Purdue Polytechnic Institute
Global mobile menu.
- Departments
- Statewide Locations
Ph.D. in Technology
- Graduate Faculty

Specialization in Cyber Forensics
The Purdue Polytechnic offers a Ph.D. in Technology with a specialization in cyber forensics. All details about the degree including the admission procedures, course structure, faculty and other resources can be found here . Additional details of the Ph.D. specific to the cyber forensics area of specialization are mentioned below.
Curriculum requirements for the cyber forensics specialization includes all the requirements of the Ph.D. in Technology degree with the added constraint that students need to complete 15 credit hours in core cyber forensics courses. The requirements are explained below.
Core Courses
CNIT 55600 - Basic Computer Forensics - 13485 Covers the fundamentals of the maturing discipline of computer forensics. The focus of the course is on gaining a broad understanding of the field of study and how technology and law interact to form this forensic science. Emerging standards and current and future issues related to the field are also explored. Examines law and public policy, the computer forensic methodology, report presentation, and expert witness testimony, as well as anti-forensic techniques that can be used to obfuscate evidence. Students are exposed to theory and practice with lab exercises, thought and term papers, and a practical, as well as written, final exam.
CNIT 55700 - Advanced Research Topics In Cyber Forensics - 45535 Provides students at the advanced degree level the opportunity to expand their knowledge of cyber forensics. Students are expected to have fundamental understanding of cyber forensics and digital forensic science. The emphasis is on directed learning and scholarly inquiry. Possible research topics range from law and public policy to software and/or hardware development. Permission of instructor required.
CNIT 58100 - Cyber Frn Cloud/Virtual Enviro - 69894 There are various architectures of virtual and cloud technology environments placing different emphasis on storage, transmission, and processing of information. The student will develop skills and abilities in evaluating the patterns of evidence within this domain. This course examines the identification and acquisition of digital evidence, residing on hosts or in transmission between hosts, from different network topologies, and protocols. This course will also examine the techniques or processes by which information can be hidden, exposed, examined, and processed in a forensics manner. The fundamental principles of forensics are applied to virtual operating environment and networks.
CNIT 58100 - Cyber Forensics Of File Sys - 69783 The plethora of strategies to store information in different formats continues to expand. This course examines the various media and strategies of storing information and the processes of documenting the collection, imaging, and processing of forensic evidence. Topics include file formats, file systems, hardware, and software involved in forensic investigation. The overall pattern of forensic evidence in file systems will be examine along with the acquisition, analysis, and reporting of evidence artifacts found in file systems. Permission of instructor or graduate standing required.
CNIT 58100 - Cyberforensics Of Malware - 69893 Consumer technologies are rapidly moving forward with items integrating processing, storage, and transmission into their base functionality. The enterprise issues with bring your own device has rapidly expanded requirements on forensics investigators to address a plethora of mobile device types. Whether it is the automobile black box or a home thermostat there are various elements of interesting evidence possible to be gained. As a simplistic example the wireless home thermostat tracks when there is activity in a house. The forensic possibilities of being able to attribute presence via the thermostat or geo-location by a cellphone are of interest to forensics investigators. This is a classic example of a device as a witness. The embedded and consumer device pantheon is developing as an important area of forensic science.
Specialization Requirements
COVID-19 Community Level: Low
- SHSU Online
- Academic Affairs
- Academic Calendar
- Academic Community Engagement (ACE)
- Academic Planning and Program Development
- Academic Success Center
- Accepted Students and Bearkat Orientation
- Admissions (Undergraduate)
- Admissions (Graduate)
- Admission Requirements
- Advising (SAM Center)
- Agricultural Sciences
- Alumni Association
- American Association of University Professors
- Analytical Laboratory
- Application for Admission
- Army ROTC - Military Science
- Arts & Media
- Auxiliary Services
- Bearkat Bundle
- Bearkat Camp
- Bearkat EduNav (BEN)
- Bearkat Express Payment
- Bearkat Kickoff
- Bearkat Marching Band
- Bearkat OneCard
- Bearkat Transfer Scholarship
- Blinn College Transfers
- Budget Office
- Business Administration
- Campus Activities & Traditions
- Campus Recreation
- Career Success Center
- Cashier's Office
- Charter School
- Class Schedule
- Computer Account Creation
- Computer Labs
- Continuing Education
- Controller's Office
- Counseling Center
- Criminal Justice
- Current Students
- Data Analytics and Decision Support
- Dean of Students' Office
- Departments
- Department of Dance
- Dining Services
- Disbursements Services
- Educator Preparation Services
- Emergency Management
- Employee Services Center
- Employment Opportunities
- Engineering Technology
- Enrollment Success
- Enrollment Marketing and Communication
- Enrollment Services - TWC
- Exchange Mail
- Facilities Management
- Faculty Senate
- Faculty/Staff Directory
- Final Exam Schedule
- Finance and Operations
- Financial Aid
- Food & Housing Access Network
- First-Generation Center
- First-Year Experience
- Free Speech & Expressive Activity
- General Information
- Garrett Center
- Global Engagement
- Golf Course
- Graduate Admissions
- The Graduate School
- Great Names
- Health Sciences
- Honors College
- Human Resources
- Humanities and Social Sciences
- IT@Sam Service Desk
- Institutional Animal Care & Use Committee (IACUC)
- Internal Grant Program
- Institutional Review Board (IRB)
- Integrated Marketing & Communications
- Internal Audit
- Joint Admission Students
- Jr. Bearkats
- Leadership Academy
- Leadership Initiatives
- LEAP Center
- Library (NGL)
- Lone Star College Transfers
- Lowman Student Center
- Mail Services
- Map - Campus
- Marketing & Communications
- McNair Program
- Military Science
- Music Choir
- MyGartner Portal
- National Student Exchange
- Office of the President
- Ombuds Office
- Online Information Request
- Organization Chart
- Orientation - New Student
- Osteopathic Medicine
- Parent & Family Relations
- Payroll Office
- PGA Golf Management
- Pre-Health Professional Student Services
- Procurement and Business Services
- Procurement Opportunities
- Program Analytics
- Prospective Students
- Quality Enhancement Plan
- Reading Center
- Registration
- Registrar's Office
- Research Administration (Post-Award)
- Research and Sponsored Programs
- Residence Life
- SACSCOC Reaffirmation
- Sam Houston Memorial Museum
- Services for Students with Disabilities
- Schedule of Classes
- Scholarships
- SHSU MarketPlace
- Spirit Programs
- Smith-Hutson Endowed Chair of Banking
- Smith-Hutson Scholarship Program
- Staff Senate
- Student Affairs
- Student Government Association
- Student Health Center
- Student Legal Services
- Student Money Management Center
- Student Success Technologies
- Study Abroad
- Summer Camps
- Supplemental Instruction
- Technology Tutorials
- Testing Center
- Theatre and Musical Theatre
- Title IX (Sexual Misconduct)
- Tour the University
- Transcripts
- Transfer Equivalency Guide
- Transfer Students (Articulation)
- Travel Services
- Undergraduate Research Symposium
- University Advancement
- University Hotel
- University Police Department
- Visitor Services
- The Woodlands Center
Digital and Cyber Forensic Science , Doctorate of Philosophy
Available: On Campus
This Ph.D. program is intended for students with a bachelor’s degree in computing science, computer engineering, or digital forensics and provides the theoretical, conceptual, methodological, and computational skills needed to understand the role of digital and cyber forensic science in post-technological societies. This degree is designed to produce graduates with the technical and leadership skills needed for leadership positions in business and industry, federal and state security agencies, and academia.
Students seeking their Ph.D. in digital and cyber forensic science must complete 85 credit hours beyond the bachelor’s degree. Previously completed master’s level coursework is evaluated on an individual basis. For advancement to candidacy, you must be enrolled full-time, maintain a 3.0 grade point average, complete 46 graduate credit hours of coursework and internship, submit a portfolio for review, and pass Comprehensive Examinations.
Students who advance to doctoral candidacy must complete and defend a doctoral dissertation, and a minimum of 15 credit hours of dissertation with continuous enrollment in the dissertation course until graduation are required.
Program Breakdown
Application deadlines.
- Fall: August 1
Please note that application deadlines will occasionally change. Please contact the program director (listed in the contact section) for confirmation on application deadlines.
Contact Info
Office of admissions.
- Graduate Admissions Website
- 936.294.1971
- [email protected]
Program Advisor
- Dr. Narasimha K. Shashidhar
- 936.294.1591
- [email protected]
Digital Forensics Association
- DFA Discussion Board
- Volunteering
- Start a Chapter
- A word on Education
- Certificates
- Free Training
- Vendor Training
- Open Source
- Case Studies
- Presentations
- Professional Journals
- Publications
- Articles & Papers
- Community Sites
- Discussion Groups
- Forensic Blogs
- Resource Sites
- Evidence Files
- Forensic Challenges
- Common Body of Knowledge
- Testimony Archive
- Tools Research
- DFA Research Publications
- Contact the DFA
- Connect with Us
Doctoral Programs
- California Sciences Institute offers a Ph.D. in Digital Forensics.
- University of Rhode Island offers a PhD in Computer Science with Digital Forensics research. The Digital Forensics classes are taken online, other classes may require residency.
- Purdue (CERIAS) offers an Interdisciplinary PhD degree with a specialization in Information Security, and many excellent projects to research on digital forensics. They also offer standard graduate degrees with the same specialization.
- MS in Digital Forensics & Cybersecurity

Graduate Programs in Digital Forensics & Cybersecurity
Our program, small, selective & diverse.
Recent STEM graduates, public & private sector practitioners, law enforcement personnel & veterans, IT professionals & more
Multi-Disciplinary
Courses in law, cybersecurity, digital forensics & research opportunities
Evening & weekend classes for working professionals, peer networking & state of the art Digital Forensics Lab

- Read more about MS in Digital Forensics & Cybersecurity

John Jay College of Criminal Justice meets the challenges of fighting cybercrime by providing professional science education in digital forensic science and cybersecurity with concern for justice. D4CS, the Digital Forensics and Cybersecurity program, offers a Master of Science in Digital Forensics and Cybersecurity degree and two advanced certificate programs.
The Master of Science in Digital Forensics and Cybersecurity degree program offers a balance of practice and theory through study in computer science, law and criminal justice. The program produces professionals qualified as digital forensic scientists who can apply and sustain their expertise as new technological and societal challenges emerge; who understand the scientific, legal and criminal justice context of high technology crime; and who can effectively communicate their knowledge to others.
212.237.8843
6.65.20 New Building

- Aviation and Astronautical Sciences
- Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence and Data Science
- Construction and Facilities
- Critical Infrastructure
- Cyber & Information Security
- Cyberpsychology
- Engineering
- Engineering Technologies
- Intelligence and Global Security Studies
- Management of Technology
- Occupational Safety and Health
- Uncrewed Systems
- Doctoral Degrees
- Master's Degrees
- Bachelor's Degrees
- Online Programs
- Associate Degrees
- Certificates
- Minor Degrees
- Summer Programs
- STEM Events
- Webinars and Podcasts
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- Transfer Students
- Military and Veterans
- International Students
- Admissions Counselor
- Capitol Connections
- Accepted Students
- Project Lead the Way
- Builder Culture
- Campus Life
- Clubs and Organizations
- Centers and Labs
- Online Classes
- The Capitol Commitment
- Top Employers
- Co-ops and Internships
- Professional Education
- Find a Mentor
- Career Services
- Capitol Online Job Board
- Recruiters and Employers
- Why Capitol Tech
- At a Glance
- Mission, Vision and Goals
- Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
- Washington, D.C.
- Capitol History
- Capitol Partners
- News and Events
- Visitors/Campus
- Accreditation
- Recognitions & Awards
- Current Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Alumni & Giving
- News & Events
- Capitology Blog
- Maps / Directions

