- Create Account

Understanding the American Education System

The American education system offers a rich field of choices for international students. There is such an array of schools, programs and locations that the choices may overwhelm students, even those from the U.S. As you begin your school search, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the American education system. Understanding the system will help you narrow your choices and develop your education plan.
The Educational Structure
Primary and secondary school.
Prior to higher education, American students attend primary and secondary school for a combined total of 12 years. These years are referred to as the first through twelfth grades.

Around age six, U.S. children begin primary school, which is most commonly called “elementary school.” They attend five or six years and then go onto secondary school.
Secondary school consists of two programs: the first is “middle school” or “junior high school” and the second program is “high school.” A diploma or certificate is awarded upon graduation from high school. After graduating high school (12th grade), U.S. students may go on to college or university. College or university study is known as “higher education.”
Grading System
Just like American students, you will have to submit your academic transcripts as part of your application for admission to university or college. Academic transcripts are official copies of your academic work. In the U.S. this includes your “grades” and “grade point average” (GPA), which are measurements of your academic achievement. Courses are commonly graded using percentages, which are converted into letter grades.
The grading system and GPA in the U.S. can be confusing, especially for international students. The interpretation of grades has a lot of variation. For example, two students who attended different schools both submit their transcripts to the same university. They both have 3.5 GPAs, but one student attended an average high school, while the other attended a prestigious school that was academically challenging. The university might interpret their GPAs differently because the two schools have dramatically different standards.
Therefore, there are some crucial things to keep in mind:
- You should find out the U.S. equivalent of the last level of education you completed in your home country.
- Pay close attention to the admission requirements of each university and college, as well as individual degree programs, which may have different requirements than the university.
- Regularly meet with an educational advisor or guidance counselor to make sure you are meeting the requirements.
Your educational advisor or guidance counselor will be able to advise you on whether or not you must spend an extra year or two preparing for U.S. university admission. If an international student entered a U.S. university or college prior to being eligible to attend university in their own country, some countries’ governments and employers may not recognize the students’ U.S. education.
Academic Year
The school calendar usually begins in August or September and continues through May or June. The majority of new students begin in autumn, so it is a good idea for international students to also begin their U.S. university studies at this time. There is a lot of excitement at the beginning of the school year and students form many great friendships during this time, as they are all adjusting to a new phase of academic life. Additionally, many courses are designed for students to take them in sequence, starting in autumn and continuing through the year.
The academic year at many schools is composed of two terms called “semesters.” (Some schools use a three-term calendar known as the “trimester” system.) Still, others further divide the year into the quarter system of four terms, including an optional summer session. Basically, if you exclude the summer session, the academic year is either comprised of two semesters or three quarter terms.
The U.S. Higher Education System: Levels of Study
- First Level: Undergraduate
"The American system is much more open. In Hong Kong you just learn what the teacher writes on the board. In America, you discuss the issues and focus more on ideas."

Paolo Kwan from Hong Kong: Studying English and Business Administration at Sierra College in California
A student who is attending a college or university and has not earned a bachelor’s degree, is studying at the undergraduate level. It typically takes about four years to earn a bachelor’s degree. You can either begin your studies in pursuit of a bachelor’s degree at a community college or a four-year university or college.
Your first two years of study you will generally be required to take a wide variety of classes in different subjects, commonly known as prerequisite courses: literature, science, the social sciences, the arts, history, and so forth. This is so you achieve a general knowledge, a foundation, of a variety of subjects prior to focusing on a specific field of study.
Many students choose to study at a community college in order to complete the first two years of prerequisite courses. They will earn an Associate of Arts (AA) transfer degree and then transfer to a four-year university or college.
A “major” is the specific field of study in which your degree is focused. For example, if someone’s major is journalism, they will earn a Bachelor of Arts in Journalism. You will be required to take a certain number of courses in this field in order to meet the degree requirements of your major. You must choose your major at the beginning of your third year of school.
A very unique characteristic of the American higher education system is that you can change your major multiple times if you choose. It is extremely common for American students to switch majors at some point in their undergraduate studies. Often, students discover a different field that they excel in or enjoy. The American education system is very flexible. Keep in mind though that switching majors may result in more courses, which means more time and money.
- Second Level: Graduate in Pursuit of a Master’s Degree
Presently, a college or university graduate with a bachelor’s degree may want to seriously think about graduate study in order to enter certain professions or advance their career. This degree is usually mandatory for higher-level positions in library science, engineering, behavioral health and education.
Furthermore, international students from some countries are only permitted to study abroad at a graduate level. You should inquire about the credentials needed to get a job in your country before you apply to a postgraduate university in the USA.
A graduate program is usually a division of a university or college. To gain admission, you will need to take the GRE (graduate record examination). Certain master’s programs require specific tests, such as the LSAT for law school, the GRE or GMAT for business school, and the MCAT for medical school.
Graduate programs in pursuit of a master’s degree typically take one to two years to complete. For example, the MBA (master of business administration) is an extremely popular degree program that takes about two years. Other master’s programs, such as journalism, only take one year.
The majority of a master’s program is spent in classroom study and a graduate student must prepare a long research paper called a “master’s thesis” or complete a “master’s project.”
- Third Level: Graduate in Pursuit of a Doctorate Degree
Many graduate schools consider the attainment of a master’s degree the first step towards earning a PhD (doctorate). But at other schools, students may prepare directly for a doctorate without also earning a master’s degree. It may take three years or more to earn a PhD degree. For international students, it may take as long as five or six years.
For the first two years of the program most doctoral candidates enroll in classes and seminars. At least another year is spent conducting firsthand research and writing a thesis or dissertation. This paper must contain views, designs, or research that have not been previously published.
A doctoral dissertation is a discussion and summary of the current scholarship on a given topic. Most U.S. universities awarding doctorates also require their candidates to have a reading knowledge of two foreign languages, to spend a required length of time “in residence,” to pass a qualifying examination that officially admits candidates to the PhD program, and to pass an oral examination on the same topic as the dissertation.

Characteristics of the U.S. Higher Education System
Classroom Environment
Classes range from large lectures with several hundred students to smaller classes and seminars (discussion classes) with only a few students. The American university classroom atmosphere is very dynamic. You will be expected to share your opinion, argue your point, participate in class discussions and give presentations. International students find this one of the most surprising aspects of the American education system.
Each week professors usually assign textbook and other readings. You will be expected to keep up-to-date with the required readings and homework so you can participate in class discussions and understand the lectures. Certain degree programs also require students to spend time in the laboratory.
Professors issue grades for each student enrolled in the course. Grades are usually based upon:
- Each professor will have a unique set of class participation requirements, but students are expected to participate in class discussions, especially in seminar classes. This is often a very important factor in determining a student’s grade.
- A midterm examination is usually given during class time.
- One or more research or term papers , or laboratory reports must be submitted for evaluation.
- Possible short exams or quizzes are given. Sometimes professors will give an unannounced “pop quiz.” This doesn’t count heavily toward the grade, but is intended to inspire students to keep up with their assignments and attendance.
- A final examination will be held after the final class meeting.
Each course is worth a certain number of credits or credit hours. This number is roughly the same as the number of hours a student spends in class for that course each week. A course is typically worth three to five credits.
A full-time program at most schools is 12 or 15 credit hours (four or five courses per term) and a certain number of credits must be fulfilled in order to graduate. International students are expected to enroll in a full-time program during each term.
If a student enrolls at a new university before finishing a degree, generally most credits earned at the first school can be used to complete a degree at the new university. This means a student can transfer to another university and still graduate within a reasonable time.
Types of U.S. higher education

Xujie Zhao from China: Studying Computer Networking at Wentworth Institute of Technology in Boston
1. State College or University
A state school is supported and run by a state or local government. Each of the 50 U.S. states operates at least one state university and possibly several state colleges. Many of these public universities schools have the name of the state, or the actual word “State” in their names: for example, Washington State University and the University of Michigan.
2. Private College or University
These schools are privately run as opposed to being run by a branch of the government. Tuition will usually be higher than state schools. Often, private U.S. universities and colleges are smaller in size than state schools.
Religiously affiliated universities and colleges are private schools. Nearly all these schools welcome students of all religions and beliefs. Yet, there are a percentage of schools that prefer to admit students who hold similar religious beliefs as those in which the school was founded.
3. Community College
Community colleges are two-year colleges that award an associate’s degrees (transferable), as well as certifications. There are many types of associate degrees, but the most important distinguishing factor is whether or not the degree is transferable. Usually, there will be two primary degree tracks: one for academic transfer and the other prepares students to enter the workforce straightaway. University transfer degrees are generally associate of arts or associate of science. Not likely to be transferrable are the associate of applied science degrees and certificates of completion.
Community college graduates most commonly transfer to four-year colleges or universities to complete their degree. Because they can transfer the credits they earned while attending community college, they can complete their bachelor’s degree program in two or more additional years. Many also offer ESL or intensive English language programs, which will prepare students for university-level courses.
If you do not plan to earn a higher degree than the associate’s, you should find out if an associate’s degree will qualify you for a job in your home country.
4. Institute of Technology
An institute of technology is a school that provides at least four years of study in science and technology. Some have graduate programs, while others offer short-term courses.

Study in the USA ®
Get matched to the best program for you.
Let us know what you're looking for so we can find the best school for you.
Useful Articles

Check Out These Schools

The Language Company
$1,000—$5,000 Session

George Mason University
$35,000—$40,000 Semester

Lawrence University
$50,000—$60,000 Year
Featured Programs

Golden West College
Typical cost per Year: $5,000—$10,000

Truckee Meadows Community College
Typical cost per Semester: $5,000—$10,000

Typical cost per Semester: $35,000—$40,000
Related Stories

Start your U.S. adventure with Study in the USA

Learn About U.S. education financing, housing, and more

campusSIMS helps international students get connected with mobile phone service in the US. Through campusSIMS’ exclusive partner Mint Mobile, students can sign up and get their US phone number while in their home country, and have mobile phone servic...

A world of greater possibility.
Follow your dreams with the TOEFL iBT® test, which has helped millions of students study abroad.

Ready to take your language learning to the next level? Have you heard about TutorABC, the World's No. 1 Online Platform for Learning English and Chinese? TutorABC is recognized as the top language platform, harnessing innovative technology to offe...
Learn about American culture and education direct from our experts at Study in the USA. Read more
Achieving Your Goal
Admissions and placement testing, beyond the basics, education system in the usa, financing your u.s. education, frequently asked questions, life in the usa, student experiences, for students age 10-18, study in canada, student voices, ask studyusa.com, subscribe to get the latest from study in the usa.
You can unsubscribe at any time.
America's Education News Source
Copyright 2024 The 74 Media, Inc
- Cyberattack
- absenteeism
Future of High School
Artificial intelligence.
- science of reading
Learning Loss, AI and the Future of Education: Our 24 Most-Read Essays of 2023
From rethinking the american high school to the fiscal cliff, tutoring and special ed, what our most incisive opinion contributors had to say.

Some of America’s biggest names in education tackled some of the thorniest issues facing the country’s schools on the op-ed pages of The 74 this year, expressing their concerns about continuing COVID-driven deficits among students and the future of education overall. There were some grim predictions, but also reasons for hope. Here are some of the most read, most incisive and most controversial essays we published in 2023.

David Steiner
America’s education system is a mess, and students are paying the price.

COVID-19, the legacy of race-based redlining, the lack of support for health care, child care and parental leave, and other social and economic policies have taken a terrible toll on student learning. But the fundamental cause of poor outcomes, writes contributor David Steiner of the Johns Hopkins Institute for Education Policy , is that policy leaders have eroded the instructional core and designed our education system for failure. As we have sown, so shall we reap. The challenges and rewards of learning are being washed away, and students are desperately the worse for the mess we have made. Read More

Margaret Raymond
The terrible truth — current solutions to covid learning loss are doomed to fail.
Despite well-intended and rapid responses to COVID learning loss, solutions such as tutoring or summer school are doomed to fail, says contributor Margaret (Macke) Raymond of the Center for Research on Education Outcomes at Stanford University. How do we know? CREDO researchers looked at learning patterns for students at three levels of achievement in 16 states and found that even with five extra years of education, only about 75% will be at grade level by high school graduation. No school can offer that much. It is time to decide whether to make necessary changes or continue to support a system that will almost certainly fail. Read More

Mark Schneider
The future is stem — but without enough students, the u.s. will be left behind.

America no longer produces the most science and engineering research publications, patents or natural-science Ph.D.s, and these trends are unlikely to change anytime soon. The problem isn’t a lack of universities to train future scientists or an economy incapable of encouraging innovation. Rather, says contributor Mark Schneider of the Institute of Education Sciences, it originates much earlier in the supply chain, in elementary school. Congress has a chance to help turn this around, by passing the New Essential Education Discoveries (NEED) Act. Read More

John Bailey
The Promise of Personalized Learning Never Delivered. Today’s AI Is Different
Educators often encounter lofty promises of technology revolutionizing learning, only to find reality fails to meet expectations. But based on his experiences with the new generation of artificial intelligence tools, contributor John Bailey believes society may be in the early stages of a transformative moment. This may very well usher in an era of individualized learning, empowering all students to realize their full potential and fostering a more equitable and effective educational experience. Read his four reasons why this generation of AI tools is likely to succeed where other technologies have failed. Read More

Chad Aldeman
Interactive — With More Teachers & Fewer Students, Districts Are Set up for Financial Trouble
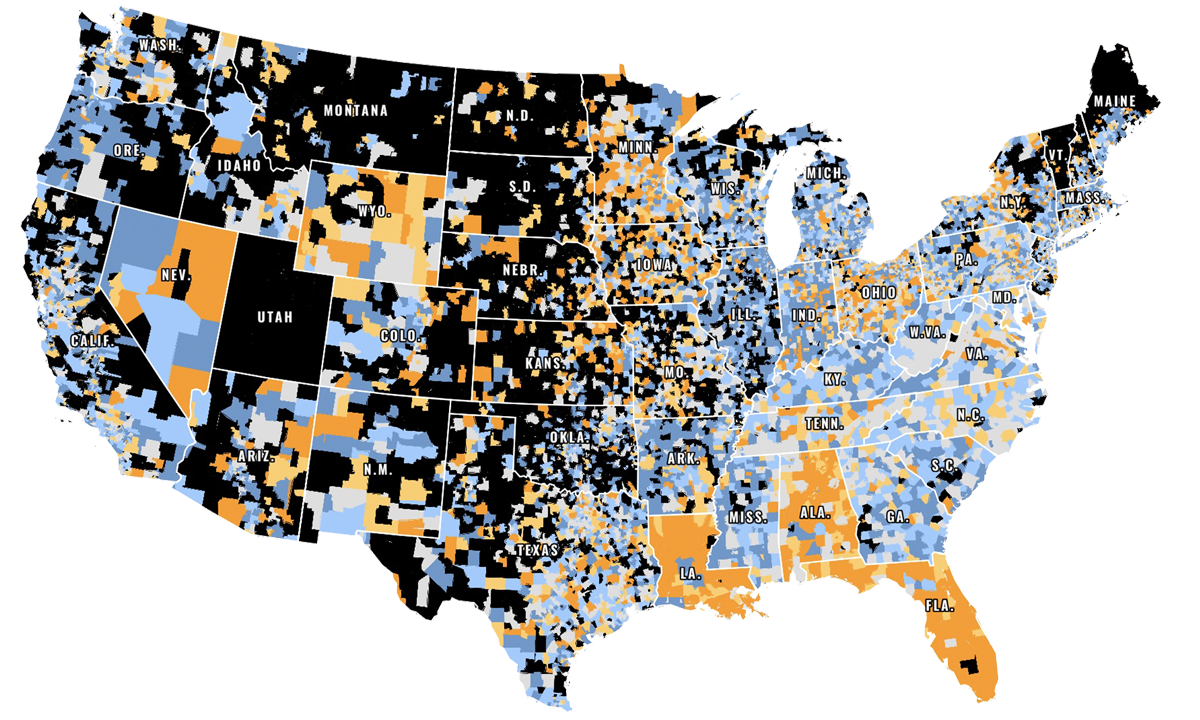
To understand the teacher labor market, you have to hold two competing narratives in your head. On one hand, teacher turnover hit new highs, morale is low and schools are facing shortages. At the same time, public schools employ more teachers than before COVID, while serving 1.9 million fewer students. Student-teacher ratios are near all-time lows. Contributor Chad Aldeman and Eamonn Fitzmaurice, The 74’s art and technology director, plotted these changes on an exclusive, interactive map — and explain how they’re putting districts in financial peril. View the Map
Fascinating, right? But these are only the tip of the iceberg. Here’s a roundup of some of the hottest topics our op-ed contributors tackled, and what they had to say:

Credit Hours Are a Relic of the Past. How States Must Disrupt High School — Now
Russlynn Ali & Timothy Knowles

Back to School — 6 Tips from Students on How to Make High School Relevant
Beth Fertig

I Changed My Shoes, and It Revolutionized How I Was Able to Rethink High School
William Blake
Fiscal Cliff & School Funding
The 50 Very Different States of American Public Education

It’s Time to Start Preparing Now for School Closures that Are Coming
Timothy Daly

Educators, Beware: As Budget Cuts Loom, Now Is NOT the Time to Quit Your Job
Katherine Silberstein & Marguerite Roza
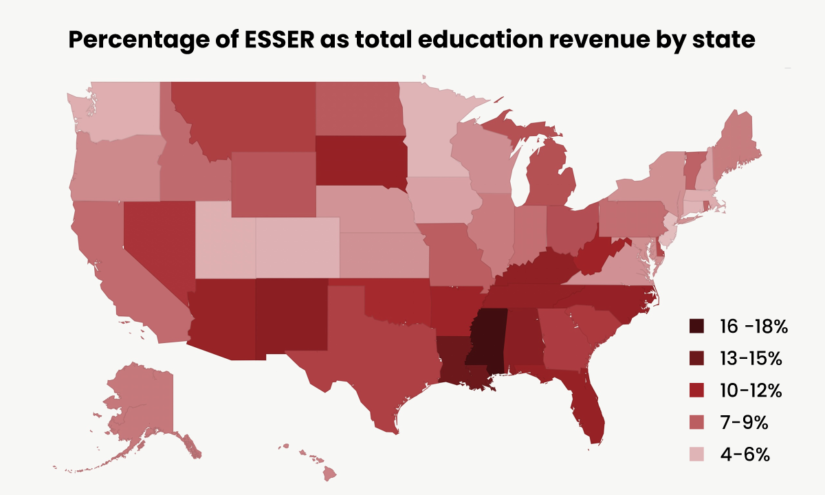
Schools Could Lose 136,000 Teaching Jobs When Federal COVID Funds Run Out

Artificial Intelligence Will Not Transform K-12 Education Without Changes to ‘the Grammar of School’

Schools Must Embrace the Looming Disruption of ChatGPT
Sarah Dillard
Personalized Education Is Not a Panacea. Neither Is Artificial Intelligence
Natalia Kucirkova

Done Right, Tutoring Can Greatly Boost Student Learning. How Do We Get There?
Kevin Huffman

As Virginia Rolls Out Ambitious Statewide High-Dosage Tutoring Effort This Week, 3 Keys to Success
Maureen Kelleher

Why This Tutoring ‘Moment’ Could Die If We Don’t Tighten Up the Models
Mike Goldstein
Learning Loss

New NAEP Scores Reveal the Failure of Pandemic Academic Recovery Efforts
Vladimir Kogan

Quarantines, Not School Closures, Led to Devastating Losses in Math and Reading
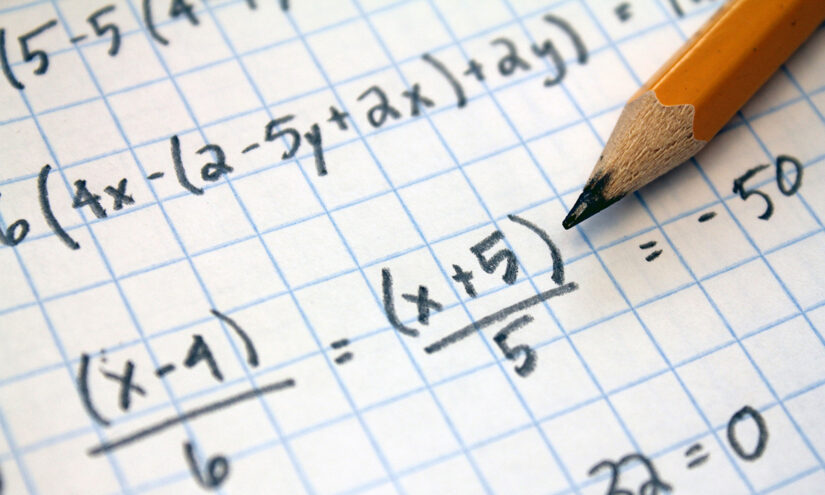
6 Teachers Tell Their Secrets for Getting Middle Schoolers up to Speed in Math
Alexandra Frost
Special Ed and Gifted & Talented

Bracing for a Tidal Wave of Unnecessary Special Education Referrals
Lauren Morando Rhim, Candace Cortiella, Lindsay Kubatzky & Laurie VanderPloeg

Why Are Schools Comfortable Accepting Failure for Students with Disabilities?
David Flink & Lauren Morando Rhim

NYC’s New Gifted & Talented Admissions Brings Chaos — and Disregards Research
Alina Adams
Help fund stories like this. Donate now!
Bev Weintraub is an Executive Editor at The 74

- best of the year
- fiscal cliff
- future of high school
- learning loss
We want our stories to be shared as widely as possible — for free.
Please view The 74's republishing terms.
By Bev Weintraub

This story first appeared at The 74 , a nonprofit news site covering education. Sign up for free newsletters from The 74 to get more like this in your inbox.
On The 74 Today
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write Any High School Essay
Last Updated: March 22, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA and by wikiHow staff writer, Hunter Rising . Emily Listmann is a private tutor in San Carlos, California. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. There are 14 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 562,752 times.
Writing an essay is an important basic skill that you will need to succeed in high school and college. While essays will vary depending on your teacher and the assignment, most essays will follow the same basic structure. By supporting your thesis with information in your body paragraphs, you can successfully write an essay for any course!
Writing Help

Planning Your Essay

- Expository essays uses arguments to investigate and explain a topic.
- Persuasive essays try to convince the readers to believe or accept your specific point of view
- Narrative essays tell about a real-life personal experience.
- Descriptive essays are used to communicate deeper meaning through the use of descriptive words and sensory details.

- Look through books or use search engines online to look at the broad topic before narrowing your ideas down into something more concise.

- For example, the statement “Elephants are used to perform in circuses” does not offer an arguable point. Instead, you may try something like “Elephants should not be kept in the circus since they are mistreated.” This allows you to find supporting arguments or for others to argue against it.
- Keep in mind that some essay writing will not require an argument, such as a narrative essay. Instead, you might focus on a pivotal point in the story as your main claim.

- Talk to your school’s librarian for direction on specific books or databases you could use to find your information.
- Many schools offer access to online databases like EBSCO or JSTOR where you can find reliable information.
- Wikipedia is a great starting place for your research, but it can be edited by anyone in the world. Instead, look at the article’s references to find the sites where the information really came from.
- Use Google Scholar if you want to find peer-reviewed scholarly articles for your sources.
- Make sure to consider the author’s credibility when reviewing sources. If a source does not include the author’s name, then it might not be a good option.

