

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, what is a hypothesis and how do i write one.
General Education

Think about something strange and unexplainable in your life. Maybe you get a headache right before it rains, or maybe you think your favorite sports team wins when you wear a certain color. If you wanted to see whether these are just coincidences or scientific fact, you would form a hypothesis, then create an experiment to see whether that hypothesis is true or not.
But what is a hypothesis, anyway? If you’re not sure about what a hypothesis is--or how to test for one!--you’re in the right place. This article will teach you everything you need to know about hypotheses, including:
- Defining the term “hypothesis”
- Providing hypothesis examples
- Giving you tips for how to write your own hypothesis
So let’s get started!

What Is a Hypothesis?
Merriam Webster defines a hypothesis as “an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument.” In other words, a hypothesis is an educated guess . Scientists make a reasonable assumption--or a hypothesis--then design an experiment to test whether it’s true or not. Keep in mind that in science, a hypothesis should be testable. You have to be able to design an experiment that tests your hypothesis in order for it to be valid.
As you could assume from that statement, it’s easy to make a bad hypothesis. But when you’re holding an experiment, it’s even more important that your guesses be good...after all, you’re spending time (and maybe money!) to figure out more about your observation. That’s why we refer to a hypothesis as an educated guess--good hypotheses are based on existing data and research to make them as sound as possible.
Hypotheses are one part of what’s called the scientific method . Every (good) experiment or study is based in the scientific method. The scientific method gives order and structure to experiments and ensures that interference from scientists or outside influences does not skew the results. It’s important that you understand the concepts of the scientific method before holding your own experiment. Though it may vary among scientists, the scientific method is generally made up of six steps (in order):
- Observation
- Asking questions
- Forming a hypothesis
- Analyze the data
- Communicate your results
You’ll notice that the hypothesis comes pretty early on when conducting an experiment. That’s because experiments work best when they’re trying to answer one specific question. And you can’t conduct an experiment until you know what you’re trying to prove!
Independent and Dependent Variables
After doing your research, you’re ready for another important step in forming your hypothesis: identifying variables. Variables are basically any factor that could influence the outcome of your experiment . Variables have to be measurable and related to the topic being studied.
There are two types of variables: independent variables and dependent variables. I ndependent variables remain constant . For example, age is an independent variable; it will stay the same, and researchers can look at different ages to see if it has an effect on the dependent variable.
Speaking of dependent variables... dependent variables are subject to the influence of the independent variable , meaning that they are not constant. Let’s say you want to test whether a person’s age affects how much sleep they need. In that case, the independent variable is age (like we mentioned above), and the dependent variable is how much sleep a person gets.
Variables will be crucial in writing your hypothesis. You need to be able to identify which variable is which, as both the independent and dependent variables will be written into your hypothesis. For instance, in a study about exercise, the independent variable might be the speed at which the respondents walk for thirty minutes, and the dependent variable would be their heart rate. In your study and in your hypothesis, you’re trying to understand the relationship between the two variables.
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
The best hypotheses start by asking the right questions . For instance, if you’ve observed that the grass is greener when it rains twice a week, you could ask what kind of grass it is, what elevation it’s at, and if the grass across the street responds to rain in the same way. Any of these questions could become the backbone of experiments to test why the grass gets greener when it rains fairly frequently.
As you’re asking more questions about your first observation, make sure you’re also making more observations . If it doesn’t rain for two weeks and the grass still looks green, that’s an important observation that could influence your hypothesis. You'll continue observing all throughout your experiment, but until the hypothesis is finalized, every observation should be noted.
Finally, you should consult secondary research before writing your hypothesis . Secondary research is comprised of results found and published by other people. You can usually find this information online or at your library. Additionally, m ake sure the research you find is credible and related to your topic. If you’re studying the correlation between rain and grass growth, it would help you to research rain patterns over the past twenty years for your county, published by a local agricultural association. You should also research the types of grass common in your area, the type of grass in your lawn, and whether anyone else has conducted experiments about your hypothesis. Also be sure you’re checking the quality of your research . Research done by a middle school student about what minerals can be found in rainwater would be less useful than an article published by a local university.

Writing Your Hypothesis
Once you’ve considered all of the factors above, you’re ready to start writing your hypothesis. Hypotheses usually take a certain form when they’re written out in a research report.
When you boil down your hypothesis statement, you are writing down your best guess and not the question at hand . This means that your statement should be written as if it is fact already, even though you are simply testing it.
The reason for this is that, after you have completed your study, you'll either accept or reject your if-then or your null hypothesis. All hypothesis testing examples should be measurable and able to be confirmed or denied. You cannot confirm a question, only a statement!
In fact, you come up with hypothesis examples all the time! For instance, when you guess on the outcome of a basketball game, you don’t say, “Will the Miami Heat beat the Boston Celtics?” but instead, “I think the Miami Heat will beat the Boston Celtics.” You state it as if it is already true, even if it turns out you’re wrong. You do the same thing when writing your hypothesis.
Additionally, keep in mind that hypotheses can range from very specific to very broad. These hypotheses can be specific, but if your hypothesis testing examples involve a broad range of causes and effects, your hypothesis can also be broad.

The Two Types of Hypotheses
Now that you understand what goes into a hypothesis, it’s time to look more closely at the two most common types of hypothesis: the if-then hypothesis and the null hypothesis.
#1: If-Then Hypotheses
First of all, if-then hypotheses typically follow this formula:
If ____ happens, then ____ will happen.
The goal of this type of hypothesis is to test the causal relationship between the independent and dependent variable. It’s fairly simple, and each hypothesis can vary in how detailed it can be. We create if-then hypotheses all the time with our daily predictions. Here are some examples of hypotheses that use an if-then structure from daily life:
- If I get enough sleep, I’ll be able to get more work done tomorrow.
- If the bus is on time, I can make it to my friend’s birthday party.
- If I study every night this week, I’ll get a better grade on my exam.
In each of these situations, you’re making a guess on how an independent variable (sleep, time, or studying) will affect a dependent variable (the amount of work you can do, making it to a party on time, or getting better grades).
You may still be asking, “What is an example of a hypothesis used in scientific research?” Take one of the hypothesis examples from a real-world study on whether using technology before bed affects children’s sleep patterns. The hypothesis read s:
“We hypothesized that increased hours of tablet- and phone-based screen time at bedtime would be inversely correlated with sleep quality and child attention.”
It might not look like it, but this is an if-then statement. The researchers basically said, “If children have more screen usage at bedtime, then their quality of sleep and attention will be worse.” The sleep quality and attention are the dependent variables and the screen usage is the independent variable. (Usually, the independent variable comes after the “if” and the dependent variable comes after the “then,” as it is the independent variable that affects the dependent variable.) This is an excellent example of how flexible hypothesis statements can be, as long as the general idea of “if-then” and the independent and dependent variables are present.
#2: Null Hypotheses
Your if-then hypothesis is not the only one needed to complete a successful experiment, however. You also need a null hypothesis to test it against. In its most basic form, the null hypothesis is the opposite of your if-then hypothesis . When you write your null hypothesis, you are writing a hypothesis that suggests that your guess is not true, and that the independent and dependent variables have no relationship .
One null hypothesis for the cell phone and sleep study from the last section might say:
“If children have more screen usage at bedtime, their quality of sleep and attention will not be worse.”
In this case, this is a null hypothesis because it’s asking the opposite of the original thesis!
Conversely, if your if-then hypothesis suggests that your two variables have no relationship, then your null hypothesis would suggest that there is one. So, pretend that there is a study that is asking the question, “Does the amount of followers on Instagram influence how long people spend on the app?” The independent variable is the amount of followers, and the dependent variable is the time spent. But if you, as the researcher, don’t think there is a relationship between the number of followers and time spent, you might write an if-then hypothesis that reads:
“If people have many followers on Instagram, they will not spend more time on the app than people who have less.”
In this case, the if-then suggests there isn’t a relationship between the variables. In that case, one of the null hypothesis examples might say:
“If people have many followers on Instagram, they will spend more time on the app than people who have less.”
You then test both the if-then and the null hypothesis to gauge if there is a relationship between the variables, and if so, how much of a relationship.

