- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing

How to Write a Theme Essay
Last Updated: January 4, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 206,255 times.
Starting the Essay

- For example, an essay prompt may ask you to reflect on the theme of good versus evil in John Steinbeck's East of Eden .

- Make a list of everything you know about the topic. This can be information you learned in class, as well as information you found on your own.
- Write down keywords or key scenes in the text that respond to the essay prompt. Think about what words or scenes from the text come to mind when you think of a specific theme.
- For example, when you brainstorm ideas on East of Eden , you may write down any moments in the text that seem to speak to the theme of good and evil.

- Your thesis statement will need to address the theme, your primary example or examples, and the stance you will take on the topic.
- For example, your thesis might be: "In East of Eden , John Steinbeck rejects the Biblical idea of good and evil and instead focuses on the contradictions and complications found in good and evil."

- Introduction: Discuss landscape as metaphor, include thesis statement.
- Body: Describe mountains in opening scene, elaborate on how they symbolize good vs. evil, state how characters live between the mountains, showing how people are caught between good and evil.
- Conclusion: Restate thesis statement, return to landscape as metaphor.
Writing Your Essay

- Questions can make fun hooks for the reader. Ask a rhetorical question that relates to the theme of the essay, such as "How does one decide what is good and what is evil?"
- You can also use a quote from the text as the hook. Find a quote in the text that explores the themes and ideas you'll be discussing in your essay.

- For example, you may introduce the role of nature plays in the text to discuss the theme of good and evil. The first sentence of your body paragraph should discuss the role of nature. This will set up the paragraph and let the reader know what the focus of the paragraph will be.

- For example, you may discuss the use of nature in the text in one paragraph. The body of the paragraph should then use quotes and scenes in the text to support this idea.
- You might write,"The descriptions of the Gabilan Mountains in the text symbolize good and evil. The characters in the story live in the Salinas Valley, trapped in a gray area between these two extremes."

- Ask yourself, "What do I want my readers to have learned through this essay?"
- Remind readers about the essay's theme. Reference some of the arguments you made in the body of your essay, reinforcing how they support your original point.
Revising Your Essay

- Check that there are transitions between paragraphs. Look at the beginning of each paragraph to make sure they all flow well together.

- Print out your paper and proofread it. Oftentimes, errors are easier to catch on paper. If you can't print out your paper, try changing the size or type of the font. Anything that alters how the work looked when you wrote it can help alert you to errors. [13] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source

- Be open to constructive feedback from friends and peers. This will only improve the essay and ensure it is at its best when you turn it in.
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 20 May 2020.
- ↑ https://penandthepad.com/write-essay-theme-book-2200.html
- ↑ https://wts.indiana.edu/writing-guides/how-to-write-a-thesis-statement.html
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/essay-outline/
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/how-to-write-a-hook/
- ↑ https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-an-essay/conclusion
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/steps_for_revising.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/proofreading_suggestions.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

When writing a theme essay, you’ll need to explore a given theme in the text you’re studying. Before you start your essay, brainstorm some notes about your theme, which you can then build your essay from. For example, if you have the theme of good and evil, think about which characters are mostly good or evil, any good or evil actions they take, description that uses light and darkness, and any religious context. In your intro, state your thesis, which should summarize your essay’s main argument. Then, choose 4 or 5 examples of your theme and write a paragraph exploring each one. Make sure you support your points with quotes from the text. In your conclusion, link your ideas back to your thesis statement. For more tips from our English co-author, including how to revise your essay to polish it up, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Mar 13, 2018
Did this article help you?

Jul 29, 2017
Dec 18, 2016
Nov 8, 2016
Ashley Ding
Nov 22, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
- Essay Guides
- Other Essays
How to Write a Theme Essay
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A thematic essay is a type of writing assignment that focuses on a specific theme or topic. It requires you to identify a central theme, discuss it in detail, and make connections between various facts. Your main goal is to demonstrate understanding and interpretation of the given subject matter. This type of essay is commonly used in literature classes or history exams.
If you’ve got an assignment to write a theme essay, you might wonder where you should even start from. No worries, we’ve got you covered here! The first thing you must know about this specific type of paper is that it aims to analyze a certain well-known theme and make an interesting statement about it. Here, you must explain meaning and relevance or complexity of your topic. You should summarize details that support your conclusion. In this article, we will conduct a detailed review of theme essay concept. We will also provide you a step by step guide on how to write a proper one. Let's dive right into it!
Thematic Essay Definition
Let’s start with defining what is a thematic essay and its purpose. In this type, one should select a thesis and form unique statement related to its aspects. You should write about it, explaining or elaborating to your audience the following:
- How is your statement related to your topic?
- Which important or interesting aspects does it highlight?
- What approaches and literary devices are you using for analysis ? How do you explain your general theme? This can be comparison, metaphor, personification etc.
When composing such an essay, you must formulate and defend your statement. Here, you will demonstrate abilities of analysis and literary devices usage. At least several paragraphs would be needed to display such skills properly.
Thematic Essay Outline: What's Inside
The best way to begin is creating a theme essay outline for your topic. An outline should contain all key parts, concepts and ideas of your paper. You should put it in a sketchy but logical manner. This way you'll quickly prepare a shortened version of your assignment. It will also help you in reviewing it. Adding missing points and correcting significant mistakes would be easier at this early stage. Outline should include all main essay parts:
- Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Body section
- Conclusion.
Keeping it brief, you should not provide complete sentences to describe your statements, ideas and arguments. A few words would suffice for each important point. Purpose is to make it readable for yourself! You should review it quickly and spot any inconsistencies.
How to Write a Thematic Essay Step-By-Step
Now it is time to focus on how to write a theme analysis essay – the complete text from scratch. Is your goal to impress readers and achieve a good grade? Then it is important that you create a proper essay structure template and don't lose any of your key questions! Stay methodical and keep it logical! Make sure your audience is engaged and don’t disappoint them in the end. Below we’ll provide a general idea for each step of this process.
Step 1. Define the Topic for Your Thematic Essay
When it comes to choosing among thematic essay topics, it is important that you pick an interesting and maybe even a controversial one. At the same time, make sure you can actually provide some meaningful input about it. Your assignment should impress readers with detailed analysis and its author’s writing skills. That's why your chosen topic must provide enough material for that. There is a diverse choice of topics. Choose the one you are really interested in whether it is Bullying essay or Happiness essay . If you need some ideas for great essay topics, feel free to check out our other articles.
Step 2. Create a Thematic Essay Outline
We've already covered the main points of theme essay outline concept. When writing it, include all the main parts of your future work. Keep it as short as possible, one paragraph per each key point will be enough. It isn’t even necessary to describe everything with complete sentences! A few words would suffice. Once done, review it first and make necessary corrections. It is advised to review an outline several times. That's how any noticeable gaps or mistakes would be spotted early.
Step 3. Start a Thematic Essay with a Hook
A good thematic essay introduction ought to captivate readers right from the start. That’s why it is always advised to add some ‘hook’ into it. You can begin with an unexpected statement, use wordplay or a plot twist. Then you can explain this in the main body part. This way your audience would be interested to hear those explanations. As a result, your paper will have better chances of success. Apart from that, introduction should contain the main statement and some information about its content.
Step 4. Write Body Paragraphs for Your Theme Essay
Goal of thematic essay body is to answer all the questions stated in an introduction. You must elaborate the meaning of each key idea. Finally, display your usage of literary devices, as we’ve specified earlier. Common practice is to use at least one paragraph per a literary device disclosure. Besides, the main body is the right place to use all relevant sources that can support your analysis or provide you with helpful analogies. Keep the main body logical, so that every paragraph is somehow connected to the previous and the next ones.
Step 5. Create a Thematic Essay Conclusion
A strong thematic essay conclusion should highlight all important points from tyourhe essay while avoiding adding new facts or evidence. Just restate your thesis, answer all questions and summarize your arguments. It might be also useful to leave some final note for readers with some deeper analysis of your topic. You can also highlight the need for further exploration of the chosen theme and thus to prepare readers for your future works on this topic.
Step 6. Proofread Your Thematic Analysis Essay
After completing theme essay, it is highly recommended to review it thoroughly, even several times if possible. The goal is to find mistakes and to spot logical gaps or missing details. Even best essays typically have inconsistencies left at the early stage. Taking a fresh look at your text often reveals some issues. If possible, ask your friends or colleagues to review your text. They might notice something you could not.
How to Format a Thematic Essay
When it comes to thematic essay format, you need to find out what are the requirements in your assignment or which format is common in the institution you will be presenting your essay for. In case no special requirements were made for you, just choose one of the most popular formats for scholarly papers:
- APA paper format : typically used in natural sciences, education and psychology fields
- MLA: typically used for works in humanities
- Chicago: typically used in business, history, and fine arts fields.
Thematic Essay Example
Let’s illustrate the explanations above with a few theme essay examples. We’ll provide some real ones here so that your every question would be answered. Hopefully you’ll find some inspiration in these examples for your own winning paper! The examples can be found below. Please scroll down to find them.
Thematic Essay: Final Thoughts
In this article we have explored the theme essay concept in detail. Its central purpose and main definition were examined and a step by step guide for writing a strong one was suggested. We’ve also provided a few working examples for your convenience. Hopefully, all this information will be useful for your scholarly endeavors!
Feel free to check out our paper writing services ! We’ve got a team of skilled writers with expertise in different literary areas, ready to help you. They deliver high quality content, always on time.
Frequently Asked Questions About Theme Essay
1. what is the thematic statement.
A thematic statement typically takes the place of a thesis in a thematic essay. It consists of 1-2 complete sentences that express a theme which you have chosen for your work. This statement must convey the main message and also show what analysis will be done. It should be brief however as most of the details are to be provided in the main body.
2. What is the goal of thematic essay?
The thematic essay goal is to express an idea or some insights about the surrounding world and to change readers' minds about certain issues. As an author, you are expected to illustrate the team, provide all necessary explanations and conduct an analysis if needed. Besides, you typically should demonstrate familiarity with some literary interpretations and methods which are used to examine your theme.
3. How long should a theme essay be?
The minimum length of a theme essay is five paragraphs. One is for introduction, one for conclusion and remaining three for the main body. Of course, it can be more than that, depending on the depth of the theme that was chosen. The main rule is to keep your essay logical and concise, avoiding adding too many details. Otherwise your audience might get tired and the effect produced by your writing would be damaged.
4. What is a thematic essay history?
Thematic essay (history class) should be written to analyze some historical facts or significance of specific literary pieces. A typical case is examining different aspects of a controversial leader from the past or a political event that has produced a number of various important consequences. Or you might argue about a specific role of a certain book during a certain period or its influence on different nations or cultural groups.

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

How to Write a Thematic Essay With Explanations and Examples
26 December 2023
last updated
Thematic essays are common essay assignments in college across all disciplines. Basically, this guide begins with a definition of a thematic essay and provides sample topics for illustration. Next, the manual deconstructs the process of writing a thematic essay. Moreover, the guide covers three core stages of thematic essay writing: preliminary actions, establishing the essay’s foundation, and writing. Finally, the manual presents a sample outline and an example of a thematic essay to demonstrate a real writing situation where a student implements these guidelines of thematic essay writing correctly. Hence, students need to learn how to write a thematic essay.
Definition of a Thematic Essay
A thematic essay is a form of academic writing that requires an author to react to a particular question or theme. In this case, instructors expect students to develop a written reaction to a question or theme by connecting various pieces of information to reach a reasonable conclusion. Moreover, a thematic essay has a high demand for research and a critical examination of subtle relationships that exist between sources. Then, the research process yields a significant amount of information, which learners may use to generate numerous unique logical relationships that lead to rational inferences. Consequently, students may select any set of evidence with a clear, logical association provided that their central claim centers on a theme of interest.

