Home Blog Design Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)

Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)
In this age of overwhelming information, the skill to effectively convey data has become extremely valuable. Initiating a discussion on data presentation types involves thoughtful consideration of the nature of your data and the message you aim to convey. Different types of visualizations serve distinct purposes. Whether you’re dealing with how to develop a report or simply trying to communicate complex information, how you present data influences how well your audience understands and engages with it. This extensive guide leads you through the different ways of data presentation.
Table of Contents
What is a Data Presentation?
What should a data presentation include, line graphs, treemap chart, scatter plot, how to choose a data presentation type, recommended data presentation templates, common mistakes done in data presentation.
A data presentation is a slide deck that aims to disclose quantitative information to an audience through the use of visual formats and narrative techniques derived from data analysis, making complex data understandable and actionable. This process requires a series of tools, such as charts, graphs, tables, infographics, dashboards, and so on, supported by concise textual explanations to improve understanding and boost retention rate.
Data presentations require us to cull data in a format that allows the presenter to highlight trends, patterns, and insights so that the audience can act upon the shared information. In a few words, the goal of data presentations is to enable viewers to grasp complicated concepts or trends quickly, facilitating informed decision-making or deeper analysis.
Data presentations go beyond the mere usage of graphical elements. Seasoned presenters encompass visuals with the art of data storytelling , so the speech skillfully connects the points through a narrative that resonates with the audience. Depending on the purpose – inspire, persuade, inform, support decision-making processes, etc. – is the data presentation format that is better suited to help us in this journey.
To nail your upcoming data presentation, ensure to count with the following elements:
- Clear Objectives: Understand the intent of your presentation before selecting the graphical layout and metaphors to make content easier to grasp.
- Engaging introduction: Use a powerful hook from the get-go. For instance, you can ask a big question or present a problem that your data will answer. Take a look at our guide on how to start a presentation for tips & insights.
- Structured Narrative: Your data presentation must tell a coherent story. This means a beginning where you present the context, a middle section in which you present the data, and an ending that uses a call-to-action. Check our guide on presentation structure for further information.
- Visual Elements: These are the charts, graphs, and other elements of visual communication we ought to use to present data. This article will cover one by one the different types of data representation methods we can use, and provide further guidance on choosing between them.
- Insights and Analysis: This is not just showcasing a graph and letting people get an idea about it. A proper data presentation includes the interpretation of that data, the reason why it’s included, and why it matters to your research.
- Conclusion & CTA: Ending your presentation with a call to action is necessary. Whether you intend to wow your audience into acquiring your services, inspire them to change the world, or whatever the purpose of your presentation, there must be a stage in which you convey all that you shared and show the path to staying in touch. Plan ahead whether you want to use a thank-you slide, a video presentation, or which method is apt and tailored to the kind of presentation you deliver.
- Q&A Session: After your speech is concluded, allocate 3-5 minutes for the audience to raise any questions about the information you disclosed. This is an extra chance to establish your authority on the topic. Check our guide on questions and answer sessions in presentations here.
Bar charts are a graphical representation of data using rectangular bars to show quantities or frequencies in an established category. They make it easy for readers to spot patterns or trends. Bar charts can be horizontal or vertical, although the vertical format is commonly known as a column chart. They display categorical, discrete, or continuous variables grouped in class intervals [1] . They include an axis and a set of labeled bars horizontally or vertically. These bars represent the frequencies of variable values or the values themselves. Numbers on the y-axis of a vertical bar chart or the x-axis of a horizontal bar chart are called the scale.
Real-Life Application of Bar Charts
Let’s say a sales manager is presenting sales to their audience. Using a bar chart, he follows these steps.
Step 1: Selecting Data
The first step is to identify the specific data you will present to your audience.
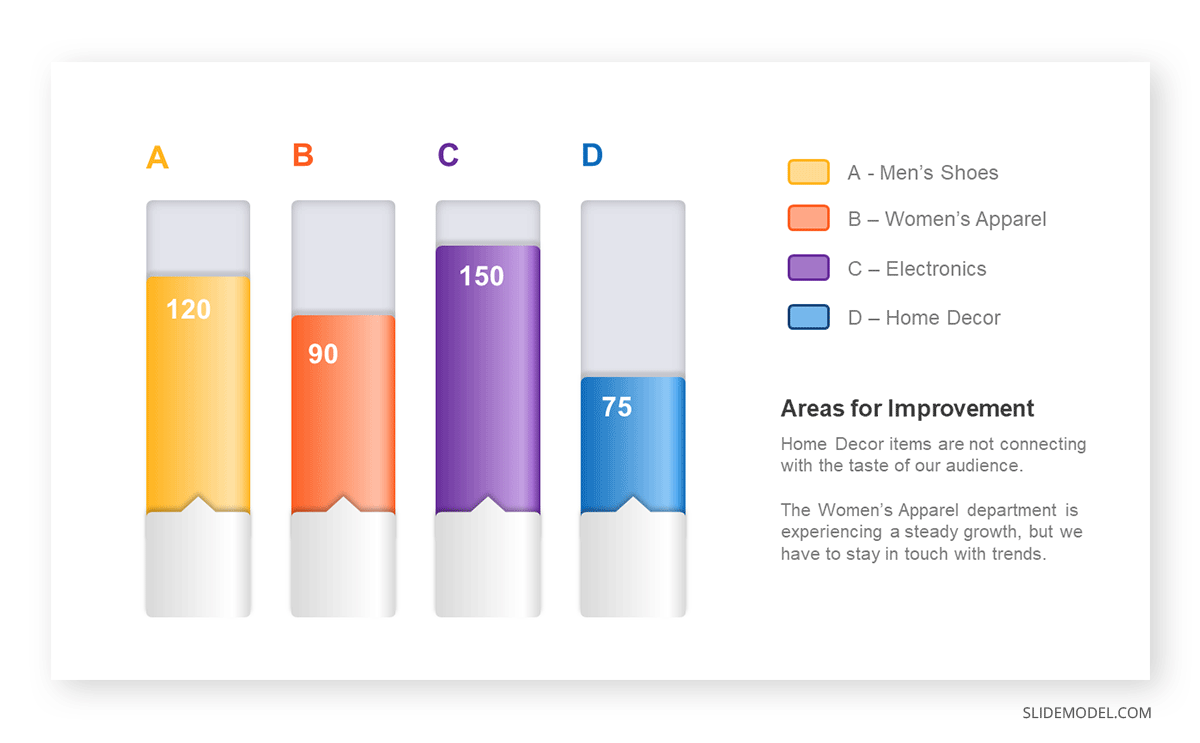
The sales manager has highlighted these products for the presentation.
- Product A: Men’s Shoes
- Product B: Women’s Apparel
- Product C: Electronics
- Product D: Home Decor
Step 2: Choosing Orientation
Opt for a vertical layout for simplicity. Vertical bar charts help compare different categories in case there are not too many categories [1] . They can also help show different trends. A vertical bar chart is used where each bar represents one of the four chosen products. After plotting the data, it is seen that the height of each bar directly represents the sales performance of the respective product.
It is visible that the tallest bar (Electronics – Product C) is showing the highest sales. However, the shorter bars (Women’s Apparel – Product B and Home Decor – Product D) need attention. It indicates areas that require further analysis or strategies for improvement.
Step 3: Colorful Insights
Different colors are used to differentiate each product. It is essential to show a color-coded chart where the audience can distinguish between products.
- Men’s Shoes (Product A): Yellow
- Women’s Apparel (Product B): Orange
- Electronics (Product C): Violet
- Home Decor (Product D): Blue
Bar charts are straightforward and easily understandable for presenting data. They are versatile when comparing products or any categorical data [2] . Bar charts adapt seamlessly to retail scenarios. Despite that, bar charts have a few shortcomings. They cannot illustrate data trends over time. Besides, overloading the chart with numerous products can lead to visual clutter, diminishing its effectiveness.
For more information, check our collection of bar chart templates for PowerPoint .
Line graphs help illustrate data trends, progressions, or fluctuations by connecting a series of data points called ‘markers’ with straight line segments. This provides a straightforward representation of how values change [5] . Their versatility makes them invaluable for scenarios requiring a visual understanding of continuous data. In addition, line graphs are also useful for comparing multiple datasets over the same timeline. Using multiple line graphs allows us to compare more than one data set. They simplify complex information so the audience can quickly grasp the ups and downs of values. From tracking stock prices to analyzing experimental results, you can use line graphs to show how data changes over a continuous timeline. They show trends with simplicity and clarity.
Real-life Application of Line Graphs
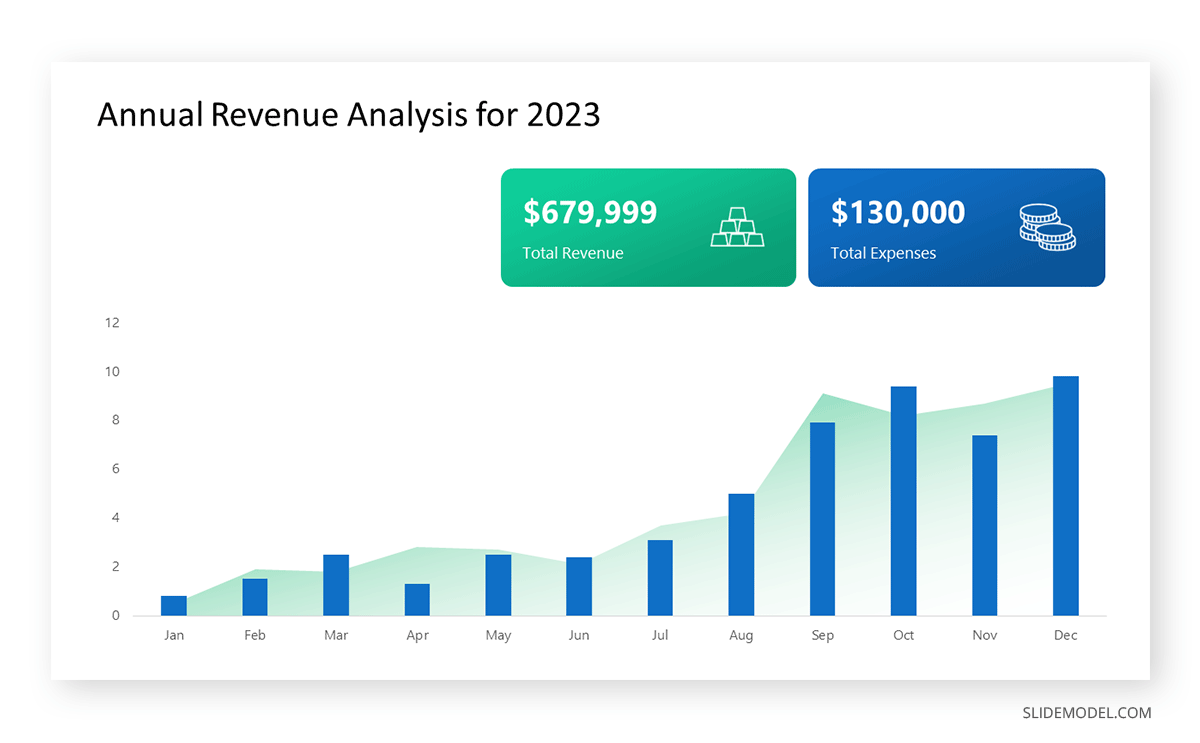
To understand line graphs thoroughly, we will use a real case. Imagine you’re a financial analyst presenting a tech company’s monthly sales for a licensed product over the past year. Investors want insights into sales behavior by month, how market trends may have influenced sales performance and reception to the new pricing strategy. To present data via a line graph, you will complete these steps.
First, you need to gather the data. In this case, your data will be the sales numbers. For example:
- January: $45,000
- February: $55,000
- March: $45,000
- April: $60,000
- May: $ 70,000
- June: $65,000
- July: $62,000
- August: $68,000
- September: $81,000
- October: $76,000
- November: $87,000
- December: $91,000
After choosing the data, the next step is to select the orientation. Like bar charts, you can use vertical or horizontal line graphs. However, we want to keep this simple, so we will keep the timeline (x-axis) horizontal while the sales numbers (y-axis) vertical.
Step 3: Connecting Trends
After adding the data to your preferred software, you will plot a line graph. In the graph, each month’s sales are represented by data points connected by a line.
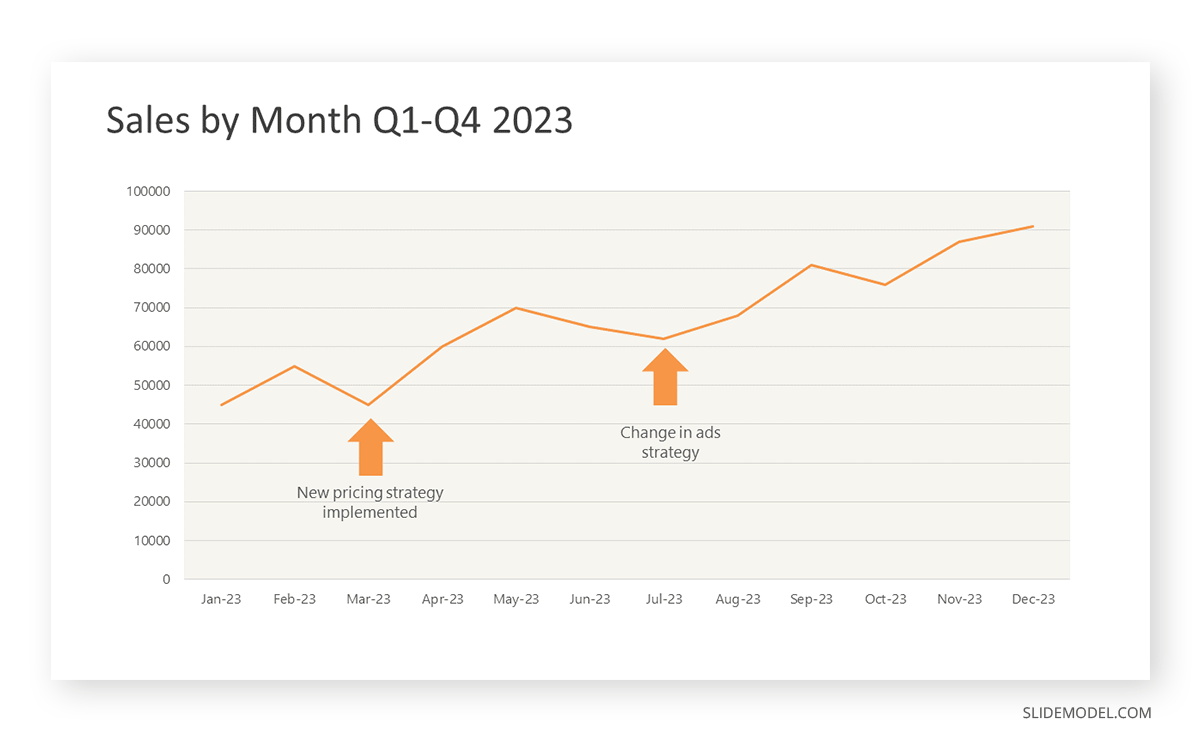
Step 4: Adding Clarity with Color
If there are multiple lines, you can also add colors to highlight each one, making it easier to follow.
Line graphs excel at visually presenting trends over time. These presentation aids identify patterns, like upward or downward trends. However, too many data points can clutter the graph, making it harder to interpret. Line graphs work best with continuous data but are not suitable for categories.
For more information, check our collection of line chart templates for PowerPoint and our article about how to make a presentation graph .
A data dashboard is a visual tool for analyzing information. Different graphs, charts, and tables are consolidated in a layout to showcase the information required to achieve one or more objectives. Dashboards help quickly see Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). You don’t make new visuals in the dashboard; instead, you use it to display visuals you’ve already made in worksheets [3] .
Keeping the number of visuals on a dashboard to three or four is recommended. Adding too many can make it hard to see the main points [4]. Dashboards can be used for business analytics to analyze sales, revenue, and marketing metrics at a time. They are also used in the manufacturing industry, as they allow users to grasp the entire production scenario at the moment while tracking the core KPIs for each line.
Real-Life Application of a Dashboard
Consider a project manager presenting a software development project’s progress to a tech company’s leadership team. He follows the following steps.
Step 1: Defining Key Metrics
To effectively communicate the project’s status, identify key metrics such as completion status, budget, and bug resolution rates. Then, choose measurable metrics aligned with project objectives.
Step 2: Choosing Visualization Widgets
After finalizing the data, presentation aids that align with each metric are selected. For this project, the project manager chooses a progress bar for the completion status and uses bar charts for budget allocation. Likewise, he implements line charts for bug resolution rates.
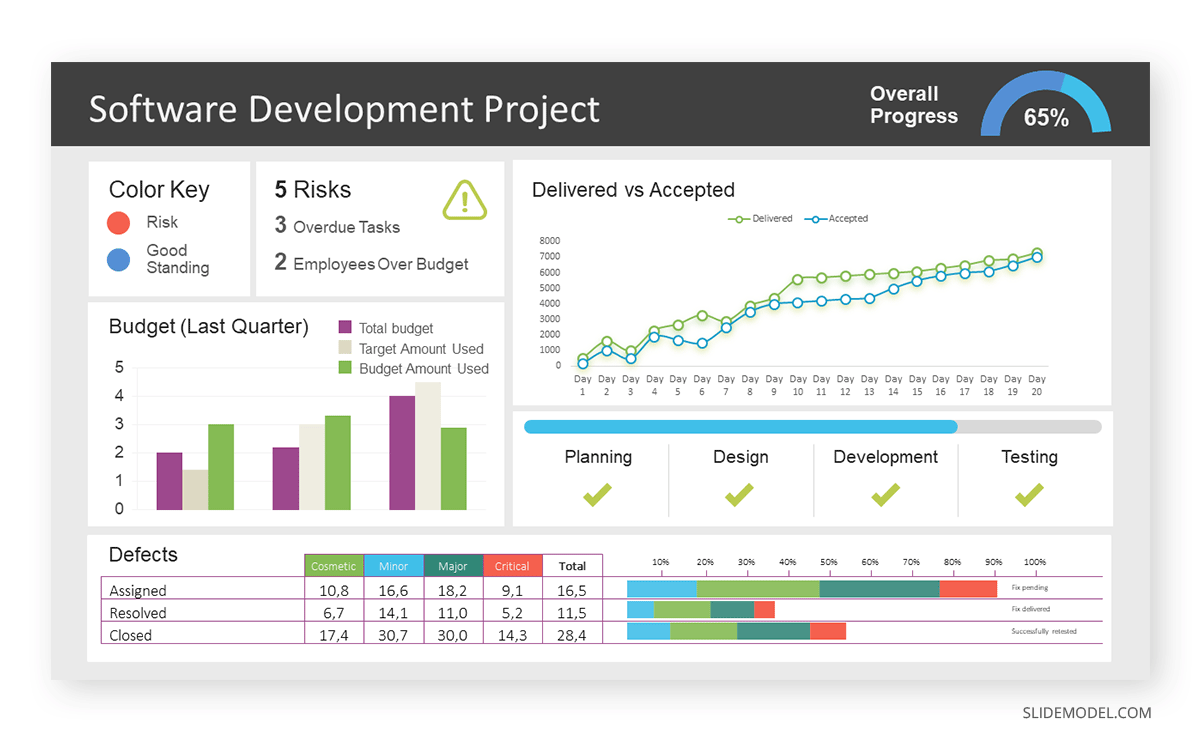
Step 3: Dashboard Layout
Key metrics are prominently placed in the dashboard for easy visibility, and the manager ensures that it appears clean and organized.
Dashboards provide a comprehensive view of key project metrics. Users can interact with data, customize views, and drill down for detailed analysis. However, creating an effective dashboard requires careful planning to avoid clutter. Besides, dashboards rely on the availability and accuracy of underlying data sources.
For more information, check our article on how to design a dashboard presentation , and discover our collection of dashboard PowerPoint templates .
Treemap charts represent hierarchical data structured in a series of nested rectangles [6] . As each branch of the ‘tree’ is given a rectangle, smaller tiles can be seen representing sub-branches, meaning elements on a lower hierarchical level than the parent rectangle. Each one of those rectangular nodes is built by representing an area proportional to the specified data dimension.
Treemaps are useful for visualizing large datasets in compact space. It is easy to identify patterns, such as which categories are dominant. Common applications of the treemap chart are seen in the IT industry, such as resource allocation, disk space management, website analytics, etc. Also, they can be used in multiple industries like healthcare data analysis, market share across different product categories, or even in finance to visualize portfolios.
Real-Life Application of a Treemap Chart
Let’s consider a financial scenario where a financial team wants to represent the budget allocation of a company. There is a hierarchy in the process, so it is helpful to use a treemap chart. In the chart, the top-level rectangle could represent the total budget, and it would be subdivided into smaller rectangles, each denoting a specific department. Further subdivisions within these smaller rectangles might represent individual projects or cost categories.
Step 1: Define Your Data Hierarchy
While presenting data on the budget allocation, start by outlining the hierarchical structure. The sequence will be like the overall budget at the top, followed by departments, projects within each department, and finally, individual cost categories for each project.
- Top-level rectangle: Total Budget
- Second-level rectangles: Departments (Engineering, Marketing, Sales)
- Third-level rectangles: Projects within each department
- Fourth-level rectangles: Cost categories for each project (Personnel, Marketing Expenses, Equipment)
Step 2: Choose a Suitable Tool
It’s time to select a data visualization tool supporting Treemaps. Popular choices include Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, PowerPoint, or even coding with libraries like D3.js. It is vital to ensure that the chosen tool provides customization options for colors, labels, and hierarchical structures.
Here, the team uses PowerPoint for this guide because of its user-friendly interface and robust Treemap capabilities.
Step 3: Make a Treemap Chart with PowerPoint
After opening the PowerPoint presentation, they chose “SmartArt” to form the chart. The SmartArt Graphic window has a “Hierarchy” category on the left. Here, you will see multiple options. You can choose any layout that resembles a Treemap. The “Table Hierarchy” or “Organization Chart” options can be adapted. The team selects the Table Hierarchy as it looks close to a Treemap.
Step 5: Input Your Data
After that, a new window will open with a basic structure. They add the data one by one by clicking on the text boxes. They start with the top-level rectangle, representing the total budget.
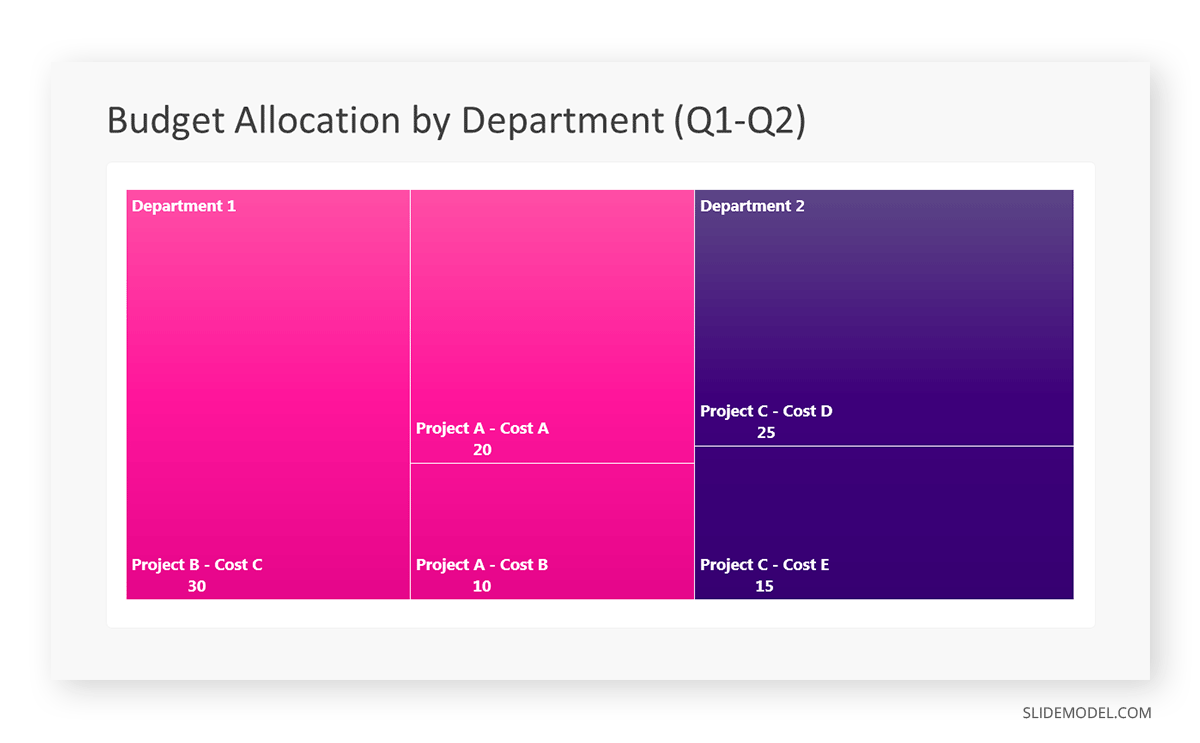
Step 6: Customize the Treemap
By clicking on each shape, they customize its color, size, and label. At the same time, they can adjust the font size, style, and color of labels by using the options in the “Format” tab in PowerPoint. Using different colors for each level enhances the visual difference.
Treemaps excel at illustrating hierarchical structures. These charts make it easy to understand relationships and dependencies. They efficiently use space, compactly displaying a large amount of data, reducing the need for excessive scrolling or navigation. Additionally, using colors enhances the understanding of data by representing different variables or categories.
In some cases, treemaps might become complex, especially with deep hierarchies. It becomes challenging for some users to interpret the chart. At the same time, displaying detailed information within each rectangle might be constrained by space. It potentially limits the amount of data that can be shown clearly. Without proper labeling and color coding, there’s a risk of misinterpretation.
A heatmap is a data visualization tool that uses color coding to represent values across a two-dimensional surface. In these, colors replace numbers to indicate the magnitude of each cell. This color-shaded matrix display is valuable for summarizing and understanding data sets with a glance [7] . The intensity of the color corresponds to the value it represents, making it easy to identify patterns, trends, and variations in the data.
As a tool, heatmaps help businesses analyze website interactions, revealing user behavior patterns and preferences to enhance overall user experience. In addition, companies use heatmaps to assess content engagement, identifying popular sections and areas of improvement for more effective communication. They excel at highlighting patterns and trends in large datasets, making it easy to identify areas of interest.
We can implement heatmaps to express multiple data types, such as numerical values, percentages, or even categorical data. Heatmaps help us easily spot areas with lots of activity, making them helpful in figuring out clusters [8] . When making these maps, it is important to pick colors carefully. The colors need to show the differences between groups or levels of something. And it is good to use colors that people with colorblindness can easily see.
Check our detailed guide on how to create a heatmap here. Also discover our collection of heatmap PowerPoint templates .
Pie charts are circular statistical graphics divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportions. Each slice represents a proportionate part of the whole, making it easy to visualize the contribution of each component to the total.
The size of the pie charts is influenced by the value of data points within each pie. The total of all data points in a pie determines its size. The pie with the highest data points appears as the largest, whereas the others are proportionally smaller. However, you can present all pies of the same size if proportional representation is not required [9] . Sometimes, pie charts are difficult to read, or additional information is required. A variation of this tool can be used instead, known as the donut chart , which has the same structure but a blank center, creating a ring shape. Presenters can add extra information, and the ring shape helps to declutter the graph.
Pie charts are used in business to show percentage distribution, compare relative sizes of categories, or present straightforward data sets where visualizing ratios is essential.
Real-Life Application of Pie Charts
Consider a scenario where you want to represent the distribution of the data. Each slice of the pie chart would represent a different category, and the size of each slice would indicate the percentage of the total portion allocated to that category.
Step 1: Define Your Data Structure
Imagine you are presenting the distribution of a project budget among different expense categories.
- Column A: Expense Categories (Personnel, Equipment, Marketing, Miscellaneous)
- Column B: Budget Amounts ($40,000, $30,000, $20,000, $10,000) Column B represents the values of your categories in Column A.
Step 2: Insert a Pie Chart
Using any of the accessible tools, you can create a pie chart. The most convenient tools for forming a pie chart in a presentation are presentation tools such as PowerPoint or Google Slides. You will notice that the pie chart assigns each expense category a percentage of the total budget by dividing it by the total budget.
For instance:
- Personnel: $40,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 40%
- Equipment: $30,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 30%
- Marketing: $20,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 20%
- Miscellaneous: $10,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 10%
You can make a chart out of this or just pull out the pie chart from the data.
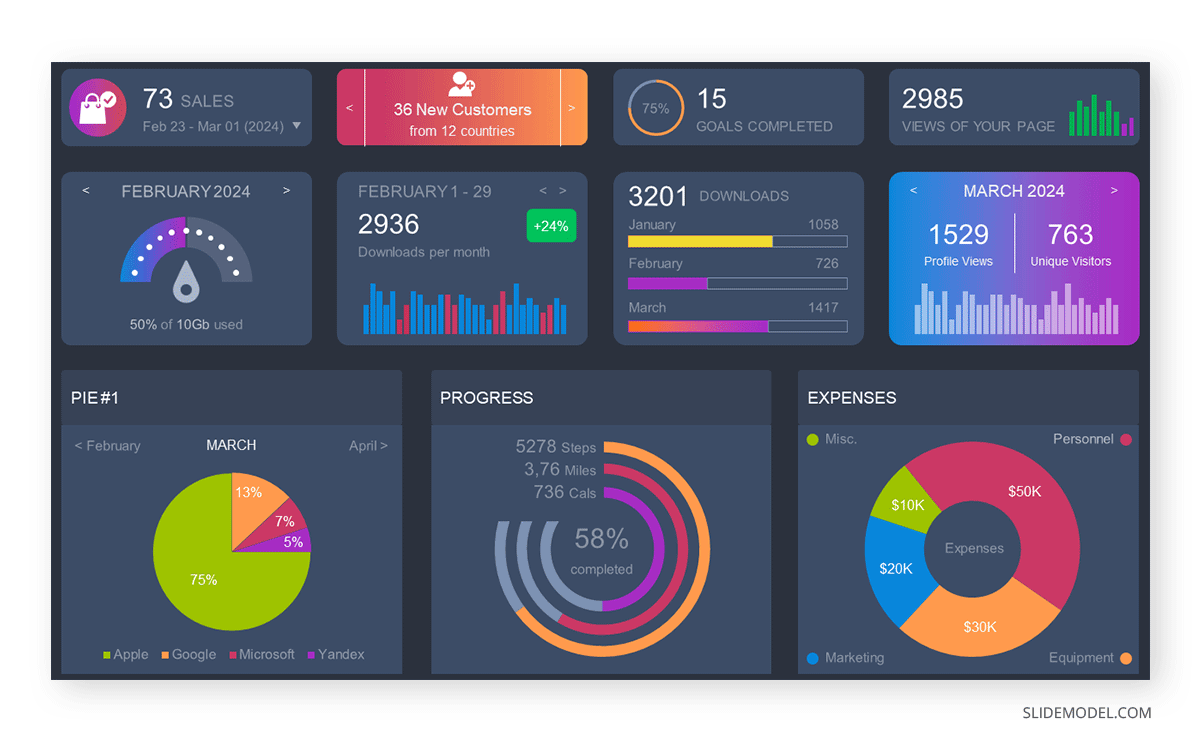
3D pie charts and 3D donut charts are quite popular among the audience. They stand out as visual elements in any presentation slide, so let’s take a look at how our pie chart example would look in 3D pie chart format.
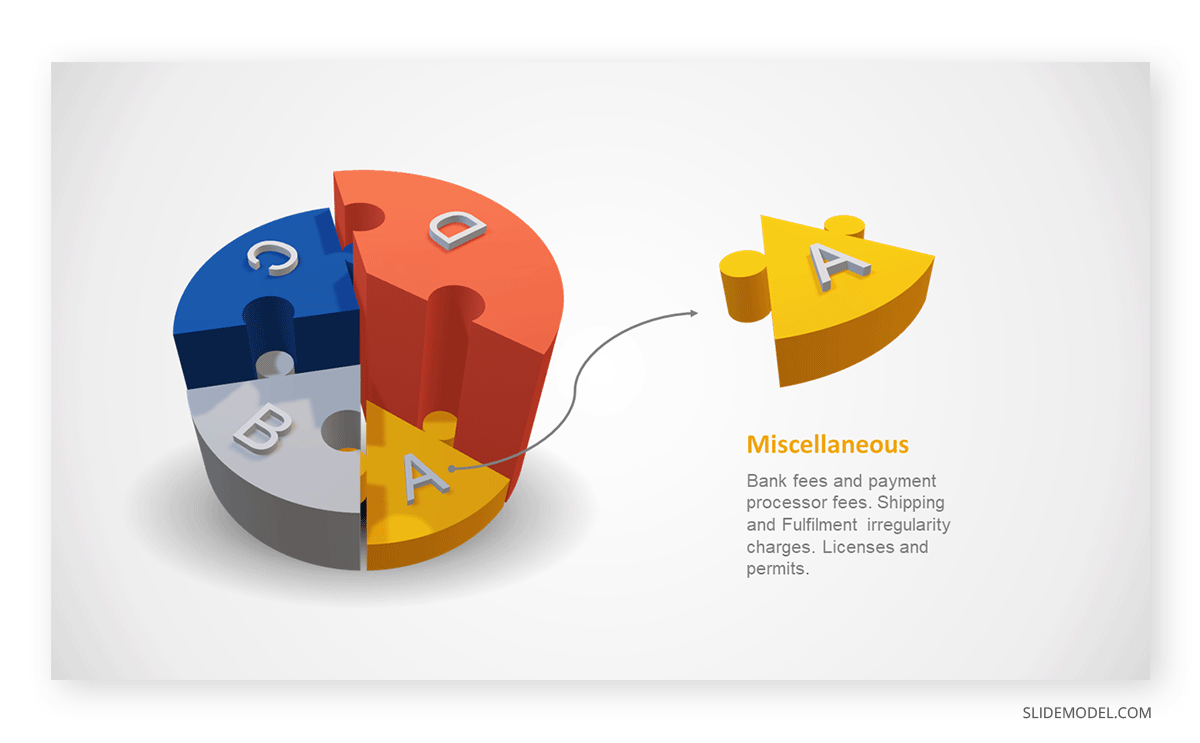
Step 03: Results Interpretation
The pie chart visually illustrates the distribution of the project budget among different expense categories. Personnel constitutes the largest portion at 40%, followed by equipment at 30%, marketing at 20%, and miscellaneous at 10%. This breakdown provides a clear overview of where the project funds are allocated, which helps in informed decision-making and resource management. It is evident that personnel are a significant investment, emphasizing their importance in the overall project budget.
Pie charts provide a straightforward way to represent proportions and percentages. They are easy to understand, even for individuals with limited data analysis experience. These charts work well for small datasets with a limited number of categories.
However, a pie chart can become cluttered and less effective in situations with many categories. Accurate interpretation may be challenging, especially when dealing with slight differences in slice sizes. In addition, these charts are static and do not effectively convey trends over time.
For more information, check our collection of pie chart templates for PowerPoint .
Histograms present the distribution of numerical variables. Unlike a bar chart that records each unique response separately, histograms organize numeric responses into bins and show the frequency of reactions within each bin [10] . The x-axis of a histogram shows the range of values for a numeric variable. At the same time, the y-axis indicates the relative frequencies (percentage of the total counts) for that range of values.
Whenever you want to understand the distribution of your data, check which values are more common, or identify outliers, histograms are your go-to. Think of them as a spotlight on the story your data is telling. A histogram can provide a quick and insightful overview if you’re curious about exam scores, sales figures, or any numerical data distribution.
Real-Life Application of a Histogram
In the histogram data analysis presentation example, imagine an instructor analyzing a class’s grades to identify the most common score range. A histogram could effectively display the distribution. It will show whether most students scored in the average range or if there are significant outliers.
Step 1: Gather Data
He begins by gathering the data. The scores of each student in class are gathered to analyze exam scores.
After arranging the scores in ascending order, bin ranges are set.
Step 2: Define Bins
Bins are like categories that group similar values. Think of them as buckets that organize your data. The presenter decides how wide each bin should be based on the range of the values. For instance, the instructor sets the bin ranges based on score intervals: 60-69, 70-79, 80-89, and 90-100.
Step 3: Count Frequency
Now, he counts how many data points fall into each bin. This step is crucial because it tells you how often specific ranges of values occur. The result is the frequency distribution, showing the occurrences of each group.
Here, the instructor counts the number of students in each category.
- 60-69: 1 student (Kate)
- 70-79: 4 students (David, Emma, Grace, Jack)
- 80-89: 7 students (Alice, Bob, Frank, Isabel, Liam, Mia, Noah)
- 90-100: 3 students (Clara, Henry, Olivia)
Step 4: Create the Histogram
It’s time to turn the data into a visual representation. Draw a bar for each bin on a graph. The width of the bar should correspond to the range of the bin, and the height should correspond to the frequency. To make your histogram understandable, label the X and Y axes.
In this case, the X-axis should represent the bins (e.g., test score ranges), and the Y-axis represents the frequency.
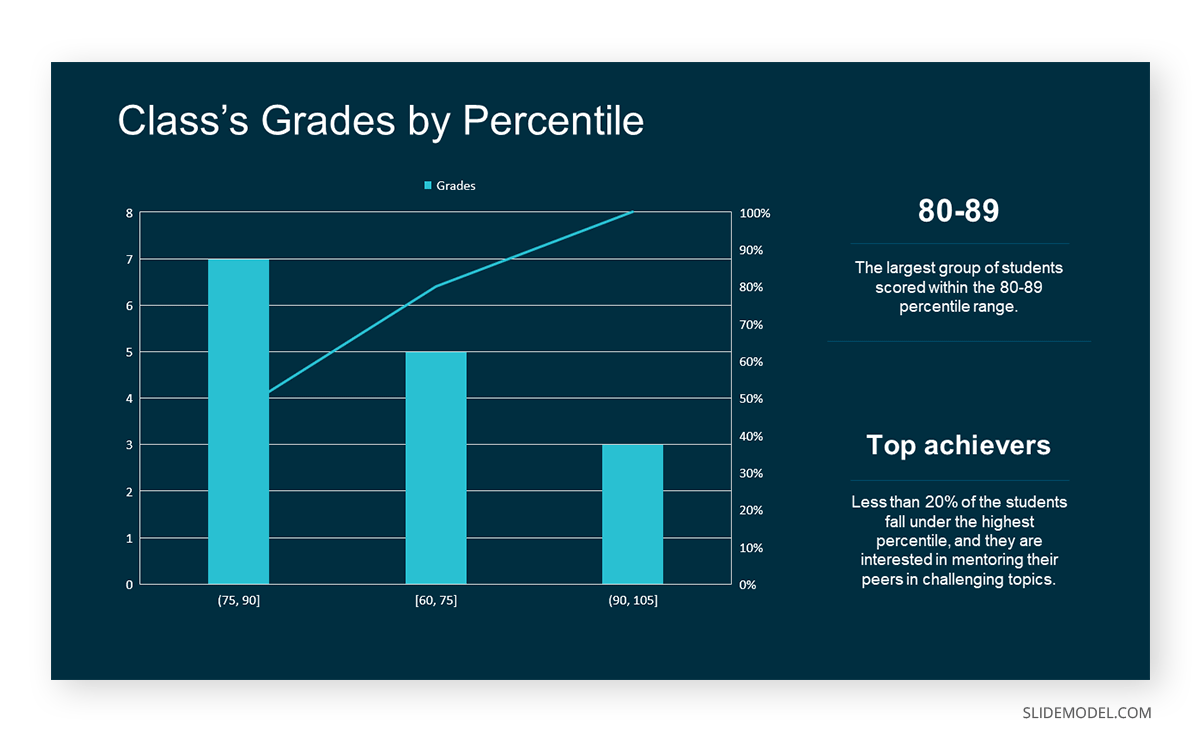
The histogram of the class grades reveals insightful patterns in the distribution. Most students, with seven students, fall within the 80-89 score range. The histogram provides a clear visualization of the class’s performance. It showcases a concentration of grades in the upper-middle range with few outliers at both ends. This analysis helps in understanding the overall academic standing of the class. It also identifies the areas for potential improvement or recognition.
Thus, histograms provide a clear visual representation of data distribution. They are easy to interpret, even for those without a statistical background. They apply to various types of data, including continuous and discrete variables. One weak point is that histograms do not capture detailed patterns in students’ data, with seven compared to other visualization methods.
A scatter plot is a graphical representation of the relationship between two variables. It consists of individual data points on a two-dimensional plane. This plane plots one variable on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. Each point represents a unique observation. It visualizes patterns, trends, or correlations between the two variables.
Scatter plots are also effective in revealing the strength and direction of relationships. They identify outliers and assess the overall distribution of data points. The points’ dispersion and clustering reflect the relationship’s nature, whether it is positive, negative, or lacks a discernible pattern. In business, scatter plots assess relationships between variables such as marketing cost and sales revenue. They help present data correlations and decision-making.
Real-Life Application of Scatter Plot
A group of scientists is conducting a study on the relationship between daily hours of screen time and sleep quality. After reviewing the data, they managed to create this table to help them build a scatter plot graph:
In the provided example, the x-axis represents Daily Hours of Screen Time, and the y-axis represents the Sleep Quality Rating.
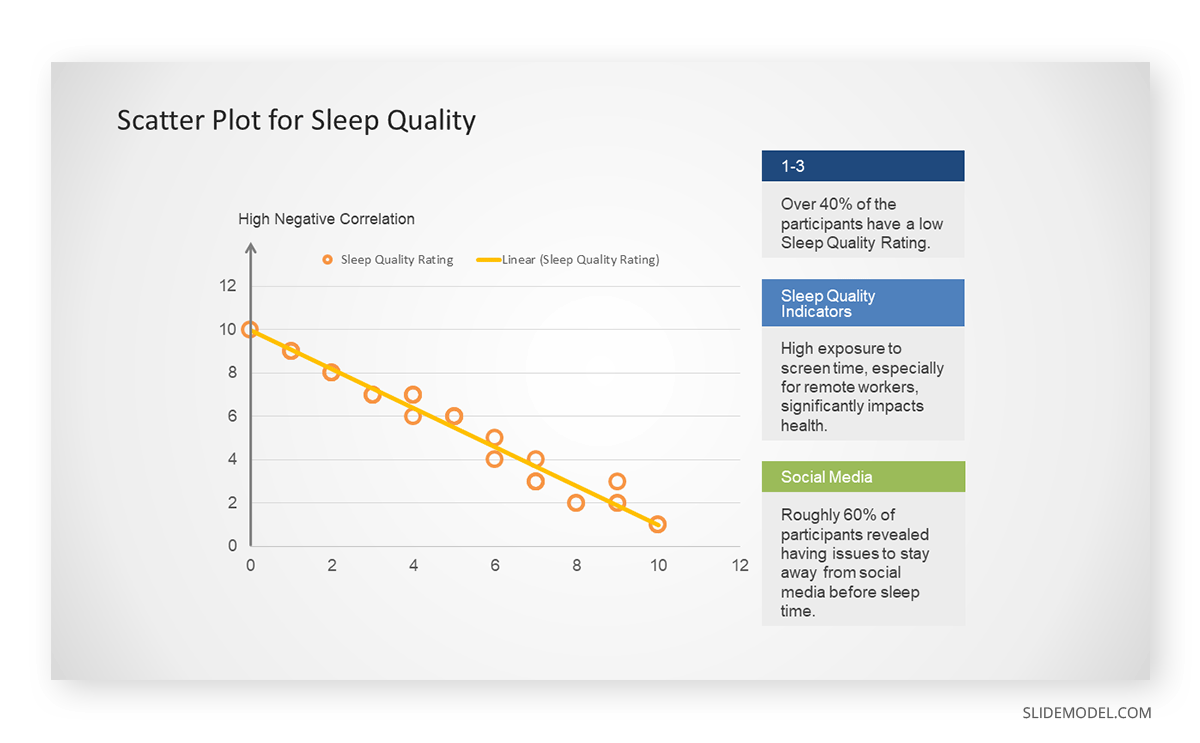
The scientists observe a negative correlation between the amount of screen time and the quality of sleep. This is consistent with their hypothesis that blue light, especially before bedtime, has a significant impact on sleep quality and metabolic processes.
There are a few things to remember when using a scatter plot. Even when a scatter diagram indicates a relationship, it doesn’t mean one variable affects the other. A third factor can influence both variables. The more the plot resembles a straight line, the stronger the relationship is perceived [11] . If it suggests no ties, the observed pattern might be due to random fluctuations in data. When the scatter diagram depicts no correlation, whether the data might be stratified is worth considering.
Choosing the appropriate data presentation type is crucial when making a presentation . Understanding the nature of your data and the message you intend to convey will guide this selection process. For instance, when showcasing quantitative relationships, scatter plots become instrumental in revealing correlations between variables. If the focus is on emphasizing parts of a whole, pie charts offer a concise display of proportions. Histograms, on the other hand, prove valuable for illustrating distributions and frequency patterns.
Bar charts provide a clear visual comparison of different categories. Likewise, line charts excel in showcasing trends over time, while tables are ideal for detailed data examination. Starting a presentation on data presentation types involves evaluating the specific information you want to communicate and selecting the format that aligns with your message. This ensures clarity and resonance with your audience from the beginning of your presentation.
1. Fact Sheet Dashboard for Data Presentation

