
- Programs & Services
- Delphi Center

Ideas to Action (i2a)
- Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Framework
Critical thinking is that mode of thinking – about any subject, content, or problem — in which the thinker improves the quality of his or her thinking by skillfully taking charge of the structures inherent in thinking and imposing intellectual standards upon them. (Paul and Elder, 2001). The Paul-Elder framework has three components:
- The elements of thought (reasoning)
- The intellectual standards that should be applied to the elements of reasoning
- The intellectual traits associated with a cultivated critical thinker that result from the consistent and disciplined application of the intellectual standards to the elements of thought
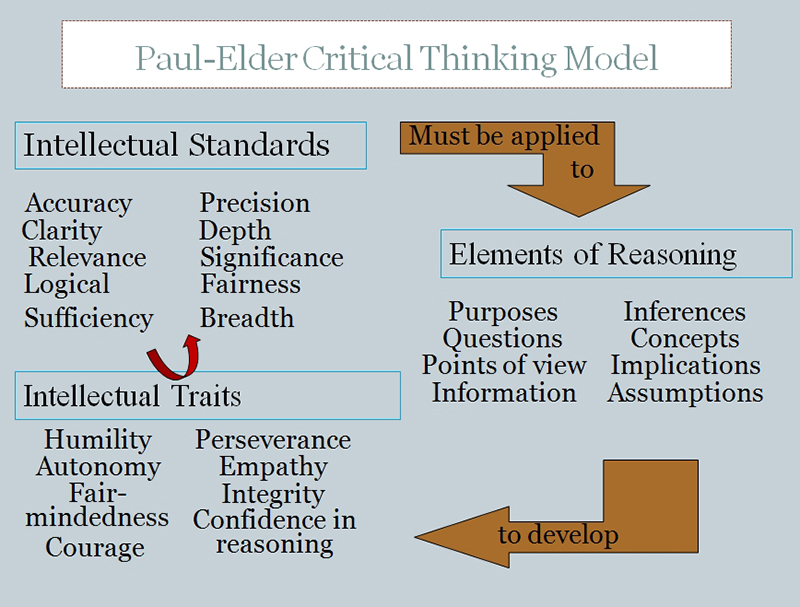
According to Paul and Elder (1997), there are two essential dimensions of thinking that students need to master in order to learn how to upgrade their thinking. They need to be able to identify the "parts" of their thinking, and they need to be able to assess their use of these parts of thinking.
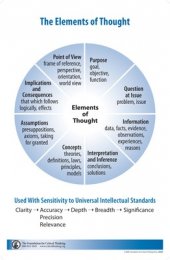
Elements of Thought (reasoning)
The "parts" or elements of thinking are as follows:
- All reasoning has a purpose
- All reasoning is an attempt to figure something out, to settle some question, to solve some problem
- All reasoning is based on assumptions
- All reasoning is done from some point of view
- All reasoning is based on data, information and evidence
- All reasoning is expressed through, and shaped by, concepts and ideas
- All reasoning contains inferences or interpretations by which we draw conclusions and give meaning to data
- All reasoning leads somewhere or has implications and consequences
Universal Intellectual Standards
The intellectual standards that are to these elements are used to determine the quality of reasoning. Good critical thinking requires having a command of these standards. According to Paul and Elder (1997 ,2006), the ultimate goal is for the standards of reasoning to become infused in all thinking so as to become the guide to better and better reasoning. The intellectual standards include:
Intellectual Traits
Consistent application of the standards of thinking to the elements of thinking result in the development of intellectual traits of:
- Intellectual Humility
- Intellectual Courage
- Intellectual Empathy
- Intellectual Autonomy
- Intellectual Integrity
- Intellectual Perseverance
- Confidence in Reason
- Fair-mindedness
Characteristics of a Well-Cultivated Critical Thinker
Habitual utilization of the intellectual traits produce a well-cultivated critical thinker who is able to:
- Raise vital questions and problems, formulating them clearly and precisely
- Gather and assess relevant information, using abstract ideas to interpret it effectively
- Come to well-reasoned conclusions and solutions, testing them against relevant criteria and standards;
- Think open-mindedly within alternative systems of thought, recognizing and assessing, as need be, their assumptions, implications, and practical consequences; and
- Communicate effectively with others in figuring out solutions to complex problems
Paul, R. and Elder, L. (2010). The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts and Tools. Dillon Beach: Foundation for Critical Thinking Press.
- SACS & QEP
- Planning and Implementation
- What is Critical Thinking?
- Why Focus on Critical Thinking?
- Culminating Undergraduate Experience
- Community Engagement
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is i2a?
Copyright © 2012 - University of Louisville , Delphi Center

Designorate
Design thinking, innovation, user experience and healthcare design
How to Apply Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Framework
The critical thinking framework provides an efficient method for designers, design students, and researchers to evaluate arguments and ideas through rational reasoning. As a result, we eliminate biases, distractions, and similar factors that negatively affect our decisions and judgments. We can use critical thinking to escape our current mindsets to reach innovative outcomes.
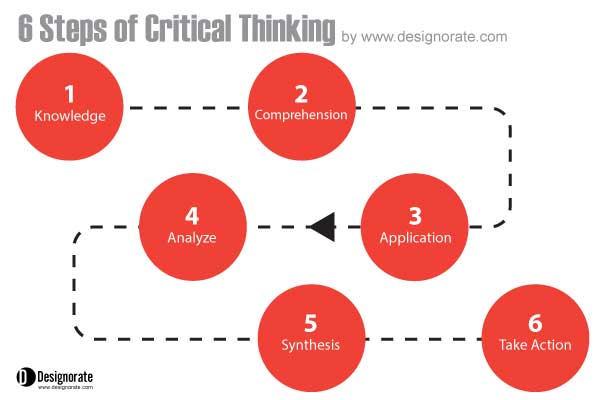
The critical thinking framework is based on three main stages; observe the problem to build rational knowledge, ask questions to analyze and evaluate data, and find answers to the questions that can be formulated into a solution. These stages are translated into six steps ( 6 Steps for Effective Critical Thinking ):
- Knowledge – Define the main topic that needs to be covered
- Comprehension – Understand the issue through researching the topic
- Application – Analyze the data and link between the collected data
- Analysis – Solve the problem, or the issue investigated
- Synthesis – Turn the solution into an implementable action plan
- Evaluate – test and evaluate the solution
Based on the above, the essential part of the critical thinking framework represents building clear, coherent reasoning for the problem, which will help ensure that the topic is addressed in the critical thinking stages.
Related articles:
- Guide for Critical Thinking for Designers
- 6 Steps for Effective Critical Thinking
- The Six Hats of Critical Thinking and How to Use Them
The Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Framework
In 2001, Paul and Elder introduced the critical thinking framework that helps students to master their thinking dimensions through identifying the thinking parts and evaluating the usage of these parts. The framework aims to improve our reasoning by identifying its different elements through three main elements; elements of reasoning, intellectual standards, and intellectual traits.
Elements of Reasoning
Whenever we have a topic or argument to discuss, we tend to use a number of thinking models to understand the topic at hand (i.e. Using Inductive Reasoning in User Experience Research ). These parts are known as the elements of thought or reasoning. Our minds may use these parts over the course to think about the idea:
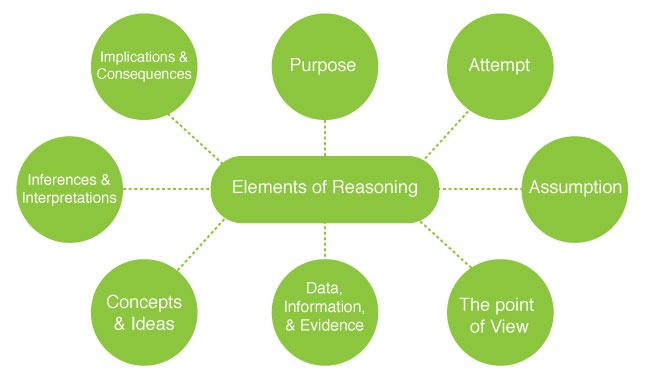
Purpose – This part of our thinking includes defining the topic’s goal or objective. For example, the goal may involve solving a problem or achieving a target. Attempt – This part includes the attempts that previously addressed the topic or attempts to solve a problem. Assumption – Before solving a problem, we don’t have much information about the topic. Therefore, we build assumptions to act as the base of our research about the issue. We usually start with inductive inferences. Then, we use the research data to validate these assumptions. For example, we assume that all apples are red and start to research the different types of trees to know that some apples are green and some are red. The point of View includes the personal perspective we take while thinking about the topic. For instance, we can think about the product from the consumer perspective rather than the business perspective. Data, Information, and Evidence – Here, we cover the data and information related to the topic. Also, here we have all the supportive evidence. Concepts and Ideas – We have all the principles, models, and theories related to the topic. For example, this part may include all the views associated with applying a specific solution. Inferences and Interpretations – The last part includes the concluded solutions based on the previous factors. The conclusion may consist of the suggested solution to a specific problem. Implications and Consequences – All the reasons must lead to consequences resulting from implementing the results of the reasoning process.
Intellectual Standards
The above reasoning parts require a good quality benchmark to achieve its goals and ensure the accuracy of results. The intellectual standards are nine factors that can evaluate the equality of the reason parts mentioned above. These standards include clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance, depth, breadth, logic, significance, and fairness. Based on these standards, we can ask ourselves questions to evaluate the parts above. The below table provides examples of the questions that we can ask to assess the equality of our ideas.