Sample Topics for Thematic Essays
- A pure democracy.
- Privacy rights in the big data age.
- Life in prison and the ex-convict experience.
2. Sociology
- Major parenting issues of the 21 st century.
- Family bonds in immigrant families.
- Escaping the cycle of poverty.
3. Literature
- The significance of a muse.
- Corruption in 18 th century short stories.
- Female authors that left a mark on classical literature.
- Memories of the holocaust.
- Landmines on the modern political landscape.
- The cause of the collapse of Middle East alliances in the 20 th century.
5. Psychology
- Teenage confidence after the emergence of social media.
- The impact of abuse on the formation of relationships.
- The efficacy of proactive counseling.
How Do You Know if Your Paper Is Thematic?
A student can readily identify a thematic essay topic because it boldly pronounces a theme but does not hint at any specific point of view. In particular, the primary goal of a topic of a thematic essay is to inform readers of a theme rather than the particular approach of an author, which becomes more apparent in the introductory paragraph. Specifically, a thematic essay topic does not allow students to develop a particular supposition concerning a theme because authors realize that there may be multiple points of view concerning the idea of a thematic essay.
3 Steps For Writing an Effective Thematic Essay
Step 1: preliminary actions, a. define a topic.
The ability of students to define a topic is dependent on the extent to which they understand essay rubric and instructions. Basically, once learners receive thematic essay instructions, they should critically read their prompts to ensure that they comprehend all demands of writing requirements. Then, writers should use keywords from their instructions to develop one or more questions, which represent the expectations of instructors. Based on developed questions, students can create a topic that adequately captures the content of possible responses holistically. Also, authors must consider the information in the instructions, which establishes the leeway that they have in the selection of a topic, for example, choose a topic not covered in-class readings.
B. Identify a Purpose for Writing a Thematic Essay
The procedure of identifying a purpose occurs in two distinct stages: the selection of a general goal and defining a specific purpose. Basically, authors may use a thematic essay to achieve two general purposes: explanation and persuasion. In this case, expectations of instructors influence the choice of the general purpose of a thematic essay to a large extent. After learners pick the general purpose for writing an essay, they should create a specific purpose that shows the particular effect that their papers must have on readers. Mostly, writers generate a specific purpose from questions that represent thematic essay instructions. In turn, the early determination of the purpose is crucial because it affects the students’ approach to research and word choice during drafting.
C. Analyze an Audience
Before writing a thematic essay, students need to determine the characteristics and expectations of readers. Basically, knowledge concerning the characteristics and expectations of the audience is valuable because it allows authors to understand the interaction between the characteristics and attitudes toward a topic, the readers’ level of expertise, and the significance of misconceptions, which aid in selecting the appropriate presentation approach. Specifically, learners can determine the most effective organization patterns, identify the best evidence, and employ an accepted documentation style. Moreover, students ensure that a suitable level of explanation accompanies specialized terms that appear in a thematic essay.
D. Generate Ideas
After learners define the purpose and comprehend the needs and traits of the audience, they begin to develop ideas for the content of a thematic essay. Mostly, thematic essay assignments for a particular subject focus on topics that lecturers discuss in classrooms and other course readings. Consequently, students may generate ideas through brainstorming based on the relevant information from the unit and other related units that they encounter during their schooling. During brainstorming, writers engage in idea mapping and clustering, which enables them to keep track of relationships between ideas.
Step 2: Establishing a Foundation of a Thematic Essay
A. search for sources.
The author’s initial ideas regarding a topic act as the starting point for acquiring credible sources that support and refine those ideas. Basically, contemporary learners engage in electronic searchers to find useful and reliable sources for thematic essays. In this case, students should begin their search on the library’s website, which provides them with material that is reliable for academic writing . Also, library search engines have complex filter functionalities, which make the process of searching for academic sources quite simple. Then, authors turn to open-web searches using Google Scholar or other public search engines that generate a significantly larger number of sources. However, some articles may not be accessible to students. Moreover, the burden of determining the reliability of sources falls on authors when they use open-web search engines. In turn, students rely entirely on keywords or keyword combinations to generate working bibliographies.
B. Evaluate Sources
Working bibliographies undergo an intensive evaluation process to establish whether they meet the necessary quality standards for inclusion in a college-level thematic essay. In this case, the evaluation process involves two primary stages: relevance determination and reliability test. During relevance determination, authors should examine each source by using three criteria:
- The level of attention that the source gives to the topic.
- The suitability of the sources’ sophistication to the purpose and audience’s needs.
- Impact of publication date on the relevance of its information.
Next, the reliability test investigates five critical aspects:
- The origin of the source.
- The level of expertise of authors.
- Biases of a source in the context of existing literature.
- Availability and quality of the evidence supporting the source’s claims.
- Objectivity in the presentation of the author’s claims and handling of evidence.
C. Write an Annotated Bibliography
At this point, the revised working bibliography now contains fewer sources that relevant and reliable. In particular, students should engage in critical reading of all sources on the working bibliography to identify useful pieces of information that they may incorporate into a thematic essay. After reading each source, learners create an annotation that contains a summary of a source, ideas for using this source, and an assessment of this source. Besides the three main elements of an annotated bibliography entry, writers may choose to mention specific pieces of evidence, which are the most significant contributions of a source to a thematic essay. Typically, writers develop an annotated bibliography from notes that they make as they read through a text.
D. Develop an Outline
Based on an annotated bibliography, students create an essay outline . Basically, the content of an annotated bibliography entries allows learners to develop relationships between sources, which is essential because it begins to shape an essay structure . In this case, writers identify and group sources that support a general point, which splits a body of a thematic essay into discernible sections. Then, authors break down each general point into specific points that can exist as a body paragraph and assign appropriate sources to individual body paragraphs. Furthermore, scholars logically organize particular points and establish some form of flow within each section of a body paragraph. In turn, writers document the organization of general and specific ideas and the distribution of evidence in a list, like a format that allows for easy identification of hierarchy.
Step 3: Writing a Thematic Essay
A. design a working thesis.
A student develops a working thesis statement , which presents his or her central claim. Basically, questions that writers derive from assignment instructions and specific minor arguments listed in a thematic essay outline are the main pieces of information that they use to generate a thesis statement. Initially, a working thesis statement may appear as a simple combination of individual responses to assignment questions in the context of the information that forms an outline. However, authors must unite individual answers under a specific inference that demonstrates the significance of a thematic essay. Also, a working thesis statement undergoes multiple revisions, which occur randomly during the writing process.
B. Review an Outline
Once an author forms a working thesis statement, a person subjects an informal outline to a revision that results in the creation of a formal outline for a thematic essay. Basically, body paragraphs of a thematic essay are building blocks for a central claim. Consequently, learners must review an informal outline to ensure that there is an apparent logical build-up to the inference, which they announce in a thesis statement. During this review, students focus on the organization of minor arguments to ensure that body paragraphs contain a single minor idea while maintaining a rational relationship with other body paragraphs. Moreover, a formal outline contains a systematic arrangement where information with the same level of significance or roles has identical indentation or numbering.
C. Select Sources
Based on a formal outline, students make a final assessment of sources for each body paragraph. In particular, a formal outline contains some changes in its organization and the framing of minor arguments of a thematic essay. Also, these changes may affect the relevance of sources to each body paragraph’s argument. Then, the subdivision or merging of minor arguments may cause some sources to become inadequate because they do not extensively cover new minor ideas. Therefore, writers should check the suitability of each source to arguments it supports to ensure that each source provides strong, relevant, and accurate evidence before commencing the drafting process.
D. Draft a Paper
During the drafting stage, authors expand a thematic outline into a complete essay by changing statements and brief notes into coherent paragraphs. Basically, there is no fixed approach to the drafting of a thematic essay because students may start drafting at any point in a thematic essay with the aid of a formal outline. Nonetheless, it is an excellent practice for learners to begin drafting from a paragraph that they understand the best because it ensures that writers waste very little time in trying to overcome the fear of creating the first draft. In turn, scholars should allocate adequate time for drafting.
How to Perfect a Thematic Essay
1. revision, a. self-critic.
After completing the first draft, students undertake a self-conducted revision process, which involves rethinking and rewriting. Basically, the process of revision focuses on the evaluation of the evidence and organization of body paragraphs to ensure that they support a working thesis statement entirely. Further, learners revisit a working thesis statement to refine its wording and the claim its presents. Before starting the revision process, writers should take a break, which allows a brain to reset and attain a higher level of objectivity while revising. Moreover, scholars should use a checklist to reduce the risk of overlooking various crucial thematic essay dynamics during individual revision.
B. Peer Review
The individual revision process identifies the apparent flaws in content presentation, but numerous flaws may go unnoticed due to the authors’ subconscious biases concerning their writing styles . As a result, students should subject their thematic essays to a peer review by a classmate, tutor, parent, or writing center staff. In this case, learners should select a peer reviewer that best represents a member of the target audience. Moreover, authors may provide peer reviewers with a checklist to guide them through the revision process, especially if a person is not an expert editor. Then, students should assign the peer review process adequate time to allow reviewers to carry out the revision task comfortably. In turn, once writers receive feedback from peer reviewers, they consider comments in making the final revision of a paper.
A. Clarity and Effectiveness
The first consideration in the editing process is the clarity and effectiveness of sentences in a thematic essay. Basically, authors should edit each sentence to ensure that statements convey the intended meaning to readers. In this case, it is advisable to focus on six clarity issues, which are the most common in thematic essays: lack of parallelism, dangling modifiers, vague references to pronouns, incomplete sentences, and incorrect separation of sentences. Besides clarity, learners should evaluate the efficacy of each statement separately and as part of a paragraph. In turn, the effectiveness of statements revolves around the smoothness of transitions, conciseness, variability in sentence structure and length, the distinctiveness of the author’s voice, and emphasis on core ideas.
B. Surface Errors
The subsequent stage of the editing process involves editing for surface errors and documentation errors. In particular, students should strive to eliminate all surface errors because they divert the readers’ attention to meaning, although some writing errors do not necessarily change the meaning of sentences. For example, learners can edit surface errors by using six-item criteria: spelling errors, comma splices, sentence fragments, verb errors, punctuation errors, and pronoun errors. Moreover, students should not attempt to conduct clarity and effectiveness editing simultaneously with surface error editing, which may result in poor editing because of the extensive nature of rules governing the English language. In turn, the final step in editing is the correction of any documentation errors while referring to the appropriate style manual.
Sample Outline for a Thematic Essay
I. introduction.
A. Hook sentence. B. Background information. C. Thesis statement.
A. First paragraph
1. The idea for the first paragraph. 2. Evidence supporting this paragraph’s claim. 3. Interpretation and analysis of the evidence.
- First specific deduction from the evidence.
- Second specific deduction from the evidence.
4. A concluding statement that demonstrates the link between the first paragraph’s claim and thesis statement.
B. Second body paragraph
1. The idea for the second paragraph. 2. Evidence supporting this paragraph’s claim. 3. Interpretation and analysis of the evidence.
4. A concluding statement that demonstrates the link between the second paragraph’s claim and thesis statement.
C. Third body paragraph
1. The idea for the third paragraph. 2. Evidence supporting this paragraph’s claim. 3. Interpretation and analysis of the evidence.
4. A concluding statement that demonstrates the link between the third paragraph’s claim and thesis statement.
III. Conclusion
A. Restatement of the thesis statement. B. Summary of the three minor arguments in the body paragraphs. C. Closing remarks emphasizing the significance of the central claim in the context of the three minor arguments.
Commentary on a Thematic Essay Outline
1. identify a central theme.
The audience can determine the central theme of a thematic essay from a thesis statement or an overview of topic statements. Basically, a well-composed thesis statement must explicitly mention the central theme or implicitly hint at the central theme. Alternatively, the audience can read through topic sentences and correctly speculate the central theme of a thematic essay because minor arguments in individual body paragraphs are building blocks of a thesis statement. However, the readers’ ability to identify the central theme from a formal outline is dependent on their pre-existing knowledge concerning a topic because an outline uses statements and annotations with little explanation.
2. Uniqueness
A thematic essay stands out from other types of essays because of the high level of freedom that writers enjoy during authorship. During the writing of a thematic essay, authors can choose any purpose or a combination of purposes to use in different sections of 5 parts of an essay , which is a luxury that argumentative essays and expository essays do not extend to writers. Also, essay instructions for a thematic essay tend to define a broad scope for research, which implies that authors may develop a wide variety of arguments. In turn, the expansive nature of the subject of a paper is not present for argumentative essays, which forces students to choose one of the two sides of a controversial issue.
Outlining a Thematic Essay
The introduction section is the first part of a thematic essay, which consists of three main elements: hook, background information, and thesis statement. Firstly, a hook is the first statement of an essay that plays the role of capturing the audience’s attention through creative wording, which gives them a reason to read the entire essay. Since students know how to write a hook , they provide the essential background information that readers require to understand a thesis statement. Moreover, the background information element does not have a fixed length. Instead, it is dependent on the complexity of a thesis statement and the overall length of a thematic essay. Also, a thesis statement is the final item of the introductory paragraph. In turn, the length of introductions is approximately 10% of the essay’s word count.
II. Body Paragraphs
A. topic sentence.
A topic sentence contains a minor claim that an author discusses within a paragraph. For example, its primary role is to establish content boundaries, which ensures that students focus on a particular idea in each paragraph. Moreover, a topic statement should present a minor argument and mention a relation that it has to the central idea or make a tacit suggestion of its link to a thesis statement. Therefore, writers should avoid the use of in-text citations in a topic statement because it implies that an idea is not original.
B. Evidence
After a topic sentence, students unveil the evidence that supports their claims. In college writing, an in-text citation should accompany any evidence that learners introduce into a thematic essay to direct readers to its origin. Also, learners should rely heavily on summary and paraphrasing as opposed to a direct quotation from sources. Nevertheless, some thematic essay instructions may specify a particular technique that writers must use when integrating evidence into a paper.
C. Evaluation
This element of a paragraph structure allows authors to explain the significance of the evidence to the paragraph’s argument. Firstly, students provide an interpretation of the evidence, which informs the audience of the meaning of the evidence in the context of a source text. Then, writers explain the value of the evidence in developing a reasonable justification for the idea proposed in topic sentences. In turn, learners should avoid the inclusion of lengthy pieces of evidence because it creates a situation where the voice of sources is more dominant than the author’s voice.
D. Concluding Statement
A concluding statement emphasizes the logical relationship that exists between the topic sentence, evidence, evaluation, and thesis statement. In some cases, it may establish the relationship of a paragraph with the preceding paragraph. Also, students should ensure that a concluding sentence of a paragraph does not contain a meaningless summary of the key pieces of evidence. Then, a concluding statement must not contain any new evidence because there is no opportunity to explain the contribution of the evidence in supporting the paragraph’s argument.
A concluding paragraph has three critical features: a restatement of the main claim, a summary of minor arguments, and closing remarks. Basically, the opening statement of a thematic essay reminds students of the central argument by using new words and syntax. After the opening statement, learners summarize minor claims that appear in individual body paragraphs while maintaining a logical organization, which is identical to the arrangement of ideas in the body. Finally, authors write a strong closing statement that knits together the introduction, thesis statement, and minor claims to create a lasting impression on the audience. Moreover, students should ensure that they do not introduce new evidence or arguments in a concluding paragraph. In turn, authors must not apologize for a lack of expertise on a topic or make absolute claims because it diminishes the efficacy of the conclusion.
Example of a Thematic Essay
Topic: Recruitment of Terrorists
I. Sample Introduction of a Thematic Essay
Terrorism is a global problem, which appears to be spreading despite an increment in the efforts to suppress its growth. Basically, the prevention of recruitment is a crucial counterterrorism strategy. Moreover, its efficacy is dependent on the understanding of the terrorists’ recruitment techniques. In turn, the terrorist groups’ recruitment methods focus on the target’s identity crisis, which puts a potential member at risk of falling for the ‘appeal’ of terrorism.
II. Examples of Body Paragraphs in a Thematic Essay
A. motivation.
An individual’s desire to be part of a movement that is effecting a radical change in society is a significant motivator for participation in terrorism. For example, recent studies show that terrorist groups begin conversations with most young recruits on social media platforms, which discuss topics concerning social, political, and economic oppression (Jacks, 2020). Basically, this finding suggests that young people in contemporary society have a desire to correct the ‘wrongs’ in society as a means of identity. Consequently, terrorists use the increased sensitivity to social injustices as a common ground to initiate and build a relationship with a prospective recruit. In turn, the youth’s strong desire to do something to stop social injustices that their respective governments ignore leaves them vulnerable to radicalization by terrorist groups.
B. Religious Beliefs
Fanatical religious belief may drive an individual to support or participate in terrorism for the sake of being part of a group. According to Mohammed (2020), the constant pressure from religious parents causes the blind indoctrination of adolescents and young adults, which enables recruiters from terrorist groups to present religious concepts as justifications for terrorism, for example, the holy war. In this case, Mohammed concedes that the mosque is an ideal site for the recruitment of terrorism because of the presence of youth with highly impressionable minds. Moreover, youths depend on teachings at places of worship for knowledge that defines their perspective of the world. As a result, terrorist recruiters disguising as spiritual leaders can easily nurture fanatical beliefs, which endorse terrorist activities. Eventually, a feeling of separation from the conservative believers pushes them to pursue groups that share their fanatical religious beliefs.
C. Recruiting
The loss of a family member to counterterrorism activities may act as a motivation factor for grievers that are trying to re-establish their identities because they no longer fit in the traditional social structures. For instance, Tobias (2020) argues that recruiters prey on the pain of grieving family members by offering them retribution as a solution to the overwhelming feeling of incompleteness. After the death of a family member, the emotional turmoil increases the susceptibility of individuals to the idea that terrorist acts are an appropriate response to the ‘killers’ of their loved ones. Often, recruitment occurs during this unstable state and encourages the individual to relive the pain each day, which results in permanent erosion of their former identity. Accordingly, grievers may find themselves as sympathizers of terrorism, which leads to active or passive participation.
III. Sample Conclusion of a Thematic Essay
Most members of terrorist organizations experience an identity crisis at the time of recruitment. Basically, the need to gain membership to a group, which fights against social injustices, tolerates fanatical religious beliefs, or seeks revenge for the death of loved ones, is a sign that identity crisis is common characteristics in recruits. In turn, current counterterrorism initiatives should seek to break the cycle of recruitment, which will weaken terrorist groups.
Takeaway on How to Write a Good Thematic Essay
- Students should define a narrow topic to guide them in generating ideas in response to a thematic essay prompt.
- The characteristics and expectations of the audience are vital in determining an appropriate presentation approach.
- Before drafting a thematic essay, authors must create a formal outline and annotated bibliography, which are critical for organization and evidence selection.
- The maintenance of a high level of fluidity during drafting is critical during drafting because it allows writers to experiment with different styles of expression.
- Revision and editing are aspects of the writing process that a student should not take lightly.
- All body paragraphs must adhere to the four-element paragraph structure.
- The conclusion of a thematic essay should not contain any new evidence or arguments.
- Learners must compose a thesis statement that captures a theme that instructors highlight in essay prompts.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles
How to write a profile essay with tips and examples, 670 personal essay topics & free ideas.
How to Write a Thematic Essay

Every piece of writing ever written has its agenda. Whether it’s to teach a lesson or show the impact of a particular emotion or action, a central theme can be developed. The goal for us as readers is to uncover what the author was trying to tell us between the lines in their literature. When we do finally discover it, we’ve accomplished the first step of thematic essay writing! Let’s see below how to write a thematic essay with our papers writing service .
What Is a Thematic Essay?
Let’s look at the thematic essay definition; a thematic essay is a piece of writing in which an author develops the central theme in some literature using literary devices like foreshadowing, imagery, personification, etc.
A professional essay writer will uncover the primary subject, elaborate upon the literary devices employed, and express the overall significance of the theme. The primary challenge comes from the fact that although there are various subjects, finding the most meaningful and impactful one can be challenging.
Naturally, each person has their own varied interpretation, making it hard to agree on a central theme wholesomely. In short, a well written thematic essay comes from a healthy central idea that is conclusively proven via literary devices and logical arguments.
If you're thinking " i need help with my homework " - contact us!
How to Pick a Thematic Topic?
A crucial aspect of writing a good thematic essay is choosing a theme. Follow the hints listed below to help you create a thematic topic:

Brainstorm from your own experiences. Recall what you were talking about in class, with your mates or parents. Do some of these conversations remind you of some book, novel or another piece of literature?
Write down every idea that comes to mind. Sometimes, your most absurd ideas are the best way to go.
List your favourite literature pieces. Which literature piece was the most touching for you? Try to analyze its subject and problems the author built upon within the story; it might help you come up with your own ideas.
Look at the details of other literature pieces: You might find some interesting details within other literature that can help you come up with your theme.
Still have no idea what to write about? No worries, we have your back.
Thematic Essay Topics
- What is George Orwell’s deliberation in portraying a “Perfect Utopia” in his book 1984?
- What main idea is George Orwell painting about Communism in the book Animal Farm?
- What is Harper Lee saying about innocence in her novel To Kill A Mockingbird?
- What is John Steinbeck saying about loneliness and isolation in Of Mice and Men?
- What is F. Scott Fitzgerald saying about the American Dream in The Great Gatsby?
Still Not in the Mood to Write Your thematic essay?
Send us your write my essays request.
How to Find and Explore the Central Theme
As stated before, uncovering the main subject and central theme respectively is the first significant step in a thematic paper. However, with so many things going on within the literature, it may be difficult to interpret the central theme accurately. To make sure you choose it correctly, follow these steps:
1. Summarize the literature: What main idea is the author trying to purvey? Usually, there will be many hints along the way, so choosing the right direction may not be so challenging.
2. Pick the most prevalent subject: One thing to note is the significant difference between a subject and a theme. A subject is the general topic of conversation—whether it be love, bravery, deception, etc. A theme is a specific point the author is making about said subject. So, find the talking point that is most commonly being brought up. This will be the focal point of the essay.
3. Read between the lines: After finding the most suitable subject, decipher what main point the author is trying to make. This will become clearer as you get deeper into the literature since clues and examples will appear frequently. After fully deciphering the central theme, there is one more significant step.
4. Overall significance: What is the overall significance that comes from the author’s point? What can be taken from this and applied to our personal lives? In other words, what is the lesson from all of this? What have we learned?
Feeling difficult to write thematic essay? Leave us a notice and our persuasive essay writer we'll help.
Thematic Essay Outline
The thematic essay has several key components. First of all, it should be five paragraphs or more, depending on the depth of the theme. Next, it should have a concrete thesis statement, which, in other words, is the thematic statement that comes from the main subject. The introduction presents the reader with the subject and the thesis statement. The body paragraphs each discuss one literary element or more to defend the validity of your thesis, all the while providing many supporting details from the text itself. Lastly, the thematic essay conclusion summarizes the main points presented and finishes off with a statement of significance.
Follow the link to learn more about HOW TO CREATE A WINNING OUTLINE
The thematic essay introduction presents the main subject of discussion in a captivating way. The first sentence of the intro should be a hook statement that makes some intriguing claim about the subject of discussion. If done correctly, this will grab your reader's attention. Afterwards, provide any necessary background information from the literature that will help the audience understand your claims later on. Lastly, put together a well thought out thesis statement that reflects the central theme of the novel.
The body paragraphs follow a thematic essay format. Since each body paragraph’s purpose should be to present a literary device as evidence, the topic sentence should introduce the claim and gateway into the evidence. Every topic sentence must mention a literary device and its relationship to the literature.
Afterwards, to validate your claim, use examples from the book that strengthen the reasoning of your statement. These can be actions from the plot or quotations that are parallel with the central theme. It’s imperative to explain how the action/quote links back to your thesis statement, as it shows that you can support your logic.
Remember: each claim must use a literary device. It can not just be a random moment or inference. Thematic essays are all about proving thesis statements through the use of critical literary devices.
The thematic essay conclusion has three main objectives to complete before wrapping up the entire paper. It should not present any new information or facts, but should summarize the information already given. First of all, restate your thesis statement in a new way. Then, summarize the central claims you made within the body of your paper and their influence on the thesis statement. To finish off the entire work, present an overall concluding statement with a global analysis of the subject. Leave your reader with another hook, making him/her interested in digging deeper into the topic.
Try also read an article on poetry analysis essay , it could be useful and can give you new insights.
Thematic Essay Example
The best way to familiarise yourself with this type of writing is to learn from an example.
Even though the ancient Greek cities of Athens and Sparta were geographically close to each other, they had very distinct cultures, lifestyles, values, and political systems that defined them. The following paper compares and contrasts the cultural impacts of the two cities by examining some of the duties and responsibilities of the citizenry as well as the different values that were deemed important. The paper further evaluates the impact of accomplishments that would have been left by both city-states on the history of western civilization.
Wrap Things Up
Before submitting your thematic essay, make sure to check a couple of things to correct any possible errors.

