[email protected]
- English English Spanish German French Turkish


Thesis vs. Research Paper: Know the Differences
It is not uncommon for individuals, academic and nonacademic to use “thesis” and “research paper” interchangeably. However, while the thesis vs. research paper puzzle might seem amusing to some, for graduate, postgraduate and doctoral students, knowing the differences between the two is crucial. Not only does a clear demarcation of the two terms help you acquire a precise approach toward writing each of them, but it also helps you keep in mind the subtle nuances that go into creating the two documents. This brief guide discusses the main difference between a thesis and a research paper.

This article discusses the main difference between a thesis and a research paper. To give you an opportunity to practice proofreading, we have left a few spelling, punctuation, or grammatical errors in the text. See if you can spot them! If you spot the errors correctly, you will be entitled to a 10% discount.
It is not uncommon for individuals, academic and nonacademic to use “thesis” and “research paper” interchangeably. After all, both terms share the same domain, academic writing . Moreover, characteristics like the writing style, tone, and structure of a thesis and research paper are also homogenous to a certain degree. Hence, it is not surprising that many people mistake one for the other.
However, while the thesis vs. research paper puzzle might seem amusing to some, for graduate, postgraduate and doctoral students, knowing the differences between the two is crucial. Not only does a clear demarcation of the two terms help you acquire a precise approach toward writing each of them, but it also helps you keep in mind the subtle nuances that go into creating the two documents.
Defining the two terms: thesis vs. research paper
The first step to discerning between a thesis and research paper is to know what they signify.
Thesis: A thesis or a dissertation is an academic document that a candidate writes to acquire a university degree or similar qualification. Students typically submit a thesis at the end of their final academic term. It generally consists of putting forward an argument and backing it up with individual research and existing data.
How to Write a Perfect Ph.D. Thesis
How to Choose a Thesis or Dissertation Topic: 6 Tips
5 Common Mistakes When Writing a Thesis or Dissertation
How to Structure a Dissertation: A Brief Guide
A Step-by-Step Guide on Writing and Structuring Your Dissertation
Research Paper: A research paper is also an academic document, albeit shorter compared to a thesis. It consists of conducting independent and extensive research on a topic and compiling the data in a structured and comprehensible form. A research paper demonstrates a student's academic prowess in their field of study along with strong analytical skills.
7 Tips to Write an Effective Research Paper
7 Steps to Publishing in a Scientific Journal
Publishing Articles in Peer-Reviewed Journals: A Comprehensive Guide
10 Free Online Journal and Research Databases for Researchers
How to Formulate Research Questions
Now that we have a fundamental understanding of a thesis and a research paper, it is time to dig deeper. To the untrained eye, a research paper and a thesis might seem similar. However, there are some differences, concrete and subtle, that set the two apart.
1. Writing objectives
The objective behind writing a thesis is to obtain a master's degree or doctorate and the ilk. Hence, it needs to exemplify the scope of your knowledge in your study field. That is why choosing an intriguing thesis topic and putting forward your arguments convincingly in favor of it is crucial.
A research paper is written as a part of a course's curriculum or written for publication in a peer-review journal. Its purpose is to contribute something new to the knowledge base of its topic.
2. Structure
Although both documents share quite a few similarities in their structures, the framework of a thesis is more rigid. Also, almost every university has its proprietary guidelines set out for thesis writing.
Comparatively, a research paper only needs to keep the IMRAD format consistent throughout its length. When planning to publish your research paper in a peer-review journal, you also must follow your target journal guidelines.
3. Time Taken
A thesis is an extensive document encompassing the entire duration of a master's or doctoral course and as such, it takes months and even years to write.
A research paper, being less lengthy, typically takes a few weeks or a few months to complete.
4. Supervision
Writing a thesis entails working with a faculty supervisor to ensure that you are on the right track. However, a research paper is more of a solo project and rarely needs a dedicated supervisor to oversee.
5. Finalization
The final stage of thesis completion is a viva voce examination and a thesis defense. It includes proffering your thesis to the examination board or a thesis committee for a questionnaire and related discussions. Whether or not you will receive a degree depends on the result of this examination and the defense.
A research paper is said to be complete when you finalize a draft, check it for plagiarism, and proofread for any language and contextual errors . Now all that's left is to submit it to the assigned authority.
What is Plagiarism | How to Avoid It
How to Choose the Right Plagiarism Checker for Your Academic Works
5 Practical Ways to Avoid Plagiarism
10 Common Grammar Mistakes in Academic Writing
Guide to Avoid Common Mistakes in Sentence Structuring
In the context of academic writing, a thesis and a research paper might appear the same. But, there are some fundamental differences that set apart the two writing formats. However, since both the documents come under the scope of academic writing, they also share some similarities. Both require formal language, formal tone, factually correct information & proper citations. Also, editing and proofreading are a must for both. Editing and Proofreading ensure that your document is properly formatted and devoid of all grammatical & contextual errors. So, the next time when you come across a thesis vs. research paper argument, keep these differences in mind.
Editing or Proofreading? Which Service Should I Choose?
Thesis Proofreading and Editing Services
8 Benefits of Using Professional Proofreading and Editing Services
Achieve What You Want with Academic Editing and Proofreading
How Much Do Proofreading and Editing Cost?
If you need us to make your thesis or dissertation, contact us unhesitatingly!
Best Edit & Proof expert editors and proofreaders focus on offering papers with proper tone, content, and style of academic writing, and also provide an upscale editing and proofreading service for you. If you consider our pieces of advice, you will witness a notable increase in the chance for your research manuscript to be accepted by the publishers. We work together as an academic writing style guide by bestowing subject-area editing and proofreading around several categorized writing styles. With the group of our expert editors, you will always find us all set to help you identify the tone and style that your manuscript needs to get a nod from the publishers.
English formatting service
You can also avail of our assistance if you are looking for editors who can format your manuscript, or just check on the particular styles for the formatting task as per the guidelines provided to you, e.g., APA, MLA, or Chicago/Turabian styles. Best Edit & Proof editors and proofreaders provide all sorts of academic writing help, including editing and proofreading services, using our user-friendly website, and a streamlined ordering process.
Get a free quote for editing and proofreading now!
Visit our order page if you want our subject-area editors or language experts to work on your manuscript to improve its tone and style and give it a perfect academic tone and style through proper editing and proofreading. The process of submitting a paper is very easy and quick. Click here to find out how it works.
Our pricing is based on the type of service you avail of here, be it editing or proofreading. We charge on the basis of the word count of your manuscript that you submit for editing and proofreading and the turnaround time it takes to get it done. If you want to get an instant price quote for your project, copy and paste your document or enter your word count into our pricing calculator.

24/7 customer support | Live support
Contact us to get support with academic editing and proofreading. We have a 24/7 active live chat mode to offer you direct support along with qualified editors to refine and furbish your manuscript.

Stay tuned for updated information about editing and proofreading services!
Follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and Medium .
For more posts, click here.
- Editing & Proofreading
- Citation Styles
- Grammar Rules
- Academic Writing
- Proofreading
- Microsoft Tools
- Academic Publishing
- Dissertation & Thesis
- Researching
- Job & Research Application
Similar Posts
How to Determine Variability in a Dataset
How to Determine Central Tendency
How to Specify Study Variables in Research Papers?
Population vs Sample | Sampling Methods for a Dissertation
7 Issues to Avoid That may Dent the Quality of Thesis Writing
How to Ensure the Quality of Academic Writing in a Thesis and Dissertation?
How to Define Population and Sample in a Dissertation?
Recent Posts
ANOVA vs MANOVA: Which Method to Use in Dissertations?
They Also Read

Whether you are new to academics or have been around for a while, you must understand that research is a critical segment of the academic field. Therefore, it is essential to know the WHATs, WHYs, and HOWs of it. Pertaining to that, this article discusses different types of research methods that you will come across. Namely, they are — quantitative research and qualitative research. Here, we will learn what these types of research are, how they are different, and when they are used. This will be especially helpful for researchers and students who are just starting with their research.

Blog writing is an effective way to share your knowledge and ideas with your target group. Here you can dive deep and talk about your favorite topics, showcase your expertise and attract an audience or readers interested in your work. However, creating a perfect blog post can sometimes get overwhelming – from choosing the right topics to selecting the proper format for your articles to picking images that generate interest and engagement, it's no less than a task.

While composing a thesis or dissertation, a student must experience some predicted traps. Falling into these traps can affect one’s academic career. However, handling potential blunders and pitfalls wisely, while developing a thesis, can lead you to success. The process of writing may be frustrating but learning about the probable pitfalls may ease your stress. Here, we bring you the list of the most common mistakes we have noticed as a professional proofreading and editing service provider.

Choosing a topic for your dissertation or thesis at the end of your master's or doctoral study can become a daunting task. You must select a topic that you find interesting to work on. A dissertation/thesis is a crucial piece of work as it carries enormous credit points at the end of the master's study or postgraduate year. Therefore, you must choose the right and the most suitable topic. Here are some helpful tips for choosing a dissertation and thesis topic that suits you the most.

Formal writing is essential to academic essays, a thesis, or a dissertation. Many issues may dent your writing. This article covers 7 critical ones to avoid that may affect the quality of thesis and dissertation writing.
Thesis vs. Research Paper: What's the Difference?
Key Differences
Comparison chart, supervision, associated with, primary contribution, thesis and research paper definitions, research paper, what is the purpose of a thesis, what is the difference between a thesis and a dissertation, how long is a typical thesis, how is a thesis graded, what is a thesis, who reads a thesis, what is the purpose of a research paper, how long is a typical research paper, what is the difference between a research paper and an essay, can a thesis include personal opinions, what is a research paper, who reads a research paper, how is a research paper structured, how do you cite a thesis, how is a research paper graded, how do you cite a research paper, how do you choose a topic for a research paper, how is a thesis structured, can a thesis be published, can a research paper be published.

Trending Comparisons

Popular Comparisons

New Comparisons

- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper
On the other hand, a research paper is analytical, argumentative and interpretative in nature. It involves the pursuit of knowledge and intelligent analysis of the information collected. It contains the idea of the author, often supported by expert opinions, research and information available in this regard.
Whether you are writing a thesis or research paper, they are equally challenging and take a lot of time to prepare. In this post, we will update you on all the points of difference between thesis and research paper.
Content: Thesis Vs Research Paper
- Key Elements
- Thesis Statement
How to start a research paper?
Comparison chart, what is thesis.
The thesis is a document containing the research and findings that students submit to get the professional qualification or degree . It has to be argumentative, which proposes a debatable point with which people could either agree or disagree. In short, it is a research report in writing that contains a problem which is yet to be dealt with.
In a thesis, the researcher puts forth his/her conclusion. The researcher also gives evidence in support of the conclusion.
Submission of the thesis is a mandatory requirement of a postgraduate course and PhD degree. In this, the primary focus is on the novelty of research along with the research methodology.
It is all about possibilities, by introducing several anti-thesis. Also, it ends up all the possibilities by nullifying all these anti-thesis.
Key Elements of Thesis
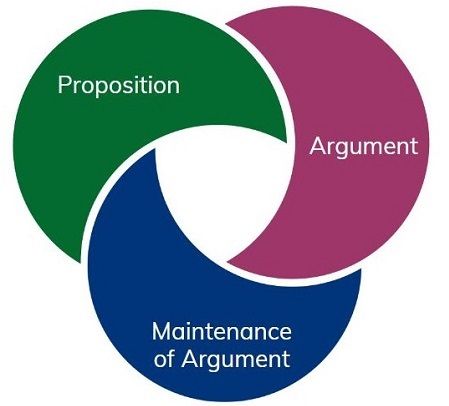
- Proposition : The thesis propagates an idea, hypothesis or recommendation.
- Argument : Gives reasons for accepting the proposition instead of just asserting a point of view.
- Maintenance of argument : The argument should be made cogent enough by providing suitable logic and adequate evidence.
Features of An Ideal Thesis
- An Ideal thesis is expected to add fresh knowledge to the existing theory.
- It communicates the central idea of the research in a clear and concise manner.
- An effective thesis is more than a simple statement, fact or question.
- It answers why and how questions concerned with the topic.
- To avoid confusion, it is worded carefully.
- It outlines the direction and scope of your essay.
- It gives reasons to the reader to continue reading.
Also Read : Difference Between Thesis and Dissertation
What is Thesis Statement?
A thesis statement is a sentence of one line, usually written at the end of your first paragraph. It presents the argument to the reader.
It is a blueprint of your thesis that directs the writer while writing the thesis and guides the reader through it.
What is Research Paper?
Research Paper is a form of academic writing. It is prepared on the basis of the original research conducted by the author on a specific topic, along with its analysis and interpretation of the findings.
An author generally starts writing a research paper on the basis of what he knows about the topic and seeks to find out what experts know. Further, it involves thorough and systematic research on a particular subject to extract the maximum information.
In short, a research paper is a written and published report containing the results of scientific research or a review of published scientific papers. Here, the scientific research is the primary research article, while the review of a published scientific paper is the review article.
In case of the primary research article, the author of the research paper provides important information about the research. This enables the scientific community members to:
- Evaluate it
- Reproduce the experiments
- Assess the reasoning and conclusions drawn
On the other hand, a review article is written to analyze, summarize and synthesize the research carried out previously.
When a research work is published in a scientific journal, it conveys the knowledge to a larger group of people and also makes people aware of the scientific work. Research work published as a research paper passes on knowledge and information to many people. The research paper provides relevant information about the disease and the treatment options at hand .
To start writing a research paper, one should always go for a topic that is interesting and a bit challenging too. Here, the key to choosing the topic is to pick the one that you can manage. So, you could avoid such topics which are very technical or specialized and also those topics for which data is not easily available. Also, do not go for any controversial topic.
The researcher’s approach and attitude towards the topic will decide the amount of effort and enthusiasm.
Steps for writing Research Paper
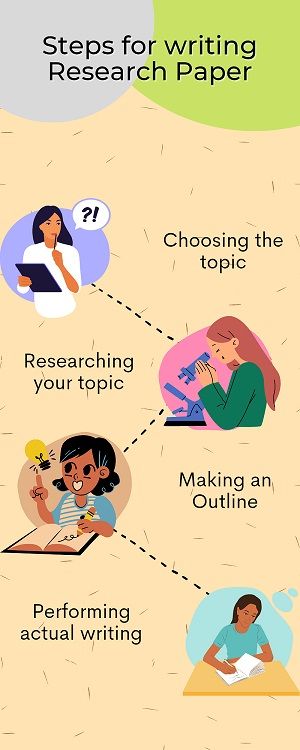
The total number of pages included in a Research Paper relies upon the research topic. It may include 8 to 10 pages, which are:
- Introduction
- Review of Literature
- Methodology
- Research Analysis
- Recommendations
Also Read : Difference Between Research Proposal and Research Report
Key Differences Between Thesis and Research Paper
- A thesis implies an original, plagiarism-free, written academic document that acts as a final project for a university degree of a higher level. But, Research Paper is a novel, plagiarism-free long essay. It portrays the interpretation, evaluation or argument submitted by a researcher.
- The thesis acts as a final project. Whereas a research paper is a kind of research manual of journals.
- The length of the thesis is around 20,000 to 80,000 words. On the contrary, the length of the research paper is relative to the study.
- The thesis focuses on the central question or statement of an intellectual argument that entails further research. On the contrary, the research paper is concerned with proving the central argument.
- The purpose of submitting the thesis is to get the degree or professional qualification. It also presents the knowledge of the candidate in the respective field. Conversely, the aim of publishing research papers is to prove credibility and contribute knowledge in the respective field.
- While the student submits the thesis to the educational committee or panel of professors who review it. In contrast, scientists and other researchers read and review the research paper.
- Preparation and completion of thesis is always under the guidance of a supervisor. For submission of the thesis, the university assigns a supervisor to each student, under whose guidance the thesis must be completed. As against, no supervisor is appointed as a guide in case of a research paper.
- The thesis contains a broader description of the subject matter. In contrast, the research paper contains a narrow description of the subject matter.
Once the research paper is published, it increases the fellowship and job opportunities for new researchers. On the other hand, thesis writing will enable the students to get the desired degree at the end of the course they have opted.
You Might Also Like:

