Change Password
Your password must have 8 characters or more and contain 3 of the following:.
- a lower case character,
- an upper case character,
- a special character

Password Changed Successfully
Your password has been changed
- Sign in / Register
Request Username
Can't sign in? Forgot your username?
Enter your email address below and we will send you your username
If the address matches an existing account you will receive an email with instructions to retrieve your username
Teaching Creativity and Inventive Problem Solving in Science
- Robert L. DeHaan
Division of Educational Studies, Emory University, Atlanta, GA 30322
Search for more papers by this author
Engaging learners in the excitement of science, helping them discover the value of evidence-based reasoning and higher-order cognitive skills, and teaching them to become creative problem solvers have long been goals of science education reformers. But the means to achieve these goals, especially methods to promote creative thinking in scientific problem solving, have not become widely known or used. In this essay, I review the evidence that creativity is not a single hard-to-measure property. The creative process can be explained by reference to increasingly well-understood cognitive skills such as cognitive flexibility and inhibitory control that are widely distributed in the population. I explore the relationship between creativity and the higher-order cognitive skills, review assessment methods, and describe several instructional strategies for enhancing creative problem solving in the college classroom. Evidence suggests that instruction to support the development of creativity requires inquiry-based teaching that includes explicit strategies to promote cognitive flexibility. Students need to be repeatedly reminded and shown how to be creative, to integrate material across subject areas, to question their own assumptions, and to imagine other viewpoints and possibilities. Further research is required to determine whether college students' learning will be enhanced by these measures.
INTRODUCTION
Dr. Dunne paces in front of his section of first-year college students, today not as their Bio 110 teacher but in the role of facilitator in their monthly “invention session.” For this meeting, the topic is stem cell therapy in heart disease. Members of each team of four students have primed themselves on the topic by reading selected articles from accessible sources such as Science, Nature, and Scientific American, and searching the World Wide Web, triangulating for up-to-date, accurate, background information. Each team knows that their first goal is to define a set of problems or limitations to overcome within the topic and to begin to think of possible solutions. Dr. Dunne starts the conversation by reminding the group of the few ground rules: one speaker at a time, listen carefully and have respect for others' ideas, question your own and others' assumptions, focus on alternative paths or solutions, maintain an atmosphere of collaboration and mutual support. He then sparks the discussion by asking one of the teams to describe a problem in need of solution.
Science in the United States is widely credited as a major source of discovery and economic development. According to the 2005 TAP Report produced by a prominent group of corporate leaders, “To maintain our country's competitiveness in the twenty-first century, we must cultivate the skilled scientists and engineers needed to create tomorrow's innovations.” ( www.tap2015.org/about/TAP_report2.pdf ). A panel of scientists, engineers, educators, and policy makers convened by the National Research Council (NRC) concurred with this view, reporting that the vitality of the nation “is derived in large part from the productivity of well-trained people and the steady stream of scientific and technical innovations they produce” ( NRC, 2007 ).
For many decades, science education reformers have promoted the idea that learners should be engaged in the excitement of science; they should be helped to discover the value of evidence-based reasoning and higher-order cognitive skills, and be taught to become innovative problem solvers (for reviews, see DeHaan, 2005 ; Hake, 2005 ; Nelson, 2008 ; Perkins and Wieman, 2008 ). But the means to achieve these goals, especially methods to promote creative thinking in scientific problem solving, are not widely known or used. An invention session such as that led by the fictional Dr. Dunne, described above, may seem fanciful as a means of teaching students to think about science as something more than a body of facts and terms to memorize. In recent years, however, models for promoting creative problem solving were developed for classroom use, as detailed by Treffinger and Isaksen (2005) , and such techniques are often used in the real world of high technology. To promote imaginative thinking, the advertising executive Alex F. Osborn invented brainstorming ( Osborn, 1948 , 1979 ), a technique that has since been successful in stimulating inventiveness among engineers and scientists. Could such strategies be transferred to a class for college students? Could they serve as a supplement to a high-quality, scientific teaching curriculum that helps students learn the facts and conceptual frameworks of science and make progress along the novice–expert continuum? Could brainstorming or other instructional strategies that are specifically designed to promote creativity teach students to be more adaptive in their growing expertise, more innovative in their problem-solving abilities? To begin to answer those questions, we first need to understand what is meant by “creativity.”
What Is Creativity? Big-C versus Mini-C Creativity
How to define creativity is an age-old question. Justice Potter Stewart's famous dictum regarding obscenity “I know it when I see it” has also long been an accepted test of creativity. But this is not an adequate criterion for developing an instructional approach. A scientist colleague of mine recently noted that “Many of us [in the scientific community] rarely give the creative process a second thought, imagining one either ‘has it’ or doesn't.” We often think of inventiveness or creativity in scientific fields as the kind of gift associated with a Michelangelo or Einstein. This is what Kaufman and Beghetto (2008) call big-C creativity, borrowing the term that earlier workers applied to the talents of experts in various fields who were identified as particularly creative by their expert colleagues ( MacKinnon, 1978 ). In this sense, creativity is seen as the ability of individuals to generate new ideas that contribute substantially to an intellectual domain. Howard Gardner defined such a creative person as one who “regularly solves problems, fashions products, or defines new questions in a domain in a way that is initially considered novel but that ultimately comes to be accepted in a particular cultural setting” ( Gardner, 1993 , p. 35).
But there is another level of inventiveness termed by various authors as “little-c” ( Craft, 2000 ) or “mini-c” ( Kaufman and Beghetto, 2008 ) creativity that is widespread among all populations. This would be consistent with the workplace definition of creativity offered by Amabile and her coworkers: “coming up with fresh ideas for changing products, services and processes so as to better achieve the organization's goals” ( Amabile et al. , 2005 ). Mini-c creativity is based on what Craft calls “possibility thinking” ( Craft, 2000 , pp. 3–4), as experienced when a worker suddenly has the insight to visualize a new, improved way to accomplish a task; it is represented by the “aha” moment when a student first sees two previously disparate concepts or facts in a new relationship, an example of what Arthur Koestler identified as bisociation: “perceiving a situation or event in two habitually incompatible associative contexts” ( Koestler, 1964 , p. 95).
In this essay, I maintain that mini-c creativity is not a mysterious, innate endowment of rare individuals. Instead, I argue that creative thinking is a multicomponent process, mediated through social interactions, that can be explained by reference to increasingly well-understood mental abilities such as cognitive flexibility and cognitive control that are widely distributed in the population. Moreover, I explore some of the recent research evidence (though with no effort at a comprehensive literature review) showing that these mental abilities are teachable; like other higher-order cognitive skills (HOCS), they can be enhanced by explicit instruction.
Creativity Is a Multicomponent Process
Efforts to define creativity in psychological terms go back to J. P. Guilford ( Guilford, 1950 ) and E. P. Torrance ( Torrance, 1974 ), both of whom recognized that underlying the construct were other cognitive variables such as ideational fluency, originality of ideas, and sensitivity to missing elements. Many authors since then have extended the argument that a creative act is not a singular event but a process, an interplay among several interactive cognitive and affective elements. In this view, the creative act has two phases, a generative and an exploratory or evaluative phase ( Finke et al. , 1996 ). During the generative process, the creative mind pictures a set of novel mental models as potential solutions to a problem. In the exploratory phase, we evaluate the multiple options and select the best one. Early scholars of creativity, such as J. P. Guilford, characterized the two phases as divergent thinking and convergent thinking ( Guilford, 1950 ). Guilford defined divergent thinking as the ability to produce a broad range of associations to a given stimulus or to arrive at many solutions to a problem (for overviews of the field from different perspectives, see Amabile, 1996 ; Banaji et al. , 2006 ; Sawyer, 2006 ). In neurocognitive terms, divergent thinking is referred to as associative richness ( Gabora, 2002 ; Simonton, 2004 ), which is often measured experimentally by comparing the number of words that an individual generates from memory in response to stimulus words on a word association test. In contrast, convergent thinking refers to the capacity to quickly focus on the one best solution to a problem.
The idea that there are two stages to the creative process is consistent with results from cognition research indicating that there are two distinct modes of thought, associative and analytical ( Neisser, 1963 ; Sloman, 1996 ). In the associative mode, thinking is defocused, suggestive, and intuitive, revealing remote or subtle connections between items that may be correlated, or may not, and are usually not causally related ( Burton, 2008 ). In the analytical mode, thought is focused and evaluative, more conducive to analyzing relationships of cause and effect (for a review of other cognitive aspects of creativity, see Runco, 2004 ). Science educators associate the analytical mode with the upper levels (analysis, synthesis, and evaluation) of Bloom's taxonomy (e.g., Crowe et al. , 2008 ), or with “critical thinking,” the process that underlies the “purposeful, self-regulatory judgment that drives problem-solving and decision-making” ( Quitadamo et al. , 2008 , p. 328). These modes of thinking are under cognitive control through the executive functions of the brain. The core executive functions, which are thought to underlie all planning, problem solving, and reasoning, are defined ( Blair and Razza, 2007 ) as working memory control (mentally holding and retrieving information), cognitive flexibility (considering multiple ideas and seeing different perspectives), and inhibitory control (resisting several thoughts or actions to focus on one). Readers wishing to delve further into the neuroscience of the creative process can refer to the cerebrocerebellar theory of creativity ( Vandervert et al. , 2007 ) in which these mental activities are described neurophysiologically as arising through interactions among different parts of the brain.
The main point from all of these works is that creativity is not some single hard-to-measure property or act. There is ample evidence that the creative process requires both divergent and convergent thinking and that it can be explained by reference to increasingly well-understood underlying mental abilities ( Haring-Smith, 2006 ; Kim, 2006 ; Sawyer, 2006 ; Kaufman and Sternberg, 2007 ) and cognitive processes ( Simonton, 2004 ; Diamond et al. , 2007 ; Vandervert et al. , 2007 ).
Creativity Is Widely Distributed and Occurs in a Social Context
Although it is understandable to speak of an aha moment as a creative act by the person who experiences it, authorities in the field have long recognized (e.g., Simonton, 1975 ) that creative thinking is not so much an individual trait but rather a social phenomenon involving interactions among people within their specific group or cultural settings. “Creativity isn't just a property of individuals, it is also a property of social groups” ( Sawyer, 2006 , p. 305). Indeed, Osborn introduced his brainstorming method because he was convinced that group creativity is always superior to individual creativity. He drew evidence for this conclusion from activities that demand collaborative output, for example, the improvisations of a jazz ensemble. Although each musician is individually creative during a performance, the novelty and inventiveness of each performer's playing is clearly influenced, and often enhanced, by “social and interactional processes” among the musicians ( Sawyer, 2006 , p. 120). Recently, Brophy (2006) offered evidence that for problem solving, the situation may be more nuanced. He confirmed that groups of interacting individuals were better at solving complex, multipart problems than single individuals. However, when dealing with certain kinds of single-issue problems, individual problem solvers produced a greater number of solutions than interacting groups, and those solutions were judged to be more original and useful.
