Music Research Paper

This sample music research paper features: 6800 words (approx. 22 pages), an outline, and a bibliography with 49 sources. Browse other research paper examples for more inspiration. If you need a thorough research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A! Feel free to contact our writing service for professional assistance. We offer high-quality assignments for reasonable rates.

Introduction
The meaning of music and dance, performance, sacred performance, chant and recitation, instruments, critical musicology, globalization, gender and sexuality, race and ethnicity, nationalism, medical ethnomusicology, applied ethnomusicology.
- Bibliography
Ethnographic approaches to music and dance in the 21st century explore how modes of expression and performance practices are involved in the making of lifeworlds. Cultural production is situated in specific contexts that generate meaning as particular sonic and kinesthetic phenomena relate to discursive processes and social structures. Scholars of music and dance engage with cultural flow through dialogic encounters and interpretative analyses. These studies help illustrate how performance practices produce meanings, mediate socialities, and configure political relations.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
Ethnomusicology, which generally encompasses anthropology, dance ethnology, folklore, musicology, and sociology, situates specific theoretical issues in comparative social and historical contexts. Up to the late 1960s, the discipline explored and indexed the musical phenomena of non-Western cultures in ways that resonated with concurrent anthropological trends in area studies. Critical analysis of these approaches led to a rethinking of music in which music became not the object of culture, but rather the product and expression of human experience. In his writings on the relations between music and society, anthropologist John Blacking (1995) proposed:
We need to know what sounds and what kinds of behavior different societies have chosen to call “musical;” and until we know more about this we cannot begin to answer the question, “How musical is man?” As “humanly organized sound,” music is a bearer of meanings insofar as it exhibits and necessarily demonstrates a set of values that the society that generates it would otherwise lack. (p. 5) Relations between music, dance, and society are thus viewed as complex networks of interdependence through which a given act embodies temporal and emplaced experiences that structure social processes. Contemporary ethnomusicology pursues a rigorous analysis of how cultural production generates social significance by positioning the individual as the agent of social change through historical encounter. (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
Theoretical Approaches to Music and Dance
Musical and social structures mutually constitute each other through human interaction. This cultural-studies approach derives from the seminal work of Raymond Williams, who claimed that culture is not fixed as a bounded work or elite mode of production, but is instead embedded in everyday experience and activity. As a cultural materialist who challenged orthodox Marxist accounts of historical epochs or phases, Williams framed cultural practices as sites of political contestation through which groups reproduce and resist modes of domination, particularly those that critique industrial capitalism (Williams, 1977). Critical to his work are structures of feeling that configure the ways in which particular generations and social classes experience difference among social relations. These feelings beget a lived experience of a particular moment in society and history that brings meaning into the lives of individuals and the lifeworlds that they constitute. The production of cultural meaning is a fluid and dynamic process that emerges as a necessary process in which “new meanings and values, new practices, new relationships, and kinds of relationship are continually being created” (Williams, 1977, pp. 122–23).
Musical meaning is not itself generated through aesthetic critique, nor by reference to something extramusical, such as an emotion, landscape, or harmonic figure. Rather, musical elements and structures discursively relate to lived experience by an act of representation that fixes musical experiences to metaphoric and metonymic structures, forms, and works. These bounded entities are placed in a network of complex relations that can be explained through systems of representation in which musical ontologies serve as interpretive frameworks for diverse musical systems, whether Western symphonic music, Hindustani classical music, or Japanese gagaku court theater, or for categorization of musical cultures as classical, folk, popular, and traditional. Categories, however, do not necessarily correlate to an intrinsic value, but more productively relate to “how they are used and embodied in community relations to become structuring forces in musical life” (Holt, 2007, p. 29).
Ethnomusicologists today explore the discursive production of musical meaning as a contemporary response to what comparative musicologist Charles Seeger (1977) problematized as the “musicological juncture” (p. 16), or the gap of representation that occurs when communicating about one system of human communication (music) through another (speech). To redress claims that music is “untranslatable and irreducible to the verbal mode” (Feld, 1982, p. 91), ethnomusicology suggests that musical practice is less a latent mode of (artistic) representation but rather a (socially) active and engaged mode of producing reality. If speech is the communication of “worldview as the intellection of reality,” then music is the communication of “worldview as the feeling of reality” (Seeger, 1977, p. 7). What we perceive as “feelingful” occurs through the “generality and multiplicity of possible messages and interpretations . . . that unite the material and mental dimensions of musical experience as fully embodied” (Seeger, 1977, p. 91). As suggested by interpretive approaches to cultural anthropology, ethnographers study not experience, per se, but the feelingful and discursive structures through which experience occurs.
Musical experience is constituted as meaningful when social structures conjoin with individual consciousness through structures of feeling. Whereas structures suggest fixed relationships that are rigid and determined, feeling inflects the intense and personal experience of what is “believed, felt, and acted upon” (Frith, 1996, p. 252). This becomes important with regard to the construction of cultural forms, whether musical genres and styles or social categories and spaces. How people behave with regard to sound relates to what they perceive and think about such behavior. Anthropologist Alan Merriam (1964) proposed a model of musical anthropology that triangulates these axes of sound, concept, and behavior. This tripartite structure has been redressed by an interpretive analysis of dialectical processes that consist of historical construction, social maintenance, and individual adaptation and experience; in other words, an agency-centered inquiry into how people create, experience, and use music (Rice, 1987).
Feelingful experiences occur through culturally specific processes that produce and perceive sound. Recent directions in the phenomenology of acoustic phenomena argue that sound is not the property of a musical object separated from its origin, but rather, sonic significance lies in the encounter of sound as musical. Sensory dimensions of experience suggest that sonorities may be heard as affective, feelingful, and emotional when perceived as musical patterns in specific cultural contexts. Phenomenological studies suggest the ways in which people relate to each other through senses of hearing. A hearing culture may make it “possible to conceptualize new ways of knowing a culture and of gaining a deepened understanding of how the members of a society know each other” (Erlmann, 2004, p. 3). In turn, individual and social processes perceive musical encounter “not through layers of cognitive categories and symbolic associations, but with a trained and responsive body, through habits copied from others and strictly reinforced, by means of musical skills” (Downey, 2002, p. 490). Listeners’ acquired habits of assimilating sensory experience to musical systems affect them viscerally, and lived bodies are fashioned by patterns of acting in relation to music at the same time that they are responsive to sonic textures.
Performance emerges through the interaction of corporeal gestures, discursive tropes, and performative utterances in social settings that situate these actions as musical or extramusical, verbal or nonverbal, cognitive or affective, sacred or secular. These actions are held together by aesthetic principles that are represented in the social and material world, just as the social and material world is imbued with extraordinary value. Performance and listening are intersubjectively and physiologically experienced in a trained and socialized set of artistic bodily movements that reflect values and ideas (Meintjes, 2003, p. 176).
Embodied realms of experience situate cultural practices in the physiological and expressive body and the social forces that operate through those bodies. Performativity asserts the materiality of nonverbal communication and expression and the presence of the body as it is mediated by the production of sound. Whether sound is produced by a singer, a musician, or mediated by technology, the presence of the medium leaves a material trace that regulates its origin (Barthes, 1978). For example, analyses of timbre consider the grain of the voice in recording—in addition to elements of texture, attack, delay, and pitch—and interpret studio techniques as signifying practices that are deeply connected to the discursive production of style and genre (Théberge, 1997).
Embodied performance by a socialized musician or dancer suggests how bodies may be regulated or may resist forces of power (Comaroff, 1991). The discourse of bodies in motion at Greek weddings, for instance, produces the dialectical relationships and mutual dependencies that are also regulated and constrained by their repetitive power as a body politic, or collective unit. By introducing nonGreek Roma musicians at wedding parties as daulia, or drums (Cowan, 1990, p. 102), Greek townspeople exert power over the materiality of both resonant and outside bodies. As sites of reception and agency, bodies bear narratives of time and place that coalesce into corporeal memories. The ways individuals perform these narratives construct identity and differences that endow sound and movement with the capacity to represent lived experience.
As forms of social action and as meaningful activity, music and dance create and give expression to human and social experience. Epistemological concerns have critically responded to the ways in which a kinetic body and a sound dialogically compose form through performance events, structured practices, and representational strategies. Rather than treat music and dance as objects of discourse that possess meaning in and of themselves, or frame body movement techniques and sonic phenomena as abstract properties that may be reconfigured according to context, ethnographers seek to localize the very terms by which understanding and knowledge of these performative dynamics are produced.
Music Research Topics and Issues
Music plays a significant role in preserving and transmitting the world’s religions in terms of history, culture, and practice. The study of music in religious practices considers the ways in which music transforms experience into sacred meanings, narrates religious myths, and structures religious ritual and communities. The performative conditions associated with religious practice consider sacred sound not as the taxonomy of a particular belief system, but rather as a sensory spectacle through which experiences become enchanted. The sacred nature mediates by sonic utterances that may induce a phantasmagoric state of being, encode sacred language, or embody affective experience. Sound indexes religious experience through the presence of sacred instruments and the act of listening to liturgical chant. Sound also marks sacred spaces through pilgrimages and festival rituals, among other religious practices (Beck, 2006; Berliner, 1993).
The efficacy of music in sacred spaces suggests the ways in which sound may be sacred and how this sacred nature may be mediated through sonic practices. How sound conveys sacred meaning and experience in specific contexts raises ontological distinctions in that what is often perceived as musical in European and North American contexts may be considered nonmusical and sacred in other sacred spaces.
Contexts may determine how sound is received and interpreted and in what ways sound may be ontologically separate from music. Interpretation of sound also structures power relations, in which religious authority is maintained by ideological boundaries of sound seeking to differentiate between sacred practices and secular forms of expression (Baily, 2003).
Ethnographies of sacred performance practices have tended to focus on the capacity of music, dance, and ritual drama to organize religious activity through modes of social interaction that produce webs of associative meaning (Reily, 2002). Performance has been conceptualized as a medium through which participants demonstrate religious conviction and commitment; as a means to structure time, narrative, and symbolic systems; and as a mode of interaction that codifies organizational patterns and the conditions of participation in religious activity. For example, the sacred voice is a medium that binds individuals communally in religious activity. How these experiences shape and are shaped by musical practice is determined by the theological ways in which individuals engage with music and music making. More recently, ethnographers have considered ways in which religious-ritual activity depends on the act of performance in order to be perceived as sacred and, in particular, how sound and movements are mediums that frame a ritual act as sacred. As individuals negotiate moral boundaries between the sacred and the profane in contemporary contexts, the act of producing sound and movement becomes a contested arena where religious authorities judge the ethics of cultural production. Performance through music and dance may allow departure from the profane and entrance into the sacred, mark the aesthetic boundaries of secular space, or itself articulate the boundaries between the sacred and the profane by which religious practices acquired enchanted and sacred meaning.
Several bodies of scholarship have addressed musical change, religious renewal, soteriological potential, musicoreligious orthodoxy, and other related issues. These different forms of religious practice, or syncretism, may be marked through distinct genres and styles that expose moments of encounter and uneven relations of power. In colonial spaces, religious repertory may occupy cultural spaces in ways that reproduce a hegemonic religious order and erase subaltern religious practices (Comaroff, 1991). Folkloric ensembles typically relate to historical or contemporary religious practices through complex processes of aestheticization that problematically blur distinctions between sacred worship, cultural traditions, and popular culture. These distinctions are in part based on a collective memory of the sacred that is translated through aesthetic ideals. The embodiment of these ideals demonstrates how religious ideologies are manifested through bodily practices that themselves produce sacred sound, movement, and performance.
The power of sound embodied in speech patterns, or chant, may preserve and transmit knowledge and religious authority as well as mark historical change. For example, the Rigvedic texts of the Harappan in Pakistan and northwestern India are considered sacred when correctly rendered through transmission and pronunciation of Vedic hymns. Recitation of these hymns occurs through three types of spoken accent with a melodic contour dependent on the succession of accent in the sung syllables, as well as the duration of each relative pitch. The consideration of Vedic chant as the foundation of contemporary Hindustani music in South Asia is, in part, attributed to its preservation through Brahman recitation. Codification of early performance practices, such as Gregorian chant in southern Europe, began when clergy notated plainchant in order to correlate its liturgical function with the medieval Roman liturgical calendar. Compositional practices that developed from these notations are widely considered to be the conceptual and historical basis for Renaissance and late European courtly arts (Bergeron, 1998).
Some religious cultures regard practices of recitation, or the sounding of religious text, as the divine act that makes speech patterns sacred by mediating the transmission of sacred texts through the vocal performance. The significance of such performances is governed not only by the syntactic conditions such as pitch and duration, but also by audition, or the appropriate response, performed by the ethical listener (Hirschkind, 2006).
Instruments embody religious experience when endowed with the capacity to produce sacred sound. In some ritual practices, performance on a particular instrument, such as batá percussion ensembles in Cuban Santería, realizes the divine potential of the ritual event and produces religious transformation. Instrumentalperformance practice marks the shift from secular to sacred contexts; produces the appropriate performance conditions for trance, ecstasy, possession, and other states of heightened sacrality; symbolizes tropes of religious narrative and function; and transfers knowledge and participation among believers (Hagedorn, 2001; Rouget, 1985; Wong, 2001).
Sacred musical practices are often narrative—telling stories and relating myths to generate a sense of historical and religious meaning. Narrative may be considered musical through, for example, the ways in which music marks the passage of time in ritual performance and in the narrative sequence of events, or through the juxtaposition of different musical genres that layer and texture religious stories. Instruments often play a significant role in narrating epic myths with sacred content, such as within bardic traditions or Sufi mysticism. One way in which narrative components of sacred music may shape a religious community is by mediating a sense of place. The act of recalling an original event, such as an act of martyrdom or a miracle, links the event to a specific site. When enacted through song and other musico-poetic genres, the act of recall layers subsequent events to that site in ways that parse history as locally meaningful in religious communities.
During the early 1990s, musicologists readjusted paradigms in which musical performance expresses a natural mode of human existence or formalizes a universal set of aesthetic ideals (Solie, 1993). The critical inquiry espoused by “new musicology” advocated for the deconstruction of ideologies into iconicities of style that are reproduced and transformed by acts of performance. Performance practices now produce social relations that are represented in different categories of gender and sexuality, race and ethnicity, generation, class and nation, and other forms of identity. Cultural meaning is discursively constructed by specific practices of signification, and links between signifier and signified are not fixed but arbitrary. These practices may construct meaningful experience in ways that depend on conventions of taste and class that are situated in a particular time and place.
Studies of place tend to be located in everyday life and explore the tactics by which people interact and engage with their environment. Gatherings, such as rehearsals among English rock musicians, are not only mediated by these practices, but also produce affective relationships to the settings in which social activities take place. Yet, as conditions of modernity separate space from place in lived experience, the physical settings of social activities are “thoroughly penetrated by and shaped in terms of social influences quite distant from them” (Giddens, as cited in Stokes, 1994, p. 1). Therefore, approaches to place, music, and dance seek to relocate cultural geographies within specific social, economic, and political spaces by addressing how individuals produce sound and movement in order “to reestablish their presence, situate events in a fixed place and time, and reembed actions within social structures” (Stokes, 1994, p. 3). Place becomes meaningful through affective processes that recognize and enable different experiences, mediate emotional relations to an environment, or produce nostalgia through acts of memory that bestow music and dance “with an intensity, power and simplicity unmatched by any other social activity” (Stokes, 1994, p. 3).
As individuals perceive what takes shape around them, they participate in the construction of a soundscape, or an environment structured by the perception and reception of sound. Soundscapes are differentiated not only by dynamics of power, class, and difference, but also by sentimentality, or the emotional and affective relationships that constitute a sense of place (Feld & Basso, 1996). An acoustemology of sound analyzes the sentimental relations to place that are embodied by sound production and reception among, for instance, Kaluli people in Papua New Guinea. Through interlocking, overlapping, and alternating singing that mimics bird calls in the rainforests, Kaluli voices index the natural environment; mediate places as sites of memory; and express an ecological sense of self, place, and time (Feld, 1982). Acoustic environments have also been critical to the historical progression of musical form in bourgeoisie European society and the displacement of instrumentalists to the role of musical interpreters. Early performance practices were comprised of extramusical, literary, or narrative material that was, in part, marked by a musician’s individualized embellishment of musical material.
In the 19th century, the concert room emerged as a performance setting that aestheticized the impression of immediate contact with the music as a listening ideal. Musical practices shifted to uphold universalist aesthetic ideals not only through listening appreciation, but also in celebration of a composer’s genius. Dramatic structures were communicated by composers such as Beethoven through “the abstract logic of pure form” and the formal properties of the music itself in ways that privileged structural-listening practices in European art music. Thus, the commodification of musical knowledge and musical emplacement fetishized sonata form in the historical development of instrumental Western art music (Leyshon, Matless, & Revill, 1998).
The commodification of musical place in a globalized world has induced a certain anxiety among critical musicologists over the ways that disembedding music and dance practices stimulates desires for authenticity by late-capital consumers in a hegemonic economic order. While the capacity for music to travel has augmented an appreciation for place and dismantled cultural borders, the poetics and politics of this have problematically differentiated relations between self and other. World music, and related configurations of art music, ritual, folk and ethnic genres, and world beat and roots music (Aubert, 2007), are authenticated by conditions of place. By privileging the geographically local as authentic, the particular can be naturalized in ways that fetishize locality through terms of belonging. The act of splitting sound from its source and reproducing it depends on uneven processes of representation that contest cultural rights and negotiate various modes of ownership (Feld & Basso, 1996). Styles associated with world music then demarcate community by linking dispersed places and allegiances that, through subjective identity, allow the strategies by which individuals register difference (Erlmann, 1999).
The globalization of world music has also been critiqued as a pastiche, or a process of reconfiguring time and space that detemporalizes the encounter between self and ethnographic others into an event beyond history, or perhaps at the horizon of a certain historical moment. For instance, the production and consumption of alternative folk rock links different historical moments into one bounded cultural space, while world-dance music may layer disparate local styles into a repetitive, temporal sequence (Erlmann, 1999). Cultural interchange and interaction in popular music thus depends upon a concept of culture that binds territory to groups in ways that demand the political engagement of cultural critique. Whereas narratives of cultural interchange such as hybridity, creolism, and syncretism tend to privilege myths of origin, postcolonial analyses encourage new approaches that no longer engender forms of being by binaries of self (self and ethnographic other), place (here and there), and time (then and now), but rather by a third space that is constituted by these boundaries.The circulatory relations of cultural flow have furthered understandings of how historical consciousness may undermine essentializing cultural strategies. Studies of the black Atlantic (Gilroy, 1993) address how black popular music and dance styles shape and are shaped by particular African retentions and situate the Atlantic as a site of crossings, mediations, and exchanges that continually reconsider the cultural flow of African and African American expressive forms.
In response to large-scale processes of migration, globalization, and transnationalism that destabilize structures of belonging, critical approaches to place have also emphasized the production of locality through cultural practices. Tropes of place may uneasily mark displacement from an imagined structure of belonging, for instance when tropes of the crowd and the machine in the South African vocal genre of isicathamiya signify a sense of nostalgia for rural agricultural economies among populations who migrated to cities in search of labor opportunities. Another example can be found in how the mapping of memory fragments onto musical events, instruments, and kinship narratives of a retired Jewish community in Liverpool, England, shapes collective relations that in turn construct an immigrant neighborhood whose identity is nurtured by newly mediated and localized imaginaries of home and community. Locality may also be produced by sound-engineering practices that index a particular place and authenticate a musical style through the technological reproduction of sound in specific performance conditions such as “live” Austin country music (Greene & Porcello, 2005).
Gender and sexuality analyses situate performers and their texts within specific musical worlds and examine how these worlds produce gendered ideologies through performance practice, singing style, repertory, performance events and occasions, lyrics and elaborations, and instrumental practice. Thus, gender and sexuality are mutually constitutive of cultural experiences, and also mutually construct processes of subjectivity and alterity in ways that have been binarily opposed to biological explanations of lived experience. As a method of cultural critique, gender and sexuality studies analyze the ways in which ideology is maintained and transformed through the performance of a gendered self. These studies also examine the ways that musical practices mediate social relations as variously gendered—masculine, feminine, and perhaps hyperreal. Because gender theorists have understood sexuality as constitutive of gendered norms, distinctions between gender and sexuality have been largely premised on identity construction as theorized in psychoanalytic discourse. Lacanian theory argues that linguistic signs triangulate the enlightened self from its other in ways that destabilize a sense of identity by the desire for an object that might represent such identity. By reading social and cultural texts for hidden and repressed desires, critical theorists reveal conditions of heteronormativity that shape and are shaped by cultural practices. Ultimately, gender and sexuality studies suggest how social distinctions may be magnified rather than ameliorated by the performative act of music making and structured movement.
A substantial body of literature has been devoted to highlighting and documenting women’s contribution and women’s roles in musical performance. As professional entertainers, as dramatic personalities, and as audiences, women convey social values and transmit cultural meanings in ways that may be different from those performed by men. The expression of sentimentality by women through forms and repertoires, such as sung poetry among Bedouin women in upper Egypt, resist, maneuver, and maintain patriarchal norms of modesty, honor, and shame that have been typified in Mediterranean studies (Abu-Lughod, 1986), whereas songs sung by Berber women in northern Morocco strategically empower potentialities of marital life (Magrini, 2003). Performance events and contexts have been analyzed with discourses surrounding these practices through elements of lyrics, style, technology, and appropriate behavior. These suggest how identity may be encoded and performed as masculine, feminine, or ambiguously gendered. Postmodernist approaches to the paradigmatic relations between musical and social structures have produced seminal readings of the gendered hierarchies in composition, such as immanent relations between the masculine and the feminine in sonata form (McClary, 1991), formulations of the Western music canon, constructions of ontological difference through gender (Solie, 1993), and the potential of music itself—as a performance rather than as text, to disrupt the masculine musicological narratives within which it is often contained (Abbate, 1991).
The broad compass of vocal performance in different registers constructs gendered and sexualized identities by embracing some, and refusing other, conventions of style and genre. Voice may characterize a range of erotic and emotional relationships among women who sing and women who listen in ways that “resonate in sonic space as lesbian difference and desire” (Brett, Wood, & Thomas, 1994, p. 28). This sapphonicvoice is found in operatic practices by female singers who assume “pants” roles, or castrato male roles sung by women, as well as other singers and singing personalities (Brett et al., 1994). Koestenbaum (1994) argued that the brea between registers is a gendered split that emplaces a voice between male and female. The ways in which the brea is negotiated may be “fatal to the act of natural voice production” (p. 220) when gender and sexuality are transferred beyond normativity, such as the sapphonicvoice’s synthesis of register; this replaces its splitting, or the falsetto register’s failure to disguise this break. The combination of different registers may refuse vocal categories and polarities of natural and unnatural, and may establish interpretations of female desire, male desire, and the relations of class, age, sexual status, and identity through vocal performance (Koestenbaum, 1994).
The performance of gender engages with the kinds of subjects that musical and dance performances engender, both onstage and among audiences, and the ways that such performance relates to everyday life as lived, embodied, and theorized. For instance, a feminized atmosphere at a wedding in Morocco is not dependent on the presence of female dancers, but rather on the performance of femininity among communal relations that may differentiate between gender, sexuality, and class. Perceptions and representations of Asian American femininity have shifted due to North American taiko performance that represents social space through gesture, movement, and the presence of women in drumming practices. In post-Apartheid South Africa, Zulu ngoma song and dance is critical to the performance of masculinity and the anxieties of retaining the presence of individualized expression and stylized body movement in the midst of unemployment, an AIDS epidemic, and a history of violence in KwaZulu-Natal (Meintjes, 2003).
Critical race studies examine how constructions of difference on the basis of body type and color are perpetuated by the representation of essentialized metaphysical conditions. Concepts of race are linked to the emergence of modern scientific inquiry into the natural world and are largely considered a product of Enlightenment thought and observation. The late 18th century produced a world “observed, processed and remapped on the imagination of Europe” (Radano & Bohlman, 2000, p. 13) in which race and music constituted logics of difference that categorized the natural world and sought to make it understandable. Moreover, racial discourse contributed to the formation of musical difference as human difference was mapped onto musical difference, that is, to the object of music itself. The epistemic model that measured harmonic relations on a mathematically proportionate scale and unified differences in pitch influenced Enlightenment thought on the structure and substance of not only resonating, but also racialized bodies. How music participates in the construction of race and racial imaginaries ultimately raises ontological questions of whether music itself represents these qualities, or whether our understandings of music are shaped by and through racial relations.
Racial constructs are connected to music through structures of understandability, that is, the capacity of sound to signify and communicate meaning, and through materiality, or the technologies, objects, and bodies that represent music and musical histories through particular ideologies (Brown, 2007). For example, the 19th-century German composer Richard Wagner claimed that the language of European opera and vocal music was degraded through the inability of European Jewish composers to fully control the language of music, which Wagner instantiated in terms of 19th-century German universalism that was first and foremost predicated on language and an assumption that music instantiates comparative linguistic properties. Elsewhere, race interacts with other systemic hierarchies, such as the historic provision of wedding and court entertainment by Jewish musicians in predominantly Muslim worlds situated along the Silk Road, from Bukharan weddings in central Asia to the Abbasid and Omayad caliphates of the 11th century. Categories in which instruments function as a racial mapping of power relations may be critiqued by participants themselves, such as Karnatak and Hindustani musicians who negotiate caste systems in South Asia that distinguish between the permissibility of Brahmin performance on the Karnatic vinalute and the delegation of instrumental performance on untouchable leather-skinned drums to less privileged castes. Conditions of difference, shaped by cultural practices, help to better understand relations of power in systems based on class, caste, kinship, religion, and other forms of belonging and ownership.
Racial conventions of blackness, whiteness, and other morphologies play a critical role in ideological distinctions of music as rational and intellectual, or as orally transmitted, communal, and embodied. The naturalization of certain structures as African retentions, such as improvised movement, antiphonal oppositions, and repeated cycles of interlocking rhythmic patterns, reinforces the putative inseparability of music and dance in the African diaspora (Meintjes, 2003). This becomes problematic when what is musical and universal is defined against conceptions of blackness as physical and embodied.Yet, performance practice and histories may join as lived experience in ways that affirm how blues practices in African American working-class communities in the southern United States influenced the emergence of jazz, gospel, soul, R&B, rock, hip-hop, and other black vernacular music. The problem of race translates into a cultural critique in which creative strategies destabilize the tropes through which they emerge by means of intertextuality, subversion, and other signifying techniques (Radano & Bohlman, 2000).
Ethnicity, like other forms of difference that participate in processes of exclusion and inclusion, is constructed on the basis of shared beliefs in a “common ancestry, memories of a shared historical past, and elements in common, such as kinship patterns, physical continuity, religious affiliation, language, or some combination of these” (Shelemay, 2001, p. 249). Musical and dance practices instantiate ethnic relations by performing social boundaries that reproduce and subvert ideologies; these relations simultaneously also produce meanings, that is, “a patterned context in which other things happen” (Waterman, 1990, p. 214). Ethnic identity is often discussed in terms of minority relations and population movements that are themselves predicated on political difference. Often, ethnic boundaries “define and maintain social identities which can only exist in context of oppositions and relativities”; thus, ethnography can engage with how “actors use music in specific local situations to erect boundaries, maintain distinctions between us and them, and use terms such as ‘authentic’ to justify these boundaries” (Stokes, 1994, p. 6).
Cultural nationalism is a complex process by which institutions and actors integrate diverse populations into structures of national belonging. Ethnography investigates the ways in which music and dance practices—and the discursive spaces that are dialogically created and inhabited by such practices—generate national imaginaries in local contexts. Early forms of nationalism celebrated the universal claim to a single shared language and a set of particular customs and traditions situated in an ethnonational framework. Scholars have since criticized collective national identity as a product of state apparatuses that seek to reify lived experience into internationally recognized forms. Thus, the invention of tradition has been linked with nation-building projects in which state power emerges through the performance of national imaginaries and the efficacy of imagined communities (Askew, 2002). The extent to which symbolic production produces and sustains state hegemony through particular genres suggests whether these processes might be “multivalent, multivocal, and polyphonic” (Askew, 2002, p. 273) and how agents and institutions are involved in negotiating, defining, and contesting that which constitutes the nation. Musical ethnographies reveal the strategic shifts that characterize nationalist projects, ask whether events coincide with or interrupt official ideologies, illustrate why specific forms are chosen to represent the nation, and address how issues of authenticity and preservation are managed in these endeavors. Though global capital flow, access to electronic media, and transnational migration of people have decentered and deterritorialized processes of nationalism, the mediating structure of the nation continues to relate how people cross lines of difference through local transactions and cultural production.
Representation of the nation through music depends on a belief in the representational potential of music, that is, music’s capacity to embody a cultural whole that exists prior to its mediation. The production of national symbols, therefore, depends upon a modern discourse that is represented by cultural mediation. This discourse emerged from Johann Gottfried Herder’s claim that based national identity on the common narratives and histories of a given people and, in particular, on the capacity of language and folksong to represent such shared experiences. Herder’s proto-nationalist theory is comprised of a geographic model where music marks a place, such as the landscape of the nation, an acoustic model whereby sound distinguishes the nation as a whole, and a narrative model in which music encodes stories that represent the history of the nation (see Bohlman, 2004). The quintessential image of the nation, or a “preexisting entity that is more indefinite than definite,” is reflected by national music, “for whom it becomes the task to bring out as much of the definition as possible” (Bohlman, 2004, p. 83).
Conversely, nationalistic music does not harbor relations among a nationalized people, but rather services competition between nation-states. Nationalistic music secures the geographic identity of the nation-state by marking borders and producing alterity through the production of national difference. Alterity may be differentiated on the basis of class, race, ethnicity, and gender dynamics that exclude those whose presence prescribes the need to regulate desires and who trigger ambivalence as a condition of modernity. The marking of borders is instantiated by a presentation of the nation that embeds power in performance, or through a means of communicative interaction in which the act itself is privileged over that which it mediates. Thus, nonverbal performance may communicate messages whose meaning is located in elements of sound and movement and in dialogic interaction between performers and audiences, or between modes of modernity—contingent on the specifics of the temporal and spatial moment.
Early studies of population movement addressed patterns of assimilation and acculturation through theories of culturecontact that failed to engage with political disparities and the contradictions of multiculturalism in modern societies. More recent approaches redressed these patterns as a postmodern condition that negotiates instantiations of nationalism, transnationalism, and displacement through the appropriation of expressive culture and the making of political alliances among transnational populations (Garofalo, 1992). However, the rigidities and essentialisms of diasporic identity created by multiculturalism may articulate or contradict the politics of national, postcolonial, and minority identities even as they stress emergent forms of culture, uneven relations of cultural hybridity, and ambivalent relations to national homelands (Ramnarine, 2007). Contemporary diaspora studies thus emphasize the “newness” of the diasporic experience, and address political belongings and further substitutions as historically specific and shaped by a historical consciousness. Fragments of this consciousness are inscribed within an in-between space by which immigrants may register a sense of loss, exile, and rupture through cultural production. Diasporic music making may thus be a practice of everyday life in local communities by individuals making strategic choices through music festivals, individual biographies, song texts, musical instruments, and intellectual movements. Politically articulated readings of these social relations and creative processes reveal economies of desire in colonial encounters, performances that mourn and remember ancestors, intercultural borrowings in African-Peruvian theater, or state interventions in the creation of broader diasporic groups (Ramnarine, 2007).
Studies of popular culture and music have helped to differentiate between experiences of voluntary and forced migration. The actions and behavior of refugees affect how groups produce and give meaning to their music as they negotiate loss and trauma, and pursue a state of stability that is represented by resettlement. For instance, Vietnamese refugee communities in the United States tend to display a preference for love songs and Western-oriented popular music that convey anticommunist nostalgia for a pre-1975 period of French, U.S., and Japanese colonial influence in Vietnam (Reyes, 1999). Other histories of dispossession and violence have prompted ethnographers to consider the social construction of place, self, and other through aesthetic experience as a means for understanding the performative capacities of particular histories and repertories of violence and “the ensuing meanings violent performances carry for victims, perpetrators, and witnesses alike” (McDonald, 2009, p. 59).
Future Directions
Medical ethnomusicology seeks to integrate disciplines of music; health sciences; integrative, complementary and alternative medicine (ICAM); the physical and social sciences; medical humanities; and the healing arts through integrative research and applied practice. Research in music, medicine, and culture recognizes the dynamic and diverse practices by which specialized music and sound phenomena function as therapeutic strategies and as a means to cure illness and disease. Ethnomusicological discourse has demonstrated the extent to which specialized music emerges from a spiritual or religious ontology and is practiced in ritual or ceremonial events. When music combines with or functions as prayer or meditation, it may constitute preventive and/or curative practices that can be situated among a set of local medical practices. Medical ethnomusicology focuses on the performance of healing and the culture of health in order to better understand disease and illness, health and healing, as well as the performative nature of diagnosis, treatment, and healing. Recent studies and interventions include locating sites of ritual healing in ngoma practice among disparate communities; correlating beliefs about spirit possession to the intricacies of indigenous health care systems in Tumbuka communities; advocating and critiquing how the decline of HIV infection rates in Uganda correspond to the use of local musical traditions that support medical initiatives; engaging with science and religion through a focus on music, prayer, meditation, and healing; and the ways that these processes intimately link with transformational cognitive states in Tajikistan (Koen, 2008).
Applied ethnomusicology refers to work in the public sector that encourages the advocacy, curation, documentation, education, and performance of music and dance. These efforts apply the perspectives, principles, theories, and methods of ethnomusicology to encourage public awareness and participation in broadly defined fields of cultural practice. Advocacy engages with public-policy issues, such as arts access and participation, artists’ rights, censorship, intellectual property, and cultural heritage through institutional and noninstitutional efforts. The Society for Ethnomusicology debates and assumes positions on the ethics of music and fair use, music and torture, and the rights of human subjects in scholarly research. Cultural initiatives facilitate opportunities for performers and performance practices through festival and concert organization, recording and documentary film production, and museum exhibitions.
Efforts to document and archive materials are encouraged through the acquisition and digitalization of archives, collaboration between institutions, improved access, and the support of scholarship, publications, and public programs. Public education and outreach develop curriculum at the primary and secondary levels; establish performance ensembles and programs to nurture skills; and foster audiences and public awareness through the promotion and distribution of related events, productions, and publications. Performance of music and dance by specialists is encouraged not only as a research method in observing participants, but also as a means to preserve, transmit, and produce communities based on knowledge production and creative expression.
Bibliography:
- Abbate, C. (1991). Unsung voices: Opera and musical narrative in the nineteenth century. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Abu-Lughod, L. (1986). Veiled sentiments: Honor and poetry in a Bedouin society. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Askew, K. M. (2002). Performing the nation: Swahili music and cultural politics in Tanzania. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Aubert, L. (2007). The music of the other: New challenges for ethnomusicology in a global age (C. Ribeiro, Trans.). Burlington, VT: Ashgate.
- Baily, J. (2003). Can you stop the birds singing? The censorship of music in Afghanistan. Copenhagen: Freemuse.
- Barthes, R. (1978). Image-music-text. New York: Hill and Wang.
- Beck, G. L. (2006). Sacred sound: Experiencing music in world religions. Waterloo, ON, Canada: Wilfrid Laurier University Press.
- Bergeron, K. (1998). Decadent enchantments: The revival of Gregorian chant at Solesmes. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Berliner, P. (1993). The soul of mbira: Music and traditions of the Shona people of Zimbabwe. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Blacking, J. (1995). Music, culture, & experience: Selected papers of John Blacking. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Bohlman, P. V. (2004). The music of European nationalism: Cultural identity and modern history. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO.
- Brett, P., Wood, E., & Thomas, G. (1994). Queering the pitch. New York: Routledge.
- Brown, J. (Ed.). (2007). Western music and race. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
- Comaroff, J. (1991). Of revelation and revolution. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Cowan, J. K. (1990). Dance and the body politic in northern Greece. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Downey, G. (2002). Listening to capoeira: Phenomenology, embodiment, and the materiality of music. Ethnomusicology, 46 (3), 487–509.
- Erlmann, V. (1999). Music, modernity, and the global imagination: South Africa and the West. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Erlmann, V. (2004). Hearing cultures: Essays on sound, listening, and modernity. New York: Berg.
- Feld, S. (1982). Sound and sentiment: Birds, weeping, poetics, and song in Kaluli expression. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press.
- Feld, S., & Basso, K. H. (1996). Senses of place. Santa Fe, NM: School of American Research Press.
- Frith, S. (1996). Performing rites: On the value of popular music. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Garofalo, R. (1992). Rockin’ the boat: Mass music and mass movements. Boston: South End Press.
- Gilroy, P. (1993). The Black Atlantic: Modernity and double consciousness. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Greene, P. D., & Porcello, T. (2005). Wired for sound: Engineering and technologies in sonic cultures. Middletown, CT: Wesleyan University Press.
- Hagedorn, K. J. (2001). Divine utterances: The performance of Afro-Cuban Santería. Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution Press.
- Hirschkind, C. (2006). Theethicalsoundscape:Cassettesermonsand Islamic counterpublics. New York: Columbia University Press.
- Holt, F. (2007). Genre in popular music. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Koen, B. D. (2008). The Oxford handbook of medical ethnomusicology. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
- Koestenbaum, W. (1994). The Queen’s throat: Opera, homosexuality, and the mystery of desire. New York: Poseidon.
- Leyshon, A., Matless, D., & Revill, G. (Eds.). (1988). The place of music. New York: Guilford Press.
- Magrini, T. (Ed.). (2003). Music and gender: Perspectives from the Mediterranean. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- McClary, S. (1991). Feminine endings: Music, gender, and sexuality. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
- McDonald, D. A. (2009). Poetics and the performance of violence in Israel/Palestine. Ethnomusicology, 53 (1), 58–85.
- Meintjes, L. (2003). Sound of Africa! Making music Zulu in a South African studio. Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
- Merriam, A. P. (1964). The anthropology of music. Evanston, IL: Northwestern University Press.
- Radano, R. M., & Bohlman, P. V. (2000). Music and the racial imagination. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Ramnarine, T. (2007). Musical performance in the diaspora. London: Routledge.
- Reily, S. A. (2002). Voices of the magi: Enchanted journeys in southeast Brazil. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Reyes, A. (1999). Songs of the caged, songs of the free: Music and the Vietnamese refugee experience. Philadelphia: Temple University Press.
- Rice, T. (1987). Toward the remodeling of ethnomusicology. Ethnomusicology, 31 (3), 469–488.
- Rouget, G. (1985). Music and trance: A theory of the relations between music and possession. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Seeger, C. (1977). Studies in musicology, 1935–1975. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Shelemay, K. K. (2001). Soundscapes: Exploring music in a changing world. New York: Norton.
- Solie, R. (Ed.). (1993). Musicology and difference: Gender and sexuality in music scholarship. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Stokes, M. (Ed.). (1994). Ethnicity, identity, and music: The musical construction of place. Oxford, UK: Berg Press.
- Théberge, P. (1997). Any sound you can imagine: Making music/ consuming technology. Hanover, NH: Wesleyan University Press.
- Waterman, C.A. (1990). Jùjú:Asocialhistoryandethnographyofan African popular music. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Williams, R. (1977). Marxism and literature. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
- Wong, D. A. (2001). Sounding the center: History and aesthetics in Thai Buddhist performance. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Research Paper Topics
120 Music Research Paper Topics
How to choose a topic for music research paper:.