- Double-check and confirm that the central theme you have decided is the one that the author likely meant to focus on. Unless you can provide a secondary issue and present it strongly enough as a primary, validate the primary subject.
- Go through and proofread your entire paper. Nothing makes reading more irritating than grammatical mistakes, clean that stuff up as much as possible.
- Get a second pair of eyes to read through your paper. It’s best to ask a classmate for help, as they most likely have or had a similar assignment. Another great way to polish things up is to ask one of our writers to give you some helpful advice.
We also recommend reading about Jem Finch character traits , our readers find it very interesting.
Having a Trouble with Your Thematic Essay?
Having a hard time thinking up a proper topic to write about? Or, do you have one but are having a hard time deciphering the theme? Let our custom essay writing service do all the work for you. Check out our price calculator to estimate the cost of your assignment.
Related Articles
%20(2).webp)

Theme Definition
What is theme? Here’s a quick and simple definition:
A theme is a universal idea, lesson, or message explored throughout a work of literature. One key characteristic of literary themes is their universality, which is to say that themes are ideas that not only apply to the specific characters and events of a book or play, but also express broader truths about human experience that readers can apply to their own lives. For instance, John Steinbeck's The Grapes of Wrath (about a family of tenant farmers who are displaced from their land in Oklahoma) is a book whose themes might be said to include the inhumanity of capitalism, as well as the vitality and necessity of family and friendship.
Some additional key details about theme:
- All works of literature have themes. The same work can have multiple themes, and many different works explore the same or similar themes.
- Themes are sometimes divided into thematic concepts and thematic statements . A work's thematic concept is the broader topic it touches upon (love, forgiveness, pain, etc.) while its thematic statement is what the work says about that topic. For example, the thematic concept of a romance novel might be love, and, depending on what happens in the story, its thematic statement might be that "Love is blind," or that "You can't buy love . "
- Themes are almost never stated explicitly. Oftentimes you can identify a work's themes by looking for a repeating symbol , motif , or phrase that appears again and again throughout a story, since it often signals a recurring concept or idea.
Theme Pronunciation
Here's how to pronounce theme: theem
Identifying Themes
Every work of literature—whether it's an essay, a novel, a poem, or something else—has at least one theme. Therefore, when analyzing a given work, it's always possible to discuss what the work is "about" on two separate levels: the more concrete level of the plot (i.e., what literally happens in the work), as well as the more abstract level of the theme (i.e., the concepts that the work deals with). Understanding the themes of a work is vital to understanding the work's significance—which is why, for example, every LitCharts Literature Guide uses a specific set of themes to help analyze the text.
Although some writers set out to explore certain themes in their work before they've even begun writing, many writers begin to write without a preconceived idea of the themes they want to explore—they simply allow the themes to emerge naturally through the writing process. But even when writers do set out to investigate a particular theme, they usually don't identify that theme explicitly in the work itself. Instead, each reader must come to their own conclusions about what themes are at play in a given work, and each reader will likely come away with a unique thematic interpretation or understanding of the work.
Symbol, Motif, and Leitwortstil
Writers often use three literary devices in particular—known as symbol , motif , and leitwortstil —to emphasize or hint at a work's underlying themes. Spotting these elements at work in a text can help you know where to look for its main themes.
- Near the beginning of Romeo and Juliet , Benvolio promises to make Romeo feel better about Rosaline's rejection of him by introducing him to more beautiful women, saying "Compare [Rosaline's] face with some that I shall show….and I will make thee think thy swan a crow." Here, the swan is a symbol for how Rosaline appears to the adoring Romeo, while the crow is a symbol for how she will soon appear to him, after he has seen other, more beautiful women.
- Symbols might occur once or twice in a book or play to represent an emotion, and in that case aren't necessarily related to a theme. However, if you start to see clusters of similar symbols appearing in a story, this may mean that the symbols are part of an overarching motif, in which case they very likely are related to a theme.
- For example, Shakespeare uses the motif of "dark vs. light" in Romeo and Juliet to emphasize one of the play's main themes: the contradictory nature of love. To develop this theme, Shakespeare describes the experience of love by pairing contradictory, opposite symbols next to each other throughout the play: not only crows and swans, but also night and day, moon and sun. These paired symbols all fall into the overall pattern of "dark vs. light," and that overall pattern is called a motif.
- A famous example is Kurt Vonnegut's repetition of the phrase "So it goes" throughout his novel Slaughterhouse Five , a novel which centers around the events of World War II. Vonnegut's narrator repeats the phrase each time he recounts a tragic story from the war, an effective demonstration of how the horrors of war have become normalized for the narrator. The constant repetition of the phrase emphasizes the novel's primary themes: the death and destruction of war, and the futility of trying to prevent or escape such destruction, and both of those things coupled with the author's skepticism that any of the destruction is necessary and that war-time tragedies "can't be helped."
Symbol, motif and leitwortstil are simply techniques that authors use to emphasize themes, and should not be confused with the actual thematic content at which they hint. That said, spotting these tools and patterns can give you valuable clues as to what might be the underlying themes of a work.
Thematic Concepts vs. Thematic Statements
A work's thematic concept is the broader topic it touches upon—for instance:
- Forgiveness
while its thematic statement is the particular argument the writer makes about that topic through his or her work, such as:
- Human judgement is imperfect.
- Love cannot be bought.
- Getting revenge on someone else will not fix your problems.
- Learning to forgive is part of becoming an adult.
Should You Use Thematic Concepts or Thematic Statements?
Some people argue that when describing a theme in a work that simply writing a thematic concept is insufficient, and that instead the theme must be described in a full sentence as a thematic statement. Other people argue that a thematic statement, being a single sentence, usually creates an artificially simplistic description of a theme in a work and is therefore can actually be more misleading than helpful. There isn't really a right answer in this debate.
In our LitCharts literature study guides , we usually identify themes in headings as thematic concepts, and then explain the theme more fully in a few paragraphs. We find thematic statements limiting in fully exploring or explaining a the theme, and so we don't use them. Please note that this doesn't mean we only rely on thematic concepts—we spend paragraphs explaining a theme after we first identify a thematic concept. If you are asked to describe a theme in a text, you probably should usually try to at least develop a thematic statement about the text if you're not given the time or space to describe it more fully. For example, a statement that a book is about "the senselessness of violence" is a lot stronger and more compelling than just saying that the book is about "violence."
Identifying Thematic Statements
One way to try to to identify or describe the thematic statement within a particular work is to think through the following aspects of the text:
- Plot: What are the main plot elements in the work, including the arc of the story, setting, and characters. What are the most important moments in the story? How does it end? How is the central conflict resolved?
- Protagonist: Who is the main character, and what happens to him or her? How does he or she develop as a person over the course of the story?
- Prominent symbols and motifs: Are there any motifs or symbols that are featured prominently in the work—for example, in the title, or recurring at important moments in the story—that might mirror some of the main themes?
After you've thought through these different parts of the text, consider what their answers might tell you about the thematic statement the text might be trying to make about any given thematic concept. The checklist above shouldn't be thought of as a precise formula for theme-finding, but rather as a set of guidelines, which will help you ask the right questions and arrive at an interesting thematic interpretation.
Theme Examples
The following examples not only illustrate how themes develop over the course of a work of literature, but they also demonstrate how paying careful attention to detail as you read will enable you to come to more compelling conclusions about those themes.
Themes in F. Scott Fitzgerald's The Great Gatsby
Fitzgerald explores many themes in The Great Gatsby , among them the corruption of the American Dream .
- The story's narrator is Minnesota-born Nick Caraway, a New York bonds salesman. Nick befriends Jay Gatsby, the protagonist, who is a wealthy man who throws extravagant parties at his mansion.
- The central conflict of the novel is Gatsby's pursuit of Daisy, whom he met and fell in love with as a young man, but parted from during World War I.
- He makes a fortune illegally by bootlegging alcohol, to become the sort of wealthy man he believes Daisy is attracted to, then buys a house near her home, where she lives with her husband.
- While he does manage to re-enter Daisy's life, she ultimately abandons him and he dies as a result of her reckless, selfish behavior.
- Gatsby's house is on the water, and he stares longingly across the water at a green light that hangs at the edge of a dock at Daisy's house which sits across a the bay. The symbol of the light appears multiple times in the novel—during the early stages of Gatsby's longing for Daisy, during his pursuit of her, and after he dies without winning her love. It symbolizes both his longing for daisy and the distance between them (the distance of space and time) that he believes (incorrectly) that he can bridge.
- In addition to the green light, the color green appears regularly in the novel. This motif of green broadens and shapes the symbolism of the green light and also influences the novel's themes. While green always remains associated with Gatsby's yearning for Daisy and the past, and also his ambitious striving to regain Daisy, it also through the motif of repeated green becomes associated with money, hypocrisy, and destruction. Gatsby's yearning for Daisy, which is idealistic in some ways, also becomes clearly corrupt in others, which more generally impacts what the novel is saying about dreams more generally and the American Dream in particular.
Gatsby pursues the American Dream, driven by the idea that hard work can lead anyone from poverty to wealth, and he does so for a single reason: he's in love with Daisy. However, he pursues the dream dishonestly, making a fortune by illegal means, and ultimately fails to achieve his goal of winning Daisy's heart. Furthermore, when he actually gets close to winning Daisy's heart, she brings about his downfall. Through the story of Gatsby and Daisy, Fitzgerald expresses the point of view that the American Dream carries at its core an inherent corruption. You can read more about the theme of The American Dream in The Great Gatsby here .
Themes in Chinua Achebe's Things Fall Apart
In Things Fall Apart , Chinua Achebe explores the theme of the dangers of rigidly following tradition .
- Okonkwo is obsessed with embodying the masculine ideals of traditional Igbo warrior culture.
- Okonkwo's dedication to his clan's traditions is so extreme that it even alienates members of his own family, one of whom joins the Christians.
- The central conflict: Okonkwo's community adapts to colonization in order to survive, becoming less warlike and allowing the minor injustices that the colonists inflict upon them to go unchallenged. Okonkwo, however, refuses to adapt.
- At the end of the novel, Okonkwo impulsively kills a Christian out of anger. Recognizing that his community does not support his crime, Okonkwo kills himself in despair.
- Clanswomen who give birth to twins abandon the babies in the forest to die, according to traditional beliefs that twins are evil.
- Okonkwo kills his beloved adopted son, a prisoner of war, according to the clan's traditions.
- Okonkwo sacrifices a goat in repentence, after severely beating his wife during the clan's holy week.
Through the tragic story of Okonkwo, Achebe is clearly dealing with the theme of tradition, but a close examination of the text reveals that he's also making a clear thematic statement that following traditions too rigidly leads people to the greatest sacrifice of all: that of personal agency . You can read more about this theme in Things Fall Apart here .
Themes in Robert Frost's The Road Not Taken
Poem's have themes just as plot-driven narratives do. One theme that Robert Frost explores in this famous poem, The Road Not Taken , is the illusory nature of free will .
- The poem's speaker stands at a fork in the road, in a "yellow wood."
- He (or she) looks down one path as far as possible, then takes the other, which seems less worn.
- The speaker then admits that the paths are about equally worn—there's really no way to tell the difference—and that a layer of leaves covers both of the paths, indicating that neither has been traveled recently.
- After taking the second path, the speaker finds comfort in the idea of taking the first path sometime in the future, but acknowledges that he or she is unlikely to ever return to that particular fork in the woods.
- The speaker imagines how, "with a sigh" she will tell someone in the future, "I took the road less travelled—and that has made all the difference."
- By wryly predicting his or her own need to romanticize, and retroactively justify, the chosen path, the speaker injects the poem with an unmistakeable hint of irony .
- The speaker's journey is a symbol for life, and the two paths symbolize different life paths, with the road "less-travelled" representing the path of an individualist or lone-wolf. The fork where the two roads diverge represents an important life choice. The road "not taken" represents the life path that the speaker would have pursued had he or she had made different choices.
Frost's speaker has reached a fork in the road, which—according to the symbolic language of the poem—means that he or she must make an important life decision. However, the speaker doesn't really know anything about the choice at hand: the paths appear to be the same from the speaker's vantage point, and there's no way he or she can know where the path will lead in the long term. By showing that the only truly informed choice the speaker makes is how he or she explains their decision after they have already made it , Frost suggests that although we pretend to make our own choices, our lives are actually governed by chance.
What's the Function of Theme in Literature?
Themes are a huge part of what readers ultimately take away from a work of literature when they're done reading it. They're the universal lessons and ideas that we draw from our experiences of works of art: in other words, they're part of the whole reason anyone would want to pick up a book in the first place!
It would be difficult to write any sort of narrative that did not include any kind of theme. The narrative itself would have to be almost completely incoherent in order to seem theme-less, and even then readers would discern a theme about incoherence and meaninglessness. So themes are in that sense an intrinsic part of nearly all writing. At the same time, the themes that a writer is interested in exploring will significantly impact nearly all aspects of how a writer chooses to write a text. Some writers might know the themes they want to explore from the beginning of their writing process, and proceed from there. Others might have only a glimmer of an idea, or have new ideas as they write, and so the themes they address might shift and change as they write. In either case, though, the writer's ideas about his or her themes will influence how they write.
One additional key detail about themes and how they work is that the process of identifying and interpreting them is often very personal and subjective. The subjective experience that readers bring to interpreting a work's themes is part of what makes literature so powerful: reading a book isn't simply a one-directional experience, in which the writer imparts their thoughts on life to the reader, already distilled into clear thematic statements. Rather, the process of reading and interpreting a work to discover its themes is an exchange in which readers parse the text to tease out the themes they find most relevant to their personal experience and interests.
Other Helpful Theme Resources
- The Wikipedia Page on Theme: An in-depth explanation of theme that also breaks down the difference between thematic concepts and thematic statements.
- The Dictionary Definition of Theme: A basic definition and etymology of the term.
- In this instructional video , a teacher explains her process for helping students identify themes.

- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1908 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,181 quotes across 1908 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
- Dynamic Character
- Falling Action
- Anadiplosis
- Rhetorical Question
- Antanaclasis
- Static Character
- Bildungsroman
- Alliteration
- Rhyme Scheme

How to Write a Thematic Essay?
06 August, 2020
12 minutes read
Author: Kate Smith
The road to graduation from any educational institution is lined with essays and written assignments – and the majority of these happen to be thematic essays, as they are supposed to demonstrate that the students understand the topic or material well. A thematic essay is almost as old as writing is, for it focuses on investigating a topic to provide detailed analysis and evidence of why a certain claim can be made.