Consistent with the findings of Brophy (2006) , many scholars acknowledge that creative discoveries in the real world such as solving the problems of cutting-edge science—which are usually complex and multipart—are influenced or even stimulated by social interaction among experts. The common image of the lone scientist in the laboratory experiencing a flash of creative inspiration is probably a myth from earlier days. As a case in point, the science historian Mara Beller analyzed the social processes that underlay some of the major discoveries of early twentieth-century quantum physics. Close examination of successive drafts of publications by members of the Copenhagen group revealed a remarkable degree of influence and collaboration among 10 or more colleagues, although many of these papers were published under the name of a single author ( Beller, 1999 ). Sociologists Bruno Latour and Steve Woolgar's study ( Latour and Woolgar, 1986 ) of a neuroendocrinology laboratory at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies make the related point that social interactions among the participating scientists determined to a remarkable degree what discoveries were made and how they were interpreted. In the laboratory, researchers studied the chemical structure of substances released by the brain. By analysis of the Salk scientists' verbalizations of concepts, theories, formulas, and results of their investigations, Latour and Woolgar showed that the structures and interpretations that were agreed upon, that is, the discoveries announced by the laboratory, were mediated by social interactions and power relationships among members of the laboratory group. By studying the discovery process in other fields of the natural sciences, sociologists and anthropologists have provided more cases that further illustrate how social and cultural dimensions affect scientific insights (for a thoughtful review, see Knorr Cetina, 1995 ).
In sum, when an individual experiences an aha moment that feels like a singular creative act, it may rather have resulted from a multicomponent process, under the influence of group interactions and social context. The process that led up to what may be sensed as a sudden insight will probably have included at least three diverse, but testable elements: 1) divergent thinking, including ideational fluency or cognitive flexibility, which is the cognitive executive function that underlies the ability to visualize and accept many ideas related to a problem; 2) convergent thinking or the application of inhibitory control to focus and mentally evaluate ideas; and 3) analogical thinking, the ability to understand a novel idea in terms of one that is already familiar.
LITERATURE REVIEW
What do we know about how to teach creativity.
The possibility of teaching for creative problem solving gained credence in the 1960s with the studies of Jerome Bruner, who argued that children should be encouraged to “treat a task as a problem for which one invents an answer, rather than finding one out there in a book or on the blackboard” ( Bruner, 1965 , pp. 1013–1014). Since that time, educators and psychologists have devised programs of instruction designed to promote creativity and inventiveness in virtually every student population: pre–K, elementary, high school, and college, as well as in disadvantaged students, athletes, and students in a variety of specific disciplines (for review, see Scott et al. , 2004 ). Smith (1998) identified 172 instructional approaches that have been applied at one time or another to develop divergent thinking skills.
Some of the most convincing evidence that elements of creativity can be enhanced by instruction comes from work with young children. Bodrova and Leong (2001) developed the Tools of the Mind (Tools) curriculum to improve all of the three core mental executive functions involved in creative problem solving: cognitive flexibility, working memory, and inhibitory control. In a year-long randomized study of 5-yr-olds from low-income families in 21 preschool classrooms, half of the teachers applied the districts' balanced literacy curriculum (literacy), whereas the experimenters trained the other half to teach the same academic content by using the Tools curriculum ( Diamond et al. , 2007 ). At the end of the year, when the children were tested with a battery of neurocognitive tests including a test for cognitive flexibility ( Durston et al. , 2003 ; Davidson et al. , 2006 ), those exposed to the Tools curriculum outperformed the literacy children by as much as 25% ( Diamond et al. , 2007 ). Although the Tools curriculum and literacy program were similar in academic content and in many other ways, they differed primarily in that Tools teachers spent 80% of their time explicitly reminding the children to think of alternative ways to solve a problem and building their executive function skills.
Teaching older students to be innovative also demands instruction that explicitly promotes creativity but is rigorously content-rich as well. A large body of research on the differences between novice and expert cognition indicates that creative thinking requires at least a minimal level of expertise and fluency within a knowledge domain ( Bransford et al. , 2000 ; Crawford and Brophy, 2006 ). What distinguishes experts from novices, in addition to their deeper knowledge of the subject, is their recognition of patterns in information, their ability to see relationships among disparate facts and concepts, and their capacity for organizing content into conceptual frameworks or schemata ( Bransford et al. , 2000 ; Sawyer, 2005 ).
Such expertise is often lacking in the traditional classroom. For students attempting to grapple with new subject matter, many kinds of problems that are presented in high school or college courses or that arise in the real world can be solved merely by applying newly learned algorithms or procedural knowledge. With practice, problem solving of this kind can become routine and is often considered to represent mastery of a subject, producing what Sternberg refers to as “pseudoexperts” ( Sternberg, 2003 ). But beyond such routine use of content knowledge the instructor's goal must be to produce students who have gained the HOCS needed to apply, analyze, synthesize, and evaluate knowledge ( Crowe et al. , 2008 ). The aim is to produce students who know enough about a field to grasp meaningful patterns of information, who can readily retrieve relevant knowledge from memory, and who can apply such knowledge effectively to novel problems. This condition is referred to as adaptive expertise ( Hatano and Ouro, 2003 ; Schwartz et al. , 2005 ). Instead of applying already mastered procedures, adaptive experts are able to draw on their knowledge to invent or adapt strategies for solving unique or novel problems within a knowledge domain. They are also able, ideally, to transfer conceptual frameworks and schemata from one domain to another (e.g., Schwartz et al. , 2005 ). Such flexible, innovative application of knowledge is what results in inventive or creative solutions to problems ( Crawford and Brophy, 2006 ; Crawford, 2007 ).
Promoting Creative Problem Solving in the College Classroom
In most college courses, instructors teach science primarily through lectures and textbooks that are dominated by facts and algorithmic processing rather than by concepts, principles, and evidence-based ways of thinking. This is despite ample evidence that many students gain little new knowledge from traditional lectures ( Hrepic et al. , 2007 ). Moreover, it is well documented that these methods engender passive learning rather than active engagement, boredom instead of intellectual excitement, and linear thinking rather than cognitive flexibility (e.g., Halpern and Hakel, 2003 ; Nelson, 2008 ; Perkins and Wieman, 2008 ). Cognitive flexibility, as noted, is one of the three core mental executive functions involved in creative problem solving ( Ausubel, 1963 , 2000 ). The capacity to apply ideas creatively in new contexts, referred to as the ability to “transfer” knowledge (see Mestre, 2005 ), requires that learners have opportunities to actively develop their own representations of information to convert it to a usable form. Especially when a knowledge domain is complex and fraught with ill-structured information, as in a typical introductory college biology course, instruction that emphasizes active-learning strategies is demonstrably more effective than traditional linear teaching in reducing failure rates and in promoting learning and transfer (e.g., Freeman et al. , 2007 ). Furthermore, there is already some evidence that inclusion of creativity training as part of a college curriculum can have positive effects. Hunsaker (2005) has reviewed a number of such studies. He cites work by McGregor (2001) , for example, showing that various creativity training programs including brainstorming and creative problem solving increase student scores on tests of creative-thinking abilities.
Model creativity—students develop creativity when instructors model creative thinking and inventiveness.
Repeatedly encourage idea generation—students need to be reminded to generate their own ideas and solutions in an environment free of criticism.
Cross-fertilize ideas—where possible, avoid teaching in subject-area boxes: a math box, a social studies box, etc; students' creative ideas and insights often result from learning to integrate material across subject areas.
Build self-efficacy—all students have the capacity to create and to experience the joy of having new ideas, but they must be helped to believe in their own capacity to be creative.
Constantly question assumptions—make questioning a part of the daily classroom exchange; it is more important for students to learn what questions to ask and how to ask them than to learn the answers.
Imagine other viewpoints—students broaden their perspectives by learning to reflect upon ideas and concepts from different points of view.
How Is Creativity Related to Critical Thinking and the Higher-Order Cognitive Skills?
It is not uncommon to associate creativity and ingenuity with scientific reasoning ( Sawyer, 2005 ; 2006 ). When instructors apply scientific teaching strategies ( Handelsman et al. , 2004 ; DeHaan, 2005 ; Wood, 2009 ) by using instructional methods based on learning research, according to Ebert-May and Hodder ( 2008 ), “we see students actively engaged in the thinking, creativity, rigor, and experimentation we associate with the practice of science—in much the same way we see students learn in the field and in laboratories” (p. 2). Perkins and Wieman (2008) note that “To be successful innovators in science and engineering, students must develop a deep conceptual understanding of the underlying science ideas, an ability to apply these ideas and concepts broadly in different contexts, and a vision to see their relevance and usefulness in real-world applications … An innovator is able to perceive and realize potential connections and opportunities better than others” (pp. 181–182). The results of Scott et al. (2004) suggest that nontraditional courses in science that are based on constructivist principles and that use strategies of scientific teaching to promote the HOCS and enhance content mastery and dexterity in scientific thinking ( Handelsman et al. , 2007 ; Nelson, 2008 ) also should be effective in promoting creativity and cognitive flexibility if students are explicitly guided to learn these skills.
Creativity is an essential element of problem solving ( Mumford et al. , 1991 ; Runco, 2004 ) and of critical thinking ( Abrami et al. , 2008 ). As such, it is common to think of applications of creativity such as inventiveness and ingenuity among the HOCS as defined in Bloom's taxonomy ( Crowe et al. , 2008 ). Thus, it should come as no surprise that creativity, like other elements of the HOCS, can be taught most effectively through inquiry-based instruction, informed by constructivist theory ( Ausubel, 1963 , 2000 ; Duch et al. , 2001 ; Nelson, 2008 ). In a survey of 103 instructors who taught college courses that included creativity instruction, Bull et al. (1995) asked respondents to rate the importance of various course characteristics for enhancing student creativity. Items ranking high on the list were: providing a social climate in which students feels safe, an open classroom environment that promotes tolerance for ambiguity and independence, the use of humor, metaphorical thinking, and problem defining. Many of the responses emphasized the same strategies as those advanced to promote creative problem solving (e.g., Mumford et al. , 1991 ; McFadzean, 2002 ; Treffinger and Isaksen, 2005 ) and critical thinking ( Abrami et al. , 2008 ).