The below two videos include Dr. Richard Paul’s lectures about the standards of thought and critical thinking.
Intellectual Traits
As a result of the application for the above reasoning parts and validating them using intellectual standards, The below characteristics are expected to evolve, known as the intellectual traits:
Intellectual Humility
This trait develops one’s ability to perceive the known limitation and the circumstances that may cause biases and self-deceptively. It depends on recognizing that one claims what one’s knows.
Intellectual Courage
Courage represents developing a consciousness to address ideas fairly regardless of its point of View or our negative emotions about it. Also, it helps us develop our ability to evaluate ideas regardless of our presumptions and perceptions about them.
Intellectual Empathy
Empathy is related to developing the ability to put ourselves in others’ shoes to understand them. Also, it forms how we can see the parts of reasoning of the others, such as the viewpoints, assumptions, and ideas.
Intellectual Integrity
This part is related to developing the ability to integrate with other intellectual reasoning and avoid the confusion of our reasoning. Unlike empathy, integrity focuses on the ability to others’ reasoning for the topic and integrate with it.
Intellectual Perseverance
Perseverance develops the need to have a proper insight about the situation regardless of the barriers faced against it, such as difficulties, frustration, and obstacles. This helps us to build rational reasoning despite what is standing against it.
Confidence in Reason
By applying the reasoning parts and encouraging people to develop their reasons, they build confidence in their reason and rational thinking.
Fair-mindedness
This trait develops the ability to start with a fair look at all the reasoning and traits of all the viewpoints, putting aside one’s feelings, raises, and interests.
The critical thinking framework can help us address topics and problems more rationally, contributing to building a clear understanding of topics. This can be achieved through having clear reasoning about the addressed topics. The Paul-Eder Critical Thinking Framework was introduced in 2001 to improve the critical thinking process by understanding the parts of the reasons and providing a method to evaluate it. You can learn more about the framework through the Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking published by the Foundation of Critical Thinking.
Understanding the thinking elements and how to evaluate our reasoning related to each part, we can improve our thoughts through time. Additionally, seven main advantages (intellectual traits) can be achieved.
Paul-Elder’s critical thinking framework identifies the thinking parts through eight elements of reasoning (purpose, attempt, assumption, point of view, data, concepts and ideas, and inference and interpretation). Nine benchmarks are used to evaluate the application of the above elements (clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance, depth, breadth, logic, significance and fairness).
What are the critical thinking framework elements?
Define the main topic that needs to be covered
Understand the issue through researching the topic
Analyze the data and link between the collected data
Solve the problem, or the issue investigated
Turn the solution into an implementable action plan
Test and evaluate the solution
The application of the Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Framework is based on identifying eight elements of reasoning: Purpose, Attempt, Assumption, Point of View, Data and Evidence, Concepts and Ideas, Inferences and Interpretations and Implications and Consequences.
Wait, Join my Newsletters!
As always, I try to come to you with design ideas, tips, and tools for design and creative thinking. Subscribe to my newsletters to receive new updated design tools and tips!
Dr Rafiq Elmansy
As an academic and author, I've had the privilege of shaping the design landscape. I teach design at the University of Leeds and am the Programme Leader for the MA Design, focusing on design thinking, design for health, and behavioural design. I've developed and taught several innovative programmes at Wrexham Glyndwr University, Northumbria University, and The American University in Cairo. I'm also a published book author and the proud founder of Designorate.com, a platform that has been instrumental in fostering design innovation. My expertise in design has been recognised by prestigious organizations. I'm a fellow of the Higher Education Academy (HEA), the Design Research Society (FDRS), and an Adobe Education Leader. Over the course of 20 years, I've had the privilege of working with esteemed clients such as the UN, World Bank, Adobe, and Schneider, contributing to their design strategies. For more than 12 years, I collaborated closely with the Adobe team, playing a key role in the development of many Adobe applications.
You May Also Like

Creative Problem Solving: How to Turn Challenges into Opportunities

How to Use the Fishbone Diagram in Root Cause Analysis?

What is Systems Thinking? And How to Use the Fifth Discipline to Understand it?

How Does Apple’s Design Process Work?
Design Thinking Tools for Ideation

Design Thinking Tools: Reverse Brainstorming
3 thoughts on “ how to apply paul-elder critical thinking framework ”.
it was really helpfull
Thank you for this helpful distillation, as well as including the videos.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Sign me up for the newsletter!
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

