- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Critical Reviews

How to Write an Article Review (With Examples)
Last Updated: April 24, 2024 Fact Checked
Preparing to Write Your Review
Writing the article review, sample article reviews, expert q&a.
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,096,303 times.
An article review is both a summary and an evaluation of another writer's article. Teachers often assign article reviews to introduce students to the work of experts in the field. Experts also are often asked to review the work of other professionals. Understanding the main points and arguments of the article is essential for an accurate summation. Logical evaluation of the article's main theme, supporting arguments, and implications for further research is an important element of a review . Here are a few guidelines for writing an article review.
Education specialist Alexander Peterman recommends: "In the case of a review, your objective should be to reflect on the effectiveness of what has already been written, rather than writing to inform your audience about a subject."
Article Review 101
- Read the article very closely, and then take time to reflect on your evaluation. Consider whether the article effectively achieves what it set out to.
- Write out a full article review by completing your intro, summary, evaluation, and conclusion. Don't forget to add a title, too!
- Proofread your review for mistakes (like grammar and usage), while also cutting down on needless information.

- Article reviews present more than just an opinion. You will engage with the text to create a response to the scholarly writer's ideas. You will respond to and use ideas, theories, and research from your studies. Your critique of the article will be based on proof and your own thoughtful reasoning.
- An article review only responds to the author's research. It typically does not provide any new research. However, if you are correcting misleading or otherwise incorrect points, some new data may be presented.
- An article review both summarizes and evaluates the article.

- Summarize the article. Focus on the important points, claims, and information.
- Discuss the positive aspects of the article. Think about what the author does well, good points she makes, and insightful observations.
- Identify contradictions, gaps, and inconsistencies in the text. Determine if there is enough data or research included to support the author's claims. Find any unanswered questions left in the article.

- Make note of words or issues you don't understand and questions you have.
- Look up terms or concepts you are unfamiliar with, so you can fully understand the article. Read about concepts in-depth to make sure you understand their full context.

- Pay careful attention to the meaning of the article. Make sure you fully understand the article. The only way to write a good article review is to understand the article.

- With either method, make an outline of the main points made in the article and the supporting research or arguments. It is strictly a restatement of the main points of the article and does not include your opinions.
- After putting the article in your own words, decide which parts of the article you want to discuss in your review. You can focus on the theoretical approach, the content, the presentation or interpretation of evidence, or the style. You will always discuss the main issues of the article, but you can sometimes also focus on certain aspects. This comes in handy if you want to focus the review towards the content of a course.
- Review the summary outline to eliminate unnecessary items. Erase or cross out the less important arguments or supplemental information. Your revised summary can serve as the basis for the summary you provide at the beginning of your review.

- What does the article set out to do?
- What is the theoretical framework or assumptions?
- Are the central concepts clearly defined?
- How adequate is the evidence?
- How does the article fit into the literature and field?
- Does it advance the knowledge of the subject?
- How clear is the author's writing? Don't: include superficial opinions or your personal reaction. Do: pay attention to your biases, so you can overcome them.

- For example, in MLA , a citation may look like: Duvall, John N. "The (Super)Marketplace of Images: Television as Unmediated Mediation in DeLillo's White Noise ." Arizona Quarterly 50.3 (1994): 127-53. Print. [9] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest.

- Your introduction should only be 10-25% of your review.
- End the introduction with your thesis. Your thesis should address the above issues. For example: Although the author has some good points, his article is biased and contains some misinterpretation of data from others’ analysis of the effectiveness of the condom.

- Use direct quotes from the author sparingly.
- Review the summary you have written. Read over your summary many times to ensure that your words are an accurate description of the author's article.

- Support your critique with evidence from the article or other texts.
- The summary portion is very important for your critique. You must make the author's argument clear in the summary section for your evaluation to make sense.
- Remember, this is not where you say if you liked the article or not. You are assessing the significance and relevance of the article.
- Use a topic sentence and supportive arguments for each opinion. For example, you might address a particular strength in the first sentence of the opinion section, followed by several sentences elaborating on the significance of the point.

- This should only be about 10% of your overall essay.
- For example: This critical review has evaluated the article "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS" by Anthony Zimmerman. The arguments in the article show the presence of bias, prejudice, argumentative writing without supporting details, and misinformation. These points weaken the author’s arguments and reduce his credibility.

- Make sure you have identified and discussed the 3-4 key issues in the article.

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libguides.cmich.edu/writinghelp/articlereview
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548566/
- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 24 July 2020.
- ↑ https://guides.library.queensu.ca/introduction-research/writing/critical
- ↑ https://www.iup.edu/writingcenter/writing-resources/organization-and-structure/creating-an-outline.html
- ↑ https://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/titles.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548565/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uconn.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/593/2014/06/How_to_Summarize_a_Research_Article1.pdf
- ↑ https://www.uis.edu/learning-hub/writing-resources/handouts/learning-hub/how-to-review-a-journal-article
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

If you have to write an article review, read through the original article closely, taking notes and highlighting important sections as you read. Next, rewrite the article in your own words, either in a long paragraph or as an outline. Open your article review by citing the article, then write an introduction which states the article’s thesis. Next, summarize the article, followed by your opinion about whether the article was clear, thorough, and useful. Finish with a paragraph that summarizes the main points of the article and your opinions. To learn more about what to include in your personal critique of the article, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Prince Asiedu-Gyan
Apr 22, 2022
Did this article help you?
Sammy James
Sep 12, 2017
Juabin Matey
Aug 30, 2017
Vanita Meghrajani
Jul 21, 2016
Nov 27, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
The Tech Edvocate
- Advertisement
- Home Page Five (No Sidebar)
- Home Page Four
- Home Page Three
- Home Page Two
- Icons [No Sidebar]
- Left Sidbear Page
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- My Speaking Page
- Newsletter Sign Up Confirmation
- Newsletter Unsubscription
- Page Example
- Privacy Policy
- Protected Content
- Request a Product Review
- Shortcodes Examples
- Terms and Conditions
- The Edvocate
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- Write For Us
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Assistive Technology
- Child Development Tech
- Early Childhood & K-12 EdTech
- EdTech Futures
- EdTech News
- EdTech Policy & Reform
- EdTech Startups & Businesses
- Higher Education EdTech
- Online Learning & eLearning
- Parent & Family Tech
- Personalized Learning
- Product Reviews
- Tech Edvocate Awards
- School Ratings
Brain Hemispheres and Learning: Everything You Need to Know
Samsung galaxy tips and tricks you need to know, top ten marketing tips for business owners with limited capital, how to successfully get a higher education while working a full-time job, ways to help and improve stuttering issues, elevating user experience with address autocomplete api, how to teach students to make story maps: everything you need to know, addressing your child’s reading issues: everything you need to know, product review of the tribit xsound plus 2, teaching reading to struggling students: everything you need to know, how to write an article review (with sample reviews) .

An article review is a critical evaluation of a scholarly or scientific piece, which aims to summarize its main ideas, assess its contributions, and provide constructive feedback. A well-written review not only benefits the author of the article under scrutiny but also serves as a valuable resource for fellow researchers and scholars. Follow these steps to create an effective and informative article review:
1. Understand the purpose: Before diving into the article, it is important to understand the intent of writing a review. This helps in focusing your thoughts, directing your analysis, and ensuring your review adds value to the academic community.
2. Read the article thoroughly: Carefully read the article multiple times to get a complete understanding of its content, arguments, and conclusions. As you read, take notes on key points, supporting evidence, and any areas that require further exploration or clarification.
3. Summarize the main ideas: In your review’s introduction, briefly outline the primary themes and arguments presented by the author(s). Keep it concise but sufficiently informative so that readers can quickly grasp the essence of the article.
4. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses: In subsequent paragraphs, assess the strengths and limitations of the article based on factors such as methodology, quality of evidence presented, coherence of arguments, and alignment with existing literature in the field. Be fair and objective while providing your critique.
5. Discuss any implications: Deliberate on how this particular piece contributes to or challenges existing knowledge in its discipline. You may also discuss potential improvements for future research or explore real-world applications stemming from this study.
6. Provide recommendations: Finally, offer suggestions for both the author(s) and readers regarding how they can further build on this work or apply its findings in practice.
7. Proofread and revise: Once your initial draft is complete, go through it carefully for clarity, accuracy, and coherence. Revise as necessary, ensuring your review is both informative and engaging for readers.
Sample Review:
A Critical Review of “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health”
Introduction:
“The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is a timely article which investigates the relationship between social media usage and psychological well-being. The authors present compelling evidence to support their argument that excessive use of social media can result in decreased self-esteem, increased anxiety, and a negative impact on interpersonal relationships.
Strengths and weaknesses:
One of the strengths of this article lies in its well-structured methodology utilizing a variety of sources, including quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews. This approach provides a comprehensive view of the topic, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of the effects of social media on mental health. However, it would have been beneficial if the authors included a larger sample size to increase the reliability of their conclusions. Additionally, exploring how different platforms may influence mental health differently could have added depth to the analysis.
Implications:
The findings in this article contribute significantly to ongoing debates surrounding the psychological implications of social media use. It highlights the potential dangers that excessive engagement with online platforms may pose to one’s mental well-being and encourages further research into interventions that could mitigate these risks. The study also offers an opportunity for educators and policy-makers to take note and develop strategies to foster healthier online behavior.
Recommendations:
Future researchers should consider investigating how specific social media platforms impact mental health outcomes, as this could lead to more targeted interventions. For practitioners, implementing educational programs aimed at promoting healthy online habits may be beneficial in mitigating the potential negative consequences associated with excessive social media use.
Conclusion:
Overall, “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is an important and informative piece that raises awareness about a pressing issue in today’s digital age. Given its minor limitations, it provides valuable
3 Ways to Make a Mini Greenhouse ...
3 ways to teach yourself to play ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.
3 Ways to Cure Goiters

How to Identify Parts of Speech

3 Ways to Win at Solitaire

4 Ways to Remove Content Lock
3 Ways to Block a Website in Google Chrome

How to Grow Carrots in Pots
How to Write an Article Review: Tips and Examples

Did you know that article reviews are not just academic exercises but also a valuable skill in today's information age? In a world inundated with content, being able to dissect and evaluate articles critically can help you separate the wheat from the chaff. Whether you're a student aiming to excel in your coursework or a professional looking to stay well-informed, mastering the art of writing article reviews is an invaluable skill.
Short Description
In this article, our research paper writing service experts will start by unraveling the concept of article reviews and discussing the various types. You'll also gain insights into the art of formatting your review effectively. To ensure you're well-prepared, we'll take you through the pre-writing process, offering tips on setting the stage for your review. But it doesn't stop there. You'll find a practical example of an article review to help you grasp the concepts in action. To complete your journey, we'll guide you through the post-writing process, equipping you with essential proofreading techniques to ensure your work shines with clarity and precision!
What Is an Article Review: Grasping the Concept
A review article is a type of professional paper writing that demands a high level of in-depth analysis and a well-structured presentation of arguments. It is a critical, constructive evaluation of literature in a particular field through summary, classification, analysis, and comparison.
If you write a scientific review, you have to use database searches to portray the research. Your primary goal is to summarize everything and present a clear understanding of the topic you've been working on.
Writing Involves:
- Summarization, classification, analysis, critiques, and comparison.
- The analysis, evaluation, and comparison require the use of theories, ideas, and research relevant to the subject area of the article.
- It is also worth nothing if a review does not introduce new information, but instead presents a response to another writer's work.
- Check out other samples to gain a better understanding of how to review the article.
Types of Review
When it comes to article reviews, there's more than one way to approach the task. Understanding the various types of reviews is like having a versatile toolkit at your disposal. In this section, we'll walk you through the different dimensions of review types, each offering a unique perspective and purpose. Whether you're dissecting a scholarly article, critiquing a piece of literature, or evaluating a product, you'll discover the diverse landscape of article reviews and how to navigate it effectively.
.webp)
Journal Article Review
Just like other types of reviews, a journal article review assesses the merits and shortcomings of a published work. To illustrate, consider a review of an academic paper on climate change, where the writer meticulously analyzes and interprets the article's significance within the context of environmental science.
Research Article Review
Distinguished by its focus on research methodologies, a research article review scrutinizes the techniques used in a study and evaluates them in light of the subsequent analysis and critique. For instance, when reviewing a research article on the effects of a new drug, the reviewer would delve into the methods employed to gather data and assess their reliability.
Science Article Review
In the realm of scientific literature, a science article review encompasses a wide array of subjects. Scientific publications often provide extensive background information, which can be instrumental in conducting a comprehensive analysis. For example, when reviewing an article about the latest breakthroughs in genetics, the reviewer may draw upon the background knowledge provided to facilitate a more in-depth evaluation of the publication.
Need a Hand From Professionals?
Address to Our Writers and Get Assistance in Any Questions!
Formatting an Article Review
The format of the article should always adhere to the citation style required by your professor. If you're not sure, seek clarification on the preferred format and ask him to clarify several other pointers to complete the formatting of an article review adequately.
How Many Publications Should You Review?
- In what format should you cite your articles (MLA, APA, ASA, Chicago, etc.)?
- What length should your review be?
- Should you include a summary, critique, or personal opinion in your assignment?
- Do you need to call attention to a theme or central idea within the articles?
- Does your instructor require background information?
When you know the answers to these questions, you may start writing your assignment. Below are examples of MLA and APA formats, as those are the two most common citation styles.
Using the APA Format
Articles appear most commonly in academic journals, newspapers, and websites. If you write an article review in the APA format, you will need to write bibliographical entries for the sources you use:
- Web : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Title. Retrieved from {link}
- Journal : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Publication Year). Publication Title. Periodical Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp.
- Newspaper : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Publication Title. Magazine Title, pp. xx-xx.
Using MLA Format
- Web : Last, First Middle Initial. “Publication Title.” Website Title. Website Publisher, Date Month Year Published. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
- Newspaper : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Newspaper Title [City] Date, Month, Year Published: Page(s). Print.
- Journal : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year Published): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
Enhance your writing effortlessly with EssayPro.com , where you can order an article review or any other writing task. Our team of expert writers specializes in various fields, ensuring your work is not just summarized, but deeply analyzed and professionally presented. Ideal for students and professionals alike, EssayPro offers top-notch writing assistance tailored to your needs. Elevate your writing today with our skilled team at your article review writing service !
.jpg)
The Pre-Writing Process
Facing this task for the first time can really get confusing and can leave you unsure of where to begin. To create a top-notch article review, start with a few preparatory steps. Here are the two main stages from our dissertation services to get you started:
Step 1: Define the right organization for your review. Knowing the future setup of your paper will help you define how you should read the article. Here are the steps to follow:
- Summarize the article — seek out the main points, ideas, claims, and general information presented in the article.
- Define the positive points — identify the strong aspects, ideas, and insightful observations the author has made.
- Find the gaps —- determine whether or not the author has any contradictions, gaps, or inconsistencies in the article and evaluate whether or not he or she used a sufficient amount of arguments and information to support his or her ideas.
- Identify unanswered questions — finally, identify if there are any questions left unanswered after reading the piece.
Step 2: Move on and review the article. Here is a small and simple guide to help you do it right:
- Start off by looking at and assessing the title of the piece, its abstract, introductory part, headings and subheadings, opening sentences in its paragraphs, and its conclusion.
- First, read only the beginning and the ending of the piece (introduction and conclusion). These are the parts where authors include all of their key arguments and points. Therefore, if you start with reading these parts, it will give you a good sense of the author's main points.
- Finally, read the article fully.
These three steps make up most of the prewriting process. After you are done with them, you can move on to writing your own review—and we are going to guide you through the writing process as well.
Outline and Template
As you progress with reading your article, organize your thoughts into coherent sections in an outline. As you read, jot down important facts, contributions, or contradictions. Identify the shortcomings and strengths of your publication. Begin to map your outline accordingly.
If your professor does not want a summary section or a personal critique section, then you must alleviate those parts from your writing. Much like other assignments, an article review must contain an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Thus, you might consider dividing your outline according to these sections as well as subheadings within the body. If you find yourself troubled with the pre-writing and the brainstorming process for this assignment, seek out a sample outline.
Your custom essay must contain these constituent parts:
- Pre-Title Page - Before diving into your review, start with essential details: article type, publication title, and author names with affiliations (position, department, institution, location, and email). Include corresponding author info if needed.
- Running Head - In APA format, use a concise title (under 40 characters) to ensure consistent formatting.
- Summary Page - Optional but useful. Summarize the article in 800 words, covering background, purpose, results, and methodology, avoiding verbatim text or references.
- Title Page - Include the full title, a 250-word abstract, and 4-6 keywords for discoverability.
- Introduction - Set the stage with an engaging overview of the article.
- Body - Organize your analysis with headings and subheadings.
- Works Cited/References - Properly cite all sources used in your review.
- Optional Suggested Reading Page - If permitted, suggest further readings for in-depth exploration.
- Tables and Figure Legends (if instructed by the professor) - Include visuals when requested by your professor for clarity.
Example of an Article Review
You might wonder why we've dedicated a section of this article to discuss an article review sample. Not everyone may realize it, but examining multiple well-constructed examples of review articles is a crucial step in the writing process. In the following section, our essay writing service experts will explain why.
Looking through relevant article review examples can be beneficial for you in the following ways:
- To get you introduced to the key works of experts in your field.
- To help you identify the key people engaged in a particular field of science.
- To help you define what significant discoveries and advances were made in your field.
- To help you unveil the major gaps within the existing knowledge of your field—which contributes to finding fresh solutions.
- To help you find solid references and arguments for your own review.
- To help you generate some ideas about any further field of research.
- To help you gain a better understanding of the area and become an expert in this specific field.
- To get a clear idea of how to write a good review.
View Our Writer’s Sample Before Crafting Your Own!
Why Have There Been No Great Female Artists?
Steps for Writing an Article Review
Here is a guide with critique paper format on how to write a review paper:
.webp)
Step 1: Write the Title
First of all, you need to write a title that reflects the main focus of your work. Respectively, the title can be either interrogative, descriptive, or declarative.
Step 2: Cite the Article
Next, create a proper citation for the reviewed article and input it following the title. At this step, the most important thing to keep in mind is the style of citation specified by your instructor in the requirements for the paper. For example, an article citation in the MLA style should look as follows:
Author's last and first name. "The title of the article." Journal's title and issue(publication date): page(s). Print
Abraham John. "The World of Dreams." Virginia Quarterly 60.2(1991): 125-67. Print.
Step 3: Article Identification
After your citation, you need to include the identification of your reviewed article:
- Title of the article
- Title of the journal
- Year of publication
All of this information should be included in the first paragraph of your paper.
The report "Poverty increases school drop-outs" was written by Brian Faith – a Health officer – in 2000.
Step 4: Introduction
Your organization in an assignment like this is of the utmost importance. Before embarking on your writing process, you should outline your assignment or use an article review template to organize your thoughts coherently.
- If you are wondering how to start an article review, begin with an introduction that mentions the article and your thesis for the review.
- Follow up with a summary of the main points of the article.
- Highlight the positive aspects and facts presented in the publication.
- Critique the publication by identifying gaps, contradictions, disparities in the text, and unanswered questions.
Step 5: Summarize the Article
Make a summary of the article by revisiting what the author has written about. Note any relevant facts and findings from the article. Include the author's conclusions in this section.
Step 6: Critique It
Present the strengths and weaknesses you have found in the publication. Highlight the knowledge that the author has contributed to the field. Also, write about any gaps and/or contradictions you have found in the article. Take a standpoint of either supporting or not supporting the author's assertions, but back up your arguments with facts and relevant theories that are pertinent to that area of knowledge. Rubrics and templates can also be used to evaluate and grade the person who wrote the article.
Step 7: Craft a Conclusion
In this section, revisit the critical points of your piece, your findings in the article, and your critique. Also, write about the accuracy, validity, and relevance of the results of the article review. Present a way forward for future research in the field of study. Before submitting your article, keep these pointers in mind:
- As you read the article, highlight the key points. This will help you pinpoint the article's main argument and the evidence that they used to support that argument.
- While you write your review, use evidence from your sources to make a point. This is best done using direct quotations.
- Select quotes and supporting evidence adequately and use direct quotations sparingly. Take time to analyze the article adequately.
- Every time you reference a publication or use a direct quotation, use a parenthetical citation to avoid accidentally plagiarizing your article.
- Re-read your piece a day after you finish writing it. This will help you to spot grammar mistakes and to notice any flaws in your organization.
- Use a spell-checker and get a second opinion on your paper.
The Post-Writing Process: Proofread Your Work
Finally, when all of the parts of your article review are set and ready, you have one last thing to take care of — proofreading. Although students often neglect this step, proofreading is a vital part of the writing process and will help you polish your paper to ensure that there are no mistakes or inconsistencies.
To proofread your paper properly, start by reading it fully and checking the following points:
- Punctuation
- Other mistakes
Afterward, take a moment to check for any unnecessary information in your paper and, if found, consider removing it to streamline your content. Finally, double-check that you've covered at least 3-4 key points in your discussion.
And remember, if you ever need help with proofreading, rewriting your essay, or even want to buy essay , our friendly team is always here to assist you.
Need an Article REVIEW WRITTEN?
Just send us the requirements to your paper and watch one of our writers crafting an original paper for you.
What Is A Review Article?
How to write an article review, how to write an article review in apa format, related articles.
.webp)
How to Write an Article Review: Template & Examples
An article review is an academic assignment that invites you to study a piece of academic research closely. Then, you should present its summary and critically evaluate it using the knowledge you’ve gained in class and during your independent study. If you get such a task at college or university, you shouldn’t confuse it with a response paper, which is a distinct assignment with other purposes (we’ll talk about it in detail below).
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
In this article, prepared by Custom-Writing experts, you’ll find:
- the intricacies of article review writing;
- the difference between an article review and similar assignments;
- a step-by-step algorithm for review composition;
- a couple of samples to guide you throughout the writing process.
So, if you wish to study our article review example and discover helpful writing tips, keep reading.
❓ What Is an Article Review?
- ✍️ Writing Steps
📑 Article Review Format
🔗 references.
An article review is an academic paper that summarizes and critically evaluates the information presented in your selected article.