Convey all the data you need to present in this one-pager format, an ideal solution tailored for users looking for presentation aids. Global maps, donut chats, column graphs, and text neatly arranged in a clean layout presented in light and dark themes.
Use This Template
2. 3D Column Chart Infographic PPT Template
Represent column charts in a highly visual 3D format with this PPT template. A creative way to present data, this template is entirely editable, and we can craft either a one-page infographic or a series of slides explaining what we intend to disclose point by point.
3. Data Circles Infographic PowerPoint Template
An alternative to the pie chart and donut chart diagrams, this template features a series of curved shapes with bubble callouts as ways of presenting data. Expand the information for each arch in the text placeholder areas.
4. Colorful Metrics Dashboard for Data Presentation
This versatile dashboard template helps us in the presentation of the data by offering several graphs and methods to convert numbers into graphics. Implement it for e-commerce projects, financial projections, project development, and more.
5. Animated Data Presentation Tools for PowerPoint & Google Slides
A slide deck filled with most of the tools mentioned in this article, from bar charts, column charts, treemap graphs, pie charts, histogram, etc. Animated effects make each slide look dynamic when sharing data with stakeholders.
6. Statistics Waffle Charts PPT Template for Data Presentations
This PPT template helps us how to present data beyond the typical pie chart representation. It is widely used for demographics, so it’s a great fit for marketing teams, data science professionals, HR personnel, and more.
7. Data Presentation Dashboard Template for Google Slides
A compendium of tools in dashboard format featuring line graphs, bar charts, column charts, and neatly arranged placeholder text areas.
8. Weather Dashboard for Data Presentation
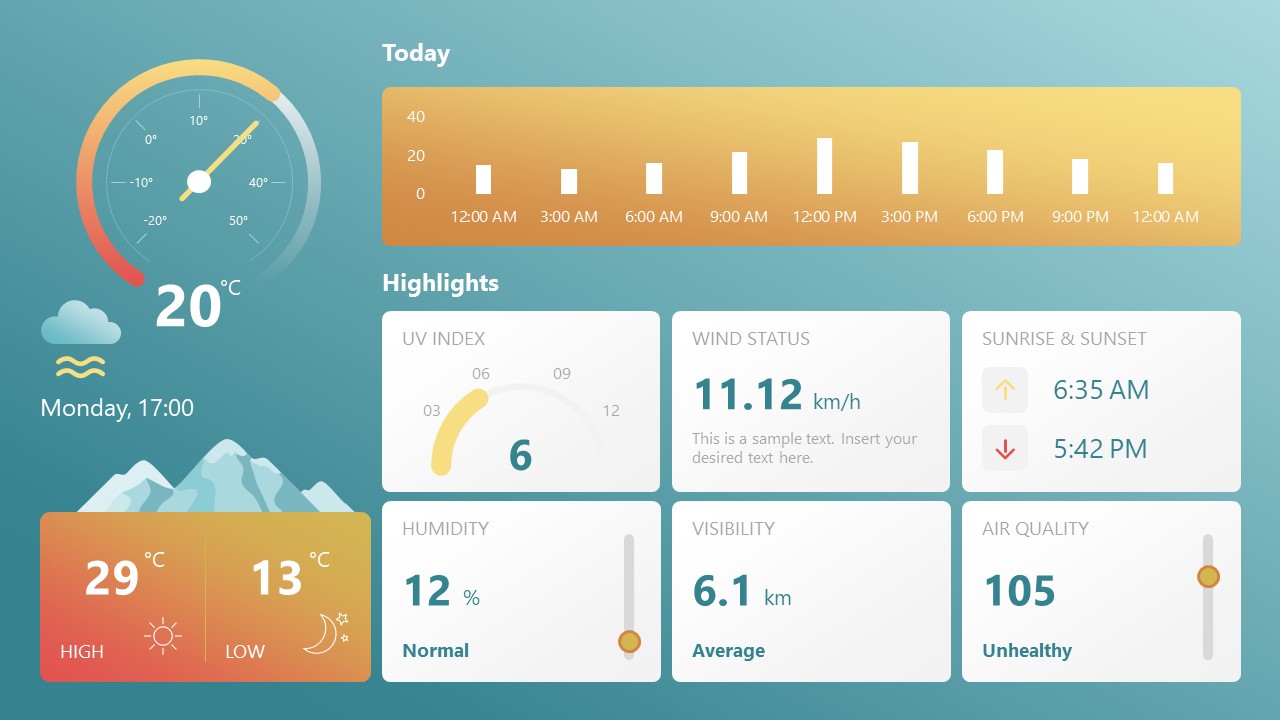
Share weather data for agricultural presentation topics, environmental studies, or any kind of presentation that requires a highly visual layout for weather forecasting on a single day. Two color themes are available.
9. Social Media Marketing Dashboard Data Presentation Template
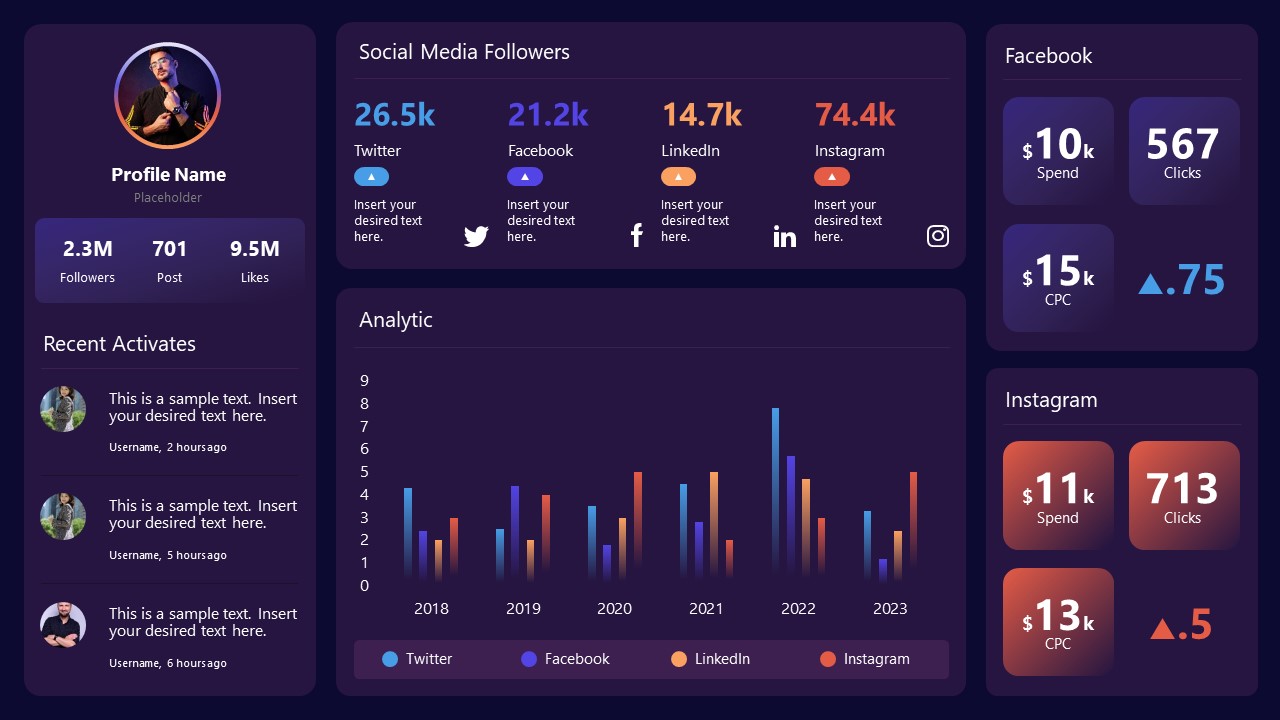
Intended for marketing professionals, this dashboard template for data presentation is a tool for presenting data analytics from social media channels. Two slide layouts featuring line graphs and column charts.
10. Project Management Summary Dashboard Template
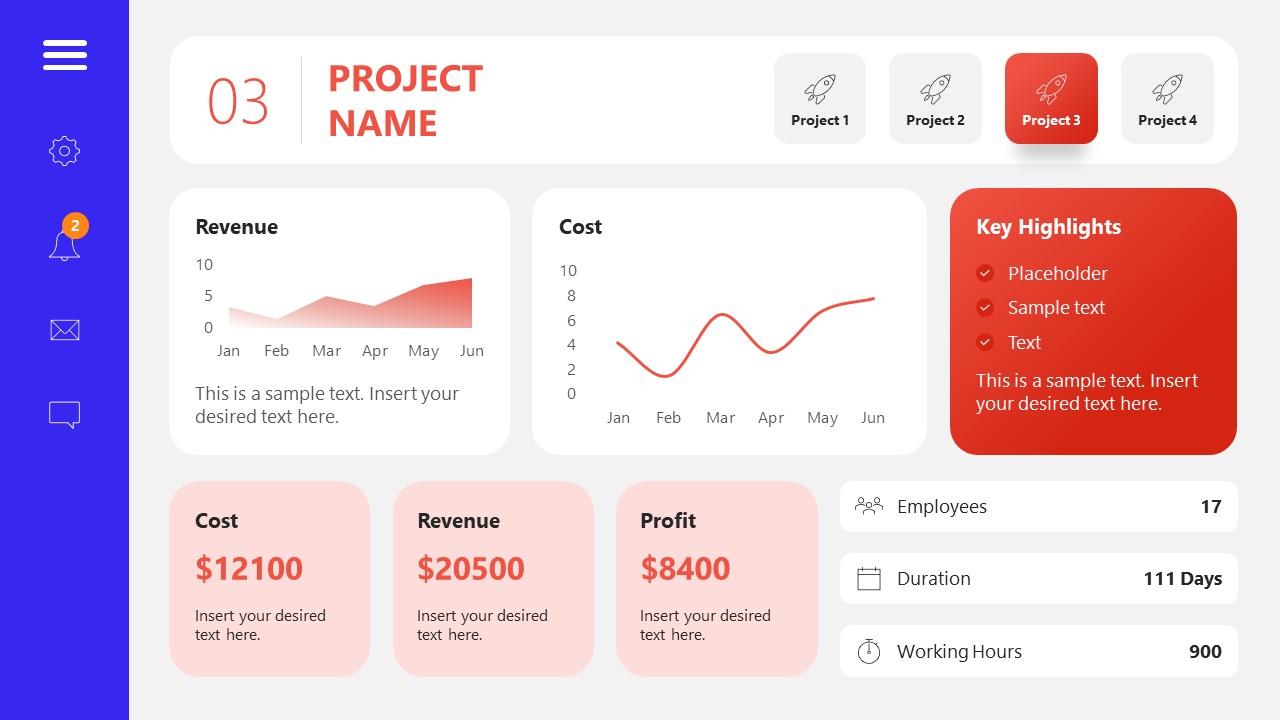
A tool crafted for project managers to deliver highly visual reports on a project’s completion, the profits it delivered for the company, and expenses/time required to execute it. 4 different color layouts are available.
11. Profit & Loss Dashboard for PowerPoint and Google Slides
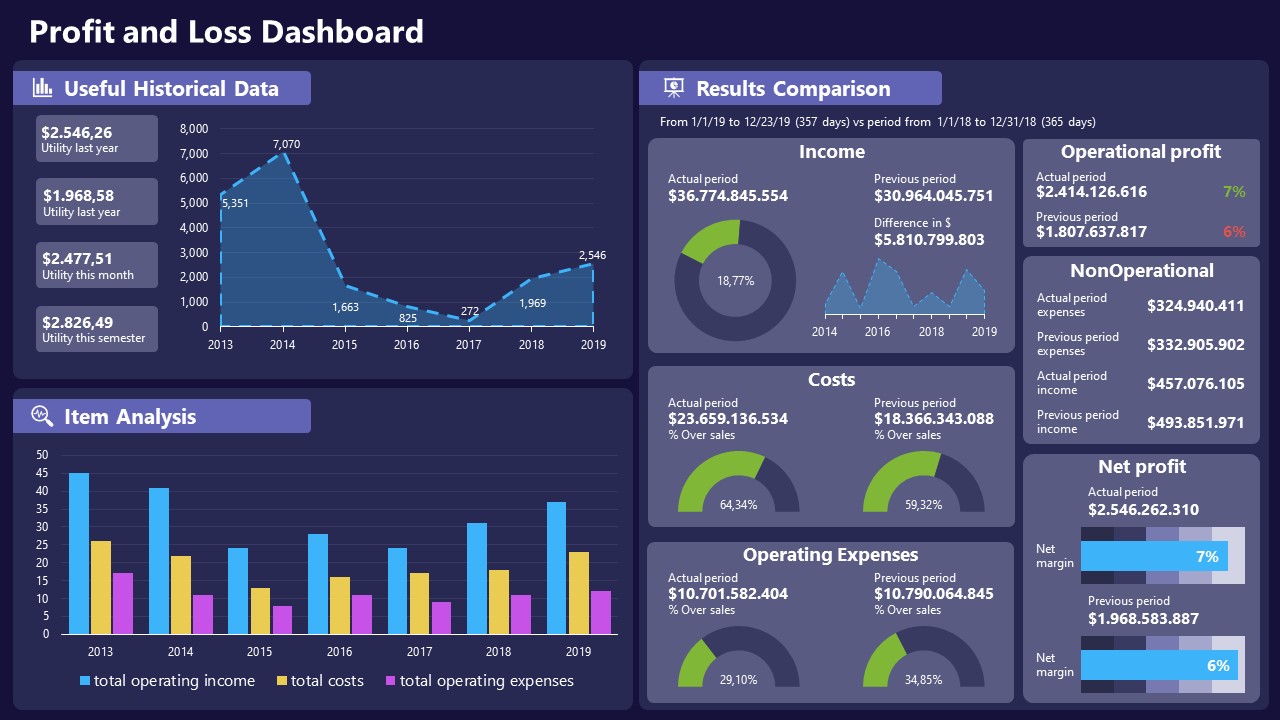
A must-have for finance professionals. This typical profit & loss dashboard includes progress bars, donut charts, column charts, line graphs, and everything that’s required to deliver a comprehensive report about a company’s financial situation.
Overwhelming visuals
One of the mistakes related to using data-presenting methods is including too much data or using overly complex visualizations. They can confuse the audience and dilute the key message.
Inappropriate chart types
Choosing the wrong type of chart for the data at hand can lead to misinterpretation. For example, using a pie chart for data that doesn’t represent parts of a whole is not right.
Lack of context
Failing to provide context or sufficient labeling can make it challenging for the audience to understand the significance of the presented data.
Inconsistency in design
Using inconsistent design elements and color schemes across different visualizations can create confusion and visual disarray.
Failure to provide details
Simply presenting raw data without offering clear insights or takeaways can leave the audience without a meaningful conclusion.
Lack of focus
Not having a clear focus on the key message or main takeaway can result in a presentation that lacks a central theme.
Visual accessibility issues
Overlooking the visual accessibility of charts and graphs can exclude certain audience members who may have difficulty interpreting visual information.
In order to avoid these mistakes in data presentation, presenters can benefit from using presentation templates . These templates provide a structured framework. They ensure consistency, clarity, and an aesthetically pleasing design, enhancing data communication’s overall impact.
Understanding and choosing data presentation types are pivotal in effective communication. Each method serves a unique purpose, so selecting the appropriate one depends on the nature of the data and the message to be conveyed. The diverse array of presentation types offers versatility in visually representing information, from bar charts showing values to pie charts illustrating proportions.
Using the proper method enhances clarity, engages the audience, and ensures that data sets are not just presented but comprehensively understood. By appreciating the strengths and limitations of different presentation types, communicators can tailor their approach to convey information accurately, developing a deeper connection between data and audience understanding.
[1] Government of Canada, S.C. (2021) 5 Data Visualization 5.2 Bar Chart , 5.2 Bar chart . https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/edu/power-pouvoir/ch9/bargraph-diagrammeabarres/5214818-eng.htm
[2] Kosslyn, S.M., 1989. Understanding charts and graphs. Applied cognitive psychology, 3(3), pp.185-225. https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/ADA183409.pdf
[3] Creating a Dashboard . https://it.tufts.edu/book/export/html/1870
[4] https://www.goldenwestcollege.edu/research/data-and-more/data-dashboards/index.html
[5] https://www.mit.edu/course/21/21.guide/grf-line.htm
[6] Jadeja, M. and Shah, K., 2015, January. Tree-Map: A Visualization Tool for Large Data. In GSB@ SIGIR (pp. 9-13). https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1393/gsb15proceedings.pdf#page=15
[7] Heat Maps and Quilt Plots. https://www.publichealth.columbia.edu/research/population-health-methods/heat-maps-and-quilt-plots
[8] EIU QGIS WORKSHOP. https://www.eiu.edu/qgisworkshop/heatmaps.php
[9] About Pie Charts. https://www.mit.edu/~mbarker/formula1/f1help/11-ch-c8.htm
[10] Histograms. https://sites.utexas.edu/sos/guided/descriptive/numericaldd/descriptiven2/histogram/ [11] https://asq.org/quality-resources/scatter-diagram