- Degrees and Programs
Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Forensic Cyberpsychology
- Request Information
Starting Summer 2023
Earn a Ph.D. in Forensic Cyberpsychology and learn all about the psychology of cybercriminal behavior.
Forensic cyberpsychology is a cutting-edge emerging discipline which presents students with an exciting opportunity to engage with this new scientific frontier and help to develop new scientific theories and protocols, or adapt existing psychological and criminological theories with a view to staging cybercrime intervention and/or prevention.
The Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in Forensic Cyberpsychology degree is a unique online program designed to broaden scientific investigation, and one of the first at a Doctoral level worldwide. Scholars from computer science to the social and behavioral sciences who join the new field of Forensic Cyberpsychology will undoubtedly contribute to crystallizing new ideas and conquering an emerging scientific frontier.
Cybercrime describes crimes carried out by both individuals and groups against computing devices, operational technology systems, or networks, as well as traditional crimes facilitated by the use of the Internet and/or information technology. Cyberpsychology focuses on the study of the impact of technology on human behavior. Cyberpsychologists study Internet psychology, virtual environments, artificial intelligence, intelligence amplification, gaming, digital convergence, social media, mobile and networking devices.
The emerging subdiscipline of Forensic Cyberpsychology focuses on the study of criminal behavior online and was first highlighted by Professor Mary Aiken almost a decade ago in the Europol 'Internet Organised Crime Threat Assessment Report' , in an appendix titled "the Cyberpsychology of Internet Facilitated Organised Crime" she outlined "the critical task for cyberpsychology as a discipline is to build up a body of established findings of how human beings experience technology, the critical task in forensic cyberpsychology is to focus on how criminal populations present in cyber environments".
In Forensic Cyberpsychology, the focus is on human factors behind cybercrime, studying offender profiling, behaviors, and what motivates criminals to act as they do, along with gaining insights and understanding into cyber deviancy, juvenile cyber delinquency, risk-taking/harmful behaviors online, and online victimology, as well as developing methods for online investigative procedures that help to mitigate and/or prevent cybercrime.
Capitol Tech has the unique resources and partnerships for students to progress in this field. In addition to learning from the world-leading expert in Cyberpsychology, Dr. Mary Aiken and other award-winning faculty, students may have opportunities for research collaborations with the National Security Agency (NSA), the Department of Defense (DoD) and other related agencies and organizations. The university’s proximity to the nation’s technology hub of Washington, D.C. and the DMV ensures prospective students will find many internships and job opportunities available to them with leaders of the industry.
The Ph.D. in Forensic Cyberpsychology program is structured for experienced professionals in this field with an appropriate graduate degree. Within the program, students will conduct original research in an approved area of Forensic Cyberpsychology.
As your Ph.D. progresses, you will move through a series of progression points and review stages by your academic supervisor. This ensures that you are engaged in research that will lead to the production of a high-quality thesis and/or publications, and that you are on track to complete this in the time available. Following submission of your Ph.D. Thesis or accepted three academic journal articles, you will have an oral presentation assessed by an external expert in your field.
Why Capitol?
Expert guidance in doctoral research
Capitol’s doctoral programs are supervised by faculty with extensive experience in chairing doctoral dissertations and mentoring students as they launch their academic careers. You’ll receive the guidance you need to successfully complete your doctoral research project and build knowledge in the field.
Proven academic excellence
Study at a university that specializes in industry-focused education in cyber and technology-based fields, nationally recognized for our academic excellence in our programs.
Program is 100% online
Our PhD in Forensic Cyberpsychology is offered 100% online.

Dr. Mary Aiken
Dr. Mary Aiken serves as Chair and Professor of the Cyberpsychology Department. She holds a Ph.D. in Forensic Cyberpsychology. Professor Mary Aiken is a world leading expert in Cyberpsychology – the study of the impact of technology on human behaviour and is a Professor of Forensic Cyberpsychology in the Department of Law and Criminology at the University of East London. Dr. Aiken is a member of INTERPOL's Global Cybercrime Expert Group and an Academic Advisor to Europol’s European Cybercrime Centre (EC3). She is a Fellow of The Royal Society of Medicine, Global Fellow at the Washington DC Wilson Center, a member of the Medico-Legal Society, an International Affiliate Member of the American Psychological Association (APA) and a Fellow of the Society for Chartered IT Professionals.

Dr. Ian McAndrew
An internationally recognized leader in research and expert on low-speed flight, Dr. McAndrew has five degrees: a PhD, two master’s degrees and two bachelor’s degrees. He is a Fellow of the Royal Aeronautical Society. Dr. McAndrew chairs several international conferences and journals and is invited to give keynote speeches all over the world. He started his career in the automotive industry as an engine designer, and has worked at several universities across the globe. Dr. McAndrew is Dean of doctoral programs at Capitol Technology University. An external examiner on the world wide stage (UK USA, Germany, Italy, Jordan, Japan, Australia, Greece and Kenya) his experience includes over 115 successful Doctorate successes.

Dr. Richard Baker
Dissertation Chair
Dr. Richard Baker is Dissertation Chair of Graduate Programs at Capitol Technology University. He previously served as associate professor in Indiana State University’s Department of Aviation Technology, and as executive director of the Center for Unmanned Systems and Human Capital Development. Richard holds a BS in mathematics and an MS in computer science from Indiana State University. He received his doctorate in information systems from Nova Southeastern University.

Dr. William Butler
Vice President
Dr. William (Bill) Butler is currently the Vice President of Academic Affairs at Capitol Technology University. Prior to this appointment in 2021, Dr. Butler served as Cybersecurity Chair for 8 years at Capitol Tech. Earlier in his career, he worked in the networking and IT industries as a network engineer and consultant for over 20 years. He also served as a joint qualified communications information systems officer in the U.S. Marine Corps and retired as a Colonel with 30 years of service (active and reserve). Dr. Butler holds a Doctorate in cybersecurity earned from Capitol focusing on preserving cellphone privacy and countering illegal cell towers (IMSI catchers).

Dr. Kellep Charles
Dr. Kellep Charles is Chair of Cybersecurity programs at Capitol Technology University. He completed his Doctorate in Cybersecurity at Capitol Technology University. He also holds a Master of Science in Telecommunication Management from the University of Maryland University College and a Bachelor of Science in Computer Science from North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University.
Career Opportunities
A degree in a cutting-edge, emerging discipline
Graduates will contribute significantly to the emerging Forensic Cyberpsychology field through the creation of new knowledge and ideas. Get the necessary credentials to take on a leadership role; work in industry, become a researcher, advisor or trusted expert.
Resources and Partnerships
Capitol Tech has the unique resources and partnerships for students to progress in this field and provides opportunities for finding internships and employment with leaders of relevant industries.
Degree Details
This program may be completed with a minimum of 60 credit hours, but may require additional credit hours, depending on the time required to complete the dissertation/publication research. Students who are not prepared to defend after completion of the 60 credits will be required to enroll in RSC-899, a one-credit, eight-week continuation course. Students are required to be continuously enrolled/registered in the RSC-899 course until they successfully complete their dissertation defense/exegesis.
The PhD program offers 2-degree completion requirement options:
- Dissertation Option : the student will produce, present, and defend a doctoral dissertation after receiving the required approvals from the student’s Committee and the PhD Review Boards.
- Publication Option: the student will produce, present, and defend doctoral research that is published as articles (3 required) in peer reviewed journals identified by the university and the student’s Committee. Students must receive the required approvals from the student’s Committee and the PhD Review Board prior to publication.
Prior Achieved Credits May Be Accepted
Doctor of Philosophy in Forensic Cyberpsychology Courses Total Credits: 60
FORENSIC CYBERPSYCHOLOGY DOCTORAL CORE: 30 CREDITS
FORENSIC CYBERPSYCHOLOGY DOCTORAL RESEARCH AND WRITING: 30 CREDITS
Educational Objectives:
1. Students will evaluate the need for Forensic Cyberpsychology.
2. Students will demonstrate advanced knowledge and competencies needed for the future in the human aspects of Forensic Cyberpsychology.
3. Students will analyze theories, tools, and frameworks used in Forensic Cyberpsychology.
4. Students will execute a plan to complete a significant piece of scholarly work.
5. Students will develop skills to implement theories into practice.
Learning Outcomes:
Upon graduation...
1. Graduates will incorporate the theoretical basis and practical applications of Forensic Cyberpsychology into their professional work.
2. Graduates will demonstrate the highest mastery the needs of Forensic Cyberpsychology.
3. Graduates will evaluate complex problems, synthesize divergent, alternative, and contradictory perspectives and ideas fully, and develop advanced solutions to Forensic Cyberpsychology challenges.
4. Graduates will contribute to the body of knowledge in the study of Forensic Cyberpsychology.
Tuition & Fees
Tuition rates are subject to change.
The following rates are in effect for the 2024-2025 academic year, beginning in Fall 2024 and continuing through Summer 2025:
- The application fee is $100
- The per-credit charge for doctorate courses is $950. This is the same for in-state and out-of-state students.
- Retired military receive a $50 per credit hour tuition discount
- Active duty military receive a $100 per credit hour tuition discount for doctorate level coursework.
- Information technology fee $40 per credit hour.
- High School and Community College full-time faculty and full-time staff receive a 20% discount on tuition for doctoral programs.
Find additional information for 2024-2025 doctorate tuition and fees.
Need more info, or ready to apply?