What is a Thematic Essay?
Although this type of essay is commonly used to analyze some historical facts or a specific literary piece and its significance, a thematic essay can be assigned on a variety of subjects. It is also a traditional classroom essay that may be a part of different exams, so students may be required to craft a thematic essay within limited time, sticking to the topic provided. This is the main reason why they consider thematic essays difficult, but whenever there’s a longer deadline and a choice of topics, the writing process is easier.
However, there’s an important thing that everyone who’s wondering ‘what is a thematic essay?’ needs to know. This type of essay mainly lets the teacher determine your knowledge of the material, and it should demonstrate your comprehension of the topic that you can back up with solid arguments and relevant examples. But proper structure is just as essential to your writing as the scope of the topic. All of the points you want to make, as well as the supporting evidence must be organized in a clear, consecutive way. If your essay lacks focus or is illogical in its organization, your readers will not be able to recognize neither the thoroughness of your research, nor the significance of your critical thinking. They might even have trouble following what evidence you found to help you arrive at a certain conclusion.
How to Find and Explore the Central Theme?
To tackle this type of essay, you often have to narrow down a topic that’s too broad before getting started on your writing. A theme is what an author portrays in a literary work, or the specific point the author is making. Often, it is the most frequently discussed one, or it is a lesson of the greatest overall significance that can be derived from the work and applied to our lives. Thus, to effectively plan out how you are going to write a thematic essay, identify the theme first. Focus on the main point the author is trying to make about a particular subject, the message he is trying to convey, why it is relevant or important at the moment, and the way the reader can benefit from it.
That’s why having a place to start and an outline to follow lays the groundwork for your thematic essay. It is the most important step in the entire essay writing process.
Thematic Essay Outline
By using an outline to shape your essay, you have a format to follow that ensures knowledge of the topic, addressing all the questions of the assignment, and keeping all of the points you want to make well-organized. A thematic essay outline lets you effectively draw parallels between different facts, formulate a coherent and detailed evaluation of the topic, and see whether something in the essay is lacking or needs to be rearranged and revised.
Some essay types may have less rigid layouts and writing requirements, allowing for more creativity and freedom when it comes to formatting. However, this is not the case with instructions on how to write a thematic essay. Just as with other traditional essays, there should be at least five paragraphs in a thematic essay, including an introduction with a thesis statement, three body paragraphs that will support your thesis with relevant arguments and examples, and a logical conclusion to wrap everything up at the end.
Introduction
Generally, to write a thematic essay you need to have an idea of what your thesis will be, how your body paragraphs will prove it, and how you are going to summarize all of the arguments detailed in the body of the essay in your conclusion. The introduction has to present the main subject of your essay as well as any necessary background information and your thesis statement. At the same time, it should be interesting enough to make the reader want to learn more about the topic. The opening sentence of the introduction is often referred to as a ‘hook’ because it is supposed to grab the reader’s attention. For this purpose, it can evoke anticipation, controversy, irony, or ask a question. The thesis statement is very important because it gives your topic a direction and a specific purpose.
The thesis statement lays the ground for further analysis, for answering a specific question, asserting an opinion or explaining how and why something works (or has worked/failed to produce an expected result). Think of your thesis statement as a compelling and concise headline that gives the reader a good idea of what the rest of the paper is about and what to expect next. It should be engaging, but not confusing to your audience. Have you ever been extremely disappointed by reading an article or watching a movie because it wasn’t what the headline, magazine cover or a movie trailer promised it to be? To make sure your reader doesn’t feel like that, you want your thesis to be integral to the essay and to all of the evidence that you provide in the following body paragraphs. Quite often, a thesis statement needs a few revisions to acquire more focus and clarity as you add the body paragraphs to your thematic essay.
Body paragraphs
While the 5-paragraph structure gives you a basic layout to work with, it should have three body paragraphs because the thesis must be supported by at least three significant arguments. However, unless the essay has a required length, you can include more supporting facts or examples. There may be more body paragraphs than just three, depending on the details of the assignment or the points you are required to address, but keep in mind that your essay should be concise and devoid of wordiness. Usually, the essay writer should focus on one point or sub-topic per paragraph, but depending on the complexity of the topic, the quantity of paragraphs for validating each claim or explaining your reasoning may vary.
You can think of body paragraphs as building blocks that include expert quotes or specific examples to add weight to them, as well as to your arguments. This is the ‘meat of your essay’ as long as you make sure that you explain the logic behind each quotation or evidence supporting your claim, and that it is in sync with your thesis statement. Such connections are essential as they tie not only the evidence and arguments, but an entire essay together.
The conclusion is not simply a reiterated thesis, but a reinforced one. However, it’s important to keep in mind that it should not introduce any new facts not discussed in the body of a thematic essay. The conclusion has to summarize the information presented in the essay, briefly going over the main ideas or claims and explaining how they influence your thesis. Finally, it should wrap up your essay in the most meaningful way, emphasizing the significance and relevance of your topic.

Thematic Essay Examples
Check the examples of thematic essays to use as writing models:
https://www.template.net/business/essay/five-paragraph-essay-template/
Thematic essay topics
To sum up, reading some properly structured thematic essay examples may be the most helpful tip for understanding what your essay should look like, and how to organize your thoughts into a logical sequence. Besides, a list of the most commonly used thematic essay topics is a frequent search query along with ‘thematic essay examples’, as it helps students to get an idea of what to expect at exams.
US History Thematic Essay
In this essay, there will be fewer words that address the reader. The purpose of this writing is to present a balanced analysis of a topic based on facts, explaining a topic in a logical and straightforward manner.
US History thematic essay example topics:
- Major movements in U.S. history
- Major advances in U.S. history
- Significant government reforms
- U.S. Presidents and their major decisions
- U.S. wars and conflicts
Global Regents Thematic Essay
These topics are likely to feature broad concepts, but they usually include tasks and suggestions that are more specific. In your essay, you are supposed to address this detailed task and the issues, concepts or questions it prompts you to explain or interpret. Using examples from your course of global history or geography is also required in your thematic essay.
Global Regents thematic essay example topics:
- Impact of colonizations on world history
- Migrations of people and their effects
- Major characteristics of world civilizations
- Cultures and their contributions
- Economic Systems
- Political Systems
- The turning points in history (revolutions, conflicts, wars)
- Revolutions and clashing of ideas
- Revolutions and new discoveries
- Scientific development
- Technological progress
- Human rights: impactful leaders and their ideas
- Human rights violations
Belief Systems Thematic Essay
A belief system is a way a group or an individual regards religious or philosophical principles. The beliefs that have formed major religions or a mainstay of a civilization may be similar or different, but each belief system has influenced the lives of its followers as well as the history, culture, politics, or economy of a specific nation or country.
Belief Systems thematic essay example topics:
- How belief systems influenced ancient civilizations?
- How did a belief form a religion?
- Cultures as systems of interconnections between humans
- The role of religion in Ancient Roman society
- The three major monotheistic religions: Judaism, Christianity and Islam
- Judaism: the first monotheistic religion
- The personal belief system and life values
- Compare Christianity to another religion. Are there more similarities or differences?
- Compare two struggles for religious freedom in different countries and time periods
- What makes all struggles for religious freedom similar?
The bottom line
While students often have difficulties writing thematic essays, these are not the most complicated tasks to complete within a certain course or subject. They just require making a detailed examination of the topic using relevant facts, examples or other evidence that you should be able to find in order to make your arguments more solid, and to show that you have gained a thorough understanding of the topic. However, you mustn’t just summarize the well-known facts or what you have learned from a course or book. In a thematic essay, you are supposed to identify and explain or compare issues, causes, patterns, outcomes, and connections between facts or events as well as their consequences or influences.


A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
The 25 Most Common Themes in Literature and Why They Matter
by Sue Weems | 0 comments
If you've ever survived a high school English class, you've likely been asked to consider the most common themes in literature. What are they and why do they matter for readers and writers? Let's take a look.

Literature's first job is to entertain. But at the same time every novel has a kernel of truth in it, or perhaps several kernels, ideas about how life works or philosophies on the best way to live or some gesture to the broader meaning of life.
Taken together, these ideas may combine into a “theme.”
I say “may” because theme is more a tool of interpretation than creativity. The writer may come into the story with an idea of what their story is about. This understanding of what their story is “about ” may even help add focus and depth to their story.
Once a book is published, though, the audience owns theme, and they may depart with a totally different message than the author intended.
Which is all to say, as a writer, theme may or may not be helpful to you.
As a reader, though, you can use theme to unlock the deeper truths both in the story and in life. Let's look at what theme is, why it matters for readers and writers, how to identify them, and some common examples of theme in literature.
Why trust Sue on theme? I'm one of those annoying English teachers who helps students analyze literature. Students ask me why we do it, and I'll tell you the secrets I share with them: analyzing literature helps us understand our humanity and world– from the misuse of power to the meaning of life.
Secondly, learning to look at a part of something and understand how it functions in the whole (AKA analysis) is a skill that transcends literature. It's a low-stakes way to practice life skills.
Want to skip ahead? Click on the topic that best answers your question.
Table of Contents
What is a literary theme? Why does theme matter for a reader? How do you identify theme in a story? Types of story: a shortcut to theme Common themes in literature with examples Why theme matters for writers Practice
What is a literary theme?
A literary theme is a universal concept, idea or message explored in a story or poem. It's often a moral, lesson, or belief that the writer wants to convey to readers.
Think of theme as the underlying message that shapes the story. It’s not always obvious at first glance – sometimes it takes some close reading and analysis to identify what’s going on beneath the surface.
A universal theme is one that transcends time and place. For example, the popular theme “love conquers all” shows up in old romances such as The Epheseian Tale from 2-50 AD to Disney's Robin Hood from 1973 to Nicholas Sparks' novel The Notebook from 2004.
Why does theme matter for a reader?
You can certainly enjoy a story without knowing the theme explicitly, but most stories are about something beyond the character's actions. And we want them to be about something more.
Stories are the way we build meaning—the way we understand human life, the way we process and confront controversial ideas, the way we sometimes relate to each other on a universal level.
When someone asks you what a book you're reading is about, you likely give a sentence or two about the character, their goal, and the conflict, but you're just as likely to identify an abstract idea that the book is about. That idea is a touchpoint for our humanness.
I may not be into a book about a boy wizard who is swept into a world where he must overcome his fears and insignificance to defeat a formidable foe, but I can certainly understand what it means to belong, what it means to find your way through inadequacy, what it means to defeat your fears.
That's the power of theme. It points to deeper meaning, connecting me to a story and to other readers like me.
How do you identify theme in a story?
If you are a student or a writer trying to identify theme, it sometimes feels like trying to crack a secret English major code. But here's a trick I teach my students.
1. Find the big idea
First, ask yourself about the big ideas or concepts that seem important throughout the entire story. These may feel abstract, such as love, beauty, despair, justice, or art. Sometimes the main character has very defined beliefs (or misbeliefs!) about the idea.
2. Ask what the story suggests about the idea
Once you have one or two overarching central ideas that seem important for the story, then ask yourself this question: What does the story seem to say about this idea?
For example, if I'm reading Shirley Jackson's chilling short story “The Lottery,” I might identify that the story is about community and tradition. If I wanted to be a little more specific I'd say tradition in the vein of conformity.
Quick summary of the story (spoiler alert!): The story opens on a summer day when an entire community participates in their annual lottery. Each family in town draws a paper until a single community member has been selected. The end of the story shows the town stoning the “winner” in a barbarous act of solidarity to maintain community traditions.
Now, to identify the central theme, I'd ask myself, what does Jackson's story seem to say about community or tradition or conformity?
Some communities are willing to maintain their traditions (or conformity) at any cost.
3. Support the theme or message with examples
If I wanted to support the central theme I identified, I would pull quotes or examples from the story that support it. In this case, I could look at the children who are willing to participate, the contrast of the summer day and the dark deed, the insistence that the stoning will keep them prosperous, even though there is no evidence of such.
Are there other possible themes? Sure. There are no wrong answers, only themes that can be defended from the texts and those that don't have enough support. It takes a little practice, but try this technique and see if it doesn't help.
Types of Story: a shortcut to finding theme in a story
As a part of his book The Write Structure , Joe has identified several types of story that help writers plan and execute their books. The detailed post is here.
In short, Joe argues that all stories are built on six values frameworks, regardless of genre. The values are directly related to the human condition and identify base needs we have for moving through the world.
Knowing your story types and the value scale can be a short cut to identifying themes in books and stories, because those universal ideas are tucked inside the values.
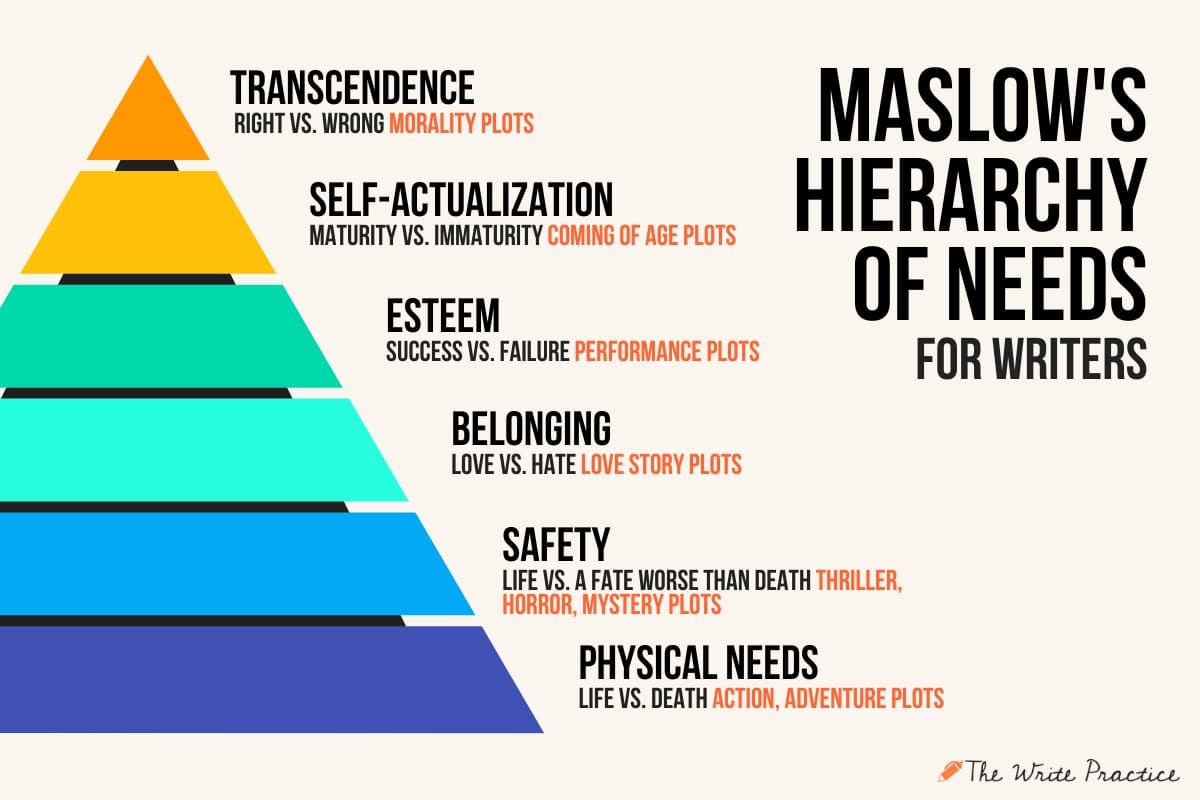
Here are the values in each type of story:
- Survival from Nature > Life vs. Death
- Survival from Others > Life vs. Fate Worse than Death
- Love/Community > Love vs. Hate
- Esteem > Accomplishment vs. Failure
- Personal Growth > Maturity vs. Immaturity
- Transcendence > Right vs. Wrong
The types can help you identify the central ideas that the story speaks into because you know that the values will be key. Your question then is what does the story seem to say about this value? Or more specifically, what does the story seem to say about the way this particular character pursues this value?
For example: If you are reading a Jack London short story or novel, you know that the protagonist is going to be facing survival from nature. The value is life versus death. So to determine the theme we ask what does the story say about life vs death or survival?
In Jack London's short story “To Build a Fire,” an arrogant man trying to survive the Yukon wilderness makes a series of novice mistakes from traveling alone to getting wet with no way to get warm and dry. Spoiler alert, he dies.
What is the theme of this story? My students usually shout out something like, “Don't be a dummy and travel alone with no way to make a fire!” And they're not wrong. The ideas here are life, death, nature, and humanity. Here are a number of ways you could frame the theme with specific support from the story:
- Nature is indifferent to human suffering.
- Human arrogance leads to death.
- There are limits to self-reliance.
As you can see, the theme is what the story suggests about the story value.
Common themes in literature with examples
James Clear collected a list of the best-selling books of all time on his website . Let's start with some of those fiction titles.
Disclaimer: I know many of these summaries and themes are vastly oversimplified and most could be fleshed out in long, complicated papers and books. But for the sake of time, let's imagine my list as limited examples of theme among many that could be argued.
Disclaimer 2: I tried to get ChatGPT to help me write the one sentence summaries for these titles even though I've read all but two of the listed books. The summaries ChatGPT wrote were weak or too general for our purposes. So if there are errors below, they are all mine—I can't blame the bots today. Let's look at the list:
1. Don Quixote by Miguel de Cervantes (1605) summary: Aging nobleman Don Quixote deludes himself into thinking he's a knight and takes on a satirical quest to prove his honor by defending the helpless and defeating the wicked.
theme: Being born a nobleman (or any class) does not automatically determine your worth.
2. Tale of Two Cities by Charles Dickens (1859) summary: In this sprawling novel of swapped (or reconstructed) identities and class warfare during the French Revolution, characters navigate the nature of love, betrayal, justice, and the possibility of transformation.
theme: Transformation is possible for enlightened individuals and societies.
3. The Lord of the Rings by J.R.R. Tolkien (1954) summary: An unlikely hobbit and his diverse team set out to find and destroy a powerful ring to save Middle-earth and defeat the dark lord Sauron.
theme: Good can defeat evil when people (or creatures) are willing to sacrifice for the common good.
4. The Little Prince by Antoine de Saint-Exupery (1943) summary: A prince visits various planets and discovers the importance of curiosity and openness to emotion.
theme: The most important things in life can't be seen with the eyes but with the heart.
5. Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone by J.K. Rowling (1997) summary: An unsuspecting orphan attends a wizard school where he discovers his true identity, a dark foe, and the belonging he craves.
theme: Love and friendship transcend time and space.
6. And Then There Were None by Agatha Christie (1939) summary: Seven guests gather at a house on an island where they are killed off one-by-one as they try to discover the murderer.
theme: Death is inevitable, justice is not.
7. The Dream of the Red Chamber by Cat Xueqin (1791) summary: In this complex family drama, a nobleman's son is born with a magic jade in his mouth, and he rebels against social norms and his father resulting in an attempted arranged wedding and illness rather than reinforce oppression.
theme: Social hierarchies maintained by oppression will eventually fall.
8. The Hobbit by J.R.R. Tolkien (1937) summary: Timid hobbit Bilbo Baggins is called by a wizard to help a band of dwarves reclaim their land from a terrible dragon, Smaug.
theme: Bravery can be found in the most unlikely places.
9. She: A History of Adventure by H. Rider Haggard (1886) summary: An professor and his ward seek out a lost kingdom in Africa to find a supernatural queen.
theme: Considering the imperialism of the time as well as worry about female empowerment, the themes here are varied and problematic, but perhaps one theme might resonate: Be careful what you seek, for you may find it.
10. The Lion, the Witch, and the Wardrobe by C.S. Lewis (1950) summary: Four children venture through a wardrobe into a magical kingdom where they must work together to save Narnia, meet Aslan, and defeat the White Witch.
theme: Evil is overwhelmingly tempting and can only be defeated through sacrifice.
11. The Catcher in the Rye by J.D. Salinger (1951) summary: An expelled prep school student, Holden Caulfield, has a number of coming-of-age misadventures on his way home for the holiday break.
theme: Innocence can only be protected from the risks of growing up for so long.
12. The Alchemist by Paolo Coelho (1988) summary: A Spanish shepherd named Santiago travels to Egypt searching for treasure he saw in a dream.
theme: Anyone can make the world better if we are willing and courageous.
13. One Hundred Years of Solitude by Gabriel Garcia Marquez (1967) summary: This circle of life novel covers seven generations of the Buendia family as they build a small dysfunctional utopia in a swamp amidst a changing political and social Latin American landscape.
theme: Solitude is an inevitability for humankind.
14. Anne of Green Gables by Lucy Maud Montgomery (1908) summary: An orphan finds her place with the Cuthbert siblings, and she brings her peculiar and delightful blend of imagination and optimism to their lives and community.
theme: Every human desires and deserves belonging.
15. Charlotte's Web by E.B. White (1952) summary: Wilbur the pig and his unconventional spider friend Charlotte join forces to save Wilbur's life from the slaughterhouse.
theme: Friendship can be found in the most unlikely places.
And let's throw in a few additional well-known stories and notable examples to see how their themes stack up:
16. Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare (1597) summary: Two teens from warring families fall in love and die rather than be kept apart from their families feud.
theme: Passion is costly.
17. Frankenstein by Mary Shelley (1818) summary: An ambitious scientist creates a monster without considering the larger implications. Chaos ensues.
theme: Knowledge can be dangerous when coupled with unbridled ambition.
18. Beloved by Toni Morrison (1987) summary: Formerly enslaved mother Sethe and her daugher Denver are haunted by the ghost of Sethe's oldest daughter who died when she was two-years-old.
theme: The physical and psychological effects of slavery are damaging and long-lasting.
19. Never Let Me Go by Kazuo Ishiguro (2005) summary: In this dystopian novel, people are cloned and held in preparation to be life-long organ donors for others.
theme: Freedom is a basic human desire.
20. Raisin in the Sun by Lorraine Hansberry (1959) summary: The Younger family grapples with identity and dreams in the wake of the death of their patriarch.
theme: Dignity and family are worth more than money.
The 5 most common themes in literature
You may have been asked to define universal themes as a part of a school assignment. Universal themes are those that transcend time and cultures, meaning they are often found to be true in real life no matter who you are or where you live.
Granted, I haven't read all the books across time and space (yet), but there's a pretty good bet that one of these major themes might apply to what you're reading regardless of time period, genre, or culture:
- Love conquers all.
- Things are not always what they seem.
- Good triumphs over evil.
- Beauty is in the eye of the beholder.
- Blood (family) is thicker than water.
Which other larger themes would you list here as some of the most common in literature? Share your theme examples in the comments .
Why theme matters for writers
Why do themes matter for writers though? After all, isn't it enough to write an entertaining story? It can be, but exploring universal themes can help take your work to the next level. You don't have to identify a theme for your story and write everything to that end—in fact that might work against you. But when done well, it can enhance your story.
Here are a few reasons you may want to think about theme in your writing:
1. Coherence
Theme can bring together the various parts of a story, including plot and subplot, characters, symbols, and motifs. Readers can feel the variations on a theme laced throughout your story and done well, it's engaging and satisfying.
If your theme is love conquers all, then you likely have two people who over come incredible odds to be together. What are the other elements that subtly underscore it? Maybe there's a house that was built with love in the setting or maybe a secondary character is failing at love because they keep putting their work first. If it's subtle, those small details reinforce the main storyline.
2. Significance
As we discussed, universal themes will resonate with readers, even when they haven't experienced the same events. Many of the works we've listed above are remembered and revered due in part to their lasting themes about human experience.
3. Expression
Theme is an opportunity to weave together your world view, experiences, perspective, and beliefs with artistic and creative possibilities. Theme serves as a unifying element as you express your vision. Try playing with theme in a story or other creative work to see how it pushes boundaries or got beyond the expected.
In summary, theme can serve as the backbone of a story, giving it structure, depth, and resonance. It can help convey the writer's intended message and engage readers on multiple levels, making it a crucial element of literary and creative expression.
Which other larger themes would you list as the most common in literature? Share your theme examples in the comments .
Set your timer for 15 minutes . Choose one of the common themes above and create a character who has strong beliefs about that theme. Now, write a scene where an event or person challenges that belief. How will the character react? Will they double-down and insist on their worldview? Or will they soften and consider alternatives? Will shock at the challenge plunge them into despair? Play with their reaction.
Once you've written for 15 minutes, post your practice in the Pro Practice Workshop and leave feedback for a few other writers.
Sue Weems is a writer, teacher, and traveler with an advanced degree in (mostly fictional) revenge. When she’s not rationalizing her love for parentheses (and dramatic asides), she follows a sailor around the globe with their four children, two dogs, and an impossibly tall stack of books to read. You can read more of her writing tips on her website .

