Assignment of Benefits 50 State Chart
State Law Charts

Document Info
Published on Sep 30, 2019
AHIP Members login info box
AHIP Member Plan employees can log in to view additional content.
Don’t have a login? Register as a Member Plan employee.
- Construction Accidents
Practice Areas
Assignment of benefits: what you need to know.
- August 17, 2022
- Steven Schwartzapfel
Insurance can be useful, but dealing with the back-and-forth between insurance companies and contractors, medical specialists, and others can be a time-consuming and ultimately unpleasant experience. You want your medical bills to be paid without having to act as a middleman between your healthcare provider and your insurer.
However, there’s a way you can streamline this process. With an assignment of benefits, you can designate your healthcare provider or any other insurance payout recipient as the go-to party for insurance claims. While this can be convenient, there are certain risks to keep in mind as well.
Below, we’ll explore what an assignment of insurance benefits is (as well as other forms of remediation), how it works, and when you should employ it. For more information, or to learn whether you may have a claim against an insurer, contact Schwartzapfel Lawyers now at 1-516-342-2200 .
What Is an Assignment of Benefits?
An assignment of benefits (AOB) is a legal process through which an insured individual or party signs paperwork that designates another party like a contractor, company, or healthcare provider as their insurance claimant .
Suppose you’re injured in a car accident and need to file a claim with your health insurance company for medical bills and related costs. However, you also need plenty of time to recover. The thought of constantly negotiating between your insurance company, your healthcare provider, and anyone else seems draining and unwelcome.
With an assignment of benefits, you can designate your healthcare provider as your insurance claimant. Then, your healthcare provider can request insurance payouts from your healthcare insurance provider directly.
Through this system, the health insurance provider directly pays your physician or hospital rather than paying you. This means you don’t have to pay your healthcare provider. It’s a streamlined, straightforward way to make sure insurance money gets where it needs to go. It also saves you time and prevents you from having to think about insurance payments unless absolutely necessary.
What Does an Assignment of Benefits Mean?
An AOB means that you designate another party as your insurance claimant. In the above example, that’s your healthcare provider, which could be a physician, hospital, or other organization.
With the assignment of insurance coverage, that healthcare provider can then make a claim for insurance payments directly to your insurance company. The insurance company then pays your healthcare provider directly, and you’re removed as the middleman.
As a bonus, this system sometimes cuts down on your overall costs by eliminating certain service fees. Since there’s only one transaction — the transaction between your healthcare provider and your health insurer — there’s only one set of service fees to contend with. You don’t have to deal with two sets of service fees from first receiving money from your insurance provider, then sending that money to your healthcare provider.
Ultimately, the point of an assignment of benefits is to make things easier for you, your insurer, and anyone else involved in the process.
What Types of Insurance Qualify for an Assignment of Benefits?
Most types of commonly held insurance can work with an assignment of benefits. These insurance types include car insurance, healthcare insurance, homeowners insurance, property insurance, and more.
Note that not all insurance companies allow you to use an assignment of benefits. For an assignment of benefits to work, the potential insurance claimant and the insurance company in question must each sign the paperwork and agree to the arrangement. This prevents fraud (to some extent) and ensures that every party goes into the arrangement with clear expectations.
If your insurance company does not accept assignments of benefits, you’ll have to take care of insurance payments the traditional way. There are many reasons why an insurance company may not accept an assignment of benefits.
To speak with a Schwartzapfel Lawyers expert about this directly, call 1-516-342-2200 for a free consultation today. It will be our privilege to assist you with all your legal questions, needs, and recovery efforts.
Who Uses Assignments of Benefits?
Many providers, services, and contractors use assignments of benefits. It’s often in their interests to accept an assignment of benefits since they can get paid for their work more quickly and make critical decisions without having to consult the insurance policyholder first.
Imagine a circumstance in which a homeowner wants a contractor to add a new room to their property. The contractor knows that the scale of the project could increase or shrink depending on the specifics of the job, the weather, and other factors.
If the homeowner uses an assignment of benefits to give the contractor rights to make insurance claims for the project, that contractor can then:
- Bill the insurer directly for their work. This is beneficial since it ensures that the contractor’s employees get paid promptly and they can purchase the supplies they need.
- Make important decisions to ensure that the project completes on time. For example, a contract can authorize another insurance claim for extra supplies without consulting with the homeowner beforehand, saving time and potentially money in the process.
Practically any company or organization that receives payments from insurance companies may choose to take advantage of an assignment of benefits with you. Example companies and providers include:
- Ambulance services
- Drug and biological companies
- Lab diagnostic services
- Hospitals and medical centers like clinics
- Certified medical professionals such as nurse anesthetists, nurse midwives, clinical psychologists, and others
- Ambulatory surgical center services
- Permanent repair and improvement contractors like carpenters, plumbers, roofers, restoration companies, and others
- Auto repair shops and mechanic organizations
Advantages of Using an Assignment of Benefits
An assignment of benefits can be an advantageous contract to employ, especially if you believe that you’ll need to pay a contractor, healthcare provider, and/or other organization via insurance payouts regularly for the near future.
These benefits include but are not limited to:
- Save time for yourself. Again, imagine a circumstance in which you are hospitalized and have to pay your healthcare provider through your health insurance payouts. If you use an assignment of benefits, you don’t have to make the payments personally or oversee the insurance payouts. Instead, you can focus on resting and recovering.
- Possibly save yourself money in the long run. As noted above, an assignment of benefits can help you circumvent some service fees by limiting the number of transactions or money transfers required to ensure everyone is paid on time.
- Increased peace of mind. Many people don’t like having to constantly think about insurance payouts, contacting their insurance company, or negotiating between insurers and contractors/providers. With an assignment of benefits, you can let your insurance company and a contractor or provider work things out between them, though this can lead to applications later down the road.
Because of these benefits, many recovering individuals, car accident victims, homeowners, and others utilize AOB agreements from time to time.
Risks of Using an Assignment of Benefits
Worth mentioning, too, is that an assignment of benefits does carry certain risks you should be aware of before presenting this contract to your insurance company or a contractor or provider. Remember, an assignment of benefits is a legally binding contract unless it is otherwise dissolved (which is technically possible).
The risks of using an assignment of benefits include:
- You give billing control to your healthcare provider, contractor, or another party. This allows them to bill your insurance company for charges that you might not find necessary. For example, a home improvement contractor might bill a homeowner’s insurance company for an unnecessary material or improvement. The homeowner only finds out after the fact and after all the money has been paid, resulting in a higher premium for their insurance policy or more fees than they expected.
- You allow a contractor or service provider to sue your insurance company if the insurer does not want to pay for a certain service or bill. This can happen if the insurance company and contractor or service provider disagree on one or another billable item. Then, you may be dragged into litigation or arbitration you did not agree to in the first place.
- You may lose track of what your insurance company pays for various services . As such, you could be surprised if your health insurance or other insurance premiums and deductibles increase suddenly.
Given these disadvantages, it’s still wise to keep track of insurance payments even if you choose to use an assignment of benefits. For example, you might request that your insurance company keep you up to date on all billable items a contractor or service provider charges for the duration of your treatment or project.
For more on this and related topic, call Schwartzapfel Lawyers now at 1-516-342-2200 .
How To Make Sure an Assignment of Benefits Is Safe
Even though AOBs do carry potential disadvantages, there are ways to make sure that your chosen contract is safe and legally airtight. First, it’s generally a wise idea to contact knowledgeable legal representatives so they can look over your paperwork and ensure that any given assignment of benefits doesn’t contain any loopholes that could be exploited by a service provider or contractor.
The right lawyer can also make sure that an assignment of benefits is legally binding for your insurance provider. To make sure an assignment of benefits is safe, you should perform the following steps:
- Always check for reviews and references before hiring a contractor or service provider, especially if you plan to use an AOB ahead of time. For example, you should stay away if a contractor has a reputation for abusing insurance claims.
- Always get several estimates for work, repairs, or bills. Then, you can compare the estimated bills and see whether one contractor or service provider is likely to be honest about their charges.
- Get all estimates, payment schedules, and project schedules in writing so you can refer back to them later on.
- Don’t let a service provider or contractor pressure you into hiring them for any reason . If they seem overly excited about getting started, they could be trying to rush things along or get you to sign an AOB so that they can start issuing charges to your insurance company.
- Read your assignment of benefits contract fully. Make sure that there aren’t any legal loopholes that a contractor or service provider can take advantage of. An experienced lawyer can help you draft and sign a beneficial AOB contract.
Can You Sue a Party for Abusing an Assignment of Benefits?
Sometimes. If you believe your assignment of benefits is being abused by a contractor or service provider, you may be able to sue them for breaching your contract or even AOB fraud. However, successfully suing for insurance fraud of any kind is often difficult.
Also, you should remember that a contractor or service provider can sue your insurance company if the insurance carrier decides not to pay them. For example, if your insurer decides that a service provider is engaging in billing scams and no longer wishes to make payouts, this could put you in legal hot water.
If you’re not sure whether you have grounds for a lawsuit, contact Schwartzapfel Lawyers today at 1-516-342-2200 . At no charge, we’ll examine the details of your case and provide you with a consultation. Don’t wait. Call now!
Assignment of Benefits FAQs
Which states allow assignments of benefits.
Every state allows you to offer an assignment of benefits to a contractor and/or insurance company. That means, whether you live in New York, Florida, Arizona, California, or some other state, you can rest assured that AOBs are viable tools to streamline the insurance payout process.
Can You Revoke an Assignment of Benefits?
Yes. There may come a time when you need to revoke an assignment of benefits. This may be because you no longer want the provider or contractor to have control over your insurance claims, or because you want to switch providers/contractors.
To revoke an assignment of benefits agreement, you must notify the assignee (i.e., the new insurance claimant). A legally solid assignment of benefits contract should also include terms and rules for this decision. Once more, it’s usually a wise idea to have an experienced lawyer look over an assignment of benefits contract to make sure you don’t miss these by accident.
Contact Schwartzapfel Lawyers Today
An assignment of benefits is an invaluable tool when you need to streamline the insurance claims process. For example, you can designate your healthcare provider as your primary claimant with an assignment of benefits, allowing them to charge your insurance company directly for healthcare costs.
However, there are also risks associated with an assignment of benefits. If you believe a contractor or healthcare provider is charging your insurance company unfairly, you may need legal representatives. Schwartzapfel Lawyers can help.
As knowledgeable New York attorneys who are well-versed in New York insurance law, we’re ready to assist with any and all litigation needs. For a free case evaluation and consultation, contact Schwartzapfel Lawyers today at 1-516-342-2200 !
Schwartzapfel Lawyers, P.C. | Fighting For You™™
What Is an Insurance Claim? | Experian
What is assignment of benefits, and how does it impact insurers? | Insurance Business Mag
Florida Insurance Ruling Sets Precedent for Assignment of Benefits | Law.com
Related Posts
What are the most common types of crane accidents.
Crane accidents can cause significant injuries, costly damages, and considerable disruptions to construction sites. Moreover, if you’re a construction worker,
Maryland Bridge Collapse: Potential Theories of Liability
In the still, pre-dawn hours of Tuesday, March 26, 2024, a critical system failure aboard the Dali cargo ship plunged
Preponderance Of Evidence: Meaning & Legal Breakdown
Understanding civil lawsuits can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re trying to wrap your head around all the legal jargon. To
We'll Fight For You
Schwartzapfel® lawyers has a 99% client satisfaction rate, quick links.
- News & Events
- Verdicts & Settlements
- Video Gallery
- Wrongful Death
- Vehicle Accidents
- Slip & Fall
- Medical Malpractice
- Workers' Compensation
- Personal Injuries
- Product Liability
- Garden City
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- COVID-19 Vaccines
- Occupational Therapy
- Healthy Aging
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
Medicare Assignment: Everything You Need to Know
Medicare assignment.
- Providers Accepting Assignment
- Providers Who Do Not
- Billing Options
- Assignment of Benefits
- How to Choose
Frequently Asked Questions
Medicare assignment is an agreement between Medicare and medical providers (doctors, hospitals, medical equipment suppliers, etc.) in which the provider agrees to accept Medicare’s fee schedule as payment in full when Medicare patients are treated.
This article will explain how Medicare assignment works, and what you need to know in order to ensure that you won’t receive unexpected bills.
fizkes / Getty Images
There are 35 million Americans who have Original Medicare. Medicare is a federal program and most medical providers throughout the country accept assignment with Medicare. As a result, these enrollees have a lot more options for medical providers than most of the rest of the population.
They can see any provider who accepts assignment, anywhere in the country. They can be assured that they will only have to pay their expected Medicare cost-sharing (deductible and coinsurance, some or all of which may be paid by a Medigap plan , Medicaid, or supplemental coverage provided by an employer or former employer).
It’s important to note here that the rules are different for the 29 million Americans who have Medicare Advantage plans. These beneficiaries cannot simply use any medical provider who accepts Medicare assignment.
Instead, each Medicare Advantage plan has its own network of providers —much like the health insurance plans that many Americans are accustomed to obtaining from employers or purchasing in the exchange/marketplace .
A provider who accepts assignment with Medicare may or may not be in-network with some or all of the Medicare Advantage plans that offer coverage in a given area. Some Medicare Advantage plans— health maintenance organizations (HMOs) , in particular—will only cover an enrollee’s claims if they use providers who are in the plan's network.
Other Medicare Advantage plans— preferred provider organizations (PPOs) , in particular—will cover out-of-network care but the enrollee will pay more than they would have paid had they seen an in-network provider.
Original Medicare
The bottom line is that Medicare assignment only determines provider accessibility and costs for people who have Original Medicare. People with Medicare Advantage need to understand their own plan’s provider network and coverage rules.
When discussing Medicare assignment and access to providers in this article, keep in mind that it is referring to people who have Original Medicare.
How to Make Sure Your Provider Accepts Assignment
Most doctors, hospitals, and other medical providers in the United States do accept Medicare assignment.
Provider Participation Stats
According to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, 98% of providers participate in Medicare, which means they accept assignment.
You can ask the provider directly about their participation with Medicare. But Medicare also has a tool that you can use to find participating doctors, hospitals, home health care services, and other providers.
There’s a filter on that tool labeled “Medicare-approved payment.” If you turn on that filter, you will only see providers who accept Medicare assignment. Under each provider’s information, it will say “Charges the Medicare-approved amount (so you pay less out-of-pocket).”
What If Your Provider Doesn’t Accept Assignment?
If your medical provider or equipment supplier doesn’t accept assignment, it means they haven’t agreed to accept Medicare’s approved amounts as payment in full for all of the services.
These providers can still choose to accept assignment on a case-by-case basis. But because they haven’t agreed to accept Medicare assignment for all services, they are considered nonparticipating providers.
Note that "nonparticipating" does not mean that a provider has opted out of Medicare altogether. Medicare will still pay claims for services received from a nonparticipating provider (i.e., one who does not accept Medicare assignment), whereas Medicare does not cover any of the cost of services obtained from a provider who has officially opted out of Medicare.
If a Medicare beneficiary uses a provider who has opted out of Medicare, that person will pay the provider directly and Medicare will not be involved in any way.
Physicians Who Have Opted Out
Only about 1% of all non-pediatric physicians have opted out of Medicare.
For providers who have not opted out of Medicare but who also don’t accept assignment, Medicare will still pay nearly as much as it would have paid if you had used a provider who accepts assignment. Here’s how it works:
- Medicare will pay the provider 95% of the amount they would pay if the provider accepted assignment.
- The provider can charge the person receiving care more than the Medicare-approved amount, but only up to 15% more (some states limit this further). This extra amount, which the patient has to pay out-of-pocket, is known as the limiting charge . But the 15% cap does not apply to medical equipment suppliers; if they do not accept assignment with Medicare, there is no limit on how much they can charge the person receiving care. This is why it’s particularly important to make sure that the supplier accepts Medicare assignment if you need medical equipment.
- The nonparticipating provider may require the person receiving care to pay the entire bill up front and seek reimbursement from Medicare (using Form CMS 1490-S ). Alternatively, they may submit a claim to Medicare on behalf of the person receiving care (using Form CMS-1500 ).
- A nonparticipating provider can choose to accept assignment on a case-by-case basis. They can indicate this on Form CMS-1500 in box 27. The vast majority of nonparticipating providers who bill Medicare choose to accept assignment for the claim being billed.
- Nonparticipating providers do not have to bill your Medigap plan on your behalf.
Billing Options for Providers Who Accept Medicare
When a medical provider accepts assignment with Medicare, part of the agreement is that they will submit bills to Medicare on behalf of the person receiving care. So if you only see providers who accept assignment, you will never need to submit your own bills to Medicare for reimbursement.
If you have a Medigap plan that supplements your Original Medicare coverage, you should present the Medigap coverage information to the provider at the time of service. Medicare will forward the claim information to your Medigap insurer, reducing administrative work on your part.
Depending on the Medigap plan you have, the services that you receive, and the amount you’ve already spent in out-of-pocket costs, the Medigap plan may pay some or all of the out-of-pocket costs that you would otherwise have after Medicare pays its share.
(Note that if you have a type of Medigap plan called Medicare SELECT, you will have to stay within the plan’s network of providers in order to receive benefits. But this is not the case with other Medigap plans.)
After the claim is processed, you’ll be able to see details in your MyMedicare.gov account . Medicare will also send you a Medicare Summary Notice. This is Medicare’s version of an explanation of benefits (EOB) , which is sent out every three months.
If you have a Medigap plan, it should also send you an EOB or something similar, explaining the claim and whether the policy paid any part of it.
What Is Medicare Assignment of Benefits?
For Medicare beneficiaries, assignment of benefits means that the person receiving care agrees to allow a nonparticipating provider to bill Medicare directly (as opposed to having the person receiving care pay the bill up front and seek reimbursement from Medicare). Assignment of benefits is authorized by the person receiving care in Box 13 of Form CMS-1500 .
If the person receiving care refuses to assign benefits, Medicare can only reimburse the person receiving care instead of paying the nonparticipating provider directly.
Things to Consider Before Choosing a Provider
If you’re enrolled in Original Medicare, you have a wide range of options in terms of the providers you can use—far more than most other Americans. In most cases, your preferred doctor and other medical providers will accept assignment with Medicare, keeping your out-of-pocket costs lower than they would otherwise be, and reducing administrative hassle.
There may be circumstances, however, when the best option is a nonparticipating provider or even a provider who has opted out of Medicare altogether. If you choose one of these options, be sure you discuss the details with the provider before proceeding with the treatment.
You’ll want to understand how much is going to be billed and whether the provider will bill Medicare on your behalf if you agree to assign benefits (note that this is not possible if the provider has opted out of Medicare).
If you have supplemental coverage, you’ll also want to check with that plan to see whether it will still pick up some of the cost and, if so, how much you should expect to pay out of your own pocket.
A medical provider who accepts Medicare assignment is considered a participating provider. These providers have agreed to accept Medicare’s fee schedule as payment in full for services they provide to Medicare beneficiaries. Most doctors, hospitals, and other medical providers do accept Medicare assignment.
Nonparticipating providers are those who have not signed an agreement with Medicare to accept Medicare’s rates as payment in full. However, they can agree to accept assignment on a case-by-case basis, as long as they haven’t opted out of Medicare altogether. If they do not accept assignment, they can bill the patient up to 15% more than the Medicare-approved rate.
Providers who opt out of Medicare cannot bill Medicare and Medicare will not pay them or reimburse beneficiaries for their services. But there is no limit on how much they can bill for their services.
A Word From Verywell
It’s in your best interest to choose a provider who accepts Medicare assignment. This will keep your costs as low as possible, streamline the billing and claims process, and ensure that your Medigap plan picks up its share of the costs.
If you feel like you need help navigating the provider options or seeking care from a provider who doesn’t accept assignment, the Medicare State Health Insurance Assistance Program (SHIP) in your state may be able to help.
A doctor who does not accept Medicare assignment has not agreed to accept Medicare’s fee schedule as payment in full for their services. These doctors are considered nonparticipating with Medicare and can bill Medicare beneficiaries up to 15% more than the Medicare-approved amount.
They also have the option to accept assignment (i.e., accept Medicare’s rate as payment in full) on a case-by-case basis.
There are certain circumstances in which a provider is required by law to accept assignment. This includes situations in which the person receiving care has both Medicare and Medicaid. And it also applies to certain medical services, including lab tests, ambulance services, and drugs that are covered under Medicare Part B (as opposed to Part D).
In 2021, 98% of American physicians had participation agreements with Medicare, leaving only about 2% who did not accept assignment (either as a nonparticipating provider, or a provider who had opted out of Medicare altogether).
Accepting assignment is something that the medical provider does, whereas assignment of benefits is something that the patient (the Medicare beneficiary) does. To accept assignment means that the medical provider has agreed to accept Medicare’s approved fee as payment in full for services they provide.
Assignment of benefits means that the person receiving care agrees to allow a medical provider to bill Medicare directly, as opposed to having the person receiving care pay the provider and then seek reimbursement from Medicare.
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare monthly enrollment .
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Annual Medicare participation announcement .
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Lower costs with assignment .
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Find providers who have opted out of Medicare .
Kaiser Family Foundation. How many physicians have opted-out of the Medicare program ?
Center for Medicare Advocacy. Durable medical equipment, prosthetics, orthotics, and supplies (DMEPOS) updates .
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Check the status of a claim .
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare claims processing manual. Chapter 26 - completing and processing form CMS-1500 data set .
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Ambulance fee schedule .
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Prescription drugs (outpatient) .
By Louise Norris Louise Norris has been a licensed health insurance agent since 2003 after graduating magna cum laude from Colorado State with a BS in psychology.
What is an assignment of benefits?

