- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers

How to Write and Publish Your Research in a Journal
Last Updated: May 26, 2024 Fact Checked
Choosing a Journal
Writing the research paper, editing & revising your paper, submitting your paper, navigating the peer review process, research paper help.
This article was co-authored by Matthew Snipp, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Cheyenne Main . C. Matthew Snipp is the Burnet C. and Mildred Finley Wohlford Professor of Humanities and Sciences in the Department of Sociology at Stanford University. He is also the Director for the Institute for Research in the Social Science’s Secure Data Center. He has been a Research Fellow at the U.S. Bureau of the Census and a Fellow at the Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences. He has published 3 books and over 70 articles and book chapters on demography, economic development, poverty and unemployment. He is also currently serving on the National Institute of Child Health and Development’s Population Science Subcommittee. He holds a Ph.D. in Sociology from the University of Wisconsin—Madison. There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 700,786 times.
Publishing a research paper in a peer-reviewed journal allows you to network with other scholars, get your name and work into circulation, and further refine your ideas and research. Before submitting your paper, make sure it reflects all the work you’ve done and have several people read over it and make comments. Keep reading to learn how you can choose a journal, prepare your work for publication, submit it, and revise it after you get a response back.
Things You Should Know
- Create a list of journals you’d like to publish your work in and choose one that best aligns with your topic and your desired audience.
- Prepare your manuscript using the journal’s requirements and ask at least 2 professors or supervisors to review your paper.
- Write a cover letter that “sells” your manuscript, says how your research adds to your field and explains why you chose the specific journal you’re submitting to.

- Ask your professors or supervisors for well-respected journals that they’ve had good experiences publishing with and that they read regularly.
- Many journals also only accept specific formats, so by choosing a journal before you start, you can write your article to their specifications and increase your chances of being accepted.
- If you’ve already written a paper you’d like to publish, consider whether your research directly relates to a hot topic or area of research in the journals you’re looking into.

- Review the journal’s peer review policies and submission process to see if you’re comfortable creating or adjusting your work according to their standards.
- Open-access journals can increase your readership because anyone can access them.

- Scientific research papers: Instead of a “thesis,” you might write a “research objective” instead. This is where you state the purpose of your research.
- “This paper explores how George Washington’s experiences as a young officer may have shaped his views during difficult circumstances as a commanding officer.”
- “This paper contends that George Washington’s experiences as a young officer on the 1750s Pennsylvania frontier directly impacted his relationship with his Continental Army troops during the harsh winter at Valley Forge.”

- Scientific research papers: Include a “materials and methods” section with the step-by-step process you followed and the materials you used. [5] X Research source
- Read other research papers in your field to see how they’re written. Their format, writing style, subject matter, and vocabulary can help guide your own paper. [6] X Research source

- If you’re writing about George Washington’s experiences as a young officer, you might emphasize how this research changes our perspective of the first president of the U.S.
- Link this section to your thesis or research objective.
- If you’re writing a paper about ADHD, you might discuss other applications for your research.

- Scientific research papers: You might include your research and/or analytical methods, your main findings or results, and the significance or implications of your research.
- Try to get as many people as you can to read over your abstract and provide feedback before you submit your paper to a journal.

- They might also provide templates to help you structure your manuscript according to their specific guidelines. [11] X Research source

- Not all journal reviewers will be experts on your specific topic, so a non-expert “outsider’s perspective” can be valuable.

- If you have a paper on the purification of wastewater with fungi, you might use both the words “fungi” and “mushrooms.”
- Use software like iThenticate, Turnitin, or PlagScan to check for similarities between the submitted article and published material available online. [15] X Research source

- Header: Address the editor who will be reviewing your manuscript by their name, include the date of submission, and the journal you are submitting to.
- First paragraph: Include the title of your manuscript, the type of paper it is (like review, research, or case study), and the research question you wanted to answer and why.
- Second paragraph: Explain what was done in your research, your main findings, and why they are significant to your field.
- Third paragraph: Explain why the journal’s readers would be interested in your work and why your results are important to your field.
- Conclusion: State the author(s) and any journal requirements that your work complies with (like ethical standards”).
- “We confirm that this manuscript has not been published elsewhere and is not under consideration by another journal.”
- “All authors have approved the manuscript and agree with its submission to [insert the name of the target journal].”

- Submit your article to only one journal at a time.
- When submitting online, use your university email account. This connects you with a scholarly institution, which can add credibility to your work.

- Accept: Only minor adjustments are needed, based on the provided feedback by the reviewers. A first submission will rarely be accepted without any changes needed.
- Revise and Resubmit: Changes are needed before publication can be considered, but the journal is still very interested in your work.
- Reject and Resubmit: Extensive revisions are needed. Your work may not be acceptable for this journal, but they might also accept it if significant changes are made.
- Reject: The paper isn’t and won’t be suitable for this publication, but that doesn’t mean it might not work for another journal.

- Try organizing the reviewer comments by how easy it is to address them. That way, you can break your revisions down into more manageable parts.
- If you disagree with a comment made by a reviewer, try to provide an evidence-based explanation when you resubmit your paper.

- If you’re resubmitting your paper to the same journal, include a point-by-point response paper that talks about how you addressed all of the reviewers’ comments in your revision. [22] X Research source
- If you’re not sure which journal to submit to next, you might be able to ask the journal editor which publications they recommend.

Expert Q&A
You might also like.

- If reviewers suspect that your submitted manuscript plagiarizes another work, they may refer to a Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) flowchart to see how to move forward. [23] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- ↑ https://www.wiley.com/en-us/network/publishing/research-publishing/choosing-a-journal/6-steps-to-choosing-the-right-journal-for-your-research-infographic
- ↑ https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
- ↑ https://libguides.unomaha.edu/c.php?g=100510&p=651627
- ↑ https://www.canberra.edu.au/library/start-your-research/research_help/publishing-research
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/conclusions
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/writing-an-abstract-for-your-research-paper/
- ↑ https://www.springer.com/gp/authors-editors/book-authors-editors/your-publication-journey/manuscript-preparation
- ↑ https://apus.libanswers.com/writing/faq/2391
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/library/keyword/search-strategy
- ↑ https://ifis.libguides.com/journal-publishing-guide/submitting-your-paper
- ↑ https://www.springer.com/kr/authors-editors/authorandreviewertutorials/submitting-to-a-journal-and-peer-review/cover-letters/10285574
- ↑ https://www.apa.org/monitor/sep02/publish.aspx
- ↑ Matthew Snipp, PhD. Research Fellow, U.S. Bureau of the Census. Expert Interview. 26 March 2020.
About This Article

To publish a research paper, ask a colleague or professor to review your paper and give you feedback. Once you've revised your work, familiarize yourself with different academic journals so that you can choose the publication that best suits your paper. Make sure to look at the "Author's Guide" so you can format your paper according to the guidelines for that publication. Then, submit your paper and don't get discouraged if it is not accepted right away. You may need to revise your paper and try again. To learn about the different responses you might get from journals, see our reviewer's explanation below. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
RAMDEV GOHIL
Oct 16, 2017
Did this article help you?
David Okandeji
Oct 23, 2019
Revati Joshi
Feb 13, 2017
Shahzad Khan
Jul 1, 2017
Apr 7, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
- Privacy Policy

Home » How to Publish a Research Paper – Step by Step Guide
How to Publish a Research Paper – Step by Step Guide
Table of Contents

Publishing a research paper is an important step for researchers to disseminate their findings to a wider audience and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their field. Whether you are a graduate student, a postdoctoral fellow, or an established researcher, publishing a paper requires careful planning, rigorous research, and clear writing. In this process, you will need to identify a research question , conduct a thorough literature review , design a methodology, analyze data, and draw conclusions. Additionally, you will need to consider the appropriate journals or conferences to submit your work to and adhere to their guidelines for formatting and submission. In this article, we will discuss some ways to publish your Research Paper.
How to Publish a Research Paper
To Publish a Research Paper follow the guide below:
- Conduct original research : Conduct thorough research on a specific topic or problem. Collect data, analyze it, and draw conclusions based on your findings.
- Write the paper : Write a detailed paper describing your research. It should include an abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
- Choose a suitable journal or conference : Look for a journal or conference that specializes in your research area. You can check their submission guidelines to ensure your paper meets their requirements.
- Prepare your submission: Follow the guidelines and prepare your submission, including the paper, abstract, cover letter, and any other required documents.
- Submit the paper: Submit your paper online through the journal or conference website. Make sure you meet the submission deadline.
- Peer-review process : Your paper will be reviewed by experts in the field who will provide feedback on the quality of your research, methodology, and conclusions.
- Revisions : Based on the feedback you receive, revise your paper and resubmit it.
- Acceptance : Once your paper is accepted, you will receive a notification from the journal or conference. You may need to make final revisions before the paper is published.
- Publication : Your paper will be published online or in print. You can also promote your work through social media or other channels to increase its visibility.
How to Choose Journal for Research Paper Publication
Here are some steps to follow to help you select an appropriate journal:
- Identify your research topic and audience : Your research topic and intended audience should guide your choice of journal. Identify the key journals in your field of research and read the scope and aim of the journal to determine if your paper is a good fit.
- Analyze the journal’s impact and reputation : Check the impact factor and ranking of the journal, as well as its acceptance rate and citation frequency. A high-impact journal can give your paper more visibility and credibility.
- Consider the journal’s publication policies : Look for the journal’s publication policies such as the word count limit, formatting requirements, open access options, and submission fees. Make sure that you can comply with the requirements and that the journal is in line with your publication goals.
- Look at recent publications : Review recent issues of the journal to evaluate whether your paper would fit in with the journal’s current content and style.
- Seek advice from colleagues and mentors: Ask for recommendations and suggestions from your colleagues and mentors in your field, especially those who have experience publishing in the same or similar journals.
- Be prepared to make changes : Be prepared to revise your paper according to the requirements and guidelines of the chosen journal. It is also important to be open to feedback from the editor and reviewers.
List of Journals for Research Paper Publications
There are thousands of academic journals covering various fields of research. Here are some of the most popular ones, categorized by field:
General/Multidisciplinary
- Nature: https://www.nature.com/
- Science: https://www.sciencemag.org/
- PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS): https://www.pnas.org/
- The Lancet: https://www.thelancet.com/
- JAMA (Journal of the American Medical Association): https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama
Social Sciences/Humanities
- Journal of Personality and Social Psychology: https://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/psp
- Journal of Consumer Research: https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/journals/jcr
- Journal of Educational Psychology: https://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/edu
- Journal of Applied Psychology: https://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/apl
- Journal of Communication: https://academic.oup.com/joc
- American Journal of Political Science: https://ajps.org/
- Journal of International Business Studies: https://www.jibs.net/
- Journal of Marketing Research: https://www.ama.org/journal-of-marketing-research/
Natural Sciences
- Journal of Biological Chemistry: https://www.jbc.org/
- Cell: https://www.cell.com/
- Science Advances: https://advances.sciencemag.org/
- Chemical Reviews: https://pubs.acs.org/journal/chreay
- Angewandte Chemie: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/15213765
- Physical Review Letters: https://journals.aps.org/prl/
- Journal of Geophysical Research: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/2156531X
- Journal of High Energy Physics: https://link.springer.com/journal/13130
Engineering/Technology
- IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/RecentIssue.jsp?punumber=5962385
- IEEE Transactions on Power Systems: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/RecentIssue.jsp?punumber=59
- IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/RecentIssue.jsp?punumber=42
- IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/RecentIssue.jsp?punumber=87
- Journal of Engineering Mechanics: https://ascelibrary.org/journal/jenmdt
- Journal of Materials Science: https://www.springer.com/journal/10853
- Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan: https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/browse/jcej
- Journal of Mechanical Design: https://asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/mechanicaldesign
Medical/Health Sciences
- New England Journal of Medicine: https://www.nejm.org/
- The BMJ (formerly British Medical Journal): https://www.bmj.com/
- Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA): https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama
- Annals of Internal Medicine: https://www.acpjournals.org/journal/aim
- American Journal of Epidemiology: https://academic.oup.com/aje
- Journal of Clinical Oncology: https://ascopubs.org/journal/jco
- Journal of Infectious Diseases: https://academic.oup.com/jid
List of Conferences for Research Paper Publications
There are many conferences that accept research papers for publication. The specific conferences you should consider will depend on your field of research. Here are some suggestions for conferences in a few different fields:
Computer Science and Information Technology:
- IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM): https://www.ieee-infocom.org/
- ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Data Communication: https://conferences.sigcomm.org/sigcomm/
- IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP): https://www.ieee-security.org/TC/SP/
- ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS): https://www.sigsac.org/ccs/
- ACM Conference on Human-Computer Interaction (CHI): https://chi2022.acm.org/
Engineering:
- IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA): https://www.ieee-icra.org/
- International Conference on Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (ICMAE): http://www.icmae.org/
- International Conference on Civil and Environmental Engineering (ICCEE): http://www.iccee.org/
- International Conference on Materials Science and Engineering (ICMSE): http://www.icmse.org/
- International Conference on Energy and Power Engineering (ICEPE): http://www.icepe.org/
Natural Sciences:
- American Chemical Society National Meeting & Exposition: https://www.acs.org/content/acs/en/meetings/national-meeting.html
- American Physical Society March Meeting: https://www.aps.org/meetings/march/
- International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology (ICEST): http://www.icest.org/
- International Conference on Natural Science and Environment (ICNSE): http://www.icnse.org/
- International Conference on Life Science and Biological Engineering (LSBE): http://www.lsbe.org/
Social Sciences:
- Annual Meeting of the American Sociological Association (ASA): https://www.asanet.org/annual-meeting-2022
- International Conference on Social Science and Humanities (ICSSH): http://www.icssh.org/
- International Conference on Psychology and Behavioral Sciences (ICPBS): http://www.icpbs.org/
- International Conference on Education and Social Science (ICESS): http://www.icess.org/
- International Conference on Management and Information Science (ICMIS): http://www.icmis.org/
How to Publish a Research Paper in Journal
Publishing a research paper in a journal is a crucial step in disseminating scientific knowledge and contributing to the field. Here are the general steps to follow:
- Choose a research topic : Select a topic of your interest and identify a research question or problem that you want to investigate. Conduct a literature review to identify the gaps in the existing knowledge that your research will address.
- Conduct research : Develop a research plan and methodology to collect data and conduct experiments. Collect and analyze data to draw conclusions that address the research question.
- Write a paper: Organize your findings into a well-structured paper with clear and concise language. Your paper should include an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. Use academic language and provide references for your sources.
- Choose a journal: Choose a journal that is relevant to your research topic and audience. Consider factors such as impact factor, acceptance rate, and the reputation of the journal.
- Follow journal guidelines : Review the submission guidelines and formatting requirements of the journal. Follow the guidelines carefully to ensure that your paper meets the journal’s requirements.
- Submit your paper : Submit your paper to the journal through the online submission system or by email. Include a cover letter that briefly explains the significance of your research and why it is suitable for the journal.
- Wait for reviews: Your paper will be reviewed by experts in the field. Be prepared to address their comments and make revisions to your paper.
- Revise and resubmit: Make revisions to your paper based on the reviewers’ comments and resubmit it to the journal. If your paper is accepted, congratulations! If not, consider revising and submitting it to another journal.
- Address reviewer comments : Reviewers may provide comments and suggestions for revisions to your paper. Address these comments carefully and thoughtfully to improve the quality of your paper.
- Submit the final version: Once your revisions are complete, submit the final version of your paper to the journal. Be sure to follow any additional formatting guidelines and requirements provided by the journal.
- Publication : If your paper is accepted, it will be published in the journal. Some journals provide online publication while others may publish a print version. Be sure to cite your published paper in future research and communicate your findings to the scientific community.
How to Publish a Research Paper for Students
Here are some steps you can follow to publish a research paper as an Under Graduate or a High School Student:
- Select a topic: Choose a topic that is relevant and interesting to you, and that you have a good understanding of.
- Conduct research : Gather information and data on your chosen topic through research, experiments, surveys, or other means.
- Write the paper : Start with an outline, then write the introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion sections of the paper. Be sure to follow any guidelines provided by your instructor or the journal you plan to submit to.
- Edit and revise: Review your paper for errors in spelling, grammar, and punctuation. Ask a peer or mentor to review your paper and provide feedback for improvement.
- Choose a journal : Look for journals that publish papers in your field of study and that are appropriate for your level of research. Some popular journals for students include PLOS ONE, Nature, and Science.
- Submit the paper: Follow the submission guidelines for the journal you choose, which typically include a cover letter, abstract, and formatting requirements. Be prepared to wait several weeks to months for a response.
- Address feedback : If your paper is accepted with revisions, address the feedback from the reviewers and resubmit your paper. If your paper is rejected, review the feedback and consider revising and resubmitting to a different journal.
How to Publish a Research Paper for Free
Publishing a research paper for free can be challenging, but it is possible. Here are some steps you can take to publish your research paper for free:
- Choose a suitable open-access journal: Look for open-access journals that are relevant to your research area. Open-access journals allow readers to access your paper without charge, so your work will be more widely available.
- Check the journal’s reputation : Before submitting your paper, ensure that the journal is reputable by checking its impact factor, publication history, and editorial board.
- Follow the submission guidelines : Every journal has specific guidelines for submitting papers. Make sure to follow these guidelines carefully to increase the chances of acceptance.
- Submit your paper : Once you have completed your research paper, submit it to the journal following their submission guidelines.
- Wait for the review process: Your paper will undergo a peer-review process, where experts in your field will evaluate your work. Be patient during this process, as it can take several weeks or even months.
- Revise your paper : If your paper is rejected, don’t be discouraged. Revise your paper based on the feedback you receive from the reviewers and submit it to another open-access journal.
- Promote your research: Once your paper is published, promote it on social media and other online platforms. This will increase the visibility of your work and help it reach a wider audience.
Journals and Conferences for Free Research Paper publications
Here are the websites of the open-access journals and conferences mentioned:
Open-Access Journals:
- PLOS ONE – https://journals.plos.org/plosone/
- BMC Research Notes – https://bmcresnotes.biomedcentral.com/
- Frontiers in… – https://www.frontiersin.org/
- Journal of Open Research Software – https://openresearchsoftware.metajnl.com/
- PeerJ – https://peerj.com/
Conferences:
- IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) – https://globecom2022.ieee-globecom.org/
- IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM) – https://infocom2022.ieee-infocom.org/
- IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM) – https://www.ieee-icdm.org/
- ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Data Communication (SIGCOMM) – https://conferences.sigcomm.org/sigcomm/
- ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS) – https://www.sigsac.org/ccs/CCS2022/
Importance of Research Paper Publication
Research paper publication is important for several reasons, both for individual researchers and for the scientific community as a whole. Here are some reasons why:
- Advancing scientific knowledge : Research papers provide a platform for researchers to present their findings and contribute to the body of knowledge in their field. These papers often contain novel ideas, experimental data, and analyses that can help to advance scientific understanding.
- Building a research career : Publishing research papers is an essential component of building a successful research career. Researchers are often evaluated based on the number and quality of their publications, and having a strong publication record can increase one’s chances of securing funding, tenure, or a promotion.
- Peer review and quality control: Publication in a peer-reviewed journal means that the research has been scrutinized by other experts in the field. This peer review process helps to ensure the quality and validity of the research findings.
- Recognition and visibility : Publishing a research paper can bring recognition and visibility to the researchers and their work. It can lead to invitations to speak at conferences, collaborations with other researchers, and media coverage.
- Impact on society : Research papers can have a significant impact on society by informing policy decisions, guiding clinical practice, and advancing technological innovation.
Advantages of Research Paper Publication
There are several advantages to publishing a research paper, including:
- Recognition: Publishing a research paper allows researchers to gain recognition for their work, both within their field and in the academic community as a whole. This can lead to new collaborations, invitations to conferences, and other opportunities to share their research with a wider audience.
- Career advancement : A strong publication record can be an important factor in career advancement, particularly in academia. Publishing research papers can help researchers secure funding, grants, and promotions.
- Dissemination of knowledge : Research papers are an important way to share new findings and ideas with the broader scientific community. By publishing their research, scientists can contribute to the collective body of knowledge in their field and help advance scientific understanding.
- Feedback and peer review : Publishing a research paper allows other experts in the field to provide feedback on the research, which can help improve the quality of the work and identify potential flaws or limitations. Peer review also helps ensure that research is accurate and reliable.
- Citation and impact : Published research papers can be cited by other researchers, which can help increase the impact and visibility of the research. High citation rates can also help establish a researcher’s reputation and credibility within their field.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and...
Home → Get Published → How to Publish a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Publish a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
Jordan Kruszynski
- January 4, 2024