Introduction to the Paul-Elder Model of Critical Thinking
Dr. sara rich .
Before choosing your own pseudoscience adventure to think critically through, let’s take a moment to explain our methodology. Namely, we have used the Paul-Elder Model of Critical Thinking to work through each question at issue and to arrive at a well-reasoned conclusion. This process has been made transparent for our readers: each section of each chapter represents one step of the Paul-Elder Model, which leads up to the written research component where all those steps are put together into a coherent argument. Each unit concludes with some critical thinking exercises pertaining to that particular pseudoscience, inspired by Gerald Nosich’s Learning to Think Things Through . This will help readers to further think and apply their learning to the pseudoscience of interest.
Step 1: Elements of Reasoning
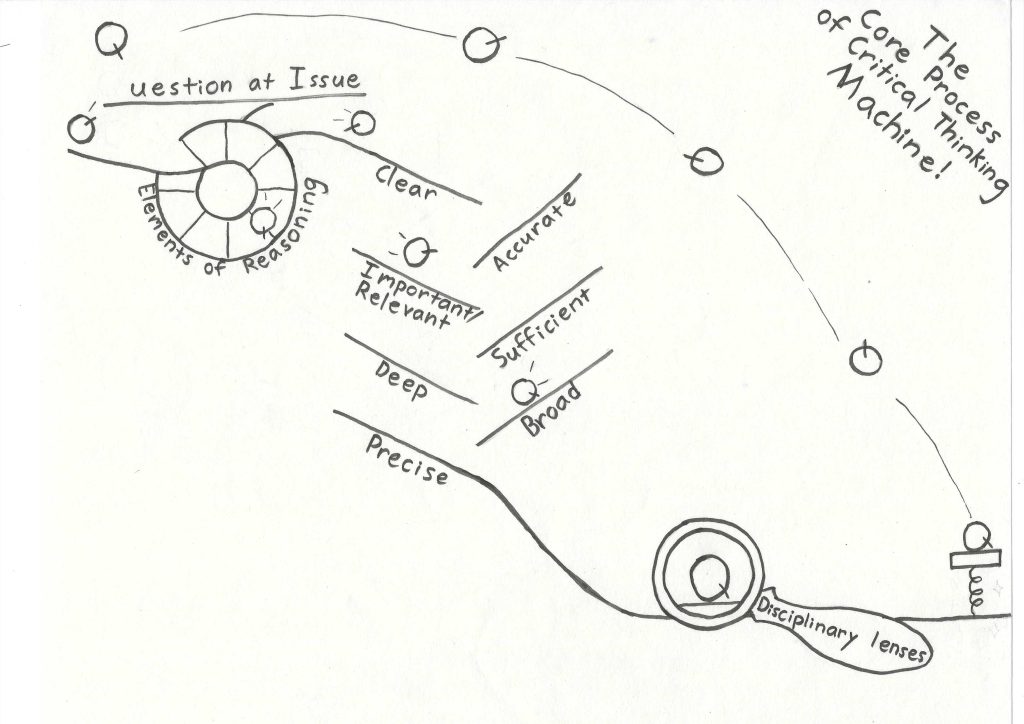
The first step of the Paul-Elder Model is the Elements of Reasoning (Fig. 1). We start with the question at issue – identifying the key question that you have about a given topic. Why? All answers first require a question. Furthermore, starting with the question at issue also sets up the thinker with a sense of epistemic humility. In other words, with every question asked, there is an implicit recognition of a gap in knowledge. The questioner becomes like Socrates, who recognized all the things that he did not know. There are limits to human knowledge, and no one knows everything. Critical thinkers recognize the gaps in their knowledge and use ambition and curiosity to rectify them with integrity and responsibility.
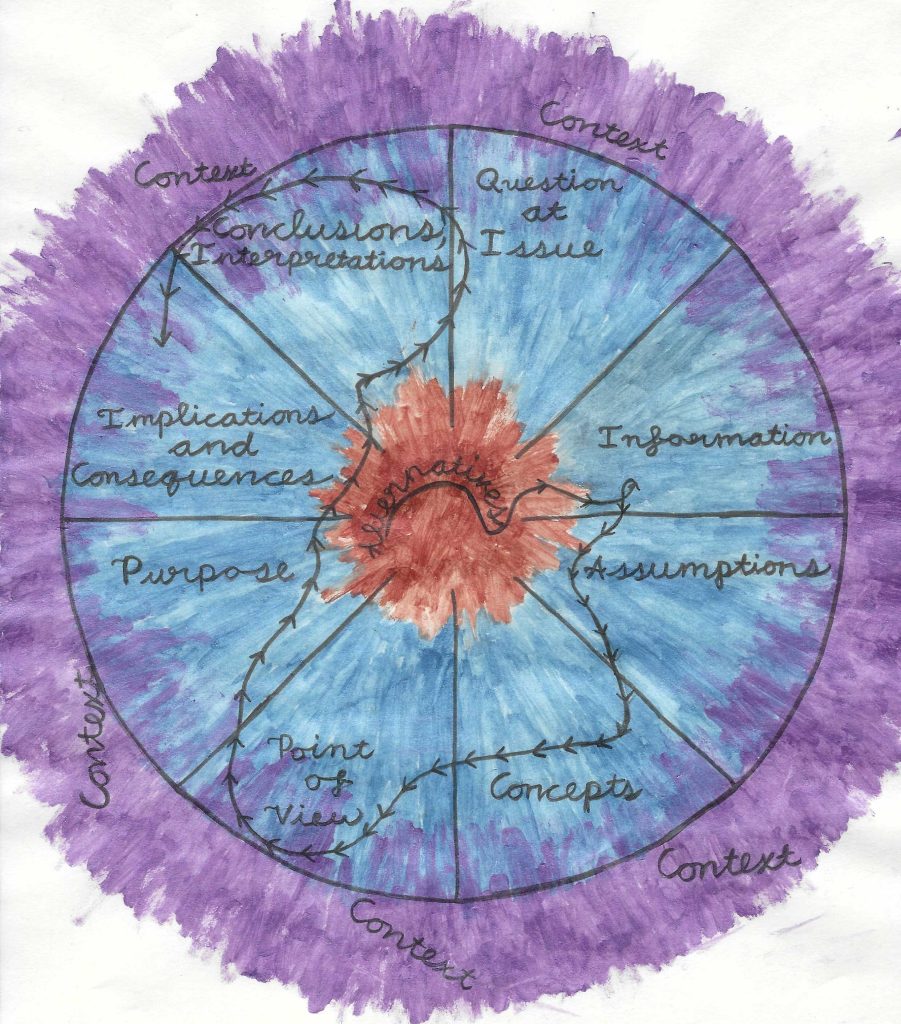
Once the question at issue is established, the critical thinker should proceed around the wheel of the 8+ Elements of Reasoning (always considering the context that undergirds the problem as a whole and alternatives to each element), until finally arriving at conclusions and interpretations. Arriving at a conclusion or interpretation is arriving at a reasoned answer to the question at issue. To go one step further, the critical thinker may return to implications and consequences in order to understand the real-world effects of the conclusion drawn. Many pseudosciences, including science denialism and the conspiracy theories that inform them, are highly consequential on individual and societal scales.
Step 2: Disciplinary Lenses
To fine-tune this conclusion even further, the critical thinker should use relevant disciplinary lenses to think about the problem the way an expert would (Fig. 2).
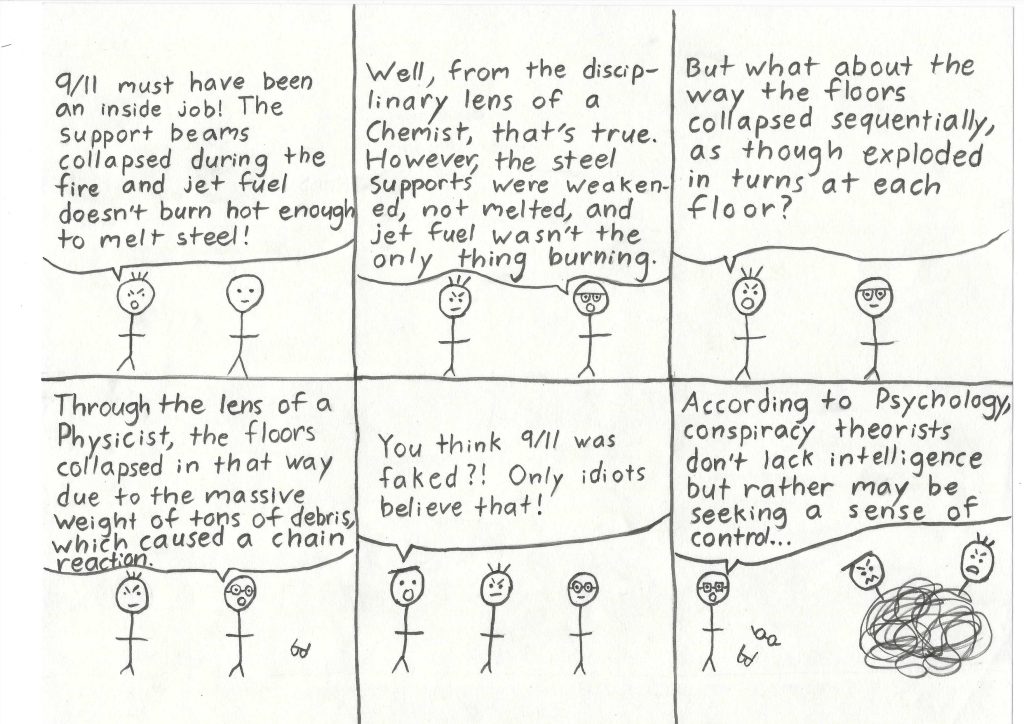
To provide another example, if your question is about Atlantis, some relevant disciplinary lenses to think with would be history, geology, and archaeology. Using the disciplinary lenses is like taking on the point of view (one of the elements of reasoning) of unbiased experts in relevant fields of study. It also offers the opportunity think using different types of reasoning: namely inductive (history), deductive (geology), and abductive (archaeology). This practice will help ensure that final conclusions are drawn from all the relevant evidence (primary source documents, geological data, and archaeological excavations), that they are placed in context (historical, geological, and archaeological), and that they demonstrate a complete understanding of the most important related concepts (Platonism, plate tectonics, artifact typologies, etc.).
Step 3: Standards of Critical Thinking
Once the fine-tuned conclusion is reached, it should be self-evaluated using the Standards of Critical Thinking (Fig. 3). These standards can be used to evaluate any empirical claim and the evidence used to support it, but it again requires a certain level of epistemic humility to apply them to your own argument. How well an argument holds up against the standards is a good indicator of how well it has been reasoned.
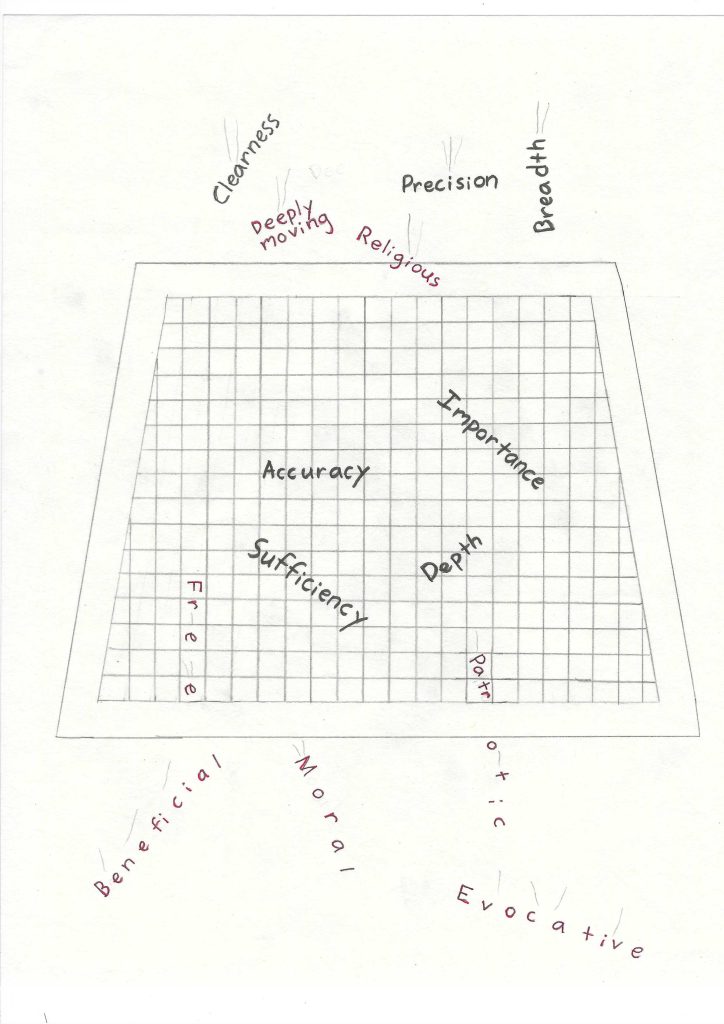
All relevant empirical claims should also be inspected for weak inductive, deductive, or abductive reasoning. Relevant claims and arguments should also be scrutinized for logical fallacies. Psuedosciences and conspiracy theories are generally brimming with logical fallacies, and learning to identify them can even be a fun pastime for the critical thinker! To learn more about logical fallacies, we recommend the open-access textbooks by Matthew Van Cleave, Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking , and Andrew Lavin, Thinking Well .
Step 4: SEE-I Method
The SEE-I method is an outline for creating a complete and coherent argument (Fig. 4). The SEE-I method can consist of as few as four sentences, or an entire doctoral dissertation can be organized this way. Effectively, the thesis statement – or concise response to the research question – comes first, followed by further elaboration and explanation (provision of context, definition of key concepts, address of the counterargument, etc.). The next section of the argument consists of examples, each in support of the thesis statement. The final step is to illustrate the thesis statement by using an analogy.
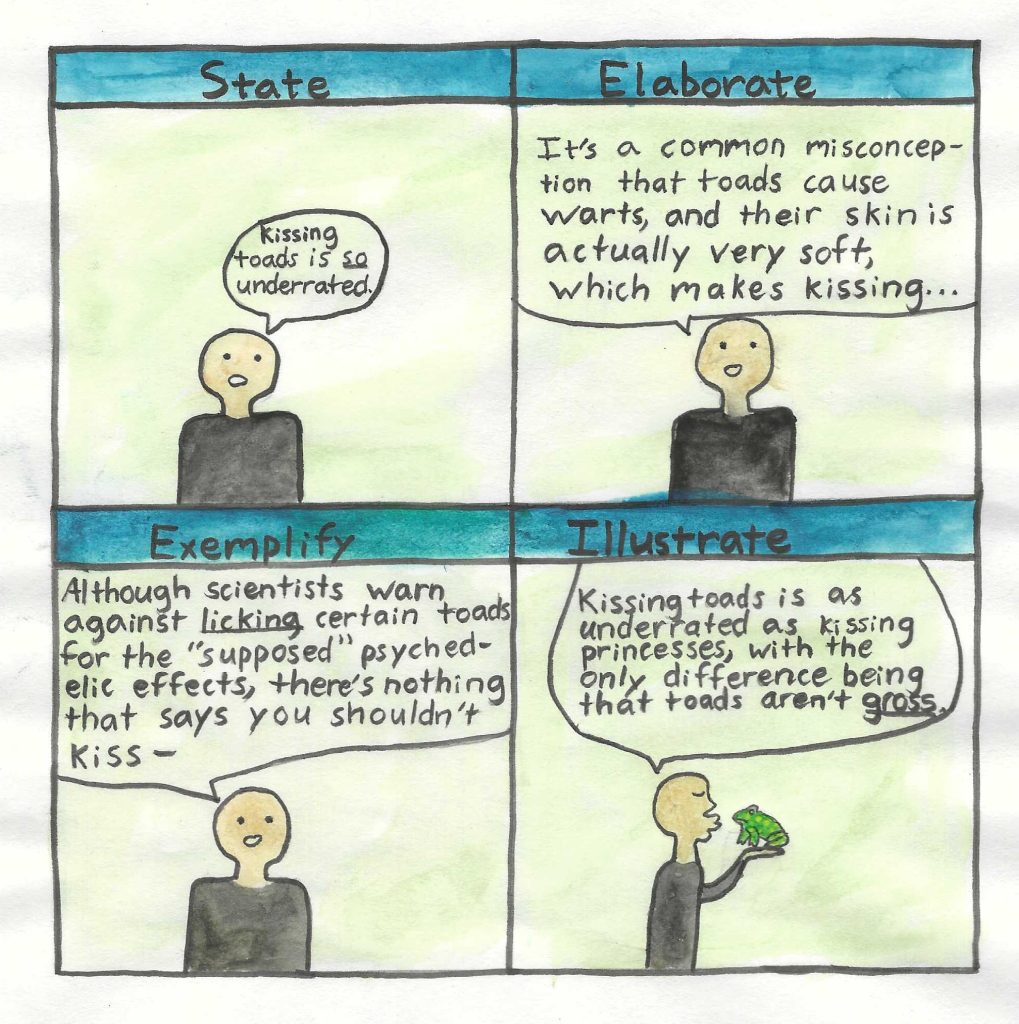
Analogy drives home the purpose of the argument and leaves an unforgettable image in the mind of the audience. Analogies compare two dissimilar things in order to make a point; in this way, analogy is different from metaphor or simile, which often function to beautify or elaborate a concept. Composing strong analogies is difficult for many people because it works at the intersection of critical and creative thinking. But as with all things, with some practice, composing original and powerful analogies to illustrate your point will become second nature, and the quality of your arguments will increase as a result. However, always be wary of the false analogy, a common logical fallacy that bring into comparison two things that only share traits in common on a superficial level. Strong analogies still work even after digging deeper into the connections and commonalities between these two dissimilar things.
Step 5: Counterarguments
Now that the argument is structured, it should again be inspected for weak points. This step requires changing your point of view to that of an audience member hearing your argument. If you were presenting this argument at a professional conference, how might a naysayer in the audience counter your claims? If you were a lawyer presenting this argument in a court of law, what might the opposition point out in your argument to prove their own case? What would a skeptical reader find fault with about your argument? Make note of those weak points and counterarguments and address them.
Step 6: Composing the Final Argument
Combining all the above steps, the final step is writing out the complete argument in the form of a research paper (Fig. 5). All the relevant information and evidence has been gathered and evaluated. The argument has been reasoned through and outlined with the SEE-I model. The standards of critical thinking are upheld in every instance. Counterarguments and weak points have been addressed and rectified as needed. Now it’s time to communicate the answer to your research question and how you followed the evidence to arrive at that conclusion.
Embarking on a research project is like setting out on a journey to a place you’ve never been; you may have some idea of the destination, but the path will almost certainly change courses many times, with unexpected encounters along the way, and where you end up will almost certainly be a little different from the idea you first had in mind. So enjoy the adventure!
