply to certain drivers or vehicles.