You’re in academia.
You’re going steady.
Your research is going well and you begin to wonder: ‘ How exactly do I get a research paper published?’
If this is the question on your lips, then this step-by-step guide is the one for you. We’ll be walking you through the whole process of how to publish a research paper.
Publishing a research paper is a significant milestone for researchers and academics, as it allows you to share your findings, contribute to your field of study, and start to gain serious recognition within the wider academic community. So, want to know how to publish a research paper? By following our guide, you’ll get a firm grasp of the steps involved in this process, giving you the best chance of successfully navigating the publishing process and getting your work out there.
Understanding the Publishing Process
To begin, it’s crucial to understand that getting a research paper published is a multi-step process. From beginning to end, it could take as little as 2 months before you see your paper nestled in the pages of your chosen journal. On the other hand, it could take as long as a year .
Below, we set out the steps before going into more detail on each one. Getting a feel for these steps will help you to visualise what lies ahead, and prepare yourself for each of them in turn. It’s important to remember that you won’t actually have control over every step – in fact, some of them will be decided by people you’ll probably never meet. However, knowing which parts of the process are yours to decide will allow you to adjust your approach and attitude accordingly.
Each of the following stages will play a vital role in the eventual publication of your paper:
- Preparing Your Research Paper
- Finding the Right Journal
- Crafting a Strong Manuscript
- Navigating the Peer-Review Process
- Submitting Your Paper
- Dealing with Rejections and Revising Your Paper
Step 1: Preparing Your Research Paper
It all starts here. The quality and content of your research paper is of fundamental importance if you want to get it published. This step will be different for every researcher depending on the nature of your research, but if you haven’t yet settled on a topic, then consider the following advice:
- Choose an interesting and relevant topic that aligns with current trends in your field. If your research touches on the passions and concerns of your academic peers or wider society, it may be more likely to capture attention and get published successfully.
- Conduct a comprehensive literature review (link to lit. review article once it’s published) to identify the state of existing research and any knowledge gaps within it. Aiming to fill a clear gap in the knowledge of your field is a great way to increase the practicality of your research and improve its chances of getting published.
- Structure your paper in a clear and organised manner, including all the necessary sections such as title, abstract, introduction (link to the ‘how to write a research paper intro’ article once it’s published) , methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
- Adhere to the formatting guidelines provided by your target journal to ensure that your paper is accepted as viable for publishing. More on this in the next section…
Step 2: Finding the Right Journal
Understanding how to publish a research paper involves selecting the appropriate journal for your work. This step is critical for successful publication, and you should take several factors into account when deciding which journal to apply for:
- Conduct thorough research to identify journals that specialise in your field of study and have published similar research. Naturally, if you submit a piece of research in molecular genetics to a journal that specialises in geology, you won’t be likely to get very far.
- Consider factors such as the journal’s scope, impact factor, and target audience. Today there is a wide array of journals to choose from, including traditional and respected print journals, as well as numerous online, open-access endeavours. Some, like Nature , even straddle both worlds.
- Review the submission guidelines provided by the journal and ensure your paper meets all the formatting requirements and word limits. This step is key. Nature, for example, offers a highly informative series of pages that tells you everything you need to know in order to satisfy their formatting guidelines (plus more on the whole submission process).
- Note that these guidelines can differ dramatically from journal to journal, and details really do matter. You might submit an outstanding piece of research, but if it includes, for example, images in the wrong size or format, this could mean a lengthy delay to getting it published. If you get everything right first time, you’ll save yourself a lot of time and trouble, as well as strengthen your publishing chances in the first place.
Step 3: Crafting a Strong Manuscript
Crafting a strong manuscript is crucial to impress journal editors and reviewers. Look at your paper as a complete package, and ensure that all the sections tie together to deliver your findings with clarity and precision.
- Begin by creating a clear and concise title that accurately reflects the content of your paper.
- Compose an informative abstract that summarises the purpose, methodology, results, and significance of your study.
- Craft an engaging introduction (link to the research paper introduction article) that draws your reader in.
- Develop a well-structured methodology section, presenting your results effectively using tables and figures.
- Write a compelling discussion and conclusion that emphasise the significance of your findings.
Step 4: Navigating the Peer-Review Process
Once you submit your research paper to a journal, it undergoes a rigorous peer-review process to ensure its quality and validity. In peer-review, experts in your field assess your research and provide feedback and suggestions for improvement, ultimately determining whether your paper is eligible for publishing or not. You are likely to encounter several models of peer-review, based on which party – author, reviewer, or both – remains anonymous throughout the process.
When your paper undergoes the peer-review process, be prepared for constructive criticism and address the comments you receive from your reviewer thoughtfully, providing clear and concise responses to their concerns or suggestions. These could make all the difference when it comes to making your next submission.
The peer-review process can seem like a closed book at times. Check out our discussion of the issue with philosopher and academic Amna Whiston in The Research Beat podcast!
Step 5: Submitting Your Paper
As we’ve already pointed out, one of the key elements in how to publish a research paper is ensuring that you meticulously follow the journal’s submission guidelines. Strive to comply with all formatting requirements, including citation styles, font, margins, and reference structure.
Before the final submission, thoroughly proofread your paper for errors, including grammar, spelling, and any inconsistencies in your data or analysis. At this stage, consider seeking feedback from colleagues or mentors to further improve the quality of your paper.
Step 6: Dealing with Rejections and Revising Your Paper
Rejection is a common part of the publishing process, but it shouldn’t discourage you. Analyse reviewer comments objectively and focus on the constructive feedback provided. Make necessary revisions and improvements to your paper to address the concerns raised by reviewers. If needed, consider submitting your paper to a different journal that is a better fit for your research.
For more tips on how to publish your paper out there, check out this thread by Dr. Asad Naveed ( @dr_asadnaveed ) – and if you need a refresher on the basics of how to publish under the Open Access model, watch this 5-minute video from Audemic Academy !
Final Thoughts
Successfully understanding how to publish a research paper requires dedication, attention to detail, and a systematic approach. By following the advice in our guide, you can increase your chances of navigating the publishing process effectively and achieving your goal of publication.
Remember, the journey may involve revisions, peer feedback, and potential rejections, but each step is an opportunity for growth and improvement. Stay persistent, maintain a positive mindset, and continue to refine your research paper until it reaches the standards of your target journal. Your contribution to your wider discipline through published research will not only advance your career, but also add to the growing body of collective knowledge in your field. Embrace the challenges and rewards that come with the publication process, and may your research paper make a significant impact in your area of study!
Looking for inspiration for your next big paper? Head to Audemic , where you can organise and listen to all the best and latest research in your field!
Keep striving, researchers! ✨
Table of Contents
Related articles.

You’re in academia. You’re going steady. Your research is going well and you begin to wonder: ‘How exactly do I get a

Behind the Scenes: What Does a Research Assistant Do?
Have you ever wondered what goes on behind the scenes in a research lab? Does it involve acting out the whims of

How to Write a Research Paper Introduction: Hook, Line, and Sinker
Want to know how to write a research paper introduction that dazzles? Struggling to hook your reader in with your opening sentences?