- Outlines will vary in size or length depending on how long your essay needs to be. Longer essays will have more body paragraphs to support your arguments.
Starting an Essay

- Make sure your quotes or information are accurate and not an exaggeration of the truth, or else readers will question your validity throughout the rest of your essay.

- For example, “Because global warming is causing the polar ice caps to melt, we need to eliminate our reliance on fossil fuels within the next 5 years.” Or, “Since flavored tobacco appeals mainly to children and teens, it should be illegal for tobacco manufacturers to sell these products.”
- The thesis is usually the last or second to last sentence in your introduction.

- Use the main topics of your body paragraphs as an idea of what to include in your mini-outline.

Writing the Body Paragraphs

- Think of your topic sentences as mini-theses so your paragraphs only argue a specific point.

- Many high school essays are written in MLA or APA style. Ask your teacher what format they want you to follow if it’s not specified.

- Unless you’re writing a personal essay, avoid the use of “I” statements since this could make your essay look less professional.

- For example, if your body paragraphs discuss similar points in a different way, you can use phrases like “in the same way,” “similarly,” and “just as” to start other body paragraphs.
- If you are posing different points, try phrases like “in spite of,” “in contrast,” or “however” to transition.
Concluding Your Essay

- For example, if your thesis was, “The cell phone is the most important invention in the past 30 years,” then you may restate the thesis in your conclusion like, “Due to the ability to communicate anywhere in the world and access information easily, the cell phone is a pivotal invention in human history.”
- If you’re only writing a 1-page paper, restating your main ideas isn’t necessary.

- For example, if you write an essay discussing the themes of a book, think about how the themes are affecting people’s lives today.

- Try to pick the same type of closing sentence as you used as your attention getter.

- Including a Works Cited page shows that the information you provided isn’t all your own and allows the reader to visit the sources to see the raw information for themselves.
- Avoid using online citation machines since they may be outdated.
Revising the Paper

- Have a peer or parent read through your essay to see if they understand what point you’re trying to make.

- For example, if your essay discusses the history of an event, make sure your sentences flow in a chronological way in the order the events happened.

- If you cut parts out of your essay, make sure to reread it to see if it affects the flow of how it reads.

Community Q&A
- Allow ample time to layout your essay before you get started writing. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- If you have writer's block , take a break for a few minutes. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 2
- Check the rubric provided by your teacher and compare your essay to it. This helps you gauge what you need to include or change. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1

- Avoid using plagiarism since this could result in academic consequences. Thanks Helpful 5 Not Helpful 1
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/types-of-essays/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/thesis-statements/
- ↑ https://guides.libs.uga.edu/reliability
- ↑ https://facultyweb.ivcc.edu/rrambo/eng1001/outline.htm
- ↑ https://examples.yourdictionary.com/20-compelling-hook-examples-for-essays.html
- ↑ https://wts.indiana.edu/writing-guides/how-to-write-a-thesis-statement.html
- ↑ https://guidetogrammar.org/grammar/five_par.htm
- ↑ https://learning.hccs.edu/faculty/jason.laviolette/persuasive-essay-outline
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/paragraphs/topicsentences
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/transitions/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/ending-essay-conclusions
- ↑ https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-an-essay/conclusion
- ↑ https://pitt.libguides.com/citationhelp
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/revising-drafts/
About This Article

Writing good essays is an important skill to have in high school, and you can write a good one by planning it out and organizing it well. Before you start, do some research on your topic so you can come up with a strong, specific thesis statement, which is essentially the main argument of your essay. For instance, your thesis might be something like, “Elephants should not be kept in the circus because they are mistreated.” Once you have your thesis, outline the paragraphs for your essay. You should have an introduction that includes your thesis, at least 3 body paragraphs that explain your main points, and a conclusion paragraph. Start each body paragraph with a topic sentence that states the main point of the paragraph. As you write your main points, make sure to include evidence and quotes from your research to back it up. To learn how to revise your paper, read more from our Writing co-author! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Ariel Arias Petzoldt
Aug 25, 2020
Did this article help you?

Nov 22, 2017
Rose Mpangala
Oct 24, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
United States Institute of Peace
National high school essay contest.
USIP partners with the American Foreign Service Association (AFSA) on the annual National High School Essay Contest. The contest each year engages high school students in learning and writing about issues of peace and conflict, encouraging appreciation for diplomacy’s role in building partnerships that can advance peacebuilding and protect national security.

The winner of the contest receives a $2,500 cash prize, an all-expense paid trip to Washington, D.C. to meet U.S. Department of State and USIP leadership, and a full-tuition paid voyage with Semester at Sea upon the student’s enrollment at an accredited university. The runner-up receives a $1,250 cash prize and a full scholarship to participate in the International Diplomacy Program of the National Student Leadership Conference.
2023 National High School Essay Contest
The American Foreign Service Association’s national high school essay contest completed its twenty-third year with over 400 submissions from 44 states. Three randomized rounds of judging produced this year’s winner, Justin Ahn, a junior from Deerfield Academy in Deerfield, Massachusetts. In his essay, “Mending Bridges: U.S.-Vietnam Reconciliation from 1995 to Today,” Ahn focuses on the successful reconciliation efforts by the Foreign Service in transforming U.S.-Vietnam relations from post-war tension to close economic and strategic partnership.
Ahn will travel to Washington, D.C. to meet with a member of the Department of State’s leadership and receive a full tuition scholarship to an educational voyage with Semester at Sea.
Niccolo Duina was this year’s runner-up. He is currently a junior at Pulaski Academy in Little Rock, Arkansas. Duina will be attending the international diplomacy program of the National Student Leadership Conference this summer.
There were eight honorable mentions:
- Santiago Castro-Luna – Chevy Chase, Maryland
- Dante Chittenden – Grimes, Iowa
- Merle Hezel – Denver, Colorado
- Adarsh Khullar – Villa Hills, Kentucky
- Nicholas Nall – Little Rock, Arkansas
- Ashwin Telang – West Windsor, New Jersey
- Himani Yarlagadda – Northville, Michigan
- Sophia Zhang – San Jose, California
Congratulations! We thank all students and teachers who took the time to research and become globally engaged citizens who care about diplomacy, development and peacebuilding.
2023 National High School Essay Contest Topic
In 2024, the U.S. Foreign Service will celebrate its 100th birthday. The Foreign Service is an important element of the American approach to peacebuilding around the world. Over the last century, U.S. diplomats have been involved in some of the most significant events in history — making decisions on war and peace, responding to natural disasters and pandemics, facilitating major treaties, and more.
As AFSA looks back on their century-long history, we invite you to do the same. This year, students are asked to explore a topic that touches upon this important history and sheds light on how vital it is for America to have a robust professional corps focused on diplomacy, development and peace in the national interest.
In your essay, you will select a country or region in which the U.S. Foreign Service has been involved in at any point since 1924 and describe — in 1,500 words or less — how the Foreign Service was successful or unsuccessful in advancing American foreign policy goals, including promoting peace, in this country/region and propose ways in which it might continue to improve those goals in the coming years.
Contest deadline: April 3, 2023
Download the study guide for the 2023 National High School Essay Contest. This study guide provides students with a basic introduction to the topic and some additional context that can assist them in answering the question. It includes the essay question, prizes and rules for the contest; an introduction to diplomacy and peacebuilding; key terms; topics and areas students might explore; and a list of other useful resources.
Learn more about the contest rules and how to submit your essay on the American Foreign Service Association’s contest webpage .
2022 National High School Essay Contest
Katherine Lam, a freshman from University High School in Tucson, Arizona, is the 2022 National High School Essay Contest winner. In her essay, “Competition and Coaction in Ethiopia: U.S. and Chinese Partnerships for International Stabilization,” Lam focuses on how the Foreign Service has partnered with other U.S. government agencies, nongovernmental organizations and — most notably — China to promote peace and development in Ethiopia. Lam will travel to Washington, D.C., to meet with a member of the U.S. Department of State’s leadership and gain full tuition for an educational voyage with Semester at Sea.
Olivia Paulsen was this year’s runner-up. She is a currently a junior receiving a home-schooled education in Concord, Massachusetts. Paulsen will be attending the international diplomacy program of the National Student Leadership Conference this summer.
The 2022 honorable mentions were: Josh Diaz (Little Rock, AR); Grace Hartman (Bethlehem, PA); Elena Higuchi (Irvine, CA); Ovea Kaushik (Oklahoma City, OK); Evan Lindemann (Palm Desert, CA); Percival Liu (Tokyo, Japan); Alexander Richter (San Jose, CA); and Gavin Sun (Woodbury, MN).
USIP congratulates all the winners of the 2022 National High School Essay Contest.
Partnerships for Peace in a Multipolar Era
The current multipolar era poses challenges for U.S. foreign policy but also provides new opportunities for partnership across world powers—including emerging great powers like China and Russia—to build peace in conflict-affected countries. Describe a current situation where American diplomats and peacebuilders are working with other world powers, as well as local and/or regional actors, in a conflict-affected country to champion democracy, promote human rights, and/or resolve violent conflict. A successful essay will lay out the strategies and tactics U.S. Foreign Service Officers and American peacebuilders are employing to build successful partnerships with other world and regional powers and with local actors in the chosen current situation. The essay will also describe specific ways that these partnerships are helping to promote stability and build peace.
Contest deadline: April 4, 2022
Download the study guide for the 2022 National High School Essay Contest. This study guide provides students with a basic introduction to the topic and some additional context that can assist them in answering the question. It includes the essay question, prizes, and rules for the contest; an introduction to diplomacy and peacebuilding; key terms; topics and areas students might explore; and a list of other useful resources.
Learn more about the contest rules and how to submit your essay on the American Foreign Service Association’s contest webpage.
2021 National High School Essay Contest
Mariam Parray, a sophomore from Pulaski Academy in Little Rock, Arkansas, is the 2021 National High School Essay Contest winner. In her essay, “Diplomats and Peacebuilders in Tunisia: Paving the Path to Democracy,” Ms. Parray focuses on how the Foreign Service partnered with other U.S. government agencies and NGOs to effect a peaceful democratic transition in Tunisia. She emphasizes the importance of multifaceted approaches as well as the importance of bringing marginalized groups into the fold. Mariam will travel to Washington to meet with a member of the Department of State’s leadership and will also gain a full tuition to an educational voyage with Semester at Sea. Harrison McCarty was this year’s runner-up. Coincidentally, he is also a sophomore from Pulaski Academy in Little Rock, Arkansas. Harrison will be attending the international diplomacy program of the National Student Leadership Conference this summer. The 2021 honorable mentions were: Louisa Eaton (Wellesley, MA); Samuel Goldston (Brooklyn, NY); Lucy King (Bainbridge Island, WA); Haan Jun Lee (Jakarta, Indonesia); Khaled Maalouf (Beirut, Lebanon); Madeleine Shaw (Bloomington, IN); Allison Srp (Austin, MN); and Daniel Zhang (Cortland, NY).
USIP congratulates all the winners of the 2021 National High School Essay Contest.
Diplomats and Peacebuilders: Powerful Partners
What characteristics lead to a successful effort by diplomats and peacebuilders to mediate or prevent violent conflict? The United States Foreign Service—often referred to as America’s first line of defense—works to prevent conflict from breaking out abroad and threats from coming to our shores. Peacebuilders work on the ground to create the conditions for peace and resolve conflicts where they are most needed.
Successful essays will identify, in no more than 1,250 words, a situation where diplomats worked on a peacebuilding initiative with partners from the country/region in question, nongovernmental organizations, and other parts of the U.S. government, and then go on to analyze what characteristics and approaches made the enterprise a success.
Contest deadline: April 5, 2021
Download the study guide for the 2021 National High School Essay Contest. This study guide provides students with a basic introduction to the topic and some additional context that can assist them in answering the question. It includes key terms in conflict management and peacebuilding and examples of peacebuilding initiatives, with reflection questions for independent learners to dig more deeply or for teachers to encourage class reflection and discussion. We hope this study guide will be a useful resource for educators and students participating in this contest, and for educators who want their students to learn more about this year’s contest topic.
2020 National High School Essay Contest
Jonas Lorincz, a junior from Marriotts Ridge High School in Marriottsville, MD, is the 2020 National High School Essay Contest winner. In his essay, “Verification, Mediation, and Peacebuilding: The Many Roles of the U.S. Foreign Service in Kosovo,” Mr. Lorincz focused on the importance of interagency cooperation in mediating the crisis in Kosovo – primarily looking into how diplomats and other civilian agencies engaged in peacebuilding throughout the conflict.
Claire Burke was this year’s runner-up. She is a junior at Mill Valley High School in Shawnee, KS.
The 2020 honorable mentions were: Grace Cifuentes (Concord, CA), Grace Lannigan (Easton, CT), Seryung Park (Tenafly, NJ), Vynateya Purimetla (Troy, MI), David Richman (Norfolk, VA), Madeleine Shaw (Bloomington, IN), Sara Smith (Fargo, ND), and Jack Viscuso (Northport, NY). USIP congratulates all the winners of the 2020 National High School Essay Contest.
2020 National High School Essay Contest Topic
Why Diplomacy and Peacebuilding Matter
How do members of the Foreign Service work with other civilian parts of the U.S. Government to promote peace, national security and economic prosperity?
Qualified essays focused on a specific challenge to U.S. peace and prosperity and included one example of the work of the Foreign Service and one or more examples of collaboration between America’s diplomats and other civilian (i.e. non-military) U.S. Government agencies or organizations.
2019 National High School Essay Contest
In its 21st year, the American Foreign Service Association (AFSA)’s National High School Essay Contest encouraged students to think about how and why the United States engages globally to build peace, and about the role that the Foreign Service plays in advancing U.S. national security and economic prosperity.
For the second year in a row, the National High School Essay Contest focused on an important aspect of operating in countries affected by or vulnerable to violent conflict: effective coordination of the many different foreign policy tools the United States has at its disposal. Whether you were addressing the prompt for a second year or new to the contest, the contest will have challenged you to expand your understanding of the role of the Foreign Service and other actors in foreign policy, identify case studies, and provide a sophisticated analysis in a concise manner.
The essay prompt and a helpful study guide are included below; you can find out more information about the rules and how to submit by checking out AFSA’s essay contest page .
2019 Essay Question
The United States has many tools to advance and defend its foreign policy and national security interests around the world—from diplomatic approaches pursued by members of the Foreign Service, to the range of options available to the U.S. military. In countries affected by or vulnerable to violent conflict, peacebuilding tools are important additions to the national security toolkit.
In such complex environments, cooperation across agencies and approaches is challenging, but it can also blend knowledge and skills in ways that strengthen the overall effort to establish a lasting peace. On the other hand, lack of coordination can lead to duplication of effort, inefficient use of limited resources and unintended consequences.
In a 1,000-1,250-word essay, identify two cases—one you deem successful and one you deem unsuccessful—where the U.S. pursued an integrated approach to build peace in a conflict-affected country. Analyze and compare these two cases, addressing the following questions:
- What relative strengths did members of the Foreign Service and military actors bring to the table? What peacebuilding tools were employed? Ultimately, what worked or did not work in each case?
- How was each situation relevant to U.S. national security interests?
- What lessons may be drawn from these experiences for the pursuit of U.S. foreign policy more broadly?
Download the study guide for the 2019 AFSA National High School Essay Contest
2018 National High School Essay Contest
Jennifer John from Redwood City, CA is the 2018 National High School Essay Contest winner, surpassing close to 1,000 other submissions. Her essay examined to what extent U.S. interagency efforts in Iraq and Bosnia were successful in building peace. Aislinn Niimi from Matthews, NC was the runner up.
The 2018 honorable mentions were: Alex, DiCenso (North Kingstown, RI),Alexandra Soo (Franklin, MI), Caroline Bellamy (Little Rock AR), Colin LeFerve (Indianapolis, IN), Elizabeth Kam (Burlingham, CA), Emma Singh (Tenafly NJ), Emma Chambers (Little Rock AR), Francesca Ciampa (Brooksville, ME), Greta Bunce (Franktown, VA), Isaac Che (Mount Vernon OH), Isabel Davis (Elk River MN), Katrina Espinoza (Watsonvile, CA), Molly Ehrig (Bethlehem, PA), Payton McGoldrick (Bristow, VA), Rachel Russell (Cabin John, MD), Sarah Chapman (Tucson, AZ), Shalia Lothe (Glen Allen VA), Sohun Modha (San Jose CA), Suhan Kacholia (Chandler, AZ), Supriya Sharma (Brewster, NY), Sydney Adams (Fort Wayne, IN), Tatum Smith (Little Rock AR), and William Milne (Fort Wayne, IN).
2017 National High School Essay Contest
Nicholas Deparle, winner of the 2017 AFSA National High School Essay Contest, comes from Sidwell Friends School in Washington DC. A rising senior at the time, Mr. Deparle covers the Internally Displaced Persons crisis in Iraq and potential ideas to help resolve the issue. Read his winning essay here . Mr. Manuel Feigl, a graduate of Brashier Middle College Charter High School in Simpsonville, SC took second place.
This year there were twenty honorable mentions: Mohammed Abuelem ( Little Rock, Ark.), Lucas Aguayo-Garber (Worcester, Mass.), Rahul Ajmera (East Williston, N.Y.), Taylor Gregory (Lolo, Mont.), Rachel Hildebrand (Sunnyvale, Calif.), Ryan Hulbert (Midland Park, N.J.), India Kirssin (Mason, Ohio), Vaibhav Mangipudy (Plainsboro, N.J.), William Marsh (Pittsburgh, Penn.), Zahra Nasser (Chicago, Ill.), Elizabeth Nemec (Milford, N.J.), David Oks (Ardsley, N.Y.), Max Pumilia (Greenwood Village, Colo.), Nikhil Ramaswamy (Plano, Texas), Aditya Sivakumar (Beaverton, Ore.), Donovan Stuard (Bethlehem, Penn.), Rachel Tanczos (Danielsville, Penn.), Isabel Ting (San Ramon, Calif.), Kimberley Tran (Clayton, Mo.), and Chenwei Wang (Walnut, Calif.).
2017 Essay Contest Topic
According to the United Nations, 65 million people worldwide have left their homes to seek safety elsewhere due to violence, conflict, persecution, or human rights violations. The majority of these people are refugees or internally displaced persons (IDPs).
Imagine you are a member of the U.S. Foreign Service —– a diplomat working to promote peace, support prosperity, and protect American citizens while advancing the interests of the United States abroad – and are now assigned to the U.S. embassy in one of these four countries.
- Turkey (Bureau of European and Eurasian Affairs)
- Kenya (Bureau of African Affairs)
- Afghanistan (Bureau of South and Central Asian Affairs)
- Iraq (Bureau of Near Eastern Affairs)
Your task is to provide recommendations to address the refugee/IDP crisis facing the country in which you are now posted. Using the resources available to you as a member of the Foreign Service, write a memo to your Ambassador outlining how the United States might help address the current unprecedented levels of displacement. You may choose to address issues related to the causes of refugee crisis, or to focus on the humanitarian crisis in your host country.
A qualifying memo will be 1,000-1,250 words and will answer the following questions:
- How does the crisis challenge U.S. interests in the country you are posted and more broadly?
- Specifically outline the steps you propose the U.S. should take to tackle the roots or the consequences of the crisis, and explain how it would help solve the issue or issues you are examining. How will your efforts help build peace or enhance stability?
- How do you propose, from your embassy/post of assignment, to foster U.S. government interagency cooperation and cooperation with the host-country government to address these issues? Among U.S. government agencies, consider U.S. Agency for International Development, the Foreign Commercial Service and the U.S. Institute of Peace.
Memo Template
TO: Ambassador ______________________
FROM: Only use your first name here
RE: Think of this as your title, make sure to include the country you are writing about
Here you want to lay out the problem, define criteria by which you will be deciding the best steps the U.S. could take, and include a short sentence or two on your final recommendation. Embassy leadership is very busy and reads many memos a day —– they should be able to get the general ““gist”” of your ideas by reading this section.
Background:
This section should provide any background information about the crisis or conflict relevant to your proposed policy. Here, you should mention why the issue is important to U.S. interests, especially peace and security.
Proposed Steps:
This is where you outline your proposed policy. Be specific in describing how the U.S. might address this issue and how these steps can contribute to peace and security. Include which organizations you propose partnering with and why.
Recommendation:
This is where you write your final recommendations for embassy leadership. Think of this as a closing paragraph.
Companion Guide for the 2017 National High School Essay Contest
It is no easy task to jump into the role of a diplomat, especially when confronted by such an urgent crisis. USIP, in consultation with AFSA, developed a guide to provide a basic introduction to the topic and some additional context that can assist you in answering the question, while still challenging you to develop your own unique response. As such, this guide should be used as a starting point to your own research and as you ultimately prepare a compelling memo outlining recommendations the U.S. government should follow to respond to the refugee and IDP crisis.
In the guide you will find: insights into the role of the Foreign Service; country, organization, and key-term briefs to provide a foundational understanding; and a list of other useful resources. Download the Companion Guide for the 2017 National High School Essay Contest (.pdf).
2016 National High School Essay Contest
USIP first partnered with AFSA for the 2016 contest and was pleased to welcome winner Dylan Borne to Washington in August. His paper describes his role as an economic officer in the U.S. Agency for International Development’s Bureau for Democracy, Conflict and Humanitarian Assistance. He writes about promoting education for girls in Afghanistan through on-line courses and dispersal of laptops. Read his winning essay (.pdf).
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write the American University Essays 2023-2024