In a careful meta-analysis, Scott et al. (2004) examined 70 instructional interventions designed to enhance and measure creative performance. The results were striking. Courses that stressed techniques such as critical thinking, convergent thinking, and constraint identification produced the largest positive effect sizes. More open techniques that provided less guidance in strategic approaches had less impact on the instructional outcomes. A striking finding was the effectiveness of being explicit; approaches that clearly informed students about the nature of creativity and offered clear strategies for creative thinking were most effective. Approaches such as social modeling, cooperative learning, and case-based (project-based) techniques that required the application of newly acquired knowledge were found to be positively correlated to high effect sizes. The most clear-cut result to emerge from the Scott et al. (2004) study was simply to confirm that creativity instruction can be highly successful in enhancing divergent thinking, problem solving, and imaginative performance. Most importantly, of the various cognitive processes examined, those linked to the generation of new ideas such as problem finding, conceptual combination, and idea generation showed the greatest improvement. The success of creativity instruction, the authors concluded, can be attributed to “developing and providing guidance concerning the application of requisite cognitive capacities … [and] a set of heuristics or strategies for working with already available knowledge” (p. 382).
Many of the scientific teaching practices that have been shown by research to foster content mastery and HOCS, and that are coming more widely into use, also would be consistent with promoting creativity. Wood (2009) has recently reviewed examples of such practices and how to apply them. These include relatively small modifications of the traditional lecture to engender more active learning, such as the use of concept tests and peer instruction ( Mazur, 1996 ), Just-in-Time-Teaching techniques ( Novak et al. , 1999 ), and student response systems known as “clickers” ( Knight and Wood, 2005 ; Crossgrove and Curran, 2008 ), all designed to allow the instructor to frequently and effortlessly elicit and respond to student thinking. Other strategies can transform the lecture hall into a workshop or studio classroom ( Gaffney et al. , 2008 ) where the teaching curriculum may emphasize problem-based (also known as project-based or case-based) learning strategies ( Duch et al. , 2001 ; Ebert-May and Hodder, 2008 ) or “community-based inquiry” in which students engage in research that enhances their critical-thinking skills ( Quitadamo et al. , 2008 ).
Another important approach that could readily subserve explicit creativity instruction is the use of computer-based interactive simulations, or “sims” ( Perkins and Wieman, 2008 ) to facilitate inquiry learning and effective, easy self-assessment. An example in the biological sciences would be Neurons in Action ( http://neuronsinaction.com/home/main ). In such educational environments, students gain conceptual understanding of scientific ideas through interactive engagement with materials (real or virtual), with each other, and with instructors. Following the tenets of scientific teaching, students are encouraged to pose and answer their own questions, to make sense of the materials, and to construct their own understanding. The question I pose here is whether an additional focus—guiding students to meet these challenges in a context that explicitly promotes creativity—would enhance learning and advance students' progress toward adaptive expertise?
Assessment of Creativity
To teach creativity, there must be measurable indicators to judge how much students have gained from instruction. Educational programs intended to teach creativity became popular after the Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking (TTCT) was introduced in the 1960s ( Torrance, 1974 ). But it soon became apparent that there were major problems in devising tests for creativity, both because of the difficulty of defining the construct and because of the number and complexity of elements that underlie it. Tests of intelligence and other personality characteristics on creative individuals revealed a host of related traits such as verbal fluency, metaphorical thinking, flexible decision making, tolerance of ambiguity, willingness to take risks, autonomy, divergent thinking, self-confidence, problem finding, ideational fluency, and belief in oneself as being “creative” ( Barron and Harrington, 1981 ; Tardif and Sternberg, 1988 ; Runco and Nemiro, 1994 ; Snyder et al. , 2004 ). Many of these traits have been the focus of extensive research of recent decades, but, as noted above, creativity is not defined by any one trait; there is now reason to believe that it is the interplay among the cognitive and affective processes that underlie inventiveness and the ability to find novel solutions to a problem.
Although the early creativity researchers recognized that assessing divergent thinking as a measure of creativity required tests for other underlying capacities ( Guilford, 1950 ; Torrance, 1974 ), these workers and their colleagues nonetheless believed that a high score for divergent thinking alone would correlate with real creative output. Unfortunately, no such correlation was shown ( Barron and Harrington, 1981 ). Results produced by many of the instruments initially designed to measure various aspects of creative thinking proved to be highly dependent on the test itself. A review of several hundred early studies showed that an individual's creativity score could be affected by simple test variables, for example, how the verbal pretest instructions were worded ( Barron and Harrington, 1981 , pp. 442–443). Most scholars now agree that divergent thinking, as originally defined, was not an adequate measure of creativity. The process of creative thinking requires a complex combination of elements that include cognitive flexibility, memory control, inhibitory control, and analogical thinking, enabling the mind to free-range and analogize, as well as to focus and test.
More recently, numerous psychometric measures have been developed and empirically tested (see Plucker and Renzulli, 1999 ) that allow more reliable and valid assessment of specific aspects of creativity. For example, the creativity quotient devised by Snyder et al. (2004) tests the ability of individuals to link different ideas and different categories of ideas into a novel synthesis. The Wallach–Kogan creativity test ( Wallach and Kogan, 1965 ) explores the uniqueness of ideas associated with a stimulus. For a more complete list and discussion, see the Creativity Tests website ( www.indiana.edu/∼bobweb/Handout/cretv_6.html ).
The most widely used measure of creativity is the TTCT, which has been modified four times since its original version in 1966 to take into account subsequent research. The TTCT-Verbal and the TTCT-Figural are two versions ( Torrance, 1998 ; see http://ststesting.com/2005giftttct.html ). The TTCT-Verbal consists of five tasks; the “stimulus” for each task is a picture to which the test-taker responds briefly in writing. A sample task that can be viewed from the TTCT Demonstrator website asks, “Suppose that people could transport themselves from place to place with just a wink of the eye or a twitch of the nose. What might be some things that would happen as a result? You have 3 min.” ( www.indiana.edu/∼bobweb/Handout/d3.ttct.htm ).
In the TTCT-Figural, participants are asked to construct a picture from a stimulus in the form of a partial line drawing given on the test sheet (see example below; Figure 1 ). Specific instructions are to “Add lines to the incomplete figures below to make pictures out of them. Try to tell complete stories with your pictures. Give your pictures titles. You have 3 min.” In the introductory materials, test-takers are urged to “… think of a picture or object that no one else will think of. Try to make it tell as complete and as interesting a story as you can …” ( Torrance et al. , 2008 , p. 2).
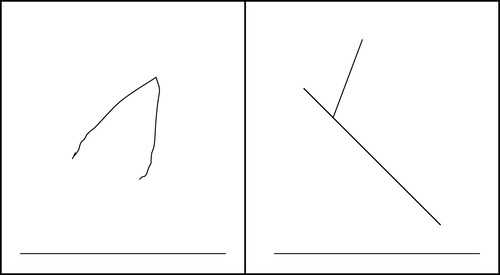
Figure 1. Sample figural test item from the TTCT Demonstrator website ( www.indiana.edu/∼bobweb/Handout/d3.ttct.htm ).
How would an instructor in a biology course judge the creativity of students' responses to such an item? To assist in this task, the TTCT has scoring and norming guides ( Torrance, 1998 ; Torrance et al. , 2008 ) with numerous samples and responses representing different levels of creativity. The guides show sample evaluations based upon specific indicators such as fluency, originality, elaboration (or complexity), unusual visualization, extending or breaking boundaries, humor, and imagery. These examples are easy to use and provide a high degree of validity and generalizability to the tests. The TTCT has been more intensively researched and analyzed than any other creativity instrument, and the norming samples have longitudinal validations and high predictive validity over a wide age range. In addition to global creativity scores, the TTCT is designed to provide outcome measures in various domains and thematic areas to allow for more insightful analysis ( Kaufman and Baer, 2006 ). Kim (2006) has examined the characteristics of the TTCT, including norms, reliability, and validity, and concludes that the test is an accurate measure of creativity. When properly used, it has been shown to be fair in terms of gender, race, community status, and language background. According to Kim (2006) and other authorities in the field ( McIntyre et al. , 2003 ; Scott et al. , 2004 ), Torrance's research and the development of the TTCT have provided groundwork for the idea that creative levels can be measured and then increased through instruction and practice.

SCIENTIFIC TEACHING TO PROMOTE CREATIVITY
How could creativity instruction be integrated into scientific teaching.
Guidelines for designing specific course units that emphasize HOCS by using strategies of scientific teaching are now available from the current literature. As an example, Karen Cloud-Hansen and colleagues ( Cloud-Hansen et al. , 2008 ) describe a course titled, “Ciprofloxacin Resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae .” They developed this undergraduate seminar to introduce college freshmen to important concepts in biology within a real-world context and to increase their content knowledge and critical-thinking skills. The centerpiece of the unit is a case study in which teams of students are challenged to take the role of a director of a local public health clinic. One of the county commissioners overseeing the clinic is an epidemiologist who wants to know “how you plan to address the emergence of ciprofloxacin resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae ” (p. 304). State budget cuts limit availability of expensive antibiotics and some laboratory tests to patients. Student teams are challenged to 1) develop a plan to address the medical, economic, and political questions such a clinic director would face in dealing with ciprofloxacin-resistant N. gonorrhoeae ; 2) provide scientific data to support their conclusions; and 3) describe their clinic plan in a one- to two-page referenced written report.
Throughout the 3-wk unit, in accordance with the principles of problem-based instruction ( Duch et al. , 2001 ), course instructors encourage students to seek, interpret, and synthesize their own information to the extent possible. Students have access to a variety of instructional formats, and active-learning experiences are incorporated throughout the unit. These activities are interspersed among minilectures and give the students opportunities to apply new information to their existing base of knowledge. The active-learning activities emphasize the key concepts of the minilectures and directly confront common misconceptions about antibiotic resistance, gene expression, and evolution. Weekly classes include question/answer/discussion sessions to address student misconceptions and 20-min minilectures on such topics as antibiotic resistance, evolution, and the central dogma of molecular biology. Students gather information about antibiotic resistance in N. gonorrhoeae , epidemiology of gonorrhea, and treatment options for the disease, and each team is expected to formulate a plan to address ciprofloxacin resistance in N. gonorrhoeae .
In this project, the authors assessed student gains in terms of content knowledge regarding topics covered such as the role of evolution in antibiotic resistance, mechanisms of gene expression, and the role of oncogenes in human disease. They also measured HOCS as gains in problem solving, according to a rubric that assessed self-reported abilities to communicate ideas logically, solve difficult problems about microbiology, propose hypotheses, analyze data, and draw conclusions. Comparing the pre- and posttests, students reported significant learning of scientific content. Among the thinking skill categories, students demonstrated measurable gains in their ability to solve problems about microbiology but the unit seemed to have little impact on their more general perceived problem-solving skills ( Cloud-Hansen et al. , 2008 ).
What would such a class look like with the addition of explicit creativity-promoting approaches? Would the gains in problem-solving abilities have been greater if during the minilectures and other activities, students had been introduced explicitly to elements of creative thinking from the Sternberg and Williams (1998) list described above? Would the students have reported greater gains if their instructors had encouraged idea generation with weekly brainstorming sessions; if they had reminded students to cross-fertilize ideas by integrating material across subject areas; built self-efficacy by helping students believe in their own capacity to be creative; helped students question their own assumptions; and encouraged students to imagine other viewpoints and possibilities? Of most relevance, could the authors have been more explicit in assessing the originality of the student plans? In an experiment that required college students to develop plans of a different, but comparable, type, Osborn and Mumford (2006) created an originality rubric ( Figure 2 ) that could apply equally to assist instructors in judging student plans in any course. With such modifications, would student gains in problem-solving abilities or other HOCS have been greater? Would their plans have been measurably more imaginative?