Blog Podcast
Privacy policy Terms of service
Subscribe to our newsletter!
Discover more from Audemic: Access any academic research via audio
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Our websites may use cookies to personalize and enhance your experience. By continuing without changing your cookie settings, you agree to this collection. For more information, please see our University Websites Privacy Notice .
Office of Undergraduate Research
Writing an academic paper as an undergraduate researcher, by ariane garrett, our peer research ambassador.
Publishing papers is the primary way that scientific knowledge is disseminated within the academic community. Therefore an essential part of becoming a successful researcher is learning how to write an academic paper. Throughout your undergraduate research career you may or may not have the opportunity to be published. Regardless, learning how academic papers are written is useful knowledge for anyone interested in pursuing a research career. Whether or not you have the opportunity to be published as an undergrad depends on a variety of factors, including the nature of your project, how often your faculty advisor publishes papers, and your particular role in the research lab. If you haven’t been published as an undergrad, no need to stress. There are many other ways your research can shine on an application.
I was tasked with writing my first paper in the spring of my junior year. As I am the primary person working on my research project, my faculty advisor expected me to write the paper by myself with his help and feedback. At first, this seemed to be a very daunting task. I had never written an entire academic paper by myself before, and I had no idea where to begin. The writing process took much longer than I expected (I didn’t finish until Fall 2019), and the paper I submitted is currently under review. In this blog post, I will share what I learned while writing my first academic paper. As a biomedical engineering major, my experience is a reflection of the norms within the engineering field. However, I hope that some of these tips will prove useful for those in all majors.
Getting Started
I began my first draft of my paper as I had begun many other papers I have written- with an introduction. When I showed my first draft to my PI, he told me that it is actually most common in the engineering field to begin writing an academic paper by constructing the figures. At first, I thought this seemed rather counterintuitive. Shouldn’t the figures be based on the writing, rather than the other way around? There are several reasons why the opposite is actually true. Firstly, the figures are the most eye-catching part of every paper and sometimes the only thing a reader will look at. In addition, many journals have figure limitations so the figures that are chosen must be carefully thought out in order to maximize their effectiveness. Lastly, constructing the figures first establishes a clear outline that you can follow as you write the rest of the paper.
Writing the Paper
Writing the actual paper is a long process that typically involves many revisions. I found it helpful to read papers from the same journal I was submitting to in order to get an idea of typical paper formats in that journal. I would also recommend seeking feedback at several stages of the writing process. Don’t wait until the entire paper is finished before showing it to your PI, instead, ask for feedback after the first draft of each section is finished. As an academic paper can have anywhere from five to hundreds of sources, I would also suggest using a citation manager as you write. This will save you from having to constantly update the sources in the paper as you add and revise.
Submitting the Paper
In my case, my PI submitted the paper and is the primary contact with the journal. However, I was expected to fully format the paper before I gave it to him to submit. If you visit the website of the journal you are submitting to, there will be details on the formatting expectations. Reformatting the entire paper after it has been written can be a lot of work, so it’s helpful to review these before you begin writing. Often, it is expected that you include a letter to the editor requesting for your paper to be considered, which you may or may not have to write depending on your PI.
After Submission
Depending on the journal, it can be up to several months before you hear back about your submission. In my case, I heard back from the reviewers about two months after submission. There were two reviewers for the paper I submitted, though this number will likely vary depending on the journal. The comments that were made were useful and provided good insight into an outsider’s perspective on my research. It is very common for journals to request revision and resubmission, so don’t expect the first paper you submit to be published!
Although writing an academic paper is challenging, I found it to be a very rewarding experience. I now appreciate how much work it takes to write a good paper and I feel like I grew as a scientific writer throughout the process. If you feel that your research deserves to be published, don’t be afraid to reach out to your PI and ask them if they think you could write a paper. Even if it is never published, writing about your research is an excellent way to become a better writer and also understand your own research area more fully.
Ariane is a senior majoring in biomedical engineering and Spanish. Click here to learn more about Ariane.
You are using an outdated browser . Please upgrade your browser today !
How to Write and Publish a Research Paper in 7 Steps
What comes next after you're done with your research? Publishing the results in a journal of course! We tell you how to present your work in the best way possible.
This post is part of a series, which serves to provide hands-on information and resources for authors and editors.
Things have gotten busy in scholarly publishing: These days, a new article gets published in the 50,000 most important peer-reviewed journals every few seconds, while each one takes on average 40 minutes to read. Hundreds of thousands of papers reach the desks of editors and reviewers worldwide each year and 50% of all submissions end up rejected at some stage.
In a nutshell: there is a lot of competition, and the people who decide upon the fate of your manuscript are short on time and overworked. But there are ways to make their lives a little easier and improve your own chances of getting your work published!
Well, it may seem obvious, but before submitting an academic paper, always make sure that it is an excellent reflection of the research you have done and that you present it in the most professional way possible. Incomplete or poorly presented manuscripts can create a great deal of frustration and annoyance for editors who probably won’t even bother wasting the time of the reviewers!
This post will discuss 7 steps to the successful publication of your research paper:
- Check whether your research is publication-ready
- Choose an article type
- Choose a journal
- Construct your paper
- Decide the order of authors
- Check and double-check
- Submit your paper
1. Check Whether Your Research Is Publication-Ready
Should you publish your research at all?
If your work holds academic value – of course – a well-written scholarly article could open doors to your research community. However, if you are not yet sure, whether your research is ready for publication, here are some key questions to ask yourself depending on your field of expertise:
- Have you done or found something new and interesting? Something unique?
- Is the work directly related to a current hot topic?
- Have you checked the latest results or research in the field?
- Have you provided solutions to any difficult problems?
- Have the findings been verified?
- Have the appropriate controls been performed if required?
- Are your findings comprehensive?
If the answers to all relevant questions are “yes”, you need to prepare a good, strong manuscript. Remember, a research paper is only useful if it is clearly understood, reproducible and if it is read and used .
2. Choose An Article Type
The first step is to determine which type of paper is most appropriate for your work and what you want to achieve. The following list contains the most important, usually peer-reviewed article types in the natural sciences:
Full original research papers disseminate completed research findings. On average this type of paper is 8-10 pages long, contains five figures, and 25-30 references. Full original research papers are an important part of the process when developing your career.
Review papers present a critical synthesis of a specific research topic. These papers are usually much longer than original papers and will contain numerous references. More often than not, they will be commissioned by journal editors. Reviews present an excellent way to solidify your research career.
Letters, Rapid or Short Communications are often published for the quick and early communication of significant and original advances. They are much shorter than full articles and usually limited in length by the journal. Journals specifically dedicated to short communications or letters are also published in some fields. In these the authors can present short preliminary findings before developing a full-length paper.
3. Choose a Journal
Are you looking for the right place to publish your paper? Find out here whether a De Gruyter journal might be the right fit.
Submit to journals that you already read, that you have a good feel for. If you do so, you will have a better appreciation of both its culture and the requirements of the editors and reviewers.
Other factors to consider are:
- The specific subject area
- The aims and scope of the journal
- The type of manuscript you have written
- The significance of your work
- The reputation of the journal
- The reputation of the editors within the community
- The editorial/review and production speeds of the journal
- The community served by the journal
- The coverage and distribution
- The accessibility ( open access vs. closed access)
4. Construct Your Paper
Each element of a paper has its purpose, so you should make these sections easy to index and search.
Don’t forget that requirements can differ highly per publication, so always make sure to apply a journal’s specific instructions – or guide – for authors to your manuscript, even to the first draft (text layout, paper citation, nomenclature, figures and table, etc.) It will save you time, and the editor’s.
Also, even in these days of Internet-based publishing, space is still at a premium, so be as concise as possible. As a good journalist would say: “Never use three words when one will do!”
Let’s look at the typical structure of a full research paper, but bear in mind certain subject disciplines may have their own specific requirements so check the instructions for authors on the journal’s home page.
4.1 The Title
It’s important to use the title to tell the reader what your paper is all about! You want to attract their attention, a bit like a newspaper headline does. Be specific and to the point. Keep it informative and concise, and avoid jargon and abbreviations (unless they are universally recognized like DNA, for example).
4.2 The Abstract
This could be termed as the “advertisement” for your article. Make it interesting and easily understood without the reader having to read the whole article. Be accurate and specific, and keep it as brief and concise as possible. Some journals (particularly in the medical fields) will ask you to structure the abstract in distinct, labeled sections, which makes it even more accessible.
A clear abstract will influence whether or not your work is considered and whether an editor should invest more time on it or send it for review.
4.3 Keywords
Keywords are used by abstracting and indexing services, such as PubMed and Web of Science. They are the labels of your manuscript, which make it “searchable” online by other researchers.
Include words or phrases (usually 4-8) that are closely related to your topic but not “too niche” for anyone to find them. Make sure to only use established abbreviations. Think about what scientific terms and its variations your potential readers are likely to use and search for. You can also do a test run of your selected keywords in one of the common academic search engines. Do similar articles to your own appear? Yes? Then that’s a good sign.
4.4 Introduction
This first part of the main text should introduce the problem, as well as any existing solutions you are aware of and the main limitations. Also, state what you hope to achieve with your research.
Do not confuse the introduction with the results, discussion or conclusion.
4.5 Methods
Every research article should include a detailed Methods section (also referred to as “Materials and Methods”) to provide the reader with enough information to be able to judge whether the study is valid and reproducible.
Include detailed information so that a knowledgeable reader can reproduce the experiment. However, use references and supplementary materials to indicate previously published procedures.
4.6 Results
In this section, you will present the essential or primary results of your study. To display them in a comprehensible way, you should use subheadings as well as illustrations such as figures, graphs, tables and photos, as appropriate.
4.7 Discussion
Here you should tell your readers what the results mean .
Do state how the results relate to the study’s aims and hypotheses and how the findings relate to those of other studies. Explain all possible interpretations of your findings and the study’s limitations.
Do not make “grand statements” that are not supported by the data. Also, do not introduce any new results or terms. Moreover, do not ignore work that conflicts or disagrees with your findings. Instead …
Be brave! Address conflicting study results and convince the reader you are the one who is correct.
4.8 Conclusion
Your conclusion isn’t just a summary of what you’ve already written. It should take your paper one step further and answer any unresolved questions.
Sum up what you have shown in your study and indicate possible applications and extensions. The main question your conclusion should answer is: What do my results mean for the research field and my community?
4.9 Acknowledgments and Ethical Statements
It is extremely important to acknowledge anyone who has helped you with your paper, including researchers who supplied materials or reagents (e.g. vectors or antibodies); and anyone who helped with the writing or English, or offered critical comments about the content.
Learn more about academic integrity in our blog post “Scholarly Publication Ethics: 4 Common Mistakes You Want To Avoid” .
Remember to state why people have been acknowledged and ask their permission . Ensure that you acknowledge sources of funding, including any grant or reference numbers.
Furthermore, if you have worked with animals or humans, you need to include information about the ethical approval of your study and, if applicable, whether informed consent was given. Also, state whether you have any competing interests regarding the study (e.g. because of financial or personal relationships.)
4.10 References
The end is in sight, but don’t relax just yet!
De facto, there are often more mistakes in the references than in any other part of the manuscript. It is also one of the most annoying and time-consuming problems for editors.
Remember to cite the main scientific publications on which your work is based. But do not inflate the manuscript with too many references. Avoid excessive – and especially unnecessary – self-citations. Also, avoid excessive citations of publications from the same institute or region.
5. Decide the Order of Authors
In the sciences, the most common way to order the names of the authors is by relative contribution.
Generally, the first author conducts and/or supervises the data analysis and the proper presentation and interpretation of the results. They put the paper together and usually submit the paper to the journal.
Co-authors make intellectual contributions to the data analysis and contribute to data interpretation. They review each paper draft. All of them must be able to present the paper and its results, as well as to defend the implications and discuss study limitations.
Do not leave out authors who should be included or add “gift authors”, i.e. authors who did not contribute significantly.
6. Check and Double-Check
As a final step before submission, ask colleagues to read your work and be constructively critical .
Make sure that the paper is appropriate for the journal – take a last look at their aims and scope. Check if all of the requirements in the instructions for authors are met.
Ensure that the cited literature is balanced. Are the aims, purpose and significance of the results clear?
Conduct a final check for language, either by a native English speaker or an editing service.
7. Submit Your Paper
When you and your co-authors have double-, triple-, quadruple-checked the manuscript: submit it via e-mail or online submission system. Along with your manuscript, submit a cover letter, which highlights the reasons why your paper would appeal to the journal and which ensures that you have received approval of all authors for submission.
It is up to the editors and the peer-reviewers now to provide you with their (ideally constructive and helpful) comments and feedback. Time to take a breather!
If the paper gets rejected, do not despair – it happens to literally everybody. If the journal suggests major or minor revisions, take the chance to provide a thorough response and make improvements as you see fit. If the paper gets accepted, congrats!
It’s now time to get writing and share your hard work – good luck!
If you are interested, check out this related blog post

[Title Image by Nick Morrison via Unsplash]
David Sleeman
David Sleeman worked as Senior Journals Manager in the field of Physical Sciences at De Gruyter.
You might also be interested in
Academia & Publishing
Library Community Gives Back: 2023 Webinar Speakers’ Charity Picks
From error to excellence: embracing mistakes in library practice, the impact of transformative agreements on scholarly publishing, visit our shop.
De Gruyter publishes over 1,300 new book titles each year and more than 750 journals in the humanities, social sciences, medicine, mathematics, engineering, computer sciences, natural sciences, and law.
Pin It on Pinterest
How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal
- Open access
- Published: 30 April 2020
- Volume 36 , pages 909–913, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Clara Busse ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0178-1000 1 &
- Ella August ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5151-1036 1 , 2
273k Accesses
15 Citations
720 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Communicating research findings is an essential step in the research process. Often, peer-reviewed journals are the forum for such communication, yet many researchers are never taught how to write a publishable scientific paper. In this article, we explain the basic structure of a scientific paper and describe the information that should be included in each section. We also identify common pitfalls for each section and recommend strategies to avoid them. Further, we give advice about target journal selection and authorship. In the online resource 1 , we provide an example of a high-quality scientific paper, with annotations identifying the elements we describe in this article.
Similar content being viewed by others

Literature reviews as independent studies: guidelines for academic practice
Open peer review: promoting transparency in open science
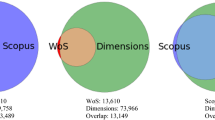
The journal coverage of Web of Science, Scopus and Dimensions: A comparative analysis
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Writing a scientific paper is an important component of the research process, yet researchers often receive little formal training in scientific writing. This is especially true in low-resource settings. In this article, we explain why choosing a target journal is important, give advice about authorship, provide a basic structure for writing each section of a scientific paper, and describe common pitfalls and recommendations for each section. In the online resource 1 , we also include an annotated journal article that identifies the key elements and writing approaches that we detail here. Before you begin your research, make sure you have ethical clearance from all relevant ethical review boards.
Select a Target Journal Early in the Writing Process
We recommend that you select a “target journal” early in the writing process; a “target journal” is the journal to which you plan to submit your paper. Each journal has a set of core readers and you should tailor your writing to this readership. For example, if you plan to submit a manuscript about vaping during pregnancy to a pregnancy-focused journal, you will need to explain what vaping is because readers of this journal may not have a background in this topic. However, if you were to submit that same article to a tobacco journal, you would not need to provide as much background information about vaping.
Information about a journal’s core readership can be found on its website, usually in a section called “About this journal” or something similar. For example, the Journal of Cancer Education presents such information on the “Aims and Scope” page of its website, which can be found here: https://www.springer.com/journal/13187/aims-and-scope .
Peer reviewer guidelines from your target journal are an additional resource that can help you tailor your writing to the journal and provide additional advice about crafting an effective article [ 1 ]. These are not always available, but it is worth a quick web search to find out.
Identify Author Roles Early in the Process
Early in the writing process, identify authors, determine the order of authors, and discuss the responsibilities of each author. Standard author responsibilities have been identified by The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) [ 2 ]. To set clear expectations about each team member’s responsibilities and prevent errors in communication, we also suggest outlining more detailed roles, such as who will draft each section of the manuscript, write the abstract, submit the paper electronically, serve as corresponding author, and write the cover letter. It is best to formalize this agreement in writing after discussing it, circulating the document to the author team for approval. We suggest creating a title page on which all authors are listed in the agreed-upon order. It may be necessary to adjust authorship roles and order during the development of the paper. If a new author order is agreed upon, be sure to update the title page in the manuscript draft.
In the case where multiple papers will result from a single study, authors should discuss who will author each paper. Additionally, authors should agree on a deadline for each paper and the lead author should take responsibility for producing an initial draft by this deadline.
Structure of the Introduction Section
The introduction section should be approximately three to five paragraphs in length. Look at examples from your target journal to decide the appropriate length. This section should include the elements shown in Fig. 1 . Begin with a general context, narrowing to the specific focus of the paper. Include five main elements: why your research is important, what is already known about the topic, the “gap” or what is not yet known about the topic, why it is important to learn the new information that your research adds, and the specific research aim(s) that your paper addresses. Your research aim should address the gap you identified. Be sure to add enough background information to enable readers to understand your study. Table 1 provides common introduction section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.