Like this article? Please share
Data Analysis, Data Science, Data Visualization Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!
Filed under Presentation Ideas • January 6th, 2024
All About Using Harvey Balls
Among the many tools in the arsenal of the modern presenter, Harvey Balls have a special place. In this article we will tell you all about using Harvey Balls.

Filed under Business • December 8th, 2023
How to Design a Dashboard Presentation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Take a step further in your professional presentation skills by learning what a dashboard presentation is and how to properly design one in PowerPoint. A detailed step-by-step guide is here!
Leave a Reply
Data presentation: A comprehensive guide
Learn how to create data presentation effectively and communicate your insights in a way that is clear, concise, and engaging.
Raja Bothra
Building presentations

Hey there, fellow data enthusiast!
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on data presentation.
Whether you're an experienced presenter or just starting, this guide will help you present your data like a pro.
We'll dive deep into what data presentation is, why it's crucial, and how to master it. So, let's embark on this data-driven journey together.
What is data presentation?
Data presentation is the art of transforming raw data into a visual format that's easy to understand and interpret. It's like turning numbers and statistics into a captivating story that your audience can quickly grasp. When done right, data presentation can be a game-changer, enabling you to convey complex information effectively.
Why are data presentations important?
Imagine drowning in a sea of numbers and figures. That's how your audience might feel without proper data presentation. Here's why it's essential:
- Clarity : Data presentations make complex information clear and concise.
- Engagement : Visuals, such as charts and graphs, grab your audience's attention.
- Comprehension : Visual data is easier to understand than long, numerical reports.
- Decision-making : Well-presented data aids informed decision-making.
- Impact : It leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
Types of data presentation
Now, let's delve into the diverse array of data presentation methods, each with its own unique strengths and applications. We have three primary types of data presentation, and within these categories, numerous specific visualization techniques can be employed to effectively convey your data.
1. Textual presentation
Textual presentation harnesses the power of words and sentences to elucidate and contextualize your data. This method is commonly used to provide a narrative framework for the data, offering explanations, insights, and the broader implications of your findings. It serves as a foundation for a deeper understanding of the data's significance.
2. Tabular presentation
Tabular presentation employs tables to arrange and structure your data systematically. These tables are invaluable for comparing various data groups or illustrating how data evolves over time. They present information in a neat and organized format, facilitating straightforward comparisons and reference points.
3. Graphical presentation
Graphical presentation harnesses the visual impact of charts and graphs to breathe life into your data. Charts and graphs are powerful tools for spotlighting trends, patterns, and relationships hidden within the data. Let's explore some common graphical presentation methods:
- Bar charts: They are ideal for comparing different categories of data. In this method, each category is represented by a distinct bar, and the height of the bar corresponds to the value it represents. Bar charts provide a clear and intuitive way to discern differences between categories.
- Pie charts: It excel at illustrating the relative proportions of different data categories. Each category is depicted as a slice of the pie, with the size of each slice corresponding to the percentage of the total value it represents. Pie charts are particularly effective for showcasing the distribution of data.
- Line graphs: They are the go-to choice when showcasing how data evolves over time. Each point on the line represents a specific value at a particular time period. This method enables viewers to track trends and fluctuations effortlessly, making it perfect for visualizing data with temporal dimensions.
- Scatter plots: They are the tool of choice when exploring the relationship between two variables. In this method, each point on the plot represents a pair of values for the two variables in question. Scatter plots help identify correlations, outliers, and patterns within data pairs.
The selection of the most suitable data presentation method hinges on the specific dataset and the presentation's objectives. For instance, when comparing sales figures of different products, a bar chart shines in its simplicity and clarity. On the other hand, if your aim is to display how a product's sales have changed over time, a line graph provides the ideal visual narrative.
Additionally, it's crucial to factor in your audience's level of familiarity with data presentations. For a technical audience, more intricate visualization methods may be appropriate. However, when presenting to a general audience, opting for straightforward and easily understandable visuals is often the wisest choice.
In the world of data presentation, choosing the right method is akin to selecting the perfect brush for a masterpiece. Each tool has its place, and understanding when and how to use them is key to crafting compelling and insightful presentations. So, consider your data carefully, align your purpose, and paint a vivid picture that resonates with your audience.
What to include in data presentation
When creating your data presentation, remember these key components:
- Data points : Clearly state the data points you're presenting.
- Comparison : Highlight comparisons and trends in your data.
- Graphical methods : Choose the right chart or graph for your data.
- Infographics : Use visuals like infographics to make information more digestible.
- Numerical values : Include numerical values to support your visuals.
- Qualitative information : Explain the significance of the data.
- Source citation : Always cite your data sources.
How to structure an effective data presentation
Creating a well-structured data presentation is not just important; it's the backbone of a successful presentation. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you craft a compelling and organized presentation that captivates your audience:
1. Know your audience
Understanding your audience is paramount. Consider their needs, interests, and existing knowledge about your topic. Tailor your presentation to their level of understanding, ensuring that it resonates with them on a personal level. Relevance is the key.
2. Have a clear message
Every effective data presentation should convey a clear and concise message. Determine what you want your audience to learn or take away from your presentation, and make sure your message is the guiding light throughout your presentation. Ensure that all your data points align with and support this central message.
3. Tell a compelling story
Human beings are naturally wired to remember stories. Incorporate storytelling techniques into your presentation to make your data more relatable and memorable. Your data can be the backbone of a captivating narrative, whether it's about a trend, a problem, or a solution. Take your audience on a journey through your data.
4. Leverage visuals
Visuals are a powerful tool in data presentation. They make complex information accessible and engaging. Utilize charts, graphs, and images to illustrate your points and enhance the visual appeal of your presentation. Visuals should not just be an accessory; they should be an integral part of your storytelling.
5. Be clear and concise
Avoid jargon or technical language that your audience may not comprehend. Use plain language and explain your data points clearly. Remember, clarity is king. Each piece of information should be easy for your audience to digest.
6. Practice your delivery
Practice makes perfect. Rehearse your presentation multiple times before the actual delivery. This will help you deliver it smoothly and confidently, reducing the chances of stumbling over your words or losing track of your message.
A basic structure for an effective data presentation
Armed with a comprehensive comprehension of how to construct a compelling data presentation, you can now utilize this fundamental template for guidance:
In the introduction, initiate your presentation by introducing both yourself and the topic at hand. Clearly articulate your main message or the fundamental concept you intend to communicate.
Moving on to the body of your presentation, organize your data in a coherent and easily understandable sequence. Employ visuals generously to elucidate your points and weave a narrative that enhances the overall story. Ensure that the arrangement of your data aligns with and reinforces your central message.
As you approach the conclusion, succinctly recapitulate your key points and emphasize your core message once more. Conclude by leaving your audience with a distinct and memorable takeaway, ensuring that your presentation has a lasting impact.
Additional tips for enhancing your data presentation
To take your data presentation to the next level, consider these additional tips:
- Consistent design : Maintain a uniform design throughout your presentation. This not only enhances visual appeal but also aids in seamless comprehension.
- High-quality visuals : Ensure that your visuals are of high quality, easy to read, and directly relevant to your topic.
- Concise text : Avoid overwhelming your slides with excessive text. Focus on the most critical points, using visuals to support and elaborate.
- Anticipate questions : Think ahead about the questions your audience might pose. Be prepared with well-thought-out answers to foster productive discussions.
By following these guidelines, you can structure an effective data presentation that not only informs but also engages and inspires your audience. Remember, a well-structured presentation is the bridge that connects your data to your audience's understanding and appreciation.
Do’s and don'ts on a data presentation
- Use visuals : Incorporate charts and graphs to enhance understanding.
- Keep it simple : Avoid clutter and complexity.
- Highlight key points : Emphasize crucial data.
- Engage the audience : Encourage questions and discussions.
- Practice : Rehearse your presentation.
Don'ts:
- Overload with data : Less is often more; don't overwhelm your audience.
- Fit Unrelated data : Stay on topic; don't include irrelevant information.
- Neglect the audience : Ensure your presentation suits your audience's level of expertise.
- Read word-for-word : Avoid reading directly from slides.
- Lose focus : Stick to your presentation's purpose.
Summarizing key takeaways
- Definition : Data presentation is the art of visualizing complex data for better understanding.
- Importance : Data presentations enhance clarity, engage the audience, aid decision-making, and leave a lasting impact.
- Types : Textual, Tabular, and Graphical presentations offer various ways to present data.
- Choosing methods : Select the right method based on data, audience, and purpose.
- Components : Include data points, comparisons, visuals, infographics, numerical values, and source citations.
- Structure : Know your audience, have a clear message, tell a compelling story, use visuals, be concise, and practice.
- Do's and don'ts : Do use visuals, keep it simple, highlight key points, engage the audience, and practice. Don't overload with data, include unrelated information, neglect the audience's expertise, read word-for-word, or lose focus.
1. What is data presentation, and why is it important in 2023?
Data presentation is the process of visually representing data sets to convey information effectively to an audience. In an era where the amount of data generated is vast, visually presenting data using methods such as diagrams, graphs, and charts has become crucial. By simplifying complex data sets, presentation of the data may helps your audience quickly grasp much information without drowning in a sea of chart's, analytics, facts and figures.
2. What are some common methods of data presentation?
There are various methods of data presentation, including graphs and charts, histograms, and cumulative frequency polygons. Each method has its strengths and is often used depending on the type of data you're using and the message you want to convey. For instance, if you want to show data over time, try using a line graph. If you're presenting geographical data, consider to use a heat map.
3. How can I ensure that my data presentation is clear and readable?
To ensure that your data presentation is clear and readable, pay attention to the design and labeling of your charts. Don't forget to label the axes appropriately, as they are critical for understanding the values they represent. Don't fit all the information in one slide or in a single paragraph. Presentation software like Prezent and PowerPoint can help you simplify your vertical axis, charts and tables, making them much easier to understand.
4. What are some common mistakes presenters make when presenting data?
One common mistake is trying to fit too much data into a single chart, which can distort the information and confuse the audience. Another mistake is not considering the needs of the audience. Remember that your audience won't have the same level of familiarity with the data as you do, so it's essential to present the data effectively and respond to questions during a Q&A session.
5. How can I use data visualization to present important data effectively on platforms like LinkedIn?
When presenting data on platforms like LinkedIn, consider using eye-catching visuals like bar graphs or charts. Use concise captions and e.g., examples to highlight the single most important information in your data report. Visuals, such as graphs and tables, can help you stand out in the sea of textual content, making your data presentation more engaging and shareable among your LinkedIn connections.
Create your data presentation with prezent
Prezent can be a valuable tool for creating data presentations. Here's how Prezent can help you in this regard:
- Time savings : Prezent saves up to 70% of presentation creation time, allowing you to focus on data analysis and insights.
- On-brand consistency : Ensure 100% brand alignment with Prezent's brand-approved designs for professional-looking data presentations.
- Effortless collaboration : Real-time sharing and collaboration features make it easy for teams to work together on data presentations.
- Data storytelling : Choose from 50+ storylines to effectively communicate data insights and engage your audience.
- Personalization : Create tailored data presentations that resonate with your audience's preferences, enhancing the impact of your data.
In summary, Prezent streamlines the process of creating data presentations by offering time-saving features, ensuring brand consistency, promoting collaboration, and providing tools for effective data storytelling. Whether you need to present data to clients, stakeholders, or within your organization, Prezent can significantly enhance your presentation-making process.
So, go ahead, present your data with confidence, and watch your audience be wowed by your expertise.
Thank you for joining us on this data-driven journey. Stay tuned for more insights, and remember, data presentation is your ticket to making numbers come alive!
Sign up for our free trial or book a demo !
Get the latest from Prezent community
Join thousands of subscribers who receive our best practices on communication, storytelling, presentation design, and more. New tips weekly. (No spam, we promise!)
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Present Your Data Like a Pro
- Joel Schwartzberg