Music Theory Research Paper Topics:
- The influence of harmonic progression on emotional response in music
- Analyzing the use of chromaticism in the compositions of Johann Sebastian Bach
- The role of rhythm and meter in creating musical tension and release
- Examining the development of tonality in Western classical music
- Exploring the impact of cultural and historical context on musical form and structure
- Investigating the use of polyphony in Renaissance choral music
- Analyzing the compositional techniques of minimalist music
- The relationship between melody and harmony in popular music
- Examining the influence of jazz improvisation on contemporary music
- The role of counterpoint in the compositions of Ludwig van Beethoven
- Investigating the use of microtonality in experimental music
- Analyzing the impact of technology on music composition and production
- The influence of musical modes on the development of different musical genres
- Exploring the use of musical symbolism in film scoring
- Investigating the role of music theory in the analysis and interpretation of non-Western music
Music Industry Research Paper Topics:
- The impact of streaming services on music consumption patterns
- The role of social media in promoting and marketing music
- The effects of piracy on the music industry
- The influence of technology on music production and distribution
- The relationship between music and mental health
- The evolution of music genres and their impact on the industry
- The economics of live music events and festivals
- The role of record labels in shaping the music industry
- The impact of globalization on the music industry
- The representation and portrayal of gender in the music industry
- The effects of music streaming platforms on artist revenue
- The role of music education in fostering talent and creativity
- The influence of music videos on audience perception and engagement
- The impact of music streaming on physical album sales
- The role of music in advertising and brand marketing
Music Therapy Research Paper Topics:
- The effectiveness of music therapy in reducing anxiety in cancer patients
- The impact of music therapy on improving cognitive function in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease
- Exploring the use of music therapy in managing chronic pain
- The role of music therapy in promoting emotional well-being in children with autism spectrum disorder
- Music therapy as a complementary treatment for depression: A systematic review
- The effects of music therapy on stress reduction in pregnant women
- Examining the benefits of music therapy in improving communication skills in individuals with developmental disabilities
- The use of music therapy in enhancing motor skills rehabilitation after stroke
- Music therapy interventions for improving sleep quality in patients with insomnia
- Exploring the impact of music therapy on reducing symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- The role of music therapy in improving social interaction and engagement in individuals with schizophrenia
- Music therapy as a non-pharmacological intervention for managing symptoms of dementia
- The effects of music therapy on pain perception and opioid use in hospitalized patients
- Exploring the use of music therapy in promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety during surgical procedures
- The impact of music therapy on improving quality of life in individuals with Parkinson’s disease
Music Psychology Research Paper Topics:
- The effects of music on mood and emotions
- The role of music in enhancing cognitive abilities
- The impact of music therapy on mental health disorders
- The relationship between music and memory recall
- The influence of music on stress reduction and relaxation
- The psychological effects of different genres of music
- The role of music in promoting social bonding and cohesion
- The effects of music on creativity and problem-solving abilities
- The psychological benefits of playing a musical instrument
- The impact of music on motivation and productivity
- The psychological effects of music on physical exercise performance
- The role of music in enhancing learning and academic performance
- The influence of music on sleep quality and patterns
- The psychological effects of music on individuals with autism spectrum disorder
- The relationship between music and personality traits
Music Education Research Paper Topics:
- The impact of music education on cognitive development in children
- The effectiveness of incorporating technology in music education
- The role of music education in promoting social and emotional development
- The benefits of music education for students with special needs
- The influence of music education on academic achievement
- The importance of music education in fostering creativity and innovation
- The relationship between music education and language development
- The impact of music education on self-esteem and self-confidence
- The role of music education in promoting cultural diversity and inclusivity
- The effects of music education on students’ overall well-being and mental health
- The significance of music education in developing critical thinking skills
- The role of music education in enhancing students’ teamwork and collaboration abilities
- The impact of music education on students’ motivation and engagement in school
- The effectiveness of different teaching methods in music education
- The relationship between music education and career opportunities in the music industry
Music History Research Paper Topics:
- The influence of African music on the development of jazz in the United States
- The role of women composers in classical music during the 18th century
- The impact of the Beatles on the evolution of popular music in the 1960s
- The cultural significance of hip-hop music in urban communities
- The development of opera in Italy during the Renaissance
- The influence of folk music on the protest movements of the 1960s
- The role of music in religious rituals and ceremonies throughout history
- The evolution of electronic music and its impact on contemporary music production
- The contribution of Latin American musicians to the development of salsa music
- The influence of classical music on film scores in the 20th century
- The role of music in the Civil Rights Movement in the United States
- The development of reggae music in Jamaica and its global impact
- The influence of Mozart’s compositions on the classical music era
- The role of music in the French Revolution and its impact on society
- The evolution of punk rock music and its influence on alternative music genres
Music Sociology Research Paper Topics:
- The impact of music streaming platforms on the music industry
- The role of music in shaping cultural identity
- Gender representation in popular music: A sociological analysis
- The influence of social media on music consumption patterns
- Music festivals as spaces for social interaction and community building
- The relationship between music and political activism
- The effects of globalization on local music scenes
- The role of music in constructing and challenging social norms
- The impact of technology on music production and distribution
- Music and social movements: A comparative study
- The role of music in promoting social change and social justice
- The influence of socioeconomic factors on music taste and preferences
- The role of music in constructing and reinforcing gender stereotypes
- The impact of music education on social and cognitive development
- The relationship between music and mental health: A sociological perspective
Classical Music Research Paper Topics:
- The influence of Ludwig van Beethoven on the development of classical music
- The role of women composers in classical music history
- The impact of Johann Sebastian Bach’s compositions on future generations
- The evolution of opera in the classical period
- The significance of Mozart’s symphonies in the classical era
- The influence of nationalism on classical music during the Romantic period
- The portrayal of emotions in classical music compositions
- The use of musical forms and structures in the works of Franz Joseph Haydn
- The impact of the Industrial Revolution on the production and dissemination of classical music
- The relationship between classical music and dance in the Baroque era
- The role of patronage in the development of classical music
- The influence of folk music on classical composers
- The representation of nature in classical music compositions
- The impact of technological advancements on classical music performance and recording
- The exploration of polyphony in the works of Johann Sebastian Bach

- Writing a Research Paper
- Research Paper Title
- Research Paper Sources
- Research Paper Problem Statement
- Research Paper Thesis Statement
- Hypothesis for a Research Paper
- Research Question
- Research Paper Outline
- Research Paper Summary
- Research Paper Prospectus
- Research Paper Proposal
- Research Paper Format
- Research Paper Styles
- AMA Style Research Paper
- MLA Style Research Paper
- Chicago Style Research Paper
- APA Style Research Paper
- Research Paper Structure
- Research Paper Cover Page
- Research Paper Abstract
- Research Paper Introduction
- Research Paper Body Paragraph
- Research Paper Literature Review
- Research Paper Background
- Research Paper Methods Section
- Research Paper Results Section
- Research Paper Discussion Section
- Research Paper Conclusion
- Research Paper Appendix
- Research Paper Bibliography
- APA Reference Page
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography vs Works Cited vs References Page
- Research Paper Types
- What is Qualitative Research
Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account
25 Most Popular Music Research Paper Topics for Writing

Research papers aren't just for history class or the social sciences. Research papers can be assigned in any course, and that includes music class. The world's musical traditions are fertile ground for research, but because we have been conditioned from childhood to think of music as entertainment rather than a subject for academic research, it is often difficult to come up with interesting and effective topics for a music research paper. Fortunately, music research papers are often more fun to write than other types of research paper because they have such a wide range of interesting topics to explore.
Choose from these stellar popular music research paper topics
Are you stuck looking for a music research topic? Well, you're in luck. We have twenty-five music research paper topics that will spark your creativity and get you started with your next paper. You can pick up one from this list, you can combine several of them, or maybe you will get inspired by this list and come with several topics on your own. In any case, make sure that the popular music topic for your research paper is interesting to you personally, and doesn't just sound potentially easy to write about.
1. How is music marketed by demographic? Explore the different ways music companies target various demographic groups such as age and gender. 2. How does the categorization of music affect consumer purchasing decisions? Examine how the emphasis on genre either enhances sales or limits consumer interest. 3. Does the album have a future in the streaming era? Consider whether the album can survive in an era when singles are streamed in customized playlists. 4. How has music changed over the past half century? Explore some of the major themes and developments that have shaped popular music since the dawn of the rock-n-roll era. 5. Research the most influential musicians of a specific era. By comparing and contrasting the careers of key figures from a particular era, you can pain a picture of a moment in time. 6. What makes music "classical"? How we define "classical" music says a lot about power and privilege. Explore who decides and what criteria get used. 7. Does music have an impact on our bodies? Research medical evidence whether music can impact human health. 8. Does music have an impact on our mental health? Examine research on the use of music for mental health and therapeutic purposes. 9. Music and children: Is the Mozart effect real? How can music education impact children's academic and social development? 10. Can music education aid in memory training and memory development? Consider the current academic research and evaluate the validity of claims for music as a memory aid. 11. How does music impact dance? Music and dance are inextricably linked. Look at some of the ways that music impacts the development of dance. 12. How does a musician become successful? Examine key routes to success and what a music student can do to set themselves up for a career. 13. What other careers does a music degree prepare a student for? Research how music degrees can set the stage for careers beyond the music industry. 14. How does music impact fashion? Look at how rock-n-roll and hip hop have shaped fashion trends. 15. How is music used in advertising? Look into the reasons that artists are licensing hit singles to sell products and how that impacts consumers' views of music. 16. Classical music vs. rock-n-roll: Which has been more influential? Examine the arguments for both sides and take a position. 17. Look into the sociology of tribute bands and consider the reasons that people would dedicate their lives to imitating other musicians. 18. It is often said that "music soothes the savage beast," and farmers often use music to calm livestock. Is there truth to the notion that music has a positive impact on animals? Explore the research and draw conclusions.
19. Music has been an important part of war throughout history, both martial music meant to rally the troops and anti-war songs. Examine the role of music in supporting and opposing war. 20. Music vs. poetry: Can song lyrics be considered a form of poetry? Why or why not? 21. How does hip-hop support African American culture and heritage? 22. Is there a problem with the close association of country music with political conservatism? 23. Select your favorite piece of music and research the influences that played a role in its creation and development. 24. Research the processes that archaeologists have used to reconstruct the sound of ancient music. 25. How do covers transform songs? Explore how covers are created now meaning.
After choosing the topic you like the most, save this list or this page to bookmarks for further references. It is good to have a library of resources at your fingertips.
Let experts rock when you are stuck
If these topics aren't enough to get you started, there is another trick to help you succeed. You can always find someone to help you with your research paper. You can contact a paper writing service online like WriteMyPaperHub and ask a professional essay writer, "Can I pay you to write my paper like an expert?" Once you do, a writer will determine what you need for your project and will begin writing a high-quality music research paper that will address your essay topic quickly, effectively, and with exceptional research and writing. You should feel free to take advantage of services like this whenever you get stuck so you can be successful with each and every music research paper.
Learning from the best and the brightest is more than beneficial. You have an opportunity to see how professional writers elaborate on a particular topic, which references they use, how they structure the whole thing. One ordered paper can be an example for your further works for months. Also, it is proven that students these days are overwhelmed with the number of assignments, and due to continuous lockdowns and limitations have less access to libraries and other necessary resources. If you feel like the pressure is too high, don't hesitate to delegate this assignment.

Astroworld Tragedy Preventable: Safety Team Questioned Crowd Capacity Before Deathly Event

Ultra Music Festival 2024 Postponed Last Minute Because of Extreme Weather: Report

Lollapalooza 2024 Lineup Announced: Where to Buy Tickets to Watch SZA, Blink-182, More

Kanye West Rolling Loud Appearance: 'No Different From a Listening Party'

Anderson .Paak Excited to Headline New Orleans Jazz Festival 2024: 'This Is What I Want to Do'

Diddy 'Manhandled' Jennifer Lopez While Dating? Fans Now Convinced After Exposure of Rapper's Dirty Laundry

Where Is Diddy? Videos About the Embattled Rapper's Alleged Arrest Spark Concerns

Aubrey O'Day Makes Smug Response to Sean 'Diddy' Combs' Home Raids: 'What You Sow, You Shall Reap'

Jennifer Lopez 'This Is Me…Now' Album 'Flopped' Because 'The World Has Moved On,' Publicist Says

TikTok Singer Anais Robin Dead at 21 Following a Tragic Accident: Report

Deleted Video of Kanye West Making Bold Diddy Accusation Mysteriously Resurfaced Amid Trafficking Probe

Michael Jackson Kids Presents United Front Amid Ongoing Estate Battle Against Katherine Jackson
Pete Townshend Brings The Who's 'Tommy' to the 'Tonight Show'
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Open access
- Published: 22 June 2021
Mental health and music engagement: review, framework, and guidelines for future studies
- Daniel E. Gustavson ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1470-4928 1 , 2 ,
- Peyton L. Coleman ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5388-6886 3 ,
- John R. Iversen 4 ,
- Hermine H. Maes 5 , 6 , 7 ,
- Reyna L. Gordon 2 , 3 , 8 , 9 &
- Miriam D. Lense 2 , 8 , 9
Translational Psychiatry volume 11 , Article number: 370 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
36k Accesses
21 Citations
73 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Medical genetics
- Psychiatric disorders
Is engaging with music good for your mental health? This question has long been the topic of empirical clinical and nonclinical investigations, with studies indicating positive associations between music engagement and quality of life, reduced depression or anxiety symptoms, and less frequent substance use. However, many earlier investigations were limited by small populations and methodological limitations, and it has also been suggested that aspects of music engagement may even be associated with worse mental health outcomes. The purpose of this scoping review is first to summarize the existing state of music engagement and mental health studies, identifying their strengths and weaknesses. We focus on broad domains of mental health diagnoses including internalizing psychopathology (e.g., depression and anxiety symptoms and diagnoses), externalizing psychopathology (e.g., substance use), and thought disorders (e.g., schizophrenia). Second, we propose a theoretical model to inform future work that describes the importance of simultaneously considering music-mental health associations at the levels of (1) correlated genetic and/or environmental influences vs. (bi)directional associations, (2) interactions with genetic risk factors, (3) treatment efficacy, and (4) mediation through brain structure and function. Finally, we describe how recent advances in large-scale data collection, including genetic, neuroimaging, and electronic health record studies, allow for a more rigorous examination of these associations that can also elucidate their neurobiological substrates.
Similar content being viewed by others
Biological principles for music and mental health
Daniel L. Bowling