- Forensics Colleges » Online Forensics Programs » Online Doctorate (PhD) in Forensic Science
Search For Schools
When you click on a sponsoring school or program advertised on our site, or fill out a form to request information from a sponsoring school, we may earn a commission. View our advertising disclosure for more details.
Online Doctoral Programs (PhD) in Forensic Science
When human life is lost, law enforcement officers and forensic science specialists must determine the motivation for a crime and the cause of death. As simple as this formula seems, humans alone cannot be trusted to provide witness testimony. Enter the work of experienced forensic scientists who prove or determine probable fault using laboratory-based and carefully constructed questions when interviewing witnesses.
Leading forensic scientists and psychologists can practice their craft with a bachelor’s or master’s degree, but to delve into the nuanced areas of forensics and leadership, some senior-level positions require a doctoral degree in forensic science.
When two witnesses point fingers at each other, saying the other is guilty, forensic science takes a multidisciplinary approach to provide essential information to bring criminals to justice. A case report involving the murder of a 55-year-old man illustrates the need for a multidisciplinary approach. The man accused of killing his neighbor admits he killed him in self-defense, but relatives of the murder victim say that there were other motivations not being admitted.
To provide more details, a forensic scientist can serve as a medical examiner, a forensic chemist can do ballistics analysis, and a forensic psychologist can conduct interviews to determine the mental health state of the accused murderer so that justice can be served with accuracy.
Forensic scientists and psychologists working in the field can pursue doctoral degree options to bolster their expertise. Read on to learn more about online doctoral programs in forensic science.
Featured Online PhDs Related to Forensic Science
At present, there are no online doctoral programs in forensic science that can be completed 100 percent online. Because forensic science is a laboratory-based discipline, most programs require students to be on campus at least part-time for research and clinical work.
However, there are PhD programs that fall under the umbrella of forensic science, such as forensic biology, chemistry, and psychology. Applicants interested in these programs are strongly encouraged to learn about the accreditation status of these programs, which is discussed in detail below.
Walden University (Related Program)
Walden University in Minneapolis, Minnesota is unique because it offers the only online PhD program in forensic psychology. Students in this program can choose from a regular or fast-track option which enables students to waive up to six courses or 53 credits from the master’s degree in forensic psychology. The program also has optional four-day intensives focused on key topics.
Students in this doctoral program can also choose from seven unique specializations to focus their studies on a specific field of forensic psychology: general, criminal justice (self-designed), crisis leadership management, crisis response, legal issues in forensic psychology, self-designed program, and victimology. This program also provides two tracks: one for students with a master’s degree in forensic psychology and one for those with a GPA of 3.0 on their bachelor’s degree or a master’s degree in another discipline.
Some of the courses in the curriculum include themes and theories of psychology; abnormal behavior; criminal behavior; understanding violence, risk, and threat assessment; advanced issues in forensic psychology; treatment of forensic populations; psychology in the courts; police psychology; and consulting for organizational change.
- Location: Minneapolis, MN
- Accreditation: Higher Learning Commission (HLC)
- Expected Time to Completion: Four to eight years
- Estimated Tuition: Tracks 1 & 2 ($600 per quarter-hour); fast track ($6,970 per term)
Fielding Graduate University (Related Program)
Fielding Graduate University offers a doctoral program in clinical psychology with an optional concentration in forensic psychology and is accredited by the American Psychological Association.
Blending in-person learning opportunities with digital formats, this PhD program includes in-person and online seminars, meetings with faculty members and other students, weeklong residential sessions, and clinical and research training experiences. The program includes a clinical practicum as well as a clinical doctoral internship. Apart from these, the program also includes two additional in-person residency requirements.
Admission requirements to the program include a bachelor’s degree, a minimum GPA of 3.0, an online application form, a curriculum vitae (CV), a statement of purpose, a critical thinking writing sample, three letters of recommendation, and official transcripts. GRE scores are not required for admission.
The curriculum includes core courses in developmental bases of behavior; history and systems of psychology; social bases of behavior; cognitive and affective bases of behavior; psychopathology; multicultural psychology. Courses in the forensic psychology concentration include forensic psychology; ethics in forensic psychology; forensic assessment in civil court; malingering and deception; evaluations for the immigration courts; forensic assessment in criminal cases; and forensic psychology lab.
- Location: Santa Barbara, CA
- Accreditation: WASC Senior College and University Commission (WSCUC); American Psychological Association (APA)
- Expected Time to Completion: Five to six years
- Estimated Tuition: $9,700 per term
University of Arizona Global Campus (Related Program)
The University of Arizona Global Campus offers an online doctor of psychology (PsyD) program that helps students in building their knowledge base in the systems and history of psychology, and then students will be able to focus their PsyD degree by selecting a concentration that aligns with their specific research and career interests.
With the criminology and justice studies specialization, students will develop their expertise in criminal behavior and the corrections systems and criminal justice. Students in this specialization will be prepared to use psychological principles to solve complex real-world issues regarding justice and crime.
The PsyD includes ten core courses, seven specialization courses, and a capstone seminar. Students will then complete an applied doctoral project, which includes two planning courses and five units of the applied doctoral project.
Comprising 62 credits, the curriculum includes courses such as contemporary criminological theory; types & characteristics of crime; advanced analysis of criminal justice processes; juvenile justice; mental health & crime; drugs, addiction, & crime; and evaluating criminal justice interventions.
- Location: Chandler, AZ
- Accreditation: WASC Senior College and University Commission (WSCUC)
- Expected Time to Completion: Four years
- Estimated Tuition: $1,082 per credit
On-Campus Doctoral Programs in Forensic Science
As previously mentioned, no fully online doctoral programs lead to a PhD in forensic science, but there are forensic science doctoral programs in related subfields.
Here are on-campus doctoral programs in forensic chemistry, forensic mental health counseling, forensic science, and forensic psychology.
West Virginia University
West Virginia University’s PhD in forensic science program is unique in that it is only the second such program in the United States. Students in this PhD will be prepared to work as professionals in government laboratories, private industries, or academia as laboratory specialists. Students in this program must successfully complete a minimum of 71 credits. The program also includes a dissertation proposal presentation, an oral defense of the dissertation, and an oral qualifying examination.
In this research-intensive program, students study the foundations of criminalistics using research design, qualitative methods, statistical analysis, and communication skills in scientific writing and presenting. All students take a common core of advanced forensic science courses and other courses determined by their dissertation committees.
- Location: Morgantown, WV
- Accreditation: Forensic Science Education Programs Accreditation Commission (FEPAC); Higher Learning Commission (HLC)
- Estimated Tuition: Resident ($513 per credit); non-resident ($1,449)
Florida International University
Florida International University offers a doctor of philosophy (PhD) in chemistry with a forensic science track. This track prepares graduates for research in environmental and biogeochemistry with an emphasis on forensic science applications. This track has two tracks to choose from: an analytical chemistry/trace concentration and a biochemistry/DNA analysis concentration.
Students in this program benefit from collaborative agreements with local, state, national, and international agencies and learn about detecting trace amounts of evidence at crime scenes, DNA typing in mass disasters, and canine screening for explosives.
Research projects are coordinated by the International Forensic Research Institute, and graduates from this program go to work in government laboratories with the FBI, Department of Homeland Security, Secret Service, and the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives.
- Location: Miami, FL
- Accreditation: Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges (SACSCOC)
- Estimated Tuition: In-state ($4,101 per semester); out-of-state ($9,015 per semester)
Sam Houston State University
Sam Houston State University offers a doctor of philosophy in forensic science program providing students with problem-solving skills; advanced, discipline-specific knowledge; and critical thinking ability allowing them to advance into leadership positions. To achieve this, students will develop the ability to perform independent research, complete multidisciplinary academic coursework, gain hands-on experience in laboratories, and collaborate with accredited forensic laboratories, partners, and institutes.
Consisting of 86 credits beyond the bachelor’s degree, students will complete 43 credits of core coursework, a minimum of 15 credits of dissertation research, and an additional 28 credits of electives. Sample some of the courses in the curriculum: forensic instrumental analysis; controlled substances; pattern and physical evidence concepts; forensic biology; forensic toxicology; law and forensic sciences; and quality assurance and ethical conduct in forensic science.
- Location: Huntsville, TX
- Expected Time to Completion: Five years
- Estimated Tuition: Texas resident ($320.25 per credit); out-of-state ($728.25 per credit)
Other Online Forensic Science Programs to Consider
Bachelor’s degree holders who want to begin graduate studies in forensic science and related fields can consider two-year master’s degree programs. This degree option offers clinical and research-based rigor to prepare students for future doctoral studies.
Here are three online master’s programs in forensic science and psychology and one hybrid (online and on-campus) forensic science program which can prepare graduates for doctoral-level coursework in forensic science or psychology.
Oklahoma State University (MS in Forensic Science)
Oklahoma State University offers a hybrid master of science in forensic science with several concentration options (two of them are FEPAC-accredited). These concentrations include arson and explosives investigation; forensic investigative sciences; forensic biology/DNA (accredited by FEPAC); forensic chemistry/toxicology (accredited by FEPAC); and forensic psychology.
The concentration in forensic biology/DNA is a 36-credit FEPAC-accredited program that can be completed part- or full-time and features a death scene investigation track for those who have taken forensic science or biology, genetics, or molecular biology courses at the undergraduate level.
In the first year of the program, students can choose to take courses on-campus or online and the second year includes laboratory and research courses that must be taken on campus. Students have seven years to complete the requirements and must maintain a 3.0 GPA throughout their time in the program.
The curriculum includes courses such as the survey of forensic sciences; molecular biology; population genetics; forensic bioscience; ethical research and scientific writing; quality assurance in forensic science; methods in forensic sciences; criminalistics and evidence analysis; advanced criminalistics; and forensic statistics.
- Location: Tulsa, OK
- Expected Time to Completion: Oklahoma residents ($233.80 per credit); non-residents ($879.75 per credit); non-residents – online only ($364 per credit)
University of North Dakota (MA in Forensic Psychology)
The University of North Dakota offers an online master of arts in forensic psychology that prepares graduates for civil and criminal justice systems work. This 30-credit program is offered fully online and part-time to meet the needs of working students.
The curriculum includes courses such as psychology and law; research methods in forensic psychology; advanced social psychology; behavior pathology; readings in psychology; cognitive psychology; diversity psychology; eyewitness testimony memory; and supervised fieldwork.
Graduates from this program are prepared to conduct focus groups in legal settings for jury selection, select and use appropriate assessment tools, evaluate programs using research-based methods, and assist in addressing forensic issues in legal settings.
- Location: Grand Forks, ND
- Expected Time to Completion: 1.5 to two years
- Estimated Tuition: $588.65 per credit
Walden University (MS in Forensic Psychology)
Walden University offers a 48-credit online master’s of science (MS) in forensic psychology. As mentioned above, students in this master’s program have the option of applying up to half of their master’s coursework towards an online PhD in forensic psychology which saves students time and money and enables them to earn MS and PhD degrees on a faster timeline.
The master’s program offers eleven specializations related to forensic psychology and other sub-fields of forensic science: criminal justice self-designed; cybercrimes; family violence; legal issues in forensic psychology; military; police psychology; self-designed learning; sex offender behavior; terrorism; victimology; and general program.
Some of the topics students will explore include foundations of graduate studies in psychology; abnormal behavior; criminal behavior; understanding forensic psychology research; understanding violence, risk, and threat assessment; psychological aspects of violent crime; victimology; and criminal investigative analysis and profiling.
- Expected Time to Completion: 18 to 24 months
- Estimated Tuition: $548 per quarter hour
Arizona State University (Master’s in Forensic Science)
Arizona State University’s online professional science master’s in forensic science (PSM) program allows currently working forensic science professionals to consider career advancement in sectors such as law enforcement, forensic science, medicolegal, and other closely related fields.
To be considered for admission, applicants must have earned a bachelor of science or bachelor of arts degree in a related field with a minimum GPA of 2.75. Additionally, applicants must complete an online application and submit official transcripts, two letters of recommendation, a personal statement, and an up-to-date resume. Proof of English language proficiency is required of applicants whose native language is not English.
The program comprises 30 credits, including coursework in forensic science and governance; ethics in forensic science; laboratory leadership, policy, and practice; advanced forensic psychology; advanced topics in human forensic DNA; applied biostatistics in medicine and informatics; biostatistics and data management; criminal procedure of investigations for social and forensic scientists; and forensic toxicology; among others.
- Location: Phoenix, AZ
- Expected Time to Completion: Two years
- Estimated Tuition: $847 per credit
Forensic Science PhD Admission Requirements
To be admitted into a forensic science PhD program, applicants must meet certain academic requirements. Here’s a list of documents commonly requested when applying for a doctoral program in forensic science:
- A personal statement (typically 1,000 words or less)
- Application fee
- A resume with one to two years of professional experience in forensic science
- A background check (especially for competitive internships for program credit)
- Competitive Graduate Record Examination (GRE) scores
- GRE Subject Test scores (generally optional)
- Interview (in-person, phone, or web-based)
- Letters of recommendation
- Official transcripts from all undergraduate (and/or graduate) institutions with a stellar GPA (e.g., >3.5)
- Proof of having completed specific coursework in a relevant major (e.g., forensic science, natural science, chemistry, biology)
- Proof of professional publications (recommended, but not always required)
- TOEFL scores (for non-native speakers of English only)
Common Courses & Requirements for Forensic Science PhD Programs
Each forensic science or psychology doctoral program has its own unique requirements for students to meet to be considered for admission and graduate from the program. Here is a list of common degree requirements and course titles.
Credit Requirements for Forensic Science Programs
- Foundational courses (3-6 credits)
- Advanced coursework (24-30 credits)
- Research methods (9-12 credits)
- Specialization courses (12-15 credits)
- Dissertation writing (3-6 credits)
- Residencies, internships, clinical practicums (timelines vary)
Common Courses for Forensic Science and Psychology Programs
- Research methods and statistics in psychology
- Psychological research and biblical worldview
- Theories and research in industrial/organizational psychology
- Teaching of psychology
- Criminal investigative analysis and profiling
- Field experience
- Vicarious trauma and compassion fatigue
- Doctoral writing assessment
- Qualitative and quantitative reasoning and analysis
- Clinical practicum
- Clinical psychopharmacology
- Dissertation writing
- Eyewitness testimony and memory
- Ethics in forensic leadership
- The chemistry of pyrotechnics and explosives
- Fire dynamics in forensic investigations
- Computer fire modeling
- Molecular biology for the forensic scientist
- Forensic pathology and medicine
- Forensic microbiology
- Forensic toxicology
- Criminalistics and evidence analysis
Online Forensic Science PhD Residencies, Internships, or Practicums
As previously discussed, the nature of forensic science or forensic psychology involves on-campus or in-person research in laboratory or clinical settings and there are few to no online opportunities for residencies, internships, or practicums.
For illustration, Walden University requires students in its PhD in clinical psychology program to spend an Academic Year in Residence (AYR) in addition to four four-day PhD residencies. The AYR earns students 40 credits and numerous opportunities to develop skills and knowledge needed for a career as a forensic psychologist.
West Virginia University also partners with several governmental and private organizations that offer forensic science internships in federal laboratories and the Department of Homeland Security for students to gain hands-on experience during summer-only experiential learning.
Forensic Science Programmatic & Institutional Accreditation
When researching educational programs, accreditation is an essential factor to consider. Accreditation is granted to programs or institutions by national, regional, or programmatic accreditation organizations tasked with ensuring that high standards of educational quality are met.
Why is it important to verify a program or institution’s accreditation? First, accreditation validates the educational quality. Future employers look for graduates from accredited programs to ensure that their professional programs and clients receive the highest level of professionalism. And most importantly, accreditation is a requirement for state or national licensure for some careers, including forensic psychology. Sometimes, candidates can only sit for licensure exams if they have completed an accredited academic program.
Programmatic Accreditation
The Forensic Science Education Programs Accreditation Commission (FEPAC) grants the gold standard in forensic science program accreditation. Forensic psychology programs are granted accreditation from the American Psychological Association (APA). To earn programmatic accreditation requires adhering to rigorously high standards in specialized areas.
Institutional Accreditation
If any institution does not hold programmatic accreditation, then a prospective student is advised to research a school’s institutional accreditation. The United States Department of Education’s Council for Higher Education (CHEA) recognizes the following regional accrediting organizations:
- Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges (SACSCOC)
- Higher Learning Commission (HLC)
- Middle States Commission on Higher Education (MSCHE)
- New England Commission of Higher Education (NECHE)
- Northwest Commission on Colleges and Universities (NWCCU)
- WASC Senior College and University Commission (WSCUC)
- Accrediting Commission for Community and Junior Colleges (ACCJC) Western Association of Schools and Colleges

