Research Methodologies
- Quantitative Research Methodologies

Qualitative Research Methodologies
- Systematic Reviews
- Finding Articles by Methodology
- Design Your Research Project
Library Help
What is qualitative research.
Qualitative research methodologies seek to capture information that often can't be expressed numerically. These methodologies often include some level of interpretation from researchers as they collect information via observation, coded survey or interview responses, and so on. Researchers may use multiple qualitative methods in one study, as well as a theoretical or critical framework to help them interpret their data.
Qualitative research methods can be used to study:
- How are political and social attitudes formed?
- How do people make decisions?
- What teaching or training methods are most effective?
Qualitative Research Approaches
Action research.
In this type of study, researchers will actively pursue some kind of intervention, resolve a problem, or affect some kind of change. They will not only analyze the results but will also examine the challenges encountered through the process.
Ethnography
Ethnographies are an in-depth, holistic type of research used to capture cultural practices, beliefs, traditions, and so on. Here, the researcher observes and interviews members of a culture — an ethnic group, a clique, members of a religion, etc. — and then analyzes their findings.
Grounded Theory
Researchers will create and test a hypothesis using qualitative data. Often, researchers use grounded theory to understand decision-making, problem-solving, and other types of behavior.
Narrative Research
Researchers use this type of framework to understand different aspects of the human experience and how their subjects assign meaning to their experiences. Researchers use interviews to collect data from a small group of subjects, then discuss those results in the form of a narrative or story.
Phenomenology
This type of research attempts to understand the lived experiences of a group and/or how members of that group find meaning in their experiences. Researchers use interviews, observation, and other qualitative methods to collect data.
Often used to share novel or unique information, case studies consist of a detailed, in-depth description of a single subject, pilot project, specific events, and so on.
- Hossain, M.S., Runa, F., & Al Mosabbir, A. (2021). Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on rare diseases: A case study on thalassaemia patients in Bangladesh. Public Health in Practice, 2(100150), 1-3.
- Nožina, M. (2021). The Czech Rhino connection: A case study of Vietnamese wildlife trafficking networks’ operations across central Europe. European Journal on Criminal Policy and Research, 27(2), 265-283.
Focus Groups
Researchers will recruit people to answer questions in small group settings. Focus group members may share similar demographics or be diverse, depending on the researchers' needs. Group members will then be asked a series of questions and have their responses recorded. While these responses may be coded and discussed numerically (e.g., 50% of group members responded negatively to a question), researchers will also use responses to provide context, nuance, and other details.
- Dichabeng, P., Merat, N., & Markkula, G. (2021). Factors that influence the acceptance of future shared automated vehicles – A focus group study with United Kingdom drivers. Transportation Research: Part F, 82, 121–140.
- Maynard, E., Barton, S., Rivett, K., Maynard, O., & Davies, W. (2021). Because ‘grown-ups don’t always get it right’: Allyship with children in research—From research question to authorship. Qualitative Research in Psychology, 18(4), 518–536.
Observational Study
Researchers will arrange to observe (usually in an unobtrusive way) a set of subjects in specific conditions. For example, researchers might visit a school cafeteria to learn about the food choices students make or set up trail cameras to collect information about animal behavior in the area.
- He, J. Y., Chan, P. W., Li, Q. S., Li, L., Zhang, L., & Yang, H. L. (2022). Observations of wind and turbulence structures of Super Typhoons Hato and Mangkhut over land from a 356 m high meteorological tower. Atmospheric Research, 265(105910), 1-18.
- Zerovnik Spela, Kos Mitja, & Locatelli Igor. (2022). Initiation of insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: An observational study. Acta Pharmaceutica, 72(1), 147–157.
Open-Ended Surveys
Unlike quantitative surveys, open-ended surveys require respondents to answer the questions in their own words.
- Mujcic, A., Blankers, M., Yildirim, D., Boon, B., & Engels, R. (2021). Cancer survivors’ views on digital support for smoking cessation and alcohol moderation: a survey and qualitative study. BMC Public Health, 21(1), 1-13.
- Smith, S. D., Hall, J. P., & Kurth, N. K. (2021). Perspectives on health policy from people with disabilities. Journal of Disability Policy Studies, 32(3), 224–232.
Structured or Semi-Structured Interviews
Researchers will recruit a small number of people who fit pre-determined criteria (e.g., people in a certain profession) and ask each the same set of questions, one-on-one. Semi-structured interviews will include opportunities for the interviewee to provide additional information they weren't asked about by the researcher.
- Gibbs, D., Haven-Tang, C., & Ritchie, C. (2021). Harmless flirtations or co-creation? Exploring flirtatious encounters in hospitable experiences. Tourism & Hospitality Research, 21(4), 473–486.
- Hongying Dai, Ramos, A., Tamrakar, N., Cheney, M., Samson, K., & Grimm, B. (2021). School personnel’s responses to school-based vaping prevention program: A qualitative study. Health Behavior & Policy Review, 8(2), 130–147.
- Call : 801.863.8840
- Text : 801.290.8123
- In-Person Help
- Email a Librarian
- Make an Appointment
- << Previous: Quantitative Research Methodologies
- Next: Systematic Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Apr 1, 2024 4:09 PM
- URL: https://uvu.libguides.com/methods
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Table of Contents

Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people’s beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and textual analysis.
Qualitative research aims to uncover the meaning and significance of social phenomena, and it typically involves a more flexible and iterative approach to data collection and analysis compared to quantitative research. Qualitative research is often used in fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, and education.
Qualitative Research Methods

Qualitative Research Methods are as follows:
One-to-One Interview
This method involves conducting an interview with a single participant to gain a detailed understanding of their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. One-to-one interviews can be conducted in-person, over the phone, or through video conferencing. The interviewer typically uses open-ended questions to encourage the participant to share their thoughts and feelings. One-to-one interviews are useful for gaining detailed insights into individual experiences.
Focus Groups
This method involves bringing together a group of people to discuss a specific topic in a structured setting. The focus group is led by a moderator who guides the discussion and encourages participants to share their thoughts and opinions. Focus groups are useful for generating ideas and insights, exploring social norms and attitudes, and understanding group dynamics.
Ethnographic Studies
This method involves immersing oneself in a culture or community to gain a deep understanding of its norms, beliefs, and practices. Ethnographic studies typically involve long-term fieldwork and observation, as well as interviews and document analysis. Ethnographic studies are useful for understanding the cultural context of social phenomena and for gaining a holistic understanding of complex social processes.
Text Analysis
This method involves analyzing written or spoken language to identify patterns and themes. Text analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative text analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Text analysis is useful for understanding media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
This method involves an in-depth examination of a single person, group, or event to gain an understanding of complex phenomena. Case studies typically involve a combination of data collection methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case. Case studies are useful for exploring unique or rare cases, and for generating hypotheses for further research.
Process of Observation
This method involves systematically observing and recording behaviors and interactions in natural settings. The observer may take notes, use audio or video recordings, or use other methods to document what they see. Process of observation is useful for understanding social interactions, cultural practices, and the context in which behaviors occur.
Record Keeping
This method involves keeping detailed records of observations, interviews, and other data collected during the research process. Record keeping is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data, and for providing a basis for analysis and interpretation.
This method involves collecting data from a large sample of participants through a structured questionnaire. Surveys can be conducted in person, over the phone, through mail, or online. Surveys are useful for collecting data on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors, and for identifying patterns and trends in a population.
Qualitative data analysis is a process of turning unstructured data into meaningful insights. It involves extracting and organizing information from sources like interviews, focus groups, and surveys. The goal is to understand people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations
Qualitative Research Analysis Methods
Qualitative Research analysis methods involve a systematic approach to interpreting and making sense of the data collected in qualitative research. Here are some common qualitative data analysis methods:
Thematic Analysis
This method involves identifying patterns or themes in the data that are relevant to the research question. The researcher reviews the data, identifies keywords or phrases, and groups them into categories or themes. Thematic analysis is useful for identifying patterns across multiple data sources and for generating new insights into the research topic.
Content Analysis
This method involves analyzing the content of written or spoken language to identify key themes or concepts. Content analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative content analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Content analysis is useful for identifying patterns in media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
Discourse Analysis
This method involves analyzing language to understand how it constructs meaning and shapes social interactions. Discourse analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as conversation analysis, critical discourse analysis, and narrative analysis. Discourse analysis is useful for understanding how language shapes social interactions, cultural norms, and power relationships.
Grounded Theory Analysis
This method involves developing a theory or explanation based on the data collected. Grounded theory analysis starts with the data and uses an iterative process of coding and analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data. The theory or explanation that emerges is grounded in the data, rather than preconceived hypotheses. Grounded theory analysis is useful for understanding complex social phenomena and for generating new theoretical insights.
Narrative Analysis
This method involves analyzing the stories or narratives that participants share to gain insights into their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. Narrative analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as structural analysis, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis. Narrative analysis is useful for understanding how individuals construct their identities, make sense of their experiences, and communicate their values and beliefs.
Phenomenological Analysis
This method involves analyzing how individuals make sense of their experiences and the meanings they attach to them. Phenomenological analysis typically involves in-depth interviews with participants to explore their experiences in detail. Phenomenological analysis is useful for understanding subjective experiences and for developing a rich understanding of human consciousness.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing and contrasting data across different cases or groups to identify similarities and differences. Comparative analysis can be used to identify patterns or themes that are common across multiple cases, as well as to identify unique or distinctive features of individual cases. Comparative analysis is useful for understanding how social phenomena vary across different contexts and groups.
Applications of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research has many applications across different fields and industries. Here are some examples of how qualitative research is used:
- Market Research: Qualitative research is often used in market research to understand consumer attitudes, behaviors, and preferences. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with consumers to gather insights into their experiences and perceptions of products and services.
- Health Care: Qualitative research is used in health care to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education: Qualitative research is used in education to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. Researchers conduct classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work : Qualitative research is used in social work to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : Qualitative research is used in anthropology to understand different cultures and societies. Researchers conduct ethnographic studies and observe and interview members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : Qualitative research is used in psychology to understand human behavior and mental processes. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy : Qualitative research is used in public policy to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
How to Conduct Qualitative Research
Here are some general steps for conducting qualitative research:
- Identify your research question: Qualitative research starts with a research question or set of questions that you want to explore. This question should be focused and specific, but also broad enough to allow for exploration and discovery.
- Select your research design: There are different types of qualitative research designs, including ethnography, case study, grounded theory, and phenomenology. You should select a design that aligns with your research question and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Recruit participants: Once you have your research question and design, you need to recruit participants. The number of participants you need will depend on your research design and the scope of your research. You can recruit participants through advertisements, social media, or through personal networks.
- Collect data: There are different methods for collecting qualitative data, including interviews, focus groups, observation, and document analysis. You should select the method or methods that align with your research design and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Analyze data: Once you have collected your data, you need to analyze it. This involves reviewing your data, identifying patterns and themes, and developing codes to organize your data. You can use different software programs to help you analyze your data, or you can do it manually.
- Interpret data: Once you have analyzed your data, you need to interpret it. This involves making sense of the patterns and themes you have identified, and developing insights and conclusions that answer your research question. You should be guided by your research question and use your data to support your conclusions.
- Communicate results: Once you have interpreted your data, you need to communicate your results. This can be done through academic papers, presentations, or reports. You should be clear and concise in your communication, and use examples and quotes from your data to support your findings.
Examples of Qualitative Research
Here are some real-time examples of qualitative research:
- Customer Feedback: A company may conduct qualitative research to understand the feedback and experiences of its customers. This may involve conducting focus groups or one-on-one interviews with customers to gather insights into their attitudes, behaviors, and preferences.
- Healthcare : A healthcare provider may conduct qualitative research to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education : An educational institution may conduct qualitative research to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. This may involve conducting classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work: A social worker may conduct qualitative research to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : An anthropologist may conduct qualitative research to understand different cultures and societies. This may involve conducting ethnographic studies and observing and interviewing members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : A psychologist may conduct qualitative research to understand human behavior and mental processes. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy: A government agency or non-profit organization may conduct qualitative research to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. This may involve conducting focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
Purpose of Qualitative Research
The purpose of qualitative research is to explore and understand the subjective experiences, behaviors, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research aims to provide in-depth, descriptive information that can help researchers develop insights and theories about complex social phenomena.
Qualitative research can serve multiple purposes, including:
- Exploring new or emerging phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring new or emerging phenomena, such as new technologies or social trends. This type of research can help researchers develop a deeper understanding of these phenomena and identify potential areas for further study.
- Understanding complex social phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring complex social phenomena, such as cultural beliefs, social norms, or political processes. This type of research can help researchers develop a more nuanced understanding of these phenomena and identify factors that may influence them.
- Generating new theories or hypotheses: Qualitative research can be useful for generating new theories or hypotheses about social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data about individuals’ experiences and perspectives, researchers can develop insights that may challenge existing theories or lead to new lines of inquiry.
- Providing context for quantitative data: Qualitative research can be useful for providing context for quantitative data. By gathering qualitative data alongside quantitative data, researchers can develop a more complete understanding of complex social phenomena and identify potential explanations for quantitative findings.
When to use Qualitative Research
Here are some situations where qualitative research may be appropriate:
- Exploring a new area: If little is known about a particular topic, qualitative research can help to identify key issues, generate hypotheses, and develop new theories.
- Understanding complex phenomena: Qualitative research can be used to investigate complex social, cultural, or organizational phenomena that are difficult to measure quantitatively.
- Investigating subjective experiences: Qualitative research is particularly useful for investigating the subjective experiences of individuals or groups, such as their attitudes, beliefs, values, or emotions.
- Conducting formative research: Qualitative research can be used in the early stages of a research project to develop research questions, identify potential research participants, and refine research methods.
- Evaluating interventions or programs: Qualitative research can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions or programs by collecting data on participants’ experiences, attitudes, and behaviors.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is characterized by several key features, including:
- Focus on subjective experience: Qualitative research is concerned with understanding the subjective experiences, beliefs, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Researchers aim to explore the meanings that people attach to their experiences and to understand the social and cultural factors that shape these meanings.
- Use of open-ended questions: Qualitative research relies on open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed, in-depth responses. Researchers seek to elicit rich, descriptive data that can provide insights into participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Sampling-based on purpose and diversity: Qualitative research often involves purposive sampling, in which participants are selected based on specific criteria related to the research question. Researchers may also seek to include participants with diverse experiences and perspectives to capture a range of viewpoints.
- Data collection through multiple methods: Qualitative research typically involves the use of multiple data collection methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation. This allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data from multiple sources, which can provide a more complete picture of participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Inductive data analysis: Qualitative research relies on inductive data analysis, in which researchers develop theories and insights based on the data rather than testing pre-existing hypotheses. Researchers use coding and thematic analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data and to develop theories and explanations based on these patterns.
- Emphasis on researcher reflexivity: Qualitative research recognizes the importance of the researcher’s role in shaping the research process and outcomes. Researchers are encouraged to reflect on their own biases and assumptions and to be transparent about their role in the research process.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research offers several advantages over other research methods, including:
- Depth and detail: Qualitative research allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data that provides a deeper understanding of complex social phenomena. Through in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation, researchers can gather detailed information about participants’ experiences and perspectives that may be missed by other research methods.
- Flexibility : Qualitative research is a flexible approach that allows researchers to adapt their methods to the research question and context. Researchers can adjust their research methods in real-time to gather more information or explore unexpected findings.
- Contextual understanding: Qualitative research is well-suited to exploring the social and cultural context in which individuals or groups are situated. Researchers can gather information about cultural norms, social structures, and historical events that may influence participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Participant perspective : Qualitative research prioritizes the perspective of participants, allowing researchers to explore subjective experiences and understand the meanings that participants attach to their experiences.
- Theory development: Qualitative research can contribute to the development of new theories and insights about complex social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data and using inductive data analysis, researchers can develop new theories and explanations that may challenge existing understandings.
- Validity : Qualitative research can offer high validity by using multiple data collection methods, purposive and diverse sampling, and researcher reflexivity. This can help ensure that findings are credible and trustworthy.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research also has some limitations, including:
- Subjectivity : Qualitative research relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers, which can introduce bias into the research process. The researcher’s perspective, beliefs, and experiences can influence the way data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted.
- Limited generalizability: Qualitative research typically involves small, purposive samples that may not be representative of larger populations. This limits the generalizability of findings to other contexts or populations.
- Time-consuming: Qualitative research can be a time-consuming process, requiring significant resources for data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Resource-intensive: Qualitative research may require more resources than other research methods, including specialized training for researchers, specialized software for data analysis, and transcription services.
- Limited reliability: Qualitative research may be less reliable than quantitative research, as it relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers. This can make it difficult to replicate findings or compare results across different studies.
- Ethics and confidentiality: Qualitative research involves collecting sensitive information from participants, which raises ethical concerns about confidentiality and informed consent. Researchers must take care to protect the privacy and confidentiality of participants and obtain informed consent.
Also see Research Methods
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on 4 April 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 30 January 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analysing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, and history.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organisation?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography, action research, phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasise different aims and perspectives.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves ‘instruments’ in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analysing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organise your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorise your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analysing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasise different concepts.
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analysing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analysing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalisability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalisable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labour-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organisation to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organise your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, January 30). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 1 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/introduction-to-qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Qualitative Research : Definition
Qualitative research is the naturalistic study of social meanings and processes, using interviews, observations, and the analysis of texts and images. In contrast to quantitative researchers, whose statistical methods enable broad generalizations about populations (for example, comparisons of the percentages of U.S. demographic groups who vote in particular ways), qualitative researchers use in-depth studies of the social world to analyze how and why groups think and act in particular ways (for instance, case studies of the experiences that shape political views).