The first thing you should note when approaching the task of an article review is that not every article is suitable for this assignment. Let’s have a look at the variety of articles to understand what you can choose from.
Popular Vs. Scholarly Articles
In most cases, you’ll be required to review a scholarly, peer-reviewed article – one composed in compliance with rigorous academic standards. Yet, the Web is also full of popular articles that don’t present original scientific value and shouldn’t be selected for a review.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Not sure how to distinguish these two types? Here is a comparative table to help you out.
Article Review vs. Response Paper
Now, let’s consider the difference between an article review and a response paper:
- If you’re assigned to critique a scholarly article , you will need to compose an article review .
- If your subject of analysis is a popular article , you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper .
The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of these two article types. Peer-reviewed, scholarly articles have clear-cut quality criteria, allowing you to conduct and present a structured assessment of the assigned material. Popular magazines have loose or non-existent quality criteria and don’t offer an opportunity for structured evaluation. So, they are only fit for a subjective response, in which you can summarize your reactions and emotions related to the reading material.
All in all, you can structure your response assignments as outlined in the tips below.
✍️ How to Write an Article Review: Step by Step
Here is a tried and tested algorithm for article review writing from our experts. We’ll consider only the critical review variety of this academic assignment. So, let’s get down to the stages you need to cover to get a stellar review.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 15% off your first order!
Read the Article
As with any reviews, reports, and critiques, you must first familiarize yourself with the assigned material. It’s impossible to review something you haven’t read, so set some time for close, careful reading of the article to identify:
- Its topic.
- Its type.
- The author’s main points and message.
- The arguments they use to prove their points.
- The methodology they use to approach the subject.
In terms of research type , your article will usually belong to one of three types explained below.
Summarize the Article
Now that you’ve read the text and have a general impression of the content, it’s time to summarize it for your readers. Look into the article’s text closely to determine:
- The thesis statement , or general message of the author.
- Research question, purpose, and context of research.
- Supporting points for the author’s assumptions and claims.
- Major findings and supporting evidence.
As you study the article thoroughly, make notes on the margins or write these elements out on a sheet of paper. You can also apply a different technique: read the text section by section and formulate its gist in one phrase or sentence. Once you’re done, you’ll have a summary skeleton in front of you.
Evaluate the Article
The next step of review is content evaluation. Keep in mind that various research types will require a different set of review questions. Here is a complete list of evaluation points you can include.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
Write the Text
After completing the critical review stage, it’s time to compose your article review.
The format of this assignment is standard – you will have an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. The introduction should present your article and summarize its content. The body will contain a structured review according to all four dimensions covered in the previous section. The concluding part will typically recap all the main points you’ve identified during your assessment.
It is essential to note that an article review is, first of all, an academic assignment. Therefore, it should follow all rules and conventions of academic composition, such as:
- No contractions . Don’t use short forms, such as “don’t,” “can’t,” “I’ll,” etc. in academic writing. You need to spell out all those words.
- Formal language and style . Avoid conversational phrasing and words that you would naturally use in blog posts or informal communication. For example, don’t use words like “pretty,” “kind of,” and “like.”
- Third-person narrative . Academic reviews should be written from the third-person point of view, avoiding statements like “I think,” “in my opinion,” and so on.
- No conversational forms . You shouldn’t turn to your readers directly in the text by addressing them with the pronoun “you.” It’s vital to keep the narrative neutral and impersonal.
- Proper abbreviation use . Consult the list of correct abbreviations , like “e.g.” or “i.e.,” for use in your academic writing. If you use informal abbreviations like “FYA” or “f.i.,” your professor will reduce the grade.
- Complete sentences . Make sure your sentences contain the subject and the predicate; avoid shortened or sketch-form phrases suitable for a draft only.
- No conjunctions at the beginning of a sentence . Remember the FANBOYS rule – don’t start a sentence with words like “and” or “but.” They often seem the right way to build a coherent narrative, but academic writing rules disfavor such usage.
- No abbreviations or figures at the beginning of a sentence . Never start a sentence with a number — spell it out if you need to use it anyway. Besides, sentences should never begin with abbreviations like “e.g.”
Finally, a vital rule for an article review is properly formatting the citations. We’ll discuss the correct use of citation styles in the following section.
When composing an article review, keep these points in mind:
- Start with a full reference to the reviewed article so the reader can locate it quickly.
- Ensure correct formatting of in-text references.
- Provide a complete list of used external sources on the last page of the review – your bibliographical entries .
You’ll need to understand the rules of your chosen citation style to meet all these requirements. Below, we’ll discuss the two most common referencing styles – APA and MLA.
Article Review in APA
When you need to compose an article review in the APA format , here is the general bibliographical entry format you should use for journal articles on your reference page:
- Author’s last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year of Publication). Name of the article. Name of the Journal, volume (number), pp. #-#. https://doi.org/xx.xxx/yyyy
Horigian, V. E., Schmidt, R. D., & Feaster, D. J. (2021). Loneliness, mental health, and substance use among US young adults during COVID-19. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 53 (1), pp. 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2020.1836435
Your in-text citations should follow the author-date format like this:
- If you paraphrase the source and mention the author in the text: According to Horigian et al. (2021), young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic.
- If you paraphrase the source and don’t mention the author in the text: Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al., 2021).
- If you quote the source: As Horigian et al. (2021) point out, there were “elevated levels of loneliness, depression, anxiety, alcohol use, and drug use among young adults during COVID-19” (p. 6).
Note that your in-text citations should include “et al.,” as in the examples above, if your article has 3 or more authors. If you have one or two authors, your in-text citations would look like this:
- One author: “According to Smith (2020), depression is…” or “Depression is … (Smith, 2020).”
- Two authors: “According to Smith and Brown (2020), anxiety means…” or “Anxiety means (Smith & Brown, 2020).”
Finally, in case you have to review a book or a website article, here are the general formats for citing these source types on your APA reference list.
Article Review in MLA
If your assignment requires MLA-format referencing, here’s the general format you should use for citing journal articles on your Works Cited page:
- Author’s last name, First name. “Title of an Article.” Title of the Journal , vol. #, no. #, year, pp. #-#.
Horigian, Viviana E., et al. “Loneliness, Mental Health, and Substance Use Among US Young Adults During COVID-19.” Journal of Psychoactive Drugs , vol. 53, no. 1, 2021, pp. 1-9.
In-text citations in the MLA format follow the author-page citation format and look like this:
- According to Horigian et al., young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (6).
- Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al. 6).
Like in APA, the abbreviation “et al.” is only needed in MLA if your article has 3 or more authors.
If you need to cite a book or a website page, here are the general MLA formats for these types of sources.
✅ Article Review Template
Here is a handy, universal article review template to help you move on with any review assignment. We’ve tried to make it as generic as possible to guide you in the academic process.
📝 Article Review Examples
The theory is good, but practice is even better. Thus, we’ve created three brief examples to show you how to write an article review. You can study the full-text samples by following the links.
📃 Men, Women, & Money
This article review examines a famous piece, “Men, Women & Money – How the Sexes Differ with Their Finances,” published by Amy Livingston in 2020. The author of this article claims that men generally spend more money than women. She makes this conclusion from a close analysis of gender-specific expenditures across five main categories: food, clothing, cars, entertainment, and general spending patterns. Livingston also looks at men’s approach to saving to argue that counter to the common perception of women’s light-hearted attitude to money, men are those who spend more on average.
📃 When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism
This is a review of Jonathan Heidt’s 2016 article titled “When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism,” written as an advocacy of right-wing populism rising in many Western states. The author illustrates the case with the election of Donald Trump as the US President and the rise of right-wing rhetoric in many Western countries. These examples show how nationalist sentiment represents a reaction to global immigration and a failure of globalization.
📃 Sleep Deprivation
This is a review of the American Heart Association’s article titled “The Dangers of Sleep Deprivation.” It discusses how the national organization concerned with the American population’s cardiovascular health links the lack of high-quality sleep to far-reaching health consequences. The organization’s experts reveal how a consistent lack of sleep leads to Alzheimer’s disease development, obesity, type 2 diabetes, etc.
Article Review Examples and Samples
Reviewing an article is not as easy as it sounds: it requires a critical mind and doing some extra research. Check out our article review samples to gain a better understanding of how to review articles yourself.
How to Write an Article Review: A Comprehensive Guide
Writing an article review can be a complex task. It requires a careful summary of the writer’s article, a thorough evaluation of its key arguments, and a clear understanding of the subject area or discipline. This guide provides guidelines and tips for preparing and writing an effective article review.
Understanding an Article Review
An article review is a critique or assessment of another’s work, typically written by experts in the field. It involves summarizing the writer’s piece, evaluating its main points, and providing an analysis of the content. A review article isn’t just a simple summary; it’s a critical assessment that reflects your understanding and interpretation of the writer’s work.
Preparing for an Article Review
Before you start writing, you need to spend time preparing. This involves getting familiar with the author’s work, conducting research, and identifying the main points or central ideas in the text. It’s crucial to understand the subject area or discipline the writer’s article falls under to provide a comprehensive review.
Writing the Summary
The first part of your article review should provide a summary of the writer’s article. This isn’t a simple recounting of the article; it’s an overview or summation that highlights the key arguments and central ideas. It should give the reader a clear understanding of the writer’s main points and the overall structure of the article.
Evaluating the Article
The evaluation or assessment is the heart of your article review. Here, you analyze the writer’s piece, critique their main points, and assess the validity of their arguments. This evaluation should be based on your research and your understanding of the subject area. It’s important to be critical, but fair in your assessment.
Consulting Experts
Consulting experts or professionals in the field can be a valuable part of writing an article review. They can provide insights, add depth to your critique, and validate your evaluation. Remember, an article review is not just about your opinion, but also about how the writer’s piece is perceived by experts in the field.
Writing the Review
Now that you have your summary and evaluation, it’s time to start writing your review. Begin with an introduction that provides a brief overview of the writer’s article and your intended critique. The body of your review should contain your detailed summary and evaluation. Finally, conclude your review by summarizing your critique and providing your final thoughts on the writer’s piece.
Following Guidelines
While writing your article review, it’s important to adhere to the guidelines provided by your instructor or the journal you’re writing for. These recommendations often include specific formatting and structure requirements, as well as suggestions on the tone and style of your review.
Revisiting the Writer’s Article
As you work on your article review, don’t forget to revisit the writer’s article from time to time. This allows you to maintain a fresh perspective on the writer’s piece and ensures that your evaluation is accurate and comprehensive. The ability to relate to the author’s work is crucial in writing an effective critique.
Highlighting the Main Points
The main points or key arguments of the writer’s article should be at the forefront of your review. These central ideas form the crux of the author’s work and are, therefore, essential to your summary and evaluation. Be sure to clearly identify these points and discuss their significance and impact in the context of the field.
Engaging with the Field
An article review isn’t just about the writer’s article – it’s also about the broader subject area or discipline. Engage with the field by discussing relevant research, theories, and debates. This not only adds depth to your review but also positions the writer’s piece within a larger academic conversation.
Incorporating Expert Opinions
Incorporating the opinions of experts or authorities in the field strengthens your review. Experts can provide valuable insights, challenge your assumptions, and help you see the writer’s article from different perspectives. They can also validate your evaluation and lend credibility to your review.
The Role of Research in Your Review
Research plays a vital role in crafting an article review. It informs your understanding of the writer’s article, the main points, and the field. It also provides the necessary context for your evaluation. Be sure to conduct thorough research and incorporate relevant studies and investigations into your review.
Finalizing Your Review
Before submitting your review, take some time to revise and refine your writing. Check for clarity, coherence, and conciseness. Ensure your summary accurately represents the writer’s article and that your evaluation is thorough and fair. Adhere to the guidelines and recommendations provided by your instructor or the journal. If you need to add citations and reference page – don’t forget to include those. You can refer to one of our tools like acm reference generator to help you do everything correctly
In summary, writing an article review is a meticulous process that requires a detailed summary of the writer’s piece, a comprehensive evaluation of its main points, and a deep engagement with the field. By preparing adequately, consulting experts, and conducting thorough research, you can write a critique that is insightful, informed, and impactful.
Psychotherapy and Collaborative Goals Essay Sample, Example
Improving Mental Health Through Collaborative Psychotherapy Initiating psychotherapy is a crucial step towards achieving mental health and wellbeing. It is a process that involves the…
Early Assessment for Depression in Teenagers Essay Sample, Example
Handling Early Teenage Depression Depression is one of the most common mental health disorders in teenagers. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, approximately…
Discussion: Pharmaceuticals and Behavioral Health Essay Sample, Example
The Correlation Between Pharmaceuticals and Behavioral Health Pharmaceuticals and behavioral health are two interconnected fields that have a significant impact on the overall health and…
Human Experience Across the Health-Illness Continuum Essay Sample, Example
The Changing Human Experience in Health and Illness Human experience is a complex and multifaceted concept that encompasses a wide range of emotions, thoughts, behaviors,…
Total Quality Management Essay Sample, Example
Total Quality Management as a Systematic Approach Total Quality Management (TQM) is a management philosophy that focuses on continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, and employee involvement.…
The Lack of Patient Access in a Healthcare Organization Essay Sample, Example
Lack of Patient Access and Its Consequences The lack of patient access in a healthcare organization is a major concern for patients, healthcare providers, and…
Innovation Management and Creativity Essay Sample, Example
Integrating Innovations into Business Management Practices Innovation management and creativity are two concepts that are closely related and have a significant impact on the success…
Background Checks Essay Sample, Example
Performing Background Checks Before Hiring a New Employee In today’s competitive and fast-paced business world, employers are vigilant about hiring the right people. One of…
Evaluating Performance Essay Sample, Example
Performance Evaluation as a Way to Uphold Business Practices to a High Standard Evaluation of performance in management is an essential aspect of organizational success.…
How the city of London shaped Shakespeare Essay Sample, Example
William Shakespeare William Shakespeare is one of the most celebrated and influential playwrights in history, and his works have endured through the ages. Shakespeare spent…
George Washington as Military Leader and President – views and attitudes Essay Sample, Example
George Washington George Washington was a man of many talents, but his greatest achievements were as a military leader and as the first President of…
Factors Affecting Stock Prices Essay Sample, Example
The Impact of Various Factors on Stock Market Valuations Stock prices are influenced by a wide range of factors that can impact the performance of…
Importance of Corporate Budget Essay Sample, Example
The Correlation Between Corporate Budgeting and Business Success Corporate budgeting is the process of creating a financial plan that outlines the expected expenditures and revenues…
COVID-19 and The Challenging Context of International Business, Trade, and Investment Essay Sample, Example
The Influence of COVID-19 on International Business, Trade, and Investment COVID-19 has presented a challenging context for international business, trade, and investment. The pandemic has…
Family Therapy and Group Work Practice in Social Work Essay Sample, Example
Family Therapy and Group Work Practice Family therapy and group work practice are two approaches to psychotherapy that focus on the interpersonal relationships between individuals.…
Group Leadership Skill: Interpersonal Process in Group Counseling and Therapy Essay Sample, Example
Group Leadership Skill As an a Valuable Part of Group Counseling and Therapy Interpersonal process is an essential group leadership skill in group counseling and…
Working with the Military and Veterans Essay Sample, Example
Social Work with the Military, Veterans and Their Families Working with the military and veterans can be a challenging and rewarding experience for social workers.…
Memory, Knowledge, and Language and Their Importance in Social Work Essay Sample, Example
Social Work and Memory, Knowledge, and Language Memory, knowledge, and language are important components in social work. Social work is a field that involves working…
Are Dress Codes a Good Idea for Schools? Essay Sample, Example
School Dress Codes Dress codes have been a topic of discussion in schools for many years. Some people believe that dress codes are a good…
Customer Satisfaction Still at 1970s Levels Essay Sample, Example
Brooks, Chad. Customer Satisfaction Still at 1970s Levels. Business News Daily, 2013. The article draws attention to the problem of relationships between American companies and…
Remember Me
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
Article Review
Article Review Writing: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with Examples