A comprehensive investigation into the genetic relationship between music engagement and mental health
Laura W. Wesseldijk, Yi Lu, … Miriam A. Mosing
The effects of playing music on mental health outcomes
Laura W. Wesseldijk, Fredrik Ullén & Miriam A. Mosing
Introduction
Music engagement, including passive listening and active music-making (singing, instrument playing), impacts socio-emotional development across the lifespan (e.g., socialization, personal/cultural identity, mood regulation, etc.), and is tightly linked with many cognitive and personality traits [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. A growing literature also demonstrates beneficial associations between music engagement and quality of life, well-being, prosocial behavior, social connectedness, and emotional competence [ 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 ]. Despite these advances linking engagement with music to many wellness characteristics, we have a limited understanding of how music engagement directly and indirectly contributes to mental health, including at the trait-level (e.g., depression and anxiety symptoms, substance use behaviors), clinical diagnoses (e.g., associations with major depressive disorder (MDD) or substance use disorder (SUD) diagnoses), or as a treatment. Our goals in this scoping review are to (1) describe the state of music engagement research regarding its associations with mental health outcomes, (2) introduce a theoretical framework for future studies that highlight the contribution of genetic and environmental influences (and their interplay) that may give rise to these associations, and (3) illustrate some approaches that will help us more clearly elucidate the genetic/environmental and neural underpinnings of these associations.
Scope of the article
People interact with music in a wide variety of ways, with the concept of “musicality” broadly including music engagement, music perception and production abilities, and music training [ 9 ]. Table 1 illustrates the breadth of music phenotypes and example assessment measures. Research into music and mental health typically focuses on measures of music engagement, including passive (e.g., listening to music for pleasure or as a part of an intervention) and active music engagement (e.g., playing an instrument or singing; group music-making), both of which can be assessed using a variety of objective and subjective measures. We focus primarily on music engagement in the current paper but acknowledge it will also be important to examine how mental health traits relate to other aspects of musicality as well (e.g., perception and production abilities).
Our scoping review and theoretical framework incorporate existing theoretical and mechanistic explanations for how music engagement relates to mental health. From a psychological perspective, studies have proposed that music engagement can be used as a tool for encouraging self-expression, developing emotion regulation and coping skills, and building community [ 10 , 11 ]. From a physiological perspective, music engagement modulates arousal levels including impacts on heart rate, electrodermal activity, and cortisol [ 12 , 13 ]. These effects may be driven in part by physical aspects of music (e.g., tempo) or rhythmic movements involved in making or listening to music, which impact central nervous system functioning (e.g., leading to changes in autonomic activity) [ 14 ], as well as by personality and contextual factors (e.g., shared social experiences) [ 15 ]. Musical experiences also impact neurochemical processes involved in reward processing [ 10 , 13 , 14 , 16 , 17 , 18 ], which are also implicated in mental health disorders (e.g., substance use; depression). Thus, an overarching framework for studying music-mental health associations should integrate the psychological, physiological, and neurochemical aspects of these potential associations. We propose expanding this scope further through consideration of genetic and environmental risk factors, which may give rise to (and/or interact with) other factors to impact health and well-being.
Regarding mental health, it is important to recognize the hierarchical structure of psychopathology [ 19 , 20 ]. Common psychological disorders share many features and cluster into internalizing (e.g., MDD, generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)), externalizing (e.g., SUDs, conduct disorder), and thought disorders (e.g., bipolar disorder, schizophrenia), with common variance shared even across these domains [ 20 ]. These higher-order constructs tend to explain much of the comorbidity among individual disorders, and have helped researchers characterize associations between psychopathology, cognition, and personality [ 21 , 22 , 23 ]. We use this hierarchical structure to organize our review. We first summarize the emerging literature on associations between music engagement and generalized well-being that provides promising evidence for associations between music engagement and mental health. Next, we summarize associations between music engagement and internalizing traits, externalizing traits/behaviors, and thought disorders, respectively. Within these sections, we critically consider the strengths and shortcomings of existing studies and how the latter may limit the conclusions drawn from this work.
Our review considers both correlational and experimental studies (typically, intervention studies; see Fig. 1 for examples of study designs). We include not only studies that examine symptoms or diagnoses based on diagnostic interviews, but also those that assess quantitative variation (e.g., trait anxiety) in clinical and nonclinical populations. This is partly because individuals with clinical diagnoses may represent the extreme end of a spectrum of similar, sub-clinical, problems in the population, a view supported by evidence that genetic influences on diagnosed psychiatric disorders or DSM symptom counts are similar to those for trait-level symptoms in the general population [ 24 , 25 ]. Music engagement may be related to this full continuum of mental health, including correlations with trait-level symptoms in nonclinical populations and alleviation of symptoms from clinical disorders. For example, work linking music engagement to subjective well-being speaks to potential avenues for mental health interventions in the population at large.
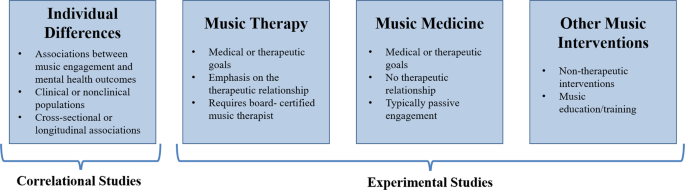
Within experimental studies, music interventions can include passive musical activities (e.g., song listening, music and meditation, lyric discussion, creating playlists) or active musical activities (e.g., creative methods, such as songwriting or improvisation and/or re-creative methods, such as song parody).
The goal of this scoping review was to integrate across related, but often disconnected, literatures in order to propose a comprehensive theoretical framework for advancing our understanding of music-mental health associations. For this reason, we did not conduct a fully systematic search or quality appraisal of documents. Rather, we first searched PubMed and Google Scholar for review articles and meta-analyses using broad search terms (e.g., “review” and “music” and [“anxiety” or “depression” or “substance use”]). Then, when drafting each section, we searched for additional papers that have been published more recently and/or were examples of higher-quality research in each domain. When giving examples, we emphasize the most recent and most well-powered empirical studies. We also conducted some targeted literature searches where reviews were not available (e.g., “music” and [“impulsivity” or “ADHD”]) using the same databases. Our subsequent framework is intended to contextualize diagnostic, symptom, and mechanistic findings more broadly within the scope of the genetic and environmental risk factors on psychopathology that give rise to these associations and (potentially) impact the efficacy of treatment efforts. As such, the framework incorporates evidence from review articles and meta-analyses from various literatures (e.g., music interventions for anxiety [ 26 ], depression [ 27 ]) in combination with experimental evidence of biological underpinnings of music engagement and the perspective provided by newly available methods for population-health approaches (i.e., complex trait genetics, gene–environment interactions).
Music engagement and well-being
A growing body of studies report associations between music engagement and general indices of mental health, including increased well-being or emotional competence, lending support for the possibility that music engagement may also be associated with better specific mental health outcomes. In over 8000 Swedish twins, hours of music practice and self-reported music achievement were associated with better emotional competence [ 5 ]. Similarly, a meta-ethnography of 46 qualitative studies revealed that participation in music activities supported well-being through management of emotions, facilitation of self-development, providing respite from problems, and facilitating social connections [ 28 ]. In a sample of 1000 Australian adults, individuals who engaged with music, such as singing or dancing with others or attending concerts reported greater well-being vs. those who engaged in these experiences alone or did not engage. Other types of music engagement, such as playing an instrument or composing music were not associated with well-being in this sample [ 4 ]. Earlier in life, social music experiences (including song familiarity and synchronous movement to music) are associated with a variety of prosocial behaviors in infants and children [ 6 ], as well as positive affect [ 7 ]. Thus, this work provides some initial evidence that music engagement is associated with better general mental health outcomes in children and adults with some heterogeneity in findings depending on the specific type of music engagement.
Music engagement and internalizing problems
MDD, GAD, and PTSD are the most frequently clustered aspects of internalizing psychopathology [ 19 , 24 , 29 , 30 ]. Experimental studies provide evidence for the feasibility of music intervention efforts and their therapeutic benefits but are not yet rigorous enough to draw strong conclusions. The most severe limitations are small samples, the lack of appropriate control groups, few interventions with multiple sessions, and publications omitting necessary information regarding the intervention (e.g., intervention fidelity, inclusion/exclusion criteria, education status of intervention leader) [ 31 , 32 , 33 ]. Correlational studies, by contrast, suggest musicians are at greater risk for internalizing problems, but that they use music engagement as a tool to help manage these problems [ 34 , 35 ].
Experimental studies
Randomized controlled trials have revealed that music interventions (including both music therapies administered by board-certified music therapists and other music interventions) are associated with reduced depression, anxiety, and PTSD symptoms [ 26 , 27 , 33 , 36 ]. A review of 28 studies reported that 26 revealed significantly reduced depression levels in music intervention groups compared to control groups, including the 9 studies which included active non-music intervention control groups (e.g., reading sessions, “conductive-behavior” psychotherapy, antidepressant drugs) [ 27 ]. A similar meta-analysis of 19 studies demonstrated that music listening is effective at decreasing self-reported anxiety in healthy individuals [ 26 ]. A review of music-based treatment studies related to PTSD revealed similar conclusions [ 36 ], though there were only four relevant studies. More recent studies confirm these findings [ 37 , 38 , 39 ], such as one randomized controlled trial that demonstrated reduced depression symptoms in older adults following musical improvisation exercises compared to an active control group (gentle gymnastic activities) [ 39 ].
This work is promising given that some studies have observed effects even when compared to traditional behavior therapies [ 40 , 41 ]. However, there are relatively few studies directly comparing music interventions to traditional therapies. Some music interventions incorporate components of other therapeutic methods in their programs including dialectic or cognitive behavior therapies [ 42 ], but few directly compare how the inclusion of music augments traditional behavioral therapy. Still other non-music therapies incorporate music into their practice (e.g., background music in mindfulness therapies) [ 43 , 44 ], but the specific contribution of music in these approaches is unclear. Thus, there is a great need for further systematic research relating music to traditional therapies to understand which components of music interventions act on the same mechanisms as traditional therapies (e.g., developing coping mechanisms and building community) and which bolster or synchronize with other approaches (e.g., by adding structure, reinforcement, predictability, and social context to traditional approaches).
Aside from comparison with other therapeutic approaches, an earlier review of 98 papers from psychiatric in-patient studies concluded that promising effects of music therapy were limited by small sample sizes and methodological shortcomings including lack of reporting of adverse events, exclusion criteria, possible confounders, and characteristics of patients lost to follow-up [ 33 ]. Other problems included inadequate reporting of information on the source population (e.g., selection of patients and proportion agreeing to take part in the study), the lack of masking of interviewers during post-test, and concealment of randomization. Nevertheless, there was some evidence that therapies with active music participation, structured sessions, and multiple sessions (i.e., four or more) improved mood, with all studies incorporating these characteristics reporting significant positive effects. However, most studies have focused on passive interventions, such as music listening [ 26 , 27 ]. Active interventions (e.g., singing, improvising) have not been directly compared with passive interventions [ 27 ], so more work is needed to clarify whether therapeutic effects are indeed stronger with more engaging and active interventions.
Correlational studies
Correlational studies have focused on the use of music in emotional self-regulation. Specifically, individuals high in neuroticism appear to use music to help regulate their emotions [ 34 , 35 ], with beneficial effects of music engagement on emotion regulation and well-being driven by cognitive reappraisal [ 45 ]. Music listening may also moderate the association between neuroticism and depression in adolescents [ 46 ], consistent with a protective effect.
A series of recent studies have used validated self-reported instruments that directly assess how individuals use music activities as an emotion regulation strategy [ 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 ]. In adults, the use of music listening for anger regulation and anxiety regulation was positively associated with subjective well-being, psychological well-being, and social well-being [ 50 ]. In studies of adolescents and undergraduates, the use of music listening for entertainment was associated with fewer depression and anxiety symptoms [ 51 ]. “Healthy” music engagement in adolescents (i.e., using music for relaxation and connection with others) was also positively associated with happiness and school satisfaction [ 49 ]. However, the use of music listening for emotional discharge was also associated with greater depression, anxiety, and stress symptoms [ 51 ], and “unhealthy” music engagement (e.g., ‘hiding’ in music to block others out) was associated with lower well-being, happiness, school satisfaction, and greater depression and rumination [ 49 ]. Other work has highlighted the role of valence in these associations, with individuals who listen to happier music when they are in a bad mood reporting stronger ability for music to influence their mood than those who listen to sad music while in a negative mood [ 52 , 53 ].
This work highlights the importance of considering individuals’ motivations for engaging with music in examining associations with well-being and mental health, and are consistent with the idea that individuals already experiencing depression, anxiety, and stress use music as a therapeutic tool to manage their emotions, with some strategies being more effective than others. Of course, these correlational effects may not necessarily reflect causal associations, but could be due to bidirectional influences, as suggested by claims that musicians may be at higher risk for internalizing problems [ 54 , 55 , 56 ]. It is also necessary to consider demographic and socioeconomic factors in these associations [ 57 ], for example, because arts engagement may be more strongly associated with self-esteem in those with higher education [ 58 ].
It is also necessary to clarify if musicians (professional and/or nonprofessional) represent an already high-risk group for internalizing problems. In one large study conducted in Norway ( N = 6372), professional musicians were higher in neuroticism than the general population [ 56 ]. Another study of musician cases ( N = 9803) vs. controls ( N = 49,015) identified in a US-based research database through text-mining of medical records found that musicians are at greater risk of MDD (Odds ratio [OR] = 1.21), anxiety disorders (OR = 1.25), and PTSD (OR = 1.13) [ 55 ]. However, other studies demonstrate null associations between musician status and depression symptoms [ 5 ] or mixed associations [ 59 ]. In N = 10,776 Swedish twins, for example, professional and amateur musicians had more self-reported burnout symptoms [ 54 ]. However, neither playing music in the past, amateur musicianship, nor professional musicianship was significantly associated with depression or anxiety disorder diagnoses.
Even if musicians are at higher risk, such findings can still be consistent with music-making being beneficial and therapeutic (e.g., depression medication use is elevated in individuals with depressive symptoms because it is a treatment). Clinical samples may be useful in disentangling these associations (i.e., examining if those who engage with music more frequently have reduced symptoms), and wider deployment of measures that capture emotion regulation strategies and motivations for engaging with music will help shed light on whether high-risk individuals engage with music in qualitatively different ways than others [ 51 , 57 ]. Later, we describe how also considering the role of genetic and environmental risk factors in these associations (e.g., if individuals at high genetic and/or environmental risk self-select into music environments because they are therapeutic) can help to clarify these questions.
Music engagement and externalizing problems
The externalizing domain comprises SUDs, and also includes impulsivity, conduct disorder, and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), especially in adolescents [ 20 , 24 , 60 , 61 ]. Similar to the conclusions for internalizing traits, experimental studies show promising evidence that music engagement interventions may reduce substance use, ADHD, and other externalizing symptoms, but conclusions are limited by methodological limitations. Correlational evidence is sparce, but there is less reason to suspect musicians are at higher risk for externalizing problems.
Intervention studies have demonstrated music engagement is helpful in patients with SUDs, including reducing withdrawal symptoms and stress, allowing individuals to experience emotions without craving substance use, and making substance abuse treatment sessions more enjoyable and motivating [ 62 , 63 , 64 ] (for a systematic review, see [ 65 ]). Similar to the experimental studies of internalizing traits, however, these studies would also benefit from larger samples, better controls, and higher-quality reporting standards.
Music intervention studies for ADHD are of similar quality. Such interventions have been shown to reduce inattention [ 66 ], decrease negative mood [ 67 ], and increase reading comprehension for those with ADHD [ 68 ]. However, there is a great amount of variability among children with ADHD, as some may find music distracting while others may focus better in the presence of music [ 69 ].
Little research has been conducted to evaluate music engagement interventions for impulsivity or conduct disorder problems, and findings are mixed. For example, a music therapy study of 251 children showed that beneficial effects on communication skills (after participating in a free improvisation intervention) was significant, though only for the subset of children above age 13 [ 70 ]. Another study suggested the promising effects of music therapy on social skills and problem behaviors in 89 students selected based on social/emotional problem behaviors, but did not have a control group [ 71 ]. Other smaller studies ( N < 20 each) show inconsistent results on disruptive behaviors and aggression [ 72 , 73 ].
Correlational studies on externalizing traits are few and far between. A number of studies examined how listening habits for different genres of music relate to more or less substance use [ 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 ]. However, these studies do not strongly illuminate associations between music engagement and substance use because musical genres are driven by cultural and socioeconomic factors that vary over the lifespan. In the previously cited large study of American electronic medical records [ 55 ] where musicianship was associated with more internalizing diagnoses, associations were nonsignificant for “tobacco use disorder” (OR = 0.93), “alcoholism” (OR = 1.01), “alcohol-related disorders” (OR = 1.00), or “substance addiction and disorders” (OR = 1.00). In fact, in sex-stratified analyses, female musicians were at significantly decreased risk for tobacco use disorder (OR = 0.85) [ 55 ]. Thus, there is less evidence musicians are at greater risk for externalizing problems than in other areas.
Regarding other aspects of externalizing, some studies demonstrate children with ADHD have poor rhythm skills, opening a possibility that working on rhythm skills may impact ADHD [ 78 , 79 ]. For example, music might serve as a helpful scaffold (e.g., for attention) due to its regular, predictable rhythmic beat. It will be important to examine whether these associations with music rhythm are also observed for measures of music engagement, especially in larger population studies. Finally, musicians were reported to have lower impulsiveness than prior population samples, but were not compared directly to non-musicians [ 80 , 81 ].
Music engagement and thought disorders
Thought disorders typically encompass schizophrenia and bipolar disorder [ 20 ]. Trait-level measures include schizotypal symptoms and depression symptoms. Much like internalizing, music interventions appear to provide some benefits to individuals with clinical diagnoses, but musicians may be at higher risk for thought disorders. Limitations of both experimental and correlational studies are similar to those for internalizing and externalizing.
Music intervention studies have been conducted with individuals with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. A recent meta-analysis of 18 music therapy studies for schizophrenia (and similar disorders) [ 82 ] demonstrated that music therapy plus standard care (compared to standard care alone) demonstrated improved general mental health, fewer negative symptoms of schizophrenia, and improved social functioning. No effects were observed for general functioning or positive symptoms of schizophrenia. Critiques echoed those described above. Most notably, although almost all studies had low risk of biases due to attrition, unclear risk of bias was evident in the vast majority of studies (>75%) for selection bias, performance bias, detection bias, and reporting bias. These concerns highlight the need for these studies to report more information about their study selection, blinding procedure, and outcomes.
More recent papers suggest similar benefits of music therapies in patients with psychosis [ 83 ] and thought disorders [ 84 ], with similar limitations (e.g., one study did not include a control group). Finally, although a 2021 review did not uncover more recent articles related to bipolar disorder, they argued that existing work suggests music therapy has the potential both to treat bipolar disorder symptoms and alleviate subthreshold symptoms in early stages of the disorder [ 85 ].
Much like internalizing, findings from the few existing studies suggest that musicians may be at higher risk for thought disorders. In the large sample of Swedish twins described earlier [ 54 ], playing an instrument was associated with more schizotypal symptoms across multiple comparisons (professional musicians vs. non-players; amateur musicians vs. non-players; still plays an instrument vs. never played). However, no associations were observed for schizophrenia or bipolar disorder diagnoses across any set of comparison groups. Another study demonstrated that individuals with higher genetic risk for schizophrenia or bipolar disorder were more likely to be a member of a creative society (i.e., actor or dancer, musician, visual artist, or writer) or work in a profession in these fields [ 86 ]. Furthermore, musician status was associated with “bipolar disorder” (OR = 1.18) and “schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders” (OR = 1.18) in US electronic health records (EHRs) [ 55 ].
Interim summary
There is promising evidence that music engagement is associated with better mental health outcomes. Music engagement is positively associated with quality of life, well-being, social connectedness, and emotional competence. However, some individuals who engage with music may be at higher risk for mental health problems, especially internalizing and thought disorders. More research is needed to disentangle these contrasting results, including clarifying how “healthy” music engagement (e.g., for relaxation or social connection) leads to greater well-being or successful emotion regulation, and testing whether some individuals are more likely to use music as a tool to regulate emotions (e.g., those with high neuroticism) [ 34 , 35 ]. Similarly, it will be important to clarify whether the fact that musicians may be an at-risk group is an extension of working in an artistic field in general (which may feature lower pay or lack of job security) and/or if similar associations are observed with continuous music engagement phenotypes (e.g., hours of practice). As we elaborate on later, genetically informative datasets can help clarify these complex associations, for example by tested whether musicians are at higher genetic risk for mental health problems but their music engagement mitigates these risks.
Music intervention studies are feasible and potentially effective at treating symptoms in individuals with clinical diagnoses, including depression, anxiety, and SUDs. However, it will be essential to expand these studies to include larger samples, random sampling, and active control groups that compare the benefits of music interventions to traditional therapies and address possible confounds. These limitations make it hard to quantify how specific factors influence the effectiveness of interventions, such as length/depth of music training, age of sample, confounding variables (e.g., socioeconomic status), and type of intervention (e.g., individual vs. group sessions, song playing vs. songwriting, receptive vs. active methods). Similarly, the tremendous breadth of music engagement activities and measures makes it difficult to identify the specific aspects of music engagement that convey the most benefits to health and well-being [ 87 ]. It is therefore necessary to improve reporting quality of studies so researchers can better identify these potential moderators or confounds using systematic approaches (e.g., meta-analyses).
Various mechanisms have been proposed to explain the therapeutic effects of music on mental health, including psychological (e.g., building communities, developing coping strategies) [ 10 , 11 ] and specific neurobiological drivers (e.g., oxytocin, cortisol, autonomic nervous system activity) [ 12 , 13 , 14 ]. However, it will be vital to conduct more systematic research comparing the effects of music interventions to existing therapeutic methods and other types of creative activities (e.g., art [ 88 ]) to quantify which effects and mechanisms are specific to music engagement. Music interventions also do not have to be an alternative to other treatments, but may instead support key elements of traditional interventions, such as being engaging, enjoyable, providing social context, and increasing structure and predictability [ 89 ]. Indeed, some music therapists incorporate principals from existing psychotherapeutic models [ 42 , 90 ] and, conversely, newer therapeutic models (e.g., mindfulness) incorporate music into their practice [ 43 , 44 ]. It is not yet possible to disentangle which aspects of music interventions best synergize with or strengthen standard psychotherapeutic practices (which are also heterogeneous), but this will be possible with better reporting standards and quality experimental design.
To encapsulate and extend these ideas, we next propose a theoretical framework that delineates key aspects of how music engagement may relate to mental health, which is intended to be useful for guiding future investigations in a more systematic way.
Theoretical framework for future studies
Associations between music engagement and mental health may take multiple forms, driven by several different types of genetic predispositions and environmental effects that give rise to, and interact with, proposed psychological and neurobiological mechanisms described earlier. Figure 2 displays our theoretical model in which potential beneficial associations with music are delineated into testable hypotheses. Four key paths characterize specific ways in which music engagement may relate to (and influence) mental health traits, and thus represent key research questions to be addressed in future studies.
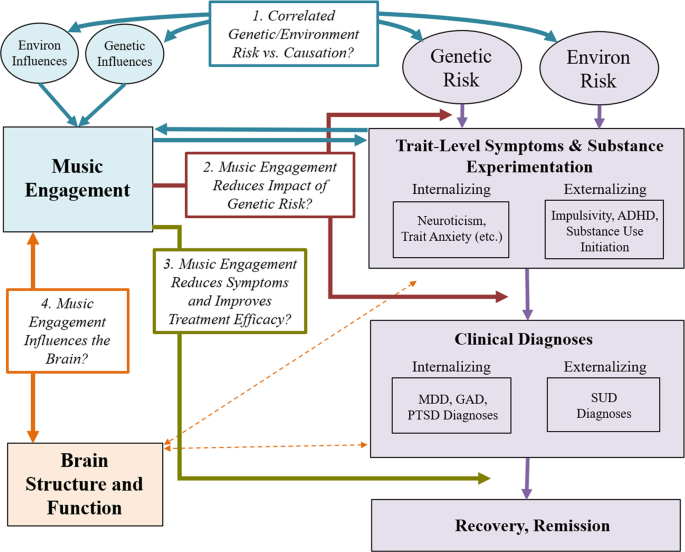
Progression of mental health problems is based on a diathesis-stress model, where genetic predispositions and environmental exposures result in later problems (which can be remedied through treatment). Potential associations with music engagement include (Path 1; blue arrows) correlated genetic/environmental influences and/or causal associations between music engagement and trait-level mental health outcomes; (Path 2; red arrows) interactions between music engagement and risk factors to predict later trait-level or clinical level symptoms; and (Path 3; gold arrow) direct effects of music engagement on reducing symptoms or improving treatment efficacy. Path 4 (orange arrows) illustrates the importance of understanding how these potential protective associations are driven by neuroanatomy and function. MDD major depressive disorder, GAD generalized anxiety disorder, PTSD posttraumatic stress disorder, SUD substance use disorder(s).
Path 1: Music engagement relates to mental health through correlated genetic and environmental risk factors and/or causation
The diathesis-stress model of psychiatric disease posits that individuals carry different genetic liabilities for any given disorder [ 91 , 92 , 93 ], with disorder onset depending on the amount of negative vs. protective environmental life events and exposures the individual experiences. Although at first glance music engagement appears to be an environmental exposure, it is actually far from it. Twin studies have demonstrated that both music experiences and music ability measures are moderately heritable and genetically correlated with cognitive abilities like non-verbal intelligence [ 94 , 95 , 96 , 97 ]. Music engagement may be influenced by its own set of environmental influences, potentially including socioeconomic factors and availability of instruments. Thus, music engagement can be viewed as a combination of genetic and environmental predispositions and availability of opportunities for engagement [ 98 ] that are necessary to consider when evaluating associations with mental health [ 54 ].
When examining music-mental health associations, it is thus important to evaluate if associations are in part explained by correlated genetic or environmental influences (see Fig. 3 for schematic and explanation for interpreting genetic/environmental correlations). On one hand, individuals genetically predisposed to engage with music may be at lower risk of experiencing internalizing or externalizing problems. Indeed, music engagement and ability appear associated with cognitive abilities through genetic correlations [ 3 , 99 ], which may apply to music-mental health associations as well. On the other, individuals at high genetic risk for neuroticism or psychopathology may be more likely to engage with music because it is therapeutic, suggesting a genetic correlation in the opposite direction (i.e., increased genetic risk for musicians). To understand and better contextualize the potential therapeutic effects of music engagement, it is necessary to quantify these potential genetic associations, while simultaneously evaluating whether these associations are explained by correlated environmental influences.
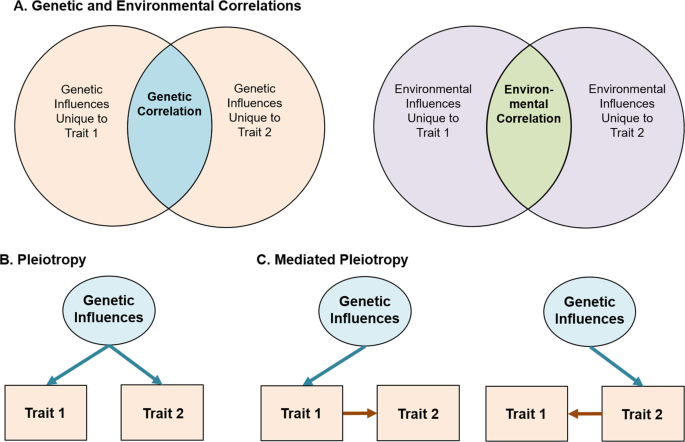
Variance in any given trait is explained by a combination of genetic influences (i.e., heritability) and environmental influences. For complex traits (e.g., MDD or depression symptoms), cognitive abilities (e.g., intelligence), and personality traits (e.g., impulsivity), many hundreds or thousands of independent genetic effects are combined together in the total heritability estimate. Similarly, environmental influences typically represent a multitude of factors, from individual life events to specific exposures (e.g., chemicals, etc.). The presence of a genetic or environmental correlation between traits indicates that some set of these influences have an impact on multiple traits. A Displayed using a Venn diagram. Identifying the strength of genetic vs. environmental correlations can be useful in testing theoretical models and pave the way for more complex genetic investigations. Beyond this, gene identification efforts (e.g., genome-wide association studies) and additional analyses of the resulting data can be used to classify whether these associations represent specific genetic influences that affect both traits equally (i.e., genetic pleiotropy ( B )) or whether a genetic influence impacts only one trait which in turn causes changes in the other (i.e., mediated genetic pleiotropy ( C )). Environmental influences can also act pleiotropically or in a mediated-pleiotropy manner, but only genetic influences are displayed for simplicity.
Beyond correlated genetic and environmental influences, music engagement and mental health problems may be associated with one another through direct influences (including causal impacts). This is in line with earlier suggestions that music activities (e.g., after-school programs, music practice) engage adolescents, removing opportunities for drug-seeking behaviors [ 100 ], increasing their social connections to peers [ 101 ], and decreasing loneliness [ 41 ]. Reverse causation is also possible, for example, if experiencing mental health problems causes some individuals to seek out music engagement as a treatment. Longitudinal and genetically informative studies can help differentiate correlated risk factors (i.e., genetic/environmental correlations) from causal effects of music engagement (Fig. 2 , blue arrows) [ 102 ].
Path 2: Engagement with music reduces the impact of genetic risk
Second, genetic and environmental influences may interact with each other to influence a phenotype. For example, individual differences in music achievement are more pronounced in those who engage in practice or had musically enriched childhood environments [ 97 , 98 ]. Thus, music exposures may not influence mental health traits directly but could impact the strength of the association between genetic risk factors and the emergence of trait-level symptoms and/or clinical diagnoses. Such associations might manifest as decreased heritability of trait-level symptoms in musicians vs. non-musicians (upper red arrow in Fig. 2 ). Alternatively, if individuals high in neuroticism use music to help regulate their emotions [ 34 , 35 ], those who are not exposed to music environments might show stronger associations between neuroticism and later depressive symptoms or diagnoses than those engaged with music (lower red arrow in Fig. 2 ). Elucidating these possibilities will help disentangle the complex associations between music and mental health and could be used to identify which individuals would benefit most from a music intervention (especially preventative interventions). Later, we describe some specific study designs that can test hypotheses regarding this gene-environment interplay.
Path 3: Music engagement improves the efficacy of treatment (or acts as a treatment)
For individuals who experience severe problems (e.g., MDD, SUDs), engaging with music may reduce symptoms or improve treatment outcomes. This is the primary goal of most music intervention studies [ 27 , 33 ] (Fig. 2 , gold arrow). However, and this is one of the central messages of this model, it is important to consider interventions in the context of the paths discussed above. For example, if music engagement is genetically correlated with increased risk for internalizing or externalizing problems (Path 1) and/or if individuals at high genetic risk for mental health problems have already been using music engagement to develop strategies to deal with subthreshold symptoms (Path 2), then may be more likely to choose music interventions over other alternatives and find them more successful. Indeed, the beneficial aspects of music training on cognitive abilities appear to be drastically reduced in samples that were randomly sampled [ 103 ]. Therefore, along with other necessary reporting standards discussed above [ 32 , 33 ], it will be useful for studies to report participants’ prior music experience and consider these exposures in evaluating the efficacy of interventions.
Path 4: Music engagement influences brain structure and function
Exploring associations between music engagement and brain structure and function will be necessary to elucidate the mechanisms driving the three paths outlined above. Indeed, there are strong links between music listening and reward centers of the brain [ 104 , 105 ] including the nucleus accumbens [ 106 , 107 ] and ventral tegmental areas [ 108 ] that are implicated in the reward system for all drugs of abuse [ 109 , 110 , 111 , 112 ] and may relate to internalizing problems [ 113 , 114 , 115 ]. Moreover, activity in the caudate may simultaneously influence rhythmic sensorimotor synchronization, monetary reward processing, and prosocial behavior [ 116 ]. Furthermore, music listening may help individuals control the effect of emotional stimuli on autonomic and physiological responses (e.g., in the hypothalamus) and has been shown to induce the endorphinergic response blocked by naloxone, an opioid antagonist [ 18 , 117 ].
This work focusing on music listening and reward processing has not been extended to music making (i.e., active music engagement), though some differences in brain structure and plasticity between musicians and non-musicians have been observed for white matter (e.g., greater fractional anisotropy in corpus callosum and superior longitudinal fasciculus) [ 118 , 119 , 120 , 121 ]. In addition, longitudinal studies have revealed that instrument players show more rapid cortical thickness maturation in prefrontal and parietal areas implicated in emotion and impulse control compared to non-musician children/adolescents [ 122 ]. Importantly, because the existing evidence is primarily correlational, these cross-sectional and longitudinal structural differences between musicians and non-musicians could be explained by genetic correlations, effects of music training, or both, making them potentially relevant to multiple paths in our model (Fig. 2 ). Examining neural correlates of music engagement in more detail will shed light on these possibilities and advance our understanding of the correlates and consequences of music engagement, and the mechanisms that drive the associations discussed above.
New approaches to studying music and mental health
Using our theoretical model as a guide, we next highlight key avenues of research that will help disentangle these music-mental health associations using state-of-the-art approaches. They include the use of (1) genetic designs, (2) neuroimaging methods, and (3) large biobanks of EHRs.
Genetic designs
Genetic designs provide a window into the biological underpinnings of music engagement [ 123 ]. Understanding the contribution of genetic risk factors is crucial to test causal or mechanistic models regarding potential associations with mental health. At the most basic level, twin and family studies can estimate genetic correlations among music ability or engagement measures and mental health traits or diagnoses. Genetic associations can be examined while simultaneously quantifying environmental correlations, as well as evaluating (bidirectional) causal associations, by testing competing models or averaging across different candidate models [ 102 , 124 ], informing Path 1.
By leveraging samples with genomic, music engagement, and mental health data, investigators can also examine whether individuals at higher genetic risk for psychopathology (e.g., for MDD) show stronger associations between music engagement measures and their mental health outcomes (Path 2). As a theoretical example, individuals with low genetic risk for MDD are unlikely to have many depressive symptoms regardless of their music engagement, so the association between depressive symptoms and music engagement may be weak if focusing on these individuals. However, individuals at high genetic risk for MDD who engage with music may have fewer symptoms than their non-musician peers (i.e., a stronger negative correlation). This is in line with recent work revealing the heritability of depression is doubled in trauma exposed compared to non-trauma exposed individuals [ 125 ].