The main elements of the introduction section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Methods Section
The purpose of the methods section is twofold: to explain how the study was done in enough detail to enable its replication and to provide enough contextual detail to enable readers to understand and interpret the results. In general, the essential elements of a methods section are the following: a description of the setting and participants, the study design and timing, the recruitment and sampling, the data collection process, the dataset, the dependent and independent variables, the covariates, the analytic approach for each research objective, and the ethical approval. The hallmark of an exemplary methods section is the justification of why each method was used. Table 2 provides common methods section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Results Section
The focus of the results section should be associations, or lack thereof, rather than statistical tests. Two considerations should guide your writing here. First, the results should present answers to each part of the research aim. Second, return to the methods section to ensure that the analysis and variables for each result have been explained.
Begin the results section by describing the number of participants in the final sample and details such as the number who were approached to participate, the proportion who were eligible and who enrolled, and the number of participants who dropped out. The next part of the results should describe the participant characteristics. After that, you may organize your results by the aim or by putting the most exciting results first. Do not forget to report your non-significant associations. These are still findings.
Tables and figures capture the reader’s attention and efficiently communicate your main findings [ 3 ]. Each table and figure should have a clear message and should complement, rather than repeat, the text. Tables and figures should communicate all salient details necessary for a reader to understand the findings without consulting the text. Include information on comparisons and tests, as well as information about the sample and timing of the study in the title, legend, or in a footnote. Note that figures are often more visually interesting than tables, so if it is feasible to make a figure, make a figure. To avoid confusing the reader, either avoid abbreviations in tables and figures, or define them in a footnote. Note that there should not be citations in the results section and you should not interpret results here. Table 3 provides common results section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Discussion Section
Opposite the introduction section, the discussion should take the form of a right-side-up triangle beginning with interpretation of your results and moving to general implications (Fig. 2 ). This section typically begins with a restatement of the main findings, which can usually be accomplished with a few carefully-crafted sentences.
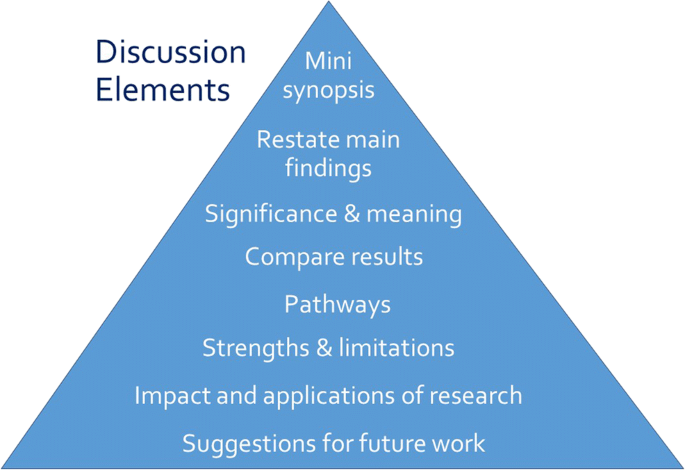
Major elements of the discussion section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Next, interpret the meaning or explain the significance of your results, lifting the reader’s gaze from the study’s specific findings to more general applications. Then, compare these study findings with other research. Are these findings in agreement or disagreement with those from other studies? Does this study impart additional nuance to well-accepted theories? Situate your findings within the broader context of scientific literature, then explain the pathways or mechanisms that might give rise to, or explain, the results.
Journals vary in their approach to strengths and limitations sections: some are embedded paragraphs within the discussion section, while some mandate separate section headings. Keep in mind that every study has strengths and limitations. Candidly reporting yours helps readers to correctly interpret your research findings.
The next element of the discussion is a summary of the potential impacts and applications of the research. Should these results be used to optimally design an intervention? Does the work have implications for clinical protocols or public policy? These considerations will help the reader to further grasp the possible impacts of the presented work.
Finally, the discussion should conclude with specific suggestions for future work. Here, you have an opportunity to illuminate specific gaps in the literature that compel further study. Avoid the phrase “future research is necessary” because the recommendation is too general to be helpful to readers. Instead, provide substantive and specific recommendations for future studies. Table 4 provides common discussion section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Follow the Journal’s Author Guidelines
After you select a target journal, identify the journal’s author guidelines to guide the formatting of your manuscript and references. Author guidelines will often (but not always) include instructions for titles, cover letters, and other components of a manuscript submission. Read the guidelines carefully. If you do not follow the guidelines, your article will be sent back to you.
Finally, do not submit your paper to more than one journal at a time. Even if this is not explicitly stated in the author guidelines of your target journal, it is considered inappropriate and unprofessional.
Your title should invite readers to continue reading beyond the first page [ 4 , 5 ]. It should be informative and interesting. Consider describing the independent and dependent variables, the population and setting, the study design, the timing, and even the main result in your title. Because the focus of the paper can change as you write and revise, we recommend you wait until you have finished writing your paper before composing the title.
Be sure that the title is useful for potential readers searching for your topic. The keywords you select should complement those in your title to maximize the likelihood that a researcher will find your paper through a database search. Avoid using abbreviations in your title unless they are very well known, such as SNP, because it is more likely that someone will use a complete word rather than an abbreviation as a search term to help readers find your paper.
After you have written a complete draft, use the checklist (Fig. 3 ) below to guide your revisions and editing. Additional resources are available on writing the abstract and citing references [ 5 ]. When you feel that your work is ready, ask a trusted colleague or two to read the work and provide informal feedback. The box below provides a checklist that summarizes the key points offered in this article.

Checklist for manuscript quality
Data Availability
Michalek AM (2014) Down the rabbit hole…advice to reviewers. J Cancer Educ 29:4–5
Article Google Scholar
International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Defining the role of authors and contributors: who is an author? http://www.icmje.org/recommendations/browse/roles-and-responsibilities/defining-the-role-of-authosrs-and-contributors.html . Accessed 15 January, 2020
Vetto JT (2014) Short and sweet: a short course on concise medical writing. J Cancer Educ 29(1):194–195
Brett M, Kording K (2017) Ten simple rules for structuring papers. PLoS ComputBiol. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005619
Lang TA (2017) Writing a better research article. J Public Health Emerg. https://doi.org/10.21037/jphe.2017.11.06
Download references
Acknowledgments
Ella August is grateful to the Sustainable Sciences Institute for mentoring her in training researchers on writing and publishing their research.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Maternal and Child Health, University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, 135 Dauer Dr, 27599, Chapel Hill, NC, USA
Clara Busse & Ella August
Department of Epidemiology, University of Michigan School of Public Health, 1415 Washington Heights, Ann Arbor, MI, 48109-2029, USA
Ella August
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ella August .
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
(PDF 362 kb)

Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Busse, C., August, E. How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal. J Canc Educ 36 , 909–913 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Download citation
Published : 30 April 2020
Issue Date : October 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Manuscripts
- Scientific writing
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal
Clara busse.
1 Department of Maternal and Child Health, University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, 135 Dauer Dr, 27599 Chapel Hill, NC USA
Ella August
2 Department of Epidemiology, University of Michigan School of Public Health, 1415 Washington Heights, Ann Arbor, MI 48109-2029 USA
Associated Data
Communicating research findings is an essential step in the research process. Often, peer-reviewed journals are the forum for such communication, yet many researchers are never taught how to write a publishable scientific paper. In this article, we explain the basic structure of a scientific paper and describe the information that should be included in each section. We also identify common pitfalls for each section and recommend strategies to avoid them. Further, we give advice about target journal selection and authorship. In the online resource 1 , we provide an example of a high-quality scientific paper, with annotations identifying the elements we describe in this article.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Introduction
Writing a scientific paper is an important component of the research process, yet researchers often receive little formal training in scientific writing. This is especially true in low-resource settings. In this article, we explain why choosing a target journal is important, give advice about authorship, provide a basic structure for writing each section of a scientific paper, and describe common pitfalls and recommendations for each section. In the online resource 1 , we also include an annotated journal article that identifies the key elements and writing approaches that we detail here. Before you begin your research, make sure you have ethical clearance from all relevant ethical review boards.
Select a Target Journal Early in the Writing Process
We recommend that you select a “target journal” early in the writing process; a “target journal” is the journal to which you plan to submit your paper. Each journal has a set of core readers and you should tailor your writing to this readership. For example, if you plan to submit a manuscript about vaping during pregnancy to a pregnancy-focused journal, you will need to explain what vaping is because readers of this journal may not have a background in this topic. However, if you were to submit that same article to a tobacco journal, you would not need to provide as much background information about vaping.
Information about a journal’s core readership can be found on its website, usually in a section called “About this journal” or something similar. For example, the Journal of Cancer Education presents such information on the “Aims and Scope” page of its website, which can be found here: https://www.springer.com/journal/13187/aims-and-scope .
Peer reviewer guidelines from your target journal are an additional resource that can help you tailor your writing to the journal and provide additional advice about crafting an effective article [ 1 ]. These are not always available, but it is worth a quick web search to find out.
Identify Author Roles Early in the Process
Early in the writing process, identify authors, determine the order of authors, and discuss the responsibilities of each author. Standard author responsibilities have been identified by The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) [ 2 ]. To set clear expectations about each team member’s responsibilities and prevent errors in communication, we also suggest outlining more detailed roles, such as who will draft each section of the manuscript, write the abstract, submit the paper electronically, serve as corresponding author, and write the cover letter. It is best to formalize this agreement in writing after discussing it, circulating the document to the author team for approval. We suggest creating a title page on which all authors are listed in the agreed-upon order. It may be necessary to adjust authorship roles and order during the development of the paper. If a new author order is agreed upon, be sure to update the title page in the manuscript draft.
In the case where multiple papers will result from a single study, authors should discuss who will author each paper. Additionally, authors should agree on a deadline for each paper and the lead author should take responsibility for producing an initial draft by this deadline.
Structure of the Introduction Section
The introduction section should be approximately three to five paragraphs in length. Look at examples from your target journal to decide the appropriate length. This section should include the elements shown in Fig. 1 . Begin with a general context, narrowing to the specific focus of the paper. Include five main elements: why your research is important, what is already known about the topic, the “gap” or what is not yet known about the topic, why it is important to learn the new information that your research adds, and the specific research aim(s) that your paper addresses. Your research aim should address the gap you identified. Be sure to add enough background information to enable readers to understand your study. Table Table1 1 provides common introduction section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.

The main elements of the introduction section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Common introduction section pitfalls and recommendations
Methods Section
The purpose of the methods section is twofold: to explain how the study was done in enough detail to enable its replication and to provide enough contextual detail to enable readers to understand and interpret the results. In general, the essential elements of a methods section are the following: a description of the setting and participants, the study design and timing, the recruitment and sampling, the data collection process, the dataset, the dependent and independent variables, the covariates, the analytic approach for each research objective, and the ethical approval. The hallmark of an exemplary methods section is the justification of why each method was used. Table Table2 2 provides common methods section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Common methods section pitfalls and recommendations
Results Section
The focus of the results section should be associations, or lack thereof, rather than statistical tests. Two considerations should guide your writing here. First, the results should present answers to each part of the research aim. Second, return to the methods section to ensure that the analysis and variables for each result have been explained.
Begin the results section by describing the number of participants in the final sample and details such as the number who were approached to participate, the proportion who were eligible and who enrolled, and the number of participants who dropped out. The next part of the results should describe the participant characteristics. After that, you may organize your results by the aim or by putting the most exciting results first. Do not forget to report your non-significant associations. These are still findings.
Tables and figures capture the reader’s attention and efficiently communicate your main findings [ 3 ]. Each table and figure should have a clear message and should complement, rather than repeat, the text. Tables and figures should communicate all salient details necessary for a reader to understand the findings without consulting the text. Include information on comparisons and tests, as well as information about the sample and timing of the study in the title, legend, or in a footnote. Note that figures are often more visually interesting than tables, so if it is feasible to make a figure, make a figure. To avoid confusing the reader, either avoid abbreviations in tables and figures, or define them in a footnote. Note that there should not be citations in the results section and you should not interpret results here. Table Table3 3 provides common results section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Common results section pitfalls and recommendations
Discussion Section
Opposite the introduction section, the discussion should take the form of a right-side-up triangle beginning with interpretation of your results and moving to general implications (Fig. 2 ). This section typically begins with a restatement of the main findings, which can usually be accomplished with a few carefully-crafted sentences.

Major elements of the discussion section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Next, interpret the meaning or explain the significance of your results, lifting the reader’s gaze from the study’s specific findings to more general applications. Then, compare these study findings with other research. Are these findings in agreement or disagreement with those from other studies? Does this study impart additional nuance to well-accepted theories? Situate your findings within the broader context of scientific literature, then explain the pathways or mechanisms that might give rise to, or explain, the results.
Journals vary in their approach to strengths and limitations sections: some are embedded paragraphs within the discussion section, while some mandate separate section headings. Keep in mind that every study has strengths and limitations. Candidly reporting yours helps readers to correctly interpret your research findings.
The next element of the discussion is a summary of the potential impacts and applications of the research. Should these results be used to optimally design an intervention? Does the work have implications for clinical protocols or public policy? These considerations will help the reader to further grasp the possible impacts of the presented work.
Finally, the discussion should conclude with specific suggestions for future work. Here, you have an opportunity to illuminate specific gaps in the literature that compel further study. Avoid the phrase “future research is necessary” because the recommendation is too general to be helpful to readers. Instead, provide substantive and specific recommendations for future studies. Table Table4 4 provides common discussion section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Common discussion section pitfalls and recommendations
Follow the Journal’s Author Guidelines
After you select a target journal, identify the journal’s author guidelines to guide the formatting of your manuscript and references. Author guidelines will often (but not always) include instructions for titles, cover letters, and other components of a manuscript submission. Read the guidelines carefully. If you do not follow the guidelines, your article will be sent back to you.
Finally, do not submit your paper to more than one journal at a time. Even if this is not explicitly stated in the author guidelines of your target journal, it is considered inappropriate and unprofessional.
Your title should invite readers to continue reading beyond the first page [ 4 , 5 ]. It should be informative and interesting. Consider describing the independent and dependent variables, the population and setting, the study design, the timing, and even the main result in your title. Because the focus of the paper can change as you write and revise, we recommend you wait until you have finished writing your paper before composing the title.
Be sure that the title is useful for potential readers searching for your topic. The keywords you select should complement those in your title to maximize the likelihood that a researcher will find your paper through a database search. Avoid using abbreviations in your title unless they are very well known, such as SNP, because it is more likely that someone will use a complete word rather than an abbreviation as a search term to help readers find your paper.
After you have written a complete draft, use the checklist (Fig. (Fig.3) 3 ) below to guide your revisions and editing. Additional resources are available on writing the abstract and citing references [ 5 ]. When you feel that your work is ready, ask a trusted colleague or two to read the work and provide informal feedback. The box below provides a checklist that summarizes the key points offered in this article.