Science or Pseudoscience? Theory or Conspiracy? Copyright © by Sara Rich. All Rights Reserved.
Video Series
- Analyze the logic of a problem or issue
- Analyze the logic of an article, essay, or text
- Analyze the logic of any book of nonfiction
- Evaluate an Author’s Reasoning
- Analyze the logic of a character in a novel
- Analyze the logic of a profession, subject, or discipline
- Analyze the logic of a concept or idea
- Distinguishing Inferences and Assumptions
- Thinking Through Conflicting Ideas
- Could you elaborate further?
- Could you give me an example?
- Could you illustrate what you mean?
- How could we check on that?
- How could we find out if that is true?
- How could we verify or test that?
- Could you be more specific?
- Could you give me more details?
- Could you be more exact?
- How does that relate to the problem?
- How does that bear on the question?
- How does that help us with the issue?
- What factors make this a difficult problem?
- What are some of the complexities of this question?
- What are some of the difficulties we need to deal with?
- Do we need to look at this from another perspective?
- Do we need to consider another point of view?
- Do we need to look at this in other ways?
- Does all this make sense together?
- Does your first paragraph fit in with your last?
- Does what you say follow from the evidence?
- Is this the most important problem to consider?
- Is this the central idea to focus on?
- Which of these facts are most important?
- Do I have any vested interest in this issue?
- Am I sympathetically representing the viewpoints of others?
Everyone thinks; it is our nature to do so. But much of our thinking, left to itself, is biased, distorted, partial, uninformed, or downright prejudiced. If we want to think well, we must understand at least the udiments of thought, the most basic structures out of which all thinking is made. We must learn how to take thinking apart.
All Thinking Is Defined by the Eight Elements That Make It Up. Eight basic structures are present in all thinking: Whenever we think, we think for a purpose within a point of view based on assumptions leading to implications and consequences. We use concepts, ideas and theories to interpret data, facts, and experiences in order to answer questions, solve problems, and resolve issues.
- generates purposes
- raises questions
- uses information
- utilizes concepts
- makes inferences
- makes assumptions
- generates implications
- embodies a point of view
- What is your, my, their purpose in doing________?
- What is the objective of this assignment (task, job, experiment, policy, strategy, etc.)?
- Should we question, refine, modify our purpose (goal, objective, etc.)?
- What is the purpose of this meeting (chapter, relationship, action)?
- What is your central aim in this line of thought?
- What is the purpose of education?
- Why did you say…?
- Take time to state your purpose clearly.
- Distinguish your purpose from related purposes.
- Check periodically to be sure you are still on target.
- Choose significant and realistic purposes.
- What is the question I am trying to answer?
- What important questions are embedded in the issue?
- Is there a better way to put the question?
- Is this question clear? Is it complex?
- I am not sure exactly what question you are asking. Could you explain it?
- The question in my mind is this: How do you see the question?
- What kind of question is this? Historical? Scientific? Ethical? Political? Economic? Or…?
- What would we have to do to settle this question?
- State the question at issue clearly and precisely.
- Express the question in several ways to clarify its meaning.
- Break the question into sub-questions.
- Distinguish questions that have definitive answers from those that are a matter of opinion or that require multiple viewpoints.
- What information do I need to answer this question?
- What data are relevant to this problem?
- Do we need to gather more information?
- Is this information relevant to our purpose or goal?
- On what information are you basing that comment?
- What experience convinced you of this? Could your experience be distorted?
- How do we know this information (data, testimony) is accurate?
- Have we left out any important information that we need to consider?
- Restrict your claims to those supported by the data you have.
- Search for information that opposes your position as well as information that supports it.
- Make sure that all information used is clear, accurate and relevant.
- Make sure you have gathered sufficient information.
- What conclusions am I coming to?
- Is my inference logical?
- Are there other conclusions I should consider?
- Does this interpretation make sense?
- Does our solution necessarily follow from our data?
- How did you reach that conclusion?
- What are you basing your reasoning on?
- Is there an alternative plausible conclusion?
- Given all the facts what is the best possible conclusion?
- How shall we interpret these data?
- Infer only what the evidence implies.
- Check inferences for their consistency with each other.
- Identify assumptions underlying your inferences.
- What idea am I using in my thinking? Is this idea causing problems for me or for others?
- I think this is a good theory, but could you explain it more fully?
- What is the main hypothesis you are using in your reasoning?
- Are you using this term in keeping with established usage?
- What main distinctions should we draw in reasoning through this problem?
- What idea is this author using in his or her thinking? Is there a problem with it?
- Identify key concepts and explain them clearly.
- Consider alternative concepts or alternative definitions of concepts.
- Make sure you are using concepts with precision.
- What am I assuming or taking for granted?
- Am I assuming something I shouldn’t?
- What assumption is leading me to this conclusion?
- What is… (this policy, strategy, explanation) assuming?
- What exactly do sociologists (historians, mathematicians, etc.) take for granted?
- What is being presupposed in this theory?
- What are some important assumptions I make about my roommate, my friends, my parents, my instructors, my country?
- Clearly identify your assumptions and determine whether they are justifiable.
- Consider how your assumptions are shaping your point of view.
- If I decide to do “X”, what things might happen?
- If I decide not to do “X”, what things might happen?
- What are you implying when you say that?
- What is likely to happen if we do this versus that?
- Are you implying that…?
- How significant are the implications of this decision?
- What, if anything, is implied by the fact that a much higher percentage of poor people are in jail than wealthy people?
- Trace the implications and consequences that follow from your reasoning.
- Search for negative as well as positive implications.
- Consider all possible consequences.
- How am I looking at this situation? Is there another way to look at it that I should consider?
- What exactly am I focused on? And how am I seeing it?
- Is my view the only reasonable view? What does my point of view ignore?
- Have you ever considered the way ____(Japanese, Muslims, South Americans, etc.) view this?
- Which of these possible viewpoints makes the most sense given the situation?
- Am I having difficulty looking at this situation from a viewpoint with which I disagree?
- What is the point of view of the author of this story?
- Do I study viewpoints that challenge my personal beliefs?
- Identify your point of view.
- Seek other points of view and identify their strengths as well as weaknesses.
- Strive to be fairminded in evaluating all points of view.

- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …
Critical Thinking Models: A Comprehensive Guide for Effective Decision Making

Critical thinking models are valuable frameworks that help individuals develop and enhance their critical thinking skills . These models provide a structured approach to problem-solving and decision-making by encouraging the evaluation of information and arguments in a logical, systematic manner. By understanding and applying these models, one can learn to make well-reasoned judgments and decisions.

Various critical thinking models exist, each catering to different contexts and scenarios. These models offer a step-by-step method to analyze situations, scrutinize assumptions and biases, and consider alternative perspectives. Ultimately, the goal of critical thinking models is to enhance an individual’s ability to think critically, ultimately improving their reasoning and decision-making skills in both personal and professional settings.
Key Takeaways
- Critical thinking models provide structured approaches for enhancing decision-making abilities
- These models help individuals analyze situations, scrutinize assumptions, and consider alternative perspectives
- The application of critical thinking models can significantly improve one’s reasoning and judgment skills.
Fundamentals of Critical Thinking

Definition and Importance
Critical thinking is the intellectual process of logically, objectively, and systematically evaluating information to form reasoned judgments, utilizing reasoning , logic , and evidence . It involves:
- Identifying and questioning assumptions,
- Applying consistent principles and criteria,
- Analyzing and synthesizing information,
- Drawing conclusions based on evidence.
The importance of critical thinking lies in its ability to help individuals make informed decisions, solve complex problems, and differentiate between true and false beliefs .
Core Cognitive Skills
Several core cognitive skills underpin critical thinking:
- Analysis : Breaking down complex information into smaller components to identify patterns or inconsistencies.
- Evaluation : Assessing the credibility and relevance of sources, arguments, and evidence.
- Inference : Drawing conclusions by connecting the dots between analyzed information.
- Synthesis : Incorporating analyzed information into a broader understanding and constructing one’s argument.
- Logic and reasoning : Applying principles of logic to determine the validity of arguments and weigh evidence.
These skills enable individuals to consistently apply intellectual standards in their thought process, which ultimately results in sound judgments and informed decisions.
Influence of Cognitive Biases
A key aspect of critical thinking is recognizing and mitigating the impact of cognitive biases on our thought processes. Cognitive biases are cognitive shortcuts or heuristics that can lead to flawed reasoning and distort our understanding of a situation. Examples of cognitive biases include confirmation bias, anchoring bias, and availability heuristic.
To counter the influence of cognitive biases, critical thinkers must be aware of their own assumptions and strive to apply consistent and objective evaluation criteria in their thinking process. The practice of actively recognizing and addressing cognitive biases promotes an unbiased and rational approach to problem-solving and decision-making.
The Critical Thinking Process

Stages of Critical Thinking
The critical thinking process starts with gathering and evaluating data . This stage involves identifying relevant information and ensuring it is credible and reliable. Next, an individual engages in analysis by examining the data closely to understand its context and interpret its meaning. This step can involve breaking down complex ideas into simpler components for better understanding.
The next stage focuses on determining the quality of the arguments, concepts, and theories present in the analyzed data. Critical thinkers question the credibility and logic behind the information while also considering their own biases and assumptions. They apply consistent standards when evaluating sources, which helps them identify any weaknesses in the arguments.
Values play a significant role in the critical thinking process. Critical thinkers assess the significance of moral, ethical, or cultural values shaping the issue, argument, or decision at hand. They determine whether these values align with the evidence and logic they have analyzed.
After thorough analysis and evaluation, critical thinkers draw conclusions based on the evidence and reasoning gathered. This step includes synthesizing the information and presenting a clear, concise argument or decision. It also involves explaining the reasoning behind the conclusion to ensure it is well-founded.
Application in Decision Making
In decision making, critical thinking is a vital skill that allows individuals to make informed choices. It enables them to:
- Analyze options and their potential consequences
- Evaluate the credibility of sources and the quality of information
- Identify biases, assumptions, and values that may influence the decision
- Construct a reasoned, well-justified conclusion
By using critical thinking in decision making, individuals can make more sound, objective choices. The process helps them to avoid pitfalls like jumping to conclusions, being influenced by biases, or basing decisions on unreliable data. The result is more thoughtful, carefully-considered decisions leading to higher quality outcomes.
Critical Thinking Models
Critical thinking models are frameworks that help individuals develop better problem-solving and decision-making abilities. They provide strategies for analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to reach well-founded conclusions. This section will discuss four notable models: The RED Model, Bloom’s Taxonomy, Paul-Elder Model, and The Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment.

The RED Model
The RED Model stands for Recognize Assumptions, Evaluate Arguments, and Draw Conclusions. It emphasizes the importance of questioning assumptions, weighing evidence, and reaching logical conclusions.
- Recognize Assumptions: Identify and challenge assumptions that underlie statements, beliefs, or arguments.
- Evaluate Arguments: Assess the validity and reliability of evidence to support or refute claims.
- Draw Conclusions: Make well-reasoned decisions based on available information and sound reasoning.
The RED Model helps individuals become more effective problem solvers and decision-makers by guiding them through the critical thinking process ^(source) .
Bloom’s Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a hierarchical model that classifies cognitive skills into six levels of complexity. These levels are remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. By progressing through these levels, individuals can develop higher-order thinking skills.
- Remembering: Recall information or facts.
- Understanding: Comprehend the meaning of ideas, facts, or problems.
- Applying: Use knowledge in different situations.
- Analyzing: Break down complex topics or problems into sub-parts.
- Evaluating: Assess the quality, relevance, or credibility of information, ideas, or solutions.
- Creating: Combine elements to form a new whole, generate new ideas, or solve complex issues.
Paul-Elder Model
The Paul-Elder Model introduces the concept of “elements of thought,” focusing on a structured approach to critical thinking. This model promotes intellectual standards, such as clarity, accuracy, and relevance. It consists of three stages:
- Critical Thinking: Employ the intellectual standards to problem-solving and decision-making processes.
- Elements of Thought: Consider purpose, question at issue, information, interpretation and inference, concepts, assumptions, implications, and point of view.
- Intellectual Traits: Develop intellectual traits, such as intellectual humility, intellectual empathy, and intellectual perseverance.
This model fosters a deeper understanding and appreciation of critical thinking ^(source) .
The Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment
The Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment is a standardized test developed by Diane Halpern to assess critical thinking skills. The evaluation uses a variety of tasks to measure abilities in core skill areas, such as verbal reasoning, argument analysis, and decision making. Pearson, a leading publisher of educational assessments, offers this test as a means to assess individuals’ critical thinking skills ^(source) .
These four critical thinking models can be used as frameworks to improve and enhance cognitive abilities. By learning and practicing these models, individuals can become better equipped to analyze complex information, evaluate options, and make well-informed decisions.
Evaluating Information and Arguments
In this section, we will discuss the importance of evaluating information and arguments in the process of critical thinking, focusing on evidence assessment, logic and fallacies, and argument analysis.
Evidence Assessment
Evaluating the relevance, accuracy, and credibility of information is a vital aspect of critical thinking. In the process of evidence assessment, a thinker should consider the following factors:
- Source reliability : Research and understand the expertise and credibility of the source to ensure that biased or inaccurate information is not being considered.
- Currency : Check the date of the information to make sure it is still relevant and accurate in the present context.
- Objectivity : Analyze the information for potential bias and always cross-reference it with other credible sources.
When practicing critical thinking skills, it is essential to be aware of your own biases and make efforts to minimize their influence on your decision-making process.
Logic and Fallacies
Logic is crucial for deconstructing and analyzing complex arguments, while identifying and avoiding logical fallacies helps maintain accurate and valid conclusions. Some common fallacies to watch out for in critical thinking include:
- Ad Hominem : Attacking the person making the argument instead of addressing the argument itself.
- Strawman : Misrepresenting an opponent’s argument to make it easier to refute.
- False Dilemma : Presenting only two options when there may be multiple viable alternatives.
- Appeal to Authority : Assuming a claim is true simply because an authority figure supports it.
Being aware of these fallacies enables a thinker to effectively evaluate the strength of an argument and make sound judgments accordingly.
Argument Analysis
Analyzing an argument is the process of evaluating its structure, premises, and conclusion while determining its validity and soundness. To analyze an argument, follow these steps:
- Identify the premises and conclusion : Determine the main point is being argued, how it is related and substance of the argument.
- Evaluate the validity : Assess whether the conclusion logically follows from the premises and if the argument’s structure is sound.
- Test the soundness : Evaluate the truth and relevance of the premises. This may require verifying the accuracy of facts and evidence, as well as assessing the reliability of sources.
- Consider counter-arguments : Identify opposing viewpoints and counter-arguments, and evaluate their credibility to gauge the overall strength of the original argument.
By effectively evaluating information and arguments, critical thinkers develop a solid foundation for making well-informed decisions and solving problems.
Enhancing Critical Thinking
Strategies for improvement.
To enhance critical thinking, individuals can practice different strategies, including asking thought-provoking questions, analyzing ideas and observations, and being open to different perspectives. One effective technique is the Critical Thinking Roadmap , which breaks critical thinking down into four measurable phases: execute, synthesize, recommend, and communicate. It’s important to use deliberate practice in these areas to develop a strong foundation for problem-solving and decision-making. In addition, cultivating a mindset of courage , fair-mindedness , and empathy will support critical thinking development.
Critical Thinking in Education
In the field of education, critical thinking is an essential component of effective learning and pedagogy. Integrating critical thinking into the curriculum encourages student autonomy, fosters innovation, and improves student outcomes. Teachers can use various approaches to promote critical thinking, such as:
- Employing open-ended questions to stimulate ideas
- Incorporating group discussions or debates to facilitate communication and evaluation of viewpoints
- Assessing and providing feedback on student work to encourage reflection and improvement
- Utilizing real-world scenarios and case studies for practical application of concepts
Developing a Critical Thinking Mindset
To truly enhance critical thinking abilities, it’s important to adopt a mindset that values integrity , autonomy , and empathy . These qualities help to create a learning environment that encourages open-mindedness, which is key to critical thinking development. To foster a critical thinking mindset:
- Be curious : Remain open to new ideas and ask questions to gain a deeper understanding.
- Communicate effectively : Clearly convey thoughts and actively listen to others.
- Reflect and assess : Regularly evaluate personal beliefs and assumptions to promote growth.
- Embrace diversity of thought : Welcome different viewpoints and ideas to foster innovation.
Incorporating these approaches can lead to a more robust critical thinking skillset, allowing individuals to better navigate and solve complex problems.
Critical Thinking in Various Contexts
The workplace and beyond.
Critical thinking is a highly valued skill in the workplace, as it enables employees to analyze situations, make informed decisions, and solve problems effectively. It involves a careful thinking process directed towards a specific goal. Employers often seek individuals who possess strong critical thinking abilities, as they can add significant value to the organization.
In the workplace context, critical thinkers are able to recognize assumptions, evaluate arguments, and draw conclusions, following models such as the RED model . They can also adapt their thinking to suit various scenarios, allowing them to tackle complex and diverse problems.
Moreover, critical thinking transcends the workplace and applies to various aspects of life. It empowers an individual to make better decisions, analyze conflicting information, and engage in constructive debates.
Creative and Lateral Thinking
Critical thinking encompasses both creative and lateral thinking. Creative thinking involves generating novel ideas and solutions to problems, while lateral thinking entails looking at problems from different angles to find unique and innovative solutions.
Creative thinking allows thinkers to:
- Devise new concepts and ideas
- Challenge conventional wisdom
- Build on existing knowledge to generate innovative solutions
Lateral thinking, on the other hand, encourages thinkers to:
- Break free from traditional thought patterns
- Combine seemingly unrelated ideas to create unique solutions
- Utilize intuition and intelligence to approach problems from a different perspective
Both creative and lateral thinking are essential components of critical thinking, allowing individuals to view problems in a holistic manner and generate well-rounded solutions. These skills are highly valued by employers and can lead to significant personal and professional growth.
In conclusion, critical thinking is a multifaceted skill that comprises various thought processes, including creative and lateral thinking. By embracing these skills, individuals can excel in the workplace and in their personal lives, making better decisions and solving problems effectively.
Overcoming Challenges
Recognizing and addressing bias.
Cognitive biases and thinking biases can significantly affect the process of critical thinking . One of the key components of overcoming these challenges is to recognize and address them. It is essential to be aware of one’s own beliefs, as well as the beliefs of others, to ensure fairness and clarity throughout the decision-making process. To identify and tackle biases, one can follow these steps:
- Be self-aware : Understand personal beliefs and biases, acknowledging that they may influence the interpretation of information.
- Embrace diverse perspectives : Encourage open discussions and invite different viewpoints to challenge assumptions and foster cognitive diversity.
- Reevaluate evidence : Continuously reassess the relevance and validity of the information being considered.
By adopting these practices, individuals can minimize the impact of biases and enhance the overall quality of their critical thinking skills.
Dealing with Information Overload
In today’s world, information is abundant, and it can become increasingly difficult to demystify and make sense of the available data. Dealing with information overload is a crucial aspect of critical thinking. Here are some strategies to address this challenge:
- Prioritize information : Focus on the most relevant and reliable data, filtering out unnecessary details.
- Organize data : Use tables, charts, and lists to categorize information and identify patterns more efficiently.
- Break down complex information : Divide complex data into smaller, manageable segments to simplify interpretation and inferences.
By implementing these techniques, individuals can effectively manage information overload, enabling them to process and analyze data more effectively, leading to better decision-making.
In conclusion, overcoming challenges such as biases and information overload is essential in the pursuit of effective critical thinking. By recognizing and addressing these obstacles, individuals can develop clarity and fairness in their thought processes, leading to well-informed decisions and improved problem-solving capabilities.
Measuring Critical Thinking
Assessment tools and criteria.
There are several assessment tools designed to measure critical thinking, each focusing on different aspects such as quality, depth, breadth, and significance of thinking. One example of a widely used standardized test is the Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal , which evaluates an individual’s ability to interpret information, draw conclusions, and make assumptions. Another test is the Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Level X and Level Z , which assess an individual’s critical thinking skills through multiple-choice questions.
Furthermore, criteria for assessing critical thinking often include precision, relevance, and the ability to gather and analyze relevant information. Some assessors utilize the Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment , which measures the application of cognitive skills such as deduction, observation, and induction in real-world scenarios.
The Role of IQ and Tests
It’s important to note that intelligence quotient (IQ) tests and critical thinking assessments are not the same. While IQ tests aim to measure an individual’s cognitive abilities and general intelligence, critical thinking tests focus specifically on one’s ability to analyze, evaluate, and form well-founded opinions. Therefore, having a high IQ does not necessarily guarantee strong critical thinking skills, as critical thinking requires additional mental processes beyond basic logical reasoning.
To build and enhance critical thinking skills, individuals should practice and develop higher-order thinking, such as critical alertness, critical reflection, and critical analysis. Using a Critical Thinking Roadmap , such as the four-phase framework that includes execution, synthesis, recommendation, and the ability to apply, individuals can continuously work to improve their critical thinking abilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main steps involved in the paul-elder critical thinking model.
The Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Model is a comprehensive framework for developing critical thinking skills. The main steps include: identifying the purpose, formulating questions, gathering information, identifying assumptions, interpreting information, and evaluating arguments. The model emphasizes clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance, depth, breadth, logic, and fairness throughout the critical thinking process. By following these steps, individuals can efficiently analyze and evaluate complex ideas and issues.
Can you list five techniques to enhance critical thinking skills?
Here are five techniques to help enhance critical thinking skills:
- Ask open-ended questions : Encourages exploration and challenges assumptions.
- Engage in active listening: Focus on understanding others’ viewpoints before responding.
- Reflect on personal biases: Identify and question any preconceived notions or judgments.
- Practice mindfulness: Develop self-awareness and stay present in the moment.
- Collaborate with others: Exchange ideas and learn from diverse perspectives.
What is the RED Model of critical thinking and how is it applied?
The RED Model of critical thinking consists of three key components: Recognize Assumptions, Evaluate Arguments, and Draw Conclusions. To apply the RED Model, begin by recognizing and questioning underlying assumptions, being aware of personal biases and stereotypes. Next, evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of different arguments, considering evidence, logical consistency, and alternative explanations. Lastly, draw well-reasoned conclusions that are based on the analysis and evaluation of the information gathered.
How do the ‘3 C’s’ of critical thinking contribute to effective problem-solving?
The ‘3 C’s’ of critical thinking – Curiosity, Creativity, and Criticism – collectively contribute to effective problem-solving. Curiosity allows individuals to explore various perspectives and ask thought-provoking questions, while Creativity helps develop innovative solutions and unique approaches to challenges. Criticism, or the ability to evaluate and analyze ideas objectively, ensures that the problem-solving process remains grounded in logic and relevance.
What characteristics distinguish critical thinking from creative thinking?
Critical thinking and creative thinking are two complementary cognitive skills. Critical thinking primarily focuses on analyzing, evaluating, and reasoning, using objectivity and logical thinking. It involves identifying problems, assessing evidence, and drawing sound conclusions. Creative thinking, on the other hand, is characterized by the generation of new ideas, concepts, and approaches to solve problems, often involving imagination, originality, and out-of-the-box thinking.
What are some recommended books to help improve problem-solving and critical thinking skills?
There are several books that can help enhance problem-solving and critical thinking skills, including:
- “Thinking, Fast and Slow” by Daniel Kahneman: This book explores the dual process theory of decision-making and reasoning.
- “The 5 Elements of Effective Thinking” by Edward B. Burger and Michael Starbird: Offers practical tips and strategies for improving critical thinking skills.
- “Critique of Pure Reason” by Immanuel Kant: A classic philosophical work that delves into the principles of reason and cognition.
- “Mindware: Tools for Smart Thinking” by Richard E. Nisbett: Presents a range of cognitive tools to enhance critical thinking and decision-making abilities.
- “The Art of Thinking Clearly” by Rolf Dobelli: Explores common cognitive biases and errors in judgment that can affect critical thinking.
You may also like