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.
Get 25% OFF new yearly plans in our Spring Sale
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
200 Common Themes in Literature

Sarah Oakley

Table of Contents
What is the theme of a story, common themes in literature, universal themes in literature, full list of themes in literature, theme examples in popular novels.
The theme of a novel is the main point of the story and what it’s really about. As a writer, it’s important to identify the theme of your story before you write it.
Themes are not unique to each novel because a theme addresses a common feeling or experience your readers can relate to. If you’re aware of what the common themes are, you’ll have a good idea of what your readers are expecting from your novel .
In this article, we’ll explain what a theme is, and we’ll explore common themes in literature.
The theme of a story is the underlying message or central idea the writer is trying to show through the actions of the main characters. A theme is usually something the reader can relate to, such as love, death, and power.
Your story can have more than one theme, as it might have core themes and minor themes that become more apparent later in the story. A romance novel can have the central theme of love, but the protagonist might have to overcome some self-esteem issues, which present the theme of identity.
Themes are great for adding conflict to your story because each theme presents different issues you could use to develop your characters. For example, a novel with the theme of survival will show the main character facing tough decisions about their own will to survive, potentially at the detriment of someone else they care about.
Sometimes a secondary character will represent the theme in the way they are characterized and the actions they take. Their role is to challenge the protagonist to learn what the story is trying to say about the theme. For example, in a novel about the fear of failure, the antagonist might be a rival in a competition who challenges the protagonist to overcome their fear so they can succeed against them.
It’s important to remember that a theme is not the same as a story’s moral message. A moral is a specific lesson you can teach your readers, whereas a story’s theme is an idea or concept your readers interpret in a way that relates to them.

Write like a bestselling author
Love writing? ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of your stories.
Common literary themes are concepts and central ideas that are relatable to most readers. Therefore, it’s a good idea to use a common theme if you want your novel to appeal to a wide range of readers.
Here’s our list of common themes in literature:
Love : the theme of love appears in novels within many genres, as it can discuss the love of people, pets, objects, and life. Love is a complex concept, so there are still unique takes on this theme being published every day.
Death/Grief : the theme of death can focus on the concept of mortality or how death affects people and how everyone processes grief in their own way.
Power : there are many books in the speculative fiction genres that focus on the theme of power. For example, a fantasy story could center on a ruling family and their internal problems and external pressures, which makes it difficult for them to stay in power.
Faith : the common theme of faith appears in stories where the events test a character’s resolve or beliefs. The character could be religious or the story could be about a character’s faith in their own ability to succeed.
Beauty : the theme of beauty is good for highlighting places where beauty is mostly overlooked by society, such as inner beauty or hard work that goes unnoticed. Some novels also use the theme of beauty to show how much we take beauty for granted.
Survival : we can see the theme of survival in many genres, such as horror, thriller, and dystopian, where the book is about characters who have to survive life-threatening situations.
Identity : there are so many novels that focus on the common theme of identity because it’s something that matters to a lot of readers. Everyone wants to know who they are and where they fit in the world.
Family : the theme of family is popular because families are ripe with opportunities for conflict. The theme of family affects everyone, whether they have one or not, so it’s a relatable theme to use in your story.

Universal themes are simply concepts and ideas that almost all cultures and countries can understand and interpret. Therefore, a universal theme is great for books that are published in several languages.
If you want to write a story you can export to readers all over the world, aim to use a universal theme. The common themes mentioned previously are all universal literary themes, but there are several more you could choose for your story.
Here are some more universal literary themes:
Human nature
Self-awareness
Coming of age
Not all themes are universal or common, but that shouldn’t put you off from using them. If you believe there is something to be said about a particular theme, your book could be the one to say it.
Your book could become popular if the theme of your book addresses a current issue. For example, a theme of art is not as common as love, but in a time when AI developments are making people talk about how AI affects art, it’s a theme people will probably appreciate.
Here’s a full list of themes you can use in your writing:
Abuse of power
American dream
Celebration
Change versus tradition
Chaos and order
Circle of life
Climate change
Colonialism
Common sense
Communication
Companionship
Conservation
Convention and rebellion
Darkness and light
Disappointment
Disillusionment
Displacement
Empowerment
Everlasting love
Forbidden love
Forgiveness
Fulfillment
Gay, lesbian, bisexual, and transgender rights
Good vs evil
Imagination
Immortality
Imperialism
Impossibility
Individuality
Inspiration
Manipulation
Materialism
Nationalism
Not giving up
Opportunity
Peer pressure
Perseverance
Personal development
Relationship
Self-discipline
Self-reliance
Self-preservation
Subjectivity
Surveillance
Totalitarianism
Unconditional love
Unrequited love
Unselfishness
Winning and losing
Working class struggles
If you’ve decided on a literary theme but you’re not sure how to present it in your novel, it’s a good idea to check out how other writers have incorporated it into their novels. We’ve found some examples of themes within popular novels that could help you get started.
The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald
The Great Gatsby is famous for the theme of the American dream, but it also includes themes of gender, race, social class, and identity. We experience the themes of the novel through the eyes of the narrator, Nick Carraway, who gradually loses his optimism for the American dream as the narrative progresses.
Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare
It’s well known that Shakespeare was a connoisseur of the theme of tragedy in his plays, and Romeo and Juliet certainly features tragedy. However, forbidden love and family are the main themes.
Charlotte’s Web by E. B. White
Charlotte’s Web is a classic children’s book that features the themes of death and mortality. From the beginning of the book, the main characters have to come to terms with their own mortality. Charlotte, the spider, does what she can to prevent the slaughter of Wilbur, the pig.
Nineteen Eighty-Four by George Orwell
George Orwell’s novel, Nineteen Eighty-Four , focuses on themes of totalitarianism, repression, censorship, and surveillance. The novel is famous for introducing the concept of Big Brother, which has become synonymous with the themes of surveillance and abuse of power.

A Game of Thrones by George R. R. Martin
The fantasy novel, A Game of Thrones , is popular for its complex storylines that present themes of family, power, love, and death. The novel has multiple points of view, which give an insight into how each main character experiences the multiple themes of the story.
The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins
The Hunger Games is a popular teen novel that focuses on themes of poverty, rebellion, survival, friendship, power, and social class. The novel highlights the horrifying consequences of rebellion, as the teenage competitors have to survive the Hunger Games pageant.
Wolf Hall by Hilary Mantel
Wolf Hall features themes of power, family, faith, and a sense of duty. It’s a historical novel about the life of Oliver Cromwell and how he became the most powerful minister in King Henry VIII’s council.
As you can see, the literary theme of a novel is one of the most important parts, as it gives the reader an instant understanding of what the story is about. Your readers will connect with your novel if you have a theme that is relatable to them.
Some themes are more popular than others, but some gain popularity based on events that are happening in the world. It’s important to consider how relevant your literary theme is to your readers at the time you intend to publish your book.
We hope this list of common themes in literature will help you with your novel writing.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Spring Sale: Get 15% off selected writing courses, only through April 19! Learn more »

When someone asks you “What is this book about?” , there are a few ways you can answer. There’s “ plot ,” which refers to the literal events in the book, and there’s “character,” which refers to the people in the book and the struggles they overcome. Finally, there are themes in literature that correspond with the work’s topic and message. But what is theme in literature?
The theme of a story or poem refers to the deeper meaning of that story or poem. All works of literature contend with certain complex ideas, and theme is how a story or poem approaches these ideas.
There are countless ways to approach the theme of a story or poem, so let’s take a look at some theme examples and a list of themes in literature. We’ll discuss the differences between theme and other devices, like theme vs moral and theme vs topic. Finally, we’ll examine why theme is so essential to any work of literature, including to your own writing.
But first, what is theme? Let’s explore what theme is—and what theme isn’t.
- Theme Definition
20 Common Themes in Literature
- Theme Examples
Themes in Literature: A Hierarchy of Ideas
Why themes in literature matter.
- Should I Decide the Themes of a Story in Advance?
Theme Definition: What is Theme?
Theme describes the central idea(s) that a piece of writing explores. Rather than stating this theme directly, the author will look at theme using the set of literary tools at their disposal. The theme of a story or poem will be explored through elements like characters , plot, settings , conflict, and even word choice and literary devices .
Theme definition: the central idea(s) that a piece of writing explores.
That said, theme is more than just an idea. It is also the work’s specific vantage point on that idea. In other words, a theme is an idea plus an opinion: it is the author’s specific views regarding the central ideas of the work.
All works of literature have these central ideas and opinions, even if those ideas and opinions aren’t immediate to the reader.
Justice, for example, is a literary theme that shows up in a lot of classical works. To Kill a Mockingbird contends with racial justice, especially at a time when the U.S. justice system was exceedingly stacked against African Americans. How can a nation call itself just when justice is used as a weapon?
By contrast, the play Hamlet is about the son of a recently-executed king. Hamlet seeks justice for his father and vows to kill Claudius—his father’s killer—but routinely encounters the paradox of revenge. Can justice really be found through more bloodshed?
What is theme? An idea + an opinion.
Clearly, these two works contend with justice in unrelated ways. All themes in literature are broad and open-ended, allowing writers to explore their own ideas about these complex topics.
Check Out Our Online Writing Courses!

Tiny and True: Creating Flash Essays with Mindfulness
with Susan Barr-Toman
April 17th, 2024
How do you tell the full truth in under 1,000 words? Learn the art of flash essays and write nuggets of wisdom in this tiny essay class.

A Poet’s Calling Card: Writing and Composing a Chapbook
with Caitlin Scarano
The poetry chapbook gives poets the chance to make a small, artful collection around a poetic obsession. Learn how to craft yours in this 8 week chapbook intensive.

Plot Your Novel
with Jack Smith
Over eight weeks, you'll develop a solid basis in the fictional elements—protagonist, setting, secondary characters, point of view, plot, and theme—while you develop the outline of your novel. You'll receive feedback at all stages from your fellow writers and your instructor.

Poems of All Sizes: Haiku, Tanka, and Japanese Poetic Forms
with Miho Kinnas
April 18th, 2024
Explore the history and poetics of Japanese poetry forms, and write haiku, tanka, renga, haiga, and linked verse poetry.