Figure 2. Originality rubric (adapted from Osburn and Mumford, 2006 , p. 183).
Answers to these questions can only be obtained when a course like that described by Cloud-Hansen et al. (2008) is taught with explicit instruction in creativity of the type I described above. But, such answers could be based upon more than subjective impressions of the course instructors. For example, students could be pretested with items from the TTCT-Verbal or TTCT-Figural like those shown. If, during minilectures and at every contact with instructors, students were repeatedly reminded and shown how to be as creative as possible, to integrate material across subject areas, to question their own assumptions and imagine other viewpoints and possibilities, would their scores on TTCT posttest items improve? Would the plans they formulated to address ciprofloxacin resistance become more imaginative?
Recall that in their meta-analysis, Scott et al. (2004) found that explicitly informing students about the nature of creativity and offering strategies for creative thinking were the most effective components of instruction. From their careful examination of 70 experimental studies, they concluded that approaches such as social modeling, cooperative learning, and case-based (project-based) techniques that required the application of newly acquired knowledge were positively correlated with high effect sizes. The study was clear in confirming that explicit creativity instruction can be successful in enhancing divergent thinking and problem solving. Would the same strategies work for courses in ecology and environmental biology, as detailed by Ebert-May and Hodder (2008) , or for a unit elaborated by Knight and Wood (2005) that applies classroom response clickers?
Finally, I return to my opening question with the fictional Dr. Dunne. Could a weekly brainstorming “invention session” included in a course like those described here serve as the site where students are introduced to concepts and strategies of creative problem solving? As frequently applied in schools of engineering ( Paulus and Nijstad, 2003 ), brainstorming provides an opportunity for the instructor to pose a problem and to ask the students to suggest as many solutions as possible in a brief period, thus enhancing ideational fluency. Here, students can be encouraged explicitly to build on the ideas of others and to think flexibly. Would brainstorming enhance students' divergent thinking or creative abilities as measured by TTCT items or an originality rubric? Many studies have demonstrated that group interactions such as brainstorming, under the right conditions, can indeed enhance creativity ( Paulus and Nijstad, 2003 ; Scott et al. , 2004 ), but there is little information from an undergraduate science classroom setting. Intellectual Ventures, a firm founded by Nathan Myhrvold, the creator of Microsoft's Research Division, has gathered groups of engineers and scientists around a table for day-long sessions to brainstorm about a prearranged topic. Here, the method seems to work. Since it was founded in 2000, Intellectual Ventures has filed hundreds of patent applications in more than 30 technology areas, applying the “invention session” strategy ( Gladwell, 2008 ). Currently, the company ranks among the top 50 worldwide in number of patent applications filed annually. Whether such a technique could be applied successfully in a college science course will only be revealed by future research.
- Abrami P. C., Bernard R. M., Borokhovski E., Wadem A., Surkes M. A., Tamim R., Zhang D. ( 2008 ). Instructional interventions affecting critical thinking skills and dispositions: a stage 1 meta-analysis . Rev. Educ. Res 78 , 1102-1134. Google Scholar
- Amabile T. M. ( 1996 ). Creativity in Context , Boulder, CO: Westview Press. Google Scholar
- Amabile T. M., Barsade S. G., Mueller J. S., Staw B. M. ( 2005 ). Affect and creativity at work . Admin. Sci. Q 50 , 367-403. Google Scholar
- Ausubel D. ( 1963 ). The Psychology of Meaningful Verbal Learning , New York: Grune and Stratton. Google Scholar
- Ausubel B. ( 2000 ). The Acquisition and Retention of Knowledge: A Cognitive View , Boston, MA: Kluwer Academic Publishers. Google Scholar
- Banaji S., Burn A., Buckingham D. ( 2006 ). The Rhetorics of Creativity: A Review of the Literature , accessed 29 December 2008 London: Centre for the Study of Children, Youth and Media, www.creativepartnerships.com/data/files/rhetorics-of-creativity-12.pdf . Google Scholar
- Barron F., Harrington D. M. ( 1981 ). Creativity, intelligence and personality . Ann. Rev. Psychol 32 , 439-476. Google Scholar
- Beller M. ( 1999 ). Quantum Dialogue: The Making of a Revolution , Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press. Google Scholar
- Blair C., Razza R. P. ( 2007 ). Relating effortful control, executive function, and false belief understanding to emerging math and literacy ability in kindergarten . Child Dev 78 , 647-663. Medline , Google Scholar
- Bodrova E., Leong D. J. ( 2001 ). The Tool of the Mind: a case study of implementing the Vygotskian approach In: American Early Childhood and Primary Classrooms , Geneva, Switzerland: UNESCO International Bureau of Education. Google Scholar
- Bransford J. D.Brown A. L.Cocking R. R. ( 2000 ). How People Learn: Brain, Mind, Experience, and School , Washington, DC: National Academies Press. Google Scholar
- Brophy D. R. ( 2006 ). A comparison of individual and group efforts to creatively solve contrasting types of problems . Creativity Res. J 18 , 293-315. Google Scholar
- Bruner J. ( 1965 ). The growth of mind . Am. Psychol 20 , 1007-1017. Medline , Google Scholar
- Bull K. S., Montgomery D., Baloche L. ( 1995 ). Teaching creativity at the college level: a synthesis of curricular components perceived as important by instructors . Creativity Res. J 8 , 83-90. Google Scholar
- Burton R. ( 2008 ). On Being Certain: Believing You Are Right Even When You're Not , New York: St. Martin's Press. Google Scholar
- Cloud-Hanson K. A., Kuehner J. N., Tong L., Miller S., Handelsman J. ( 2008 ). Money, sex and drugs: a case study to teach the genetics of antibiotic resistance . CBE Life Sci. Educ 7 , 302-309. Medline , Google Scholar
- Craft A. ( 2000 ). Teaching Creativity: Philosophy and Practice , New York: Routledge. Google Scholar
- Crawford V. M. ( 2007 ). Adaptive expertise as knowledge building in science teachers' problem solving accessed 1 July 2008 Proceedings of the Second European Cognitive Science Conference Delphi, Greece http://ctl.sri.com/publications/downloads/Crawford_EuroCogSci07Proceedings.pdf . Google Scholar
- Crawford V. M., Brophy S. ( 2006 ). Adaptive Expertise: Theory, Methods, Findings, and Emerging Issues; September 2006 In: accessed 1 July 2008 Menlo Park, CA: SRI International, http://ctl.sri.com/publications/downloads/AESymposiumReportOct06.pdf . Google Scholar
- Crossgrove K., Curran K. L. ( 2008 ). Using clickers in nonmajors- and majors-level biology courses: student opinion, learning, and long-term retention of course material . CBE Life Sci. Educ 7 , 146-154. Link , Google Scholar
- Crowe A., Dirks C., Wenderoth M. P. ( 2008 ). Biology in bloom: implementing Bloom's taxonomy to enhance student learning in biology . CBE Life Sci. Educ 7 , 368-381. Link , Google Scholar
- Davidson M. C., Amso D., Anderson L. C., Diamond A. ( 2006 ). Development of cognitive control and executive functions from 4–13 years: evidence from manipulations of memory, inhibition, and task switching . Neuropsychologia 44 , 2037-2078. Medline , Google Scholar
- DeHaan R. L. ( 2005 ). The impending revolution in undergraduate science education . J. Sci. Educ. Technol 14 , 253-270. Google Scholar
- Diamond A., Barnett W. S., Thomas J., Munro S. ( 2007 ). Preschool program improves cognitive control . Science 318 , 1387-1388. Medline , Google Scholar
- Duch B. J., Groh S. E., Allen D. E. ( 2001 ). The Power of Problem-based Learning , Sterling, VA: Stylus Publishers. Google Scholar
- Durston S., Davidson M. C., Thomas K. M., Worden M. S., Tottenham N., Martinez A., Watts R., Ulug A. M., Caseya B. J. ( 2003 ). Parametric manipulation of conflict and response competition using rapid mixed-trial event-related fMRI . Neuroimage 20 , 2135-2141. Medline , Google Scholar
- Ebert-May D., Hodder J. ( 2008 ). Pathways to Scientific Teaching , Sunderland, MA: Sinauer. Google Scholar
- Finke R. A., Ward T. B., Smith S. M. ( 1996 ). Creative Cognition: Theory, Research and Applications , Boston, MA: MIT Press. Google Scholar
- Freeman S., O'Connor E., Parks J. W., Cunningham M., Hurley D., Haak D., Dirks C., Wenderoth M. P. ( 2007 ). Prescribed active learning increases performance in introductory biology . CBE Life Sci. Educ 6 , 132-139. Link , Google Scholar
- Gabora L. ( 2002 ). Hewett T.Kavanagh E. Cognitive mechanisms underlying the creative process Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Creativity and Cognition 2002 October 13–16 Loughborough University, United Kingdom 126-133. Google Scholar
- Gaffney J.D.H., Richards E., Kustusch M. B., Ding L., Beichner R. ( 2008 ). Scaling up education reform . J. Coll. Sci. Teach 37 , 48-53. Google Scholar
- Gardner H. ( 1993 ). Creating Minds: An Anatomy of Creativity Seen through the Lives of Freud, Einstein, Picasso, Stravinsky, Eliot, Graham, and Ghandi In: New York: Harper Collins. Google Scholar
- Gladwell M. ( 2008 ). In the air; who says big ideas are rare? The New Yorker accessed 19 May 2008 www.newyorker.com/reporting/2008/05/12/080512fa_fact_gladwell . Google Scholar
- Guilford J. P. ( 1950 ). Creativity . Am. Psychol 5 , 444-454. Medline , Google Scholar
- Hake R. ( 2005 ). The physics education reform effort: a possible model for higher education . Natl. Teach. Learn. Forum 15 , 1-6. Google Scholar
- Halpern D. E., Hakel M. D. ( 2003 ). Applying the science of learning to the university and beyond . Change 35 , 36-42. Google Scholar
- Handelsman J. ( 2004 ). Scientific teaching . Science 304 , 521-522. Medline , Google Scholar
- Handelsman J, Miller S., Pfund C. ( 2007 ). Scientific Teaching , New York: W. H. Freeman and Co. Google Scholar
- Haring-Smith T. ( 2006 ). Creativity research review: some lessons for higher education. Association of American Colleges and Universities . Peer Rev 8 , 23-27. Google Scholar
- Hatano G., Ouro Y. ( 2003 ). Commentary: reconceptualizing school learning using insight from expertise research . Educ. Res 32 , 26-29. Google Scholar
- Hrepic Z., Zollman D. A., Rebello N. S. ( 2007 ). Comparing students' and experts' understanding of the content of a lecture . J. Sci. Educ. Technol 16 , 213-224. Google Scholar
- Hunsaker S. L. ( 2005 ). Outcomes of creativity training programs . Gifted Child Q 49 , 292-298. Google Scholar
- Kaufman J. C., Baer J. ( 2006 ). Intelligent testing with Torrance . Creativity Res. J 18 , 99-102. Google Scholar
- Kaufman J. C., Beghetto R. A. ( 2008 , Ed. R. L. DeHaanK.M.V. Narayan , Exploring mini-C: creativity across cultures In: Education for Innovation: Implications for India, China and America , Rotterdam, The Netherlands: Sense Publishers, 165-180. Google Scholar