American University has one optional prompt for all applicants about why you want to attend AU. Additionally, the school has prompts for each of its special programs.
There are three prompts for Honors Program applicants, two prompts for Global Scholars Program applicants, three prompts for Lincoln Scholars Program applicants, three prompts for Politics, Policy and Law Scholars applicants, two prompts for Public Health Scholars applicants, two prompts for Sakura Scholars Program applicants, and five prompts for AU Emerging Global Leader Scholarship (International Students) applicants.
Since AU receives thousands of applications from academically strong students, your essays are your chance to stand out. In this post, we’ll discuss how to craft an engaging response to each of these options.
Want to know your chances at AU? Calculate your chances for free right now.
All Applicants Prompt
At american university, inclusive excellence is a cornerstone of the academic experience for our students, and we deeply value the learning that is inspired by the diversity of backgrounds and life experiences that all our community members bring with them. please share why you would like to join this community. (150 words).
This is a standard instance of the common “Why This College?” prompt . Unless this is the first college you are applying to, chances are you’ve already seen a prompt like this before. There are no tricks here; this straightforward prompt is meant to gauge your interest in AU.
The admissions committee will use your answer to determine how you fit with the University and how you’ll make the most of all its opportunities. To help them figure these things out, your essay should show how your personal goals and the AU’s resources intersect.
A good approach to an essay like this is establishing a connection with AU. There are two kinds of connections—tangible and intangible. Ideally, you’ll be able to establish both, but a good response will establish at least a tangible connection.
Establishing a tangible connection can be done by explicitly discussing resources and opportunities offered by AU that resonate with you personally. To have a strong, specific response, you’re going to need to do some research. Don’t fret if you haven’t done this before; we’ve created a handy guide to help you research colleges effectively!
To begin, try to find your desired major’s webpage by consulting this list of degree programs . You should also look into faculty members in your department. To do that, you can use this searchable directory to find your department, which will have its own faculty list. Finally, look into the wealth of centers, institutes, and initiatives at AU.
Here’s an example of what a successful, specific response might look like:
“I am from a multicultural family; my mother is Jewish and my father Muslim. This background exposed me to some profound discussions of geopolitical affairs from a fairly young age. I am fascinated by international studies and I wish to contribute to initiatives that aim to reduce conflict between Israel and Palestine. AU’s International Studies program at the School of International Service offers in-depth classes that are highly relevant to this passion of mine. RELG-475 Religion and Violence and SISU-319 Arab-Israeli Relations specifically will grant me insights into the religious roots of the conflict that I simply cannot learn by just talking to my parents.
I am particularly interested in the work of Professor Mohammed Abu-Nimer. My mother showed me his book Evaluating Interreligious Peacebuilding earlier this year, and I found his thoughts on conducting evaluations in conflict areas illuminating, as they explain some consequences of fieldwork.”
This response does a few things effectively. First, it gives the admissions committee an idea of who the student is and where she comes from. Second, it establishes her motivations and passions. Third, it specifically discusses several courses and the work of one of AU’s faculty members, as well as why those resources are important to the student. You can do all these things while remaining within the small word limit.
Besides describing the particular resources to intend to make use of, you might also wish to express an intangible connection with AU. This isn’t necessary, but it would add to your application if you can do it. An intangible connection is just what it sounds like—a connection that isn’t based on the tangible resources offered by the University. Often, an intangible connection involves alignment between your personal values and those of the institution.
For example, perhaps you’re deeply invested in environmental conservation. You’ll be happy to know that AU is “the first urban campus, the first research university, and the largest higher education institution in the United States to achieve carbon neutrality.” It also achieved this goal two years ahead of schedule! You could write a bit about how much you appreciate AU’s sustainability initiatives to your response to establish an intangible connection.
Finally, there are a few things you’ll want to avoid doing in your essay:
- Name-dropping. Don’t write a laundry list of activities, classes, or professors that interest you without explaining why those things are important to you. Even though you are discussing facets of the university, this essay needs to be primarily focused on you.
- Empty flattery. Anyone can write that “AU is a well-respected institution with an amazing international studies program.” It’s nice to compliment the university, but you don’t have a lot of space, and empty flattery suggests that you don’t have anything more substantive to say.
- Generic remarks. Talking about AU’s good location, a strong program in some field, or small class sizes won’t add much to your response. These are generic things that apply to many schools.
Make sure that you do ample research, develop nuanced reasons for choosing AU, and write a sincere response, and you will be off to a great start!
American University Special Program Essay Prompts
Click on the link to be taken to the special program prompts.
- AU Honors Program
- Global Scholars Program
- Lincoln Scholars Program
- Politics, Policy and Law Scholars Program
- Public Health Scholars Program
- Sakura Scholars Program
- AU Emerging Global Leader Scholarship
AU Honors Program Applicants, Prompt 1
Au honors students are distinguished by their sense of intellectual curiosity, both inside and outside of the classroom. tell us what you are most curious about, and how that curiosity has influenced your life thus far. (300 words).
This prompt is fairly broad, so you can approach it in a few different ways. We recommend writing a sort of blend between a “Why This Major?” essay and an extracurricular activities essay . Focusing on an aspect of your intended major will show your passion for something inherently intellectual, and throwing in some of your other interests/hobbies will add nuance and personality to your response.
Before you begin writing, you’ll want to gather your thoughts so that your essay will have structure. Think of the following questions as a way to focus your thoughts:
1. What piques your curiosity and interest the most? What are your authentic reasons for being interested in this thing?
2. What are some specific examples of things that you enjoy with regard to this interest?
If this is something you’re truly curious about, you shouldn’t describe it generically. Instead of thinking “I love reading,” think “I enjoy reading novels that explore existentialist philosophical themes.”
3. How might pursuing this thing serve your life and/or career goals?
Is your curiosity about this thing a driving force in your plans for your future? For example, are you so curious about ocean life that your biggest life goal is to become a marine biologist?
4. Is this interest primarily academic or extracurricular? What are your best experiences with this interest both inside and out of the classroom?
5. Is there any recurring emotional experience that you have when exploring this thing that piques your curiosity? Why do you find that experience or state of mind appealing?
6. How has this thing influenced your development as a person? Have you developed or strengthened any personality traits or skills as a result of your object of interest?
Questions 4, 5, and 6 will be especially helpful when you’re trying to recall some anecdotes to support your interest and curiosity in it.
You only have 300 words to work with, so you should keep your response limited to one thing you’re deeply curious about (or maybe two if they’re related). A strong essay will do a few things:
- First, it will show that you have nuanced interests with intellectual depth.
- Second, it will talk a bit about the trajectory your life has been on as a result of your interests.
- Finally, it will display an important part of your personality that can give the admissions committee an idea of who you are as an individual.
There are a couple of common mistakes you should avoid when writing your response:
- Picking the wrong topic. Bad topics include: an interest you already wrote about somewhere else in the application; an interest that sounds impressive, but that you aren’t very invested in; one you haven’t spent much time on.
- Writing a generic statement about why the interest you chose is interesting or cool without addressing the personal connection you have with it. It’s great to appreciate your own interests, but you need to show the admissions committee why the thing that makes you curious is so important to you.
Some examples of strong topics would be:
- A student who’s a second-generation Japanese immigrant might be curious about the relationship between language and identity. She’s noticed while learning Japanese that it’s easier to have more complex conversations with her parents in their native tongue, and that they’re better able to express their personality. And as she’s become more comfortable speaking Japanese, she’s able to connect more with her heritage. This has led her to attend local language exchanges and start a podcast about the stories of the attendees and their thoughts on language and identity. She hopes to study Japanese at AU and become a translator.
- A runner who got tendonitis in his junior year may be curious about how the tendons and ligaments in our body work to support us during exercise. After doing physical therapy and healing his tendon, he decided to take an anatomy course and shadow his physical therapist. He wants to become a physical therapist or sports medicine doctor to help other athletes rehab their injuries.
AU Honors Program Applicants, Prompt 2
What aspect of the au honors program piques your interest the most (300 words).
This prompt is a slightly more specific version of the “Why This College?” prompt . However, you’re being asked why you’re drawn to the AU Honors Program in particular rather than to American University as a whole.
The prompt is meant to assess a few things:
- First, it’s meant to see if you know what you’re getting into with the program. If you’ve done your research on the Honors Program, you should have something detailed to say about it.
- Second, it’s intended to determine how you will fit in the program. The admissions committee wants to know what role you’ll have in the program and how you’ll make use of its resources to achieve your goals.
- Finally, it’s an effective way for the admissions committee to see which students are genuinely interested in the program.
Before you begin writing, make a list of the reasons you decided to apply to the program. You might find it helpful to explicitly jot down the things that drew you to the Honors Program in the first place. One of these reasons might very well be the subject of your essay. You should also explore the Honors Program website to make sure you don’t miss any of your reasons.
The prompt asks specifically for the aspect that most piques your interest, so you have to figure out if you want to write about an academic reason, an extracurricular one, or an intangible one. Let’s go over what makes each of these unique.
Academic reasons are as straightforward as they sound. Things such as the Honors Colloquium courses, the Honors Capstone , and research opportunities are academic aspects of the program that you might want to write about.
Extracurricular reasons include activities and opportunities that are supplementary to academics. Things such as Honors housing , the Student Advisory Council , and the Honors “Have You Ever Wondered?” discussion series are extracurricular aspects of the program.
Intangible reasons are those that involve values, beliefs, and other nonphysical things. The program’s commitment to interdisciplinary thinking and the BIPOC Affinity Group ’s dedication to “an empowering and supportive environment” are examples of intangible aspects of the program.
Your reasons for being interested in the program don’t have to be the most exotic or outlandish; you can write an effective straightforward response to this prompt. The thing that piques your interest the most might be the Honors Colloquia, the opportunity to engage with Program Associates, or the opportunities in Honors housing. All these options are valid ways to establish a tangible connection with the program.
For example, consider a student who wants to do political science research in her future career. She might be most interested in the Honors Program’s curriculum. Her response can cover the rigorous nature of the program, discuss some of the Honors-specific courses, and talk about the ample opportunities to conduct undergraduate research (such as HNRS-398 Honors Challenge Course and the Honors Capstone).
Avoid name-dropping random courses, activities, or faculty members without elaborating on how they resonate with you personally. Doing so will make your interest look superficial or disingenuous.
As long as you can describe what in particular has drawn you to the Honors Program as well as why it did so, you will be able to write an effective response to this prompt.
AU Honors Program Applicants, Prompt 3
We all have meaningful experiences that shape us and inform our worldview. what aspect of your background would you most like to share with other students in the honors program (300 words).
This is, in essence, a version of the common diversity prompt that many colleges provide. Colleges often include diversity prompts so they can learn something about your personal background and its influence on your worldview.
In June 2023, the United States Supreme Court struck down the use of affirmative action in college admissions. Nevertheless, the ruling allows colleges to consider race on an individual basis, which is one reason many schools are now including diversity prompts as one of their supplemental essay prompts. If you feel that your racial background specifically has impacted you significantly, this is the response in which you should write about that.
More generally, you can respond to this common prompt with a fairly traditional answer. One tried-and-true method you could use involves identifying the most important part of your identity, then discussing how that aspect of your background is relevant to you and your life experiences.
Before you jump into writing your response, think of aspects of your background that may have had an impact on the way you look at the world or the way you live your life. Some examples of things that have likely influenced your worldview include:
- Personal identity. Your race, ethnicity, gender identity, sexual orientation, age, etc. all have a profound influence on the way you think and perceive the world.
- Cultural identity. Your religious affiliations, political views, socioeconomic status, social class, and even the place you are from influence what issues you see the most, and what solutions you envision for these issues.
- Personal history. Things in your life may have an average trajectory. Maybe you’ve had a fortunate life with few obstacles to overcome so far, or maybe you’ve experienced a great deal of adversity or tragedy. The way things generally tend to go in your life will have a great impact on how you view life and the world around you.
- Interests. The things you’re really invested in can change how you perceive the world. If you’re a musician, for example, you might find musicality in the most mundane sounds out in the world on a daily basis.
That said, there are several angles with which you could approach this prompt. Some more specific examples of aspects of identity you might write about include:
- Having a disability that has changed your perspective on something in the world.
- Being a member of an ethnic group that has an interesting cultural practice.
- Fluency in another language that you use to help members of your community.
- Being a member of a fandom.
You have 300 words to work with, which is a considerable length, so feel free to structure your essay using an anecdote. You might begin with a time when your worldview was different, then describe how it changed due to the aspect of your background that is the subject of your essay.
One thing you should avoid is simply listing out things that generate diversity. Diversity includes everything mentioned above and more, but just writing out a list of things contributes very little to your application and also fails to respond to the prompt. The prompt asks you which singular aspect of your background you would like to share, so make sure to choose wisely and elaborate.
This prompt is one of the few opportunities you have to showcase your unique perspectives. Whatever aspect of your background you choose to write about here, make sure your response is sincere. Try to show as much individuality and specificity as you can in your response.
Global Scholars Program Applicants, Prompt 1
In your view, what is the greatest challenge facing humanity today and how do you envision yourself being part of the solution (no word count given).
In this prompt, you are asked to give your opinion on the greatest challenge facing humanity today. This sounds like a very tall order, but don’t worry; it’s an opinion question, so any reasonable challenge you choose will be fine.
Admissions committees want to see specifics, so we often recommend not identifying too broad a problem. In the brainstorming stage, however, you can think as broadly as you’d like. Global poverty, world hunger, illiteracy in developing countries, human rights abuses—each of these things can be an effective starting point.
Thinking about your identity and values might help you determine which issues are most important to you. Aspects of your identity include your ethnicity, race, country of origin, language, religion, gender identity, sexual orientation, hometown, income class, socioeconomic status, illnesses/disabilities, and even interests and activities!
Consider these different aspects of your background and list broad world issues that may have an impact on some part of your identity. For example, you might be Ukrainian and have family members directly affected by the current war. In this case, your ethnic background may compel you to write about geopolitical conflicts or human rights issues.
Be sure to narrow your topic to something specific once you begin writing. Even though the prompt asks what you think is “the greatest challenge facing humanity today,” you should be prepared to discuss concrete examples of that challenge.
For instance, if you want to write about world hunger, try to also describe particular situations and specific problems related to that broader issue—some things you might want to examine in such an essay can include widespread food and water shortages in Venezuela as a result of governmental policies, hunger in Haiti due to food insecurity and currency inflation, and the impending famine in Sudan as a result of internal conflicts.
The aforementioned examples can add a great deal of nuance to your essay for a couple of reasons. First, citing specific instances of your chosen challenge goes beyond simply stating that your challenge exists. It creates tangible reasons to be concerned about the issue. Second, having a few concrete examples demonstrates that you are informed and knowledgeable about the issue.
Once you have decided on a global challenge and have thought of a few examples to support your point, reflect on how you might be able to contribute to a solution to this problem. This program is offered by the School of International Service, so you will be pursuing a degree in International Studies.
You might already have some ideas about how you wish to help solve your chosen problem, but your essay will be even better if you can connect your goals to the school and degree. Read up on the BA in International Studies and the Global Scholars Program to inspire your writing!
There really is no wrong way to envision yourself as part of the solution. Consider the following hypothetical students to see how contributions can vary:
- A student who’s passionate about the environment might say that climate change is the greatest challenge facing humanity, and might describe how it has devastated different communities around the world, including his small coastal town, which has experienced worsening floods. He might hope to major in International Studies to eventually work in the United Nations and be a part of climate change conferences and agreements.
- A student who wants to be a doctor might say that lack of access to good, inexpensive healthcare is the greatest global challenge. She could describe how the U.S. healthcare system fails many low-income people, and how poorer countries lack the infrastructure and resources to treat easily treatable illnesses. She hopes to go to medical school then join Doctors Without Borders to help those in conflict zones and those facing disasters get the treatment they need.
This prompt is meant to gauge which global issues you deem important and how you intend to use your college education and degree to contribute to ongoing efforts to solve these issues. You’ll have a strong essay as long as you’re sincere and write about a problem you’re personally invested in.
Global Scholars Program Applicants, Prompt 2
Describe a situation in which you had to work harder than you expected. when and how did you know that your current efforts were not enough how did you adjust (500 words).
This prompt asks you to describe a time in your life when you faced a challenge that required you to put in an unprecedented amount of time and effort. What you choose to write about doesn’t have to be a singular experience; a situation in this context can be something much larger.
You can choose to describe any experience—academic, personal, extracurricular, and so forth—in your answer. Like most other prompts, the key will be in how you not only relate your chosen situation to your personality, but to the Global Scholars program at large.
Think first about your identity and your environment—are there any distinguishable experiences in which you have always felt that you’ve had an uphill battle or unfair disadvantage? Think about periods of your life in which you may have had to undergo a major transition or change.
Regardless of the situation you choose, remember that the best answers come out of asking yourself questions. This applies equally to a situation you may describe that does not involve your identity or environment—you can also approach this prompt by thinking about any life-altering events that forced you to pivot or make a change.
For example, maybe COVID-19 left one or both of your parents unemployed, and you had to pick up a job on top of your schoolwork. While you may have expected to be able to handle the part-time job, perhaps you saw your schoolwork and relationships begin to slip through the cracks and you were forced to really reevaluate your time management skills.
You may end up writing about an experience that is similar to that of other applicants, so it’s how you relate it to yourself and to your environment that will make you stand out from the crowd. Make sure you continue to emphasize your emotions and honesty throughout your answer, and lastly, try to relate your chosen experience back to the Global Scholars program at large.
You can conclude by writing about how you hope to apply what you learned from your life experiences to your participation in the Global Scholars program—how you hope to apply your newfound understanding of various financial or personal circumstances to learning about various cultural and global circumstances.
Lincoln Scholars Program Applicants, Prompt 1
Tell us about a morally complicated text that you think would lead to good discussion for first year college students. in what way is the text morally complicated and why do you recommend it (no more than 500 words).
This might seem like a daunting prompt, but it can be easier than it seems. Don’t worry about having some grandiose, impressive tome to talk about for this essay. If you think creatively, you should be able to identify moral complications in simpler texts. This is the kind of essay that really benefits from careful argumentation.
Brainstorming your topic:
There are two kinds of texts that would probably make for a strong essay:
- Texts you’ve read recently, which should still be fresh in your mind
- Texts you’ve read a long time ago and still remember because they were impactful or profound to you
It’s important that you pick one of these kinds of texts because you’ll want to write about something you know well enough. If you choose a text that you don’t really remember, or worse, a text you haven’t read that looks impressive, your points will probably be shallow and superficial, which will drag the overall quality of your essay down.
As far as the text itself is concerned, you can write about nearly anything (just make sure it’s not too trivial, like a children’s book). Perhaps you have read a clearly morally complex text, such as Victor Hugo’s Les Misérables or Harper Lee’s To Kill a Mockingbird . If you have, and you remember the details well enough to explain your choice, then by all means write about it!
However, if you haven’t read a text like that, that’s fine too. Think of things you’ve read recently that have moral dilemmas you might discuss. For some idea on how you might stretch the theme of morality, consider some examples:
- Lois Lowry’s The Giver, a young adult novel, discusses themes related to individuality and emotional depth and can be pitted against order and conformity. This moral conflict leaves a lot of room for debate, as the balance between individuality and societal conformity is one that is often hard for individuals to navigate.
- Marvel Comics’ Civil War, a seven-issue comic book storyline from 2007, has a plot centered around the U.S. government requiring super-powered individuals to reveal their identities to be superheroes under official regulation. While this may not be a traditional text, it has been acclaimed for its exploration of the conflicting desires of security and freedom that are still discussed in American politics today.
- Walter Isaacson’s Steve Jobs, the authorized biography of Apple’s co-founder, is a thorough look at the life of the controversial business magnate. It discusses not only his great achievements in the worlds of business and technology, but also his personality, which has been described as abrasive or difficult at times. This text allows students to examine the ways in which massive corporations, their employees, and their consumers can be directly affected by the very human individuals who lead them.
As you can see from the above examples, you can find and argue for moral complications almost anywhere you look. You might use a traditional example of a large, classic novel with clear and distinctive moral ambiguity, or you might explore some more creative options, such as biographies, YA novels, and even comic books or graphic novels!
Tips for writing your essay:
A good response will answer every part of the prompt. You should strive to identify the text, explain how it’s morally complicated, and detail your reasons for recommending it. The first and last part shouldn’t be too hard once you’ve settled on your text—naming the text and talking about why you’re recommending it are tasks that you can probably do easily if you know your chosen text well. After all, you know why you like the book.
It’s the second part of the prompt that will require some more careful thought. Effectively explaining how the text is morally complicated is only something you can do if you’re familiar enough with the text and its themes. Oftentimes, the moral complications of a book aren’t directly relevant to the plot—they’re often a thematic consequence of a character’s actions or are intended to be seen behind the main narrative, but not the focal point of the text itself.
That said, it might actually be a good idea to consult online summaries, videos, and study guides of the text you chose. Of course, you should absolutely have read the text and have a decent grasp of its material, but this isn’t a test for school—you can and should see how the moral themes are discussed by other readers. This will inform your argument that this text should be used in discussions among first year students.
Mistakes to avoid:
There aren’t too many ways to tackle this prompt incorrectly, but there are a couple of things you should avoid , which have already been mentioned but are worth repeating:
- Choosing a text you aren’t familiar with, just because it looks more impressive. It’s better to write a thoughtful, intelligent essay on a text that might be seen as lackluster than to write a shallow, generic essay on a text seen as impressive. Remember, the admissions officers aren’t making decisions based on books you have or haven’t read—they’re making decisions based on the quality of your essays.
- Choosing a trivial or juvenile text. Most young adult novels should be complex enough to be valid texts for this essay, but don’t try to be overly creative by writing about something for little children. Children’s books are intentionally written in a way that does not deal with the complex, intellectual themes that you’re tasked with discussing here.
As long as you pick a decent text (i.e., one you’re familiar with that isn’t too trivial), describe the ways in which it deals with questions of moral complexity, and make a good case for its use in Caltech’s first year classrooms, you’ll be well on your way to crafting a strong response.