Checklist for manuscript quality
(PDF 362 kb)
Acknowledgments
Ella August is grateful to the Sustainable Sciences Institute for mentoring her in training researchers on writing and publishing their research.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Data Availability
Compliance with ethical standards.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications . If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

- Library Catalogue

The latest news and answers to your questions about scholarly publishing and open access.
How can I publish an academic article as an undergraduate student?
Choosing where to submit your work as an undergrad.
As a researcher, where you submit will really depend on the details of the submission and where it best fits, as well as where you're likely to be successful at this point in your career. Journals will often consider any original research and will assess it based on the novelty and contribution to the field of research. However, there are a few steps you can take to increase your chances of being successful in getting your work published at this stage.
- Check out our post on Getting Published: Tips for choosing an academic journal for general suggestions about journal publishing, including where to look for possible journals and options for making your work open access.
- Check the journals' rejection rates. Journals with very high rejection rates may be more challenging to publish in as a student, simply because they accept fewer articles.
- Consider whether you can work with a faculty member to co-author the paper that you submit.
- Do some research to find out where other undergraduate students in your department have been successful in getting published.
Journals dedicated to publishing undergraduate research
More information about undergraduate publishing.
Visit the following resources to learn more about Scholarly Publishing, and contact your liaison librarian or [email protected] for additional support.
- Scholarly Publishing and Open Access webpages
- Introduction to Scholarly Publishing at SFU - Canvas Course
- Attend a Research Commons publishing workshop, such as the Publishing Symposium (while the Research Commons workshops are primarily offered to graduate students, undergraduate students interested in publishing are welcome to attend).
*Don't see an SFU student journal in your discipline? Consider starting one! Visit the SFU Library Digital Publishing webpages and contact [email protected] to learn more.
Contact us : For assistance with scholarly publishing, please contact [email protected] .
An Undergraduate's Guide to Funding and Publishing Research
- URECA and other SBU Research Programs and Opportunities
- Funding Your Research
- Publishing Your Research: Why and How?
- Publishing Your Research: List of Undergraduate Journals
SBU's own publications
Note that among the journals listed here are SBU's own publications such as SBU Brooklogue , Young Investigator's Review and the Stony Brook Undergraduate History Journal .
How do I know whether my discipline is considered a Humanities or Social Science field?
Humanities includes fields such as Art History, Classics, English, Comparative Literature, History, Musicology, and Philosophy. Sometimes History can be considered broadly as either a Humanities or Social Science discipline, but for the sake of this list, most history journals are listed in the Arts & Humanities category. Likewise, Women's, Gender, and Sexuality Studies and related fields often use methods from both Humanities and Social Science research, so you might find related topics on either the Humanities or Social Science list. Psychology is another borderline discipline that might be classified as either a social science or STEM field. For the sake of this list, Psychology is listed with the Social Sciences. STEM fields are those affiliated with science, technology, engineering, or math.
Journals that publish undergraduate research
There are many journals that focus specifically on publishing undergraduate research. The Council on Undergraduate Research (CUR) keeps an ever growing list of journals that feature undergraduate work . However, many of those listed by CUR are hosted by a specific institution and might only publish the work of their own students, and others might not be peer-reviewed or have publishing fees, so read the descriptions carefully. And, as always, carefully review each journal's website, published articles, and the author submission guidelines before submitting your work.
Below is a list of selected journals that SBU undergraduates are eligible to submit to, organized into the following categories:
- Broad Scope: Journals that publish research in any disciplinary area.
- Arts and Humanities : Fields such as Art History, Classics, English, Comparative Literature, Cultural Studies, History, Musicology, Philosophy, Theology, and Writing & Rhetoric. Sometimes History-related fields are also classified as a Social Science, but on this page, most history journals are in the Arts & Humanities category.
- Social Sciences: Fields such as Sociology, Psychology, Economics, International Affairs, Geography, Sustainability, Political Science, and Human Rights are included here.
- STEM : Fields in the hard sciences, technology, engineering and mathematics.
Broad Scope: Journals that publish research in any discipline
- Aletheia: The Alpha Chi Journal of Undergraduate Scholarship Peer-reviewed journal for undergraduate scholarship run by the Alpha Chi National College Honor Society.
- American Journal of Undergraduate Research (AJUR) AJUR is a national, independent, faculty peer-reviewed, open-source, quarterly, multidisciplinary student research journal.
- Butler Journal of Undergraduate Research (BJUR) Submission of original, scholarly research articles is open to undergraduates from any accredited college or university. BJUR publishes scholarship across the humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences.
- Discussions: The Undergraduate Research Journal of Case Western Reserve University The journal accepts research papers written by current undergraduate students from accredited colleges and universities around the globe. The research can be on any topic.
- Inquiries: Social Sciences, Arts, & Humanities An open access academic journal focusing on publishing high quality original work across a range of disciplines, especially on work in the social sciences, arts, and humanities.
- International Journal of Undergraduate Research & Creative Activities (IJURCA) Peer-reviewed, open-access journal dedicated to the publication of outstanding scholarship by undergraduates and their mentors. Accepts submissions from all academic disciplines, including original research in the the form of articles and literature reviews, as well as creative work in a variety of media.
- Journal of Student Research Multidisciplinary and faculty-reviewed journal devoted to the rapid dissemination of current research done by high school, undergraduate, and graduate students.
- Midwest Journal of Undergraduate Research Multidisciplinary scholarly journal produced by a team of Monmouth College student editors and faculty members with peer and faculty reviewers for each article.
- SBU Brooklogue SBU's exclusively undergraduate, peer-reviewed journal for humanities and social sciences.
- Undergraduate Research Journal Double-blind, educator-reviewed print and electronic journal published annually. A forum for multidisciplinary undergraduate research and creative endeavors including case studies, conceptual pieces, creative writing, journalism writings, literature reviews, original art, photography, and scientific studies. Highlights mentored undergraduate scholarly products across all disciplines from all types of higher education institutions.
- UReCA: The NCHC Journal of Undergraduate Research & Creative Activity The official undergraduate journal of the National Collegiate Honors Council. Submissions are accepted from undergraduates in the following categories: STEM, Social Science, Humanities, Fine Art, and Creative Writing.
Arts and Humanities
- Animus: The Undergraduate Classical Journal of the University of Chicago Supports undergraduate scholarship in the Classics and related fields.
- Apollon Undergraduate Journal A peer-reviewed journal run by faculty and students at Fairfield University. Any undergraduate student whose research was produced through coursework in the humanities may submit.
- Archive: An Undergraduate Journal of History Accepts submissions of History scholarship, including scholarly papers, articles, book reviews, and historical essays from undergraduate students of all majors from colleges and universities in the U.S. or abroad.
- Berkeley Undergraduate Journal of Classics Original manuscripts on any topic related to Classics from undergraduate students in any major at an institution which confers a bachelor's degree are eligible to submit.
- Clio's Scroll: The Berkeley Undergraduate History Journal The journal publishes articles by undergraduates and recent graduates of any university on historical topics.
- Dies Ligibiles: An Undergraduate Journal of Medieval Studies The journal accepts research papers, book reviews, translations, and art in English, French, and Spanish from any undergraduate student at any college or university. The work must pertain to the time period 400 - 1600 CE.
- Epistemai: An Undergraduate Philosophy Journal A student-run philosophy journal at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities. The journal publishes short, original philosophical work done by undergraduates from universities across the country, and internationally.
- Falsafa: Undergraduate Journal of Philosophy Run by the Philosophy Club at the University of California, Irvine, this journal highlights philosophical ideas and research by undergraduates.
- Forbes & Fifth This undergraduate journal of the Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences at the University of Pittsburgh considers both scholarly and creative work from students at any accredited university in the world.
- The Gettysburg College Journal of the Civil War Era Open access peer-reviewed undergraduate journal that publishes academic essays, public history essays, and book reviews on the Civil War Era.
- History Matters: An Undergraduate Journal of Historical Research An undergraduate history journal published annually by the Department of History at Appalachian State University. The journal is indexed by EBSCOhost's America: History and Life.
- Journal of Art History and Museum Studies (JAHMS) An undergraduate peer-reviewed journal that publishes undergraduate scholarship by a diverse coalition of student artists and historians.
- The Kennesaw Tower: Undergraduate Foreign Language Research Journal Annual undergraduate double blind and peer-reviewed journal publishes scholarly work of advanced undergraduates students in Chinese, FLED, French, German, Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish.
- Mysterion: The Theology Journal of Boston College Publishes undergraduate research from around the world on topics related to theology.
- Nota Bene: Canadian Undergraduate Journal of Musicology Publishes essays written by undergraduate students from universities around the world. Topics include historical musicology, ethnomusicology, popular music studies, music theory, music education, and interdisciplinary subjects. Double blind review by professors across Canada.
- The Oswald Review: An International Journal of Undergraduate Research and Criticism in the Discipline of English Published annually, and requiring a faculty member's endorsement, the refereed journal in indexed in EBSCO and accepts undergraduate criticism and research in the field of English from students throughout the U.S. and abroad.
- Queen City Writers: a journal of undergraduate writing & composing Refereed journal that publishes essays and multimedia work by undergraduate students affiliated with any post-secondary institution. Topics covered include writing, rhetoric, reading, pedagogy, literacy broadly conceived, popular culture and media, community discourses and multimodal and digital composing.
- Rock Creek Review An undergraduate journal edited, produced and published at Heidelberg University in partnership with the English Department. The journal publishes literary research from schools around the world for an annual publication. Check the website for the "call for papers," which will explain the theme of the next issue.
- RhetTech Undergraduate Journal Run by students at James Madison University, this journal showcases exemplary work being done in undergraduate writing, rhetoric, and technical communication courses around the country.
- Simpliciter: Brandies Philosophy Journal Run by students at Brandeis University, this journal aims to recognize excellent works of philosophy produced by undergraduates from universities anywhere in the world.
- sprinkle: an undergraduate journal of feminist and queer studies A peer-reviewed journal devoted to the diverse voices of emerging scholar-activists, authors, and artists in Women's Gender & Queer Studies and related fields. First established at McGill University, sprinkle is now published at Cal Poly San Luis Obispo and welcomes submissions from around the world.
- Stance: An International Undergraduate Philosophy Journal Peer-reviewed journal publishes original work by undergraduates from around the world.
- Stony Brook Undergraduate History Journal Peer-reviewed publication that showcases the research of SBU students writing about history at the local, national and international levels.
- UC Berkeley Comparative Literature Undergraduate Journal Publishes undergraduate research in comparative texts and media, treating a broad range of topics including theoretical literary discourse, international trends in literature, and comparisons for national literature. Showcases the best work across the U.S. and also highlight more contemplative writing by students regarding multicultural issues, culture shock, or transnational experiences such as studying abroad.
- UC Santa Barbara Undergraduate Journal of History A space for undergraduates to share original research other scholarly works of history. Reviewed by graduate students with faculty mentorship.
- The Word: The Stanford Journal of Student Hiphop Research Continually solicits research papers and blog content related to hiphop culture. An open-source, open peer-refereed journal. Open to undergraduates from any college or university.
- Xchanges: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Technical Communication, Rhetoric, and Writing Across the Curriculum The fall issues publishes these and research projects of upper-level undergraduate students. Submissions may be traditional articles or multimodal "webtexts." Based in the English Department at the University of New Mexico.
- Yale Historical Review Welcomes works from undergraduates at any institution on any historically relevant topic.
- Young Scholars in Writing (YSW) An international peer-reviewed journal. Publishes original research and theoretical articles by undergraduates of all majors and years on the subjects of rhetoric, writing, writers, discourse, language, and related topics.
Social Sciences
- Afkar: The Undergraduate Journal of Middle East Studies International peer-reviewed journal that accepts research articles, essays, and book reviews that focus on the politics, history, culture, and society of the Middle East and North Africa.
- Al Noor Boston College's Middle Eastern Studies journal. It is run by undergraduates and publishes work from students around the world.
- Chicago Journal of Foreign Policy: University of Chicago's Premiere Undergraduate Journal of International Affairs Accepts submissions from undergraduates from around the world on articles related to foreign policy, international relations, and related topics, preferably pertaining to the period since 1945..
- Compass: An Undergraduate Journal of American Political Ideas A joint project of Northern Illinois University and Arizona State University, Compass publishes work related to American democracy understood in the broad contexts of political philosophy, history, literature, economics, and culture.
- Consilience: The Journal of Sustainable Development To encourage an international community to think more broadly, deeply, and analytically about sustainable development, the journal publishes work by students, researchers, professors, and practitioners from a variety of academic fields and geographic regions.
- Critique: a worldwide student journal of politics Peer-reviewed journal that publishes scholarship by students of political science. The journal is recognized by the American Political Science Association and indexed by EBSCO.
- The Developing Economist Student-run undergraduate economics research journal, published with support from the Longhorn Chapter of the Omicron Delta Epsilon Economics Honor Society and the Department of Economics at the University of Texas at Austin.
- Issues in Political Economy Co-edited by undergraduates at Elon University and the University of Mary Washington, the journal publishes undergraduate research in the field of economics and is indexed in Cabell's Directory of Publishing Opportunities in Economics and Finance.
- Journal of Integrated Social Sciences A web-based, peer-reviewed journal committed to the scholarly investigation of social phenomena. We especially encourage students and their faculty advisors to submit the results of their investigations in Psychology, Sociology, and Gender Studies.
- Journal of Interpersonal Relations, Intergroup Relations, and Identity (JIRIRI) Affiliated with the Universite de Montreal, the international peer-reviewed journal publishes the work of undergraduates on new theoretical ideas in the fields of psychology, identity, interpersonal and intergroup relations. It publishes both theoretical and empirical articles.
- Journal of Politics and Society Published by the student group Helvidius at Columbia University, the journal focuses on undergraduate interdisciplinary research in the social sciences.
- The Journal of Undergraduate Ethnic Minority Psychology (JUEMP) Open access, double blind, peer-reviewed journal devoted to publishing research authored or co-authored by undergraduates. The journal is especially interested in submissions that are from ethnic minorities perspectives, that focus on the thoughts and behaviors of ethnic minority populations, or both.
- New Errands: The Undergraduate Journal of American Studies Sponsored by The Eastern American Studies Association and the American Studies Program at Penn State Harrisburg, this journal publishes undergraduate research in the field of American Studies.
- The Philosophy, Politics, and Economics Review International undergraduate journal housed in the Kellogg Center for Philosophy, Politics, and Economics at Virginia Tech. Through a double blind review process, the journal publishes original research in the humanities and social sciences from undergraduates worldwide.
- Process: Journal of Multidisciplinary Undergraduate Scholarship Published quarterly, the journal publishes undergraduate writings that rigorously engage with issues of social justice, transformative education, politics, identity, and cultural production. Publishes both critical essays and non-traditional or multimodal compositions.
- Righting Wrongs: A Journal of Human Rights Based at Webster University's Institute for Human Rights and Humanitarian Studies, this peer-reviewed academic journal publishes undergraduate research papers, book reviews, opinion pieces, and photo essays that explore human rights issues.
- Social Moments: A Student Journal of Social Relations Interdisciplinary peer-reviewed journal examining the social and cultural world through a social science lens. All undergraduate and graduate students are invited to submit work in any social science discipline.
- Sociology between the Gaps: Forgotten and Neglected Topics Undergraduates, graduates, and professionals in sociology and related fields may submit their articles, books and film reviews, and point of view essays. Double blind peer review.
- Undergraduate Economic Review (UER) Supported by the Department of Economics and The Ames Library at Illinois Wesleyan University, this is an open access peer-reviewed journal that publishes undergraduate research in the field of economics from around the world.
- Undergraduate Journal of Global Citizenship Based at Fairfield University, the journal publishes undergraduate research on topics related to International Studies such as global awareness, interdependence, environmental responsibility, social justice, humanitarianism, and other themes that promote the understanding of global citizenship.
- Undergraduate Journal of Service Learning & Community-Based Research Refereed, multidisciplinary, open access undergraduate journal that publishes articles from students all around the world. Accepted articles contribute to the literature on service learning and community-based research through reflection, research, or analysis. Based at University of North Carolina Wilmington.
- The Undergraduate Research Journal of Psychology at UCLA (URJP) Based at UCLA, but accepting submissions of undergraduate research from institutions all over the world, this peer-reviewed journal aims to empower undergraduate students to engage in and with research and facilitate scientific conversation and inquiry in the field of psychology.
STEM Fields
- Columbia Undergraduate Science Journal (CUSJ) Open access science journal that publishes manuscripts resulting from significant scientific research or analysis. Each paper undergoes a double-blind peer review process and a faculty review by the CUSJ Faculty Advisory Board.
- EvoS: The Evolutional Studies Consortium A peer-reviewed open access journal, EvoS welcomes work from all academic disciplines and interdisciplinary scholarship that incorporates evolutionary theory.
- Illumin Magazine: A Review of Engineering in Everyday Life An online magazine dedicated to exploring the science and technology behind the things we encounter every day. Features the work of University of Southern California undergraduate engineers, as well as submissions from universities across the U.S.
- Impulse: The Premier Undergraduate Neuroscience Journal International online neuroscience journal for undergraduate publications.
- International Journal of Exercise Science This journal engages undergraduate and graduate students in scholarly activity as both authors and reviewers. Articles on exercise science undergo peer review.
- Intersect: The Stanford Journal of Science, Technology, and Society An open access international science, technology, and society research journal that accepts undergraduate, graduate, and PhD submissions at the intersection of history, culture, sociology, art, literature, business, law, health, and design with science and technology. Students from around the world are invited to submit.
- Involve: A Journal of Mathematics High quality mathematical research involving students from all academic levels. Submissions should include substantial faculty input; faculty co-authorship is required and the submission should come from a faculty member.
- Journal of Undergraduate Chemistry Research Peer-reviewed journal that publishes undergraduate students' work in chemistry, including analytical, organic, inorganic, physical, polymers, and biochemistry.
- Journal of Undergraduate Kinesiology Research Published by the Kinesiology Department at the University of Wisconsin Eau Claire, the peer-reviewed, journal is dedicated to original undergraduate research in Kinesiology. Currently, the research originates from students at the University of Wisconsin, but undergraduates from all institutions are invited to submit.
- Journal of Undergraduate Reports in Physics (JURP) Peer-reviewed publication of the Society of Physics Students comprised of undergraduate research, outreach, and scholarly reporting.
- Journal of Young Investigators (JYI) JYI publishes original work in the sciences written by undergraduates mentored by a faculty member. The mission of the journal is to improve undergraduate science training by providing innovative, high quality educational experiences in science writing, publication, and the peer-review process.
- Psi Chi Journal Undergraduate, graduate, and faculty submissions welcome year round to this peer-reviewed psychology journal.
- Rose-Hulman Undergraduate Mathematics Journal Devoted entirely to papers written by undergraduates on topics in the mathematical sciences. Sponsored by the Mathematics Department at Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology, the journal accepts submissions from undergraduates around the world and faculty co-authors are not permitted.
- RURALS: Review of Undergraduate Research in Agricultural and Life Sciences Faculty-refereed international journal devoted to the publication of high quality research by undergraduates in all agricultural research problem areas.
- SIAM Undergraduate Research Online (SIURO) Run by the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM), SIURO publishes articles written by undergraduates from all over the world in the field of computational mathematics. Each paper must be submitted with a letter from a faculty advisor.
- Spectrum Published by the University of Alberta, this multidisciplinary journal publishes research completed by undergraduates in a variety of formats including research articles, review articles, music, video, visual arts, and creative writing.
- Spora: A Journal of Biomathematics Published by Illinois State, this is an open access refereed research journal dedicated to publishing high quality manuscripts by undergraduate or graduate students that describe mathematical and statistical techniques to solve problems in biological settings, as well as in experimental biology. Requires an article processing charge.
- PUMP Journal of Undergraduate Research PUMP stands for Preparing Undergraduate Mathematicians for Ph.D.s, and the journal publishes articles by undergraduates students who want to pursue doctoral studies in the Mathematical Sciences. The journal especially encourages submissions by students from underrepresented groups. Topics include pure and applied mathematics and statistics and authors may submit research papers, papers containing new proofs of known results, and expository papers which propose original points of view.
- Undergraduate Journal of Experimental Microbiology and Immunology (UJEMI+) Based at the University of British Columbia, the journal has two versions -- one that publishes only UBC students (UJEMI) and the other that is open to external submissions (UJEMI+). Dedicated to the publication of undergraduate articles in fields related to microbiology and immunology, the journal requires a formal endorsement from a course instructor or researcher who mentored the student authors.
- Young Investigator's Review Stony Brook's own student-run science journal!
- << Previous: Publishing Your Research: Why and How?
- Next: Contact >>
- Last Updated: Mar 26, 2024 11:42 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.stonybrook.edu/undergraduate_research
- Request a Class
- Hours & Locations
- Ask a Librarian
- Special Collections
- Library Faculty & Staff
Library Administration: 631.632.7100
- Stony Brook Home
- Campus Maps
- Web Accessibility Information
- Accessibility Barrier Report Form