Rachel Drummond, MEd
Rachel Drummond has given her writing expertise to ForensicsColleges.com since 2019, where she provides a unique perspective on the intersection of education, mindfulness, and the forensic sciences. Her work encourages those in the field to consider the role of mental and physical well-being in their professional success.
Rachel is a writer, educator, and coach from Oregon. She has a master’s degree in education (MEd) and has over 15 years of experience teaching English, public speaking, and mindfulness to international audiences in the United States, Japan, and Spain. She writes about the mind-body benefits of contemplative movement practices like yoga on her blog , inviting people to prioritize their unique version of well-being and empowering everyone to live healthier and more balanced lives.
- Online Bachelor's in Biochemistry
- Online Bachelor's in Biology
- Online Bachelor's in Criminal Justice
- Online Bachelor's in Cybersecurity
- Online Bachelor's in Forensic Accounting
- Online Bachelor's in Forensic Psychology
- Online Bachelor's in Forensic Science
- Online Bachelor's in Legal Studies
- Online Bachelor’s in Digital Forensics
- Online Master's in Biochemistry
- Online Master's in Biology
- Online Master's in Criminal Justice
- Online Master's in Forensic Science
- Online Master’s in Crime Scene Investigation
- Online Master’s in Cybersecurity
- Online Master’s in Digital Forensics
- Online Master’s in Forensic Accounting
- Online Master’s in Forensic Nursing
- Online Master’s in Forensic Psychology
- Online Master’s in Legal Studies
- Online MBA in Criminal Justice
- Online Certificates in Crime Scene Investigation
- Online Certificates in Cybersecurity
- Online Certificates in Forensic Psychology
- Online Graduate Certificate Programs in Legal Studies
- Online Graduate Certificates in Criminal Justice
- Online Graduate Certificates in Digital Forensics
- Online Graduate Certificates in Forensic Accounting
- Online Graduate Certificates in Forensic Science
- Online Post-Master's Certificates in Forensic Nursing
- Online Doctorate (PhD) in Forensic Psychology
- Online PhD Programs in Criminal Justice
- Online PhD Programs in Cybersecurity
- Online PsyD in Forensic Psychology
Back to Top
Cybersecurity Guide
From classroom to career: Digital forensics degrees explained
- Career steps
- Career overview
- Important skills
- What do digital forensics do?
- Job description
- Salary and outlook
Pursuing a digital forensics degree opens up a world of opportunities in our increasingly digital and cyber-centric society. This degree and career path is beneficial for several compelling reasons:
- Growing demand : The integration of technology into every facet of our lives has led to a surge in the need for digital forensics experts.
- High salary potential : The specialized nature of the work and market demand often equate to competitive compensation.
- Career variety : A degree in this field can lead to numerous roles, such as a digital forensic investigator or cybersecurity analyst.
- Constant learning : The ever-evolving nature of digital forensics promises continuous learning and professional growth.
- Impact : Digital forensics professionals play a vital role in safeguarding information systems, offering a sense of fulfillment.
- Skill transferability : The skills acquired during the study are highly transferable across various tech jobs.
- Job security : Given the relentless rise of cyber threats, job security is typically high in this field.
The digital CSIs of the infosec universe, and digital forensics (sometimes known as DFOR) experts are critical in minimizing any harm done by cybercrimes, and reconstructing the crime to help bring criminals to justice.
Anytime law enforcement officials are involved, following the letter of the law is vital to a successful culmination of an investigation. Adhering to proper evidence-handling procedures will be of paramount concern for digital forensics experts.
Many digital forensic experts are employed by governments or government contractors. For a large portion of these positions, a security clearance is necessary .
Four steps to becoming a digital forensics expert
1. Education : There are a variety of college degree programs that lend themselves to careers in digital forensics. These include computer engineering, computer science , electrical engineering, applied mathematics, cybersecurity , information technology, and digital forensics. More advanced positions in digital forensics sometimes require master’s degrees.
Cyberseek data indicates that 1 percent of employed cyber crime analysts, a role similar to digital forensics, have obtained at least an associate degree. Meanwhile, 61 percent of this group have graduated with a bachelor’s degree, and about 38 percent have pursued a master’s degree.
2. Career path : There are entry-level positions available in digital forensics that provide excellent avenues of entry into the field. Honing technical skills as a prelude to developing infosec skills is also a viable path. So too are positions in information technology fields with a special focus on cybersecurity. Software development is another track that can lead to digital forensics careers.
3. Professional certifications : There are many different digital forensics certifications available, but some of the most popular and highly regarded include:
- GIAC Certified Forensic Analyst (GCFA) : Covers the essential skills needed to conduct digital forensic investigations. It is a good choice for beginners and experienced professionals alike.
- GIAC Certified Forensic Examiner (GCFE) : This more advanced certification is designed for experienced digital forensic investigators. It covers a wider range of topics, including incident response, malware analysis, and network forensics.
- EnCase™ Certified Examiner (EnCE) : Certification for both private and public sector professionals in the use of EnCase forensic software
- AccessData Certified Examiner (ACE) : Demonstrates proficiency with Forensic Toolkit (FTK) technology.
- Certified Forensic Computer Examiner (CFCE) : Vendor-neutral certification that is designed for experienced digital forensic investigators.
- Certified Computer Examiner (CCE) : Covers the process of digital forensics examination including the ability to handle and process digital evidence.
Other certifications include:
- Professional Certified Investigator (PCI)
- Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator (CHFI)
- GIAC Reverse Engineering Malware (GREM)
- GIAC Network Forensic Analyst (GNFA)
- GIAC Advanced Smartphone Forensics (GASF)
- GIAC Cyber Threat Intelligence (GCTI)
- Certified Mobile Device Examiner (CMDE)
- Certified Digital Forensics Examiner (CDFE)
- Certified Network Forensic Analysis Manager (CNFAM)
- Advanced Digital Forensic Certification (ADFC)
Some employers may also require more basic certifications, such as CompTIA A+ or Net+, which relate to IT operational and technical support skills or a more focused on one or a few specific types of hardware or operation systems like iOS Forensics , which delves into Apple’s notoriously challenging iPhone operating system.
4. Keep current : As with most cybersecurity career paths, it is vital to remain current with what is happening in the industry. Keeping skills and knowledge up to date with all of the latest trends is made easier when the field has its professional trade association. One example within the digital forensics community is the High Technology Crime Investigation Association .
Offering relevant continuing education, professional training, and proficiency testing for digital forensics professionals.
The Scientific Working Group on Digital Evidence (SWGDE) is another cybercrime forensics organization dedicated to keeping industry professionals’ knowledge and skills current. SWGDE focuses on fostering open communication between industry organizations and professionals.
What is a digital forensics expert?
Job titles for digital forensics professionals vary quite a bit but are generally variations on a theme. Titles seen frequently include digital forensics engineer, digital forensics investigator, digital forensics specialist, digital forensics analyst, digital forensics examiner, digital forensics technician, and others.
Job scope probably varies a little less than titles, but will depend on seniority and experience levels. Cybercrime forensics experts primarily enter the picture after there has been a breach of information security. That’s the time to put on the CSI trench coat and dig deep into the evidence. No blood and guts, just digital trails.
Digital forensics degree, skills, and experience
The investigations of digital crimes (and just about everything else) involve delving into computing devices, including mobile devices, software, network traffic analysis, memory analysis, media analysis, databases, and internet-of-things (IoT) devices. This means that digital forensic experts must possess in-depth and low-level knowledge of as many such systems as possible.
Technical Skills may include:
- Operating Systems Proficiency : An understanding of various operating systems such as Windows, MacOS, Linux, and their respective file systems.
- Forensic Tool Expertise : Familiarity with popular digital forensic tools such as EnCase, Forensic Toolkit (FTK), Autopsy, Cellebrite, X-Ways, and others.
- Mobile Forensics : Skills related to extracting and analyzing data from mobile devices like smartphones and tablets.
- Network Forensics : Knowledge of network protocols, packet analysis, and the ability to analyze network logs for signs of malicious activity.
- Cryptography : Understanding encryption and decryption techniques, recognizing encrypted files or data streams, and methods to potentially decrypt or analyze them.
- Malware Analysis : Ability to detect, isolate, and analyze malicious software.
- Cloud Forensics : Skills to investigate data stored on cloud platforms such as AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure.
- Database Forensics : Ability to navigate and analyze database structures, logs, and data.
- Data Recovery : Techniques to retrieve data from damaged, encrypted, or formatted storage devices.
- Computer Languages : Python, Bash/Shell, and PowerShell are the most useful scripting languages for most digital forensics practitioners. If you are interested in specialized areas like malware analysis, then deeper knowledge in C/C++, Assembly, and Java may be more relevant
Soft skills sought by employers include Written and oral communication, excellent analytical skills, the ability to organize complex investigations, and the ability to document and report findings to stakeholders.
What do digital forensics experts do?
Today, there is a digital element to almost every legal investigation. From civil cases like infidelity, child custody, accident reconstruction, civil disputes, and missing persons, to criminal cases such as fraud, espionage, arson, larceny, and wrongful death, digital forensics is now used as a critical element of most investigations. Breach of information security is a major focus for digital forensics experts.
In the pursuit of finding answers, digital forensics professionals utilize skills and knowledge of all elements of information systems and security to extract all relevant data. This includes a wide variety of computer hardware and software, networking systems, and mobile devices and systems.
With this knowledge, digital forensics professionals will attempt to restore deleted data, analyze recovered data, and perform a complete forensic examination of all computers, databases, and systems.
This information is assembled and used to reconstruct what actually happened and then reported on to affected parties. In civil or criminal cases that have progressed to legal courts, digital forensics experts are often called on to provide expert testimony.
Digital forensics expert job description
The specific functions of digital forensics experts will vary substantially based on the employer’s agenda and the specific case being worked on. Potentially, tasks will include some or all of the following:
- Utilize leading forensic software to identify, collect, preserve, and analyze electronic data from laptops, desktops, servers, backup media, mobile devices, and a wide variety of other media
- Recover deleted user data, hidden data, file fragments, and temporary files
- Managing and tracking electronic evidence
- Identify and document tactics, techniques, and procedures used by an attacker to gain unauthorized access
- Develop and disseminate engagement reports, technical reports, and briefs based on analytic findings
- Follow industry-standard forensic best practices while imaging, preserving, transporting, and handling electronic data and associated physical devices.
- Provide expert witness testimony
Outlook for digital forensics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that the employment of forensic science technicians, which includes digital forensics investigators, will grow 13 percent from 2022 to 2032.
Digital forensics investigators are in high demand in a variety of industries, including law enforcement, government, and private companies. As organizations become more reliant on digital technology, the need for digital forensics investigators to investigate cybercrimes and incidents will continue to grow.
In addition to the growing demand for digital forensics investigators, the field is also becoming increasingly complex as technology evolves. Digital forensics investigators need to be able to stay up-to-date on the latest trends and technologies to effectively investigate cybercrimes.
Law enforcement agencies, including district attorney offices, police, the FBI, DEA, and CIA, are often hiring digital forensics investigators. The FBI recently created the Forensic Examiner Talent Network to attract and retain top talent in cybercrime forensics.
How much do digital forensics experts make?
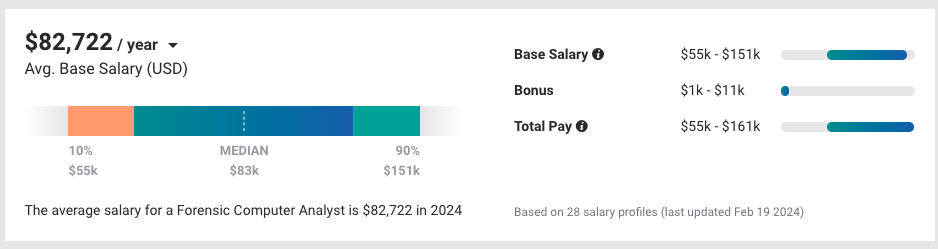
Glassdoor reports that in 2024, Digital forensics professionals make an average annual salary of $132,000 Bonuses, commissions, and profit-sharing can add as much as $21,716 annually. A quick search of job posting sites uncovered one position that paid $111,000.
On the other hand, Payscale shared that the salary of a Forensic Computer Analyst with digital forensic skills may range from $55,000 up to $151,000, with an average salary of $82,722.
Frequently asked questions
Digital forensics experts identify, acquire, process, analyze, and report data. They usually come into play when a breach of information security has occurred.
A digital forensic expert helps retrieve, analyze, and complete a forensic examination of all computers, databases, and systems for affected parties.
Obtain a relevant degree (e.g., Computer Science or Digital Forensics) and consider certifications like CCE or GCFA. Develop technical and soft skills, emphasizing hands-on experience with forensics tools. Gain practical experience through internships and simulated labs and continuously update your knowledge in this rapidly evolving field. As you progress, consider specializing in areas like mobile forensics or malware analysis for advanced opportunities
Digital forensics is highly promising. As our reliance on digital platforms grows and the cyber threat landscape becomes more intricate, the expertise of digital forensic professionals will be indispensable in ensuring digital justice, security, and resilience.
Essential skills for digital forensic experts include proficiency in operating systems, file systems, digital forensic tools, encryption, malware analysis, cloud forensics, data examination, pattern recognition, legal procedures, and evidence admissibility. Recognized certifications, such as CCE, CFCE, or EnCE, are also valuable.
- Digital Forensics career pathway | Sourced from cyberseek.org in April 2024.
- Salary info for Digital Forensics | Sourced from Payscale and Glassdoor in April 2024.
- Outlook info for Digital Forensics | Sourced from Bureau of Labor Statistics in April 2024.
- Current Students
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
Online Master's Degree
Digital forensics & cyber investigation, degree at a glance.
- Transfer exactly 6 credits
- All courses available online
- Select hybrid courses available
TUITION RATES
- $694 per credit (in-state)
- $694 per credit (out-of-state)
- $480 per credit (military)
- Other fees may apply
Next Session Starts
Develop the cutting-edge skills and knowledge you need to become a digital forensics expert..
The online master’s degree in digital forensics and cyber investigation from University of Maryland Global Campus is designed to prepare you to meet the growing demand for investigative, leadership, and executive skills in analyzing and mitigating cyber crime. Learn how to determine whether a digital system has been attacked or compromised, and master reliable methods to identify, preserve, analyze, and present evidence for legal prosecution and administrative proceedings.
- Requirements
Total Credits Required: 36
Take the following courses in the order listed:
Foundation Course
Core courses.
- Cyberspace and Cybersecurity Foundations (6 Credits, DFC 610)
- Digital Forensics Technology and Practices (6 Credits, DFC 620)
- Digital Forensic Response and Analysis (6 Credits, DFC 630)
- Advanced Forensics (6 Credits, DFC 640)
Capstone Course
- Cybersecurity Capstone (6 Credits, CYB 670)
General Master's Degree Requirements
- You must maintain a GPA of 3.0 or higher at all times.
- All degree requirements must be fulfilled within five consecutive years.
- Any transfer credits must have been earned within the five-year time frame to be applied toward a graduate degree.
- Please review the overall master’s degree requirements for additional considerations.
Additional Program-Specific Requirements
- All courses must be taken in the order listed.
- You must complete each course with a grade of B or better to advance to the next course.
- The grade of C is not available for these courses.
- The courses in this program will have seven-day and 60-day options for the grade of Incomplete.
Accelerated Pathway
If you completed your undergraduate degree at UMGC with a major in cybersecurity technology, an accelerated pathway between UMGC's graduate and undergraduate degree programs in this field may allow you to reduce your total coursework for this program by up to 6 credits .
Explore the MARS Program in Your Courses
Some of UMGC's online cyber graduate courses utilize the Multi-Dimensional Applied Relevant System (MARS), an AI-driven virtual learning platform that allows students to demonstrate their abilities and apply their cyber skills in a practical, immersive environment.
Search Course Catalog
These requirements are for students who enroll in the 2023–2024 academic year . For prior year requirements, visit our catalog archive.
Master’s Degree Requirements
Program highlights.
Develop skills and gain knowledge through coursework that draws from the expertise and experience of our respected faculty.
Industry Snapshot
This program is designed to help prepare you for work in government organizations, the private sector, and law enforcement agencies in the areas of computer and digital crime.
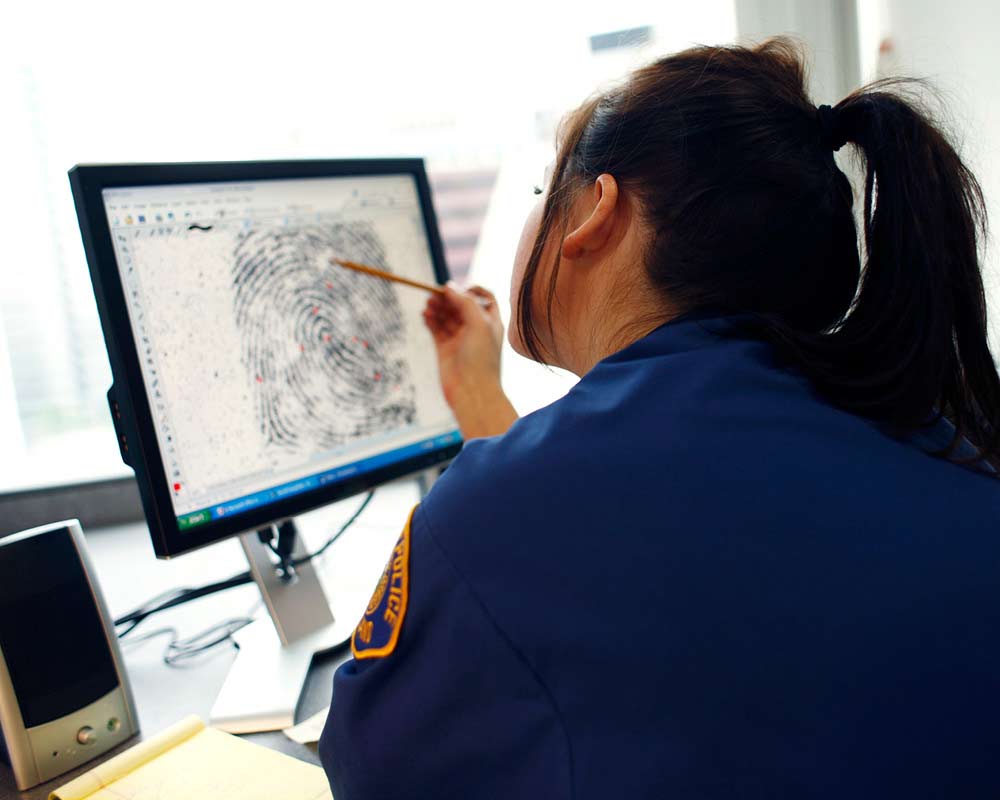