People also read
Learn How to Write an Editorial on Any Topic
Best Tips on How to Avoid Plagiarism
How to Write a Movie Review - Guide & Examples
A Complete Guide on How to Write a Summary for Students
Write Opinion Essay Like a Pro: A Detailed Guide
Evaluation Essay - Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
How to Write a Thematic Statement - Tips & Examples
How to Write a Bio - Quick Tips, Structure & Examples
How to Write a Synopsis – A Simple Format & Guide
How to Write a Comparative Essay – A Complete Guide
Visual Analysis Essay - A Writing Guide with Format & Sample
List of Common Social Issues Around the World
Writing Character Analysis - Outline, Steps, and Examples
11 Common Types of Plagiarism Explained Through Examples
A Detailed Guide on How to Write a Poem Step by Step
Detailed Guide on Appendix Writing: With Tips and Examples
Struggling to write a review that people actually want to read? Feeling lost in the details and wondering how to make your analysis stand out?
You're not alone!
Many writers find it tough to navigate the world of article reviews, not sure where to start or how to make their reviews really grab attention.
No worries!
In this blog, we're going to guide you through the process of writing an article review that stands out. We'll also share tips, and examples to make this process easier for you.
Let’s get started.
- 1. What is an Article Review?
- 2. Types of Article Reviews
- 3. Article Review Format
- 4. How to Write an Article Review? 10 Easy Steps
- 5. Article Review Outline
- 6. Article Review Examples
- 7. Tips for Writing an Effective Article Review
What is an Article Review?
An article review is a critical evaluation and analysis of a piece of writing, typically an academic or journalistic article.
It goes beyond summarizing the content; it involves an in-depth examination of the author's ideas, arguments, and methodologies.
The goal is to provide a well-rounded understanding of the article's strengths, weaknesses, and overall contribution to the field.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Types of Article Reviews
Article reviews come in various forms, each serving a distinct purpose in the realm of academic or professional discourse. Understanding these types is crucial for tailoring your approach.
Here are some common types of article reviews:
Journal Article Review
A journal article review involves a thorough evaluation of scholarly articles published in academic journals.
It requires summarizing the article's key points, methodology, and findings, emphasizing its contributions to the academic field.
Take a look at the following example to help you understand better.
Example of Journal Article Review
Research Article Review
A research article review focuses on scrutinizing articles with a primary emphasis on research.
This type of review involves evaluating the research design, methodology, results, and their broader implications.
Discussions on the interpretation of results, limitations, and the article's overall contributions are key.
Here is a sample for you to get an idea.
Example of Research Article Review
Science Article Review
A science article review specifically addresses articles within scientific disciplines. It includes summarizing scientific concepts, hypotheses, and experimental methods.
The type of review assesses the reliability of the experimental design, and evaluates the author's interpretation of findings.
Take a look at the following example.
Example of Science Article Review
Critical Review
A critical review involves a balanced critique of a given article. It encompasses providing a comprehensive summary, highlighting key points, and engaging in a critical analysis of strengths and weaknesses.
To get a clearer idea of a critical review, take a look at this example.
Critical Review Example
Article Review Format
When crafting an article review in either APA or MLA format, it's crucial to adhere to the specific guidelines for citing sources.
Below are the bibliographical entries for different types of sources in both APA and MLA styles:
How to Write an Article Review? 10 Easy Steps
Writing an effective article review involves a systematic approach. Follow this step-by-step process to ensure a comprehensive and well-structured analysis.
Step 1: Understand the Assignment
Before diving into the review, carefully read and understand the assignment guidelines.
Pay attention to specific requirements, such as word count, formatting style (APA, MLA), and the aspects your instructor wants you to focus on.
Step 2: Read the Article Thoroughly
Begin by thoroughly reading the article. Take notes on key points, arguments, and evidence presented by the author.
Understand the author's main thesis and the context in which the article was written.
Step 3: Create a Summary
Summarize the main points of the article. Highlight the author's key arguments and findings.
While writing the summary ensure that you capture the essential elements of the article to provide context for your analysis.
Step 4: Identify the Author's Thesis
In this step, pinpoint the author's main thesis or central argument. Understand the purpose of the article and how the author supports their position.
This will serve as a foundation for your critique.
Step 5: Evaluate the Author's Evidence and Methodology
Examine the evidence provided by the author to support their thesis. Assess the reliability and validity of the methodology used.
Consider the sources, data collection methods, and any potential biases.
Step 6: Analyze the Author's Writing Style
Evaluate the author's writing style and how effectively they communicate their ideas.
Consider the clarity of the language, the organization of the content, and the overall persuasiveness of the article.
Step 7: Consider the Article's Contribution
Reflect on the article's contribution to its field of study. Analyze how it fits into the existing literature, its significance, and any potential implications for future research or applications.
Step 8: Write the Introduction
Craft an introduction that includes the article's title, author, publication date, and a brief overview.
State the purpose of your review and your thesis—the main point you'll be analyzing in your review.
Step 9: Develop the Body of the Review
Organize your review by addressing specific aspects such as the author's thesis, methodology, writing style, and the article's contribution.
Use clear paragraphs to structure your analysis logically.
Step 10: Conclude with a Summary and Evaluation
Summarize your main points and restate your overall assessment of the article.
Offer insights into its strengths and weaknesses, and conclude with any recommendations for improvement or suggestions for further research.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Article Review Outline
Creating a well-organized outline is an essential part of writing a coherent and insightful article review.
This outline given below will guide you through the key sections of your review, ensuring that your analysis is comprehensive and logically structured.
Refer to the following template to understand outlining the article review in detail.
Article Review Format Template
Article Review Examples
Examining article review examples can provide valuable insights into the structure, tone, and depth of analysis expected.
Below are sample article reviews, each illustrating a different approach and focus.
Example of Article Review
Sample of article review assignment pdf
Tips for Writing an Effective Article Review
Crafting an effective article review involves a combination of critical analysis, clarity, and structure.
Here are some valuable tips to guide you through the process:
- Start with a Clear Introduction
Kick off your article review by introducing the article's main points and mentioning the publication date, which you can find on the re-title page. Outline the topics you'll cover in your review.
- Concise Summary with Unanswered Questions
Provide a short summary of the article, emphasizing its main ideas. Highlight any lingering questions, known as "unanswered questions," that the article may have triggered. Use a basic article review template to help structure your thoughts.
- Illustrate with Examples
Use examples from the article to illustrate your points. If there are tables or figures in the article, discuss them to make your review more concrete and easily understandable.
- Organize Clearly with a Summary Section
Keep your review straightforward and well-organized. Begin with the start of the article, express your thoughts on what you liked or didn't like, and conclude with a summary section. This follows a basic plan for clarity.
- Constructive Criticism
When providing criticism, be constructive. If there are elements you don't understand, frame them as "unanswered questions." This approach shows engagement and curiosity.
- Smoothly Connect Your Ideas
Ensure your thoughts flow naturally throughout your review. Use simple words and sentences. If you have questions about the article, let them guide your review organically.
- Revise and Check for Clarity
Before finishing, go through your review. Correct any mistakes and ensure it sounds clear. Check if you followed your plan, used simple words, and incorporated the keywords effectively. This makes your review better and more accessible for others.
In conclusion , writing an effective article review involves a thoughtful balance of summarizing key points, and addressing unanswered questions.
By following a simple and structured approach, you can create a review that not only analyzes the content but also adds value to the reader's understanding.
Remember to organize your thoughts logically, use clear language, and provide examples from the article to support your points.
Ready to elevate your article reviewing skills? Explore the valuable resources and expert assistance at MyPerfectWords.com.
Our team of experienced writers is here to help you with article reviews and other school tasks.
So why wait? Place your " write my essays online " request today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
How to Write an Article Review: Practical Tips and Examples
Table of contents
- 1 What Is an Article Review?
- 2 Different Types of Article Review
- 3.1 Critical review
- 3.2 Literature review
- 3.3 Mapping review/systematic map
- 3.4 Meta-analysis
- 3.5 Overview
- 3.6 Qualitative Systematic Review/Qualitative Evidence Synthesis
- 3.7 Rapid review
- 3.8 Scoping review
- 3.9 Systematic review
- 3.10 Umbrella review
- 4 Formatting
- 5 How To Write An Article Review
- 6 Article Review Outline
- 7 10 Tips for Writing an Article Review
- 8 An Article Review Example
What Is an Article Review?
Before you get started, learn what an article review is. It can be defined as a work that combines elements of summary and critical analysis. If you are writing an article review, you should take a close look at another author’s work. Many experts regularly practice evaluating the work of others. The purpose of this is to improve writing skills.
This kind of work belongs to professional pieces of writing because the process of crafting this paper requires reviewing, summarizing, and understanding the topic. Only experts are able to compose really good reviews containing a logical evaluation of a paper as well as a critique.
Your task is not to provide new information. You should process what you have in a certain publication.
Different Types of Article Review
In academic writing, the landscape of article reviews is diverse and nuanced, encompassing a variety of formats that cater to different research purposes and methodologies. Among these, three main types of article reviews stand out due to their distinct approaches and applications:
- Narrative. The basic focus here is the author’s personal experience. Judgments are presented through the prism of experiences and subsequent realizations. Besides, the use of emotional recollections is acceptable.
- Evidence. There is a significant difference from the narrative review. An in-depth study of the subject is assumed, and conclusions are built on arguments. The author may consider theories or concrete facts to support that.
- Systematic. The structure of the piece explains the approach to writing. The answer to what’s a systematic review lies on the surface. The writer should pay special attention to the chronology and logic of the narrative.
Understanding 10 Common Types
Don`t rush looking at meta-analysis vs. systematic review. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with other formats and topics of texts. This will allow you to understand the types of essays better and select them based on your request. For this purpose, we`ll discuss the typology of reviews below.
Critical review
The critical review definition says that the author must be objective and have arguments for each thought. Sometimes, amateur authors believe that they should “criticize” something. However, it is important to understand the difference since objectivity and the absence of emotional judgments are prioritized. The structure of this type of review article is as follows:
- Introduction;
- Conclusion.
“Stuffing” of the text is based on such elements as methodology, argumentation, evidence, and theory base. The subject of study is stated at the beginning of the material. Then follows the transition to the main part (facts). The final word summarizes all the information voiced earlier.
It is a mistake to believe that critical reviews are devoid of evaluation. The author’s art lies in maneuvering between facts. Smooth transition from one argument to another and lays out the conclusions in the reader. That is why such texts are used in science. The critical reviews meaning is especially tangible in medical topics.
Literature review
Literature is the basis for this type of work ─ books, essays, and articles become a source of information. Thus, the author should rethink the voiced information. After that, it is possible to proceed to conclusions. The methodology aims to find interconnections, repetitions, and even “gaps” in the literature. One important item is the referencing of sources. Footnotes are possible in the work itself or the list of resources used.
These types of research reviews often explore myths since there are often inconsistencies in mythology. Sometimes, there is contrary information. In this case, the author has to gather all existing theories. The essence does not always lie in the confirmation of facts. There are other different types of reviews for this purpose. In literary reviews, the object of study may be characters or traditions. This is where the author’s space for discovery opens up. Inconsistencies in the data can tell important details about particular periods or cultures. At the same time, patterns reveal well-established facts. Make sure to outline your work before you write. This will help you with essay writing .
Mapping review/systematic map
A mapping review, also known as a systematic map, is a unique approach to surveying and organizing existing literature, providing a panoramic view of the research landscape. This paper systematically categorizes and maps out the available literature on a particular topic, emphasizing breadth over depth. Its primary goal is to present a comprehensive visual representation of the research distribution, offering insights into the overall scope of a subject.
One of the strengths of systematic reviews is that they deeply focus on a research question with detailed analysis and synthesis, while mapping review prioritizes breadth. It identifies and categorizes a broad range of studies without necessarily providing in-depth critique or content synthesis. This approach allows for a broader understanding of the field, making it especially useful in the early stages of research. Mapping reviews excel in identifying gaps in the existing body of literature.
By systematically mapping the distribution of research, researchers can pinpoint areas where studies are scarce or nonexistent, helping to guide future research directions. This makes mapping reviews a valuable tool for researchers seeking to contribute meaningfully to a field by addressing unexplored or underexplored areas.
Meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a powerful statistical technique. It systematically combines the results of multiple studies to derive comprehensive and nuanced insights. This method goes beyond the limitations of individual studies, offering a more robust understanding of a particular phenomenon by synthesizing data from diverse sources.
Meta-analysis employs a rigorous methodology. It involves the systematic collection and statistical integration of data from multiple studies. This methodological rigor ensures a standardized and unbiased approach to data synthesis. It is applied across various disciplines, from medicine and psychology to social sciences, providing a quantitative assessment of the overall effect of an intervention or the strength of an association.
In evidence-based fields, where informed decision-making relies on a thorough understanding of existing research, meta-analysis plays a pivotal role. It offers a quantitative overview of the collective evidence, helping researchers, policymakers, and practitioners make more informed decisions. By synthesizing results from diverse studies, meta-analysis contributes to the establishment of robust evidence-based practices, enhancing the reliability and credibility of findings in various fields. To present your research findings in the most readable way possible, learn how to write a summary of article .
If the key purpose of systematic review is to maximize the disclosure of facts, the opposite is true here. Imagine a video shot by a quadcopter from an altitude. The viewer sees a vast area of terrain without focusing on individual details. Overviews follow the same principle. The author gives a general picture of the events or objects described.
These types of reviews often seem simple. However, the role of the researcher becomes a very demanding one. The point is not just to list facts. Here, the search for information comes to the fore. After all, it is such reports that, in the future, will provide the basis for researching issues more narrowly. In essence, you yourself create a new source of information ─ students who worry that somebody may critique the author’s article love this type of material. However, there are no questions for the author; they just set the stage for discussions in different fields.
An example of this type of report would be a collection of research results from scientists. For example, statistics on the treatment of patients with certain diseases. In such a case, reference is made to scientific articles and doctrines. Based on this information, readers can speak about the effectiveness of certain treatment methods.
Qualitative Systematic Review/Qualitative Evidence Synthesis
One of the next types of review articles represents a meticulous effort to synthesize and analyze qualitative studies within a specific research domain.
The focus is synthesizing qualitative studies, employing a systematic and rigorous approach to extract meaningful insights. Its significance lies in its ability to provide a nuanced understanding of complex phenomena, offering a qualitative lens to complement quantitative analyses. Researchers can uncover patterns, themes, and contextual nuances that may elude traditional quantitative approaches by systematically reviewing and synthesizing qualitative data.
Often, you may meet discussion: is a systematic review quantitative or qualitative? The application of qualitative systematic reviews extends across diverse research domains, from healthcare and social sciences to education and psychology. For example, this approach can offer a comprehensive understanding of patient experiences and preferences in healthcare. In social sciences, it can illuminate cultural or societal dynamics. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool for researchers exploring, interpreting, and integrating qualitative findings to enrich their understanding of complex phenomena within their respective fields.
Rapid review
If you don’t know how to write an article review , try starting with this format. It is the complete opposite of everything we talked about above. The key advantage and feature is speed. Quick overviews are used when time is limited. The focus can go to individual details (key). Often, the focus is still on the principal points.
Often, these types of review papers are critically needed in politics. This method helps to communicate important information to the reader quickly. An example can be a comparison of the election programs of two politicians. The author can show the key differences. Or it can make an overview based on the theses of the opponents’ proposals on different topics.
Seeming simplicity becomes power. Such texts allow the reader to make a quick decision. The author’s task is to understand potential interests and needs. Then, highlight and present the most important data as concisely as possible. In addition to politics, such reports are often used in communications, advertising, and marketing. Experienced writers mention the one-minute principle. This means you can count on 60 seconds of the reader’s attention. If you managed to hook them ─ bravo, you have done the job!
Scoping review
If you read the official scoping review definition, you may find similarities with the systematic type of review. However, recall is a sequential and logical study in the second case. It’s like you stack things on a shelf by color, size, and texture.
This type of review can be more difficult to understand. The basic concept is to explore what is called the field of subjects. This means, on the one hand, exploring a particular topic through the existing data about it. The author tries to find gaps or patterns by drawing on sources of information.
Another good comparison between systematic and this type of review is imagining as if drawing a picture. In the first case, you will think through every nuance and detail, why it is there, and how it “moves the story.” In the second case, it is as if you are painting a picture with “broad strokes.” In doing so, you can explain your motives for choosing the primary color. For example: “I chose the emerald color because all the cultural publications say it’s a trend”. The same goes for texts.
Systematic review
Sometimes, you may encounter a battle: narrative review vs. systematic review. The point is not to compare but to understand the different types of papers. Once you understand their purpose, you can present your data better and choose a more readable format. The systematic approach can be called the most scientific. Such a review relies on the following steps:
- Literature search;
- Evaluating the information;
- Data processing;
- Careful analysis of the material.
It is the fourth point that is key. The writer should carefully process the information before using it. However, 80% of your work’s result depends on this stage’s seriousness.
A rigorous approach to data selection produces an array of factual data. That is why this method is so often used in science, education, and social fields. Where accuracy is important. At the same time, the popularity of this approach is growing in other directions.
Systematic reviews allow for using different data and methodologies,, but with one important caveat ─ if the author manages to keep the narrative structured and explain the reason for certain methods. It is not about rigor. The task of this type of review is to preserve the facts, which dictates consistency and rationality.
Umbrella review
An umbrella review is a distinctive approach that involves the review of existing reviews, providing a comprehensive synthesis of evidence on a specific topic. The methodology of an umbrella review entails systematically examining and summarizing findings from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
This method ensures a rigorous and consolidated analysis of the existing evidence. The application of an umbrella review is broad, spanning various fields such as medicine, public health, and social sciences. It is particularly useful when a substantial body of systematic reviews exists, allowing researchers to draw overarching conclusions from the collective findings.
It allows the summarization of existing reviews and provides a new perspective on individual subtopics of the main object of study. In the context of the umbrella method, the comparison “bird’s eye view” is often cited. A bird in flight can see the whole panorama and shift its gaze to specific objects simultaneously. What becomes relevant at a particular moment? The author will face the same task.
On the one hand, you must delve into the offshoots of the researched topic. On the other hand, focus on the topic or object of study as a whole. Such a concept allows you to open up new perspectives and thoughts.