4 Tips to Write the Best Hypothesis
If you’re going to take the time to hold an experiment, whether in school or by yourself, you’re also going to want to take the time to make sure your hypothesis is a good one. The best hypotheses have four major elements in common: plausibility, defined concepts, observability, and general explanation.
#1: Plausibility
At first glance, this quality of a hypothesis might seem obvious. When your hypothesis is plausible, that means it’s possible given what we know about science and general common sense. However, improbable hypotheses are more common than you might think.
Imagine you’re studying weight gain and television watching habits. If you hypothesize that people who watch more than twenty hours of television a week will gain two hundred pounds or more over the course of a year, this might be improbable (though it’s potentially possible). Consequently, c ommon sense can tell us the results of the study before the study even begins.
Improbable hypotheses generally go against science, as well. Take this hypothesis example:
“If a person smokes one cigarette a day, then they will have lungs just as healthy as the average person’s.”
This hypothesis is obviously untrue, as studies have shown again and again that cigarettes negatively affect lung health. You must be careful that your hypotheses do not reflect your own personal opinion more than they do scientifically-supported findings. This plausibility points to the necessity of research before the hypothesis is written to make sure that your hypothesis has not already been disproven.
#2: Defined Concepts
The more advanced you are in your studies, the more likely that the terms you’re using in your hypothesis are specific to a limited set of knowledge. One of the hypothesis testing examples might include the readability of printed text in newspapers, where you might use words like “kerning” and “x-height.” Unless your readers have a background in graphic design, it’s likely that they won’t know what you mean by these terms. Thus, it’s important to either write what they mean in the hypothesis itself or in the report before the hypothesis.
Here’s what we mean. Which of the following sentences makes more sense to the common person?
If the kerning is greater than average, more words will be read per minute.
If the space between letters is greater than average, more words will be read per minute.
For people reading your report that are not experts in typography, simply adding a few more words will be helpful in clarifying exactly what the experiment is all about. It’s always a good idea to make your research and findings as accessible as possible.

Good hypotheses ensure that you can observe the results.
#3: Observability
In order to measure the truth or falsity of your hypothesis, you must be able to see your variables and the way they interact. For instance, if your hypothesis is that the flight patterns of satellites affect the strength of certain television signals, yet you don’t have a telescope to view the satellites or a television to monitor the signal strength, you cannot properly observe your hypothesis and thus cannot continue your study.
Some variables may seem easy to observe, but if you do not have a system of measurement in place, you cannot observe your hypothesis properly. Here’s an example: if you’re experimenting on the effect of healthy food on overall happiness, but you don’t have a way to monitor and measure what “overall happiness” means, your results will not reflect the truth. Monitoring how often someone smiles for a whole day is not reasonably observable, but having the participants state how happy they feel on a scale of one to ten is more observable.
In writing your hypothesis, always keep in mind how you'll execute the experiment.
#4: Generalizability
Perhaps you’d like to study what color your best friend wears the most often by observing and documenting the colors she wears each day of the week. This might be fun information for her and you to know, but beyond you two, there aren’t many people who could benefit from this experiment. When you start an experiment, you should note how generalizable your findings may be if they are confirmed. Generalizability is basically how common a particular phenomenon is to other people’s everyday life.
Let’s say you’re asking a question about the health benefits of eating an apple for one day only, you need to realize that the experiment may be too specific to be helpful. It does not help to explain a phenomenon that many people experience. If you find yourself with too specific of a hypothesis, go back to asking the big question: what is it that you want to know, and what do you think will happen between your two variables?

Hypothesis Testing Examples
We know it can be hard to write a good hypothesis unless you’ve seen some good hypothesis examples. We’ve included four hypothesis examples based on some made-up experiments. Use these as templates or launch pads for coming up with your own hypotheses.
Experiment #1: Students Studying Outside (Writing a Hypothesis)
You are a student at PrepScholar University. When you walk around campus, you notice that, when the temperature is above 60 degrees, more students study in the quad. You want to know when your fellow students are more likely to study outside. With this information, how do you make the best hypothesis possible?
You must remember to make additional observations and do secondary research before writing your hypothesis. In doing so, you notice that no one studies outside when it’s 75 degrees and raining, so this should be included in your experiment. Also, studies done on the topic beforehand suggested that students are more likely to study in temperatures less than 85 degrees. With this in mind, you feel confident that you can identify your variables and write your hypotheses:
If-then: “If the temperature in Fahrenheit is less than 60 degrees, significantly fewer students will study outside.”
Null: “If the temperature in Fahrenheit is less than 60 degrees, the same number of students will study outside as when it is more than 60 degrees.”
These hypotheses are plausible, as the temperatures are reasonably within the bounds of what is possible. The number of people in the quad is also easily observable. It is also not a phenomenon specific to only one person or at one time, but instead can explain a phenomenon for a broader group of people.
To complete this experiment, you pick the month of October to observe the quad. Every day (except on the days where it’s raining)from 3 to 4 PM, when most classes have released for the day, you observe how many people are on the quad. You measure how many people come and how many leave. You also write down the temperature on the hour.
After writing down all of your observations and putting them on a graph, you find that the most students study on the quad when it is 70 degrees outside, and that the number of students drops a lot once the temperature reaches 60 degrees or below. In this case, your research report would state that you accept or “failed to reject” your first hypothesis with your findings.
Experiment #2: The Cupcake Store (Forming a Simple Experiment)
Let’s say that you work at a bakery. You specialize in cupcakes, and you make only two colors of frosting: yellow and purple. You want to know what kind of customers are more likely to buy what kind of cupcake, so you set up an experiment. Your independent variable is the customer’s gender, and the dependent variable is the color of the frosting. What is an example of a hypothesis that might answer the question of this study?
Here’s what your hypotheses might look like:
If-then: “If customers’ gender is female, then they will buy more yellow cupcakes than purple cupcakes.”
Null: “If customers’ gender is female, then they will be just as likely to buy purple cupcakes as yellow cupcakes.”
This is a pretty simple experiment! It passes the test of plausibility (there could easily be a difference), defined concepts (there’s nothing complicated about cupcakes!), observability (both color and gender can be easily observed), and general explanation ( this would potentially help you make better business decisions ).

Experiment #3: Backyard Bird Feeders (Integrating Multiple Variables and Rejecting the If-Then Hypothesis)
While watching your backyard bird feeder, you realized that different birds come on the days when you change the types of seeds. You decide that you want to see more cardinals in your backyard, so you decide to see what type of food they like the best and set up an experiment.
However, one morning, you notice that, while some cardinals are present, blue jays are eating out of your backyard feeder filled with millet. You decide that, of all of the other birds, you would like to see the blue jays the least. This means you'll have more than one variable in your hypothesis. Your new hypotheses might look like this:
If-then: “If sunflower seeds are placed in the bird feeders, then more cardinals will come than blue jays. If millet is placed in the bird feeders, then more blue jays will come than cardinals.”
Null: “If either sunflower seeds or millet are placed in the bird, equal numbers of cardinals and blue jays will come.”
Through simple observation, you actually find that cardinals come as often as blue jays when sunflower seeds or millet is in the bird feeder. In this case, you would reject your “if-then” hypothesis and “fail to reject” your null hypothesis . You cannot accept your first hypothesis, because it’s clearly not true. Instead you found that there was actually no relation between your different variables. Consequently, you would need to run more experiments with different variables to see if the new variables impact the results.
Experiment #4: In-Class Survey (Including an Alternative Hypothesis)
You’re about to give a speech in one of your classes about the importance of paying attention. You want to take this opportunity to test a hypothesis you’ve had for a while:
If-then: If students sit in the first two rows of the classroom, then they will listen better than students who do not.
Null: If students sit in the first two rows of the classroom, then they will not listen better or worse than students who do not.
You give your speech and then ask your teacher if you can hand out a short survey to the class. On the survey, you’ve included questions about some of the topics you talked about. When you get back the results, you’re surprised to see that not only do the students in the first two rows not pay better attention, but they also scored worse than students in other parts of the classroom! Here, both your if-then and your null hypotheses are not representative of your findings. What do you do?
This is when you reject both your if-then and null hypotheses and instead create an alternative hypothesis . This type of hypothesis is used in the rare circumstance that neither of your hypotheses is able to capture your findings . Now you can use what you’ve learned to draft new hypotheses and test again!
Key Takeaways: Hypothesis Writing
The more comfortable you become with writing hypotheses, the better they will become. The structure of hypotheses is flexible and may need to be changed depending on what topic you are studying. The most important thing to remember is the purpose of your hypothesis and the difference between the if-then and the null . From there, in forming your hypothesis, you should constantly be asking questions, making observations, doing secondary research, and considering your variables. After you have written your hypothesis, be sure to edit it so that it is plausible, clearly defined, observable, and helpful in explaining a general phenomenon.
Writing a hypothesis is something that everyone, from elementary school children competing in a science fair to professional scientists in a lab, needs to know how to do. Hypotheses are vital in experiments and in properly executing the scientific method . When done correctly, hypotheses will set up your studies for success and help you to understand the world a little better, one experiment at a time.