- Next: Choose an approach >>
- Choose an approach
- Find studies
- Learn methods
- Get software
- Get data for secondary analysis
- Network with researchers

- Last Updated: Jan 31, 2024 9:21 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.stanford.edu/qualitative_research
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Emotions
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music and Media
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Oncology
- Medical Toxicology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business Ethics
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic History
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

The Oxford Handbook of Qualitative Research

Patricia Leavy Independent Scholar Kennebunk, ME, USA
A newer edition of this book is available.
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This handbook provides a broad introduction to qualitative research to those with little to no background in the subject while simultaneously providing substantive contributions to the field that will be of interest to even the most experienced researchers. The first two sections explore the history of qualitative research, ethical perspectives, and philosophical/theoretical approaches. The next three sections focus on the major methods of qualitative practice, as well as on newer approaches (such as arts-based research and internet research); area studies often excluded (such as museum studies and disaster studies); and mixed methods and participatory methods (such as community-based research). The next section covers key issues including data analysis, interpretation, writing, and assessment. The final section offers a commentary about politics and research and the move toward public scholarship. The Oxford Handbook of Qualitative Research is intended for students of all levels, faculty, and researchers across the social sciences.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
Published on August 25, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 20, 2023.
Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation , or research paper , the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research and your dissertation topic .
It should include:
- The type of research you conducted
- How you collected and analyzed your data
- Any tools or materials you used in the research
- How you mitigated or avoided research biases
- Why you chose these methods
- Your methodology section should generally be written in the past tense .
- Academic style guides in your field may provide detailed guidelines on what to include for different types of studies.
- Your citation style might provide guidelines for your methodology section (e.g., an APA Style methods section ).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to write a research methodology, why is a methods section important, step 1: explain your methodological approach, step 2: describe your data collection methods, step 3: describe your analysis method, step 4: evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made, tips for writing a strong methodology chapter, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about methodology.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
Your methods section is your opportunity to share how you conducted your research and why you chose the methods you chose. It’s also the place to show that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated .
It gives your research legitimacy and situates it within your field, and also gives your readers a place to refer to if they have any questions or critiques in other sections.
You can start by introducing your overall approach to your research. You have two options here.
Option 1: Start with your “what”
What research problem or question did you investigate?
- Aim to describe the characteristics of something?
- Explore an under-researched topic?
- Establish a causal relationship?
And what type of data did you need to achieve this aim?
- Quantitative data , qualitative data , or a mix of both?
- Primary data collected yourself, or secondary data collected by someone else?
- Experimental data gathered by controlling and manipulating variables, or descriptive data gathered via observations?
Option 2: Start with your “why”
Depending on your discipline, you can also start with a discussion of the rationale and assumptions underpinning your methodology. In other words, why did you choose these methods for your study?
- Why is this the best way to answer your research question?
- Is this a standard methodology in your field, or does it require justification?
- Were there any ethical considerations involved in your choices?
- What are the criteria for validity and reliability in this type of research ? How did you prevent bias from affecting your data?
Once you have introduced your reader to your methodological approach, you should share full details about your data collection methods .
Quantitative methods
In order to be considered generalizable, you should describe quantitative research methods in enough detail for another researcher to replicate your study.
Here, explain how you operationalized your concepts and measured your variables. Discuss your sampling method or inclusion and exclusion criteria , as well as any tools, procedures, and materials you used to gather your data.
Surveys Describe where, when, and how the survey was conducted.
- How did you design the questionnaire?
- What form did your questions take (e.g., multiple choice, Likert scale )?
- Were your surveys conducted in-person or virtually?
- What sampling method did you use to select participants?
- What was your sample size and response rate?
Experiments Share full details of the tools, techniques, and procedures you used to conduct your experiment.
- How did you design the experiment ?
- How did you recruit participants?
- How did you manipulate and measure the variables ?
- What tools did you use?
Existing data Explain how you gathered and selected the material (such as datasets or archival data) that you used in your analysis.
- Where did you source the material?
- How was the data originally produced?
- What criteria did you use to select material (e.g., date range)?
The survey consisted of 5 multiple-choice questions and 10 questions measured on a 7-point Likert scale.
The goal was to collect survey responses from 350 customers visiting the fitness apparel company’s brick-and-mortar location in Boston on July 4–8, 2022, between 11:00 and 15:00.
Here, a customer was defined as a person who had purchased a product from the company on the day they took the survey. Participants were given 5 minutes to fill in the survey anonymously. In total, 408 customers responded, but not all surveys were fully completed. Due to this, 371 survey results were included in the analysis.
- Information bias
- Omitted variable bias
- Regression to the mean
- Survivorship bias
- Undercoverage bias
- Sampling bias
Qualitative methods
In qualitative research , methods are often more flexible and subjective. For this reason, it’s crucial to robustly explain the methodology choices you made.
Be sure to discuss the criteria you used to select your data, the context in which your research was conducted, and the role you played in collecting your data (e.g., were you an active participant, or a passive observer?)
Interviews or focus groups Describe where, when, and how the interviews were conducted.
- How did you find and select participants?
- How many participants took part?
- What form did the interviews take ( structured , semi-structured , or unstructured )?
- How long were the interviews?
- How were they recorded?
Participant observation Describe where, when, and how you conducted the observation or ethnography .
- What group or community did you observe? How long did you spend there?
- How did you gain access to this group? What role did you play in the community?
- How long did you spend conducting the research? Where was it located?
- How did you record your data (e.g., audiovisual recordings, note-taking)?
Existing data Explain how you selected case study materials for your analysis.
- What type of materials did you analyze?
- How did you select them?
In order to gain better insight into possibilities for future improvement of the fitness store’s product range, semi-structured interviews were conducted with 8 returning customers.
Here, a returning customer was defined as someone who usually bought products at least twice a week from the store.
Surveys were used to select participants. Interviews were conducted in a small office next to the cash register and lasted approximately 20 minutes each. Answers were recorded by note-taking, and seven interviews were also filmed with consent. One interviewee preferred not to be filmed.
- The Hawthorne effect
- Observer bias
- The placebo effect
- Response bias and Nonresponse bias
- The Pygmalion effect
- Recall bias
- Social desirability bias
- Self-selection bias
Mixed methods
Mixed methods research combines quantitative and qualitative approaches. If a standalone quantitative or qualitative study is insufficient to answer your research question, mixed methods may be a good fit for you.
Mixed methods are less common than standalone analyses, largely because they require a great deal of effort to pull off successfully. If you choose to pursue mixed methods, it’s especially important to robustly justify your methods.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Next, you should indicate how you processed and analyzed your data. Avoid going into too much detail: you should not start introducing or discussing any of your results at this stage.
In quantitative research , your analysis will be based on numbers. In your methods section, you can include:
- How you prepared the data before analyzing it (e.g., checking for missing data , removing outliers , transforming variables)
- Which software you used (e.g., SPSS, Stata or R)
- Which statistical tests you used (e.g., two-tailed t test , simple linear regression )
In qualitative research, your analysis will be based on language, images, and observations (often involving some form of textual analysis ).
Specific methods might include:
- Content analysis : Categorizing and discussing the meaning of words, phrases and sentences
- Thematic analysis : Coding and closely examining the data to identify broad themes and patterns
- Discourse analysis : Studying communication and meaning in relation to their social context
Mixed methods combine the above two research methods, integrating both qualitative and quantitative approaches into one coherent analytical process.
Above all, your methodology section should clearly make the case for why you chose the methods you did. This is especially true if you did not take the most standard approach to your topic. In this case, discuss why other methods were not suitable for your objectives, and show how this approach contributes new knowledge or understanding.
In any case, it should be overwhelmingly clear to your reader that you set yourself up for success in terms of your methodology’s design. Show how your methods should lead to results that are valid and reliable, while leaving the analysis of the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results for your discussion section .
- Quantitative: Lab-based experiments cannot always accurately simulate real-life situations and behaviors, but they are effective for testing causal relationships between variables .
- Qualitative: Unstructured interviews usually produce results that cannot be generalized beyond the sample group , but they provide a more in-depth understanding of participants’ perceptions, motivations, and emotions.
- Mixed methods: Despite issues systematically comparing differing types of data, a solely quantitative study would not sufficiently incorporate the lived experience of each participant, while a solely qualitative study would be insufficiently generalizable.
Remember that your aim is not just to describe your methods, but to show how and why you applied them. Again, it’s critical to demonstrate that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated.
1. Focus on your objectives and research questions
The methodology section should clearly show why your methods suit your objectives and convince the reader that you chose the best possible approach to answering your problem statement and research questions .
2. Cite relevant sources
Your methodology can be strengthened by referencing existing research in your field. This can help you to:
- Show that you followed established practice for your type of research
- Discuss how you decided on your approach by evaluating existing research
- Present a novel methodological approach to address a gap in the literature
3. Write for your audience
Consider how much information you need to give, and avoid getting too lengthy. If you are using methods that are standard for your discipline, you probably don’t need to give a lot of background or justification.
Regardless, your methodology should be a clear, well-structured text that makes an argument for your approach, not just a list of technical details and procedures.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Thematic analysis
- Cohort study
- Peer review
- Ethnography
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Conformity bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Availability heuristic
- Attrition bias
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research project . It involves studying the methods used in your field and the theories or principles behind them, in order to develop an approach that matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyze data (for example, experiments, surveys , and statistical tests ).
In shorter scientific papers, where the aim is to report the findings of a specific study, you might simply describe what you did in a methods section .
In a longer or more complex research project, such as a thesis or dissertation , you will probably include a methodology section , where you explain your approach to answering the research questions and cite relevant sources to support your choice of methods.
In a scientific paper, the methodology always comes after the introduction and before the results , discussion and conclusion . The same basic structure also applies to a thesis, dissertation , or research proposal .
Depending on the length and type of document, you might also include a literature review or theoretical framework before the methodology.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
Reliability and validity are both about how well a method measures something:
- Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure (whether the results can be reproduced under the same conditions).
- Validity refers to the accuracy of a measure (whether the results really do represent what they are supposed to measure).
If you are doing experimental research, you also have to consider the internal and external validity of your experiment.
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population . Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research. For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
In statistics, sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 20). What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/methodology/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research design | types, guide & examples, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research Methods & Data Analysis
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative?
The main difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the type of data they collect and analyze.
Quantitative research collects numerical data and analyzes it using statistical methods. The aim is to produce objective, empirical data that can be measured and expressed in numerical terms. Quantitative research is often used to test hypotheses, identify patterns, and make predictions.
Qualitative research , on the other hand, collects non-numerical data such as words, images, and sounds. The focus is on exploring subjective experiences, opinions, and attitudes, often through observation and interviews.
Qualitative research aims to produce rich and detailed descriptions of the phenomenon being studied, and to uncover new insights and meanings.
Quantitative data is information about quantities, and therefore numbers, and qualitative data is descriptive, and regards phenomenon which can be observed but not measured, such as language.
What Is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting non-numerical data, such as language. Qualitative research can be used to understand how an individual subjectively perceives and gives meaning to their social reality.
Qualitative data is non-numerical data, such as text, video, photographs, or audio recordings. This type of data can be collected using diary accounts or in-depth interviews and analyzed using grounded theory or thematic analysis.
Qualitative research is multimethod in focus, involving an interpretive, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 2)
Interest in qualitative data came about as the result of the dissatisfaction of some psychologists (e.g., Carl Rogers) with the scientific study of psychologists such as behaviorists (e.g., Skinner ).
Since psychologists study people, the traditional approach to science is not seen as an appropriate way of carrying out research since it fails to capture the totality of human experience and the essence of being human. Exploring participants’ experiences is known as a phenomenological approach (re: Humanism ).
Qualitative research is primarily concerned with meaning, subjectivity, and lived experience. The goal is to understand the quality and texture of people’s experiences, how they make sense of them, and the implications for their lives.
Qualitative research aims to understand the social reality of individuals, groups, and cultures as nearly as possible as participants feel or live it. Thus, people and groups are studied in their natural setting.
Some examples of qualitative research questions are provided, such as what an experience feels like, how people talk about something, how they make sense of an experience, and how events unfold for people.
Research following a qualitative approach is exploratory and seeks to explain ‘how’ and ‘why’ a particular phenomenon, or behavior, operates as it does in a particular context. It can be used to generate hypotheses and theories from the data.
Qualitative Methods
There are different types of qualitative research methods, including diary accounts, in-depth interviews , documents, focus groups , case study research , and ethnography.
The results of qualitative methods provide a deep understanding of how people perceive their social realities and in consequence, how they act within the social world.
The researcher has several methods for collecting empirical materials, ranging from the interview to direct observation, to the analysis of artifacts, documents, and cultural records, to the use of visual materials or personal experience. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 14)
Here are some examples of qualitative data:
Interview transcripts : Verbatim records of what participants said during an interview or focus group. They allow researchers to identify common themes and patterns, and draw conclusions based on the data. Interview transcripts can also be useful in providing direct quotes and examples to support research findings.
Observations : The researcher typically takes detailed notes on what they observe, including any contextual information, nonverbal cues, or other relevant details. The resulting observational data can be analyzed to gain insights into social phenomena, such as human behavior, social interactions, and cultural practices.
Unstructured interviews : generate qualitative data through the use of open questions. This allows the respondent to talk in some depth, choosing their own words. This helps the researcher develop a real sense of a person’s understanding of a situation.
Diaries or journals : Written accounts of personal experiences or reflections.
Notice that qualitative data could be much more than just words or text. Photographs, videos, sound recordings, and so on, can be considered qualitative data. Visual data can be used to understand behaviors, environments, and social interactions.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative research is endlessly creative and interpretive. The researcher does not just leave the field with mountains of empirical data and then easily write up his or her findings.
Qualitative interpretations are constructed, and various techniques can be used to make sense of the data, such as content analysis, grounded theory (Glaser & Strauss, 1967), thematic analysis (Braun & Clarke, 2006), or discourse analysis.
For example, thematic analysis is a qualitative approach that involves identifying implicit or explicit ideas within the data. Themes will often emerge once the data has been coded.
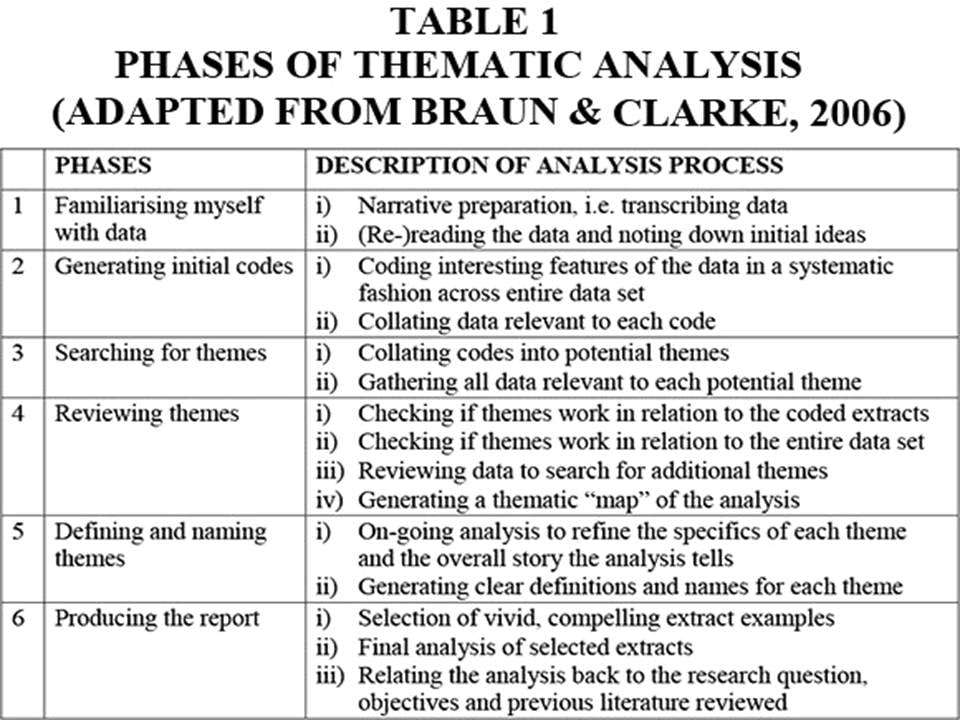
Key Features
- Events can be understood adequately only if they are seen in context. Therefore, a qualitative researcher immerses her/himself in the field, in natural surroundings. The contexts of inquiry are not contrived; they are natural. Nothing is predefined or taken for granted.
- Qualitative researchers want those who are studied to speak for themselves, to provide their perspectives in words and other actions. Therefore, qualitative research is an interactive process in which the persons studied teach the researcher about their lives.
- The qualitative researcher is an integral part of the data; without the active participation of the researcher, no data exists.
- The study’s design evolves during the research and can be adjusted or changed as it progresses. For the qualitative researcher, there is no single reality. It is subjective and exists only in reference to the observer.
- The theory is data-driven and emerges as part of the research process, evolving from the data as they are collected.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
- Because of the time and costs involved, qualitative designs do not generally draw samples from large-scale data sets.
- The problem of adequate validity or reliability is a major criticism. Because of the subjective nature of qualitative data and its origin in single contexts, it is difficult to apply conventional standards of reliability and validity. For example, because of the central role played by the researcher in the generation of data, it is not possible to replicate qualitative studies.