Gene–environment interaction studies using polygenic scores (i.e., summed indices of genetic risk based on genome-wide association studies; GWAS) are becoming more common [ 126 , 127 ]. There are already multiple large GWAS of internalizing and externalizing traits [ 128 , 129 , 130 ], and the first large-scale GWAS of a music measure indicates that music rhythm is also highly polygenic [ 131 ]. Importantly, is not necessary to have all traits measured in the same sample to examine cross-trait relationships. Studies with only music engagement and genetic data, for example, can still examine how polygenic scores for depression predict music engagement, or interact with music engagement measures to predict other study outcomes. Figure 4 displays an example of a GWAS and how it can be used to compute and apply a polygenic score to test cross-trait predictions.
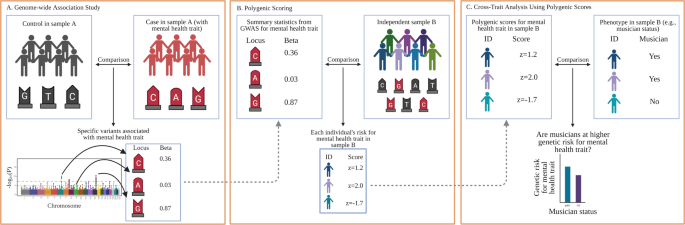
A GWAS are conducted by examining whether individual genetic loci (i.e., single-nucleotide polymorphisms, or SNPs, depicted with G, A, C, and T labels within a sample (or meta-analysis) differentiate cases from controls. The example is based on a dichotomous mental health trait (e.g., major depressive disorder diagnosis), but GWAS can be applied to other dichotomous and continuous phenotypes, such as trait anxiety, musician status, or hours of music practice. Importantly, rather than examining associations on a gene-by-gene basis, GWAS identify relevant genetic loci using SNPs from across the entire genome (typically depicted using a Manhattan plot, such as that displayed at the bottom of A ). B After a GWAS has been conducted on a given trait, researchers can use the output to generate a polygenic score (sometimes called a polygenic risk score) in any new sample with genetic data by summing the GWAS effect sizes for each SNP allele present in a participant’s genome. An individual with a z = 2.0 would have many risk SNPs for that trait, whereas an individual with z = −2 would have much fewer risk SNPs. C Once a polygenic score is generated for all participants, it can be applied like any other variable in the new sample. In this example, researchers could examine whether musicians are at higher (or lower) genetic risk for a specific disorder. Other more complex analyses are also possible, such as examining how polygenic scores interact with existing predictors (e.g., trauma exposure) or polygenic scores for other traits to influence a phenotype or predict an intervention outcome. Created with BioRender.com.
Finally, longitudinal twin and family studies continue to be a promising resource for understanding the etiology and developmental time-course of the correlates of mental health problems. Such designs can be used to examine whether associations between music and mental health are magnified based on other exposures or psychological constructs (gene-by-environment interactions) [ 132 ], and whether parents engaged with music are more likely to pass down environments that are protective or hazardous for later mental health (gene-environment correlations) in addition to passing on their genes. These studies also provide opportunities to examine whether these associations change across key developmental periods. The publicly available Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development study, for example, is tracking over 10,000 participants (including twin and sibling pairs) throughout adolescence, with measures of music engagement and exhaustive measures of mental health, cognition, and personality, as well as neuroimaging and genotyping [ 133 , 134 ]. Although most large samples with genomic data still lack measures of music engagement, key musical phenotypes could be added to existing study protocols (or to similar studies under development) with relatively low participant burden [ 135 ]. Musical questionnaires and/or tasks may be much more engaging and enjoyable than other tasks, improving volunteers’ research participation experience.
Neuroimaging
Another way to orient the design of experiments is through the exploration of neural mechanisms by which music might have an impact on mental health. This is an enormous, growing, and sometimes fraught literature, but there is naturally a great potential to link our understanding of neural underpinnings of music listening and engagement with the literature on neural bases of mental health. These advances can inform the mechanisms driving successful interventions and inform who may benefit the most from such interventions. We focus on two areas among many: (1) the activation of reward circuitry by music and (2) the impact music has on dynamic patterns of neural activity, both of which are likely vectors for the interaction of music and mental health and provide examples of potential interactions.
Music and reward
The strong effect of music on our emotions has been clearly grounded in its robust activation of reward circuitry in the brain, and motivational and hedonic effects of music listening have been shown to be specifically modulated by dopamine [ 16 , 105 , 136 ]. The prevalence of reward and dopaminergic dysfunction in mental illness makes this a rich area for future studies. For example, emotional responses to music might be used as a substitute for reward circuit deficiencies in depression, and it is intriguing to consider if music listening or music engagement could potentiate such function [ 137 , 138 ].
Music and brain network dynamics
The search for neuronally based biomarkers of aspects of mental illness has been a central thrust within the field [ 139 ], holding promise for the understanding of heterogeneity within disorders and identification of common mechanistic pathways [ 140 ]. A thorough review is beyond the scope of this paper, but several points of contact can be highlighted that might suggest neuro-mechanistic mediators of musical effects on mental health. For example, neurofeedback-directed upregulation of activity in emotion circuitry has been proposed as a therapy for MDD [ 141 ]. Given the emotional effects of music, there is potential for using musical stimuli as an adjuvant, or as a more actively patient-controlled output target for neurofeedback. Growing interest in measures of the dynamic complexity of brain activity in health and disease as measured by magnetic resonance imaging or magneto/electroencephalography (M/EEG) [ 142 ] provides a second point of contact, with abnormalities in dynamic complexity suggested as indicative of mental illness [ 143 ], while music engagement has been suggested to reflect and perhaps affect dynamic complexity [ 144 , 145 ].
The caveats identified in this review apply equally to such neuro-mechanistic studies [ 146 ]. High-quality experimental design (involving appropriate controls and randomized design) has been repeatedly shown to be critical to providing reliable evidence for non-music outcomes of music engagement [ 103 ]. For such studies to have maximal impact, analysis of M/EEG activity not at the scalp level, but at the source level, has been shown to improve the power of biomarkers, and their mechanistic interpretability [ 147 , 148 ]. Moreover, as with genetic influences that typically influence a trait through a multitude of small individual effects [ 149 ], the neural underpinnings of music-mental health associations may be highly multivariate. In the longer term, leveraging large-scale studies and large-scale data standardization and aggregation hold the promise of gleaning deeper cross-domain insights, for which current experimentalists can prepare by adopting standards for the documentation, annotation, and storage of data [ 150 ].
Biobanks and electronic health records
Finally, the use of EHR databases can be useful in quantifying associations between music engagement and mental health in large samples. EHR databases can include hundreds of thousands of records and allow for examination with International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems codes, including MDD, SUD, and schizophrenia diagnoses. This would allow for powerful estimates of music-mental health associations, and exploration of music engagement with other health outcomes.
The principal roadblock to this type of research is that extensive music phenotypes are not readily available in EHRs. However, there are multiple ways to bypass this limitation. First, medical records can be scraped using text-mining tools to identify cases of musician-related terms (e.g., “musician”, “guitarist”, “violinist”). For example, the phenome-wide association study described earlier [ 55 ] compared musician cases and controls identified in a large EHR database through text-mining of medical records and validated with extensive manual review charts. This study was highly powered to detect associations with internalizing and thought disorders (but showed null or protective effects for musicians for SUDs). Many EHR databases also include genomic data, allowing for integration with genetic models even in the absence of music data (e.g., exploring whether individuals with strong genetic predispositions for musical ability are at elevated or reduced risk for specific health diagnosis).
EHRs could also be used as recruitment tools, allowing researchers to collect additional data for relevant music engagement variables and compare with existing mental health diagnoses without having to conduct their own diagnostic interviews. These systems are not only relevant to individual differences research but could also be used to identify patients for possible enrollment in intervention studies. Furthermore, if recruitment for individual differences or intervention studies is done in patient waiting rooms of specific clinics, researchers can target specific populations of interest, have participants complete some relevant questionnaires while they wait, and be granted access to medical record data without having to conduct medical interviews themselves.
Concluding remarks
Music engagement, a uniquely human trait which has a powerful impact on our everyday experience, is deeply tied with our social and cultural identities as well as our personality and cognition. The relevance of music engagement to mental health, and its potential use as a therapeutic tool, has been studied for decades, but this research had not yet cohered into a clear picture. Our scoping review and framework integrated across a breadth of smaller literatures (including extant reviews and meta-analyses) relating music engagement to mental health traits and treatment effects, though it was potentially limited due to the lack of systematic literature search or formal quality appraisal of individual studies. Taken together, the current body of literature suggests that music engagement may provide an outlet for individuals who are experiencing internalizing, externalizing, or thought disorder problems, potentially supporting emotion regulation through multiple neurobiological pathways (e.g., reward center activity). Conducting more rigorous experimental intervention studies, improving reporting standards, and harnessing large-scale population-wide data in combination with new genetic analytic methods will help us achieve a better understanding of how music engagement relates to these mental health traits. We have presented a framework that illustrates why it will be vital to consider genetic and environmental risk factors when examining these associations, leading to new avenues for understanding the mechanisms by which music engagement and existing risk factors interact to support mental health and well-being.
Mankel K, Bidelman GM. Inherent auditory skills rather than formal music training shape the neural encoding of speech. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2018;115:13129–34.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Swaminathan S, Schellenberg EG. Musical competence is predicted by music training, cognitive abilities, and personality. Sci Rep. 2018;8:9223.
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Mosing MA, Pedersen NL, Madison G, Ullen F. Genetic pleiotropy explains associations between musical auditory discrimination and intelligence. PLos One. 2014;9:e113874.
Weinberg MK, Joseph D. If you’re happy and you know it: Music engagement and subjective wellbeing. Psychol Music. 2017;45:257–67.
Article Google Scholar
Theorell TP, Lennartsson AK, Mosing MA, Ullen F. Musical activity and emotional competence - a twin study. Front Psychol. 2014;5:774.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cirelli LK, Trehub SE, Trainor LJ. Rhythm and melody as social signals for infants. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018;1423:66–72.
Zentner M, Eerola T. Rhythmic engagement with music in infancy. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2010;107:5768–73.
Lense MD, Beck S, Liu C, Pfeiffer R, Diaz N, Lynch M, et al. Parents, peers, and musical play: Integrated parent-child music class program supports community participation and well-being for families of children with and without Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front Psychol. 2020;11:11.
Honing H. On the biological basis of musicality. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018;1423:51–6.
Maratos AS, Gold C, Wang X, Crawford MJ. Music therapy for depression. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;1:CD004517.
Ansdell G, Meehan J. “Some Light at the End of the Tunnel”: exploring Users’ evidence for the effectiveness of music therapy in adult mental health settings. Music Med. 2010;2:29–40.
Khalfa S, Bella SD, Roy M, Peretz I, Lupien SJ. Effects of relaxing music on salivary cortisol level after psychological stress. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;999:374–6.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
McKinney CH, Antoni MH, Kumar M, Tims FC, McCabe PM. Effects of guided imagery and music (GIM) therapy on mood and cortisol in healthy adults. Health Psychol. 1997;16:390–400.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Chanda ML, Levitin DJ. The neurochemistry of music. Trends Cogn Sci. 2013;17:179–93.
Olff M, Koch SB, Nawijn L, Frijling JL, Van Zuiden M, Veltman DJ. Social support, oxytocin, and PTSD. Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2014;5:26513.
Ferreri L, Mas-Herrero E, Zatorre RJ, Ripollés P, Gomez-Andres A, Alicart H, et al. Dopamine modulates the reward experiences elicited by music. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2019;116:3793–8.
Evers S, Suhr B. Changes of the neurotransmitter serotonin but not of hormones during short time music perception. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2000;250:144–7.
Blum K, Simpatico T, Febo M, Rodriquez C, Dushaj K, Li M, et al. Hypothesizing music intervention enhances brain functional connectivity involving dopaminergic recruitment: Common neuro-correlates to abusable drugs. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54:3753–58.
Kotov R, et al. The hierarchical Taxonomy of psychopathology (HiTOP): a dimensional alternative to traditional nosologies. J Abnorm Psychol. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1037/abn0000258 .
Caspi A, Houts RM, Belsky DW, Goldman-Mellor SJ, Harrington H, Israel S, et al. The p factor: one general psychopathology factor in the structure of psychiatric disorders? Clin Psychological Sci. 2014;2:119–37.
Whiteside SP, Lynam DR. Understanding the role of impulsivity and externalizing psychopathology in alcohol abuse: Application of the UPPS impulsive behavior scale. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2003;11:210–7.
Tackett JL, Lahey BB, van Hulle C, Waldman I, Krueger RF, Rathouz PJ. Common genetic influences on negative emotionality and a general psychopathology factor in childhood and adolescence. J Abnorm Psychol. 2013;122:1142–53.
Young SE, Friedman NP, Miyake A, Willcutt EG, Corley RP, Haberstick BC, et al. Behavioral disinhibition: liability for externalizing spectrum disorders and its genetic and environmental relation to response inhibition across adolescence. J Abnorm Psychol. 2009;118:117–30.
Gustavson DE, Franz CE, Panizzon MS, Lyons MJ, Kremen WS. Internalizing and externalizing psychopathology in middle age: Genetic and environmental architecture and stability of symptoms over 15 to 20 years. Psychological Med. 2019;50:1–9.
Google Scholar
Martin J, Taylor MJ, Lichtenstein P. Assessing the evidence for shared genetic risks across psychiatric disorders and traits. Psychological Med. 2018;48:1759–74.
Panteleeva Y, Ceschi G, Glowinski D, Courvoisier DS, Grandjean D. Music for anxiety? Meta-analysis of anxiety reduction in non-clinical samples. Psychol Music. 2017;46:473–87.
Leubner D, Hinterberger T. Reviewing the effectiveness of music interventions in treating depression. Front Psychol. 2017;8:1109.
Perkins R, Mason-Bertrand A, Fancourt D, Baxter L, Williamon A. How participatory music engagement supports mental well-being: a meta-ethnography. Qualitative Health Res. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732320944142 .
Lilienfeld SO. Comorbidity between and within childhood externalizing and internalizing disorders: reflections and directions. J. Abnorm Child Psychol. 2003;31:285–91.
Kendler KS, Myers J. The boundaries of the internalizing and externalizing genetic spectra in men and women. Psychological Med. 2014;44:647–55.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Robb SL, Burns DS, Carpenter JS. Reporting guidelines for music-based interventions. J Health Psychol. 2011;16:342–52.
Robb SL, Hanson-Abromeit D, May L, Hernandez-Ruiz E, Allison M, Beloat A, et al. Reporting quality of music intervention research in healthcare: a systematic review. Complement Ther Med. 2018;38:24–41.
Carr C, Odell-Miller H, Priebe S. A systematic review of music therapy practice and outcomes with acute adult psychiatric in-patients. PLos One. 2013;8:e70252.
Miranda D, Blais-Rochette C. Neuroticism and emotion regulation through music listening: a meta-analysis. Musica Sci. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1177/1029864918806341 .
Miranda D. The emotional bond between neuroticism and music. Psychomusicology: Music, Mind, Brain. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1037/pmu0000250 .
Landis-Shack N, Heinz AJ, Bonn-Miller MO. Music therapy for posttraumatic stress in adults: a theoretical review. Psychomusicology. 2017;27:334–342.
Schäfer K, Saarikallio S, Eerola T. Music may reduce loneliness and act as social surrogate for a friend: evidence from an experimental listening study. Music Sci. 2020;3. https://doi.org/10.1177/2059204320935709 .
Braun Janzen T, Al Shirawi MI, Rotzinger S, Kennedy SH, Bartel L. A pilot study investigating the effect of music-based intervention on depression and anhedonia. Front Psychol. 2019;10:1038.
Biasutti M, Mangiacotti A. Music training improves depressed mood symptoms in elderly people: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Aging Hum Dev. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091415019893988 .
Castillo-Pérez S, Gómez-Pérez V, Velasco MC, Pérez-Campos E, Mayoral M-A. Effects of music therapy on depression compared with psychotherapy. Arts Psychother. 2010;37:387–390.
Hendricks CB, Robinson B, Bradley LJ, Davis K. Using music techniques to treat adolescent depression. J Humanist Counseling. 1999;38:39–46.
Chwalek CM, McKinney CH. The use of dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) in music therapy: a sequential explanatory study. J. Music Ther. 2015;52:282–318.
Tang YY, Yang L, Leve LD, Harold GT. Improving executive function and its neurobiological mechanisms through a mindfulness-based intervention: advances within the field of developmental neuroscience. Child Dev. Perspect. 2012;6:361–66.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Didonna F. Mindfulness-based interventions in an inpatient setting. In: Clinical handbook of mindfulness. Springer, New York, NY; 2009. p. 447–62.
Chin T, Rickard NS. Beyond positive and negative trait affect: flourishing through music engagement. Psychol Well-Being. 2014;4:25.
Miranda D, Claes M. Personality traits, music preferences and depression in adolescence. Int J Adolescence Youth. 2008;14:277–98.
Fancourt D, Garnett C, Spiro N, West R, Mullensiefen D. How do artistic creative activities regulate our emotions? Validation of the Emotion Regulation Strategies for Artistic Creative Activities Scale (ERS-ACA). PLos One. 2019;14:e0211362.
Saarikallio S. Development and validation of the brief music in mood regulation scale (B-MMR). Music Percept. 2012;30:97–105.
Saarikallio S, Gold C, McFerran K. Development and validation of the healthy-unhealthy music scale. Child Adolesc Ment Health. 2015;20:210–17.
Groarke JM, Hogan MJ. Development and psychometric evaluation of the adaptive functions of music listening scale. Front Psychol. 2018;9:516.
Thomson CJ, Reece JE, Di Benedetto M. The relationship between music-related mood regulation and psychopathology in young people. Musica Sci. 2014;18:150–65.
Shifriss R, Bodner E, Palgi Y. When you’re down and troubled: views on the regulatory power of music. Psychol Music. 2014;43:793–807.
Garrido S, Schubert E. Moody melodies: do they cheer us up? A study of the effect of sad music on mood. Psychol Music. 2013;43:244–261.
Wesseldijk LW, Ullen F, Mosing MA. The effects of playing music on mental health outcomes. Sci Rep. 2019;9:12606.
Niarchou M, Lin G, Lense MD, Gordon RL, Davis LK. The medical signature of musicians: a phenome-wide association study using an electronic health record database. medRxiv. 2020;10:51. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.14.20175109 .
Vaag J, Sund ER, Bjerkeset O. Five-factor personality profiles among Norwegian musicians compared to the general workforce. Musica Sci. 2017;22:434–445.
Fancourt D, Garnett C, Müllensiefen D. The relationship between demographics, behavioral and experiential engagement factors, and the use of artistic creative activities to regulate emotions. Psychol Aesthet Creat Arts. 2020.(advance online publication)
Mak HW, Fancourt D. Longitudinal associations between ability in arts activities, behavioural difficulties and self-esteem: Analyses from the 1970 British Cohort Study. Sci Rep. 2019;9:14236.
West SG, Taylor AB, Wu W. Model fit and model selection in structural equation modeling. In: Hoyle RH, editor. Handbook of structural equation modeling. New York, NY: The Guilford Press; 2012. p. 209–31.
Weiss B, Susser K, Catron T. Common and specific features of childhood psychopathology. J Abnorm Psychol. 1998;107:118–27.
Krueger RF, McGue M, Iacono WG. The higher-order structure of common DSM mental disorders: Internalization, externalization, and their connections to personality. Personal Individ Differences. 2001;30:1245–159.
Morse S, et al. Audio therapy significantly attenuates aberrant mood in residential patient addiction treatment: putative activation of dopaminergic pathways in the meso-limbic reward circuitry of humans. J Addict Res Ther. 2011;3:2.
Baker FA, Gleadhill LM, Dingle GA. Music therapy and emotional exploration: exposing substance abuse clients to the experiences of non-drug-induced emotions. Arts Psychother. 2007;34:321–330.
Dingle GA, Gleadhill L, Baker FA. Can music therapy engage patients in group cognitive behaviour therapy for substance abuse treatment? Drug Alcohol Rev. 2008;27:190–6.
Hohmann L, Bradt J, Stegemann T, Koelsch S. Effects of music therapy and music-based interventions in the treatment of substance use disorders: A systematic review. PLos One. 2017;12:e0187363.
Swope PM. Effects of learning the drums on inattention, vigilance, and sustained attention in adolescents with ADHD. Spalding University; 2018.
Zimmermann MB, Diers K, Strunz L, Scherbaum N, Mette C. Listening to Mozart improves current mood in adult ADHD: a randomized controlled pilot study. Front Psychol. 2019;10:1104.
Madjar N, Gazoli R, Manor I, Shoval G. Contrasting effects of music on reading comprehension in preadolescents with and without ADHD. Psychiatry Res. 2020;291:113207.
Pelham WE, Waschbusch DA, Hoza B, Gnagy EM, Greiner AR, Sams SE, et al. Music and video as distractors for boys with ADHD in the classroom: comparison with controls, individual differences, and medication effects. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2011;39:1085–98.
Porter S, McConnell T, McLaughlin K, Lynn F, Cardwell C, Braiden HJ, et al. Music therapy for children and adolescents with behavioural and emotional problems: a randomised controlled trial. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2017;58:586–94.
Chong HJ, Kim SJ. Education-oriented music therapy as an after-school program for students with emotional and behavioral problems. Arts Psychother. 2010;37:190–96.
Rickson DJ, Watkins WG. Music therapy to promote prosocial behaviors in aggressive adolescent boys—a pilot study. J. Music Ther. 2003;40:283–301.
Montello L, Coons EE. Effects of active versus passive group music therapy on preadolescents with emotional, learning, and behavioral disorders. J Music Ther. 1999;35:49–67.
Mulder J, Ter Bogt TF, Raaijmakers QA, Gabhainn SN, Monshouwer K, Vollebergh WA. The soundtrack of substance use: Music preference and adolescent smoking and drinking. Subst Use Misuse. 2009;44:514–31.
Mulder J, Ter Bogt TF, Raaijmakers QA, Nic Gabhainn S, Monshouwer K, Vollebergh WA. Is it the music? Peer substance use as a mediator of the link between music preferences and adolescent substance use. J Adolescence. 2010;33:387–94.
Chen MJ, Miller BA, Grube JW, Waiters ED. Music, substance use, and aggression. J Stud Alcohol. 2006;67:373–81.
ter Bogt TF, Gabhainn SN, Simons-Morton BG, Ferreira M, Hublet A, Godeau E, et al. Dance is the new metal: adolescent music preferences and substance use across Europe. Subst Use Misuse. 2012;47:130–42.
Slater JL, Tate MC. Timing deficits in ADHD: insights from the neuroscience of musical rhythm. Front Comput Neurosci. 2018;12:51.
Carrer LR. Music and sound in time processing of children with ADHD. Front Psychiatry. 2015;6:127.
Miksza P. Relationships among impulsivity, achievement goal motivation, and the music practice of high school wind players. Bull Council Res Music Educ. 2009;180:9–27.
Miksza P. Relationships among achievement goal motivation, impulsivity, and the music practice of collegiate brass and woodwind players. Psychol Music. 2010;39:50–67.
Geretsegger M, Mössler KA, Bieleninik Ł, Chen XJ, Heldal TO, Gold C. Music therapy for people with schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;5:CD004025.
PubMed Google Scholar
Volpe U, Gianoglio C, Autiero L, Marino ML, Facchini D, Mucci A, et al. Acute effects of music therapy in subjects with psychosis during inpatient treatment. Psychiatry. 2018;81:218–27.
Pavlov A, Kameg K, Cline TW, Chiapetta L, Stark S, Mitchell AM. Music therapy as a nonpharmacological intervention for anxiety in patients with a thought disorder. Issues Ment Health Nurs. 2017;38:285–8.
Haugwitz, B. (2021). Music therapy in the early detection and indicated prevention in persons at risk of bipolar disorders: state of knowledge and potential. Br J Music Ther. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359457521997386 .
Power RA, Steinberg S, Bjornsdottir G, Rietveld CA, Abdellaoui A, Nivard MM, et al. Polygenic risk scores for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder predict creativity. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18:953–5.
Fancourt D, Ockelford A, Belai A. The psychoneuroimmunological effects of music: a systematic review and a new model. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014;36:15–26.
Baker FA, Metcalf O, Varker T, O’Donnell M. A systematic review of the efficacy of creative arts therapies in the treatment of adults with PTSD. Psychol Trauma. 2018;10:643–51.
Lense MD, Camarata S. PRESS-Play: musical engagement as a motivating platform for social interaction and social play in young children with ASD. Music Sci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1177/2059204320933080 .
Walker EF, Diforio D. Schizophrenia: a neural diathesis-stress model. Psychological Rev. 1997;104:667–85.
Zuckerman M, Riskind JH. Vulnerability to psychopathology: a biosocial model. J Cogn Psychother. 2000;14:407–8.
Trucco EM, Madan B, Villar M. The impact of genes on adolescent substance use: a developmental perspective. Curr Addict Rep. 2019;6:522–531.
Butkovic A, Ullen F, Mosing MA. Personality related traits as predictors of music practice: underlying environmental and genetic influences. Personal Individ Differences. 2015;74:133–8.
Coon H, Carey G. Genetic and environmental determinants of musical ability in twins. Behav Genet. 1989;19:183–93.
Ullén F, Mosing MA, Holm L, Eriksson H, Madison G. Psychometric properties and heritability of a new online test for musicality, the Swedish Musical Discrimination Test. Personal Individ Differences. 2014;63:87–93.
Hambrick DZ, Tucker-Drob EM. The genetics of music accomplishment: evidence for gene-environment correlation and interaction. Psychonomic Bull Rev. 2015;22:112–20.
Wesseldijk LW, Mosing MA, Ullen F. Gene-environment interaction in expertise: the importance of childhood environment for musical achievement. Dev Psychol. 2019;55:1473–9.
Ullen F, Mosing MA, Madison G. Associations between motor timing, music practice, and intelligence studied in a large sample of twins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015;1337:125–9.
Botvin GJ. Substance abuse prevention: theory, practice, and effectiveness. Crime Justice. 1990;13:461–519.
Fredricks JA, Simpkins S, Eccles JS. Family socialization, gender, and participation in sports and instrumental music. In: Developmental pathways through middle childhood. Mahwah, NJ: Psychology Press; 2006. p. 53–74.
Maes HH, Neale MC, Kirkpatrick RM, Kendler KS. Using multimodal inference/model averaging to model causes of covariation between variables in twins. Behav Genet. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-020-10026-8 .
Sala G, Gobet F. When the music’s over. Does music skill transfer to children’s and young ado escents’ cognitive and academic skills? A meta-analysis. Educ Res Rev. 2017;20:55–67.
Salimpoor VN, Zald DH, Zatorre RJ, Dagher A, McIntosh AR. Predictions and the brain: how musical sounds become rewarding. Trends Cogn Sci. 2015;19:86–91.
Loui P, Patterson S, Sachs ME, Leung Y, Zeng T, Przysinda E. White matter correlates of musical anhedonia: Implications for evolution of music. Front Psychol. 2017;8:1664.
Salimpoor VN, van den Bosch I, Kovacevic N, McIntosh AR, Dagher A, Zatorre RJ. Interactions between the nucleus accumbens and auditory cortices predict music reward value. Science. 2013;340:216–9.
Zatorre RJ, Salimpoor VN. From perception to pleasure: music and its neural substrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2013;110:10430–7. Suppl 2
Alluri V, Brattico E, Toiviainen P, Burunat I, Bogert B, Numminen J, et al. Musical expertise modulates functional connectivity of limbic regions during continuous music listening. Psychomusicology. 2015;25:443–54.
Vanyukov MM, Tarter RE, Kirisci L, Kirillova GP, Maher BS, Clark DB. Liability to substance use disorders: 1. Common mechanisms and manifestations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2003;27:507–515.
Volkow ND, Morales M. The brain on drugs: from reward to addiction. Cell. 2015;162:712–25.
Wise RA. Dopamine and reward: the anhedonia hypothesis 30 years on. Neurotox Res. 2008;14:169–83.
Koob GF, Volkow ND. Neurocircuitry of addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010;35:217–38.
Mukherjee S, Coque L, Cao JL, Kumar J, Chakravarty S, Asaithamby A, et al. Knockdown of Clock in the ventral tegmental area through RNA interference results in a mixed state of mania and depression-like behavior. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;68:503–11.
Kaufling J. Alterations and adaptation of ventral tegmental area dopaminergic neurons in animal models of depression. Cell Tissue Res. 2019;377:59–71.
Small KM, Nunes E, Hughley S, Addy NA. Ventral tegmental area muscarinic receptors modulate depression and anxiety-related behaviors in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2016;616:80–5.
Kokal I, Engel A, Kirschner S, Keysers C. Synchronized drumming enhances activity in the caudate and facilitates prosocial commitment-if the rhythm comes easily. PLos One. 2011;6:e27272.
Goldstein A. Thrills in response to music and other stimuli. Physiological Psychol. 1980;8:126–9.
Moore E, Schaefer RS, Bastin ME, Roberts N, Overy K. Can musical training influence brain connectivity? Evidence from diffusion tensor MRI. Brain Sci. 2014;4:405–27.
Imfeld A, Oechslin MS, Meyer M, Loenneker T, Jancke L. White matter plasticity in the corticospinal tract of musicians: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Neuroimage. 2009;46:600–7.
Han Y, Yang H, Lv YT, Zhu CZ, He Y, Tang HH, et al. Gray matter density and white matter integrity in pianists’ brain: a combined structural and diffusion tensor MRI study. Neurosci Lett. 2009;459:3–6.
Schmithorst VJ, Wilke M. Differences in white matter architecture between musicians and non-musicians: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Neurosci Lett. 2002;321:57–60.
Hudziak JJ, Albaugh MD, Ducharme S, Karama S, Spottswood M, Crehan E, et al. Cortical thickness maturation and duration of music training: Health-promoting activities shape brain development. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014;53:1153–61.
Gingras B, Honing H, Peretz I, Trainor LJ, Fisher SE. Defining the biological bases of individual differences in musicality. Philos Trans R Soc B. 2015;370:20140092.
Heath AC, Kessler RC, Neale MC, Hewitt JK, Eaves LJ, Kendler KS. Testing hypotheses about direction of causation using cross-sectional family data. Behav Genet. 1993;23:29–50.
Coleman JRI, Peyrot WJ, Purves KL, Davis KAS, Rayner C, Choi SW, et al. Genome-wide gene-environment analyses of major depressive disorder and reported lifetime traumatic experiences in UK Biobank. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25:247353–1446.
Domingue BW, Liu HX, Okbay A, Belsky DW. Genetic heterogeneity in depressive symptoms following the death of a spouse: polygenic score analysis of the US Health and Retirement Study. Am J Psychiatry. 2017;174:963–970.
Barcellos SH, Carvalho LS, Turley P. Education can reduce health differences related to genetic risk of obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:E9765–E9772.
Howard DM, Adams MJ, Shirali M, Clarke TK, Marioni RE, Davies G, et al. Genome-wide association study of depression phenotypes in UK Biobank identifies variants in excitatory synaptic pathways. Nat Commun. 2018;9:1470.
Okbay A, Baselmans BM, De Neve JE, Turley P, Nivard MG, Fontana MA, et al. Genetic variants associated with subjective well-being, depressive symptoms, and neuroticism identified through genome-wide analyses. Nat Genet. 2016;48:624–33.
Walters RK, Polimanti R, Johnson EC, McClintick JN, Adams MJ, Adkins AE, et al. Transancestral GWAS of alcohol dependence reveals common genetic underpinnings with psychiatric disorders. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21:1656–69.
Niarchou M, et al. Unraveling the genetic architecture of music rhythm. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/836197v1 . 2019 ; 29:S62.
Purcell S. Variance components models for gene-environment interaction in twin analysis. Twin Res. 2002;5:554–71.
Barch DM, Albaugh MD, Avenevoli S, Chang L, Clark DB, Glantz MD, et al. Demographic, physical and mental health assessments in the adolescent brain and cognitive development study: rationale and description. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2018;32:55–66.
Uban KA, Horton MK, Jacobus J, Heyser C, Thompson WK, Tapert SF, et al. Biospecimens and the ABCD study: rationale, methods of collection, measurement and early data. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2018;32:97–106.
Mullensiefen D, Gingras B, Musil J, Stewart L. The musicality of non-musicians: an index for assessing musical sophistication in the general population. PLos One. 2014;9:e89642.
Blood AJ, Zatorre RJ. Intensely pleasurable responses to music correlate with activity in brain regions implicated in reward and emotion. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2001;98:11818–23.
Jenkins LM, Skerrett KA, DelDonno SR, Patrón VG, Meyers KK, Peltier S, et al. Individuals with more severe depression fail to sustain nucleus accumbens activity to preferred music over time. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 2018;275:21–7.
Belfi AM, Loui P. Musical anhedonia and rewards of music listening: current advances and a proposed model. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020;1464:99–114.
Insel T, et al. Research domain criteria (RDoC): toward a new classification framework for research on mental disorders. Am Psychiatric Assoc. 2010;167:748–51.
Loo SK, McGough JJ, McCracken JT, Smalley SL. Parsing heterogeneity in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder using EEG-based subgroups. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2018;59:223–31.
Zotev V, Mayeli A, Misaki M, Bodurka J. Emotion self-regulation training in major depressive disorder using simultaneous real-time fMRI and EEG neurofeedback. Neuroimage Clin. 2020;27:102331.
Yang AC, Jann K, Michel CM, Wang DJJ. Editorial: advances in multi-scale analysis of brain complexity. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:337.
Lin C, Lee SH, Huang CM, Chen GY, Ho PS, Liu HL, et al. Increased brain entropy of resting-state fMRI mediates the relationship between depression severity and mental health-related quality of life in late-life depressed elderly. J Affect Disord. 2019;250:270–7.
Bhattacharya J, Lee EJ. Modulation of EEG theta band signal complexity by music therapy. Int J Bifurc Chaos. 2016;26:1650001.
Carpentier SM, McCulloch AR, Brown TM, Faber S, Ritter P, Wang Z, et al. Complexity matching: brain signals mirror environment information patterns during music listening and reward. J Cogn Neurosci. 2020;32:734–45.
Etkin A. A reckoning and research agenda for neuroimaging in psychiatry. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176:507–11.
Rissling AJ, Makeig S, Braff DL, Light GA. Neurophysiologic markers of abnormal brain activity in schizophrenia. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2010;12:572–8.
Loo SK, Makeig S. Clinical utility of EEG in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a research update. Neurotherapeutics. 2012;9:569–87.
Boyle EA, Li YI, Pritchard JK. An expanded view of complex traits: from polygenic to omnigenic. Cell. 2017;169:1177–86.
Sivagnanam S, Yoshimoto K, Carnevale T, Nadeau D, Kandes M, Petersen T, et al. Neuroscience Gateway enabling large scale modeling and data processing in neuroscience research. In: Practice and Experience in Advanced Research Computing. Association for Computing Machinery, Portland, OR, USA ; 2020. p.510–513.
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH grants DP2HD098859, R01AA028411, R61MH123029, R21DC016710, U01DA04112, and R03AG065643, National Endowment for the Arts (NEA) research lab grants 1863278-38 and 1855526-38, and National Science Foundation grant 1926794. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health or National Endowment for the Arts. The authors would like to thank Navya Thakkar and Gabija Zilinskaite for their assistance.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Medicine, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, USA
- Daniel E. Gustavson
Vanderbilt Genetics Institute, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, USA
Daniel E. Gustavson, Reyna L. Gordon & Miriam D. Lense
Department of Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, USA
Peyton L. Coleman & Reyna L. Gordon
Swartz Center for Computational Neuroscience, Institute for Neural Computation, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA, USA
John R. Iversen
Department of Human and Molecular Genetics, Virginia Institute for Psychiatric and Behavioral Genetics, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA, USA
- Hermine H. Maes
Department of Psychiatry, Virginia Institute for Psychiatric and Behavioral Genetics, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA, USA
Massey Cancer Center, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA, USA
Vanderbilt Brain Institute, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, USA
Reyna L. Gordon & Miriam D. Lense
The Curb Center, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Daniel E. Gustavson .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Gustavson, D.E., Coleman, P.L., Iversen, J.R. et al. Mental health and music engagement: review, framework, and guidelines for future studies. Transl Psychiatry 11 , 370 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-021-01483-8
Download citation
Received : 23 November 2020
Revised : 03 June 2021
Accepted : 10 June 2021
Published : 22 June 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-021-01483-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
- Laura W. Wesseldijk
- Miriam A. Mosing
Translational Psychiatry (2023)
Effects of music-based interventions on cancer-related pain, fatigue, and distress: an overview of systematic reviews
- Ana Trigueros-Murillo
- Javier Martinez-Calderon
- Alberto Marcos Heredia-Rizo
Supportive Care in Cancer (2023)
A Systematic Review of Music-Based Interventions to Improve Treatment Engagement and Mental Health Outcomes for Adolescents and Young Adults
- Aaron H. Rodwin
- Rei Shimizu
- Michelle R. Munson
Child and Adolescent Social Work Journal (2023)
Heritability of Childhood Music Engagement and Associations with Language and Executive Function: Insights from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study
- Srishti Nayak
Behavior Genetics (2023)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