Comments or Suggestions? | Library Webmaster

Except where otherwise noted, this work by SBU Libraries is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License .

How to Write a Research Paper
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Research Paper Fundamentals
How to choose a topic or question, how to create a working hypothesis or thesis, common research paper methodologies, how to gather and organize evidence , how to write an outline for your research paper, how to write a rough draft, how to revise your draft, how to produce a final draft, resources for teachers .
It is not fair to say that no one writes anymore. Just about everyone writes text messages, brief emails, or social media posts every single day. Yet, most people don't have a lot of practice with the formal, organized writing required for a good academic research paper. This guide contains links to a variety of resources that can help demystify the process. Some of these resources are intended for teachers; they contain exercises, activities, and teaching strategies. Other resources are intended for direct use by students who are struggling to write papers, or are looking for tips to make the process go more smoothly.
The resources in this section are designed to help students understand the different types of research papers, the general research process, and how to manage their time. Below, you'll find links from university writing centers, the trusted Purdue Online Writing Lab, and more.
What is an Academic Research Paper?
"Genre and the Research Paper" (Purdue OWL)
There are different types of research papers. Different types of scholarly questions will lend themselves to one format or another. This is a brief introduction to the two main genres of research paper: analytic and argumentative.
"7 Most Popular Types of Research Papers" (Personal-writer.com)
This resource discusses formats that high school students commonly encounter, such as the compare and contrast essay and the definitional essay. Please note that the inclusion of this link is not an endorsement of this company's paid service.
How to Prepare and Plan Out Writing a Research Paper
Teachers can give their students a step-by-step guide like these to help them understand the different steps of the research paper process. These guides can be combined with the time management tools in the next subsection to help students come up with customized calendars for completing their papers.
"Ten Steps for Writing Research Papers" (American University)
This resource from American University is a comprehensive guide to the research paper writing process, and includes examples of proper research questions and thesis topics.
"Steps in Writing a Research Paper" (SUNY Empire State College)
This guide breaks the research paper process into 11 steps. Each "step" links to a separate page, which describes the work entailed in completing it.
How to Manage Time Effectively
The links below will help students determine how much time is necessary to complete a paper. If your sources are not available online or at your local library, you'll need to leave extra time for the Interlibrary Loan process. Remember that, even if you do not need to consult secondary sources, you'll still need to leave yourself ample time to organize your thoughts.
"Research Paper Planner: Timeline" (Baylor University)
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment.
"Research Paper Planner" (UCLA)
UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
There's a reason teachers spend a long time talking about choosing a good topic. Without a good topic and a well-formulated research question, it is almost impossible to write a clear and organized paper. The resources below will help you generate ideas and formulate precise questions.
"How to Select a Research Topic" (Univ. of Michigan-Flint)
This resource is designed for college students who are struggling to come up with an appropriate topic. A student who uses this resource and still feels unsure about his or her topic should consult the course instructor for further personalized assistance.
"25 Interesting Research Paper Topics to Get You Started" (Kibin)
This resource, which is probably most appropriate for high school students, provides a list of specific topics to help get students started. It is broken into subsections, such as "paper topics on local issues."
"Writing a Good Research Question" (Grand Canyon University)
This introduction to research questions includes some embedded videos, as well as links to scholarly articles on research questions. This resource would be most appropriate for teachers who are planning lessons on research paper fundamentals.
"How to Write a Research Question the Right Way" (Kibin)
This student-focused resource provides more detail on writing research questions. The language is accessible, and there are embedded videos and examples of good and bad questions.
It is important to have a rough hypothesis or thesis in mind at the beginning of the research process. People who have a sense of what they want to say will have an easier time sorting through scholarly sources and other information. The key, of course, is not to become too wedded to the draft hypothesis or thesis. Just about every working thesis gets changed during the research process.
CrashCourse Video: "Sociology Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is tailored to sociology students, it is applicable to students in a variety of social science disciplines. This video does a good job demonstrating the connection between the brainstorming that goes into selecting a research question and the formulation of a working hypothesis.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement for an Analytical Essay" (YouTube)
Students writing analytical essays will not develop the same type of working hypothesis as students who are writing research papers in other disciplines. For these students, developing the working thesis may happen as a part of the rough draft (see the relevant section below).
"Research Hypothesis" (Oakland Univ.)
This resource provides some examples of hypotheses in social science disciplines like Political Science and Criminal Justice. These sample hypotheses may also be useful for students in other soft social sciences and humanities disciplines like History.
When grading a research paper, instructors look for a consistent methodology. This section will help you understand different methodological approaches used in research papers. Students will get the most out of these resources if they use them to help prepare for conversations with teachers or discussions in class.
"Types of Research Designs" (USC)
A "research design," used for complex papers, is related to the paper's method. This resource contains introductions to a variety of popular research designs in the social sciences. Although it is not the most intuitive site to read, the information here is very valuable.
"Major Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is a bit on the dry side, it provides a comprehensive overview of the major research methodologies in a format that might be more accessible to students who have struggled with textbooks or other written resources.
"Humanities Research Strategies" (USC)
This is a portal where students can learn about four methodological approaches for humanities papers: Historical Methodologies, Textual Criticism, Conceptual Analysis, and the Synoptic method.
"Selected Major Social Science Research Methods: Overview" (National Academies Press)
This appendix from the book Using Science as Evidence in Public Policy , printed by National Academies Press, introduces some methods used in social science papers.
"Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: 6. The Methodology" (USC)
This resource from the University of Southern California's library contains tips for writing a methodology section in a research paper.
How to Determine the Best Methodology for You
Anyone who is new to writing research papers should be sure to select a method in consultation with their instructor. These resources can be used to help prepare for that discussion. They may also be used on their own by more advanced students.
"Choosing Appropriate Research Methodologies" (Palgrave Study Skills)
This friendly and approachable resource from Palgrave Macmillan can be used by students who are just starting to think about appropriate methodologies.
"How to Choose Your Research Methods" (NFER (UK))
This is another approachable resource students can use to help narrow down the most appropriate methods for their research projects.
The resources in this section introduce the process of gathering scholarly sources and collecting evidence. You'll find a range of material here, from introductory guides to advanced explications best suited to college students. Please consult the LitCharts How to Do Academic Research guide for a more comprehensive list of resources devoted to finding scholarly literature.
Google Scholar
Students who have access to library websites with detailed research guides should start there, but people who do not have access to those resources can begin their search for secondary literature here.
"Gathering Appropriate Information" (Texas Gateway)
This resource from the Texas Gateway for online resources introduces students to the research process, and contains interactive exercises. The level of complexity is suitable for middle school, high school, and introductory college classrooms.
"An Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative Data Collection Methods" (NSF)
This PDF from the National Science Foundation goes into detail about best practices and pitfalls in data collection across multiple types of methodologies.
"Social Science Methods for Data Collection and Analysis" (Swiss FIT)
This resource is appropriate for advanced undergraduates or teachers looking to create lessons on research design and data collection. It covers techniques for gathering data via interviews, observations, and other methods.
"Collecting Data by In-depth Interviewing" (Leeds Univ.)
This resource contains enough information about conducting interviews to make it useful for teachers who want to create a lesson plan, but is also accessible enough for college juniors or seniors to make use of it on their own.
There is no "one size fits all" outlining technique. Some students might devote all their energy and attention to the outline in order to avoid the paper. Other students may benefit from being made to sit down and organize their thoughts into a lengthy sentence outline. The resources in this section include strategies and templates for multiple types of outlines.
"Topic vs. Sentence Outlines" (UC Berkeley)
This resource introduces two basic approaches to outlining: the shorter topic-based approach, and the longer, more detailed sentence-based approach. This resource also contains videos on how to develop paper paragraphs from the sentence-based outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL)
The Purdue Online Writing Lab's guide is a slightly less detailed discussion of different types of outlines. It contains several sample outlines.
"Writing An Outline" (Austin C.C.)
This resource from a community college contains sample outlines from an American history class that students can use as models.
"How to Structure an Outline for a College Paper" (YouTube)
This brief (sub-2 minute) video from the ExpertVillage YouTube channel provides a model of outline writing for students who are struggling with the idea.
"Outlining" (Harvard)
This is a good resource to consult after completing a draft outline. It offers suggestions for making sure your outline avoids things like unnecessary repetition.
As with outlines, rough drafts can take on many different forms. These resources introduce teachers and students to the various approaches to writing a rough draft. This section also includes resources that will help you cite your sources appropriately according to the MLA, Chicago, and APA style manuals.
"Creating a Rough Draft for a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
This resource is useful for teachers in particular, as it provides some suggested exercises to help students with writing a basic rough draft.
Rough Draft Assignment (Duke of Definition)
This sample assignment, with a brief list of tips, was developed by a high school teacher who runs a very successful and well-reviewed page of educational resources.
"Creating the First Draft of Your Research Paper" (Concordia Univ.)
This resource will be helpful for perfectionists or procrastinators, as it opens by discussing the problem of avoiding writing. It also provides a short list of suggestions meant to get students writing.
Using Proper Citations
There is no such thing as a rough draft of a scholarly citation. These links to the three major citation guides will ensure that your citations follow the correct format. Please consult the LitCharts How to Cite Your Sources guide for more resources.
Chicago Manual of Style Citation Guide
Some call The Chicago Manual of Style , which was first published in 1906, "the editors' Bible." The manual is now in its 17th edition, and is popular in the social sciences, historical journals, and some other fields in the humanities.
APA Citation Guide
According to the American Psychological Association, this guide was developed to aid reading comprehension, clarity of communication, and to reduce bias in language in the social and behavioral sciences. Its first full edition was published in 1952, and it is now in its sixth edition.
MLA Citation Guide
The Modern Language Association style is used most commonly within the liberal arts and humanities. The MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing was first published in 1985 and (as of 2008) is in its third edition.
Any professional scholar will tell you that the best research papers are made in the revision stage. No matter how strong your research question or working thesis, it is not possible to write a truly outstanding paper without devoting energy to revision. These resources provide examples of revision exercises for the classroom, as well as tips for students working independently.
"The Art of Revision" (Univ. of Arizona)
This resource provides a wealth of information and suggestions for both students and teachers. There is a list of suggested exercises that teachers might use in class, along with a revision checklist that is useful for teachers and students alike.
"Script for Workshop on Revision" (Vanderbilt University)
Vanderbilt's guide for leading a 50-minute revision workshop can serve as a model for teachers who wish to guide students through the revision process during classtime.
"Revising Your Paper" (Univ. of Washington)
This detailed handout was designed for students who are beginning the revision process. It discusses different approaches and methods for revision, and also includes a detailed list of things students should look for while they revise.
"Revising Drafts" (UNC Writing Center)
This resource is designed for students and suggests things to look for during the revision process. It provides steps for the process and has a FAQ for students who have questions about why it is important to revise.
Conferencing with Writing Tutors and Instructors
No writer is so good that he or she can't benefit from meeting with instructors or peer tutors. These resources from university writing, learning, and communication centers provide suggestions for how to get the most out of these one-on-one meetings.
"Getting Feedback" (UNC Writing Center)
This very helpful resource talks about how to ask for feedback during the entire writing process. It contains possible questions that students might ask when developing an outline, during the revision process, and after the final draft has been graded.
"Prepare for Your Tutoring Session" (Otis College of Art and Design)
This guide from a university's student learning center contains a lot of helpful tips for getting the most out of working with a writing tutor.
"The Importance of Asking Your Professor" (Univ. of Waterloo)
This article from the university's Writing and Communication Centre's blog contains some suggestions for how and when to get help from professors and Teaching Assistants.
Once you've revised your first draft, you're well on your way to handing in a polished paper. These resources—each of them produced by writing professionals at colleges and universities—outline the steps required in order to produce a final draft. You'll find proofreading tips and checklists in text and video form.
"Developing a Final Draft of a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
While this resource contains suggestions for revision, it also features a couple of helpful checklists for the last stages of completing a final draft.
Basic Final Draft Tips and Checklist (Univ. of Maryland-University College)
This short and accessible resource, part of UMUC's very thorough online guide to writing and research, contains a very basic checklist for students who are getting ready to turn in their final drafts.
Final Draft Checklist (Everett C.C.)
This is another accessible final draft checklist, appropriate for both high school and college students. It suggests reading your essay aloud at least once.
"How to Proofread Your Final Draft" (YouTube)
This video (approximately 5 minutes), produced by Eastern Washington University, gives students tips on proofreading final drafts.
"Proofreading Tips" (Georgia Southern-Armstrong)
This guide will help students learn how to spot common errors in their papers. It suggests focusing on content and editing for grammar and mechanics.
This final set of resources is intended specifically for high school and college instructors. It provides links to unit plans and classroom exercises that can help improve students' research and writing skills. You'll find resources that give an overview of the process, along with activities that focus on how to begin and how to carry out research.
"Research Paper Complete Resources Pack" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, rubrics, and other resources is designed for high school students. The resources in this packet are aligned to Common Core standards.
"Research Paper—Complete Unit" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, notes, PowerPoints, and other resources has a 4/4 rating with over 700 ratings. It is designed for high school teachers, but might also be useful to college instructors who work with freshmen.
"Teaching Students to Write Good Papers" (Yale)
This resource from Yale's Center for Teaching and Learning is designed for college instructors, and it includes links to appropriate activities and exercises.
"Research Paper Writing: An Overview" (CUNY Brooklyn)
CUNY Brooklyn offers this complete lesson plan for introducing students to research papers. It includes an accompanying set of PowerPoint slides.
"Lesson Plan: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper" (San Jose State Univ.)
This lesson plan is designed for students in the health sciences, so teachers will have to modify it for their own needs. It includes a breakdown of the brainstorming, topic selection, and research question process.
"Quantitative Techniques for Social Science Research" (Univ. of Pittsburgh)
This is a set of PowerPoint slides that can be used to introduce students to a variety of quantitative methods used in the social sciences.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1934 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,762 quotes across 1934 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