- Also, contexts, situations, events, conditions, and interactions cannot be replicated to any extent, nor can generalizations be made to a wider context than the one studied with confidence.
- The time required for data collection, analysis, and interpretation is lengthy. Analysis of qualitative data is difficult, and expert knowledge of an area is necessary to interpret qualitative data. Great care must be taken when doing so, for example, looking for mental illness symptoms.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
- Because of close researcher involvement, the researcher gains an insider’s view of the field. This allows the researcher to find issues that are often missed (such as subtleties and complexities) by the scientific, more positivistic inquiries.
- Qualitative descriptions can be important in suggesting possible relationships, causes, effects, and dynamic processes.
- Qualitative analysis allows for ambiguities/contradictions in the data, which reflect social reality (Denscombe, 2010).
- Qualitative research uses a descriptive, narrative style; this research might be of particular benefit to the practitioner as she or he could turn to qualitative reports to examine forms of knowledge that might otherwise be unavailable, thereby gaining new insight.
What Is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research involves the process of objectively collecting and analyzing numerical data to describe, predict, or control variables of interest.
The goals of quantitative research are to test causal relationships between variables , make predictions, and generalize results to wider populations.
Quantitative researchers aim to establish general laws of behavior and phenomenon across different settings/contexts. Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Quantitative Methods
Experiments typically yield quantitative data, as they are concerned with measuring things. However, other research methods, such as controlled observations and questionnaires , can produce both quantitative information.
For example, a rating scale or closed questions on a questionnaire would generate quantitative data as these produce either numerical data or data that can be put into categories (e.g., “yes,” “no” answers).
Experimental methods limit how research participants react to and express appropriate social behavior.
Findings are, therefore, likely to be context-bound and simply a reflection of the assumptions that the researcher brings to the investigation.
There are numerous examples of quantitative data in psychological research, including mental health. Here are a few examples:
Another example is the Experience in Close Relationships Scale (ECR), a self-report questionnaire widely used to assess adult attachment styles .
The ECR provides quantitative data that can be used to assess attachment styles and predict relationship outcomes.
Neuroimaging data : Neuroimaging techniques, such as MRI and fMRI, provide quantitative data on brain structure and function.
This data can be analyzed to identify brain regions involved in specific mental processes or disorders.
For example, the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) is a clinician-administered questionnaire widely used to assess the severity of depressive symptoms in individuals.
The BDI consists of 21 questions, each scored on a scale of 0 to 3, with higher scores indicating more severe depressive symptoms.
Quantitative Data Analysis
Statistics help us turn quantitative data into useful information to help with decision-making. We can use statistics to summarize our data, describing patterns, relationships, and connections. Statistics can be descriptive or inferential.
Descriptive statistics help us to summarize our data. In contrast, inferential statistics are used to identify statistically significant differences between groups of data (such as intervention and control groups in a randomized control study).
- Quantitative researchers try to control extraneous variables by conducting their studies in the lab.
- The research aims for objectivity (i.e., without bias) and is separated from the data.
- The design of the study is determined before it begins.
- For the quantitative researcher, the reality is objective, exists separately from the researcher, and can be seen by anyone.
- Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Limitations of Quantitative Research
- Context: Quantitative experiments do not take place in natural settings. In addition, they do not allow participants to explain their choices or the meaning of the questions they may have for those participants (Carr, 1994).
- Researcher expertise: Poor knowledge of the application of statistical analysis may negatively affect analysis and subsequent interpretation (Black, 1999).
- Variability of data quantity: Large sample sizes are needed for more accurate analysis. Small-scale quantitative studies may be less reliable because of the low quantity of data (Denscombe, 2010). This also affects the ability to generalize study findings to wider populations.
- Confirmation bias: The researcher might miss observing phenomena because of focus on theory or hypothesis testing rather than on the theory of hypothesis generation.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
- Scientific objectivity: Quantitative data can be interpreted with statistical analysis, and since statistics are based on the principles of mathematics, the quantitative approach is viewed as scientifically objective and rational (Carr, 1994; Denscombe, 2010).
- Useful for testing and validating already constructed theories.
- Rapid analysis: Sophisticated software removes much of the need for prolonged data analysis, especially with large volumes of data involved (Antonius, 2003).
- Replication: Quantitative data is based on measured values and can be checked by others because numerical data is less open to ambiguities of interpretation.
- Hypotheses can also be tested because of statistical analysis (Antonius, 2003).
Antonius, R. (2003). Interpreting quantitative data with SPSS . Sage.
Black, T. R. (1999). Doing quantitative research in the social sciences: An integrated approach to research design, measurement and statistics . Sage.
Braun, V. & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology . Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3, 77–101.
Carr, L. T. (1994). The strengths and weaknesses of quantitative and qualitative research : what method for nursing? Journal of advanced nursing, 20(4) , 716-721.
Denscombe, M. (2010). The Good Research Guide: for small-scale social research. McGraw Hill.
Denzin, N., & Lincoln. Y. (1994). Handbook of Qualitative Research. Thousand Oaks, CA, US: Sage Publications Inc.
Glaser, B. G., Strauss, A. L., & Strutzel, E. (1968). The discovery of grounded theory; strategies for qualitative research. Nursing research, 17(4) , 364.
Minichiello, V. (1990). In-Depth Interviewing: Researching People. Longman Cheshire.
Punch, K. (1998). Introduction to Social Research: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches. London: Sage

Further Information
- Designing qualitative research
- Methods of data collection and analysis
- Introduction to quantitative and qualitative research
- Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog?
- Qualitative research in health care: Analysing qualitative data
- Qualitative data analysis: the framework approach
- Using the framework method for the analysis of
- Qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research
- Content Analysis
- Grounded Theory
- Thematic Analysis
- Open access
- Published: 28 March 2024
Using the consolidated Framework for Implementation Research to integrate innovation recipients’ perspectives into the implementation of a digital version of the spinal cord injury health maintenance tool: a qualitative analysis
- John A Bourke 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- K. Anne Sinnott Jerram 1 , 2 ,
- Mohit Arora 1 , 2 ,
- Ashley Craig 1 , 2 &
- James W Middleton 1 , 2 , 4 , 5
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 390 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
69 Accesses
Metrics details
Despite advances in managing secondary health complications after spinal cord injury (SCI), challenges remain in developing targeted community health strategies. In response, the SCI Health Maintenance Tool (SCI-HMT) was developed between 2018 and 2023 in NSW, Australia to support people with SCI and their general practitioners (GPs) to promote better community self-management. Successful implementation of innovations such as the SCI-HMT are determined by a range of contextual factors, including the perspectives of the innovation recipients for whom the innovation is intended to benefit, who are rarely included in the implementation process. During the digitizing of the booklet version of the SCI-HMT into a website and App, we used the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) as a tool to guide collection and analysis of qualitative data from a range of innovation recipients to promote equity and to inform actionable findings designed to improve the implementation of the SCI-HMT.
Data from twenty-three innovation recipients in the development phase of the SCI-HMT were coded to the five CFIR domains to inform a semi-structured interview guide. This interview guide was used to prospectively explore the barriers and facilitators to planned implementation of the digital SCI-HMT with six health professionals and four people with SCI. A team including researchers and innovation recipients then interpreted these data to produce a reflective statement matched to each domain. Each reflective statement prefaced an actionable finding, defined as alterations that can be made to a program to improve its adoption into practice.
Five reflective statements synthesizing all participant data and linked to an actionable finding to improve the implementation plan were created. Using the CFIR to guide our research emphasized how partnership is the key theme connecting all implementation facilitators, for example ensuring that the tone, scope, content and presentation of the SCI-HMT balanced the needs of innovation recipients alongside the provision of evidence-based clinical information.
Conclusions
Understanding recipient perspectives is an essential contextual factor to consider when developing implementation strategies for healthcare innovations. The revised CFIR provided an effective, systematic method to understand, integrate and value recipient perspectives in the development of an implementation strategy for the SCI-HMT.
Trial registration
Peer Review reports
Injury to the spinal cord can occur through traumatic causes (e.g., falls or motor vehicle accidents) or from non-traumatic disease or disorder (e.g., tumours or infections) [ 1 ]. The onset of a spinal cord injury (SCI) is often sudden, yet the consequences are lifelong. The impact of a SCI is devastating, with effects on sensory and motor function, bladder and bowel function, sexual function, level of independence, community participation and quality of life [ 2 ]. In order to maintain good health, wellbeing and productivity in society, people with SCI must develop self-management skills and behaviours to manage their newly acquired chronic health condition [ 3 ]. Given the increasing emphasis on primary health care and community management of chronic health conditions, like SCI, there is a growing responsibility on all parties to promote good health practices and minimize the risks of common health complications in their communities.
To address this need, the Spinal Cord Injury Health Maintenance Tool (SCI-HMT) was co-designed between 2018 and 2023 with people living with SCI and their General Practitioners (GPs) in NSW, Australia [ 4 ] The aim of the SCI-HMT is to support self-management of the most common and arguably avoidable potentially life-threatening complications associated with SCI, such as mental health crises, autonomic dysreflexia, kidney infections and pressure injuries. The SCI-HMT provides comprehensible information with resources about the six highest priority health areas related to SCI (as indicated by people with SCI and GPs) and was developed over two phases. Phase 1 focused on developing a booklet version and Phase 2 focused on digitizing this content into a website and smartphone app [ 4 , 5 ].
Enabling the successful implementation of evidence-based innovations such as the SCI-HMT is inevitably influenced by contextual factors: those dynamic and diverse array of forces within real-world settings working for or against implementation efforts [ 6 ]. Contextual factors often include background environmental elements in which an intervention is situated, for example (but not limited to) demographics, clinical environments, organisational culture, legislation, and cultural norms [ 7 ]. Understanding the wider context is necessary to identify and potentially mitigate various challenges to the successful implementation of those innovations. Such work is the focus of determinant frameworks, which focus on categorising or classing groups of contextual determinants that are thought to predict or demonstrate an effect on implementation effectiveness to better understand factors that might influence implementation outcomes [ 8 ].
One of the most highly cited determinant frameworks is the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) [ 9 ], which is often posited as an ideal framework for pre-implementation preparation. Originally published in 2009, the CFIR has recently been subject to an update by its original authors, which included a literature review, survey of users, and the creation of an outcome addendum [ 10 , 11 ]. A key contribution from this revision was the need for a greater focus on the place of innovation recipients, defined as the constituency for whom the innovation is being designed to benefit; for example, patients receiving treatment, students receiving a learning activity. Traditionally, innovation recipients are rarely positioned as key decision-makers or innovation implementers [ 8 ], and as a consequence, have not often been included in the application of research using frameworks, such as the CFIR [ 11 ].
Such power imbalances within the intersection of healthcare and research, particularly between those receiving and delivering such services and those designing such services, have been widely reported [ 12 , 13 ]. There are concerted efforts within health service development, health research and health research funding, to rectify this power imbalance [ 14 , 15 ]. Importantly, such efforts to promote increased equitable population impact are now being explicitly discussed within the implementation science literature. For example, Damschroder et al. [ 11 ] has recently argued for researchers to use the CFIR to collect data from innovation recipients, and that, ultimately, “equitable population impact is only possible when recipients are integrally involved in implementation and all key constituencies share power and make decisions together” (p. 7). Indeed, increased equity between key constituencies and partnering with innovation recipients promotes the likelihood of sustainable adoption of an innovation [ 4 , 12 , 14 ].
There is a paucity of work using the updated CFIR to include and understand innovation recipients’ perspectives. To address this gap, this paper reports on a process of using the CFIR to guide the collection of qualitative data from a range of innovation recipients within a wider co-design mixed methods study examining the development and implementation of SCI-HMT. The innovation recipients in our research are people living with SCI and GPs. Guided by the CFIR domains (shown in the supplementary material), we used reflexive thematic analysis [ 16 ]to summarize data into reflective summaries, which served to inform actionable findings designed to improve implementation of the SCI-HMT.
The procedure for this research is multi-stepped and is summarized in Fig. 1 . First, we mapped retrospective qualitative data collected during the development of the SCI-HMT [ 4 ] against the five domains of the CFIR in order to create a semi-structured interview guide (Step 1). Then, we used this interview guide to collect prospective data from health professionals and people with SCI during the development of the digital version of the SCI-HMT (Step 2) to identify implementation barriers and facilitators. This enabled us to interpret a reflective summary statement for each CFIR domain. Lastly, we developed an actionable finding for each domain summary. The first (RESP/18/212) and second phase (2019/ETH13961) of the project received ethical approval from The Northern Sydney Local Health District Human Research Ethics Committee. The reporting of this study was conducted in line with the consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) guidelines [ 17 ]. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Procedure of synthesising datasets to inform reflective statements and actionable findings. a Two health professionals had a SCI (one being JAB); b Two co-design researchers had a SCI (one being JAB)
Step one: retrospective data collection and analysis
We began by retrospectively analyzing the data set (interview and focus group transcripts) from the previously reported qualitative study from the development phase of the SCI-HMT [ 4 ]. This analysis was undertaken by two team members (KASJ and MA). KASJ has a background in co-design research. Transcript data were uploaded into NVivo software (Version 12: QSR International Pty Ltd) and a directed content analysis approach [ 18 ] was applied to analyze categorized data a priori according to the original 2009 CFIR domains (intervention characteristics, outer setting, inner setting, characteristics of individuals, and process of implementation) described by Damschroder et al. [ 9 ]. This categorized data were summarized and informed the specific questions of a semi-structured interview guide. The final output of step one was an interview guide with context-specific questions arranged according to the CFIR domains (see supplementary file 1). The interview was tested with two people with SCI and one health professional.
Step two: prospective data collection and analysis
In the second step, semi-structured interviews were conducted by KASJ (with MA as observer) with consenting healthcare professionals who had previously contributed to the development of the SCI-HMT. Healthcare professionals included GPs, Nurse Consultants, Specialist Physiotherapists, along with Health Researchers (one being JAB). In addition, a focus group was conducted with consenting individuals with SCI who had contributed to the SCI-HMT design and development phase. The interview schedule designed in step one above guided data collection in all interviews and the focus group.
The focus group and interviews were conducted online, audio recorded, transcribed verbatim and uploaded to NVivo software (Version 12: QSR International Pty Ltd). All data were subject to reflexive, inductive and deductive thematic analysis [ 16 , 19 ] to better understand participants’ perspectives regarding the potential implementation of the SCI-HMT. First, one team member (KASJ) read transcripts and began a deductive analysis whereby data were organized into CFIR domains-specific dataset. Second, KASJ and JAB analyzed this domain-specific dataset to inductively interpret a reflective statement which served to summarise all participant responses to each domain. The final output of step two was a reflective summary statement for each CFIR domain.
Step three: data synthesis
In the third step we aimed to co-create an actionable finding (defined as tangible alteration that can be made to a program, in this case the SCI-HMT [ 20 ]) based on each domain-specific reflective statement. To achieve this, three codesign researchers (KAS and JAB with one person with SCI from Step 2 (deidentified)) focused on operationalising each reflective statement into a recommended modification for the digital version of the SCI-HMT. This was an iterative process guided by the specific CFIR domain and construct definitions, which we deemed salient and relevant to each reflective statement (see Table 2 for example). Data synthesis involved line by line analysis, group discussion, and repeated refinement of actionable findings. A draft synthesis was shared with SCI-HMT developers (JWM and MA) and refinement continued until consensus was agreed on. The final outputs of step three were an actionable finding related to each reflective statement for each CFIR domain.
The characteristics of both the retrospective and prospective study participants are shown in Table 1 . The retrospective data included data from a total of 23 people: 19 people with SCI and four GPs. Of the 19 people with SCI, 12 participated in semi-structured interviews, seven participated in the first focus group, and four returned to the second focus group. In step 2, four people with SCI participated in a focus group and six healthcare professionals participated in one-on-one semi-structured interviews. Two of the healthcare professionals (a GP and a registrar) had lived experience of SCI, as did one researcher (JAB). All interviews and focus groups were conducted either online or in-person and ranged in length between 60 and 120 min.
In our overall synthesis, we actively interpreted five reflective statements based on the updated CFIR domain and construct definitions by Damschroder et al. [ 11 ]. Table 2 provides a summary of how we linked the updated CFIR domain and construct definitions to the reflective statements. We demonstrate this process of co-creation below, including illustrative quotes from participants. Importantly, we guide readers to the actionable findings related to each reflective statement in Table 2 . Each actionable statement represents an alteration that can be made to a program to improve its adoption into practice.
Participants acknowledged that self-management is a major undertaking and very demanding, as one person with SCI said, “ we need to be informed without being terrified and overwhelmed”. Participants felt the HMT could indeed be adapted, tailored, refined, or reinvented to meet local needs. For example, another person with SCI remarked:
“Education needs to be from the get-go but in bite sized pieces from all quarters when readiness is most apparent… at all time points , [not just as a] a newbie tool or for people with [long-term impairment] ” (person with SCI_02).
Therefore, the SCI-HMT had to balance complexity of content while still being accessible and engaging, and required input from both experts in the field and those with lived experience of SCI, for example, a clinical nurse specialist suggested:
“it’s essential [the SCI-HMT] is written by experts in the field as well as with collaboration with people who have had a, you know, the lived experience of SCI” (healthcare professional_03).
Furthermore, the points of contact with healthcare for a person with SCI can be challenging to navigate and the SCI-HMT has the potential to facilitate a smoother engagement process and improve communication between people with SCI and healthcare services. As a GP suggested:
“we need a tool like this to link to that pathway model in primary health care , [the SCI-HMT] it’s a great tool, something that everyone can read and everyone’s reading the same thing” (healthcare professional_05).