Difference between intelligence and critical thinking
Some scientists have concluded that traditional intelligence tests don’t accurately test the critical thinking required in making real-life decisions. Hence, many people […]

Online Learning and Critical Thinking: How to Choose the Right Course
Online learning gives more people access to education because of its convenience. It allows those with little time to take courses that […]

Riddles for creative thinking
Creative thinking is a person’s ability to figure out solutions to seemingly unsolvable problems by conceiving innovative ideas that conventional or logical […]

Critical Thinking Vs. Negative Thinking
When someone is being ‘critical’ of something, it generally means they are looking on it unfavorably, pointing out its flaws and shortcomings. […]

Learning Meta Data
Content source, first published, learning topics, learning blockchain.

For more lessons on how to Improve Communication check out the free classes below.

You must be a member of the @lantis Learning Network to Add Classes, Lessons, Beliefs, Arguments, and other New Content.
The Paul & Elder Critical Thinking Framework is a common standard use to help us model how we think and how we can use that knowledge to help us make better decisions.
Critical thinking is that mode of thinking – about any subject, content, or problem — in which the thinker improves the quality of his or her thinking by skillfully taking charge of the structures inherent in thinking and imposing intellectual standards upon them. (Paul and Elder, 2001).
The Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Framework has three components:
- Elements of Reasoning
- Intellectual Standards applied to the elements of reasoning
- intellectual traits associated with a cultivated critical thinker that result from the consistent and disciplined application of intellectual standards to the elements of thought

According to Paul and Elder (1997), there are two essential dimensions of thinking that decision-makers need to master in order to learn how to upgrade their thinking.
- They need to be able to identify the “parts” of their thinking
- They need to be able to assess their use of these parts of thinking
@lantis adds that Communication is important for the ‘parts” to exchange information effectively.
Elements of Thought (reasoning)
The “parts” or elements of thinking are as follows:
- All reasoning has a purpose
- All reasoning is an attempt to figure something out, to settle some question, to solve some problem
- All reasoning is based on assumptions
- All reasoning is done from some point of view
- All reasoning is based on data, information, and evidence
- All reasoning is expressed through, and shaped by, l anguage, culture, concepts, and ideas
- All reasoning contains inferences or interpretations by which we draw conclusions and give meaning to data
- All reasoning leads somewhere or has implications and consequences
Universal Intellectual Standards
The intellectual standards that are to these elements are used to determine the quality of reasoning. Good critical thinking requires having a command of these standards. According to Paul and Elder (1997, 2006), the ultimate goal is for the standards of reasoning to become infused in all thinking so as to become the guide to better and better reasoning. The intellectual standards include:
Clarity Could you elaborate? Could you illustrate what you mean? Could you give me an example? Accuracy How could we check on that? How could we find out if that is true? How could we verify or test that? Precision Could you be more specific? Could you give me more details? Could you be more exact? Relevance How does that relate to the problem? How does that bear on the question? How does that help us with the issue? Depth What factors make this difficult? What are some of the complexities of this question? What are some of the difficulties we need to deal with? Breadth Do we need to look at this from another perspective? Do we need to consider another point of view? Do we need to look at this in other ways? Logic Does all of this make sense together? Does your first paragraph fit in with your last one? Does what you say follow from the evidence? Significance Is this the most important problem to consider? Is this the central idea to focus on? Which of these facts are most important? Fairness Is my thinking justifiable in context? Am I taking into account the thinking of others? Is my purpose fair given the situation? Am I using my concepts in keeping with educated usage, or am I distorting them to get what I want?
Intellectual Traits
Consistent application of the standards of thinking to the elements of thinking result in the development of intellectual traits of:
- Intellectual Humility
- Intellectual Courage
- Intellectual Empathy
- Intellectual Autonomy
- Intellectual Integrity
- Intellectual Perseverance
- Confidence in Reason
- Fair-mindedness
Characteristics of a Well-Cultivated Critical Thinker
Habitual utilization of intellectual traits produces a well-cultivated critical thinker who is able to:
- Raise vital questions and problems, formulating them clearly and precisely
- Gather and assess relevant information, using abstract ideas to interpret it effectively
- Come to well-reasoned conclusions and solutions, testing them against relevant criteria and standards;
- Think open-mindedly within alternative systems of thought, recognizing and assessing, as need be, their assumptions, implications, and practical consequences; and
- Communicate effectively with others in figuring out solutions to complex problems
Paul, R. and Elder, L. (2010). The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts and Tools. Dillon Beach: Foundation for Critical Thinking Press.
Being Critical is Not Thinking Critically
How you can protect yourself from misinformation
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Reconciling Four Models of Critical Thinking: FSU QEP, Paul-Elder, CLA, and APA Delphi