Demystify the numbers. Your audience will thank you.
While a good presentation has data, data alone doesn’t guarantee a good presentation. It’s all about how that data is presented. The quickest way to confuse your audience is by sharing too many details at once. The only data points you should share are those that significantly support your point — and ideally, one point per chart. To avoid the debacle of sheepishly translating hard-to-see numbers and labels, rehearse your presentation with colleagues sitting as far away as the actual audience would. While you’ve been working with the same chart for weeks or months, your audience will be exposed to it for mere seconds. Give them the best chance of comprehending your data by using simple, clear, and complete language to identify X and Y axes, pie pieces, bars, and other diagrammatic elements. Try to avoid abbreviations that aren’t obvious, and don’t assume labeled components on one slide will be remembered on subsequent slides. Every valuable chart or pie graph has an “Aha!” zone — a number or range of data that reveals something crucial to your point. Make sure you visually highlight the “Aha!” zone, reinforcing the moment by explaining it to your audience.
With so many ways to spin and distort information these days, a presentation needs to do more than simply share great ideas — it needs to support those ideas with credible data. That’s true whether you’re an executive pitching new business clients, a vendor selling her services, or a CEO making a case for change.
- JS Joel Schwartzberg oversees executive communications for a major national nonprofit, is a professional presentation coach, and is the author of Get to the Point! Sharpen Your Message and Make Your Words Matter and The Language of Leadership: How to Engage and Inspire Your Team . You can find him on LinkedIn and X. TheJoelTruth
Partner Center
10 Methods of Data Presentation with 5 Great Tips to Practice, Best in 2024
Leah Nguyen • 05 Apr 2024 • 11 min read
There are different ways of presenting data, so which one is suited you the most? You can end deathly boring and ineffective data presentation right now with our 10 methods of data presentation . Check out the examples from each technique!
Have you ever presented a data report to your boss/coworkers/teachers thinking it was super dope like you’re some cyber hacker living in the Matrix, but all they saw was a pile of static numbers that seemed pointless and didn’t make sense to them?
Understanding digits is rigid . Making people from non-analytical backgrounds understand those digits is even more challenging.
How can you clear up those confusing numbers in the types of presentation that have the flawless clarity of a diamond? So, let’s check out best way to present data. 💎
Table of Contents
- What are Methods of Data Presentations?
- #1 – Tabular
#2 – Text
#3 – pie chart, #4 – bar chart, #5 – histogram, #6 – line graph, #7 – pictogram graph, #8 – radar chart, #9 – heat map, #10 – scatter plot.
- 5 Mistakes to Avoid
- Best Method of Data Presentation
Frequently Asked Questions
More tips with ahaslides.
- Marketing Presentation
- Survey Result Presentation
- Types of Presentation

Start in seconds.
Get any of the above examples as templates. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
What are Methods of Data Presentation?
The term ’data presentation’ relates to the way you present data in a way that makes even the most clueless person in the room understand.
Some say it’s witchcraft (you’re manipulating the numbers in some ways), but we’ll just say it’s the power of turning dry, hard numbers or digits into a visual showcase that is easy for people to digest.
Presenting data correctly can help your audience understand complicated processes, identify trends, and instantly pinpoint whatever is going on without exhausting their brains.
Good data presentation helps…
- Make informed decisions and arrive at positive outcomes . If you see the sales of your product steadily increase throughout the years, it’s best to keep milking it or start turning it into a bunch of spin-offs (shoutout to Star Wars👀).
- Reduce the time spent processing data . Humans can digest information graphically 60,000 times faster than in the form of text. Grant them the power of skimming through a decade of data in minutes with some extra spicy graphs and charts.
- Communicate the results clearly . Data does not lie. They’re based on factual evidence and therefore if anyone keeps whining that you might be wrong, slap them with some hard data to keep their mouths shut.
- Add to or expand the current research . You can see what areas need improvement, as well as what details often go unnoticed while surfing through those little lines, dots or icons that appear on the data board.
Methods of Data Presentation and Examples
Imagine you have a delicious pepperoni, extra-cheese pizza. You can decide to cut it into the classic 8 triangle slices, the party style 12 square slices, or get creative and abstract on those slices.
There are various ways for cutting a pizza and you get the same variety with how you present your data. In this section, we will bring you the 10 ways to slice a pizza – we mean to present your data – that will make your company’s most important asset as clear as day. Let’s dive into 10 ways to present data efficiently.
#1 – Tabular
Among various types of data presentation, tabular is the most fundamental method, with data presented in rows and columns. Excel or Google Sheets would qualify for the job. Nothing fancy.
This is an example of a tabular presentation of data on Google Sheets. Each row and column has an attribute (year, region, revenue, etc.), and you can do a custom format to see the change in revenue throughout the year.
When presenting data as text, all you do is write your findings down in paragraphs and bullet points, and that’s it. A piece of cake to you, a tough nut to crack for whoever has to go through all of the reading to get to the point.
- 65% of email users worldwide access their email via a mobile device.
- Emails that are optimised for mobile generate 15% higher click-through rates.
- 56% of brands using emojis in their email subject lines had a higher open rate.
(Source: CustomerThermometer )
All the above quotes present statistical information in textual form. Since not many people like going through a wall of texts, you’ll have to figure out another route when deciding to use this method, such as breaking the data down into short, clear statements, or even as catchy puns if you’ve got the time to think of them.
A pie chart (or a ‘donut chart’ if you stick a hole in the middle of it) is a circle divided into slices that show the relative sizes of data within a whole. If you’re using it to show percentages, make sure all the slices add up to 100%.
The pie chart is a familiar face at every party and is usually recognised by most people. However, one setback of using this method is our eyes sometimes can’t identify the differences in slices of a circle, and it’s nearly impossible to compare similar slices from two different pie charts, making them the villains in the eyes of data analysts.
Bonus example: A literal ‘pie’ chart! 🥧
The bar chart is a chart that presents a bunch of items from the same category, usually in the form of rectangular bars that are placed at an equal distance from each other. Their heights or lengths depict the values they represent.
They can be as simple as this:
Or more complex and detailed like this example of presentation of data. Contributing to an effective statistic presentation, this one is a grouped bar chart that not only allows you to compare categories but also the groups within them as well.
Similar in appearance to the bar chart but the rectangular bars in histograms don’t often have the gap like their counterparts.
Instead of measuring categories like weather preferences or favourite films as a bar chart does, a histogram only measures things that can be put into numbers.
Teachers can use presentation graphs like a histogram to see which score group most of the students fall into, like in this example above.
Recordings to ways of displaying data, we shouldn’t overlook the effectiveness of line graphs. Line graphs are represented by a group of data points joined together by a straight line. There can be one or more lines to compare how several related things change over time.
On a line chart’s horizontal axis, you usually have text labels, dates or years, while the vertical axis usually represents the quantity (e.g.: budget, temperature or percentage).
A pictogram graph uses pictures or icons relating to the main topic to visualise a small dataset. The fun combination of colours and illustrations makes it a frequent use at schools.
Pictograms are a breath of fresh air if you want to stay away from the monotonous line chart or bar chart for a while. However, they can present a very limited amount of data and sometimes they are only there for displays and do not represent real statistics.
If presenting five or more variables in the form of a bar chart is too stuffy then you should try using a radar chart, which is one of the most creative ways to present data.
Radar charts show data in terms of how they compare to each other starting from the same point. Some also call them ‘spider charts’ because each aspect combined looks like a spider web.
Radar charts can be a great use for parents who’d like to compare their child’s grades with their peers to lower their self-esteem. You can see that each angular represents a subject with a score value ranging from 0 to 100. Each student’s score across 5 subjects is highlighted in a different colour.
If you think that this method of data presentation somehow feels familiar, then you’ve probably encountered one while playing Pokémon .
A heat map represents data density in colours. The bigger the number, the more colour intense that data will be represented.
Most U.S citizens would be familiar with this data presentation method in geography. For elections, many news outlets assign a specific colour code to a state, with blue representing one candidate and red representing the other. The shade of either blue or red in each state shows the strength of the overall vote in that state.
Another great thing you can use a heat map for is to map what visitors to your site click on. The more a particular section is clicked the ‘hotter’ the colour will turn, from blue to bright yellow to red.
If you present your data in dots instead of chunky bars, you’ll have a scatter plot.
A scatter plot is a grid with several inputs showing the relationship between two variables. It’s good at collecting seemingly random data and revealing some telling trends.
For example, in this graph, each dot shows the average daily temperature versus the number of beach visitors across several days. You can see that the dots get higher as the temperature increases, so it’s likely that hotter weather leads to more visitors.
5 Data Presentation Mistakes to Avoid
#1 – assume your audience understands what the numbers represent.
You may know all the behind-the-scenes of your data since you’ve worked with them for weeks, but your audience doesn’t.
Showing without telling only invites more and more questions from your audience, as they have to constantly make sense of your data, wasting the time of both sides as a result.
While showing your data presentations, you should tell them what the data are about before hitting them with waves of numbers first. You can use interactive activities such as polls , word clouds , online quiz and Q&A sections , combined with icebreaker games , to assess their understanding of the data and address any confusion beforehand.
#2 – Use the wrong type of chart
Charts such as pie charts must have a total of 100% so if your numbers accumulate to 193% like this example below, you’re definitely doing it wrong.
Before making a chart, ask yourself: what do I want to accomplish with my data? Do you want to see the relationship between the data sets, show the up and down trends of your data, or see how segments of one thing make up a whole?
Remember, clarity always comes first. Some data visualisations may look cool, but if they don’t fit your data, steer clear of them.
#3 – Make it 3D
3D is a fascinating graphical presentation example. The third dimension is cool, but full of risks.
Can you see what’s behind those red bars? Because we can’t either. You may think that 3D charts add more depth to the design, but they can create false perceptions as our eyes see 3D objects closer and bigger than they appear, not to mention they cannot be seen from multiple angles.
#4 – Use different types of charts to compare contents in the same category
This is like comparing a fish to a monkey. Your audience won’t be able to identify the differences and make an appropriate correlation between the two data sets.
Next time, stick to one type of data presentation only. Avoid the temptation of trying various data visualisation methods in one go and make your data as accessible as possible.
#5 – Bombard the audience with too much information
The goal of data presentation is to make complex topics much easier to understand, and if you’re bringing too much information to the table, you’re missing the point.
The more information you give, the more time it will take for your audience to process it all. If you want to make your data understandable and give your audience a chance to remember it, keep the information within it to an absolute minimum. You should set your session with open-ended questions , to avoid dead-communication!
What are the Best Methods of Data Presentation?
Finally, which is the best way to present data?
The answer is…
There is none 😄 Each type of presentation has its own strengths and weaknesses and the one you choose greatly depends on what you’re trying to do.
For example:
- Go for a scatter plot if you’re exploring the relationship between different data values, like seeing whether the sales of ice cream go up because of the temperature or because people are just getting more hungry and greedy each day?
- Go for a line graph if you want to mark a trend over time.
- Go for a heat map if you like some fancy visualisation of the changes in a geographical location, or to see your visitors’ behaviour on your website.
- Go for a pie chart (especially in 3D) if you want to be shunned by others because it was never a good idea👇
What is chart presentation?
A chart presentation is a way of presenting data or information using visual aids such as charts, graphs, and diagrams. The purpose of a chart presentation is to make complex information more accessible and understandable for the audience.
When can I use charts for presentation?
Charts can be used to compare data, show trends over time, highlight patterns, and simplify complex information.
Why should use charts for presentation?
You should use charts to ensure your contents and visual look clean, as they are the visual representative, provide clarity, simplicity, comparison, contrast and super time-saving!
What are the 4 graphical methods of presenting data?
Histogram, Smoothed frequency graph, Pie diagram or Pie chart, Cumulative or ogive frequency graph, and Frequency Polygon.
Leah Nguyen
Words that convert, stories that stick. I turn complex ideas into engaging narratives - helping audiences learn, remember, and take action.
More from AhaSlides

We use cookies
This website uses cookies to provide better user experience and user's session management. By continuing visiting this website you consent the use of these cookies.
ChartExpo Survey