You might be interested in similar programs
Compare All Programs
Industry Certification Exams
This program is designed to help prepare you for the following certification exams:
- EC-Council Certified Incident Handler
- EnCase Certified Examiner (EnCE)
- GIAC Certified Forensic Analyst (GCFA)
- GIAC Certified Forensic Examiner (GCFE)
- GIAC Network Forensic Analyst (GNFA)
Additional Program Information
- Experience Recommended for Success
- Technology Requirements
- Student Organizations
We recommend having a background in computing and programming for this program. Strong writing skills are also encouraged.
For some of the upper-level cybersecurity and IT courses in this program, you will need equipment that meets the following specifications. Courses in graphics- or computing-intensive disciplines may require a higher processing speed, more RAM, and/or better screen resolution.
Hardware Requirements
- 64-bit processor, Intel Core i5 (7th generation or higher), or equivalent (e.g., AMD, M1)
- Processor speed: 1.5 GHz or higher (2 GHz recommended)
- Storage: At least 250 GB (SSD [preferred] or HD), with at least 30 percent free space
- RAM: At least 4 GB (8 GB recommended)
- Display/monitor: Minimum 13”
- Screen resolution: Minimum 1280 px x 1024 px
- Keyboard and mouse/trackpad
- High-speed Internet connection (Ethernet or Wi-Fi)
- 32-bit video card
Operating System
Choose one of the following:
- Windows 10 (recommended; version 1909 or higher required for any course using Adobe Creative Cloud)
- Mac OS X 10.15 or higher
- Ubuntu 18.04+ (or other Linux LTS)
- Microsoft Office 2019 or later (Office 365 Education is available for free with your student email address.)
- Most recent version/update of a web browser (Firefox, Safari, or Chrome)
- Antivirus software
- Adobe Acrobat PDF Reader
Additional Recommendations
- Built-in camera (or USB port for a webcam)
- Built-in microphone and speakers (or USB ports for external audio devices)
Computing Club
The Computing Club provides a dynamic environment where members can work collaboratively, share innovative ideas, enhance their career-readiness, and gain marketable experience in their respective fields. It is available to graduate or undergraduate students, alumni, faculty, and staff members. Students and alumni can join the Computing Club group on CareerQuest .
Cyber Competition Team
The Cyber Competition Team represents UMGC at various cybersecurity events and tournaments nationwide. Being a member of the team gives students an opportunity to develop their cybersecurity skills and network with other students. The team is open to undergraduate and graduate students and alumni through a tryout process. Email jesse.varsalone@umgc.edu or visit the team webpage to learn more.
Upsilon Pi Epsilon (Computing & Technology Disciplines)
Upsilon Pi Epsilon, the international honor society for the computing and IT disciplines, is designed to promote the computing and information sciences and to encourage the enhancement of knowledge in the field. Upsilon Pi Epsilon is open to both undergraduate and graduate students who are pursuing a degree in the computing and information science disciplines. Membership is by invitation only.
Undergraduate membership is open to students majoring in one of the computing disciplines who have completed at least 45 credit hours towards their degree, including 30 or more credits at UMGC (in graded coursework) and at least 15 credits from information technology and computer science courses. Undergraduate students need to have a cumulative GPA of a 3.5 or higher and a GPA of 3.5 or higher in all coursework taken from the information technology and computer science courses.
Graduate student membership is open to students pursuing a master's degree in cloud computing systems, cyber operations, cybersecurity management and policy, cybersecurity technology, data analytics, or digital forensics and cyber investigation; a master's degree in information technology with a specialization in database systems technology, informatics, information assurance, software engineering, or systems engineering; or a legacy master's degree in cybersecurity. Graduate students must have completed at least 18 resident credits towards their degree at UMGC, with a cumulative GPA of a 3.5 or higher.
For more information, please email upe@umgc.edu .
What is a master's in digital forensics and cyber investigation?
A master's in digital forensics and cyber investigation is a graduate-level program that focuses on the identification, preservation, analysis, and presentation of digital evidence in a legal context. UMGC's online Master of Science in Digital Forensics and Cyber Investigation degree is a 36-credit program that covers topics like forensic examination tools and technologies, best practices in forensic examinations, artifact reconstruction and recovery, evidentiary volume and encryption, and more. Graduates of the program are prepared for careers as digital forensic analysts, forensic examiners, forensic consultants, and information security managers.
Is a master's degree in digital forensics and cyber investigation worth it?
At UMGC, we want you to be happy with the investment you make in your education, and we work hard to keep our programs affordable . When you choose to pursue your master's in digital forensics and cyber investigation at UMGC, you can rest assured that the quality of our curriculum is backed by the reputation of an accredited state university and a member institution of the University System of Maryland . Deciding whether an online master's degree in digital forensics and cyber investigation is worth it for you ultimately depends on your individual needs and goals. If you're not sure whether this is the right program for you or need help figuring out how to fit the program into your life, don't hesitate to reach out to us —our advisors and success coaches are happy to help.
How long does it take to get a master's in digital forensics and cyber investigation?
UMGC's online master's degree in digital forensics and cyber investigation is a 36-credit program with courses offered year-round. Each course is 6 credits, and students typically take them one at a time, which means they can finish the program in as little as 18 months. If you recently completed an undergraduate degree in cybersecurity technology at UMGC, you may be able to apply 6 credits toward your graduate degree and shorten your time to completion by one term.

How much does a master's in digital forensics and cyber investigation cost?
UMGC is committed to keeping our tuition and fees as affordable as possible. The master's degree in digital forensics and cyber investigation follows the specialty graduate program tuition rates, which appear at the top of this webpage. We also offer scholarships , an interest-free monthly payment plan , and no-cost digital materials in place of most textbooks to help make your education more affordable.
What background do I need to get a master's in digital forensics and cyber investigation?
You don't need to have majored in any specific area to be successful in the master's in digital forensics and cyber investigation at UMGC. However, we do recommend you have a background in computing and programming. Strong writing skills are also encouraged.
Whom is the Master of Science in Digital Forensics and Cyber Investigation geared toward?
This program is designed for those who want to develop skills and competencies in the analysis of digital evidence. This may lead to positions tracking cyber intruders or digital evidence within government and private organizations as well as law enforcement.
What will I get from the Master of Science in digital forensics and cyber investigation?
This program focuses on the investigation area of a cyber attack and collecting evidence from digital assets of other specific activity. It will help you develop your competencies in finding, accessing and analyzing digital evidence left on a variety of devices from computers to smartphones and tablets. The program will require that you become adept with network, computer, and digital analysis technologies at an intermediate level.