Dr. Owenga says
February 23, 2023 at 2:38 pm
So good and informative. These are quite beneficial insights. Thanks
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Home » Education » What is the Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper
What is the Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper
The main difference between thesis and research paper is that thesis is a long academic paper that typically serves as the final project for a university degree, while research paper is a piece of academic writing on a particular topic.
In brief, both thesis and research paper are types of academic writing students need to complete in their academic life. While there are many similarities between the two, including the use of academic writing and structure, they are not the same.
Key Areas Covered
1. What is a Thesis – Definition, Features 2. What is a Research Paper – Definition, Features 3. Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper – Comparison of Key Differences

What is a Thesis
A thesis is a long paper that typically serves as the final project for a university degree. Submitting a thesis is generally required for completing undergraduate honours, masters , and doctoral degrees . The theses are very long and may contain hundreds of pages. They are also scholarly in nature and allows students to contribute valuable research in their field of study.
Moreover, a major part of a thesis work involves research and writing. It generally has advanced research design and analysis. When writing a thesis, the students will have to prove or disapprove a hypothesis , and their conclusions have to be backed by extensive research and an insightful, learned description of how they got to that conclusion. In some degree programs, students also have to perform an oral defence of the thesis paper in front of a panel of experts.
Components of a Thesis
These are the components you will usually find in a thesis paper.
- Title Page
- Abstract
- Table of Contents
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- Introduction
- Methods
- Discussion
- Conclusions
- Recommendations
- Acknowledgements
- References
What is a Research Paper
A research paper is a type of academic writing that involves research, source evaluation, critical thinking, organization, and composition. Moreover, through a research paper, students can explore, interpret, and evaluate sources related to a particular topic. In fact, primary and secondary sources are very important components of a research paper. But it’s important to note that a research paper is not just a summary of a topic using primary and secondary sources. It’s not just an opinion essay or an expository essay that contains the writer’s opinions and views, either. A research paper is a type of writing that requires evaluating different sources and interpreting the information of these sources through one’s own lens. Furthermore, the main purpose of this type of writing is to offer a unique perspective on a topic analyzing and evaluating what others have already said about it.

In addition, there are different types of research papers. Argumentative research papers and analytical research papers are two of the main types of research papers.
Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper
A thesis or dissertation is a long academic paper that typically serves as the final project for a university degree while a research paper is a type of academic writing that involves research, source evaluation, critical thinking, organization, and composition.
In an Academic Context
In an academic context, students may be required to write research papers for assignments and homework, but a thesis is usually the final project.
A thesis tends to be longer than a research paper; in fact, a thesis can take many months, sometimes years, to complete.
Supervision
The thesis is written under the supervision of one or more academic supervisors whereas research papers usually do not have supervisors.
Students have to complete a thesis in order to complete their degree, whereas students write research papers to expand their knowledge.
In brief, the main difference between thesis and research paper is that thesis is a long research paper that typically serves as the final project for a university degree, while a research paper is a piece of academic writing on a particular topic. Moreover, in an academic context, students may be required to write research papers for assignments and homework. But the thesis is usually the final project.
1. Stute, Martin. “ How to Write Your Thesis .” Columbia University. 2. “ Genre and the Research Paper .” Purdue Writing Lab.
Image Courtesy:
1. “ Research Paper ” (CC BY-SA 3.0) By Nick Youngson via Alpha Stock Images
About the Author: Hasa
Hasanthi is a seasoned content writer and editor with over 8 years of experience. Armed with a BA degree in English and a knack for digital marketing, she explores her passions for literature, history, culture, and food through her engaging and informative writing.
You May Also Like These
Leave a reply cancel reply.

- Master Your Homework
- Do My Homework
Thesis vs. Research Paper: What’s the Difference?
At universities around the world, students are often required to produce scholarly research pieces in the form of a thesis or research paper. While these two types of documents may appear similar on the surface, there is an important distinction between them that needs to be understood by both instructors and students alike. This article will outline the differences between a thesis and a research paper in order to provide readers with greater clarity regarding each type’s purpose, structure, and format. By examining key elements such as length requirements, citation style preferences, amount of source material needed for support arguments made within either document type; we can further explore what makes up each one’s unique character while understanding how they differ from one another at their core.
- I. Introduction to Thesis vs. Research Paper
- II. Definition of a Thesis
- III. Definition of a Research Paper
- IV. Similarities between Theses and Research Papers
- V. Differences between Theses and Research Papers
Realizing the Potential of Blockchain Technology
- Recent advances in blockchain technology have made it a viable solution to many different challenges.
- Blockchain is best known as an immutable, distributed ledger for secure data storage and management.
The application possibilities for this technology are practically endless, ranging from financial services to healthcare systems. For example, research has shown that blockchain could revolutionize the banking industry by improving transaction speed and security while also reducing costs.
In addition to its use in financial markets, there have been several studies exploring how blockchain can be used within academia. A recent paper published in Nature Communications argues that it could play a key role in enhancing scholarly publishing processes such as peer review and manuscript tracking. The authors suggest using smart contracts built on top of the Ethereum platform to create automated workflows between researchers, publishers and readers.
I. Introduction to Thesis vs. Research Paper
Choosing between a thesis and a research paper is often daunting, but understanding the difference can be key to crafting an effective piece of academic writing. While both papers require extensive research into various topics or arguments, there are notable differences that set each apart.
A thesis , typically written for graduate students pursuing advanced degrees such as master’s or doctoral programs, serves as the final project necessary for graduation. Students craft this type of essay after conducting independent research in their chosen field in order to prove proficiency within said area. A thesis should provide readers with insight on a specific topic while showing competence and knowledge acquired during one’s years spent studying at an institution. Therefore, its length will vary depending upon the scope and depth of the subject matter covered by its author(s).
- Research Paper:
In contrast to a thesis, which focuses primarily on original ideas generated through primary sources (i.e., books authored by experts) collected throughout one’s studies; a research paper , generally assigned during undergraduate courses rather than graduate ones due to their shorter length requirement (usually 8-10 pages), requires deep exploration into existing texts/data collected from multiple secondary sources. It aims not only to demonstrate comprehension of related material found online or elsewhere but also convey them clearly in accordance with established guidelines regarding grammar usage and other formalities expected when submitting this kind of assignment
II. Definition of a Thesis
When speaking of academic writing, the research paper and thesis , two distinct yet closely related documents, are often discussed together. To better understand these works of scholarly discourse it is helpful to clarify their definitions.
A research paper is a written document that presents evidence or information in an effort to support a specific argument. It can be about any subject imaginable but must include primary sources such as surveys or interviews which have been conducted by the author themselves. While there may also be some secondary source material included, this should not form the main body of work.
In contrast to a research paper, a thesis is more comprehensive document typically produced when pursuing advanced degrees such as masters’s and doctoral programs. A thesis requires much greater depth than what one would find in a typical essay or project report – often hundreds of pages long – requiring significant original thought and analysis on behalf of its creator(s). It generally includes several sections including an introduction (statement), literature review (critique), discussion (analysis) and conclusion.
III. Definition of a Research Paper
A research paper is an academic writing that reports on the findings of a particular topic and communicates them to its readers. It is based on previously published research, such as books, journals, or other sources. The purpose of this type of paper is to demonstrate how the writer has conducted original research in order to gain knowledge about their subject matter.
In most cases, a thesis statement appears at the beginning of a research paper as part of an introduction. This statement conveys the main idea or argument for which you are making your case in relation to your chosen topic and should be written with clarity and precision. Once this foundation has been laid down, it will then serve as a guidepost throughout the rest of your essay by providing clear structure around which you can build up evidence supporting your claims through different types:
- Qualitative
- Quantitative
- “Mixed-Methods” Research.
. For example; if exploring gender roles within religion one could cite textual analysis from scriptures such survey data from interviews with religious practitioners examining their views on these topics among others.. Ultimately no matter what type or method used all valid information gathered must fit into respective parts that make up overall thesis statement presented early while conducting effective analysis accompanied by sufficient support provided via cited sources reviewed beforehand when composing entire work piece – thus forming concise project known as ‘Research Paper’.
IV. Similarities between Theses and Research Papers
Comparative Analysis
The purpose of both a research paper and a thesis is to further explore and develop knowledge on an assigned topic. Both documents require extensive amounts of research, referencing credible sources, and in-depth analysis. Additionally, these two pieces share common elements such as an introduction, body text containing arguments or evidence that support the writer’s hypothesis or conclusion, and a final summary which ties all the ideas together into one cohesive document.
Despite similarities between them though, there are fundamental differences between papers & theses that distinguish their purposes from each other. For instance; while research papers focus more on exploring existing literature about said topics through secondary data collection methods with little emphasis placed upon developing new ideas/concepts for readers – Thesis projects concentrate more on producing original academic works based upon primary data collected by its author(s) themselves using various empirical methodologies & models presented throughout their texts . Therefore it’s clear to see how these two writing styles contrast yet still find some overlaps within each respective form of written work!
V. Differences between Theses and Research Papers
It is important to understand the differences between a thesis and research paper, as it can have an effect on how you present your work. Although there are similarities between the two genres, they differ in several ways.
- A research paper , which is also referred to as a report or essay, is written for academic purposes and aims to answer an open-ended question or analyze specific data points within a given topic. It typically includes multiple sources of information from different sources such as books, magazines, newspapers etc., with quotes being used throughout the text.
- Research papers tend to be longer than other types of writing due to their depth and scope; usually ranging from 5 pages up to 50 pages or more depending upon your subject matter.
Theses =are often considered one step above regular research paper because these require greater level of hardwork & efforts involved than latter due mainly lengthy nature..In addition ,the content should include extensive analysis alongwith authors perspective about current understanding about context within area covered so far . They must include originality among peer’s previous work done previously .
In conclusion, the differences between a thesis and research paper are multifaceted. A thesis is typically longer than a research paper due to its depth of content and higher level of analysis that it requires. The topics for these two types of documents also differ in terms of scope, focus on making an original contribution to knowledge within their respective fields, as well as the audience being addressed by each type. As such, understanding these distinctions can provide students with better insight into when they should be using either format or writing style. Ultimately, this article has outlined the basic criteria necessary for distinguishing between a thesis versus a research paper so readers may make more informed decisions in selecting which one best suits their individual needs.

Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper: Unraveling the Distinction in 2023
Are you puzzled in the difference between Thesis and Research Paper? If yes, then have a close look at this blog post to explore everything about the difference between Thesis and Research Paper
In the realm of academia, students and researchers encounter various types of written assignments that require rigorous investigation and analysis. Among these assignments, the thesis and research paper are two common forms of scholarly writing.
While both contribute to the advancement of knowledge and demonstrate a student’s research capabilities, there are distinct differences between them in terms of purpose, scope, originality, structure, evaluation, and length.
Understanding these differences is essential for students embarking on their academic journey or researchers seeking to make meaningful contributions to their respective fields.
By grasping the unique characteristics of a thesis and a research paper, individuals can navigate the academic landscape more effectively, align their research objectives, and tailor their writing to meet the specific expectations of each form of scholarly communication.
In this discussion, we will delve into the dissimilarities between a thesis and a research paper, shedding light on the distinct purposes they serve, the scope of their investigations, the level of originality they demand, the structure they adhere to, the evaluation criteria they face, and the length of time they require for completion.
By examining these aspects, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how a thesis and a research paper differ, allowing students and researchers to approach these academic assignments with greater clarity and confidence.
Whether you are a student embarking on your undergraduate or postgraduate journey, or a researcher striving to contribute to the scholarly discourse in your field, gaining a thorough understanding of the differences between a thesis and a research paper will serve as a valuable guide in effectively formulating research questions, conducting comprehensive investigations, and presenting your findings in a manner that aligns with the expectations of your academic community.
So, let us explore the unique characteristics that set a thesis and a research paper apart, empowering you to navigate the academic landscape and engage in scholarly pursuits with distinction and purpose.
Definition and Purpose of a Thesis
Table of Contents
A thesis is a significant academic document that showcases a student’s in-depth understanding of a particular subject and their ability to conduct independent research.
It is a formal written work that presents original findings, arguments, or theories, aiming to contribute new knowledge to the academic community. A thesis is typically pursued as a requirement for obtaining a higher academic degree, such as a Master’s or Ph.D.
The purpose of a thesis is multifold. Firstly, it serves as a demonstration of the student’s comprehensive understanding of the chosen field of study. It requires an extensive exploration of the existing literature, theories, methodologies, or experiments related to the research topic.
By delving deeply into the subject matter, a thesis allows students to showcase their analytical and critical thinking abilities, as well as their proficiency in synthesizing and evaluating complex information.
Secondly, a thesis aims to contribute to the existing body of knowledge within the specific academic discipline. It demands original research and the identification of a research gap, which the student then strives to fill through their investigations.
By conducting thorough research, collecting and analyzing data, and drawing meaningful conclusions, a thesis can offer new insights, propose novel theories, or develop innovative methodologies. Through their contribution, students endeavor to advance the understanding and knowledge within their field of study.
Lastly, a thesis serves as a requirement for obtaining a higher academic degree. It demonstrates the student’s research capabilities and scholarly competence, validating their readiness to contribute to their chosen field as a qualified professional or researcher.
Successful completion of a thesis signifies the mastery of research skills, the ability to work independently, and the capacity to engage in academic discourse.
Overall, a thesis represents a significant academic achievement, reflecting the culmination of a student’s academic journey and their dedication to expanding knowledge within their field. It serves as a testament to their intellectual capabilities, research prowess, and their potential to make meaningful contributions to their respective disciplines.
Definition and Purpose of a Research Paper
A research paper is a scholarly document that presents the results of a study or investigation conducted by a researcher or a group of researchers. It is a written work that focuses on addressing a specific research question, exploring a hypothesis, or investigating a particular topic within a given academic field. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute to the existing body of knowledge by presenting new insights, analyzing data, or providing a critical analysis of existing information.
Research papers are essential in various academic disciplines, including sciences, social sciences, humanities, and more. They serve as a means to communicate research findings, share knowledge, and engage in scholarly discussions.
Through research papers, researchers aim to advance understanding, challenge existing theories or assumptions, or propose new perspectives on a particular subject.
The primary purpose of a research paper is to contribute to the existing knowledge within a specific field of study. Researchers conduct a thorough review of relevant literature and studies to identify gaps or areas that require further investigation.
They formulate a research question or hypothesis and design a methodology to collect and analyze data that can answer the research question or test the hypothesis. The research paper then presents the findings, interpretations, and conclusions derived from the analysis of the collected data.
Research papers also play a crucial role in the dissemination of knowledge. They provide a platform for researchers to share their findings with the broader academic community.
By publishing research papers in academic journals, presenting them at conferences, or sharing them through other scholarly channels, researchers contribute to the ongoing conversations within their field. Other researchers can build upon the findings, validate or challenge the results, and collectively advance knowledge in a collaborative manner.
Moreover, research papers help researchers develop critical thinking skills, enhance their research methodology expertise, and contribute to their academic and professional growth.
Engaging in the research process, from formulating a research question to conducting data analysis, strengthens researchers’ abilities to think analytically, critically evaluate information, and draw meaningful conclusions. Research papers also provide opportunities for researchers to develop their academic writing skills, allowing them to effectively communicate their research findings and insights.
Difference Between Thesis and Research paper (Tabular Form)
Here’s a comparison between a thesis and a research paper in tabular form:
Please note that the specific characteristics may vary depending on the institution and academic discipline. This table provides a general overview of the key differences between a thesis and a research paper.
Difference Between Thesis and Research paper
Thesis and research paper are two distinct academic documents that have several differences. Here are the key dissimilarities between a thesis and a research paper:
Purpose and Objective
Have a close look at the purpose and objective comparison.
A thesis serves the purpose of demonstrating a student’s in-depth understanding of a subject, showcasing their analytical and critical thinking abilities, and contributing new knowledge to the academic community.
It aims to obtain a higher degree, such as a Master’s or Ph.D. For example, a Ph.D. thesis in biology may involve conducting original research to discover a new species or proposing a novel scientific theory.
Research Paper
The primary purpose of a research paper is to contribute to existing knowledge on a subject and engage in scholarly discussions. It focuses on exploring a research question or hypothesis, presenting findings, and analyzing the collected data.
For example, a research paper in economics may investigate the impact of a specific policy on economic growth by analyzing data from various sources.
Scope and Depth
Have a close look at the scope and depth comparison.
A thesis requires extensive research and an exhaustive exploration of the chosen topic. It involves delving deeply into the existing literature, critically analyzing previous studies, and offering an extensive review of relevant theories, methodologies, or experiments.
The scope of a thesis is broader, aiming to cover various aspects of the chosen field. For example, a thesis in history may involve examining multiple historical events, analyzing primary sources, and comparing different historical interpretations.
While a research paper also requires research, its scope of exploration is usually narrower compared to a thesis. Research papers often focus on addressing specific research questions, providing detailed analysis, or presenting findings within a limited context.
The scope of a research paper is more focused on a specific aspect or angle of the topic. For example, a research paper in psychology may investigate the effects of a particular therapy technique on a specific group of individuals.
Originality and Contribution
Have a close look at the originality and contribution comparison.
A thesis demands original research and substantial contribution to the existing body of knowledge in the field. It requires students to identify a research gap, formulate research questions, and conduct extensive investigations to fill that gap.
A thesis should provide novel insights, theories, or methodologies that contribute to the advancement of the field. For example, a thesis in computer science may involve developing a new algorithm or software application to solve a complex problem.
While a research paper also requires originality, its scope of contribution is typically narrower compared to a thesis. Research papers often focus on addressing specific aspects or angles of a topic, providing detailed analysis, or presenting findings within a limited context.
They may offer new perspectives or interpretations but may not be as extensive in terms of contributing to the overall knowledge in the field. For example, a research paper in sociology may present a new analysis of existing survey data to support or challenge existing sociological theories.
Structure and Formatting
Have a close look at structure and formatting comparison.
A thesis follows a specific structure that includes various sections such as a title page, abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results and analysis, discussion, conclusion, references, and appendices (if applicable).
This structured format provides a comprehensive framework for presenting the research and analysis conducted. Each section has its purpose and contributes to the overall coherence of the thesis.
A research paper usually has a more flexible structure, depending on the field of study and the specific requirements of the assignment or publication. However, it commonly includes sections like a title, abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results and analysis, discussion, conclusion, and references.
The structure may vary based on the specific guidelines or preferences of the intended publication. The flexibility allows researchers to adapt the structure to the needs of their study while maintaining the logical flow of information.
Evaluation and Audience
Have a close look at evolution and audience comparison.
A thesis is primarily evaluated by a committee of professors or experts in the field. The evaluation process involves comprehensive scrutiny of the research methodology, data analysis, theoretical frameworks, and the overall contribution to the field.
The audience for a thesis is typically limited to the academic community, including the student’s advisors, faculty members, and fellow researchers. The evaluation focuses on the originality, quality, and depth of the research conducted.
Research papers cater to a broader audience, including scholars, researchers, and professionals in the respective field. They are often evaluated through peer review processes before being published in academic journals or presented at conferences.
The evaluation criteria for research papers may vary depending on the publication or assignment guidelines, but they generally emphasize the clarity of research objectives, methodology, data analysis, and the significance of the findings. The evaluation focuses on the validity and contribution of the research to the existing knowledge.
Length and Time Frame
Have a close look at length and time frame comparison.
A thesis is typically longer in length compared to a research paper. It requires a more extensive investigation and analysis, resulting in a higher word count. The time frame to complete a thesis is also longer, often spanning several semesters or years.
The extended length and timeframe allow students to engage in thorough research, conduct experiments, gather data, and provide a comprehensive analysis of the chosen topic.
Research papers are generally shorter in length compared to a thesis. They focus on specific aspects or angles of a topic, resulting in a relatively shorter word count. The time frame to complete a research paper is shorter, often within a semester or a few weeks.
The shorter length and timeframe require researchers to narrow down their focus and present a concise analysis of the chosen research question.
Have a close look at purpose and objective comparison.
A thesis serves as a culmination of a student’s academic journey, demonstrating their mastery of a subject area and their ability to conduct independent research. It aims to contribute new knowledge, theories, or methodologies to the academic community, advancing the understanding of the chosen field.
The primary objective is to obtain a higher degree, such as a Master’s or Ph.D., and showcase expertise in a specialized area of study.
The primary purpose of a research paper is to communicate the results of a specific study or investigation to the academic community. It aims to contribute to existing knowledge by presenting new findings, interpretations, or analyses on a specific research question or topic.
Research papers can be standalone publications or part of a broader research project, providing insights and contributing to ongoing scholarly discussions.
Have a close look at scope and depth comparison.
A thesis requires a comprehensive and in-depth exploration of a subject, often involving extensive literature review, data collection, and analysis. It typically covers a broader scope within the chosen field, aiming to provide a holistic understanding of the topic and its various aspects.
A thesis often requires a more extensive examination of theoretical frameworks, methodologies, and relevant literature, presenting a well-rounded analysis.
Research papers often focus on a specific aspect or angle of a topic, narrowing down the scope of the study. The depth of exploration in a research paper is more limited compared to a thesis, as it emphasizes detailed analysis and findings related to the specific research question.
While research papers may include literature review and references, the analysis is usually more targeted and specific to the research question being addressed.
Have a close look at originality and contribution comparison.
A thesis requires a higher level of originality and contribution to the field. It should offer new insights, theories, methodologies, or empirical evidence that expand existing knowledge and advance the field of study.
A thesis often addresses a research gap or poses new research questions, aiming to fill a void in the existing body of knowledge.
While research papers also require originality, their contribution is typically more limited in scope. Research papers often build upon existing theories, methodologies, or data, offering new interpretations or perspectives within a specific context.
They may present incremental findings, replication studies, or comparative analyses that deepen understanding in a focused area of study.
A thesis follows a structured format that varies across institutions and disciplines. It typically includes sections such as a title page, abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results and analysis, discussion, conclusion, references, and appendices (if applicable).
The structure ensures logical flow, provides context, and allows for comprehensive presentation of research and analysis.
Research papers also have a flexible structure, but they commonly include sections like a title, abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results and analysis, discussion, conclusion, and references. The specific structure may vary based on publication guidelines or the nature of the study.
The structure aims to present the research question, methodology, findings, and analysis in a coherent and understandable manner.
Have a close look at evaluation and audience comparison.
Theses are primarily evaluated by a committee of professors or experts in the field. The evaluation process involves rigorous scrutiny of the research methodology, data analysis, theoretical frameworks, and overall contribution to the field.
The audience for a thesis is typically limited to the academic community, including the student’s advisors, faculty members, and fellow researchers.
Research papers are evaluated through peer review processes before publication or presentation. The evaluation criteria may vary depending on the specific guidelines or intended publication, but they generally assess the clarity of research objectives, methodology, data analysis, and the significance of the findings.
The audience for research papers includes scholars, researchers, and professionals in the respective field, aiming to contribute to ongoing scholarly discussions and inform future research.
Theses are typically longer in length compared to research papers. The word count for a thesis can vary significantly, ranging from tens of thousands to over a hundred thousand words, depending on the level of study and institution’s requirements.
The time frame to complete a thesis is longer, often spanning several semesters or years, allowing for thorough research, data collection, analysis, and the writing process.
Research papers are generally shorter in length compared to theses. The word count for research papers varies depending on the specific requirements of the publication or assignment, but it is typically more concise compared to a thesis.
The time frame to complete a research paper is shorter, often within a semester or a few weeks, necessitating focused research, analysis, and writing within a more limited timeframe.
In conclusion, the difference between a thesis and a research paper lies in their purpose, scope, originality, structure, evaluation, and length. A thesis represents the culmination of a student’s academic journey, aiming to obtain a higher degree and contribute new knowledge to the academic community.
It requires extensive research, in-depth exploration of the chosen topic, and a broader scope that covers various aspects of the field. A thesis demands originality and substantial contribution, often addressing research gaps and presenting novel insights or methodologies.
On the other hand, a research paper focuses on presenting specific findings, interpretations, or analyses within a narrower scope. While it also requires originality, its contribution is usually more limited, building upon existing theories or data to offer new perspectives or interpretations.
Research papers have a flexible structure, adapting to the requirements of the publication or assignment, while the thesis follows a specific and comprehensive format.
Theses are primarily evaluated by a committee of experts in the field, targeting the academic community, while research papers undergo peer review processes for publication and cater to a broader audience of scholars, researchers, and professionals.
Furthermore, the length and time frame differ between the two. Theses are generally longer, spanning several semesters or years, allowing for thorough research and analysis, while research papers are shorter and completed within a semester or a few weeks, requiring focused research and concise presentation of findings.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for students and researchers to navigate their academic endeavors effectively. Whether one aims to pursue advanced degrees or contribute to scholarly discussions, recognizing the unique characteristics of the thesis and research paper helps in formulating research objectives, selecting appropriate methodologies, and presenting research outcomes in a manner suitable to their intended audience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main objective of a thesis.
The main objective of a thesis is to demonstrate a student’s in-depth understanding of a subject, showcase their analytical and critical thinking abilities, and contribute new knowledge to the academic community.
Can a research paper be considered a thesis?
No, a research paper and a thesis are distinct academic documents. While both involve research and analysis, a thesis is more comprehensive, requires a higher level of originality, and aims for a higher academic degree.
How long does it take to complete a thesis?
The duration to complete a thesis can vary depending on the program and the nature of the research. It often takes several semesters or years to conduct the necessary research, collect data, analyze findings, and write the thesis.
Who evaluates a thesis?
A thesis is typically evaluated by a committee of professors or experts in the field. They assess the research methodology, data analysis, theoretical frameworks, and the overall contribution to the field.
What is the audience for a research paper?
The audience for a research paper includes scholars, researchers, and professionals in the respective field. Research papers are often published in academic journals or presented at conferences to engage in scholarly discussions.
Similar Articles

Top 19 Tips & Tricks On How To Improve Grades?
Do you want to improve your grades? If yes, then don’t worry! In this blog, I have provided 19 tips…