Performing Music Research: Methods in Music Education, Psychology, and Performance Science

Professor of Performance Science
Associate Director of Research
Reader in Performance Science
Research Associate in Performance Science
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Performing Music Research is a comprehensive guide to research in music performance. It reviews the knowledge and skills needed to critique existing studies in music education, psychology, and performance science, and to design and carry out new investigations. Methodological approaches are highlighted across the book in ways that help aspiring researchers bring precision to their research questions, select methods that are appropriate for addressing their questions, and apply those methods systematically and rigorously. Each chapter contains a study guide, comprising a chapter summary, a list of keywords, and suggestions for further discussion. The book concludes with a resources section, including a glossary and supplementary material to support advanced statistical analysis. The book’s companion website provides information designed to facilitate access to original research and to test knowledge and understanding.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.

Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Music: Research Methods
- Popular Music
- Databases and indexes
- Call numbers
Research Methods
- Dictionaries and encyclopedias
- Composition and Creative Music Technology
- Music, culture and place
- Music history
- Music in Australia
- Teaching Music
- Drumming Traditions of West Africa
- Digital collections
- Special collections
- Academic writing
- Introduction
- Qualitative and Quantitative Methodology
- Artistic Research
- Autoethnography
- Creative Practice
- Ethnography
- Indigenous Methodologies
- Narrative Inquiry
- Practice as Research
- Oxford Handbooks
- Methodology of Music Research
Many books about research methodology introduce the reader to a range of existing methods. This page selects online resources relevant to music and interdisciplinary studies and some books only have a chapter, or a case study, that applies to music, performance or creative practice. If you are seeking a particular kind of research methodology, you can meet a librarian online , or email [email protected].
SAGE research methods online SAGE Research Methods Online (SRMO) is a research methods tool created to help researchers, faculty and students with their research projects. Researchers can browse by methods to help them design research projects, understand particular methods or identify a new method. Since SRMO focuses on methodology rather than disciplines, it is best to use music as a keyword in order to find applications to music research. You can also use the Methods Map to read definitions of key terminology, or to find narrower definitions for qualitative data analysis or research design.
Sage research methods foundations SAGE Research Methods Foundations provides a concise introduction to methods and research terms for those who are new to research in general or to that particular method. While a general search can provide an overwhelming number of results, SAGE Research Methods Foundations offers a targeted list of entries to guide users through the content. The navigation menu puts the entry in context, so users can easily find more general topics related to a method or continue on to more specific sub-topics. There is an A-Z section on the innovators of methods, with profiles that evaluate their contributions. The content ranges from Participatory and Arts-Based Research, Analysis of Material Culture, Narrative Research, Autobiography to Sampling.
The Sage Encyclopedia of Qualitative Research Methods includes the following entry: Music in Qualitative Research
The SAGE Handbook of Digital Dissertations and Theses includes the following chapter: Practice-as-Research in Music Performance
The Orpheus Institute Series aims to enhance and advance discourse in the field of artistic research in music and to generate future work. A number of titles in the series are found below. The library has access to all the titles through JSTOR .
Oxford Handbooks Online brings together the world's leading scholars to write review essays that evaluate the current thinking on a field or topic. You can search simultaneously across all handbooks by keywords. Methodologies are discussed in the following selectied chapters:
Toward a Methodology for Research into the Revival of Musical Life after War, Natural Disaster, Bans on All Music, or Neglect by Margaret Kartomi from The Oxford handbook of music revival (2014) Music-Making As Data: Collection and Analysis by Kristen Pellegrino from The Oxford Handbook of Qualitative Research in American Music Education (2014) Creating a Framework for Music Making and Leisure: Max Kaplan Leads the Way by Marie McCarthy from the Oxford handbook of music making and leisure (2017) Introduction: Situating Country Music Studies by Travis D. Stimeling from The Oxford handbook of country music studies (2017)
Methodology of Music Research is a series published by Peter Lang in Switzerland.
- Research Catalogue A non-commercial, collaboration and publishing platform for artistic research provided by the Society for Artistic Research which is free to use for artists and researchers. It aims to provide resources for teaching purposes, student assessment, peer review workflows and research funding administration.
- << Previous: Call numbers
- Next: Dictionaries and encyclopedias >>
Custom Essay, Term Paper & Research paper writing services
- testimonials
Toll Free: +1 (888) 354-4744
Email: [email protected]
Writing custom essays & research papers since 2008
Best 100 music research topics (just updated).

If you are reading this, you are probably looking for the best music research topics for your next essay. Truth be told, choosing the right topic is very important. It can make the difference between a B and an A, or even between an A and an A+. Unfortunately, choosing the best topics is not as simple as you think. Even though the internet is full of music research topics, most of them are plain and, quite frankly, boring.
Your professor wants more than this. Let’s see why you need the most interesting topics and where you can find them. Of course, you are free to use any of our 100 topics for free and even reword them as you see fit. Read on!
Choosing Good Music Research Topics
By now, you are probably wondering why everyone keeps telling you to come up with the best music topics. The truth is that there are many, many benefits to choosing an awesome topic. Here are just some of them, so you can get a better idea of the importance of a great idea:
- Excellent music research paper topics show your professor that you really did your best to get a top grade.
- A good topic is one that you know much about. It should be relatively easy to you to research it and to write about it.
- An awesome topic will pique the interest of your professor and will keep him or her reading. You will often get bonus points for this.
- Great topics make you stand out from your classmates. Your professor will notice you, and the grade will reflect this.
Where Can You Find Decent Music Topics?
Finding amazing music research topics is easier said than done. Yes, the Internet is full of websites that are offering ideas. There are even websites where you can buy bundles of topics. However, the music argumentative essay topics you will get from these websites are not of the highest quality. Most of them are actually quite boring. And remember, you classmates are probably searching for music history research paper topics on the same websites as you do. You want your research topics on music or book review topics to be original, so your professor can have a reason to award your paper some bonus points. The best place to get excellent music topics to write about is this page. The list of ideas is updated frequently, so you can get an original topic for free right now.
Music History Research Topics
Are you looking for the most interesting music history research topics? If you do, just pick one from our list for free:
- How did the Catholic church influence Renaissance music?
- Social issues described in Baroque-period music.
- Analyze the evolution of Romantic-era music.
- How did the Baroque Opera come to be?
- Who invented Medieval music and when?
- Why has western music almost disappear in the last 10 years?
- Analyze the evolution of music in the Classical era.
- Analyzing violin music performance during the Romantic Era.
Music Argument Topics
Are you looking to find an argument and support it? Then you absolutely need to check out our exceptional list of music argument topics:
- Music today is better than music in the 90s.
- The most lucrative career for a musician.
- Music helps you memorize faster.
- The most popular kind of metal music.
- The evolution of blues songs over the last 30 years.
- Music helps children develop faster.
- Hip-hop is a misunderstood music genre.
- Jazz music is not obsolete.
Music Theory Topics
Interested in writing about music theory? Our amazing academic writers have put together a list of music theory topics for you:
- Analyze the most important aspects of modern music.
- Classical music has specific medical applications.
- Hidden symbols in Renaissance-period music.
- The unique features of Baroque-age music.
- Analyze the evolution of music in the Baroque era.
- The best music compositors in the Romantic era.
- Remarkable characteristics of Romantic-age songs.
- The peculiarities of Asian modern music.
Music Industry Topics
Writing about the music industry can be fun and entertaining. Your professor will love it. Pick one of our music industry topics and start writing:
- What do you associate rock music with and why?
- Should the music industry pay songwriters more?
- How does illegal pirating of songs affect the music industry?
- Do music sharing sites help new artists become famous.
- Analyze the evolution of music labels in the US.
- What differentiates a music label from all others?
- Music talent shows and their effects on a musician’s career.
- The difficulties of signing a contract with a major music label in the US.
Research Paper Topics on Music for High School
Are you a high school student? In this case, you will need our research paper topics on music for high school:
- The best compositors of the Baroque Era.
- What differentiates modern music from classical music?
- Notable women in classical music.
- Analyze the evolution of music in the Modern age.
- How was Beethoven’s music influenced by his loss of hearing?
- How would our world be without music?
- Does music cause negative effects on US teens?
Music Thesis Topics
Writing a thesis about music is not easy. In fact, it can be one of the most difficult projects in your academic career. Start right now by choosing one of the best music thesis topics:
- What made a musician stand out in the Baroque Age?
- The most notable musical experiments in the Classical age.
- Comparing Renaissance and Medieval music styles.
- Analyze the evolution of music in the Renaissance age.
- How did royalty in the UK benefit from music in the Renaissance era?
- Discuss a folk song from the Renaissance age.
- Differences between Asian and European classical music.
Music Controversial Topics
Music, like most other disciplines, has plenty of controversial topics you can talk about. Don’t waste any time and pick one of these music controversial topics:
- Does digital music cut the profits of musicians?
- Who owns the intellectual property to a song?
- The difficulties of getting songwriting credit.
- Illegal downloads are changing the music industry.
- Should music education still be included in the curriculum?
- Analyze medieval liturgical music.
- Music should be free for everyone to download and use.
Persuasive Speech Topics About Music
Are you required the write a persuasive speech about music? If you are, you may need a bit of help. Pick one of these persuasive speech topics about music (updated for 2023):
- Music has a significant effect on advertising.
- The changes rap music has brought to the US culture.
- Indie is a term that should not apply to music.
- Metal music should be banned from the US.
- Does listening to music have a great influence on mental health?
- The amazing evolution of music in the Medieval age.
- People should be free to listen to the music they like for free.
- The fashion industry wouldn’t be where it is today without music.
Easy Topics About Music
Perhaps you don’t want to spend 5 or 6 hours writing the research paper . You need an easier topic. Choose one of these easy topics about music and write the essay fast:
- How can one become a symbol of modern music?
- My favorite singer today.
- Which musician from the past would you bring back to life and why?
- Do politics influence modern music?
- Compare and contrast two music genres.
- Analyze the evolution of music in the modern age in the United States.
- The side effects of turning the volume too loud.
- How is classical music used in Disney movies?
Music Education Research Topics
Are you interested in talking about music education? Perhaps you’ll have some suggestions to make after you’ve done the research. Just choose one of the music education research topics below:
- Can E-Learning be applied to music education?
- Can music teachers offer distance learning services?
- The advantages and disadvantages of Zoom music lessons.
- Why are music worksheets so important for high school students?
- How did the Internet change music education?
- Why are modern music studies so important?
- Should we learn more about Asian music in school?
- How can students learn music while respecting COVID19 measures?
Highly Interesting Music Topics
We know you want a top grade on your next music research paper. We advise you to select one of these highly interesting music topics and surprise your professor:
- How did pop music came to existence and why?
- Analyze the history of hip-hop music.
- Compare metal music with classical music.
- Why is rock music so popular in the United Kingdom?
- Which song would best present our species to aliens?
- Compare and contrast Korean and Chinese music.
- Analyze the popular themes of Japanese music.
- The stunning rise of K-pop bands.
Informative Speech Topics About Music
It’s difficult to find good informative speech topics about music these days. If you want to stand out from the rest of your classmates, choose one of our topics:
- Discuss the ideas presented in romantic music.
- What do people who appreciate classic music have in common?
- Analyze the most popular Bach music.
- Describe the role of market music in the Baroque era.
- Analyze the evolution of European music.
- Ways to make classical music popular with teens in the UK.
- Discuss the most popular musical instrument in the Classical age.
Music Essay Topics for College
Are you a college student? If you want an A+ on your next research paper, use one of these music essay topics for college students:
- Does modern music contain medieval themes?
- Analyze a song from the Renaissance age.
- Why is blues music so important for our culture?
- Who invented the blues genre and when?
- Analyze the evolution of American folk music.
- Most popular names in Baroque-age songs.
- Modern interpretations of medieval songs.
- Listening to blues music can lead to depression.
Need some more music history paper topics? Or perhaps you need a list of music related research topics to choose from for your thesis. Our best paper writer can help you in no time. Get in touch with us and we guarantee that we will find the perfect music topic for your needs. You will be well on your way to getting the A+ you need. Give us a try and get an amazing research topic on music in 10 minutes or less!

- Paper writing help
- Buy an Essay
- Pay for essay
- Buy Research Paper
- Write My Research Paper
- Research Paper Help
- Custom Research Paper
- Custom Dissertation
- Dissertation Help
- Buy Dissertation
- Dissertation Writer
- Write my Dissertation
- How it works
200 Best Music Research Paper Topics For Students
Music research topics are an excellent opportunity to trace the history of the development of individual genres or entire eras. You can create an essay or research paper with an emphasis on certain stylistic features, or delve deeper into the technical aspects of album making. Also, the research topics in music allow you to learn more about popular composers, musicians, and individual bands. You can find out the history of creating certain songs or finding out the nuances of the breakup of groups.
While music research paper topics seem easy, it still requires a good outline and reliable sources to gather information. The life of many musicians is very busy, so certain topics for music research papers may require a more thorough analysis. For example, you will need to research the biography and all creation stages of famous music industry personalities.
Any research topic about music should be analyzed, and only verified facts added. You should also avoid using emotional coloring and bias. And don't forget about formatting. Any interesting music topics require clear structuring into paragraphs, lists, and subheadings.
By popular genres & styles
Individual styles are especially appreciated in research paper topics on music. You can choose the genre or group that interests you. This will allow you to get additional motivation and focus more on facts. The main challenge in this case is to find authoritative sources.
- The impact of rock and roll on the modern music industry.
- The basic concepts of creating musical songs.
- Rock performers and their popularity in society.
- Reasons for the negative attitude towards the rock vocalist.
- Rock musicians and problems with the law.
- The nuances of alcohol addiction of rock musicians.
- The main features of creating rock songs.
- Musical agitation as the main motive of rock songs.
- The main reasons for making rock songs.
- Symbiosis of rock and classical music.
- Rock performers and popular musicians.
- The analysis of the creative personality on the example of Kurt Cobain.
- The modern musical trend in culture.
- Top 10 most popular metal groups.
- Why has metal music become so popular?
- The mix of traditional music and heavy metal.
- Analysis of lyrical constructions of metal performers.
- The symbiosis of musical instruments in metal music.
- The analysis of seventh chords in the construction of metal songs.
- The influence of metal on other genres.
- The symbiosis of metal and pop music.
- The influence of metal vocalists on American culture.
- The symbiosis of genres as the reason for the creation of metal.
- The modern icons of the metal scene.
- The best metal bands in the last thirty years.
- The analysis of the dynamics of the popularity of metal bands.
- The modern concerts on the example of metal bands
- Female vocalists in pop music.
- The reason for the creation of numerous female musical groups.
- Pop music as a tuning fork of public morality.
- Why is pop music degrading?
- How can pop music be used to improve college grades?
- The nuances of using pop music in contemporary American culture.
- How can pop music be used to improve mood?
- The symbiosis of pop music and rap culture.
- How does contemporary pop music affect young people?
- The study of pop music in the context of the social culture of Harlem.
- The classic examples of pop artists.
- Madonna: the most popular popes of personalities.
- The analysis of the popularity of Britney Spears.
- Pop icons of the past decade.
- Hip-hop as the basis of the movement for social equality.
- The origins of hip-hop and the reasons for its popularization.
- How does hip-hop affect contemporary pop artists?
- The analysis of hip-hop performers on the example of the best vocalists of the decade.
- How does hip-hop allow athletes to train?
- Modern hip-hop and new musical trends.
- The symbiosis of hip-hop and metal music.
- How does hip-hop motivate people for sporting achievements?
- The analysis of hip-hop performers on the example of female vocalists.
- Modern hip-hop and its impact on youth.
- The main aspects of the integration of hip-hop music in the modern community.
- All technical aspects of creating hip-hop music.
- The classic approach to the formation of hip-hop motives.
- The analysis of the structure of hip-hop songs.
- The best hip-hop artists of the last decade.
- The stages of the formation of jazz as a separate musical genre.
- Why is jazz so popular these days?
- The nuances of studying jazz musical combinations.
- How Jess influences the structuring of student learning.
- The nuances of jazz performers in modern America.
- The best American jazz performers.
- Jazz as the most structured musical theory.
- How can you quickly learn to create jazz compositions?
- The influence of jazz on the cultural and political elite of the United States.
- Can jazz replace other musical styles?
- Jazz fusion as an example of musical prowess.
- The technical aspects of creating a pentatonic scale in a jazz style.
- The selection of jazz musicians.
- The development of jazz in the United States.
- The main reasons for the popularization of jazz in modern society.
- Blues and its influence on the development of the music industry.
- The symbiosis of blues and jazz.
- Can the Blues be compared to classical music?
- How do contemporary artists use the Blues in pop music?
- Historical context creation of blues compositions.
- How does the Blues affect rock music?
- Can the Blues help students learn?
- How blues musicians are developing in the USA.
- Can blues be used as a springboard for classical music production?
- The best US blues artists of the last 20 years.
- Blues performers of the last ten years.
- The influence of the blues on the formation of other genres.
- The analysis of the statistical popularity of the blues.
- The critical aspects when creating Blues compositions.
- The selection of blues parties when creating music.
- The influence of classical music on pop culture.
- The classical music and the best composers of the last century.
- Beethoven and his best works.
- How did Mozart influence classical music?
- Is the symbiosis of jazz and classical music possible?
- The structure of making classical music.
- The stages of the formation of classical music in modern society.
- Can you replace pop culture with classical music?
- How does classical music affect the psychological state of people?
- The classical music and symbiosis with opera.
- The basic concept of the analysis of classical music.
- A technical comparison of the mastery of classical composers.
- The choice of classical music for the mood.
- The classical music and its influence on rock culture.
- The main technical aspects of creating a score.
The region is important for those looking for musical topics for research paper. Most genres of European music and some information about composers are open to general use. If your research topic on music is aimed at analyzing the Arab countries, then you will need more time looking for reliable information. The fact is that not all Muslim archives are in the public domain.
Western music
- The features of musical motives of Western music.
- The history of Western music with real examples.
- How has Western music changed over the past two hundred years?
- Is it possible to combine Western music with European motives?
- The features of the use of traditional Western musical instruments.
- How do Western countries use music for meditation?
- Western music in the context of modern society.
- The role of Western music in the life of native people.
- How melodic is oriental music?
- The stages of the formation of Western music in American culture.
European music
- European music and modern trends.
- British pop bands and their worldwide popularity.
- How popular are German pop bands in the USA?
- European music and national musical instruments.
- How does European music affect well-being?
- The analysis of European music with specific examples.
- Top 10 of the greatest European musical groups.
- The analysis of European music on the example of instrumental groups.
- The best pop music performers in Europe.
- How does pop music influence the development of culture?
Asian music
- Asian music: the example of ethnic trends.
- The influence of Asian music on world culture.
- The main musical instruments of Asia.
- Can you compare Asian music with European motives?
- How has Asian music changed over the past hundred years?
- The nuances of creating Asian music.
- How does Asian music influence contemporary cinema?
- The best Asian performers.
- Top 10 Asian vocalists who have conquered the whole world.
- Do national instruments influence the creation of Asian music?
By history periods
You can use music appreciation research paper topics to analyse a specific period in history. Baroque, Renaissance and other eras are especially relevant for research as they allow you to see the history of the development of music. You can concentrate on a specific time period and the most famous composers.
- Medieval music and its influence on the Crusades.
- The major trends in the medieval music industry.
- The influence of kings on the creation of medieval music.
- The main musical instruments in medieval Europe.
- Musical instruments in Central Asia during the Middle Ages.
- What kind of music was popular in the Middle Ages.
- How difficult was the life of a musician in the Middle Ages?
- The analysis of medieval music on modern examples.
- How has contemporary music influenced pop culture?
- Historical aspects of the creation of medieval music.
- The influence of medieval music and culture.
- The rhythmic pattern of medieval music.
- The medieval music during the feast.
- The influence of medieval music on classical music.
- The medieval music channel and musical comparison.
Renaissance
- The dawn of musical culture during the Renaissance.
- The analysis of Renaissance music with specific examples.
- How has Renaissance music influenced contemporary pop culture?
- The analysis of Renaissance music as a constructive masterpiece.
- The nuances of Renaissance music and, most importantly, musical instruments.
- How difficult is it to reproduce Renaissance music in today's environment?
- The analysis of structural compositions of the Renaissance.
- Renaissance music as a tuning fork of public morality.
- How has music changed since the Renaissance?
- Can Renaissance music be used to create a modern instrumental ensemble?
Baroque Age (XVI-XVIII)
- The influence of politicians on the formation of music during the Baroque period.
- How has Baroque influenced contemporary instrumental music?
- The nuances of musical constructions during the Baroque period.
- How has the baroque influenced modern instruments?
- The nuances of the Baroque in the context of the complexity of musical compositions.
- The main effect of the Baroque in contemporary music.
- The historical aspects of the creation of the Baroque as a separate genre of music.
- The influence of the Baroque on the creation of contemporary musical groups.
- The analysis of the structure and musical motives of Baroque in detail.
- Baroque in contemporary music.
- The nuances of creating songs in the Baroque style.
Classical Age (XVIII-XIV)
- The Classical Age of music in modern society.
- How did the Classical Age influence the formation of musical trends?
- The general concept of the Classical Age in instrumental music.
- The nuances of creating music based on the Classical Age.
- How did the Classical Age influence the creation of pop culture?
- The theory of creating musical compositions on the example of the Classical Age.
- The general factors of the Classical Age in instrumental music.
- The main trends and popular instruments of the Classical Age.
- The main musical compositions of the 14th century.
- The main factors in the creation of musical compositions in the 13th century.
Romantic Era (XIV-XX)
- The Romantic Era and its impact on contemporary music.
- The main principles of structuring music into the Romantic Era.
- Features of creating instrumental compositions in the Romantic Era.
- The Romantic Era and modern music trends.
- The main factors influencing the Romantic Era in the music industry.
- Key figures in the music industry and their passion for the Romantic Era.
- How did the Romantic Era form the modern style?
- How has the Romantic Era influenced rhythmic music?
- The Romantic Era in the music industry.
- The main aspects of the formation of the Romantic Era in musical culture.
- Making marching music in the Romantic Era.
- Features of creating musical compositions.
- The technical aspects that influenced modern romantic motives.
Modern Era (XX-XXI)
- Jazz music as a phenomenon of the modern roar the influence of the modern era on instrumental music.
- Technical aspects of hip-hop and Reggae.
- How is contemporary classical music created?
- Can modern music genres be combined to create something new?
- Why is the modern music industry stagnating?
- The aspects of contemporary music.
- How does instrumental music affect culture?
- Contemporary music and technical innovation.
- How is contemporary music created?
- The nuances of creating hip-hop albums.
How To Write On Music Related Research Topics
By choosing topics about music for an essay, you get the opportunity to prepare a detailed paper work with facts, genre nuances and detailed biographies of famous musicians. You need to stick to the formatting and your outline. Find reliable information for music history research topics and talk about the emergence of certain genres.
Music business research topics are especially important, as you need to consider not only the stylistic but also the commercial nuances of the bands. For example, you can prepare detailed data on annual music tours or album sales.
All music appreciation presentation topics require detailed factual focus, which can be difficult for many people. If you are not ready to do it yourself, then we can help you.
Our service will solve your problem with music research topics high school. We also guarantee that you will get a good grade. We will help you organize all the nuances so that your music history paper topics become a reason for pride and high scores.
An Inspiration List
- popular music | Description, History, & Facts | Britannica
- History of music
- Music History from Primary Sources
- Brief History of Music: An Introduction
- How Music and Instruments Began

Dissertation Consulting Services Since 2004
Our services
- Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Consulting
- Dissertation Editing
- Write My Dissertation
Music Research Paper Sample
Music research paper sample will help you to accomplish your work.
Writing a research paper on music differs greatly from a research paper on other subjects. Music research paper has a wide range of good research topics that you can select to study. If you want to study a history of any instrument, you are welcome. May be it will be better to make research on a certain type of music. If you find it very difficult, you can write about a biography of a composer. To write an A+ research paper on music, try to feel a subject matter by your soul.
Music can be called a weapon that struggles against darkness, for freedom against tyranny. There are some tips that will probably help you to accomplish your work perfectly well. There exist different types of music which can be easily researched:
• Classical music: there is a tradition to use classical music with particular reference to the music of the past and including the 19th century. So, we may speak about modern classical music because this term comprises music being written nowadays. This kind of music refers to any serious art music, traditions of which can be traced.
• Light classical: it is used in short classical works which can be easily listened to. The composers create such kind of art not only to play, but to entertain. So, if you decide to write about light classical music in your music research paper, you have to describe a performer’s feelings as well.
• Serious music: sometimes it is related to classical music; however, it has a wider concept than classical one. It comprises folk music, jazz and classical music.
• Light music: it includes light classical music, popular songs from different sources, both traditional and new, dance music, film music, etc.
• Jazz: it is considered to be a popular music. It was played by Negro groups in the early 20th century. Its characteristic features are the following: freestyle and strong rhythms. It was called traditional jazz. Later, it was removed by similar music played by large bands. Such kind of music was a perfect improvisation for dancing. After all, modern jazz appeared. It characterized by the blues that aimed to produce an unhurried emotive style.
• Pop music: it is modern music presented nowadays. It is performed by a singer or a pop group mainly with electric guitars and drums.
• Dance music: it is a kind of music that includes pop music and jazz.
• Background music can be of any kind produced as a background for conversation, meeting, arrangement, etc. It is put on records intentionally and heard increasingly in hotel foyers, airports, etc.
• Chamber music is written for a chamber orchestra.
If you do not want to make a research on a particular kind of music, find interesting information about their founders, but tell about composers’ biography first.
To write music research paper is the same difficult as well other types of research paper. You can make use of music research paper sample found online. To ease your work greatly, you may visit custom research writing assistant PhDify.com .
How it works
1 make your order, 2 monitor the progress, 3 download the paper, get dissertation writing help.
- Flipped Classroom: What You Didn’t Knew About It
- Why Use KBS?
- How To Write Excellent Research Paper: Thesis
- Sample Of Research Paper On National Security
- Writing Research Paper On Afghanistan War
Testimonials
The topic of my dissertation seemed easy but only at first glance - I couldn't sleep well any more. I was stressed and I felt broken. Phdify saved me from a total disaster, and now I have my PhD.
Most friends of mine encountered the same difficulties. I wrote some chapters by myself, but another chapters were moving on slowly! So, I never hesitated to ask for a help and I've got a great experience at phdify.com!
At one moment I felt an absolute despair to finish my thesis! To my luck a good friend of my gave me this site, and I understood: this is my salvation! Thanks to Phdify team I finished my thesis in time!
Ask support
Get answers Immediately

© Ph Dify 2024. All rights reserved
PhDify.com is owned and operated by RATATATA LTD Registered address: 48, Vitosha Blvd., ground floor, city of Sofia, Triaditsa Region, Bulgaria, 1000.
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7
- Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

Music Research Topics: 40 Topic Examples for Paper or Essay

Music Research Paper Topic Examples
Music is a universal language that transcends borders and cultures, touching the depths of human emotions and shaping societies throughout history.
It is a dynamic field with many facets, making it a fascinating subject for research and exploration.
This article provides a treasure trove of music research topics. Each topic offers a unique lens through which researchers can analyze the art form that harmonizes our world.