High School Guide: How to Publish a Research Paper in 5 Easy Steps
Indigo Research Team

We understand how overwhelming the idea of publishing research as a high schooler may seem. It’s true, that the process of submitting and publishing a paper can be very complex and daunting. It needs a lot of preparation and perseverance.
However, publishing research increasingly becomes the " gold " that a college Admission Officer is looking for. Publication in leading journals, like Concord Review, or International Journal for High School Students can showcase your ability and determination to a college admission officer when you apply for college.
Although it seems complicated, worry not! We’ll simplify the steps for you.

This article will break down 5 steps on how to publish a research paper.
1. Find the Right Mentor for Your Research Purposes
Can you write a research paper on your own? Yes, you can. But, it would be extremely difficult. Finding the perfect mentor is key to having a smooth ride. As an aspiring high school student, you'll want guidance from someone who shares your intellectual interests and can offer expertise in your field of study. Mentors can also help you find information about publishing research as well as where to publish a research paper.
“If you cannot see where you are going, find someone who has been there before.” - J.L. Norris
To find a mentor, first , you need to reflect on your goals and needs. Ask yourself these questions:
• Do you want help developing research questions? • Feedback on a draft? • Opportunities to co-author a paper?
Defining what you hope to gain from mentorship will help determine who may be the best fit.
Secondly, once you know (in general) who you want to work with, you can start your search by browsing the faculty profiles on your school’s website or research database like academia.edu or you can also utilize social media platforms like LinkedIn. Look for professors with expertise in your areas of interest.
It’s important to reach out in the right manner for them to notice you. Remember, you are the one who needs their help and not the other way around. Therefore, the way you reach out online is very crucial to get their attention. Keep in mind that you should do thorough research about this person before sending a message. Here’s an example of a short template message you can use for initial communication on LinkedIn:
Dear Professor [Last Name],
I'm [Your Name], a high school student passionate about [Your Research Interest]. Impressed by your work in [Their Field]. I'm very intrigued by your argumentation about [Topic]. I’m looking for a mentorship for a project I'm planning. Your guidance would be invaluable. Could we discuss this possibility
Looking forward to hearing from you. Best,
[Your Name]
Third, if you still can’t find an available mentor, you should also expose yourself to new ideas by attending guest lectures, joining online forums, and reading publications in your field. You can also find mentors who have published research papers that you are interested in. Engage with the material by asking questions. This demonstrates your passion for learning and can lead to finding a mentor.
While finding a mentor can be a bit of a hassle, you can check out our mentors and find the mentor of your preferences. After you have found your mentor, you can start doing the second step.
2. Choose an Exciting Research Topic That Interests You
Choosing topics that you are deeply passionate about or interested in is the key to keeping you motivated until the end of the research.
Discover Your Passions or Interests
There are many passion project ideas that you can explore. But you can always start by asking:
• What do you love to read about or discuss with friends? • Are there any social issues you care deeply about? • What are the topics related to your hobbies, favorite books or movies, sports teams, and travel destinations? • Or do you like more of the popular subjects in your school like biology, chemistry, computer science, psychology, or genetics? Look for topics that spark your curiosity or creativity.
Find an Opportunity Gap
Review what research has already been done on topics that interest you. Look for areas that could use more exploration or that you could investigate further. Think about new angles, questions, or perspectives you might bring to the subject. Finding an unexplored niche in a broader topic area can lead to an exciting, original research paper.
Talk to Your Mentor
Discuss ideas with your mentor, especially if you have an area of study in mind but need guidance narrowing down to a specific, manageable research question. Your mentor may be able to suggest topics that would work well for a research paper and align with standards or curriculum. They can also help determine if a topic idea is too broad or narrow, or if resources will be readily available.
Application of the Research in Reality
Choose a topic that could have real-world implications or applications. How can your research paper help real-world problems?
Think about local issues in your community or school that could be addressed or improved through research. Papers investigating practical solutions or the effectiveness of policies, programs, or interventions tend to be very compelling.

3. Choose the Right Journal or Conference to Publish Your Research Paper
“Where can I publish my research paper?”
You can publish your research paper through respectable journals, conferences, or research paper competitions. It's important to have a goal in mind before starting any research paper. Determining this in the beginning might help you to stay on course and motivated.
Consider the Scope of the Selected Journals
Decide the scope then look for publications that focus on your area of study or research topic. Are you looking to publish a research paper in an international journal? Or are you aiming for more local journals?
Double-check that the journal accepts submissions from high school students and check their reputation. Aim high, but be realistic. See if any professors or mentors can recommend appropriate platforms. Review the editorial board and see if top researchers in your field are involved.
Examples of the journals that can publish your research paper as a high schooler include:
- Concord Review
- The National High School Journal of Science
- STEM Fellowship Journal
- Journal of Student Research
- Journal of High School Science (JHSS)
- International Journal of High School Research (IJHSR)
“Where can I publish my research paper for free?”
Here are some journals where you can submit your research paper for free, but be aware some of them require a publication fee:
- Journal of Emerging Investigators (JEI)
- Young Scientist Journal
- Youth Medical Journal
- Journal Research High School
- Hope Humanities Journal
- International Youth Neuroscience Association Journal
- Whitman Journal of Psychology
Review Submission Guidelines
Once you’ve set your mind and chosen your goal, carefully read and follow the instructions for authors. Pay attention to formatting, abstract length, images, and anything else specified. Following the guidelines shows you understand publishing norms in your field.
4. Conduct Thorough Research, Write and Format Your Research Paper Properly
Now that you have selected a topic and compiled sources, it's time to dive into your research and start writing. Publishing a research paper in a journal requires thorough research and a properly formatted paper.
- Analyze and read all of your resources and take notes on the key ideas, facts, questions, examples, data, quotes, and arguments that might be relevant to your research project. Keep it organized into an outline.
- Determine your research question and consult with your mentor. Once you begin drafting your paper, be sure to paraphrase, summarize, and quote the right citation.
- Carefully proofread and format your paper. Double-check for any spelling, grammar, or punctuation errors. Ensure your paper follows the recommended style guide for font type and size, spacing, margins, page numbers, headings, and image captions.
Of course, writing a research paper is not as easy. If you need guidance, you can also try to join research programs that will allow you to finish the research paper easier.
5. Review Before Submitting Your Research Paper and Respond to Feedback
Once your paper is complete, it's time to share your work with the world.
Review Your Research Paper
Before making this incredible step, review your research paper once again. Have a teacher or mentor check your paper to ensure it meets the journal's standards. Put together a cover letter introducing yourself and your research. Explain the importance of your work and most importantly, why they need to publish your work.
Anticipate Feedback
Even after submitting, your work isn't done. Journals will send your paper out for peer review by experts in the field. Reviewers may suggest changes to strengthen your paper before it can be accepted. Don't get discouraged—even professional researchers incorporate feedback! Address each comment thoroughly and openly. Making revisions will improve your paper and help you become a better writer and researcher.
How Long Does it Take to Publish a Research Paper?
In general, the publication process can take several months to a year or more from the initial submission to final publication. It depends on the institutions and the availability of the peer reviewers. If your paper is accepted for publication, congratulations! If not, use the experience as an opportunity to improve. Carefully consider the feedback and see it as a chance to strengthen your methods, arguments, and writing. Don't hesitate to submit to another journal or work with your mentor to revise and resubmit.
That’s it! Congratulations on finishing all the steps!
Whether or not you get published, finishing the research paper is an achievement in itself. We hope that this article on how to publish a research paper will help you to get your research paper published. Remember that persistence, attention to detail, and a clear understanding of your target journal's guidelines are key. Stay determined and keep researching. You got this!
Need more guidance to do your research paper and most importantly, publish your paper? Don't worry, we've got you! At Indigo Research, we connect you with leading professors from renowned universities who are eager to mentor you and support you in publishing your research!
Click to discover more about how we can help!
How to Publish a Research Paper In High School: 18 Journals and Conferences to Consider