What’s Next?
If you’re studying for the science portion of the ACT, there’s definitely a lot you need to know. We’ve got the tools to help, though! Start by checking out our ultimate study guide for the ACT Science subject test. Once you read through that, be sure to download our recommended ACT Science practice tests , since they’re one of the most foolproof ways to improve your score. (And don’t forget to check out our expert guide book , too.)
If you love science and want to major in a scientific field, you should start preparing in high school . Here are the science classes you should take to set yourself up for success.
If you’re trying to think of science experiments you can do for class (or for a science fair!), here’s a list of 37 awesome science experiments you can do at home

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

Scientific Method: Step 3: HYPOTHESIS
- Step 1: QUESTION
- Step 2: RESEARCH
- Step 3: HYPOTHESIS
- Step 4: EXPERIMENT
- Step 5: DATA
- Step 6: CONCLUSION
Step 3: State your hypothesis
Now it's time to state your hypothesis . The hypothesis is an educated guess as to what will happen during your experiment.
The hypothesis is often written using the words "IF" and "THEN." For example, " If I do not study, then I will fail the test." The "if' and "then" statements reflect your independent and dependent variables .
The hypothesis should relate back to your original question and must be testable .
A word about variables...
Your experiment will include variables to measure and to explain any cause and effect. Below you will find some useful links describing the different types of variables.
- "What are independent and dependent variables" NCES
- [VIDEO] Biology: Independent vs. Dependent Variables (Nucleus Medical Media) Video explaining independent and dependent variables, with examples.
Resource Links
- What is and How to Write a Good Hypothesis in Research? (Elsevier)
- Hypothesis brochure from Penn State/Berks
- << Previous: Step 2: RESEARCH
- Next: Step 4: EXPERIMENT >>
- Last Updated: Jan 26, 2024 10:39 AM
- URL: https://harford.libguides.com/scientific_method

- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
Hypothesis Examples

A hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a test. It forms the basis for designing an experiment in the scientific method . A good hypothesis is testable, meaning it makes a prediction you can check with observation or experimentation. Here are different hypothesis examples.
Null Hypothesis Examples
The null hypothesis (H 0 ) is also known as the zero-difference or no-difference hypothesis. It predicts that changing one variable ( independent variable ) will have no effect on the variable being measured ( dependent variable ). Here are null hypothesis examples:
- Plant growth is unaffected by temperature.
- If you increase temperature, then solubility of salt will increase.
- Incidence of skin cancer is unrelated to ultraviolet light exposure.
- All brands of light bulb last equally long.
- Cats have no preference for the color of cat food.
- All daisies have the same number of petals.
Sometimes the null hypothesis shows there is a suspected correlation between two variables. For example, if you think plant growth is affected by temperature, you state the null hypothesis: “Plant growth is not affected by temperature.” Why do you do this, rather than say “If you change temperature, plant growth will be affected”? The answer is because it’s easier applying a statistical test that shows, with a high level of confidence, a null hypothesis is correct or incorrect.
Research Hypothesis Examples
A research hypothesis (H 1 ) is a type of hypothesis used to design an experiment. This type of hypothesis is often written as an if-then statement because it’s easy identifying the independent and dependent variables and seeing how one affects the other. If-then statements explore cause and effect. In other cases, the hypothesis shows a correlation between two variables. Here are some research hypothesis examples:
- If you leave the lights on, then it takes longer for people to fall asleep.
- If you refrigerate apples, they last longer before going bad.
- If you keep the curtains closed, then you need less electricity to heat or cool the house (the electric bill is lower).
- If you leave a bucket of water uncovered, then it evaporates more quickly.
- Goldfish lose their color if they are not exposed to light.
- Workers who take vacations are more productive than those who never take time off.
Is It Okay to Disprove a Hypothesis?
Yes! You may even choose to write your hypothesis in such a way that it can be disproved because it’s easier to prove a statement is wrong than to prove it is right. In other cases, if your prediction is incorrect, that doesn’t mean the science is bad. Revising a hypothesis is common. It demonstrates you learned something you did not know before you conducted the experiment.
Test yourself with a Scientific Method Quiz .
- Mellenbergh, G.J. (2008). Chapter 8: Research designs: Testing of research hypotheses. In H.J. Adèr & G.J. Mellenbergh (eds.), Advising on Research Methods: A Consultant’s Companion . Huizen, The Netherlands: Johannes van Kessel Publishing.
- Popper, Karl R. (1959). The Logic of Scientific Discovery . Hutchinson & Co. ISBN 3-1614-8410-X.
- Schick, Theodore; Vaughn, Lewis (2002). How to think about weird things: critical thinking for a New Age . Boston: McGraw-Hill Higher Education. ISBN 0-7674-2048-9.
- Tobi, Hilde; Kampen, Jarl K. (2018). “Research design: the methodology for interdisciplinary research framework”. Quality & Quantity . 52 (3): 1209–1225. doi: 10.1007/s11135-017-0513-8
Related Posts
What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
If...,Then...
Angela Lumsden/Getty Images
- Scientific Method
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for an observation. The definition depends on the subject.
In science, a hypothesis is part of the scientific method. It is a prediction or explanation that is tested by an experiment. Observations and experiments may disprove a scientific hypothesis, but can never entirely prove one.
In the study of logic, a hypothesis is an if-then proposition, typically written in the form, "If X , then Y ."
In common usage, a hypothesis is simply a proposed explanation or prediction, which may or may not be tested.
Writing a Hypothesis
Most scientific hypotheses are proposed in the if-then format because it's easy to design an experiment to see whether or not a cause and effect relationship exists between the independent variable and the dependent variable . The hypothesis is written as a prediction of the outcome of the experiment.
- Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis
Statistically, it's easier to show there is no relationship between two variables than to support their connection. So, scientists often propose the null hypothesis . The null hypothesis assumes changing the independent variable will have no effect on the dependent variable.
In contrast, the alternative hypothesis suggests changing the independent variable will have an effect on the dependent variable. Designing an experiment to test this hypothesis can be trickier because there are many ways to state an alternative hypothesis.
For example, consider a possible relationship between getting a good night's sleep and getting good grades. The null hypothesis might be stated: "The number of hours of sleep students get is unrelated to their grades" or "There is no correlation between hours of sleep and grades."
An experiment to test this hypothesis might involve collecting data, recording average hours of sleep for each student and grades. If a student who gets eight hours of sleep generally does better than students who get four hours of sleep or 10 hours of sleep, the hypothesis might be rejected.
But the alternative hypothesis is harder to propose and test. The most general statement would be: "The amount of sleep students get affects their grades." The hypothesis might also be stated as "If you get more sleep, your grades will improve" or "Students who get nine hours of sleep have better grades than those who get more or less sleep."
In an experiment, you can collect the same data, but the statistical analysis is less likely to give you a high confidence limit.
Usually, a scientist starts out with the null hypothesis. From there, it may be possible to propose and test an alternative hypothesis, to narrow down the relationship between the variables.
Example of a Hypothesis
Examples of a hypothesis include:
- If you drop a rock and a feather, (then) they will fall at the same rate.
- Plants need sunlight in order to live. (if sunlight, then life)
- Eating sugar gives you energy. (if sugar, then energy)
- White, Jay D. Research in Public Administration . Conn., 1998.
- Schick, Theodore, and Lewis Vaughn. How to Think about Weird Things: Critical Thinking for a New Age . McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2002.
- Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples
- Definition of a Hypothesis
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- Six Steps of the Scientific Method
- What Are Examples of a Hypothesis?
- Understanding Simple vs Controlled Experiments
- Scientific Method Flow Chart
- Scientific Method Vocabulary Terms
- What Is a Testable Hypothesis?
- Null Hypothesis Examples
- What 'Fail to Reject' Means in a Hypothesis Test
- How To Design a Science Fair Experiment
- What Is an Experiment? Definition and Design
- Hypothesis Test for the Difference of Two Population Proportions
- How to Conduct a Hypothesis Test
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Biology library
Course: biology library > unit 1, the scientific method.
- Controlled experiments
- The scientific method and experimental design
Introduction
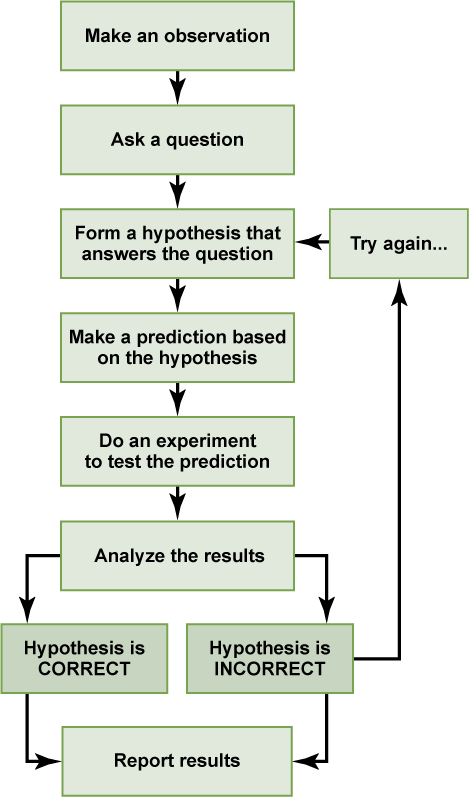
- Make an observation.
- Ask a question.
- Form a hypothesis , or testable explanation.
- Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
- Test the prediction.
- Iterate: use the results to make new hypotheses or predictions.
Scientific method example: Failure to toast
1. make an observation..
- Observation: the toaster won't toast.
2. Ask a question.
- Question: Why won't my toaster toast?