Participants highlighted that the ability of the SCI-HMT to facilitate effective communication was very much dependent on the delivery format. The idea of digitizing the SCI-HMT garnered equal support from people with SCI and health care professionals, with one participant with SCI deeming it to be “ essential” ( person with SCI_01) and a health professional suggesting a “digitalized version will be an advantage for most people” (healthcare professional_02).
Outer setting
There was strong interest expressed by both people with SCI and healthcare professionals in using the SCI-HMT. The fundamental premise was that knowledge is power and the SCI-HMT would have strong utility in post-acute rehabilitation services, as well as primary care. As a person with SCI said,
“ we need to leave the [spinal unit] to return to the community with sufficient knowledge, and to know the value of that knowledge and then need to ensure primary healthcare provider [s] are best informed” (person with SCI_04).
The value of the SCI-HMT in facilitating clear and effective communication and shared decision-making between healthcare professionals and people with SCI was also highlighted, as shown by the remarks of an acute nurse specialist:
“I think this tool is really helpful for the consumer and the GP to work together to prioritize particular tests that a patient might need and what the regularity of that is” (healthcare professional_03).
Engaging with SCI peer support networks to promote the SCI-HMT was considered crucial, as one person with SCI emphasized when asked how the SCI-HMT might be best executed in the community, “…peers, peers and peers” (person with SCI_01). Furthermore, the layering of content made possible in the digitalized version will allow for the issue of approachability in terms of readiness for change, as another person with SCI said:
“[putting content into a digital format] is essential and required and there is a need to put summarized content in an App with links to further web-based information… it’s not likely to be accessed otherwise” (person with SCI_02).
Inner setting
Participants acknowledged that self-management of health and well-being is substantial and demanding. It was suggested that the scope, tone, and complexity of the SCI-HMT, while necessary, could potentially be resisted by people with SCI if they felt overwhelmed, as one person with SCI described:
“a manual that is really long and wordy, like, it’s [a] health metric… they maybe lack the health literacy to, to consume the content then yes, it would impede their readiness for [self-management]” (person with SCI_02).
Having support from their GPs was considered essential, and the HMT could enable GP’s, who are under time pressure, to provide more effective health and advice to their patients, as one GP said:
“We GP’s are time poor, if you realize then when you’re time poor you look quickly to say oh this is a patient tool - how can I best use this?” (healthcare professional_05).
Furthermore, health professional skills may be best used with the synthesis of self-reported symptoms, behaviors, or observations. A particular strength of a digitized version would be its ability to facilitate more streamlined communication between a person with SCI and their primary healthcare providers developing healthcare plans, as an acute nurse specialist reflected, “ I think that a digitalized version is essential with links to primary healthcare plans” (healthcare professional_03).
Efficient communication with thorough assessment is essential to ensure serious health issues are not missed, as findings reinforce that the SCI-HMT is an educational tool, not a replacement for healthcare services, as a clinical nurse specialist commented, “ remember, things will go wrong– people end up very sick and in acute care “ (healthcare professional_02).
The SCI-HMT has the potential to provide a pathway to a ‘hope for better than now’ , a hope to ‘remain well’ and a hope to ‘be happy’ , as the informant with SCI (04) declared, “self-management is a long game, if you’re keeping well, you’ve got that possibility of a good life… of happiness”. Participants with SCI felt the tool needed to be genuine and
“acknowledge the huge amount of adjustment required, recognizing that dealing with SCI issues is required to survive and live a good life” (person with SCI_04).
However, there is a risk that an individual is completely overwhelmed by the scale of the SCI-HMT content and the requirement for lifelong vigilance. Careful attention and planning were paid to layering the information accordingly to support self-management as a ‘long game’, which one person with SCI reflected in following:
“the first 2–3 year [period] is probably the toughest to get your head around the learning stuff, because you’ve got to a stage where you’re levelling out, and you’ve kind of made these promises to yourself and then you realize that there’s no quick fix” (person with SCI_01).
It was decided that this could be achieved by providing concrete examples and anecdotes from people with SCI illustrating that a meaningful, healthy life is possible, and that good health is the bedrock of a good life with SCI.
There was universal agreement that the SCI-HMT is aspirational and that it has the potential to improve knowledge and understanding for people with SCI, their families, community workers/carers and primary healthcare professionals, as a GP remarked:
“[different groups] could just read it and realize, ‘Ahh, OK that’s what that means… when you’re doing catheters. That’s what you mean when you’re talking about bladder and bowel function or skin care” (healthcare professional_04).
Despite the SCI-HMT providing an abundance of information and resources to support self-management, participants identified four gaps: (i) the priority issue of sexuality, including pleasure and identity, as one person with SCI remarked:
“ sexuality is one of the biggest issues that people with SCI often might not speak about that often cause you know it’s awkward for them. So yeah, I think that’s a that’s a serious issue” (person with SCI_03).
(ii) consideration of the taboo nature of bladder and bowel topics for indigenous people, (iii) urgent need to ensure links for SCI-HMT care plans are compatible with patient management systems, and (iv) exercise and leisure as a standalone topic taking account of effects of physical activity, including impact on mental health and wellbeing but more especially for fun.
To ensure longevity of the SCI-HMT, maintaining a partnership between people with SCI, SCI community groups and both primary and tertiary health services is required for liaison with the relevant professional bodies, care agencies, funders, policy makers and tertiary care settings to ensure ongoing education and promotion of SCI-HMT is maintained. For example, delivery of ongoing training of healthcare professionals to both increase the knowledge base of primary healthcare providers in relation to SCI, and to promote use of the tools and resources through health communities. As a community nurse specialist suggested:
“ improving knowledge in the health community… would require digital links to clinical/health management platforms” (healthcare professional_02).
In a similar vein, a GP suggested:
“ our common GP body would have continuing education requirements… especially if it’s online, in particular for the rural, rural doctors who you know, might find it hard to get into the city” (healthcare professional_04).
The successful implementation of evidence-based innovations into practice is dependent on a wide array of dynamic and active contextual factors, including the perspectives of the recipients who are destined to use such innovations. Indeed, the recently updated CFIR has called for innovation recipient perspectives to be a priority when considering contextual factors [ 10 , 11 ]. Understanding and including the perspectives of those the innovation is being designed to benefit can promote increased equity and validation of recipient populations, and potentially increase the adoption and sustainability of innovations.
In this paper, we have presented research using the recently updated CFIR to guide the collection of innovation recipients’ perspectives (including people with SCI and GPs working in the community) regarding the potential implementation barriers and facilitators of the digital version of the SCI-HMT. Collected data were synthesized to inform actionable findings– tangible ways in which the SCI-HMT could be modified according of the domains of the CFIR (e.g., see Keith et al. [ 20 ]). It is important to note that we conducted this research using the original domains of the CFIR [ 9 ] prior to Damschroder et al. publishing the updated CFIR [ 11 ]. However, in our analysis we were able to align our findings to the revised CFIR domains and constructs, as Damschroder [ 11 ] suggests, constructs can “be mapped back to the original CFIR to ensure longitudinal consistency” (p. 13).
One of the most poignant findings from our analyses was the need to ensure the content of the SCI-HMT balanced scientific evidence and clinical expertise with lived experience knowledge. This balance of clinical and experiential knowledge demonstrated genuine regard for lived experience knowledge, and created a more accessible, engaging, useable platform. For example, in the innovation and individual domains, the need to include lived experience quotes was immediately apparent once the perspective of people with SCI was included. It was highlighted that while the SCI-HMT will prove useful to many parties at various stages along the continuum of care following onset of SCI, there will be those individuals that are overwhelmed by the scale of the content. That said, the layering of information facilitated by the digitalized version is intended to provide an ease of navigation through the SCI-HMT and enable a far greater sense of control over personal health and wellbeing. Further, despite concerns regarding e-literacy the digitalized version of the SCI-HMT is seen as imperative for accessibility given the wide geographic diversity and recent COVID pandemic [ 21 ]. While there will be people who are challenged by the technology, the universally acceptable use of the internet is seen as less of a barrier than printed material.
The concept of partnership was also apparent within the data analysis focusing on the outer and inner setting domains. In the outer setting domain, our findings emphasized the importance of engaging with SCI community groups, as well as primary and tertiary care providers to maximize uptake at all points in time from the phase of subacute rehabilitation onwards. While the SCI-HMT is intended for use across the continuum of care from post-acute rehabilitation onwards, it may be that certain modules are more relevant at different times, and could serve as key resources during the hand over between acute care, inpatient rehabilitation and community reintegration.
Likewise, findings regarding the inner setting highlighted the necessity of a productive partnership between GPs and individuals with SCI to address the substantial demands of long-term self-management of health and well-being following SCI. Indeed, support is crucial, especially when self-management is the focus. This is particularly so in individuals living with complex disability following survival after illness or injury [ 22 ], where health literacy has been found to be a primary determinant of successful health and wellbeing outcomes [ 23 ]. For people with SCI, this tool potentially holds the most appeal when an individual is ready and has strong partnerships and supportive communication. This can enable potential red flags to be recognized earlier allowing timely intervention to avert health crises, promoting individual well-being, and reducing unnecessary demands on health services.
While the SCI-HMT is an educational tool and not meant to replace health services, findings suggest the current structure would lead nicely to having the conversation with a range of likely support people, including SCI peers, friends and family, GP, community nurses, carers or via on-line support services. The findings within the process domain underscored the importance of ongoing partnership between innovation implementers and a broad array of innovation recipients (e.g., individuals with SCI, healthcare professionals, family, funding agencies and policy-makers). This emphasis on partnership also addresses recent discussions regarding equity and the CFIR. For example, Damschroder et al. [ 11 ] suggests that innovation recipients are too often not included in the CFIR process, as the CFIR is primarily seen as a tool intended “to collect data from individuals who have power and/or influence over implementation outcomes” (p. 5).
Finally, we feel that our inclusion of innovation recipients’ perspectives presented in this article begins to address the notion of equity in implementation, whereby the inclusion of recipient perspectives in research using the CFIR both validates, and increases, the likelihood of sustainable adoption of evidence-based innovations, such as the SCI-HMT. We have used the CFIR in a pragmatic way with an emphasis on meaningful engagement between the innovation recipients and the research team, heeding the call from Damschroder et al. [ 11 ], who recently argued for researchers to use the CFIR to collect data from innovation recipients. Adopting this approach enabled us to give voice to innovation recipient perspectives and subsequently ensure that the tone, scope, content and presentation of the SCI-HMT balanced the needs of innovation recipients alongside the provision of evidence-based clinical information.
Our research is not without limitations. While our study was successful in identifying a number of potential barriers and facilitators to the implementation of the SCI-HMT, we did not test any implementation strategies to impact determinants, mechanisms, or outcomes. This will be the focus of future research on this project, which will investigate the impact of implementation strategies on outcomes. Focus will be given to the context-mechanism configurations which give rise to particular outcomes for different groups in certain circumstances [ 7 , 24 ]. A second potential concern is the relatively small sample size of participants that may not allow for saturation and generalizability of the findings. However, both the significant impact of secondary health complications for people with SCI and the desire for a health maintenance tool have been established in Australia [ 2 , 4 ]. The aim our study reported in this article was to achieve context-specific knowledge of a small sample that shares a particular mutual experience and represents a perspective, rather than a population [ 25 , 26 ]. We feel our findings can stimulate discussion and debate regarding participant-informed approaches to implementation of the SCI-HMT, which can then be subject to larger-sample studies to determine their generalisability, that is, their external validity. Notably, future research could examine the interaction between certain demographic differences (e.g., gender) of people with SCI and potential barriers and facilitators to the implementation of the SCI-HMT. Future research could also include the perspectives of other allied health professionals working in the community, such as occupational therapists. Lastly, while our research gave significant priority to recipient viewpoints, research in this space would benefit for ensuring innovation recipients are engaged as genuine partners throughout the entire research process from conceptualization to implementation.
Employing the CFIR provided an effective, systematic method for identifying recipient perspectives regarding the implementation of a digital health maintenance tool for people living with SCI. Findings emphasized the need to balance clinical and lived experience perspectives when designing an implementation strategy and facilitating strong partnerships with necessary stakeholders to maximise the uptake of SCI-HMT into practice. Ongoing testing will monitor the uptake and implementation of this innovation, specifically focusing on how the SCI-HMT works for different users, in different contexts, at different stages and times of the rehabilitation journey.
Data availability
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are available available upon request and with permission gained from the project Steering Committee.
Abbreviations
spinal cord injury
HMT-Spinal Cord Injury Health Maintenance Tool
Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research
Kirshblum S, Vernon WL. Spinal Cord Medicine, Third Edition. New York: Springer Publishing Company; 2018.
Middleton JW, Arora M, Kifley A, Clark J, Borg SJ, Tran Y, et al. Australian arm of the International spinal cord Injury (Aus-InSCI) Community Survey: 2. Understanding the lived experience in people with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2022;60(12):1069–79.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Craig A, Nicholson Perry K, Guest R, Tran Y, Middleton J. Adjustment following chronic spinal cord injury: determining factors that contribute to social participation. Br J Health Psychol. 2015;20(4):807–23.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Middleton JW, Arora M, Jerram KAS, Bourke J, McCormick M, O’Leary D, et al. Co-design of the Spinal Cord Injury Health Maintenance Tool to support Self-Management: a mixed-methods Approach. Top Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation. 2024;30(1):59–73.
Article Google Scholar
Middleton JW, Arora M, McCormick M, O’Leary D. Health maintenance Tool: how to stay healthy and well with a spinal cord injury. A tool for consumers by consumers. 1st ed. Sydney, NSW Australia: Royal Rehab and The University of Sydney; 2020.
Google Scholar
Nilsen P, Bernhardsson S. Context matters in implementation science: a scoping review of determinant frameworks that describe contextual determinants for implementation outcomes. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):189.
Jagosh J. Realist synthesis for Public Health: building an Ontologically Deep understanding of how Programs Work, for whom, and in which contexts. Annu Rev Public Health. 2019;40(1):361–72.
Nilsen P. Making sense of implementation theories, models and frameworks. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):53.
Damschroder LJ, Aron DC, Keith RE, Kirsh SR, Alexander JA, Lowery JC. Fostering implementation of health services research findings into practice: a consolidated framework for advancing implementation science. Implement Sci. 2009;4(1):50.
Damschroder LJ, Reardon CM, Opra Widerquist MA, Lowery JC. Conceptualizing outcomes for use with the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR): the CFIR outcomes Addendum. Implement Sci. 2022;17(1):7.
Damschroder LJ, Reardon CM, Widerquist MAO, Lowery JC. The updated Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research based on user feedback. Implement Sci. 2022;17(1):75.
Plamondon K, Ndumbe-Eyoh S, Shahram S. 2.2 Equity, Power, and Transformative Research Coproduction. Research Co-Production in Healthcare2022. p. 34–53.
Verville L, Cancelliere C, Connell G, Lee J, Munce S, Mior S, et al. Exploring clinicians’ experiences and perceptions of end-user roles in knowledge development: a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):926.
Gainforth HL, Hoekstra F, McKay R, McBride CB, Sweet SN, Martin Ginis KA, et al. Integrated Knowledge Translation Guiding principles for conducting and Disseminating Spinal Cord Injury Research in Partnership. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;102(4):656–63.
Langley J, Knowles SE, Ward V. Conducting a Research Coproduction Project. Research Co-Production in Healthcare2022. p. 112– 28.
Braun V, Clarke V. One size fits all? What counts as quality practice in (reflexive) thematic analysis? Qualitative Research in Psychology. 2020:1–25.
Tong A, Sainsbury p, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qulaitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007;19(6):349–57.
Bengtsson M. How to plan and perform a qualitative study using content analysis. NursingPlus Open. 2016;2:8–14.
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Res Psychol. 2006;3(2):77–101.
Keith RE, Crosson JC, O’Malley AS, Cromp D, Taylor EF. Using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) to produce actionable findings: a rapid-cycle evaluation approach to improving implementation. Implement Science: IS. 2017;12(1):15.
Choukou M-A, Sanchez-Ramirez DC, Pol M, Uddin M, Monnin C, Syed-Abdul S. COVID-19 infodemic and digital health literacy in vulnerable populations: a scoping review. Digit HEALTH. 2022;8:20552076221076927.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Daniels N. Just Health: Meeting Health needs fairly. Cambridge University Press; 2007. p. 397.
Parker SM, Stocks N, Nutbeam D, Thomas L, Denney-Wilson E, Zwar N, et al. Preventing chronic disease in patients with low health literacy using eHealth and teamwork in primary healthcare: protocol for a cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2018;8(6):e023239–e.
Salter KL, Kothari A. Using realist evaluation to open the black box of knowledge translation: a state-of-the-art review. Implement Sci. 2014;9(1):115.
Sebele-Mpofu FY. The Sampling Conundrum in qualitative research: can Saturation help alleviate the controversy and alleged subjectivity in Sampling? Int’l J Soc Sci Stud. 2021;9:11.
Malterud K, Siersma VD, Guassora AD. Sample size in qualitative interview studies: guided by Information Power. Qual Health Res. 2015;26(13):1753–60.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Authors of this study would like to thank all the consumers with SCI and healthcare professionals for their invaluable contribution to this project. Their participation and insights have been instrumental in shaping the development of the SCI-HMT. The team also acknowledges the support and guidance provided by the members of the Project Steering Committee, as well as the partner organisations, including NSW Agency for Clinical Innovation, and icare NSW. Author would also like to acknowledge the informant group with lived experience, whose perspectives have enriched our understanding and informed the development of SCI-HMT.