Suzan L., Guam MS in Digital Forensics & Cyber Investigation
Our helpful admissions advisors can help you choose an academic program to fit your career goals, estimate your transfer credits, and develop a plan for your education costs that fits your budget. If you’re a current UMGC student, please visit the Help Center .
Personal Information
Contact information, additional information.
By submitting this form, you acknowledge that you intend to sign this form electronically and that your electronic signature is the equivalent of a handwritten signature, with all the same legal and binding effect. You are giving your express written consent without obligation for UMGC to contact you regarding our educational programs and services using e-mail, phone, or text, including automated technology for calls and/or texts to the mobile number(s) provided. For more details, including how to opt out, read our privacy policy or contact an admissions advisor .
Please wait, your form is being submitted.
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
Department of Information Security and Communication Technology
- Master's programmes in English
- For exchange students
- PhD opportunities
- All programmes of study
- Language requirements
- Application process
- Academic calendar
- NTNU research
- Research excellence
- Strategic research areas
- Innovation resources
- Student in Trondheim
- Student in Gjøvik
- Student in Ålesund
- For researchers
- Life and housing
- Faculties and departments
- International researcher support
Språkvelger
Ntnu digital forensics.
The research group focuses on research and development of advanced computational methods to establish and prove the scientific basis of forensic investigative procedures, with the objective to support forensic examiners in their daily casework.
About our Research Group
We conduct fundamental and applied research to enhance prevention, investigation and prosecution of cybercrime, cyber-enabled fraud, and high technology crime.
We also contribute to advisory services, forensic casework, and expert witness in cooperation with partners from national, European and international law enforcement agencies (LEA), academia and the private sector.
Learn more about our research

- Research in the area of large-scale investigations; automatic search through terabytes of electronic data storage within closed systems and the Internet,
- Research and development for the rapid acquisition, correlation and analysis of Internet-related evidence,
- Technologies for cross-media search and data integration to access diverse sources of information, in particular data enrichment from Internet sources,
- Algorithms for the analysis of encrypted evidence and cryptographic credentials,
- Design of advanced computing technologies to achieve more objective evidence analysis and final decision making by implementing computational intelligence.
- Development of methods and tools for digital penetrator attribution and profiling, visualization of serious criminal relationships and associations, and geographical mapping of digital and physical evidence.
Mission statement
Teaching on Bachelor, Master , and PhD Level
- Postgraduate Education and Training
- Curiosity-driven, fundamental research and publications
- Applied Research and Development on behalf of Industrial and Governmental Entities
- Forensic Casework, Expert Witnesses, and Advisory Services in Cooperation with Partners
- Networking and Community-building Activities, e.g., Workshops, Tutorials, Competitions,…
- Assist in basic and applied forensic research, e.g. to establish or prove the scientific basis of a particular forensic investigative procedure,
- Support the forensic examiner in their daily casework.
- Modern crime investigation, prosecution and prevention shall profit from the joint intelligence of humans and machines.
Research activity
Vacant positions, key academic staff, key academic staff, person-portlet, katrin franke professor of computer science, jan william johnsen researcher, carl stuart leichter adjunct associate professor, kyle andrew porter researcher, andrii shalaginov associate professor, part-time academic staff, part-time academic staff, stefan axelsson associate professor, geir olav dyrkolbotn associate professor, hanno langweg associate professor, thomas walmann, part-time without person portlet.
André Årnes , Adjunct Associate Professor
Jefferey D. Hamm , Lecturer, Mandiant/FireEye
Affiliated Academic Staff
Christoffer vargtass hallstensen head of soc, anna maria henningsson adviser, basel katt head of department and professor, mariusz nowostawski associate professor, affiliated without person portlet.
Inger Marie Sunde , Professor, The Norwegian Police University College (PHS)
Hallstein A. Hansen , PhD, Oslo Police District (OPD)
Jul Fredrik Kaltenborn , PhD Research Fellow, Department of Information Security and Communication Technology
News and events
News and events, digital forensics map.
Teknologivegen 22 Gjøvik
Phd research fellows
Ph.d. research fellows, jens-petter sandvik, academic partners.
- United Nations Interregional Crime and Justice Research Institute
- University California Santa Cruz, USA
- Kyushu Institute of Technology, Japan
- University of Groningen, The Netherlands
- Norwegian Computing Centre (NR) , Norway
- Norwegian Police University College (PHS), Norway
- University in Oslo, Norway
- University of Malta, Malta
- National Research Council of Italy, Italy
- National Intelligence Academy, Romania
- Edith Cowan University, Australia
- Fraunhofer Society, Germany
- Hitachi Central Research Laboratory, Japan
- École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Switzerland
- Ellinki Aeroporiki Viomichania Anonymi Etairei, Greece
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), USA
- Universität Stuttgart, Germany
User partners from public sector
- Norwegian National Police Directorate (POD), Norway
- Kripos, Norway
- Økokrim, Norway
- Oslo Police District (OPD), Norway
- Netherlands Forensics Institute (NFI), Netherlands
- Advance Technology Institute, Romania
- NorSIS – Norsk Senter for Informasjonssikring, Norway
- Misa SA, Norway
- Raufoss Technology AS, Norway
- SINTEF Raufoss Manufacturing, Norway
Security-service providers
- FinansCERT, Norway
- mnemonic AS, Norway
- Synergetics N.V. Group, Belgium
- Xensics, USA
- KraftCERT AS, Norway
- National Sikkerhetsmyndighet (NSM), Norway
- REALITY NET System Solutions, Italy
- Ericsson AB, Sweden
- C 3 M d.o.o., Slovenia
- Promon, Norway
- RD&T Technology AB, Sweden
Contacts:
Website: .
https://thecollege.syr.edu/degree-programs/digital-forensics-ms/
Overview:
The M.S. in Digital Forensics is a 36-credit program that combines the iSchool’s expertise in information security, digital forensics, and data analytics with the forensic science expertise of the Forensic and National Security Sciences Institute in the College of Arts and Sciences. Digital forensics is the acquisition and analysis of evidentiary information that is stored or transferred in binary form. Digital evidence is found on computers, networks, mobile devices, drones, “smart devices,” and in “the cloud.” Single investigations often generate dozens of digital devices with terabytes of data. It is the fastest growing area in forensics science. Courses will provide training and experience in the collection, examination, analysis, reporting, and legal proceedings involving digital evidence, preparing graduates for careers in in digital forensics, information security, business intelligence, investigations, and traditional forensic science.
I. Primary Core
(21 credits) - Students are required to take the following seven courses.
- FSC 606 - Advanced Forensic Science 3 credit(s)
- FSC 633 - Quality Assurance and Ethics 3 credit(s)
- FSC 656 - Mobile Forensics and Social Networking 3 credit(s)
- FSC 668 - Crime Scene Investigation 3 credit(s)
- IST 602 - Digital Forensics 3 credit(s)
- IST 623 - Introduction to Information Security 3 credit(s)
- IST 687 - Introduction to Data Science 3 credit(s)
II Secondary Core
(3 credits) - Students must take one from the courses listed below.
- IST 618 - Information Policy 3 credit(s)
- IST 704 - Applied Information Security 3 credit(s)
- IST 707 - Applied Machine Learning 3 credit(s)
III. Electives
- FSC 631 - Statistics for Forensic Science 3 credit(s)
- FSC 632 - Research and Career Resources 3 credit(s)
- FSC 655 - Computational Forensics 3 credit(s)
- IST 634 - Security in Networked Environments 3 credit(s)
- IST 636 - Leading Issues in Information Security 3 credit(s)
- IST 659 - Data Administration Concepts and Database Management 3 credit(s)
- IST 718 - Big Data Analytics 3 credit(s)
- IST 719 - Information Visualization 3 credit(s)
- LAW 759 - Computer Crimes 3 credit(s)
- LAW 832 - Cyber Security Law and Policy 3 credit(s)
IV. Research
Each student is required to participate in original research, write a detailed report of publishable quality, and successfully defend the results in front of a committee of three faculty members in a public seminar. This research should be conducted as part of an on- or off-campus research project, internship, or independent study. Additional credits of independent study or internship may be used to satisfy elective credit by petition.
- FSC 690 - Independent Study 1-6 credit(s)
- IST 690 - Independent Study 1-6 credit(s)

- Blog and News
The Evolution of Digital Forensics
What is digital forensics? With people relying on computer systems to exchange information more than ever, digital forensics is increasingly vital from a cybersecurity and information security perspective.
Digital forensics is a part of cybersecurity that focuses on retrieving, analyzing, and examining digital evidence, usually in criminal or legal proceedings. If you are considering a career in digital or computer forensics, it is necessary to understand the history of digital forensics, current principles, and the complicated legal issues surrounding it. This will enable you to make a more informed decision about whether this career path is right for you.
Tracing the Origins of Digital Forensics
The history of digital forensics dates back to the 1980s—making it a relatively new field in the grand scheme of things. Despite its comparatively recent beginnings, the field has come quite a long way.
Emergence in the 1980s and 1990s
Early forms of digital data first emerged in the late 1970s, but it wasn't until the 1980s that the digital forensics field gained traction. During this time, more people began to purchase personal computers, and computer-related crimes started to occur. In its earliest stages, digital forensics strategies were used to analyze computer systems and collect evidence for criminal investigations.
By the 1990s, the field established foundational techniques and formal methodologies for collecting evidence and investigating crimes. Later in the decade, Internet use became more widespread, resulting in a need for more robust digital forensic methods to address growing issues like identity theft and hacking.
Standardization Efforts in the 2000s
By the early 2000s, more people were using the web globally, resulting in widespread cybercrime. In response, the digital forensics field began working toward standardizing its processes. During this time, the International Association of Computer Investigative Specialists (IACIS) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) were founded and began guiding best practices.
Through the remainder of the early 2000s, digital forensic investigators worked to refine these strategies while adapting to the changing digital landscape.
The Evolution of Digital Forensic Tools
Forensic tools have evolved over the years, aiding in investigations as the scope and ubiquity of technology has changed. One of the earlier tools still in use today is the hard-drive duplicator, a piece of hardware that can copy all files from one device onto a clean drive for more accessible investigation and research.
Decryption tools have also come a long way, especially when cracking device passwords for analysis and investigation. Today, password recovery devices use algorithms like brute force and even dictionary attacks to access password-protected devices. Some examples of other digital forensics tools commonly used today include:
- File viewers and file analysis tools
- Database and network forensics tools
- Registry analysis tools
Understanding the Digital Forensic Process
The digital forensic process can vary depending on the type of investigation being conducted or the type of crime being analyzed. In general, however, a basic series of steps are followed during a digital forensic investigation to yield the best results.
In the initial stage of the process, the specific digital media is seized, usually by law enforcement agencies. Then, a hard drive duplicator or a similar tool is employed to generate a forensic replica of the data in question. This allows the original device to be returned safely to storage while files and other digital evidence are analyzed.
During the analysis or investigation portion of the process, files are scrutinized for evidence. Specific evidence collected may include emails, chat logs, and browsing history and files. From there, the findings from the investigation are documented in a report. Law enforcement and relevant agencies may continue to be involved in this investigation aspect.
Exploring the Application of Digital Forensics
With so many digital devices and forms of digital data, the potential applications of digital forensics are seemingly endless. Some common examples of applications include:
- Computer crime investigation
- Intellectual property theft
- Data and security breaches
- Uncovering evidence of fraud or unauthorized access
- Civil litigation in court proceedings
- Incident response during or after a cybersecurity incident
- Malware analysis
- Investigation of unauthorized traffic and network traffic in a web attack
Practical Limitations in Real-World Scenarios
Industry professionals still face practical challenges despite significant advancements in digital forensics over the past few decades. Data encryption is a challenge that makes it difficult to decode passwords and analyze data in criminal and civil investigations. Encryption involves converting the text or data into an unreadable code that can be interpreted only with a decryption code. The text or data can only be interpreted with a decryption code. Over the years, hackers and other cybercriminals have become more advanced in encrypting their data, requiring digital forensics investigators to step up their decryption game.
Likewise, as cloud computing and the use of mobile devices become more widespread, the field of digital forensics has struggled to keep up with these evolving technologies.
Legal Aspects Surrounding Digital Forensics
In addition to practical limitations surrounding the field of digital forensics, professionals working in this field must also consider the many legal aspects that come into play. This is especially true regarding the use of digital evidence in courts and the integrity and authenticity of data.
The Use of Digital Evidence in Courts
In the United States, many laws limit members of law enforcement and digital investigators regarding what kind of evidence can be admitted and used in court.
For example, the Electronic Communications Privacy Act (ECPA) makes obtaining search warrants for transmitted communication (such as VOIP data) more difficult than stored communication.
Meanwhile, even when digital evidence can be used in court, requirements over the chain of custody and audit trails make it extremely challenging for computer forensics professionals to submit authentic evidence in every case. Those working in this field must understand the ins and outs of these laws and follow best practices for maintaining data integrity.
The Role of Investigative Tools in Legal Cases
Investigative tools have come a long way in digital forensics and continue to play an important role in criminal and civil cases. Tools and methods such as forensic imaging, forensic analysis, data analysis, and forensic testing make it possible for experts to gather evidence and conduct meaningful data analysis that can crack a case wide open.
Diversified Branches of Digital Forensics
Within the field of digital forensics, various branches focus on different areas of expertise. From computer forensics and mobile device forensics to digital image and database forensics, there's bound to be a niche that suits your interests.
Exploring Computer Forensics
This branch of digital forensics concerns data found on computers and in digital storage media. Computer forensics practices tend to be used most in civil and criminal cases involving computers, using common methods like data recovery and following a clear chain of custody to ensure the strongest case.
Unveiling Mobile Device Forensics
In recent years, the branch of mobile device forensics has grown significantly as more people use mobile devices (such as smartphones and tablets) to generate and share data worldwide. The branch of mobile device forensics focuses on any type of device with communication abilities and some form of internal memory. Examples include cell phones, tablets, GPS (global positioning system), and PDA (personal digital assistant) devices.
Understanding Network Forensics
Another aspect of digital forensics to consider is network forensics, which focuses on monitoring and analyzing network traffic for legal evidence or intrusion detection. Network forensics is generally used when law enforcement agencies need to capture network traffic as part of a criminal investigation or when a network is being monitored for unauthorized traffic and other intrusions. Network forensics investigations work can be challenging, especially since network traffic is constantly changing and thus can be difficult to study.
The World of Forensic Data Analysis
Forensic data analysis (FDA) examines structured data, often related to financial crime. Someone working in forensic data analysis may be looking to uncover a pattern that indicates fraudulent activities on a device or account. Such data can come from specific software devices, apps, or even email communication—and analyzing this type of data requires a great deal of expertise.
Grasping Digital Image Forensics
Digital image forensics (or digital media forensics) is another growing branch of digital forensics that has emerged in recent years. This field focuses on multimedia files, including audio recordings, images, and videos. Often, investigators look for signs of tampering or manipulation, but this can vary from one investigation to the next.
An Insight Into Database Forensics
Another complex niche in the broader field of digital forensics is database forensics, which involves investigating and analyzing individual databases to uncover signs of crime. Crimes committed on a database can include unauthorized access and data tampering. Such investigations are often necessary after a significant data breach or when suspicions of a more extensive and ongoing crime occur.
Learning About IoT Forensics
In recent years, the use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has grown significantly across the globe. These devices (from smart assistants to Wi-Fi-connected doorbells) aim to make our lives easier—unfortunately, they can also lead to security breaches and cybercrime. Specifically, hackers use IoT devices to carry out larger-scale attacks (such as botnet attacks).
In response, a new branch of digital forensics known as IoT forensics has been born out of necessity. This niche is focused on investigating and analyzing smart devices, other IoT technologies, and the data generated by these devices. While this branch of the field is still relatively nascent, it has already successfully provided digital evidence useful for cases related to privacy and data breaches.
The Significance of Digital Forensics in Today's World
There's no overstating how digital forensics solves and even prevents cybercrime in today's always-connected world. The field itself has come a long way since its beginnings in the 1980s—and it will continue to evolve and meet the world's changing needs as new technological innovations emerge.
If you're interested in joining the fight against cybercrime and making a positive difference in the digital world, then a career in digital forensic science may be right for you.
Not sure where to begin? If you already have a bachelor's degree, Champlain College Online offers an online graduate certificate program in digital forensics and incident response . Our program is offered 100 percent online and can be completed in as little as three terms. Request more information or get started with your online application today.
- Digital Forensics
About the Author
Champlain college online, related programs, digital forensics & incident response, you may also like.