3. Propose a hypothesis.
- Hypothesis: Maybe the outlet is broken.
4. Make predictions.
- Prediction: If I plug the toaster into a different outlet, then it will toast the bread.
5. Test the predictions.
- Test of prediction: Plug the toaster into a different outlet and try again.
- If the toaster does toast, then the hypothesis is supported—likely correct.
- If the toaster doesn't toast, then the hypothesis is not supported—likely wrong.
Logical possibility
Practical possibility, building a body of evidence, 6. iterate..
- Iteration time!
- If the hypothesis was supported, we might do additional tests to confirm it, or revise it to be more specific. For instance, we might investigate why the outlet is broken.
- If the hypothesis was not supported, we would come up with a new hypothesis. For instance, the next hypothesis might be that there's a broken wire in the toaster.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
Published on May 6, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection .
Example: Hypothesis
Daily apple consumption leads to fewer doctor’s visits.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more types of variables .
- An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls.
- A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
If there are any control variables , extraneous variables , or confounding variables , be sure to jot those down as you go to minimize the chances that research bias will affect your results.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Step 1. ask a question.
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2. Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to ensure that you’re embarking on a relevant topic . This can also help you identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalize more complex constructs.
Step 3. Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
4. Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis . The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
- H 0 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has no effect on their final exam scores.
- H 1 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has a positive effect on their final exam scores.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
A hypothesis is not just a guess — it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/hypothesis/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, construct validity | definition, types, & examples, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, operationalization | a guide with examples, pros & cons, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Shona McCombes .
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more variables . An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls. A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Step 1: ask a question.
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2: Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalise more complex constructs.
Step 3: Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
Step 4: Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
Step 6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
A hypothesis is not just a guess. It should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, May 06). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/hypothesis-writing/
Is this article helpful?
1.2: The Scientific Process
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 64696
Biologists study the living world by posing questions about it and seeking science-based responses. This approach is common to other sciences as well and is often referred to as the scientific method . The scientific process was used even in ancient times, but it was first documented by England’s Sir Francis Bacon (1561–1626) ( Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) ), who set up inductive methods for scientific inquiry. The scientific method is not exclusively used by biologists but can be applied to almost anything as a logical problem solving method.