The SCI Wellness project was a collaborative project between John Walsh Centre for Rehabilitation Research at The University of Sydney and Royal Rehab. Both organizations provided in-kind support to the project. Additionally, the University of Sydney and Royal Rehab received research funding from Insurance and Care NSW (icare NSW) to undertake the SCI Wellness Project. icare NSW do not take direct responsibility for any of the following: study design, data collection, drafting of the manuscript, or decision to publish.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
John Walsh Centre for Rehabilitation Research, Northern Sydney Local Health District, St Leonards, NSW, Australia
John A Bourke, K. Anne Sinnott Jerram, Mohit Arora, Ashley Craig & James W Middleton
The Kolling Institute, Faculty of Medicine and Health, The University of Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Burwood Academy Trust, Burwood Hospital, Christchurch, New Zealand
John A Bourke
Royal Rehab, Ryde, NSW, Australia
James W Middleton
State Spinal Cord Injury Service, NSW Agency for Clinical Innovation, St Leonards, NSW, Australia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Project conceptualization: KASJ, MA, JWM; project methodology: JWM, MA, KASJ, JAB; data collection: KASJ and MA; data analysis: KASJ, JAB, MA, JWM; writing—original draft preparation: JAB; writing—review and editing: JAB, KASJ, JWM, MA, AC; funding acquisition: JWM, MA. All authors contributed to the revision of the paper and approved the final submitted version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to John A Bourke .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The first (RESP/18/212) and second phase (2019/ETH13961) of the project received ethical approval from The Northern Sydney Local Health District Human Research Ethics Committee. All participants provided informed, written consent. All data were to be retained for 7 years (23rd May 2030).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
MA part salary (from Dec 2018 to Dec 2023), KASJ part salary (July 2021 to Dec 2023) and JAB part salary (Jan 2022 to Aug 2022) was paid from the grant monies. Other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Bourke, J.A., Jerram, K.A.S., Arora, M. et al. Using the consolidated Framework for Implementation Research to integrate innovation recipients’ perspectives into the implementation of a digital version of the spinal cord injury health maintenance tool: a qualitative analysis. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 390 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10847-x
Download citation
Received : 14 August 2023
Accepted : 11 March 2024
Published : 28 March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10847-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Spinal Cord injury
- Self-management
- Innovation recipients
- Secondary health conditions
- Primary health care
- Evidence-based innovations
- Actionable findings
- Consolidated Framework for implementation research
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]

9 methodologies for a successful qualitative research assignment
Qualitative research is important in the educational and scientific domains. It enables a deeper understanding of phenomena, experiences, and context. Many researchers employ such research activities in the fields of history, sociology, and anthropology. For such researchers, learning quality analysis insights is crucial. This way, they can perform well throughout their research journey. Writing a qualitative research assignment is one such way to practice qualitative interpretations. When students address various qualitative questions in these projects, they become efficient in conducting these activities at a higher level, such as for a master’s or Ph.D. thesis.
The FormPlus highlights why researchers prefer qualitative research over quantitative research. It is faster, scientific, objective, focused, and acceptable. Researchers who don’t know what to expect from the research outcomes usually choose qualitative research. In this guide, we will discuss the top methodologies that students can employ while writing their qualitative research assignments. This way, you can write an appealing document that perfectly demonstrates your qualitative research skills.
However, being stressed with academic and daily life commitments, if you find it challenging to manage time exclusively for such projects, availing of assignment writing services can make it manageable. Instead of doing anything wrong in the hustle, get it done by the professionals specifically working to handle these academic write-ups. Now, let’s define quality research before we discuss the actual topic.
What is meant by qualitative research?
Quality research is a market research method that gathers data from conversational and open-ended communication. In simple words, it is about what people think and why they think so. It relates to the nature or standard of something rather than dealing with its quantity. Such researchers collect nonnumerical data to understand opinions, concepts, and ideas.
How do you write a qualitative research assignment? Top 9 methodologies
Writing an assignment requires your command of various tasks. Qualitative research assignment design involves research, writing, structuring, and providing citations of the resources used. Assignment writing plays a crucial role in upgrading your grades.
So, you must make it accurate and authentic. Write it with the utmost care without skipping any important aspects. Sometimes, it can be hard, but it becomes easy if you correctly use effective methodologies. This is why we have brought together some of the common methodologies you can use to write your qualitative research assignments.
1. Interviews
A qualitative interview is mostly used in projects that involve market research. In this study personal interaction is required to collect in-depth information of the participants. In qualitative research for assignment, consider the interview as a personal form of research agenda rather than a focused group study. A qualitative interview requires careful planning so that you can gather meaningful data.
Here are the simple steps to consider for its implementation in a qualitative research assignment:
- Define research objectives.
- Identify the target population.
- Obtain informed consent of participants.
- Make an interview guideline.
- Select a suitable location.
- Conduct the interview.
- Show respect for participant’s perspectives.
- Analyse the data.
2. Observation
In qualitative observation, the researcher gathers data from five senses: sight, hearing, touch, smell, and taste. It is a subject approach that depends on the sensory organ of the researcher. This method allows you to better understand the culture, process, and people under study. Some of its characteristics to consider for writing a qualitative research assignment include,
- It is a naturalistic inquiry of the participants in a natural environment.
- This approach is subjective and depends on the researcher’s observation.
- It does not seek a definite answer to a query.
- The researcher can recognise their own biases when compiling findings.
3. Questionnaires
In this type of survey, the researcher asks open-ended questions to participants. This way, they price the long written or typed document. In writing qualitative research assignments, these questions aim to reveal the participants’ narratives and experiences. Once you know what type of information you need, you can start curating your questionnaire form. The questions must be specific and clear enough that the participants can comprehend them.
Below are the main points that must be considered when creating qualitative research questionnaires.
- Avoid jargon and ambiguity in the questions.
- Each question should contribute to the research objectives.
- Use simple language.
- The questions should be neutral and unbiased.
- Be precise, as the complex questions can overwhelm the respondents.
- Always conduct a pilot test.
- Put yourself in the respondent’s shoes while asking questions.
4. Case Study
A case study is a detailed analysis of a person, place, thing, organisation, or phenomenon. This method is appropriate when you want to gain a contextual, concrete, and in-depth understanding of the real-world problem for writing your qualitative research assignment. This method is especially helpful when you need more time to conduct large-scale research activities.
The four crucial steps below can be followed up with this methodology.
- Select a case that has the potential to provide new and unexpected insights into the subject.
- Make a theoretical framework.
- Collect your data from various primary and secondary resources.
- Describe and analyse the case to provide a clear picture of the subject.
5. Focus Groups
Focused group research has some interesting properties. In this method, a planned interview is conducted within a small group. For this purpose, some of the participants are sampled from the study population to record data for writing a qualitative research assignment. Typically, a focused group has features like,
- At least four to ten participants must meet for up to two hours.
- There must be a facilitator who can guide the discussion by asking open-ended questions.
- The emphasis must be put on the group discussion rather than the discussion of the group members with the facilitator.
- The discussion should be recorded and transcribed by the researchers.
6. Ethnographic Research
It is the most in-depth research method that involves studying people in their natural environment. It requires the researcher to adopt the target audience environment. The environment can be anything from an organisation to a city or any remote location.
However, the geographical constraints can be a problem in this study. For students who are writing their qualitative research assignment, some of the features of ethnographic research to write in their document include,
- The researcher can get a more realistic picture of the study.
- It uncovers extremely valuable insights.
- Provides accurate predictions.
- You can extend the observation to create more in-depth data.
- You can interact with people within a particular context.
7. Record Keeping
This method is similar to going to the library to collect data from books. You consult various relayed books, note the important points, and take note of the referencing. So, the researcher uses already existing data rather than introducing new things in the field.
Later on, this data can be used to conduct new research. Yet, when faced with the vast resources available in your institution’s library, seeking assistance from UK-based assignment writing services is an excellent solution if you need help pinpointing the most relevant information for your topic. Proficient in data gathering and adept at structuring qualitative research assignments, these professionals can significantly elevate your academic results.
This method is mostly used by companies to understand a group of customers’ behaviour, characteristics, and motivation. It allows respondents to ask in-depth questions about their experience. In a business market, it helps you understand how your customers make decisions. The intent is to understand them at their level and make related changes in your setup. The researcher must ask generic and precise questions that have a clear purpose.
Consider the below examples of qualitative survey questions. It can be useful in recording data and writing qualitative research assignments.
- Why did you buy this skin care product?
- What is the overall narrative of this brand?
- How do you feel after buying this product?
- What sets this brand apart from others?
- How will this product fulfil your needs?
- What are the things that you expect from this brand to grant you?
9. Action Research
This method involves collaboration and empowerment of the participants. It is mostly appropriate for marginalised groups where there is no flexibility.
The primary characteristics of the action research that can be quoted in your qualitative research assignment include,
- It is action-oriented, and participants are actively involved in the research.
- There is a collaborative process between participants and researchers.
- The nature of action research is flexible to the changing situation.
However, the survey also accompanies some of the limitations, including,
- The researcher can misinterpret the open-ended questions.
- The data ownership between the researcher and participants needs to be negotiated.
- The ethical considerations must be kept.
- It is not considered a scientific method as it is fluid in data collection. Consequently, it may not attract the finding.
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative research?
Both research types share the common aim of knowledge acquisition. In quantitative research, the use of numbers and objective measures is used. It seeks answers to questions like when and where.
On the other hand, in qualitative research, the researcher is concerned with subjective phenomena. Such data can’t be numerically measured. For example, you might conduct a survey to analyse how different people experience grief.
What are the 4 types of qualitative research?
There are various types of qualitative research. It may include,
● Phenomenological studies:
It examines the human experience via description provided by the people involved. These are the lived experiences of the people. It is usually used in research areas where little knowledge is known.
● Ethnographic studies:
It involves the analysis of data about cultural groups. In such analysis, the researcher mostly lives with different communities and becomes part of their culture to provide solid interpretations.
● Grounded theory studies:
In this qualitative approach, the researcher collects and analyses the data. Later on, a theory is developed that is grounded in the data. It used both inductive and deductive approaches for theory development.
● Historical studies:
It is concerned with the location, identification, evaluation, and synthesis of data from the past. These researchers are not concerned with discovering past events but with relating these events to the present happenings.
The Research Gate provides a flow chart illustrating various qualitative research methods.
What are The 7 characteristics of qualitative research?
The following are some of the distinct features of qualitative research. You can write about them in your qualitative research assignment, as they are collected from reliable sources.
- It can even capture the changing attitude within the target group.
- It is beyond the limitations associated with quantitative research
- It explains something that numbers alone can’t describe.
- It is a flexible approach to improve the outcomes.
- A researcher is not supposed to become more speculative about the results.
- This approach is more targeted.
- It keeps the cost of data collection down.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative research?
The pros of qualitative research can’t be denied. However, some cons are also associated with this research.
- Explore attitudes and behaviours in depth.
- It encourages discussions for better results.
- Generate descriptive data that can formulate new theories.
- The small sample size can be a problem.
- Bias in the sample collection.
- Lack of privacy if you are covering a sensitive topic.
Qualitative research assignment examples
The Afe Babalola University ePortal provides an example of a qualitative assignment. Here is the description of quality questions and related answers. You can get an idea about how to handle your quality research assignment project with this sample.
The questions asked in the paper are displayed below.
The Slide Team presents a template for further compressing other details, such as the qualitative research assignment template. You can use it to make your presentation look professional.
Writing a qualitative research assignment is crucial, especially if you want to engage in research activities for your master’s thesis. Most researchers choose this method because of the associated credibility and reliability of the results. In the above guide, we have discussed some of the prominent features of this method. All of the given data can help you in writing your assignments. We have discussed the benefits of each methodology and a brief account of how you can carry it.
However, even after going through this whole guideline, if the concepts of the Qualitative Research methods assignment seem ambiguous and you think you can’t write a good project, then ask professional to “ write my assignment .” These experts can consult the best sources for the data collection of your project. Consequently, they will deliver you the winning document that can stand out among other write-ups.
- Frontiers in Psychology
- Quantitative Psychology and Measurement
- Research Topics
Best Practice Approaches for Mixed Methods Research in Psychological Science - Volume II
Total Downloads
Total Views and Downloads
About this Research Topic
Having started as a small movement in the 1980’s, the study of mixed methods research burst onto the scene around the beginning of the second millennium. After decades of intense dispute between supporters of the qualitative perspective and their quantitative counterparts—with both sides having grown deeply ...
Keywords : Symmetry, Quantitizing, Qualitizing, Record Transformation, Qual-Quan Integration
Important Note : All contributions to this Research Topic must be within the scope of the section and journal to which they are submitted, as defined in their mission statements. Frontiers reserves the right to guide an out-of-scope manuscript to a more suitable section or journal at any stage of peer review.
Topic Editors
Topic coordinators, recent articles, submission deadlines, participating journals.
Manuscripts can be submitted to this Research Topic via the following journals:
total views
- Demographics
No records found
total views article views downloads topic views
Top countries
Top referring sites, about frontiers research topics.
With their unique mixes of varied contributions from Original Research to Review Articles, Research Topics unify the most influential researchers, the latest key findings and historical advances in a hot research area! Find out more on how to host your own Frontiers Research Topic or contribute to one as an author.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Can J Hosp Pharm
- v.67(6); Nov-Dec 2014

Qualitative Research: Getting Started
Introduction.
As scientifically trained clinicians, pharmacists may be more familiar and comfortable with the concept of quantitative rather than qualitative research. Quantitative research can be defined as “the means for testing objective theories by examining the relationship among variables which in turn can be measured so that numbered data can be analyzed using statistical procedures”. 1 Pharmacists may have used such methods to carry out audits or surveys within their own practice settings; if so, they may have had a sense of “something missing” from their data. What is missing from quantitative research methods is the voice of the participant. In a quantitative study, large amounts of data can be collected about the number of people who hold certain attitudes toward their health and health care, but what qualitative study tells us is why people have thoughts and feelings that might affect the way they respond to that care and how it is given (in this way, qualitative and quantitative data are frequently complementary). Possibly the most important point about qualitative research is that its practitioners do not seek to generalize their findings to a wider population. Rather, they attempt to find examples of behaviour, to clarify the thoughts and feelings of study participants, and to interpret participants’ experiences of the phenomena of interest, in order to find explanations for human behaviour in a given context.
WHAT IS QUALITATIVE RESEARCH?
Much of the work of clinicians (including pharmacists) takes place within a social, clinical, or interpersonal context where statistical procedures and numeric data may be insufficient to capture how patients and health care professionals feel about patients’ care. Qualitative research involves asking participants about their experiences of things that happen in their lives. It enables researchers to obtain insights into what it feels like to be another person and to understand the world as another experiences it.
Qualitative research was historically employed in fields such as sociology, history, and anthropology. 2 Miles and Huberman 2 said that qualitative data “are a source of well-grounded, rich descriptions and explanations of processes in identifiable local contexts. With qualitative data one can preserve chronological flow, see precisely which events lead to which consequences, and derive fruitful explanations.” Qualitative methods are concerned with how human behaviour can be explained, within the framework of the social structures in which that behaviour takes place. 3 So, in the context of health care, and hospital pharmacy in particular, researchers can, for example, explore how patients feel about their care, about their medicines, or indeed about “being a patient”.
THE IMPORTANCE OF METHODOLOGY
Smith 4 has described methodology as the “explanation of the approach, methods and procedures with some justification for their selection.” It is essential that researchers have robust theories that underpin the way they conduct their research—this is called “methodology”. It is also important for researchers to have a thorough understanding of various methodologies, to ensure alignment between their own positionality (i.e., bias or stance), research questions, and objectives. Clinicians may express reservations about the value or impact of qualitative research, given their perceptions that it is inherently subjective or biased, that it does not seek to be reproducible across different contexts, and that it does not produce generalizable findings. Other clinicians may express nervousness or hesitation about using qualitative methods, claiming that their previous “scientific” training and experience have not prepared them for the ambiguity and interpretative nature of qualitative data analysis. In both cases, these clinicians are depriving themselves of opportunities to understand complex or ambiguous situations, phenomena, or processes in a different way.
Qualitative researchers generally begin their work by recognizing that the position (or world view) of the researcher exerts an enormous influence on the entire research enterprise. Whether explicitly understood and acknowledged or not, this world view shapes the way in which research questions are raised and framed, methods selected, data collected and analyzed, and results reported. 5 A broad range of different methods and methodologies are available within the qualitative tradition, and no single review paper can adequately capture the depth and nuance of these diverse options. Here, given space constraints, we highlight certain options for illustrative purposes only, emphasizing that they are only a sample of what may be available to you as a prospective qualitative researcher. We encourage you to continue your own study of this area to identify methods and methodologies suitable to your questions and needs, beyond those highlighted here.
The following are some of the methodologies commonly used in qualitative research:
- Ethnography generally involves researchers directly observing participants in their natural environments over time. A key feature of ethnography is the fact that natural settings, unadapted for the researchers’ interests, are used. In ethnography, the natural setting or environment is as important as the participants, and such methods have the advantage of explicitly acknowledging that, in the real world, environmental constraints and context influence behaviours and outcomes. 6 An example of ethnographic research in pharmacy might involve observations to determine how pharmacists integrate into family health teams. Such a study would also include collection of documents about participants’ lives from the participants themselves and field notes from the researcher. 7
- Grounded theory, first described by Glaser and Strauss in 1967, 8 is a framework for qualitative research that suggests that theory must derive from data, unlike other forms of research, which suggest that data should be used to test theory. Grounded theory may be particularly valuable when little or nothing is known or understood about a problem, situation, or context, and any attempt to start with a hypothesis or theory would be conjecture at best. 9 An example of the use of grounded theory in hospital pharmacy might be to determine potential roles for pharmacists in a new or underserviced clinical area. As with other qualitative methodologies, grounded theory provides researchers with a process that can be followed to facilitate the conduct of such research. As an example, Thurston and others 10 used constructivist grounded theory to explore the availability of arthritis care among indigenous people of Canada and were able to identify a number of influences on health care for this population.