The last time you sought medical care, you likely made an appointment with your provider, got the treatment you needed, paid your copay or deductible, and that was it. No paperwork, no waiting to be reimbursed; your doctor received payment from your insurance company and you both went on with your lives.
This is how most people receive health care in the U.S. This system, known as assignment of benefits or AOB, is now being used with other types of insurance, including auto and homeowners coverage .
What is an assignment of benefits?
An AOB is a legal agreement that allows your insurance company to directly pay a third party for services performed on your behalf. In the case of health care, it could be your doctor or another medical professional providing care. With a homeowners, renters, or auto insurance claim, the third party could be a contractor, auto repair shop, or other facility.
Assignment of benefits is legal, thanks to a concept known as freedom of contract, which says two parties may make a private agreement, including the forfeiture of certain rights, and the government may not interfere. There are exceptions, making freedom of contract something less than an absolute right. For example, the contract may not violate the law or contain unfair terms.
Not all doctors or contractors utilize AOBs. Therefore, it’s a good idea to make sure the doctor or service provider and you are on the same page when it comes to AOBs before treatment or work begins.
How an AOB works
The function of an AOB agreement varies depending on the type of insurance policy involved, the healthcare provider, contractor, or service provider, and increasingly, state law. Although an AOB is normal in health insurance, other applications of assignment of benefits have now included the auto and homeowners insurance industry.
Because AOBs are common in health care, you probably don’t think twice about signing a piece of paper that says “assignment of benefits” across the top. But once you sign it, you’re likely turning over your right to deal with your insurance company regarding service from that provider. Why would you do this?
According to Dr. David Berg of Redirect Health , the reason is simple: “Without an AOB in place, the patient themselves would be responsible for paying the cost of their service and would then file a claim with their insurance company for reimbursement.”
With homeowners or auto insurance, the same rules apply. Once you sign the AOB, you are effectively out of the picture. The contractor who reroofs your house or the mechanic who rebuilds your engine works with your insurance company by filing a claim on your behalf and receiving their money without your help or involvement.
“Each state has its own rules, regulations, and permissions regarding AOBs,” says Gregg Barrett, founder and CEO of WaterStreet , a cloud-based P&C insurance administration platform. “Some states require a strict written breakdown of work to be done, while others allow assignment of only parts of claims.”
Within the guidelines of the specific insurance rules for AOBs in your state, the general steps include:
- You and your contractor draw up an AOB clause as part of the contract.
- The contract stipulates the exact work that will be completed and all necessary details.
- The contractor sends the completed AOB to the insurance company where an adjuster reviews, asks questions, and resolves any discrepancies.
- The contractor’s name (or that of an agreed-upon party) is listed to go on the settlement check.
After work is complete and signed off, the insurer will issue the check and the claim will be considered settled.
Example of an assignment of benefits
If you’re dealing with insurance, how would an AOB factor in? Let’s take an example. “Say you have a water leak in the house,” says Angel Conlin, chief insurance officer at Kin Insurance . “You call a home restoration company to stop the water flow, clean up the mess, and restore your home to its former glory. The restoration company may ask for an assignment of benefits so it can deal directly with the insurance company without your input.”
In this case, by eliminating the homeowner, whose interests are already represented by an experienced insurance adjustor, the AOB reduces redundancy, saves time and money, and allows the restoration process to proceed with much greater efficiency.
When would you need to use an assignment of benefits?
An AOB can simplify complicated and costly insurance transactions and allow you to turn these transactions over to trusted experts, thereby avoiding time-consuming negotiations.
An AOB also frees you from paying the entire bill upfront and seeking reimbursement from your insurance company after work has been completed or services rendered. Since you are not required to sign an assignment of benefits, failure to sign will result in you paying the entire medical bill and filing for reimbursement. The three most common uses of AOBs are with health insurance, car insurance, and homeowners insurance.
Assignment of benefits for health insurance
As discussed, AOBs in health insurance are commonplace. If you have health insurance, you’ve probably signed AOBs for years. Each provider (doctor) or practice requires a separate AOB. From your point of view, the big advantages of an AOB are that you receive medical care, your doctor and insurance company work out the details and, in the event of a disagreement, those two entities deal with each other.
Assignment of benefits for car owners
If your car is damaged in an accident and needs extensive repair, the benefits of an AOB can quickly add up. Not only will you have your automobile repaired with minimal upfront costs to you, inconvenience will be almost nonexistent. You drop your car off (or have it towed), wait to be called, told the repair is finished, and pick it up. Similar to a health care AOB, disagreements are worked out between the provider and insurer. You are usually not involved.
Assignment of benefits for homeowners
When your home or belongings are damaged or destroyed, your primary concern is to “return to normal.” You want to do this with the least amount of hassle. An AOB allows you to transfer your rights to a third party, usually a contractor, freeing you to deal with the crisis at hand.
When you sign an AOB, your contractor can begin immediately working on damage repair, shoring up against additional deterioration, and coordinating with various subcontractors without waiting for clearance or communication with you.
The fraud factor
No legal agreement, including an AOB, is free from the possibility of abuse or fraud. Built-in safeguards are essential to ensure the benefits you assign to a third party are as protected as possible.
In terms of what can and does go wrong, the answer is: plenty. According to the National Association of Mutual Insurance Companies (NAMICs), examples of AOB fraud include inflated invoices or charges for work that hasn’t been done. Another common tactic is to sue the insurance company, without the policyholder’s knowledge or consent, something that can ultimately result in the policyholder being stuck with the bill and higher insurance premiums due to losses experienced by the insurer.
State legislatures have tried to protect consumers from AOB fraud and some progress has been made. Florida, for example, passed legislation in 2019 that gives consumers the right to rescind a fraudulent contract and requires that AOB contracts include an itemized description of the work to be done. Other states, including North Dakota, Kansas, and Iowa have all signed NAMIC-backed legislation into law to protect consumers from AOB fraud.
The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC), offers advice for consumers to help avoid AOB fraud and abuse:
- File a claim with your insurer before you hire a contractor. This ensures you know what repairs need to be made.
- Don’t pay in full upfront. Legitimate contractors do not require it.
- Get three estimates before selecting a contractor.
- Get a full written contract and read it carefully before signing.
- Don’t be pressured into signing an AOB. You are not required to sign an AOB.
Pros and cons of an assignment of benefits
The advantages and disadvantages of an AOB agreement depend largely on the amount and type of protection your state’s insurance laws provide.
Pros of assignment of benefits
With proper safeguards in place to reduce opportunities for fraud, AOBs have the ability to streamline and simplify the insurance claims process.
- An AOB frees you from paying for services and waiting for reimbursement from your insurer.
- Some people appreciate not needing to negotiate with their insurer.
- You are not required to sign an AOB.
Cons of assignment of benefits
As with most contracts, AOBs are a double-edged sword. Be aware of potential traps and ask questions if you are unsure.
- Signing an AOB could make you the victim of a scam without knowing it until your insurer refuses to pay.
- An AOB doesn’t free you from the ultimate responsibility to pay for services rendered, which could drag you into expensive litigation if things go south.
- Any AOB you do sign is legally binding.
The takeaway
An AOB, as the health insurance example shows, can simplify complicated and costly insurance transactions and help consumers avoid time-consuming negotiations. And it can save upfront costs while letting experts work out the details.
It can also introduce a nightmare scenario laced with fraud requiring years of costly litigation. Universal state-level legislation with safeguards is required to avoid the latter. Until that is in place, your best bet is to work closely with your insurer when signing an AOB. Look for suspicious or inflated charges when negotiating with contractors, providers, and other servicers.
EDITORIAL DISCLOSURE : The advice, opinions, or rankings contained in this article are solely those of the Fortune Recommends ™ editorial team. This content has not been reviewed or endorsed by any of our affiliate partners or other third parties.