Mastering Art of Data Presentation for Compelling Insights
You have a bunch of numbers, and you want to make them look good. You could just throw them all onto a spreadsheet and call it a day.
But where’s the fun in that?
Instead, you can use presentation of data methods to bring your data to life and make it more engaging. Data presentation is like a fancy dress party for numbers. Here, data puts on their finest outfits and strut their stuff.
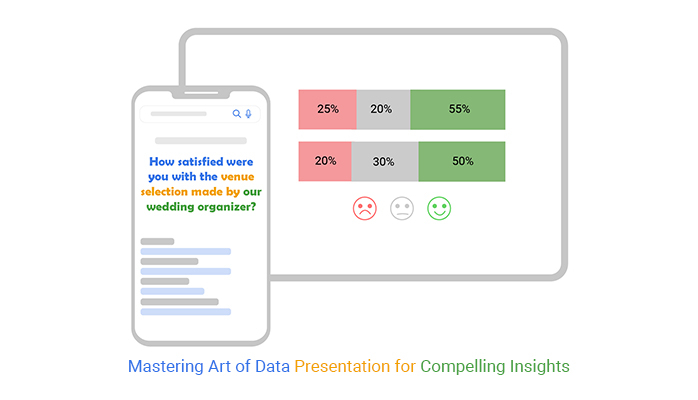
But, like at any party, there are different ways to make an entrance. Various methods of data presentation can make your information shine brighter than a disco ball.
You can dress them up in bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, etc. Each method has a unique style and purpose. All you have to do is choose the one that best suits your data. Then, tailor it to tell your story.
Let’s explore the different methods of data presentation and discover how to transform data into a captivating spectacle.
Table of Content:
What is data presentation.
- Significance of Effective
- Various Approaches
Tips for Effective Presentation of Data
- Implementation
Data presentation refers to organizing and displaying data meaningfully and clearly. It involves transforming raw data into perfect data storytelling that can be easily interpreted and analyzed. Effective presentation enhances comprehension, facilitates decision-making, and supports communication.
Significance of Effective Data Presentation
Data presentation plays a crucial role in conveying information, insights, and trends effectively. Here are some reasons why it is invaluable:
- Clarity and comprehension: Data in its raw form can be complex and overwhelming. Data presentation simplifies the information and presents it in a manner that is easy to understand. It transforms numbers and statistics into visual and structured formats, facilitating a swift grasp of the key points.
- Facilitates decision-making: Whether in business, research, or government, decision-makers rely on data to make informed choices. The presentation helps identify trends, patterns, and areas needing attention.
- Effective communication: Data presentation bridges the gap between data experts and non-experts. Consequently, it makes it possible to effectively communicate findings, research, and insights to a broader audience.
- Comparison and analysis: Data presentation methods like charts and graphs facilitate comparisons and data analysis. Visualizing data side by side or over time can reveal patterns and relationships not evident in raw data.
- Audience engagement: Effective presentation techniques help engage the audience by presenting information in a visually stimulating way. This enhances understanding and increases the likelihood of the audience retaining the information.
- Persuasion and influence: Data presentation is often used for persuasion and influence. It helps to highlight key data points, emphasize important information, and support the presenter’s arguments. Thus making it easier to convince and persuade others of a particular viewpoint or argument.
- Problem-solving and analysis: Presenting data in a structured and organized manner makes identifying patterns, correlations, and anomalies easier. Consequently, this leads to more accurate analysis and problem-solving.
- Collaboration and teamwork: Effective presentation of data promotes collaboration and teamwork. Team members can easily share and discuss information, leading to better collaboration and effective decision-making.
- Real-time analysis: With the advent of data visualization tools and dashboards, the presentation of data allows for real-time analysis. Consequently, you can monitor key metrics and respond to changing conditions swiftly.
- Data transparency: Transparent ways of presenting data are essential for building trust, especially in government and research contexts. They provide a clear view of the data sources, methodology, and results, fostering accountability.
Various Approaches to Data Presentation
Tables are one of the most straightforward and widely used methods for the presentation of data. They consist of rows and columns, with each cell containing data. Tables are handy for presenting structured and detailed information in a clear and organized format. They excel at showing precise values and directly comparing categories or data points.
Charts and Graphs
Charts and graphs visually simplify complex data, enhancing comprehension. Charts employ bars, lines, or columns for data display. On the other hand, graphs use points, lines, and curves to illustrate variable relationships.
Charts and graphs come in various types:
- Bar charts: Used to compare discrete categories or values, bar charts display data as rectangular bars. They are excellent for showing comparisons and ranking items.
- Line graphs: Ideal for illustrating trends and changes over time, line graphs connect data points with lines. This makes them suitable for time-series data.
- Pie charts: These circular charts depict parts of a whole, showing the proportions and percentages of a data set.
- Scatter plots: Scatter plots display data points on a grid, illustrating relationships and correlations between variables.
- Histograms: Histograms are used to represent data distributions and frequencies. They provide insights into the spread and skewness of data.
Infographics
Infographics merge text, graphics, and visuals to present data concisely and captivatingly. They excel at simplifying complex ideas and presenting statistics in an easily understandable, visually pleasing way. They find common use in marketing, journalism, and education, enhancing data accessibility for a wide audience.
Dashboards are dynamic, tailor-made interfaces that provide real-time data visualization and analytics. They streamline monitoring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metric tracking and facilitate data-driven decision-making .
Heatmaps use color intensity to represent data values, showing the concentration/distribution of data across a specific area. They are valuable for visualizing data patterns, such as website user activity (click heatmaps). Or areas of high and low interest in an image.
Effective data presentation is essential for conveying information clearly and engagingly. Here are tips to help you achieve effective data presentation:
- Understand your audience: Consider the knowledge level and expectations of your audience. Then, tailor your data presentation to match their needs. This ensures the information is accessible and relevant to your target audience.
- Select the appropriate visualization method: Choose the right chart, graph, or data presentation method for your data and objectives. For instance, bar charts are excellent for comparisons, while line graphs show trends over time .
- Simplify and focus: Avoid clutter and complexity to keep your presentation clean and straightforward. Moreover, highlight the most critical data points or insights and remove distracting elements.
- Use consistent design: Maintain a consistent design throughout your presentation. Use the same color scheme, fonts, and labeling style to provide visual coherence. This consistency enhances readability.
- Label clearly: Ensure that all elements of your presentation of data are clearly labeled. Include titles, axis labels, and data source references to prevent confusion.
- Provide context: Help your audience understand the context of the data. Explain what the data represents, its importance, and any relevant background information.
- Test for clarity: Run a test presentation to a small group to gauge how well the information is received. This allows you to identify any areas that may need clarification or adjustment.
- Stay up to date: Stay current with the presentation of data best practices and tools. Technology and design trends evolve, so it’s important to keep learning to improve your skills.
Best Data Presentation Implementation
Excel, the old stalwart of spreadsheets, is excellent for crunching numbers and organizing data. But when it comes to data visualization , it doesn’t quite “excel.”
We have a solution – ChartExpo.
ChartExpo breathes life into your Google Forms survey data when analyzed in Excel.
It turns your survey data into captivating visual masterpieces, all in just a few clicks.
Benefits of Using ChartExpo
- ChartExpo’s got it all – a visual feast for your data. With a wide array of visualizations, you can cherry-pick the perfect one to dazzle your audience.
- No more data headaches – ChartExpo streamlines analysis and presentation, making data look more attractive.
- Say goodbye to coding dilemmas; ChartExpo’s user-friendly interface helps you create jaw-dropping visualizations with zero coding skills.
- Unleash your creativity with ChartExpo’s customization options. You can spice up your visuals with colors, fonts, and styles that reflect your flair.
- And the best part? It won’t break the bank. You get a full-on data visualization extravaganza with a free 7-day trial and a $10 monthly plan.
How to Install ChartExpo in Excel?
- Open your Excel application.
- Open the worksheet and click the “ Insert ” menu.
- You’ll see the “ My Apps ” option.
- In the office Add-ins window, click “ Store ” and search for ChartExpo on my Apps Store.
- Click the “ Add ” button to install ChartExpo in your Excel.
ChartExpo charts are available both in Google Sheets and Microsoft Excel. Please use the following CTA’s to install the tool of your choice and create beautiful visualizations in a few clicks in your favorite tool.
Assume the responses to your survey are as shown in the table below.
This table contains sample data. Expect many responses and questions in real life.
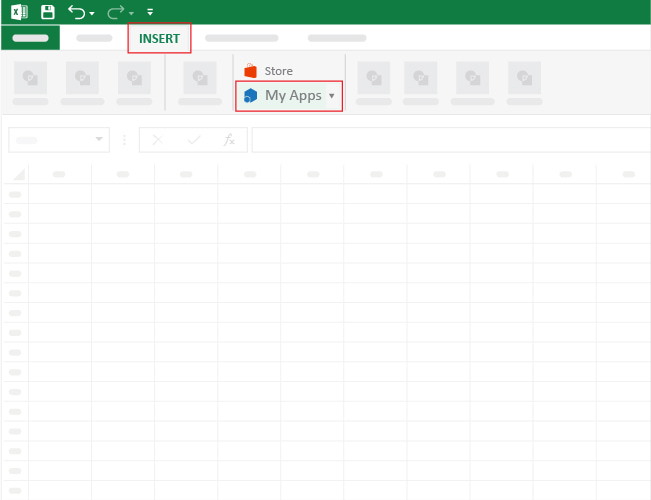
- To get started with ChartExpo, install ChartExpo in Excel .
- Now Click on My Apps from the INSERT menu.
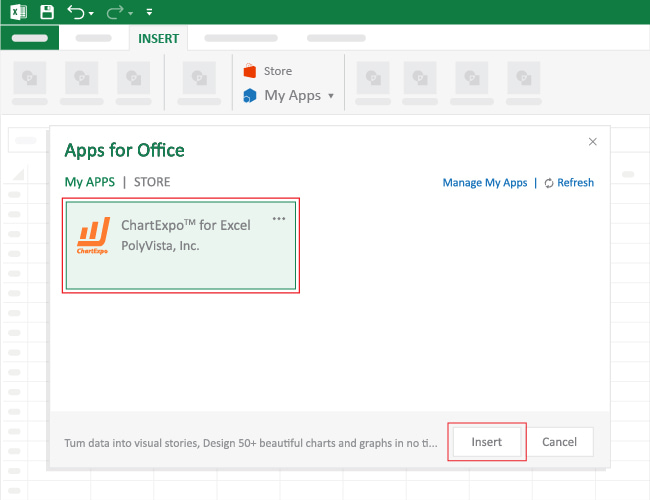
- Choose ChartExpo from My Apps , then click Insert.
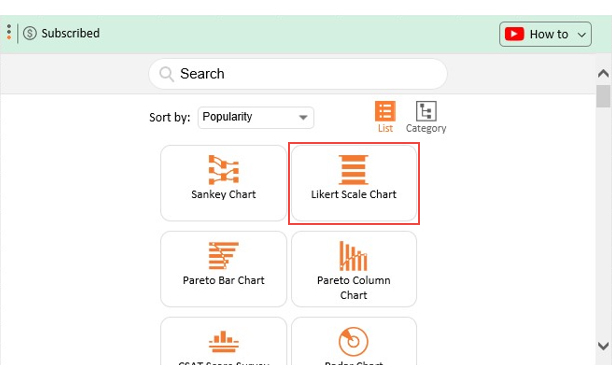
- Once it loads, choose the “ Likert Scale Chart ” from the charts list.
- Click the “ Create Chart From Selection ” button after selecting the data from the sheet, as shown.
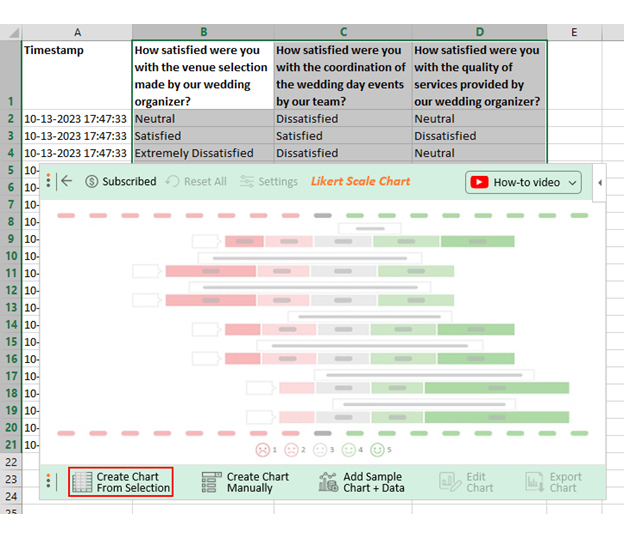
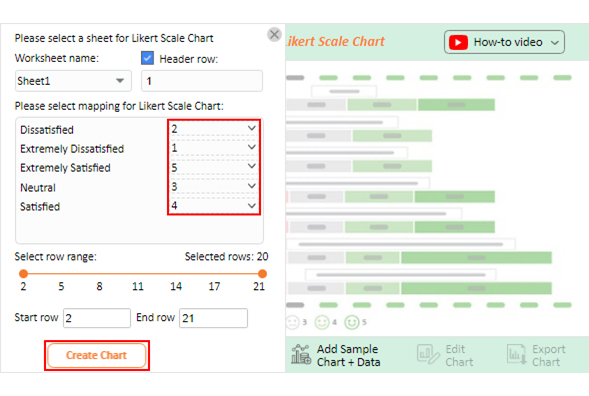
- When you click the “ Create Chart From Selection ” button, you have to map responses with numbers manually. The Likert scale has this arrangement:
- Extremely Dissatisfied = 1
- Dissatisfied = 2
- Neutral = 3
- Satisfied = 4
- Extremely Satisfied = 5
- Once all is set, click the “ Create Chart ” button.
- ChartExpo will generate the visualization below for you.
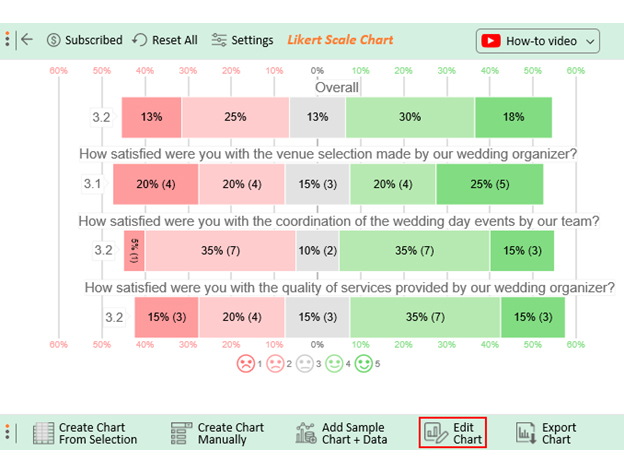
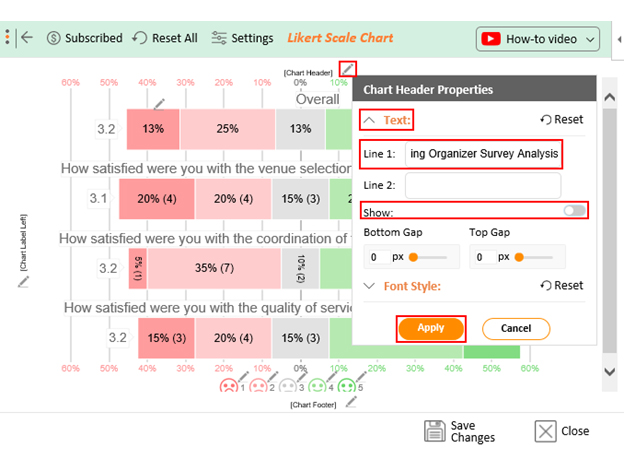
- If you want to have the chart’s title, click Edit Chart , as shown in the above image.
- Click the pencil icon next to the Chart Header to change the title.
- It will open the properties dialog. Under the Text section, you can add a heading in Line 1 and enable Show .
- Give the appropriate title of your chart and click the Apply button.
- Let’s say you want to add text responses instead of numbers against every emoji.
- Click the pencil icon next to the respective emoji. Expand the “ Label ” properties and write the required text. Then click the “ Apply All ” button.
- Click the “ Save Changes ” button to persist the changes.
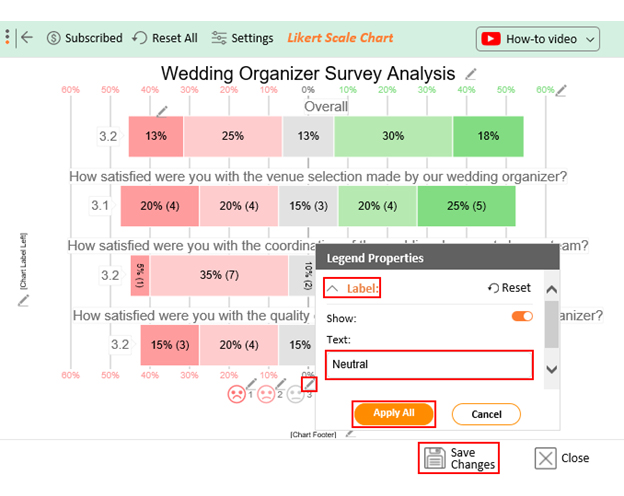
- Your final chart will appear below.
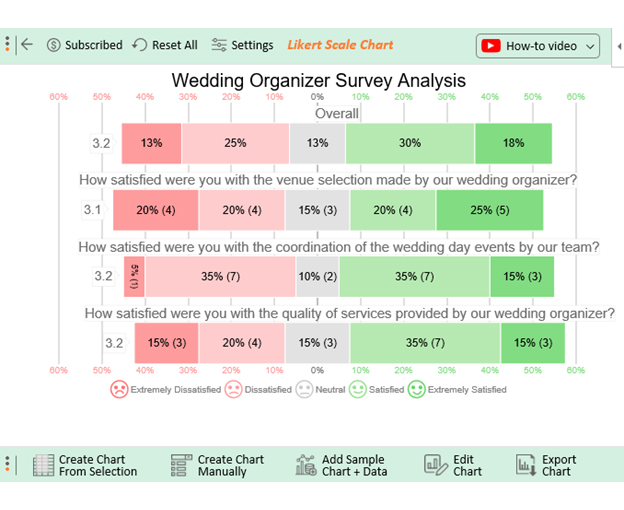
- 45% of customers expressed satisfaction with the venue selection, 40% were dissatisfied, and 15% remained neutral.
- Regarding the coordination of the wedding day events, 50% were satisfied, while 40% expressed dissatisfaction.
- Regarding the quality of services provided by the wedding organizer, 50% were satisfied, and 35% were dissatisfied.
- 48% of customers expressed satisfaction with the wedding organizer, with 18% extremely satisfied.
- 38% expressed dissatisfaction, with 13% extremely dissatisfied.
- 13% remained neutral.
What are the types of data presentation methods?
Data presentation methods include;
- Tables for structured data.
- Charts and graphs for visual representation.
- Infographics for concise visuals.
- Dashboards for interactive data.
- Heatmaps for data concentration
What is the difference between data analysis and data presentation?
Data analysis involves examining and interpreting data to extract insights and patterns. Data presentation focuses on visualizing those findings to make information understandable and engaging.
Understanding the different methods of data presentation is essential for effective communication in our data-driven world. Tables, charts, infographics, dashboards, and other techniques enable us to transform complex data into clear, engaging visual stories.
Each method has unique strengths, making it suitable for specific data types and audience preferences. For instance, tables enhance simplicity, charts and graphs promote clarity, and infographics improve visual appeal. Either way, each method enhances comprehension and enables informed decision-making.
Moreover, interactivity facilitated by dashboards and heatmaps empowers you to explore data independently. This fosters a culture of data-driven exploration and analysis.
Ultimately, data presentation goes beyond mere aesthetics; its core purpose is to infuse data with meaning. When we tell stories with data, we can inspire change, improve understanding, and unlock the power of information.
Choose the right method, practice effective design, and know your audience. These are the keys to presenting data that informs, engages, and makes a lasting impact.
How much did you enjoy this article?

Related articles
How to Change the Chart Style in Excel?
Learn essential strategies for how to change the chart style in Excel & revolutionize your charts. Elevate insights and craft appealing visuals with your audience.
What is a Good Price-to-Earnings Ratio? Grasp Insights
Navigate the complexities of determining what is a good price-to-earnings ratio with insightful analysis tailored to your investment objectives and risk tolerance.
What is Net Working Capital: A Visual Guide
Stop wondering "What is Net Working Capital?" and start analyzing it! Our guide empowers you to assess a company's financial health through NWC analysis.

How to Calculate Return on Investment Capital?
Uncover the keys to financial success with our guide on How to Calculate Return on Investment Capital. Explore the ROIC formula, & evaluate its applications.
How to Edit a Chart in Excel? A Step-by-Step Guide
Learn essential techniques for Excel chart editing in our guide. Discover step-by-step instructions to master how to edit a chart in Excel with practical guidance.
Data Topics
- Data Architecture
- Data Literacy
- Data Science
- Data Strategy
- Data Modeling
- Governance & Quality
- Education Resources For Use & Management of Data
Types of Data Visualization and Their Uses
In today’s data-first business environment, the ability to convey complex information in an understandable and visually appealing manner is paramount. Different types of data visualization help transform analyzed data into comprehensible visuals for all types of audiences, from novices to experts. In fact, research has shown that the human brain can process images in as little as […]

In today’s data-first business environment, the ability to convey complex information in an understandable and visually appealing manner is paramount. Different types of data visualization help transform analyzed data into comprehensible visuals for all types of audiences, from novices to experts. In fact, research has shown that the human brain can process images in as little as 13 milliseconds.

In essence, data visualization is indispensable for distilling complex information into digestible formats that support both quick comprehension and informed decision-making. Its role in analysis and reporting underscores its value as a critical tool in any data-centric activity.
Types of Data Visualization: Charts, Graphs, Infographics, and Dashboards
The diverse landscape of data visualization begins with simple charts and graphs but moves beyond infographics and animated dashboards. Charts , in their various forms – be it bar charts for comparing quantities across categories or line charts depicting trends over time – serve as efficient tools for data representation. Graphs extend this utility further: Scatter plots reveal correlations between variables, while pie graphs offer a visual slice of proportional relationships within a dataset.
Venturing beyond these traditional forms, infographics emerge as powerful storytelling tools, combining graphical elements with narrative to enlighten audiences on complex subjects. Unlike standard charts or graphs that focus on numerical data representation, infographics can incorporate timelines, flowcharts, and comparative images to weave a more comprehensive story around the data.
A dashboard, when effectively designed , serves as an instrument for synthesizing complex data into accessible and actionable insights. Dashboards very often encapsulate a wide array of information, from real-time data streams to historical trends, and present it through an amalgamation of charts, graphs, and indicators.
A dashboard’s efficacy lies in its ability to tailor the visual narrative to the specific needs and objectives of its audience. By selectively filtering and highlighting critical data points, dashboards facilitate a focused analysis that aligns with organizational goals or individual projects.
The best type of data visualization to use depends on the data at hand and the purpose of its presentation. Whether aiming to highlight trends, compare values, or elucidate complex relationships, selecting the appropriate visual form is crucial for effectively communicating insights buried within datasets. Through thoughtful design and strategic selection among these varied types of visualizations, one can illuminate patterns and narratives hidden within numbers – transforming raw data into meaningful knowledge.
Other Types of Data Visualization: Maps and Geospatial Visualization
Utilizing maps and geospatial visualization serves as a powerful method for uncovering and displaying insightful patterns hidden within complex datasets. At the intersection of geography and data analysis, this technique transforms numerical and categorical data into visual formats that are easily interpretable, such as heat maps, choropleths, or symbolic representations on geographical layouts. This approach enables viewers to quickly grasp spatial relationships, distributions, trends, and anomalies that might be overlooked in traditional tabular data presentations.
For instance, in public health, geospatial visualizations can highlight regions with high incidences of certain diseases, guiding targeted interventions. In environmental studies, they can illustrate changes in land use or the impact of climate change across different areas over time. By embedding data within its geographical context, these visualizations foster a deeper understanding of how location influences the phenomena being studied.
Furthermore, the advent of interactive web-based mapping tools has enhanced the accessibility and utility of geospatial visualizations. Users can now engage with the data more directly – zooming in on areas of interest, filtering layers to refine their focus, or even contributing their own data points – making these visualizations an indispensable tool for researchers and decision-makers alike who are looking to extract meaningful patterns from spatially oriented datasets.
Additionally, scatter plots excel in revealing correlations between two variables. By plotting data points on a two-dimensional graph, they allow analysts to discern potential relationships or trends that might not be evident from raw data alone. This makes scatter plots a staple in statistical analysis and scientific research where establishing cause-and-effect relationships is crucial.
Bubble charts take the concept of scatter plots further by introducing a third dimension – typically represented by the size of the bubbles – thereby enabling an even more layered understanding of data relationships. Whether it’s comparing economic indicators across countries or visualizing population demographics, bubble charts provide a dynamic means to encapsulate complex interrelations within datasets, making them an indispensable tool for advanced data visualization.
Innovative Data Visualization Techniques: Word Clouds and Network Diagrams
Some innovative techniques have emerged in the realm of data visualization that not only simplify complex datasets but also enhance engagement and understanding. Among these, word clouds and network diagrams stand out for their unique approaches to presenting information.
Word clouds represent textual data with size variations to emphasize the frequency or importance of words within a dataset. This technique transforms qualitative data into a visually appealing format, making it easier to identify dominant themes or sentiments in large text segments.
Network diagrams introduce an entirely different dimension by illustrating relationships between entities. Through nodes and connecting lines, they depict how individual components interact within a system – be it social networks, organizational structures, or technological infrastructures. This visualization method excels in uncovering patterns of connectivity and influence that might remain hidden in traditional charts or tables.
Purpose and Uses of Each Type of Data Visualization
The various types of data visualization – from bar graphs and line charts to heat maps and scatter plots – cater to different analytical needs and objectives. Each type is meticulously designed to highlight specific aspects of the data, making it imperative to understand their unique applications and strengths. This foundational knowledge empowers users to select the most effective visualization technique for their specific dataset and analysis goals.
Line Charts: Tracking Changes Over Time Line charts are quintessential in the realm of data visualization for their simplicity and effectiveness in showcasing trends and changes over time. By connecting individual data points with straight lines, they offer a clear depiction of how values rise and fall across a chronological axis. This makes line charts particularly useful for tracking the evolution of quantities – be it the fluctuating stock prices in financial markets, the ebb and flow of temperatures across seasons, or the gradual growth of a company’s revenue over successive quarters. The visual narrative that line charts provide helps analysts, researchers, and casual observers alike to discern patterns within the data, such as cycles or anomalies.
Bar Charts and Histograms: Comparing Categories and Distributions Bar charts are highly suitable for representing comparative data. By plotting each category of comparison with a bar whose height or length reflects its value, bar charts make it easy to visualize relative values at a glance.
Histograms show the distribution of groups of data in a dataset. This is particularly useful for understanding the shape of data distributions – whether they are skewed, normal, or have any outliers. Histograms provide insight into the underlying structure of data, revealing patterns that might not be apparent.
Pie Charts: Visualizing Proportional Data Pie charts serve as a compelling visualization tool for representing proportional data, offering a clear snapshot of how different parts contribute to a whole. By dividing a circle into slices whose sizes are proportional to their quantity, pie charts provide an immediate visual comparison among various categories. This makes them especially useful in illustrating market shares, budget allocations, or the distribution of population segments.
The simplicity of pie charts allows for quick interpretation, making it easier for viewers to grasp complex data at a glance. However, when dealing with numerous categories or when precise comparisons are necessary, the effectiveness of pie charts may diminish. Despite this limitation, their ability to succinctly convey the relative significance of parts within a whole ensures their enduring popularity in data visualization across diverse fields.
Scatter Plots: Identifying Relationship and Correlations Between Variables Scatter plots are primarily used for spotting relationships and correlations between variables. These plots show data points related to one variable on one axis and a different variable on another axis. This visual arrangement allows viewers to determine patterns or trends that might indicate a correlation or relationship between the variables in question.
For instance, if an increase in one variable consistently causes an increase (or decrease) in the other, this suggests a potential correlation. Scatter plots are particularly valuable for preliminary analyses where researchers seek to identify variables that warrant further investigation. Their straightforward yet powerful nature makes them indispensable for exploring complex datasets, providing clear insights into the dynamics between different factors at play.
Heat Maps: Representing Complex Data Matrices through Color Gradients Heat maps serve as a powerful tool in representing complex data matrices, using color gradients to convey information that might otherwise be challenging to digest. At their core, heat maps transform numerical values into a visual spectrum of colors, enabling viewers to quickly grasp patterns, outliers, and trends within the data. This method becomes more effective when the complex relationships between multiple variables need to be reviewed.
For instance, in fields like genomics or meteorology, heat maps can illustrate gene expression levels or temperature fluctuations across different regions and times. By assigning warmer colors to higher values and cooler colors to lower ones, heat maps facilitate an intuitive understanding of data distribution and concentration areas, making them indispensable for exploratory data analysis and decision-making processes.
Dashboards and Infographics: Integrating Multiple Data Visualizations Dashboards and infographics represent a synergistic approach in data visualization, blending various graphical elements to offer a holistic view of complex datasets. Dashboards, with their capacity to integrate multiple data visualizations such as charts, graphs, and maps onto a single interface, are instrumental in monitoring real-time data and tracking performance metrics across different parameters. They serve as an essential tool for decision-makers who require a comprehensive overview to identify trends and anomalies swiftly.
Infographics, on the other hand, transform intricate data sets into engaging, easily digestible visual stories. By illustrating strong narratives with striking visuals and solid statistics, infographics make complex information easily digestible to any type of audience.
Together, dashboards and infographics convey multifaceted data insights in an integrated manner – facilitating informed decisions through comprehensive yet clear snapshots of data landscapes.
16 Best Types of Charts and Graphs for Data Visualization [+ Guide]
Published: June 08, 2023
There are more type of charts and graphs than ever before because there's more data. In fact, the volume of data in 2025 will be almost double the data we create, capture, copy, and consume today.