From the Source: Journaling for Self-Knowledge and Creativity
with Amy Bonnaffons
April 24th, 2024
Journal to discover yourself, find a wellspring of creativity, and produce publication-ready pieces.
Let’s look at some common themes in literature. The ideas presented within this list of themes in literature show up in novels, memoirs, poems, and stories throughout history.
Theme Examples in Literature
Let’s take a closer look at how writers approach and execute theme. Themes in literature are conveyed throughout the work, so while you might not have read the books in the following theme examples, we’ve provided plot synopses and other relevant details where necessary. We analyze the following:
- Power and Corruption in the novel Animal Farm
- Loneliness in the short story “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place”
- Love in the poem “How Do I Love Thee”
Theme Examples: Power and Corruption in the Novel Animal Farm
At its simplest, the novel Animal Farm by George Orwell is an allegory that represents the rise and moral decline of Communism in Russia. Specifically, the novel uncovers how power corrupts the leaders of populist uprisings, turning philosophical ideals into authoritarian regimes.
Most of the characters in Animal Farm represent key figures during and after the Russian Revolution. On an ailing farm that’s run by the negligent farmer Mr. Jones (Tsar Nicholas II), the livestock are ready to seize control of the land. The livestock’s discontent is ripened by Old Major (Karl Marx/Lenin), who advocates for the overthrow of the ruling elite and the seizure of private land for public benefit.
After Old Major dies, the pigs Napoleon (Joseph Stalin) and Snowball (Leon Trotsky) stage a revolt. Mr. Jones is chased off the land, which parallels the Russian Revolution in 1917. The pigs then instill “Animalism”—a system of government that advocates for the rights of the common animal. At the core of this philosophy is the idea that “all animals are equal”—an ideal that, briefly, every animal upholds.
Initially, the Animalist Revolution brings peace and prosperity to the farm. Every animal is well-fed, learns how to read, and works for the betterment of the community. However, when Snowball starts implementing a plan to build a windmill, Napoleon drives Snowball off of the farm, effectively assuming leadership over the whole farm. (In real life, Stalin forced Trotsky into exile, and Trotsky spent the rest of his life critiquing the Stalin regime until he was assassinated in 1940.)
Napoleon’s leadership quickly devolves into demagoguery, demonstrating the corrupting influence of power and the ways that ideology can breed authoritarianism. Napoleon uses Snowball as a scapegoat for whenever the farm has a setback, while using Squealer (Vyacheslav Molotov) as his private informant and public orator.
Eventually, Napoleon changes the tenets of Animalism, starts walking on two legs, and acquires other traits and characteristics of humans. At the end of the novel, and after several more conflicts , purges, and rule changes, the livestock can no longer tell the difference between the pigs and humans.
Themes in Literature: Power and Corruption in Animal Farm
So, how does Animal Farm explore the theme of “Power and Corruption”? Let’s analyze a few key elements of the novel.
Plot: The novel’s major plot points each relate to power struggles among the livestock. First, the livestock wrest control of the farm from Mr. Jones; then, Napoleon ostracizes Snowball and turns him into a scapegoat. By seizing leadership of the farm for himself, Napoleon grants himself massive power over the land, abusing this power for his own benefit. His leadership brings about purges, rule changes, and the return of inequality among the livestock, while Napoleon himself starts to look more and more like a human—in other words, he resembles the demagoguery of Mr. Jones and the abuse that preceded the Animalist revolution.
Thus, each plot point revolves around power and how power is wielded by corrupt leadership. At its center, the novel warns the reader of unchecked power, and how corrupt leaders will create echo chambers and private militaries in order to preserve that power.
Characters: The novel’s characters reinforce this message of power by resembling real life events. Most of these characters represent real life figures from the Russian Revolution, including the ideologies behind that revolution. By creating an allegory around Lenin, Trotsky, Stalin, and the other leading figures of Communist Russia’s rise and fall, the novel reminds us that unchecked power foments disaster in the real world.
Literary Devices: There are a few key literary devices that support the theme of Power and Corruption. First, the novel itself is a “satirical allegory.” “ Satire ” means that the novel is ridiculing the behaviors of certain people—namely Stalin, who instilled far-more-dangerous laws and abuses that created further inequality in Russia/the U.S.S.R. While Lenin and Trotsky had admirable goals for the Russian nation, Stalin is, quite literally, a pig.
Meanwhile, “allegory” means that the story bears symbolic resemblance to real life, often to teach a moral. The characters and events in this story resemble the Russian Revolution and its aftermath, with the purpose of warning the reader about unchecked power.
Finally, an important literary device in Animal Farm is symbolism . When Napoleon (Stalin) begins to resemble a human, the novel suggests that he has become as evil and negligent as Mr. Jones (Tsar Nicholas II). Since the Russian Revolution was a rejection of the Russian monarchy, equating Stalin to the monarchy reinforces the corrupting influence of power, and the need to elect moral individuals to posts of national leadership.
Theme Examples: Loneliness in “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place”
Ernest Hemingway’s short story “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place” is concerned with the theme of loneliness. You can read this short story here . Content warning for mentions of suicide.
There are very few plot points in Hemingway’s story, so most of the story’s theme is expressed through dialogue and description. In the story, an old man stays up late drinking at a cafe. The old man has no wife—only a niece that stays with him—and he attempted suicide the previous week. Two waiters observe him: a younger waiter wants the old man to leave so they can close the cafe, while an older waiter sympathizes with the old man. None of these characters have names.
The younger waiter kicks out the old man and closes the cafe. The older waiter walks to a different cafe and ruminates on the importance of “a clean, well-lighted place” like the cafe he works at.
Themes in Literature: Loneliness in “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place”
Hemingway doesn’t tell us what to think about the old man’s loneliness, but he does provide two opposing viewpoints through the dialogue of the waiters.
The younger waiter has the hallmarks of a happy life: youth, confidence, and a wife to come home to. While he acknowledges that the old man is unhappy, he also admits “I don’t want to look at him,” complaining that the old man has “no regard for those who must work.” The younger waiter “did not wish to be unjust,” he simply wanted to return home.
The older waiter doesn’t have the privilege of turning away: like the old man, he has a house but not a home to return to, and he knows that someone may need the comfort of “a clean and pleasant cafe.”
The older waiter, like Hemingway, empathizes with the plight of the old man. When your place of rest isn’t a home, the world can feel like a prison, so having access to a space that counteracts this feeling is crucial. What kind of a place is that? The older waiter surmises that “the light of course” matters, but the place must be “clean and pleasant” too. Additionally, the place should not have music or be a bar: it must let you preserve the quiet dignity of yourself.
Lastly, the older waiter’s musings about God clue the reader into his shared loneliness with the old man. In a stream of consciousness, the older waiter recites traditional Christian prayers with “nada” in place of “God,” “Father,” “Heaven,” and other symbols of divinity. A bartender describes the waiter as “otro locos mas” (translation: another crazy), and the waiter concludes that his plight must be insomnia.
This belies the irony of loneliness: only the lonely recognize it. The older waiter lacks confidence, youth, and belief in a greater good. He recognizes these traits in the old man, as they both share a need for a clean, well-lighted place long after most people fall asleep. Yet, the younger waiter and the bartender don’t recognize these traits as loneliness, just the ramblings and shortcomings of crazy people.
Does loneliness beget craziness? Perhaps. But to call the waiter and old man crazy would dismiss their feelings and experiences, further deepening their loneliness.
Loneliness is only mentioned once in the story, when the young waiter says “He’s [the old man] lonely. I’m not lonely. I have a wife waiting in bed for me.” Nonetheless, loneliness consumes this short story and its older characters, revealing a plight that, ironically, only the lonely understand.
Theme Examples: Love in the Poem “How Do I Love Thee”
Let’s turn towards brighter themes in literature: namely, love in poetry . Elizabeth Barrett Browning’s poem “ How Do I Love Thee ” is all about the theme of love.
Themes in Literature: Love in “How Do I Love Thee”
Browning’s poem is a sonnet , which is a 14-line poem that often centers around love and relationships. Sonnets have different requirements depending on their form, but between lines 6-8, they all have a volta —a surprising line that twists and expands the poem’s meaning.
Let’s analyze three things related to the poem’s theme: its word choice, its use of simile and metaphor , and its volta.
Word Choice: Take a look at the words used to describe love. What do those words mean? What are their connotations? Here’s a brief list: “soul,” “ideal grace,” “quiet need,” “sun and candle-light,” “strive for right,” “passion,” “childhood’s faith,” “the breath, smiles, tears, of all my life,” “God,” “love thee better after death.”
These words and phrases all bear positive connotations, and many of them evoke images of warmth, safety, and the hearth. Even phrases that are morose, such as “lost saints” and “death,” are used as contrasts to further highlight the speaker’s wholehearted rejoicing of love. This word choice suggests an endless, benevolent, holistic, all-consuming love.
Simile and Metaphor: Similes and metaphors are comparison statements, and the poem routinely compares love to different objects and ideas. Here’s a list of those comparisons:
The speaker loves thee:
- To the depths of her soul.
- By sun and candle light—by day and night.
- As men strive to do the right thing (freely).
- As men turn from praise (purely).
- With the passion of both grief and faith.
- With the breath, smiles, and tears of her entire life.
- Now in life, and perhaps even more after death.
The speaker’s love seems to have infinite reach, flooding every aspect of her life. It consumes her soul, her everyday activities, her every emotion, her sense of justice and humility, and perhaps her afterlife, too. For the speaker, this love is not just an emotion, an activity, or an ideology: it’s her existence.
Volta: The volta of a sonnet occurs in the poem’s center. In this case, the volta is the lines “I love thee freely, as men strive for right. / I love thee purely, as they turn from praise.”
What surprising, unexpected comparisons! To the speaker, love is freedom and the search for a greater good; it is also as pure as humility. By comparing love to other concepts, the speaker reinforces the fact that love isn’t just an ideology, it’s an ideal that she strives for in every word, thought, and action.
“Theme” is part of a broader hierarchy of ideas. While the theme of a story encompasses its central ideas, the writer also expresses these ideas through different devices.
You may have heard of some of these devices: motif, moral, topic, etc. What is motif vs theme? What is theme vs moral? These ideas interact with each other in different ways, which we’ve mapped out below.
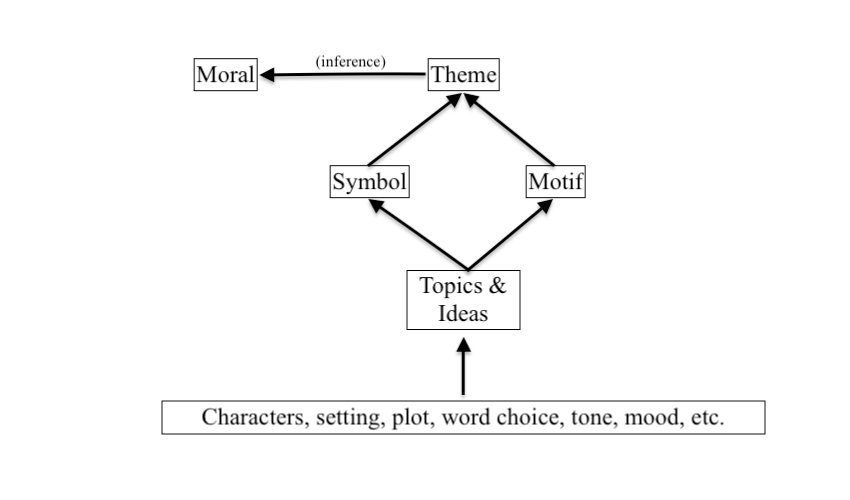
Theme vs Topic
The “topic” of a piece of literature answers the question: What is this piece about? In other words, “topic” is what actually happens in the story or poem.
You’ll find a lot of overlap between topic and theme examples. Love, for instance, is both the topic and the theme of Elizabeth Barrett Browning’s poem “How Do I Love Thee.”
The difference between theme vs topic is: topic describes the surface level content matter of the piece, whereas theme encompasses the work’s apparent argument about the topic.
Topic describes the surface level content matter of the piece, whereas theme encompasses the work’s apparent argument about the topic.
So, the topic of Browning’s poem is love, while the theme is the speaker’s belief that her love is endless, pure, and all-consuming.
Additionally, the topic of a piece of literature is definitive, whereas the theme of a story or poem is interpretive. Every reader can agree on the topic, but many readers will have different interpretations of the theme. If the theme weren’t open-ended, it would simply be a topic.
Theme vs Motif
A motif is an idea that occurs throughout a literary work. Think of the motif as a facet of the theme: it explains, expands, and contributes to themes in literature. Motif develops a central idea without being the central idea itself .
Motif develops a central idea without being the central idea itself.
In Animal Farm , for example, we encounter motif when Napoleon the pig starts walking like a human. This represents the corrupting force of power, because Napoleon has become as much of a despot as Mr. Jones, the previous owner of the farm. Napoleon’s anthropomorphization is not the only example of power and corruption, but it is a compelling motif about the dangers of unchecked power.
Theme vs Moral
The moral of a story refers to the story’s message or takeaway. What can we learn from thinking about a specific piece of literature?
The moral is interpreted from the theme of a story or poem. Like theme, there is no single correct interpretation of a story’s moral: the reader is left to decide how to interpret the story’s meaning and message.
For example, in Hemingway’s “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place,” the theme is loneliness, but the moral isn’t quite so clear—that’s for the reader to decide. My interpretation is that we should be much more sympathetic towards the lonely, since loneliness is a quiet affliction that many lonely people cannot express.
Great literature does not tell us what to think, it gives us stories to think about.
However, my interpretation could be miles away from yours, and that’s wonderful! Great literature does not tell us what to think, it gives us stories to think about, and the more we discuss our thoughts and interpretations, the more we learn from each other.
The theme of a story affects everything else: the decisions that characters make, the mood that words and images build, the moral that readers interpret, etc. Recognizing how writers utilize various themes in literature will help you craft stronger, more nuanced works of prose and poetry .
“To produce a mighty book, you must choose a mighty theme.” —Herman Melville
Whether a writer consciously or unconsciously decides the themes of their work, theme in literature acts as an organizing principle for the work as a whole. For writers, theme is especially useful to think about in the process of revision: if some element of your poem or story doesn’t point towards a central idea, it’s a sign that the work is not yet finished.
Moreover, literary themes give the work stakes . They make the work stand for something. Remember that our theme definition is an idea plus an opinion. Without that opinion element, a work of literature simply won’t stand for anything, because it is presenting ideas in the abstract without giving you something to react to. The theme of a story or poem is never just “love” or “justice,” it’s the author’s particular spin and insight on those themes. This is what makes a work of literature compelling or evocative. Without theme, literature has no center of gravity, and all the words and characters and plot points are just floating in the ether.
Should I Decide the Theme of a Story or Poem in Advance?
You can, though of course it depends on the actual story you want to tell. Some writers certainly start with a theme. You might decide you want to write a story about themes like love, family, justice, gender roles, the environment, or the pursuit of revenge.
From there, you can build everything else: plot points, characters, conflicts, etc. Examining themes in literature can help you generate some strong story ideas !
Nonetheless, theme is not the only way to approach a creative writing project. Some writers start with plot, others with character, others with conflicts, and still others with just a vague notion of what the story might be about. You might not even realize the themes in your work until after you finish writing it.
You certainly want your work to have a message, but deciding what that message is in advance might actually hinder your writing process. Many writers use their poems and stories as opportunities to explore tough questions, or to arrive at a deeper insight on a topic. In other words, you can start your work with ideas, and even opinions on those ideas, but don’t try to shoehorn a story or poem into your literary themes. Let the work explore those themes. If you can surprise yourself or learn something new from the writing process, your readers will certainly be moved as well.
So, experiment with ideas and try different ways of writing. You don’t have think about the theme of a story right away—but definitely give it some thought when you start revising your work!
Develop Great Themes at Writers.com
As writers, it’s hard to know how our work will be viewed and interpreted. Writing in a community can help. Whether you join our Facebook group or enroll in one of our upcoming courses , we have the tools and resources to sharpen your writing.
Sean Glatch
18 comments.
Sean Glatch,Thank you very much for your discussion on themes. It was enlightening and brought clarity to an abstract and sometimes difficult concept to explain and illustrate. The sample stories and poem were appreciated too as they are familiar to me. High School Language Arts Teacher
Hi Stephanie, I’m so glad this was helpful! Happy teaching 🙂
Wow!!! This is the best resource on the subject of themes that I have ever encountered and read on the internet. I just bookmarked it and plan to use it as a resource for my teaching. Thank you very much for publishing this valuable resource.
Hi Marisol,
Thank you for the kind words! I’m glad to hear this article will be a useful resource. Happy teaching!
Warmest, Sean
builders beams bristol
What is Theme? A Look at 20 Common Themes in Literature | writers.com
Hello! This is a very informative resource. Thank you for sharing.
farrow and ball pigeon
This presentation is excellent and of great educational value. I will employ it already in my thesis research studies.
John Never before communicated with you!
Brilliant! Thank you.
[…] THE MOST COMMON THEMES IN LITERATURE […]
marvellous. thumbs up
Thank you. Very useful information.
found everything in themes. thanks. so much
In college I avoided writing classes and even quit a class that would focus on ‘Huck Finn’ for the entire semester. My idea of hell. However, I’ve been reading and learning from the writers.com articles, and I want to especially thank Sean Glatch who writes in a way that is useful to aspiring writers like myself.
You are very welcome, Anne! I’m glad that these resources have been useful on your writing journey.
Thank you very much for this clear and very easy to understand teaching resources.
Hello there. I have a particular question.
Can you describe the exact difference of theme, issue and subject?
I get confused about these.
I love how helpful this is i will tell my class about it!
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Do Thematic Analysis | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
How to Do Thematic Analysis | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Published on September 6, 2019 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Thematic analysis is a method of analyzing qualitative data . It is usually applied to a set of texts, such as an interview or transcripts . The researcher closely examines the data to identify common themes – topics, ideas and patterns of meaning that come up repeatedly.
There are various approaches to conducting thematic analysis, but the most common form follows a six-step process: familiarization, coding, generating themes, reviewing themes, defining and naming themes, and writing up. Following this process can also help you avoid confirmation bias when formulating your analysis.
This process was originally developed for psychology research by Virginia Braun and Victoria Clarke . However, thematic analysis is a flexible method that can be adapted to many different kinds of research.
Table of contents
When to use thematic analysis, different approaches to thematic analysis, step 1: familiarization, step 2: coding, step 3: generating themes, step 4: reviewing themes, step 5: defining and naming themes, step 6: writing up, other interesting articles.
Thematic analysis is a good approach to research where you’re trying to find out something about people’s views, opinions, knowledge, experiences or values from a set of qualitative data – for example, interview transcripts , social media profiles, or survey responses .
Some types of research questions you might use thematic analysis to answer:
- How do patients perceive doctors in a hospital setting?
- What are young women’s experiences on dating sites?
- What are non-experts’ ideas and opinions about climate change?
- How is gender constructed in high school history teaching?
To answer any of these questions, you would collect data from a group of relevant participants and then analyze it. Thematic analysis allows you a lot of flexibility in interpreting the data, and allows you to approach large data sets more easily by sorting them into broad themes.
However, it also involves the risk of missing nuances in the data. Thematic analysis is often quite subjective and relies on the researcher’s judgement, so you have to reflect carefully on your own choices and interpretations.
Pay close attention to the data to ensure that you’re not picking up on things that are not there – or obscuring things that are.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Once you’ve decided to use thematic analysis, there are different approaches to consider.
There’s the distinction between inductive and deductive approaches:
- An inductive approach involves allowing the data to determine your themes.
- A deductive approach involves coming to the data with some preconceived themes you expect to find reflected there, based on theory or existing knowledge.
Ask yourself: Does my theoretical framework give me a strong idea of what kind of themes I expect to find in the data (deductive), or am I planning to develop my own framework based on what I find (inductive)?
There’s also the distinction between a semantic and a latent approach:
- A semantic approach involves analyzing the explicit content of the data.
- A latent approach involves reading into the subtext and assumptions underlying the data.
Ask yourself: Am I interested in people’s stated opinions (semantic) or in what their statements reveal about their assumptions and social context (latent)?
After you’ve decided thematic analysis is the right method for analyzing your data, and you’ve thought about the approach you’re going to take, you can follow the six steps developed by Braun and Clarke .
The first step is to get to know our data. It’s important to get a thorough overview of all the data we collected before we start analyzing individual items.
This might involve transcribing audio , reading through the text and taking initial notes, and generally looking through the data to get familiar with it.
Next up, we need to code the data. Coding means highlighting sections of our text – usually phrases or sentences – and coming up with shorthand labels or “codes” to describe their content.
Let’s take a short example text. Say we’re researching perceptions of climate change among conservative voters aged 50 and up, and we have collected data through a series of interviews. An extract from one interview looks like this:
In this extract, we’ve highlighted various phrases in different colors corresponding to different codes. Each code describes the idea or feeling expressed in that part of the text.
At this stage, we want to be thorough: we go through the transcript of every interview and highlight everything that jumps out as relevant or potentially interesting. As well as highlighting all the phrases and sentences that match these codes, we can keep adding new codes as we go through the text.
After we’ve been through the text, we collate together all the data into groups identified by code. These codes allow us to gain a a condensed overview of the main points and common meanings that recur throughout the data.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Next, we look over the codes we’ve created, identify patterns among them, and start coming up with themes.
Themes are generally broader than codes. Most of the time, you’ll combine several codes into a single theme. In our example, we might start combining codes into themes like this:
At this stage, we might decide that some of our codes are too vague or not relevant enough (for example, because they don’t appear very often in the data), so they can be discarded.
Other codes might become themes in their own right. In our example, we decided that the code “uncertainty” made sense as a theme, with some other codes incorporated into it.
Again, what we decide will vary according to what we’re trying to find out. We want to create potential themes that tell us something helpful about the data for our purposes.
Now we have to make sure that our themes are useful and accurate representations of the data. Here, we return to the data set and compare our themes against it. Are we missing anything? Are these themes really present in the data? What can we change to make our themes work better?
If we encounter problems with our themes, we might split them up, combine them, discard them or create new ones: whatever makes them more useful and accurate.
For example, we might decide upon looking through the data that “changing terminology” fits better under the “uncertainty” theme than under “distrust of experts,” since the data labelled with this code involves confusion, not necessarily distrust.
Now that you have a final list of themes, it’s time to name and define each of them.
Defining themes involves formulating exactly what we mean by each theme and figuring out how it helps us understand the data.
Naming themes involves coming up with a succinct and easily understandable name for each theme.
For example, we might look at “distrust of experts” and determine exactly who we mean by “experts” in this theme. We might decide that a better name for the theme is “distrust of authority” or “conspiracy thinking”.
Finally, we’ll write up our analysis of the data. Like all academic texts, writing up a thematic analysis requires an introduction to establish our research question, aims and approach.
We should also include a methodology section, describing how we collected the data (e.g. through semi-structured interviews or open-ended survey questions ) and explaining how we conducted the thematic analysis itself.
The results or findings section usually addresses each theme in turn. We describe how often the themes come up and what they mean, including examples from the data as evidence. Finally, our conclusion explains the main takeaways and shows how the analysis has answered our research question.
In our example, we might argue that conspiracy thinking about climate change is widespread among older conservative voters, point out the uncertainty with which many voters view the issue, and discuss the role of misinformation in respondents’ perceptions.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Discourse analysis
- Cohort study
- Peer review
- Ethnography
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Conformity bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Availability heuristic
- Attrition bias
- Social desirability bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, June 22). How to Do Thematic Analysis | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 13, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/thematic-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, what is qualitative research | methods & examples, inductive vs. deductive research approach | steps & examples, critical discourse analysis | definition, guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
- Human Editing
- Free AI Essay Writer
- AI Outline Generator
- AI Paragraph Generator
- Paragraph Expander
- Essay Expander
- Literature Review Generator
- Research Paper Generator
- Thesis Generator
- Paraphrasing tool
- AI Rewording Tool
- AI Sentence Rewriter
- AI Rephraser
- AI Paragraph Rewriter
- Summarizing Tool
- AI Content Shortener
- Plagiarism Checker
- AI Detector
- AI Essay Checker
- Citation Generator
- Reference Finder
- Book Citation Generator
- Legal Citation Generator
- Journal Citation Generator
- Reference Citation Generator
- Scientific Citation Generator
- Source Citation Generator
- Website Citation Generator
- URL Citation Generator
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- AI Writing Guides
- AI Detection Guides
- Citation Guides
- Grammar Guides
- Paraphrasing Guides
- Plagiarism Guides
- Summary Writing Guides
- STEM Guides
- Humanities Guides
- Language Learning Guides
- Coding Guides
- Top Lists and Recommendations
- AI Detectors
- AI Writing Services
- Coding Homework Help
- Citation Generators
- Editing Websites
- Essay Writing Websites
- Language Learning Websites
- Math Solvers
- Paraphrasers
- Plagiarism Checkers
- Reference Finders
- Spell Checkers
- Summarizers
- Tutoring Websites
Most Popular
12 days ago
Why Congress Cares About Media Literacy and You Should Too
How educators can reinvent teaching and learning with ai.
13 days ago
Who vs Whom
Plagiarism vs copyright, top 20 best books on american history, themes of “night” by elie wiesel.
Image: artstation.com