40 Topic Examples for Paper or Essay

- The Impact of Climate Change on Coastal Ecosystems
- Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Challenges and Opportunities
- The History and Significance of the Suffragette Movement
- Cybersecurity Threats in the Age of Digital Transformation
- The Influence of Social Media on Mental Health
- The Role of Women in STEM: Breaking Barriers
- The Economics of Renewable Energy Adoption
- The Evolution of Urbanization and Its Effects on Society
- The Cultural Significance of Traditional Foods
- The Globalization of Pop Culture: A Double-Edged Sword
- The Ethics of Genetic Engineering and Designer Babies
- The Impact of Mass Media on Political Discourse
- The Art of Storytelling: Its Power in Literature and Film
- Environmental Conservation and Biodiversity Preservation
- The Influence of Music on Emotions and Behavior
- The Role of NGOs in International Development
- The Future of Space Exploration and Colonization
- The Psychology of Addiction: Causes and Treatment
- The Evolution of Artificial Life: From Turing to Deep Learning
- The Importance of Financial Literacy in Modern Society
- The Historical Development of Human Rights
- The Impact of E-Commerce on Traditional Retail
- The Intersection of Art and Technology in the Digital Age
- The Rise of Populism and Its Implications for Democracy
- The Benefits and Challenges of Remote Work
- The Cultural Significance of Festivals and Celebrations
- The Philosophy of Mind: Dualism vs. Materialism
- The Influence of Gaming on Cognitive Skills and Social Behavior
- The Role of Education in Promoting Gender Equality
- The Implications of 5G Technology on Communication
- The Ethical Considerations in Animal Testing
- The Evolution of Language and Communication
- The Impact of Artificial Sweeteners on Health
- The Cultural Exchange in World Literature
- The Challenges of Cyberbullying and Online Harassment
- The Role of Sports in Building Character and Leadership
- The Importance of Early Childhood Education
- The Psychological Effects of Color on Human Behavior
- The Intersection of Religion and Science: Debates and Harmonies
- The Socioeconomic Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic
How to Write a Good Music Research Paper
1. introduction.
Engage the reader with a compelling start. You can use an anecdote, a thought-provoking quote, or an interesting fact related to your music research topic. The goal is to pique the reader’s interest and encourage them to continue reading.

Provide context for your research topic and explain its significance. This is where you introduce the broader issues or themes related to your case and explain why it’s worth studying.
State your primary research question or thesis. This is the heart of your introduction, where you clearly define the specific focus of your research.
Briefly outline the scope of your paper and the topics you will cover. Give readers an overview of what to expect in the coming sections.
Present your central argument or hypothesis. This statement should be concise and clear, summarizing the main point of your research.
2. Literature Review
A literature review is a critical component of research, as it provides an essential foundation for a study. It serves to summarize existing knowledge, identify gaps, and establish the context for the research.
After reviewing relevant literature, researchers can build on past work, avoid redundancy, and ensure that their research contributes new insights.
It also helps in shaping research questions, theoretical frameworks, and methodologies. A comprehensive literature review adds credibility and depth to research, making it an indispensable step in the research process.
3. Methodology
The methodology section outlines the systematic approach used to conduct the research, ensuring its rigor and applicability.
Data will be collected from a diverse sample of participants through structured surveys and in-depth interviews.
The study aims to recruit participants with varied musical backgrounds, age groups, and experiences to gain a comprehensive perspective.
Quantitative data will undergo statistical analysis, while qualitative data will be thematically coded to unearth patterns and insights.
4. Analysis and Findings
In this section, you present the outcomes of your research, for instance, on the psychological and emotional effects of music.

Your quantitative analysis reveals significant correlations between musical genres and distinct emotional responses.
Notably, participants report should elevate feelings of joy, nostalgia, and relaxation in response to specific genres.
The qualitative findings should enrich your understanding, emphasizing the significance of individual preferences and contextual factors in shaping emotional experiences.
5. Discussion
Here, you interpret the implications of your findings, demonstrating music’s profound impact on emotional well-being and cognitive processes.
The observed correlations between specific musical genres and emotional states underscore the therapeutic potential of music, offering new avenues for stress reduction and memory enhancement.
Mostly, this substantiates your central thesis that music is a potent tool for improving mental and emotional health, supporting the idea that it extends beyond entertainment.
However, it is crucial to acknowledge the study’s limitations, including potential biases in self-reporting and the cross-sectional design.
6. Conclusion
In the conclusion section, the research should shed light on the remarkable influence of music on human psychology.
Your findings highlight music’s significant role in shaping emotional well-being and cognitive processes.
Specific musical genres should evoke distinct emotional responses, indicating music’s potential for therapeutic applications in stress reduction and memory enhancement.
The study should underscore the need for a deeper understanding of the intricate relationship between music and the human psyche.
After harnessing music’s emotional and cognitive effects, you can explore innovative interventions to enhance psychological well-being.
While your research provides valuable insights, it is essential to acknowledge its limitations and encourage further investigation into the multifaceted dimensions of music’s impact on the human experience.
7. References
References validate the credibility and academic rigor of your research. After citing reputable sources, you demonstrate that your work is built on a foundation of established knowledge and research within the field.
References provide evidence to support your arguments and claims. They show that your research is based not solely on your personal opinions but on existing and expert opinions.
Properly citing sources helps you avoid plagiarism, a serious academic offense. Plagiarism involves using someone else’s work without giving them credit, which can lead to academic penalties and damage your reputation.
References serve as a guide for readers interested in delving deeper into the topic. They can use your reference list to access the sources you consulted, promoting further learning and research.
References provide context for your research, allowing readers to see how your work fits within the broader academic conversation. This can help establish the significance of your research.
8. Appendices

Appendices are essential in research to provide additional information, such as raw data, charts, or lengthy explanations, without cluttering the main text.
They enhance comprehension and allow readers to explore details at their discretion.
9. Acknowledgments
Acknowledgments in research papers serve several vital purposes.
First and foremost, they express gratitude and recognition for the contributions of individuals, organizations, or institutions that supported the research.
Acknowledgments enhance transparency by disclosing financial support, resource access, or partnerships. They demonstrate ethical research practices and ensure that potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Acknowledgments play a vital role in maintaining research integrity, respecting intellectual contributions, and building a sense of academic community and collaboration.

Josh Jasen or JJ as we fondly call him, is a senior academic editor at Grade Bees in charge of the writing department. When not managing complex essays and academic writing tasks, Josh is busy advising students on how to pass assignments. In his spare time, he loves playing football or walking with his dog around the park.
Related posts
parts of introduction paragraph
5 Parts of an Introduction Paragraph in an Essay or Paper

How to write a good Painted Essay
How to write a Good Painted Essay: Structure, Template, and Examples

Turnitin or SafeAssign
Turnitin or SafeAssign: Which Plagiarism Detection Tool is Right for You?
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » 500+ Music Research Topics
500+ Music Research Topics

Music is a universal language that has the power to evoke emotions, bring people together, and express complex ideas and feelings. As a result, it has been the subject of extensive research and analysis across a wide range of fields, from psychology and neuroscience to sociology and cultural studies. Whether you are a music student, researcher , or simply a curious enthusiast, there are countless fascinating and important topics to explore within the realm of music research. From the history and evolution of different musical genres to the impact of music on human behavior and cognition, the possibilities for investigation and discovery are virtually endless. In this post, we will highlight some of the most interesting and relevant music research topics that you can explore in your own studies or simply as a way to deepen your appreciation and understanding of this rich and diverse art form.
Music Research Topics
Music Research Topics are as follows:
- The impact of music on memory retention.
- The evolution of hip-hop music and its influence on popular culture.
- The relationship between music and emotions.
- The role of music in religious and spiritual practices.
- The effects of music on mental health.
- The impact of music on athletic performance.
- The role of music in therapy and rehabilitation.
- The evolution of classical music through the ages.
- The impact of technology on music creation and distribution.
- The relationship between music and language acquisition.
- The cultural significance of music in different parts of the world.
- The influence of popular music on politics and social issues.
- The impact of music on academic performance.
- The role of music in film and television.
- The use of music in advertising and marketing.
- The psychology of musical preferences.
- The effects of music on sleep patterns and quality.
- The impact of music on creativity and productivity.
- The influence of music on fashion and style.
- The impact of music education on childhood development.
- The role of music in memory recall and nostalgia.
- The effects of music on physical health.
- The relationship between music and brain development.
- The impact of music on the immune system.
- The influence of music on social behavior.
- The evolution of jazz music and its impact on society.
- The role of music in cultural preservation and identity.
- The effects of music on stress levels and anxiety.
- The relationship between music and social movements.
- The impact of music on language learning and pronunciation.
- The effects of music on learning and cognition.
- The influence of music on political ideologies and movements.
- The impact of music on academic achievement.
- The relationship between music and cultural assimilation.
- The role of music in international diplomacy.
- The effects of music on physical performance and endurance.
- The impact of music on memory consolidation and recall.
- The influence of music on fashion trends and subcultures.
- The role of music in socialization and identity formation.
- The effects of music on perception and attention.
- The impact of music on decision making and judgment.
- The relationship between music and romantic attraction.
- The role of music in social justice movements.
- The effects of music on motor skills and coordination.
- The influence of music on cultural exchange and globalization.
- The impact of music on language and cultural barriers.
- The relationship between music and cultural appropriation.
- The role of music in community building and activism.
- The effects of music on motivation and goal setting.
- The influence of music on fashion advertising and marketing.
- The impact of music on social inequality and discrimination.
- The relationship between music and cultural hegemony.
- The role of music in political propaganda and manipulation.
- The effects of music on physical therapy and rehabilitation.
- The influence of music on cultural diplomacy and international relations.
- The impact of music on the environment and sustainability.
- The relationship between music and social hierarchies.
- The role of music in cultural exchange and intercultural communication.
- The effects of music on creative thinking and problem solving.
- The influence of music on consumer behavior and product preferences.
- The impact of music on social mobility and economic inequality.
- The relationship between music and cultural diversity.
- The role of music in intergenerational communication and conflict resolution.
- The effects of music on mood and emotional regulation.
- The influence of music on cultural authenticity and representation.
- The impact of music on memory in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
- The impact of music on recovery and rehabilitation in individuals with physical injuries.
- The role of music in promoting cultural exchange and understanding in international education.
- The role of music in promoting cultural sensitivity and understanding in international relations.
- The role of music in promoting cultural sensitivity and understanding in international human rights.
- The effects of music on cognitive functioning and mental health in individuals with ADHD.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the food and beverage industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-sexual orientations.
- The impact of music on job satisfaction and retention in the finance industry.
- The role of music in promoting cultural diversity and understanding in international development.
- The effects of music on emotional regulation and depression in individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the transportation industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-abilities.
- The impact of music on academic performance and motivation in college students.
- The role of music in promoting cross-cultural understanding and acceptance in international cooperation.
- The effects of music on social skills and behavior in individuals with autism spectrum disorder.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the entertainment industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-language backgrounds.
- The impact of music on creativity and innovation in the tech startup industry.
- The role of music in promoting cultural sensitivity and understanding in international peacekeeping.
- The effects of music on cognitive functioning and mental health in individuals with traumatic brain injury.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the travel industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-socioeconomic backgrounds.
- The impact of music on job satisfaction and productivity in the education industry.
- The role of music in promoting cultural diversity and understanding in international cooperation.
- The effects of music on emotional regulation and anxiety in individuals with generalized anxiety disorder.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the home appliance industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-culture backgrounds.
- The impact of music on academic performance and motivation in graduate students.
- The role of music in promoting cross-cultural understanding and acceptance in international diplomacy.
- The effects of music on social skills and behavior in individuals with attention deficit disorder.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the construction industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-spiritual backgrounds.
- The impact of music on creativity and productivity in the healthcare industry.
- The role of music in promoting cultural sensitivity and understanding in international justice.
- The effects of music on cognitive functioning and mental health in individuals with Parkinson’s disease.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the hospitality industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-political backgrounds.
- The impact of music on job satisfaction and retention in the automotive industry.
- The role of music in promoting cultural diversity and understanding in international diplomacy.
- The effects of music on emotional regulation and depression in individuals with major depressive disorder.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the telecommunications industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-ethnic and racial backgrounds.
- The impact of music on academic performance and motivation in high school students with disabilities.
- The role of music in promoting cross-cultural understanding and acceptance in international trade.
- The effects of music on social skills and behavior in individuals with borderline personality disorder.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the fashion industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-heritage backgrounds.
- The effects of music on cognitive functioning and mental health in individuals with schizophrenia.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the technology industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-race identities.
- The impact of music on job satisfaction and retention in the hospitality industry.
- The role of music in promoting cultural diversity and understanding in global development.
- The effects of music on emotional regulation and anxiety in individuals with social phobia.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the toy industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-faith backgrounds.
- The impact of music on academic performance and motivation in high school students.
- The effects of music on social skills and behavior in individuals with oppositional defiant disorder.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the beauty industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-ethnicity backgrounds.
- The impact of music on creativity and productivity in the fashion industry.
- The role of music in promoting cultural sensitivity and understanding in international aid.
- The effects of music on cognitive functioning and mental health in individuals with dementia.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the fitness industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-gender identities.
- The impact of music on job satisfaction and productivity in the technology industry.
- The role of music in promoting cultural diversity and understanding in international tourism.
- The effects of music on emotional regulation and depression in individuals with anxiety disorders.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the pet industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-education backgrounds.
- The impact of music on academic performance and motivation in middle school students.
- The effects of music on social skills and behavior in individuals with obsessive-compulsive disorder.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the home decor industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-sex identities.
- The impact of music on creativity and innovation in the gaming industry.
- The role of music in promoting cultural sensitivity and understanding in international conflict resolution.
- The effects of music on cognitive functioning and mental health in individuals with bipolar disorder.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the sports industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-nationality and mixed-linguistic backgrounds.
- The impact of music on job satisfaction and retention in the retail industry.
- The role of music in promoting cultural diversity and understanding in global governance.
- The effects of music on emotional regulation and anxiety in individuals with panic disorder.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the electronics industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-citizenship backgrounds.
- The impact of music on academic performance and motivation in elementary school students.
- The role of music in promoting cross-cultural understanding and acceptance in international security.
- The effects of music on social skills and behavior in individuals with conduct disorder.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the agriculture industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-religious backgrounds.
- The effects of music on cognitive functioning and mental health in individuals with traumatic brain injuries.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with disability identities.
- The role of music in promoting cross-cultural understanding and acceptance in the healthcare industry.
- The effects of music on emotional regulation and anxiety in individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with LGBTQ+ identities.
- The impact of music on job satisfaction and productivity in the gig economy.
- The role of music in promoting cultural sensitivity and understanding in education policy.
- The effects of music on social skills and behavior in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-age identities.
- The impact of music on creativity and innovation in the advertising industry.
- The role of music in promoting cultural diversity and understanding in urban planning.
- The effects of music on cognitive functioning and mental health in individuals with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the food industry.
- The impact of music on job satisfaction and retention in the nonprofit sector.
- The role of music in promoting cultural understanding and acceptance in international business.
- The effects of music on emotional regulation and depression in individuals with chronic pain.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the gaming industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-sexual orientation identities.
- The role of music in promoting cross-cultural communication and understanding in foreign policy.
- The effects of music on social skills and behavior in individuals with social anxiety disorder.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the craft industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-disability identities.
- The impact of music on creativity and productivity in the media industry.
- The role of music in promoting cultural sensitivity and understanding in corporate social responsibility.
- The effects of music on cognitive functioning and mental health in individuals with substance use disorders.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the automotive industry.
- The impact of music on job satisfaction and productivity in the education sector.
- The role of music in promoting cultural diversity and understanding in international law.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the wellness industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-nationality backgrounds.
- The impact of music on academic performance and motivation in adult learners.
- The role of music in promoting cultural understanding and acceptance in global governance.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the furniture industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-generational backgrounds.
- The impact of music on creativity and innovation in the film industry.
- The role of music in promoting cultural integration and social cohesion in diverse communities.
- The effects of music on cognitive functioning and mental health in individuals with multiple sclerosis.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the tech industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in second-generation immigrants.
- The role of music in promoting cross-cultural communication and understanding in diplomacy.
- The effects of music on emotional regulation and self-esteem in individuals with eating disorders.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the publishing industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in biracial and multiracial families.
- The impact of music on creativity and innovation in the workplace.
- The role of music in promoting cultural awareness and sensitivity in the criminal justice system.
- The effects of music on social skills and behavior in individuals with schizophrenia.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with refugee backgrounds.
- The role of music in promoting cultural understanding and acceptance in global marketing.
- The effects of music on emotional regulation and anxiety in individuals with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed religious backgrounds.
- The impact of music on academic achievement and retention in community college students.
- The role of music in promoting cultural exchange and understanding in international development.
- The effects of music on social skills and behavior in individuals with bipolar disorder.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the luxury goods industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with immigrant parents.
- The impact of music on creativity and productivity in the tech industry.
- The role of music in promoting cultural sensitivity and understanding in journalism.
- The effects of music on emotional regulation and depression in individuals with chronic fatigue syndrome.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the wine industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with non-binary gender identities.
- The impact of music on job satisfaction and productivity in remote workers.
- The role of music in promoting cultural diversity and understanding in international relations.
- The role of music in promoting cultural awareness and sensitivity in diplomacy.
- The effects of music on emotional regulation and self-esteem in individuals with body dysmorphia.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with immigrant grandparents.
- The role of music in promoting cultural understanding and acceptance in global advertising.
- The effects of music on social skills and behavior in individuals with borderline intellectual functioning.
- The relationship between music and cultural representation in the fragrance industry.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and mental health in individuals with mixed-citizenship status.
- The impact of music on creativity and productivity in the creative industries
- The relationship between music and social cohesion in diverse communities.
- The role of music in social justice movements and protests.
- The effects of music on pain management and perception.
- The influence of music on cultural hybridity and globalization.
- The impact of music on social identity and self-esteem.
- The relationship between music and cultural imperialism.
- The role of music in therapeutic settings for children and adolescents.
- The effects of music on language development in bilingual children.
- The influence of music on cultural representation in the media.
- The impact of music on interpersonal relationships and communication.
- The relationship between music and cultural hegemony in the digital age.
- The role of music in community-based initiatives for social change.
- The effects of music on mental health in marginalized communities.
- The influence of music on cultural identity and self-expression.
- The impact of music on academic engagement and success in at-risk students.
- The relationship between music and cultural appropriation in popular culture.
- The role of music in cultural diplomacy and international relations in the 21st century.
- The effects of music on cognitive processing in individuals with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
- The influence of music on cultural hybridity and transnationalism.
- The impact of music on social justice advocacy and awareness-raising.
- The relationship between music and cultural resistance in marginalized communities.
- The role of music in the negotiation of cultural identities in the diaspora.
- The effects of music on language processing and learning in second language acquisition.
- The influence of music on cultural exchange and intercultural communication in the digital age.
- The impact of music on academic achievement in students with disabilities.
- The relationship between music and cultural hegemony in the music industry.
- The role of music in the socialization and empowerment of girls and women.
- The effects of music on physical health in individuals with chronic pain.
- The influence of music on cultural authenticity and representation in the tourism industry.
- The impact of music on the construction of gender and sexuality in popular culture.
- The relationship between music and cultural appropriation in the fashion industry.
- The role of music in promoting cross-cultural understanding and empathy.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