This makes data visualization essential for businesses. Different types of graphs and charts can help you:
- Motivate your team to take action.
- Impress stakeholders with goal progress.
- Show your audience what you value as a business.
Data visualization builds trust and can organize diverse teams around new initiatives. Let's talk about the types of graphs and charts that you can use to grow your business.
.png)
Free Excel Graph Templates
Tired of struggling with spreadsheets? These free Microsoft Excel Graph Generator Templates can help.
- Simple, customizable graph designs.
- Data visualization tips & instructions.
- Templates for two, three, four, and five-variable graph templates.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Different Types of Graphs for Data Visualization
1. bar graph.
A bar graph should be used to avoid clutter when one data label is long or if you have more than 10 items to compare.
Best Use Cases for These Types of Graphs
Bar graphs can help you compare data between different groups or to track changes over time. Bar graphs are most useful when there are big changes or to show how one group compares against other groups.
The example above compares the number of customers by business role. It makes it easy to see that there is more than twice the number of customers per role for individual contributors than any other group.
A bar graph also makes it easy to see which group of data is highest or most common.
For example, at the start of the pandemic, online businesses saw a big jump in traffic. So, if you want to look at monthly traffic for an online business, a bar graph would make it easy to see that jump.
Other use cases for bar graphs include:
- Product comparisons.
- Product usage.
- Category comparisons.
- Marketing traffic by month or year.
- Marketing conversions.
Design Best Practices for Bar Graphs
- Use consistent colors throughout the chart, selecting accent colors to highlight meaningful data points or changes over time.
- Use horizontal labels to improve readability.
- Start the y-axis at 0 to appropriately reflect the values in your graph.
2. Line Graph
A line graph reveals trends or progress over time, and you can use it to show many different categories of data. You should use it when you chart a continuous data set.
Line graphs help users track changes over short and long periods. Because of this, these types of graphs are good for seeing small changes.
Line graphs can help you compare changes for more than one group over the same period. They're also helpful for measuring how different groups relate to each other.
A business might use this graph to compare sales rates for different products or services over time.
These charts are also helpful for measuring service channel performance. For example, a line graph that tracks how many chats or emails your team responds to per month.
Design Best Practices for Line Graphs
- Use solid lines only.
- Don't plot more than four lines to avoid visual distractions.
- Use the right height so the lines take up roughly 2/3 of the y-axis' height.
3. Bullet Graph
A bullet graph reveals progress towards a goal, compares this to another measure, and provides context in the form of a rating or performance.
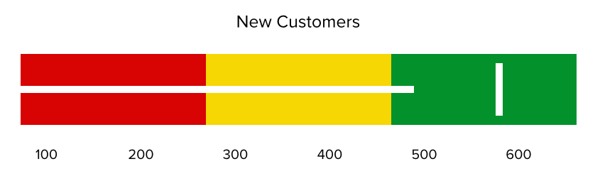
In the example above, the bullet graph shows the number of new customers against a set customer goal. Bullet graphs are great for comparing performance against goals like this.
These types of graphs can also help teams assess possible roadblocks because you can analyze data in a tight visual display.
For example, you could create a series of bullet graphs measuring performance against benchmarks or use a single bullet graph to visualize these KPIs against their goals:
- Customer satisfaction.
- Average order size.
- New customers.
Seeing this data at a glance and alongside each other can help teams make quick decisions.
Bullet graphs are one of the best ways to display year-over-year data analysis. You can also use bullet graphs to visualize:
- Customer satisfaction scores.
- Customer shopping habits.
- Social media usage by platform.
Design Best Practices for Bullet Graphs
- Use contrasting colors to highlight how the data is progressing.
- Use one color in different shades to gauge progress.
Different Types of Charts for Data Visualization
To better understand these chart types and how you can use them, here's an overview of each:
1. Column Chart
Use a column chart to show a comparison among different items or to show a comparison of items over time. You could use this format to see the revenue per landing page or customers by close date.
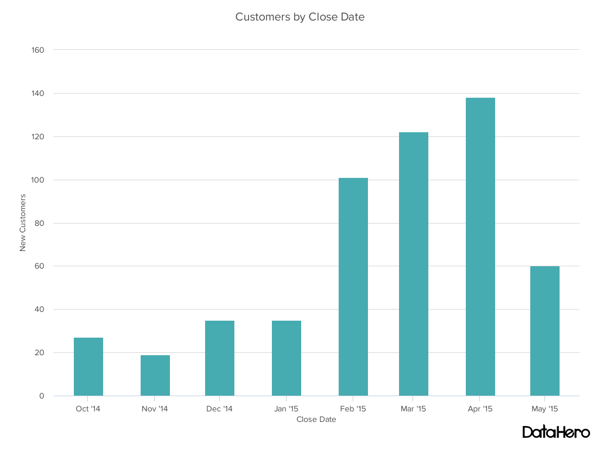
Best Use Cases for This Type of Chart
You can use both column charts and bar graphs to display changes in data, but column charts are best for negative data. The main difference, of course, is that column charts show information vertically while bar graphs show data horizontally.
For example, warehouses often track the number of accidents on the shop floor. When the number of incidents falls below the monthly average, a column chart can make that change easier to see in a presentation.
In the example above, this column chart measures the number of customers by close date. Column charts make it easy to see data changes over a period of time. This means that they have many use cases, including:
- Customer survey data, like showing how many customers prefer a specific product or how much a customer uses a product each day.
- Sales volume, like showing which services are the top sellers each month or the number of sales per week.
- Profit and loss, showing where business investments are growing or falling.
Design Best Practices for Column Charts
2. dual-axis chart.
A dual-axis chart allows you to plot data using two y-axes and a shared x-axis. It has three data sets. One is a continuous data set, and the other is better suited to grouping by category. Use this chart to visualize a correlation or the lack thereof between these three data sets.
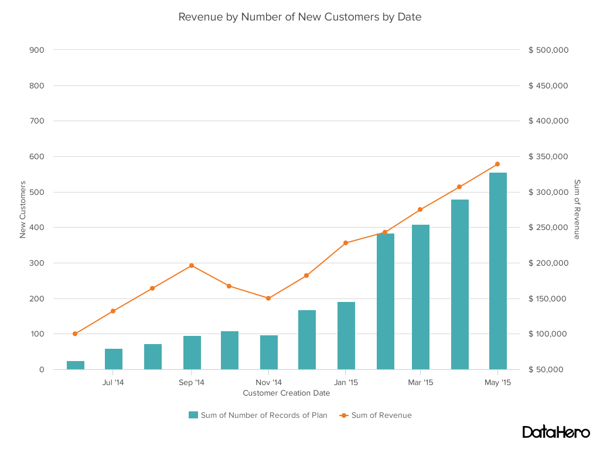
A dual-axis chart makes it easy to see relationships between different data sets. They can also help with comparing trends.
For example, the chart above shows how many new customers this company brings in each month. It also shows how much revenue those customers are bringing the company.
This makes it simple to see the connection between the number of customers and increased revenue.
You can use dual-axis charts to compare:
- Price and volume of your products.
- Revenue and units sold.
- Sales and profit margin.
- Individual sales performance.
Design Best Practices for Dual-Axis Charts
- Use the y-axis on the left side for the primary variable because brains naturally look left first.
- Use different graphing styles to illustrate the two data sets, as illustrated above.
- Choose contrasting colors for the two data sets.
3. Area Chart
An area chart is basically a line chart, but the space between the x-axis and the line is filled with a color or pattern. It is useful for showing part-to-whole relations, like showing individual sales reps’ contributions to total sales for a year. It helps you analyze both overall and individual trend information.
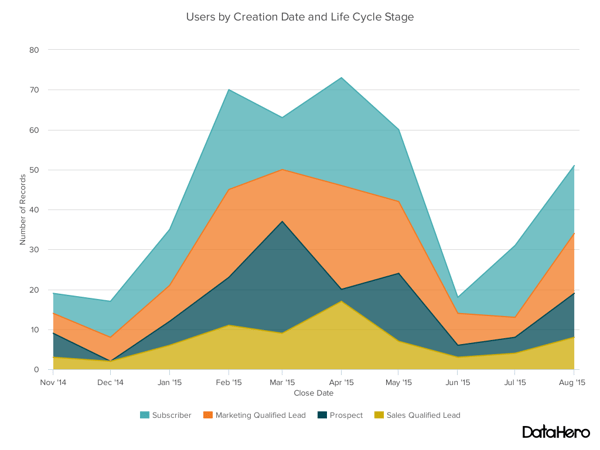
Best Use Cases for These Types of Charts
Area charts help show changes over time. They work best for big differences between data sets and help visualize big trends.
For example, the chart above shows users by creation date and life cycle stage.
A line chart could show more subscribers than marketing qualified leads. But this area chart emphasizes how much bigger the number of subscribers is than any other group.
These charts make the size of a group and how groups relate to each other more visually important than data changes over time.
Area graphs can help your business to:
- Visualize which product categories or products within a category are most popular.
- Show key performance indicator (KPI) goals vs. outcomes.
- Spot and analyze industry trends.
Design Best Practices for Area Charts
- Use transparent colors so information isn't obscured in the background.
- Don't display more than four categories to avoid clutter.
- Organize highly variable data at the top of the chart to make it easy to read.
4. Stacked Bar Chart
Use this chart to compare many different items and show the composition of each item you’re comparing.
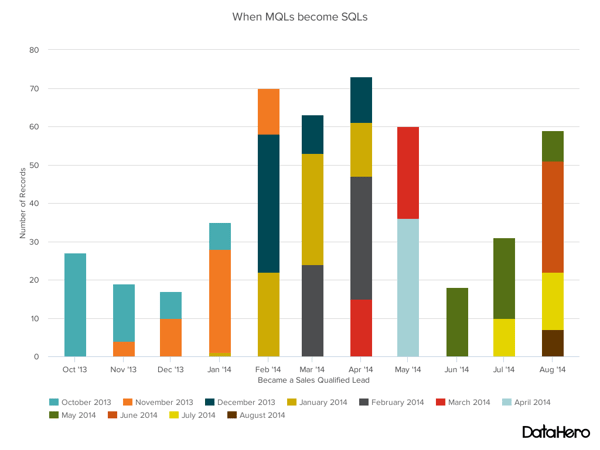
These graphs are helpful when a group starts in one column and moves to another over time.
For example, the difference between a marketing qualified lead (MQL) and a sales qualified lead (SQL) is sometimes hard to see. The chart above helps stakeholders see these two lead types from a single point of view — when a lead changes from MQL to SQL.
Stacked bar charts are excellent for marketing. They make it simple to add a lot of data on a single chart or to make a point with limited space.
These graphs can show multiple takeaways, so they're also super for quarterly meetings when you have a lot to say but not a lot of time to say it.
Stacked bar charts are also a smart option for planning or strategy meetings. This is because these charts can show a lot of information at once, but they also make it easy to focus on one stack at a time or move data as needed.
You can also use these charts to:
- Show the frequency of survey responses.
- Identify outliers in historical data.
- Compare a part of a strategy to its performance as a whole.
Design Best Practices for Stacked Bar Graphs
- Best used to illustrate part-to-whole relationships.
- Use contrasting colors for greater clarity.
- Make the chart scale large enough to view group sizes in relation to one another.
5. Mekko Chart
Also known as a Marimekko chart, this type of graph can compare values, measure each one's composition, and show data distribution across each one.
It's similar to a stacked bar, except the Mekko's x-axis can capture another dimension of your values — instead of time progression, like column charts often do. In the graphic below, the x-axis compares the cities to one another.
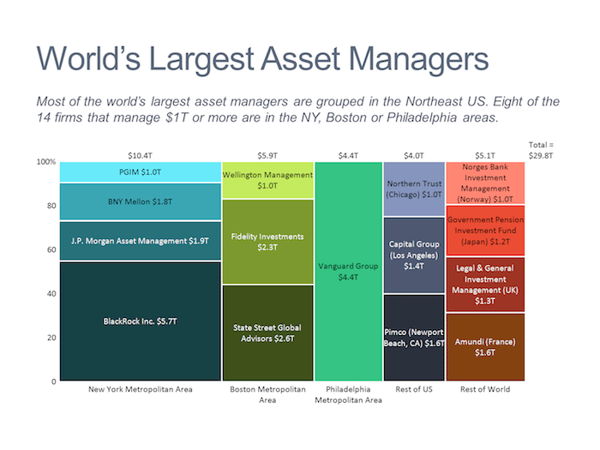
Image Source
You can use a Mekko chart to show growth, market share, or competitor analysis.
For example, the Mekko chart above shows the market share of asset managers grouped by location and the value of their assets. This chart clarifies which firms manage the most assets in different areas.
It's also easy to see which asset managers are the largest and how they relate to each other.
Mekko charts can seem more complex than other types of charts and graphs, so it's best to use these in situations where you want to emphasize scale or differences between groups of data.
Other use cases for Mekko charts include:
- Detailed profit and loss statements.
- Revenue by brand and region.
- Product profitability.
- Share of voice by industry or niche.
Design Best Practices for Mekko Charts
- Vary your bar heights if the portion size is an important point of comparison.
- Don't include too many composite values within each bar. Consider reevaluating your presentation if you have a lot of data.
- Order your bars from left to right in such a way that exposes a relevant trend or message.
6. Pie Chart
A pie chart shows a static number and how categories represent part of a whole — the composition of something. A pie chart represents numbers in percentages, and the total sum of all segments needs to equal 100%.
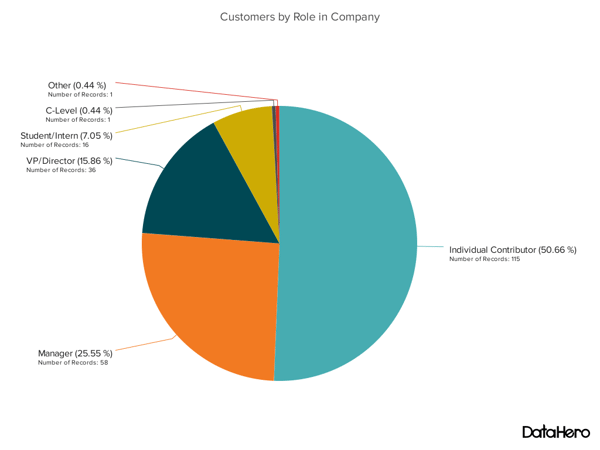
The image above shows another example of customers by role in the company.
The bar graph example shows you that there are more individual contributors than any other role. But this pie chart makes it clear that they make up over 50% of customer roles.
Pie charts make it easy to see a section in relation to the whole, so they are good for showing:
- Customer personas in relation to all customers.
- Revenue from your most popular products or product types in relation to all product sales.
- Percent of total profit from different store locations.
Design Best Practices for Pie Charts
- Don't illustrate too many categories to ensure differentiation between slices.
- Ensure that the slice values add up to 100%.
- Order slices according to their size.
7. Scatter Plot Chart
A scatter plot or scattergram chart will show the relationship between two different variables or reveal distribution trends.
Use this chart when there are many different data points, and you want to highlight similarities in the data set. This is useful when looking for outliers or understanding your data's distribution.
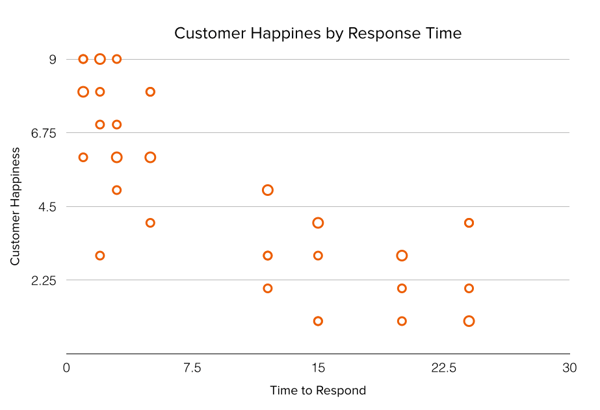
Scatter plots are helpful in situations where you have too much data to see a pattern quickly. They are best when you use them to show relationships between two large data sets.
In the example above, this chart shows how customer happiness relates to the time it takes for them to get a response.
This type of graph makes it easy to compare two data sets. Use cases might include:
- Employment and manufacturing output.
- Retail sales and inflation.
- Visitor numbers and outdoor temperature.
- Sales growth and tax laws.
Try to choose two data sets that already have a positive or negative relationship. That said, this type of graph can also make it easier to see data that falls outside of normal patterns.
Design Best Practices for Scatter Plots
- Include more variables, like different sizes, to incorporate more data.
- Start the y-axis at 0 to represent data accurately.
- If you use trend lines, only use a maximum of two to make your plot easy to understand.
8. Bubble Chart
A bubble chart is similar to a scatter plot in that it can show distribution or relationship. There is a third data set shown by the size of the bubble or circle.
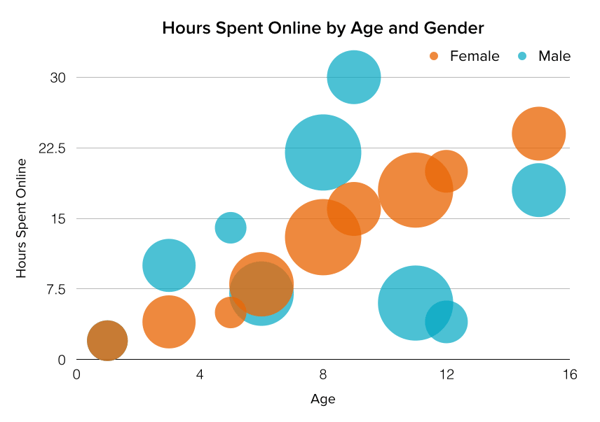
In the example above, the number of hours spent online isn't just compared to the user's age, as it would be on a scatter plot chart.
Instead, you can also see how the gender of the user impacts time spent online.
This makes bubble charts useful for seeing the rise or fall of trends over time. It also lets you add another option when you're trying to understand relationships between different segments or categories.
For example, if you want to launch a new product, this chart could help you quickly see your new product's cost, risk, and value. This can help you focus your energies on a low-risk new product with a high potential return.
You can also use bubble charts for:
- Top sales by month and location.
- Customer satisfaction surveys.
- Store performance tracking.
- Marketing campaign reviews.
Design Best Practices for Bubble Charts
- Scale bubbles according to area, not diameter.
- Make sure labels are clear and visible.
- Use circular shapes only.
9. Waterfall Chart
Use a waterfall chart to show how an initial value changes with intermediate values — either positive or negative — and results in a final value.
Use this chart to reveal the composition of a number. An example of this would be to showcase how different departments influence overall company revenue and lead to a specific profit number.
The most common use case for a funnel chart is the marketing or sales funnel. But there are many other ways to use this versatile chart.
If you have at least four stages of sequential data, this chart can help you easily see what inputs or outputs impact the final results.
For example, a funnel chart can help you see how to improve your buyer journey or shopping cart workflow. This is because it can help pinpoint major drop-off points.
Other stellar options for these types of charts include:
- Deal pipelines.
- Conversion and retention analysis.
- Bottlenecks in manufacturing and other multi-step processes.
- Marketing campaign performance.
- Website conversion tracking.
Design Best Practices for Funnel Charts
- Scale the size of each section to accurately reflect the size of the data set.
- Use contrasting colors or one color in graduated hues, from darkest to lightest, as the size of the funnel decreases.
11. Heat Map
A heat map shows the relationship between two items and provides rating information, such as high to low or poor to excellent. This chart displays the rating information using varying colors or saturation.
Best Use Cases for Heat Maps
In the example above, the darker the shade of green shows where the majority of people agree.
With enough data, heat maps can make a viewpoint that might seem subjective more concrete. This makes it easier for a business to act on customer sentiment.
There are many uses for these types of charts. In fact, many tech companies use heat map tools to gauge user experience for apps, online tools, and website design .
Another common use for heat map graphs is location assessment. If you're trying to find the right location for your new store, these maps can give you an idea of what the area is like in ways that a visit can't communicate.
Heat maps can also help with spotting patterns, so they're good for analyzing trends that change quickly, like ad conversions. They can also help with:
- Competitor research.
- Customer sentiment.
- Sales outreach.
- Campaign impact.
- Customer demographics.
Design Best Practices for Heat Map
- Use a basic and clear map outline to avoid distracting from the data.
- Use a single color in varying shades to show changes in data.
- Avoid using multiple patterns.
12. Gantt Chart
The Gantt chart is a horizontal chart that dates back to 1917. This chart maps the different tasks completed over a period of time.
Gantt charting is one of the most essential tools for project managers. It brings all the completed and uncompleted tasks into one place and tracks the progress of each.
While the left side of the chart displays all the tasks, the right side shows the progress and schedule for each of these tasks.
This chart type allows you to:
- Break projects into tasks.
- Track the start and end of the tasks.
- Set important events, meetings, and announcements.
- Assign tasks to the team and individuals.
Download the Excel templates mentioned in the video here.
5 Questions to Ask When Deciding Which Type of Chart to Use
1. do you want to compare values.
Charts and graphs are perfect for comparing one or many value sets, and they can easily show the low and high values in the data sets. To create a comparison chart, use these types of graphs:
- Scatter plot
2. Do you want to show the composition of something?
Use this type of chart to show how individual parts make up the whole of something, like the device type used for mobile visitors to your website or total sales broken down by sales rep.
To show composition, use these charts:
- Stacked bar
3. Do you want to understand the distribution of your data?
Distribution charts help you to understand outliers, the normal tendency, and the range of information in your values.
Use these charts to show distribution:
4. Are you interested in analyzing trends in your data set?
If you want more information about how a data set performed during a specific time, there are specific chart types that do extremely well.
You should choose one of the following:
- Dual-axis line
5. Do you want to better understand the relationship between value sets?
Relationship charts can show how one variable relates to one or many different variables. You could use this to show how something positively affects, has no effect, or negatively affects another variable.
When trying to establish the relationship between things, use these charts:
Featured Resource: The Marketer's Guide to Data Visualization

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

9 Great Ways to Use Data in Content Creation

Data Visualization: Tips and Examples to Inspire You

17 Data Visualization Resources You Should Bookmark
![common types of data presentation An Introduction to Data Visualization: How to Create Compelling Charts & Graphs [Ebook]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/data-visualization-guide.jpg)
An Introduction to Data Visualization: How to Create Compelling Charts & Graphs [Ebook]

Why Data Is The Real MVP: 7 Examples of Data-Driven Storytelling by Leading Brands
![common types of data presentation How to Create an Infographic Using Poll & Survey Data [Infographic]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/00-Blog_Thinkstock_Images/Survey_Data_Infographic.jpg)
How to Create an Infographic Using Poll & Survey Data [Infographic]
Data Storytelling 101: Helpful Tools for Gathering Ideas, Designing Content & More

What Great Data Visualization Looks Like: 12 Complex Concepts Made Easy
Stats Shouldn't Stand Alone: Why You Need Data Visualization to Teach and Convince

How to Harness the Power of Data to Elevate Your Content
Tired of struggling with spreadsheets? These free Microsoft Excel Graph Generator Templates can help
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Beginner Guides 8 Types of Presentations You Should Know [+Examples & Tips]
8 Types of Presentations You Should Know [+Examples & Tips]
Written by: Krystle Wong Aug 11, 2023

From persuasive pitches that influence opinions to instructional demonstrations that teach skills, the different types of presentations serve a unique purpose, tailored to specific objectives and audiences.
Presentations that are tailored to its objectives and audiences are more engaging and memorable. They capture attention, maintain interest and leave a lasting impression.
Don’t worry if you’re no designer — Whether you need data-driven visuals, persuasive graphics or engaging design elements, Venngage can empower you to craft presentations that stand out and effectively convey your message.
Venngage’s intuitive drag-and-drop interface, extensive presentation template library and customizable design options make it a valuable tool for creating slides that align with your specific goals and target audience.
Click to jump ahead:
8 Different types of presentations every presenter must know
How do i choose the right type of presentation for my topic or audience, types of presentation faq, 5 steps to create a presentation with venngage .