- Kaufman J. C., Sternberg R. J. ( 2007 ). Creativity . Change 39 , 55-58. Google Scholar
- Kim K. H. ( 2006 ). Can we trust creativity tests: a review of the Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking (TTCT) . Creativity Res. J 18 , 3-14. Google Scholar
- Knight J. K., Wood W. B. ( 2005 ). Teaching more by lecturing less . Cell Biol. Educ 4 , 298-310. Link , Google Scholar
- Cetina Knorr K. ( 1995 , Ed. S. JasanoffG. MarkleJ. PetersenT. Pinch , Laboratory studies: the cultural approach to the study of science In: Handbook of Science and Technology Studies , Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 140-166. Google Scholar
- Koestler A. ( 1964 ). The Act of Creation , New York: Macmillan. Google Scholar
- Latour B., Woolgar S. ( 1986 ). Laboratory Life: The Construction of Scientific Facts , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. Google Scholar
- MacKinnon D. W. ( 1978 , Ed. D. W. MacKinnon , What makes a person creative? In: In Search of Human Effectiveness , New York: Universe Books, 178-186. Google Scholar
- Martindale C. ( 1999 , Ed. R. J. Sternberg , Biological basis of creativity In: Handbook of Creativity , Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press, 137-152. Google Scholar
- Mazur E. ( 1996 ). Peer Instruction: A User's Manual , Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. Google Scholar
- McFadzean E. ( 2002 ). Developing and supporting creative problem-solving teams: Part 1—a conceptual model . Manage. Decis 40 , 463-475. Google Scholar
- McGregor G. D. ( 2001 ). Creative thinking instruction for a college study skills program: a case study. . Dissert Abstr. Intl 62 , 3293A UMI No. AAT 3027933. Google Scholar
- McIntyre F. S., Hite R. E., Rickard M. K. ( 2003 ). Individual characteristics and creativity in the marketing classroom: exploratory insights . J. Mark. Educ 25 , 143-149. Google Scholar
- Mestre J. P. ( 2005 ). Transfer of Learning: From a Modern Multidisciplinary Perspective , Greenwich, CT: Information Age Publishing. Google Scholar
- Mumford M. D., Mobley M. I., Uhlman C. E., Reiter-Palmon R., Doares L. M. ( 1991 ). Process analytic models of creative capacities . Creativity Res. J 4 , 91-122. Google Scholar
- National Research Council ( 2007 ). Rising Above the Gathering Storm: Energizing and Employing America for a Brighter Economic Future, Committee on Science, Engineering and Public Policy In: Washington, DC: National Academies Press. Google Scholar
- Neisser U. ( 1963 ). The multiplicity of thought . Br. J. Psychol 54 , 1-14. Medline , Google Scholar
- Nelson C. E. ( 2008 ). Teaching evolution (and all of biology) more effectively: strategies for engagement, critical reasoning, and confronting misconceptions Integrative and Comparative Biology Advance Access accessed 15 September 2008 http://icb.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/reprint/icn027v1.pdf . Google Scholar
- Novak G, Gavrin A., Christian W, Patterson E. ( 1999 ). Just-in-Time Teaching: Blending Active Learning with Web Technology , San Francisco, CA: Pearson Benjamin Cummings. Google Scholar
- Osborn A. F. ( 1948 ). Your Creative Power , New York: Scribner. Google Scholar
- Osborn A. F. ( 1979 ). Applied Imagination , New York: Scribner. Google Scholar
- Osburn H. K., Mumford M. D. ( 2006 ). Creativity and planning: training interventions to develop creative problem-solving skills . Creativity Res. J 18 , 173-190. Google Scholar
- Paulus P. B., Nijstad B. A. ( 2003 ). Group Creativity: Innovation through Collaboration , New York: Oxford University Press. Google Scholar
- Perkins K. K., Wieman C. E. ( 2008 , Ed. R. L. DeHaanK.M.V. Narayan , Innovative teaching to promote innovative thinking In: Education for Innovation: Implications for India, China and America , Rotterdam, The Netherlands: Sense Publishers, 181-210. Google Scholar
- Plucker J. A., Renzulli J. S. ( 1999 , Ed. R. J. Sternberg , Psychometric approaches to the study of human creativity In: Handbook of Creativity , Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press, 35-61. Google Scholar
- Quitadamo I. J., Faiola C. L., Johnson J. E., Kurtz M. J. ( 2008 ). Community-based inquiry improves critical thinking in general education biology . CBE Life Sci. Educ 7 , 327-337. Link , Google Scholar
- Runco M. A. ( 2004 ). Creativity . Annu. Rev. Psychol 55 , 657-687. Medline , Google Scholar
- Runco M. A., Nemiro J. ( 1994 ). Problem finding, creativity, and giftedness . Roeper Rev 16 , 235-241. Google Scholar
- Sawyer R. K. ( 2005 ). Educating for Innovation Thinking Skills Creativity accessed 13 August 2008 1 41-48 www.artsci.wustl.edu/∼ksawyer/PDFs/Thinkjournal.pdf . Google Scholar
- Sawyer R. K. ( 2006 ). Explaining Creativity: The Science of Human Innovation , New York: Oxford University Press. Google Scholar
- Schwartz D. L., Bransford J. D., Sears D. ( 2005 , Ed. J. P. Mestre , Efficiency and innovation in transfer In: Transfer of Learning from a Modern Multidisciplinary Perspective , Greenwich, CT: Information Age Publishing, 1-51. Google Scholar
- Scott G., Leritz L. E., Mumford M. D. ( 2004 ). The effectiveness of creativity training: a quantitative review . Creativity Res. J 16 , 361-388. Google Scholar
- Simonton D. K. ( 1975 ). Sociocultural context of individual creativity: a transhistorical time-series analysis . J. Pers. Soc. Psychol 32 , 1119-1133. Medline , Google Scholar
- Simonton D. K. ( 2004 ). Creativity in Science: Chance, Logic, Genius, and Zeitgeist , Oxford, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. Google Scholar
- Sloman S. ( 1996 ). The empirical case for two systems of reasoning . Psychol. Bull 9 , 3-22. Google Scholar
- Smith G. F. ( 1998 ). Idea generation techniques: a formulary of active ingredients . J. Creative Behav 32 , 107-134. Google Scholar
- Snyder A., Mitchell J., Bossomaier T., Pallier G. ( 2004 ). The creativity quotient: an objective scoring of ideational fluency . Creativity Res. J 16 , 415-420. Google Scholar
- Sternberg R. J. ( 2003 ). What is an “expert student?” . Educ. Res. 32 , 5-9. Google Scholar
- Sternberg R., Williams W. M. ( 1998 ). Teaching for creativity: two dozen tips accessed 25 March 2008 www.cdl.org/resource-library/articles/teaching_creativity.php . Google Scholar
- Tardif T. Z., Sternberg R. J. ( 1988 , Ed. R. J. Sternberg , What do we know about creativity? In: The Nature of Creativity , New York: Cambridge University Press, 429-440. Google Scholar
- Torrance E. P. ( 1974 ). Norms and Technical Manual for the Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking , Bensenville, IL: Scholastic Testing Service. Google Scholar
- Torrance E. P. ( 1998 ). The Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking Norms—Technical Manual Figural (Streamlined) Forms A and B , Bensenville, IL: Scholastic Testing Service. Google Scholar
- Torrance E. P., Ball O. E., Safter H. T. ( 2008 ). Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking: Streamlined Scoring Guide for Figural Forms A and B , Bensenville, IL: Scholastic Testing Service. Google Scholar
- Treffinger D. J., Isaksen S. G. ( 2005 ). Creative problem solving: the history, development, and implications for gifted education and talent development . Gifted Child Q 49 , 342-357. Google Scholar
- Vandervert L. R., Schimpf P. H., Liu H. ( 2007 ). How working memory and the cerebellum collaborate to produce creativity and innovation . Creativity Res. J 9 , 1-18. Google Scholar
- Wallach M. A., Kogan N. ( 1965 ). Modes of Thinking in Young Children: A Study of the Creativity-Intelligence Distinction , New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Google Scholar
- Wood W. B. ( 2009 ). Innovations in undergraduate biology teaching and why we need them . Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol in press. Medline , Google Scholar
- ChatGPT improves creative problem-solving performance in university students: An experimental study Computers & Education, Vol. 215
- Educators as agents of breadth-biased learning: using social reconstructionism as rationale for embracing media multitasking and enhancing teaching practices in higher education 3 April 2024 | Frontiers in Psychology, Vol. 15
- Searching for creativity: How people search to generate new ideas 1 December 2023 | Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, Vol. 75, No. 4
- Fostering creativity in low-engagement students through socratic dialogue: An experiment in an operations class The International Journal of Management Education, Vol. 22, No. 1
- Cognitive flexibility and academic performance: Individual and cross-national patterns among adolescents in 57 countries Personality and Individual Differences, Vol. 217
- Are we teaching novice instructional designers to be creative? A qualitative case study 16 January 2024 | Instructional Science, Vol. 4
- What's in a word? Student beliefs and understanding about green chemistry 1 January 2024 | Chemistry Education Research and Practice, Vol. 25, No. 1
- Preservice Physical Education Teachers’ Resistance to Change: The Importance of Occupational Socialization Experiences 26 October 2023 | Trends in Higher Education, Vol. 2, No. 4
- How can we measure metacognition in creative problem-solving? Standardization of the MCPS scale Thinking Skills and Creativity, Vol. 49
- TOWARDS ENHANCING CREATIVITY AND INNOVATION IN EDUCATION SYSTEM FOR YOUTH IN HAIL REGION 1 August 2023 | Advanced Education, Vol. 10, No. 22
- Investigating the impact of innovation competence instruction in higher engineering education 12 June 2023 | European Journal of Engineering Education, Vol. 10
- Regaining creativity in science: insights from conversation 17 May 2023 | Royal Society Open Science, Vol. 10, No. 5
- How transdisciplinary integration, creativity and student motivation interact in three STEAM projects for gifted education? 29 March 2023 | Gifted Education International, Vol. 39, No. 2
- Does creative coursework predict educational, career, and community engagement outcomes for arts alumni? 15 November 2022 | Creativity Research Journal, Vol. 35, No. 2
- Make science disruptive again 27 March 2023 | Nature Biotechnology, Vol. 41, No. 4
- Promoting Creativity in Undergraduate Recreation and Leisure Services Classrooms: An Overview 19 March 2021 | SCHOLE: A Journal of Leisure Studies and Recreation Education, Vol. 38, No. 1
- A Positive Association between Working Memory Capacity and Human Creativity: A Meta-Analytic Evidence 13 January 2023 | Journal of Intelligence, Vol. 11, No. 1
- Students Creativity Through Digital Mind Map 26 July 2023
- Pedagogical and School Practices to Foster Key Competences and Domain-General Literacy 23 August 2023
- Coping with Challenges and Uncertainty in Scientific Research Asia-Pacific Science Education, Vol. 8, No. 2
- Teaching design thinking as a tool to address complex public health challenges in public health students: a case study 12 April 2022 | BMC Medical Education, Vol. 22, No. 1