Different types of formatting styles are used for article review writing. It mainly depends on the guidelines that are provided by the instructor, sometimes, professors even provide an article review template that needs to be followed.
Here are some common types of formatting styles that you should be aware of when you start writing an article review:
- APA (American Psychological Association) – An APA format article review is commonly used for social sciences. It has guidelines for formatting the title, abstract, body paragraphs, and references. For example, the title of an article in APA format is in sentence case, whereas the publication title is in title case.
- MLA (Modern Language Association): This is a formatting style often used in humanities, such as language studies and literature. There are specific guidelines for the formatting of the title page, header, footer, and citation style.
- Chicago Manual of Style: This is one of the most commonly used formatting styles. It is often used for subjects in humanities and social sciences, but also commonly found in a newspaper title. This includes guidelines for formatting the title page, end notes, footnotes, publication title, article citation, and bibliography.
- Harvard Style: Harvard style is commonly used for social sciences and provides specific guidelines for formatting different sections of the pages, including publication title, summary page, website publisher, and more.
To ensure that your article review paper is properly formatted and meets the requirements, it is crucial to adhere to the specific guidelines for the formatting style you are using. This helps you write a good article review.
- Free unlimited checks
- All common file formats
- Accurate results
- Intuitive interface
How To Write An Article Review
There are several steps that must be followed when you are starting to review articles. You need to follow these to make sure that your thoughts are organized properly. In this way, you can present your ideas in a more concise and clear manner. Here are some tips on how to start an article review and how to cater to each writing stage.
- Read the Article Closely: Even before you start to write an article review, it’s important to make sure that you have read the specific article thoroughly. Write down the central points and all the supporting ideas. It’s important also to note any questions or comments that you have about the content.
- Identify the Thesis: Make sure that you understand the author’s main points, and identify the main thesis of the article. This will help you focus on your review and ensure that you are addressing all of the key points.
- Formulate an Introduction: The piece should start with an introduction that has all the necessary background information, possibly in the first paragraph or in the first few paragraphs. This can include a brief summary of the important points or an explanation of the importance.
- Summarize the Article : Summarize the main points when you review the article, and make sure that you include all supporting elements of the author’s thesis.
- Start with Personal Critique : Now is the time to include a personal opinion on the research article or the journal article review. Start with evaluating all the strengths and weaknesses of the reviewed article. Discuss all of the flaws that you found in the author’s evidence and reasoning. Also, point out whether the conclusion provided by the author was well presented or not.
- Add Personal Perspective: Offer your perspective on the original article, do you agree or disagree with the ideas that the article supports or not. Your critical review, in your own words, is an essential part of a good review. Make sure you address all unanswered questions in your review.
- Conclude the Article Review : In this section of the writing process, you need to be very careful and wrap up the whole discussion in a coherent manner. This is should summarize all the main points and offer an overall assessment.
Make sure to stay impartial and provide proof to back up your assessment. By adhering to these guidelines, you can create a reflective and well-structured article review.
Article Review Outline
Here is a basic, detailed outline for an article review you should be aware of as a pre-writing process if you are wondering how to write an article review.
Introduction
- Introduce the article that you are reviewing (author name, publication date, title, etc.) Now provide an overview of the article’s main topic
Summary section
- Summarize the key points in the article as well as any arguments Identify the findings and conclusion
Critical Review
- Assess and evaluate the positive aspects and the drawbacks
- Discuss if the authors arguments were verified by the evidence of the article
- Identify if the text provides substantial information for any future paper or further research
- Assess any gaps in the arguments
- Restate the thesis statement
- Provide a summary for all sections
- Write any recommendations and thoughts that you have on the article
- Never forget to add and cite any references that you used in your article

10 Tips for Writing an Article Review
Have you ever written such an assignment? If not, study the helpful tips for composing a paper. If you follow the recommendations provided here, the process of writing a summary of the article won’t be so time-consuming, and you will be able to write an article in the most effective manner.
The guidelines below will help to make the process of preparing a paper much more productive. Let’s get started!
- Check what kind of information your work should contain. After answering the key question “What is an article review?” you should learn how to structure it the right way. To succeed, you need to know what your work should be based on. An analysis with insightful observations is a must for your piece of writing.
- Identify the central idea: In your first reading, focus on the overall impression. Gather ideas about what the writer wants to tell, and consider whether he or she managed to achieve it.
- Look up unfamiliar terms. Don’t know what certain words and expressions mean? Highlight them, and don’t forget to check what they mean with a reliable source of information.
- Highlight the most important ideas. If you are reading it a second time, use a highlighter to highlight the points that are most important to understanding the passage.
- Write an outline. A well-written outline will make your life a lot easier. All your thoughts will be grouped. Detailed planning helps not to miss anything important. Think about the questions you should answer when writing.
- Brainstorm headline ideas. When choosing a project, remember: it should reflect the main idea. Make it bold and concise.
- Check an article review format example. You should check that you know how to cite an article properly. Note that citation rules are different in APA and MLA formats. Ask your teacher which one to prioritize.
- Write a good introduction. Use only one short paragraph to state the central idea of the work. Emphasize the author’s key concepts and arguments. Add the thesis at the end of the Introduction.
- Write in a formal style. Use the third person, remembering that this assignment should be written in a formal academic writing style.
- Wrap up, offer your critique, and close. Give your opinion on whether the author achieved his goals. Mention the shortcomings of the job, if any, and highlight its strengths.
If you have checked the tips and you still doubt whether you have all the necessary skills and time to prepare this kind of educational work, follow one more tip that guarantees 100% success- ask for professional assistance by asking the custom writing service PapersOwl to craft your paper instead of you. Just submit an order online and get the paper completed by experts.

An Article Review Example
If you have a task to prepare an analysis of a certain piece of literature, have a look at the article review sample. There is an article review example for you to have a clear picture of what it must look like.
Journal Article on Ayn Rand’s Works Review Example
“The purpose of the article is to consider the features of the poetics of Ayn Rand’s novels “Atlas Shrugged,” “We the living,” and “The Fountainhead.” In the analysis of the novels, the structural-semantic and the method of comparative analysis were used.
With the help of these methods, genre features of the novels were revealed, and a single conflict and a cyclic hero were identified.
In-depth reading allows us to more fully reveal the worldview of the author reflected in the novels. It becomes easier to understand the essence of the author’s ideas about the connection between being and consciousness, embodied in cyclic ideas and images of plot twists and heroes. The author did a good job highlighting the strong points of the works and mentioning the reasons for the obvious success of Ayn Rand.“
You can also search for other relevant article review examples before you start.
In conclusion, article reviews play an important role in evaluating and analyzing different scholarly articles. Writing a review requires critical thinking skills and a deep understanding of the article’s content, style, and structure. It is crucial to identify the type of article review and follow the specific guidelines for formatting style provided by the instructor or professor.
The process of writing an article review requires several steps, such as reading the article attentively, identifying the thesis, and formulating an introduction. By following the tips and examples provided in this article, students can write a worthy review that demonstrates their ability to evaluate and critique another writer’s work.
Learning how to write an article review is a critical skill for students and professionals alike. Before diving into the nitty-gritty of reviewing an article, it’s important to understand what an article review is and the elements it should include. An article review is an assessment of a piece of writing that summarizes and evaluates a work. To complete a quality article review, the author should consider the text’s purpose and content, its organization, the author’s style, and how the article fits into a larger conversation. But if you don’t have the time to do all of this work, you can always purchase a literature review from Papers Owl .
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.

Get Started
Take the first step and invest in your future.

Online Programs
Offering flexibility & convenience in 51 online degrees & programs.

Prairie Stars
Featuring 15 intercollegiate NCAA Div II athletic teams.

Find your Fit
UIS has over 85 student and 10 greek life organizations, and many volunteer opportunities.

Arts & Culture
Celebrating the arts to create rich cultural experiences on campus.

Give Like a Star
Your generosity helps fuel fundraising for scholarships, programs and new initiatives.

Bragging Rights
UIS was listed No. 1 in Illinois and No. 3 in the Midwest in 2023 rankings.
- Quick links Applicants & Students Important Apps & Links Alumni Faculty and Staff Community Admissions How to Apply Cost & Aid Tuition Calculator Registrar Orientation Visit Campus Academics Register for Class Programs of Study Online Degrees & Programs Graduate Education International Student Services Study Away Student Support Bookstore UIS Life Dining Diversity & Inclusion Get Involved Health & Wellness COVID-19 United in Safety Residence Life Student Life Programs UIS Connection Important Apps UIS Mobile App Advise U Canvas myUIS i-card Balance Pay My Bill - UIS Bursar Self-Service Email Resources Bookstore Box Information Technology Services Library Orbit Policies Webtools Get Connected Area Information Calendar Campus Recreation Departments & Programs (A-Z) Parking UIS Newsroom The Observer Connect & Get Involved Update your Info Alumni Events Alumni Networks & Groups Volunteer Opportunities Alumni Board News & Publications Featured Alumni Alumni News UIS Alumni Magazine Resources Order your Transcripts Give Back Alumni Programs Career Development Services & Support Accessibility Services Campus Services Campus Police Facilities & Services Registrar Faculty & Staff Resources Website Project Request Web Services Training & Tools Academic Impressions Career Connect CSA Reporting Cybersecurity Training Faculty Research FERPA Training Website Login Campus Resources Newsroom Campus Calendar Campus Maps i-Card Human Resources Public Relations Webtools Arts & Events UIS Performing Arts Center Visual Arts Gallery Event Calendar Sangamon Experience Center for Lincoln Studies ECCE Speaker Series Community Engagement Center for State Policy and Leadership Illinois Innocence Project Innovate Springfield Central IL Nonprofit Resource Center NPR Illinois Community Resources Child Protection Training Academy Office of Electronic Media University Archives/IRAD Institute for Illinois Public Finance
Request Info