How To Do Homework Fast – 11 Tips To Do Homework Fast
Homework is one of the most important parts that have to be done by students. It has been around for…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Thesis vs Research Paper
Published 16 October, 2023
A thesis and a research paper are two different writing formats used for academic purposes. A thesis is usually an in-depth study of the topic that considers all aspects of the situation, while a research paper provides more specific information on the subject matter or problem. They are both very different in nature and content, as well as length and structure. A thesis is typically more formal and academic in tone while a research paper can be less formal with more of an emphasis on the findings. This blog post will explore some of the differences between writing a thesis and researching for a paper.
Introduction of Thesis
The thesis is basically an academic document that students write for obtaining an academics degree. Students studying in the final year of their graduation need to prepare a thesis before the issuance of a degree from educational institutions. You need to write a thesis under the supervision of a Supervisor who will provide guidance and give feedback on the draft of the thesis. The main purpose of writing a thesis is to gather, analyze and present information in front of mentors from the respective universities. A thesis is broader. Students have to select the topic which should be relevant to the field to the area of specialty. You need to get your thesis to approve by your supervisor. You may have to spend a number of months writing a thesis because it is quite difficult to collect and analyze data. Therefore, it is very much essential for you to follow the proper process. In many of the countries where students call a thesis a Dissertation.
Introduction of Research Paper
A research paper is basically an individual academic document. It is basically a publication of research findings which you need to publish after properly analyzing the data which you have collected by applying different techniques. Basically, research papers are short in length in comparison to the thesis. The research paper only contains descriptions of specific and relevant information. On the other hand, the thesis mainly concentrates on a broader field. A research paper is basically a document that contains the research results which you draw from information that you have collected. It has its own document, there is a specific research methodology that you need to follow. Every academic paper has its own journal in which you can publish. For instance, for the journal of international marketing you need to publish information related to marketing only. Researcher papers are a contribution of the researcher in the field of specialty.
Read Also: How to write a good research paper
Major Differences between research paper and Thesis
Comparison between the structure of the thesis and research paper.
The main difference between the research paper and thesis is related to their structure, shown below:
Structure of Research paper
- Title page: The research paper begins with the title page. On the title page of the research paper, you need to mention the name of the author, year of publication, and all other relevant information.
- Abstract: Abstract for a research paper basically contains a detailed overview of a research paper.
- Introduction: In the research paper introduction , you need to clearly state the topic. Students also need to provide a reason for selecting a particular topic.
- Methodology: Here, you need to clearly define the research methodology which you are going to use for performing research.
- Results: in this Section, the author describes the results and research findings which are the outcome of the data analysis.
- Discussions: You need to have a research discussion on the basis of results and findings.
- Conclusion: Here, you need to provide a research conclusion or summary of key points. Students should also demonstrate the importance of the study, s it will help you in developing interest of reading among the reader.
- References: This section contains a list of resources that you are going to use for writing a research paper.
Structure of Thesis
On the other hand, the Thesis begins with a research proposal which you need to submit to the tutor. After getting the approval from the supervisor, you need to follow the below structure
- Title page: On the title page of the thesis, you need to write the name of the students and instructor, date, and other relevant information related to the subject.
- Abstract: Abstract in thesis mainly consists of a single-page summary of the complete thesis. It only includes the main point of the Thesis.
- Introduction: Students need to include background information about the topic in the introduction section. It is also very much essential for students to clearly states the aims and objectives of their study.
- Literature Review: In the literature section of the thesis, you need to include debates, opinions of different authors about a specific topic.
- Methods: Here, in this section of the thesis, you need to clearly state the techniques which you are going to use for data collection, analysis, and interpretations. It also contains a description of the research design, questionnaire, etc.
- Results: It is basically an important part of the thesis. You need to provide a description of the results on the basis of information that you have collected from different sources.
- Discussion: In this section of the Thesis, students need to have a discussion on all terms or main ideas.
- Conclusion: It is basically the end of all chapters in the Thesis. Here, students need to provide a summary of important results.
- Recommendations: In this section of the Thesis, you need to address gaps in the literature and need to provide suggestions for filing the same.
- References: Here, you need to include the names of authors and articles which you have used for writing the thesis.
- Bibliography: It is the section in the Thesis that contains the links which you or another researcher may use for gathering information. You can also include the research questionnaire form in this section.
Thesis and research papers are the two most common types of academic writing. They both have similarities but also distinct differences in their format, content, length, purpose, and audience. It is important to understand these distinctions so you can decide which one fits your needs best for any given project or assignment. If you need help choosing between thesis vs research paper formats, we’re here to guide you through this process with our knowledgeable team members who specialize in different subject areas. You can seek professional help for completing different types of assignments at reasonable costs. My Research Topics is basically a reliable support system for the students for all those students who really need help finishing the assignments.
Stuck During Your Dissertation
Our top dissertation writing experts are waiting 24/7 to assist you with your university project,from critical literature reviews to a complete PhD dissertation.

Other Related Guides
- Research Project Questions
- Types of Validity in Research – Explained With Examples
- Schizophrenia Sample Research Paper
- Quantitative Research Methods – Definitive Guide
- Research Paper On Homelessness For College Students
- How to Study for Biology Final Examination
- Textual Analysis in Research / Methods of Analyzing Text
A Guide to Start Research Process – Introduction, Procedure and Tips
Research findings – objectives , importance and techniques.
- Topic Sentences in Research Paper – Meaning, Parts, Importance, Procedure and Techniques

Recent Research Guides for 2023

Get 15% off your first order with My Research Topics
Connect with a professional writer within minutes by placing your first order. No matter the subject, difficulty, academic level or document type, our writers have the skills to complete it.

My Research Topics is provides assistance since 2004 to Research Students Globally. We help PhD, Psyd, MD, Mphil, Undergrad, High school, College, Masters students to compete their research paper & Dissertations. Our Step by step mentorship helps students to understand the research paper making process.
Research Topics & Ideas
- Sociological Research Paper Topics & Ideas For Students 2023
- Nurses Research Paper Topics & Ideas 2023
- Nursing Capstone Project Research Topics & Ideas 2023
- Unique Research Paper Topics & Ideas For Students 2023
- Teaching Research Paper Topics & Ideas 2023
- Literary Research Paper Topics & Ideas 2023
- Nursing Ethics Research Topics & Ideas 2023
Research Guide
Disclaimer: The Reference papers provided by the Myresearchtopics.com serve as model and sample papers for students and are not to be submitted as it is. These papers are intended to be used for reference and research purposes only.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

What is a thesis | A Complete Guide with Examples

Table of Contents
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It’s typically submitted at the end of your master’s degree or as a capstone of your bachelor’s degree.
However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners. From the initial challenge of pinpointing a compelling research topic to organizing and presenting findings, the process is filled with potential pitfalls.
Therefore, to help you, this guide talks about what is a thesis. Additionally, it offers revelations and methodologies to transform it from an overwhelming task to a manageable and rewarding academic milestone.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic.
Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research, which not only fortifies your propositions but also confers credibility to your entire study.
Furthermore, there's another phenomenon you might often confuse with the thesis: the ' working thesis .' However, they aren't similar and shouldn't be used interchangeably.
A working thesis, often referred to as a preliminary or tentative thesis, is an initial version of your thesis statement. It serves as a draft or a starting point that guides your research in its early stages.
As you research more and gather more evidence, your initial thesis (aka working thesis) might change. It's like a starting point that can be adjusted as you learn more. It's normal for your main topic to change a few times before you finalize it.
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper.
Typically found within the introductory section, a strong thesis statement acts as a roadmap of your thesis, directing readers through your arguments and findings. By delineating the core focus of your investigation, it offers readers an immediate understanding of the context and the gravity of your study.
Furthermore, an effectively crafted thesis statement can set forth the boundaries of your research, helping readers anticipate the specific areas of inquiry you are addressing.
Different types of thesis statements
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers.
Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements:
Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
Purpose : To convince the reader of a particular stance or point of view by presenting evidence and formulating a compelling argument.
Example : Reducing plastic use in daily life is essential for environmental health.
Analytical thesis statement
Purpose : To break down an idea or issue into its components and evaluate it.
Example : By examining the long-term effects, social implications, and economic impact of climate change, it becomes evident that immediate global action is necessary.
Expository (or Descriptive) thesis statement
Purpose : To explain a topic or subject to the reader.
Example : The Great Depression, spanning the 1930s, was a severe worldwide economic downturn triggered by a stock market crash, bank failures, and reduced consumer spending.
Cause and effect thesis statement
Purpose : To demonstrate a cause and its resulting effect.
Example : Overuse of smartphones can lead to impaired sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and increased levels of anxiety.
Compare and contrast thesis statement
Purpose : To highlight similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example : "While both novels '1984' and 'Brave New World' delve into dystopian futures, they differ in their portrayal of individual freedom, societal control, and the role of technology."
When you write a thesis statement , it's important to ensure clarity and precision, so the reader immediately understands the central focus of your work.
What is the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement?
While both terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings.
A thesis refers to the entire research document, encompassing all its chapters and sections. In contrast, a thesis statement is a brief assertion that encapsulates the central argument of the research.
Here’s an in-depth differentiation table of a thesis and a thesis statement.
Now, to craft a compelling thesis, it's crucial to adhere to a specific structure. Let’s break down these essential components that make up a thesis structure
15 components of a thesis structure
Navigating a thesis can be daunting. However, understanding its structure can make the process more manageable.
Here are the key components or different sections of a thesis structure:
Your thesis begins with the title page. It's not just a formality but the gateway to your research.

Here, you'll prominently display the necessary information about you (the author) and your institutional details.
- Title of your thesis
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date
- Your Supervisor's name (in some cases)
- Your Department or faculty (in some cases)
- Your University's logo (in some cases)
- Your Student ID (in some cases)
In a concise manner, you'll have to summarize the critical aspects of your research in typically no more than 200-300 words.

This includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. For many, the abstract will determine if they delve deeper into your work, so ensure it's clear and compelling.
Acknowledgments
Research is rarely a solitary endeavor. In the acknowledgments section, you have the chance to express gratitude to those who've supported your journey.

This might include advisors, peers, institutions, or even personal sources of inspiration and support. It's a personal touch, reflecting the humanity behind the academic rigor.
Table of contents
A roadmap for your readers, the table of contents lists the chapters, sections, and subsections of your thesis.

By providing page numbers, you allow readers to navigate your work easily, jumping to sections that pique their interest.
List of figures and tables
Research often involves data, and presenting this data visually can enhance understanding. This section provides an organized listing of all figures and tables in your thesis.

It's a visual index, ensuring that readers can quickly locate and reference your graphical data.
Introduction
Here's where you introduce your research topic, articulate the research question or objective, and outline the significance of your study.

- Present the research topic : Clearly articulate the central theme or subject of your research.
- Background information : Ground your research topic, providing any necessary context or background information your readers might need to understand the significance of your study.
- Define the scope : Clearly delineate the boundaries of your research, indicating what will and won't be covered.
- Literature review : Introduce any relevant existing research on your topic, situating your work within the broader academic conversation and highlighting where your research fits in.
- State the research Question(s) or objective(s) : Clearly articulate the primary questions or objectives your research aims to address.
- Outline the study's structure : Give a brief overview of how the subsequent sections of your work will unfold, guiding your readers through the journey ahead.
The introduction should captivate your readers, making them eager to delve deeper into your research journey.
Literature review section
Your study correlates with existing research. Therefore, in the literature review section, you'll engage in a dialogue with existing knowledge, highlighting relevant studies, theories, and findings.

It's here that you identify gaps in the current knowledge, positioning your research as a bridge to new insights.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI tools. For example, the SciSpace literature review tool enables you to efficiently explore and delve into research papers, simplifying your literature review journey.
Methodology
In the research methodology section, you’ll detail the tools, techniques, and processes you employed to gather and analyze data. This section will inform the readers about how you approached your research questions and ensures the reproducibility of your study.

Here's a breakdown of what it should encompass:
- Research Design : Describe the overall structure and approach of your research. Are you conducting a qualitative study with in-depth interviews? Or is it a quantitative study using statistical analysis? Perhaps it's a mixed-methods approach?
- Data Collection : Detail the methods you used to gather data. This could include surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, archival research, etc. Mention where you sourced your data, the duration of data collection, and any tools or instruments used.
- Sampling : If applicable, explain how you selected participants or data sources for your study. Discuss the size of your sample and the rationale behind choosing it.
- Data Analysis : Describe the techniques and tools you used to process and analyze the data. This could range from statistical tests in quantitative research to thematic analysis in qualitative research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings to ensure that your results are both accurate and consistent.
- Ethical Considerations : Highlight any ethical issues related to your research and the measures you took to address them, including — informed consent, confidentiality, and data storage and protection measures.
Moreover, different research questions necessitate different types of methodologies. For instance:
- Experimental methodology : Often used in sciences, this involves a controlled experiment to discern causality.
- Qualitative methodology : Employed when exploring patterns or phenomena without numerical data. Methods can include interviews, focus groups, or content analysis.
- Quantitative methodology : Concerned with measurable data and often involves statistical analysis. Surveys and structured observations are common tools here.
- Mixed methods : As the name implies, this combines both qualitative and quantitative methodologies.
The Methodology section isn’t just about detailing the methods but also justifying why they were chosen. The appropriateness of the methods in addressing your research question can significantly impact the credibility of your findings.
Results (or Findings)
This section presents the outcomes of your research. It's crucial to note that the nature of your results may vary; they could be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.

Quantitative results often present statistical data, showcasing measurable outcomes, and they benefit from tables, graphs, and figures to depict these data points.
Qualitative results , on the other hand, might delve into patterns, themes, or narratives derived from non-numerical data, such as interviews or observations.
Regardless of the nature of your results, clarity is essential. This section is purely about presenting the data without offering interpretations — that comes later in the discussion.
In the discussion section, the raw data transforms into valuable insights.
Start by revisiting your research question and contrast it with the findings. How do your results expand, constrict, or challenge current academic conversations?
Dive into the intricacies of the data, guiding the reader through its implications. Detail potential limitations transparently, signaling your awareness of the research's boundaries. This is where your academic voice should be resonant and confident.
Practical implications (Recommendation) section
Based on the insights derived from your research, this section provides actionable suggestions or proposed solutions.
Whether aimed at industry professionals or the general public, recommendations translate your academic findings into potential real-world actions. They help readers understand the practical implications of your work and how it can be applied to effect change or improvement in a given field.
When crafting recommendations, it's essential to ensure they're feasible and rooted in the evidence provided by your research. They shouldn't merely be aspirational but should offer a clear path forward, grounded in your findings.
The conclusion provides closure to your research narrative.
It's not merely a recap but a synthesis of your main findings and their broader implications. Reconnect with the research questions or hypotheses posited at the beginning, offering clear answers based on your findings.

Reflect on the broader contributions of your study, considering its impact on the academic community and potential real-world applications.
Lastly, the conclusion should leave your readers with a clear understanding of the value and impact of your study.
References (or Bibliography)
Every theory you've expounded upon, every data point you've cited, and every methodological precedent you've followed finds its acknowledgment here.

In references, it's crucial to ensure meticulous consistency in formatting, mirroring the specific guidelines of the chosen citation style .
Proper referencing helps to avoid plagiarism , gives credit to original ideas, and allows readers to explore topics of interest. Moreover, it situates your work within the continuum of academic knowledge.
To properly cite the sources used in the study, you can rely on online citation generator tools to generate accurate citations!
Here’s more on how you can cite your sources.
Often, the depth of research produces a wealth of material that, while crucial, can make the core content of the thesis cumbersome. The appendix is where you mention extra information that supports your research but isn't central to the main text.

Whether it's raw datasets, detailed procedural methodologies, extended case studies, or any other ancillary material, the appendices ensure that these elements are archived for reference without breaking the main narrative's flow.
For thorough researchers and readers keen on meticulous details, the appendices provide a treasure trove of insights.
Glossary (optional)
In academics, specialized terminologies, and jargon are inevitable. However, not every reader is versed in every term.
The glossary, while optional, is a critical tool for accessibility. It's a bridge ensuring that even readers from outside the discipline can access, understand, and appreciate your work.