Lincoln Scholars Program Applicants, Prompt 2
One goal of the lincoln scholars program is to encourage intellectual and political diversity on campus. what does this goal mean to you and why does a program with this goal interest you (no more than 500 words).
This prompt puts a specific spin on the common “Why This College?” and “Why This Major?” prompts, with a couple of key differences:
- First, you’re asked about a particular goal and what it means to you.
- Second, rather than discussing the University as a whole or a particular major, you’re tasked with describing why a program like the Lincoln Scholars Program appeals to you.
Make sure to address both parts of the question to have a full response. You have up to 500 words to work with, so you can really go into detail about each part. A good approach would be to answer each portion of the question in turn.
Before you begin writing, think about what intellectual and political diversity mean to you. Note the wording of the prompt: “What does this goal mean to you?” You can take advantage of the nuanced meanings of the word “mean.” In a literal sense, the question is asking how you would define such a goal. But in another sense, it’s asking why the goal is significant or important to you.
It might be helpful to jot down some bullet points that you might want to build on in your response. You might end up with a list that looks something like this:
- Having a group of people with different fields of expertise work on one project from various angles
- Different viewpoints creating points for intellectual debate
- Multiple people of various backgrounds informing each other’s perspectives
- Generating varied approaches to the same problem with the shared goal of solving it
Whatever you think of, try to come up with a solid personal definition of intellectual and political diversity. From there, you can begin to describe why these kinds of diversity are important to you. Using an anecdote-driven narrative to explain this point is a good approach. For example, perhaps you participated in a school project in which a different perspective was the one that led to a solution. Or, maybe you were part of a debate club and learned to see a topic differently because of a well-informed persuasive argument on the other side.
As you develop your thoughts on why such a goal is important to you, transition into a discussion of the program and why it interests you. Here, it’s essential that you establish a connection to the program. Do some research on the program’s webpage to learn about resources and opportunities that are offered.
Perhaps one of the program’s courses is appealing to you because of its content. Or, maybe you resonate with the program’s mission “to explore the great questions of moral and political life in a context of intellectual and political diversity.” Be sure to describe how and why a program like this piques your interest.
Connect the goal of intellectual and political diversity to your personal goals and values. This is the strongest way to convey your interest in the Lincoln Scholars Program and in exploring big questions from multiple viewpoints.
Lincoln Scholars Program Applicants, Prompt 3
List five texts, magazines, movies, websites, podcasts, music, or other media that you regularly engage with and explain briefly why you like each one. please list a variety of types of media. (1-2 sentences per item, no more than 400 total)..
This is a more niche prompt that you probably haven’t seen often, if at all. Luckily, there’s really no right or wrong answer! In fact, the program’s webpage lists some of the books that students have applied to the program with this year, and they include all kinds of works—ancient epic poems, classic novels, niche novellas, poetry collections, philosophical dialogues, and memoirs!
AU is curious about what interests you, how you think, how you’ve developed intellectually, and how you may have challenged yourself with the media you consume. Choose your examples carefully, but also be honest.
One great way to think about this prompt is through the idea of a “capsule wardrobe.” In a capsule wardrobe, each piece of clothing is unique and works well on its own—you might have a graphic tee, a leather jacket, a button-up shirt, and a few pairs of jeans. Even though each article of clothing has its own character, each also works toward your overall style—the entire wardrobe. Combining items into outfits can highlight different aspects of each item as well as similarities they share
The same idea applies to the texts, movies, websites, and music in your list. Each item should be compelling on its own, but should also contribute to the wardrobe that is your intellectual style. A great list will have items that complement each other, like a belt that matches with a pair of shoes. Some more style tips:
1. List items that build on each other. You want your list to have synergy . Just like wearing two matching items together can convey your sense of style, including two similar items in your list can display a sustained interest in a subject. For example, if you include both Romeo and Juliet and West Side Story in my list of films, you’re showing the admissions officer that you’re interested in exploring how the same story has been interpreted by different creatives from different times and places. Neither Romeo and Juliet nor West Side Story could demonstrate this idea alone—when included together, the message is greater than just the sum of its parts!
- Show multidimensionality. There’s something to be careful about. It’s possible to show sustained interest in a topic without indicating growth, and this is something you’ll want to avoid. For example, if your entire list consists of true-crime podcasts, it will look a bit one-dimensional and bland because each item effectively conveys the same message. Aim to list works that show your interest in the multiple angles of a topic. For example, listing the true-crime podcast Serial and Criminal Perspective as well as the journal Psychological Review and a blog on forensic psychology will add levels of intellectual nuance to your interest in the broad theme.
- Don’t overdress. You might want to only include the most impressive, difficult, intellectual media you’ve consumed to show that you’re intelligent and academic, but too much of that will probably make you look like you’re exaggerating for the admissions committee. Instead of doing that, balance the weightier, deeper items with some more relaxed or jocular ones. Hawking’s A Brief History of Time and Einstein’s Relativity: The Special and General Theory are going to look less like you’re pandering if you include something like Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy in your list. Balance the intellectual interests you wish to show off with your some distinctive personality.
- Don’t underdress. The opposite of the previous tip is also true. While throwing in some fun little books, movies, or music can add some dimension and personality to your list, they shouldn’t be the only things you include. You absolutely can (and should) include a sitcom or a non-academic novel on your media list, but make sure you don’t overfill the list with items of lesser substance. Also avoid including items that are too juvenile. Think smart casual clothing—you don’t need to wear a suit everywhere you go, but some places (like this supplemental essay) require a bit more than sweatpants and flip flops. Some nice jeans and a polo can be enough.
- Recognizable brands can be effective. Mentioning a couple of notable pop culture items will increase your list’s relatability in the admissions officer’s eyes. And, psychologically speaking , similarities on paper can help you in non-personal interactions. Just make sure you pick something that is well received both critically and by the masses, like a Beatles album or the movie Parasite —something that you and your reader could have a robust intellectual debate about.
- Moderation. If it’s not already clear by now, making a strong list is going to be a delicate task. You’re going to need to find the middle ground between casual and intellectual, specific and general, fiction and nonfiction, books and movies, etc. Don’t wait until the last minute to cobble together a list of random things just because this isn’t a fully fledged essay. Remember that you still need to explain and defend your choices. Devote as much time to this list and you do to your essays. The list reveals as much about you as an individual as a full essay does—be sure to treat it with the same respect.
- Be honest! You may be asked about this list somewhere down the road during the admissions process. Don’t get caught off guard by what you’re passing off as your own list. Nothing is more embarrassing and detrimental during this process than not having a clue about something you purport to have read/seen.
Politics, Policy and Law Scholars Program Applicants, Prompt 1
The politics, policy, and law scholars program is an intensive course of study in which students from diverse backgrounds live and learn together. given its intense and unique nature, why do you want to be a part of the program why do you think you would be a good fit for the politics, policy and law scholars program (250 words).
This is essentially a “Why This College?” prompt , but applied to a special program rather than AU as a whole. Moreover, in addition to describing how the program is a good fit for you, you’re tasked with describing how you are a good fit for the program.
Brainstorming your essay:
A recommended strategy for prompts like this is to establish a connection to the program. Two kinds of connection you might try to establish are a tangible connection and an intangible one.
A tangible connection can be made by identifying specific program offerings that resonate with you personally. To find such resources, you should do some in-depth research on the program. A good place to start is the PPL Scholars website . There you’ll find the course of study, the applicable majors, information about the living learning community, and more.
You might write about things like the campus culture, specific classes or academic opportunities, particular professors, etc. Given the rather low word limit, try to stick to academic features, as others might come off as less important.
An intangible connection can be made by discussing how your personal values align with those of the program. The PPL program emphasizes “the principles, practices, and institutions of politics and law from quantitative and qualitative, philosophical, and social science perspectives.”
If your personal values deeply resonate with the ideas of practicing law, government, public policy, criminal justice, or a similar field, you might wish to discuss how those values will be supported and informed by those of the program. Be sure to take a look at the PPL Scholars FAQ webpage to get a little more insight into the program.
Since you only have 250 words to work with, it would be a good idea to choose either a tangible connection or intangible one to discuss, rather than both. Remember, you need to save some space to discuss how you’re a good fit for the program.
Also note that it’s okay if you can’t develop a really strong intangible connection to the program—that is usually the harder kind of connection to write about. A strong tangible connection and a good explanation of how you’re a good fit for the PPL Scholars Program will make for a good response.
For example, consider a hypothetical student whose mother is a lawyer and whose father is a police officer. She might feel deeply connected to issues of justice and reform through the stories her parents tell her. She might write a response that begins like this:
“My parents are both deeply involved in the legal professions—my dad is a police officer and my mom is a lawyer. They have told me how the justice system isn’t perfect—both of them have seen the system succeed and fail many times. The passion with which they describe their careers has inspired me to go into a legal field too.
Having been raised by two parents in intense careers in legal fields has given me the resolve I will need to undertake such a career myself. I believe that my passion and determination, as well as my existing background knowledge about these fields make me uniquely equipped to take on the challenges of the Politics, Policy and Law Scholars Program…”
This excerpt is an excellent start to this prompt because it explains the unique features of the students past that equip her with the skills needed to succeed in the PPL Scholars Program. Note that this blurb is only half the word limit, which should give you some perspective on how much detail you might go into.
With prompts like this one, there are three things you will want to avoid doing in your response. These include the following:
- Name-dropping. It looks superficial and insincere to simply name certain courses or professors without elaborating on the ways in which these resources are meaningful or useful to you.
- Empty flattery. Don’t waste your word count talking about the prestige of the program or the University. There’s nothing wrong with being nice, but overdoing that in a prompt with a word limit might lead to you writing an essay that doesn’t answer the question.
- Naming general resources that are applicable to many schools. Don’t base your essay on things like good class sizes, strong political science courses, a nice location, etc.—these things apply to many schools and programs, and don’t showcase a personal connection to this particular program.
Politics, Policy and Law Scholars Program Applicants, Prompt 2
The living learning community and cohort aspects are integral parts of the politics, policy & law scholars program. describe a specific project, course, or other experience that required you to work with others toward a shared goal or to resolve conflict and build consensus. how did you contribute to accomplishing the goal or resolving conflict how did you engage with others how has this experience prepared you for the ppl program be specific. (250 words).
This prompt asks you to elaborate on a team-based problem-solving experience that will give the admissions reader insight into how you will fit in with the PPL program at large. As an intensive program, PPL requires all students to be a part of their Living Learning Community, meaning that you’ll be working alongside fellow PPL students both in and outside of the classroom. As such, the admissions committee wants to ensure that you’re able to support a larger community of like-minded (or even sometimes diversely minded) students.
First, think back over your time in high school and try to identify any large-scale projects that you were involved in with a group. At the same time, keep in mind that this response should not just be more explanation of something that may already appear on your application. When selecting what to write about, try to fill in the gaps your application has.
For instance, perhaps you were on the Executive Board of Model UN, and hope to share an experience about how you organized a conference hosted at your high school. While that’s definitely a valid experience, this answer should be less about the what and more about the how .
How did that conference come together? How did you delegate responsibilities among your peers and which responsibilities did you take on? What challenges or obstacles did you face as a team and how did you overcome them together? Did you have to work through any conflicts when working with one another?
Ultimately, reflect not only on your accomplishments with whichever experience you choose, but also on the failures, conflicts, and honest strategies you chose to employ to keep the ship afloat. The next step will be highlighting the crucial lessons that the experience taught you, and how you hope to apply those lessons to your time in the PPL program.
In order to brainstorm how you wish to close out your response, remember that the PPL program will require you to live and learn alongside your peers—make sure your answer emphasizes that you were able to come together as a group to tackle a complicated problem, and ultimately come out not just successful, but as a closer group overall.
Politics, Policy and Law Scholars Program Applicants, Prompt 3
You have been hired to advise a member of congress or a state legislator (you can choose which one, but you should pick one) about the issues that affect americans aged 18-26. you have been asked to identify one legal, political, or policy issue that will resonate with this group of americans and recommend a policy proposal that he or she should support and promote. explain the issue, explain why the elected official should highlight it, and propose a specific original policy solution. provide support for your proposed solution. your proposal should not simply be to support another individual’s already created policy. (650 words).
This prompt is less of a by-the-books response and more of an exercise, asking you to not only identify a major issue facing the country but also persuading a hypothetical elected official to pay attention to it and also brainstorm a possible solution.
The purpose of this prompt is to get a sense of your level of political engagement, as well as to give you a chance to attempt your first case study, which will serve as a gateway to the PPL program at large. This essay will require thorough research and deliberation, but, at its core, it’s just an expanded version of a typical Political/Global Issues prompt.
First, decide the scale of your chosen issue. Trying to brainstorm a list of possible issues to focus on will end up generating a laundry list of options, and might exhaust your brain before you even begin writing your response.
Something that may help guide you is remembering that you should have a unique perspective on your chosen issue. For example, you wouldn’t want to write your response about something general like the dangers of climate change if you genuinely don’t have anything to add to the conversation—the point is not to reiterate discourse that is already out there, but rather to think creatively and critically about the world and the ways in which your unique perspective can be valuable in trying to solve your chosen issue.
Therefore, it may be more useful to start small and then expand outwards. Look at your environment—what issues impact your community, your state, or your region? Looking again at the issue of climate change, perhaps you come from a state where fracking is not only legal, but still actively occurs. Perhaps your own family or a family you know has ties to the fracking business, and you feel as though current legislation and efforts to outlaw fracking stall because of pushback from these communities.
Tie your belief to your perspective—you may believe that fracking should be illegal, and your perspective can guide you in persuading an elected official to provide various incentives to those who rely on fracking for their livelihoods. As such, starting small will make your answer more specific and unique while still tackling a national issue like climate change.
If you don’t feel as though your environment has given you a distinct perspective on a current event, do some research on what issues have most recently surfaced in the country. For example, recent months have called attention to a migrant crisis that the United States is facing and how resources for these migrants are quickly diminishing.
Regarding this example, perhaps you are very active in community service and volunteering—how can you use that interest to frame your answer? Your proposed solution can involve rallying young people to volunteer and provide support to these migrant communities, while also trying to work with the opposing party to reach a solution.
Remember, your answer still needs an official policy proposal, so perhaps your proposed solution can immediately provide temporary shelter and resources for migrants while also opening the door to a firmer long-term solution. Your proposed solution doesn’t have to completely close the door on an issue, but it should showcase your understanding of the political process.
Public Health Scholars Program Applicants, Prompt 1
Discuss a public health issue of local, national, international, or personal importance to you. explain why it is important to you and describe how you envision impacting this issue (500 words)..
This prompt is meant to gauge two things. First, it’s trying to find out which public health issues you consider important and why. Second, it wants to discern how you intend to use your college education and life experience to contribute to a solution to this issue.
Admissions committees are constantly looking for nuance and specificity, so we recommend that you choose a problem that isn’t very broad. A problem like “COVID-19” is too vague to write an effective essay on. Instead, choose something more narrow, such as “COVID-19 in impoverished communities.”
If you’re having trouble settling on a topic to write about, think about your identity and values. Aspects of your identity include your ethnicity, race, country of origin, language, religion, gender identity, sexual orientation, hometown, income class, socioeconomic status, illnesses/disabilities, and even interests and activities! There might be an aspect of your identity that is directly related to a public health issue.
Consider these different aspects of your background and make a list of public health issues that may have an impact on part of your identity. For example, African Americans are more likely to suffer from cardiovascular disease or stroke than white Americans. In cases like this, people with your racial background may be affected by a health issue more than people of other backgrounds.
To help add nuance to your essay, be sure to cite specific examples or your chosen issue. Concrete examples will make your essay more specific as well as help you transition into a discussion of how you intend to help contribute to solving the issue.
For instance, if you want to write about substance misuse and substance abuse, discuss some specific situations in which these issues take hold. In such an essay, you might want to write about things you have seen firsthand—these can include opiate abuse by the homeless population in your home city, overprescription of certain drugs in your area, a persistent community habit of failing to finish a full course of antibiotics, etc.
The above examples can add nuance to your essay for two reasons. First, simply stating that your issue exists and is important (even if that’s true) is not a compelling argument without concrete evidence. Providing examples shows your reader that there are tangible reasons to care about the issue. Second, having some real-life examples in your essay shows that you are both inquisitive and informed.
Once you’ve picked a public health issue that you can support with tangible evidence, ponder how your future college education and life experience can afford you the ability to help solve this issue. AU’s Three-Year Public Health Scholars Program is an accelerated course of study designed to help you get a BA or BS in Public Health in 3 years (possibly on a pre-med track as well).
You might already have plans for your future contributions to solving your chosen issue, but you can potentially elevate your essay if you’re able to connect your goals to the school and degree. Look at AU’s Three-Year Public Health Scholars Program website as well as the Public Health BA website and BS website to inspire your writing!
This essay is about your plans for a career in public health, so don’t worry too much about having a “right” or “wrong” answer. Here are a couple of hypothetical student bios to show you just how different effective ideas can look:
- Jane has been curious about psychology and mental health since middle school. Throughout high school, she has had many conversations with her uncle, a cognitive behavioral therapist, about the staggering lack of mental health resources across the United States. Jane is pursuing a degree in Public Health because she feels that this field is the key to developing lasting reform in the domain of mental health.
- Robert is a Chinese-American with a family history of cardiovascular disease. Intrigued by this recurrent issue, he has done a lot of independent research on prevalence rates. Robert found that Asian-Americans are disproportionately affected by cardiovascular disease due to several social determinants. He hopes to get a degree in Public Health so he can help spearhead initiatives that will provide care to his underserved ethnic community.
Public Health Scholars Program Applicants, Prompt 2
Why do you want to join a 3-year degree program what skills and insight do you hope to acquire through this experience respond in no more than 250 words..
This prompt is a bit of a mix of two common types of prompt—the “Why This College?” and the “Why This Major?” prompts. It’s a very straightforward question meant to gauge your interest in the University, the field of public health, and the 3-Year Public Health Scholars Program. The admissions committee wants to see how you fit with the program and how you’ll make the most of its resources.
You’ll want to establish at least a tangible connection to the program. The best way to do this is to describe your interest in the field then connect it to your reasons for applying to the program.
Think about why you’re passionate about public health. For what reasons do you want to study it? What are some career and life goals of yours? How will this 3-year program help you achieve these goals?
Explore the program’s website as well as the sites for the Public Health BA degree and BS degree to help inspire your writing! Try to find unique features of the program that you can use to inform your response.
Look at this hypothetical response to see how you might establish a connection with the program:
“Growing up, I had a lot of problems with my weight and health, and I was shamed for not making ‘healthy choices.’ It was only when my dad got a promotion and we moved to a new neighborhood that I realized what the main issue was. In my old, poorer neighborhood, all we had access to were fast food restaurants and corner stores. In my new neighborhood, there were several grocery stores with fresh, healthy food within a mile. My weight and health have improved significantly ever since our move.
I want to get a BS in Public Health because I hope to make it easier for young, poor kids like I was to gain access to the resources to live a healthier life. A 3-year program will allow me to help these communities more effectively.
I look forward to taking the course Gender, Poverty and Health, which will explore the intersections between these topics and allow me to reflect on systemic ways to bring much-needed health resources to impoverished communities. Furthermore, the course Multicultural Health will allow me to approach my work through an intersectional lens, as there are many immigrants in low-income communities who face unique health disparities based on their backgrounds.
Good health is not as simple as just ‘making the right choices’ when there are systemic barriers to making those choices. I hope to help remove those barriers in my work.”
This example is effective for a couple of reasons. First, it gives the admissions committee an idea of the student’s background, motivations, and passion. Second, it answers each point of the prompt explicitly and clearly. The student describes why he is interested in a 3-year program, then lists the main skills he hopes to acquire through this program.
There are a few things you should avoid when crafting your essay:
- Empty flattery. Writing about how unique or prestigious the University/program is might sound nice, but you shouldn’t talk about how cool a program is to you without elaborating on why . This kind of approach is vague and doesn’t add any nuance to your essay.
- Name-dropping. Don’t simply list a bunch of classes, professors, or activities that appeal to you without describing why they’re interesting to you.
- Being generic. A good location, a strong program in public health, a nice core curriculum, etc. are things that apply to many schools and programs. They are too vague and will make your essay stand out less.
As long as you give a genuine answer and you have solid goals that this program will help you achieve, you’ll craft an effective essay that is sure to stand out to admissions officers.
Sakura Scholars Program Applicants, Prompt 1
The sakura scholars program requires students to study in both the united states and japan, learn the japanese language, focus on regional topics in east asia and the pacific, and complete a capstone for the joint bachelor’s degree in global international relations. why are you interested in this program what are your personal and/or professional goals and how will this program help you to reach them (500 words).
This prompt is similar to the common “Why This College?” prompt , but more specifically applies to the intercollegiate Sakura Scholars program. This prompt is meant to gauge your reasons for applying to the program to see if you’re a good fit for it and if it’s a good fit for you.
To write a successful essay, you‘ll need to establish a connection with the program and express how your goals are best served by being a part of it.
There are two kinds of connections that you can make with a college, program, major, etc. The first kind is the tangible connection. This involves identifying specific concrete reasons for applying to the program. To do this effectively, you will need to do in-depth research on the program and its offerings.
If you’ve made it to this point, you have probably written your response to the All Applicants prompt that was covered at the beginning of this guide. If you have, doing research on the program will be very similar to doing research on American University broadly, as you did earlier. If you haven’t done that essay yet, don’t worry! We have created a guide to help you research colleges (and programs) for this type of essay.
Go to the program’s website to begin your research. Scroll through the main site and the FAQ page to learn more about the program. In this program you have the choice of starting your undergraduate career at American University or Ritsumeikan University, so be sure to check out Ritsumeikan University’s program site as well! This will help you determine where you want to spend your first semester. Regardless of which school you choose, you’ll spend four semesters at AU and four semesters abroad.
The program awards a degree in Global International Relations, so a good approach to this essay is to describe why the field of international relations is important to you and how the program is uniquely equipped to help you achieve your goals in this field.
One direct way to establish a tangible connection between the program and your goals is to find courses or faculty members that really resonate with you. Since the program is between two universities, you should look through the faculty lists of both American and Ritsumeikan .
Consider the following excerpt from a response that might be written by a hypothetical Uyghur student, whose ethnic background has many people suffering human rights violations abroad:
“The Sakura Scholars program is the perfect opportunity for me to study international relations in the United States and Japan. It would give me unprecedented access to Western and Eastern perspectives. I am particularly interested in the work of Professor Jeffrey Bachman at American University and that of Professor Rieko Kitamura at Ritsumeikan University.
Prof. Bachman studies genocide, political violence, and human rights, and Prof. Kitamura has done work on human rights protections. Studying under the supervision of these professors will offer me the chance to delve deeper into specific regional issues. The degree awarded by this program will offer me new ways to help end the plight of my people.”
This response is very effective for a number of reasons:
- First, it establishes a personal background that helps the admissions committee understand the student’s personal motivations.
- Second, it showcases the student’s sincere interest in the Sakura Scholars program.
- Finally, it explicitly names resources (specifically professors) at both universities that will be assets to the student’s education and to the realization of the student’s personal goals.
The second kind of connection you can make with the program is an intangible connection. This involves things like seeing if your values and those of the program are aligned. For example, you might appreciate how the program takes place in the East and West, emphasizing “voices, experiences, and theory from a truly multicultural, multiregional, global perspective.”
There are some things you’ll want to avoid when writing your response:
- Name-dropping. Don’t simply list activities, courses, or professors that interest you without explaining why you’re interested in them. This essay needs to be about you more than the program itself.
- Empty flattery. Anyone can write about the reputations of AU and Ritsumeikan. Compliments are nice, but empty flattery suggests that you don’t have anything more substantive to say.
- Generic aspects of the program. Talking about good locations, a strong program in international relations, or small class sizes won’t really add to your essay. Try to write about unique aspects of the program or things that are rare .
Make sure you give yourself plenty of time to do deep research before you begin writing. Also be sure to write about nuanced personal motivations for applying to the program. Most importantly, write a sincere response! Honestly will go a long way, both in the application process and beyond.
Sakura Scholars Program Applicants, Prompt 2
In this joint degree program, you will gain first-hand comparative international experience as you spend two years at american university and two years at ritsumeikan university. think of a time when you faced a challenge or found yourself in an unexpected situation. explain what happened, what you learned, and how this experience might help you adapt to different intercultural situations, and work through future challenges as a sakura scholar. (no word count given).
This prompt is a very standard example of the Overcoming Challenges essay . You’re being asked about a challenge you faced as well as the lessons you learned from it. These questions are to give the admissions committee an idea of how you handle moments of adversity or surprise, and how you learn from adverse or unexpected experiences.
Before you begin writing, you should plan out your topic as thoroughly as you can so that the writing process can move smoothly. When trying to decide on a topic, think about any major challenges you’ve faced in life. Also consider any unexpected life events that may have turned out to be formative experiences. The prompt specifies that challenges and unexpected situations are both fair game, so don’t feel restricted to thinking only of negative experiences.
Once you’ve thought about possible experiences you could write about, create a list of the challenges that came to mind and a separate list of unexpected situations. For each list, ask yourself which experiences taught you the most important or influential lessons about yourself or the world.
Finally, after deciding on the best experience to talk about in this essay, ask yourself the following questions about it:
- What happened?
- In the moment, what was your reaction to the situation? How did it affect you, your thoughts, and your emotions? How have these emotions changed over time?
- Why was this experience so important to you? What is its personal significance?
- Consider the steps you took to manage the situation. Were they successful? Why or why not?
- Reflecting on the outcome of the event, how did the experience allow you to grow and mature as an individual? What did you learn from the success or failure of your approach? What lessons did you learn, both broadly and specifically?
- How did the experience prepare you to face occurrences like it in the future? How has it equipped you to adapt to different intercultural situations?
Once you’ve chosen a topic and answered these questions, writing the essay shouldn’t be so daunting.
Maybe you don’t have a clear answer for every question above. That’s fine, but be sure that you can do at least three things to effectively respond to the prompt:
- Describe the event/experience.
- Explain the most important lessons you learned from the experience.
- Detail the ways in which these lessons have improved your ability to adapt to different potential intercultural situations and your capacity to be a strong Sakura Scholar.
With regard to structuring your essay, you may find it helpful to frame it with a narrative format. After all, part of your response requires an explanation of the experience, which would benefit from an anecdote.
Here’s an outline to help you organize your writing:
- If you choose to use a narrative format, begin with an anecdote—a vivid and evocative retelling of the event to draw your reader in.
- After introducing the topic through an anecdote, describe yourself (your attitudes, beliefs, motivations, etc.) prior to the event that you learned from.
- State specifically how the experience was a turning point for you. How did your life change? What did you learn about yourself, others, and/or the world? The lesson should ideally reflect the way you now embrace challenges or unanticipated occurrences, and the ways in which you’re better equipped to tackle intercultural issues.
- If storytelling is one of your strong suits, you might choose to rearrange the order in which you describe events. For example, you might start with a summary of who you are now and how you’re able to approach intercultural situations, then transition to a discussion of who you were before the experience, then discuss the experience and how it affected you.
A hypothetical student might write about an experience related to his multiracial background. Perhaps the student felt like he had to deny both of his ethnic backgrounds to fit in with the American teens around him at school. He began to embrace his identity and eventually overcame his fear of being judged. He learned that innocent childhood ignorance was not a reason to detract from his own identity, a lesson that will help him later on because he has spent years confronting issues of identity in a multicultural context.
This example would be effective because it explicitly outlines the challenge the student had to confront, his response to adversity, what he learned about himself from overcoming the challenge, and how it has prepared him to undertake life as a Sakura Scholar in this multicultural program.
There is no word count given, but you should try to keep your response around 300 words. An essay longer than 350 words might become drawn out or redundant, and one shorter than 250 words might not leave you with enough space to be sufficiently detailed.
A Note About the AU Emerging Global Leader Scholarship Prompts
The following five prompts are all required for applicants to the AU Emerging Global Leader Scholarship. This scholarship covers all billable AU expenses (full tuition, room, and board) for one international student who will need a non-immigrant visa (preferably an F-1 or J-1 student visa) to study in the United States.
Since the scholarship is only being offered to international student applicants, you can disregard the next five prompts if you’re a U.S. citizen, U.S. permanent resident, U.S. pending permanent resident, or dual citizen of the U.S. and another country. You are also not eligible to apply if you’re enrolled in or have already begun any post-secondary studies at another university in your home country or the U.S., or if you graduated secondary school earlier than 2022.
AU Emerging Global Leader Scholarship Applicants (International Students), Prompt 1
Discuss a significant issue in your home country about which you are passionate and describe how you would use the education you obtain at our institution, american university (au), washington, dc, to create positive civic and social change once you return home. (250 words).
This prompt is intended to help you reveal a few important things about yourself—your ability to find significant civic and social issues around you, the types of problems that are important and interesting to you, your critical-thinking and problem-solving skills, and your plans for using your college education to its full potential after graduation.
This prompt is a bit like the common community service prompt , albeit in the future tense. It’s different in that rather than describing how you helped solve an issue in the past, you’re tasked with writing about how you foresee yourself contributing to the solution to a problem in the future.
Before you begin writing, think about the issues that truly bother you in your home country. Since you’re just brainstorming a list right now, these problems can be big or small. To have an essay that stands out, however, you should ultimately pick something substantial when you begin writing.
Your problem doesn’t have to be within any specific domain as long as you can envision civic and social change being integral to the problem’s resolution. As you think, consider social, economic, political, governmental, environmental, war-related, and public health issues.
The prompt isn’t asking you to write a whole textbook on the issue, but be sure that you research it well enough to describe its important points at the very least. You need to write a description of the problem, as well as some ways in which your American University education will help you tackle the problem back in your home country.
That being said, you should have a good understanding of what the problem entails. You might want to pick an issue in which you have some personal investment so you can add a nuanced perspective to your essay.
You only have 250 words to address every part of the prompt, so be succinct and direct in your explanation of the issue. Don’t only talk about the basic facts, though. Be sure to also touch on why the problem is important to you. Be careful not to let bias direct how you report the facts. Try to strike a balance between straightforward reportage and personal interest.
For example, consider a hypothetical student from Ethiopia, a country still facing the effects of a yearslong civil war. Perhaps he has noticed that the problem primarily stems from a lack of communication between the government and the rebelling military faction. He might write a response like this:
“In December 2020, my family fled its home, the Tigray Region of Ethiopia, at the outset of war. The Tigray People’s Liberation Front, a political party that ruled Ethiopia for decades, held an election during the COVID-19 pandemic that the current federal government ruled illegal. This debate escalated to violence, beginning a war that, despite a ceasefire, still has lasting impacts.
My family fled and thankfully found a safe haven in Europe, but so many other families did not have such luck. Hundreds of thousands of people have been displaced or killed in this senseless conflict that is ravaging my homeland.
It is my hope that a strong education will equip me with the skills and knowledge to go back home and contribute to a more definite end to this conflict. Despite the ceasefire, some occupations continue and famine is widespread. I believe a degree in International Studies will help me better understand the causes of war and the preconditions necessary to end it.
I cannot solve this issue myself, but I can no longer watch my home get torn apart. I want to help resolve this conflict by participating directly in the peace and rebuilding processes. If nothing else, I can at least use my education on the global stage to direct more eyes to this dreadful time period. Ghanaian diplomat Kofi Annan once said, ‘Education is the premise of progress, in every society, in every family.’ I know in my heart that he was right.”
This is an effective response. First, it provides a fairly detailed outline of an issue in the student’s home country. Second, it describes why the issue is such an important problem and why it’s so hard to solve. And finally, it discusses how a degree from AU can help the student contribute to awareness of the issue and attempts to resolve it.
You will craft a strong essay if you can address three things:
- What – Define the issue thoroughly but concisely.
- Why – Describe why the issue is important to you and to the people it directly affects.
- How – Detail how your AU education will prepare you to contribute to efforts to resolve the issue.
AU Emerging Global Leader Scholarship Applicants (International Students), Prompt 2
Discuss your current involvement in community service projects and volunteer activities. describe what you have learned about yourself as a result of these activities. (250 words).
This is a prime example of the community service essay. Schools that use this prompt want to know about your level of engagement with the people and environment around you. The Emerging Global Leader Scholarship—a program that emphasizes “leadership development and global engagement” —is especially interested in your impact on your community.
Be sure to check out CollegeVine’s guide to writing the community service essay for some in-depth tips and examples!
Since you only have 250 words, you won’t be able to write about many activities. In fact, we recommend sticking to 1-2 really meaningful and long-term projects. These are the projects that tend to show a genuine commitment to community service. If you only have short-term projects to write about, then you can mention 2-3 in your response.
When picking a topic, try to think about any projects you do that might be less common. For example, painting murals on old buildings to brighten up the neighborhood is less common than volunteering at a food drive or soup kitchen. There’s nothing wrong with writing about a more common volunteering experience in this essay, but if you have a unique project to write about, it may make your essay more engaging.
If you deem all your volunteering activities and community service projects are fairly commonplace, try to choose the ones that are more meaningful to you. If you feel more connected to a particular experience over the others, your writing about it will be more passionate and vivid.
Once you have decided on an activity (or a few), think about these questions:
- What happened during the activity?
- What went through your mind and how did you feel as this was happening?
- How have your emotions regarding the activity changed over time?
With your activity and motivations in mind, think about how you want to structure your essay. If you’re writing about a singular experience, consider taking a narrative approach. An essay that simply lists facts lacks important emotion. Tell about your experience with vivid imagery—show, don’t tell. This is a good way to draw your reader into the experience.
For example, perhaps you speak Spanish and do volunteer work where you can serve as a translator. Maybe you have seen firsthand the impact that speaking someone’s native language can have. Lessons this experience might have taught you about yourself can include the following:
- Your ability to switch between two languages is better than you thought.
- You can take on a leadership role even under the pressure of needing to speak a second language.
- You have more patience than you thought you did.
- You’re really good at working with the elderly, and you didn’t know that before.
As you can see, there are plenty of lessons you can glean from even one volunteering experience. These might include skills, abilities, personal attributes, or something else entirely.
This shouldn’t be a difficult essay to write, but you should note that there are three particular things to avoid :
- Listing out everything that happened. You have 250 words to work with. While this is ample space, you should use it wisely. This isn’t a play-by-play, so stick to the most important details. Your essay should focus more on the lessons you learned.
- Using a privileged tone. You’ll want to maintain a balanced, humble tone. Looking entitled or pretentious is not going to help your application in the least. Show how the experience is important to you without painting yourself as some kind of savior.
- Clichés. You might think it’s a good idea to quote a famous person or to use a trite, old life lesson, but we actually recommend avoiding these strategies. Admissions officers have seen them hundreds of times, so they won’t contribute much to your application.
When you write your response, be genuine about your motivations, honest about your impact on the local community, and specific in your descriptions of activities. Doing all those things will ensure a strong essay.
AU Emerging Global Leader Scholarship Applicants (International Students), Prompt 3
Describe an obstacle or challenge you have faced in your life. how have you overcome this challenge and grown from this experience (250 words).
This is the classic Overcoming Challenges prompt , so we recommend that you read our linked guide for advice and examples.
AU Emerging Global Leader Scholarship Applicants (International Students), Prompt 4
The au diplomats are a diverse group of current au international students and us global nomads who have been selected by the au admissions team to form and maintain connections with new and prospective american university (au) students, and to represent au to the international community., our emerging global leader scholar is expected to play an impactful role in the work of our au diplomats group. what outreach, communication, and/or intake strategies would you employ to inform and welcome new and prospective students to american university, washington, dc (250 words).
This prompt tasks you with highlighting how you envision yourself connecting with new and prospective students who may also be international students. While it may seem daunting to have to think ahead to welcoming and guiding others to a University you yourself are currently applying to, the answer is really based more on your experience than you may think.
Think about how your application process has felt so far. Applying to a school in a country different from your own may have been an overwhelming process, and it’s perfectly all right to write about that feeling—in fact, it may even guide your answer.
Imagine you were in contact with an AU Diplomat or a current Emerging Global Leader scholar. What questions would you ask now or would you have asked in the past? Doing some role-reversal will help you imagine the kind of Emerging Global Leader Scholar you can be to help new and prospective students like yourself.
Additionally, reflect on what you wish you knew prior to the application process. How did you find American University? Did anything or anyone help you along the way? How did you engage with American University prior to applying? And eventually, what advice would you give to a younger student who will soon be in your shoes?
For example, perhaps you live halfway across the world, and had trouble attending virtual information events at many schools because of the time difference. Maybe American University offered some information sessions specific to your country or region of the world—how did that make you feel more connected to the school? Maybe you want to volunteer for these events to give more prospective students the opportunity to learn about the school, and maybe even reach areas that haven’t yet been reached.
Your strategies will come from your personal experiences, so be open and honest about your past and present—even though your own future may still be undetermined.
AU Emerging Global Leader Scholarship Applicants, Prompt 3
This is the classic Overcoming Challenges essay, so we recommend that you read our linked guide for advice and examples.
AU Emerging Global Leader Scholarship Applicants, Prompt 4
The au diplomats are a diverse group of current au international students and us global nomads who have been selected by the au admissions team to form and maintain connections with new and prospective american university (au) students, and to represent au to the international community. our emerging global leader scholar is expected to play an impactful role in the work of our au diplomats group. what outreach, communication, and/or intake strategies would you employ to inform and welcome new and prospective students to american university, washington, dc (250 words).
This prompt tasks you with highlighting how you envision yourself connecting with new and prospective students who may also be international students. While it may seem daunting to have to think ahead to welcoming and guiding others to a University you are applying to, the answer is really based more in your experience than you may think.
Think about how your application process has felt so far. Applying to a school in a different country than your own may have been overwhelming, and it is perfectly all right to write about that feeling – in fact, it may even guide your answer.
Imagine you were in contact with an AU Diplomat or a current Emerging Global Leader scholar. What questions would you ask or would you have asked in the past? Doing some role-reversal will help you imagine the kind of Emerging Global Leader Scholar you can be to help new and prospective students like yourself.
Additionally, reflect on what you wish you knew prior to the application process. How did you find American University? Did anything or anyone help you along the way? How did you engage with American University prior to applying? And eventually, what advice would you give a younger student who will soon be in your shoes?
For example, perhaps you live halfway across the world, and had trouble attending virtual information events at many schools because of the time difference. Maybe American University offered some information sessions specific to your country or region of the world – how did that make you feel more connected to the school? Maybe you want to volunteer for these events to give more prospective students the opportunity to learn about the school, and maybe even reach areas that haven’t yet been reached.
Your strategies will come from your personal experiences, so be open and honest even though your own future may still be undetermined.
AU Emerging Global Leader Scholarship Applicants (International Students), Prompt 5
What are the characteristics of leadership that you most admire who is a leader that exemplifies those qualities, and why (250 words).
There are two main approaches you can use to navigate this prompt. You can certainly begin by brainstorming a list of leadership qualities you find most important and then find a leader you admire, but it may actually be wise to work backwards and reverse-engineer your answer—essentially, choose a leader you admire first and then identify the qualities that make them a great leader. Choosing someone you already admire may make your response more sincere and detailed.
There are no real wrong answers to this prompt, which also means that the more specific and unique you can get, the better. It is, however, best to avoid leaders who would be generally named immediately. For example, you would not want to pick a figure like the current President of the United States, other former Presidents, or other well-renowned world leaders, as they will likely be a common answer to this question.
Instead, think about whether your home country has any leaders—political, social, environmental, etc.—that would make for a strong response. Remember, this answer isn’t just about proving why your choice is a strong leader, it’s about showing the admissions committee your perception of what makes for great leadership.
After you’ve selected a leader, analyze the characteristics of that leader that resonate with people. Are they a great public speaker? Have they managed to unify a wide populace of differing perspectives? What is their public image? What impresses you most about their accomplishments?
These questions can help you identify how your chosen leader reflects your perspectives on great leadership as a whole, and will allow you to craft an answer around your thesis rather than the other way around.
Where to Get Your American University Essays Edited
Do you want feedback on your AU essays? After rereading your essays over and over again, it can be difficult to spot where your writing could use some improvement. That’s why we created our free Peer Essay Review tool , where you can get a free review of your essay from another student. You can also improve your own writing skills by reviewing other students’ essays.
If you want a college admissions expert to review your essay, advisors on CollegeVine have helped students refine their writing and submit successful applications to top schools. Find the right advisor for you to improve your chances of getting into your dream school!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Learn How to Support Stressed and Anxious Students.
The Big List of Essay Topics for High School (120+ Ideas!)
Ideas to inspire every young writer!