Our Positions | Assignment of Benefits
Issues | Our Positions
- Aftermarket Parts
- Anti-Steering
- Automated Vehicles
- Auto Affordability
- Distracted/Impaired Driving
- No-Fault Insurance
- Ride-Sharing (TNCs)
- Uninsured/Underinsured
- Corporate Governance Annual Disclosure (CGAD)
- Group Supervision
- Holding Company Act
- Own Risk Solvency Assessment (ORSA)
- Consumer Financial Protection Bureau
- Covered Agreement
- Crop Insurance
- Disparate Impact Rule
- Federal Insurance Office
- Federal Reserve Regulation Impacting Insurers
- Fiduciary Rule
- Financial Stability Oversight Council
- McCarran-Ferguson
- Overtime Rule
- Risk Retention Act
- Capital Adequacy
- Current Expected Credit Loss (CECL)
- Financial Analysis and Examination
- Financial Stability - Macroprudential Oversight
- Group Capital
- Insurance Contracts
- Investment Regulation
- Other Public Accounting Standards
- Receivership/Insolvency - Recovery/Resolutions Plans
- Reinsurance Collateral
- Statutory Accounting Standards
- Cadillac Tax
- Cost-Shifting
- Medicare Secondary Payer
- Cybersecurity
- Drones/Unmanned Aerial Systems
- Electronic Policyholder Communications
- InsurTech/FinTech
- American Law Institute
- Assignment of Benefits
- Civil Justice Reform
- Depreciation of Labor
- Joint and Several Liability
- Noneconomic Damages Caps
- Phantom Damages
- Prejudgment Damages Caps
- Prejudgment Interest Reform
- Self-Evaluative Privilege
- Sunshine Litigation Legislation
- Third Party Litigation Funding
- Conduct of Business
- Market Conduct Annual Statement
- Market Conduct Certification
- Market Conduct Regulation
- Anti-Concurrent Causation Clauses
- Building Codes
- Catastrophe Funds
- Climate Risk
- Disaster Deductibles
- Disaster Mitigation
- Hurricane Deductibles
- National Flood Insurance Program
- Storm Chasers
- Open Rating in Competitive Markets
- Flex-Rating
- Commercial Lines Modernization
- Price Optimization
- Speed to Market
- Federal Tax Reform
- Premium Taxes
- Small Mutual Inflation Update
- TRIA Data Reporting
- Risk-Based Pricing
- Use of Education & Occupation in Undwriting (predictive modeling, big data, tech-driving underwriting tools)
- Use of Weather-Related Claims
- Federalizing the WC System
- Drug Compounding
- Drug Formularies
- Fee Schedules
- Physician Dispensing
- State Reforms
- Opioid Abuse
- Insurance Core Principles
An assignment of benefits, or AOB, is a legal tool that allows an insurer to directly pay a third party for services performed rather than reimbursing a claimant afterwards. In recent years, insurers have experienced an increase in fraud and abuse of assignment of benefit provisions, resulting in higher costs.
Assignment of rights to collect under an insurance policy after a loss are common. In many cases, homeowners will assign the right to collect to contractors or other service providers following a loss. Vendors soliciting AOBs from policyholders are typically associated with property insurance, auto repair, and personal insurance claims. While such assignment may allow policyholders to make emergency repairs more quickly, the practice has resulted in many homeowners becoming the victims of scam artists and other unscrupulous service providers. Contractors have sought to unilaterally establish the value of the claim and demand payment for inflated invoices. Many contractors also work with attorneys that then sue the insurance company over the claim.
State legislatures have sought to protect insurance consumers from AOB abuse by imposing common sense limitations, and 2019 finally saw some progress. For example, for the past several years, the Florida legislature has sought to put some parameters around the use of assignment of benefits to curtail the explosion of lawsuits filed by contractors and attorneys allegedly on behalf of consumers who knew nothing about the lawsuits. The only beneficiary of such fraud were the unscrupulous lawyers and contractors. In 2019, AOB reform legislation finally passed the Florida legislature, and was signed into law by the governor. Among other things, the new law gives policyholders the right to rescind the contract, and mandates that the assignment include an itemized description of the work to be done. Similarly, governors in North Dakota, Kansas, and Iowa all signed into law NAMIC-backed legislation to protect consumers from abusive assignment of benefit practices.
NAMIC Position
Namic news on assignment of benefits.

Erin Collins Senior Vice President - State and Policy Affairs
804.878.6473
Erin
Political Action
News & media.

Assignment of benefits
Assignment of benefits is a legal agreement where a patient authorizes their healthcare provider to receive direct payment from the insurance company for services rendered.
Boost patient experience and your bottom line by automating patient cost estimates, payer underpayment detection, and contract optimization in one place.
What is Assignment of Benefits?
Assignment of benefits (AOB) is a crucial concept in the healthcare revenue cycle management (RCM) process. It refers to the legal transfer of the patient's rights to receive insurance benefits directly to the healthcare provider. In simpler terms, it allows healthcare providers to receive payment directly from the insurance company, rather than the patient being responsible for paying the provider and then seeking reimbursement from their insurance company.
Understanding Assignment of Benefits
When a patient seeks medical services, they typically have health insurance coverage that helps them pay for the cost of their healthcare. In most cases, the patient is responsible for paying a portion of the bill, known as the copayment or deductible, while the insurance company covers the remaining amount. However, in situations where the patient has assigned their benefits to the healthcare provider, the provider can directly bill the insurance company for the services rendered.
The assignment of benefits is a legal agreement between the patient and the healthcare provider. By signing this agreement, the patient authorizes the healthcare provider to receive payment directly from the insurance company on their behalf. This ensures that the provider receives timely payment for the services provided, reducing the financial burden on the patient.
Difference between Assignment of Benefits and Power of Attorney
While the assignment of benefits may seem similar to a power of attorney (POA) in some respects, they are distinct legal concepts. A power of attorney grants someone the authority to make decisions and act on behalf of another person, including financial matters. On the other hand, an assignment of benefits only transfers the right to receive insurance benefits directly to the healthcare provider.
In healthcare, a power of attorney is typically used in situations where a patient is unable to make decisions about their medical care. It allows a designated individual, known as the healthcare proxy, to make decisions on behalf of the patient. In contrast, an assignment of benefits is used to streamline the payment process between the healthcare provider and the insurance company.