200+ Funny Research Topics

500+ Sports Research Topics

300+ American History Research Paper Topics

500+ Cyber Security Research Topics

500+ Environmental Research Topics

500+ Economics Research Topics
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychol
The psychological functions of music listening
Thomas schäfer.
1 Department of Psychology, Chemnitz University of Technology, Chemnitz, Germany
Peter Sedlmeier
Christine städtler, david huron.
2 School of Music, Cognitive and Systematic Musicology Laboratory, Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA
Why do people listen to music? Over the past several decades, scholars have proposed numerous functions that listening to music might fulfill. However, different theoretical approaches, different methods, and different samples have left a heterogeneous picture regarding the number and nature of musical functions. Moreover, there remains no agreement about the underlying dimensions of these functions. Part one of the paper reviews the research contributions that have explicitly referred to musical functions. It is concluded that a comprehensive investigation addressing the basic dimensions underlying the plethora of functions of music listening is warranted. Part two of the paper presents an empirical investigation of hundreds of functions that could be extracted from the reviewed contributions. These functions were distilled to 129 non-redundant functions that were then rated by 834 respondents. Principal component analysis suggested three distinct underlying dimensions: People listen to music to regulate arousal and mood , to achieve self-awareness , and as an expression of social relatedness . The first and second dimensions were judged to be much more important than the third—a result that contrasts with the idea that music has evolved primarily as a means for social cohesion and communication. The implications of these results are discussed in light of theories on the origin and the functionality of music listening and also for the application of musical stimuli in all areas of psychology and for research in music cognition.
Introduction
Music listening is one of the most enigmatic of human behaviors. Most common behaviors have a recognizable utility that can be plausibly traced to the practical motives of survival and procreation. Moreover, in the array of seemingly odd behaviors, few behaviors match music for commandeering so much time, energy, and money. Music listening is one of the most popular leisure activities. Music is a ubiquitous companion to people's everyday lives.
The enthusiasm for music is not a recent development. Recognizably musical activities appear to have been present in every known culture on earth, with ancient roots extending back 250,000 years or more (see Zatorre and Peretz, 2001 ). The ubiquity and antiquity of music has inspired considerable speculation regarding its origin and function.
Throughout history, scholars of various stripes have pondered the nature of music. Philosophers, psychologists, anthropologists, musicologists, and neuroscientists have proposed a number of theories concerning the origin and purpose of music and some have pursued scientific approaches to investigating them (e.g., Fitch, 2006 ; Peretz, 2006 ; Levitin, 2007 ; Schäfer and Sedlmeier, 2010 ).
The origin of music is shrouded in prehistory. There is little physical evidence—like stone carvings or fossilized footprints—that might provide clues to music's past. Necessarily, hypotheses concerning the original functions of music will remain speculative. Nevertheless, there are a number of plausible and interesting conjectures that offer useful starting-points for investigating the functions of music.
A promising approach to the question of music's origins focuses on how music is used—that is, it's various functions. In fact, many scholars have endeavored to enumerate various musical functions (see below). The assumption is that the function(s) that music is presumed to have served in the past would be echoed in at least one of the functions that music serves today. Of course, how music is used today need have no relationship with music's function(s) in the remote past. Nevertheless, evidence from modern listeners might provide useful clues pertinent to theorizing about origins.
In proposing various musical functions, not all scholars have related these functions to music's presumed evolutionary roots. For many scholars, the motivation has been simply to identify the multiple ways in which music is used in everyday lives (e.g., Chamorro-Premuzic and Furnham, 2007 ; Boer, 2009 ; Lonsdale and North, 2011 ; Packer and Ballantyne, 2011 ). Empirical studies of musical functions have been very heterogeneous. Some studies were motivated by questions related to development. Many related to social identity. Others were motivated by cognitive psychology, aesthetics, cultural psychology, or personality psychology. In addition, studies differed according to the target population. While some studies attempted to assemble representative samples of listeners, others explicitly focused on specific populations such as adolescents. Most studies rely on convenient samples of students. Consequently, the existing literature is something of a hodgepodge.
The aim of the present study is to use the extant literature as a point of departure for a fresh re-appraisal of possible musical functions. In Part 1 of our study, we summarize the results of an extensive literature survey concerning the possible functions of music. Specifically, we identified and skimmed hundreds of publications that explicitly suggest various functions, uses, or benefits for music. We provide separate overviews for the empirical literatures and the theoretical literatures. This survey resulted in just over 500 proposed musical functions. We do not refer to each of the identified publications but concentrate on the ones that have identified either more than one single function of music listening or a single unique function that is not captured in any other publication. In Part 2, we present the results of an empirical study whose purpose was to distill—using principal components analysis (PCA)—the many proposed functions of music listening. To anticipate our results, we will see that PCA suggests three main dimensions that can account for much of the shared variance in the proposed musical functions.
Review of the research on the functions of music
Discussions and speculations regarding the functions of music listening can be found in both theoretical literature concerning music as well as in empirical studies of music. Below, we offer a review of both literatures. The contents of the reviews are summarized in Tables TablesA1, A1 , ,A2. A2 . Table TableA1 A1 provides an overview of theoretical proposals regarding musical function, whereas Table TableA2 A2 provides an overview of empirical studies regarding musical function. Together, the two tables provide a broad inventory of potential functions for music.
Theoretical approaches
Many scholars have discussed potential functions of music exclusively from a theoretical point of view. The most prominent of these approaches or theories are the ones that make explicit evolutionary claims. However, there are also other, non-evolutionary approaches such as experimental aesthetics or the uses-and-gratifications approach. Functions of music were derived deductively from these approaches and theories. In addition, in the literature, one commonly finds lists or collections of functions that music can have. Most of these lists are the result of literature searches; in other cases authors provide no clear explanation for how they came up with the functions they list. Given the aim of assembling a comprehensive list, all works are included in our summary.
Functions of music as they derive from specific approaches or theories
Evolutionary approaches. Evolutionary discussions of music can already be found in the writings of Darwin. Darwin discussed some possibilities but felt there was no satisfactory solution to music's origins (Darwin, 1871 , 1872 ). His intellectual heirs have been less cautious. Miller ( 2000 ), for instance, has argued that music making is a reasonable index of biological fitness, and so a manifestation of sexual selection—analogous to the peacock's tail. Anyone who can afford the biological luxury of making music must be strong and healthy. Thus, music would offer an honest social signal of physiological fitness.
Another line of theorizing refers to music as a means of social and emotional communication. For example, Panksepp and Bernatzky ( 2002 , p. 139) argued that
in social creatures like ourselves, whose ancestors lived in arboreal environments where sound was one of the most effective ways to coordinate cohesive group activities, reinforce social bonds, resolve animosities, and to establish stable hierarchies of submission and dominance, there could have been a premium on being able to communicate shades of emotional meaning by the melodic character (prosody) of emitted sounds.
A similar idea is that music contributes to social cohesion and thereby increases the effectiveness of group action. Work and war songs, lullabies, and national anthems have bound together families, groups, or whole nations. Relatedly, music may provide a means to reduce social stress and temper aggression in others. The idea that music may function as a social cement has many proponents (see Huron, 2001 ; Mithen, 2006 ; Bicknell, 2007 ).
A novel evolutionary theory is offered by Falk ( 2004a , b ) who has proposed that music arose from humming or singing intended to maintain infant-mother attachment. Falk's “putting-down-the-baby hypothesis” suggests that mothers would have profited from putting down their infants in order to make their hands free for other activities. Humming or singing consequently arose as a consoling signal indicating caretaker proximity in the absence of physical touch.
Another interesting conjecture relates music to human anxiety related to death, and the consequent quest for meaning. Dissanayake ( 2009 ), for example, has argued that humans have used music to help cope with awareness of life's transitoriness. In a manner similar to religious beliefs about the hereafter or a higher transcendental purpose, music can help assuage human anxiety concerning mortality (see, e.g., Newberg et al., 2001 ). Neurophysiological studies regarding music-induced chills can be interpreted as congruent with this conjecture. For example, music-induced chills produce reduced activity in brain structures associated with anxiety (Blood and Zatorre, 2001 ).
Related ideas stress the role music plays in feelings of transcendence. For example, (Frith, 1996 , p. 275) has noted that: “We all hear the music we like as something special, as something that defies the mundane, takes us “out of ourselves,” puts us somewhere else.” Thus, music may provide a means of escape. The experience of flow states (Nakamura and Csikszentmihalyi, 2009 ), peaks (Maslow, 1968 ), and chills (Panksepp, 1995 ), which are often evoked by music listening, might similarly be interpreted as forms of transcendence or escapism (see also Fachner, 2008 ).
More generally, Schubert ( 2009 ) has argued that the fundamental function of music is its potential to produce pleasure in the listener (and in the performer, as well). All other functions may be considered subordinate to music's pleasure-producing capacity. Relatedly, music might have emerged as a safe form of time-passing—analogous to the sleeping behaviors found among many predators. As humans became more effective hunters, music might have emerged merely as an entertaining and innocuous way to pass time during waking hours (see Huron, 2001 ).
The above theories each stress a single account of music's origins. In addition, there are mixed theories that posit a constellation of several concurrent functions. Anthropological accounts of music often refer to multiple social and cultural benefits arising from music. Merriam ( 1964 ) provides a seminal example. In his book, The anthropology of music , Merriam proposed 10 social functions music can serve (e.g., emotional expression, communication, and symbolic representation). Merriam's work has had a lasting influence among music scholars, but also led many scholars to focus exclusively on the social functions of music. Following in the tradition of Merriam, Dissanayake ( 2006 ) proposed six social functions of ritual music (such as display of resources, control, and channeling of individual aggression, and the facilitation of courtship).
Non-evolutionary approaches. Many scholars have steered clear of evolutionary speculation about music, and have instead focused on the ways in which people use music in their everyday lives today. A prominent approach is the “uses-and-gratifications” approach (e.g., Arnett, 1995 ). This approach focuses on the needs and concerns of the listeners and tries to explain how people actively select and use media such as music to serve these needs and concerns. Arnett ( 1995 ) provides a list of potential uses of music such as entertainment, identity formation, sensation seeking, or culture identification.
Another line of research is “experimental aesthetics” whose proponents investigate the subjective experience of beauty (both artificial or natural), and the ensuing experience of pleasure. For example, in discussing the “recent work in experimental aesthetics,” Bullough ( 1921 ) distinguished several types of listeners and pointed to the fact that music can be used to activate associations, memories, experiences, moods, and emotions.
By way of summary, many musical functions have been proposed in the research literature. Evolutionary speculations have tended to focus on single-source causes such as music as an indicator of biological fitness, music as a means for social and emotional communication, music as social glue, music as a way of facilitating caretaker mobility, music as a means of tempering anxiety about mortality, music as escapism or transcendental meaning, music as a source of pleasure, and music as a means for passing time. Other accounts have posited multiple concurrent functions such as the plethora of social and cultural functions of music found in anthropological writings about music. Non-evolutionary approaches are evident in the uses-and-gratifications approach—which revealed a large number of functions that can be summarized as cognitive, emotional, social, and physiological functions—and the experimental aesthetics approach, whose proposed functions can similarly be summarized as cognitive and emotional functions.
Functions of music as they derive from literature research
As noted, many publications posit musical functions without providing a clear connection to any theory. Most of these works are just collections of functions of music from the literature. Not least, there are also accounts of such collections where it remained unclear how the author(s) came up with the functions contained. Some of these works refer to only one single function of music—most often because this functional aspect was investigated not with the focus on music but with a focus on other psychological phenomena. Yet other works list extensive collections of purported musical functions.
Works that refer to only one single functional aspect of music include possible therapeutic functions for music in clinical settings (Cook, 1986 ; Frohne-Hagemann and Pleß-Adamczyk, 2005 ), the use of music for symbolic exclusion in political terms (Bryson, 1996 ), the syntactic, semantic, and mediatizing use of film music (Maas, 1993 ), and the use of music to manage physiological arousal (Bartlett, 1996 ).
The vast majority of publications identify several possible musical functions, most of which—as stated above—are clearly focused on social aspects. Several comprehensive collections have been assembled, such as those by Baacke ( 1984 ), Gregory ( 1997 ), Ruud ( 1997 ), Roberts and Christenson ( 2001 ), Engh ( 2006 ), and Laiho ( 2004 ). Most of these studies identified a very large number of potential functions of music.
By way of summary, there exists a long tradition of theorizing about the potential functions of music. Although some of these theories have been deduced from a prior theoretical framework, none was the result of empirical testing or exploratory data-gathering. In the ensuing section, we turn to consider empirically-oriented research regarding the number and nature of potential musical functions.
Empirical investigations
A number of studies have approached the functions of music from an empirical perspective. Two main approaches might be distinguished. In the first approach, the research aim is to uncover or document actual musical functioning. That is, the research aims to observe or identify one or more ways in which music is used in daily life. In the second approach, the research goal is to infer the structure or pattern underlying the use of music. That is, the research aims to uncover potential basic or fundamental dimensions implied by the multiple functions of music. This is mostly done using PCA or factor analyses or cluster analyses that reduce a large number of functions to only a few basic dimensions. In some cases, the analyses are run exploratively whereas in other cases, they are run in a confirmatory way, that is—with a predefined number of dimensions. The empirical studies can be categorized according to several criteria (see Table TableA2). A2 ). However, when discussing some of the most important works here, we will separate studies where respondents were asked for the functions of music in open surveys from studies where the authors provided their own collections of functions, based on either literature research or face validity.
Surveys about the functions music can have
A number of studies have attempted to chronicle the broad range of musical functions. Most of these studies employed surveys in which people were asked to identify the ways in which they make use of music in their lives. In some studies, expert interviews were conducted in order to identify possible functions. Table TableA2 A2 provides a summary of all the pertinent studies including their collections of functions and—where applicable—their derived underlying dimensions. We will restrict our ensuing remarks to the largest and most comprehensive studies.
Chamorro-Premuzic and Furnham ( 2007 ) identified 15 functions of music among students and subsequently ran focus groups from which they distilled three distinct dimensions: emotional use, rational use, and background use. Some of the largest surveys have been carried out by Boer ( 2009 ). She interviewed more than a thousand young people in different countries and assembled a comprehensive collection of musical functions. Using factor analysis, she found 10 underlying dimensions: emotion, friends, family, venting, background, dancing, focus, values, politic, and culture. (Lonsdale and North, 2011 , Study 1) pursued a uses-and-gratifications approach. They identified 30 musical uses that could be reduced to six distinct dimensions. In a related study employing a larger sample, the same authors came up with eight distinct dimensions: identity, positive and negative mood management, reminiscing, diversion, arousal, surveillance, and social interaction (Lonsdale and North, 2011 , Study 4). When interviewing older participants, Hays and Minichiello ( 2005 ) qualitatively identified six dimensions: linking, life events, sharing and connecting, wellbeing, therapeutic benefits, escapism, and spirituality.
The various surveys and interview studies clearly diverge with regard to the number of different musical functions. Similarly, the various cluster and factor analyses often end up producing different numbers of distinct dimensions. Nevertheless, the results are often quite similar. On a very broad level, there are four categories that appear consistently: social functions, emotional functions, cognitive or self-related functions, and physiological or arousal-related functions (see also Hargreaves and North, 1999 ; Schäfer and Sedlmeier, 2009 , 2010 ).
Empirical studies using predefined collections of functions of music
Apart from the open-ended surveys and interview methods, a number of studies investigating musical functions begin with researcher-defined collections or even categories/dimensions. Some of these predefined collections or categories/dimensions were simply borrowed from the existing published research, whereas others were derived from specific theoretical perspectives.
Empirical studies on functions of music emerging from specific theoretical approaches. Some of the above mentioned theoretical approaches to the functionality of music have been investigated in empirical studies. Boehnke and Münch ( 2003 ) developed a model of the relationship of adolescents' development, music, and media use. They proposed seven functions of music that relate to the developmental issues of young people (such as peer group integration, physical maturation, or identity development). In two studies with a large number of participants, Lonsdale and North ( 2011 ) applied the model of media gratification (from McQuail et al., 1972 ) and used a collection of 30 functions of music they assembled from literature research and interviews. In both studies, they ran factor analyses—reducing the number of functions to six dimensions and eight dimensions, respectively. Lehmann ( 1994 ) developed a situations-functions-preference model and proposed that music preferences emerge from the successful use of music to serve specific functions for the listener, depending on the current situation. Lehmann identified 68 ways in which people use music, from which he was able to reduce them to 15 music reception strategies (Rezeptionsweisen) such as compensation/escapism, relaxation, and identification. Misenhelter and Kaiser ( 2008 ) adopted Merriam's ( 1964 ) anthropological approach and attempted to identify the functions of music in the context of music education. They surveyed teachers and students and found six basic functions that were quite similar to the ones proposed by Merriam ( 1964 ). Wells and Hakanen ( 1997 ) adopted Zillmann's ( 1988a , b ) mood management theory and identified four types of users regarding the emotional functions of music: mainstream, music lover, indifferent, and heavy rockers.
Empirical studies on functions of music emerging from literature research. A number of studies have made use of predefined musical functions borrowed from the existing research literature. The significance of these functions and/or their potential underlying structure has then been empirically investigated using different samples. As mentioned, not all of those studies tried to assemble an exhaustive collection of musical functions in order to produce a comprehensive picture of the functions of music; but many studies were focused on specific aspects such as the emotional, cognitive, or social functions of music.
Schäfer and Sedlmeier ( 2009 ) collected 17 functions of music from the literature and found functions related to the management of mood and arousal as well as self-related functions to be the ones that people highly ascribe to their favorite music. Tarrant et al. ( 2000 ) used a collection of 10 functions of music from the literature and factor analyzed them resulting in three distinct dimensions of music use: self-related, emotional, and social.
Sun and Lull ( 1986 ) collected 18 functions of music videos and were able to reduce them to four dimensions: social learning, passing time, escapism/mood, and social interaction. Melton and Galician ( 1987 ) identified 15 functions of radio music and music videos; and Greasley and Lamont ( 2011 ) collected 15 functions of music, as well. Ter Bogt et al. ( 2011 ) collected 19 functions of music from the literature and used confirmatory factor analysis to group them into five dimensions. In a clinical study with adolescents, Walker Kennedy ( 2010 ) found 47 functions of music that could be reduced to five dimensions.
By way of summary, extant empirical studies have used either an open approach—trying to capture the variety of musical functions in the course of surveys or questionnaire studies—or predefined collections of functions as they resulted from specific theoretical approaches or from literature research. These different approaches have led to quite heterogeneous collections of possible musical functions—from only few functions posited by a specific hypothesis, to long lists arising from open surveys. Moreover, although the many attempts to distill the functions of music to fewer dimensions have produced some points of agreement, the overall picture remains unclear.
The structure among the functions of music
With each successive study of musical functions, the aggregate list of potential uses has grown longer. Questionnaire studies, in particular, have led to the proliferation of possible ways in which music may be relevant in people's lives. Even if one sidesteps the question of possible evolutionary origins, the multitude of hundreds of proposed functions raises the question of whether these might not be distilled to a smaller set of basic dimensions.
As noted earlier, previous research appears to converge on four dimensions: social functions (such as the expression of one's identity or personality), emotional functions (such as the induction of positive feelings), cogni tive or self-related functions (such as escapism), and arousal-related functions (such as calming down or passing time). These four dimensions might well account for the basic ways in which people use music in their daily lives.
Notice that cluster analysis and PCA/factor analysis presume that the research begins with a range of variables that ultimately capture all of the factors or dimensions pertaining to the phenomenon under consideration. The omission of even a single variable can theoretically lead to incomplete results if that variable proves to share little variance in common with the other variables. For example, in studying the factors that contribute to a person's height, the failure to include a variable related to developmental nutrition will led to deceptive results; one might wrongly conclude that only genetic factors are important. The validity of these analyses depends, in part, on including a sufficient range of variables so that all of the pertinent factors or dimensions are likely to emerge.
Accordingly, we propose to address the question of musical functions anew, starting with the most comprehensive list yet of potential music-related functions. In addition, we will aim to recruit a sample of participants covering all age groups, a wide range of socio-economic backgrounds, and pursue our analysis without biasing the materials to any specific theory.
Fundamental functions of music—a comprehensive empirical study
The large number of functions of music that research has identified during the last decades has raised the question of a potential underlying structure: Are there functions that are more fundamental and are there others that can be subsumed under the fundamental ones? And if so, how many fundamental functions are there? As we have outlined above, many scientists have been in search of basic distinct dimensions among the functions of music. They have used statistical methods that help uncover such dimensions among a large number of variables: factor analyses or cluster analyses.
However, as we have also seen, the approaches and methods have been as different as the various functions suggested. For instance, some scholars have focused exclusively on the social functions of music while others have been interested in only the emotional ones; some used only adolescent participants while others consulted only older people. Thus, these researchers arrived at different categorizations according to their particular approach. To date, there is still no conclusive categorization of the functions of music into distinct dimensions, which makes psychological studies that rely on the use of music and its effects on cognition, emotion, and behavior still difficult (see also Stefanija, 2007 ). Although there exist some theoretically driven claims about what fundamental dimensions there might be (Tarrant et al., 2000 ; Laiho, 2004 ; Schubert, 2009 ; Lonsdale and North, 2011 ), there has been no large-scale empirical study that analyzed the number and nature of distinct dimensions using the broad range of all potential musical functions—known so far—all at once.
We sought to remedy this deficiency by assembling an exhaustive list of the functions of music that have been identified in past research and putting them together in one questionnaire study. Based on the research reviewed in the first part of this study, we identified more than 500 items concerned with musical use or function. Specifically, we assembled an aggregate list of all the questions and statements encountered in the reviewed research that were either theoretically derived or used in empirical studies. Of course, many of the items are similar, analogous, or true duplicates. After eliminating or combining redundant items, we settled on a list of 129 distinct items. All of the items were phrased as statements in the form “I listen to music because … ” The complete list of items is given in Table TableA3, A3 , together with their German versions as used in our study.
Participants were asked to rate how strongly they agreed with each item-statement on a scale from 0 ( not at all ) to 6 ( fully agree ). When responding to items, participants were instructed to think of any style of music and of any situation in which they would listen to music. In order to obtain a sample that was heterogeneous with regard to age and socioeconomic background, we distributed flyers promoting the Internet link to our study in a local electronics superstore. Recruitment of participants was further pursued via some mailing lists of German universities, students from comprehensive schools, and members of a local choir. As an incentive, respondents got the chance to win a tablet computer. A total of 834 people completed the survey. Respondents ranged from 8 to 85 years of age ( M = 26, SD = 10.4, 57% female).
Notice that in carrying out such a survey, we are assuming that participants have relatively accurate introspective access to their own motivations in pursuing particular musical behaviors, and that they are able to accurately recall the appropriate experiences. Of course, there exists considerable empirical research casting doubt on the accuracy of motivational introspection in self-report tasks (e.g., Wilson, 2002 ; Hirstein, 2005 ; Fine, 2006 ). These caveats notwithstanding, in light of the limited options for gathering pertinent empirical data, we nevertheless chose to pursue a survey-based approach.
Principal component analysis revealed three distinct dimensions behind the 129 items (accounting for about 40% of the variance), based on the scree plot. This solution was consistent over age groups and genders. The first dimension (eigenvalue: 15.2%) includes statements about self-related thoughts (e.g., music helps me think about myself), emotions and sentiments (e.g., music conveys feelings), absorption (e.g., music distracts my mind from the outside world), escapism (e.g., music makes me forget about reality), coping (e.g., music makes me believe I'm better able to cope with my worries), solace (e.g., music gives comfort to me when I'm sad), and meaning (e.g., music adds meaning to my life). It appears that this dimension expresses a very private relationship with music listening. Music helps people think about who they are, who they would like to be, and how to cut their own path. We suggest labeling this dimension self-awareness . The second dimension (eigenvalue: 13.7%) includes statements about social bonding and affiliation (e.g., music helps me show that I belong to a given social group; music makes me feel connected to my friends; music tells me how other people think). People can use music to feel close to their friends, to express their identity and values to others, and to gather information about their social environment. We suggest labeling this dimension social relatedness . The third dimension (eigenvalue: 10.2%) includes statements about the use of music as background entertainment and diversion (e.g., music is a great pastime; music can take my mind off things) and as a means to get into a positive mood and regulate one's physiological arousal (e.g., music can make me cheerful; music helps me relax; music makes me more alert). We suggest labeling this dimension arousal and mood regulation . All factor loadings are reported in Table TableA3 A3 .
In order to analyze the relative significance of the three derived dimensions for the listeners, we averaged the ratings for all items contained in each dimension (see Figure Figure1). 1 ). Arousal and mood regulation proved to be the most important dimension of music listening closely followed by self-awareness. These two dimensions appear to represent the two most potent reasons offered by people to explain why they listen to music, whereas social relatedness seems to be a relatively less important reason (ranging below the scale mean). This pattern was consistent across genders, socioeconomic backgrounds, and age groups. All differences between the three dimensions are significant (all p s < 0.001). The reliability indices (Cronbach's α) for the three dimensions are α = 0.97 for the first, α = 0.96 for the second, and α = 0.92 for the third dimension.

The three distinct dimensions emerging from 129 reasons for listening to music . Error bars are 95% confidence intervals. Self-awareness: M = 3.59 ( SE = 0.037); social relatedness: M = 2.01 ( SE = 0.035); arousal and mood regulation: M = 3.78 ( SE = 0.032).
General discussion
Since the earliest writing on the psychology of music, researchers have been concerned with the many ways in which people use music in their lives. In the first part of this paper, we reviewed literature spanning psychological, musicological, biological, and anthropological perspectives on musical function. The picture that emerged from our review was somewhat confusing. Surveying the literature from the past 50 years, we identified more than 500 purported functions for music. From this list, we assembled a somewhat catholic list of 129 non-redundant musical functions. We then tested the verisimilitude of these posited functions by collecting survey responses from a comparatively large sample. PCA revealed just three distinct dimensions: People listen to music to achieve self-awareness , social relatedness , and arousal and mood regulation . We propose calling these the Big Three of music listening.
In part one of our study we noted that several empirical studies suggest grouping musical functions according to four dimensions: cognitive, emotional, social/cultural, and physiological/arousal-related functions. This raises the question of how our three-dimensional result might be reconciled with the earlier work. We propose that there is a rather straightforward interpretation that allows the four-dimensional perspective to be understood within our three-dimensional result. Cognitive functions are captured by the first dimension (self-awareness); social/cultural functions are captured by the second dimensions (social relatedness); physiological/arousal-related functions are captured by the third dimension (arousal and mood regulation); and emotional functions are captured by the first and third dimensions (self-awareness + arousal and mood regulation). Notably—as can be seen with the items in Table TableA3—there A3 —there is a dissociation of emotion-related and mood-related functions. Emotions clearly appear in the first dimension (e.g., music conveys feelings; music can lighten my mood; music helps me better understand my thoughts and emotions), indicating that they might play an important role in achieving self-awareness, probably in terms of identity formation and self-perception, respectively. However, the regulation of moods clearly appears in the third dimension (e.g., music makes me cheerful; music can enhance my mood; I'm less bored when I listen to music), suggesting that moods are not central issues pertaining to identity. Along with the maintenance of a pleasant level of physiological arousal, the maintenance of pleasant moods is an effect of music that might rather be utilized as a “background” strategy, that is, not requiring a deep or aware involvement in the music. The regulation of emotions, on the other side, could be a much more conscious strategy requiring deliberate attention and devotion to the music. Music psychology so far has not made a clear distinction between music-related moods and emotions; and the several conceptions of music-related affect remain contentious (see Hunter and Schellenberg, 2010 ). Our results appear to call for a clearer distinction between moods and emotions in music psychology research.
As noted earlier, a presumed evolutionary origin for music need not be reflected in modern responses to music. Nevertheless, it is plausible that continuities exist between modern responses and possible archaic functions. Hence, the functions apparent in our study may echo possible evolutionary functions. The three functional dimensions found in our study are compatible with nearly all of the ideas about the potential evolutionary origin of music mentioned in the introduction. The idea that music had evolved as a means for establishing and regulating social cohesion and communication is consistent with the second dimension. The idea of music satisfying the basic human concerns of anxiety avoidance and quest for meaning is consistent with the first dimension. And the notion that the basic function of music could have been to produce dissociation and pleasure in the listener is consistent with the third dimension.
In light of claims that music evolved primarily as a means for promoting social cohesion and communication—a position favored by many scholars—the results appear noteworthy. Seemingly, people today hardly listen to music for social reasons, but instead use it principally to relieve boredom, maintain a pleasant mood, and create a comfortable private space. Such a private mode of music listening might simply reflect a Western emphasis on individuality: self-acknowledgement and well-being appear to be more highly valued than social relationships and relatedness (see also Roberts and Foehr, 2008 ; Heye and Lamont, 2010 ).
The results of the present study may be of interest to psychologists who make use of music as a tool or stimulus in their research. The way people usually listen to music outside the laboratory will surely influence how they respond to musical stimuli in psychological experiments. For those researchers who make use of music in psychological studies, some attention should be paid to how music is used in everyday life. The three dimensions uncovered in this study can provide a parsimonious means to identify the value a person sets on each of three different types of music use. It is also conceivable that individual patterns of music use are related to personality traits, a conjecture which may warrant future research.
With regard to music cognition, the present results are especially relevant to studies about aesthetic preferences, style or genre preferences, and musical choice. Recent research suggests that musical functions play an important role in the formation and development of music preferences (e.g., Schäfer and Sedlmeier, 2009 ; Rentfrow et al., 2011 ). It will be one of the future tasks of music cognition research to investigate the dependence of music preference and music choice on the functional use of music in people's lives.
By way of summary, in a self-report study, we found that people appear to listen to music for three major reasons, two of which are substantially more important than the third: music offers a valued companion, helps provide a comfortable level of activation and a positive mood, whereas its social importance may have been overvalued.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Overview of theoretical contributions that have derived, proposed, or addressed more than one function or functional aspect of music listening .

Overview about empirical studies that have identified and/or investigated more than one function or functional aspect of music listening .

In some places, we could only provide exemplary functions because either the total number of functions was too large to be displayed here or not all functions were given in the original publications .
The 129 statements referring to the functions of music exhaustively derived from past research, together with their means, standard deviations, and factor loadings (varimax rotated) .
Dimension 1, self-awareness; Dimension 2, social relatedness; Dimension 3, arousal and mood regulation .
- Arnett J. J. (1995). Adolescents' uses of media for self-socialisation . J. Youth Adolesc . 24 , 519–533 [ Google Scholar ]
- Baacke D. (1984). Kommunikations-kultur der Jugend , in Medienpädagogik and Kommunikationskultur. Referate und Texte Nach Dem Ersten “Forum Kommunikationskultur,” ed de Haen I. (Frankfurt am Main: GEP; ), 37–53 [ Google Scholar ]
- Bartlett D. L. (1996). Physiological responses to music and sound stimuli , in Handbook of Music Psychology, 2nd Edn , ed Hodges D. A. (St. Louis, MO: MMB Music; ), 343–385 [ Google Scholar ]
- Bicknell J. (2007). Explaining strong emotional responses to music: sociality and intimacy . J. Conscious. Stud . 14 , 5–23 [ Google Scholar ]
- Blood A. J., Zatorre R. J. (2001). Intensely pleasurable responses to music correlate with activity in brain regions implicated in reward and emotion . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 98 , 11818–11823 10.1073/pnas.191355898 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Boehnke K., Münch T. (2003). Jugendsozialisation und Medien. Helfen Medien und Musik beim Erwachsenwerden? in Neue Medien im Alltag. Nutzung, Vernetzung, Interaktion , eds Keitel E., Boehnke K., Wenz K. (Lengerich: Pabst Science Publishers; ), 203–227 [ Google Scholar ]
- Boer D. (2009). Music Makes the People Come Together: Social Functions of Music Listening for Young People Across Cultures . Department of Psychology. Victoria University of Wellington, Wellington. Available online at: http://researcharchive.vuw.ac.nz/bitstream/handle/10063/1155/thesis.pdf?sequence=1
- Brown J. D., Campbell K., Fischer L. (1986). American adolescents and music videos: why do they watch . Int. Commun. Gaz . 37 , 19–32 10.1177/001654928603700104 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown S. (2006). How does music work? Toward a pragmatics of musical communication , in Music and Manipulation: On the Social Uses and Social Control of Music , eds Brown S., Volgsten U. (New York, NY: Berghahn Books; ), 1–30 [ Google Scholar ]
- Bryson B. (1996). “Anything but heavy metal”: symbolic exclusion and musical dislikes . Am. Soc. Rev . 61 , 884–899 10.2307/2096459 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bullough E. (1921). Recent work in experimental aesthetics . Br. J. Psychol . 12 , 76–99 [ Google Scholar ]
- Campbell C., Connell S., Beegle A. P. (2007). Adolescents' expressed meanings of music in and out of school . J. Res. Music Educ . 55 , 220–236 [ Google Scholar ]
- Chamorro-Premuzic T., Furnham A. (2007). Personality and music: can traits explain how people use music in everyday life . Br. J. Psychol . 98 , 175–185 10.1348/000712606X111177 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Coleman J. S. (1961). Psychological effects of the social system , in The Adolescents Society: The Social Life of the Teenager and its Impact on Education , ed Coleman J. S. (Oxford: Free Press of Glencoe; ), 220–243 [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook J. D. (1986). Music as an intervention in the oncology setting . Cancer Nurs . 9 , 23–28 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Darwin C. (1871). The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex . London: John Murray [ Google Scholar ]
- Darwin C. (1872). The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals . London: John Murray [ Google Scholar ]
- DeNora T. (1999). Music as a technology of the self . Poetics 27 , 31–56 10.1016/S0304-422X(99)00017-0 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dissanayake E. (2006). Ritual and ritualization: musical means of conveying and shaping emotion in humans and other animals , in Music and Manipulation: On the Social Uses and Social Control of Music , eds Brown S., Volgsten U. (New York, NY: Berghahn Books; ), 31–56 [ Google Scholar ]
- Dissanayake E. (2009). Root, leaf, blossom, or bole: concerning the origin and adaptive function of music , in Communicative Musicality: Exploring the Basis of Human Companionship , eds Malloch S., Trevarthen C. (New York, NY: Oxford University Press; ), 17–30 [ Google Scholar ]
- Engh M. (2006). Popstars als Marke: Identitätsorientiertes Marken-management für die Musikindustrielle Künstlerentwicklung und –Vermarktung . Wiesbaden: Deutscher Universitäts-Verlag [ Google Scholar ]
- Fachner J. (2008). Musik und veränderte Bewusstseinszustände [Music and altered states of consciousness] , in Musikpsychologie. Das neue Handbuch , eds Bruhn H., Kopiez R., Lehmann A. C. (Reinbek: Rowohlt; ), 594–612 [ Google Scholar ]
- Falk D. (2004a). Prelinguistic evolution in early hominins: whence motherese . Behav. Brain Sci . 27 , 491–503 10.1017/S0140525X04000111 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Falk D. (2004b). The “putting the baby down” hypothesis: bipedalism, babbling, and baby slings . Behav. Brain Sci . 27 , 526–534 10.1017/S0140525X0448011X [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fine C. (2006). A Mind of Its Own: How Your Brain Distorts and Deceives . New York, NY: W.W. Norton [ Google Scholar ]
- Fitch W. T. (2006). The biology and evolution of music: a comparative perspective . Cognition 100 , 173–215 10.1016/j.cognition.2005.11.009 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Frith S. (1996). Performing Rites. On the Value of Popular Music . Oxford: Oxford University Press [ Google Scholar ]
- Frohne-Hagemann I., Pleß-Adamczyk H. (2005). Indikation Musiktherapie bei psychischen Problemen im Kindes- und Jugendalter. Musiktherapeutische Diagnostik und Manual nach ICD-10 . Göttingen: Vandenhoeck and Ruprecht [ Google Scholar ]
- Gantz W., Gartenberg H. M., Pearson M. L., Schiller S. O. (1978). Gratifications and expectations associated with Pop music among adolescents . Pop. Music Soc . 6 , 81–89 10.1080/03007767808591113 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Greasley A. E., Lamont A. (2011). Exploring engagement with music in everyday life using experience sampling methodology . Music. Sci . 15 , 45–71 10.1177/1029864910393417 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gregory A. H. (1997). The roles of music in society: the ethnomusicological perspective , in The Social Psychology of Music , eds Hargreaves D. J., North A. C. (New York, NY: Oxford University Press; ), 123–140 [ Google Scholar ]
- Hargreaves D. J., North A. C. (1999). The functions of music in everyday life: redefining the social in music psychology . Psychol. Music 27 , 71–83 10.1177/0305735699271007 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hays T., Minichiello V. (2005). The meaning of music in the lives of older people: a qualitative study . Psychol. Music 33 , 437–451 10.1177/0305735605056160 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Heister H.-W. (1993). Stellenwert der Musik im gesellschaftlichen System , in Musikpsychologie. Ein Handbuch , eds Bruhn H, Oerter R., Rösing H. (Reinbek: Rowohlt; ), 103–112 [ Google Scholar ]
- Herbert R. (2011). Everyday Music Listening: Absorption, Dissociation and Trancing . Farnham, Burlington: Ashgate Publishing Limited [ Google Scholar ]
- Heye A., Lamont A. (2010). Mobile listening situations in everyday life: the use of MP3 players while travelling . Music. Sci . 14 , 95–120 [ Google Scholar ]
- Hirstein W. (2005). Brain Fiction: Self-Deception and the Riddle of Confabulation . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press [ Google Scholar ]
- Hunter P. G., Schellenberg E. G. (2010). Music and emotion , in Music Perception , Vol. 36 , eds Jones M. R., Fay R. R., Popper A. N. (New York, NY: Springer; ), 129–164 [ Google Scholar ]
- Huron D. (2001). Is music an evolutionary adaptation? , in The Biological Foundations of Music , eds Zatorre R. J., Peretz I. (New York, NY: New York Academy of Sciences; ), 43–61 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Juslin P. N., Liljeström S., Västfjäll D., Barradas G., Silva A. (2008). An experience sampling study of emotional reactions to music: listener, music, and situation . Emotion 8 , 668–683 10.1037/a0013505 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kapteina H. (2010). Was Geschieht, Wenn Wir Musik Hören. Fragmente Zur Psychologie Des Hörens . Available online at: http://www.musiktherapie.uni-siegen.de/kapteina/material/forschungsgebiete/neu_was_geschieht_wenn_wir_musik_hoeren.pdf
- Laiho S. (2004). The psychological functions of music in adolescence . Nord. J. Music Ther . 13 , 47–63 10.1080/08098130409478097 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Larson R. (1995). Secrets in the bedroom: adolescents' private use of media . J. Youth Adolesc . 24 , 535–550 10.1007/BF01537055 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Laukka P. (2007). Uses of music and psychological well-being among the elderly . J. Happiness Stud . 8 , 215–241 10.1007/s10902-006-9024-3 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lehmann A. C. (1994). Habituelle Und Situative Rezeptionsweisen Beim Musikhören. Eine Einstellungstheoretische Untersuchung . Frankfurt: Peter Lang [ Google Scholar ]
- Levitin D. J. (2007). Life Soundtrack: The Uses of Music in Everyday Life . Montreal, QC: McGill University; Available online at: http://levitin.mcgill.ca/pdf/LifeSoundtracks.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Lonsdale A. J., North A. C. (2011). Why do we listen to music. a uses and gratifications analysis . Br. J. Psychol . 102 , 108–134 10.1348/000712610X506831 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maas G. (1993). Filmmusik , in Musikpsychologie. Ein Handbuch , eds Bruhn H., Oerter R., Rösing H. (Reinbek: Rowohlt; ), 203–207 [ Google Scholar ]
- Maslow A. H. (1968). Toward a Psychology of Being . 2nd Edn New York, NY: Van Nostr and Company [ Google Scholar ]
- McQuail D., Blumler J. G., Brown J. (1972). The television audience: a revised perspective , in Sociology of Mass Communication , ed McQuail D. (Middlesex: Penguin; ), 135–165 [ Google Scholar ]
- Melton G. W., Galician M. Lou. (1987). A sociological approach to the pop music phenomenon: radio and music video utilization for expectation, motivation and satisfaction . Pop. Music Soc . 11 , 35–46 10.1080/03007768708591286 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Merriam A. P. (1964). The Anthropology of Music . Evanston, IL: Northwestern University Press [ Google Scholar ]
- Miller G. (2000). Evolution of human music through sexual selection , in The Origins of Music , eds Wallin N. L., Merker B., Brown S. (Cambridge: The MIT Press; ), 329–360 [ Google Scholar ]
- Misenhelter D., Kaiser K. (2008). Social functions of music in music education . J. Artistic Creat. Educ . 2 , 61–74 [ Google Scholar ]
- Mithen S. (2006). The Singing Neanderthals: The Origins of Music, Language, Mind, and Body . Cambridge: Harvard University Press [ Google Scholar ]
- Münch T., Bommersheim U., Müller-Bachmann E. (2005). Jugendliches Musikverhalten. Musikinvolvement, Nutzungsmotive und Musikpräferenzen , in Jugendsozialisation und Medien , eds Boehnke K., Münch T. (Lengerich: Pabst Science Publishers; ), 167–199 [ Google Scholar ]
- Nakamura J., Csikszentmihalyi M. (2009). Flow theory and research , in Oxford Handbook of Positive Psychology, 2nd Edn , eds Lopez S. J., Snyder C. R. (New York, NY: Oxford University Press; ), 195–206 [ Google Scholar ]
- Newberg A., D'Aquili E., Rause V. (2001). Why God Won't Go Away: Brain Science and the Biology of Belief . New York, NY: Ballantine Books [ Google Scholar ]
- North A. C., Hargreaves D. J., O'Neill S. A. (2000). The importance of music to adolescents . Br. J. Educ. Psychol . 70 , 255–272 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Packer J., Ballantyne J. (2011). The impact of music festival attendance on young people's psychological and social well-being . Psychol. Music 39 , 164–181 10.1177/0305735610372611 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Panksepp J. (1995). The emotional sources of “chills” induced by music . Music Percept . 13 , 171–207 [ Google Scholar ]
- Panksepp J., Bernatzky G. (2002). Emotional sounds and the brain: the neuro-affective foundations of musical appreciation . Behav. Process . 60 , 133–155 10.1016/S0376-635700080-3 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Peretz I. (2006). The nature of music from a biological perspective . Cognition 100 , 1–32 10.1016/j.cognition.2005.11.004 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rentfrow P. J., Goldberg L. R., Levitin D. J. (2011). The structure of musical preferences: a five-factor model . J. Pers. Soc. Psychol . 100 , 1139–1157 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Roberts D. F., Christenson P. G. (2001). Popular music in childhood and adolescence , in Handbook of Children and the Media , eds Singer D. G., Singer J. L. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, Inc; ), 395–414 [ Google Scholar ]
- Roberts D. F., Foehr U. G. (2008). Trends in media use . Future Child . 18 , 11–37 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Roe K. (1985). Swedish youth and music: listening patterns and motivations . Commun. Res . 12 , 353–362 10.1177/009365085012003007 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rösing H. (1993). Musik im Alltag , in Musikpsychologie. Ein Handbuch , eds Bruhn H., Oerter R., Rösing H. (Reinbek: Rowohlt; ), 113–130 [ Google Scholar ]
- Ruud E. (1997). Music and the quality of life . Nord. J. Music Ther . 6 , 86–97 10.1080/08098139709477902 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schäfer T., Sedlmeier P. (2009). From the functions of music to music preference . Psychol. Music 37 , 279–300 10.1177/0305735608097247 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schäfer T., Sedlmeier P. (2010). What makes us like music. Determinants of music preference . Psychol. Aesthe. Creativity Arts 4 , 223–234 10.1037/a0018374 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schubert E. (2009). The fundamental function of music . Music. Sci . 13 , 63–81 10.1177/1029864909013002051 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Steele J. R., Brown J. D. (1995). Adolescent room culture: studying the media in the context of everyday life . J. Youth Adolesc . 24 , 551–576 10.1007/BF01537056 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stefanija L. (2007). Functions of music: a survey of research vocabularies . Muzikos funkcijos: tyrimø terminologijos apžvalga. (Lithuanian) 7 , 6–17 [ Google Scholar ]
- Sun S., Lull J. (1986). The adolescent audience for music videos and why they watch . J. Commun . 36 , 115–125 10.1111/j.1460-2466.1986.tb03043.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tarrant M., North A. C., Hargreaves D. J. (2000). English and American adolescents' reasons for listening to music . Psychol. Music 28 , 166–173 10.1177/0305735600282005 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ter Bogt T. F. M., Mulder J., Raaijmakers Q. A. W., Gabhainn S. N. (2011). Moved by music: a typology of music listeners . Psychol.Music 39 , 147–163 10.1177/0305735610370223 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Troldahl V. C., Skolnik R. (1967). The meanings people have for radio today . J. Broadcast . 12 , 57–67 10.1080/08838156709386226 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Walker Kennedy S. (2010). An Exploration of Differences in Response to Music Related to Levels of Psychological Health in Adolescents . Toronto, ON: University of Toronto [ Google Scholar ]
- Wells A., Hakanen E. A. (1997). The emotional use of popular music by adolescents , in Mass Media and Society , eds Wells A., Hakanen E. A. (Greenwich: Ablex Publishing Corporation; ), 217–228 [ Google Scholar ]
- Wilson T. D. (2002). Strangers to Ourselves: Discovering the Adaptive Unconscious . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press [ Google Scholar ]
- Zatorre R. J., Peretz I. (2001). The Biological Foundations of Music . New York, NY: New York Academy of Sciences [ Google Scholar ]
- Zillmann D. (1988a). Mood management through communication choices . Am. Behav. Sci . 31 , 327–341 [ Google Scholar ]
- Zillmann D. (1988b). Mood management: using entertainment to full advantage , in Communication, Social Cognition, and Affect , eds Donohew L., Sypher H. E., Higgins E. T. (Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; ), 147–171 [ Google Scholar ]
EDITORIAL article
Editorial: the impact of music on human development and well-being.