- Phenomenology attempts to understand problems, ideas, and situations from the perspective of common understanding and experience rather than differences. 10 Phenomenology is about understanding how human beings experience their world. It gives researchers a powerful tool with which to understand subjective experience. In other words, 2 people may have the same diagnosis, with the same treatment prescribed, but the ways in which they experience that diagnosis and treatment will be different, even though they may have some experiences in common. Phenomenology helps researchers to explore those experiences, thoughts, and feelings and helps to elicit the meaning underlying how people behave. As an example, Hancock and others 11 used a phenomenological approach to explore health care professionals’ views of the diagnosis and management of heart failure since publication of an earlier study in 2003. Their findings revealed that barriers to effective treatment for heart failure had not changed in 10 years and provided a new understanding of why this was the case.
ROLE OF THE RESEARCHER
For any researcher, the starting point for research must be articulation of his or her research world view. This core feature of qualitative work is increasingly seen in quantitative research too: the explicit acknowledgement of one’s position, biases, and assumptions, so that readers can better understand the particular researcher. Reflexivity describes the processes whereby the act of engaging in research actually affects the process being studied, calling into question the notion of “detached objectivity”. Here, the researcher’s own subjectivity is as critical to the research process and output as any other variable. Applications of reflexivity may include participant-observer research, where the researcher is actually one of the participants in the process or situation being researched and must then examine it from these divergent perspectives. 12 Some researchers believe that objectivity is a myth and that attempts at impartiality will fail because human beings who happen to be researchers cannot isolate their own backgrounds and interests from the conduct of a study. 5 Rather than aspire to an unachievable goal of “objectivity”, it is better to simply be honest and transparent about one’s own subjectivities, allowing readers to draw their own conclusions about the interpretations that are presented through the research itself. For new (and experienced) qualitative researchers, an important first step is to step back and articulate your own underlying biases and assumptions. The following questions can help to begin this reflection process:
- Why am I interested in this topic? To answer this question, try to identify what is driving your enthusiasm, energy, and interest in researching this subject.
- What do I really think the answer is? Asking this question helps to identify any biases you may have through honest reflection on what you expect to find. You can then “bracket” those assumptions to enable the participants’ voices to be heard.
- What am I getting out of this? In many cases, pressures to publish or “do” research make research nothing more than an employment requirement. How does this affect your interest in the question or its outcomes, or the depth to which you are willing to go to find information?
- What do others in my professional community think of this work—and of me? As a researcher, you will not be operating in a vacuum; you will be part of a complex social and interpersonal world. These external influences will shape your views and expectations of yourself and your work. Acknowledging this influence and its potential effects on personal behaviour will facilitate greater self-scrutiny throughout the research process.
FROM FRAMEWORKS TO METHODS
Qualitative research methodology is not a single method, but instead offers a variety of different choices to researchers, according to specific parameters of topic, research question, participants, and settings. The method is the way you carry out your research within the paradigm of quantitative or qualitative research.
Qualitative research is concerned with participants’ own experiences of a life event, and the aim is to interpret what participants have said in order to explain why they have said it. Thus, methods should be chosen that enable participants to express themselves openly and without constraint. The framework selected by the researcher to conduct the research may direct the project toward specific methods. From among the numerous methods used by qualitative researchers, we outline below the three most frequently encountered.
DATA COLLECTION
Patton 12 has described an interview as “open-ended questions and probes yielding in-depth responses about people’s experiences, perceptions, opinions, feelings, and knowledge. Data consists of verbatim quotations and sufficient content/context to be interpretable”. Researchers may use a structured or unstructured interview approach. Structured interviews rely upon a predetermined list of questions framed algorithmically to guide the interviewer. This approach resists improvisation and following up on hunches, but has the advantage of facilitating consistency between participants. In contrast, unstructured or semistructured interviews may begin with some defined questions, but the interviewer has considerable latitude to adapt questions to the specific direction of responses, in an effort to allow for more intuitive and natural conversations between researchers and participants. Generally, you should continue to interview additional participants until you have saturated your field of interest, i.e., until you are not hearing anything new. The number of participants is therefore dependent on the richness of the data, though Miles and Huberman 2 suggested that more than 15 cases can make analysis complicated and “unwieldy”.
Focus Groups
Patton 12 has described the focus group as a primary means of collecting qualitative data. In essence, focus groups are unstructured interviews with multiple participants, which allow participants and a facilitator to interact freely with one another and to build on ideas and conversation. This method allows for the collection of group-generated data, which can be a challenging experience.
Observations
Patton 12 described observation as a useful tool in both quantitative and qualitative research: “[it involves] descriptions of activities, behaviours, actions, conversations, interpersonal interactions, organization or community processes or any other aspect of observable human experience”. Observation is critical in both interviews and focus groups, as nonalignment between verbal and nonverbal data frequently can be the result of sarcasm, irony, or other conversational techniques that may be confusing or open to interpretation. Observation can also be used as a stand-alone tool for exploring participants’ experiences, whether or not the researcher is a participant in the process.
Selecting the most appropriate and practical method is an important decision and must be taken carefully. Those unfamiliar with qualitative research may assume that “anyone” can interview, observe, or facilitate a focus group; however, it is important to recognize that the quality of data collected through qualitative methods is a direct reflection of the skills and competencies of the researcher. 13 The hardest thing to do during an interview is to sit back and listen to participants. They should be doing most of the talking—it is their perception of their own life-world that the researcher is trying to understand. Sophisticated interpersonal skills are required, in particular the ability to accurately interpret and respond to the nuanced behaviour of participants in various settings. More information about the collection of qualitative data may be found in the “Further Reading” section of this paper.
It is essential that data gathered during interviews, focus groups, and observation sessions are stored in a retrievable format. The most accurate way to do this is by audio-recording (with the participants’ permission). Video-recording may be a useful tool for focus groups, because the body language of group members and how they interact can be missed with audio-recording alone. Recordings should be transcribed verbatim and checked for accuracy against the audio- or video-recording, and all personally identifiable information should be removed from the transcript. You are then ready to start your analysis.
DATA ANALYSIS
Regardless of the research method used, the researcher must try to analyze or make sense of the participants’ narratives. This analysis can be done by coding sections of text, by writing down your thoughts in the margins of transcripts, or by making separate notes about the data collection. Coding is the process by which raw data (e.g., transcripts from interviews and focus groups or field notes from observations) are gradually converted into usable data through the identification of themes, concepts, or ideas that have some connection with each other. It may be that certain words or phrases are used by different participants, and these can be drawn together to allow the researcher an opportunity to focus findings in a more meaningful manner. The researcher will then give the words, phrases, or pieces of text meaningful names that exemplify what the participants are saying. This process is referred to as “theming”. Generating themes in an orderly fashion out of the chaos of transcripts or field notes can be a daunting task, particularly since it may involve many pages of raw data. Fortunately, sophisticated software programs such as NVivo (QSR International Pty Ltd) now exist to support researchers in converting data into themes; familiarization with such software supports is of considerable benefit to researchers and is strongly recommended. Manual coding is possible with small and straightforward data sets, but the management of qualitative data is a complexity unto itself, one that is best addressed through technological and software support.
There is both an art and a science to coding, and the second checking of themes from data is well advised (where feasible) to enhance the face validity of the work and to demonstrate reliability. Further reliability-enhancing mechanisms include “member checking”, where participants are given an opportunity to actually learn about and respond to the researchers’ preliminary analysis and coding of data. Careful documentation of various iterations of “coding trees” is important. These structures allow readers to understand how and why raw data were converted into a theme and what rules the researcher is using to govern inclusion or exclusion of specific data within or from a theme. Coding trees may be produced iteratively: after each interview, the researcher may immediately code and categorize data into themes to facilitate subsequent interviews and allow for probing with subsequent participants as necessary. At the end of the theming process, you will be in a position to tell the participants’ stories illustrated by quotations from your transcripts. For more information on different ways to manage qualitative data, see the “Further Reading” section at the end of this paper.
ETHICAL ISSUES
In most circumstances, qualitative research involves human beings or the things that human beings produce (documents, notes, etc.). As a result, it is essential that such research be undertaken in a manner that places the safety, security, and needs of participants at the forefront. Although interviews, focus groups, and questionnaires may seem innocuous and “less dangerous” than taking blood samples, it is important to recognize that the way participants are represented in research can be significantly damaging. Try to put yourself in the shoes of the potential participants when designing your research and ask yourself these questions:
- Are the requests you are making of potential participants reasonable?
- Are you putting them at unnecessary risk or inconvenience?
- Have you identified and addressed the specific needs of particular groups?
Where possible, attempting anonymization of data is strongly recommended, bearing in mind that true anonymization may be difficult, as participants can sometimes be recognized from their stories. Balancing the responsibility to report findings accurately and honestly with the potential harm to the participants involved can be challenging. Advice on the ethical considerations of research is generally available from research ethics boards and should be actively sought in these challenging situations.
GETTING STARTED
Pharmacists may be hesitant to embark on research involving qualitative methods because of a perceived lack of skills or confidence. Overcoming this barrier is the most important first step, as pharmacists can benefit from inclusion of qualitative methods in their research repertoire. Partnering with others who are more experienced and who can provide mentorship can be a valuable strategy. Reading reports of research studies that have utilized qualitative methods can provide insights and ideas for personal use; such papers are routinely included in traditional databases accessed by pharmacists. Engaging in dialogue with members of a research ethics board who have qualitative expertise can also provide useful assistance, as well as saving time during the ethics review process itself. The references at the end of this paper may provide some additional support to allow you to begin incorporating qualitative methods into your research.
CONCLUSIONS
Qualitative research offers unique opportunities for understanding complex, nuanced situations where interpersonal ambiguity and multiple interpretations exist. Qualitative research may not provide definitive answers to such complex questions, but it can yield a better understanding and a springboard for further focused work. There are multiple frameworks, methods, and considerations involved in shaping effective qualitative research. In most cases, these begin with self-reflection and articulation of positionality by the researcher. For some, qualitative research may appear commonsensical and easy; for others, it may appear daunting, given its high reliance on direct participant– researcher interactions. For yet others, qualitative research may appear subjective, unscientific, and consequently unreliable. All these perspectives reflect a lack of understanding of how effective qualitative research actually occurs. When undertaken in a rigorous manner, qualitative research provides unique opportunities for expanding our understanding of the social and clinical world that we inhabit.
Further Reading
- Breakwell GM, Hammond S, Fife-Schaw C, editors. Research methods in psychology. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications Ltd; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Strauss A, Corbin J. Basics of qualitative research. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications Ltd; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- Willig C. Introducing qualitative research in psychology. Buckingham (UK): Open University Press; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- Guest G, Namey EE, Mitchel ML. Collecting qualitative data: a field manual for applied research. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications Ltd; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ogden R. Bias. In: Given LM, editor. The Sage encyclopedia of qualitative research methods. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications Inc; 2008. pp. 61–2. [ Google Scholar ]
This article is the seventh in the CJHP Research Primer Series, an initiative of the CJHP Editorial Board and the CSHP Research Committee. The planned 2-year series is intended to appeal to relatively inexperienced researchers, with the goal of building research capacity among practising pharmacists. The articles, presenting simple but rigorous guidance to encourage and support novice researchers, are being solicited from authors with appropriate expertise.
Previous article in this series:
Bond CM. The research jigsaw: how to get started. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(1):28–30.
Tully MP. Research: articulating questions, generating hypotheses, and choosing study designs. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(1):31–4.
Loewen P. Ethical issues in pharmacy practice research: an introductory guide. Can J Hosp Pharm. 2014;67(2):133–7.
Tsuyuki RT. Designing pharmacy practice research trials. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(3):226–9.
Bresee LC. An introduction to developing surveys for pharmacy practice research. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(4):286–91.
Gamble JM. An introduction to the fundamentals of cohort and case–control studies. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(5):366–72.
Competing interests: None declared.
- Open access
- Published: 01 April 2024
Midwives’ lived experiences of caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in Eswatini: a qualitative study
- Annie M. Temane 1 ,
- Fortunate N. Magagula 2 &
- Anna G. W. Nolte 1
BMC Women's Health volume 24 , Article number: 207 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Midwives encounter various difficulties while aiming to achieve excellence in providing maternity care to women with mobility disabilities. The study aimed to explore and describe midwives’ experiences of caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in Eswatini.
A qualitative, exploratory, descriptive, contextual research design with a phenomenological approach was followed. Twelve midwives working in maternal health facilities in the Hhohho and Manzini regions in Eswatini were interviewed. Purposive sampling was used to select midwives to participate in the research. In-depth phenomenological interviews were conducted, and Giorgi’s descriptive phenomenological method was used for data analysis.
Three themes emerged from the data analysis: midwives experienced physical and emotional strain in providing maternity care to women with mobility disabilities, they experienced frustration due to the lack of equipment to meet the needs of women with mobility disabilities, and they faced challenges in providing support and holistic care to women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium.
Conclusions
Midwives experienced challenges caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and the puerperium in Eswatini. There is a need to develop and empower midwives with the knowledge and skill to implement guidelines and enact protocols. Moreover, equipment and infrastructure are required to facilitate support and holistic maternity care for women with mobility disabilities.
Peer Review reports
Globally, few studies have focused on midwives’ views of providing maternity care to women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and the puerperium [ 1 ]. In The Disabled World [ 2 ], the World Health Organisation (WHO) defines ‘disability’ as an umbrella term covering impairments, activity limitations, and participation restrictions. Furthermore, the WHO defines an ‘impairment’ as a problem in bodily function or structure; an ‘activity limitation’ as a difficulty encountered by an individual in executing a task or action; and ‘participation restriction’ as a problem experienced by an individual in various life situations [ 2 ]. In this study, mobility disabilities refer to an impairment in the functioning of the upper and lower extremities as experienced by women during pregnancy, labour and the puerperium.
Midwives, as frontline workers in the delivery of maternity care [ 3 ] responsible for the lives of the mother and the baby, are accountable for providing competent and holistic care for women during pregnancy, labour and puerperium. As part of healthcare provision, midwives play an important role in ensuring that every woman, including women with mobility disabilities, receives the best maternity care during pregnancy, labour and puerperium. Moridi et al. [ 4 ] state that women with mobility disabilities are entitled to feel safe, respected and well cared for by midwives, who must be sufficiently prepared to care for these women.
According to the Global Population Report, [ 5 ] more than one billion people have some form of disability. Eswatini is classified as a middle-income setting in the southern African region, measuring 17 000 square kilometres with a population of 1 093 238. Of the population, 76.2% reside in rural areas (833 472), and 23.8% (259 766) reside in urban areas [ 6 ]. The economy is largely agricultural as most industries manufacture agricultural products [ 7 ]. Of the Eswatini population, 146 554 (13%) live with disabilities, with most being women (87 258; 16%), 22,871 (14.1%) and 26,270 (14.3%) of them reside in the Hhohho and Manzini regions respectively [ 8 ]. 15% (125 545) of people with disabilities live in rural areas, and 85% of the disabled population is unemployed [ 8 ], which means most of these individuals are economically disadvantaged. Furthermore, according to the Eswatini Central Statistics Office, 8 26.5% of people with disabilities have a mobility (walking) disability, with 63.5% of these being women.
Midwives may encounter difficulties while aiming to achieve excellence in providing maternity care to women with mobility disabilities in what may be challenging circumstances [ 9 ]. The WHO [ 10 ] claims people with disabilities do not receive the health services they need and are thus likely to find healthcare providers have inadequate skills. Lawler et al. [ 11 ] argue that ineffective interactions and poor communication with women needing care, particularly among health professionals engaged in providing maternity services, limit these women’s opportunities to participate in decision-making processes during pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum care. According to the University of Johannesburg, [ 12 ] the midwife, together with the mother, have to engage collaboratively in order to come up with opportunities to promote health while removing any challenges that could impede the achievement thereof.
Walsh-Gallagher et al. [ 13 ] postulate that healthcare professionals tend to view women with disabilities as liabilities and regard them as high risk; they often exclude them from the individualised plan of care, which leads to an increase in these women’s fears about their maternity care. These challenges frequently result in health disparities and prevent women with mobility disabilities from receiving optimal maternity care. By exploring midwives’ experiences of this phenomenon, guidelines for support can be developed to extend available knowledge on maternity care for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium.
Study design
The aim of the study was to explore and describe midwives’ experiences of caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in the Hhohho and Manzini regions of Eswatini. A qualitative, [ 14 ] exploratory, [ 15 ] descriptive, [ 16 ] contextual [ 17 ] research design with a phenomenological approach [ 18 ] was applied for this study to gain insight and understanding of the research phenomenon [ 19 ]. The phenomenon under study was midwives’ lived experiences caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium. The participants were approached face-to-face to participate in the study. The researchers followed the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) to report on this qualitative study [ 20 ].
The setting for the study was the Hhohho and Manzini regions of Eswatini. The researcher collected data at the site where participants experienced the phenomenon, as emphasised by Yildiz, [ 21 ] within the context in which they were comfortable to be interviewed [ 22 ]. This setting included maternal health facilities in hospitals and public health units.