How to Review a Journal Article

- Request Info Request info for.... Undergraduate/Graduate Online Study Away Continuing & Professional Education International Student Services General Inquiries
For many kinds of assignments, like a literature review , you may be asked to offer a critique or review of a journal article. This is an opportunity for you as a scholar to offer your qualified opinion and evaluation of how another scholar has composed their article, argument, and research. That means you will be expected to go beyond a simple summary of the article and evaluate it on a deeper level. As a college student, this might sound intimidating. However, as you engage with the research process, you are becoming immersed in a particular topic, and your insights about the way that topic is presented are valuable and can contribute to the overall conversation surrounding your topic.
IMPORTANT NOTE!!
Some disciplines, like Criminal Justice, may only want you to summarize the article without including your opinion or evaluation. If your assignment is to summarize the article only, please see our literature review handout.
Before getting started on the critique, it is important to review the article thoroughly and critically. To do this, we recommend take notes, annotating , and reading the article several times before critiquing. As you read, be sure to note important items like the thesis, purpose, research questions, hypotheses, methods, evidence, key findings, major conclusions, tone, and publication information. Depending on your writing context, some of these items may not be applicable.
Questions to Consider
To evaluate a source, consider some of the following questions. They are broken down into different categories, but answering these questions will help you consider what areas to examine. With each category, we recommend identifying the strengths and weaknesses in each since that is a critical part of evaluation.
Evaluating Purpose and Argument
- How well is the purpose made clear in the introduction through background/context and thesis?
- How well does the abstract represent and summarize the article’s major points and argument?
- How well does the objective of the experiment or of the observation fill a need for the field?
- How well is the argument/purpose articulated and discussed throughout the body of the text?
- How well does the discussion maintain cohesion?
Evaluating the Presentation/Organization of Information
- How appropriate and clear is the title of the article?
- Where could the author have benefited from expanding, condensing, or omitting ideas?
- How clear are the author’s statements? Challenge ambiguous statements.
- What underlying assumptions does the author have, and how does this affect the credibility or clarity of their article?
- How objective is the author in his or her discussion of the topic?
- How well does the organization fit the article’s purpose and articulate key goals?
Evaluating Methods
- How appropriate are the study design and methods for the purposes of the study?
- How detailed are the methods being described? Is the author leaving out important steps or considerations?
- Have the procedures been presented in enough detail to enable the reader to duplicate them?
Evaluating Data
- Scan and spot-check calculations. Are the statistical methods appropriate?
- Do you find any content repeated or duplicated?
- How many errors of fact and interpretation does the author include? (You can check on this by looking up the references the author cites).
- What pertinent literature has the author cited, and have they used this literature appropriately?
Following, we have an example of a summary and an evaluation of a research article. Note that in most literature review contexts, the summary and evaluation would be much shorter. This extended example shows the different ways a student can critique and write about an article.
Chik, A. (2012). Digital gameplay for autonomous foreign language learning: Gamers’ and language teachers’ perspectives. In H. Reinders (ed.), Digital games in language learning and teaching (pp. 95-114). Eastbourne, UK: Palgrave Macmillan.
Be sure to include the full citation either in a reference page or near your evaluation if writing an annotated bibliography .
In Chik’s article “Digital Gameplay for Autonomous Foreign Language Learning: Gamers’ and Teachers’ Perspectives”, she explores the ways in which “digital gamers manage gaming and gaming-related activities to assume autonomy in their foreign language learning,” (96) which is presented in contrast to how teachers view the “pedagogical potential” of gaming. The research was described as an “umbrella project” consisting of two parts. The first part examined 34 language teachers’ perspectives who had limited experience with gaming (only five stated they played games regularly) (99). Their data was recorded through a survey, class discussion, and a seven-day gaming trial done by six teachers who recorded their reflections through personal blog posts. The second part explored undergraduate gaming habits of ten Hong Kong students who were regular gamers. Their habits were recorded through language learning histories, videotaped gaming sessions, blog entries of gaming practices, group discussion sessions, stimulated recall sessions on gaming videos, interviews with other gamers, and posts from online discussion forums. The research shows that while students recognize the educational potential of games and have seen benefits of it in their lives, the instructors overall do not see the positive impacts of gaming on foreign language learning.
The summary includes the article’s purpose, methods, results, discussion, and citations when necessary.
This article did a good job representing the undergraduate gamers’ voices through extended quotes and stories. Particularly for the data collection of the undergraduate gamers, there were many opportunities for an in-depth examination of their gaming practices and histories. However, the representation of the teachers in this study was very uneven when compared to the students. Not only were teachers labeled as numbers while the students picked out their own pseudonyms, but also when viewing the data collection, the undergraduate students were more closely examined in comparison to the teachers in the study. While the students have fifteen extended quotes describing their experiences in their research section, the teachers only have two of these instances in their section, which shows just how imbalanced the study is when presenting instructor voices.
Some research methods, like the recorded gaming sessions, were only used with students whereas teachers were only asked to blog about their gaming experiences. This creates a richer narrative for the students while also failing to give instructors the chance to have more nuanced perspectives. This lack of nuance also stems from the emphasis of the non-gamer teachers over the gamer teachers. The non-gamer teachers’ perspectives provide a stark contrast to the undergraduate gamer experiences and fits neatly with the narrative of teachers not valuing gaming as an educational tool. However, the study mentioned five teachers that were regular gamers whose perspectives are left to a short section at the end of the presentation of the teachers’ results. This was an opportunity to give the teacher group a more complex story, and the opportunity was entirely missed.
Additionally, the context of this study was not entirely clear. The instructors were recruited through a master’s level course, but the content of the course and the institution’s background is not discussed. Understanding this context helps us understand the course’s purpose(s) and how those purposes may have influenced the ways in which these teachers interpreted and saw games. It was also unclear how Chik was connected to this masters’ class and to the students. Why these particular teachers and students were recruited was not explicitly defined and also has the potential to skew results in a particular direction.
Overall, I was inclined to agree with the idea that students can benefit from language acquisition through gaming while instructors may not see the instructional value, but I believe the way the research was conducted and portrayed in this article made it very difficult to support Chik’s specific findings.
Some professors like you to begin an evaluation with something positive but isn’t always necessary.
The evaluation is clearly organized and uses transitional phrases when moving to a new topic.
This evaluation includes a summative statement that gives the overall impression of the article at the end, but this can also be placed at the beginning of the evaluation.
This evaluation mainly discusses the representation of data and methods. However, other areas, like organization, are open to critique.
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Writing Guide
- Article Writing
How To Write an Article Review
- Definition of article review
- Why do students write article reviews
- Types of article review
- Structure and outline
- Step-by-step guide
Article review format
- How to write a good article review
- Article review examples
Definition of article review assignments
Why do students write article reviews.
- Article writing is a deeply analytical process that helps students to correct vague terms when and if they are present. Likewise, when composing an article review or an original assignment, such work provides more clarity regarding using appropriate words. If an article has colloquial language or logical gaps, it is one of those aspects to mention in an article review. It also allows writers to determine whether certain terms must be replaced and edited.
- Article review essay writing helps to clarify scientific questions.
- Writing an article review allows students to see and understand how others approach specific issues and what perspectives should be studied regarding the problems at hand. Once a person reads the review, it makes it easier to get rid of bias.
- Article review assignments also provide students with editing and grammar work to help with more accurate papers.
- Most importantly, an article review is a way to encourage better work and provide critical analysis with due criticism and evaluation of the original article.
Types of article review tasks
- Original Research Article Review. The original research article review is close to what is often seen as the literature review. An author must explore the author’s hypothesis and some background studies with due analysis to outline scientific methods. It’s one of the most challenging tasks to write as one must interpret the findings and talk about future implications. This type of work can also get lengthy and be up to 6,000 words in subjects like History or Sociology.
- Critical Analysis. As the name implies, it critically evaluates the author’s work and can be up to 3,000 words.
- Literature Review. It stands for the review of secondary literature sources. As a rule, such reviews do not present much new data and only evaluate the importance of sources and information that supports the author’s arguments.
- Systematic Review. This case stands for research questions and articles that require a deeper synthesis of available facts or certain evidence. The purpose here is to define and evaluate the quality of the data obtained by the author.
- Meta-Analysis Reviews. Once again, it is a systematic review focusing on a specific topic, the literature issues. You must provide a special quantitative estimate for exposure and intervention.
- Clinical Trial Reviews. It means that one must provide a study related to an investigation offered by the author. It can relate to a drug or talk about a sample group of people, thus bringing it into the field of a defined population or a group of participants.
- Perspective or Opinion Article Review. This is where one poses an opinion, meaning things can get biased toward a certain opinion. In writing a good review, a student can look for perspectives and evaluate the importance of the original article. Likewise, posing an opinion is one of the obligatory aspects.
Article review structure and outline
Article review structure.
- Title page.
- An article introduction presenting the main subject and/or a problem.
- Brief article summary.
- Critical article evaluation and/or a summary.
- Conclusion with the moral lesson and discussion on the findings’ pros/cons.
- Bibliography with relevant citations.
Article review outline
- You provide an evaluation and summary of the author’s article.
- Your audience can receive sufficient knowledge regarding the subject.
- You have made points about the strongest arguments of the author.
- You have criticized the author’s work and explained how it contributes to the scientific field.
- You conclude your article review with your original thoughts and opinions without turning to additional research unless the grading rubric required it.
Step-by-step writing guide
Step 1: learn about the article’s agenda., step 2: summarize the main article ideas, step 3: organization aspect of the review, step 4: article preview and take notes, step 5: paraphrasing and analysis, step 6: final evaluation.

- An introduction. The topic of your study must be mentioned here in the first sentence. Indicate what your article contains and talk about the author’s background. Provide an order of the subjects you plan to discuss to explain what your readers expect. The introduction should provide the author’s claims and the main arguments that result in your thesis statement. When writing an introduction, you must determine the main argument.
- Body paragraphs. This is where you provide an evaluation with a summary and write about the author’s work.
- Conclusion. Speak of your reasons for providing a review and talk about whether you could support your thesis and what you have learned.
- Works Cited page. Refer to your grading rubric to identify what citation style must be used.
How to write a good article review?
- Do not write the statements in the first person. It is recommended to use the third person instead by turning to a formal academic tone.
- Your introduction with the information about the original article should take from 10 to 25% of your assignment’s volume.
- An introduction must end with a strong thesis and make an assumption or research the author’s main claim. A typical thesis to start an article review for an assignment may look this way:
- Write down all the important points and share your findings. It will help to show that you have done your homework correctly.
- Discuss how the article supports the claims and whether it provides good evidence.
- Always provide background information about the author.
- Use direct quotes to support your claims by turning to the original article.
- Read your summary twice to evaluate whether it follows the main thesis.
- Talk about the contributions of the author to the academic community.
- Provide reasons for whether you support the author’s view or not. Why or why not?
- Summarize all the important points in a conclusion part.
Why choose article review examples?
- Wright State University’s Journal Article Review Example .
- University of Illinois Springfield’s Article How-to Review Guide .
- UC Merced Library’s Article Review Sample
- Identify recent and important changes in your field of study.
- Determine who works in a specific field of science and why.
- Narrow things down and identify essential information to help you start with research.
- Use obtained information in school debates, and references work.
- Generate new ideas and conduct lab experiments.
- Write an article review through the lens of personal experience and expertise.

Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

Want to make a difference? Try working at an environmental non-profit organization
Career Feature 26 APR 24

Scientists urged to collect royalties from the ‘magic money tree’
Career Feature 25 APR 24

NIH pay rise for postdocs and PhD students could have US ripple effect
News 25 APR 24

Algorithm ranks peer reviewers by reputation — but critics warn of bias
Nature Index 25 APR 24

How young people benefit from Swiss apprenticeships
Spotlight 17 APR 24

Researchers want a ‘nutrition label’ for academic-paper facts
Nature Index 17 APR 24

How reliable is this research? Tool flags papers discussed on PubPeer
News 29 APR 24
Postdoctoral Associate- Molecular Cell Biology
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Associate or Senior Editor, Communications Medicine
Job Title: Associate or Senior Editor, Communications Medicine Location: Philadelphia, New York, Jersey City, Washington DC (Hybrid Working) Closin...
Jersey City, New Jersey
Springer Nature Ltd
Associate or Senior Editor, BMC Psychology and BMC Psychiatry
Job Title: Associate Editor or Senior Editor, BMC Psychology and BMC Psychiatry Location(s): New York or Shanghai Deadline: May 21st, 2024 You w...
New York (US)
W2 Professorship with tenure track to W3 in Animal Husbandry (f/m/d)
The Faculty of Agricultural Sciences at the University of Göttingen invites applications for a temporary professorship with civil servant status (g...
Göttingen (Stadt), Niedersachsen (DE)
Georg-August-Universität Göttingen
W1 professorship for „Tissue Aspects of Immunity and Inflammation“
Kiel University (CAU) and the University of Lübeck (UzL) are striving to increase the proportion of qualified female scientists in research and tea...
University of Luebeck
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- All eBooks & Audiobooks
- Academic eBook Collection
- Home Grown eBook Collection
- Off-Campus Access
- Literature Resource Center
- Opposing Viewpoints
- ProQuest Central
- Course Guides
- Citing Sources
- Library Research
- Websites by Topic
- Book-a-Librarian
- Research Tutorials
- Use the Catalog
- Use Databases
- Use Films on Demand
- Use Home Grown eBooks
- Use NC LIVE
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary vs. Secondary
- Scholarly vs. Popular
- Make an Appointment
- Writing Tools
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing Center
Service Alert

Article Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing an article SUMMARY
Writing an article REVIEW
- Writing an article CRITIQUE
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- About RCC Library
Text: 336-308-8801
Email: [email protected]
Call: 336-633-0204
Schedule: Book-a-Librarian
Like us on Facebook
Links on this guide may go to external web sites not connected with Randolph Community College. Their inclusion is not an endorsement by Randolph Community College and the College is not responsible for the accuracy of their content or the security of their site.
A journal article review is written for a reader who is knowledgeable in the discipline and is interested not just in the coverage and content of the article being reviewed, but also in your critical assessment of the ideas and argument that are being presented by the author.
Your review might be guided by the following questions:
Additional Resources
All links open in a new window.
How to Write an Article Review (from Essaypro.com)
How to Review a Journal Article (from University of Illinois Springfield)
Writing Critical Reviews (from Queen's University Library)
- << Previous: Writing an article SUMMARY
- Next: Writing an article CRITIQUE >>
- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 9:32 AM
- URL: https://libguides.randolph.edu/summaries
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Article review writing format, steps, examples and illustration PDF Compiled by Mohammed Yismaw

2021, Article review writing format, steps, examples and illustration PDF Compiled by Mohammed Yismaw
The purpose of this document is to help students and researchers understand how a review of an academic journal is conducted and reported in different fields of study. Review articles in academic journals that analyze or discuss researches previously published by others, rather than reporting new research results or findings. Summaries and critiques are two ways to write a review of a scientific journal article. Both types of writing ask you first to read and understand an article from the primary literature about your topic. The summary involves briefly but accurately stating the key points of the article for a reader who has not read the original article. The critique begins by summarizing the article and then analyzes and evaluates the author’s research. Summaries and critiques help you learn to synthesize information from different sources and are usually limited to two pages maximum.
Related Papers
Harald von Kortzfleisch , Christoph Kahle
Neue Technologien und Innovationen stellen heutzutage wichtige Schlüsselelemente der Wachstums und Erfolgssicherung von Unternehmen dar. Durch einen in Geschwindigkeit und Intensität immer schneller zunehmenden Wettbewerb nehmen Innovationen eine immer zentralere Rolle im Praxisalltag von Unternehmen ein. Dieser technische Fortschritt treibt auch in der Wissenschaft das Thema des Innovationsmanagements in den letzten Jahrzehnten immer stärker voran und wird dort ausgiebig diskutiert. Die Bedeutung von Innovationen wächst dabei ebenfalls aus der Sicht der Kunden, welche heutzutage viel differenzierter als früher Produkte und Dienste nachfragen und somit Unternehmen vor neue Herausforderungen stellen. Ãberdies stellen Innovationen heute ein entscheidendes Bindeglied zwischen Marktorientierung und erhofften Unternehmenserfolg dar. Seit einigen Jahren lässt sich eine Ãffnung der Unternehmensgrenzen für externe Quellen wie Kunden, Zulieferer, Universitäten oder teilweise auch M...
SSRN Electronic Journal
Helmut Krcmar
Dominic Lindner
Alexandra Waluszewski
Research Policy
Nuria Gonzalez Alvarez
Creativity and Innovation Management
Matti Pihlajamaa
Firms tap into user knowledge to learn about the users’ needs. While users have been recognized as a valuable source of knowledge for innovation, few studies have investigated how their knowledge is integrated into innovation processes in the context of complex products and systems (CoPS). The purpose of this study is to reveal the practices of CoPS manufacturers to facilitate user knowledge utilization for innovation. We investigate two case companies, a medical device manufacturer and an aircraft manufacturer, and report on seven managerial practices for utilizing user knowledge. We adopt the absorptive capacity model in structuring our findings and elaborate three of the model's sub-capabilities (recognition of the value of user knowledge, acquisition of user knowledge, and assimilation/transformation of user knowledge) by proposing that each is associated with a distinct managerial goal and related practices: (1) Sensitizing the organization to the innovation potential of user knowledge, (2) identifying and gaining access to suitable user knowledge, and (3) analyzing and interpreting user knowledge and integrating it into product development. Our study contributes to the innovation management literature by analyzing the capabilities required to utilize user knowledge throughout the CoPS innovation process.
Information & Management
Diffusion of digital technologies into the manufacturing industry has created new opportunities for innovation that firms must address to remain competitive. We investigate the role of customer and user knowledge in the digital innovation processes of three global B2B manufacturing companies. We find that the B2B manufacturing industry's characteristics influence how users and customers may be leveraged. Customers making the purchasing decisions are considered for knowledge about short-term changes in market needs, while users working directly with the products provide long-term guidance for digital innovation. We identify practices for acquiring, distributing, and using customer and user knowledge for digital innovation.
Journal of business market management
Patricia Sandmeier
Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management and Innovation
Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management and Innovation JEMI
Given the rising role of users in innovation processes and the increasing amount of research in this field the aim of this paper is to explore the limits of our understanding of the user innovation (UI) concept. In doing so, the study addresses four basic questions: (1) Why do users create and share innovation? (2) Who is the user-innovator? (3) What type of innovation do users create? (4) How do users innovate? The results of a systematic literature review identified the main research streams on user innovation, together with weaknesses of past research and perspectives for future studies.
RELATED PAPERS
Gernot Grabher
Journal of Computer‐ …
Petra Schubert , Kathrin Möslein
Mossimo Sesom
Shahab Zare
Arthur Shulman
International Journal of Technology Management
Richard Farr
European Journal of Dental Education
Y.P. CHANDRA
Chandra Yanto
Management Science
John Roberts
Maria Antikainen
Johanna Bragge
intechopen.com
Ivona Vrdoljak Raguz
Service Science
Tuure Tuunanen
Jouni K Juntunen
Benji Decker
Eva Heiskanen
Handbook of Marketing
Jerome Hauser
Service Industries Journal
Christian Kowalkowski
Journal of Engineering Design
Ola Isaksson , Anna Rönnbäck
Journal of Management
Bettina Bastian
International Journal of Innovation Management
Harald von Kortzfleisch
Guido H Baltes
Technology Analysis & Strategic Management
Raimo Lovio
Marco Bertoni , Christian Johansson
Dominik Walcher
Managing Service Quality
Tor W. Andreassen
Journal of Product Innovation Management
Gary Schirr
System Sciences, 2004. …
Ralf Reichwald , Dominik Walcher
Edina Vadovics
Jouni Similä
Luis Cancino Muñoz
Shell Artillery
Ralf Reichwald
Journal of the Academy of …
Ian Wilkinson , Subroto Roy
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Article Review