By defining complex terms and providing context, you're inviting a wider audience to engage with your research, enhancing its reach and impact.
Remember, while these components provide a structured framework, the essence of your thesis lies in the originality of your ideas, the rigor of your research, and the clarity of your presentation.
As you craft each section, keep your readers in mind, ensuring that your passion and dedication shine through every page.
Thesis examples
To further elucidate the concept of a thesis, here are illustrative examples from various fields:
Example 1 (History): Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807 by Suchait Kahlon.
Example 2 (Climate Dynamics): Influence of external forcings on abrupt millennial-scale climate changes: a statistical modelling study by Takahito Mitsui · Michel Crucifix
Checklist for your thesis evaluation
Evaluating your thesis ensures that your research meets the standards of academia. Here's an elaborate checklist to guide you through this critical process.
Content and structure
- Is the thesis statement clear, concise, and debatable?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background and context?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, relevant, and well-organized?
- Does the methodology section clearly describe and justify the research methods?
- Are the results/findings presented clearly and logically?
- Does the discussion interpret the results in light of the research question and existing literature?
- Is the conclusion summarizing the research and suggesting future directions or implications?
Clarity and coherence
- Is the writing clear and free of jargon?
- Are ideas and sections logically connected and flowing?
- Is there a clear narrative or argument throughout the thesis?
Research quality
- Is the research question significant and relevant?
- Are the research methods appropriate for the question?
- Is the sample size (if applicable) adequate?
- Are the data analysis techniques appropriate and correctly applied?
- Are potential biases or limitations addressed?
Originality and significance
- Does the thesis contribute new knowledge or insights to the field?
- Is the research grounded in existing literature while offering fresh perspectives?
Formatting and presentation
- Is the thesis formatted according to institutional guidelines?
- Are figures, tables, and charts clear, labeled, and referenced in the text?
- Is the bibliography or reference list complete and consistently formatted?
- Are appendices relevant and appropriately referenced in the main text?
Grammar and language
- Is the thesis free of grammatical and spelling errors?
- Is the language professional, consistent, and appropriate for an academic audience?
- Are quotations and paraphrased material correctly cited?
Feedback and revision
- Have you sought feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the field?
- Have you addressed the feedback and made the necessary revisions?
Overall assessment
- Does the thesis as a whole feel cohesive and comprehensive?
- Would the thesis be understandable and valuable to someone in your field?
Ensure to use this checklist to leave no ground for doubt or missed information in your thesis.
After writing your thesis, the next step is to discuss and defend your findings verbally in front of a knowledgeable panel. You’ve to be well prepared as your professors may grade your presentation abilities.
Preparing your thesis defense
A thesis defense, also known as "defending the thesis," is the culmination of a scholar's research journey. It's the final frontier, where you’ll present their findings and face scrutiny from a panel of experts.
Typically, the defense involves a public presentation where you’ll have to outline your study, followed by a question-and-answer session with a committee of experts. This committee assesses the validity, originality, and significance of the research.
The defense serves as a rite of passage for scholars. It's an opportunity to showcase expertise, address criticisms, and refine arguments. A successful defense not only validates the research but also establishes your authority as a researcher in your field.
Here’s how you can effectively prepare for your thesis defense .
Now, having touched upon the process of defending a thesis, it's worth noting that scholarly work can take various forms, depending on academic and regional practices.
One such form, often paralleled with the thesis, is the 'dissertation.' But what differentiates the two?
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct research projects undertaken at different levels of higher education.
To the uninitiated, understanding their meaning might be elusive. So, let's demystify these terms and delve into their core differences.
Here's a table differentiating between the two.
Wrapping up
From understanding the foundational concept of a thesis to navigating its various components, differentiating it from a dissertation, and recognizing the importance of proper citation — this guide covers it all.
As scholars and readers, understanding these nuances not only aids in academic pursuits but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relentless quest for knowledge that drives academia.
It’s important to remember that every thesis is a testament to curiosity, dedication, and the indomitable spirit of discovery.
Good luck with your thesis writing!
Frequently Asked Questions
A thesis typically ranges between 40-80 pages, but its length can vary based on the research topic, institution guidelines, and level of study.
A PhD thesis usually spans 200-300 pages, though this can vary based on the discipline, complexity of the research, and institutional requirements.
To identify a thesis topic, consider current trends in your field, gaps in existing literature, personal interests, and discussions with advisors or mentors. Additionally, reviewing related journals and conference proceedings can provide insights into potential areas of exploration.
The conceptual framework is often situated in the literature review or theoretical framework section of a thesis. It helps set the stage by providing the context, defining key concepts, and explaining the relationships between variables.
A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or point of your research. Start by pinpointing the central question or issue your research addresses, then condense that into a single statement, ensuring it reflects the essence of your paper.
You might also like

AI for Meta Analysis — A Comprehensive Guide

How To Write An Argumentative Essay

Beyond Google Scholar: Why SciSpace is the best alternative
While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.
Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis
- How it works
Published by Nicolas at January 17th, 2024 , Revised On January 23, 2024
Dissertation Vs Thesis: How Are They Different
Dissertation vs thesis! What are you writing?
Table of Contents
Many graduate students from universities in Canada often get confused and mix both terms. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they carry distinct meanings and purposes in academia. Read this blog to fully understand the difference between a thesis and a dissertation.
What Is A Dissertation
A dissertation is a substantial piece of academic writing typically required to complete a doctoral degree (such as a Ph.D.). It represents an original and significant contribution to the field of study and is usually the culmination of several years of research and study.
What Is A Thesis
A thesis is a scholarly piece of writing, usually at the master’s or undergraduate level, that presents an original research question, methodology, and findings. It represents the culmination of a student’s academic work and demonstrates their ability to contribute to the field of study.
The Evolution Of Dissertation Vs Thesis
The history of the thesis and dissertation dates back several centuries, and the evolution of these academic documents reflects changes in scholarly practices, educational systems, and the expectations of advanced degree programs.
Medieval Origins
The concept of a scholarly thesis has roots in medieval universities. In the 12th and 13th centuries, institutions like the University of Paris introduced the practice of disputations, where students defended their theses in a public forum. These early theses were often theological or philosophical in nature.
Renaissance And Early Modern Period
During the Renaissance, the practice of defending theses continued to evolve. The 16th and 17th centuries saw an increasing emphasis on empirical observation and scientific inquiry. The thesis became more diverse, covering topics in natural philosophy, mathematics, and other emerging disciplines.

18th And 19th Centuries
The 18th century marked the formalization of the thesis as a requirement for academic degrees. Universities started to mandate the submission of a written document along with the oral defence. This practice became more standardized in the 19th century as universities across Europe and North America adopted similar academic norms.
Evolution Of The Dissertation
The term “dissertation” has its roots in the Latin word “dissertatio,” meaning “discussion.” Dissertations, as we understand them today, emerged in the 19th century, primarily in German universities. Doctoral candidates were required to produce substantial research demonstrating their ability to contribute original knowledge to their field.
20th Century
The 20th century saw a global expansion of higher education and an increase in the number of doctoral programs. The thesis and dissertation became integral components of graduate education worldwide. The structure, format (eg, APA or MLA ), and expectations for these documents varied among disciplines and institutions.
Electronic Theses And Dissertations (ETDs)
With the advent of digital technology in the late 20th century, there was a shift toward electronic submission of theses and dissertations. This made research papers more accessible and facilitated the dissemination of knowledge. Many universities now require the submission of ETDs.
Contemporary Trends In Dissertation Vs Thesis
In the 21st century, the thesis and dissertation continue to evolve. Educational institutions are adapting to new forms of scholarship , interdisciplinary research, and varied modes of dissemination. The focus is often on producing high-quality, original research that contributes significantly to the academic community.
What Is The Difference Between A Dissertation And A Thesis
Thesis vs dissertation: length and depth.
One of the key differences between a thesis vs dissertation lies in their length and depth of research:
Theses are typically shorter in length, ranging from 50 to 100 pages, depending on the institution and program requirements. The research conducted for a thesis is expected to contribute to the existing literature but may not need to be as exhaustive as that of a dissertation.
Dissertation
Dissertations, being the pinnacle of doctoral research, are substantially longer, often exceeding 100 pages and sometimes reaching several hundred pages. Doctoral candidates are expected to delve deeply into their chosen topic, conducting extensive research and offering a unique contribution to the academic community.
Dissertation Vs Thesis: Scope And Purpose
Another significant distinction between a dissertation vs thesis is the scope and purpose of the research:
The primary goal of a thesis is to demonstrate a student’s understanding of the subject and their ability to conduct independent research within a defined scope. A thesis is often more focused and may be an exploration or analysis of a specific aspect of a broader topic. For example, a finance thesis could be about any topic within the subject.
Dissertations, being doctoral-level projects, have a broader scope. Doctoral candidates are expected to make an original and substantial contribution to the field, advancing existing knowledge and addressing gaps in the current literature. Dissertations often involve more extensive data collection, analysis, and synthesis of information.
The research paper we write have:
- Precision and Clarity
- Zero Plagiarism
- High-level Encryption
- Authentic Sources
Dissertation Vs Thesis: The Similarities
While there are distinct differences between a thesis vs dissertation, they also share several similarities, reflecting their common purpose within academic research papers . Here are some key similarities between a dissertation and a thesis.
Research Component
Both dissertations and theses involve original research and scholarly inquiry. Students are expected to engage in a systematic investigation of a chosen topic, demonstrate a deep understanding of existing literature, and contribute new knowledge or insights to their field.
Academic Rigour
Both documents adhere to high standards of academic rigour and integrity. They require meticulous attention to detail, adherence to citation and referencing styles, and a commitment to intellectual honesty.
Formal Structure
Dissertations and theses typically follow a formal structure, including elements such as a thesis statement , an introduction, a literature review, methodology, results, a discussion, and a conclusion. This structured format ensures a comprehensive presentation of the research.
Faculty Guidance
In both cases, students work closely with faculty advisors or mentors throughout the research process. Advisors guide research design, literature review, data analysis, and other aspects of the project.
Oral Defense
A commonality between dissertations and theses is the requirement for an oral defence. In many academic institutions, students must defend their research findings before a committee of faculty members. This defence allows students to articulate their research methods, results, and conclusions, while also responding to questions and critiques.
Degree Requirement
Both a thesis and a dissertation serve as a crucial component for the completion of an academic degree. Thesis is typically associated with master’s programs, while dissertations are a requirement for doctoral degrees. In both cases, successfully completing the research project is essential for obtaining the respective degrees.
Contribution To Knowledge
Whether a thesis or a dissertation, the primary goal is to contribute to the existing body of knowledge in a particular field. Both documents aim to advance understanding, address gaps in the literature, and offer meaningful insights that can inform future research.
Literature Review
A comprehensive literature review is a common element in both dissertations and theses. This section provides context for the research by summarizing and critiquing relevant scholarly works, helping establish the rationale and significance of the study.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a dissertation and a thesis.
A thesis is a shorter, master’s-level research document demonstrating mastery of a subject. A dissertation, typically for a doctoral degree, is longer and requires a more extensive, original contribution to the field.
What is the difference between a master thesis and dissertation?
A master’s thesis is a shorter research document showcasing mastery of a specific subject. A dissertation, associated with a doctoral degree, is more extensive, requiring a substantial, original contribution to the field.
Are thesis and dissertation the same thing?
No, a thesis and a dissertation are not the same. A thesis is a research document associated with a master’s degree, demonstrating mastery of a subject. A dissertation is a more extensive research document required for a doctoral degree, emphasizing original contribution to the field.
Where to find thesis and dissertations?
There are several online sources that can help you in finding the perfect thesis and dissertation for your research. ResearchProspect Canada is one of the leading and trustworthy brands, helping students achieve academic excellence.
What is electronic thesis and dissertation?
An Electronic Thesis and Dissertation (ETD) is a digital version of a student’s thesis or dissertation. It is submitted and stored electronically, allowing easy access, distribution, and archiving, reflecting the shift towards digital formats in academia.
How to cite theses and dissertation?
To cite theses and dissertations, follow the citation style specified by your academic institution or the preferred style guide (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Include author, title, publication year, institution, and retrieval information for online sources, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
How to cite pro quest dissertation and theses APA?
To cite a ProQuest dissertation or thesis in APA format, use the following template: Author, A. A. (Year). Title of dissertation/thesis (Publication No.). ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global. Include the ProQuest publication number for online sources.
You May Also Like
Introduction establishes context, states research question, and justifies study. The abstract is a concise summary of key paper elements.
Welcome to the most comprehensive resource page of climate change research topics, a crucial field of study central to understanding […]
Check out this comprehensive guide to learn how to write a literature review with the help of multiple good literature review examples.
Ready to place an order?
USEFUL LINKS
Learning resources, company details.
- How It Works
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance
Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper
Edited by Diffzy | Updated on: May 28, 2023
Why read @ Diffzy
Our articles are well-researched
We make unbiased comparisons
Our content is free to access
We are a one-stop platform for finding differences and comparisons
We compare similar terms in both tabular forms as well as in points
- Introduction
Some of the basic confusion introduced in our schools has yet to be cleared. It is the reason why we decided to select the often confused topic of the distinction between a thesis and a research paper. Many times in our academic projects, we have a thesis or research paper to work on.
Thesis and research papers are generally submitted as the final
assignment. In our country, we hardly get to see such assignments for the completion of courses, but in foreign countries, we often see such assignments.
Many of our students claim that they find it difficult to understand the difference between a thesis and a research paper. So it is important to familiarise ourselves with and understand these important topics. Although this difference is a bit difficult to understand because of the high degree of confusion,
- Thesis vs. Research paper
The aspects that are common in a research paper and a thesis are that both are academic documents. But we know that there are a lot of differences between both documents. This difference can be caused by style, purpose, or specific components.
The basic difference between a thesis and a research paper is the purpose. The purpose of a thesis is to present it as a document written to support an academic qualification. It is longer in comparison to a research paper, and thus it is finished in several years. A thesis, also known as a dissertation, is usually connected with PG studies, i.e., taught at the Master’s degree, M.Phil., or Ph.D. level, and is performed under the guidance of an academic professional of the respective university. A guide or supervisor is the person who oversees and guides the progress of the person writing the thesis. One of the supervisor’s tasks is to develop presentation and writing skills and capability for research. In most universities, the guide or supervisor has the responsibility to meet with every student frequently and discuss how progress is going. But a research paper is usually written as a collective part of a topic and is not counted as a separate module or subject. This is the reason why it does not require an individual supervisor or guide.
- Difference between a thesis and a research paper in tabular form
- What is a thesis?
The term thesis is taken from the Greek word tithenai. It means "to place." This initial definition was related to the origins of an intentional infinitive, which indicates "putting forth" of something. After this, the Greek word transformed into 'thesis'. In Greek, it means "to put forth something," akin to a proposal. This theme is a matter of argument today and is popularly called a ‘thesis’.
When we discuss a thesis, it is defined as a document that contains the findings and research. Students submit these to get a professional degree.
It starts a debatable point on which one could agree or disagree. In simple terms, it is described as a research report in written format that includes a problem that needs to be dealt with. The researcher presents the conclusion. This researcher also makes statements that support the conclusion. Thesis writing is compulsory. In the thesis, our primary focus is always on the novelty of the research.
Introduction to the thesis statement
The thesis statement is simply a one-line sentence. It is usually presented in written form at the end of the first paragraph. It provides an argument for the person reading it. It is a sort of blueprint for the thesis, which directs the writer when writing a thesis and provides guidance to the reader who reads it.
An important key element of a thesis
Argument: The first important element is that the reason for agreeing with the proposition is more than just focusing on point of view.
Maintenance of Argument: The second element is the maintenance of the argument.
The argument must be cogent enough by presenting appropriate logic and evidence.
Proposition: The third important element in a thesis is the proposition. It propagates an idea or recommendation.
Features of a good thesis .
- A good thesis adds freshness and new knowledge to a pre-existing thesis.
- It helps to communicate the core idea of research in a simple, clear, and shorter way.
- An efficient thesis is an important statement or question.
- A good thesis gives answers to how and why various questions are associated with a topic.
- To get rid of confusion. It is presented carefully.
- The thesis at the end gives a good reason for those who are reading and keeps them engaged.
- What is a research paper?
A research paper might be defined as a piece of plagiarism-free and original research. Here the term research is associated with the repetition of the term research. Recurring searches in various realms prove that the questions of the central thesis are called research.
A research paper consists of questions about the central thesis, if not regularly, then usually. A research paper can be classified into two parts. In this classification, one is qualitative and the other is quantitative. Academic writing takes the form of a research paper. It is created using the author's unique study on a particular subject, coupled with its analysis and interpretation of the results.
An author typically begins writing a research paper using what he already knows about the subject and then attempts to learn from specialists. Gathering the most information possible also entails a comprehensive and organized study on a certain topic. Simply put, a research paper is a written and published report. It abstracts or make appear the outcomes of a scientific research. In this example, the review article is a critique of a previously published scientific publication. while the original research article is basically a scientific study
In the case of the primary research article, the research paper's author offers crucial details regarding the study.
How is a research paper started?
I t is very pivotal to entail all the important sequences involved in writing a research paper. Without following all steps, a research paper will not be considered appropriate and right. When someone starts writing a research paper. One should always consider a topic that seems interesting but is also a bit challenging. Here, topic selection must be such that one can manage that topic easily. So, we can avoid these types of topics that are not simple and too technical, and the topic must not be such that very little information is available on it. The approach of researchers is an important factor that determines their efforts.
Steps of writing a research paper.
Picking the topic: The first and foremost step involved in writing a research paper is to choose a topic, which must be simple and as per the reader's interest. If we are starting with a topic that is not simple and per our likings, then it will be difficult for us to go through the topic and prepare a good research paper. So a good topic is indispensable. The selected topic can make a research project good or bad, which is why a lot of assertion is placed on the selection of an good topic.
Topic research : The second step is to do proper research on the topic. The research should be appropriate and factual. A research paper prepared without proper research will include wrong facts and information, which will not make it a good research paper. Research about a topic can be done through various sources to get the research correct, and these sources are selected as per the topic of the research.
Outlining: Outlining is necessary for the purpose of preparing a research paper. It helps to get what the framework of the research paper is. The framework of a research paper gives a basic outline that needs to be followed while preparing a good research paper.
Performing actual writing: After choosing a topic, researching the topic, and making an outline, the next important step is to perform the actual writing of the research paper. It is possible only in circumstances when the writer has selected the apt topic. Then Conducted appropriate research. After this prepared a good framework to do the work of writing. In the end, after following all the steps, we can easily determine if our research paper is as per the mark or not. If it is not as expected, then changes can be made.
It can be done only when the writer has selected the appropriate topic, conducted proper research, and prepared a good framework to perform the writing. In the end, after following all the steps, we can easily determine if our research paper is as per the mark or not. If it is not as expected, then changes can be made.
Difference between a thesis and a research paper in tabular form .
- The thesis is a type of document that has a broader description of the subject. In contrast, the research paper includes a less detailed description of that particular subject.
- While the student submits the thesis for review by a committee of professors or an educational committee. In contrast, the research report is read and evaluated by scientists and other researchers.
- The primary question or claim of an intellectual argument that calls for additional inquiry is the topic of the thesis. The research article, on the other hand, is concerned with supporting the main contention.
- A thesis serves as a capstone undertaking. A research article, however, functions more like a journal's research manual.
- A document like a thesis is generally for a particular audience, usually at the graduate level. A research paper-type document can be presented for graduate- or undergraduate-level audiences.
- The fundamental question or claim of a scholarly argument that motivates additional research is the focus of a thesis, whereas the main goal of a research paper is to support that claim.
- Sometimes the term "thesis" is used in place of "research paper," but this is a rhetorical mistake when a part is used in place of the whole. The research paper normally includes the thesis statement, not the other way around.
- When we talk about a thesis statement, we can see that it does not include methodology. But a research paper exhibits methodology. It may be quantitative or qualitative.
As we know that there are a lot of anti-foundational theories working against the classical model, as per these models, the lines of inquiry that come up as anti-theses must not be nullified. It might be presented conclusively that a research paper and a thesis have differences and similarities between them. Here the difference cause confusion to those who are dealing in these.
We have discussed various important points that will help you understand the difference between a thesis and a research paper. When the research paper is made public, it opens up job opportunities and fellowships for those who are new researchers. On the other hand, thesis writing helps students get a degree when the course is finished. These sound similar, but this can be elaborated on various grounds, and we hope this will help you understand the difference.
Table of Contents
- Difference between a thesis and a research paper in tabular form.
Cite this article
Use the citation below to add this article to your bibliography:
MLA Style Citation
"Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper." Diffzy.com , 2024. Thu. 11 Apr. 2024. < https://www.diffzy.com/article/difference-between-thesis-and-research-paper >.
Chicago Style Citation
Diffzy.com , 2024. "Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper." Accessed April 11, 2024. https://www.diffzy.com/article/difference-between-thesis-and-research-paper .
APA Style Citation
Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper. (n.d.). diffzy.com , Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.diffzy.com/article/difference-between-thesis-and-research-paper .
Edited by Diffzy
Share this article
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences
Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences

Dissertation vs Thesis
“Dissertation” and “ thesis ” are often used interchangeably, but there are some differences between them, depending on the context and country in which they are used. Here is a brief overview of their differences:
In the United States and Canada, a thesis is usually associated with a master’s degree, while a dissertation is associated with a doctoral degree. A thesis involves original research and is usually shorter than a dissertation, with a typical length of 50-100 pages. A dissertation, on the other hand, is a longer piece of original research, with a typical length of 100-300 pages or more.
In the United Kingdom, the opposite is true: a thesis is usually associated with a doctoral degree, while a dissertation is associated with a master’s degree. However, the terms are sometimes used interchangeably.
In some other countries, such as Australia and New Zealand, the terms “thesis” and “dissertation” are used interchangeably, and the length and content of these documents depend on the degree program and the requirements of the institution.
In general, both a thesis and a dissertation involve original research and are used to demonstrate the candidate’s expertise in a particular field of study. However, the specific requirements and expectations for each may vary depending on the degree program, institution, and country.
Both a thesis and a dissertation typically involve conducting original research and presenting findings in a formal document. They often include a literature review, methodology section, analysis of data, and conclusions based on the findings.
The purpose of both a thesis and a dissertation is to contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field and demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter. They are also important for advancing academic and professional careers in fields such as academia, research, and policy-making.
While the requirements and expectations for a thesis or dissertation may vary, it is important for students to work closely with their advisors and follow all guidelines provided by their institution. This includes adhering to formatting and citation styles, conducting ethical research, and submitting drafts and revisions in a timely manner.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

Differences Finder
What is the Difference Between Thesis and Report
Thesis and Report are two commonly confused terms, each with its own unique features, purposes, and formats. While both are written in an academic setting, there are several distinct differences between the two that should …
Published on: Education
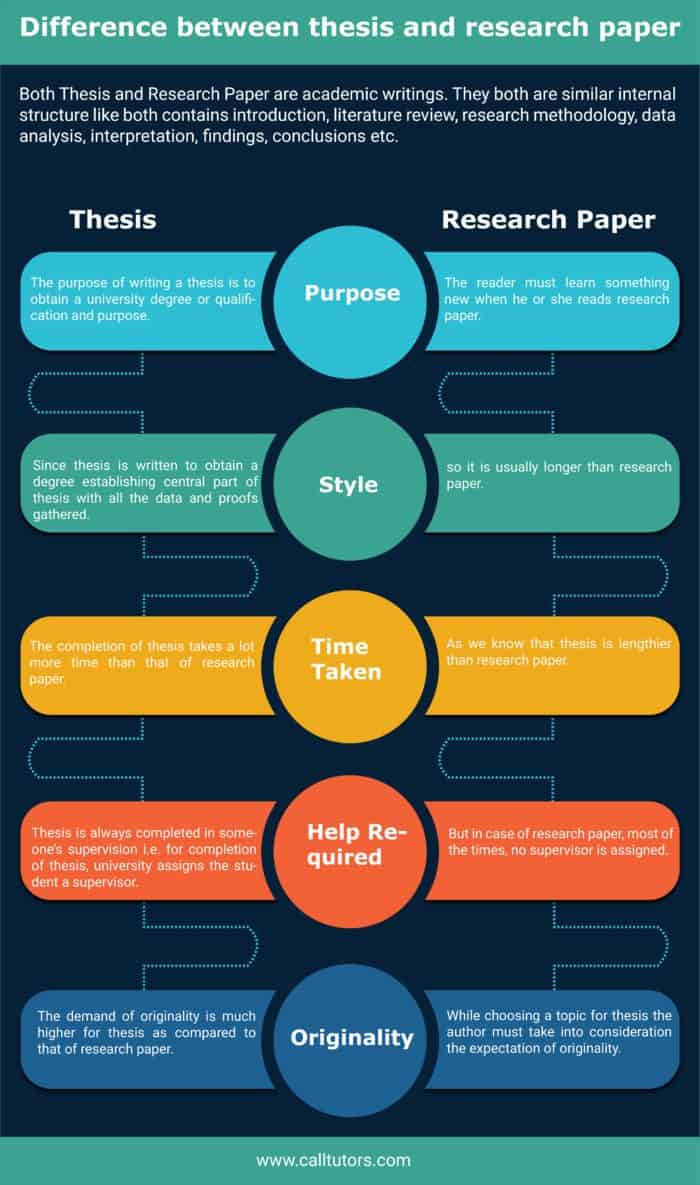
Thesis and Report are two commonly confused terms, each with its own unique features, purposes, and formats. While both are written in an academic setting, there are several distinct differences between the two that should be taken into consideration.
A thesis is typically a long, research-based essay that is written as part of a student’s degree program. It is an in-depth exploration of a specific topic and involves the student’s own research and analysis. The primary purpose of a thesis is to demonstrate that the student has a comprehensive understanding of the topic, and is capable of applying the knowledge they have acquired during their degree program to a specific problem or issue. A thesis is usually written in the form of a book, which includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, and conclusion.
On the other hand, a report is a shorter document that is typically written in response to a specific problem or issue. It may be based on research, but its primary purpose is to provide an accurate description of a current situation or past event. Reports are generally written in a more concise and descriptive format, as opposed to the more analytical style of a thesis. Reports also usually include recommendations for further action based on the findings.
In conclusion, while both a thesis and a report are written in an academic setting, there are several differences between the two that should be taken into consideration. A thesis is an in-depth exploration of a specific topic and is typically written in the form of a book, while a report is a shorter document that is usually written in response to a specific problem or issue. Additionally, the primary purpose of a thesis is to demonstrate that the student has a comprehensive understanding of the topic, while a report is primarily designed to provide an accurate description of a current situation or past event.
Thesis vs Report: An Overview
Thesis and report writing are two distinct processes that are used in academic writing to convey different types of information. To understand the differences between the two, we must first define them. A thesis is an extensive paper that is written as a requirement for a degree or diploma at a university or college. It is typically a long-term project that involves a considerable amount of research and analysis. A report, on the other hand, is a shorter written work, usually composed of facts and figures, that is used to present information in a concise manner.
Thesis vs Report: Content and Structure
The content and structure of a thesis and a report are very different. A thesis is typically an in-depth exploration of a specific topic, and it may include a series of chapters that discuss related concepts, theories, and research. The structure of the thesis typically follows the standard academic format, with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The introduction of a thesis typically explains the topic that will be explored and provides an overview of the structure of the document. The body paragraphs of the thesis will then discuss the research, theories, and evidence that relate to the topic. Finally, the conclusion will summarize the research and offer a conclusion or opinion on the topic.
A report, on the other hand, is typically shorter than a thesis and is generally used to present specific information in a concise manner. Reports often contain a title page, an executive summary, a table of contents, and sections that present the data and discuss the implications of the findings. Reports are typically used to present data related to a particular field or topic, such as a market analysis or a financial statement. Reports may also include charts and graphs to help illustrate the data.
Thesis vs Report: Purpose and Style
The purpose and style of a thesis and a report also differ significantly. The purpose of a thesis is typically to explore a particular topic in depth, and the document should be written in an academic style with formal language. The thesis should also include citations to sources that are used to support the arguments that are presented.
The purpose of a report, on the other hand, is typically to present facts and figures in a concise manner. Reports are typically written in a more formal style than a thesis and should include citations to sources when necessary. Reports may also include visuals such as charts and graphs to help illustrate the data. Additionally, reports should be written in a clear and concise manner to ensure that the information is easily understood by the reader.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
About Diffinder
Difference Between Anova and Ancova
Difference between left and right handed scissors.
Difference between a research paper, dissertation & thesis
When it comes to writing academic papers, students should have the right skills if they must succeed. Whether it is doing a weekly essay assignment, crafting a term paper, or doing research, the best learners are those who have mastered the art of literary composition. You should also note that understanding how each school paper differs from the other puts you ahead of the pack. Most of the schools, universities and institutions require you to undertake research at some point or another in form of coursework .
Often, students mistake research for term papers or thesis for dissertations. The worst-case scenario is when instead of writing a thesis; you end up with a dissertation paper. Such is an occurrence that often denies students marks. And so, the big question we want to answer in this post is what the differences between research, dissertation, and thesis are? Keep reading to learn more.