High school students generally do a lot of writing, learning to use language clearly, concisely, and persuasively. When it’s time to choose an essay topic, though, it’s easy to come up blank. If that’s the case, check out this huge round-up of essay topics for high school. You’ll find choices for every subject and writing style.
- Argumentative Essay Topics
- Cause-and-Effect Essay Topics
- Compare-Contrast Essay Topics
- Descriptive Essay Topics
- Expository and Informative Essay Topics
- Humorous Essay Topics
Literary Essay Topics
- Narrative and Personal Essay Topics
- Personal Essay Topics
- Persuasive Essay Topics
Research Essay Topics
Argumentative essay topics for high school.
When writing an argumentative essay, remember to do the research and lay out the facts clearly. Your goal is not necessarily to persuade someone to agree with you, but to encourage your reader to accept your point of view as valid. Here are some possible argumentative topics to try. ( Here are 100 more compelling argumentative essay topics. )
- The most important challenge our country is currently facing is … (e.g., immigration, gun control, economy)
- The government should provide free internet access for every citizen.
- All drugs should be legalized, regulated, and taxed.
- Vaping is less harmful than smoking tobacco.
- The best country in the world is …
- Parents should be punished for their minor children’s crimes.
- Should all students have the ability to attend college for free?
- Should physical education be part of the standard high school curriculum?

WeAreTeachers
- Schools should require recommended vaccines for all students, with very limited exceptions.
- Is it acceptable to use animals for experiments and research?
- Does social media do more harm than good?
- Capital punishment does/does not deter crime.
- What one class should all high schools students be required to take and pass in order to graduate?
- Do we really learn anything from history, or does it just repeat itself over and over?
- Are men and women treated equally?
Cause-and-Effect Essay Topics for High School
A cause-and-effect essay is a type of argumentative essay. Your goal is to show how one specific thing directly influences another specific thing. You’ll likely need to do some research to make your point. Here are some ideas for cause-and-effect essays. ( Get a big list of 100 cause-and-effect essay topics here. )
- Humans are causing accelerated climate change.
- Fast-food restaurants have made human health worse over the decades.
- What caused World War II? (Choose any conflict for this one.)
- Describe the effects social media has on young adults.

- How does playing sports affect people?
- What are the effects of loving to read?
- Being an only/oldest/youngest/middle child makes you …
- What effect does violence in movies or video games have on kids?
- Traveling to new places opens people’s minds to new ideas.
- Racism is caused by …
Compare-Contrast Essay Topics for High School
As the name indicates, in compare-and-contrast essays, writers show the similarities and differences between two things. They combine descriptive writing with analysis, making connections and showing dissimilarities. The following ideas work well for compare-contrast essays. ( Find 80+ compare-contrast essay topics for all ages here. )
- Public and private schools
- Capitalism vs. communism
- Monarchy or democracy
- Dogs vs. cats as pets

- Paper books or e-books
- Two political candidates in a current race
- Going to college vs. starting work full-time
- Working your way through college as you go or taking out student loans
- iPhone or Android
- Instagram vs. Twitter (or choose any other two social media platforms)
Descriptive Essay Topics for High School
Bring on the adjectives! Descriptive writing is all about creating a rich picture for the reader. Take readers on a journey to far-off places, help them understand an experience, or introduce them to a new person. Remember: Show, don’t tell. These topics make excellent descriptive essays.
- Who is the funniest person you know?
- What is your happiest memory?
- Tell about the most inspirational person in your life.
- Write about your favorite place.
- When you were little, what was your favorite thing to do?
- Choose a piece of art or music and explain how it makes you feel.
- What is your earliest memory?

- What’s the best/worst vacation you’ve ever taken?
- Describe your favorite pet.
- What is the most important item in the world to you?
- Give a tour of your bedroom (or another favorite room in your home).
- Describe yourself to someone who has never met you.
- Lay out your perfect day from start to finish.
- Explain what it’s like to move to a new town or start a new school.
- Tell what it would be like to live on the moon.
Expository and Informative Essay Topics for High School
Expository essays set out clear explanations of a particular topic. You might be defining a word or phrase or explaining how something works. Expository or informative essays are based on facts, and while you might explore different points of view, you won’t necessarily say which one is “better” or “right.” Remember: Expository essays educate the reader. Here are some expository and informative essay topics to explore. ( See 70+ expository and informative essay topics here. )
- What makes a good leader?
- Explain why a given school subject (math, history, science, etc.) is important for students to learn.
- What is the “glass ceiling” and how does it affect society?
- Describe how the internet changed the world.
- What does it mean to be a good teacher?

- Explain how we could colonize the moon or another planet.
- Discuss why mental health is just as important as physical health.
- Describe a healthy lifestyle for a teenager.
- Choose an American president and explain how their time in office affected the country.
- What does “financial responsibility” mean?
Humorous Essay Topics for High School
Humorous essays can take on any form, like narrative, persuasive, or expository. You might employ sarcasm or satire, or simply tell a story about a funny person or event. Even though these essay topics are lighthearted, they still take some skill to tackle well. Give these ideas a try.
- What would happen if cats (or any other animal) ruled the world?
- What do newborn babies wish their parents knew?
- Explain the best ways to be annoying on social media.
- Invent a wacky new sport, explain the rules, and describe a game or match.

- Imagine a discussion between two historic figures from very different times, like Cleopatra and Queen Elizabeth I.
- Retell a familiar story in tweets or other social media posts.
- Describe present-day Earth from an alien’s point of view.
- Choose a fictional character and explain why they should be the next president.
- Describe a day when kids are in charge of everything, at school and at home.
Literary essays analyze a piece of writing, like a book or a play. In high school, students usually write literary essays about the works they study in class. These literary essay topic ideas focus on books students often read in high school, but many of them can be tweaked to fit other works as well.
- Discuss the portrayal of women in Shakespeare’s Othello .
- Explore the symbolism used in The Scarlet Letter .
- Explain the importance of dreams in Of Mice and Men .
- Compare and contrast the romantic relationships in Pride and Prejudice .

- Dissect the allegory of Animal Farm and its relation to contemporary events.
- Interpret the author’s take on society and class structure in The Great Gatsby .
- Explore the relationship between Hamlet and Ophelia.
- Discuss whether Shakespeare’s portrayal of young love in Romeo and Juliet is accurate.
- Explain the imagery used in Beowulf .
Narrative and Personal Essay Topics for High School
Think of a narrative essay like telling a story. Use some of the same techniques that you would for a descriptive essay, but be sure you have a beginning, middle, and end. A narrative essay doesn’t necessarily need to be personal, but they often are. Take inspiration from these narrative and personal essay topics.
- Describe a performance or sporting event you took part in.
- Explain the process of cooking and eating your favorite meal.
- Write about meeting your best friend for the first time and how your relationship developed.
- Tell about learning to ride a bike or drive a car.
- Describe a time in your life when you’ve been scared.