- ‘Allowing them to dream’: fostering creativity in mathematics undergraduates 26 May 2022 | Journal of Further and Higher Education, Vol. 46, No. 10
- Interaction with metaphors enhances creative potential 1 July 2022 | Journal of Poetry Therapy, Vol. 35, No. 4
- Creative problem solving in knowledge-rich contexts Trends in Cognitive Sciences, Vol. 26, No. 10
- Teaching Protein–Ligand Interactions Using a Case Study on Tau in Alzheimer’s Disease 1 July 2022 | Journal of Chemical Education, Vol. 99, No. 8
- The Effectiveness of Collaborative Learning on Critical Thinking, Creative Thinking, and Metacognitive Skill Ability: Meta-Analysis on Biological Learning 15 July 2022 | European Journal of Educational Research, Vol. volume-11-2022, No. volume-11-issue-3-july-2022
- Student approaches to creative processes when participating in an open-ended project in science 30 June 2022 | International Journal of Science Education, Vol. 44, No. 10
- Arts, Machines, and Creative Education
- Perceived Learning Effectiveness and Student Satisfaction
- A Contribution to Scientific Creativity: A Validation Study Measuring Divergent Problem Solving Ability 3 September 2021 | Creativity Research Journal, Vol. 34, No. 2
- Problem Solving and Digital Transformation: Acquiring Skills through Pretend Play in Kindergarten 28 January 2022 | Education Sciences, Vol. 12, No. 2
- Growing Innovation and Collaboration Through Assessment and Feedback: A Toolkit for Assessing and Developing Students’ Soft Skills in Biological Experimentation 12 May 2022
- The Role of Creativity in Teaching Mathematics Online 1 December 2022
- Breathing Life Into Marketing Scholarship Through Creativity Learning and Teaching
- Mobilizing Research-Based Learning (RBL) in Higher Education
- Trends and opportunities by fostering creativity in science and engineering: a systematic review 2 September 2021 | European Journal of Engineering Education, Vol. 46, No. 6
- The effect of a scientific board game on improving creative problem solving skills Thinking Skills and Creativity, Vol. 41
- Create Teaching Creativity through Training Management, Effectiveness Training, and Teacher Quality in the Covid-19 Pandemic 6 August 2021 | Journal of Ethnic and Cultural Studies, Vol. 8, No. 4
- Creativity and technology in teaching and learning: a literature review of the uneasy space of implementation 11 January 2021 | Educational Technology Research and Development, Vol. 69, No. 4
- Üstün Yetenekli Öğrencilerin Bilimsel Yaratıcılık ve Bilimsel Problem Çözme ile İlgili Öz Değerlendirmeleri 15 July 2021 | Yuzunci Yil Universitesi Egitim Fakultesi Dergisi
- Cultivating creative thinking in engineering student teams: Can a computer‐mediated virtual laboratory help? 23 November 2020 | Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, Vol. 37, No. 2
- Entrepreneurial competencies of undergraduate students: The case of universities in Nigeria The International Journal of Management Education, Vol. 19, No. 1
- Promoting Creativity in General Education Mathematics Courses 5 August 2019 | PRIMUS, Vol. 31, No. 1
- Methodological Considerations for Understanding Students’ Problem Solving Processes and Affective Trajectories During Game-Based Learning: A Data Fusion Approach 3 July 2021
- The main trends in the process of building the creative potential of engineering students 18 June 2021 | E3S Web of Conferences, Vol. 274
- Research on the Present Situation and Countermeasures of Cultivating Graduate Students’ Innovation Ability under Cooperative Innovation Environment Creative Education Studies, Vol. 09, No. 02
- Innovation Centers and the Information Schools: The Influence of LIS Faculty Journal of Education for Library and Information Science, Vol. 61, No. 4
- Biomimetics: teaching the tools of the trade 28 September 2020 | FEBS Open Bio, Vol. 10, No. 11
- STEM academic teachers’ experiences of undertaking authentic assessment-led reform: a mixed method approach 21 March 2019 | Studies in Higher Education, Vol. 45, No. 9
- Problems of forming marketing competencies in the digital economy IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Vol. 940, No. 1
- Culturally Responsive Assessment of Physical Science Skills and Abilities: Development, Field Testing, Implementation, and Results 2 June 2020 | Journal of Advanced Academics, Vol. 31, No. 3
- Culturally Responsive Assessment of Life Science Skills and Abilities: Development, Field Testing, Implementation, and Results 3 June 2020 | Journal of Advanced Academics, Vol. 31, No. 3
- Curriculum Differentiation’s Capacity to Extend Gifted Students in Secondary Mixed-ability Science Classes 27 June 2020 | Talent, Vol. 10, No. 1
- Student Motivation from and Resistance to Active Learning Rooted in Essential Science Practices 23 December 2017 | Research in Science Education, Vol. 50, No. 1
- Integrating Entrepreneurship and Art to Improve Creative Problem Solving in Fisheries Education 27 February 2020 | Fisheries, Vol. 45, No. 2
- Concepts Re-imagined: Relational Signs Beyond Definitional Rigidity 15 August 2020
- Promoting Student Creativity and Inventiveness in Science and Engineering 24 October 2020
- Teaching for Leadership, Innovation, and Creativity
- Problem Çözme Becerileri Eğitim Programının Çocukların Karar Verme Becerileri Üzerindeki Etkisi 30 December 2019 | Erzincan Üniversitesi Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi, Vol. 21, No. 3
- Mento’s change model in teaching competency-based medical education 27 December 2019 | BMC Medical Education, Vol. 19, No. 1
- The Effects of Individual Preparations on Group Creativity 21 January 2020
- The Value of Creativity for Enhancing Translational Ecologies, Insights, and Discoveries 9 July 2019 | Frontiers in Psychology, Vol. 10
- Using the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health to Guide Students' Clinical Approach to Aging With Pathology Topics in Geriatric Rehabilitation, Vol. 35, No. 3
- Impact of Brainstorming Strategy in Dealing With Knowledge Retention Skill: An Insight Into Special Learners' Needs In Saudi Arabia 1 January 2021 | MIER Journal of Educational Studies Trends & Practices
- The potential of students’ creative disposition as a perspective to develop creative teaching and learning for senior high school biological science 12 March 2019 | Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Vol. 1157
- Evaluating Remote Experiment from a Divergent Thinking Point of View 25 July 2018
- Exploring Creative Education Practices and Implications: A Case study of National Chengchi University, Taiwan 4 April 2022 | Journal of Business and Economic Analysis, Vol. 02, No. 02
- Exploring Creative Education Practices and Implications: A Case study of National Chengchi University, Taiwan 1 January 2020 | Journal of Business and Economic Analysis, Vol. 02, No. 02
- Diverging from the Dogma: A Call to Train Creative Thinkers in Science 14 September 2018 | The Bulletin of the Ecological Society of America, Vol. 100, No. 1
- Comparison of German and Japanese student teachers’ views on creativity in chemistry class 16 May 2018 | Asia-Pacific Science Education, Vol. 4, No. 1
- The use of humour during a collaborative inquiry 27 August 2018 | International Journal of Science Education, Vol. 40, No. 14
- Connecting creative coursework exposure and college student engagement across academic disciplines 29 August 2019 | Gifted and Talented International, Vol. 33, No. 1-2
- Views of German chemistry teachers on creativity in chemistry classes and in general 1 January 2018 | Chemistry Education Research and Practice, Vol. 19, No. 3
- Embedding Critical and Creative Thinking in Chemical Engineering Practice
- Introducing storytelling to educational robotic activities
- Investigating Undergraduates’ Perceptions of Science in Courses Taught Using the CREATE Strategy Journal of Microbiology & Biology Education, Vol. 19, No. 1
- Teachers’ learning on the workshop of STS approach as a way of enhancing inventive thinking skills
- Creativity Development Through Inquiry-Based Learning in Biomedical Sciences
- The right tool for the right task: Structured techniques prove less effective on an ill-defined problem finding task Thinking Skills and Creativity, Vol. 26
- The influential factors and hierarchical structure of college students’ creative capabilities—An empirical study in Taiwan Thinking Skills and Creativity, Vol. 26
- Teacher perceptions of professional role and innovative teaching at elementary schools in Taiwan 10 November 2017 | Educational Research and Reviews, Vol. 12, No. 21
- Evaluation of creative problem-solving abilities in undergraduate structural engineers through interdisciplinary problem-based learning 28 July 2016 | European Journal of Engineering Education, Vol. 42, No. 6
- What Shall I Write Next? 19 September 2017
- Inquiry-based Laboratory Activities on Drugs Analysis for High School Chemistry Learning 3 October 2017 | Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Vol. 895
- BARRIERS TO STUDENTS’ CREATIVE EVALUATION OF UNEXPECTED EXPERIMENTAL FINDINGS 25 June 2017 | Journal of Baltic Science Education, Vol. 16, No. 3
- Kyle J. Frantz ,
- Melissa K. Demetrikopoulos ,
- Shari L. Britner ,
- Laura L. Carruth ,
- Brian A. Williams ,
- John L. Pecore ,
- Robert L. DeHaan , and
- Christopher T. Goode
- Elizabeth Ambos, Monitoring Editor
- A present absence: undergraduate course outlines and the development of student creativity across disciplines 3 October 2016 | Teaching in Higher Education, Vol. 22, No. 2
- Exploring differences in creativity across academic majors for high-ability college students 16 February 2018 | Gifted and Talented International, Vol. 32, No. 1
- Creativity in chemistry class and in general – German student teachers’ views 1 January 2017 | Chemistry Education Research and Practice, Vol. 18, No. 2
- IMPORTANCE OF CREATIVITY IN ENTREPRENEURSHIP 1 January 2017
- Accessing the Finest Minds
- Science and Innovative Thinking for Technical and Organizational Development
- Learning High School Biology in a Social Context Creative Education, Vol. 08, No. 15
- Possibilities and limitations of integrating peer instruction into technical creativity education 6 September 2016 | Instructional Science, Vol. 44, No. 6
- Creative Cognitive Processes in Higher Education 20 November 2014 | The Journal of Creative Behavior, Vol. 50, No. 4
- An Evidence-Based Review of Creative Problem Solving Tools 6 April 2016 | Human Resource Development Review, Vol. 15, No. 2
- Case-based exams for learning and assessment: Experiences in an information systems course
- Case exams for assessing higher order learning: A comparative social media analytics usage exam
- Beyond belief: Structured techniques prove more effective than a placebo intervention in a problem construction task Thinking Skills and Creativity, Vol. 19
- A Belief System at the Core of Learning Science
- Student Research Work and Modeled Situations in Order to Bridge the Gap between Basic Science Concepts and Those from Preventive and Clinical Practice. Meaningful Learning and Informed beneficience Creative Education, Vol. 07, No. 07