Examples of Assignment of Benefits
To better understand how assignment of benefits works, let's consider a few examples:
Sarah visits her primary care physician for a routine check-up. She has health insurance coverage through her employer. Before the appointment, Sarah signs an assignment of benefits form, authorizing her physician to receive payment directly from her insurance company. After the visit, the physician submits the claim to the insurance company, and they reimburse the physician directly for the covered services.
John undergoes a surgical procedure at a hospital. He has health insurance coverage through a private insurer. Prior to the surgery, John signs an assignment of benefits form, allowing the hospital to receive payment directly from his insurance company. The hospital submits the claim to the insurance company, and they reimburse the hospital for the covered services. John is responsible for paying any copayments or deductibles directly to the hospital.
Mary visits a specialist for a specific medical condition. She has health insurance coverage through a government program. Mary signs an assignment of benefits form, granting the specialist the right to receive payment directly from the government program. The specialist submits the claim to the program, and they reimburse the specialist for the covered services. Mary is responsible for any applicable copayments or deductibles.
In each of these examples, the assignment of benefits allows the healthcare provider to receive payment directly from the insurance company, simplifying the billing and reimbursement process for both the provider and the patient.
Assignment of benefits is a fundamental concept in healthcare revenue cycle management. It enables healthcare providers to receive payment directly from the insurance company, reducing the financial burden on patients and streamlining the billing process. By understanding the assignment of benefits, patients can make informed decisions about their healthcare and ensure that their providers receive timely payment for the services rendered.
Improve your financial performance while providing a more transparent patient experience
Related terms.
Exclusion is the process of identifying and removing claims that do not meet the criteria for reimbursement, ensuring compliance and accurate revenue capture.
Single coverage
Single coverage is a healthcare insurance plan that provides benefits to only one individual, typically excluding dependents or other family members.
Subscribe to the

Healthcare Clarified newsletter
Get the latest insights on RCM and healthcare policy in your inbox
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
Client Alerts, News Articles, Blog Posts, & Multimedia
Everything you need to know about BMD and the industry.
The Current State of Assignment of Benefits Litigation in Florida

By: Senior Counsel Nhan T. Lee with Associate Wayne A. Comstock

Homeowners typically experience property damage and use contractors to repair the damage as quickly as possible. [4] An assignment of benefits, or AOB, is an agreement “in which a contractor begins the work [on the property owner’s home] without charging the property owner and agrees to seek compensation from the insurer.” [5] An AOB can be beneficial to a homeowner because an AOB eliminates the processing of a claim through the insurance company. [6] Without contacting the insurance company, “the insured can hire a contractor, wait for the contractor to finish the work, then pay the deductible.” [7] Despite the time saving benefit to a homeowner, AOBs can lead to costly litigation and higher premiums. [8]
In Florida, AOB abuse first started with Personal Injury Protection (“PIP”) claims. [9] A PIP claim works similar to an AOB property damage claim. [10] In a PIP claim, “[t]he assignment lets a medical provider seek reimbursement for their services directly from an insurer. The injured person receives medical care and does not have to deal directly with their insurance company.” [11] PIP claims led to abuse because plaintiff’s attorneys filed many lawsuits on behalf of the assignee “for inflated claims or potentially unnecessary medical treatment.” [12]
Prior to 2019, AOBs frequently resulted in costly litigation primarily because Florida law provided for one-way attorney’s fee provisions. [13] In a first-party lawsuit, Florida law required insurers to pay plaintiff’s attorneys a court determined “reasonable sum.” [14] However, Florida law did not require plaintiffs to compensate the insurer’s attorneys. [15] This imbalance pressured insurers to settle claims “rather than face expensive litigation, which, if they lose, means they must pay the other side’s lawyers.” [16]
The public policy rationale supporting one-way attorney’s fee provisions in Florida stems from Feller v. Equitable Life Assurance Soc. [17] In Feller , the Supreme Court of Florida described the purpose of one-way attorney’s fee provisions as “to discourage the contesting of policies in Florida courts, and to reimburse plaintiffs reasonably their outlay for attorney’s fees when suing in Florida courts.” [18] In Ivey v. Allstate Ins. Co. , the Supreme Court of Florida further described the rationale behind one-way attorney’s fee provisions as “to level the playing field so that the economic power of insurance companies is not so overwhelming that injustice may be encouraged because people will not have the necessary means to seek redress in the courts.” [19] AOBs defeat the purpose of one-way attorney’s fee provisions because AOBs do not serve those individuals one-way attorney’s fee provisions are meant to protect: the policyholder and any beneficiaries the policyholder designates. [20]
The Florida legislature enacted PIP reforms in 2012 that curbed “AOB abuse in auto insurance.” [21] However, around the same time, AOB abuse began spreading to property damage claims. [22] Vendors targeted homeowners insurers because Florida is home to a large number of insured homes, “which ensures large claimant and plaintiff pools.” [23] In addition, hurricanes and tropical storms in Florida carry the risk of water damage. [24] In Florida, “[w]ater damage repairs often need to be undertaken immediately to prevent further damage.” [25] To complicate matters further, “the standard homeowners policy requires that policyholders protect their property from further damage by making reasonable and necessary repairs.” [26] A homeowners policy is more attractive than an auto insurance policy because the average loss is higher: $11,000 compared with $1,300. [27] The higher threshold means that a homeowner assignee in a property claim can potentially “inflate repair bills to a greater degree.” [28] As a result of increasing AOB litigation, insurers raised premiums. [29] For example, “the average premium [in Florida] rose 30 percent between 2007 and 2015.” [30] AOB abuse is most pronounced in Florida because “insurers’ legal costs are rising much faster than losses from homeowners claims” compared with other states. [31]
In an effort to curtail AOB abuse, the Florida legislature enacted significant reforms to AOBs and the one-way attorney’s fee provision. [32] The legislation, enacted on July 1, 2019, “require[d] assignment agreements to be in writing and signed by both the assignee and assignor.” [33] Other changes to AOB agreements included allowing “assignors to rescind without penalty within seven days of the execution of the agreement” and obligating “[a]ssignees . . . [to] provide a copy of an assignment agreement to an insurer within three business days of the execution of the agreement.” [34] The most notable difference, however, involved the one-way attorney’s fee provision where the provision “no longer applies to an assignee.” [35] Instead, the 2019 reforms encouraged insurers to avoid litigation through negotiation or appraisal. [36] In a lawsuit involving an AOB agreement, attorney’s fees may only be recovered as follows:
- Less than 25 percent of the disputed amount, the insurer is entitled to an award of reasonable attorney fees.
- At least 25 percent but less than 50 percent of the disputed amount, no party is entitled to an award of attorney fees.
- At least 50 percent of the disputed amount, the assignee is entitled to an award of reasonable attorney fees. [37]
As companion legislation, the Florida legislature also passed Fla. Stat. 627.7153. [38] Under Fla. Stat. 627.1753, an insurer may restrict an insured’s “right to execute an assignment agreement” if the insurer provides (1) an insurance policy that does not restrict the insured’s “right to an execute an assignment agreement[,]” (2) the restricted policy at a lower cost compared with the unrestricted policy, (3) the policy restricting or prohibiting assignment in whole at a “lower cost than any policy [restricting or] prohibiting assignment in part[,]” and (4) specific language in any restricted policy as described in the statute. [39]
The Florida legislature enacted the 2019 reforms, in part, to reduce insurance premiums for Florida homeowners. [40] In the year following the reform, Citizens Property Insurance Corporation (“CPIC”), reported that insurance premiums dropped for almost 44,000 policyholders. [41] In addition, the reform helped reduce AOB litigation. [42] In 2020, “Florida [saw] less first party cases being filed . . . . CPIC alone [saw] their caseload drop from 2,000 to 1,750 suit per month.” [43] Despite the reduction, Florida lawmakers remained concerned about AOB abuse. [44]
In May 2022, the Florida Legislature approved additional property insurance reforms. [45] The reforms further limit the awarding of attorney’s fees in AOB cases. [46] The reform, titled SB 2D, prohibits a court from awarding attorney’s fees to an assignee in AOB litigation. [47] The reforms also severely “restrict the awarding of fee multipliers in property insurance disputes to ‘rare and exceptional circumstances.’” [48] Florida lawmakers believed such reforms necessary given Florida’s excessive contribution to homeowner insurance lawsuits across the United States. [49] Florida, responsible for “just 9% of property insurance claims, generates 79% of the nation’s homeowner insurance lawsuits.” [50] Florida lawmakers approved the reforms under the belief that “lawsuits . . . exploded in the past several years” despite the 2019 reforms. [51]
While Florida lawmakers acted to protect homeowners, [52] contractors rallied against the reform. [53] In June 2022, the Restoration Association of Florida and Air Quality Assessors, LLC, “filed [a] lawsuit in Leon County circuit court” testing the constitutional validity of the legislation. [54] In filing the lawsuit, “contractors contend that assignment of benefits helps homeowners who are unfamiliar with making sure insurance claims are handled properly.” [55] Contractors believe that AOBs help homeowners quickly address home damage due to inclement weather and other unforeseen circumstances. [56]
In Florida, contractors and Florida lawmakers are seemingly at odds with respect to AOBs. [57] The 2022 reforms remove the awarding of attorney’s fees altogether from AOB litigation, [58] which may both help and hurt homeowners in Florida by lowering property insurance premiums but making immediate home repair less accessible. AOBs will remain a contentious issue moving forward, and the reforms may lead to additional challenges.
[1] Jim Ash, Governor Signs Property Insurance Reforms and Condo Safety Measures , Florida Bar (May 27, 2022), https://www.floridabar.org/the-florida-bar-news/governor-signs-property-insurance-reforms-and-condo-safety-measures/.
[2] Mark Delegal & Ashley Kalifeh, Restoring Balance in Insurance Litigation: Curbing Abuses of Assignments of Benefits and Reaffirming Insureds’ Unique Right to Unilateral Attorney’s Fees 9 (2015), https://www.fljustice.org/files/123004680.pdf.
[3] Douglas Scott MacGregor, Florida Takes Aim at Assignment of Benefits Abuse: A Home Run or a Swing and a Miss? , in New Appleman on Insurance: Current Critical Issues in Insurance Law (2021).
[9] Ins. Info. Inst., Florida’s Assignment of Benefits Crisis: Runaway Litigation Is Spreading, and Consumers Are Paying the Price 7 (2018).
[12] Id. at 8.
[13] Id. at 4.
[17] Feller v. Equitable Life Assurance Soc. , 57 So. 2d 581, 583 (Fla. 1952).
[19] Ivey v. Allstate Ins. Co. , 774 So. 2d 679, 684 (Fla. 2000).
[20] Delegal & Kalifeh, supra note 2, at 3.
[21] Ins. Info. Inst., supra note 9, at 12.
[23] Id. at 13.
[24] What You Should Know About Water Damage in Your Home or Business , Kanner & Pintaluga, https://hurricanedamage.com/blog/what-to-know-about-water-damage/.
[25] Ins. Info. Inst., supra note 9, at 13.
[29] Id. at 14.
[32] Fred E. Karlinsky, Esq., Florida Assignment of Benefit Abuse: Recent Developments, Fed’n of Regul. Couns., https://www.forc.org/Public/Journals/2019/Articles/Summer/Vol30Ed2Article1.aspx.
[36] Cozen O’Connor, Florida’s “Assignment of Benefits” Bill: A Guide Through the New Statutory Framework , JDSupra (Apr. 26, 2019), https://www.jdsupra.com/legalnews/florida-s-assignment-of-benefits-bill-a-29861/.
[37] Fla. Stat. § 627.7152(10)(a) (2019).
[38] Fla. Stat. § 627.7153 (2019).
[39] Id. § 627.7153(2)(a)-(d).
[40] O’Connor, supra note 36.
[41] Rumberger Kirk, Impact of Florida’s New Assignment of Benefits Law: HB 7065 , JDSupra (May 26, 2020), https://www.jdsupra.com/legalnews/impact-of-florida-s-new-assignment-of-80753/.
[44] Ash, supra note 1.
[53] Jim Saunders, Contractors Challenge New Florida Insurance Law , Law (June 1, 2022), https://www.law.com/dailybusinessreview/2022/06/01/contractors-challenge-new-florida-insurance-law/.
[57] Ash, supra note 1; Saunders, supra note 53.
[58] Ash, supra note 1.
Chemical Dependency Professionals Board Rule Changes: Part 2
Board of pharmacy rule changes, counselor, social workers, and marriage and family therapist (cswmft) board rule changes, latest batch of ohio chemical dependency professionals board rules: what providers should know, now in effect: dol final rule on classification of independent contractors.
- Applicant Information
- Breaking CMS Medicare Updates
- Catastrophe Modeling
- Commercial Auto
- Commercial Property
- Community Hazard Mitigation
- Core Lines Services
- IoT/Telematics
- Life Insurance
- Personal Auto
- Personal Property
- Predictive Analytics
- Rating Integrity
- Risk Assessment
- Verisk InsurTech – Reimagining the Future
- Workers’ Compensation
1/30/2024 - 2 Min Read
Quarterly reconstruction costs stabilize as inflation recedes