When it comes to presentations, versatility is the name of the game. Having a variety of presentation styles up your sleeve can make a world of difference in keeping your audience engaged. Here are 8 essential presentation types that every presenter should be well-acquainted with:
1. Informative presentation
Ever sat through a presentation that left you feeling enlightened? That’s the power of an informative presentation.
This presentation style is all about sharing knowledge and shedding light on a particular topic. Whether you’re diving into the depths of quantum physics or explaining the intricacies of the latest social media trends, informative presentations aim to increase the audience’s understanding.
When delivering an informative presentation, simplify complex topics with clear visuals and relatable examples. Organize your content logically, starting with the basics and gradually delving deeper and always remember to keep jargon to a minimum and encourage questions for clarity.
Academic presentations and research presentations are great examples of informative presentations. An effective academic presentation involves having clear structure, credible evidence, engaging delivery and supporting visuals. Provide context to emphasize the topic’s significance, practice to perfect timing, and be ready to address anticipated questions.
2. Persuasive presentation
If you’ve ever been swayed by a passionate speaker armed with compelling arguments, you’ve experienced a persuasive presentation .
This type of presentation is like a verbal tug-of-war, aiming to convince the audience to see things from a specific perspective. Expect to encounter solid evidence, logical reasoning and a dash of emotional appeal.
With persuasive presentations, it’s important to know your audience inside out and tailor your message to their interests and concerns. Craft a compelling narrative with a strong opening, a solid argument and a memorable closing. Additionally, use visuals strategically to enhance your points.
Examples of persuasive presentations include presentations for environmental conservations, policy change, social issues and more. Here are some engaging presentation templates you can use to get started with:

3. Demonstration or how-to presentation
A Demonstration or How-To Presentation is a type of presentation where the speaker showcases a process, technique, or procedure step by step, providing the audience with clear instructions on how to replicate the demonstrated action.
A demonstrative presentation is particularly useful when teaching practical skills or showing how something is done in a hands-on manner.
These presentations are commonly used in various settings, including educational workshops, training sessions, cooking classes, DIY tutorials, technology demonstrations and more. Designing creative slides for your how-to presentations can heighten engagement and foster better information retention.
Speakers can also consider breaking down the process into manageable steps, using visual aids, props and sometimes even live demonstrations to illustrate each step. The key is to provide clear and concise instructions, engage the audience with interactive elements and address any questions that may arise during the presentation.

4. Training or instructional presentation
Training presentations are geared towards imparting practical skills, procedures or concepts — think of this as the more focused cousin of the demonstration presentation.
Whether you’re teaching a group of new employees the ins and outs of a software or enlightening budding chefs on the art of soufflé-making, training presentations are all about turning novices into experts.
To maximize the impact of your training or instructional presentation, break down complex concepts into digestible segments. Consider using real-life examples to illustrate each point and create a connection.
You can also create an interactive presentation by incorporating elements like quizzes or group activities to reinforce understanding.
5. Sales presentation
Sales presentations are one of the many types of business presentations and the bread and butter of businesses looking to woo potential clients or customers. With a sprinkle of charm and a dash of persuasion, these presentations showcase products, services or ideas with one end goal in mind: sealing the deal.
A successful sales presentation often has key characteristics such as a clear value proposition, strong storytelling, confidence and a compelling call to action. Hence, when presenting to your clients or stakeholders, focus on benefits rather than just features.
Anticipate and address potential objections before they arise and use storytelling to showcase how your offering solves a specific problem for your audience. Utilizing visual aids is also a great way to make your points stand out and stay memorable.
A sales presentation can be used to promote service offerings, product launches or even consultancy proposals that outline the expertise and industry experience of a business. Here are some template examples you can use for your next sales presentation:

6. Pitch presentation
Pitch presentations are your ticket to garnering the interest and support of potential investors, partners or stakeholders. Think of your pitch deck as your chance to paint a vivid picture of your business idea or proposal and secure the resources you need to bring it to life.
Business presentations aside, individuals can also create a portfolio presentation to showcase their skills, experience and achievements to potential clients, employers or investors.
Craft a concise and compelling narrative. Clearly define the problem your idea solves and how it stands out in the market. Anticipate questions and practice your answers. Project confidence and passion for your idea.
7. Motivational or inspirational presentation
Feeling the need for a morale boost? That’s where motivational presentations step in. These talks are designed to uplift and inspire, often featuring personal anecdotes, heartwarming stories and a generous serving of encouragement.
Form a connection with your audience by sharing personal stories that resonate with your message. Use a storytelling style with relatable anecdotes and powerful metaphors to create an emotional connection. Keep the energy high and wrap up your inspirational presentations with a clear call to action.
Inspirational talks and leadership presentations aside, a motivational or inspirational presentation can also be a simple presentation aimed at boosting confidence, a motivational speech focused on embracing change and more.
8. Status or progress report presentation
Projects and businesses are like living organisms, constantly evolving and changing. Status or progress report presentations keep everyone in the loop by providing updates on achievements, challenges and future plans. It’s like a GPS for your team, ensuring everyone stays on track.
Be transparent about achievements, challenges and future plans. Utilize infographics, charts and diagrams to present your data visually and simplify information. By visually representing data, it becomes easier to identify trends, make predictions and strategize based on evidence.

Now that you’ve learned about the different types of presentation methods and how to use them, you’re on the right track to creating a good presentation that can boost your confidence and enhance your presentation skills .
Selecting the most suitable presentation style is akin to choosing the right outfit for an occasion – it greatly influences how your message is perceived. Here’s a more detailed guide to help you make that crucial decision:
1. Define your objectives
Begin by clarifying your presentation’s goals. Are you aiming to educate, persuade, motivate, train or perhaps sell a concept? Your objectives will guide you to the most suitable presentation type.
For instance, if you’re aiming to inform, an informative presentation would be a natural fit. On the other hand, a persuasive presentation suits the goal of swaying opinions.
2. Know your audience
Regardless if you’re giving an in-person or a virtual presentation — delve into the characteristics of your audience. Consider factors like their expertise level, familiarity with the topic, interests and expectations.
If your audience consists of professionals in your field, a more technical presentation might be suitable. However, if your audience is diverse and includes newcomers, an approachable and engaging style might work better.

3. Analyze your content
Reflect on the content you intend to present. Is it data-heavy, rich in personal stories or focused on practical skills? Different presentation styles serve different content types.
For data-driven content, an informative or instructional presentation might work best. For emotional stories, a motivational presentation could be a compelling choice.
4. Consider time constraints
Evaluate the time you have at your disposal. If your presentation needs to be concise due to time limitations, opt for a presentation style that allows you to convey your key points effectively within the available timeframe. A pitch presentation, for example, often requires delivering impactful information within a short span.
5. Leverage visuals
Visual aids are powerful tools in presentations. Consider whether your content would benefit from visual representation. If your PowerPoint presentations involve step-by-step instructions or demonstrations, a how-to presentation with clear visuals would be advantageous. Conversely, if your content is more conceptual, a motivational presentation could rely more on spoken words.

6. Align with the setting
Take the presentation environment into account. Are you presenting in a formal business setting, a casual workshop or a conference? Your setting can influence the level of formality and interactivity in your presentation. For instance, a demonstration presentation might be ideal for a hands-on workshop, while a persuasive presentation is great for conferences.
7. Gauge audience interaction
Determine the level of audience engagement you want. Interactive presentations work well for training sessions, workshops and small group settings, while informative or persuasive presentations might be more one-sided.
8. Flexibility
Stay open to adjusting your presentation style on the fly. Sometimes, unexpected factors might require a change of presentation style. Be prepared to adjust on the spot if audience engagement or reactions indicate that a different approach would be more effective.
Remember that there is no one-size-fits-all approach, and the best type of presentation may vary depending on the specific situation and your unique communication goals. By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the most effective presentation type to successfully engage and communicate with your audience.
To save time, use a presentation software or check out these presentation design and presentation background guides to create a presentation that stands out.
What are some effective ways to begin and end a presentation?
Capture your audience’s attention from the start of your presentation by using a surprising statistic, a compelling story or a thought-provoking question related to your topic.
To conclude your presentation , summarize your main points, reinforce your key message and leave a lasting impression with a powerful call to action or a memorable quote that resonates with your presentation’s theme.
How can I make my presentation more engaging and interactive?
To create an engaging and interactive presentation for your audience, incorporate visual elements such as images, graphs and videos to illustrate your points visually. Share relatable anecdotes or real-life examples to create a connection with your audience.
You can also integrate interactive elements like live polls, open-ended questions or small group discussions to encourage participation and keep your audience actively engaged throughout your presentation.
Which types of presentations require special markings
Some presentation types require special markings such as how sales presentations require persuasive techniques like emphasizing benefits, addressing objections and using compelling visuals to showcase products or services.
Demonstrations and how-to presentations on the other hand require clear markings for each step, ensuring the audience can follow along seamlessly.
That aside, pitch presentations require highlighting unique selling points, market potential and the competitive edge of your idea, making it stand out to potential investors or partners.
Need some inspiration on how to make a presentation that will captivate an audience? Here are 120+ presentation ideas to help you get started.
Creating a stunning and impactful presentation with Venngage is a breeze. Whether you’re crafting a business pitch, a training presentation or any other type of presentation, follow these five steps to create a professional presentation that stands out:
- Sign up and log in to Venngage to access the editor.
- Choose a presentation template that matches your topic or style.
- Customize content, colors, fonts, and background to personalize your presentation.
- Add images, icons, and charts to enhancevisual style and clarity.
- Save, export, and share your presentation as PDF or PNG files, or use Venngage’s Presentation Mode for online showcasing.
In the realm of presentations, understanding the different types of presentation formats is like having a versatile set of tools that empower you to craft compelling narratives for every occasion.
Remember, the key to a successful presentation lies not only in the content you deliver but also in the way you connect with your audience. Whether you’re informing, persuading or entertaining, tailoring your approach to the specific type of presentation you’re delivering can make all the difference.
Presentations are a powerful tool, and with practice and dedication (and a little help from Venngage), you’ll find yourself becoming a presentation pro in no time. Now, let’s get started and customize your next presentation!
Discover popular designs