Article reviews are an essential part of academic article writing , providing an opportunity to evaluate and analyze published research. A well-written review can help readers understand the simple subject matter and determine the value of the article. In this article, we’ll cover what is an article review, provide step-by-step guidance on how to write one, and answer some common questions.
1. Journal Article Review Form

Size: 84 KB
2. Article Review & Critique

Size: 420 KB
3. Formal Article Review

Size: 188 KB
4. Article Review Guideline

Size: 157 KB
5. Book and Article Reviews

Size: 284 KB
6. Format for Review Article

Size: 71 KB
7. Scientific Article Review

Size: 258 KB
8. Critical Reviews of Journal Articles

Size: 50 KB
9. Research Experience Article Review

Size: 31 KB
10. Review for Article Psychological Bulletin

11. Article Format Guide Review
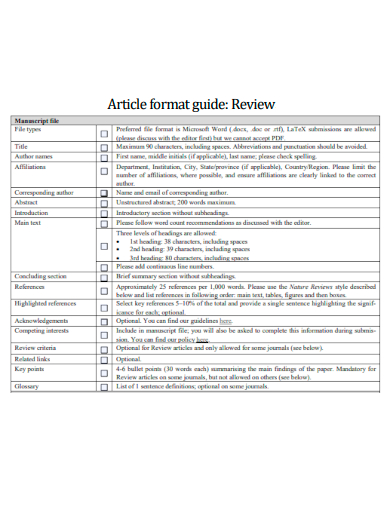
Size: 449 KB
12. Value Of Review Article

Size: 51 KB
13. Articles for Peer-Review Publications

Size: 181 KB
14. Law Review Article Selection Process

15. Creative Article Review

Size: 46 KB
16. Club Article Review

Size: 77 KB
17. Review of Research Articles

Size: 152 KB
What is an Article Review
An article review is a critical assessment of a scholarly article or research paper. It involves analyzing the content, methodology, and findings of the article and providing an evaluation of its strengths and weaknesses. The review typically includes a summary of the article’s main points, an evaluation of its contribution to the subject, and suggestions for improvement.
How to Write an Article Review
Writing an article review can be a challenging task, but it’s an essential skill for students and researchers alike. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you write an effective article review:
Choose the article to review
Select an article that is relevant to your subject and interests you. Make sure the article is recent, reputable, and published in a peer-reviewed journal.
Read the article carefully
Read the article thoroughly and take notes as you go. Pay attention to the author’s thesis statement, research question, methodology, and findings.
Identify the main points and key arguments
Determine the main points and arguments of the article. Look for evidence that supports the author’s thesis statement.
Evaluate the article’s methodology and research design
Evaluate the methodology and research design used in the article. Determine if the research methods were appropriate and effective in answering the research question.
Assess the article’s strengths and weaknesses
Identify the strengths and weaknesses of the article. Evaluate the quality of the evidence presented and the logic of the arguments made.
Write a summary of the article
Summarize the article in your own words. Include the main points, key arguments, and findings of the article.
Write the main body of the review
In the main body of the review, analyze and evaluate the article. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the article and provide evidence to support your claims.
Conclude with a final evaluation and recommendations for improvement
Conclude your review with a final evaluation conclusion of the article. Highlight its strengths and weaknesses and provide recommendations for improvement.
Proofread and edit the review
After completing your review, proofread and edit it carefully. Check for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. Make sure your review is clear, concise, and well-organized.
What is the difference between an article review and a literature review?
A literature review is a comprehensive analysis of published research on a particular subject, while an article review focuses specifically on one article.
Can I use first-person sentences in an article review?
It depends on the guidelines given by your instructor or the publication you are submitting the review to. Generally, using the third person is more appropriate for academic writing sentences .
Should I include the abstract of the article in my review?
Yes, including a brief summary of the article’s abstract is usually a good idea.
How long should an article review be?
The length of an article review varies depending on the subject and the publication requirements. Generally, a review should be between 500 and 1000 words.
Writing an effective article review requires careful analysis, evaluation, and critique of the article. By following our step-by-step guide, you can develop the skills to write a comprehensive and insightful review that provides valuable information to readers. Whether you’re reviewing an academic article, book or manuscript , or any other subject, the tips and techniques outlined here will help you write an effective article review.
AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Viltrox AF 40mm F2.5 Z sample gallery
The Viltrox AF 40mm F2.5 Z is a full-frame lens for Nikon Z-mount cameras. The lightweight prime lens provides a normal field of view, roughly approximating the perspective of human vision.
We put the AF 40mm F2.5 on a Nikon Z7 and captured photos from rain-soaked Seattle to the sunny high desert of central Oregon, in a variety of lighting conditions. Check out our sample gallery to get a better idea of how this lens performs in the field.
View our Viltrox AF 40mm F2.5 Z sample gallery
Gear in this story

- Discuss in the forums
- See full product details
- View sample images
When you use DPReview links to buy products, the site may earn a commission.

If you choose this over the sure-bet Nikkor Z 40mm, good luck! Present and future compatibility issues may occur. https://www.dpreview.com/forums/post/67650141
If there are comparisons of images from this and Nikon's own 40/F2, then folks can decide for themselves if the extra $140 for Nikon's lens is worth spending.
I have their 16mm f1.8 which is epic for the price, and this new 40mm looks decent enough for its intended use, but what I'm really waiting for is the new Viltrox LAB series announcement and reviews to start to drop. Rumors said April, but today is going fast... so May-be-May? Hmmm...
I do like Viltrox lenses. They have a great value of perf/$.
You may also like
Latest sample galleries.

Latest in-depth reviews

The Panasonic Lumix S5II launched the second generation of Panasonic’s full-frame mirrorless camera system and was the first Panasonic to feature phase detect autofocus. As our review reveals, it’s a heck of an all-around camera for both still and video shooters.

The latest Lumix puts a Four Thirds sensor in a full-frame body with boosted AF and a wealth of stills and video capabilities to create a Swiss Army Knife of a Micro Four Thirds camera.

The fourth camera in Leica's SL series of full-frame mirrorless cameras sees the 60MP BSI sensor from the Q3 and M11 models arrive with a significant interface redesign.

The Fujifilm X100VI is the sixth iteration of Fujifilm's classically-styled large sensor compact. A 40MP X-Trans sensor, in-body stabilization and 6.2K video are among the updates.

The Nikon Zf is a 24MP full-frame mirrorless camera with classic looks that brings significant improvements to Nikon's mid-price cameras. We just shot a sample reel to get a better feel for its video features and have added our impressions to the review.
Latest buying guides

What’s the best camera for around $2000? This price point gives you access to some of the most all-round capable cameras available. Excellent image quality, powerful autofocus and great looking video are the least you can expect. We've picked the models that really stand out.

What's the best camera for travel? Good travel cameras should be small, versatile, and offer good image quality. In this buying guide we've rounded-up several great cameras for travel and recommended the best.

If you want a compact camera that produces great quality photos without the hassle of changing lenses, there are plenty of choices available for every budget. Read on to find out which portable enthusiast compacts are our favorites.

'What's the best mirrorless camera?' We're glad you asked.

Above $2500 cameras tend to become increasingly specialized, making it difficult to select a 'best' option. We case our eye over the options costing more than $2500 but less than $4000, to find the best all-rounder.

We paired the Viltrox AF 40mm F2.5 with a Nikon Z7 and took photos from rain-soaked Seattle to the high desert of central Oregon. Check out our sample gallery to see how this inexpensive lens performed.

Every week, we ask newsletter subscribers a question about gear, creativity or life. This week we looked back in time to ponder which classic cameras are overdue for a comeback.

Peakto Search, a new plug-in for Lightroom Classic on macOS, uses AI tech to index your photos so you can perform searches across one or more catalogs using descriptive text prompts or visual similarity to other images.

In part two of his photography tour of Madagascar, landscape photographer Erez Marom introduces us to the visually stunning Red Tsingy.

The small, lightweight prime lens features internal focusing and EXIF communication with Nikon Z-mount cameras. (Includes sample gallery.)

7Artisans has revealed a full-frame autofocus 50mm F1.8 lens for Nikon's Z mount. It will be available soon at a price of $228.

7Artisans has announced a $130 27mm F2.8 autofocus lens for Sony APS-C E-mount cameras.

For our twenty-fifth anniversary, we asked camera and lens makers what they believe to be the most significant products of the past quarter century.

40MP sensor shows lots of detail, with its lens delivering good levels of sharpness at our standard F5.6 test aperture.

mood.camera is a new iOS camera app that aims to emulate film photography by offering 14 'film stock' filters, but which, like film, only shows you the results after you take a photo. We found it to be surprisingly fun.

Sigma has announced it will be offering six of its DC DN APS-C lenses for Canon's RF mount, making it one of the first third-party manufacturers to sell RF lenses under license.

Tamron has announced it's developing a version of its 11-20mm F2.8 Di III-A RXD fast wide-angle zoom for Canon RF mount APS-C cameras.

Moment's T-series lenses are well-built, offering the look and feel of a premium product. But with high-end smartphone cameras getting so good, can they still up your photo game? We decided to find out.

Popular photo sharing service Photobucket recently revealed that the 13 billion images it hosts online could be used to train AI models. We explain what changes made this possible and suggest some cloud storage alternatives to keep your data private.

A few weeks ago in Japan, we had the opportunity to interview the team at Ricoh behind the new Pentax film camera that's expected to arrive later this year. Find out why the designers settled on a half-frame design that favors a vertical format, what inspired the optics, and the added complexity of including a manual film-winding mechanism.

TTArtisan has released a 56mm F1.8 autofocus lens for Sony and Fujifilm APS-C cameras, targeting portrait photographers looking for a budget third-party option.

We're almost a third of the way through the year already! Here's a recap of the reviews and testing we've done this year so far, with more (and more and more) to come as the year goes on!

Sign up for our free weekly newsletter and discover a world of DPReview beyond the website.

7Artisans has released a new 50mm F1.4 Tilt lens, available for Sony and Fujifilm APS-C cameras, as well as Panasonic and Olympus Micro Four Thirds cameras.

Fujifilm US's free-to-enter raffle is now open, offering the chance to purchase a Limited Edition X100VI.

Blackmagic Designs has announced the Pyxis, a $3000, 6K full-frame (36 x 24mm) modular video camera. It will be available with PL, locking Canon EF or Leica L mounts.

Who wouldn't want to use the IS mechanism they've paid for to squeeze a bit more resolution our of their camera? People like Richard Butler, who question the effort/reward balance they offer.

We took the Sony FE 16-25mm F2.8 G to the streets of Seattle. And then to the library when the rain robbed us of sunshine.

Sony has announced the FE 16-25mm F2.8 G, a compact, fast wide-angle lens designed to complement its recent 24-50mm F2.8.

The Blackmagic Ursa Cine 12K is available now, starting at $14,995.

"We have not made any significant progress since last year, " says Sigma owner and CEO Kazuto Yamaki, when asked about the planned full-frame Foveon camera. But he still believes in the project and discussed with us what such a camera could still offer.

The Legacy Survey of Space and Time camera recently completed by the US Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory risks making your camera setup seem inadequate.

In this first article of a new series, globetrotting landscape and nature photographer Erez Marom takes us to the island nation of Madagascar, sharing his experience photographing lemurs and chameleons.

With similar goals to its standalone Ninja monitors/recorders, the Phone Ninja connects a camera's HDMI out to a compatible iPhone for live view, recording, live streaming and file transfer.

The best of the best from the DPReview community, see our favorite photos you made from the North American eclipse.
- Gear Patrol
- Work for us
- Advertise with us
- Feedback / Contact us
- Camera reviews
- Lens reviews
- Printer reviews
- Buying guides
- Sample images
- Editorial enquiries
- Camera search
- Camera comparison
- Lens search
- Product timeline
- Browse all products
- Community Guidelines
- My Settings
- My GearList
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
5 Strategies for Improving Mental Health at Work
- Morra Aarons-Mele

Benefits and conversations around mental health evolved during the pandemic. Workplace cultures are starting to catch up.
Companies are investing in — and talking about — mental health more often these days. But employees aren’t reporting a corresponding rise in well-being. Why? The author, who wrote a book on mental health and work last year, explores several key ways organizations haven’t gone far enough in implementing a culture of well-being. She also makes five key suggestions on what they can do to improve the mental health of their employees.
“I have never felt so seen.”
- Morra Aarons-Mele is a workplace mental health consultant and author of The Anxious Achiever: Turn Your Biggest Fears Into Your Leadership Superpower (Harvard Business Review Press, 2023). She has written for The New York Times, The Wall Street Journal, O the Oprah Magazine, TED, among others, and is the host of the Anxious Achiever podcast from LinkedIn Presents. morraam
Partner Center
Trending News
Related Practices & Jurisdictions
- ADR / Arbitration / Mediation
- Corporate & Business Organizations
- Litigation / Trial Practice

A recent unpublished California Court of Appeal decision, Hegemier v. A Better Life Recovery LLC, Cal. Ct. App., 4th Dist., No. G061892 , demonstrates the potential consequence of drafting an arbitration agreement without foreseeing every way a future plaintiff might attempt to pick it apart.
Almost two years ago , in Viking River Cruises, Inc. v. Moriana , 596 U.S. 639 (2022),the United States Supreme Court held that the Federal Arbitration Act preempts the rule from Iskanian v. CLS Transp. Los Angeles, LLC , 59 Cal. 4th 348 (2014) that Private Attorneys General Act (PAGA) actions could not be divided into individual and representative claims brought on behalf of other allegedly “aggrieved employees.” This decision paved the way for employers to enforce agreements requiring individual arbitration even in the context of a PAGA action, by compelling the “individual” component of the PAGA claim to arbitration. (Under California Supreme Court precedent , the “non-individual” component remains in court, where it is generally stayed until arbitration concludes.)
In attempting to follow this now-familiar playbook, the employer in Hegemier hit a snag. The arbitration agreement contained a provision exempting from arbitration “claims that are not subject to arbitration under current law.” The trial court interpreted this to mean that PAGA claims categorically were excluded from the agreement, because at the time the agreement was signed, Viking River had not yet been decided, and Iskanian would have precluded arbitration of the PAGA claims.
The Court of Appeal agreed. Without further clarifying language such as “under current law, as it may be interpreted in the future,” the court interpreted the reference to “current law” to mean “a fixed ‘snapshot’ of claims that were deemed not arbitrable at the time the agreement was signed.” Slip op. at 11. Therefore, “among the types of claims the alleged agreement exempts from binding arbitration is that which Iskanian declared an employee could not be compelled to arbitrate based on a predispute agreement — both the individual and non-individual components of a PAGA claim.” Id. at 2.
The Hegemier court acknowledged other Court of Appeal decisions reversed orders denying arbitration of individual PAGA claims based on pre- Viking River arbitration agreements (for example, as we reported here ). However, it distinguished those cases based on the “unambiguous language” limiting the scope of the agreement to arbitrable claims under “current law.” Id. at 12.
Hegemier ’s interpretation of “current law” is certainly open to criticism. Ordinarily, we consider the task of a court interpreting statutory law as explaining what the law meant all along, rather than creating new law. Indeed, the Viking River decision concludes that Iskanian ’s prohibition against arbitration of the individual component of a PAGA claim was wrong the day it was decided. Viking River , 596 U.S. at 662 (holding this rule “is incompatible with the [Federal Arbitration Act]”).
Ironically, while the exclusion of claims not arbitrable under “current law” in Hegemier was meant to ensure the arbitration agreement was enforced to the fullest extent, it was turned against the employer and ultimately excluded claims from arbitration that otherwise would have been arbitrable. As we have reported ( here and here ), Hegemier was hardly the first case to do so. Rather, it is the latest sober reminder that reminder that class and representative action plaintiffs will often seize on any plausible argument to avoid an arbitration agreement, and will sometimes find a receptive audience.
Current Legal Analysis
More from proskauer rose llp, upcoming legal education events.