3/20/2024 - 12 min read

2/26/2024 - 7 min read

2/26/2024 - 3 min read

2/20/2024 - 8 min read

1/31/2024 - 5 min read

1/30/2024 - 21 min read
1/30/2024 - 2 min read

1/23/2024 - 20 min read

1/18/2024 - 22 min read

1/4/2024 - 1 min read

12/21/2023 - 2 min read

12/13/2023 - 3 min read

12/11/2023 - 1 min read

12/11/2023 - 17 min read

12/7/2023 - 11 min read
- 855-717-0022
- Log In / Create an Account
Assignment of benefits
Assignment of benefits is an agreement that gives your claims benefits to someone else.
What is an assignment of benefits?
An assignment of benefits (or AOB for short) is an agreement that gives your claims benefits, and in some instances complete control of your claim, to someone else. It’s usually used so that a contractor can "stand in your shoes" and file a claim, make decisions about repairs, and collect insurance payments from your insurance company directly for covered repairs. In some states, the contractor will even file a lawsuit against your insurer as your assignee.
Why do homeowners agree to an assignment of benefits?
Homeowners may sign an assignment of benefits form because they think it’s more convenient and efficient than dealing with the claims process firsthand.
Once a contractor has been assigned your benefits, they tell the insurance company what work they believe is required and negotiate the claim. For example, say you have a water leak in the house. You call a home restoration company to stop the water flow, clean up the mess, and restore your home to its former glory. The restoration company may ask for an assignment of benefits so it can deal directly with the insurance company without your input. That may sound like a relief at first glance – someone else can deal with all that!
But signing away your rights in the claims process may not be worth the risk.
Assignment of benefits in Florida: a case of rampant fraud
Because the assignment of benefits takes control out of the homeowner’s hands, insurance fraud is a major concern. Some contractors may take advantage of the situation and inflate repair needs and costs or bill for work that was never completed. They may also hire attorneys to sue the insurance company if it does not pay the full amount of their estimate or denies claims.
These lawsuits became a huge problem in Florida – by 2018, there were 135,000 AOB lawsuits , a 70 percent increase in 15 years. On the whole, the FBI estimates fraudulent claims account for nearly $6 billion of the $80 billion appropriated for post-hurricane reconstruction.
Florida eventually passed a bill in 2019 to curb the abuse of the assignment of benefits.
Ultimately, AOB fraud hurts homeowners the most. It increases homeowners insurance rates across the board, and you may be stuck with incomplete work and no recourse.
What responsibilities does the AOB contractor have?
Once you sign an AOB, a contractor has full power to make all decisions about the claim without consulting you. The assignment of benefits gives contractors the ability to:
- File the insurance claim .
- Work directly with insurance claims adjusters.
- Make repair decisions.
- Complete repairs.
- Directly bill the insurance carrier for all work completed.
- Sue your insurance company regarding your claim.
Sometimes the assignment of benefits limits the scope of the work the contractor was hired for. For example, say your home has a leaky pipe. You may hire a plumber to fix the leak, a remediation company to dry the walls and carpet, and a general contractor to replace the bathroom cabinets. Each of the three contractors may have a respective assignment of benefits for their part of the job.
How assignment of benefits impact homeowners
Under some circumstances, an assignment of benefits agreement could work out for homeowners who don’t want to handle their insurance claim. If the contractor is reputable, performs the work, and knows what information the insurance company needs, it can be a big help.
For example:
- The claims adjuster will work directly with the contractor.
- The contractor would handle remediation and repairs.
- The contractor would bill the insurance company, not the homeowner.
AOB arrangements only work for covered damage in need of repair. If you must replace belongings or appliances, you’d still need to work directly with your insurer and payments would go to you.
Protecting yourself in an assignment of benefits agreement
Don’t sign an assignment of benefits agreement right off the bat. Before you hire any contractor:
- Get multiple quotes.
- Check references, licenses, and their insurance.
- Get written estimates for potential work.
- Get a guarantee to back the workmanship.
- Make sure you get to approve the completed work.
- Request copies of all paperwork sent to your insurance company.
- Require that the contractor show you the documents you are actually signing.
You might be tempted to hire the first contractor you find, but you save yourself headaches if you do some due diligence before signing an assignment of benefits. Great contractors use this to expedite repairs and spare you some work. Take a beat to find that great contractor .
Related Posts: Keep exploring
Displaying post 1 / 3
Handling Assignment of Benefit (“AOB”) Claims in the Wake of Hurricanes Irma and Harvey
Overview | Blog Posts | First-Party Coverage | Timothy Engelbrecht , T. Nicholas Goanos , L. Andrew Watson | Related | Print | Share
Timothy Engelbrecht
Partner | First-Party Coverage , Extra-Contractual 813-281-1900 [email protected]
T. Nicholas Goanos
Partner | Extra-Contractual , Arson & Fraud , Casualty Defense Litigation , Third-Party Coverage , First-Party Coverage 704-940-9811 [email protected]
L. Andrew Watson
Partner | First-Party Coverage , Extra-Contractual , Casualty Defense Litigation , Arson & Fraud , Third-Party Coverage 704-543-2321 [email protected]
September 12, 2017
Hurricanes Irma and Harvey have damaged large areas of Florida, Texas, and Louisiana, as well as brought heavy rain and wind to Georgia, North Carolina, and South Carolina. As insurers handle thousands of property damage claims in these areas, they will undoubtedly be presented with claims that have been assigned from insureds to damage-repair contractors. These are often referred to as assignments of benefits or “AOB” claims. This article explains briefly what an AOB claim is, how Florida, Texas, Louisiana, Georgia, North Carolina, and South Carolina address AOB claims, and the best practices for handling AOB claims.
WHAT IS AN AOB CLAIM?
The classic example of an AOB claim is the following: an insured suffers property damage and hires a repair contractor to repair that damage. The repair contractor requires the insured to execute a written document, usually entitled “Assignment of Insurance Benefits”, which says something to the effect of “for and in consideration of the contractor’s agreement to protect the property from further damage and/or make repairs, the insured assigns his/her/its insurance benefits to the contractor.” The contractor thereafter makes a claim directly to the insurer using the AOB.
HOW DOES FLORIDA, TEXAS, LOUISIANA, GEORGIA, NORTH CAROLINA, AND SOUTH CAROLINA ADDRESS AOB CLAIMS?
Florida has allowed AOB claims for over 100 years. Sec. First Ins. Co. v. State, Office of Ins. Regulation , 177 So. 3d 627, 628 (Fla. 1st DCA 2015). Post-loss property damage claims are freely assignable in Florida regardless of whether the insurer consents or not. Start to Finish Restoration, LLC v. Homeowners Choice Prop. & Cas. Ins. Co. , 192 So. 3d 1275, 1276 (Fla. 2d DCA 2016). An insurance policy that has a “non-assignment” clause only bars the assignment of the entire insurance policy, not an assignment of a post-loss insurance claim. Bioscience West, Inc. v. Gulfstream Prop. & Cas. Ins. Co. , 185 So. 3d 638, 640-41 (Fla. 2d DCA 2016).
Texas has adopted the opposite approach to AOBs. The general rule in Texas is that an insured cannot assign an insurance claim if the insurance policy has a non-assignment clause. ARM Props. Mgmt. Group v. RSUI Indem . Co., 642 F.Supp.2d 592, 609-10 (W.D. Tex. 2009) relying on Tex. Farmers Ins. Co. v. Gerdes , 880 S.W. 2d 215, 218 (Tex. App. 1994). This is true even if the non-assignment clause is general and broadly worded.
Louisiana takes a hybrid approach to AOBs. Louisiana allows an insurer to place a clause in an insurance policy that prohibits post-loss assignments. In re Katrina Canal Breaches Litig ., 63 So. 3d 955, 962-63 (La. 2011). However, in order for such a clause to be enforceable, the clause must clearly and unambiguously express that it applies to post-loss assignments. Id . The general and a broadly worded non-assignment clause that has traditionally appeared in most insurance policies is not sufficient. Id.
Georgia , much like many of the States above and across the Country, permits AOBs. See Santiago v. Safeway Ins. Co. , 196 Ga. App. 480, 481, 396 S.E.2d 506, 608 (App. Ct. 1990). Unlike North Carolina and South Carolina, which are discussed below, an assignee in Georgia may pursue his own extra-contractual claim only after first establishing a breach of the insurance policy. Southern Gen. Ins. Co. v. Holt , 262 Ga. 267, 416 S.E.2d 274, 276-77 (1992). Further, before pursuing an extra-contractual claim, an assignee (or insured) in Georgia must provide the insurer an opportunity to “cure” the alleged “bad faith”. See Ga. Code Ann. § 33-4-6.
Lastly, North Carolina and South Carolina also allow AOBs. In upholding the validity of an assignment, courts in these States have ruled not only that assignments of benefits are indeed valid, but also, that they are governed by each State’s general contract law. See e.g., Alaimo Family Chiropractic v. Allstate Ins. Co. , 155 N.C. App. 194, 197, 574 S.E.2d 496, 498 (App. Ct. 2002); Gray v. State Farm Auto. Ins. Co. , 327 S.C. 646, 491 S.E.2d 272 (App. Ct. 1997). The “rubber” meets the proverbial “road”, though, when an extra-contractual claim is alleged. In North Carolina and South Carolina, a plaintiff may assert an extra-contractual claim, even if the insurer has not breached the insurance policy. See Tadlock Painting Co. v. Maryland Cas. Co. , 322 S.C. 498, 473 S.E.2d 52 (1996); Kielbania v. Indian Harbor Ins. Co., 2012 WL 3957926 (M.D.N.C. 2012). However, an assignee is limited in the sense that it may pursue only his own extra-contractual claim, and not the assignors. Horton v. New S. Ins. Co. , 122 N.C. App. 265, 268, 468 S.E.2d 856, 858 (1996); Davis v. Liberty Mut. Ins. Co. , 2015 WL 6163243, at *4 (D.S.C. 2015).
WHAT ARE THE BEST PRACTICES FOR HANDLING AN AOB CLAIM?
First, as noted above, an adjuster needs to know if the state law where the AOB claim is being made allows for AOB claims.
Second, assuming the state allows for AOB claims, the adjuster needs to carefully read what the actual AOB document says. They are not all the same. Some AOBs assign the entire claim. Other AOBs only assign part of the claim. For example, imagine an insured’s property is damaged by water. The insured needs the water extracted and the structure rebuilt. An AOB might assign both the water extraction and the rebuild claim to a single contractor. Or, the insured might execute one AOB to a water extraction contractor and a separate AOB to a different rebuild contractor. Or, an insured might execute an AOB to a water extraction contractor and the insured will retain the remaining rights to make the rebuild claim. If the AOB is unclear what – exactly – is being assigned, it is important for the adjuster to speak with the insured and the contractor to ensure everyone is on the same page.
Third, the adjuster should speak to the insured to gather information necessary to understand and adjust the assigned claim. In Florida, an adjuster likely cannot require a contractor to perform the insurance policy’s post-loss conditions of giving documents, executing a sworn statement in proof of loss, or appearing for an examination under oath. Shaw v. State Farm Fire & Cas. Co., 37 So. 3d 329, 332-33 (Fla. 5th DCA 2010) disapproved on other grounds in Nunez v. Geico Gen. Ins. Co. , 117 So. 3d 388 (Fla. 2013). However, the insured is still responsible for fulfilling those conditions even with regard to the assigned claim. Id. The insured’s failure to do so may bar the assigned claim. Id.
Fourth, assuming payment will be made on the assigned claim, the adjuster should determine who will be listed on the settlement check. If there is a valid AOB, it may be improper to list the insured on the settlement check since the insured’s rights have been assigned to the contractor. Many AOBs will state that only the contractor be listed on the settlement check. However, it is good for an adjuster to confirm with the insured that the insured understands that he/she/it will not be listed on the settlement check. It is also important for the adjuster to correctly determine if a mortgagee needs to be listed on the settlement check. Situations vary depending on the nature of the work that the contractor is doing (damage prevention versus repair) and whether the work has been completed or is still to be done. The adjuster should discuss the situation with the insured, the contractor, and the mortgagee if the adjuster is at all unsure if the mortgagee needs to be on the settlement check.
Fifth, an adjuster should know whether an assigned claim can be resolved using the insurance policy’s appraisal provision. Appraisal can be an inexpensive and expedient way to resolve a claim. In Florida, an insurer usually can require a contractor with an assigned claim to go to appraisal if the insurance policy provides for the mandatory appraisal upon request. Certified Priority Restoration v. State Farm Florida Ins. Co ., 191 So. 3d 961, 962 (Fla. 4th DCA 2016).
Insurers will continue to be presented with AOB claims in the wake of Hurricanes Irma and Harvey. We have been helping insurers and adjusters navigate the unique issues associated with AOB claims for many years. Please contact us if you have any questions or need assistance.
For any further questions, please contact Timothy Engelbrecht, T. Nicholas Goanos, or L. Andrew Watson.