- Share the most embarrassing thing that ever happened to you.
- Tell about a time when you overcame a big challenge.
- Tell the story of how you learned an important life lesson.
- Describe a time when you or someone you know experienced prejudice or oppression.
- Explain a family tradition, how it developed, and its importance today.
- What is your favorite holiday? How does your family celebrate it?
- Retell a familiar story from the point of view of a different character.
- Describe a time when you had to make a difficult decision.
- Tell about your proudest moment.
Persuasive Essay Topics for High School
Persuasive essays are similar to argumentative , but they rely less on facts and more on emotion to sway the reader. It’s important to know your audience, so you can anticipate any counterarguments they might make and try to overcome them. Try these topics to persuade someone to come around to your point of view. ( Discover 60 more intriguing persuasive essay topics here. )
- Do you think homework should be required, optional, or not given at all?
- Everyone should be vegetarian or vegan.
- What animal makes the best pet?
- Visit an animal shelter, choose an animal that needs a home, and write an essay persuading someone to adopt that animal.
- Who is the world’s best athlete, present or past?
- Should little kids be allowed to play competitive sports?
- Are professional athletes/musicians/actors overpaid?
- The best music genre is …

- Is democracy the best form of government?
- Is capitalism the best form of economy?
- Students should/should not be able to use their phones during the school day.
- Should schools have dress codes?
- If I could change one school rule, it would be …
- Is year-round school a good idea?
A research essay is a classic high school assignment. These papers require deep research into primary source documents, with lots of supporting facts and evidence that’s properly cited. Research essays can be in any of the styles shown above. Here are some possible topics, across a variety of subjects.
- Which country’s style of government is best for the people who live there?
- Choose a country and analyze its development from founding to present day.
- Describe the causes and effects of a specific war.
- Formulate an ideal economic plan for our country.
- What scientific discovery has had the biggest impact on life today?
- Analyze the way mental health is viewed and treated in this country.
- Explore the ways systemic racism impacts people in all walks of life.
- Defend the importance of teaching music and the arts in public schools.
- Choose one animal from the endangered species list, and propose a realistic plan to protect it.
What are some of your favorite essay topics for high school? Come share your prompts on the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, check out the ultimate guide to student writing contests .
We Are Teachers
You Might Also Like

100 Thought-Provoking Argumentative Writing Prompts for Kids and Teens
Practice making well-reasoned arguments using research and facts. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
"The American Scholar" is considered one of Emerson's most important works and is widely regarded as a seminal text in American literature. The essay is often studied as a statement of Emerson's views on the importance of individualism and intellectual freedom and continues to be widely read and discussed today.
An Oration delivered before the Phi Beta Kappa Society, at Cambridge, August 31, 1837

Summary of The American Scholar
"The American Scholar" is an essay by Ralph Waldo Emerson in which he calls for the development of a new type of scholar in America who is independent and self-reliant. Emerson argues that the traditional European model of scholarship is outdated and that American scholars should break free from it and develop their own unique voice and perspective. He believes that the American scholar should be influenced primarily by nature, which provides a source of spiritual and intellectual inspiration. He also stresses the importance of personal experience, intellectual curiosity, and creative imagination in shaping the American scholar. Through this essay, Emerson encourages the creation of a new generation of scholars who are unafraid to challenge the status quo and who are guided by their own instincts and ideas. He believes that this kind of scholar will be a leader in shaping a distinct American culture and intellectual tradition.
The American Scholar - The Complete Essay
Mr. President and Gentlemen,
I greet you on the re-commencement of our literary year. Our anniversary is one of hope and, perhaps, not enough labor. We do not meet for games of strength or skill, for the recitation of histories, tragedies, and odes, like the ancient Greeks; for parliaments of love and poesy, like the Troubadours; nor for the advancement of science, like our cotemporaries in the British and European capitals. Thus far, our holiday has been simply a friendly sign of the survival of the love of letters amongst people too busy to give letters anymore. As such, it is precious as the sign of an indestructible instinct. Perhaps the time has already come when it ought to be, and will be, something else; when the sluggard intellect of this continent will look from under its iron lids and fill the postponed expectation of the world with something better than the exertions of mechanical skill. Our day of dependence, our long apprenticeship to the learning of other lands, draws to a close. The millions that around us are rushing into life, and cannot always be fed on the sere remains of foreign harvests. Events and actions arise that must be sung, that will sing themselves. Who can doubt that poetry will revive and lead in a new age, as the star in the constellation Harp, which now flames in our zenith, astronomers announce, shall one day be the pole star for a thousand years?
In this hope, I accept the topic which not only usage, but the nature of our association, seem to prescribe to this day — the AMERICAN SCHOLAR. Year by year, we come up hither to read one more chapter of his biography. Let us inquire about what light new days and events have thrown on his character and his hopes.
It is one of those fables, which, out of an unknown antiquity, convey an unlooked-for wisdom, that the gods, in the beginning, divided Man into men, that he might be more helpful to himself; just as the hand was divided into fingers, the better to answer its end.
The old fable covers a doctrine ever new and sublime; that there is One Man — present to all particular men only partially or through one faculty; and that you must take the whole society to find the whole man. Man is not a farmer, a professor, or an engineer, but he is all. Man is a priest, scholar, statesman, and producer, and soldier. In the divided or social state, these functions are parcelled out to individuals, each of whom aims to do his stint of the joint work while the other performs his. The fable implies, that the individual, to possess himself, must sometimes return from his own labor to embrace all the other laborers. But unfortunately, this original unit, this fountain of power, has been so distributed to multitudes, has been so minutely subdivided and peddled out, that it is spilled into drops and cannot be gathered. The state of society is one in which the members have suffered amputation from the trunk, and strut about so many walking monsters, — a good finger, a neck, a stomach, an elbow, but never a man.
Man is thus metamorphosed into a thing, into many things. The planter, who is Man sent out into the field to gather food, is seldom cheered by any idea of the true dignity of his ministry. He sees his bushel and his cart, and nothing beyond, and sinks into the farmer, instead of Man on the farm. The tradesman scarcely ever gives an ideal worth to his work, but is ridden by the routine of his craft, and the soul is subject to dollars. The priest becomes a form; the attorney, a statute book; the mechanic, a machine; the sailor, a rope of a ship.

In this distribution of functions, the scholar is the delegated intellect. In the right state, he is Man Thinking . In the degenerate state, when the victim of society, he tends to become a mere thinker or, still worse, the parrot of other men's thinking.
In this view of him, as Man Thinking, the theory of his office is contained. Him nature solicits with all her placid, all her monitory pictures; him the past instructs; him the future invites. Is not, indeed, every man a student, and do not all things exist for the student's behoof? And, finally, is not the true scholar the only true master? But the old oracle said, `All things have two handles: beware of the wrong one.' In life, too often, the scholar errs with mankind and forfeits his privilege. Let us see him in his school, and consider him in reference to the main influences he receives.
I. The first in time and the first in importance of the influences upon the mind is that of nature. Every day, the sun; and, after sunset, night and her stars. Ever the winds blow; ever the grass grows. Every day, men and women, conversing, beholding and beholden. The scholar is he of all men whom this spectacle most engages. He must settle its value in his mind. What is nature to him? There is never a beginning, there is never an end, to the inexplicable continuity of this web of God, but always circular power returning into itself. Therein it resembles his own spirit, whose beginning, whose ending, he never can find, — so entire, so boundless. Far, too, as her splendors shine, system on system shooting like rays, upward, downward, without centre, without circumference — in the mass and in the particle, nature hastens to render an account of herself to the mind. Classification begins. To the young mind, everything is individual, stands by itself. By and by, it finds how to join two things, and see in them one nature; then three, then three thousand; and so, tyrannized over by its own unifying instinct, it goes on tying things together, diminishing anomalies, discovering roots running under ground, whereby contrary and remote things cohere, and flower out from one stem. It presently learns, that, since the dawn of history, there has been a constant accumulation and classifying of facts. But what is classification but the perceiving that these objects are not chaotic, and are not foreign, but have a law which is also a law of the human mind? The astronomer discovers that geometry, a pure abstraction of the human mind, is the measure of planetary motion. The chemist finds proportions and intelligible method throughout matter; and science is nothing but the finding of analogy, and identity, in the most remote parts. The ambitious soul sits down before each refractory fact, one after another, reduces all strange constitutions, all new powers, to their class and their law, and goes on forever to animate the last fiber of organization, the outskirts of nature, by insight.
Thus to him, to this school-boy under the bending dome of day, is suggested, that he and it proceed from one root; one is leaf and one is flower; relation, sympathy, stirring in every vein. And what is that Root? Is not that the soul of his soul? — A thought too bold, — a dream too wild. Yet when this spiritual light shall have revealed the law of more earthly natures, — when he has learned to worship the soul, and to see that the natural philosophy that now is, is only the first gropings of its gigantic hand, he shall look forward to an ever expanding knowledge as to a becoming creator. He shall see, that nature is the opposite of the soul, answering to it part for part. One is seal, and one is print. Its beauty is the beauty of his own mind. Its laws are the laws of his own mind. Nature then becomes to him the measure of his attainments. So much of nature as he is ignorant of, so much of his own mind does he not yet possess. And, in fine, the ancient precept, "Know thyself," and the modern precept, "Study nature," become at last one maxim.
II. The next great influence on the spirit of the scholar, is, the mind of the Past, — in whatever form, whether of literature, of art, of institutions, that mind is inscribed. Books are the best type of influence of the past, and perhaps we shall get at the truth, — learn the amount of this influence more conveniently — by considering their value alone.
The theory of books is noble. The scholar of the first age received into him the world around; brooded thereon; gave it the new arrangement of his own mind, and uttered it again. It came into him, life; it went out from him, truth. It came to him, short-lived actions; it went out from him, immortal thoughts. It came to him, business; it went from him, poetry. It was a dead fact; now, it is quick thought. It can stand, and it can go. It now endures, it now flies, it now inspires. Precisely in proportion to the depth of mind from which it issued, so high does it soar, so long does it sing.

Or, I might say, it depends on how far the process had gone of transmuting life into truth. In proportion to the completeness of the distillation, so will the purity and imperishableness of the product be. But none is quite perfect. As no air-pump can by any means make a perfect vacuum, so neither can any artist entirely exclude the conventional, the local, the perishable from his book, or write a book of pure thought, that shall be as efficient, in all respects, to a remote posterity, as to cotemporaries, or rather to the second age. Each age, it is found, must write its own books; or rather, each generation for the next succeeding. The books of an older period will not fit this.
Yet hence arises a grave mischief. The sacredness which attaches to the act of creation, — the act of thought — is transferred to the record. The poet chanting, was felt to be a divine man: henceforth the chant is divine also. The writer was a just and wise spirit: henceforward it is settled, the book is perfect; as love of the hero corrupts into worship of his statue. Instantly, the book becomes noxious: the guide is a tyrant. The sluggish and perverted mind of the multitude, slow to open to the incursions of Reason, having once so opened, having once received this book, stands upon it, and makes an outcry, if it is disparaged. Colleges are built on it. Books are written on it by thinkers, not by Man Thinking; by men of talent, that is, who start wrong, who set out from accepted dogmas, not from their own sight of principles. Meek young men grow up in libraries, believing it their duty to accept the views, which Cicero, which Locke, which Bacon, have given, forgetful that Cicero, Locke, and Bacon were only young men in libraries, when they wrote these books.
Hence, instead of Man Thinking, we have the bookworm. Hence, the book-learned class, who value books, as such; not as related to nature and the human constitution, but as making a sort of Third Estate with the world and the soul. Hence, the restorers of readings, the emendators, and the bibliomaniacs of all degrees.
Books are the best of things, well used; abused, among the worst. What is the right use? What is the one end, which all means go to effect? They are for nothing but to inspire. I had better never see a book than to be warped by its attraction clean out of my own orbit, and made a satellite instead of a system. The one thing in the world, of value, is the active soul. This every man is entitled to; this every man contains within him, although, in almost all men, obstructed, and as yet unborn. The soul active sees absolute truth; and utters truth, or creates. In this action, it is genius; not the privilege of here and there a favorite, but the sound estate of every man. In its essence, it is progressive. The book, the college, the school of art, the institution of any kind, stop with some past utterance of genius. This is good, say they, — let us hold by this. They pin me down. They look backward and not forward. But genius looks forward: the eyes of man are set in his forehead, not in his hindhead: man hopes: genius creates. Whatever talents may be, if the man create not, the pure efflux of the Deity is not his; — cinders and smoke there may be, but not yet flame. There are creative manners , there are creative actions, and creative words; manners , actions, words, that is, indicative of no custom or authority, but springing spontaneous from the mind's own sense of good and fair.
On the other part, instead of being its own seer, let it receive from another mind its truth, though it were in torrents of light, without periods of solitude, inquest, and self-recovery, and a fatal disservice is done. Genius is always sufficiently the enemy of genius by over influence. The literature of every nation bear me witness. The English dramatic poets have been Shakspearized now for two hundred years.
Undoubtedly there is a right way of reading, so it is sternly subordinated. Man's Thinking must not be subdued by his instruments. Books are for the scholar's idle times. When he can read God directly, the hour is too precious to be wasted in other men's transcripts of their readings. But when the intervals of darkness come, as come they must, — when the sun is hid, and the stars withdraw their shining, — we repair to the lamps which were kindled by their ray, to guide our steps to the East again, where the dawn is. We hear, that we may speak. The Arabian proverb says, "A fig tree, looking on a fig tree, becometh fruitful."
It is remarkable, the character of the pleasure we derive from the best books. They impress us with the conviction, that one nature wrote and the same reads. We read the verses of one of the great English poets, of Chaucer, of Marvell, of Dryden, with the most modern joy, — with a pleasure, I mean, which is in great part caused by the abstraction of all time from their verses. There is some awe mixed with the joy of our surprise, when this poet, who lived in some past world, two or three hundred years ago, says that which lies close to my own soul, that which I also had wellnigh thought and said. But for the evidence thence afforded to the philosophical doctrine of the identity of all minds, we should suppose some preestablished harmony, some foresight of souls that were to be, and some preparation of stores for their future wants, like the fact observed in insects, who lay up food before death for the young grub they shall never see.
I would not be hurried by any love of system, by any exaggeration of instincts, to underrate the Book. We all know that, as the human body can be nourished on any food, though it were boiled grass and the broth of shoes, so the human mind can be fed by any knowledge. And great and heroic men have existed, who had almost no other information than by the printed page. I only would say, that it needs a strong head to bear that diet. One must be an inventor to read well. As the proverb says, "He that would bring home the wealth of the Indies, must carry out the wealth of the Indies." There is then creative reading as well as creative writing. When the mind is braced by labor and invention, the page of whatever book we read becomes luminous with manifold allusion. Every sentence is doubly significant, and the sense of our author is as broad as the world. We then see, what is always true, that, as the seer's hour of vision is short and rare among heavy days and months, so is its record, perchance, the least part of his volume. The discerning will read, in his Plato or Shakespeare, only that least part, — only the authentic utterances of the oracle; — all the rest he rejects, were it never so many times Plato's and Shakespeare's.
Of course, there is a portion of reading quite indispensable to a wise man. History and exact science he must learn by laborious reading. Colleges, in like manner, have their indispensable office, — to teach elements. But they can only highly serve us, when they aim not to drill, but to create; when they gather from far every ray of various genius to their hospitable halls, and, by the concentrated fires, set the hearts of their youth on flame. Thought and knowledge are natures in which apparatus and pretension avail nothing. Gowns, and pecuniary foundations, though of towns of gold, can never countervail the least sentence or syllable of wit. Forget this, and our American colleges will recede in their public importance, whilst they grow richer every year.

III. There goes in the world a notion, that the scholar should be a recluse, a valetudinarian, — as unfit for any handiwork or public labor, as a penknife for an axe. The so-called `practical men' sneer at speculative men, as if, because they speculate or see , they could do nothing. I have heard it said that the clergy — who are always, more universally than any other class, the scholars of their day, — are addressed as women; that the rough, spontaneous conversation of men they do not hear, but only a mincing and diluted speech. They are often virtually disfranchised, and, indeed, there are advocates for their celibacy. As far as this is true of the studious classes, it is not just and wise. Action is with the scholar subordinate, but it is essential. Without it, he is not yet man. Without it, thought can never ripen into truth. Whilst the world hangs before the eye as a cloud of beauty, we cannot even see its beauty. Inaction is cowardice, but there can be no scholar without the heroic mind. The preamble of thought, the transition through which it passes from the unconscious to the conscious, is action. Only so much do I know, as I have lived. Instantly we know whose words are loaded with life, and whose not.
The world, — this shadow of the soul, or other me , lies wide around. Its attractions are the keys which unlock my thoughts and make me acquainted with myself. I run eagerly into this resounding tumult. I grasp the hands of those next me, and take my place in the ring to suffer and to work, taught by an instinct, that so shall the dumb abyss be vocal with speech. I pierce its order; I dissipate its fear; I dispose of it within the circuit of my expanding life. So much only of life as I know by experience, so much of the wilderness have I vanquished and planted, or so far have I extended my being, my dominion. I do not see how any man can afford, for the sake of his nerves and his nap, to spare any action in which he can partake. It is pearls and rubies to his discourse. Drudgery, calamity, exasperation, want, are instructers in eloquence and wisdom. The true scholar grudges every opportunity of action past by, as a loss of power.
It is the raw material out of which the intellect molds her splendid products. A strange process too, this, by which experience is converted into thought, as a mulberry leaf is converted into satin. The manufacture goes forward at all hours.
The actions and events of our childhood and youth, are now matters of calmest observation. They lie like fair pictures in the air. Not so with our recent actions, — with the business which we now have in hand. On this we are quite unable to speculate. Our affections as yet circulate through it. We no more feel or know it, than we feel the feet, or the hand, or the brain of our body. The new deed is yet a part of life, — remains for a time immersed in our unconscious life. In some contemplative hour, it detaches itself from the life like a ripe fruit, to become a thought of the mind. Instantly, it is raised, transfigured; the corruptible has put on incorruption. Henceforth it is an object of beauty, however base its origin and neighborhood. Observe, too, the impossibility of antedating this act. In its grub state, it cannot fly, it cannot shine, it is a dull grub. But suddenly, without observation, the selfsame thing unfurls beautiful wings, and is an angel of wisdom. So is there no fact, no event, in our private history, which shall not, sooner or later, lose its adhesive, inert form, and astonish us by soaring from our body into the empyrean. Cradle and infancy, school and playground, the fear of boys, and dogs, and ferules, the love of little maids and berries, and many another fact that once filled the whole sky, are gone already; friend and relative, profession and party, town and country, nation and world, must also soar and sing.
Of course, he who has put forth his total strength in fit actions, has the richest return of wisdom. I will not shut myself out of this globe of action, and transplant an oak into a flower-pot, there to hunger and pine; nor trust the revenue of some single faculty, and exhaust one vein of thought, much like those Savoyards, who, getting their livelihood by carving shepherds, shepherdesses, and smoking Dutchmen, for all Europe, went out one day to the mountain to find stock, and discovered that they had whittled up the last of their pine-trees. Authors we have, in numbers, who have written out their vein, and who, moved by a commendable prudence , sail for Greece or Palestine, follow the trapper into the prairie, or ramble round Algiers, to replenish their merchantable stock.
If it were only for a vocabulary, the scholar would be covetous of action. Life is our dictionary. Years are well spent in country labors; in town, — in the insight into trades and manufactures; in frank intercourse with many men and women; in science; in art; to the one end of mastering in all their facts a language by which to illustrate and embody our perceptions. I learn immediately from any speaker how much he has already lived, through the poverty or the splendor of his speech. Life lies behind us as the quarry from whence we get tiles and copestones for the masonry of to-day. This is the way to learn grammar. Colleges and books only copy the language which the field and the work-yard made.
But the final value of action, like that of books, and better than books, is, that it is a resource. That great principle of Undulation in nature, that shows itself in the inspiring and expiring of the breath; in desire and satiety; in the ebb and flow of the sea; in day and night; in heat and cold; and as yet more deeply ingrained in every atom and every fluid, is known to us under the name of Polarity, — these "fits of easy transmission and reflection," as Newton called them, are the law of nature because they are the law of spirit.
The mind now thinks; now acts; and each fit reproduces the other. When the artist has exhausted his materials, when the fancy no longer paints, when thoughts are no longer apprehended, and books are a weariness, — he has always the resource to live . Character is higher than intellect. Thinking is the function. Living is the functionary. The stream retreats to its source. A great soul will be strong to live, as well as strong to think. Does he lack organ or medium to impart his truths? He can still fall back on this elemental force of living them. This is a total act. Thinking is a partial act. Let the grandeur of justice shine in his affairs. Let the beauty of affection cheer his lowly roof. Those 'far from fame,' who dwell and act with him, will feel the force of his constitution in the doings and passages of the day better than it can be measured by any public and designed display. Time shall teach him, that the scholar loses no hour which the man lives. Herein he unfolds the sacred germ of his instinct, screened from influence. What is lost in seemliness is gained in strength. Not out of those, on whom systems of education have exhausted their culture, comes the helpful giant to destroy the old or to build the new, but out of unhandselled savage nature, out of terrible Druids and Berserkirs, come at last Alfred and Shakespeare.

I hear therefore with joy whatever is beginning to be said of the dignity and necessity of labor to every citizen. There is virtue yet in the hoe and the spade, for learned as well as for unlearned hands. And labor is everywhere welcome; always we are invited to work; only be this limitation observed, that a man shall not for the sake of wider activity sacrifice any opinion to the popular judgments and modes of action.
I have now spoken of the education of the scholar by nature, by books, and by action. It remains to say somewhat of his duties.
They are such as become Man Thinking. They may all be comprised in self-trust. The office of the scholar is to cheer, to raise, and to guide men by showing them facts amidst appearances. He plies the slow, unhonored, and unpaid task of observation. Flamsteed and Herschel, in their glazed observatories, may catalogue the stars with the praise of all men, and, the results being splendid and useful, honor is sure. But he, in his private observatory, cataloguing obscure and nebulous stars of the human mind, which as yet no man has thought of as such, — watching days and months, sometimes, for a few facts; correcting still his old records; — must relinquish display and immediate fame. In the long period of his preparation, he must betray often an ignorance and shiftlessness in popular arts, incurring the disdain of the able who shoulder him aside. Long he must stammer in his speech; often forego the living for the dead. Worse yet, he must accept, — how often! poverty and solitude. For the ease and pleasure of treading the old road, accepting the fashions, the education, the religion of society, he takes the cross of making his own, and, of course, the self-accusation, the faint heart, the frequent uncertainty and loss of time, which are the nettles and tangling vines in the way of the self-relying and self-directed; and the state of virtual hostility in which he seems to stand to society, and especially to educated society. For all this loss and scorn, what offset? He is to find consolation in exercising the highest functions of human nature. He is one, who raises himself from private considerations, and breathes and lives on public and illustrious thoughts. He is the world's eye. He is the world's heart. He is to resist the vulgar prosperity that retrogrades ever to barbarism, by preserving and communicating heroic sentiments, noble biographies, melodious verse, and the conclusions of history. Whatsoever oracles the human heart, in all emergencies, in all solemn hours, has uttered as its commentary on the world of actions, — these he shall receive and impart. And whatsoever new verdict Reason from her inviolable seat pronounces on the passing men and events of to-day, — this he shall hear and promulgate.
These being his functions, it becomes him to feel all confidence in himself, and to defer never to the popular cry. He and he only knows the world. The world of any moment is the merest appearance. Some great decorum, some fetish of a government, some ephemeral trade, or war, or man, is cried up by half mankind and cried down by the other half, as if all depended on this particular up or down. The odds are that the whole question is not worth the poorest thought which the scholar has lost in listening to the controversy. Let him not quit his belief that a popgun is a popgun, though the ancient and honorable of the earth affirm it to be the crack of doom. In silence, in steadiness, in severe abstraction, let him hold by himself; add observation to observation, patient of neglect, patient of reproach; and bide his own time, — happy enough, if he can satisfy himself alone, that this day he has seen something truly. Success treads on every right step. For the instinct is sure, that prompts him to tell his brother what he thinks. He then learns, that in going down into the secrets of his own mind, he has descended into the secrets of all minds. He learns that he who has mastered any law in his private thoughts, is master to that extent of all men whose language he speaks, and of all into whose language his own can be translated. The poet , in utter solitude remembering his spontaneous thoughts and recording them, is found to have recorded that, which men in crowded cities find true for them also. The orator distrusts at first the fitness of his frank confessions, — his want of knowledge of the persons he addresses, — until he finds that he is the complement of his hearers; — that they drink his words because he fulfils for them their own nature; the deeper he dives into his privatest, secretest presentiment, to his wonder he finds, this is the most acceptable, most public, and universally true. The people delight in it; the better part of every man feels, This is my music; this is myself.
In self-trust, all the virtues are comprehended. Free should the scholar be, — free and brave. Free even to the definition of freedom, "without any hindrance that does not arise out of his own constitution." Brave; for fear is a thing, which a scholar by his very function puts behind him. Fear always springs from ignorance. It is a shame to him if his tranquillity, amid dangerous times, arise from the presumption, that, like children and women, his is a protected class; or if he seek a temporary peace by the diversion of his thoughts from politics or vexed questions, hiding his head like an ostrich in the flowering bushes, peeping into microscopes, and turning rhymes, as a boy whistles to keep his courage up. So is the danger a danger still; so is the fear worse. Manlike let him turn and face it. Let him look into its eye and search its nature, inspect its origin, — see the whelping of this lion, — which lies no great way back; he will then find in himself a perfect comprehension of its nature and extent; he will have made his hands meet on the other side, and can henceforth defy it, and pass on superior. The world is his, who can see through its pretension. What deafness, what stone-blind custom, what overgrown error you behold, is there only by sufferance, — by your sufferance. See it to be a lie, and you have already dealt it its mortal blow.
Yes, we are the cowed, — we the trustless. It is a mischievous notion that we are come late into nature; that the world was finished a long time ago. As the world was plastic and fluid in the hands of God, so it is ever to so much of his attributes as we bring to it. To ignorance and sin, it is flint. They adapt themselves to it as they may; but in proportion as a man has any thing in him divine, the firmament flows before him and takes his signet and form. Not he is great who can alter matter, but he who can alter my state of mind. They are the kings of the world who give the color of their present thought to all nature and all art, and persuade men by the cheerful serenity of their carrying the matter, that this thing which they do, is the apple which the ages have desired to pluck, now at last ripe, and inviting nations to the harvest. The great man makes the great thing. Wherever Macdonald sits, there is the head of the table. Linnaeus makes botany the most alluring of studies, and wins it from the farmer and the herb-woman; Davy, chemistry; and Cuvier, fossils. The day is always his, who works in it with serenity and great aims. The unstable estimates of men crowd to him whose mind is filled with a truth, as the heaped waves of the Atlantic follow the moon.
For this self-trust, the reason is deeper than can be fathomed, — darker than can be enlightened. I might not carry with me the feeling of my audience in stating my own belief. But I have already shown the ground of my hope, in adverting to the doctrine that man is one. I believe man has been wronged; he has wronged himself. He has almost lost the light, that can lead him back to his prerogatives. Men are become of no account. Men in history, men in the world of to-day are bugs, are spawn, and are called `the mass' and `the herd.' In a century, in a millennium, one or two men; that is to say, — one or two approximations to the right state of every man. All the rest behold in the hero or the poet their own green and crude being, — ripened; yes, and are content to be less, so that may attain to its full stature. What a testimony, — full of grandeur, full of pity, is borne to the demands of his own nature, by the poor clansman, the poor partisan, who rejoices in the glory of his chief. The poor and the low find some amends to their immense moral capacity, for their acquiescence in a political and social inferiority. They are content to be brushed like flies from the path of a great person, so that justice shall be done by him to that common nature which it is the dearest desire of all to see enlarged and glorified. They sun themselves in the great man's light, and feel it to be their own element. They cast the dignity of man from their downtrod selves upon the shoulders of a hero, and will perish to add one drop of blood to make that great heart beat, those giant sinews combat and conquer. He lives for us, and we live in him.
Men such as they are, very naturally seek money or power; and power because it is as good as money, — the "spoils," so called, "of office." And why not? for they aspire to the highest, and this, in their sleep-walking, they dream is highest. Wake them, and they shall quit the false good, and leap to the true, and leave governments to clerks and desks. This revolution is to be wrought by the gradual domestication of the idea of Culture. The main enterprise of the world for splendor, for extent, is the upbuilding of a man. Here are the materials strown along the ground. The private life of one man shall be a more illustrious monarchy, — more formidable to its enemy, more sweet and serene in its influence to its friend, than any kingdom in history. For a man, rightly viewed, comprehendeth the particular natures of all men. Each philosopher, each bard, each actor, has only done for me, as by a delegate, what one day I can do for myself. The books which once we valued more than the apple of the eye, we have quite exhausted. What is that but saying, that we have come up with the point of view which the universal mind took through the eyes of one scribe; we have been that man, and have passed on. First, one; then, another; we drain all cisterns, and, waxing greater by all these supplies, we crave a better and more abundant food. The man has never lived that can feed us ever. The human mind cannot be enshrined in a person, who shall set a barrier on any one side to this unbounded, unboundable empire. It is one central fire, which, flaming now out of the lips of Etna, lightens the capes of Sicily; and, now out of the throat of Vesuvius, illuminates the towers and vineyards of Naples. It is one light which beams out of a thousand stars. It is one soul which animates all men.
But I have dwelt perhaps tediously upon this abstraction of the Scholar. I ought not to delay longer to add what I have to say, of nearer reference to the time and to this country.