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

10.3: Types of Quantitative Data Analysis and Presentation Format
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 194132
If your thesis is quantitative research, you will be conducting various types of analyses (see the following table).
6 Types of Data in Statistics & Research: Key in Data Science
Understanding the different types of data (in statistics, marketing research, or data science) allows you to pick the data type that most closely matches your needs and goals.
Whether you are a businessman, marketer, data scientist, or another professional who works with some kinds of data, you should be familiar with the key list of data types.
Why? Because the various data classifications allow you to correctly use measurements and thus to correctly make decisions.
On this page:
- The most common data types (with examples) in statistics, research, and data science. Simply explained.
- Infographics in PDF
Qualitative vs Quantitative Data
1. Quantitative data
Quantitative data seems to be the easiest to explain. It answers key questions such as “how many, “how much” and “how often”.
Quantitative data can be expressed as a number or can be quantified. Simply put, it can be measured by numerical variables.
Quantitative data are easily amenable to statistical manipulation and can be represented by a wide variety of statistical types of graphs and charts such as line, bar graph, scatter plot, and etc.
Examples of quantitative data:
- Scores on tests and exams e.g. 85, 67, 90 and etc.
- The weight of a person or a subject.
- Your shoe size.
- The temperature in a room.
There are 2 general types of quantitative data: discrete data and continuous data. We will explain them later in this article.
2. Qualitative data
Qualitative data can’t be expressed as a number and can’t be measured. Qualitative data consist of words, pictures, and symbols, not numbers.
Qualitative data is also called categorical data because the information can be sorted by category, not by number.
Qualitative data can answer questions such as “how this has happened” or and “why this has happened”.
Examples of qualitative data:
- Colors e.g. the color of the sea
- Your favorite holiday destination such as Hawaii, New Zealand and etc.
- Names as John, Patricia,…..
- Ethnicity such as American Indian, Asian, etc.
More you can see on our post qualitative vs quantitative data .
There are 2 general types of qualitative data: nominal data and ordinal data. We will explain them after a while.
Download the following infographic in PDF
Nominal vs Ordinal Data
3. Nominal data
Nominal data is used just for labeling variables, without any type of quantitative value. The name ‘nominal’ comes from the Latin word “nomen” which means ‘name’.
The nominal data just name a thing without applying it to order. Actually, the nominal data could just be called “labels.”
Examples of Nominal Data:
- Gender (Women, Men)
- Hair color (Blonde, Brown, Brunette, Red, etc.)
- Marital status (Married, Single, Widowed)
- Ethnicity (Hispanic, Asian)
As you see from the examples there is no intrinsic ordering to the variables.
Eye color is a nominal variable having a few categories (Blue, Green, Brown) and there is no way to order these categories from highest to lowest.
4. Ordinal data
Ordinal data shows where a number is in order. This is the crucial difference from nominal types of data.
Ordinal data is data which is placed into some kind of order by their position on a scale. Ordinal data may indicate superiority.
However, you cannot do arithmetic with ordinal numbers because they only show sequence.
Ordinal variables are considered as “in between” qualitative and quantitative variables.
In other words, the ordinal data is qualitative data for which the values are ordered.
In comparison with nominal data, the second one is qualitative data for which the values cannot be placed in an ordered.
We can also assign numbers to ordinal data to show their relative position. But we cannot do math with those numbers. For example: “first, second, third…etc.”
Examples of Ordinal Data:
- The first, second and third person in a competition.
- Letter grades: A, B, C, and etc.
- When a company asks a customer to rate the sales experience on a scale of 1-10.
- Economic status: low, medium and high.
Much more on the topic plus a quiz, you can learn in our post: nominal vs ordinal data .
Discrete vs Continuous Data
As we mentioned above discrete and continuous data are the two key types of quantitative data.
In statistics, marketing research, and data science, many decisions depend on whether the basic data is discrete or continuous.
5. Discrete data
Discrete data is a count that involves only integers. The discrete values cannot be subdivided into parts.
For example, the number of children in a class is discrete data. You can count whole individuals. You can’t count 1.5 kids.
To put in other words, discrete data can take only certain values. The data variables cannot be divided into smaller parts.
It has a limited number of possible values e.g. days of the month.
Examples of discrete data:
- The number of students in a class.
- The number of workers in a company.
- The number of home runs in a baseball game.
- The number of test questions you answered correctly
6. Continuous data
Continuous data is information that could be meaningfully divided into finer levels. It can be measured on a scale or continuum and can have almost any numeric value.
For example, you can measure your height at very precise scales — meters, centimeters, millimeters and etc.
You can record continuous data at so many different measurements – width, temperature, time, and etc. This is where the key difference from discrete types of data lies.
The continuous variables can take any value between two numbers. For example, between 50 and 72 inches, there are literally millions of possible heights: 52.04762 inches, 69.948376 inches and etc.
A good great rule for defining if a data is continuous or discrete is that if the point of measurement can be reduced in half and still make sense, the data is continuous.
Examples of continuous data:
- The amount of time required to complete a project.
- The height of children.
- The square footage of a two-bedroom house.
- The speed of cars.
Much more on the topic you can see in our detailed post discrete vs continuous data : with a comparison chart.
All of the different types of data have a critical place in statistics, research, and data science.
Data types work great together to help organizations and businesses from all industries build successful data-driven decision-making process .
Working in the data management area and having a good range of data science skills involves a deep understanding of various types of data and when to apply them. If you’re looking to enhance your data analysis skills, taking the best data science courses online can provide you with a solid foundation in understanding these essential data types.
About The Author
Silvia Valcheva
Silvia Valcheva is a digital marketer with over a decade of experience creating content for the tech industry. She has a strong passion for writing about emerging software and technologies such as big data, AI (Artificial Intelligence), IoT (Internet of Things), process automation, etc.
It’s a great blog. A great blog. Thanks for sharing this helpful post.
The blog is very informative and useful. Great article.
Brilliant, thanks
Educative article indeed
Wow! Well explained.
Thank you for taking the time to explain with such clarity.This has been of great help to me.
Informative and Easy
excellent explanation. you provided clarity on this topic. thanks to you i am saved from endless search of a simple and concise explanation. kudos
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Lacunar stroke.
Meghana Gore ; Kamna Bansal ; Mahammed Z. Khan Suheb ; Ria Monica D. Asuncion .
Affiliations
Last Update: January 16, 2023 .
- Continuing Education Activity
Ischemic strokes are due to the occlusion of vascular supply to a specific part of the brain leading to tissue hypoxia and damage. Lacunar stroke is a common occlusive stroke with significant morbidity and mortality. Advancement in knowledge about modifying risk factors and early diagnosis has led to a favorable outcome. Most lacunar strokes remain asymptomatic due to the involvement of small vessels causing small-sized infarcts. However, accumulating multiple small lacunar infarcts can lead to significant physical and cognitive disabilities. This article reviews the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management options and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in treating patients suffering from a lacunar stroke.
- Summarize the pathophysiology of lacunar stroke.
- Review history and physical examination findings of patients suffering from lacunar infarctions.
- Outline various treatment options, including medications and rehabilitation for managing lacunar stroke.
- Describe the importance of improving care coordination among interprofessional team members to ensure the best outcomes.
- Introduction
Stroke is one of the most common illnesses causing functional impairment and disability. According to American Stroke Association data, ischemic stroke accounts for 87 percent of all strokes, while hemorrhagic stroke accounts for the rest. Lacunar strokes, a type of ischemic stroke, are small and located in non-cortical areas. [1]
Lacunar infarctions are caused by the occlusion of small deep penetrating branches of the cerebral vessels from the circle of Willis, including branches from the middle cerebral artery, anterior cerebral artery, posterior cerebral artery, or basilar artery. [2]
Most lacunar strokes remain asymptomatic due to the involvement of small vessels causing small-sized infarcts. However, accumulating multiple small lacunar infarcts can lead to significant physical and cognitive disabilities.
Ischemic strokes are due to the occlusion of vascular supply to a specific part of the brain leading to tissue hypoxia and damage. In lacunar infarction, the small penetrating cerebral vessels supplying the subcortical areas are occluded due to various vascular pathologies, including lipohyalinosis and microatheromas. [3]
In some cases, small embolic fragments from a cardiac source or large vessel disease can cause deep penetrating artery occlusion. [4] [5] [6]
The development of small vessel disease, causing a lacunar stroke, is mainly due to underlying medical conditions such as hypertension and diabetes mellitus. Other risk factors include smoking, LDL levels, carotid artery atherosclerosis, peripheral artery disease, previous TIA, and hyperhomocysteinemia. [7] [3]
Certain genetic factors also increase the risk of developing small vessel disease. APOE e4 alleles and carriers are at increased risk of developing white matter lesions. Also, cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) is one of the rare genetic disorders that can cause small vessel arteriopathy. [8]
- Epidemiology
Stroke is the fifth leading cause of death in the United States. [9] [10] Lacunar strokes are the most common among ischemic strokes; they constitute 25% of ischemic strokes. [11] [12]
According to the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2016 lifetime risk of stroke, the estimates include almost equivalent risk of stroke among women and men. GBD estimated lifetime risk of 18.3% with ischemic stroke and 8.2% risk of hemorrhagic stroke. [10]
In a community-based study, the incidence rate of lacunar infarct in a predominantly White community was 29 per 100,000 population, while in another community-based research with a mostly Black population, the incidence rate of lacunar infarct was 52 per 100,000 people. [13] [14]
In a follow-up study, patients with lacunar infarcts are diagnosed with dementia 4 to 12 times more frequently than the average population. [15] Post-stroke dementia in accumulated lacunar infarct is common despite their small size and association with small vessel disease. [16] Also, lacunar stroke at an older age is associated with worse long-term disability. [17]
- Pathophysiology
Cerebral circulation mainly comprises the arterial system, which forms the circle of Willis. [18] The main cerebral branches include the middle cerebral artery, anterior cerebral artery, posterior cerebral artery, basilar artery, and vertebral arteries that supply the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. These arteries have deep branches that penetrate and feed deep gray and white matter of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. [18]
Occlusion or blockage of the small penetrating arteries causes small lacunar strokes. Their size varies from 3 mm to 20 mm in dimension. However, only 17% of lacunar strokes are less than 10 mm in size. [3]
Small arterial occlusion is the fundamental pathogenesis for lacunar strokes. The primary underlying pathophysiological process is lipohyalinosis and micro-atheroma formation. [19]
In lipohyalinosis, the media of small vessels thickens, followed by fibrinoid deposition and hypertrophy of smooth muscle and other connective tissue elements. This arterial pathology is caused by hypertension, diabetes, and other risk factors, including hyperlipidemia and hyperhomocysteinemia. Such segmental arteriolar disorganization causes a significant reduction in the luminal diameter of small arteries (less than 200 μm in diameter) and causes hypoperfusion to subcortical areas. [3]
Microatheroma is an atheromatous arterial lesion within the brain parenchyma. They cause occlusion or stenosis of a deep penetrating brain artery. Histologically, microatheroma is identical to large-vessel atheroma. Microatheroma has the subintimal deposition of lipids and proliferation of fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, and lipid-laden macrophages. Microatheroma is generally located in the proximal region near the origin of the parent artery. [19]
Other mechanisms can cause small vessel arteriopathy, which can cause subcortical strokes. Sometimes arterial media may get foreign deposits, as in amyloid angiopathy and genetic conditions like cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL). [8]
APOE gene is responsible for making apolipoprotein; it helps transport cholesterol across different tissues and cells. APOE represents three alleles, e2, e3, and e4. The APOE e4 allele may confer some risk of developing small vessel pathology. There is evidence that APOE e4 carriers are at increased risk for atherosclerosis. APOE is responsible for clearing beta-amyloid from the brain; e4 may be less efficient, causing atherosclerosis. [20]
Deep penetrating branch occlusion via direct emboli or thrombus from a cardiac or large artery source, micro atheroma involving the lenticulostriate branch, or macroatheroma caused by parent artery occlusion can also cause a lacunar stroke.
Other rare postulated reasons for small cerebral infarcts include embolism, vasculitis, infections, and vasospasm, which are not proven by autopsy.
- Histopathology
A lacune is generally identified on autopsy as a fluid-filled cavity that marks the healed stage of small infarcted brain tissue. There are three types of lacunes, as described per histopathology. Type 1 is classified as an ischemic infarct, type 2 is a small hemorrhage, and type 3 includes dilated perivascular space. [21] [22]
Atherosclerosis of small cerebral arteries originating from the brain's base is involved in subcortical ischemia and lacunar syndromes.
On autopsy, Miller Fisher observed specific pathological changes in lacunar infarcts. It showed a characteristic histopathological finding of segmental arterial disorganization, fibrinoid degeneration, and lipohyalinosis (hyaline wall thickening). [23]
Lipohyalinosis is described as microangiopathy with loss of normal arterial architecture with mural foam cells and fibrinoid necrotic changes in the vessel wall. [24] [19]
Histologically, microatheroma is very much like a large-vessel atheromatous plaque. It involves the subintimal deposition of lipids, a proliferation of fibroblasts and smooth muscles, and lipid-laden macrophages. [23]
Hyaline atherosclerosis of small cerebral vessels is a common finding in patients with lacunar infarcts.
- History and Physical
As with ischemic strokes, lacunar infarcts usually present with sudden onset neurological deficits. However, a subset of lacunar infarctions may present in a stepwise pattern and are known to worsen even during admission. Lacunar infarcts are common in the deep brain nuclei, including the thalamus, basal ganglia, pons, and white matter of the internal capsule. Lacunar infarcts can be asymptomatic and are noted on imaging as incidental findings. Silent lacunar infarcts are more common than symptomatic lacunar infarcts. [25]
Clinical presentation depends on the area of brain involvement. Lacunar infarcts in the centrum semiovale may present without symptoms and can be found incidentally on brain imaging for some other cause. However, certain lacunar infarcts, like in the posterior limb of the internal capsule or the pons, can present with severe hemiplegia. Often, cortical findings, such as neglect, visual disturbances, aphasia, and behavioral changes, are absent in the clinical presentation of lacunar stroke as they occur in subcortical areas of the brain.
Lacunar strokes seldom affect memory, language, and judgment. There are about 20 different types of lacunar syndromes described in the literature. The most common lacunar syndromes are described below:
- Pure motor hemiparesis involves the posterior limb of the internal capsule, corona radiata. This type presents with contralateral hemiparesis of the face, arm, and leg. Mild dysarthria may be present with the absence of sensory symptoms. These are the most common lacunar syndromes. They account for 45% of cases of lacunar strokes. Cortical signs like aphasia, cognitive deficit, or visual symptoms are always absent. Pure motor stroke can be a combination of weakness in the arm, leg, or face on one side or any of these parts alone.
- Ataxic hemiparesis comprises 10 to 18% of cases. It involves the internal capsule, pons, or corona radiata. It causes hemiparesis of the contralateral face and leg and ataxia of the contralateral limb. Ataxia is the prominent feature of this stroke.
- Pure sensory stroke involves the thalamus or corona radiata; it presents with the absent or abnormal sensation of the contralateral of the face, arm, and leg. It accounts for 7% of cases of lacunar strokes. The sensations affected are pain, temperature, touch, pressure, vision, hearing, and taste. A common form of thalamic lacunar stroke is known as Dejerine Roussy syndrome. [26]
- Dysarthria: clumsy hand syndrome involves the pons or internal capsule and presents with dysarthria and problems pronouncing words due to voice box muscle weakness, including tongue, larynx, and other facial muscle weakness. Contralateral clumsiness of the upper extremity is present with preserved motor strength. There may be difficulty with subtle fine movements such as writing or tying a shoelace.
- A sensory: motor stroke involves the thalamus, internal capsule, or putamen-capsule-caudate and presents clinically with a combination of contralateral sensory and motor loss. Sensory-motor lacunar strokes are the second most common type of lacunar strokes. They account for 20% of cases. [27] [28] [29]
Most penetrating branches arise from the middle cerebral artery; the intracranial non-stenotic atheroma in the large vessel may cause a lacunar stroke by blocking the penetrating branch artery at its takeoff point. [30]
Neurological fluctuation and deterioration is a common feature of subcortical strokes. More than 40% with subcortical infarct deteriorate neurologically within the first week of onset of stroke symptoms. One-third of the deteriorated patients reverse spontaneously. The rest of them suffer a physical disability. [31] Lacunar strokes are a common cause of vascular dementia and mild cognitive impairment, often overlooked in clinical practice. Multiple silent lacunar strokes are documented on brain MRI, with patients presenting with mild cognitive impairment and early dementia. [32]
Sudden onset neurological deficit requires emergent neuroimaging. An initial non-contrast head CT scan is preferred in an acute setting as it is readily available, quick, and useful to rule out life-threatening conditions such as intracerebral bleeding or herniation and clear the patient for possible intervention.
CT scan seldom identifies lacunar ischemic insult within the first 24 hours due to its small size. If seen, lacunar strokes are ill-defined hypodensities on CT scans unless there is a hemorrhagic component to the acute stroke. A hyperdensity of a large artery on non-contrast head CT indicates the presence of a thrombus inside the arterial lumen or vessel calcification. Early infarct signs on non-contrast CT include loss of gray-white differentiation and focal hypoattenuation of brain parenchyma. These details are difficult to read in small subcortical strokes. Chronic lesions may appear as hypodense foci.
CT angiogram of the head and neck can also be done. This can show a filling defect consistent with a thrombus blocking a specified vessel. It may also show arterial narrowing, and extensive vessel disease, like in the carotid arteries, which may be a source of an embolus or the middle cerebral artery features consistent with an atheroma. Neurovascular imaging modality is essential to determine the presence of large artery occlusion as it helps determine the need for catheter-guided thrombolysis.
MRI is a superior imaging modality in acute and subacute settings to detect lacunar infarction. In the acute stage, the MRI diffusion-weighted image (DWI) has the most diagnostic accuracy. MRI-DWI helps to differentiate between acute and chronic infarction. [33] In an acute setting, on T1-weighted images, lacunes appear as focal areas of decreased signal intensity and as focal areas of hyperintensity on T2-weighted images. Chronic lesions are isointense to CSF on all sequences.
In cases where a neck angiogram is not done, carotid ultrasound helps diagnose an atherosclerotic narrowing of the extracranial carotid artery. The risk of stroke is higher in patients with severe carotid artery stenosis (CAS). The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force considers 70%-99% of carotid stenosis clinically significant. Carotid artery intervention is recommended in clinically significant lesions.
Extensive embolic workup, including echocardiography and vascular imaging evaluation, is very low yield in cases of lacunar strokes. [34] However, this may be necessary in some cases, like in young patients with no apparent medical issues.
Other immediate tests to be performed include blood glucose levels, electrocardiogram, complete blood count including platelets, troponin, prothrombin time, and international normalized ratio (INR), activated partial thromboplastin time, and a complete metabolic panel and lipid panel. These tests are helpful in the assessment of underlying stroke risk factors.
- Treatment / Management
Treatment principles for acute lacunar stroke are similar to any acute ischemic stroke. The initial goal of acute-stage treatment is ensuring medical stability and determining candidacy for thrombolysis. Tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) improves outcomes for patients with ischemic stroke if administered within 4.5 hours of symptom onset. Once intracerebral bleed is ruled out, intravenous thrombolysis is an important step in the treatment. An acute lacunar infarct is efficiently treated with TPA. [35] [36]
If symptom onset duration is more than 4.5 hours and there is suspicion of intracranial arterial occlusion in the anterior circulation, CTA/MRA is useful for selecting candidates for mechanical thrombectomy between 6 to 24 hours from the last known well.
Management of a patient who presents with acute lacunar infarct out of TPA window consistent with a non-cardioembolic stroke includes dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) with aspirin and clopidogrel within 24 hours of symptom onset and continued for 21 days. DAPT in the acute phase effectively lowers recurrent ischemic stroke for 90 days from symptom onset. Antiplatelet therapy should be delayed for 24 hours in patients who received TPA.
Management of hypertension includes allowing for permissive hypertension unless the blood pressure is markedly elevated (i.e., more than 220/120 mmHg); in this case, lower blood pressure by 15% during the first 24 hours, hold any outpatient antihypertensive medications at admission for the early 24 hours, unless other comorbid conditions require the immediate lowering of blood pressure. In patients where TPA is given or who undergo thrombectomy, lowering the blood pressure below 185/110 mmHg is ideal.
Blood sugar management is done to maintain euglycemia with recommended blood glucose levels at 60–180 mg/dL. Both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia should be monitored and corrected. The recommended HbA1c goal is 6.5 to 7.
Correct volume status by giving isotonic saline as stroke patients tend to be volume depleted. Keep oxygen saturation above 90%. Continue statin therapy with a goal LDL of less than 70 mg/dl. Assess swallowing function before advancing diet. VTE prophylaxis and early mobilization efforts are essential parts of the treatment plan. [37]
Stroke Prevention
Primary and secondary stroke prevention remains an essential part of the treatment plan. Primary prevention includes the prevention of the first episode of stroke, and secondary prevention includes the prevention of recurrence.
Primary stroke prevention measures include risk factor management that uses antihypertensive medications, diabetes control, cholesterol-lowering agents, smoking cessation, dietary intervention, weight loss, and exercise.
Secondary prevention includes antithrombotic agents like aspirin, clopidogrel, extended-release dipyridamole, and ticlopidine and managing underlying risk factors. Antiplatelet agents reduce the risk of recurrence in patients with lacunar strokes. [38] Blood pressure control, diabetes control, lipid management, smoking cessation, weight loss, and regular exercise are included in secondary prevention strategies. Blood pressure reduction at a systolic blood pressure target of less than 130 mmHg is beneficial. [39]
Dual antiplatelet therapy (clopidogrel and aspirin) for secondary prevention has not shown a further reduction in the risk of recurrence in lacunar stroke. [40] Secondary stroke prevention is an essential strategy; it can prevent as much as 80% of all recurrent strokes. [41]
Oral anticoagulants are not considered for small cerebral vessel disease-related stroke prevention, including recurrent lacunar infarcts, as they disproportionately increase intracranial cerebral hemorrhage risk. [42]
Physical therapy and rehabilitation are essential steps for managing patients who suffer lacunar strokes that cause physical disability. These patients require rehabilitation. The goal of rehabilitation is to optimize functional recovery after a stroke and level of independence and maintain quality of life.
- Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnoses of lacunar infarcts include the following:
- Large vessel ischemic stroke in the middle cerebral artery territory: it is clinically differentiated from lacunar strokes by the presence of cortical signs, including altered mental status, aphasia, hemineglect, etc.
- Intracranial hemorrhages can be easily seen on neuroimaging modalities like brain CT scans.
- Seizures are caused by excess neuronal activity and can be differentiated clinically by their tonic-clonic activity and postictal state after having seizures.
- Complicated migraine: symptoms are usually accompanied by headache and aura. A typical aura may involve visual disturbances, sensory symptoms, motor weakness, or speech disturbances.
- Brain tumors: are distinguished by their characteristic appearance on MRI.
- Multiple sclerosis (MS): can cause paroxysmal attacks of ataxia and dysarthria. MRI helps distinguish the presence of plaques due to MS from a stroke. Further cerebral vasoreactivity measured by transcranial Doppler (TCD) sonography can be used for differentiating ischemic and demyelinating lesions. The presence of oligoclonal bands on lumbar puncture is characteristic of multiple sclerosis.
Earlier studies suggested that lacunar stroke has a better prognosis compared to other strokes. It has a high survival rate, a low recurrence rate, and a relatively good functional recovery. In general, lacunar infarcts have a relatively favorable prognosis. [43]
However, recent studies showed that in the earlier stages of the disease, the prognosis of lacunar stroke appears to be benign. Still, long-term prognosis with lacunar stroke constitutes an increased risk of death, mainly from cardiovascular causes. The risk of stroke recurrence is similar to any other type of stroke. Patients with recurrent small vessel disease are at increased risk of developing cognitive decline and dementia. [44] [16]
- Complications
Lacunar strokes are thought to be the leading cause of vascular dementia and cognitive impairment. [16] Accumulated lacunar infarcts can lead to other disease-related complications due to physical disability, including, but not limited to, aspiration pneumonia, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, urinary tract infection, depression, and decubitus ulcers.
- Postoperative and Rehabilitation Care
Most patients with lacunar infarctions have significant improvements in neurologic deficits. Physical therapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy, and rehabilitation services remain essential after hospital care to regain maximum strength and functional level after stroke.
- Deterrence and Patient Education
Patients need to be aware of risk factors that increase stroke risk. Compliance with antithrombotic agents to prevent the recurrence of stroke is essential. Patients are advised to maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, avoid smoking, and avoid excessive alcohol use. Together, these habits reduce the risk of having strokes in general. If patients have high blood pressure, lipid disorder, or diabetes, regular follow-up with their primary care provider is essential to keep these risk factors optimally controlled.
The timeline of recovery from a lacunar stroke is different for everyone. Home safety is essential. Fall risk due to physical disability is common. Depression is common in people who have experienced a stroke and should be addressed if present. Cognitive impairment due to multiple subcortical strokes can progress to vascular dementia and should be monitored.
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Patients with lacunar infarctions must be managed by a neurologist, family clinicians, nursing staff, and physical, occupational, and social therapists, all operating as an interprofessional team, to receive comprehensive care. Physical deficits like ataxia and motor hemiparesis are managed with physical therapy, while muscle relaxants like baclofen and tizanidine can be used for spasticity. Pharmacists remain crucial in patients receiving multiple medications to check drug interactions. Rehabilitation therapy must be continued to maximize the patient’s neurologic function to bring them close to their baseline before the infarction. All interprofessional team members must maintain open communication lines with each other and maintain accurate and updated patient records to serve as an accurate information source for everyone involved in care. This interprofessional approach to care will result in the best possible patient outcomes. [Level 5]
Long-term care coordination is the responsibility of the primary care provider. Emphasis on managing stroke risk factors includes intense antihypertensive therapy, lipid management, and strict control of blood sugars after the lacunar ischemic event.
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Meghana Gore declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Kamna Bansal declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Mahammed Khan Suheb declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Ria Monica Asuncion declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Gore M, Bansal K, Khan Suheb MZ, et al. Lacunar Stroke. [Updated 2023 Jan 16]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Ischemic lacunar stroke in patients with and without potential mechanism other than small-artery disease. [Stroke. 2003] Ischemic lacunar stroke in patients with and without potential mechanism other than small-artery disease. Baumgartner RW, Sidler C, Mosso M, Georgiadis D. Stroke. 2003 Mar; 34(3):653-9. Epub 2003 Feb 27.
- Association between arterial calcifications and nonlacunar and lacunar ischemic strokes. [Stroke. 2014] Association between arterial calcifications and nonlacunar and lacunar ischemic strokes. van Dijk AC, Fonville S, Zadi T, van Hattem AM, Saiedie G, Koudstaal PJ, van der Lugt A. Stroke. 2014 Mar; 45(3):728-33. Epub 2014 Jan 23.
- Should computed tomography appearance of lacunar stroke influence patient management? [J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry....] Should computed tomography appearance of lacunar stroke influence patient management? Mead GE, Lewis SC, Wardlaw JM, Dennis MS, Warlow CP. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999 Nov; 67(5):682-4.
- Review Lacunar stroke. [Expert Rev Neurother. 2009] Review Lacunar stroke. Arboix A, Martí-Vilalta JL. Expert Rev Neurother. 2009 Feb; 9(2):179-96.
- Review Penetrating artery territory pontine infarction. [Rev Neurol Dis. 2011] Review Penetrating artery territory pontine infarction. Field TS, Benavente OR. Rev Neurol Dis. 2011; 8(1-2):30-8.
Recent Activity
- Lacunar Stroke - StatPearls Lacunar Stroke - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples) Design • March 20th, 2024. In this age of overwhelming information, the skill to effectively convey data has become extremely valuable. Initiating a discussion on data presentation types involves thoughtful consideration of the nature of your data and the message you aim to convey.
Definition: Data presentation is the art of visualizing complex data for better understanding. Importance: Data presentations enhance clarity, engage the audience, aid decision-making, and leave a lasting impact. Types: Textual, Tabular, and Graphical presentations offer various ways to present data.
8. Tabular presentation. Presenting data in rows and columns, often used for precise data values and comparisons. Tabular data presentation is all about clarity and precision. Think of it as presenting numerical data in a structured grid, with rows and columns clearly displaying individual data points.
TheJoelTruth. While a good presentation has data, data alone doesn't guarantee a good presentation. It's all about how that data is presented. The quickest way to confuse your audience is by ...
Among various types of data presentation, tabular is the most fundamental method, with data presented in rows and columns. Excel or Google Sheets would qualify for the job. Nothing fancy. This is an example of a tabular presentation of data on Google Sheets.
5. Histograms. It is a perfect Presentation of the spread of numerical data. The main differentiation that separates data graphs and histograms are the gaps in the data graphs. 6. Box plots. Box plot or Box-plot is a way of representing groups of numerical data through quartiles. Data Presentation is easier with this style of graph dealing with ...
Key Objectives of Data Presentation. Here are some key objectives to think about when presenting financial analysis: Visual communication. Audience and context. Charts, graphs, and images. Focus on important points. Design principles. Storytelling. Persuasiveness.
Problem-solving and analysis: Presenting data in a structured and organized manner makes identifying patterns, correlations, and anomalies easier. Consequently, this leads to more accurate analysis and problem-solving. Collaboration and teamwork: Effective presentation of data promotes collaboration and teamwork.
Thankfully, we're here to help. Here are 10 data presentation tips to effectively communicate with executives, senior managers, marketing managers, and other stakeholders. 1. Choose a Communication Style. Every data professional has a different way of presenting data to their audience. Some people like to tell stories with data, illustrating ...
Presentation length. This is my formula to determine how many slides to include in my main presentation assuming I spend about five minutes per slide. (Presentation length in minutes-10 minutes for questions ) / 5 minutes per slide. For an hour presentation that comes out to ( 60-10 ) / 5 = 10 slides.
The Power of Good Data Visualization. Data visualization involves the use of graphical representations of data, such as graphs, charts, and maps. Compared to descriptive statistics or tables, visuals provide a more effective way to analyze data, including identifying patterns, distributions, and correlations and spotting outliers in complex ...
Types of data presentation Depending on the data type and purpose, there are different ways you can present data, including: Textual representation The most common way to represent data is through text. Here, you may include the data in a text document that's easy to read and understand. Some common text formats are doc files, portable document ...
Make sure your data is accurate, up-to-date, and relevant to your presentation topic. Your goal will be to create clear conclusions based on your data and highlight trends. 2. Know your audience. Knowing who your audience is and the one thing you want them to get from your data is vital.
This method of displaying data uses diagrams and images. It is the most visual type for presenting data and provides a quick glance at statistical data. There are four basic types of diagrams, including: Pictograms: This diagram uses images to represent data. For example, to show the number of books sold in the first release week, you may draw ...
The best type of data visualization to use depends on the data at hand and the purpose of its presentation. Whether aiming to highlight trends, compare values, or elucidate complex relationships, selecting the appropriate visual form is crucial for effectively communicating insights buried within datasets.
In the case of a live presentation, you can have fewer comments on charts since you can talk about all the needed context, while in an e-mail, it's better to provide all the details. A table with many numbers won't work for live presentations since the slide with so much information might distract the audience from your speech.
Consider reevaluating your presentation if you have a lot of data. Order your bars from left to right in such a way that exposes a relevant trend or message. 6. Pie Chart ... Choosing the wrong visual aid or defaulting to the most common type of data visualization could confuse your viewer or lead to mistaken data interpretation.
CREATE THIS PRESENTATION. 2. Persuasive presentation. If you've ever been swayed by a passionate speaker armed with compelling arguments, you've experienced a persuasive presentation . This type of presentation is like a verbal tug-of-war, aiming to convince the audience to see things from a specific perspective.
Table 10.1 - Some Common Forms of Quantitative Analysis; Type of Analysis Appropriate Quantitative Analysis Presentation Format; Univariate: Descriptive statistics (range, mean, median, mode, standard deviation, skewness, kurtosis)
6. Scatter Plot. The scatter plot is also among the popular data visualization types and has other names such as a scatter diagram, scatter graph, and correlation chart. Scatter plot helps in many areas of today's world - business, biology, social statistics, data science and etc.
In this article, the techniques of data and information presentation in textual, tabular, and graphical forms are introduced. Text is the principal method for explaining findings, outlining trends, and providing contextual information. A table is best suited for representing individual information and represents both quantitative and ...
The types of data presentation used will depend on the data collected; Graphical Skills. Much of the data collected will be presented in the form of graphs of some form; Each type of graph is suitable for particular data sets; The graphs also may have advantages and disadvantages; Bar graphs One of the simplest methods to display discrete data
As we mentioned above discrete and continuous data are the two key types of quantitative data. In statistics, marketing research, and data science, many decisions depend on whether the basic data is discrete or continuous. 5. Discrete data. Discrete data is a count that involves only integers.
There are two main types of data: quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative data can be continuous, representing measurements, or discrete, representing countable items. Qualitative data includes categorical data for characteristics, binary data with two options, and nominal or ordinal scales. Choosing the right statistical test is challenging.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue.
Data and its Types. DATA BY S.P.ARTHI B COM CA. Data • Facts,statistics used. What is data? Data. Types of Data Data. Data collection Depending on. Discrete and continuous. Data and its Types - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Stroke is one of the most common illnesses causing functional impairment and disability. According to American Stroke Association data, ischemic stroke accounts for 87 percent of all strokes, while hemorrhagic stroke accounts for the rest. Lacunar strokes, a type of ischemic stroke, are small and located in non-cortical areas.[1]