Texas Supreme Court Answers Certified Question in Favor of Insurer on Preclusion of Attorney’s Fees Under Texas Insurance Code Chapter 542A
By Jeffery Allcorn | Blog Posts
March 5, 2024

Analyzing AOBs: Are the Courts Splitting Hairs or Seeking Statutory Compliance?
By Kimberly Matot | Blog Posts , News
February 23, 2024

Bad Faith in Florida: Development of, and Changes to, First-Party Bad Faith Law
By William Collum | Events
January 26, 2024

Hurricane and Wind Forces on Building Envelope Components
By T. Wiley Hodges | Events

Hurricane Ian Shoreline Loss: Four Policies, Oh Joy!
By Thomas Keller | Events
October 19, 2023
- Received a document?

Assignment of Benefits for Contractors: Pros & Cons of Accepting an AOB

22 articles
Insurance , Restoration , Slow Payment

When a property owner files an insurance claim to cover a restoration or roofing project, the owner typically deals directly with the insurance company. They may not have the funds available to pay the contractor out of pocket, so they’re counting on that insurance check to cover the construction costs.
But insurance companies often drag their feet, and payments can take even longer than normal. Contractors often wish they could simply deal with the insurance company directly through an assignment of benefits. In some circumstances, an AOB can be an effective tool that helps contractors collect payment faster — but is it worth it?
In this article, we’ll explain what an assignment of benefits is, and how the process works. More importantly, we’ll look at the pros and cons for restoration and roofing contractors to help you decide if an AOB is worth it .
What is an assignment of benefits?
An assignment of benefits , or AOB, is an agreement to transfer insurance claim rights to a third party. It gives the assignee authority to file and negotiate a claim directly with the insurance company, without involvement from the property owner.
An AOB also allows the insurer to pay the contractor directly instead of funneling funds through the customer. AOBs take the homeowner out of the claims equation.
Here’s an example: A property owner’s roof is damaged in a hurricane. The owner contacts a restoration company to repair the damage, and signs an AOB to transfer their insurance rights to the contractor. The contractor, now the assignee, negotiates the claim directly with the insurance company. The insurer will pay the claim by issuing a check for the repairs directly to the restoration contractor.
Setting up an AOB
A property owner and contractor can set up an assignment of benefits in two steps:
- The owner and the contractor sign an AOB agreement
- The contractor sends the AOB to the insurance company
Keep in mind that many states have their own laws about what the agreement can or should include .
For example, Florida’s assignment of benefits law contains relatively strict requirements when it comes to an assignment of benefits:
- The AOB agreements need to be in writing. The agreement must contain a bolded disclosure notifying the customer that they are relinquishing certain rights under the homeowners policy. You can’t charge administrative fees or penalties if a homeowner decides to cancel the AOB.
- The AOB must include an itemized, per-unit breakdown of the work you plan to do. The services can only involve how you plan to make repairs or restore the home’s damage or protect the property from any further harm. A copy must be provided to the insurance company.
- A homeowner can rescind an AOB agreement within 14 days of signing, or within 30 days if no work has begun and no start date was listed for the work. If a start date is listed, the 30-day rule still applies if substantial progress has not been made on the job.
Before signing an AOB agreement, make sure you understand the property owner’s insurance policy, and whether the project is likely to be covered.
Learn more: Navigating an insurance claim on a restoration project
Pros & cons for contractors
It’s smart to do a cost-benefit analysis on the practice of accepting AOBs. Listing pros and cons can help you make a logical assessment before deciding either way.
Pro: Hiring a public adjuster
An insurance carrier’s claims adjuster will inspect property damage and arrive at a dollar figure calculated to cover the cost of repairs. Often, you might feel this adjuster may have overlooked some details that should factor into the estimate.
If you encounter pushback from the insurer under these circumstances, a licensed, public adjuster may be warranted. These appraisers work for the homeowner, whose best interests you now represent as a result of the AOB. A public adjuster could help win the battle to complete the repairs properly.
Pro: More control over payment
You may sink a considerable amount of time into preparing an estimate for a customer. You may even get green-lighted to order materials and get started. Once the ball starts rolling, you wouldn’t want a customer to back out on the deal.
Klark Brown , Co-founder of The Alliance of Independent Restorers, concedes this might be one of the very situations in which an AOB construction agreement might help a contractor. “An AOB helps make sure the homeowner doesn’t take the insurance money and run,” says Brown.
Pro: Build a better relationship with the homeowner
A homeowner suffers a substantial loss and it’s easy to understand why push and pull with an insurance company might be the last thing they want to undertake. They may desire to have another party act on their behalf.
As an AOB recipient, the claims ball is now in your court. By taking some of the weight off a customer’s shoulders during a difficult period, it could help build good faith and further the relationship you strive to build with that client.
Learn more : 8 Ways for Contractors to Build Trust With a Homeowner
Con: It confuses payment responsibilities
Even if you accept an AOB, the property owner still generally bears responsibility for making payment. If the insurance company is dragging their feet, a restoration contractor can still likely file a mechanics lien on the property .
A homeowner may think that by signing away their right to an insurance claim, they are also signing away their responsibility to pay for the restoration work. This typically isn’t true, and this expectation could set you up for a more contentious dispute down the line if there is a problem with the insurance claim.
Con: Tighter margins
Insurance companies will want repairs made at the lowest cost possible. Just like you, carriers run a business and need to cut costs while boosting revenue.
While some restoration contractors work directly with insurers and could get a steady stream of work from them, Brown emphasizes that you may be sacrificing your own margins. “Expect to accept work for less money than you’d charge independently,” he adds.
The takeaway here suggests that any contractor accepting an AOB could subject themselves to the same bare-boned profit margins.
Con: More administrative work
Among others, creating additional administrative busywork is another reason Brown recommends that you steer clear of accepting AOBs. You’re committing additional resources while agreeing to work for less money.
“Administrative costs are a burden,” Brown states. Insurers may reduce and/or delay payments to help their own bottom lines. “Insurers will play the float with reserves and claims funds,” he added. So, AOBs can be detrimental to your business if you’re spending more while chasing payments.
Con: Increase in average collection period
Every contractor should use some financial metrics to help gauge the health of the business . The average collection period for receivables measures the average time it takes you to get paid on your open accounts.
Insurance companies aren’t known for paying claims quickly. If you do restoration work without accepting an AOB, you can often take action with the homeowner to get paid faster. When you’re depending on an insurance company to make your payment, rather than the owner, collection times will likely increase.
The literal and figurative bottom line is: If accepting assignment of benefits agreements increases the time it takes to get paid and costs you more in operational expense, these are both situations you want to avoid.
Learn more: How to calculate your collection effectiveness
AOBs and mechanics liens
A mechanics lien is hands down a contractor’s most effective tool to ensure they get paid for their work. Many types of restoration services are protected under lien laws in most states. But what happens to lien rights when a contractor accepts an assignment of benefits?
An AOB generally won’t affect a contractor’s ability to file a mechanics lien on the property if they don’t receive payment. The homeowner is typically still responsible to pay for the improvements. This is especially true if the contract involves work that wasn’t covered by the insurance policy.
However, make sure you know the laws in the state where your project is located. For example, Florida’s assignment of benefits law, perhaps the most restrictive in the country, appears to prohibit an AOB assignee from filing a lien.
Florida AOB agreements are required to include language that waives the contractor’s rights to collect payment from the owner. The required statement takes it even further, stating that neither the contractor or any of their subs can file a mechanics lien on the owner’s property.
On his website , Florida’s CFO says: “The third-party assignee and its subcontractors may not collect, or attempt to collect money from you, maintain any action of law against you, file a lien against your property or report you to a credit reporting agency.”
That sounds like a contractor assignee can’t file a lien if they aren’t paid . But, according to construction lawyer Alex Benarroche , it’s not so cut-and-dry.
“Florida’s AOB law has yet to be tested in court, and it’s possible that the no-lien provision would be invalid,” says Benarroche. “This is because Florida also prohibits no-lien clauses in a contract. It is not legal for a contractor to waive their right to file a lien via an agreement prior to performance.”
Learn more about no-lien clauses and their enforceability state-by-state
Remember that every state treats AOBs differently, and conflicting laws can create additional risk. It’s important to consult with a construction lawyer in the project’s state before accepting an assignment of benefits.
Best practices for contractors
At the end of the day, there are advantages and disadvantages to accepting an assignment of benefits. While it’s possible in some circumstances that an AOB could help a contractor get paid faster, there are lots of other payment tools that are more effective and require less administrative costs. An AOB should never be the first option on the table .
If you do decide to become an assignee to the property owner’s claim benefits, make sure you do your homework beforehand and adopt some best practices to effectively manage the assignment of benefits process. You’ll need to keep on top of the administrative details involved in drafting AOBs and schedule work in a timely manner to stay in compliance with the conditions of the agreement.
Make sure you understand all the nuances of how insurance works when there’s a claim . You need to understand the owner’s policy and what it covers. Home insurance policy forms are basically standardized for easy comparisons in each state, so what you see with one company is what you get with all carriers.
Since you’re now the point of contact for the insurance company, expect more phone calls and emails from both clients and the insurer . You’ll need to have a strategy to efficiently handle ramped-up communications since the frequency will increase. Keep homeowners and claims reps in the loop so you can build customer relationships and hopefully get paid faster by the insurer for your work.
Ask an expert for free
I am doing some part-time administrative work for a friend who has an owner/operator pressure washing business located in NC in its first year of business. Recently, my friend has expressed interest in expanding his operations to FL so that he can eventually live and work between both...
I am a homeowner, 4 days prior to Ida, we had solar panels installed. Half were damaged and blown off of course, so after we allowed the solar panel co to do our roof and redo our panel system. After a year, they finally replaced our roof and...
I believe a person was impersonating as a licensed general contractor. When I verified the license in GA, the license belonged to a completely different individual. When I called the provided insurance carrier of the general contractor, the insurance company said the company did not have an active...
Thomas Tracy
View Profile
About the author
Recommended for you
Construction contracts: what does “workmanlike manner” mean.
Just about every construction contract will require that work be done in a "workmanlike manner." But what exactly does that...
What Is Underbilling? | Construction Industry Accounting
Underbilling occurs when a contractor does not bill for all the labor and materials delivered in a billing cycle. It...
Conditional vs. Unconditional Lien Waivers: The Difference & Why It Matters
Unconditional vs. conditional lien waivers: which type of lien waiver should you use on your construction projects and jobs? We...
Guide to Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) in Construction
With a proper dispute resolution clause in place, contractors, subs, and suppliers can avoid taking their disputes into litigation.
Do I Have to Sign a Lien Waiver to Get Paid?
Lien waivers are an important part of optimizing construction payment. Property owners and GCs rely on waivers to manage the...
What Is a Work in Progress Schedule? | Construction Accounting
The Work In Progress (WIP) schedule is an accounting schedule that's a component of a company's balance sheet. It's calculated...
6 Construction Project Delivery Methods Compared
The steps required in a project’s journey to completion are importation to how successful the project will be. That’s why...
What is Overbilling? | Construction Industry Accounting
Overbilling occurs when a contractor bills for contracted labor and materials prior to that work actually being completed. For example,...
Don't Make a Costly Mistake!
Understanding florida assignment of benefits (aob).
Don't make a costly MISTAKE!
We want to make Floridians aware of an important issue called AOB (Assignment of Benefits). Click here to view the AOB Fact Sheet and Red Flag Checklist from the Florida Office of Insurance Regulation .
If you are insured with State Farm, please follow these tips to keep your rights with your claim:
- If you have a property damage loss in your home, contact State Farm immediately to report the claim. We are here to help 24/7. 1-800-SFCLAIM (1-800-732-5246)
- Be careful before signing anything without fully reading the documents. An AOB transfers the payment and many rights of your claim to the vendor or contractor for the services provided or to be provided. Keep your rights!
- Preserve all building and/or plumbing materials removed by any contractor or vendor until you speak with State Farm.
If you have any additional questions about AOB, contact your local State Farm agent or www.fightfraud.today for additional details.
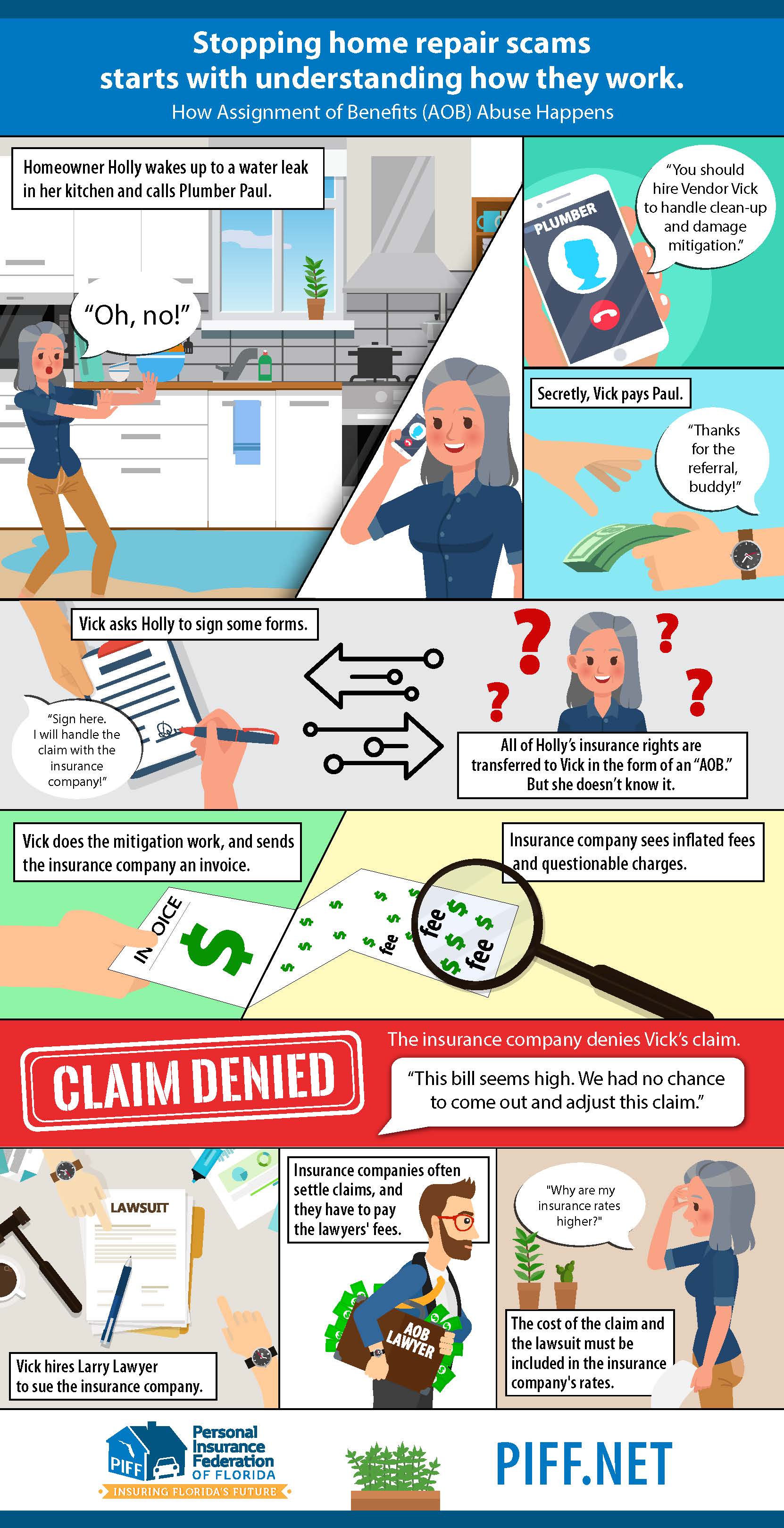
Media Contact
In Solvency
Understandable Insights from Fox Rothschild's National Bankruptcy Practice
Assignments for the Benefit of Creditors – an often-overlooked state law alternative to Chapter 7 bankruptcy
by Magdalena Schardt
For some folks the three letters ABC are a reminder of elementary school and singing a song to learn the alphabet. For others, it is a throw back to the early 70’s when the Jackson Five and its lead singer Michael, still with his adolescent high voice, sang a catchy love song. Then there is a select group of people in the world of corporate workouts, liquidations and bankruptcies, who know those three letters to stand for the A ssignment for the B enefit of C reditors – a voluntary state law liquidation process that may arguably offer a hospitable and friendly alternative to federal bankruptcy. This article is a brief summary of this potentially attractive alternative to bankruptcy.
The Assignment for the Benefit of Creditors (“ABC”), also known as a General Assignment, is a state law procedure governed by state statute or common law. Over 30 states have codified statutes, and the remainder of states rely on common law. See Practical Issues in Assignments for the Benefit of Creditors , by Robert Richards & Nancy Ross, ABI Law Review Vol. 17:5 (2009) at p. 6 (listing state statutes). In some states, the statutory authority and common law can coexist. At its most basic, the ABC process involves the transfer of all assets by a financially distressed debtor (the assignor) to an individual or entity (the assignee) with fiduciary obligations who then liquidates the assets and pays creditors. The assignment agreement is essentially a contract involving the transfer and control of property, in trust, to a third party. In some states that have enacted a statute, state courts may supervise the process (and at different levels of involvement depending on the statute). The statutory scheme in other states such as California and Nevada, and in states where common law govern, do not provide for judicial oversight..
ABCs are promoted as less expensive and more flexible than a chapter 7 liquidation and may proceed substantially faster than bankruptcy liquidation. See generally Practical Issues in Assignments for the Benefit of Creditors , ABI Law Review Vol. 17:5 (2009) at p. 8 (citations omitted). In addition, the ABC process may provide four other noteworthy benefits not available in a bankruptcy. First, the liquidating company chooses the assignee, there is no appointment of a random trustee or formal election required like in a bankruptcy. This freedom of choice allows the assignor to evaluate the reputation and experience of proposed assignees, as well as select an assignee with familiarity in the nature of the assignor’s business and/or with more expansive contacts in the industry to facilitate the sale/liquidation. Second, the ABC process generally falls under the radar of the media (particularly in states that do not require court supervision), and the assignor may avoid publicity, often negative, that can be associated with bankruptcy proceedings. Third, with an ABC, the assignee has the ability to sell the assets without the imposition of potentially cumbersome requirements of Section 363 of the Bankruptcy Code, and in some cases, can conduct a sale the same day as the general assignment. Finally, the ABC process generally authorizes the sale of assets free of unsecured creditor debt. In essence, in an ABC, a company buying assets from a distressed business does not acquire the debt of the assignor.
On the down side, ABCs do not provide the protection of the automatic stay that is triggered upon the filing of a bankruptcy petition. In some situations, the debtor entity needs to stop the pursuit of creditors immediately, and a bankruptcy proceeding will supply this relief. Unlike bankruptcy, the sale through an ABC: i) is not free and clear of liens; ii) unexpired leases cannot be assumed and assigned without the consent of the contract counter-party; and iii) insolvency can trigger a default under an unexpired lease or executory contract. See generally Practical Issues in Assignments for the Benefit of Creditors , ABI Law Review Vol. 17:5 (2009) at p. 20. In general, an ABC is not a good choice for debtors that have secured creditors that do not consent because there is no mechanism for using cash collateral or transferring assets free and clear of liens without the secured creditors’ consent. In cases where junior lienholders are out of the money, there is no incentive for those creditors to voluntarily release their liens. In addition, while unsecured creditors do not have to consent to the general assignment for it to be valid, choosing this alternative forum may cause concern for creditors (particularly those used to the transparency of a court-supervised bankruptcy or receivership proceeding) and invite the filing of an involuntary bankruptcy. Therefore, it is prudent to involve major creditors in the process, and perhaps even in the pre-assignment planning. In addition, if an involuntary petition is filed, the assignee could request that the bankruptcy court abstain in order to proceed with the ABC.
Using the ABC state process in lieu of filing for bankruptcy in federal court may result in a more streamlined, efficient liquidation process that is less expensive and likely completed quicker than a federal bankruptcy proceeding. In some jurisdictions, such as New Jersey, workout professionals note anecdotally that corporate clients fare better under this state law alternative rather than the lengthy, more complicated federal bankruptcy proceedings.
Many bankruptcy professionals are unfamiliar with the procedures of ABC and are reluctant to recommend it as a method for liquidating assets and administering claims. This lack of familiarity may be a disservice to potential clients. Fox Rothschild attorneys in the financial restructuring department have experience in representing all parties involved in an ABC, from assignee, assignor, acquiring entity/individual to creditors. If you have questions or are looking for more information about the ABC process, contact Magdalena Schardt or one of our financial restructuring and bankruptcy professionals in one of the 29 offices.
RIA Members Login with Your Membership Credentials and Access Your Member Only Benefits Here.