The scientific process typically starts with an observation (often a problem to be solved) that leads to a question. Remember that science is very good at answering questions having to do with observations about the natural world, but is very bad at answering questions having to do with morals, ethics, or personal opinions.
Let’s think about a simple problem that starts with an observation and apply the scientific method to solve the problem. Imagine that one morning when you wake up and flip the switch to turn on your bedside lamp, the light won’t turn on. That is an observation that also describes a problem: the lights won’t turn on. Of course, you would next ask the question: “Why won’t the light turn on?”
Recall that a hypothesis is a suggested explanation that can be tested. A hypothesis is NOT the question you are trying to answer – it is what you think the answer to the question will be and why . To solve a problem, several hypotheses may be proposed. For example, one hypothesis might be, “The light won’t turn on because the bulb is burned out.” But there could be other answers to the question, and therefore other hypotheses may be proposed. A second hypothesis might be, “The light won’t turn on because the lamp is unplugged” or “The light won’t turn on because the power is out.” A hypothesis should be based on credible background information. A hypothesis is NOT just a guess (not even an educated one), although it can be based on your prior experience (such as in the example where the light won’t turn on). In general, hypotheses in biology should be based on a credible, referenced source of information.
A hypothesis must be testable to ensure that it is valid. For example, a hypothesis that depends on what a dog thinks is not testable, because we can’t tell what a dog thinks. It should also be falsifiable, meaning that it can be disproven by experimental results. An example of an unfalsifiable hypothesis is “Red is a better color than blue.” There is no experiment that might show this statement to be false. To test a hypothesis, a researcher will conduct one or more experiments designed to eliminate one or more of the hypotheses. This is important: a hypothesis can be disproven, or eliminated, but it can never be proven. Science does not deal in proofs like mathematics. If an experiment fails to disprove a hypothesis, then that explanation (the hypothesis) is supported as the answer to the question. However, that doesn’t mean that later on, we won’t find a better explanation or design a better experiment that will be found to falsify the first hypothesis and lead to a better one.
A variable is any part of the experiment that can vary or change during the experiment. Typically, an experiment only tests one variable and all the other conditions in the experiment are held constant.
- The variable that is tested is known as the independent variable .
- The dependent variable is the thing (or things) that you are measuring as the outcome of your experiment.
- A constant is a condition that is the same between all of the tested groups.
- A confounding variable is a condition that is not held constant that could affect the experimental results.
A hypothesis often has the format “If [I change the independent variable in this way] then [I will observe that the dependent variable does this] because [of some reason].” For example, the first hypothesis might be, “If you change the light bulb, then the light will turn on because the bulb is burned out.” In this experiment, the independent variable (the thing that you are testing) would be changing the light bulb and the dependent variable is whether or not the light turns on. It would be important to hold all the other aspects of the environment constant, for example not messing with the lamp cord or trying to turn the lamp on using a different light switch. If the entire house had lost power during the experiment because a car hit the power pole, that would be a confounding variable.
You may have learned that a hypothesis can be phrased as an “If..then…” statement. Simple hypotheses can be phrased that way (but they must also include a “because”), but more complicated hypotheses may require several sentences. It is also very easy to get confused by trying to put your hypothesis into this format. Hypotheses do not have to be phrased as “if..then..” statements, it is just sometimes a useful format.
Query \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Query \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Query \(\PageIndex{3}\)
The results of your experiment are the data that you collect as the outcome. In the light experiment, your results are either that the light turns on or the light doesn’t turn on. Based on your results, you can make a conclusion. Your conclusion uses the results to answer your original question.
We can put the experiment with the light that won’t go in into the figure above:
- Observation: the light won’t turn on.
- Question: why won’t the light turn on?
- Hypothesis: the lightbulb is burned out.
- Prediction: if I change the lightbulb (independent variable), then the light will turn on (dependent variable).
- Experiment: change the lightbulb while leaving all other variables the same.
- Analyze the results: the light didn’t turn on.
- Conclusion: The lightbulb isn’t burned out. The results do not support the hypothesis, time to develop a new one!
- Hypothesis 2: the lamp is unplugged.
- Prediction 2: if I plug in the lamp, then the light will turn on.
- Experiment: plug in the lamp
- Analyze the results: the light turned on!
- Conclusion: The light wouldn’t turn on because the lamp was unplugged. The results support the hypothesis, it’s time to move on to the next experiment!
In practice, the scientific method is not as rigid and structured as it might at first appear. Sometimes an experiment leads to conclusions that favor a change in approach; often, an experiment brings entirely new scientific questions to the puzzle. Many times, science does not operate in a linear fashion; instead, scientists continually draw inferences and make generalizations, finding patterns as their research proceeds. Scientific reasoning is more complex than the scientific method alone suggests.
Control Groups
Another important aspect of designing an experiment is the presence of one or more control groups. A control group allows you to make a comparison that is important for interpreting your results. Control groups are samples that help you to determine that differences between your experimental groups are due to your treatment rather than a different variable – they eliminate alternate explanations for your results (including experimental error and experimenter bias). They increase reliability, often through the comparison of control measurements and measurements of the experimental groups. Often, the control group is a sample that is not treated with the independent variable, but is otherwise treated the same way as your experimental sample. This type of control group contains every feature of the experimental group except it is not given the manipulation that is hypothesized about (it does not get treated with the independent variable). Therefore, if the results of the experimental group differ from the control group, the difference must be due to the hypothesized manipulation, rather than some outside factor. It is common in complex experiments (such as those published in scientific journals) to have more control groups than experimental groups.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Question: Which fertilizer will produce the greatest number of tomatoes when applied to the plants?
Prediction and Hypothesis: If I apply different brands of fertilizer to tomato plants, the most tomatoes will be produced from plants watered with Brand A because Brand A advertises that it produces twice as many tomatoes as other leading brands.
Experiment: Purchase 10 tomato plants of the same type from the same nursery. Pick plants that are similar in size and age. Divide the plants into two groups of 5. Apply Brand A to the first group and Brand B to the second group according to the instructions on the packages. After 10 weeks, count the number of tomatoes on each plant.
Independent Variable: Brand of fertilizer.
Dependent Variable: Number of tomatoes.
The number of tomatoes produced depends on the brand of fertilizer applied to the plants.
Constants: amount of water, type of soil, size of pot, amount of light, type of tomato plant, length of time plants were grown.
Confounding variables: any of the above that are not held constant, plant health, diseases present in the soil or plant before it was purchased.
Results: Tomatoes fertilized with Brand A produced an average of 20 tomatoes per plant, while tomatoes fertilized with Brand B produced an average of 10 tomatoes per plant.
You’d want to use Brand A next time you grow tomatoes, right? But what if I told you that plants grown without fertilizer produced an average of 30 tomatoes per plant! Now what will you use on your tomatoes?
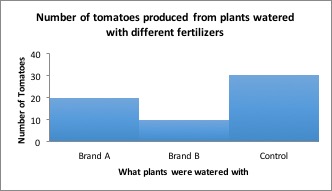
Results including control group: Tomatoes which received no fertilizer produced more tomatoes than either brand of fertilizer.
Conclusion: Although Brand A fertilizer produced more tomatoes than Brand B, neither fertilizer should be used because plants grown without fertilizer produced the most tomatoes!
Positive control groups are often used to show that the experiment is valid and that everything has worked correctly. You can think of a positive control group as being a group where you should be able to observe the thing that you are measuring (“the thing” should happen). The conditions in a positive control group should guarantee a positive result. If the positive control group doesn’t work, there may be something wrong with the experimental procedure.
Negative control groups are used to show whether a treatment had any effect. If your treated sample is the same as your negative control group, your treatment had no effect. You can also think of a negative control group as being a group where you should NOT be able to observe the thing that you are measuring (“the thing” shouldn’t happen), or where you should not observe any change in the thing that you are measuring (there is no difference between the treated and control group). The conditions in a negative control group should guarantee a negative result. A placebo group is an example of a negative control group.
As a general rule, you need a positive control to validate a negative result, and a negative control to validate a positive result.
- You observe growth . Does this mean that your spinach is really contaminated? Consider an alternate explanation for growth: the swab, the water, or the plate is contaminated with bacteria. You could use a negative control to determine which explanation is true. If a swab is wet and wiped on a nutrient plate, do bacteria grow?
- You don’t observe growth. Does this mean that your spinach is really safe? Consider an alternate explanation for no growth: Salmonella isn’t able to grow on the type of nutrient you used in your plates. You could use a positive control to determine which explanation is true. If you wipe a known sample of Salmonella bacteria on the plate, do bacteria grow?
- In a drug trial, one group of subjects are given a new drug, while a second group is given a placebo drug (a sugar pill; something which appears like the drug, but doesn’t contain the active ingredient). Reduction in disease symptoms are measured. The second group receiving the placebo is a negative control group. You might expect a reduction in disease symptoms purely because the person knows they are taking a drug so they should be getting better. If the group treated with the real drug does not show more a reduction in disease symptoms than the placebo group, the drug doesn’t really work. The placebo group sets a baseline against which the experimental group (treated with the drug) can be compared. A positive control group is not required for this experiment.
- In an experiment measuring the preference of birds for various types of food , a negative control group would be a “placebo feeder”. This would be the same type of feeder, but with no food in it. Birds might visit a feeder just because they are interested in it; an empty feeder would give a baseline level for bird visits. A positive control group might be a food that squirrels are known to like. This would be useful because if no squirrels visited any of the feeders, you couldn’t tell if this was because there were no squirrels around or because they didn’t like any of your food offerings!
- To test the effect of pH on the function of an enzyme , you would want a positive control group where you knew the enzyme would function (pH not changed) and a negative control group where you knew the enzyme would not function (no enzyme added). You need the positive control group so you know your enzyme is working: if you didn’t see a reaction in any of the tubes with the pH adjusted, you wouldn’t know if it was because the enzyme wasn’t working at all or because the enzyme just didn’t work at any of your tested pH. You need the negative control group so you can ensure that there is no reaction taking place in the absence of enzyme: if the reaction proceeds without the enzyme, your results are meaningless.
Text adapted from: OpenStax, Biology. OpenStax CNX. May 27, 2016 http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:RD6ERYiU@5/The-Process-of-Science .