First things first note that variations between different types of academic papers could be in the form of writing style , definition, presentation of arguments, not to mention the purpose of writing and level of academia. You should not expect high school students, for example, to partake in thesis writing. But when it comes to writing research papers, it can happen at any level of academia right from high school through college and university.
Note: There are differences in how these terminologies are used. In few countries they are used interchangeably, while in other countries thesis is related to bachelor’s or master’s degree course and dissertation is used in the context of a doctorate degree, whereas in some countries the reverse is true. For example, in Indian context, PhD students are required to submit a “thesis” whereas M. Phil students are required to submit a dissertation. Thesis is considered to be much longer form of research which is opposite in case of USA.
Differences based on the definition
Definitive differences between academic papers simplify things for a college newbie yet to write his or her academic paper. Now, on defining the thesis, research and dissertation, the following are worth noting:
- A research paper refers to a piece of literary composition, often a class requirement. The most notable aspect of research papers is that before you craft them, you must gather knowledge independently. After collecting data and information, students then put together findings in a descriptive format. Learners must also present their arguments based on their evaluation of a subject under study. A good research paper opens the gates to advanced academic writing which will involve the implementation of findings.
- A dissertation is a paper that students write as a requirement for the conferment of a diploma or degree. In some countries, Ph.D. students also write dissertations.
- A thesis is a paper students craft as a requirement for a degree at college or university level. You do realize that all the three types of academic papers lead to something, often an academic qualification that would see one earn a degree or get admitted to the next level of academia.
Length of paper and methodology
While the methodology of writing these papers is similar, often constituting sections such as introduction, abstract, literature review, research method, presentation/finings, discussions, conclusion and recommendations, the length of each paper does vary. Research papers and dissertations are generally long. However, thesis papers tend to be short hence requiring less time to write. Dissertations and research require a comprehensive study of a study and gathering information/data. You, therefore, spend more time on them before and during writing. You may even use an editing service to help you research, write, and proofread your dissertation properly.
Differences based on knowledge inference and hypothesis
A hypothesis is an educated guess. Before you conduct a study, assumptions have to be made that something will turn out in some way. Most importantly, how the outcome will impact a population informs the construction of a hypothesis/thesis statement. In research and dissertation writing, students must exhibit a rigorous understanding of a subject based on a study. It is on this premise that they must come up with/infer a meaningful conclusion. However, when writing thesis papers, the formulation of a hypothesis comes after researching and writing on a subject.
Differences based on the approach
How students go about crafting research, dissertation and thesis is another way of differentiating the three papers. In writing research and dissertation papers, students must use existing pieces of literature to back their findings. However, thesis papers more often rely on existing research work to prove a point. You can, for example, sample different research papers on climate change to prove your study on the same. Ostensibly, you are using existing and published academic papers to ascertain that phenomena or a problem exist.
Mode of publication and utilization
You should also note that academic papers exhibit differences based on the reason for which they get published and also how people use them. Dissertation papers are like complete and newly published books given their voluminous nature. You could refer to yours as an academic book. It makes you a published author. However, thesis and research work are like articles that shed light on a subject but not as comprehensively as dissertations.
Differences based on the level of academia
While students can write research papers at any level, they are most common at the undergraduate level. Completion of a research paper often leads to the conferment of an undergraduate degree. And when it comes to writing dissertation papers, the bargain is qualifying for a master’s degree, thusly; postgraduate, Mphil or MBA. It means if you are not writing a dissertation to obtain a postgraduate degree, you do so as a means of enrolling in a postgraduate program. Thesis papers lead to the conferment of a Ph.D. degree or a doctorate as some scholars call it. Students who write thesis papers do so within the last two years of their academic life.
Final Thoughts
Many factors distinguish academic papers. But regardless of the methodology or purpose of these papers, the most important thing is that students showcase their literary skills. Moreover, academic paper tests the knowledge of students on different issues and subjects. Whether it is writing about how past events led to present-day situations or how human activities will lead to something happening in the future, knowledge dispensation helps societies grow.
In the interest of time, research work involved in crafting academic papers is meant to unearth critical findings on a subject and provide solutions to an existing problem. As a rule of the thumb, students who write research, dissertation or thesis papers must demonstrate their understanding of the society and problems that bedevil it. It is through doing so that recommendations for solving a problem become trustworthy, dependable, acceptable and applicable. Most importantly, learners must meet a set academic threshold before writing the above papers.
About The Author
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.

Thesis vs. Research Paper — What's the Difference?
Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper
Table of contents, key differences, comparison chart, requirement, compare with definitions, research paper, common curiosities, is a thesis longer than a research paper, do all master's programs require a thesis, can a research paper be published in a journal, is a thesis mandatory for obtaining a ph.d., what is the central component of a thesis, are research papers peer-reviewed, what is the main goal of a research paper, are citations crucial for both thesis and research papers, can i write a research paper independently, outside of academic settings, is the topic for a thesis more specific than for a research paper, which is more challenging: writing a thesis or a research paper, how are the findings presented in a thesis compared to a research paper, can one research project lead to both a thesis and research papers, is professional experience valued in writing a thesis or research paper, what's the significance of a thesis statement in a research paper, share your discovery.

Author Spotlight
Popular Comparisons

Trending Comparisons

New Comparisons

Trending Terms

New User? Start here.
Differences Thesis and Research Paper: Academic Evaluation

Table of Contents
Several students wrongly assume that a thesis and a research paper are the same. But that’s a misconception.
Indeed, thesis and research papers are academic writing tasks that students must learn during their learning tenure.
While the purpose for both remains the same – ‘explaining the performed study in detail,’ several differences exist between them.
Below we discuss the differences between a research paper and a thesis.
Explaining the Definition – Thesis Vs Research Paper
Thesis paper.
It is a long academic piece, the last assignment before the university degree. Such detailed papers need students to complete UG honours, Master, and doctorate degrees.
Typically, the thesis comprises 80-100 pages (even more). They are written in a scholarly tone and enable learners to present crucial research in their chosen study field.
Furthermore, the thesis writing process can be hectic and tiresome. Students must have sound writing prowess and research and analysing skills. Using them, learners must prove or disapprove of the researched theory with their written pieces. With authentic evidence and arguments, they also give an insightful description of how they reached that conclusion.
In certain degree programs, learners must conduct an oral statement to substantiate their thesis paper before an expert panel.
Chief Facets to Incorporate into a Thesis Paper
- Thesis title page
- An Abstract
- Content index (Table of Content)
- Listing of figures and tables
- A strong intro
- Methodology
- Research outcome
- Discussions on the study
- A compelling conclusion with your stance backed with evidence
- Suggestions
- An acknowledgment section to appreciate everyone who helped you
- Reference list (bibliography)
- An Appendices section
Research Paper
Contrastingly, a research paper comprises quality analysis and research on the study. Students must evaluate their primary and secondary sources and organise and compose the paper using critical thinking skills. Such papers also investigate, interpret and analyse research findings for a specific topic.
Moreover, a research paper isn’t simply an expository essay presenting the writer’s perspectives and ideas. Nor is it a topic summary written using legitimate sources. Such papers need students to evaluate various sources, interpret the information in their voice and compare their views with that of others.
Research Papers Can Be the Following Assignments:
- Analytical research papers
- Argumentative research papers
- Expository research papers
Thesis Vs Research Paper – A COMPARATIVE TABLE
Explaining the differences in details – thesis vs. research paper.
Comparing Scope & Depth
A thesis paper will need comprehensive research on the subject title. Writers must dig deep into the present Literature, critically analyses past studies and present a precise review of pertaining experiments, theories, and chosen methods.
Due to this, the scope and depth of research are more in a thesis paper. It focuses on all facets of the topic.
For instance, a thesis paper on the History of World Wars will need exhaustive research on all lead-up events, causes, and consequences. It will also compare historic interpretations from both primary and secondary sources.
Research papers must also need wide research. However, the scope for such tasks is narrower. It focuses on particular idea/questions, gives detailed analysis and research findings within a limited word limit.
The research paper’s scope will be on an exact field or topic angle per the coverage.
For example, a research paper on a psychological treatment may cover the influence of the therapy on a targeted group of people.
Contribution to the Field & Authenticity
Thesis papers require authentic research on the field of study. Students must find gaps in the previously performed research, form related questions, and perform wide-ranging analyses to fill those holes.
Everything in the thesis paper must share novel insights, methods, and hypotheses contributing to the field’s advancement.
For instance, a computer science thesis will require students to find a fresh algorithm or application for solving intricate issues.
A research paper also needs authenticity, except on a narrower scope than a thesis. It highlights several angles and facets of the title topic and presents deep analysis and research findings in a restricted context.
Formatting & Structuring
A thesis paper adheres to a particular format and structure. It features different sections (stated above).
The format presents a detailed framework for performing research and analysis. Plus, every segment comprises a purpose and helps achieve proper coherence throughout the paper.
A research paper’s structure is more flexible. Most times, it depends on the study and assignment guidelines.
Still, its standard format includes the following –
- Literature review
- Research analysis and outcome
- Study discussion
- Citation index
Students find it easier to write research papers due to the format’s flexibility. They can tweak the structure to suit the study while sustaining a proper flow of data and arguments.
Task Evaluation & Target Audience
The thesis paper is written for university professors, committee members, or field exponents. These delegates review the research methods, framework, analysis of different data, and importance to its study field.
The target readers are lesser and only restricted to the academic fraternity. Occasionally, it involves the faculty team, student mentors, and other budding researchers. During the evaluation, the focus is on originality, research depth, and overall work quality.
A research paper has a larger audience, researchers, tutors, scholars, and other professionals in the study field. The evaluation process is also different. It is done through peer review before publishing or shown at conferences.
The review process also differs per the assignment guidelines. The focus is on originality, relevance, contextual accuracy, clear framework, and significance of the study for improving current field knowledge and data.
Completion Time & Paper Length
A thesis is lengthier, so it will take longer to finish. Furthermore, it needs more analysis and research to compensate for its higher word limit.
Generally, the time for finishing a thesis paper can extend to many semesters, months, or even years. Students can properly perform in-depth research, collect data and supporting evidence, perform various experiments, etc, within that duration.
A research paper takes less time to complete. The length is shorter, and the topic coverage is often limited. Moreover, students can take a stance after reviewing what others say for writing clarity to finish the paper concisely in a semester or a week.
Objective & Intention
A thesis is a compilation of a learner’s academic tenure. It shows their increased knowledge, writing confidence, and mastery over their chosen study field. Moreover, it also reveals their skills to perform research independently.
It aims to present fresh knowledge, hypothesis, and methods/approaches to its target audience and community. Its objective is also to progress the understanding of the study among experts and build awareness.
For students, the thesis objective is to establish themselves as specialists in the presented study and procure their advanced PhD or Master’s degree without hitches.
The research paper aims to showcase the outcome of a particular investigative study to its targeted audience. It shares new data, analysis and raises vital questions or topics for further research.
Moreover, research papers can either be impartial or concise pieces of a larger field of research. It always shares useful knowledge for current academic debates.
Now that you know the difference between a research paper and a thesis, let’s shift to the next segment.
Thesis Statement Example for Research Paper
What is a thesis statement.
A thesis statement concisely describes the topic’s main arguments and ideas. It informs readers what follows in the body section and creates interest and anticipation.
Every academic writing piece – thesis, research paper, academic essay/article, etc., must have a thesis statement. It should be 1-2 lines and can be viewed as qualitative, quantitative, or mixed research approaches.
A Thesis Statement’s Importance:
- A thesis statement hints at the author’s main argument. It outlines the research focus and evidence supporting it.
- Such statements help writers maintain focus and allow them to organise and refine their views and stance on the coverage.
- Moreover, thesis statements determine the connection between facts and its substantiating evidence.
The Formula for Compiling a Thesis Statement
Many students ask how to craft a solid thesis statement on their topic. It’s not that difficult.
- Firstly, you must specify coverage and have a sound understanding of it.
For example – Increasing suicides among American teenagers
- Secondly, you must present your assertion on the chosen title topic.
For example – Face–to–faceconversations or therapy can help determine a teen’s suicidal cause and reduce it from happening. (Topic assertion).
- Thirdly, you must justify your topic assertion.
For example – Openly talking about problems face-to-face or in therapy can ease teenagers’ minds and comfort them. (Justifying the assertion)
Thesis Statement Example for Your Writing Aid
Teens today face a lot of stress to meet daily expectations, and talking to parents/therapists can help them confront their issues and overcome suicidal tendencies with proper help.
More Thesis Statement Example for Research Paper
(A) Thesis Statement for Expository Research Papers
It highlights an issue and lists crucial facets worth discussing in the research paper.
Take, for instance –
- Topic – Kid’s anxiety
- Crucial facets –higher intelligence levels, peer pressure, and meeting everyone’s expectations
Thesis statement – Kid’s anxiety results and further increases due to constant peer pressure, meeting everyone’s expectations and achieving higher intelligence levels to match standards.
(B) Thesis Statement for Analytical Research Papers
It analyses, interprets, and investigates the title topic’s every angle. The statement hints at all major points researched and presents a rational outcome.
Take for instance
- Topic – Fossil Fuel & its Alternative energy sources.
- Crucial facets –Hydroelectric power and solar energy are prominent alternative sources to fossil fuels.
Thesis Statement – After analysing extensively, the outcome is that Hydroelectric power and solar energy are currently the prominent alternatives to fossil fuels.
(C) Thesis Statement for Argumentative Research Papers
The statement denotes the author/writer’s stance on a particular topic covered with reasons and supporting evidence to convince target readers.
Take for Instance
- Topic – Should animal cruelty be banned?
- Writer’s Stance –Animal cruelty, like inhumane experimentation, must be banned!
Thesis statement – Inhumane animal experiments and cruelty must be prohibited as it is immoral, abusive, and hurtful, and that 80% of experiments conducted are novice and flawed.
More Tips on Writing Thesis Statements for Research Papers
- Thesis statements must always be proven. So, provide supporting evidence for your topic arguments.
- The topic must be interesting and known to the general masses. Furthermore, since research papers have limited topic coverage, restrict your focus to a particular aspect.
- Include the coverage’s major points that immediately capture the reader’s interest.
- Ensure the statement is concise but precise and presents the necessary scope for detailed arguments and validations.
- The statement must also be forceful to show the audience that you are presenting a compelling argument worth knowing. You must have an assertive tone for your position against others’ existing opinions.
What to Avoid in a Thesis Statement?
- A research thesis statement must not make outrageous claims. Nor should it mock or insult the views of others.
For Example – US Religious extremists will ban HS textbooks and legislate their Puritanical principles.
- It must not mention any obvious or vague fact that doesn’t inform anything new but leads to a dead end.
For Example –Ad firms use sex to promote and sell their products!
- It must not hint at something too expansive.
For Example – Abraham Lincoln’s life was troublesome, long, and challenging at every step.
- The thesis statement must also not be too narrow.
For Example – Beer commercials are considered offensive to the viewers.
- It must not be a blatant declaration of what you will write below.
For Example, I will explain how the digestive system functions in this paper.
How Can MyAssignmenthelp.com Tutor You on Writing Thesis & Research Papers from the Concept Stage?
Most first-year students struggle to grasp their assignment requirements. Statistics reveal that 65% of them fail to understand the topic and what the instructor expects from them.
While this data may seem alarming, there is no serious cause for concern. Writing academic research papers is always challenging for the best of writers. So, it’s no surprise to see freshman-year apprentices struggling.
MyAssignmenthelp.com aims to end its assignment troubles. We have dedicated tutors to guide students on their various writing tasks. Our experts have Masters/Ph.D. credentials with sufficient academic writing experience.
Once we receive an order, we assign a competent tutor to work with the student side-by-side and guide them at every step.
Our Academic Writing Help Covers the Following Assignments
- Thesis/Dissertations
- Research papers
- Academic Essays
- Case Study tasks
- Subject-wise homework
- Programming and other technical writing projects
- Business reports
- Lab reports
- Term papers
- Coursework help
- Research proposals
Additional Assignment Writing Assistance
- Editing and proofreading services
- Referencing guidance
- Bibliography help
- Assignment tutoring and brainstorming
- Free academic tools to use
- Pre-crafted samples/examples on all types of academic assignments.
These services will be tailored to your assignment requirements and will take you closer to your desired grades.
We will have your back, regardless of whether you wish to know more about thesis vs research paper differences or seek appropriate writing samples.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can thesis be called a research paper.
Ans: Yes, a thesis is a type of research paper. It comprises the original research that you submit as the final step to your Master’s/university degree.
However, they vary per the type of assignment. Contrary to the above thesis definition, a research paper is a novel plagiarism-free essay. It depicts the writer’s evaluation or viewpoints of specific research.
What Is the Different Between Research Papers and Journal Articles?
Ans: A research paper is crafted traditionally by a college/university student on a specific research theme. The professor typically assigns the task.
A journal article deals with a recently researched or reviewed subject by a field exponent.
What Is the Accepted Thesis Paper Format?
Ans: The thesis paper must have 5 ( or more ) chapters depending on the writer and scope of research.
It must also have these sections –
- An introduction
- Literature review
- The methodology
- Research findings
- A strong conclusion
Furthermore, the thesis paper must be lengthy and incorporate 8-12 quality references for each 1000 words. The professor determines the word count, and writers must adhere to it.
What Should Be the Tone for A Thesis?
Ans: It must also adopt a scholarly/informative tone and avoid jargon and boring terms. You must use multisyllabic phrases and present unbiased arguments or perspectives.
What Is the Writing Tone for A Research Paper?
Ans: You must follow a scholarly writing tone for research papers. It should be formal, consistent, to the point, and objective. The arguments must be error-free and backed with legitimate substantiating evidence.
Experts suggest using the writer’s voice in the paper to communicate with readers clearly.
How to Work A Thesis Paper from Scratch?
Ans: Follow the below tips if this is your first attempt at crafting a thesis paper.
- Pick a good thesis title on the suggested subject.
- Determine the literature review.
- Read texts from reliable sources and list primary and secondary reference links.
- Evaluate your sources and check for ambiguity, controversy, complexities, interest, etc.
- Create an outline for the thesis paper
- Brainstorm the thesis idea and write down the initial draft.
- Keep the thesis statement prominent in the introduction section
- Arrange all arguments and also focus on counterarguments in the body.
Consult with experts today to know more about crafting an excellent thesis paper.
What Are 3 Must-Include Components of a Thesis Paper?
Ans: All thesis papers must comprise these 3 components. They include as follows –
- A captivating topic that expresses the main focus of the paper
- A controlling idea that describes what you intend to discuss and share on the coverage
- Several sub-topics –depict each facet of the thesis topic with logical reasons, examples, and supporting data.
Connect with our thesis experts today and learn about other key thesis paper components.
Are There Any Similarities Between the Two?
Ans: The purpose of the thesis and research paper are the same, explaining a study in detail. Some even say the writing tone is similar.
Ask our experts for more similarities between the two.
Can I Find Writing Samples for Both Online?
Ans: You will find plenty of writing samples for thesis and research papers online. We can provide you with writing references and customised guidance if you want.
Does the Research Paper Require A Thesis Statement?
Ans: The thesis statement is mandatory for all academic essays and research paper assignments. It provides focus and writing direction. Plus, it hints at what the paper will cover in the body.
We are here to solve your queries and deliver apt solutions. Get in touch immediately.