AOBs and Assignments of Insurance Rights

There are a multitude of hardships that Restoration Industry Association members face every day but one issue that is gaining more traction in the restoration industry is “assignment of benefits” (AOB). We talked in depth to attorney Ed Cross, RIA’s Restoration Advocate, and founding Chair of the Association’s Advocacy & Government Affairs (AGA) Committee, about the incredible opportunities AOBs present for the restoration industry — and to gather some tips when signing one.
What Is “Assignment of Benefits?” To put it plainly, assignment of benefits is a transfer of the legal title to a portion of an insurance claim over to a service provider. When someone has a loss on their property and they make a claim using their insurance policy, that claim can be transferred to another party. This allows contractors to control their own destinies and make legal claims directly against insurance companies who fail to pay the fair market value for restoration work, or insist on using standardized price lists as universal pricing. Xactware has repeatedly made clear that its pricing data is not intended to be used as global pricing and that contractors should set their own prices.
Many people do not have the money to restore their buildings after they’ve been damaged by a flood, fire, or other instances, but they need the restoration work done immediately.
“Contractors take an assignment of benefits in order to have security that their bill is going to get paid,” Cross said. “They do this in exchange for the assurance of immediate payment. So, there's an expectation that the insurance company is going to pay the bill.”
A Game of Cat and Mouse According to Cross, many times when the policyholder receives the insurance money, they aren’t interested in paying for anything. This puts the restoration contractor in a bind.
“Sometimes the policyholder will use it to pay off the mortgage on their house,” Cross said. “So now, not only do they have essentially a brand new house, it's also paid for, free and clear, at the expense of the restoration contractor who is not in a position to take back the work.”
Unlike a car being repossessed if you can’t make the payments on it, a restoration contractor isn’t in the position to take back their work. A contractor could file a lien, but that is a long, complex, and expensive process which could one day put a property into foreclosure, but that’s a rare outcome.
To increase the chance that the contractor’s name will appear on an insurance check, contractors in most states may obtain ownership of the portion of the insurance claim they were hired to address. This frequently allows the contractor to step into the shoes of the policyholder and collect directly from the insurance company. If the insurance company does not name the contractor on the check and the insured runs with the money, the contractor may be able to force the insurance company to pay again. Cross has done this many times against major insurance carriers.
Restoration contractors have the resources, the energy, and the wherewithal to pursue this collection and to press the insurance company to pay fair value, whereas a typical policyholder doesn't have the resources, the expertise, or the desire to ensure that the contractor gets paid in full. This can leave the restoration contractors in a rough spot: those needing work will go with whatever the policy will pay, and if it pays too little, who should they go after?
“Many contractors agree to work for the amount of insurance proceeds,” Cross said. “And if the insurance company decides it wants to pay little or nothing, as they often want to do, the contractor gets left holding the bag. It places them in the predicament of trying to decide, do I sue my customer? Or do I try to go after this insurance company?”
Assignments got a bad rap because of an extraordinary law in the State of Florida that encouraged litigation by allowing the holder of an assignment to collect attorney’s fees in a lawsuit against an insurance company, even if there was no wrongdoing by the insurance company. The insurance lobby put an end to that when F.S. 627.7152 was passed. Among other things, it says that the holder of an assignment waives the right to collect money from an insured. It also greatly limited the scenarios when the holder of an assignment could collect attorney’s fees. This effectively eliminated assignments in State of Florida. Cross warns contractors against using assignments in the State of Florida, but points out that the issues there are present nowhere else in the country. Assignments should not be judged by unique circumstances in Florida that ended three years ago.
The States of Texas and Oregon generally refuse to enforce assignments of benefits, but they allow the assignment of a legal claim. Thus, if the insurance company breaches the insurance contract by underpaying on a claim, for example, or commits insurance bad faith, the contractor may be able to take ownership of the legal claim and sue the insurance company directly. But in most other states, contractors can and should seek assignments.
When policyholders either run off with the insurance money or use it to pay something off, (such as their mortgage), with a well-executed AOB you can go back to the insurance company and demand that they pay a second time.
“Ultimately, they write a second check when they're unable to get the policyholder to pay out the money,” Cross said. “And we're often able to do that without filing a lawsuit.”
Unfortunately, the insurance industry does not train adjusters to know that assignments of benefits need to be honored. Adjusters are often dismissive of them and give all the money to the policyholder — which is when things get out of control.
The AGA is out to change all of that. It will be releasing a 50-state Summary of the Law of Assignments regarding the enforceability of assignment of benefits which contractors can use in their communications and negotiations with stubborn insurance companies. At the RIA Convention in Orlando on June 29, 2021, Cross will present the first session of the AGA Academy, which will teach contractors how to prepare, present, and prosecute assignments using RIA’s Summary of the Law of Assignments. The event is rapidly selling out and contractors should sign up now to avoid missing this special opportunity.
Tips for Contractors and AOB’s Cross offers three points that every restoration contractor should take into account when looking to sign an AOB.
The first is that most restorers mistakenly believe that they have an AOB, when in fact, all they have is a direction to pay.
“The typical restoration work authorization says that the policyholder instructs the insurance company to name the contractor on the check and correctly to name the contractor on the check,” Cross said. “Contractors think that's an assignment. It's not an assignment; it is merely a direction to pay.”
An assignment is a transfer of legal title, meaning that ownership of part of the insurance claim is being transferred to the contractor. This puts the contractor in “privity” (a legal relationship) with the insurer that allows the contractor to obtain remedies based on the insurance policy. A direction to pay should be included in an assignment of benefits document. But it is not, in and of itself, an assignment because it does not transfer ownership.
Second is that an assignment should include more than the assignment of “benefits.” It should also include an assignment of the right to go to appraisal. Appraisal is a process under the insurance policy where if a policyholder and an insurance company are unable to agree on the amount of loss, they can submit the matter to independent appraiser, who sets the amount of the loss.
Last, and most important, the assignment should also include an assignment of the right to sue the insurance company for breach of the policy and for insurance bad faith in jurisdictions that recognize this. This is why Cross no longer generates “Assignments of benefits” for his clients; he generates “Assignments of Insurance Rights .” A well-drafted Assignment of Insurance rights includes assignments of benefits, the right to appraisal, and the rights to sue, as well as a direction to pay.
Don’t miss out on the 75 th Diamond Anniversary International Restoration Convention + Industry Expo! Click here to register and find out more!
Back to Top