By Alex Yang
Graduate student at Southern Methodist University
9 minute read
So you've been working super hard writing a research paper , and you’ve finally finished. Congrats! It’s a very impressive accolade already, but there’s a way to take it a level further. As we’ve talked about before in our Polygence blog, “ Showcasing your work and sharing it with the world is the intellectual version of ‘pics or it didn’t happen.’ ” Of course, there are lot of different ways to showcase your work , from creating a Youtube video to making a podcast. But one of the most popular ways to showcase your research is to publish your research. Publishing your research can take the great work you’ve already done and add credibility to it, and will make a stronger impression than unpublished research. Further, the process of having your work reviewed by advanced degree researchers can be a valuable experience in itself. You can receive feedback from experts and learn how to improve upon the work you’ve already done.
Before we dive into the various journals and conferences to publish your work, let’s distinguish between the various publishing options that you have as a high schooler, as there are some nuances. Quick disclaimer: this article focuses on journals and conferences as ways to showcase your work. There are also competitions where you can submit your work, and we have written guides on competing in premier competitions like Regeneron STS and competing in Regeneron ISEF .
Publishing Options for High School Students
Peer-reviewed journals.
This is rather self-explanatory, but these journals go through the peer review process, where author(s) submit their work to the journal, and the journal's editors send the work to a group of independent experts (typically grad students or other scientists with advanced degrees) in the same field or discipline. These experts are peer reviewers, who evaluate the work based on a set of predetermined criteria, including the quality of the research, the validity of the methodology, the accuracy of the data, and the originality of the findings. The peer reviewers may suggest revisions or leave comments, but ultimately the editors will decide which suggestions to give to the student.
Once you’ve received suggestions, you have the opportunity to make revisions before submitting your final product back to the journal. The editor then decides whether or not your work is published.
Non-Peer-Reviewed Journals
These are just journals that do not undergo a review process. In general, peer-reviewed journals may be seen as more credible and prestigious. However, non-peer-reviewed journals may make it easier and faster to publish your work, which can be helpful if you are pressed for time and applying to colleges soon .
Pre Print Archives
Preprint archives or servers are online repositories where student researchers can upload and share their research papers without undergoing any review process. Preprints allow students to share their findings quickly and get feedback from the scientific community, which can help improve the research while you’re waiting to hear back from journals, which typically have longer timelines and can take up to several months to publish research. Sharing your work in a preprint archive does not prohibit you from, or interfere with submitting the same work to a journal afterwards.
Research Conferences
Prefer to present your research in a presentation or verbal format? Conferences can be a great way to “publish” your research, showcase your public speaking skills, speak directly to your audience, and network with other researchers in your field.
Student-led Journals vs Graduate Student / Professor-led Journals
Some student-led journals may have peer-review, but the actual people peer-reviewing your work may be high school students. Other journals will have graduate students, PhD students, or even faculty reviewing your work. As you can imagine, there are tradeoffs to either option. With an advanced degree student reviewing your work, you can likely expect better and more accurate feedback. Plus, it’s cool to have an expert look over your work! However, this may also mean that the journal is more selective, whereas student-led journals may be easier to publish in. Nonetheless, getting feedback from anyone who’s knowledgeable can be a great way to polish your research and writing.
Strategy for Submitting to Multiple Journals
Ultimately, your paper can only be published in one peer-reviewed journal. Submitting the same paper to multiple peer-reviewed journals at the same time is not allowed, and doing so may impact its publication at any peer-reviewed journal. If your work is not accepted at one journal, however, then you are free to submit that work to your next choice and so on. Therefore, it is best to submit to journals with a strategy in mind. Consider: what journal do I ideally want to be published in? What are some back-ups if I don’t get published in my ideal journal? Preprints, like arXiv and the Research Archive of Rising Scholars, are possible places to submit your work in advance of seeking peer-reviewed publication. These are places to “stake your claim” in a research area and get feedback from the community prior to submitting your paper to its final home in a peer-reviewed journal. You can submit your work to a preprint prior to submitting at a peer-reviewed journal. However, bioRxiv, a reputable preprint server, recommends on their website that a preprint only be posted on one server, so that’s something to keep in mind as well.
Citation and Paper Formats
All of the journals listed below have specific ways that they’d like you to cite your sources, varying from styles like MLA to APA, and it’s important that you double-check the journal’s requirements for citations, titling your paper, writing your abstract, etc. Most journal websites have very detailed guides for how they want you to format your paper, so follow those closely to avoid having to wait to hear back and then resubmit your paper. If you’re looking for more guidance on citations and bibliographies check out our blog post!
18 Journals and Conferences to Publish Your Research as a High Schooler
Now that we’ve distinguished the differences between certain journals and conferences, let’s jump into some of our favorite ones. We’ve divided up our selections based on prestige and reliability, and we’ve made these selections using our experience with helping Polygence students showcase their research .
Most Prestigious Journals
Concord review.
Cost: $70 to Submit and $200 Publication Cost (if accepted)
Deadline: Fixed Deadlines in Feb 1 (Summer Issue), May 1 (Fall), August 1 (Winter), and November 1 (Spring)
Subject area: History / Social Sciences
Type of research: All types of academic articles
The Concord Review is a quarterly journal that publishes exceptional essays written by high school students on historical topics. The journal has been around since 1987 and has a great reputation, with many student winners going to great universities. Further, if your paper is published, your essays will be sent to subscribers and teachers all around the world, which is an incredible achievement.
Papers submitted tend to be around 8,000 words, so there is definitely a lot of writing involved, and the Concord Review themselves say that they are very selective, publishing only about 5% of the essays they receive.
We’ve posted our complete guide on publishing in the Concord Review here.
Journal of Emerging Investigators (JEI)
Deadline: Rolling
Subject area: STEM
Type of research: Original hypothesis-driven scientific research
JEI is an open-access publication that features scientific research papers written by middle and high school students in the fields of biological and physical sciences. The journal includes a comprehensive peer-review process, where graduate students and other professional scientists with advanced degrees will review the manuscripts and provide suggestions to improve both the project and manuscript itself. You can expect to receive feedback in 6-8 weeks.
This should be the go-to option for students that are doing hypothesis-driven, original research or research that involves original analyses of existing data (meta-analysis, analyzing publicly available datasets, etc.). This is not an appropriate fit for students writing literature reviews. Finally, a mentor or parent must submit on behalf of the student.
We’ve had many Polygence students successfully submit to JEI. Check out Hana’s research on invasive species and their effects in drought times.
STEM Fellowship Journal (SFJ)
Cost: $400 publication fee
Subject area: All Scientific Disciplines
Type of research: Conference Proceedings, Review Articles, Viewpoint Articles, Original Research
SFJ is a peer-reviewed journal published by Canadian Science Publishing that serves as a platform for scholarly research conducted by high school and university students in the STEM fields. Peer review is conducted by undergraduate, graduate student, and professional reviewers.
Depending on the kind of research article you choose to submit, SFJ provides very specific guidelines on what to include and word limits.
Other Great Journal Options
National high school journal of science (nhsjs).
Cost: $250 for publication
Deadline: Rolling
Subject area: All science disciplines
Type of research: Original research, literature review
NHSJS is a journal peer reviewed by high schoolers from around the world, with an advisory board of adult academics. Topics are STEM related, and submission types can vary from original research papers to shorter articles.
Curieux Academic Journal
Cost: $185-215
Subject area: Engineering, Humanities, and Natural Science, Mathematics, and Social Science
Type of research: Including but not limited to research papers, review articles, and humanity/social science pieces.
Curieux Academic Journal is a non-profit run by students and was founded in 2017 to publish outstanding research by high school and middle school students. Curieux publishes one issue per month (twelve per year), so there are many opportunities to get your research published.
The Young Scientists Journal
Deadline: December
Subject area: Sciences
Type of research: Original research, literature review, blog post
The Young Scientists Journal , while a popular option for students previously, has paused submissions to process a backlog. The journal is an international peer-reviewed journal run by students, and creates print issues twice a year.
The journal has also been around for a decade and has a clear track record of producing alumni who go on to work in STEM.
Here’s an example of research submitted by Polygence student Ryan to the journal.
Journal of Research High School (JRHS)
Subject area: Any academic subject including the sciences and humanities
Type of research: Original research and significant literature reviews.
JRHS is an online research journal edited by volunteer professional scientists, researchers, teachers, and professors. JRHS accepts original research and significant literature reviews in Engineering, Humanities, Natural Science, Math, and Social Sciences.
From our experience working with our students to help publish their research, this journal is currently operating with a 15-20 week turnaround time for review. This is a bit on the longer side, so be mindful of this turnaround time if you’re looking to get your work published soon.
Youth Medical Journal
Deadline: March (currently closed)
Subject area: Medical or scientific topics
Type of research: Original research, review article, blog post, magazine article
The Youth Medical Journal is an international, student-run team of 40 students looking to share medical research.
We’ve found that this journal is a good entry point for students new to research papers, but when submissions are busy, in the past they have paused submissions.
Journal of High School Science (JHSS)
Subject area: All topics
Type of research: Original research, literature review, technical notes, opinion pieces
This peer-reviewed STEAM journal publishes quarterly, with advanced degree doctors who sit on the journal’s editorial board. In addition to typical STEM subjects, the journal also accepts manuscripts related to music and theater, which is explicitly stated on their website.
Due to the current large volume of submissions, the review process takes a minimum of 4 weeks from the time of submission.
Whitman Journal of Psychology
Subject area: Psychology
Type of research: Original research, podcasts
The WWJOP is a publication run entirely by students, where research and literature reviews in the field of psychology are recognized. The journal is run out of a high school with a teacher supervisor and student staff.
The WWJOP uniquely also accepts podcast submissions, so if that’s your preferred format for showcasing your work, then this could be the journal for you!
Cost: $180 submission fee
Subject area: Humanities
Type of research: Essay submission
The Schola is a peer-reviewed quarterly journal that showcases essays on various humanities and social sciences topics authored by high school students worldwide. They feature a diverse range of subjects such as philosophy, history, art history, English, economics, public policy, and sociology.
Editors at Schola are academics who teach and do research in the humanities and social sciences
Critical Debates in Humanities, Science and Global Justice
Cost: $10 author fee
Subject area: Ethics and frontiers of science, Biology and ecosystems, Technology and Innovation, Medical research and disease, Peace and civil society, Global citizenship, identity and democracy, Structural violence and society, Psychology, Education, AI, Sociology, Computer Science, Neuroscience, Cultural politics, Politics and Justice, Computer science and math as related to policy, Public policy, Human rights, Language, Identity and Culture, Art and activism
Critical Debates is an international academic journal for critical discourse in humanities, science and contemporary global issues for emerging young scholars
International Youth Neuroscience Association Journal
Subject area: Neuroscience
Type of research: Research papers
Although this student peer-reviewed journal is not currently accepting submissions, we’ve had students recently publish here.
Here’s an example of Nevenka’s research that was published in the November 2022 issue of the journal.
Preprint Archives to Share Your Work In
Subject area: STEM, Quantitative Finance, Economics
arXiv is an open access archive supported by Cornell University, where more than 2 million scholarly articles in a wide variety of topics have been compiled. arXiv articles are not peer-reviewed, so you will not receive any feedback on your work from experts. However, your article does go through a moderation process where your work is classified into a topic area and checked for scholarly value. This process is rather quick however and according to arXiv you can expect your article to be available on the website in about 6 hours.
Although there’s no peer review process, that means the submission standards are not as rigorous and you can get your article posted very quickly, so submitting to arXiv or other preprint archives can be something you do before trying to get published in a journal.
One slight inconvenience of submitting to arXiv is that you must be endorsed by a current arXiv author, which can typically be a mentor or teacher or professor that you have. Here’s an example of a Polygence student submitting their work to arXiv, with Albert’s research on Hamiltonian Cycles.
Subject area: Biology
Type of research: Original research
bioRxiv is a preprint server for biology research, where again the research is not peer-reviewed but undergoes a check to make sure that the material is relevant and appropriate.
bioRxiv has a bit of a longer posting time, taking around 48 hours, but that’s still very quick. bioRxiv also allows for you to submit revised versions of your research if you decide to make changes.
Research Archive of Rising Scholars (RARS)
Subject area: STEM and Humanities
Type of research: Original research, review articles, poems, short stories, scripts
Research Archive of Rising Scholars is Polygence’s own preprint server! We were inspired by arXiv so we created a repository for articles and other creative submissions in STEM and the Humanities.
We launched RARS in 2022 and we’re excited to offer a space for budding scholars as they look to publish their work in journals. Compared to other preprint archives, RARS also accepts a wider range of submission types, including poems, short stories, and scripts.
Conferences to Participate In
Symposium of rising scholars.
Deadline: Twice a year - February and July
Polygence’s very own Symposium of Rising Scholars is a bi-annual academic conference where students present and share their research with their peers and experts. The Symposium also includes a College Admissions Panel and Keynote Speech. In our 8th edition of the Symposium this past March, we had 60 students presenting live, approximately 70 students presenting asynchronously, and over 100 audience members. The keynote speaker was Chang-rae Lee, award-winning novelist and professor at Stanford University.
We’re looking to have our 9th Symposium in Fall of 2023, and you can express your interest now. If you’re interested to see what our Polygence scholars have presented in the past for the Symposium, you can check out their scholar pages here.
Junior Science and Humanities Symposium (JSHS)
Deadline: Typically in November, so for 2024’s competition look to submit in Fall 2023
Subject area: STEM topics
JSHS is a Department of Defense sponsored program and competition that consists of first submitting a written report of your research. If your submission is selected, you’ll be able to participate in the regional symposium, where you can present in oral format or poster format. A select group from the regional symposium will then qualify for the national symposium.
One of the great things about JSHS compared to the journals mentioned above is that you’re allowed to work in teams and you don’t have to be a solo author. This can make the experience more fun for you and your teammates, and allow you to combine your strengths for your submission.
Related Content:
Top 8 Business Journals to Publish Your Research
Why Teens Should Attend the National Student Leadership Conference (NSLC)
How to Brainstorm Your Way to Perfect Research Topic Ideas
Top 20 Most Competitive Summer Programs for High School Students
Research Opportunities for High School Students
Want to start a project of your own?
Click below to get matched with one of our expert mentors who can help take your project off the ground!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
3. Submit your article according to the journal's submission guidelines. Go to the "author's guide" (or similar) on the journal's website to review its submission requirements. Once you are satisfied that your paper meets all of the guidelines, submit the paper through the appropriate channels.
To Publish a Research Paper follow the guide below: Conduct original research: Conduct thorough research on a specific topic or problem. Collect data, analyze it, and draw conclusions based on your findings. Write the paper: Write a detailed paper describing your research.
Step 2: Finding the Right Journal. Understanding how to publish a research paper involves selecting the appropriate journal for your work. This step is critical for successful publication, and you should take several factors into account when deciding which journal to apply for: Conduct thorough research to identify journals that specialise in ...
2. Prepare your paper for submission. Download our get published quick guide opens in new tab/window, which outlines the essential steps in preparing a paper.(This is also available in Chinese opens in new tab/window).It is very important that you stick to the specific "guide for authors" of the journal to which you are submitting.
If you want to prepare for publication, consider some of the following steps: 1. Determine your topic. One of the first steps toward creating a published paper is by carefully choosing your topic. An important part of your topic selection depends on your studies and on what topics you're qualified to discuss. There are also some topics that may ...
As an academic paper can have anywhere from five to hundreds of sources, I would also suggest using a citation manager as you write. This will save you from having to constantly update the sources in the paper as you add and revise. Submitting the Paper. In my case, my PI submitted the paper and is the primary contact with the journal.
What you will achieve: In this project-based course, you will outline a complete scientific paper, choose an appropriate journal to which you'll submit the finished paper for publication, and prepare a checklist that will allow you to independently judge whether your paper is ready to submit.
Step 1: Choosing a journal. Why choose your target journal before you start writing? Choosing which journal to publish your research paper in is one of the most significant decisions you have to make as a researcher. Where you decide to submit your work can make a big difference to the reach and impact your research has.
This post will discuss 7 steps to the successful publication of your research paper: Check whether your research is publication-ready. Choose an article type. Choose a journal. Construct your paper. Decide the order of authors. Check and double-check. Submit your paper. 1.
The introduction section should be approximately three to five paragraphs in length. Look at examples from your target journal to decide the appropriate length. This section should include the elements shown in Fig. 1. Begin with a general context, narrowing to the specific focus of the paper.
The introduction section should be approximately three to five paragraphs in length. Look at examples from your target journal to decide the appropriate length. This section should include the elements shown in Fig. 1. Begin with a general context, narrowing to the specific focus of the paper.
Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist. Free lecture slides.
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature. As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question.More specifically, that's called a research question, and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What's important to understand though is that you'll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources - for ...
Formatting a Chicago paper. The main guidelines for writing a paper in Chicago style (also known as Turabian style) are: Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Use 1 inch margins or larger. Apply double line spacing. Indent every new paragraph ½ inch. Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center.
Some journals are dedicated to publishing undergraduate research - For example, the Canadian Journal of Undergraduate Research (CJUR) based out of UBC. Student journals are another great option: SFU hosts a number of student journals* run by and for students, and many of these accept undergraduate student work in a particular discipline. The Library's Student Learning Commons also hosts the ...
An undergraduate journal edited, produced and published at Heidelberg University in partnership with the English Department. The journal publishes literary research from schools around the world for an annual publication. Check the website for the "call for papers," which will explain the theme of the next issue.
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment. "Research Paper Planner" (UCLA) UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
Carefully proofread and format your paper. Double-check for any spelling, grammar, or punctuation errors. Ensure your paper follows the recommended style guide for font type and size, spacing, margins, page numbers, headings, and image captions. . Of course, writing a research paper is not as easy.
Step 2: Organize Your Schedule. Once you've read the rubric, note in your planner or on your calendar when your research paper is due. Then, make a schedule so that you can accomplish this task in small steps rather than over the course of one (likely stressful) night. Having a plan in place can help you feel better and write a stronger ...
🔥Join me for my Certification Course on 'A-Z of Research Writing & Presentation' 😃: https://wiseupcommunications.com/course/research-writing/In this video,...
To address the first issue, yes, it is possible to publish without a professor. People at corporations and small companies publish all the time without academic collaborators (and without PhD level staffers). The challenge is having a topic that is worth publishing, and finding an appropriate venue to publish it in.
Getting published in the Journal of Student Research takes careful prep and following specific guidelines. Here are some tips to boost your manuscript's chances of acceptance and make it stand out to reviewers. 1. Make sure your claims are unique.
STEM Fellowship Journal (SFJ) SFJ is a peer-reviewed journal published by Canadian Science Publishing that serves as a platform for scholarly research conducted by high school and university students in the STEM fields. Peer review is conducted by undergraduate, graduate student, and professional reviewers.
Publishing a research paper for the first time? In this video, we talk about the process of how you can do a research project and then build it into a resear...