Sign Up for e-NewsBulletins

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Take action
- Report an antitrust violation
- File adjudicative documents
- Find banned debt collectors
- View competition guidance
- Competition Matters Blog
New HSR thresholds and filing fees for 2024
View all Competition Matters Blog posts
We work to advance government policies that protect consumers and promote competition.
View Policy
Search or browse the Legal Library
Find legal resources and guidance to understand your business responsibilities and comply with the law.
Browse legal resources
- Find policy statements
- Submit a public comment

Vision and Priorities
Memo from Chair Lina M. Khan to commission staff and commissioners regarding the vision and priorities for the FTC.
Technology Blog
Consumer facing applications: a quote book from the tech summit on ai.
View all Technology Blog posts
Advice and Guidance
Learn more about your rights as a consumer and how to spot and avoid scams. Find the resources you need to understand how consumer protection law impacts your business.
- Report fraud
- Report identity theft
- Register for Do Not Call
- Sign up for consumer alerts
- Get Business Blog updates
- Get your free credit report
- Find refund cases
- Order bulk publications
- Consumer Advice
- Shopping and Donating
- Credit, Loans, and Debt
- Jobs and Making Money
- Unwanted Calls, Emails, and Texts
- Identity Theft and Online Security
- Business Guidance
- Advertising and Marketing
- Credit and Finance
- Privacy and Security
- By Industry
- For Small Businesses
- Browse Business Guidance Resources
- Business Blog
Servicemembers: Your tool for financial readiness
Visit militaryconsumer.gov
Get consumer protection basics, plain and simple
Visit consumer.gov
Learn how the FTC protects free enterprise and consumers
Visit Competition Counts
Looking for competition guidance?
- Competition Guidance
News and Events
Latest news, ftc expands patent listing challenges, targeting more than 300 junk listings for diabetes, weight loss, asthma and copd drugs.
View News and Events
Upcoming Event
Older adults and fraud: what you need to know.
View more Events
Sign up for the latest news
Follow us on social media
--> --> --> --> -->

Playing it Safe: Explore the FTC's Top Video Game Cases
Learn about the FTC's notable video game cases and what our agency is doing to keep the public safe.
Latest Data Visualization
FTC Refunds to Consumers
Explore refund statistics including where refunds were sent and the dollar amounts refunded with this visualization.
About the FTC
Our mission is protecting the public from deceptive or unfair business practices and from unfair methods of competition through law enforcement, advocacy, research, and education.
Learn more about the FTC

Meet the Chair
Lina M. Khan was sworn in as Chair of the Federal Trade Commission on June 15, 2021.
Chair Lina M. Khan
Looking for legal documents or records? Search the Legal Library instead.
- Cases and Proceedings
- Premerger Notification Program
- Merger Review
- Anticompetitive Practices
- Competition and Consumer Protection Guidance Documents
- Warning Letters
- Consumer Sentinel Network
- Criminal Liaison Unit
- FTC Refund Programs
- Notices of Penalty Offenses
- Advocacy and Research
- Advisory Opinions
- Cooperation Agreements
- Federal Register Notices
- Public Comments
- Policy Statements
- International
- Office of Technology Blog
- Military Consumer
- Consumer.gov
- Bulk Publications
- Data and Visualizations
- Stay Connected
- Commissioners and Staff
- Bureaus and Offices
- Budget and Strategy
- Office of Inspector General
- Careers at the FTC
Fact Sheet on FTC’s Proposed Final Noncompete Rule
- Competition
- Office of Policy Planning
- Bureau of Competition
The following outline provides a high-level overview of the FTC’s proposed final rule :
- Specifically, the final rule provides that it is an unfair method of competition—and therefore a violation of Section 5 of the FTC Act—for employers to enter into noncompetes with workers after the effective date.
- Fewer than 1% of workers are estimated to be senior executives under the final rule.
- Specifically, the final rule defines the term “senior executive” to refer to workers earning more than $151,164 annually who are in a “policy-making position.”
- Reduced health care costs: $74-$194 billion in reduced spending on physician services over the next decade.
- New business formation: 2.7% increase in the rate of new firm formation, resulting in over 8,500 additional new businesses created each year.
- This reflects an estimated increase of about 3,000 to 5,000 new patents in the first year noncompetes are banned, rising to about 30,000-53,000 in the tenth year.
- This represents an estimated increase of 11-19% annually over a ten-year period.
- The average worker’s earnings will rise an estimated extra $524 per year.
The Federal Trade Commission develops policy initiatives on issues that affect competition, consumers, and the U.S. economy. The FTC will never demand money, make threats, tell you to transfer money, or promise you a prize. Follow the FTC on social media , read consumer alerts and the business blog , and sign up to get the latest FTC news and alerts .
Press Release Reference
Contact information, media contact.
Victoria Graham Office of Public Affairs 415-848-5121
Independent review panel releases final report on UNRWA

Facebook Twitter Print Email
An independent panel released its much-awaited report on Monday about the UN relief agency for Palestine refugees (UNRWA), providing 50 recommendations and noting that Israeli authorities have yet to provide proof of their claims that UN staff are involved with terrorist organisations.
“Israel made public claims that a significant number of UNRWA employees are members of terrorist organisations. However, Israel has yet to provide supporting evidence of this,” according to the 54-page final report , Independent review of mechanisms and procedures to ensure adherence by UNRWA to the humanitarian principle of neutrality .
The UN Secretary-General, who received the final report at the weekend, had appointed the independent review group days after Israel announced the allegations against UNRWA, which employees 30,000 people and serves 5.9 million Palestine refugees in the West Bank, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria and war-torn Gaza.
The much-awaited final report found that UNRWA, established by the General Assembly in 1949, has extensive tools in place to ensure it remains unbiased in its work and routinely provides Israel with employee lists and “ the Israeli Government has not informed UNRWA of any concerns relating to any UNRWA staff based on these staff lists since 2011.”
UNRWA has ‘most elaborate’ rules within UN system
“The set of rules and the mechanisms and procedures in place [at UNRWA] are the most elaborate within the UN system, precisely because it is such a difficult issue to work in such a complex and sensitive environment,” Catherine Colonna, former French foreign minister and head of the review group, told journalists at UN Headquarters following the report’s launch. “What needs to be improved will be improved. I’m confident that implementing these measures will help UNRWA deliver on its mandate .”
Strongly encouraging "the international community to work side by side with the agency so it can perform its mission and overcome the challenges when they are there", she said “this is the purpose of the review.”
In its nine-week-long review of existing mechanisms, the group conducted more than 200 interviews, met with Israeli and Palestinian authorities and directly contacted 47 countries and organisations, presenting a set of 50 recommendations on issues ranging from education to fresh vetting processes for recruiting staff.

Report steers new UN action plan
The report’s recommendations include creating a centralised “neutrality investigations unit”, rolling out an updated Code of Ethics and associated training to all staff, and identifying and implementing additional ways to screen UNRWA applicants at an early stage of the recruitment process.
The report also suggested exploring the possibility of third-party monitoring for sensitive projects and establishing a framework with interested donors to ensure transparency.
In a statement on Monday, the UN Secretary-General’s Spokesperson said the UN chief accepts the recommendations contained in Ms. Colonna’s report. He has agreed with Commissioner General Philippe Lazzarini that UNRWA, with the Secretary-General’s support, will establish an action plan to implement the recommendations contained in the final report.”
Claims financially hobbled UNRWA
According to the review group’s final report, Israel’s claims against UNRWA triggered the suspension of funding amounting to around $450 million.
The direct impact of Israel’s allegations swiftly hobbled UNRWA’s ability to continue its work. Operating solely on voluntary donations, UNRWA saw major donors, including the United States, cancelling or suspending funds for the agency.
In April, Washington banned funding for UNRWA until at least 2025, but other donors have pledged additional funding or restored their donations.
The new report recommended increasing the frequency and strengthening the transparency of UNRWA’s communication with donors on its financial situation and on neutrality allegations and breaches. The review group suggested regular updates and “integrity briefings” for donors interested in supporting UNRWA on integrity and related issues.
Findings on UNRWA schools
The UN agency delivers on its obligation to ensure neutrality of its 1,000 installations, including schools, healthcare centres and warehouses, according to the report, which also stated that “security and capacity challenges may hamper” existing due diligence mechanisms.
The review group said UNRWA “has consistently worked on ensuring neutrality in education” as it provides elementary and preparatory education for 500,000 pupils in 706 schools with 20,000 educational staff, including in Gaza, where right now all children are out of school following attacks destroying the enclave’s education system amid the ongoing conflict.

Claims of anti-Semitic textbooks
Investigating “sustained criticism, mainly from Israel”, about the alleged presence of hate speech, incitement to violence and anti-Semitism in Palestinian Authority educational material, the review group examined three major international assessments and studies.
The new report showed that two identified bias and non-compliant content, but did not provide evidence of anti-Semitic reference . A third, the Eckert report, identified two examples that displayed anti-Semitic content, but noted that one had already been removed and the other significantly altered.
As such, the report recommended several actions, including the review of the content of all textbooks with host countries, Israel and the Palestinian Authority .
UNRWA remains a pivotal ‘lifeline’ for Palestine
The report stated that “in the absence of a political solution between Israel and the Palestinians, UNRWA remains pivotal in providing lifesaving humanitarian aid and essential social services, particularly in health and education, to Palestinian refugees in Gaza, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria and the West Bank” and is “irreplaceable and indispensable to Palestinians’ human and economic development”.
“In addition, many view UNRWA as a humanitarian lifeline ,” according to the report.
The UN chief on Monday said he counted on the cooperation of the donor community, the host countries and the staff to fully cooperate in the implementation of the new report’s final recommendations, the UN Spokesperson said.
“Moving forward, the Secretary-General appeals to all stakeholders to actively support UNRWA, as it is a lifeline for Palestine refugees in the region,” he said.
Other top UN officials have voiced strong support for the agency, calling on donors to reverse funding cuts and allow UNRWA to perform its work, especially in Gaza.
In late March, Israel announced it would reject UNRWA’s requests to deliver aid into northern Gaza, where a famine is unfolding as Israeli authorities continue to block or severely delay lifesaving aid shipments , according to UN officials, who launched an appeal last week for emergency funding.

Lazzarini: Report will further strengthen UNRWA
UNRWA chief Lazzarini welcomed the report’s findings and recommendations.
“ UNRWA is developing an action plan , with a timeline and budget to take forward the report’s recommendations,” he said in a statement on Monday.
He said implementing some of the recommendations will require extensive engagement with staff and partners, including Member States, host nations and donor countries, adding that the UN agency looks forward to cooperating with all concerned stakeholders to implement the recommendations.
“UNRWA is firmly dedicated to applying UN values and humanitarian principles,” he said. “The recommendations in this report will further strengthen our efforts and response during one of the most difficult moments in the history of the Palestinian people.”
First of two investigations
Following Israel’s allegations against UNRWA in late January, the UN agency immediately fired the staff members in question and requested a swift, impartial investigation. The UN chief ordered two.
Days later, the Secretary-General appointed an independent review team , led by Ms. Colonna and researched by Raoul Wallenberg Institute in Sweden, the Michelsen Institute in Norway and the Danish Institute for Human Rights, to investigate the UNRWA’s process of ensuring neutrality in its work.
At the same time, the UN chief ordered the UN’s top watchdog, the Office of Internal Oversight (OIOS), to investigate the veracity of Israel’s claims against the 12 UNRWA staff members.
At the outset , OIOS investigators reached out to Member States concerned, visited UNRWA headquarters in Jordan and reviewed initial information received by the agency from Israeli authorities and from a variety of sources, including that released through the media and other public outlets.
That investigation is ongoing.
- Data, AI, & Machine Learning
- Managing Technology
- Social Responsibility
- Workplace, Teams, & Culture
- AI & Machine Learning
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Big ideas Research Projects
- Artificial Intelligence and Business Strategy
- Responsible AI
- Future of the Workforce
- Future of Leadership
- All Research Projects
- AI in Action
- Most Popular
- The Truth Behind the Nursing Crisis
- Work/23: The Big Shift
- Coaching for the Future-Forward Leader
- Measuring Culture

The spring 2024 issue’s special report looks at how to take advantage of market opportunities in the digital space, and provides advice on building culture and friendships at work; maximizing the benefits of LLMs, corporate venture capital initiatives, and innovation contests; and scaling automation and digital health platform.
- Past Issues
- Upcoming Events
- Video Archive
- Me, Myself, and AI
- Three Big Points

The Anomalies of Disruption
Innovative examples from Apple, Uber, and Tesla show the importance of expanding views, getting granular, and using multiple models.