Trending News

Related Practices & Jurisdictions
- Health Law & Managed Care
- Insurance Reinsurance & Surety
- Litigation / Trial Practice
- All Federal

When a patient sees a provider, the patient signs an “assignment of benefits” contract with the provider, assigning the patient’s legal rights to recover benefits from the insurance company to the provider so that the provider can be directly reimbursed for the services rendered to the patient. When the provider is in-network, this process is executed with little fanfare. However, for an out-of network provider, the road to reimbursement is not always as smooth. Not all states expressly permit assignment-of-benefits clauses, and as a result, insurers send the reimbursement to the beneficiary rather than the provider. The beneficiary is then supposed to forward the reimbursement onto the provider, which many of them do. However, if they do not, providers are put in the uncomfortable and difficult position of suing the patient, which has an uncertain likelihood of success. Given this arduous task, some providers contend that insurance companies have begun to utilize direct payment to patients in retaliation against providers for refusing to join the insurer’s networks.
In fact, in 2015, providers of inpatient and outpatient substance abuse and/or mental health treatment to chemically-dependent individuals filed suit against a group of insurers that includes several Blue Cross entities for this exact practice. In Dual Diagnosis Treatment Center, Inc., et al. v. Blue Cross of California, et. al., the providers alleged that defendants purposefully ignored valid assignments of benefits and instead directly reimbursed providers’ patients in order to punish the providers for being a few of a small number of providers who had not joined the insurers’ networks.
In their defense, the insurers stated that some of the plans contained anti-assignment provisions, prohibiting beneficiaries from entering into assignment-of-benefits contracts with providers. The original complaint sought to recover benefits, remove breaching fiduciaries and, against the Blue Cross insurers, injunctive and declaratory relief that Blue Cross’ pattern of denying providers’ assigned claims without reviewing the operative plan document or informing providers of the denial violates the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA), the federal law that regulates employee sponsored retirement and welfare benefit plans. The court granted insurers’ motion to dismiss without prejudice, specifically to allow the providers to amend their complaint to demonstrate that waiver or estoppel would apply to the anti-assignment provisions.
The providers filed a second amended complaint, which was dismissed by the court with leave to amend, and the providers filed a third amended complaint in October 2017. The third amended complaint brought two claims: a claim for plan benefits under ERISA and a state law claim under California law alleging that the Blue Cross insurers misled providers about the assignability of benefits (specifically, misrepresenting that benefits were assignable when they were not and also representing that benefits were not assignable when they were). The insurers filed a motion to dismiss on the state law claim, which the court granted on the grounds of insufficient standing because the providers did not properly allege an economic injury. Specifically, the court held that collection costs, bad debt, preventing the providers from assisting their patients in the administrative appeals process and denying providers the opportunity to make alternate payment arrangements or collect additional money from their patients up front were insufficient to allege that the insurers’ conduct resulted in economic injury to the providers. The providers’ claim for benefits under ERISA still stands. However, there is no date set for hearing at this time.
The outcome of this case will set the stage for future litigation and out-of-network payment strategies. In addition to this and other pending cases, out-of-network providers or those considering an out-of-network strategy should closely monitor proposed legislation in their states of operation regarding direct-pay-to-patient methods. Some states, such as Indiana, have proposed legislation requiring insurers to directly reimburse out-of-network providers for certain services. These types of laws, in combination with litigation, will significantly influence the risk associated with pursuing an out-of-network payment strategy.
Current Legal Analysis
More from polsinelli pc, upcoming legal education events.

Sign Up for e-NewsBulletins

IMAGES
COMMENTS
State Affairs Dashboard ; Professional Development. Professional Development Online Learning . Online Learning Medicare + Fraud, Waste, and Abuse Training ... Assignment of Benefits 50 State Chart. State Law Charts Document Info. Published on Sep 30, 2019 ...
There are many reasons why an insurance company may not accept an assignment of benefits. To speak with a Schwartzapfel Lawyers expert about this directly, call 1-516-342-2200 for a free consultation today. It will be our privilege to assist you with all your legal questions, needs, and recovery efforts.
Here's how it works: Medicare will pay the provider 95% of the amount they would pay if the provider accepted assignment. The provider can charge the person receiving care more than the Medicare-approved amount, but only up to 15% more (some states limit this further). This extra amount, which the patient has to pay out-of-pocket, is known as ...
Pros of assignment of benefits. With proper safeguards in place to reduce opportunities for fraud, AOBs have the ability to streamline and simplify the insurance claims process. An AOB frees you ...
What is an Assignment of Benefits? In the context of insured property claims, an assignment of benefits (AOB) is an agreement between you and a contractor in which you give the contractor your right to insurance payments for a specific scope of work.In exchange, the contractor agrees that it will not seek payment from you for that scope of work, except for the amount of any applicable deductible.
Assignment of benefits is legal, thanks to a concept known as freedom of contract, which says two parties may make a private agreement, including the forfeiture of certain rights, and the ...
As used in this section, "assignment of benefits" means the transfer of dental care coverage reimbursement benefits or other rights under an insurance policy, subscription contract, or dental services plan by an insured, subscriber, or enrollee to a dentist or oral surgeon. 627.638.
Assignment of Benefits (AOB) is an agreement that transfers the insurance claims rights or benefits of the policy to a third party. An AOB gives the third party authority to file a claim, make repair decisions, and collect insurance payments without the involvement of the homeowner. AOBs are commonly used in homeowners' insurance claims by ...
An assignment of benefits, or AOB, is a legal tool that allows an insurer to directly pay a third party for services performed rather than reimbursing a claimant afterwards. In recent years, insurers have experienced an increase in fraud and abuse of assignment of benefit provisions, resulting in higher costs. ... State legislatures have sought ...
Assignment of benefits. Assignment of benefits is a legal agreement where a patient authorizes their healthcare provider to receive direct payment from the insurance company for services rendered. Boost patient experience and your bottom line by automating patient cost estimates, payer underpayment detection, and contract optimization in one place.
The American Dental Association working closely with our state dental society partners have helped pass legislation in 23 states basically requiring a dental plan to honor assignment of benefits if the patient has authorized assignment to the dentist on the dental claim form. See the list of these states below.
An assignment of benefits, or AOB, is an agreement "in which a contractor begins the work [on the property owner's home] without charging the property owner and agrees to seek compensation from the insurer.". [5] An AOB can be beneficial to a homeowner because an AOB eliminates the processing of a claim through the insurance company. [6]
In the 1917 landmark case of West Florida Grocery Co. v. Teutonia Fire Ins. Co., 77 So. 209, 210-, the state Supreme Court rendered a decision holding that the insured was able to assign the benefits of the policy following a loss directly to a third party without the written consent of the insurance provider.
An assignment of benefits (or AOB for short) is an agreement that gives your claims benefits, and in some instances complete control of your claim, to someone else. It's usually used so that a contractor can "stand in your shoes" and file a claim, make decisions about repairs, and collect insurance payments from your insurance company ...
In July 2019, Florida enacted section 627.7152, Florida Statutes, which set forth specific requirements and limitations for assignment of benefits agreements for construction projects. After the passage of that act, approximately 20 trial court orders were entered along with two appellate decisions were issued, providing guidance on the statute.
Assignment of benefits is legal, thanks to a concept known as freedom of contract, which says two parties may make a private agreement, including the forfeiture of certain rights, and the government may not interfere. There are exceptions, making freedom of contract something less than an absolute right.
This article explains briefly what an AOB claim is, how Florida, Texas, Louisiana, Georgia, North Carolina, and South Carolina address AOB claims, and the best practices for handling AOB claims.
An assignment of benefits, or AOB, is an agreement to transfer insurance claim rights to a third party. It gives the assignee authority to file and negotiate a claim directly with the insurance company, without involvement from the property owner. ... Keep in mind that many states have their own laws about what the agreement can or should ...
If you have a property damage loss in your home, contact State Farm immediately to report the claim. We are here to help 24/7. 1-800-SFCLAIM (1-800-732-5246) Be careful before signing anything without fully reading the documents. An AOB transfers the payment and many rights of your claim to the vendor or contractor for the services provided or ...
The Assignment for the Benefit of Creditors ("ABC"), also known as a General Assignment, is a state law procedure governed by state statute or common law. Over 30 states have codified statutes, and the remainder of states rely on common law. ... Review Vol. 17:5 (2009) at p. 8 (citations omitted). In addition, the ABC process may provide ...
The States of Texas and Oregon generally refuse to enforce assignments of benefits, but they allow the assignment of a legal claim. Thus, if the insurance company breaches the insurance contract by underpaying on a claim, for example, or commits insurance bad faith, the contractor may be able to take ownership of the legal claim and sue the ...
Not all states expressly permit assignment-of-benefits clauses, and as a result, insurers send the reimbursement to the beneficiary rather than the provider. The beneficiary is then supposed to ...
balance. A photocopy of this assignment shall be considered as affective and valid as the original. I authorize the provider to initiate a complaint or file appeal to the insurance commissioner or any payer authority for any reason on my behalf and personally will be active in the resolution of claims delay or unjustified reductions or denials.
assignment of benefits. the assignment of benefits statement states which of the following? - receiver payment directly from the payer. - accepts a payers allowed chharge. what are the most common ways that prior authorization can be performed - on the insurance carrier's website - over the phone.