- FOSTERING FIFTH GRADERS’ SCIENTIFIC CREATIVITY THROUGH PROBLEM-BASED LEARNING 25 October 2015 | Journal of Baltic Science Education, Vol. 14, No. 5
- Scaffolding for Creative Product Possibilities in a Design-Based STEM Activity 16 November 2014 | Research in Science Education, Vol. 45, No. 5
- Intuition and insight: two concepts that illuminate the tacit in science education 18 June 2015 | Studies in Science Education, Vol. 51, No. 2
- Arts and crafts as adjuncts to STEM education to foster creativity in gifted and talented students 28 March 2015 | Asia Pacific Education Review, Vol. 16, No. 2
- Initiatives Towards an Education for Creativity Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, Vol. 180
- Brian A. Couch ,
- Tanya L. Brown ,
- Tyler J. Schelpat ,
- Mark J. Graham , and
- Jennifer K. Knight
- Michèle Shuster, Monitoring Editor
- Kim Quillin , and
- Stephen Thomas
- Mary Lee Ledbetter, Monitoring Editor
- The Design of IdeaWorks: Applying Social Learning Networks to Support Tertiary Education 21 July 2015
- Video Games and Malevolent Creativity
- Modelling a Laboratory for Ideas as a New Tool for Fostering Engineering Creativity Procedia Engineering, Vol. 100
- “Development of Thinking Skills” Course: Teaching TRIZ in Academic Setting Procedia Engineering, Vol. 131
- Leadership in the Future Experts’ Creativity Development with Scientific Research Activities 4 November 2014
- Developing Deaf Children's Conceptual Understanding and Scientific Argumentation Skills: A Literature Review 3 January 2014 | Deafness & Education International, Vol. 16, No. 3
- Leslie M. Stevens , and
- Sally G. Hoskins
- Nancy Pelaez, Monitoring Editor
- Cortex, Vol. 51
- A Sociotechnological Theory of Discursive Change and Entrepreneurial Capacity: Novelty and Networks SSRN Electronic Journal, Vol. 3
- GEOverse: An Undergraduate Research Journal: Research Dissemination Within and Beyond the Curriculum 1 August 2013
- Learning by Practice, High-Pressure Student Ateliers 2 August 2013
- Relating Inter-Individual Differences in Verbal Creative Thinking to Cerebral Structures: An Optimal Voxel-Based Morphometry Study 5 November 2013 | PLoS ONE, Vol. 8, No. 11
- 21st Century Biology: An Interdisciplinary Approach of Biology, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics Education Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, Vol. 102
- Reclaiming creativity in the era of impact: exploring ideas about creative research in science and engineering Studies in Higher Education, Vol. 38, No. 9
- An Evaluation of Alternative Ways of Computing the Creativity Quotient in a Design School Sample Creativity Research Journal, Vol. 25, No. 3
- A.-M. Hoskinson ,
- M. D. Caballero , and
- J. K. Knight
- Eric Brewe, Monitoring Editor
- Understanding, attitude and environment International Journal for Researcher Development, Vol. 4, No. 1
- Promoting Student Creativity and Inventiveness in Science and Engineering
- Building creative thinking in the classroom: From research to practice International Journal of Educational Research, Vol. 62
- A Demonstration of a Mastery Goal Driven Learning Environment to Foster Creativity in Engineering Design SSRN Electronic Journal, Vol. 111
- The development of creative cognition across adolescence: distinct trajectories for insight and divergent thinking 8 October 2012 | Developmental Science, Vol. 16, No. 1
- A CROSS-NATIONAL STUDY OF PROSPECTIVE ELEMENTARY AND SCIENCE TEACHERS’ CREATIVITY STYLES 10 September 2012 | Journal of Baltic Science Education, Vol. 11, No. 3
- Evaluation of fostering students' creativity in preparing aided recalls for revision courses using electronic revision and recapitulation tools 2.0 Behaviour & Information Technology, Vol. 31, No. 8
- Scientific Creativity: The Missing Ingredient in Slovenian Science Education 15 April 2012 | European Journal of Educational Research, Vol. volume-1-2012, No. volume1-issue2.html
- Could the ‘evolution’ from biology to life sciences prevent ‘extinction’ of the subject field? 6 March 2012 | Suid-Afrikaanse Tydskrif vir Natuurwetenskap en Tegnologie, Vol. 31, No. 1
- Mobile innovations, executive functions, and educational developments in conflict zones: a case study from Palestine 1 October 2011 | Educational Technology Research and Development, Vol. 60, No. 1
- Informing Pedagogy Through the Brain-Targeted Teaching Model Journal of Microbiology & Biology Education, Vol. 13, No. 1
- Teaching Creative Science Thinking Science, Vol. 334, No. 6062
- Sally G. Hoskins ,
- David Lopatto , and
- Leslie M. Stevens
- Diane K. O'Dowd, Monitoring Editor
- Embedding Research-Based Learning Early in the Undergraduate Geography Curriculum Journal of Geography in Higher Education, Vol. 35, No. 3
- Jared L. Taylor ,
- Karen M. Smith ,
- Adrian P. van Stolk , and
- George B. Spiegelman
- Debra Tomanek, Monitoring Editor
- IFAC Proceedings Volumes, Vol. 43, No. 17
- Critical and Creative Thinking Activities for Engaged Learning in Graphics and Visualization Course
- Creativity Development through Inquiry-Based Learning in Biomedical Sciences
Submitted: 31 December 2008 Revised: 14 May 2009 Accepted: 28 May 2009
© 2009 by The American Society for Cell Biology
Frontiers for Young Minds

- Download PDF
Can We Improve Problem Solving by Nurturing Creativity?

Did you ever face a problem you needed to solve? Most of us face such problems daily—for example, finding the shortest route to school, locating the source of a bad smell, fixing a broken home appliance, or settling a disagreement. Problem solving is an essential life skill. Problem solving is also a creative process, and creativity is considered an important life skill, too. In this study, we tested whether we could improve problem solving among teenagers by increasing their creativity using a simple method. We found that we could improve participants’ creativity, and that this led to improved problem-solving ability.
The Importance of Problem Solving
Problem solving is an important part of our lives. We all solve problems every day. You probably face many problems in school. Some of these problems relate to the stuff you learn, for example, how to complete the assignment the teacher gave you, how to recognize parts of speech in a sentence or properties of a matter, or how to memorize historical facts. However, you probably face many other types of problems, too—such as how to play with as many of your friends as possible during recess, how to cope with upsetting situations with other students, or how to get home by the shortest route.
In addition, children, teens, and adults face many problems that are not related to school—for example, how to fix a broken appliance, how to trace the source of a bad smell, how to settle a disagreement, or how to plan a fun family trip. Overall, problem solving is considered a key life skill that everybody needs to master.
What Is Creativity?
Creativity is somewhat difficult to define. First, it is important to know that creativity is a skill that can be learned, practiced, and improved. It is not something that you are either born with or not. Scientists know this for sure after decades of studying creativity among various populations. Second, it should be clearly noted that creativity applies to all aspects of life and not just to the arts. Many people are creative in what they do, even if they are teachers, mathematicians, mechanics, pediatricians, or programmers. Furthermore, creativity can be shown in everyday activities, like playing (especially when pretending), cooking, or debating a topic with others.
With that in mind, creativity is traditionally defined as producing something that is both new and useful [ 1 ]. Imagine trying to bake a creative cake for a school contest. If your recipe is original (new) but the result is inedible (not useful), then your cake is not creative. On the other hand, if the cake looks or tastes amazing (useful) but the recipe is someone else’s (not new), your cake is also not creative. For your cake to be considered creative, it should be both based on an original (new) recipe and it should be edible (useful).
How Can You Measure Creativity?
Most people can appreciate that something is creative when they see or hear it, but how can we measure just how creative something is? This is a critical issue when we want to study creativity and test whether it has changed. One of the common ways to measure creativity is by giving a creativity test, and then calculating a few values to get the results. In the test that we used, called Torrance’s Test for Creative Thinking [ 2 ], the test page consists of 12 identical empty circles. The person taking the test is asked to draw as many drawings as possible using the circles as part of them, in just a few minutes. So, one circle can be turned into a pizza pie, another circle can be turned into an emoji, and another into a basketball. Furthermore, two circles could be combined to form wheels of a bicycle, and multiple circles could be connected and turned into a caterpillar. The options are endless ( Figure 1 ).

- Figure 1 - A filled-up page from Torrance’s Test for Creative Thinking, which we used in our study.
- Participants were given with a sheet of paper that has 12 empty circles, and were asked to draw as many drawings as possible while making use of the circles as an integral part of these drawing. Note that, in more than one case, two circles were used to form a single drawing (glasses and a Google logo). Note also that this participant felt that it was ok to draw outside the original circles (which is indeed ok).
Once the test is finished and the papers are collected, we can calculate various dimensions of creativity. One such dimension is how many drawings the person completed. Another dimension has to do with how many different types of drawings the test-taker drew; for example, a basketball, soccer ball, and tennis ball are different drawings but are of the same type. A third dimension involves how original the drawings are compared to other participants. The final dimension involves how many details were included in the drawings. These dimensions can be easily computed, and they can help researchers assign a numerical value to each test.
How Does Creativity Relate to Problem Solving?
Creativity has a lot to do with problem solving. In many cases, people demonstrate creativity when they try to solve problems. Recall the example of the cake contest from above—in that case, we could say that the problem was how to win the contest. So, it is probably not surprising that creativity has been suggested as a way to improve problem solving in several areas, for example when learning mathematics, science, foreign language, literature, or history [ 3 ].
Also, remember that creativity can be learned, practiced, and improved. This means we can ask whether we can improve creativity in a way that also improves problem solving—and this is exactly the question that we posed in our study.