- 1 Department of Culture, Communication and Media, University College London, London, United Kingdom
- 2 Department of Philosophy, Sociology, Education and Applied Psychology, University of Padua, Padua, Italy
- 3 School of Humanities and Communication Arts, Western Sydney University, Penrith, NSW, Australia
- 4 Melbourne Conservatorium of Music, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
Editorial on the Research Topic The Impact of Music on Human Development and Well-Being
Music is one of the most universal ways of expression and communication for humankind and is present in the everyday lives of people of all ages and from all cultures around the world ( Mehr et al., 2019 ). Hence, it seems more appropriate to talk about musics (plural) rather than in the singular ( Goble, 2015 ). Furthermore, research by anthropologists as well as ethnomusicologists suggests that music has been a characteristic of the human condition for millennia (cf. Blacking, 1976 ; Brown, 1999 ; Mithen, 2005 ; Dissanayake, 2012 ; Higham et al., 2012 ; Cross, 2016 ). Nevertheless, whilst the potential for musical behavior is a characteristic of all human beings, its realization is shaped by the environment and the experiences of individuals, often within groups ( North and Hargreaves, 2008 ; Welch and McPherson, 2018 ). Listening to music, singing, playing (informally, formally), creating (exploring, composing, improvising), whether individually and collectively, are common activities for the vast majority of people. Music represents an enjoyable activity in and of itself, but its influence goes beyond simple amusement.
These activities not only allow the expression of personal inner states and feelings, but also can bring about many positive effects in those who engage in them. There is an increasing body of empirical and experimental studies concerning the wider benefits of musical activity, and research in the sciences associated with music suggests that there are many dimensions of human life—including physical, social, educational, psychological (cognitive and emotional)—which can be affected positively by successful engagement in music ( Biasutti and Concina, 2013 ). Learning in and through music is something that can happen formally (such as part of structured lessons in school), as well as in other-than-formal situations, such as in the home with family and friends, often non-sequentially and not necessarily intentional, and where participation in music learning is voluntary, rather than mandated, such as in a community setting (cf. Green, 2002 ; Folkestad, 2006 ; Saether, 2016 ; Welch and McPherson, 2018 ).
Such benefits are evidenced across the lifespan, including early childhood ( Gerry et al., 2012 ; Williams et al., 2015 ; Linnavalli et al., 2018 ), adolescence ( McFerran et al., 2018 ), and older adulthood ( Lindblad and de Boise, 2020 ). Within these lifespan perspectives, research into music's contribution to health and well-being provides evidence of physical and psychological impacts ( MacDonald et al., 2013 ; Fancourt and Finn, 2019 ; van den Elzen et al., 2019 ). Benefits are also reported in terms of young people's educational outcomes ( Guhn et al., 2019 ), and successful musical activity can enhance an individual's sense of social inclusion ( Welch et al., 2014 ) and social cohesion ( Elvers et al., 2017 ).
This special issue provides a collection of 21, new research articles that deepen and develop our understanding of the ways and means that music can impact positively on human development and well-being. The collection draws on the work of 88 researchers from 17 different countries across the world, with each article offering an illustration of how music can relate to other important aspects of human functioning. In addition, the articles collectively illustrate a wide range of contemporary research approaches. These provide evidence of how different research aims concerning the wider benefits of music require sensitive and appropriate methodologies.
In terms of childhood and adolescence, for example, Putkinen et al. demonstrate how musical training is likely to foster enhanced sound encoding in 9 to 15-year-olds and thus be related to reading skills. A separate Finnish study by Saarikallio et al. provides evidence of how musical listening influences adolescents' perceived sense of agency and emotional well-being, whilst demonstrating how this impact is particularly nuanced by context and individuality. Aspects of mental health are the focus for an Australian study by Stewart et al. of young people with tendencies to depression. The article explores how, despite existing literature on the positive use of music for mood regulation, music listening can be double-edged and could actually sustain or intensify a negative mood.
A Portuguese study by Martins et al. shifts the center of attention from mental to physical benefits in their study of how learning music can support children's coordination. They provide empirical data on how a sustained, 24-week programme of Orff-based music education, which included the playing of simple tuned percussion instruments, significantly enhanced the manual dexterity and bimanual coordination in participant 8-year-olds compared to their active control (sports) and passive control peers. A related study by Loui et al. in the USA offers insights into the neurological impact of sustained musical instrument practice. Eight-year-old children who play one or more musical instruments for at least 0.5 h per week had higher scores on verbal ability and intellectual ability, and these correlated with greater measurable connections between particular regions of the brain related to both auditory-motor and bi-hemispheric connectivity.
Younger, pre-school children can also benefit from musical activities, with associations being reported between informal musical experiences in the home and specific aspects of language development. A UK-led study by Politimou et al. found that rhythm perception and production were the best predictors of young children's phonological awareness, whilst melody perception was the best predictor of grammar acquisition, a novel association not previously observed in developmental research. In another pre-school study, Barrett et al. explored the beliefs and values held by Australian early childhood and care practitioners concerning the value of music in young children's learning. Despite having limited formal qualifications and experience of personal music learning, practitioners tended overall to have positive attitudes to music, although this was biased toward music as a recreational and fun activity, with limited support for the notion of how music might be used to support wider aspects of children's learning and development.
Engaging in music to support a positive sense of personal agency is an integral feature of several articles in the collection. In addition to the Saarikallio team's research mentioned above, Moors et al. provide a novel example of how engaging in collective beatboxing can be life-enhancing for throat cancer patients in the UK who have undergone laryngectomy, both in terms of supporting their voice rehabilitation and alaryngeal phonation, as well as patients' sense of social inclusion and emotional well-being.
One potential reason for these positive findings is examined in an Australian study by Krause et al. . They apply the lens of self-determination theory to examine musical participation and well-being in a large group of 17 to 85-year-olds. Respondents to an online questionnaire signaled the importance of active music making in their lives in meeting three basic psychological needs embracing a sense of competency, relatedness and autonomy.
The use of public performance in music therapy is the subject of a US study by Vaudreuil et al. concerning the social transformation and reintegration of US military service members. Two example case studies are reported of service members who received music therapy as part of their treatment for post-traumatic stress disorder, traumatic brain injury, and other psychological health concerns. The participants wrote, learned, and refined songs over multiple music therapy sessions and created song introductions to share with audiences. Subsequent interviews provide positive evidence of the beneficial psychological effects of this programme of audience-focused musical activity.
Relatedly, McFerran et al. in Australia examined the ways in which music and trauma have been reported in selected music therapy literature from the past 10 years. The team's critical interpretive synthesis of 36 related articles led them to identify four different ways in which music has been used beneficially to support those who have experienced trauma. These approaches embrace the use of music for stabilizing (the modulation of physiological processes) and entrainment (the synchronization of music and movement), as well as for expressive and performative purposes—the fostering of emotional and social well-being.
The therapeutic potential of music is also explored in a detailed case study by Fachner et al. . Their research focuses on the nature of critical moments in a guided imagery and music session between a music therapist and a client, and evidences how these moments relate to underlying neurological function in the mechanics of music therapy.
At the other end of the age span, and also related to therapy, an Australian study by Brancatisano et al. reports on a new Music, Mind, and Movement programme for people in their eighties with mild to moderate dementia. Participants involved in the programme tended to show an improvement in aspects of cognition, particularly verbal fluency and attention. Similarly, Wilson and MacDonald report on a 10-week group music programme for young Scottish adults with learning difficulties. The research data suggest that participants enjoyed the programme and tended to sustain participation, with benefits evidenced in increased social engagement, interaction and communication.
The role of technology in facilitating access to music and supporting a sense of agency in older people is the focus for a major literature review by Creech , now based in Canada. Although this is a relatively under-researched field, the available evidence suggests that that older people, even those with complex needs, are capable of engaging with and using technology in a variety of ways that support their musical perception, learning and participation and wider quality of life.
Related to the particular needs of the young, children's general behavior can also improve through music, as exampled in an innovative, school-based, intensive 3-month orchestral programme in Italy with 8 to 10-year-olds. Fasano et al. report that the programme was particularly beneficial in reducing hyperactivity, inattention and impulsivity, whilst enhancing inhibitory control. These benefits are in line with research findings concerning successful music education with specific cases of young people with ADHD whose behavior is characterized by these same disruptive symptoms (hyperactivity, inattention, and impulsivity).
Extra-musical benefits are also reported in a study of college students (Bachelors and Masters) and amateur musicians in a joint Swiss-UK study. Antonini Philippe et al. suggest that, whilst music making can offer some health protective effects, there is a need for greater health awareness and promotion among advanced music students. Compared to the amateur musicians, the college music students evaluated their overall quality of life and general and physical health more negatively, as did females in terms of their psychological health. Somewhat paradoxically, the college students who had taken part in judged performances reported higher psychological health ratings. This may have been because this sub-group were slightly older and more experienced musicians.
Music appears to be a common accompaniment to exercise, whether in the gym, park or street. Nikol et al. in South East Asia explore the potential physical benefits of synchronous exercise to music, especially in hot and humid conditions. Their randomized cross-over study (2019) reports that “time-to-exhaustion” under the synchronous music condition was 2/3 longer compared to the no-music condition for the same participants. In addition, perceived exertion was significantly lower, by an average of 22% during the synchronous condition.
Comparisons between music and sport are often evidenced in the body of existing Frontiers research literature related to performance and group behaviors. Our new collection contains a contribution to this literature in a study by Habe et al. . The authors investigated elite musicians and top athletes in Slovenia in terms of their perceptions of flow in performance and satisfaction with life. The questionnaire data analyses suggest that the experience of flow appears to influence satisfaction with life in these high-functioning individuals, albeit with some variations related to discipline, participant sex and whether considering team or individual performance.
A more formal link between music and movement is the focus of an exploratory case study by Cirelli and Trehub . They investigated a 19-month-old infant's dance-like, motorically-complex responses to familiar and unfamiliar songs, presented at different speeds. Movements were faster for the more familiar items at their original tempo. The child had been observed previously as moving to music at the age of 6 months.
Finally, a novel UK-based study by Waddington-Jones et al. evaluated the impact of two professional composers who were tasked, individually, to lead a 4-month programme of group composing in two separate and diverse community settings—one with a choral group and the other in a residential home, both funded as part of a music programme for the Hull City of Culture in 2017. In addition to the two composers, the participants were older adults, with the residential group being joined by schoolchildren from a local Primary school to collaborate in a final performance. Qualitative data analyses provide evidence of multi-dimensional psychological benefits arising from the successful, group-focused music-making activities.
In summary, these studies demonstrate that engaging in musical activity can have a positive impact on health and well-being in a variety of ways and in a diverse range of contexts across the lifespan. Musical activities, whether focused on listening, being creative or re-creative, individual or collective, are infused with the potential to be therapeutic, developmental, enriching, and educational, with the caveat provided that such musical experiences are perceived to be engaging, meaningful and successful by those who participate.
Collectively, these studies also celebrate the multiplicity of ways in which music can be experienced. Reading across the articles might raise a question as to whether or not any particular type of musical experience is seen to be more beneficial compared with another. The answer, at least in part, is that the empirical evidence suggests that musical engagement comes in myriad forms along a continuum of more or less overt activity, embracing learning, performing, composing and improvising, as well as listening and appreciating. Furthermore, given the multidimensional neurological processing of musical experience, it seems reasonable to hypothesize that it is perhaps the level of emotional engagement in the activity that drives its degree of health and well-being efficacy as much as the activity's overt musical features. And therein are opportunities for further research!
Author Contributions
The editorial was drafted by GW and approved by the topic Co-editors. All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the Edited Collection, and have approved this editorial for publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to all the contributing authors and their participants for their positive engagement with this Frontiers Research Topic, and also for the Frontiers staff for their commitment and support in bringing this topic to press.
Biasutti, M., and Concina, E. (2013). “Music education and transfer of learning,” in Music: Social Impacts, Health Benefits and Perspectives , eds P. Simon and T. Szabo (New York, NY: Nova Science Publishers, Inc Series: Fine Arts, Music and Literature), 149–166.
Google Scholar
Blacking, J. (1976). How Musical Is Man? London: Faber & Faber.
Brown, S. (1999). “The ‘musilanguage’ model of music evolution,” in The Origins of Music , eds N. L. Wallin, B. Merker, and S. Brown (Cambridge: The MIT Press), 271–301. doi: 10.7551/mitpress/5190.003.0022
CrossRef Full Text
Cross, I. (2016). “The nature of music and its evolution,” in Oxford Handbook of Music Psychology , eds S. Hallam, I. Cross, and M. Thaut (New York, NY: Oxford University Press), 3–18. doi: 10.1093/oxfordhb/9780198722946.013.5
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Dissanayake, E. (2012). The earliest narratives were musical. Res. Stud. Music Educ. 34, 3–14. doi: 10.1177/1321103X12448148
Elvers, P., Fischinger, T., and Steffens, J. (2017). Music listening as self-enhancement: effects of empowering music on momentary explicit and implicit self-esteem. Psychol. Music 46, 307–325. doi: 10.1177/0305735617707354
Fancourt, D., and Finn, S. (2019). What Is the Evidence on the Role of the Arts in Improving Health and Well-Being? A Scoping Review . Copenhagen: World Health Organisation.
Folkestad, G. (2006). Formal and informal learning situations or practices vs formal and informal ways of learning. Br. J. Music Educ. 23, 135–145. doi: 10.1017/S0265051706006887
Gerry, D., Unrau, A., and Trainor, L. J. (2012). Active music classes in infancy enhance musical, communicative and social development. Dev. Sci. 15, 398–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7687.2012.01142.x
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Goble, J. S. (2015). Music or musics?: an important matter at hand. Act. Crit. Theor. Music Educ. 14, 27–42. Available online at: http://act.maydaygroup.org/articles/Goble14_3.pdf
Green, L. (2002). How Popular Musicians Learn. Aldershot: Ashgate Press.
Guhn, M., Emerson, S. D., and Gouzouasis, P. (2019). A population-level analysis of associations between school music participation and academic achievement. J. Educ. Psychol. 112, 308–328. doi: 10.1037/edu0000376
Higham, T., Basell, L., Jacobi, R., Wood, R., Ramsey, C. B., and Conard, N.J. (2012). Testing models for the beginnings of the Aurignacian and the advent of figurative art and music: the radiocarbon chronology of GeißenklÃsterle. J. Hum. Evol. 62, 664-676. doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2012.03.003
Lindblad, K., and de Boise, S. (2020). Musical engagement and subjective wellbeing amongst men in the third age. Nordic J. Music Therapy 29, 20–38. doi: 10.1080/08098131.2019.1646791
Linnavalli, T., Putkinen, V., Lipsanen, J., Huotilainen, M., and Tervaniemi, M. (2018). Music playschool enhances children's linguistic skills. Sci. Rep. 8:8767. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27126-5
MacDonald, R., Kreutz, G., and Mitchell, L. (eds.), (2013). Music, Health and Wellbeing. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. doi: 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199586974.001.0001
McFerran, K. S., Hense, C., Koike, A., and Rickwood, D. (2018). Intentional music use to reduce psychological distress in adolescents accessing primary mental health care. Clin. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 23, 567–581. doi: 10.1177/1359104518767231
Mehr, A., Singh, M., Knox, D., Ketter, D. M., Pickens-Jones, D., Atwood, S., et al. (2019). Universality and diversity in human song. Science 366:eaax0868. doi: 10.1126/science.aax0868
Mithen, S., (ed.). (2005). Creativity in Human Evolution and Prehistory . London: Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9780203978627
North, A. C., and Hargreaves, D. J. (2008). The Social and Applied Psychology of Music . New York, NY: Oxford University Press. doi: 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198567424.001.0001
Saether, M. (2016). Music in informal and formal learning situations in ECEC. Nordic Early Childhood Educ. Res. J. 13, 1–13. doi: 10.7577/nbf.1656
van den Elzen, N., Daman, V., Duijkers, M., Otte, K., Wijnhoven, E., Timmerman, H., et al. (2019). The power of music: enhancing muscle strength in older people. Healthcare 7:82. doi: 10.3390/healthcare7030082
Welch, G.F., and McPherson, G. E., (eds.). (2018). “Commentary: Music education and the role of music in people's lives,” in Music and Music Education in People's Lives: An Oxford Handbook of Music Education (New York, NY: Oxford University Press), 3–18. doi: 10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199730810.013.0002
Welch, G. F., Himonides, E., Saunders, J., Papageorgi, I., and Sarazin, M. (2014). Singing and social inclusion. Front. Psychol. 5:803. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00803
Williams, K. E., Barrett, M. S., Welch, G. F., Abad, V., and Broughton, M. (2015). Associations between early shared music activities in the home and later child outcomes: findings from the longitudinal study of Australian Children. Early Childhood Res. Q. 31, 113–124. doi: 10.1016/j.ecresq.2015.01.004
Keywords: music, wider benefits, lifespan, health, well-being
Citation: Welch GF, Biasutti M, MacRitchie J, McPherson GE and Himonides E (2020) Editorial: The Impact of Music on Human Development and Well-Being. Front. Psychol. 11:1246. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01246
Received: 12 January 2020; Accepted: 13 May 2020; Published: 17 June 2020.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2020 Welch, Biasutti, MacRitchie, McPherson and Himonides. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Graham F. Welch, graham.welch@ucl.ac.uk ; Michele Biasutti, michele.biasutti@unipd.it
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Music Research Paper. This sample music research paper features: 6800 words (approx. 22 pages), an outline, and a bibliography with 49 sources. Browse other research paper examples for more inspiration. If you need a thorough research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help.
Music Industry Research Paper Topics: The impact of streaming services on music consumption patterns. The role of social media in promoting and marketing music. The effects of piracy on the music industry. The influence of technology on music production and distribution. The relationship between music and mental health.
Writing a Music Research Paper: A Primer Like most other disciplines, research that you will do in the area of music can get interdisciplinary very quickly—after all, music is an inexorable component of most of our daily lives. Some examples include looking at music through: a historical, cultural studies, religious, or political lens.
Music is a vast and ever-growing field. Because of this, it can be challenging to find excellent music research topics for your essay or thesis. Although there are many examples of music research topics online, not all are appropriate. This article covers all you need to know about choosing suitable music research paper topics.
theses and dissertations. The primary role of this Guide is to serve as a first stop for music students writing research papers, but significant portions of it are also relevant to other writing projects. The six sections of the Guide are organized chronologically according to the resources a writer needs at different stages of a research paper.
Examine the arguments for both sides and take a position. 17. Look into the sociology of tribute bands and consider the reasons that people would dedicate their lives to imitating other musicians ...
Table 1 illustrates the breadth of music phenotypes and example assessment measures. Research into music and mental health typically focuses on measures of music engagement, including passive (e.g ...
Performing Music Research is a comprehensive guide to research in music performance. It reviews the knowledge and skills needed to critique existing studies in music education, psychology, and performance science, and to design and carry out new investigations. Methodological approaches are highlighted across the book in ways that help aspiring ...
Finally, a research paper calls for thorough documentation, careful construction, and a highly precise style. It generally works best to approach writing about music in an "inductive" way, first establishing facts and then using them as the basis for conclusions and judgments.
This journal provides a platform for researchers to communicate important new insights in music research from the full spectrum of relevant scientific and schol ... Music & Science is a new peer-reviewed open access online journal published by Sage in association with SEMPRE. The journal's point of departure is the idea that science—or, more ...
Good chapters on writing about music, analysis and research, from choosing a topic through outlining, writing the draft, editing and revising. It offers tips on seminar presentations, concert reports, and program notes. There is a sample research paper in the appendix that illustrates formats.
Then you absolutely need to check out our exceptional list of music argument topics: Music today is better than music in the 90s. The most lucrative career for a musician. Music helps you memorize faster. The most popular kind of metal music. The evolution of blues songs over the last 30 years. Music helps children develop faster.
Analysis of lyrical constructions of metal performers. The symbiosis of musical instruments in metal music. The analysis of seventh chords in the construction of metal songs. The influence of metal on other genres. The symbiosis of metal and pop music. The influence of metal vocalists on American culture.
How it works. 1 Make your order. provide the writing instructions and pay when prompted to do go. 2 Monitor the progress. ensure that the project is completed on time. 3 Download the paper. release the money for completed parts and download the completed project.
Music Research Paper Topic Examples Music is a universal language that transcends borders and cultures, touching the depths of human emotions and shaping societies throughout history. It is a dynamic field with many facets, making it a fascinating subject for research and exploration.
Abstract. This article gives basic guidelines and procedures in analyzing a music composition for the activity in music. In order for you to analyze music, you should familiarize yourself first ...
Research on the effect of background music (BgM) on cognitive task performance is marked by inconsistent methods and inconclusive findings. In order to provide clarity to this area, we performed a systematic review on the impact of BgM on performances in a variety of tasks whilst considering the contributions of various task, music, and population characteristics.
Music is a universal language that has the power to evoke emotions, bring people together, and express complex ideas and feelings. As a result, it has been the subject of extensive research and analysis across a wide range of fields, from psychology and neuroscience to sociology and cultural studies. Whether you are a music student, researcher, or simply a curious enthusiast, there are ...
Part one of the paper reviews the research contributions that have explicitly referred to musical functions. It is concluded that a comprehensive investigation addressing the basic dimensions underlying the plethora of functions of music listening is warranted. ... For example, music-induced chills produce reduced activity in brain structures ...
According to Fassbender, Richards, Bilgin, Thompson, and Heiden (2012), music affects memory. Music during a study or learning phase hindered memory but increased mood and sports performance. The ...
Editorial on the Research TopicThe Impact of Music on Human Development and Well-Being. Music is one of the most universal ways of expression and communication for humankind and is present in the everyday lives of people of all ages and from all cultures around the world ( Mehr et al., 2019 ). Hence, it seems more appropriate to talk about ...
Download sample Academic Papers along with scoring guidelines and scoring distributions. If you are using assistive technology and need help accessing these PDFs in another format, contact Services for Students with Disabilities at 212-713-8333 or by email at [email protected]. 2020: Through-Course Assessment. Performance Task Overview.
Sample Student Paper paper title, 2.4, 2.27, Table 2.1, Figure 2.4 parenthetical citation of a work with two authors, 8.17 parenthetical citation of a work with one author, 8.17 group author, 9.11 use of first person, 4.16 italics to highlight a key term, 6.22 narrative citation in parenthetical running text, 8.11 repeated citation needed, 8.1