The following review example can serve as a guide for students trying to find inspiration when writing an assignment.
What makes the story real? Not the reliability of facts or the fact that it’s based on real events. The main element is honesty. Integrity to share the happiest and the saddest moments, success and despair. The real story is raw to the bone, and the real author never hides behind the pen and paper.
This is the case for Elie Wiesel. The writer chooses memoir to go uncensored with his thoughts and memories about the most challenging moment in his life and the scariest event in history – war.
Elie Wiesel’s “Night” is a powerful narrative that delves into the darkest chapters of human history through the eyes of a young Jewish boy, Eliezer. This semi-autobiographical novel, though woven with fictional elements, deeply reflects Wiesel’s harrowing experiences in Nazi concentration camps. “Night” is not just a story of survival but also a testament to the human spirit facing unimaginable horrors. In this article, we’ll explore the central themes that emerge from this profound work, rendered in simple text for clarity and understanding.
In this article, we’ll discover the main themes in “Night” and their meaning.
Loss of Identity
The themes of “Night” by Elie Wiesel explore profound aspects of human nature and spirituality. Eliezer’s journey begins in his hometown, where he is deeply immersed in Jewish teachings and traditions. His profound identity as a young, devout Jew is starkly contrasted with the dehumanization he endures under the Nazi regime. The camps strip him of his name, his hair, and eventually, his faith, reducing him to a mere number. The transformation is so drastic that Eliezer, along with other prisoners, begins to see themselves as nothing more than animals, fighting over scraps of bread. This theme highlights not just a loss of personal identity but the obliteration of humanity itself.
“In the afternoon, they made us line up. Three prisoners brought a table and some medical instruments. We were told to roll up our left sleeves and file past the table. The three “veteran” prisoners, needles in hand, tattooed numbers on our left arms. I became A-7713. From then on, I had no other name.”
Loss of identity, faith, the oppressive silence, and the ubiquity of suffering are not just historical reflections but also universal questions that resonate across time. Wiesel’s narrative serves as a stark reminder of the depths of darkness humanity can reach, and the resilience required to search for light amid such darkness.

Loss of Faith
The core of Eliezer’s being is his faith, which is deeply challenged by the atrocities he witnesses. At the beginning of the narrative, Eliezer declares, “I believed profoundly.”
“I was twelve. I believed profoundly. During the day I studied the Talmud, and at night I ran to the synagogue to weep over the destruction of the Temple.”
In the concentration camps of Birkenau-Auschwitz, the horrors Eliezer witnesses begin to shake his faith in God. The crematoriums burn without end, devouring countless lives, including the most innocent of all—children. The cruelty he observes and endures is unimaginable, more brutal than one would ever treat animals. He struggles with the idea of a just God who would allow such atrocities.
“Night. No one prayed, so that the night would pass quickly. The stars were only sparks of the fire which devoured us. Should that fire die out one day, there would be nothing left in the sky but dead stars, dead eyes.”
Despite the terror surrounding them, Eliezer is struck by the sight of fellow Jews clinging to their faith, praying and seeking solace in their beliefs. This perseverance in the face of such evil puzzles him; it seems to demonstrate a strength and a capacity for forgiveness that surpasses the deity they worship.
As time goes on, death becomes a constant companion in the camps, and despair takes root. Eliezer, along with others, loses any remaining belief in a benevolent God. This sentiment is shared by others, like Akiba Drumer and a rabbi Eliezer speaks with, who conclude that a God cannot exist in a world that allows the Holocaust to happen.
“Behind me, I heard the same man asking: “Where is God now?” And I heard a voice within me answer him: “Where is He? Here He is—He is hanging here on this gallows. . . . “”
Eliezer’s faith is irreparably damaged during an execution at Buna, where a young boy is hanged before the eyes of the prisoners. A voice from the crowd pierces the air with the question, “ Where is God now? ” In his heart, Eliezer believes that if God exists, He is present in the suffering of the boy on the gallows, who dies a slow, agonizing death while the prisoners are forced to witness.

Silence permeates “Night,” symbolizing both the incomprehensible absence of God and the muted response of the world to the Holocaust. Eliezer grapples with God’s silence, unable to reconcile it with the loving deity he was raised to worship.
This theme is painfully illustrated when Eliezer fails to answer his dying father’s call, a silence born of utter despair and hopelessness. Wiesel uses this motif to challenge the reader, posing difficult questions about divine and human inaction in the face of atrocity.

Fathers and Sons
Eliezer’s story begins with him witnessing his father cry for the first time when they are forced to leave their home. This is significant because it shows a crack in the strong figure his father has always been. The memoir “Night” delves into the breakdown of father-son bonds under the extreme conditions of the Holocaust. Central to this theme is the changing relationship between Eliezer and his father, which also reflects on the relationships between other fathers and sons in the concentration camps.
Before the Holocaust, Eliezer’s father is a respected figure both in the community and at home. Their relationship is based on tradition, where honoring one’s parents is a key commandment, especially in Jewish families like theirs. But once Eliezer and his father are separated from the rest of their family at Birkenau, they only have each other. As his father becomes weaker, the roles they once played change. Eliezer finds himself in the position of being the protector, rather than the one protected.
Life in the camps tests their relationship in many ways. Eliezer often feels guilty for being mad at his father when he can’t defend himself or keep up with the march. Despite his weakening state, his father still tries to look after Eliezer by giving him tools for survival and even saving him from being strangled on the train. But there’s only so much they can do to shield one another from suffering. As the conditions worsen and the weaker prisoners start dying, fathers start to be seen as burdens. Sons struggle with guilt over their survival instincts and their inability to save their fathers. Eliezer witnesses the extreme of this when a young man abandons his exhausted father, a rabbi, during a death march, and again on a train when a son kills his father for food.
These harsh realities force Eliezer to confront his feelings for his father. However, by the end of “Night,” these feelings become irrelevant. His father falls ill, no one is willing to provide medical help, and Eliezer is powerless to protect him or to stop others from causing harm. The roles and relationships that once defined them are irreversibly altered.
“Oh, to strangle the doctor and the others! To burn the whole world! My father’s murderers! But the cry stayed in my throat.”

Final thoughts
Elie Wiesel’s “Night” shares a heart-wrenching story of how the Holocaust tore apart people’s lives and faith. It shows the painful change in a son’s duty to his father and the struggle to keep hope alive. The book makes us think deeply about the harsh truths of survival and loss during one of history’s darkest times.
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.
Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More from Critical Essay Examples and Samples

Nov 27 2023
Lord of the Flies Themes

Nov 21 2023
One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest Book Summary

Nov 20 2023
Was Helen Keller racist?
Remember Me
Is English your native language ? Yes No
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
Essay Topics – List of 500+ Essay Writing Topics and Ideas
List of 500+ essay writing topics and ideas.
Essay topics in English can be difficult to come up with. While writing essays , many college and high school students face writer’s block and have a hard time to think about topics and ideas for an essay. In this article, we will list out many good essay topics from different categories like argumentative essays, essays on technology, environment essays for students from 5th, 6th, 7th, 8th grades. Following list of essay topics are for all – from kids to college students. We have the largest collection of essays. An essay is nothing but a piece of content which is written from the perception of writer or author. Essays are similar to a story, pamphlet, thesis, etc. The best thing about Essay is you can use any type of language – formal or informal. It can biography, the autobiography of anyone. Following is a great list of 100 essay topics. We will be adding 400 more soon!
But Before that you may wanna read some awesome Essay Writing Tips here .

Get the Huge list of 100+ Speech Topics here
Argumentative Essay Topics
- Should plastic be banned?
- Pollution due to Urbanization
- Education should be free
- Should Students get limited access to the Internet?
- Selling Tobacco should be banned
- Smoking in public places should be banned
- Facebook should be banned
- Students should not be allowed to play PUBG
Essay Topics on Technology
- Wonder Of Science
- Mobile Phone
Essay Topics on Festivals on Events
- Independence Day (15 August)
- Teachers Day
- Summer Vacation
- Children’s Day
- Swachh Bharat Abhiyan
- Janmashtami
- Republic Day
Essay Topics on Education
- Education Essay
- Importance of Education
- Contribution of Technology in Education