Population and sampling
The study’s population comprised midwives working in maternal health facilities in hospitals and public health units, that is, one referral hospital and one public health unit in the Hhohho region and two referral hospitals and one public health unit in the Manzini region of Eswatini. Purposive sampling was used to select midwives to participate in the study; [ 16 ] 12 midwives from both regions were included. The midwives were between the ages of 35 and 55, and all midwives were black in race and identified as females. The years of experience in the field ranged between 5 and 15 years. The criteria for inclusion were midwives who had provided maternity care to women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium for a period of not more than two to three years, willing to participate in the study. The sample size was determined by repetitions of key statements about the research phenomenon during data collection, termed data saturation [ 23 ]. None of the participants refused to participate in the study.
Table 1 summarises the participants’ demographic characteristics.
Data collection
In-depth phenomenological, face-to-face, individual interviews were conducted to collect data [ 17 ]. The researcher who was a Midwifery lecturer held a Master’s Degree in Maternal and Neonatal science at the time of the study requested approval from the Unit manager to seek permission from the midwives to take part in the study. The midwives were given an information letter which included objectives of the study and the reasons for conducting the study. After recruiting midwives and obtaining their written consent to participate in the study and permission to audio-record the interviews, the researcher set up appointments with them for the interviews, and the data collection process commenced. The central question posed to participants was: How was it for you to care for a woman with a mobility disability during pregnancy, labour and puerperium? A pilot of the tool was performed on the first participant who met the inclusion criteria and possessed the same characteristics as those of the study sample. The pre-testing question yielded positive results, the participant responded to the question asked and there was no need to rephrase it or further test it.
The interviews were conducted from March 2019 to July 2019 and lasted 30–45 min. The researcher conducted interviews until the data became redundant and repetitive, reflecting that saturation had been reached, in congruence with Fouché et al. [ 25 ] In addition, field notes were recorded in a notebook after each in-depth phenomenological interview. No repeat interviews were held. The researcher ensured bracketing by omitting any perceptions from her past experiences that were likely to influence her interpretation of the research findings.
Data analysis
Before data analysis commenced, data were organised in computer files after being transcribed and translated into narrative form. Data from each participant were coded and stored in the relevant file and kept in a safe place; only the researcher could access the information. Back-up copies were made of all the data, and the master copies were stored in a safe to which only the researcher had access.
Data collection and analysis occurred concurrently. The researcher was guided by Giorgi et al.’s [ 26 ] five-step method of data analysis. This entailed the researcher reading all the transcribed data and the entire ‘naïve description’ provided by the participants during the interviews. The demarcation of ‘meaning units’ within narratives followed. In addition, the researcher marked where meaning shifts occurred and transformed meaning units into descriptive expressions. The researcher laid out the general structure of midwives’ experiences. Moreover, an independent coder was provided with the raw data (after signing a confidentiality agreement) to analyse the findings. The researcher and independent coder analysed the data separately and met for a consensus discussion. Both agreed on all the units of analysis, with an inter-coder reliability of 100%.
Measures of trustworthiness
The research was informed by Guba and Lincoln’s [ 27 ] model in relation to credibility, transferability, dependability and confirmability. For credibility, the researcher ensured prolonged engagement in the field [ 28 ], peer debriefing, [ 29 ] member checking, and an external auditor was used [ 25 ]. The study was also presented at a national conference. Transferability refers to the ability to extend the findings of one’s study to comparable environments or participants, as stated by Pitney et al. [ 30 ] The researcher ensured the study’s transferability by providing a richly documented account and in-depth description of all aspects and processes of the study protocol. Data saturation also confirmed transferability [ 23 ]. Dependability is evident in a study when other researchers are able to follow the researcher’s decision trail [ 31 ]. The researcher ensured dependability by densely describing the research process in congruence with Fouché et al.’s [ 25 ] guidelines, so that other researchers can follow similar steps of the same research methodology. Confirmability occurs when the research is judged by the way in which the findings and conclusions achieve their aim and are not the result of the researcher’s prior assumptions and preconceptions [ 32 ]. The researcher ensured this by remaining true to the research process through reflexivity and not compromising the research process in any way [ 28 ]. In addition, the researcher engaged an independent coder and provided a chain of evidence of the entire research process to enable an audit. Therefore, all forms of collected data, including raw data, reflexive journals, [ 29 ] notes and transcriptions, were recorded.
Ethical clearance to conduct this study was obtained from the University of Johannesburg Faculty of Health Sciences Higher Degrees Committee (ref. no. HDC-01-50-2018), University of Johannesburg Faculty of Health Research Ethics Committee (ref. no. REC-01-82-2018), and the Eswatini National Health Research Review Board (ref. no. NHRRB982/2018). The researcher applied and adhered to the four principles to be considered when conducting research: autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence and justice [ 33 ]. Autonomy was adhered to by affording the participants the right to choose to participate in the study and by signing a written informed consent form a week after it was given to them before the interviews commenced. Beneficence was ensured through doing good and doing no harm to participants by prioritising the participants’ interests above those of the researcher, and did not engage in any practice that jeopardised their rights. Non-maleficence was observed by eradicating any possible harmful risks in the study; the researcher ensured the safety of the participants by conducting interviews in a familiar, private environment where they felt free and safe from harm. Furthermore, justice was observed by treating all participants equally regardless of their biographical, social and economic status.
Three themes and categories emerged from the data analysis. Table 2 summarises the themes and categories of midwives’ lived experiences caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in Eswatini.
Theme 1: physical and emotional efforts required from midwives to provide maternity care to women with mobility disabilities
Category 1.1: midwives experienced that woman with mobility disabilities needed assistance getting onto the bed during labour and delivery.
According to the participants, caring for women with mobility disabilities weighed heavily on them physically as they were required to assist the women onto delivery beds, which were too high for the women to climb up on their own:
“The beds are too high, they need to be adjustable…unless you change her to another room, we only have one in the other room…but to be honest she delivered on the same high bed with the help…It’s uncomfortable even with me who is normal, how about someone who has a disability? Getting the woman onto the bed is also uncomfortable for us we end up having pain on our backs.” (M3) . “The challenge is that I couldn’t help her to climb on to the bed, because I needed someone to assist when she came for postnatal care as she was even carrying 3 babies, I didn’t know what to do…I eventually went out and asked for assistance from my colleague…” (M10) . “I believe that the equipment should accommodate the women with disability, however, ours is not accommodative to the women…there are no special delivery beds, specifically designed for them because in my opinion the beds have to be shorter so they can be able to get on to them easily…yes so that they can be able to climb on the beds” (M1) .
Category 1.2: midwives experienced challenges in manoeuvring women with mobility disabilities during labour
Midwives reported it was difficult to perform some procedures while progressing these women during labour and delivery. This situation called for some adjustment and improvisation on their part, and they were unsure if it was the right thing to do.
“Even though she was a bit uncomfortable and anxious because the leg was just straight and could not bend, I reassured her…She had to remove the artificial leg and remain with the stump. I placed her on the lithotomy position. With the other hand she had to hold on to the ankle of the normal foot, even though it was awkward and difficult to manoeuvre, she managed to deliver the baby.” (M1) . “Luckily for us, she didn’t sustain a tear and we were saved from suturing her cause we foresaw difficulties as how we could have done it as she couldn’t open her thighs well due to the disability…yes I had to get a partner to assist, since she couldn’t even open her thighs. She also couldn’t cooperate possibly because of the pain that is also more reason I asked for my colleague to assist.” (M6) . “…yes…let me make an example, in my case she had a fracture, even if the pelvis was gynaecoid, there were problems of finding the right position for her during delivery, when she had to push the baby out…” (M8) . “The one that I saw did not have one leg. She had come for her postnatal care. We assisted and her on the couch, with my colleague. Since she couldn’t keep her legs open, I asked my colleague to keep one of her legs open whilst I examined her.” (M12) .
Category 1.3: midwives experienced anxiety and the need to exercise patience when caring for women with mobility disabilities
The participants experienced an emotional and psychological burden when caring for women with mobility disabilities. They felt unqualified and foresaw difficulties that triggered anxiety, which led to them not knowing what to do and how to handle these women.
“It was during labour…the woman was limping the woman she was on crutches. The moment she came into the ward I am a human being I just felt sorry for her kutsi (as to) how is she going to take care of the baby, and the hand was somehow deformed.” (M3) . “At first its emotionally draining as an individual you cause you start sympathising…(other midwife chips in)…yes you even find yourself saying things just because you pity her, and in the process they get hurt.” (M6) . “It came as a shock and it was my first experience, it came as a shock as to how I was going to help her as even my experience was limited in that area.” (M7) . “As I was taking care of her it became necessary for me to put myself into her shoes and to bear with her considering her situation….When you see her for the first time you would pity her yet she is now used to it.” (M1) .
Theme 2: lack of equipment to meet the needs of women with mobility disabilities
Category 2.1: midwives reported a lack of special beds and infrastructure to meet the needs of women with mobility disabilities.
Midwives reported their frustration at the lack of sufficient equipment like special beds and examination tables, tailored for women with mobility disabilities. It was a challenge to provide maternity care for women without this equipment.
“I believe that the infrastructure and equipment should accommodate the women with mobility disability, however, ours is not accommodative to the women…Usually we don’t have the prenatal ward in the maternity, most women who come in the latent phase have to ambulate, or go to the waiting huts and come back when the labour pains are stronger…There are no special delivery beds, specifically designed for them because in my opinion the beds have to be shorter so they can be able to get on to them easily. We do not even have toilets meant for them.” (M1) . “I was anxious as to how was she going to push how to push cause we do not have the right beds when it was time for pushing I asked for assistance…” (M2) . “The challenge is that I couldn’t help her to climb on to the bed, because I needed someone to assist when she came for postnatal care…the beds need to be adjustable so that they are able to be pushed lower for the mother to move from wheel chair to the bed and we pull the bed up again to examine her.” (M11) .
Theme 3: challenges in providing holistic care to women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour, and puerperium
Category 3.1: midwives reported a lack of guidelines and protocols in caring holistically for women with mobility disabilities.
Midwives emphasised a lack of guidelines, protocols and knowledge about caring holistically for women with mobility disabilities. This resulted in everyone making their own decisions and doing as they saw fit in caring for these women:
“I think during antenatal care they (the women with mobility disabilities) need to be prepared for labour cause for others the pain is extraordinary, apart from the pain threshold, they also face self-esteem issues, they are looked down upon…I only saw that she was disabled during assessment cause nothing was recorded on the antenatal care card.” (M2) . “I was not aware of the disability at first, I only discovered when she was pushing…she was admitted and progressed by another midwife, I only attended to her when she was pushing… there was nothing written on the nurse’s notes/ handover notes about her disability.” (M5) . “There is no normal practice for a woman with mobility disability when they come and they are in labour, I usually admit regardless of the stage of labour or dilatation…It is not a protocol, it’s a midwife’s prerogative.” (M1) . “We assess and come up with our own discretion even in terms of admitting them (women with mobility disability). Some midwives will admit them regardless of the stage of labour and disregard the protocol that women who come into labour have to ambulate if they are in the latent phase.” (M8) . “There is one that came the past 3 days she has 3 children now and we just scheduled her for c/section because we know that she has been having c/section since she started. Just from looking at the way she walked, we could tell that she couldn’t deliver normally.” (M9) .
Category 3.2: midwives experienced challenges in allowing significant others to support women with mobility disabilities during labour and delivery
Consequent to the challenges in providing holistic care to women with mobility disabilities, midwives experienced challenges in allowing significant others to support these women during labour and delivery.
“It can depend on the patients themselves, they should decide and we need to be flexible for it to happen…as you can see our labour room also has the issue of privacy…we would need to restructure cause we have beds for 5 or more women in labour room…and then bringing someone from outside could be tricky” (M6) . “Maybe…not sure though, that they can bring their relatives, but maybe, considering staffing limitation…also the issue of discrimination and privacy, they (the women with disabilities) might feel we discriminate against them because they are disabled we now treat them differently.” (M7) . “Maybe if she can (bring her relative) but that’s not necessary, because I can always ask my colleague to assist, unless there is no one…” (M12) .
Childbirth is a special experience that requires a personal connection between the midwife and the woman giving birth, characterised by successful communication and respect [ 34 ]. However, the themes identified in the study indicated that midwives experienced challenges caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium based on their limited capacity and preparedness, and lack of protocols to care for these women. They also reported a lack of supportive equipment for women with mobility disabilities. This posed a challenge for them in attending to these women’s specific needs, and they did not always know how to handle the situation appropriately.
One of the themes centred on midwives’ experiences of the physical and emotional efforts required of them to provide maternity care to women with mobility disabilities. They explained women with mobility disabilities required assistance getting onto the bed during labour and delivery, and more manoeuvring was expected of them (as midwives) as they had to adjust their performance and some procedures. The midwives also reported challenges in providing holistic care to women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium. Konig-Bachmann et al. [ 35 ] reiterate that caring for women with disabilities requires a level of flexibility, adaptation beyond routine procedures, and demands a high degree of improvisation from healthcare providers to ensure high-quality care. Morrison et al. [ 36 ] also found that healthcare providers reported difficulties with equipment when providing healthcare for women with physical disabilities; particularly the beds being too high for them to access. Smeltzer et al. [ 37 ] similarly allude to the importance of educating and training clinicians to equip them with knowledge and technical skills to provide more effective care to women with physical disabilities.
The midwives also shared that labour and deliveries were further complicated by some women with mobility disabilities not being able to cooperate due to the pain they experienced; others could not change position due to their disability. In a study by Sonalkar et al., [ 38 ] healthcare providers described the gynaecologic examination as challenging to complete as it required patience and the ability to be adaptable to different methods and positioning. Similarly, Konig-Bachmann et al. [ 35 ] indicate that in order to provide high-quality care for women with disabilities, healthcare providers need to exercise strong flexibility, adapt beyond routine procedures, and engage in a high degree of improvisation. Byrnes and Hickey [ 39 ] concur with this study’s findings and state that due to mobility restrictions, it may be difficult to assess the fundal height and foetal growth in women with physical disabilities.
Some midwives reported their caregiving role was emotionally draining as they felt sorry and pitied the women with mobility disabilities; thus, they needed to show compassion and reassure them. According to Mgwili et al., [ 40 ] psychoanalytic thinkers associate pity among staff members upon first contact with a physically disabled person as being instigated by personal feelings, stimulated by the disability. The midwives in this study stated they needed to be more patient and adjust their approach to caring for these women. Tarasoff [ 41 ] and Schildberger et al. [ 42 ] reiterated that healthcare providers seemed uncomfortable with women’s disability, consequently failing to offer needed support. According to Sonalkar et al., [ 38 ] healthcare providers reported there would be less fear and concern about hurting women with disabilities if midwives had increased training. Similarly, Mitra et al. [ 43 ] mentioned that healthcare providers had a general lack of confidence in their ability to provide adequate maternity care for women with physical disabilities.
Another theme was midwives’ challenges in providing competent and quality care for women with mobility disabilities due to a lack of equipment, including special beds and examination tables to meet these women’s needs. The examination, labour and delivery beds were too high and could not be adjusted for the women to get on by themselves, or even with the assistance of a midwife. In addition, the midwives reported there was no prenatal ward or waiting huts where they could place these women during the latent phase of labour. The midwives further emphasised there were no special toilets for women with mobility disabilities, which made it hazardous and difficult for them. Mitra et al. [ 43 ] concur on the barriers to providing maternity care to women with physical disabilities presented from health professionals’ perspectives. The authors indicated that participants from their study reported inaccessible equipment, including examination tables, as a barrier, making it more difficult and time-consuming to care for women with physical disabilities. In addition, Sonalkar et al. [ 38 ] said healthcare providers shared their concern about the lack of adjustable examination tables and transfer equipment, thus presenting a barrier to equitable care for women with disabilities.
Midwives further reported a lack of guidelines and protocols. This resulted in everyone making their own decisions and doing as they saw fit in caring for these women, and, in most instances, not recording the disability at all during antenatal care and admission into labour records. They often only discovered that the woman had a mobility disability at a later stage, when they were in labour. Sonalkar et al. [ 38 ] reported that healthcare providers felt frustrated and overwhelmed by the uncertainty of whether they made the correct decisions when caring for women with physical disabilities due to the lack of guidelines forcing them to use their own judgement. Mitra et al. [ 43 ] determined that most healthcare providers reported a lack of maternity practice guidelines for women with physical disabilities. Also, healthcare providers highlighted the importance of learning about disabilities and having a better understanding of a condition, particularly if it is likely to be exacerbated during pregnancy [ 44 ]. The need to make and read the notes on these women’s antenatal care cards or reports was emphasised.
Due to the lack of clear guidelines and protocols in caring for women with mobility disabilities, the midwives reported they sometimes admitted the woman into the labour ward regardless of the stage of labour, while other midwives did not and wanted them to walk around and come back for admission once they are in the active phase of labour. Furthermore, the midwives explained they often referred these women for caesarean sections right away, regardless of whether the woman could deliver normally due to mere panic from just seeing the disability or based on a previous record of surgery. Smeltzer et al. [ 45 ] researched obstetric clinicians’ experiences and educational preparation in caring for pregnant women with physical disabilities, and they agree on the lack of knowledge among health professionals caring for women with mobility disability.
Devkota et al. [ 46 ] also agree regarding midwives’ inefficiency in providing quality care for women with mobility disabilities. They claim healthcare providers often struggle to understand women with disabilities’ needs as they are not formally trained to provide services to this population. These healthcare providers were found to be undertrained in specific skills that would equip them to provide better and more targeted services for women with disabilities.