Historically, there is thought to be a difference in the ideas which predominate over successive epochs, and there are data for marking the genius of the Classic, of the Romantic, and now of the Reflective or Philosophical age. With the views I have intimated of the oneness or the identity of the mind through all individuals, I do not much dwell on these differences. In fact, I believe each individual passes through all three. The boy is a Greek; the youth, romantic; the adult, reflective. I deny not, however, that a revolution in the leading idea may be distinctly enough traced.
Our age is bewailed as the age of Introversion. Must that needs be evil? We, it seems, are critical; we are embarrassed with second thoughts; we cannot enjoy any thing for hankering to know whereof the pleasure consists; we are lined with eyes; we see with our feet; the time is infected with Hamlet's unhappiness, —
"Sicklied o'er with the pale cast of thought."
Is it so bad then? Sight is the last thing to be pitied. Would we be blind? Do we fear lest we should outsee nature and God, and drink truth dry? I look upon the discontent of the literary class, as a mere announcement of the fact, that they find themselves not in the state of mind of their fathers, and regret the coming state as untried; as a boy dreads the water before he has learned that he can swim. If there is any period one would desire to be born in, — is it not the age of Revolution; when the old and the new stand side by side, and admit of being compared; when the energies of all men are searched by fear and by hope; when the historic glories of the old, can be compensated by the rich possibilities of the new era? This time, like all times, is a very good one, if we but know what to do with it.
I read with joy some of the auspicious signs of the coming days, as they glimmer already through poetry and art, through philosophy and science, through church and state.
One of these signs is the fact, that the same movement which effected the elevation of what was called the lowest class in the state, assumed in literature a very marked and as benign an aspect. Instead of the sublime and beautiful; the near, the low, the common, was explored and poetized. That, which had been negligently trodden under foot by those who were harnessing and provisioning themselves for long journeys into far countries, is suddenly found to be richer than all foreign parts. The literature of the poor, the feelings of the child, the philosophy of the street, the meaning of household life, are the topics of the time. It is a great stride. It is a sign, — is it not? of new vigor, when the extremities are made active, when currents of warm life run into the hands and the feet. I ask not for the great, the remote, the romantic; what is doing in Italy or Arabia; what is Greek art, or Provencal minstrelsy; I embrace the common, I explore and sit at the feet of the familiar, the low. Give me insight into to-day, and you may have the antique and future worlds. What would we really know the meaning of? The meal in the firkin; the milk in the pan; the ballad in the street; the news of the boat; the glance of the eye; the form and the gait of the body; — show me the ultimate reason of these matters; show me the sublime presence of the highest spiritual cause lurking, as always it does lurk, in these suburbs and extremities of nature; let me see every trifle bristling with the polarity that ranges it instantly on an eternal law; and the shop, the plough, and the leger, referred to the like cause by which light undulates and poets sing; — and the world lies no longer a dull miscellany and lumber-room, but has form and order; there is no trifle; there is no puzzle; but one design unites and animates the farthest pinnacle and the lowest trench.
This idea has inspired the genius of Goldsmith, Burns, Cowper, and, in a newer time, of Goethe , Wordsworth, and Carlyle. This idea they have differently followed and with various success. In contrast with their writing, the style of Pope, of Johnson, of Gibbon, looks cold and pedantic. This writing is blood-warm. Man is surprised to find that things near are not less beautiful and wondrous than things remote. The near explains the far. The drop is a small ocean. A man is related to all nature. This perception of the worth of the vulgar is fruitful in discoveries. Goethe, in this very thing the most modern of the moderns, has shown us, as none ever did, the genius of the ancients.
There is one man of genius, who has done much for this philosophy of life, whose literary value has never yet been rightly estimated; — I mean Emanuel Swedenborg . The most imaginative of men, yet writing with the precision of a mathematician, he endeavored to engraft a purely philosophical Ethics on the popular Christianity of his time. Such an attempt, of course, must have difficulty, which no genius could surmount. But he saw and showed the connection between nature and the affections of the soul. He pierced the emblematic or spiritual character of the visible, audible, tangible world. Especially did his shade-loving muse hover over and interpret the lower parts of nature; he showed the mysterious bond that allies moral evil to the foul material forms, and has given in epical parables a theory of isanity, of beasts, of unclean and fearful things.
Another sign of our times, also marked by an analogous political movement, is, the new importance given to the single person. Every thing that tends to insulate the individual, — to surround him with barriers of natural respect, so that each man shall feel the world is his, and man shall treat with man as a sovereign state with a sovereign state; — tends to true union as well as greatness. "I learned," said the melancholy Pestalozzi, "that no man in God's wide earth is either willing or able to help any other man." Help must come from the bosom alone. The scholar is that man who must take up into himself all the ability of the time, all the contributions of the past, all the hopes of the future. He must be an university of knowledges. If there be one lesson more than another, which should pierce his ear, it is, The world is nothing, the man is all; in yourself is the law of all nature, and you know not yet how a globule of sap ascends; in yourself slumbers the whole of Reason; it is for you to know all, it is for you to dare all. Mr. President and Gentlemen, this confidence in the unsearched might of man belongs, by all motives, by all prophecy, by all preparation, to the American Scholar. We have listened too long to the courtly muses of Europe. The spirit of the American freeman is already suspected to be timid, imitative, tame. Public and private avarice make the air we breathe thick and fat. The scholar is decent, indolent, complaisant. See already the tragic consequence . The mind of this country, taught to aim at low objects, eats upon itself. There is no work for any but the decorous and the complaisant. Young men of the fairest promise, who begin life upon our shores, inflated by the mountain winds, shined upon by all the stars of God, find the earth below not in unison with these, — but are hindered from action by the disgust which the principles on which business is managed inspire, and turn drudges, or die of disgust, — some of them suicides. What is the remedy? They did not yet see, and thousands of young men as hopeful now crowding to the barriers for the career, do not yet see, that, if the single man plant himself indomitably on his instincts, and there abide, the huge world will come round to him. Patience, — patience; — with the shades of all the good and great for company; and for solace, the perspective of your own infinite life; and for work, the study and the communication of principles, the making those instincts prevalent, the conversion of the world. Is it not the chief disgrace in the world, not to be an unit; — not to be reckoned one character; — not to yield that peculiar fruit which each man was created to bear, but to be reckoned in the gross, in the hundred, or the thousand, of the party, the section, to which we belong; and our opinion predicted geographically, as the north, or the south? Not so, brothers and friends, — please God, ours shall not be so. We will walk on our own feet; we will work with our own hands; we will speak our own minds. The study of letters shall be no longer a name for pity, for doubt, and for sensual indulgence. The dread of man and the love of man shall be a wall of defence and a wreath of joy around all. A nation of men will for the first time exist, because each believes himself inspired by the Divine Soul which also inspires all men.
What is The American Scholar by Ralph Waldo Emerson about?
"The American Scholar" is an essay by Ralph Waldo Emerson delivered as a lecture to the Phi Beta Kappa Society at Harvard College in 1837. In the essay, Emerson calls for an American scholar who is independent and self-reliant and who can lead the country in a new direction. He argues that the traditional European model of scholarship is outdated and that the American scholar must develop his unique voice and perspective. He also stresses the importance of personal experience, intellectual curiosity, and creative imagination in shaping the American scholar. Emerson argues that the American scholar must embrace his individuality and be true to his intellectual and artistic instincts rather than merely following the conventional wisdom of his time. Through this essay, Emerson encourages the development of a distinct American culture and intellectual tradition and calls for a new generation of scholars who are unafraid to challenge the status quo.
What is the most important influence for The American Scholar, according to Emerson?
According to Ralph Waldo Emerson in "The American Scholar," the most important influence is nature. Emerson believed studying nature was crucial to developing a truly independent and self-reliant scholar. He saw nature as a source of spiritual and intellectual inspiration. He argued that the American scholar must be in close contact with the natural world to cultivate a sense of wonder and curiosity. He also believed that the American scholar should study the laws and patterns of nature to develop a deeper understanding of the universe and our place in it. By embracing nature as a source of knowledge and inspiration, Emerson believed that the American scholar could develop a unique and original perspective that would set him apart from the traditional European model of scholarship. Ultimately, for Emerson, nature was the foundation for developing an independent and self-reliant American scholar.

Ralph Waldo Emerson left the ministry to pursue a career in writing and public speaking. Emerson became one of America's best known and best-loved 19th-century figures. More About Emerson
Quick Links
Self-reliance.
- Address at Divinity College
- English Traits
- Representative Men
- The Conduct of Life
- Essays: First Series
- Essays: Second Series
- Nature: Addresses/Lectures
- Lectures / Biographies
- Letters and Social Aims
Early Emerson Poems
- Uncollected Prose
- Government of Children
Emerson Quotes
"Every man has his own courage, and is betrayed because he seeks in himself the courage of other persons." – Ralph Waldo Emerson
“Do not go where the path may lead, go instead where there is no path and leave a trail.” – Ralph Waldo Emerson
“The purpose of life is not to be happy. It is to be useful, to be honorable, to be compassionate, to have it make some difference that you have lived and lived well.” – Ralph Waldo Emerson
Emerson's Essays
Research the collective works of Ralph Waldo Emerson. Read More Essay
Emerson's most famous work that can truly change your life. Check it out
America's best known and best-loved poems. More Poems

The National Society Daughters of the American Revolution
- DAR’s Continuing Commitment to Equality
- National Headquarters
- DAR Publications
- DAR History
- DAR's 125th Anniversary
- Did you know?
- What is DAR
- Who Are DAR Members
- Member Interests
- Volunteer Projects
- How to Join
- Chapter Locator
- Membership Interest Form
- Million Members Celebration
- Media Center
- Marian Anderson
- Preservation Efforts
- Historic Sites and Properties
- Honoring Our Patriots
- Inside This Issue
- Writers and Contributors
- Media and Advertising
- Our Patriots DAR Podcast
- Start With What You Know
- Speak With Relatives
- Start Looking Online
- Specialty Research
- Visit Libraries, Archives and Courthouses
- Work With A DAR Chapter
- Genealogical Research (GRS)
- Suggested Reading
- GRS for Educators
- Genie Clips
- Plan your Visit
- Hours of Operation
- Directions & Parking
- Education Resources
Essay Contests
- Youth Programs
- DAR Schools
- DAR Manual for Citizenship
- Constitution Week
- DAR Good Citizens
- Resources for Teachers
- Education Grant Program
- General Information
- Merit Scholarship
- Children and Step Children of DAR Members
- History, Economics, Government and Political Science
- Medical & Nursing
- Elementary and Secondary Teacher Education
- Specific Scholarships
- American Indians
- Scholarship FAQs
- Military Support & Service for Veterans
- Public Outreach
- Patriotic Awards
- DAR Historic Preservation Grants Poster
- Recipients and Photos
- Booking Process
- Event Rates
- Photography and Filming
- Schedule a Tour
- Job Openings
- Internships
- Equal Employment Opportunity Statement
- Employee Benefits
- Service to America
- America 250
- Celebrate 125!
- Who Is Margaret Cochran Corbin?
- Margaret Corbin Video
- Molly Pitcher Folklore
- 1926 DAR Efforts
- Discovery at West Point
- Margaret Corbin’s Legacy Lives On
- Margaret Corbin Rededication Ceremony
- DAR 2018 Search Efforts
- Resources and Further Reading
Member Resources
- Seating Map
- Visitor Services
- Technical Information
- FAQ - Constitution Hall
Upcoming Events
Trevor noah: off the record, mother's day celebration.
- Girl Scouts
- Calendar of Events
- Featured Objects
- Online Quilt Index
- Search the Collection
- Current Exhibition
- Upcoming Exhibition
- Past Exhibitions
- Period Room Tours
- Online Exhibitions
- Teacher Resources
- Portable Education Program
- Online Exhibits
- Docent Website
- Correspondent Docent Website
- Museum Shop
- Museum Shop Trunk Show
UnFinished Objects (UFO) Craft Circle
Kids make and take: sampler bookmarks, dar library.
- Mission Statement & Collection Development Policy
- Planning Your Visit
- Donation Info
- FAQ - Library
- DAR Lineage Resources
- Digital Resources
- Print Resources
- DAR Special Collections
- DAR Library Catalog
- How-To Guides
- Pathfinders
- Collection Finding Aids
- Forgotten Patriots
- E Pluribus Unum Educational Initiative
- Researching British-Occupied Areas
- Search Services
- Family History Library Affiliate
- Group Visits
- Programming
- Online Library Lectures
- Genealogical Research System (GRS)
- Ancestor Search
- Member Search
- Descendants Search
- Library Catalog
DAR Americana Collection and NSDAR Archives
- History of the Collections
- Americana Collection
- NSDAR Archives
- Searching the DAR Americana Collection and NSDAR Archives
- DAR Applications and Genealogy
- DAR Magazine
- Contact a DAR Chapter
- FAQ – Archives and History
Learn how DAR members selflessly and tirelessly dedicated themselves to the war relief effort of World War I

Giving to the DAR
- Guardian Trust Endowment
- President General's Project
- General Fund/Area of Greatest Need
- Special Gift Opportunities
- The Daughters Tribute
- Download My Donor History
- Donor Information At A Glance
- Matching Gifts
- Planned Giving
- Sustaining Supporter
- Current Campaign
- 1890 Annual Giving Circle
- The Founders Club
- The Heritage Club
- Donation Pins
- President General's Project Donor Wall
- Virtual Donor Recognition
- Wall of Honor
- Daughters Tribute Recognition Wall
- Gift Acceptance
- Membership Challenge
- President General's Benefactor

American History Essay Contest
The American History Essay Contest was established to encourage young people to think creatively about our nation's great history and learn about history in a new light.
This contest is open to students in public, private, and parochial schools, and registered home-study programs. Students in grades five through eight are encouraged to participate. Each year, a selected topic for use during the academic year is announced, and contest instructions are published online and sent to schools by participating DAR chapters. Essays are judged for historical accuracy, adherence to the topic, organization of materials, interest, originality, spelling, grammar, punctuation, and neatness.
Participating chapters send one winning essay from each of the four grades for judging on the state level. The state will send one winning essay from each of the four grades to be judged on a divisional level. The winning essay from each of the four grades will then be judged on the national level and the winners are announced.
Each student participant receives a certificate of participation from the chapter and the chapter winners receive bronze medals and certificates. State winners receive certificates and silver medals. National winners receive special certificates, medals, and a monetary award.
Click here for an informational PDF handout . For additional contest information or guidelines, please contact your local DAR chapter .
Patriots of the American Revolution High School Essay Contest
In preparation for the 250th anniversary of the nation’s founding, the DAR has launched the "Patriots of the American Revolution DAR High School Essay Contest.” This contest will focus on the men and women who figured in the events of the American Revolution (1773 – 1783), and it is hoped that students will find Patriots to write about who will interest and inspire them.
These Patriots may be one of our famous Founders, or an everyday man, woman, or child who supported the American Revolution in ways both large and small. Students will be asked to discuss how their chosen Patriot contributed to the founding of the nation. Essays will be judged for historical accuracy, organization of materials, interest, originality, spelling, grammar, punctuation, and the quality and scope of references, particularly the use of primary sources.
This contest is open to students in public, private, and parochial schools, and registered home-study programs, in grades 9 through 12. Essays from students from all grades will be judged together, with one winning essay chosen at each level. Participating DAR Chapters will select one essay as the chapter winner, to be sent on to the State level; the State will select one essay winner to represent the state for judging at the Division level, and each Division level will also have one winner which will be sent on to the National contest. Each student participant receives a certificate of participation from the chapter and the chapter winners receive a bronze medal and certificate set. State winners receive a silver medal and certificate set. Division level winners receive certificates and a book. National winners receive special certificates, medals, and a monetary award.
The National Society will select first-, second- and third-place winners. The national winner will receive a National Winner Certificate, pin and monetary award, presented at NSDAR’s annual Continental Congress, and the winning essay may appear in official DAR communications. National second- and third-place winners will also receive a certificate and monetary award.
This essay contest is being launched to engage students during the 250 th anniversary of the American Revolution, and is designed to encourage students to think more about the many different people, known and unknown, who were a part of the American Revolution, and perhaps even see themselves in the figures they write about.
For additional contest information or guidelines, please contact your local DAR chapter .
Looking for a Scholarship?
DAR offers a wide range of scholarships for a variety of different disciplines. Learn more ...
Celebrate Constitution Week!
September 17-23 Learn More
Interested in Getting Involved?
DAR has Youth Programs in many local communities. Learn More...
Archives mega Menu Title
Forms & publications.

Learn more about the relationship between Marian Anderson and the DAR.
Library Mega Menu Title
Member resources mega menu title, museum mega menu title, shopping cart.
DAR members selflessly dedicated themselves to the war relief effort of World War I

- Department of State
American Foreign Service Association
- Publications
- AFSA Scholarships
- AFSA High School Essay Contest
- AFSA Resources for Students
- Education Supplement
- Foreign Affairs Internships and Other Foreign Service-Related Opportunities
- Educational Resources for Students and Teachers
- Foreign Service HS Clubs - Get Involved!
- Educational Partners
- Awards & Honors
National High School Essay Contest
You are here, in this section, applications have closed for the 2024 essay contest.