Digital Forensics and the Chain of Custody: How Is Electronic Evidence Collected and Safeguarded?
Blog topics.

What Can You Do With A Degree In Cybersecurity?

Champlain College Recognized for Nearly 40 Top Online Programs in the U.S.
Request information.
Connect with our admissions team to learn more about Champlain College Online today.

I acknowledge that, by clicking the "submit" button, I am giving my express written consent to Champlain College and its representatives to contact me about educational opportunities via email, text, or phone, at the phone number above, including my mobile phone, using an automatic dialer, or pre-recorded message. Message and data rates may apply. I understand that my consent is not a requirement for enrollment, and I may withdraw my consent at any time.

Online Digital Forensics Graduate Certificate
Quicklinks: Curriculum • Faculty • Tuition & Financial Aid • Careers
Program at a Glance
- 16 Credits Required
- 8–12 months Completion Time
- $15,400 Tuition & Fees—Part-Time Study*
*Based on 2023–2024 Boston University tuition and fees. Merit scholarship may reduce cost.
Related Programs
- Applied Data Analytics
- Computer Networks
- Data Analytics
- Database Management & Business Intelligence
- Health Informatics
- IT Project Management
- Web Application Development
- Crime Analysis
- Cybercrime Investigation & Cybersecurity
- Strategic Management
- Health Information Management
- Software Development
- Advanced Information Technology
- Applied Business Analytics
- Criminal Justice
- Information Security
- Information Technology
- Medical Information Security & Privacy
- Software Engineering
The online Graduate Certificate in Digital Forensics at Boston University’s Metropolitan College (MET) is designed to develop proficiency in digital crime scene investigation.
The fundamental role of digital systems in business—from computers and networks to all manner of smart devices—brings serious security challenges. According to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), more than $10 billion in losses have been reported since 2015, much of that as a result of hackers, criminals, and other “bad actors” attacking organizations through schemes such as business email compromise (BEC), ransomware, phishing, extortion, and personal data breaches (to name just a few).
To mitigate such risks to valuable information, it is important for IT specialists to obtain a comprehensive overview of digital forensics. The specialized BU MET online certificate program in Digital Forensics provides you with a comprehensive knowledge of digital crime scene investigation and introduces topics such as forensic analysis policy and procedures, forensic analysis tools, data recovery, and investigation, among others.
Students who complete the Online Graduate Certificate in Digital Forensics will be able to demonstrate:
- Advanced knowledge of the computer and mobile forensics tools necessary to launch a complete and successful digital forensics investigation in civil, criminal, or administrative cases.
- Proficiency in conducting network forensics analysis, including determining how a perpetrator or an attacker gained access to a network and transmitted felonious digital data.
- Competence sufficient to conduct a comprehensive “digital crime scene investigation” and mastery of skills pertaining to acquisition of digital evidence, conducting analysis, presenting a report, and being an expert witness in a court.
Why Choose BU’s Online Graduate Certificate in Digital Forensics?
- Four-course certificate program comprises courses shared by the MS in Computer Information Systems, ranked #8 among the nation’s Best Online Master's in Computer Information Technology Programs ( U.S. News & World Report 2024).
- Students benefit from a supportive online network, with courses developed and taught by PhD-level full-time faculty and professionals with hands-on expertise in the industry.
- Small course sections ensure that students get the attention they need, while case studies and real-world projects ensure that they gain in-depth, practical experience with the latest technologies.
Digital Forensics Career Outlook
Information security analysts.
31% increase in jobs through 2029
$99,730 median annual pay in 2019
Police and Detectives
5% increase in jobs through 2029
$65,170 median annual pay in 2019
Forensic Science Technicians
14% increase in jobs through 2029
$59,150 median annual pay in 2019
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, September 2020
Internet Crime: A Growing Concern
A total of 4,883,231 complaints have been reported to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) since its inception in 2000. From 2015 to 2019, the IC3 has received an average of 340,000 complaints per year. In 2019 alone, the Center received a total of 467,361 complaints with reported losses exceeding $3.5 billion— the highest number of complaints and the highest dollar losses reported since the center was established .
2019 Internet Crime Report, FBI Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3)
Best Technology Jobs, 2024 U.S. News & World Report
- #1 Software Developer
- #2 IT Manager
- #3 Information Security Analyst
- #4 Data Scientist
- #5 Web Developer
- #6 Computer Systems Analyst
- #7 Computer Network Architect
- #8 Database Administrator
- #9 Computer Support Specialist
- #10 Computer Systems Administrator
- #11 Computer Programmer
Tuition & Financial Assistance
Money matters.
Boston University Metropolitan College (MET) offers competitive tuition rates that meet the needs of part-time students seeking an affordable education. These rates are substantially lower than those of the traditional, full-time residential programs yet provide access to the same high-quality BU education. To learn more about current tuition rates, visit the MET website .
Financial Assistance
Comprehensive financial assistance services are available at MET, including scholarships , graduate loans, and payment plans. There is no cost to apply for financial assistance, and you may qualify for a student loan regardless of your income. Learn more .
Boston University’s Graduate Certificate in Digital Forensics consists of four required online courses (16 credits).
Academic credits earned toward the online Graduate Certificate in Digital Forensics may be transferred to the Master of Science degree in Computer Information Systems .
(Four courses/16 credits)
METCS625 Business Data Communication and Networks
This course presents the foundations of data communications and takes a bottom-up approach to computer networks. The course concludes with an overview of basic network security and management concepts. Prereq: MET CS 200, or instructor's consent. This course may not be taken in conjunction with MET CS 425 (undergraduate) or MET CS 535. Only one of these courses can be counted towards degree requirements. [4 credits]
METCS693 Digital Forensics and Investigations
Provides a comprehensive understanding of digital forensics and investigation tools and techniques. Learn what computer forensics and investigation is as a profession and gain an understanding of the overall investigative process. Operating system architectures and disk structures are discussed. Studies how to set up an investigator's office and laboratory, as well as what computer forensic hardware and software tools are available. Other topics covered include importance of digital evidence controls and how to process crime and incident scenes, details of data acquisition, computer forensic analysis, e-mail investigations, image file recovery, investigative report writing, and expert witness requirements. Provides a range of laboratory and hands-on assignments either in solo or in teams. With rapid growth of computer systems and digital data this area has grown in importance. Prereq: Working knowledge of windows computers, including installing and removing software. Access to a PC meeting the minimum system requirements defined in the course syllabus. [4 credits]
METCS694 Mobile Forensics and Security
Overview of mobile forensics investigation techniques and tools. Topics include mobile forensics procedures and principles, related legal issues, mobile platform internals, bypassing passcode, rooting or jailbreaking process, logical and physical acquisition, data recovery and analysis, and reporting. Provides in-depth coverage of both iOS and Android platforms. Laboratory and hands-on exercises using current tools are provided and required. [4 credits]
Plus one of the following:
METCS690 Network Security
This course will cover advanced network security issues and solutions. The main focus on the first part of the course will be on Security basics, i.e. security services, access controls, vulnerabilities, threats and risk, network architectures and attacks. In the second part of the course, particular focus and emphasis will be given to network security capabilities and mechanisms (Access Control on wire-line and wireless networks), IPsec, Firewalls, Deep Packet Inspection and Transport security. The final portion of the course will address Network Application security (Email, Ad-hoc, XML/SAML and Services Oriented Architecture security. As part of our course review we will explore a number of Network Use Cases. Prereq: MET CS 535 or MET CS 625; Familiarity with OSI and TCP/IP protocol stack; Background-familiarity with binary numbers, prime numbers, binary- hexadecimal-decimal conversions, etc; Familiarity with computer programming concepts; or instructor's consent. [4 credits]
METCS695 Cybersecurity
This course introduces fundamental concepts, principles of cybersecurity and their use in the development of security mechanisms and policies. Topics include basic risk assessment and management; basic legal and ethics issues, various cyber attacks, defense methods and tools; security principles, models and components; different crypto protocols, techniques and tools, including symmetric and asymmetric encryption algorithms, hashing, public key infrastructure, and how they can be used; security threats and defense to hardware, operating systems, networks and applications in modern computing environments. Hands-on labs using current tools are provided and required. Prerequisite: METCS535 or METCS625 or instructor's consent. [4 credits]
Admission & Prerequisite Information
- Completed Application for Graduate Admission and application fee
- All college transcripts
- Personal statement
- One letter of recommendation
- Official English proficiency exam results ( International students )
Prerequisites
Applicants are not required to have a degree in computer science for entry to a program within the Department of Computer Science. Upon review of your application, the department will determine if the completion of prerequisite coursework will be required, based on your academic and professional background.
A maximum of two graduate-level courses (8 credits) taken at Metropolitan College before acceptance into the program may be applied towards the certificate.