In this White Paper, submitted to FSU's Quality Enhancement Plan Writing Committee (a comprehensive 5-year QEP is one requirement for SACS reaccreditation of educational institutions), I discuss four models of Critical Thinking which are relevant to their process of QEP writing, given their decision to make Critical Thinking in the majors the governing idea of their QEP. Specifically, I discuss the APA Delphi Report Model, the Paul-Elder Model, a reconstruction of the model of CT involved in the Collegiate Learning Assessment (CLA), and the proposed QEP model of "evidence-based decision-making in the majors". for each, I highlight strengths and weaknesses, and argue that these are in fact compatible models.
Related Papers
Martin Davies
There has been no shortage of definitions of the concept of “critical thinking” over the years and the concept has been subject to much detailed scholarly work. In social and educational terms critical thinking is an important topic. Of late, critical thinking has also been widely discussed in the popular media, and the concept has been regarded as one of the most important graduate outcomes expected of a university education. However, despite this, scholars have yet to arrive at a holistic conception of critical thinking—a model of critical thinking as it were—that might usefully underpin the range of considerations about critical thinking that occur in the higher education literature. This paper: (1) reviews the various definitions and approaches to critical thinking, and (2) incorporates them into a single, coherent model. A number of disagreements in critical thinking scholarship are outlined as ‘axis disputes’ arising from the proposed model.
Brian Frank , Jake Kaupp
BRAIN. Broad Research in Artificial Intelligence and Neuroscience ISSN 2067-3957
Academia EduSoft , Ali Taghinezhad
This study was intended to investigate the effectiveness of teaching critical thinking on students' writing performance and their critical thinking dispositions. To this end, 140 students were selected. 73 students were assigned to the experimental group and 67 were assigned to the control group. The experimental group received instruction in critical thinking strategies whereas the control group did not. The instruments used in this study were the researcher-developed essay test, the Ennis-Weir critical thinking essay test, and the California Critical Thinking Dispositions Inventory (CCTDI). A 2-group pretest/posttest quasi-experimental design was utilized to determine the outcome measures. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and independent-samples t-test. Statistically significant differences were observed in the experimental and the control groups in the total scores of the three instruments. The results indicated an improvement in students' writing performance and their dispositions toward using critical thinking strategies. Nonetheless, some dispositional aspects such as truth-seeking, cognitive maturity, and open-mindedness did not differ significantly after the intervention.
Laurie Miller
Veornita Sims
محمد محمد السر محمد
Noreen Facione , Peter A Facione
This invited paper appeared in the Journal INQUIRY which chronicles theory and research in logic and critical thinking. In this , Peter and Noreen Facione describe their passionate involvement with critical thinking, its definition, measurement, training, and practical application to everyday decisions, big and small. In reflecting on their work they say “we have identified three groups of questions: those vexing, recurring questions that motivate us to explore critical thinking, those scholarly questions around which we organized our empirical and conceptual research, and those urgent practical questions which demand the development of applications and assessment solutions. We conclude with two recommendations for the consideration of all those who value fair-minded, well-reasoned, reflective decision making.”
Gregory Sadler
The FSU Rising Junior Examination in 2010 involved use of the Collegiate Learning Assessment (CLA). The process and the results for the Institutional CLA are summarized in this report. A CLA Performance Task requires students to investigate and take a position on real-life-like situations. They must address another person’s claims, argument, and position, and they must do so in reference to seven documents containing different types of information. The documents also contain a mixture of relevant and irrelevant, and reliable and unreliable, information. The examination is scored holistically using rubrics. The report provides recommendations
RELATED PAPERS
Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education
Journal of the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning
Christine M Morgan
LITERARY STUDY, MEASUREMENT, AND THE SUBLIME: DISCIPLINARY ASSESSMENT
Kathleen McCoy
Lucinda Cole
Tantatape Brahmasrene
Andrews Daklo Kwame
Carol Ann Gittens , Peter A Facione
Journal of Athletic Training
Stacy E Walker
Tanju Deveci , Nader Ayish
Nurse Education Today
Christos Andreou
Nurse education today
Amanda J . Carter
Alubabari Desmond Nbete
European Journal of Teacher Education
Banu Yücel Toy
Educational Technology Research and Development
Owen Harney
Sophie Kennedy
English Language Teaching (ELT)
Journal of Modern Research in English Language Studies
julie baroody
Innovative Higher Education
Abdel Salam El-Koumy
Assessing Writing
Secret Belanger , Emily Saxton
Heidi Hyytinen
Akan Deniz Yazgan
STEM Assessment …
Laurie Poklop
katherine velasquez
YEE CHUNG GOH
don millard
The International Journal of Art & Design, 37(2), 265-276
Jeffrey Broome , Adriane Pereira
Peter A Facione
Dawit Tibebu Tiruneh , Jan Elen
International Education Studies
Mohammad H Yarmohammadian
Ronald Barnett
Philline Deraney , Amani Hamdan
Steven E Higgins
Amani Hamdan , Philline Deraney
Emily Isaacson
Hui Meng Kow
Najia Abdallaoui- Maan
Kevin Crichlow
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- International Center for the Assessment of Higher Order Thinking
- Our Team of Presenters
- Fellows of the Foundation
- Dr. Richard Paul
- Dr. Linda Elder
- Dr. Gerald Nosich
- Permission to Use Our Work
- Create a CriticalThinking.Org Account
- Contributions to the Foundation for Critical Thinking
- Contact Us - Office Information
- Testimonials
- Center for Critical Thinking
- The National Council for Excellence in Critical Thinking
- Library of Critical Thinking Resources
- The Center for Critical Thinking Community Online
- Customized Webinars and Online Courses for Faculty
Certification in the Paul-Elder Approach to Critical Thinking
- Consulting for Leaders and Key Personnel at Your Organization
- K-12 Instruction
- Higher Education
- Business & Professional Groups
- Build a Local Critical Thinking Town Hall
- Critical Thinking Training for Law Enforcement
- Online Courses for Instructors
- Critical Thinking Therapy
- Bring Critical Thinking Into Your Website's Discussion
- The State of Critical Thinking Today
- Professional Development Model for K-12
- Professional Development Model - College and University
- Workshop Descriptions
- Mentor Program
- Inservice Information Request Form
- Institutions Using Our Approach to Critical Thinking
- Upcoming Events in Critical Thinking
- 44th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Focal Session Descriptions
- Daily Schedule
- Call for Proposals
- Presuppositions of the 44th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Recommended Reading
- 2024 Fall Academy on Critical Thinking
- Academy Presuppositions
- Conference Archives
- 43rd Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Guest Presentation Program
- Register as an Ambassador
- Testimonials from Past Attendees
- Thank You to Our Donors
- Presuppositions of the Conference
- 42nd Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Overview of Sessions (Flyer)
- Presuppositions of the Annual International Conference
- Testimonials from Past Conferences
- 41st Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Recommended Publications
- Dedication to Our Donors
- 40th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Session Descriptions
- Testimonials from Prior Conferences
- International Critical Thinking Manifesto
- Scholarships Available
- 39th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Travel and Lodging Info
- FAQ & General Announcements
- Focal and Plenary Session Descriptions
- Program and Proceedings of the 39th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- The Venue: KU Leuven
- Call for Critical Thinking Ambassadors
- Conference Background Information
- 38th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Call for Ambassadors for Critical Thinking
- Conference Focal Session Descriptions
- Conference Concurrent Session Descriptions
- Conference Roundtable Discussions
- Conference Announcements and FAQ
- Conference Program and Proceedings
- Conference Daily Schedule
- Conference Hotel Information
- Conference Academic Credit
- Conference Presuppositions
- What Participants Have Said About the Conference
- 37th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Registration & Fees
- FAQ and Announcements
- Conference Presenters
- 37th Conference Flyer
- Program and Proceedings of the 37th Conference
- 36th International Conference
- Conference Sessions
- Conference Flyer
- Program and Proceedings
- Academic Credit
- 35th International Conference
- Conference Session Descriptions
- Available Online Sessions
- Bertrand Russell Distinguished Scholar - Daniel Ellsberg
- 35th International Conference Program
- Concurrent Sessions
- Posthumous Bertrand Russell Scholar
- Hotel Information
- Conference FAQs
- Visiting UC Berkeley
- 34th INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
- Bertrand Russell Distinguished Scholar - Ralph Nader
- Conference Concurrent Presenters
- Conference Program
- Conference Theme
- Roundtable Discussions
- Flyer for Bulletin Boards
- 33rd INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
- 33rd International Conference Program
- 33rd International Conference Sessions
- 33rd International Conference Presenters
- The Bertrand Russell Distinguished Scholars Critical Thinking Conversations
- 33rd International Conference - Fees & Registration
- 33rd International Conference Concurrent Presenters
- 33rd International Conference - Hotel Information
- 33rd International Conference Flyer
- 32nd INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
- 32nd Annual Conference Sessions
- 32nd Annual Conference Presenter Information
- 32nd Conference Program
- The Bertrand Russell Distinguished Scholars Critical Thinking Lecture Series
- 32nd Annual Conference Concurrent Presenters
- 32nd Annual Conference Academic Credit
- 31st INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
- 31st Conference Sessions
- Comments about previous conferences
- Conference Hotel (2011)
- 31st Concurrent Presenters
- Registration Fees
- 31st International Conference
- 30th INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CRITICAL THINKING