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.6: Exercises
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 182609
1.1: Soda Pop Fizz
1.2: Chemicals Compose Ordinary Things
1.3: All Things Are Made of Atoms and Molecules
1.4: The Scientific Method: How Chemists Think
Use the following paragraph to answer the first two questions. In 1928, Sir Alexander Fleming was studying Staphylococcus bacteria growing in culture dishes. He noticed that a mold called Penicillium was also growing in some of the dishes. In Figure 1.13, Petri dish A represents a dish containing only Staphylococcus bacteria. The red dots in dish B represent Penicillium colonies. Fleming noticed that a clear area existed around the mold because all the bacteria grown in this area had died. In the culture dishes without the mold, no clear areas were present. Fleming suggested that the mold was producing a chemical that killed the bacteria. He decided to isolate this substance and test it to see if it would kill bacteria. Fleming grew some Penicillium mold in a nutrient broth. After the mold grew in the broth, he removed all the mold from the broth and added the broth to a culture of bacteria. All the bacteria died.
- Nutrient broth kills bacteria.
- There are clear areas around the Penicillium mold where Staphylococcus doesn't grow.
- Mold kills bacteria.
- Penicillium mold produces a substance that kills Staphylococcus.
- Without mold in the culture dish, there were no clear areas in the bacteria.
- Collecting and organizing data
- Making a hypothesis
- Testing a hypothesis by experiment
- Rejecting the old hypothesis and making a new one
- None of these
A scientific investigation is NOT valid unless every step in the scientific method is present and carried out in the exact order listed in this chapter.
Which of the following words is closest to the same meaning as hypothesis ?
Why do scientists sometimes discard theories?
- the steps in the scientific method were not followed in order
- public opinion disagrees with the theory
- the theory is opposed by the church
- contradictory observations are found
- congress voted against it
Gary noticed that two plants which his mother planted on the same day, that were the same size when planted, were different in size after three weeks. Since the larger plant was in the full sun all day and the smaller plant was in the shade of a tree most of the day, Gary believed the sunshine was responsible for the difference in the plant sizes. In order to test this, Gary bought ten small plants of the same size and type. He made sure they had the same size and type of pot. He also made sure they had the same amount and type of soil. Then Gary built a frame to hold a canvas roof over five of the plants while the other five were nearby but out in the sun. Gary was careful to make sure that each plant received exactly the same amount of water and plant food every day.
- Different plants have different characteristics.
- Plants that get more sunshine grow larger than plants that get less sunshine.
- Plants that grow in the shade grow larger.
- Plants that don’t receive water will die.
- Plants that receive the same amount of water and plant food will grow the same amount.
- Gary wanted to determine if the size of the container would affect the plant growth.
- Gary wanted to make sure the size of the container did not affect differential plant growth in his experiment.
- Gary want to control how much plant food his plants received.
- Gary wanted his garden to look organized.
- There is no possible scientific reason for having the same size containers.
- Gary wanted to test the effect of shade on plant growth and therefore, he wanted to have no variables other than the amount of sunshine on the plants.
- Gary wanted to test the effect of the amount of water on plant growth.
- Gary's hypothesis was that water quality was affecting plant growth.
- Gary was conserving water.
- There is no possible scientific reason for having the same amount of water for each plant every day.
- the amount of water
- the amount of plant food
- the amount of soil
- the amount of sunshine
- the type of soil
- individual plant variation
- soil temperature due to different colors of containers
- water loss due to evaporation from the soil
- the effect of insects which may attack one set of plants but not the other
- All of the above are possible factors that Gary did not control.
When a mosquito sucks blood from its host, it penetrates the skin with its sharp beak and injects an anti-coagulant so the blood will not clot. It then sucks some blood and removes its beak. If the mosquito carries disease-causing microorganisms, it injects these into its host along with the anti-coagulant. It was assumed for a long time that the virus typhus was injected by the louse when sucking blood in a manner similar to the mosquito. But apparently this is not so. The infection is not in the saliva of the louse, but in the feces. The disease is thought to be spread when the louse feces come in contact with scratches or bite wounds in the host's skin. A test of this was carried out in 1922 when two workers fed infected lice on a monkey, taking great care that no louse feces came into contact with the monkey. After two weeks, the monkey had NOT become ill with typhus. The workers then injected the monkey with typhus and it became ill within a few days. Why did the workers inject the monkey with typhus near the end of the experiment?
- to prove that the lice carried the typhus virus
- to prove the monkey was similar to man
- to prove that the monkey was not immune to typhus
- to prove that mosquitoes were not carriers of typhus
- the workers were mean
Eijkman fed a group of chickens exclusively on rice whose seed coat had been removed (polished rice or white rice). The chickens all developed polyneuritis (a disease of chickens) and died. He fed another group of chickens unpolished rice (rice that still had its seed coat). Not a single one of them contracted polyneuritis. He then gathered the polishings from rice (the seed coats that had been removed) and fed the polishings to other chickens that were sick with polyneuritis. In a short time, the birds all recovered. Eijkman had accurately traced the cause of polyneuritis to a faulty diet. For the first time in history, a food deficiency disease had been produced and cured experimentally. Which of the following is a reasonable statement of Eijkman’s hypothesis?
- Polyneuritis is a fatal disease for chickens.
- White rice carries a virus for the disease polyneuritis.
- Unpolished rice does not carry the polyneuritis virus.
- The rice seed coat contains a nutrient that provides protection for chickens against polyneuritis.
- None of these is a reasonable statement of Eijkman's hypothesis.
The three questions below relate to the following paragraphs.
Scientist A noticed that in a certain forest area, the only animals inhabiting the region were giraffes. He also noticed that the only food available for the animals was on fairly tall trees and as the summer progressed, the animals ate the leaves high and higher on the trees. The scientist suggested that these animals were originally like all other animals but generations of animals stretching their necks to reach higher up the trees for food, caused the species to grow very long necks.
Scientist B conducted experiments and observed that stretching muscles does NOT cause bones to grow longer nor change the DNA of animals so that longer muscles would be passed on to the next generation. Scientist B, therefore, discarded Scientist A's suggested answer as to why all the animals living in the area had long necks. Scientist B suggested instead that originally many different types of animals including giraffes had lived in the region but only the giraffes could survive when the only food was high in the trees, and so all the other species had left the area.
- The only animals living in the area were giraffes.
- The only available food was on tall trees.
- Animals which constantly stretch their necks will grow longer necks.
- A, B, and C are all interpretations.
- A, B, and C are all observations.
- the only animals living in the area were giraffes.
- the only available food was on tall trees.
- animals which constantly stretch their necks will grow longer necks.
- the animals which possess the best characteristics for living in an area, will be the predominant species.
- None of the above are reasonable statements of Scientist A's hypothesis.
- evidence that the scientific method doesn’t always work.
- a result achieved without use of the scientific method.
- an example of what happened before the scientific method was invented.
- an example of the normal functioning of the scientific method.
- an unusual case.
When a theory has been known for a long time, it becomes a law.
During Pasteur's time, anthrax was a widespread and disastrous disease for livestock. Many people whose livelihood was raising livestock lost large portions of their herds to this disease. Around 1876, a horse doctor in eastern France named Louvrier, claimed to have invented a cure for anthrax. The influential men of the community supported Louvrier's claim to have cured hundreds of cows of anthrax. Pasteur went to Louvrier's hometown to evaluate the cure. The cure was explained to Pasteur as a multi-step process during which: 1) the cow was rubbed vigorously to make her as hot as possible; 2) long gashes were cut into the cows skin and turpentine was poured into the cuts; 3) an inch-thick coating of cow manure mixed with hot vinegar was plastered onto the cow and the cow was completely wrapped in a cloth. Since some cows recover from anthrax with no treatment, performing the cure on a single cow would not be conclusive, so Pasteur proposed an experiment to test Louvrier's cure. Four healthy cows were to be injected with anthrax microbes, and after the cows became ill, Louvrier would pick two of the cows (A and B) and perform his cure on them while the other two cows (C and D) would be left untreated. The experiment was performed and after a few days, one of the untreated cows died and one of them got better. Of the cows treated by Louvrier's cure, one cow died and one got better. In this experiment, what was the purpose of infecting cows C and D?
- So that Louvrier would have more than two cows to choose from.
- To make sure the injection actually contained anthrax.
- To serve as experimental controls (a comparison of treated to untreated cows).
- To kill as many cows as possible.
A hypothesis is