Eric Braude
Associate Professor and Director of Digital Learning, Computer Science PhD, Columbia University; MS, University of Miami; MS, University of Illinois; BS, University of Natal (South Africa)

Lou Chitkushev
Associate Dean, Academic Affairs; Associate Professor, Computer Science; Director, Health Informatics and Health Sciences PhD, Boston University; MS, Medical College of Virginia; MS, BS, University of Belgrade

Lecturer, Computer Science MSEE, BSEE, University of Illinois
View all Faculty

Lecturer, Computer Science MS, Southern Connecticut State University; BS, University of Wisconsin, Madison

Suresh Kalathur
Assistant Professor, Computer Science; Director, Analytics PhD, Brandeis University; MS, Indian Institute of Technology; BS, Regional Engineering College (Warangal, India)

Vijay Kanabar, PMP
Associate Professor, Computer Science and Administrative Sciences; Director, Project Management PhD, University of Manitoba (Canada); MS, Florida Institute of Technology; MBA, Webber College; BS, University of Madras (India)

Jae Young Lee
Assistant Professor, Computer Science; Coordinator, Databases PhD, MS, University of Texas at Arlington; BS, Seoul National University (Korea)

Robert Schudy
Associate Professor Emeritus, Computer Science PhD, MS, University of Rochester; BA, University of California San Diego

Victor Shtern
Associate Professor Emeritus, Computer Science PhD, Leningrad Aluminum Institute (Russia); MS, Leningrad Institute of Technology; MBA, Boston University

Anatoly Temkin
Assistant Professor and Chair, Computer Science PhD, Kazan University (Russia); MS, Moscow University

Guanglan Zhang
Associate Professor, Computer Science; Coordinator, Health Informatics PhD, MEng, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore; BS, Luoyang Institute of Technology

Yuting Zhang
Assistant Professor, Computer Science; Coordinator, Information Security PhD, Boston University; MS, BS University of Science and Technology Beijing

Tanya Zlateva
Dean, Metropolitan College; Professor of the Practice, Computer Science and Education; Director, Information Security PhD, Dresden University of Technology (Germany); MS, Dresden University of Technology; BS, Dresden University of Technology
Getting Started
To learn more or to contact an enrollment advisor before you get started, request information using the button below and tell us a little about yourself. Someone will be in touch to answer any questions you may have about the program and detail the next steps in earning your degree. You can also start your application or register for a course at Metropolitan College.
- Request Information Have a Metropolitan College enrollment advisor get in touch with you.
PhD Research Topics in Digital Forensics
PhD Research Topics in Digital Forensics bring out the best days when you work with us. Surely, you will have a good mindset with our work for you. Unless you are satisfied, we will not back off from our work.
Digital Forensics will give the means to find the digital proofs in electrical devices. Singularly, it will pave the way to analyze the gathered proofs. Also, it is used to predict illegal actions through the found data……….
Our experts will direct you to all the nooks and corners of your area. Indeed, we will help you to uplift the value of your research digital forensics thesis work. Though we have done many projects in this field, we still do even more. We have given them in the following section for you.
CURRENT KEY CONCEPTS IN DIGITAL FORENSICS
- Audio visual biometric and also Multimedia
- Fake colorized image study
- Median Filtering analysis
- Multigranularity study
- Behavioral anomaly detection
- Biometric analysis of crime scene
- And also in Live event prediction
PhD Research Topics in Digital Forensics help you to be bold and best in your work. We promise to provide in-depth research thought from top vibrating areas. To point out, this field gets well with other chief research areas.
HYBRID DOMAIN WITH DIGITAL FORENSICS
- Internet of Things
- Cloud and Fog Computing
- Wireless Network
- Mobile-Cloud
- Blockchain Technology
- Cyber Security
PhD Research Topics in Digital Forensics will always fight for the head of the table for your work. Digital Forensics can influence a wide range of technologies that could adapt and progress every minute. To this end, you have got a glimpse into the area of digital forensics.
To know further, take a look at the following topics we have given for you,
An inventive mechanism for Identification of Attack-based on Digital Forensic Evidences intended for WAMPAC Systems
On the use of Grayscale Image Conversion and Deep Learning in Digital Forensics based on File Fragment Classification scheme
A novel method for Neural Network based on Digital Forensics Classification system
The novel mechanism for Analyzing Data from an Android Smartphone while Comparing between Two Forensic Tools
A novel Techniques for Comprehensive Display of Digital Image Copy-Move Forensics method
An efficient method for Adaptive Sliding Window Algorithm designed for Mining Frequent Itemsets in Computer Forensics system
A novel Research based on Electronic Data Forensics Model under Cloud Computing practice
An effectual method for Band Energy Difference intended for Source Attribution in Audio Forensics scheme
Design an effectual process of Digital Forensic Analysis of Instant Messaging Applications on Android Smartphones system
A creative mechanism for Forensics and Deep Learning meant for Botnets in IoTs
An innovative methodology for Tuning function of Monitoring System designed for Network Forensics in Cloud Environment
The firsthand method for Blockchain-based IoT Forensics Framework with Identity Privacy
The new design for Android Applications of Private Data Acquisition Method Based on System-Level Data Migration and Volatile Memory Forensics
An inventive method for Live Forensic Acquisition & Analysis of Mac OS Systems
The novel approach for Face Verification and Recognition for Digital Forensics and Information Security
A new framework function for Probe-IoT based on public digital ledger in forensic investigation for IoT
On the use of Deep Residual Learning based Data Augmentation intended for Median Filtering Forensics of Digital Images system
An inventive mechanism for Framework based on IoT Data Acquisition and Forensics Analysis system
On the use of Multiple Models in Residual Domain based on Median Filtering Forensics system
An innovative function for Coarse-to-Fine Copy-Move Forgery Detection for Video Forensics scheme

Why Work With Us ?
Senior research member, research experience, journal member, book publisher, research ethics, business ethics, valid references, explanations, paper publication, 9 big reasons to select us.
Our Editor-in-Chief has Website Ownership who control and deliver all aspects of PhD Direction to scholars and students and also keep the look to fully manage all our clients.
Our world-class certified experts have 18+years of experience in Research & Development programs (Industrial Research) who absolutely immersed as many scholars as possible in developing strong PhD research projects.
We associated with 200+reputed SCI and SCOPUS indexed journals (SJR ranking) for getting research work to be published in standard journals (Your first-choice journal).
PhDdirection.com is world’s largest book publishing platform that predominantly work subject-wise categories for scholars/students to assist their books writing and takes out into the University Library.
Our researchers provide required research ethics such as Confidentiality & Privacy, Novelty (valuable research), Plagiarism-Free, and Timely Delivery. Our customers have freedom to examine their current specific research activities.
Our organization take into consideration of customer satisfaction, online, offline support and professional works deliver since these are the actual inspiring business factors.
Solid works delivering by young qualified global research team. "References" is the key to evaluating works easier because we carefully assess scholars findings.
Detailed Videos, Readme files, Screenshots are provided for all research projects. We provide Teamviewer support and other online channels for project explanation.
Worthy journal publication is our main thing like IEEE, ACM, Springer, IET, Elsevier, etc. We substantially reduces scholars burden in publication side. We carry scholars from initial submission to final acceptance.
Related Pages
Phd Research Topics In Ns2
Phd Research Topics In Cse
Phd Research Topics In Cryptography
Phd Research Topics In Nlp
Phd Research Topics In Cybersecurity
Phd Research Topics In Neural Networks
Phd Research Topics In Computer Graphics
Phd Research Topics In Information Technology
Phd Research Topics In Face Recognition
Phd Research Topics In Information Security
Phd Research Topics In Augmented Reality
Phd Research Topics In Audio Speech Language Processing
Phd Research Topics In Information Forensics Security
Phd Research Topics In Artificial Neural Network
Phd Research Topics In Audio Speech And Language Processing
Our Benefits
Throughout reference, confidential agreement, research no way resale, plagiarism-free, publication guarantee, customize support, fair revisions, business professionalism, domains & tools, we generally use, wireless communication (4g lte, and 5g), ad hoc networks (vanet, manet, etc.), wireless sensor networks, software defined networks, network security, internet of things (mqtt, coap), internet of vehicles, cloud computing, fog computing, edge computing, mobile computing, mobile cloud computing, ubiquitous computing, digital image processing, medical image processing, pattern analysis and machine intelligence, geoscience and remote sensing, big data analytics, data mining, power electronics, web of things, digital forensics, natural language processing, automation systems, artificial intelligence, mininet 2.1.0, matlab (r2018b/r2019a), matlab and simulink, apache hadoop, apache spark mlib, apache mahout, apache flink, apache storm, apache cassandra, pig and hive, rapid miner, support 24/7, call us @ any time, +91 9444829042, [email protected].
Questions ?
Click here to chat with us

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn how to perform research, analysis, and leadership in digital and cyber forensics and security. This program offers coursework, internship, and dissertation in the field of computational and scientific basis for forensic and cyber technologies.
Learn about the Ph.D. in Technology degree with a specialization in cyber forensics from Purdue Polytechnic Institute. The degree requires 15 credit hours in core cyber forensics courses, 30 credit hours in discovery foundations, 18 credit hours in cognate courses, and 15-30 credit hours in dissertation research. The curriculum covers the fundamentals, methods, and applications of digital forensics.
Learn how to apply forensically sound digital data capture and analysis and develop new tools and methods for handling digital and cyber forensic evidence with the PhD in digital and cyber forensic science from Sam Houston State University. The program offers research areas such as multimedia, 3D printing, computational, and hardware forensics, as well as the DoD Cyber Scholarship Program for eligible students.
Students seeking their Ph.D. in digital and cyber forensic science must complete 85 credit hours beyond the bachelor's degree. Previously completed master's level coursework is evaluated on an individual basis. For advancement to candidacy, you must be enrolled full-time, maintain a 3.0 grade point average, complete 46 graduate credit hours ...
Find out the available doctoral programs in digital forensics in higher education, such as California Sciences Institute, University of Rhode Island, and Purdue (CERIAS). Learn about the specialization, research, and requirements of each program.
Learn how to apply and sustain your expertise in digital forensic science and cybersecurity at John Jay College of Criminal Justice. The program offers a balance of practice and theory through study in computer science, law and criminal justice.
Learn about the few doctoral programs in forensic science and the subfields of psychology, chemistry, and anthropology. Find out the admission criteria, curriculum, and accreditation status of these programs.
Behavioural Analysis for Ransomware and Extortion-based Attack Detection. Edinburgh Napier University's Cyber Security and Forensics Research Group focuses on applied research in areas of threat analysis and detection, digital forensic triage, trust, identity and cryptography, and has had successful real world impact with several spin-out ...
Learn about the admission requirements, coursework, dissertation, and graduation procedures for the Doctor of Philosophy degree in Digital and Cyber Forensic Science at Sam Houston State University. The program is offered by the Department of Computer Science in the College of Science and Engineering Technology.
Starting Summer 2023. Earn a Ph.D. in Forensic Cyberpsychology and learn all about the psychology of cybercriminal behavior. Forensic cyberpsychology is a cutting-edge emerging discipline which presents students with an exciting opportunity to engage with this new scientific frontier and help to develop new scientific theories and protocols, or adapt existing psychological and criminological ...
Here are on-campus doctoral programs in forensic chemistry, forensic mental health counseling, forensic science, and forensic psychology. West Virginia University. West Virginia University's PhD in forensic science program is unique in that it is only the second such program in the United States. Students in this PhD will be prepared to work ...
$17,580 is the most affordable PhD program option and it is available at the Georgia Institute of Technology. ... Program: Ph.D. in Digital and Cyber Forensic Science CAE designation: CAE-CD Number of credits: 85 Cost per credit: $321 in state | $728 out of state Delivery method: Not Required
1. Education: There are a variety of college degree programs that lend themselves to careers in digital forensics. These include computer engineering, computer science, electrical engineering, applied mathematics, cybersecurity, information technology, and digital forensics. More advanced positions in digital forensics sometimes require master ...
PhD Thesis . Digital Forensics Practices: A Road Map for Building Digital Forensics Capability . Ahmed Jasim Almarzooqi . A Doctoral Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfilment of the Award of Doctor of Philosophy . Faculty of Technology . De Montfort University . Leicester, United Kingdome . 1st November, 2016
Learn how to analyze and mitigate cyber crime with this online degree from University of Maryland Global Campus. Develop skills in digital forensics, cyber investigation, and legal presentation with state-of-the-art tools and technologies.
The Ph.D. in Digital and Cyber Forensic Science requires the completion of 85 credit hours beyond the bachelor's degree. Students complete: Code Title Hours Requirements Core Coursework 52 Dissertation Research 15 Electives 12 Internship 6 Total Hours 85 The curriculum is designed to deliver an essential core curriculum in digital and cyber ...
NTNU Digital Forensics. The research group focuses on research and development of advanced computational methods to establish and prove the scientific basis of forensic investigative procedures, with the objective to support forensic examiners in their daily casework. ... Teaching on Bachelor, Master, and PhD Level. Postgraduate Education and ...
Digital Forensics. Offered by the College of Engineering and Computing Office of Graduate Studies in conjunction with the Digital Forensics Master's Program. Students in the Digital Forensics concentration must enter the program with a prior conferred concentration-specific Master's Degree or elect a Secondary Master's Degree.
Overview: The M.S. in Digital Forensics is a 36-credit program that combines the iSchool's expertise in information security, digital forensics, and data analytics with the forensic science expertise of the Forensic and National Security Sciences Institute in the College of Arts and Sciences. Digital forensics is the acquisition and analysis ...
Digital forensics is a part of cybersecurity that focuses on retrieving, analyzing, and examining digital evidence, usually in criminal or legal proceedings. If you are considering a career in digital or computer forensics, it is necessary to understand the history of digital forensics, current principles, and the complicated legal issues ...
PhD Thesis Alleviating the Digital Forensic Backlog: A Methodology for Automated Digital Evidence Processing Xiaoyu Du A thesis submitted in ful lment of the degree of PhD in Computer Science Supervisor: Dr. Mark Scanlon Head of School: Assoc. Prof. Chris Bleakley UCD School of Computer Science
Graduate Certificate. 16 Credits Required. 8-12 months Completion Time. $15,400 Tuition & Fees—Part-Time Study*. The online Graduate Certificate in Digital Forensics at Boston University's Metropolitan College (MET) is designed to develop proficiency in digital crime scene investigation. The fundamental role of digital systems in business ...
Learn about the current key concepts, domains and tools of digital forensics, a field that investigates the digital proofs of crime scenes and illegal actions. Explore various topics for PhD research projects in digital forensics, such as audio visual biometric, multimedia, median filtering, behavior analysis, and more. Find out how to work with us and get benefits from our services.