- 30th International Conference Theme
- 30th Conference Sessions
- PreConference Sessions
- 30th Concurrent Presenters
- 30th Conference Presuppositions
- Hilton Garden Inn
- 29th International Conference
- 29th Conference Theme
- 29th Conference Sessions
- 29th Preconference Sessions
- 29th Conference Concurrent Sessions
- 2008 International Conference on Critical Thinking
- 2008 Preconference Sessions (28th Intl. Conference)
- 2007 Conference on Critical Thinking (Main Page)
- 2007 Conference Theme and sessions
- 2007 Pre-Conference Workshops
- 2006 Annual International Conference (archived)
- 2006 International Conference Theme
- 2005 International Conference (archived)
- Prior Conference Programs (Pre 2000)
- Workshop Archives
- Spring 2022 Online Workshops
- 2021 Online Workshops for Winter & Spring
- 2019 Seminar for Military and Intelligence Trainers and Instructors
- Transportation, Lodging, and Recreation
- Seminar Flyer
- 2013 Spring Workshops
- Our Presenters
- 2013 Spring Workshops - Hotel Information
- 2013 Spring Workshops Flyer
- 2013 Spring Workshops - Schedule
- Spring Workshop 2012
- 2012 Spring Workshop Strands
- 2012 Spring Workshop Flier
- 2011 Spring Workshop
- Spring 2010 Workshop Strands
- 2009 Spring Workshops on Critical Thinking
- 2008 SPRING Workshops and Seminars on Critical Thinking
- 2008 Ethical Reasoning Workshop
- 2008 - On Richard Paul's Teaching Design
- 2008 Engineering Reasoning Workshop
- 2008 Academia sobre Formulando Preguntas Esenciales
- Fellows Academy Archives
- 2017 Fall International Fellows Academy
- 4th International Fellows Academy - 2016
- 3rd International Fellows Academy
- 2nd International Fellows Academy
- 1st International Fellows Academy
- Academy Archives
- October 2019 Critical Thinking Academy for Educators and Administrators
- Transportation, Lodging, and Leisure
- Advanced Seminar: Oxford Tutorial
- Recreational Group Activities
- Limited Scholarships Available
- September 2019 Critical Thinking Educators and Administrators Academy
- 2019 Critical Thinking Training for Trainers and Advanced Academy
- Academy Flyer
- Seattle, WA 2017 Spring Academy
- San Diego, CA 2017 Spring Academy
- 2016 Spring Academy -- Washington D.C.
- 2016 Spring Academy -- Houston, TX
- The 2nd International Academy on Critical Thinking (Oxford 2008)
- 2007 National Academy on Critical Thinking Testing and Assessment
- 2006 Cambridge Academy (archived)
- 2006 Cambridge Academy Theme
- 2006 Cambridge Academy Sessions
- Accommodations at St. John's College
- A Model for the National Assessment of Higher Order Thinking
- International Critical Thinking Essay Test
- Online Critical Thinking Basic Concepts Test
- Online Critical Thinking Basic Concepts Sample Test
- Consequential Validity: Using Assessment to Drive Instruction
- News & Announcements
- Newest Pages Added to CriticalThinking.Org
- Critical Thinking Online Courses
- Critical Thinking Blog
- 2019 Blog Entries
- 2020 Blog Entries
- 2021 Blog Entries
- 2022 Blog Entries
- 2023 Blog Entries
- Online Courses for Your Students
- 2023 Webinar Archives
- 2022 Webinar Archives
- 2021 Webinar Archive
- 2020 Webinar Archive
- Guided Study Groups
- Critical Thinking Channel on YouTube
- CT800: Spring 2024
Translate this page from English...
*Machine translated pages not guaranteed for accuracy. Click Here for our professional translations.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Paul-Elder framework has three components: According to Paul and Elder (1997), there are two essential dimensions of thinking that students need to master in order to learn how to upgrade their thinking. They need to be able to identify the "parts" of their thinking, and they need to be able to assess their use of these parts of thinking.
These stages are translated into six steps (6 Steps for Effective Critical Thinking): Knowledge - Define the main topic that needs to be covered. Comprehension - Understand the issue through researching the topic. Application - Analyze the data and link between the collected data. Analysis - Solve the problem, or the issue investigated.
ConCepts and tools. By Dr. Richard Paul and Dr. Linda Elder. The Foundation for Critical Thinking. www.criticalthinking.org 707-878-9100 [email protected]. Why A Critical Thinking Mini-Guide? This miniature guide focuses on of the essence of critical thinking concepts and tools distilled into pocket size.
Adapted from Elder, L., & Paul, R. (2010). The thinker's guide to analytic thinking. Dillon Beach, CA: Foundation for Critical Thinking Press. Paul‐Elder Model of Critical Thinking Can be used to help learners critically evaluate information during learning and think critically, to probe
Elder, L ., & Paul, R . (2012) . The thinker's guide to intellectual standards: The words that name them and the criteria that define them. Tomales, CA: Foundation for Critical ˜inking Press . Linda Elder is an Educational Psychologist and President of the Foundation for Critical Thinking. Richard Paul is Director of the Center for Critical ...
Fig. 1. Elements of Reasoning according to the Paul-Elder Model of Critical Thinking. Courtesy of Charis Williams, 2023. Once the question at issue is established, the critical thinker should proceed around the wheel of the 8+ Elements of Reasoning (always considering the context that undergirds the problem as a whole and alternatives to each element), until finally arriving at conclusions and ...
This powerful book introduces core critical thinking concepts and principles as an empowering problem-solving framework for every profession, course of study, and indeed every area of life. The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts and Tools distills the groundbreaking work of Richard Paul and Linda Elder, targeting how to deconstruct thinking through the elements of reasoning and how ...
She is President of the Foundation for Critical Thinking and Executive Director of the Center for Critical Thinking. Dr. Elder has taught psychology and critical thinking at the college level and has given presentations to more than 50,000 educators at all levels. Useful model because "Paul-Elder framework's comprehensiveness, discipline ...
This powerful book introduces core critical thinking concepts and principles as an empowering problem-solving framework for every profession, course of study, and indeed every area of life. The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts and Tools distills the groundbreaking work of Richard Paul and Linda Elder, targeting how to deconstruct thinking through the elements of reasoning and how ...
9. Seeing the development of critical thinking as unfolding in stages, and as involving deep commitment on the part of the learner. 10. Designing professional development in critical thinking for business managers and employees, using the Paulian Framework™ (Paul- Elder Model™). Mechanics of the Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Certification ...
This model is based fundamentally in the original work of Dr. Richard Paul, and is an essential component in the Paul- Elder framework for critical thinking™. Refer back to this model frequently to refresh your memory as to the eight elements of reasoning that are present in your thinking whenever you reason through anything.
The Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Model is a comprehensive framework for developing critical thinking skills. The main steps include: identifying the purpose, formulating questions, gathering information, identifying assumptions, interpreting information, and evaluating arguments. The model emphasizes clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance ...
Published 2019. Education, Philosophy. TLDR. The critical thinking competency standards articulated in this guide serve as a resource for teachers, curriculum designers, administrators and accrediting bodies to ensure that critical thinking is fostered in the teaching of any subject to all students at every grade level. Expand. View via Publisher.
Paul and Elder (2006), a theorist in critical thinking, describes critical thinking as "the art of thinking about your thinking while you are thinking in order to make your thinking better: more clear, more accurate, and more defensible" (p. 17).Paul's Model for Critical Thinking is a prominent critical thinking model and has been used to improve critical thinking for all levels of students.
AC 2012-3648: ENGAGING FRESHMAN ENGINEERS USING THE PAUL-ELDER MODEL OF CRITICAL THINKING. Dr. Angela Thompson P.E., University of Louisville Dr. Patricia A. Ralston, University of Louisville Dr. Jeffrey Lloyd Hieb, University of Louisville. Jeffrey Hieb is currently an Assistant Professor in the Department of Engineering Fundamentals at the ...
The Paul & Elder Critical Thinking Framework is a common standard use to help us model how we think and how we can use that knowledge to help us make better decisions. Critical thinking is that mode of thinking - about any subject, content, or problem — in which the thinker improves the quality of his or her thinking by skillfully taking ...
9. Seeing the development of critical thinking as unfolding in stages, and as involving deep commitment on the part of the learner. 10. Designing professional development in critical thinking for business managers and employees, using the Paulian Framework (Paul- Elder Model). Mechanics of the Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Certification Program:
Critical Thinking: Strategies for Improving Student Learning, Part III. Linda Elder, Richard W. Paul. Published 1 April 2009. Education. Journal of Developmental Education. In the last column we focused (as a primary goal of instruction) on the importance of teaching so that students learn to think their way into and through content.
Skilled analysis and evaluation of one's emotions and values. Intelligent choices in human relationships. Skilled decision-making in the workplace. Teaching students, colleagues, employees, clients, etc. how to take command of their own reasoning in all parts of life. Skilled civic choices, personal choices, etc. . . .
FMU's Critical Thinking Component Paul-Elder Model of Critical Thinking Bloom's Taxonomy Conceptualizing Concepts or Key Ideas Knowledge Analyzing Point of View Analysis ... Connections between FMU's Critical Thinking Components, Paul-Elder Model and Bloom's Taxonomy. Intellectual Standards Are Used to Assess Critical Thinking. The ...
The Paul-Elder Model of Critical Thinking comprises three groups of components: Intellectual Standards; Elements of Reasoning; and Intellectual Traits. Intellectual Standards are the standards which are to be applied to thinking in order to make it, or determine whether it is, Critical Thinking. ...
The Paul-Elder Framework for Critical Thinking - also referred to as the Paulian Approach to Critical Thinking - is the most integrated conception of critical thinking in the world, and is based in the natural languages we speak every day. Our framework provides an internationally recognized, comprehensive approach to analyzing, assessing ...