- a description of a consistent pattern in observations.
- an observation that remains constant.
- a theory that has been proven.
- a tentative explanation for a phenomenon.
A number of people became ill after eating oysters in a restaurant. Which of the following statements is a hypothesis about this occurrence?
- Everyone who ate oysters got sick.
- People got sick whether the oysters they ate were raw or cooked.
- Symptoms included nausea and dizziness.
- The cook felt really bad about it.
- Bacteria in the oysters may have caused the illness.
Which statement best describes the reason for using experimental controls?
- Experimental controls eliminate the need for large sample sizes.
- Experimental controls eliminate the need for statistical tests.
- Experimental controls reduce the number of measurements needed.
- Experimental controls allow comparison between groups that are different in only one independent variable.
A student decides to set up an experiment to determine the relationship between the growth rate of plants and the presence of detergent in the soil. He sets up 10 seed pots. In five of the seed pots, he mixes a precise amount of detergent with the soil and the other five seed pots have no detergent in the soil. The five seed pots with detergent are placed in the sun and the five seed pots with no detergent are placed in the shade. All 10 seed pots receive the same amount of water and the same number and type of seeds. He grows the plants for two months and charts the growth every two days. What is wrong with his experiment?
- The student has too few pots.
- The student has two independent variables.
- The student has two dependent variables.
- The student has no experimental control on the soil.
A scientist plants two rows of corn for experimentation. She puts fertilizer on row 1 but does not put fertilizer on row 2. Both rows receive the same amount of sun and water. She checks the growth of the corn over the course of five months. What is acting as the control in this experiment?
- Corn without fertilizer.
- Corn with fertilizer.
- Amount of water.
- Height of corn plants.
If you have a control group for your experiment, which of the following is true?
- There can be more than one difference between the control group and the test group, but not more three differences, or else the experiment is invalid.
- The control group and the test group may have many differences between them.
- The control group must be identical to the test group except for one variable.
- None of these are true.
If the hypothesis is rejected by the experiment, then:
- the experiment may have been a success.
- the experiment was a failure.
- the experiment was poorly designed.
- the experiment didn't follow the scientific method.
A well-substantiated explanation of an aspect of the natural world is a:
- hypothesis.
- None of these.
1.5: A Beginning Chemist: How to Succeed
Module 1: Introduction to Biology
Experiments and hypotheses, learning outcomes.
- Form a hypothesis and use it to design a scientific experiment
Now we’ll focus on the methods of scientific inquiry. Science often involves making observations and developing hypotheses. Experiments and further observations are often used to test the hypotheses.
A scientific experiment is a carefully organized procedure in which the scientist intervenes in a system to change something, then observes the result of the change. Scientific inquiry often involves doing experiments, though not always. For example, a scientist studying the mating behaviors of ladybugs might begin with detailed observations of ladybugs mating in their natural habitats. While this research may not be experimental, it is scientific: it involves careful and verifiable observation of the natural world. The same scientist might then treat some of the ladybugs with a hormone hypothesized to trigger mating and observe whether these ladybugs mated sooner or more often than untreated ones. This would qualify as an experiment because the scientist is now making a change in the system and observing the effects.
Forming a Hypothesis
When conducting scientific experiments, researchers develop hypotheses to guide experimental design. A hypothesis is a suggested explanation that is both testable and falsifiable. You must be able to test your hypothesis, and it must be possible to prove your hypothesis true or false.
For example, Michael observes that maple trees lose their leaves in the fall. He might then propose a possible explanation for this observation: “cold weather causes maple trees to lose their leaves in the fall.” This statement is testable. He could grow maple trees in a warm enclosed environment such as a greenhouse and see if their leaves still dropped in the fall. The hypothesis is also falsifiable. If the leaves still dropped in the warm environment, then clearly temperature was not the main factor in causing maple leaves to drop in autumn.
In the Try It below, you can practice recognizing scientific hypotheses. As you consider each statement, try to think as a scientist would: can I test this hypothesis with observations or experiments? Is the statement falsifiable? If the answer to either of these questions is “no,” the statement is not a valid scientific hypothesis.
Practice Questions
Determine whether each following statement is a scientific hypothesis.
Air pollution from automobile exhaust can trigger symptoms in people with asthma.
- No. This statement is not testable or falsifiable.
- No. This statement is not testable.
- No. This statement is not falsifiable.
- Yes. This statement is testable and falsifiable.
Natural disasters, such as tornadoes, are punishments for bad thoughts and behaviors.
a: No. This statement is not testable or falsifiable. “Bad thoughts and behaviors” are excessively vague and subjective variables that would be impossible to measure or agree upon in a reliable way. The statement might be “falsifiable” if you came up with a counterexample: a “wicked” place that was not punished by a natural disaster. But some would question whether the people in that place were really wicked, and others would continue to predict that a natural disaster was bound to strike that place at some point. There is no reason to suspect that people’s immoral behavior affects the weather unless you bring up the intervention of a supernatural being, making this idea even harder to test.
Testing a Vaccine
Let’s examine the scientific process by discussing an actual scientific experiment conducted by researchers at the University of Washington. These researchers investigated whether a vaccine may reduce the incidence of the human papillomavirus (HPV). The experimental process and results were published in an article titled, “ A controlled trial of a human papillomavirus type 16 vaccine .”
Preliminary observations made by the researchers who conducted the HPV experiment are listed below:
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted virus in the United States.
- There are about 40 different types of HPV. A significant number of people that have HPV are unaware of it because many of these viruses cause no symptoms.
- Some types of HPV can cause cervical cancer.
- About 4,000 women a year die of cervical cancer in the United States.
Practice Question
Researchers have developed a potential vaccine against HPV and want to test it. What is the first testable hypothesis that the researchers should study?
- HPV causes cervical cancer.
- People should not have unprotected sex with many partners.
- People who get the vaccine will not get HPV.
- The HPV vaccine will protect people against cancer.
Experimental Design
You’ve successfully identified a hypothesis for the University of Washington’s study on HPV: People who get the HPV vaccine will not get HPV.
The next step is to design an experiment that will test this hypothesis. There are several important factors to consider when designing a scientific experiment. First, scientific experiments must have an experimental group. This is the group that receives the experimental treatment necessary to address the hypothesis.
The experimental group receives the vaccine, but how can we know if the vaccine made a difference? Many things may change HPV infection rates in a group of people over time. To clearly show that the vaccine was effective in helping the experimental group, we need to include in our study an otherwise similar control group that does not get the treatment. We can then compare the two groups and determine if the vaccine made a difference. The control group shows us what happens in the absence of the factor under study.
However, the control group cannot get “nothing.” Instead, the control group often receives a placebo. A placebo is a procedure that has no expected therapeutic effect—such as giving a person a sugar pill or a shot containing only plain saline solution with no drug. Scientific studies have shown that the “placebo effect” can alter experimental results because when individuals are told that they are or are not being treated, this knowledge can alter their actions or their emotions, which can then alter the results of the experiment.
Moreover, if the doctor knows which group a patient is in, this can also influence the results of the experiment. Without saying so directly, the doctor may show—through body language or other subtle cues—their views about whether the patient is likely to get well. These errors can then alter the patient’s experience and change the results of the experiment. Therefore, many clinical studies are “double blind.” In these studies, neither the doctor nor the patient knows which group the patient is in until all experimental results have been collected.
Both placebo treatments and double-blind procedures are designed to prevent bias. Bias is any systematic error that makes a particular experimental outcome more or less likely. Errors can happen in any experiment: people make mistakes in measurement, instruments fail, computer glitches can alter data. But most such errors are random and don’t favor one outcome over another. Patients’ belief in a treatment can make it more likely to appear to “work.” Placebos and double-blind procedures are used to level the playing field so that both groups of study subjects are treated equally and share similar beliefs about their treatment.
The scientists who are researching the effectiveness of the HPV vaccine will test their hypothesis by separating 2,392 young women into two groups: the control group and the experimental group. Answer the following questions about these two groups.