Paolo Beghini/Ikon Images
On his office door, Clayton Christensen — who at one point I called my teacher, mentor, boss, colleague, coauthor, and, most importantly, friend — had a handcrafted sign saying, “Anomalies Wanted.” Like a good scientist, Christensen believed that the things you didn’t expect provided the richest sources of learning. And indeed, many big changes after 2000 that just feel disruptive don’t quite fit Christensen’s theory of disruptive innovation model.
Lessons from these anomalies — the iPhone, Uber, and Tesla — strengthen our ability to predict the impact of in-process innovations like additive manufacturing and artificial intelligence by showing the importance of expanding our view, getting granular in our analysis, and using multiple models to analyze complex change.
Get Updates on Innovative Strategy
The latest insights on strategy and execution in the workplace, delivered to your inbox once a month.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up
Privacy Policy
Recall the basic idea of disruption, summarized in Christensen’s 1997 blockbuster book The Innovator’s Dilemma : Incumbents generally win when the game is about sustaining innovations that improve along known performance dimensions and lose to upstarts when the game is about disruptive innovations that intentionally trade off performance along traditional dimensions in the name of simplicity, convenience, or affordability.
The driver of disruption is the resource allocation process inside companies. That diffuse, difficult-to-manage process naturally prioritizes innovations that appeal to a company’s best customers. Those customers initially dismiss disruptions because of their limitations, so disruptive innovators take root with customers at the fringes of the market who relish their simplicity and affordability. Since companies innovate faster than people’s lives change, that which is initially not good enough for mainstream customers gets better and better until the disrupter combines good-enough performance with better simplicity and affordability. The market leader, which did everything you are supposed to do, fails in the face of disruptive change.
Anomaly 1: The iPhone
Here’s what Christensen had to say about the iPhone when it launched: “The iPhone is a sustaining technology relative to Nokia. In other words, Apple is leaping ahead on the sustaining curve [by building a better phone]. But the prediction of the theory would be that Apple won’t succeed with the iPhone. They’ve launched an innovation that the existing players in the industry are heavily motivated to beat: It’s not [truly] disruptive. History speaks pretty loudly on that, that the probability of success is going to be limited.”
Christensen would later recant. Why? He said he compared the iPhone to other phones, where he really should have been comparing it to laptop computers. And when you make that comparison, the disruptive nature of the iPhone comes into focus.
The early iPhone certainly had its limitations. Its battery didn’t last long. Typing wasn’t easy. There were only a handful of applications. It had new advantages, such as a cutting-edge internet browser and the kind of radical simplicity that had been Apple’s hallmark for decades. In classic disruptive fashion, the iPhone brought computing to new contexts, where people were delighted with a somewhat limited product.
Also, the iPhone wasn’t just a product play by Apple, it was an ecosystem play. Ron Adner from the Tuck School of Business at Dartmouth College has deeply studied ecosystems in his books The Wide Lens and Winning the Right Game . His research shows how innovation success requires smartly thinking about how to work with suppliers, channels to market, complementary industries, and more. That’s one reason, he argues, that Amazon’s e-reading platform Kindle crushed Sony’s e-reader. Even though Sony’s reader was technologically more sophisticated, Amazon made it incredibly easy to obtain content, making its device significantly more usable.
In classic disruptive fashion, the iPhone brought computing to new contexts, where people were delighted with a somewhat limited product.
Similarly, the full power of Apple’s disruption only became apparent about a year after the iPhone launched. While the elegance of its design captivated reviewers and early adopters, early sales weren’t that great. The browser was cool, but slow networks limited its functionality, and Apple did not allow third-party developers to create applications for the iPhone. Why would it need to? “What’s the killer app?” Steve Jobs said at the iPhone’s launch in January 2007. “The killer app is making calls. It’s amazing how hard it is to make calls on most phones.”
If you were Nokia, Research in Motion, Motorola, Palm, Handspring, or Ericsson, maybe you took solace in the iPhone’s slow start. By the end of 2007, however, Jobs changed course, and it shouldn’t have really been a surprise. When Apple’s iPod music player first came out, it was limited because it seamlessly worked only with Apple’s Mac computers. Then, when Apple ported iTunes to Windows-based computers, the product took off. Jobs had demonstrated that he was willing to be … flexibly controlling.
This time, Jobs announced that Apple would have a software development kit for third-party apps within four months. And the rest is history. In 2023, the App Store generated close to $100 billion in revenues for Apple. By way of comparison, The Coca-Cola Co. earns approximately $50 billion a year in revenue. Think about that the next time you start playing a silly game on your phone.
The anomaly of the iPhone teaches us to expand our view in three ways. First, think carefully about the comparison set. What job does a customer hire an innovation to get done? What else could it hire to get that job done? Second, zoom out to look at the broader ecosystem. Does the innovation change industry dynamics in a broader way? Finally, don’t just look at the snapshot of an innovation at a given time; watch the full movie and be flexible as a company’s full strategy comes into full focus.
Anomaly 2: Uber
Analyzing innovation has gotten harder as the world has gotten more complicated.
The iPhone was a combination of many innovations. When it launched, you could focus on its multi-touch interface, how it ported the Macintosh operating system onto a handheld device, the uniqueness of its web browser, the power of its camera, the Gorilla Glass screen, its unique partnership with Google, and on and on and on. It’s increasingly hard to say a company is or isn’t following a disruptive path, because a company’s product or service combines so many different facets.
Take one of the weirdest podcasts I have ever been on as part of a panel of disruptive experts. It was the 15th episode of The Disruptive Voice , created by the Forum for Growth and Innovation, a group at Harvard Business School that helped to augment Christensen’s research. Titled “Is Uber Disruptive?” it was 36 minutes long.
That’s a long time to answer what seems self-evident, as saying that Uber was categorically not disruptive would seem to require significant logical and theoretical contortions. Yet, parts of Uber seemed anomalous. In a December 2015 Harvard Business Review article, Christensen and coauthors Rory McDonald and Michael Raynor wrote, “The theory of disruption predicts that when an entrant takes the incumbent competitors head-on, offering better products or services, the incumbents will accelerate their innovations to defend their business.”
Evaluating Uber requires a multidimensional analysis. Is the customer the person seeking to get from point A to point B? Or is it the driver, who wants to get compensated for getting the person from point A to point B? And how do you think about the difference between Uber, UberX, UberX Share, Uber Black, Uber Eats, and so on? And how does the reality that the taxicab industry is fragmented and generally horrifically run factor in?
Taking Uber apart and looking at each of these components leads to the clear conclusion that some pieces of it squarely fit the original disruptive model, and some pieces don’t. While the “incumbents” would increase their investment to defend their position, fragmented local competitors couldn’t compete against a global company with significant venture capital backing.
The lesson? Get granular. Pick an innovation apart. Consider how it creates, captures, and delivers value. Look at the competitive set. Are there factors that could inhibit or enhance your ability to respond to new competition?
Anomaly 3: Tesla
Disruption purists look at Tesla with skepticism. Disruption starts with simple solutions at the low end of the market, or in new contexts. Tesla started with a premium-priced sophisticated solution. Yet, it seems to have played out in a disruptive way with market leaders struggling to respond.
Tesla highlights the importance of avoiding overreliance on a single, relatively simple model, as tempting as it might be. The real world is a complicated place. A powerful model or framework is useful, but it is always important to remember that the world of business is not Newtonian physics. Stuff happens. Tesla, for example, got hundreds of millions of dollars from the U.S. government in 2010, when it was still a young company (it repaid the loan in 2013). And then governments around the world gave ample tax credits to people who bought electric vehicles. A single model struggles to make sense of the real world’s complexity.
I recommend using a combination of models to make the best predictions possible, be clear about assumptions, and identify what you would see that indicates your prediction was wrong. And, critically, be happy with being wrong.
Tesla highlights the importance of avoiding overreliance on a single, relatively simple model, as tempting as it might be.
There are undoubtedly some disruptive elements to Tesla. Its cars offer new benefits, of course, but drivers have to wait for it to charge and suffer from the dreaded range anxiety. A range of models beyond disruption help to explain why incumbent car manufacturers have struggled to respond. Beyond Adner’s ecosystem frame, a seminal 1990 paper by Rebecca Henderson and Kim Clark (which influenced Christensen’s research) demonstrated that market leaders struggled with “architectural” innovations that changed the way they interacted internally, even if the technology was trivial. 1 Electrification certainly has architectural components, helping to explain the challenges of incumbent response.
Another useful lens comes from the systems psychodynamics world. The research of scholars such as Gianpiero Petriglieri and Susan Long shows that groups create powerful defense mechanisms when they feel threatened. 2 Moving from a mechanical engineering mindset to a software mindset is exactly the kind of threat that triggers those defense mechanisms. Even if top leaders make big resource allocation decisions, those defense mechanisms make change incredibly challenging.
A good strategist has multiple arrows in their quiver. To augment my own understanding of disruptive change, I try to keep up with relevant literature in a range of fields, most notably strategy, innovation, leadership, organizational behavior, systems psychodynamics, and behavioral psychology. Each of those lenses provides unique insight into a rich, complex challenge.
Apple, Uber, and Tesla all led to results that matched those of disruptions detailed in The Innovator’s Dilemma , but didn’t quite fit Christensen’s original model. That’s OK. The anomalies have taught us to carefully consider the comparison set, evaluate the ecosystem, unpack an innovation, and use alternative frameworks. Anomalies wanted, indeed.
About the Author
Scott D. Anthony (@scottdanthony) is a clinical professor at the Tuck School of Business at Dartmouth College and a senior adviser and managing partner emeritus at growth strategy consultancy Innosight. He is a coauthor of Eat, Sleep, Innovate (Harvard Business Review Press, 2020).
1. R.M. Henderson and K.B. Clark, “ Architectural Innovation: The Reconfiguration of Existing Product Technologies and the Failure of Established Firms ,” Administrative Science Quarterly, 35, no. (1) (1990): 9-30.
2. G. Petriglieri and J.L. Petriglieri, “ The Return of the Oppressed: A Systems Psychodynamic Approach to Organization Studies ,” Academy of Management Annals 14, no. (1) (2020): 411-449.
More Like This
Add a comment cancel reply.
You must sign in to post a comment. First time here? Sign up for a free account : Comment on articles and get access to many more articles.
- Create an email message
- Suggested recipients
- Use @mentions
- Create a signature
- Add attachments
- Check spelling
- Add a reaction
- Out of office replies
- Delay or schedule
- Recall a message
- Automatic forwarding
- Read receipt
- Save a file or draft
- Change display name
- Create a folder
- Use inbox rules
- Conditional formatting
- Use Favorites
- Custom views
- Message font size
- Message list view
- Focused Inbox
- View as conversations
- Filter and sort messages
- Number of messages
- Chat with recipients
- Share an email
- Status in Outlook
- Phishing and suspicious behavior
- Blocked senders
- Protected messages
- Open a protected message
- More to explore

Create and add an email signature in Outlook
In Outlook, you can create one or more personalized signatures for your email messages. Your signature can include text, links, pictures, and images (such as your handwritten signature or a logo).
Note: If the steps under this New Outlook tab don't work, you may not be using new Outlook for Windows yet. Select Classic Outlook and follow those steps instead.
Create and add an email signature
On the View tab, select View Settings .
Select Accounts > Signatures .
Select New signature , then give it a distinct name.
In the editing box below the new name, type your signature, then format it with the font, color, and styles to get the appearance you want.
Select Save when you're done.
With your new signature selected from the list above the editing box, go to Select default signatures and choose whether to apply the signature to new messages and to replies and forwards.
Select Save again.
Note: If you have a Microsoft account, and you use Outlook and Outlook on the web or Outlook on the web for business, you need to create a signature in both products.
Create your signature and choose when Outlook adds a signature to your messages
If you want to watch how it's done, you can go directly to the video below .
Open a new email message.

Under Select signature to edit , choose New , and in the New Signature dialog box, type a name for the signature.
Under Edit signature , compose your signature. You can change fonts, font colors, and sizes, as well as text alignment. If you want to create a more robust signature with bullets, tables, or borders, use Word to create and format your signature text, then copy and paste it into the Edit signature box. You can also use a pre-designed template to create your signature. Download the templates in Word, customize with your personal information, and then copy and paste into the Edit signature box.
You can add links and images to your email signature, change fonts and colors, and justify the text using the mini formatting bar under Edit signature .
You can also add social media icons and links in your signature or customize one of our pre-designed temlates. For more information, see Create a signature from a template .
To add images to your signature, see Add a logo or image to your signature .
Under Choose default signature , set the following options.
In the E-mail account drop-down box, choose an email account to associate with the signature. You can have different signatures for each email account.
You can have a signature automatically added to all new messages. Go to in the New messages drop-down box and select one of your signatures. If you don't want to automatically add a signature to new messages, choose (none). This option does not add a signature to any messages you reply to or forward.
You can select to have your signature automatically appear in reply and forward messages. In the Replies/forwards drop-down, select one of your signatures. Otherwise, accept the default option of (none).
Choose OK to save your new signature and return to your message. Outlook doesn't add your new signature to the message you opened in Step 1, even if you chose to apply the signature to all new messages. You'll have to add the signature manually to this one message. All future messages will have the signature added automatically. To add the signature manually, select Signature from the Message menu and then pick the signature you just created.
Add a logo or image to your signature
If you have a company logo or an image to add to your signature, use the following steps.
Open a new message and then select Signature > Signatures .
In the Select signature to edit box, choose the signature you want to add a logo or image to.

To resize your image, right-click the image, then choose Picture . Select the Size tab and use the options to resize your image. To keep the image proportions, make sure to keep the Lock aspect ratio checkbox checked.
When you're done, select OK , then select OK again to save the changes to your signature.
Insert a signature manually
If you don't choose to insert a signature for all new messages or replies and forwards, you can still insert a signature manually.
In your email message, on the Message tab, select Signature .
Choose your signature from the fly-out menu that appears. If you have more than one signature, you can select any of the signatures you've created.
See how it's done

Top of page
Note: Outlook on the web is the web version of Outlook for business users with a work or school account.
Automatically add a signature to a message
You can create an email signature that you can add automatically to all outgoing messages or add manually to specific ones.
Select Settings at the top of the page.
Select Mail > Compose and reply .
Under Email signature , type your signature and use the available formatting options to change its appearance.
Select the default signature for new messages and replies.
Manually add your signature to a new message
If you've created a signature but didn't choose to automatically add it to all outgoing messages, you can add it later when you write an email message.
In a new message or reply, type your message.

If you created multiple signatures, choose the signature you want to use for your new message or reply.
When your email message is ready, choose Send .
Note: Outlook.com is the web version of Outlook for users signing in with a personal Microsoft account such as an Outlook.com or Hotmail.com account.
Related articles
Create and add an email signature in Outlook for Mac
Create an email signature from a template

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Find solutions to common problems or get help from a support agent.

Online support
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Start your review by referring to the title and author of the article, the title of the journal, and the year of publication in the first paragraph. For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest. 4. Write the introduction.
2. Read the article thoroughly: Carefully read the article multiple times to get a complete understanding of its content, arguments, and conclusions. As you read, take notes on key points, supporting evidence, and any areas that require further exploration or clarification. 3. Summarize the main ideas: In your review's introduction, briefly ...
Step 1: Define the right organization for your review. Knowing the future setup of your paper will help you define how you should read the article. Here are the steps to follow: Summarize the article — seek out the main points, ideas, claims, and general information presented in the article.
Article Review vs. Response Paper . Now, let's consider the difference between an article review and a response paper: If you're assigned to critique a scholarly article, you will need to compose an article review.; If your subject of analysis is a popular article, you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper.; The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of ...
An article review is a critique or assessment of another's work, typically written by experts in the field. It involves summarizing the writer's piece, evaluating its main points, and providing an analysis of the content. A review article isn't just a simple summary; it's a critical assessment that reflects your understanding and ...
Step 2: Read the Article Thoroughly. Begin by thoroughly reading the article. Take notes on key points, arguments, and evidence presented by the author. Understand the author's main thesis and the context in which the article was written.
Here is a basic, detailed outline for an article review you should be aware of as a pre-writing process if you are wondering how to write an article review. Introduction. Introduce the article that you are reviewing (author name, publication date, title, etc.) Now provide an overview of the article's main topic.
For many kinds of assignments, like a literature review, you may be asked to offer a critique or review of a journal article.This is an opportunity for you as a scholar to offer your qualified opinion and evaluation of how another scholar has composed their article, argument, and research.That means you will be expected to go beyond a simple summary of the article and evaluate it on a deeper ...
Article review format. The formatting of an article review will always come down to what type of assignment you plan to write and your citation style. Still, you should provide a title page, the course title, your name, and the work date. In certain cases, it may be required to include an abstract of 200 to 300 words.
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
For an article review, your task is to identify, summarize, and evaluate the ideas and information the author has presented. You are being asked to make judgments, positive or negative, about the content of the article. The criteria you follow to do this will vary based upon your particular academic discipline and the parameters of your ...
A journal article review is written for a reader who is knowledgeable in the discipline and is interested not just in the coverage and content of the article being reviewed, but also in your critical assessment of the ideas and argument that are being presented by the author. Your review might be guided by the following questions:
A reader will obtain a copy of the article if more information is needed. Write the literature review in the past tense; the research has already been completed. The article cannot "do", "find", or "say" anything. The authors are the people who conducted the study. The above format is a guideline.
Ev en better you might. consider doing an argument map (see Chapter 9, Critical thinking). Step 5: Put the article aside and think about what you have read. Good critical review. writing requires ...
Here, I provide tips on planning and writing a review article, with examples of well-crafted review articles published in The FEBS Journal. ... Most review articles are between 4000 and 6000 words in length and as a rule of thumb, 80-90% of the text should be within the main section/devoted to the core topic—make sure that your outline ...
Actions to Take. 1. Skim the article without taking notes: Read the abstract. The abstract will tell you the major findings of the article and why they matter. Read first for the "big picture.". Note any terms or techniques you need to define. Jot down any questions or parts you don't understand.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
2. Benefits of Review Articles to the Author. Analysing literature gives an overview of the "WHs": WHat has been reported in a particular field or topic, WHo the key writers are, WHat are the prevailing theories and hypotheses, WHat questions are being asked (and answered), and WHat methods and methodologies are appropriate and useful [].For new or aspiring researchers in a particular ...
Review articles are divided into 2 categories as narrative, and systematic reviews. Narrative reviews are written in an easily readable format, and allow consideration of the subject matter within a large spectrum. ... The second problem is that, most of the researches have been performed with small sample sizes. In statistical methods in meta ...
- What are the article's shortcomings and limitations? - Are all important aspects and issues of its domain covered? - Examine and comment the logic given in the article Suggested Format of an article review uous information. Illustrative Example for article review Article Reviewed: Matthias, M., Sascha, V., & Jonathan, L. (2014).
An article review is a critical assessment of a scholarly article or research paper. It involves analyzing the content, methodology, and findings of the article and providing an evaluation of its strengths and weaknesses. The review typically includes a summary of the article's main points, an evaluation of its contribution to the subject ...
A review article can also be called a literature review, or a review of literature. It is a survey of previously published research on a topic. It should give an overview of current thinking on the topic. And, unlike an original research article, it will not present new experimental results. Writing a review of literature is to provide a ...
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels ...
We put the AF 40mm F2.5 on a Nikon Z7 and captured photos from rain-soaked Seattle to the sunny high desert of central Oregon, in a variety of lighting conditions. Check out our sample gallery to get a better idea of how this lens performs in the field. View our Viltrox AF 40mm F2.5 Z sample gallery
Morra Aarons-Mele is a workplace mental health consultant and author of The Anxious Achiever: Turn Your Biggest Fears Into Your Leadership Superpower (Harvard Business Review Press, 2023). She has ...
The National Law Review - National Law Forum LLC 3 Grant Square #141 Hinsdale, IL 60521 Telephone (708) 357-3317 or toll free (877) 357-3317. If you would ike to contact us via email please click ...
The following outline provides a high-level overview of the FTC's proposed final rule:. The final rule bans new noncompetes with all workers, including senior executives after the effective date.
"Israel made public claims that a significant number of UNRWA employees are members of terrorist organisations. However, Israel has yet to provide supporting evidence of this," according to the 54-page final report, Independent review of mechanisms and procedures to ensure adherence by UNRWA to the humanitarian principle of neutrality.. The UN Secretary-General, who received the final ...
In a December 2015 Harvard Business Review article, Christensen and coauthors Rory McDonald and Michael Raynor wrote, "The theory of disruption predicts that when an entrant takes the incumbent competitors head-on, offering better products or services, the incumbents will accelerate their innovations to defend their business."
Under Choose default signature, set the following options.. In the E-mail account drop-down box, choose an email account to associate with the signature. You can have different signatures for each email account. You can have a signature automatically added to all new messages. Go to in the New messages drop-down box and select one of your signatures. If you don't want to automatically add a ...