Hi, I am Mark, a Literature writer by profession. Fueled by a lifelong passion for Literature, story, and creative expression, I went on to get a PhD in creative writing. Over all these years, my passion has helped me manage a publication of my write ups in prominent websites and e-magazines. I have also been working part-time as a writing expert for myassignmenthelp.com for 5+ years now. It’s fun to guide students on academic write ups and bag those top grades like a pro. Apart from my professional life, I am a big-time foodie and travel enthusiast in my personal life. So, when I am not working, I am probably travelling places to try regional delicacies and sharing my experiences with people through my blog.
Related Post
Writing Get your essay and assignment written from scratch by PhD expert
Rewriting: Paraphrase or rewrite your friend's essay with similar meaning at reduced cost
Editing: Proofread your work by experts and improve grade at Lowest cost
Enter phone no. to receive critical updates and urgent messages !
Please upload all relevant files for quick & complete assistance.
Get original papers written according to your instructions and save time for what matters most.

Thesis Vs. Dissertation — Know the difference and similarities!
The academic world is filled with many different types of writing assignments, each with its own unique set of requirements and expectations. One common source of confusion for students is the distinction between a thesis and a dissertation. Both are long-form academic works, but there are several key differences between the two that are important to understand.
In Shakespeare’s day, a candidate for a master’s degree would write a thesis, an original paper in which he maintained a certain proposition. Whereas, completion of a doctoral program required submission and defense of a dissertation. He would read his thesis to his committee, after which he sat in silence while two faculty members gave point-by-point refutations of everything the candidate said.
The focus here was on the student’s ideas and his ability to arrange and express them clearly. If a student wished to advance further in academia he could pursue a dissertation. This was more of a literature review . He would read widely in a particular area and write up his findings, discussing the various authorities and their opinions. The point was to demonstrate that he was well-versed in the literature of the field. While the confusion between the two terms is understandable, we shall tackle the dissertation vs. thesis topic in this article and provide unambiguous insights on it.
Table of Contents
What Is a Thesis?
A thesis is a critically written scholarly piece of research work. Typically, it is submitted by students graduating from a master’s program. The purpose of a thesis is to allow students to showcase their knowledge and expertise within the subject matter they have been studying as part of the program.
What Is a Dissertation?
A dissertation is a comparatively lengthier piece of scholarly writing that accounts for your research work throughout the doctoral program. A researcher earns the Ph.D. after submitting and defending his/her dissertation. It includes all information about the original research or expanded research on a new or existing topic conducted by the Ph.D. candidate.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: Differences
- The primary difference between a thesis and a dissertation is the time when they are completed. As mentioned earlier, a thesis is presented at the culmination of a master’s program, whereas, a dissertation is presented to earn a Ph.D.
- A thesis is a compilation of research ensuring that the researcher is well-informed and has knowledge about the research topic learned in the study program. On the other hand, a dissertation provides an opportunity for the researcher to contribute new theories and information to the existing literature in the research field.
- A thesis is a presentation of learned and existing information, while the purpose of a dissertation is to develop a unique concept and defend it based on theoretical and practical results.
- A master’s thesis is approximately 100 pages in length. However, a Ph.D. dissertation should be much longer than a thesis and must include background and research information. A dissertation must include your research proposal, grant proposal, literature review , ideation of research topic, and every other minute detail about your research. Ideally, a dissertation inclusive of all details mentioned above should be three times the length of a master’s thesis.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: Similarities
- Both a thesis and a dissertation are considered final projects and are required to graduate from respective programs.
- The thesis and dissertation both require a deep and accurate understanding of the research problem.
- Both forms of scholarly written pieces must address specific research questions.
- Academic writing skills are imperative for a thesis as well as a dissertation.
- Ethical practices must be followed while collating and documenting research data.
- Plagiarism is not accepted in either.
- Both require analytical skills to support the findings.
- It is essential that both undergo intense dissertation/ thesis editing and critical proofreading before final submission.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: Europe
In Europe, the original distinction between a thesis and a dissertation has been largely retained. A doctoral thesis is a focused piece of original research that is performed to obtain a Ph.D. A dissertation is part of a broader post-graduate research project.

However, the thesis has evolved since original research nowadays requires plenty of background research . So, a thesis will contain extensive citations and references to earlier work, although the focus remains on the original work that comes out of it.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: USA
In the United States, the definition of a thesis is almost the opposite of that in Europe. Because a thesis is shorter than a dissertation it gradually came to mean a preliminary degree on the way to a doctorate. A thesis is now performed to earn a Master’s degree. In scientific fields, a master’s candidate takes advanced coursework and gains hands-on experience in a research project but does not direct the project to the same extent that he would in a doctoral program. In a master’s project, the student’s ideas are welcomed and expected but the focus is on obtaining technical expertise, not doing original research. Engineering students commonly obtain Master’s degrees and seldom go on to get PhDs. In other fields such as Chemistry, the opposite is true, with a Master’s degree no longer being required as the first step for a doctorate. Almost everyone I know who received a Master’s degree in Chemistry got one because they dropped out of graduate school and wrote their truncated research as a Master’s project.
In a Nutshell
Needless to say, the dissertation vs. thesis facts are real. Therefore, using one term instead of another is not acceptable as an academic. One must remember the purpose of each and use them accordingly. However, one is not undermined by the other. Whether you are writing a thesis or a dissertation, both must be done with the same seriousness. Both require critical technical and soft skills. Improving your time management and academic writing skills plays a major role in acing both forms of scholarly writing.
How do you decipher dissertation vs. thesis? Should the interchanged usage of these terms be acceptable? How is your approach to writing a thesis different from that of a dissertation? What are the other differences associated with the thesis and dissertation? Let us know in the comments section below!
Frequently Asked Questions
"Dissertation" and "thesis" are used interchangeably but differ in: Academic Level: Thesis for master's, dissertation for doctoral degrees (US). Scope and Depth: Thesis shorter, demonstrates mastery; dissertation extensive, original research. Originality: Thesis may involve original analysis; dissertation presents significant new insights. Time and Effort: Dissertations require more resources and time than theses.
The length of a dissertation varies depending on factors like academic discipline, research topic, institution, and country. Generally, dissertations are longer than theses, ranging from 10,000 to over 100,000 words. However, word count alone does not reflect the quality or depth of the research. Guidelines from the academic institution should be consulted for specific requirements.
The length of a thesis varies depending on factors like academic discipline, research topic, institution, and country. Generally, the word count ranges from around 10,000 to 50,000 words. Specific guidelines from the academic institution should be consulted for precise requirements.
Has helped develop my writing skills through science-based study.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Defining the two terms: thesis vs. research paper. The first step to discerning between a thesis and research paper is to know what they signify. Thesis: A thesis or a dissertation is an academic document that a candidate writes to acquire a university degree or similar qualification. Students typically submit a thesis at the end of their final ...
A thesis and research paper both pertain to academic writing but serve different functions. A thesis is typically the culmination of a graduate program, representing original research and findings that contribute new knowledge to the field. It's often required for obtaining advanced degrees. On the other hand, a research paper can be a stand ...
But, Research Paper is a novel, plagiarism-free long essay. It portrays the interpretation, evaluation or argument submitted by a researcher. The thesis acts as a final project. Whereas a research paper is a kind of research manual of journals. The length of the thesis is around 20,000 to 80,000 words.
Conclusion. In brief, the main difference between thesis and research paper is that thesis is a long research paper that typically serves as the final project for a university degree, while a research paper is a piece of academic writing on a particular topic. Moreover, in an academic context, students may be required to write research papers ...
I. Introduction to Thesis vs. Research Paper Choosing between a thesis and a research paper is often daunting, but understanding the difference can be key to crafting an effective piece of academic writing. While both papers require extensive research into various topics or arguments, there are ...
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
In conclusion, the difference between a thesis and a research paper lies in their purpose, scope, originality, structure, evaluation, and length. A thesis represents the culmination of a student's academic journey, aiming to obtain a higher degree and contribute new knowledge to the academic community. It requires extensive research, in-depth ...
Thesis vs Research Paper. A thesis and a research paper are two different writing formats used for academic purposes. A thesis is usually an in-depth study of the topic that considers all aspects of the situation, while a research paper provides more specific information on the subject matter or problem.
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic. Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research ...
Thesis. Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master's or Doctoral degree, although it ...
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
Contemporary Trends In Dissertation Vs Thesis. In the 21st century, the thesis and dissertation continue to evolve. Educational institutions are adapting to new forms of scholarship, interdisciplinary research, and varied modes of dissemination. The focus is often on producing high-quality, original research that contributes significantly to ...
Thesis vs. Research paper. The aspects that are common in a research paper and a thesis are that both are academic documents. But we know that there are a lot of differences between both documents. This difference can be caused by style, purpose, or specific components. The basic difference between a thesis and a research paper is the purpose.
A thesis involves original research and is usually shorter than a dissertation, with a typical length of 50-100 pages. A dissertation, on the other hand, is a longer piece of original research, with a typical length of 100-300 pages or more. In the United Kingdom, the opposite is true: a thesis is usually associated with a doctoral degree ...
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
A thesis is typically a long, research-based essay that is written as part of a student's degree program. It is an in-depth exploration of a specific topic and involves the student's own research and analysis. ... Thesis vs Report: An Overview. Thesis and report writing are two distinct processes that are used in academic writing to convey ...
A good research paper opens the gates to advanced academic writing which will involve the implementation of findings. A dissertation is a paper that students write as a requirement for the conferment of a diploma or degree. In some countries, Ph.D. students also write dissertations. A thesis is a paper students craft as a requirement for a ...
A thesis is often a requirement for higher-level academic degrees and encapsulates a student's entire course of study into a single document. On the other hand, a research paper, while also academic, can be written for various reasons, whether for a class assignment or to share findings in a journal.
Explaining the Definition - Thesis Vs Research Paper Thesis Paper. It is a long academic piece, the last assignment before the university degree. Such detailed papers need students to complete UG honours, Master, and doctorate degrees. Typically, the thesis comprises 80-100 pages (even more). They are written in a scholarly tone and enable ...
Dissertation vs. Thesis: Differences. The primary difference between a thesis and a dissertation is the time when they are completed. As mentioned earlier, a thesis is presented at the culmination of a master's program, whereas, a dissertation is presented to earn a Ph.D. A thesis is a compilation of research ensuring that the researcher is ...
Following are the concepts discussed in this video:#researchpaper #thesis #researchpapers is thesis and dissertation the same,research paper vs thesis vs di...