- This group is given a placebo.
- This group is deliberately infected with HPV.
- This group is given nothing.
- This group is given the HPV vaccine.
- a: This group is given a placebo. A placebo will be a shot, just like the HPV vaccine, but it will have no active ingredient. It may change peoples’ thinking or behavior to have such a shot given to them, but it will not stimulate the immune systems of the subjects in the same way as predicted for the vaccine itself.
- d: This group is given the HPV vaccine. The experimental group will receive the HPV vaccine and researchers will then be able to see if it works, when compared to the control group.
Experimental Variables
A variable is a characteristic of a subject (in this case, of a person in the study) that can vary over time or among individuals. Sometimes a variable takes the form of a category, such as male or female; often a variable can be measured precisely, such as body height. Ideally, only one variable is different between the control group and the experimental group in a scientific experiment. Otherwise, the researchers will not be able to determine which variable caused any differences seen in the results. For example, imagine that the people in the control group were, on average, much more sexually active than the people in the experimental group. If, at the end of the experiment, the control group had a higher rate of HPV infection, could you confidently determine why? Maybe the experimental subjects were protected by the vaccine, but maybe they were protected by their low level of sexual contact.
To avoid this situation, experimenters make sure that their subject groups are as similar as possible in all variables except for the variable that is being tested in the experiment. This variable, or factor, will be deliberately changed in the experimental group. The one variable that is different between the two groups is called the independent variable. An independent variable is known or hypothesized to cause some outcome. Imagine an educational researcher investigating the effectiveness of a new teaching strategy in a classroom. The experimental group receives the new teaching strategy, while the control group receives the traditional strategy. It is the teaching strategy that is the independent variable in this scenario. In an experiment, the independent variable is the variable that the scientist deliberately changes or imposes on the subjects.
Dependent variables are known or hypothesized consequences; they are the effects that result from changes or differences in an independent variable. In an experiment, the dependent variables are those that the scientist measures before, during, and particularly at the end of the experiment to see if they have changed as expected. The dependent variable must be stated so that it is clear how it will be observed or measured. Rather than comparing “learning” among students (which is a vague and difficult to measure concept), an educational researcher might choose to compare test scores, which are very specific and easy to measure.
In any real-world example, many, many variables MIGHT affect the outcome of an experiment, yet only one or a few independent variables can be tested. Other variables must be kept as similar as possible between the study groups and are called control variables . For our educational research example, if the control group consisted only of people between the ages of 18 and 20 and the experimental group contained people between the ages of 30 and 35, we would not know if it was the teaching strategy or the students’ ages that played a larger role in the results. To avoid this problem, a good study will be set up so that each group contains students with a similar age profile. In a well-designed educational research study, student age will be a controlled variable, along with other possibly important factors like gender, past educational achievement, and pre-existing knowledge of the subject area.
What is the independent variable in this experiment?
- Sex (all of the subjects will be female)
- Presence or absence of the HPV vaccine
- Presence or absence of HPV (the virus)
List three control variables other than age.
What is the dependent variable in this experiment?
- Sex (male or female)
- Rates of HPV infection
- Age (years)
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- Revision and adaptation. Authored by : Shelli Carter and Lumen Learning. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Scientific Inquiry. Provided by : Open Learning Initiative. Located at : https://oli.cmu.edu/jcourse/workbook/activity/page?context=434a5c2680020ca6017c03488572e0f8 . Project : Introduction to Biology (Open + Free). License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
There are basic methods of gaining knowledge that is common to all of science. At the heart of science is the scientific investigation. A scientific investigation is a plan for asking questions and testing possible answers in order to advance scientific knowledge. Figure 1.8.2 1.8. 2 outlines the steps of the scientific method.
2. The cooler the temperature in a lake, the more oxygen the water holds. Daniel notices that he catches more fish in a lake that is cooler than 55 degrees.
The scientific method is central to the study of biology: it is a process of acquiring and verifying information through experimentation. The general steps of the scientific method are depicted in the figure below. The hypothesis, or suggested explanation for the observation, is the basis for setting up experiments.
Merriam Webster defines a hypothesis as "an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument.". In other words, a hypothesis is an educated guess. Scientists make a reasonable assumption--or a hypothesis--then design an experiment to test whether it's true or not.
It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis. 7.
Now it's time to state your hypothesis. The hypothesis is an educated guess as to what will happen during your experiment. The hypothesis is often written using the words "IF" and "THEN." For example, "If I do not study, then I will fail the test." The "if' and "then" statements reflect your independent and dependent variables.
Here are some research hypothesis examples: If you leave the lights on, then it takes longer for people to fall asleep. If you refrigerate apples, they last longer before going bad. If you keep the curtains closed, then you need less electricity to heat or cool the house (the electric bill is lower). If you leave a bucket of water uncovered ...
Scientific Hypothesis Examples. By Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D. If you get at least 6 hours of sleep, you will do better on tests than if you get less sleep. If you drop a ball, it will fall toward the ground. If you drink coffee before going to bed, then it will take longer to fall asleep. If you cover a wound with a bandage, then it will ...
A hypothesis is a conjecture. A researcher hypothesizes to predict what is going on or what is expected to occur. The hypothesis is a claim of how it works a relation between two or more variables. Usually, it is written in the present time. According to Fleming's experiment and his accident in the lab, we can postulate the following hypothesis.
Meaning. Biology. The study of living things. Observation. Noticing and describing events in an orderly way. Hypothesis. A scientific explanation that can be tested through experimentation or observation. Controlled experiment. An experiment in which only one variable is changed.
Choose 1 answer: The facts collected from an experiment are written in the form of a hypothesis. A. The facts collected from an experiment are written in the form of a hypothesis. A hypothesis is the correct answer to a scientific question. B. A hypothesis is the correct answer to a scientific question. A hypothesis is a possible, testable ...
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for an observation. The definition depends on the subject. In science, a hypothesis is part of the scientific method. It is a prediction or explanation that is tested by an experiment. Observations and experiments may disprove a scientific hypothesis, but can never entirely prove one.
The scientific method. At the core of biology and other sciences lies a problem-solving approach called the scientific method. The scientific method has five basic steps, plus one feedback step: Make an observation. Ask a question. Form a hypothesis, or testable explanation. Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
A prediction is similar to a hypothesis but it typically has the format "If . . . then . . . ." For example, the prediction for the first hypothesis might be, "If the student turns on the air conditioning, then the classroom will no longer be too warm." A hypothesis must be testable to ensure that it is valid.
A hypothesis is a tentative, testable answer to a scientific question. Once a scientist has a scientific question she is interested in, the scientist reads up to find out what is already known on the topic. Then she uses that information to form a tentative answer to her scientific question. Sometimes people refer to the tentative answer as "an ...
If the hypothesis is rejected by the experiment, then: the experiment may have been a success. the experiment was a failure. the experiment was poorly designed. the experiment didn't follow the scientific method. A well-substantiated explanation of an aspect of the natural world is a: theory. law. hypothesis. None of these.
The scientific process was used even in ancient times, but it was first documented by England's Sir Francis Bacon (1561-1626) ( Figure 1.2.1 1.2. 1 ), who set up inductive methods for scientific inquiry. The scientific method is not exclusively used by biologists but can be applied to almost anything as a logical problem solving method.
If the hypothesis is rejected by the experiment, then: the experiment may have been a success. the experiment was a failure. the experiment was poorly designed. the experiment didn't follow the scientific method. A well-substantiated explanation of an aspect of the natural world is a: theory. law. hypothesis. None of these.
This would qualify as an experiment because the scientist is now making a change in the system and observing the effects. Forming a Hypothesis. When conducting scientific experiments, researchers develop hypotheses to guide experimental design. A hypothesis is a suggested explanation that is both testable and falsifiable.