Insights From Our Study
In our study, we tested teens’ creative thinking and problem-solving skills before and after an activity that was aimed at promoting their creativity. This way, we could check whether the creativity training improved their creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The problem-solving activity was done in an online learning environment. The participants were asked to lead a virtual astronaut through several tasks to get her to her destination. In each task, participants were presented with a path the astronaut should follow and with a pool of blocks that each represent a certain action, like “move forward” or “turn right.” The blocks could be dragged and connected like Lego bricks to construct a sequence of actions. For example, if a participant wanted the astronaut to go one step forward and then turn right, they used a “move forward” block connected to a “turn right” block ( Figure 2 ). We tested how well participants solved these problems by measuring the time it took them and the number of tries they needed to complete the tasks. The creative thinking test we gave them was just like the one we described above, with 12 empty circles.
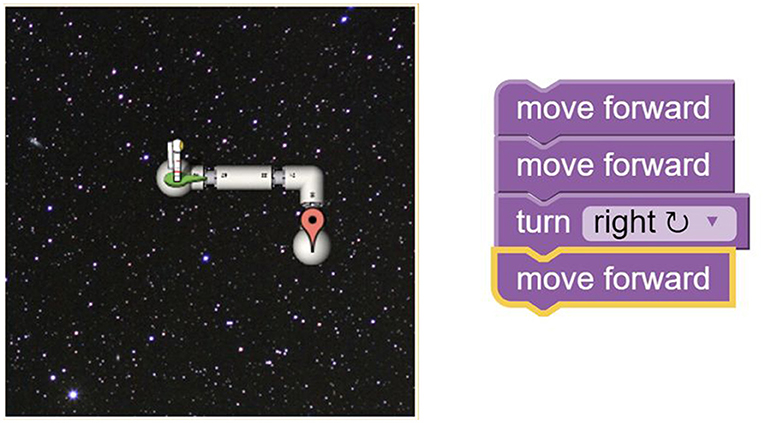
- Figure 2 - A task from the online learning environment that we used in our study, and its solution.
- Participants had to put together steps to guide the astronaut through the path to her destination. We measured how many attempts it took participants until solving this task, how much time did it take then, and how original were their solutions.
Then, we gave some participants a special activity, called an intervention , for nurturing their creativity. This involved one 15-min meeting per week for 10 weeks. In each meeting, we presented the participants with pictures of everyday objects—like a paper cup, ruler, car wheel, basketball, etc.—and for each object, we asked participants to write down as many uses as they could think of ( Figure 3 ). They worked independently, so no one could see or hear what the others wrote, and we recorded their responses anonymously. Once in a few intervention sessions, we shared with them interesting uses that were mentioned by the group. This way, we helped them to practice thinking creatively. We also had a control group made up of a group of participants that did not take part in this intervention. Using a control group allows to test whether the results of the experiment replicate with no intervention.

- Figure 3 - During our intervention, we presented the participants with daily objects—one at a time—just like the ones shown here.
- For each object, participants were asked to write down as many uses as possible. This intervention was shown to improve their creative thinking and problem-solving abilities.
After this intervention, all the participants were given another problem-solving test, this time with different, more difficult tasks, and another creativity drawing test, this time with squares instead of circles.
When we analyzed the data by comparing their performance on the pre/post-tests , we observed two fascinating patterns. First, all participants improved in measures of creativity, but those who did the intervention improved more than those in the control group. Second, everybody improved their problem-solving skills, but those who participated in the intervention improved these skills more than those in the control group.
So, in our study, we were able to improve creativity and, by doing so, we also improved problem solving!
You Too Can Be More Creative and a Better Problem Solver!
These findings are promising, especially because our intervention was simple and it could be given by anyone, anywhere, without special equipment or special knowledge. This means that you too can use this intervention to improve your own creativity, or you can help your friends or classmates improve their creativity. Simply think of a daily object you are familiar with, and think of as many possible uses to it. By doing so, you will probably become a better problem solver, which can help you in school and throughout life.
Problem Solving : ↑ Finding correct solutions to challenges, tasks of puzzles.
Creativity : ↑ A mental skill that helps produce something that is both new and useful.
Intervention : ↑ An action researchers take to test the impact on research participants.
Control Group : ↑ A control group holds part of a research population who do not get an intervention. Comparing the control group to the other participants helps scientists deduce that the intervention worked.
Pre/Post-Tests : ↑ Similar or identical tests that are given to research participants before (“pre”) and after (“post”) an intervention, to determine the impact of the intervention.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Original Source Article
↑ Israel Fishelson, R., and Hershkovitz, A. 2022. Cultivating creativity improves middle school students’ computational thinking skills. Inter. Learn. Environ . doi: 10.1080/10494820.2022.2088562
[1] ↑ Runco, M. A., and Jaeger, G. J. 2012. The standard definition of creativity. Creat. Res. J. 24:92–96. doi: 10.1080/10400419.2012.650092
[2] ↑ Torrance, E. P. 1974. Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking . Bensenville, IL: Scholastic Testing Service..
[3] ↑ Treffinger, D. J. 1995. Creative problem solving: overview and educational implications. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 7:301–312.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Creative Porblem Solving (CPS) is framework which individuals or groups can use to: formulate problems, opportunities, or challenges; generate and analyze many, varied, and novel options; and plan for effective implementation of new solutions or courses of action. Today's CPS framework bulds on more than four decades of theory, research, and application in a variety of contexts. CPS involves ...
Educational Implications. Donald J. TVeffïnger12. Creative Problem Solving (CPS) is a framework which individuals or groups can use to: formulate problems, opportunities, or challenges; generate and. analyze many, varied, and novel options; and plan for effective implementation of new solutions or courses of action.
Discusses the development and current status of Creative Problem Solving (CPS), an approach that was developed by S. G. Isaksen et al (1994) and D. J. Treffinger et al (1994). CPS is a framework that individuals or groups can use to: (1) formulate problems, opportunities, or challenges; (2) generate and analyze many, varied, and novel options; and (3) plan for effective implementation of new ...
This article presents a summary of research, development, and applications of Creative Problem Solving (CPS) in educational settings and, more specifically, in gifted education. The CPS framework is widely known and applied as one important goal in contemporary gifted education, as well as in relation to initiatives for "teaching thinking ...
Creative Problem Solving in Primary Education: Exploring the Role of Fact Finding, Problem Finding, and Solution Finding across T asks, Thinking Skills and Creativity (2020), doi: https://doi.org ...
This text provides a comprehensive and contemporary overview and description of Creative Problem Solving (CPS). Accessible and highly practical for a broad base of researchers and practitioners, the book provides a framework, a language, guidelines, and a set of easy-to-use tools for understanding challenges, generating ideas, and transforming promising ideas into action.
Humans are innate creative problem-solvers. Since early humans developed the first stone tools to crack open fruit and nuts more than 2 million years ago, the application of creative thinking to solve problems has been a distinct competitive advantage for our species (Puccio 2017).Originally used to solve problems related to survival, the tendency toward the use of creative problem-solving to ...
Highlights. Creative problem solving (CPS) relies on the reorganization of existing knowledge to serve new, problem-relevant functions. Extant creativity research, especially brain-based research, largely does not reflect the knowledge-rich contexts in which the application of previously-acquired knowledge is critical, as is frequently the case ...
CPS is a comprehensive system built on our own natural thinking processes that deliberately ignites creative thinking and produces innovative solutions. Through alternating phases of divergent and convergent thinking, CPS provides a process for managing thinking and action, while avoiding premature or inappropriate judgment. It is built upon a ...
Creative Problem Solving (CPS) can help your students to approach problems and deal with change in a deliberate and constructive way, building their confidence and success in working with complex issues. This revised and updated fourth edition includes: practical suggestions for those new to Creative Problem Solving. Educational Resource.
Abstract. Four processes are at the core of "creative" problem-solving: finding problems, generating novelty, defining solutions, and recognizing solutions. The statement of the problem itself ...
The purpose of this exploratory study of creative problem-solving characteristics of young children was to (a) determine whether the percentage of creativity-relevant behaviors declined, stayed the same, or increased as children entered school and progressed to the first grade (ages 4, 5, and 6) and (b) describe differences and similarities across the three ages and ten domains in the assessment.
The thinking skills and powerful practice are promoted by the creative problem solving (CPS) method, which conform to the OEP. There are five steps for using OER through OEP: 1) Learning to "Open" 2) Goals setting and Collaborative learning 3) Retrieving and Brainstorming 4) Reuse, Revise and co-creating and 5) Evaluate, Feedback and Retain.
We identify five reasons why it is important for at-risk students to learn and be able to apply Creative Problem Solving (CPS). CPS builds on both creative and critical thinking (in harmony with each other). The CPS Version 6.1TM framework incorporates guidelines and specific tools for generating ideas ("creative" thinking) and focusing ideas ("critical" thinking), and involves four components ...
This article presents a summary of research, development, and applications of Creative Problem Solving (CPS) in educational settings and, more specifically, in gifted education. The CPS framework is widely known and applied as one important goal in contemporary gifted education, as well as in relation to initiatives for "teaching thinking" in the broader context of general education. This ...
Creative problem solving: the history, development, and implications for gifted education and talent development. Gifted Child Q 49, 342-357. Google Scholar; Vandervert L. R., Schimpf P. H., Liu H. (2007). How working memory and the cerebellum collaborate to produce creativity and innovation. Creativity Res. J 9, 1-18. Google Scholar
More recently, Treffinger's study (1995), "Creative Problem solving: Overview and Educational Implications", reviews the later trends in creative problem solving. According to his article, CPS is … Representing process dimensions in a natural, rather than in a contrived way. Undergoing a transformation from a prescriptive to a descriptive ...
Creative Problem Solving (CPS) techniques could support such thinking, for they encourage students to be open-minded and curious, think out of the box, conceptualise and reflect, allowing them to take a multi-perspective approach that is conducive to original and new insights. ... Practical implications for medical education. ... Treffinger DJ ...
Donald J. Treffinger t,2. Creative Problem Solving (CPS) is aframework hich individuals or groups can use to: formulate problems, opportunities, orchallenges; gen rate and analyze many, varied, annovel options; andplan for effective implementation of new solutions or courses of action. Today's CPS framework builds on more than four decades ...
So, it is probably not surprising that creativity has been suggested as a way to improve problem solving in several areas, for example when learning mathematics, science, foreign language, literature, or history [ 3 ]. Also, remember that creativity can be learned, practiced, and improved. This means we can ask whether we can improve creativity ...
Understanding, measuring, and enhancing individual creative problem-solving efforts. Creativity Research Journal, 11 (2) (1998), pp. 123-150. ... Overview and educational implications. Educational psychology review, 7 (1995), pp. 301-312. View in Scopus Google Scholar. VanderWeele, 2016.
The Evaluation of Potential Creativity (EpoC) battery is described as a relevant new tool to assess convergent thinking, with a focus on the integrative, original synthesis, which is ultilmately essential to the creative process, and the potential for resulting creative productions. Implications for measuring creativity and education are discussed.