Essay Topics on Famous Leaders
- Mahatma Gandhi
- APJ Abdul Kalam
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- Swami Vivekananda
- Mother Teresa
- Rabindranath Tagore
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
- Subhash Chandra Bose
- Abraham Lincoln
- Martin Luther King
- Lal Bahadur Shashtri
Essay Topics on Animals and Birds
- My Favorite Animal
Essays Topics About Yourself
- My Best Friend
- My Favourite Teacher
- My Aim In Life
- My Favourite Game – Badminton
- My Favourite Game – Essay
- My Favourite Book
- My Ambition
- How I Spent My Summer Vacation
- India of My Dreams
- My School Life
- I Love My Family
- My Favourite Subject
- My Favourite Game Badminton
- My Father My Hero
- My School Library
- My Favourite Author
- My plans for summer vacation
Essay Topics Based on Environment and Nature
- Global Warming
- Environment
- Air Pollution
- Environmental Pollution
- Water Pollution
- Rainy Season
- Climate Change
- Importance Of Trees
- Winter Season
- Deforestation
- Natural Disasters
- Save Environment
- Summer Season
- Trees Our Best Friend Essay In English
Essay Topics Based on Proverbs
- Health Is Wealth
- A Stitch in Time Saves Nine
- An Apple a Day Keeps Doctor Away
- Where there is a will, there is way
- Time and Tide wait for none
Toppr provides free study materials like NCERT Solutions for Students, Previous 10 Years of Question Papers, 1000+ hours of video lectures for free. Download Toppr app for Android and iOS or signup for free.
Essay Topics for Students from 6th, 7th, 8th Grade
- Noise Pollution
- Environment Pollution
- Women Empowerment
- Time and Tide Wait for none
- Science and Technology
- Importance of Sports
- Sports and Games
- Time Management
- Cleanliness is next to Godliness
- Cleanliness
- Rome was not Built in a Day
- Unemployment
- Clean India
- Cow Essay In English
- Describe Yourself
- Festivals Of India
- Ganesh Chaturthi
- Healthy Food
- Importance Of Water
- Plastic Pollution
- Value of Time
- Honesty is the Best Policy
- Gandhi Jayanti
- Human Rights
- Knowledge Is Power
- Same Sex Marriage
- Childhood Memories
- Cyber Crime
- Kalpana Chawla
- Punctuality
- Rani Lakshmi Bai
- Spring Season
- Unity In Diversity
- Artificial Intelligence
- Online Shopping
- Indian Culture
- Healthy Lifestyle
- Indian Education System
- Disaster Management
- Environmental Issues
- Freedom Fighters
- Grandparents
- Save Fuel For Better Environment
- Importance Of Newspaper
- Lal Bahadur Shastri
- Raksha Bandhan
- World Environment Day
- Narendra Modi
- What Is Religion
- Charity Begins at Home
- A Journey by Train
- Ideal student
- Save Water Save Earth
- Indian Farmer
- Safety of Women in India
- Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan
- Capital Punishment
- College Life
- Natural Resources
- Peer Pressure
- Nature Vs Nurture
- Romeo And Juliet
- Generation Gap
- Makar Sankranti
- Constitution of India
- Girl Education
- Importance of Family
- Importance of Independence Day
- Brain Drain
- A Friend In Need Is A Friend Indeed
- Action Speaks Louder Than Words
- All That Glitters Is Not Gold
- Bhagat Singh
- Demonetization
- Agriculture
- Importance of Discipline
- Population Explosion
- Poverty in India
- Uses Of Mobile Phones
- Water Scarcity
- Train Journey
- Land Pollution
- Environment Protection
- Indian Army
- Uses of Internet
- All that Glitters is not Gold
- Balanced Diet
- Blood Donation
- Digital India
- Dussehra Essay
- Energy Conservation
- National Integration
- Railway Station
- Sachin Tendulkar
- Health And Hygiene
- Importance Of Forest
- Indira Gandhi
- Laughter Is The Best Medicine
- Career Goals
- Mental Health
- Save Water Save Life
- International Yoga Day
- Winter Vacation
- Soil Pollution
- Every Cloud Has A Silver Lining
- Indian Culture And Tradition
- Unity Is Strength
- Unity is Diversity
- Wildlife Conservation
- Cruelty To Animals
- Nelson Mandela
- Of Mice And Men
- Organ Donation
- Life in a Big City
- Democracy in India
- Waste Management
- Biodiversity
- Afforestation
- Female Foeticide
- Harmful Effects Of Junk Food
- Rain Water Harvesting
- Save Electricity
- Social Media
- Social Networking Sites
- Sound Pollution
- Procrastination
- Life in an Indian Village
- Life in Big City
- Population Growth
- World Population Day
- Greenhouse Effect
- Statue of Unity
- Traffic Jam
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao
- Importance of Good Manners
- Good Manners
- Cyber Security
- Green Revolution
- Health And Fitness
- Incredible India
- Make In India
- Surgical Strike
- Triple Talaq
- A Good Friend
- Importance of Friends in our Life
- Should Plastic be Banned
- Nationalism
- Traffic Rules
- Effects of Global Warming
- Fundamental Rights
- Solar System
- National Constitution Day
- Good Mother
- Importance of Trees in our Life
- City Life Vs Village Life
- Importance of Communication
- Conservation of Nature
- Man vs. Machine
- Indian Economy
- Mothers Love
- Importance of National Integration
- Black Money
- Greenhouse effect
- Untouchability
- Self Discipline
- Global Terrorism
- Conservation of Biodiversity
- Newspaper and Its Uses
- World Health Day
- Conservation of Natural Resources
- A Picnic with Family
- Indian Heritage
- Status of Women in India
- Child is Father of the Man
- Reading is Good Habit
- Plastic Bag
- Terrorism in India
- Library and Its Uses
- Life on Mars
- Urbanization
- Pollution Due to Diwali
- National Flag of India
- Vocational Education
- Importance of Tree Plantation
- Summer Camp
- Vehicle Pollution
- Women Education in India
- Seasons in India
- Freedom of the Press
- Caste System
- Environment and Human Health
- Mountain Climbing
- Depletion of Natural Resources
- Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar
- Health Education
- Effects of Deforestation
- Life after School
- Starvation in India
- Jan Dhan Yojana
- Impact of Privatization
- Election Commission of India
- Election and Democracy
- Prevention of Global Warming
- Impact of Cinema in Life
- Subhas Chandra Bose
- Dowry System
- Ganesh Chaturthi Festival
- Role of Science in Making India
- Impact of Global Warming on Oceans
- Pollution due to Festivals
- Ambedkar Jayanti
- Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat
- Family Planning in India
- Democracy vs Dictatorship
- National Festivals of India
- Sri Aurobindo
- Casteism in India
- Organ trafficking
- Consequences of Global Warming
- Role of Human Activities in Global Warming
- Issues and Problems faced by Women in India
- Role of Judiciary in the Country Today
- Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan
- PUBG Mobile Game Addiction
- Role of Youths in Nation Building
- Value of Oxygen and Water in Life/Earth
- Farmer Suicides in India
- Start-up India
- Pollution Due to Firecrackers
- Life of Soldiers
- Child Labour
- Save Girl Child
- Morning Walk
- My School Fete
- Essay on Financial Literacy
- Essay On Sustainable Development
- Essay On Punjab
- Essay On Travel
- My Home Essay
- Child Marriage Essay
- Importance Of English Language Essay
- Essay On Mass Media
- Essay On Horse
- Essay On Police
- Essay On Eid
- Essay On Solar Energy
- Animal Essay
- Essay On Mango
- Gender Discrimination Essay
- Essay On Advertisement
- My First Day At School Essay
- My Neighborhood Essay
- True Friendship Essay
- Work Is Worship Essay
- Essay On Self Confidence
- Essay On Superstition
- Essay On Bangalore
- Sex Vs Gender Essay
- Essay On Social Issues
- Time Is Money Essay
- Essay About Grandmothers
- Essay On Hard Work
- First Day Of School Essay
- Flowers Essay
- My Favorite Food Essay
- Essay on Birds
- Essay on Humanity
- Essay on Sun
- Essay on Kargil War
- Every Cloud Has a Silver Lining Essay
- Francis Bacon Essays
- Importance of Cleanliness Essay
- My Sister Essay
- Self Introduction Essay
- Solar Energy Essay
- Sports Day Essa
- Value Of Education Essay
- Essay On Isro
- Essay On Balance Is Beneficial
- Essay On Reservation In India
- Essay On Water Management
- Essay On Smoking
- Essay On Stress Management
- Essay On William Shakespeare
- Essay on Apple
- Essay On Albert Einstein
- Essay On Feminism
- Essay On Kindness
- Essay On Domestic Violence
- Essay on English as a Global Language
- Essay On Co-Education
- Importance Of Exercise Essay
- Overpopulation Essay
- Smartphone Essay
- Essay on River
- Essay on Cyclone
- Essay On Facebook
- Essay On Science In Everyday Life
- Essay On Women Rights
- Essay On Right To Education
- Essay on Quotes
- Essay On Peace
- Essay On Drawing
- Essay On Bicycle
- Essay On Sexual Harassment
- Essay On Hospital
- Essay On Srinivasa Ramanujan
- Essay On Golden Temple
- Essay On Art
- Essay On Ruskin Bond
- Essay On Moon
- Birthday Essay
- Dont Judge A Book By Its Cover Essay
- Draught Essay
- Gratitude Essay
- Indian Politics Essay
- Who am I Essay
- Essay on Positive Thinking
- Essay on Dance
- Essay on Navratri
- Essay on Onam
- Essay on New Education Policy 2020
- Esasy on Thank you Coronavirus Helpers
- Essay on Coronavirus and Coronavirus Symptoms
- Essay on Baseball
- Essay on coronavirus vaccine
- Fitness beats pandemic essay
- Essay on coronavirus tips
- Essay on coronavirus prevention
- Essay on coronavirus treatment
- Essay on essay on trees
- Essay on television
- Gender inequality essay
- Water conservation essay
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on Types of sports
- Essay on road safety
- Essay on my favourite season
- My pet essay
- Student life essay
- Essay on Railway station
- Essay on earth
- Essay on knowledge is power
- Essay on favourite personality
- Essay on memorable day of my life
- My parents essay
- Our country essay
- Picnic essay
- Travelling essay
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Letter Writing
- It So Happened Summary
- Honey Dew Chapter Summaries
- The Alien Hand
- Malu Bhalu Summary
- Sing a Song of People Summary
- The Little Bully Summary
- Nobody’s Friend Summary
- Class Discussion Summary
- Crying Summary in English
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Home — Essay Samples — Literature — The Outsiders — The Outsiders Themes
The Outsiders Themes
- Categories: Social Class The Outsiders
About this sample

Words: 472 |
Published: Mar 13, 2024
Words: 472 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Table of contents
Social identity and division, impact of violence, power of empathy.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Sociology Literature

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1070 words
1 pages / 610 words
1 pages / 607 words
2 pages / 887 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on The Outsiders
Dallas Winston, a character from S.E. Hinton's novel "The Outsiders," is known for his rebellious and tough nature. Throughout the book, Dallas Winston, also known as Dally, makes several memorable quotes that reflect his [...]
In S. E. Hinton's novel "The Outsiders," the character of Darrel Curtis, also known as Darry, plays a significant role. As the eldest sibling and caretaker of his two younger brothers, Darry is portrayed as a responsible and [...]
In S. E. Hinton's novel "The Outsiders," the character of Dallas Winston, also known as Dally, plays a significant role in the story. Dally is portrayed as a tough, rebellious, and troubled teenager who often finds himself in [...]
In S.E. Hinton's novel "The Outsiders," the character of Dallas Winston, also known as Dally, stands out as a complex and intriguing figure. His tough exterior and rebellious nature mask a deeper vulnerability and inner turmoil [...]
In the vast landscape of literature, there are certain works that stand out not only for their storytelling prowess but also for their ability to weave in elements of other literary works, historical events, and popular culture. [...]
Johnny Cade is a character in S.E. Hinton's novel, The Outsiders, who stands out for his quiet demeanor and inner strength. Despite being a member of the Greasers, a tough and rebellious gang, Johnny is portrayed as a sensitive [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
The Themes of Diego Rivera
This essay about Diego Rivera explores the multifaceted themes within his art, revealing how Rivera’s work serves as a mirror reflecting the essence of Mexican culture. Through his paintings and murals, Rivera chronicles Mexican history, portraying the struggles and triumphs of its people, from ancient civilizations to the Mexican Revolution. He also captures the everyday lives of Mexicans, particularly laborers, while celebrating indigenous folklore and mythology. Rivera’s art evolves stylistically, reflecting his personal journey and ideological shifts. Overall, Rivera’s themes encompass a wide range of subjects, offering viewers a profound glimpse into the soul of Mexico and the enduring power of art to inspire and unite.
How it works
Diego Rivera, the towering colossus of Mexican art, stands as a luminary whose brushstrokes weave tales of passion, pain, and the indomitable spirit of his homeland. Through a kaleidoscope of themes, Rivera’s artistic journey unveils the multifaceted essence of Mexican culture, captivating audiences with its raw honesty and profound introspection.
Central to Rivera’s oeuvre is his unwavering commitment to portraying the tumultuous narrative of Mexican history. From the ancient civilizations of Mesoamerica to the tumultuous echoes of the Mexican Revolution, Rivera’s murals serve as poignant chronicles, narrating the triumphs and tribulations of a nation in perpetual flux.
With each stroke of his brush, Rivera immortalizes the heroes and heroines who dared to defy tyranny and champion the cause of social justice, their indelible legacies emblazoned upon the walls of the National Palace and beyond.
Yet, amidst the grandeur of historical epics, Rivera’s art also delves into the intimate tapestry of everyday life, illuminating the struggles and aspirations of the Mexican people. From the sun-drenched fields of rural agrarians to the clangorous factories of urban laborers, Rivera’s canvases pulsate with the rhythmic heartbeat of a nation at work. Through his empathetic gaze, he invites viewers to bear witness to the dignity and resilience of those who toil in obscurity, their silent labor a testament to the collective spirit of Mexico.
Moreover, Rivera’s artistic vision transcends the temporal confines of history, embracing the rich tapestry of Mexican folklore and mythology. Drawing inspiration from the vibrant traditions of indigenous cultures, Rivera’s imagery teems with the vibrant hues of Aztec cosmology and the mystical allure of ancient deities. In his hands, Quetzalcoatl dances alongside revolutionaries, their intertwined destinies weaving a seamless narrative of continuity and change, bridging the chasm between past and present.
Yet, for all its mythic grandeur and historical resonance, Rivera’s art remains a deeply personal reflection of his own journey of self-discovery. From the early echoes of European modernism to the fiery fervor of socialist realism, Rivera’s stylistic evolution mirrors the shifting tides of his own ideological awakening. With each brushstroke, he wrestles with the complexities of identity and belonging, his art a mirror reflecting the indomitable spirit of a nation in constant flux.
In summation, Diego Rivera’s themes encapsulate the vibrant mosaic of Mexican culture, weaving a tapestry of history, labor, and mythology that resonates with timeless relevance. Through his art, Rivera invites us to embark on a journey of discovery, to traverse the labyrinthine corridors of the Mexican soul and behold its myriad wonders. In a world fraught with division and discord, Rivera’s legacy serves as a beacon of hope, reminding us of the transformative power of art to unite, inspire, and ignite the flames of revolution.
Cite this page
The Themes Of Diego Rivera. (2024, Apr 14). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-themes-of-diego-rivera/
"The Themes Of Diego Rivera." PapersOwl.com , 14 Apr 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-themes-of-diego-rivera/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Themes Of Diego Rivera . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-themes-of-diego-rivera/ [Accessed: 14 Apr. 2024]
"The Themes Of Diego Rivera." PapersOwl.com, Apr 14, 2024. Accessed April 14, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-themes-of-diego-rivera/
"The Themes Of Diego Rivera," PapersOwl.com , 14-Apr-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-themes-of-diego-rivera/. [Accessed: 14-Apr-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Themes Of Diego Rivera . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-themes-of-diego-rivera/ [Accessed: 14-Apr-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Download Article. 1. Read the essay prompt carefully. A theme essay usually responds to a specific prompt given to you by a teacher or professor. Most essay prompts will ask you to identify the theme, or the overarching message, in a text. Look at the terms used in the prompt and highlight keywords or important terms.
Step 4. Write Body Paragraphs for Your Theme Essay. Goal of thematic essay body is to answer all the questions stated in an introduction. You must elaborate the meaning of each key idea. Finally, display your usage of literary devices, as we've specified earlier. Common practice is to use at least one paragraph per a literary device disclosure.
Thematic writing is a staple of high school English and college writing courses. The idea behind thematic writing is to create a piece that uses a theme to tie together different ideas or topics. Thematic writing can be used for essays, short stories, novels, and even non-fiction pieces. In academic writing, thematic essays often center on a ...
1. Identify a Central Theme. The audience can determine the central theme of a thematic essay from a thesis statement or an overview of topic statements. Basically, a well-composed thesis statement must explicitly mention the central theme or implicitly hint at the central theme.
2. Pick the most prevalent subject: One thing to note is the significant difference between a subject and a theme. A subject is the general topic of conversation—whether it be love, bravery, deception, etc. A theme is a specific point the author is making about said subject. So, find the talking point that is most commonly being brought up.
1 Map out themes and literary devices. Your story's theme should be on your mind throughout every stage of the writing process. As you brainstorm, think about the statements you want to make in your work. Jot these down, then jot down any potential symbols or concepts you can use to illustrate these statements.
A theme is a universal idea, lesson, or message explored throughout a work of literature. One key characteristic of literary themes is their universality, which is to say that themes are ideas that not only apply to the specific characters and events of a book or play, but also express broader truths about human experience that readers can ...
Introduction. Generally, to write a thematic essay you need to have an idea of what your thesis will be, how your body paragraphs will prove it, and how you are going to summarize all of the arguments detailed in the body of the essay in your conclusion. The introduction has to present the main subject of your essay as well as any necessary ...
Customize your theme essay outline accordingly; don't make it as generic as this example here. Fill it with details like what ideas you will include in your first paragraph, what your thesis statement will be, and what your introduction hook is. With this thematic essay format, you are now ready to do the write-up. 5. Write the Essay
Stay focused in order not to miss important things that may help you to write your essay. Differentiate the theme from the subject of the work under analysis. The general topic of the conversation is a subject. For example: love, hate, or brevity. A theme is more specific and is based on the subject.
Add relevant supporting details to the main body that defend your theme. Conclusion should be precise and finishes off the essay stating the overall significance. Be relevant and precise. Add necessary examples where needed. Refer to the author and avoid giving your personal opinion.
theme: The most important things in life can't be seen with the eyes but with the heart. 5. Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone by J.K. Rowling (1997) summary: An unsuspecting orphan attends a wizard school where he discovers his true identity, a dark foe, and the belonging he craves.
Here's our list of common themes in literature: Love: the theme of love appears in novels within many genres, as it can discuss the love of people, pets, objects, and life. Love is a complex concept, so there are still unique takes on this theme being published every day. Death/Grief: the theme of death can focus on the concept of mortality ...
Examples of essay outlines. Examples of outlines for different types of essays are presented below: an argumentative, expository, and literary analysis essay. Argumentative essay outline. This outline is for a short argumentative essay evaluating the internet's impact on education. It uses short phrases to summarize each point.
Theme definition: the central idea (s) that a piece of writing explores. That said, theme is more than just an idea. It is also the work's specific vantage point on that idea. In other words, a theme is an idea plus an opinion: it is the author's specific views regarding the central ideas of the work.
This example guides you through the structure of an essay. It shows how to build an effective introduction , focused paragraphs , clear transitions between ideas, and a strong conclusion . Each paragraph addresses a single central point, introduced by a topic sentence , and each point is directly related to the thesis statement .
How to Do Thematic Analysis | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Published on September 6, 2019 by Jack Caulfield.Revised on June 22, 2023. Thematic analysis is a method of analyzing qualitative data.It is usually applied to a set of texts, such as an interview or transcripts.The researcher closely examines the data to identify common themes - topics, ideas and patterns of meaning that come up ...
The themes of "Night" by Elie Wiesel explore profound aspects of human nature and spirituality. Eliezer's journey begins in his hometown, where he is deeply immersed in Jewish teachings and traditions. His profound identity as a young, devout Jew is starkly contrasted with the dehumanization he endures under the Nazi regime.
While writing essays, many college and high school students face writer's block and have a hard time to think about topics and ideas for an essay. In this article, we will list out many good essay topics from different categories like argumentative essays, essays on technology, environment essays for students from 5th, 6th, 7th, 8th grades.
The theme of guilt in Macbeth is further reinforced by the portrayal of the witches and their manipulation of Macbeth's psyche. The witches' prophecies and manipulative tactics serve to fuel Macbeth's ambition and ultimately lead him to commit the murder of King Duncan. However, their influence also plays a significant role in exacerbating ...
Theme Essay Theme Theme Essay Don't judge a book by it's cover. This theme shows up all over the story "The Girl who was Born with only Two Arms and Two Legs" By Stuart Baum. People where they live have four arms and four legs. Judging happens in many ways. In this story it happens in two ways. First off,
Revenge is a powerful and enduring theme in William Shakespeare's tragedy, Macbeth. From the very beginning of the play, we see the seeds of vengeance planted in the hearts of the characters, driving their actions and ultimately leading to their downfall. In Macbeth, the titular character's desire for revenge is sparked by the prophecies of the ...
The Outsiders Themes. A novel by S.E. Hinton, is a timeless classic that explores the themes of friendship, loyalty, and the struggle between social classes. Set in the 1960s, the book follows the lives of two rival gangs, the Greasers and the Socs, and their constant battles for dominance. Through the experiences of the main character, Ponyboy ...
Essay Example: Diego Rivera, the towering colossus of Mexican art, stands as a luminary whose brushstrokes weave tales of passion, pain, and the indomitable spirit of his homeland. Through a kaleidoscope of themes, Rivera's artistic journey unveils the multifaceted essence of Mexican culture