Consequent to the challenges in providing holistic care to women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium, midwives experienced challenges in allowing significant others to support these women. They reported that as much as they needed assistance caring for these women, and as much as the women would prefer to have their family members or significant others assisting them, this is not possible due to the lack of privacy, especially in public health facilities. Walsh-Gallager et al.’s [ 13 ] study on the ambiguity of disabled women’s experiences of pregnancy, childbirth and motherhood resonate with this study’s findings. The authors reported that women with disabilities’ partners were denied access or had their visits curtailed on several occasions due to inflexible hospital visiting policies. Redshaw et al. [ 47 ] reiterated the same in their study; disabled women were less likely to say their companion or partner was welcome to visit, let alone provide any form of assistance. In addition, a study by Bassoumah and Mohammad [ 48 ] reported that women with disabilities were denied their spouses’ support while receiving maternity care. Byrnes and Hickey [ 39 ] also concur that every effort should be made to allow women with disabilities who are in labour to receive support from significant others, and they should be active partners in the labour process.
Limitations
The study was limited to two of the four regions of Eswatini, namely Hhohho and Manzini; hence, the results could not be generalised for the whole country. The study also only focused on mobility disabilities due to time constraints and limited funds. Future research could be conducted to cover all other forms of disabilities.
This study focused on midwives’ lived experiences caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in Eswatini. In-depth phenomenological interviews were conducted, the findings were analysed, and themes were established. The findings illustrate that midwives experienced challenges caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in Eswatini. There is a need to develop and implement guidelines to empower midwives with knowledge and skill to provide support and holistic maternity care, and enact protocols. They should also have access to appropriate equipment and infrastructure specifically tailored towards promoting optimal health for women with mobility disabilities.
Data availability
The data analysed is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
González-Timoneda A, Hernández Hernández V, Pardo Moya S, Alfaro Blazquez R. Experiences and attitudes of midwives during the birth of a pregnant woman with COVID-19 infection: a qualitative study. Women Birth. 2021;34(5):467.
Article Google Scholar
Disabled World. Definitions of disability [home page on the internet]. C2009 [updated 2021; cited 2023 July 26]. Available from: https://disabled-world.com/definitions/disability-definitions.php .
Aune I, Tysland T, Vollheim SA. Norwegian midwives’ experiences of relational continuity of midwifery care in the primary health care service: a qualitative descriptive study. Nordic J Nurs Res. 2021;4(1):5–13.
Moridi M, Pazandeh F, Hajian S, Potrata B. Midwives’ perspectives of respectful maternity care during childbirth: a qualitative study. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(3):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0229941 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
United Nations. Background: International Day of Persons with Disabilities. [homepage on the internet]. c2022 [updated 2022 December 1; cited 2023 July 20]. Available from: https://un.org/en/observances/day-of-persons-with-disabilities/background .
Central Statistics Office. Population and housing census: 2017. Volume 3. Mbabane: Swaziland Government Printing Office; 2019a.
Google Scholar
Central Statistics Office. National accounts estimates. Mbabane: Swaziland Government Printing Office; 2018.
Central Statistics Office. Population and housing census: 2017. Volume 6. Mbabane: Swaziland Government Printing Office; 2019b.
Magqadiyane S. Experiences of midwives for caring un-booked pregnant mothers in a maternity unit at a district hospital in the Eastern Cape Province. Advances in reproductive sciences [serial online]. 2020. [cited 2021 August 5];8:186–200. https://doi.org/10.4236/arsci.2020.84016 .
World Health Organisation (WHO). Global report on health equity for persons with disabilities. [homepage on the internet]. c2022 [updated 2022 December 2; cited 2023 July 20]. Available from: https://who.int/health-topics/disability#tab=tab_1 .
Lawler D, Lalor J, Begley C. Access to maternity services for women with physical disability: a systematic review of literature. Int J Childbirth. 2013;3(4):203–17.
University of Johannesburg. Department of nursing paradigm. Johannesburg: University of Johannesburg;2017.
Walsh-Gallagher D, McConkey R, Sinclair M, Clarke R. Normalising birth for women with a disability: the challenges facing practitioners. Midwifery. 2013;29:294–9.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Silverman D, editor. Qualitative research. 5th ed. Los Angeles: SAGE; 2021.
Nassaji H. Good qualitative research. Language Teaching Research [serial online]. 2020. [cited 2021 August 6];24(4):427–431. Available from: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1362168820941288 .
Doyle L, McCabe C, Keogh B, Brady A, McCann M. An overview of the qualitative design within nursing research. Journal of Research in Nursing [serial online]. 2020. [cited 2021 August 6];25(5):444–446. Available from: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1744987119880234 .
Hennink M, Hutter I, Bailey A. Qualitative research methods. 2nd ed. London: SAGE; 2020.
Frechette J, Bitzas V, Aubry M, Kilpatrick K, Lavoie-Tremblay M. Capturing lived experience: methodological considerations for interpretive phenomenological inquiry. Int J Qual Meth. 2022;19:2–11.
Flick U. The SAGE handbook of qualitative research design. London: SAGE; 2022.
Book Google Scholar
Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007;19(6):349–57. https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzm042 .
Yildiz A. A discussion on accurate and effective data collection for qualitative research. J Curr Researches Educational Stud. 2020;10(2):17–24.
Papakitsou V. Qualitative research: narrative approaches in sciences. Dialogues Clin Neurosci Mental Health. 2020;3(1):63–70.
Johnson JL, Adkins D, Chauvin S. Qualitative research in pharmacy education: a review of the quality indicators of rigor in qualitative research. Am J Pharm Educ. 2020;84(1):138–46.
Magagula T. The guidelines of maternity care of women with mobility disabilities in the Hhohho and Manzini regions: Eswatini [unpublished thesis]. University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg; 2021.
Fouché CB, Strydom H, Roestenburg WJH, editors. Research at grassroots for social sciences and human services professions. 5th ed. Pretoria: Van Schaik; 2021.
Giorgi A, Giorgi B, Morley J. The descriptive phenomenological psychological method. In: The SAGE handbook of qualitative research in psychology. 2nd edition. Los Angeles: SAGE; 2017.
Guba EG, Lincoln YS. Fourth generation evaluation. Newbury Park, CA: SAGE; 1989.
Rose J, Johnson W. Contextualising reliability and validity in qualitative research: toward more rigorous and trustworthy qualitative social science in leisure research. J Leisure Res. 2020;1:10–3. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222216.2020.1722042 .
Creswell JW, Creswell JD. Research Design: qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods approaches. 5th Ed. California: SAGE; 2018.
Pitney WA, Parker J, Singe SM, Potteiger K. Qualitative research in health professions. Thorofare: SLACK Incorporated; 2020.
Leavy P, editor. The Oxford handbook of qualitative research. New York: Oxford University Press; 2020.
Kyngäs H, Mikkonen K, Kääriäinen M, editors. The application of content analysis in nursing science research. 2020. [cited 2022 April 27]. Available from: https://dl1tarjomac.ir/nursing-ebooks/TPC202203.pdf .
Dhai A, McQuoid-Mason DJ. Bioethics, human rights and health law: principles and practice. Cape Town: Juta; 2020.
Hallam J, Howard C, Locke A, Thomas M. Communicating choice: an exploration of mothers’ experiences of birth. J Reprod Infant Psyc. 2016;34(2):175–84.
König-Bachmann M, Zenzmaier C, Schildberger B. Health professionals’ views on maternity care for women with physical disabilities: a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(551):1–11.
Morrison J, Basnet M, Buthathoki B, et al. Disabled women’s maternal and newborn health care in rural Nepal: a qualitative study. Midwifery. 2014;30:1132–9.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Smeltzer S, Wint A, Ecker J, Iezzoni L. Labor, delivery, and anaesthesia experiences of women with physical disability. Birth. 2017;44(4):315–24.
Sonalkar S, Chavez V, McClusky J, Hunter TA, Mollen CJ. Gynaecologic care for women with physical disabilities: a qualitative study of patients and providers. Women Health Iss. 2020;30(2):136–41.
Byrnes L, Hickey M. Perinatal care for women with disabilities: clinical considerations. J Nurse Practitioners. 2016;12(8):506–7.
Mgwili VN, Watermayer B. Physically disabled women and discrimination in reproductive health care: Psychoanalytic reflections. In: Disability and Social Change: A South African agenda [serial online]. 2006. [cited 2020 June 01]. Available from: https://www.hsrcpress.ac.za .
Tarasoff LA. Improving perinatal care for women with physical disabilities [Abstract]. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2016;38(5):501.
Schildberger B, Zenzmaier C, König-Bachmann M. Experiences of Austrian mothers with mobility or sensory impairments during pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium: a qualitative study. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2017;17(201):1–11.
Mitra M, Akobirshoev I, Moring N, et al. Access to and satisfaction with prenatal care among pregnant women with physical disabilities: findings from a national survey. J Womens Health. 2017;26(12):1356–63.
Hall J, Hundley V, Collins B, Ireland J. Dignity and respect during pregnancy and childbirth: a survey of experience of disabled women. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2018;18(328):1–13.
Smeltzer S, Mitra M, Long-Bellil L, Iezzoni L, Smith L. Obstetric clinicians’ experiences and educational preparation for caring for pregnant women with physical disabilities: a qualitative study. Disabil Health J. 2018;11(1):8–13.
Devkota HR, Murray EA, Kett M, Groce N. Health care provider’s attitude towards disability and experience of women with disabilities in the use of maternal healthcare service in rural Nepal. Reprod Health. 2017;14(79):1–14.
Redshaw M, Malouf R, Gao H, Gray R. Women with disability: the experience of maternity care during pregnancy, labour and birth and the postnatal period. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2013;13(174):1–14.
Bassoumah B, Mohammed A. The socio-cultural challenges to maternal and neonatal care: the views of women with disabilities receiving maternity care in the Chereponi district of Northern Ghana. Sci Afr. 2020;7:1–10.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the midwives in the Hhohho and Manzini regions of Eswatini who participated in the study and provided their own experiences of providing maternity care to women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium.
The research received funding from the University of Johannesburg Postgraduate Supervisor-linked Bursary.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Health Sciences, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Annie M. Temane & Anna G. W. Nolte
Mother and Child Nursing, University of Eswatini, Kwaluseni, Eswatini
Fortunate N. Magagula
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
F.N.M conducted the research and wrote the manuscript. A.M.T supervised, reviewed, and finalised the manuscript. A.G.W.N co-supervised the study and edited the manuscript for final submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Annie M. Temane .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate.
Ethical clearance to conduct this study was obtained from the University of Johannesburg Faculty of Health Sciences Higher Degrees Committee (ref. no. HDC-01-50-2018), University of Johannesburg Faculty of Health Research Ethics Committee (ref. no. REC-01-82-2018) and the Eswatini National Health Research Review Board (ref. no. NHRRB982/2018). Participation in this study was voluntary, and informed consent was obtained from participants before the interviews commenced.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Temane, A.M., Magagula, F.N. & Nolte, A.G.W. Midwives’ lived experiences of caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in Eswatini: a qualitative study. BMC Women's Health 24 , 207 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-024-03032-z
Download citation
Received : 18 August 2023
Accepted : 18 March 2024
Published : 01 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-024-03032-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Experiences
- Maternity care
- Women with mobility disabilities
- Labour and the puerperium
BMC Women's Health
ISSN: 1472-6874
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
We will keep fighting for all libraries - stand with us!
Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
QUALITATIVE RESEARCH METHODS
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
Download options, in collections.
Uploaded by FREE-EDUCATIONAL-BOOKS on March 27, 2024
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Qualitative research methodologies seek to capture information that often can't be expressed numerically. These methodologies often include some level of interpretation from researchers as they collect information via observation, coded survey or interview responses, and so on. Researchers may use multiple qualitative methods in one study, as ...
Qualitative Research. Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people's beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus ...
Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences, perceptions, and behavior. It answers the hows and whys instead of how many or how much. It could be structured as a stand-alone study, purely relying on qualitative data or it could be part of mixed-methods research that combines qualitative and quantitative data.
Qualitative research methods. Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods.These are some of the most common qualitative methods: Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes. Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations. Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among ...
INTRODUCTION. Qualitative research methods refer to techniques of investigation that rely on nonstatistical and nonnumerical methods of data collection, analysis, and evidence production. Qualitative research techniques provide a lens for learning about nonquantifiable phenomena such as people's experiences, languages, histories, and cultures.
Abstract. This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions ...
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
Definition. Qualitative research is the naturalistic study of social meanings and processes, using interviews, observations, and the analysis of texts and images. In contrast to quantitative researchers, whose statistical methods enable broad generalizations about populations (for example, comparisons of the percentages of U.S. demographic ...
The final section offers a commentary about politics and research and the move toward public scholarship. The Oxford Handbook of Qualitative Research is intended for students of all levels, faculty, and researchers across the social sciences. Keywords: qualitative research, museum studies, disaster studies, data analysis, assessment, ethical ...
Methods? qualitative research. introduction to the subject, with helpful, practical pointers on how to conduct research and how to access . methods. What is Research? research. 1. 2. and . social.
It introduces qualitative methods in an interesting and hands-on way to provide you with an understanding of key concepts and methods in qualitative research as applied to the fi eld of health. All three authors are trained anthropologists who have been working in health and development for many years.
This guide to using qualitative research methodology is designed to help you think about all the steps you need to take to ensure that you produce a good quality piece of work. The guide starts by telling you what qualitative methodology is and when to use it in the field (understand people's belief system, perspectives, experiences). It
Qualitative research is a type of research that aims to gather and analyse non-numerical (descriptive) data in order to gain an understanding of individuals' social reality, including understanding their attitudes, beliefs, and motivation. This type of research typically involves in-depth interviews, focus groups, or observations in order to collect data that is rich in detail and context.
About Research Methods. This guide provides an overview of research methods, how to choose and use them, and supports and resources at UC Berkeley. As Patten and Newhart note in the book Understanding Research Methods, "Research methods are the building blocks of the scientific enterprise. They are the "how" for building systematic knowledge.
When collecting and analyzing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge. Quantitative research. Quantitative research is expressed in numbers and graphs. It is used to test or confirm theories and assumptions.
Mixed methods combine the above two research methods, integrating both qualitative and quantitative approaches into one coherent analytical process. Step 4: Evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made. Above all, your methodology section should clearly make the case for why you chose the methods you did.
However, qualitative research methodologies can often present a formidable challenge to new researchers, particularly those at the master's level. The complexity and depth required in approaches like phenomenology, grounded theory, or ethnography can be overwhelming for beginners who are yet to navigate the intricate nuances of qualitative ...
The main difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the type of data they collect and analyze. Quantitative research collects numerical data and analyzes it using statistical methods. The aim is to produce objective, empirical data that can be measured and expressed in numerical terms.
A fourth issue is that the "implicit use of methods in qualitative research makes the field far less standardized than the quantitative paradigm" (Goertz and Mahoney 2012:9). Relatedly, the National Science Foundation in the US organized two workshops in 2004 and 2005 to address the scientific foundations of qualitative research involving ...
A different type of lighting research - A qualitative methodology. Show details Hide details. K Kelly. Lighting Research & Technology. Jul 2016. Restricted access. Understanding and Reporting Qualitative Research: An Analytical Review and Recommendations for Submitting Authors.
Employing IPA as a Qualitative Methodology in Educational Research Christine Robinson The University of Notre Dame Australia, [email protected] Heath Williams ... Social research methods: Qualitative and quantitative approaches (7. th. ed.). Pearson. Noon, E. (2018). Interpretive phenomenological analysis: An appropriate methodology for
Procedure. The procedure for this research is multi-stepped and is summarized in Fig. 1.First, we mapped retrospective qualitative data collected during the development of the SCI-HMT [] against the five domains of the CFIR in order to create a semi-structured interview guide (Step 1).Then, we used this interview guide to collect prospective data from health professionals and people with SCI ...
Top 9 methodologies. 1. Interviews. Define research objectives. Identify the target population. Obtain informed consent of participants. Make an interview guideline. Select a suitable location ...
Having started as a small movement in the 1980's, the study of mixed methods research burst onto the scene around the beginning of the second millennium. After decades of intense dispute between supporters of the qualitative perspective and their quantitative counterparts—with both sides having grown deeply entrenched in their respective views—a complementary approach promising the ...
In this Rip Out, we describe 3 different qualitative research approaches commonly used in medical education: grounded theory, ethnography, and phenomenology. Each acts as a pivotal frame that shapes the research question (s), the method (s) of data collection, and how data are analyzed. 4, 5. Go to:
This course concentrates on the use of qualitative methods for educational research. Strategies for conducting qualitative studies are described and techniques for analyzing and reporting findings are emphasized. Students will also examine strategies for the ethical conduct of qualitative research. Prerequisites, Notes & Instructor
Qualitative research methodology is not a single method, but instead offers a variety of different choices to researchers, according to specific parameters of topic, research question, participants, and settings. The method is the way you carry out your research within the paradigm of quantitative or qualitative research.
Midwives encounter various difficulties while aiming to achieve excellence in providing maternity care to women with mobility disabilities. The study aimed to explore and describe midwives' experiences of caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in Eswatini. A qualitative, exploratory, descriptive, contextual research design with a phenomenological ...
QUALITATIVE RESEARCH METHODS. Collection. success-series; additional_collections. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH METHODS PDF MCQ (multiple choice questions) book. Addeddate. 2024-03-27 18:04:26. Collection_added. additional_collections. Identifier.