2024 Essay Contest Topic
This year, AFSA celebrates the 100th anniversary of the United States Foreign Service. Over the last century, our diplomats and development professionals have been involved in groundbreaking events in history – decisions on war and peace, supporting human rights and freedom, creating joint prosperity, reacting to natural disasters and pandemics and much more. As AFSA looks back on this century-long history, we invite you to join us in also looking ahead to the future. This year students are asked to explore how diplomats can continue to evolve their craft to meet the needs of an ever-changing world that brings fresh challenges and opportunities to the global community and America’s place in it.
Over the past 100 years the Foreign Service has faced a multitude of challenges such as world war, terrorism, nuclear proliferation, humanitarian disasters, global pandemics, and economic crises. In a 1,000-1,500-word essay please identify what you believe will be the biggest challenge to face the Foreign Service in the future. The essay will describe this challenge and clearly define how American diplomats can help mitigate it.
Successful essays will use past or current diplomatic efforts to support what you believe to be the best course of action to tackle this obstacle.
For more information on Essay Contest Rules and Guidance please visit this page . For additional resources and to view the 2024 Study Guide please visit this page .
AFSA Announces the Winner of the 2023 High School Essay Contest

The American Foreign Service Association’s national high school essay contest completed its twenty-third year with over 400 submissions from 44 states.
Three randomized rounds of judging produced this year’s winner, Justin Ahn, a junior from Deerfield Academy in Deerfield, Massachusetts. In his essay, “Mending Bridges: US-Vietnam Reconciliation from 1995 to Today,” Justin focuses on the successful reconciliation efforts by the Foreign Service in transforming US-Vietnam relations from post-war tension to close economic and strategic partnership.
Justin traveled to Washington in AUgust 2023, where he met with Secretary of State Antony Blinken. He also received a full tuition scholarship to an educational voyage with Semester at Sea.
Niccolo Duina was this year’s runner-up. He is a senior at Pulaski Academy in Little Rock, Arkansas. Niccolo attended the international diplomacy program of the National Student Leadership Conference in summer 2023.
There were eight honorable mentions:
- Santiago Castro-Luna – Chevy Chase, Maryland
- Dante Chittenden – Grimes, Iowa
- Merle Hezel – Denver, Colorado
- Adarsh Khullar – Villa Hills, Kentucky
- Nicholas Nall – Little Rock, Arkansas
- Ashwin Telang – West Windsor, New Jersey
- Himani Yarlagadda – Northville, Michigan
- Sophia Zhang – San Jose, California
Congratulations! We thank all students and teachers who took the time to research and become globally engaged citizens who care about diplomacy, development, and peacebuilding.
If you are not graduating this year, please consider submitting another essay for next year’s contest. The new prompt will be published in fall 2023.
PRIVACY POLICY:
AFSA collects your information for this contest and for AFSA partners. You may be signed up to receive updates or information from AFSA and our partners. You will receive confirmation from AFSA that your submission has been received and a notification if you are the winner or an honorable mention in June . You may also receive a message from our sponsor regarding their program offerings.
PLEASE NOTE:

Students whose parents are not in the Foreign Service are eligible to participate if they are in grades nine through twelve in any of the fifty states, the District of Columbia, the U.S. territories, or if they are U.S. citizens attending high school overseas. Students may be attending a public, private, or parochial school. Entries from home-schooled students are also accepted. Previous first-place winners and immediate relatives of directors or staff of AFSA, NLSC and Semester at Sea are not eligible to participate. Previous honorable mention recipients are eligible to enter. $2,500 to the writer of the winning essay, in addition to an all-expense paid trip to the nation’s capital from anywhere in the U.S. for the winner and his or her parents, and an all-expense paid educational voyage courtesy of Semester at Sea.
The winner's school also receives a donation of 10 copies of AFSA's Inside a U.S. Embassy: Diplomacy at Work

The Fund for American Diplomacy is AFSA's 501(c)(3) charitable organization that supports AFSA’s outreach goals. AFSA National High School Essay contest is AFSA’s main outreach initiative to high school students. We appreciate your willingness to contribute. Rest assured that your contribution will be put to good use. Donations to the FAD are fully tax deductible.
Contest Information
- Current & Past Winning Essays
- Rules and Guidelines
- Writer's Resources
- Writer's Checklist
- Description of the Foreign Service
- What Diplomats Do and Why It Matters
- Oral Histories and Country Readers
- Semester at Sea
- Educational Voyage Details
- National Student Leadership Conference


ALA Americanism Essay Contest: Stimulating students’ patriotism through writing

- Celebration
ALA Mission Statement
In the spirit of Service, Not Self, the mission of the American Legion Auxiliary is to support The American Legion and to honor the sacrifice of those who serve by enhancing the lives of our veterans, military, and their families, both at home and abroad. For God and Country, we advocate for veterans, educate our citizens, mentor youth, and promote patriotism, good citizenship, peace and security.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Copyright © 2024 American Legion Auxiliary
Creative local students win historical essay and video contests
RIDGEFIELD – Three high school students from Vancouver and Ridgefield displayed their creativity in winning first place in the Fort Vancouver Sons of The American Revolution Chapter’s 2024 Eagle Scout Essay, Knight Essay and youth video contests. Each contest challenged the high school students to research and write about or produce a video featuring a compelling person from the American Revolution. Each winner received a $100 award and certificate for their achievement at the local level and advanced to the state level for further competition.
Josephine Abbott, a Seton High School junior, wrote a descriptive essay about Cherokee Nation War Chief Dragging Canoe and his many efforts to lead his people during the American Revolution. Abbott’s entry in the SAR Arthur M. and Berdena King Eagle Scout Essay Contest earned a first-place finish at the local level. Abbott had a special connection to her essay subject as she is the eighth great-granddaughter of Chief Dragging Canoe. In addition to writing her essay, Abbott was required to prepare a four-generation family lineage chart and document her many accomplishments as an Eagle Scout.
Elizabeth Swift, a Ridgefield High School senior, also choose a Native American as the subject for her George S. and Stella M. Knight Essay Contest entry. Nicholas Cusick was a member of the Tuscarora tribe, which supported the American patriots’ cause during the Revolution. He served with French Marquis de Lafayette as an interpreter and guide, and for his service he was granted a pension after the war. Swift’s essay on Cusick also earned her second place at state this year and a $500 award.
Lincoln Swift, a sophomore at Ridgefield High School, used video to tell the story of Patrick Carr, an Irish immigrant and leather worker, who was one of the victims of the Boston Massacre. Swift choreographed Carr’s tragic story with the use of stick puppets. Swift’s three-minute video not only won accolades at the local level, it earned him first place in the Washington State SAR Society Youth Video Contest. Swift received a $1,000 award and certificate for first place.
“These three contests challenge high school students to research and document important events and people from the American Revolution,” said Fort Vancouver SAR Chapter President Paul Winter. “In fact, we have programs designed for students at the elementary school level up through high school. Each program encourages the students to be creative, have some fun, and, as in the case of our Eagle Scout this year, find personal connections to the struggle for independence.”
Related Stories
Oral History Offers a Model for How Schools Can Introduce Students to Complex Topics

- Share article
As historian David McCullough said, history is the study of who we are and why we are the way we are.
That’s why teachers in the Memphis-Shelby County public schools, as racially isolated now as they were when the U.S. Supreme Court outlawed school segregation, have launched a curriculum to introduce their students to the 13 children who helped integrate these Tennessee city schools in 1961.
Memphis-Shelby County teachers, researchers from the University of Memphis, and the local Memphis 13 Foundation worked with seven of the 10 surviving members of the Memphis 13—a group of Black 1st graders who peacefully enrolled in four all-white schools at the height of the civil rights era—to develop teacher training, lesson plans, and oral history activities for elementary students.

“Just going home and talking to grandparents or talking to the elders in their community was never going to be enough,” said Anna Falkner, an assistant professor at the University of Memphis and a co-developer of the curriculum, “because it wouldn’t provide [students] with the context that they needed in order to understand what happened and understand the ongoing effects of, for example, the way segregation looks today.”
The Memphis 13 project offers a model for how schools can introduce complex subjects to students, even in early grades, while also giving them opportunities to investigate social studies in their communities
“Really consider the context,” Falkner said. “What are the specifics that can help students understand their Southern context or the context wherever they are and what that means in relation to the larger experience. It’s not just focusing on that national narrative, not just sharing Brown v. Board , but really thinking about, what did this look like in my backyard? What did it look like for my family members or my community members?”
For example, teachers met with surviving members of the Memphis 13 to identify projects for students in 2nd and 5th grades, when Tennessee social studies standards cover civil rights issues. Sheila Malone, one of the students who first integrated into the district’s Bruce Elementary as a 1st grader, suggested that 5th graders record the experiences of others who had attended the district schools during desegregation.
“[Malone] wanted the students to go back home and share the story and have intergenerational conversations about the history of our schools,” said Gina Tillis, the director of curriculum and instruction for the Memphis 13 Foundation, who co-developed the Memphis curriculum. “One of the things that I’ve noticed with the members of Memphis 13 is, as they’re sharing their stories, they’re unpacking memories that have been silenced. … This is a really powerful space for students to reflect on their education, their parents’ and their elders’ education, and what we’re doing collectively to create a more inclusive and equitable school system.”
Second graders, for example, watch documentaries and review news accounts about the school desegregation decisions in Memphis and other cities, identifying ways children their age participated. In 5th grade , students review collected oral history interviews and collect their own, as well as analyze modern policies related to school integration. Tillis said the project plans to expand the curriculum to 8th and 11th grades in the future.
Building school integration history projects
Emerging technology has made it easier for educators to engage their students in active historical research, according to the Center for Public History and Digital Humanities at Cleveland State University in Ohio. The center, for example, has developed apps to help students record interviews and archive historical documents.
Efforts like those of the Memphis 13 helped integrate public schools in the decades following the landmark U.S. Supreme Court ruling in Brown v. Board of Education . However, these trends began to reverse in the 1990s and have worsened to this day, even as the overall public school population has grown more diverse. Studies find schools serving high populations of students of color continue to have on average fewer educational opportunities —including challenging courses, experienced teachers, and other resources—compared with schools serving mostly white students.
While the Memphis 13 are well known, Tillis stressed that schools can use community history to engage students regardless of where they are. “Everyone has a school desegregation story. Every district, every person ... and every district story is unique,” she said. “It’s, I think, one of the most powerful stories to share because it offers you this platform to really deconstruct what’s going on in our schools.”
Researchers recommended that schools interested in developing similar projects:
- Work with local historians and groups to identify social studies topics and events that had strong effects on the local community. This can include school district librarians or archivists, for example.
- Provide teachers with training in both the historical context and strategies and tools for documenting community history.
- Focus on topics that encourage students to make connections between history and current issues in their community.
“One of the lessons that we’re hoping to share with other school districts is just the power of listening to your community members who are historians, even if they don’t work for the local archive: the neighbor down the street who kept all the newspapers, the person who knew everybody in the neighborhood,” Falkner said. “Finding those community members and making a meaningful way for them to participate in the curriculum development is the most important piece.”
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

We travel a lot, and our son attends local classrooms along the way. We noticed primary schools in Europe let kids be kids.
- My husband and I homeschool our son, which allows us to travel.
- In addition to his homeschooling curriculum, he has attended schools in different countries.
- We've noticed differences — and similarities — between the schools he attended in Europe and the US.

My son has been homeschooled, essentially, his whole academic life. Because of this, we're able to travel multiple times each month without worrying about him missing school. I am a writer and my husband is a film and TV composer as well as an investor, which also makes this possible.
Not only can we take my son's work with us, but he has also been able to experience schooling in various countries by joining classrooms and homeschool groups throughout our travels. His curriculum is based in the United States, but integrating local schools helps him learn different languages, culture, and of course, make friends.
Because we have spent extended periods of time in Portugal, the Netherlands, and Italy, we have been able to experience how a few schools in these places approach education more intimately. While we've experienced some similarities across the schools he's attended, like classroom size and curriculum structure, we also noticed distinct differences in approach.
School was low-stress in the Netherlands
Where we lived in the Netherlands, children as young as four years old often happily walked themselves to school. The school my son attended in the Netherlands was run like a well-oiled machine, yet they still maintained a playful and innocent atmosphere.
The school administrators were strict about timeliness — I often witnessed that if students arrived even one minute late, they were considered late, with no exceptions. However, discipline for kids was simply a stern talking-to from teachers. Teachers told us that if children had issues with each other, they were expected to sort it amongst themselves, while the adults observed from a distance.
Friends who had kids at other schools in the Netherlands confirmed that this focus on independent conflict resolution with minimal adult intervention was common. Play was the central focus of the day for children until they were about seven years old. The primary focus during those early years was on children learning to coexist with one another rather than academics.
Learning to swim was also a significant focus in the early years in the Netherlands and considered more critical than learning to read by many locals we spoke with. Once compulsory, now only some schools integrate swim classes into the curriculum. Given the numerous canals everywhere, this emphasis is understandable.
Related stories
Children at my son's school spent a large portion of their day outdoors, regardless of the weather, which parents said was typical. The Dutch often say, "There is no such thing as bad weather, only bad clothing." At school, my son assisted in preparing daily vegan meals, and occasionally brought home crafts to do.
Friends who had older kids in the Netherlands told me that the homework increased once they hit middle school, where there was more of an emphasis on academics. I truly appreciated this low-stress setting we encountered during our son's primary school years.
We saw more emphasis on collaboration than individual performance in Portugal
In Portugal, there was an emphasis on projects that children completed together to enhance their collaboration skills, and praise was often based on the collaboration itself rather than individual performance.
We noticed that children rarely had packed schedules filled with extracurricular activities like in the US, and often stayed up very late at night with their families, based on our own observations and talking to Portuguese parents.
While I adored the genuinely "crunchy" vibe of the schools my son attended and the kindness of the teachers, I believed our son would benefit from more structure and consistency in his routine . So, for a time, we supplemented even more than our usual load of schoolwork at home to provide more academic consistency during his short stint at a Portuguese school and eventually transitioned to only homeschooling again and met with a homeschool group for field trips.
We noticed less encouragement of competition in Italy than in the US
At the school my son goes to in Italy , it was immediately evident that food and dining is treated as an important part of the school day. Students are given a proper dining experience with formal table settings. The primary schools get a full two-hour break in the middle of the day including lunch and free time, known as riposo , lending to a much longer school day overall.
Football (soccer) is also taken seriously, so most schools we visited have specialized schedules specifically for children who play and perhaps want to pursue it as a career. Participation in the arts, football, and music is encouraged, but football is by far the most popular activity at our school and in our region.
As for the emphasis on the curriculum, so far, it seems far less rigid than in the US. Cognitive and social skills appear to be the primary objectives, rather than a heavy focus on testing. There is almost no encouragement of competition that we witnessed, as collaboration seems to be the focus until middle school.
My son is not yet in middle school, but from what I've heard both in preliminary conversations with schools, open days, and from Facebook groups with other expat parents , it sounds like middle school takes a more rigorous academic approach across Europe. For example, some countries, like Italy, expect children to know their primary focus of study by the time they enter high school, and then are placed in a specialized school program geared towards that interest area. Middle school seems to help form this decision by focusing on more specific subjects like robotics, engineering and anatomy, as they are already expected to know how to work together.
The unifying theme we observed throughout the schools in Europe that our son has attended, regardless of the country, was to allow children to be children and let the serious learning come later. At almost all the schools my son attended or toured, more importance was placed on children's ability to coexist together, work on projects and tasks collaboratively, than on core subjects like math, science, and history in those early years.
Each country had something we cherished and something we had to learn to adjust to. Overall, compared to our group homeschooling experience in the US, I would say that the primary schools in the European cities we joined were far less stressful. The academics seemed to get prioritized more as the kids got older. This makes me really appreciate how the lower grades focused on collaboration and coexistence.
- Main content
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
The Most Important Thing I Teach My Students Isn’t on the Syllabus

By Frank Bruni
Mr. Bruni is a contributing Opinion writer and the author of the forthcoming book “The Age of Grievance,” from which this essay is adapted.
I warn my students. At the start of every semester, on the first day of every course, I confess to certain passions and quirks and tell them to be ready: I’m a stickler for correct grammar, spelling and the like, so if they don’t have it in them to care about and patrol for such errors, they probably won’t end up with the grade they’re after. I want to hear everyone’s voice — I tell them that, too — but I don’t want to hear anybody’s voice so often and so loudly that the other voices don’t have a chance.
And I’m going to repeat one phrase more often than any other: “It’s complicated.” They’ll become familiar with that. They may even become bored with it. I’ll sometimes say it when we’re discussing the roots and branches of a social ill, the motivations of public (and private) actors and a whole lot else, and that’s because I’m standing before them not as an ambassador of certainty or a font of unassailable verities but as an emissary of doubt. I want to give them intelligent questions, not final answers. I want to teach them how much they have to learn — and how much they will always have to learn.
I’d been on the faculty of Duke University and delivering that spiel for more than two years before I realized that each component of it was about the same quality: humility. The grammar-and-spelling bit was about surrendering to an established and easily understood way of doing things that eschewed wild individualism in favor of a common mode of communication. It showed respect for tradition, which is a force that binds us, a folding of the self into a greater whole. The voices bit — well, that’s obvious. It’s a reminder that we share the stages of our communities, our countries, our worlds, with many other actors and should conduct ourselves in a manner that recognizes this fact. And “it’s complicated” is a bulwark against arrogance, absolutism, purity, zeal.
I’d also been delivering that spiel for more than two years before I realized that humility is the antidote to grievance.
We live in an era defined and overwhelmed by grievance — by too many Americans’ obsession with how they’ve been wronged and their insistence on wallowing in ire. This anger reflects a pessimism that previous generations didn’t feel. The ascent of identity politics and the influence of social media, it turned out, were better at inflaming us than uniting us. They promote a self-obsession at odds with community, civility, comity and compromise. It’s a problem of humility.
The Jan. 6 insurrectionists were delusional, frenzied, savage. But above all, they were unhumble. They decided that they held the truth, no matter all the evidence to the contrary. They couldn’t accept that their preference for one presidential candidate over another could possibly put them in the minority — or perhaps a few of them just reasoned that if it did, then everybody else was too misguided to matter. They elevated how they viewed the world and what they wanted over tradition, institutional stability, law, order.
It’s no accident that they were acting in the service of Donald Trump, whose pitch to Americans from the very start was a strikingly — even shockingly — unhumble one. “I alone can fix it,” he proclaimed in his 2016 speech accepting the Republican Party’s nomination for president; and at his inauguration in January of the following year, the word “humbled,” which had been present in the first inaugural remarks of both Barack Obama and George W. Bush, was nowhere to be found. Nor were any of its variants. That whole sentiment and politesse were missing, as they had been during a campaign centered on his supposed omniscience.
There are now mini-Trumps aplenty in American politics, but anti-Trumps will be our salvation, and I say that not along partisan or ideological lines. I’m talking about character and how a society holds itself together. It does that with concern for the common good, with respect for the institutions and procedures that protect that and with political leaders who ideally embody those traits or at least promote them.
Those leaders exist. When Charlie Baker, a former Massachusetts governor, was enjoying enormous favor and lofty approval ratings as a Republican in a predominantly Democratic state, he was also stressing the importance of humility. He was fond of quoting Philippians 2:3, which he invoked as a lodestar for his administration. “Do nothing out of selfish ambition or vain conceit,” it says. “Rather, in humility value others above yourself.”
That’s great practical advice for anyone in government, where most meaningful success hinges on teamwork and significant progress requires consensus. Governing, as opposed to demagoguery, is about earning others’ trust and cooperation. Exhibiting a willingness to listen to and to hear them goes a long way toward that.
“Insight and knowledge come from curiosity and humility,” Mr. Baker wrote in a 2022 book, “Results,” coauthored with his chief of staff, Steve Kadish, a Democrat. “Snap judgments — about people or ideas — are fueled by arrogance and conceit. They create blind spots and missed opportunities. Good ideas and interesting ways to accomplish goals in public life exist all over the place if you have the will, the curiosity, and the humility to find them.”
Humble politicians don’t insist on one-size-fits-all answers when those aren’t necessary as a matter of basic rights and fundamental justice. Humble activists don’t either. The campaign for same-sex marriage — one of the most successful social movements of recent decades — showed that progress can be made not by shaming people, not by telling them how awful they are, but by suggesting how much better they could be. Marriage-equality advocates emphasized a brighter future that they wanted to create, not an ugly past that they wanted to litigate. They also wisely assured Americans that gay and lesbian people weren’t trying to explode a cherished institution and upend a system of values, but instead wanted in.
“I don’t want to disparage shouting and demands — everything has its place,” Evan Wolfson, the founder of the pivotal advocacy group Freedom to Marry, told me when we revisited the movement’s philosophy and tactics. At times, he acknowledged, champions of a cause “need to break the silence, we need to push, we need to force.”
“But I used to say, ‘Yes, there’s demanding, but there’s also asking,’” he recalled. “And one is not the enemy of the other. People don’t like being accused, people don’t like being condemned, people don’t like being alienated. It’s a matter of conversation and persuasion.”
That’s consistent with the message delivered by Loretta Ross, a longtime racial justice and human rights advocate, through her teaching, public speaking and writing. Troubled by the frequent targeting and pillorying of people on social media, she urged the practice of calling in rather than calling out those who’ve upset you. “Call-outs make people fearful of being targeted,” she wrote in a guest essay for Times Opinion . “People avoid meaningful conversations when hypervigilant perfectionists point out apparent mistakes, feeding the cannibalistic maw of the cancel culture.” Instead, she advised, engage them. If you believe they need enlightenment, try that route, “without the self-indulgence of drama,” she wrote.
She was preaching humility.
She was also recognizing other people’s right to disagree — to live differently, to talk differently. Pluralism is as much about that as it is about a multiracial, multifaith, multigender splendor. That doesn’t mean a surrender or even a compromise of principles; a person can hold on to those while practicing tolerance, which has been supplanted by grievance. Tolerance shares DNA with respect. It recognizes that other people have rights and inherent value even when we disagree vehemently with them.
We all carry wounds, and some of us carry wounds much graver than others. We confront obstacles, including unjust and senseless ones. We must tend to those wounds. We must push hard at those obstacles. But we mustn’t treat every wound, every obstacle, as some cosmic outrage or mortal danger. We mustn’t lose sight of the struggle, imperfection and randomness of life. We mustn’t overstate our vulnerability and exaggerate our due.
While grievance blows our concerns out of proportion, humility puts them in perspective. While grievance reduces the people with whom we disagree to caricature, humility acknowledges that they’re every bit as complex as we are — with as much of a stake in creating a more perfect union.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Frank Bruni is a professor of journalism and public policy at Duke University, the author of the book "The Age of Grievance" and a contributing Opinion writer. He writes a weekly email newsletter . Instagram Threads @ FrankBruni • Facebook
Home — Essay Samples — Geography & Travel — Travel and Tourism Industry — The History of Moscow City
The History of Moscow City
- Categories: Russia Travel and Tourism Industry
About this sample

Words: 614 |
Published: Feb 12, 2019
Words: 614 | Page: 1 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Geography & Travel

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
13 pages / 6011 words
1 pages / 657 words
4 pages / 2143 words
6 pages / 3010 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Travel and Tourism Industry
The ethics in the hospitality industry play a pivotal role in shaping the reputation and success of businesses within this sector. Ethics encompass the principles and values that guide behavior, decision-making, and interactions [...]
Traveling is an enriching experience that allows individuals to explore new cultures, meet people from different backgrounds, and broaden their perspectives. In the summer of 2019, I had the opportunity to embark on an amazing [...]
Travelling is a topic that has been debated for centuries, with some arguing that it is a waste of time and money, while others believe that it is an essential part of life. In this essay, I will argue that travelling is not [...]
Traveling has always been a significant part of my life. From a young age, I have been fortunate enough to explore different cultures, experience new traditions, and immerse myself in the beauty of our world. My passion for [...]
When planning a business trip all aspects and decisions rely heavily on the budget set by the company for the trip. Once Sandfords have confirmed the location careful consideration should be used to choose the travel method and [...]
Tourism is an action of worldwide imperativeness and importance as it is a major force in the economy (Cooper et al. 2008). Tourism has undeniably developed as one of the most significant economic and social phenomena of the [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
2018 Primetime Emmy & James Beard Award Winner
R&K Insider
Join our newsletter to get exclusives on where our correspondents travel, what they eat, where they stay. Free to sign up.
A History of Moscow in 13 Dishes
Featured city guides.
- Contributors : About the Site
Newgeography.com
- Urban Issues
- Small Cities
- Demographics
Moscow, like other international urban areas , is decentralizing, despite considerable barriers. The expansion will lead to even more decentralization, which is likely to lead to less time "stuck in traffic" and more comfortable lifestyles. Let's hope that Russia's urban development policies, along with its plans to restore population growth, will lead to higher household incomes and much improved economic performance.
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris and the author of “ War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life ”
Note 1: The 23 ward (ku) area of Tokyo is the geography of the former city of Tokyo, which was abolished in the 1940s. There is considerable confusion about the geography of Tokyo. For example, the 23 ward area is a part of the prefecture of Tokyo, which is also called the Tokyo Metropolis, which has led some analysts to think of it as the Tokyo metropolitan area (labor market area). In fact, the Tokyo metropolitan area, variously defined, includes, at a minimum the prefectures of Tokyo, Kanagawa, Chiba and Saitama with some municipalities in Gunma, Ibaraki and Tochigi. The metropolitan area contains nearly three times the population of the "Tokyo Metropolis."
Note 2: The expansion area (556 square miles or 1,440 square kilometers) has a current population of 250,000.
Note 3: Includes all residents in suburban districts with at least part of their population in the urban area.
Note 4: Urban area data not yet available.
Photo: St. Basil's Cathedral (all photos by author)
- Login to post comments
- Evolving Urban Form: Development Profiles of World Urban Areas
- Transportation
Comment viewing options
Road in city area.
The roads and ways of the city areas are very clumsy and many accidents are happening due to the short road. But you need to maintain the driving properly otherwise you may face accident. So now the government decided to expand the road which may put the positive effect on automobile sector. I think it is a helpful service for the society people. If you have a BMW car and you have faced any problem then better to repair it at BMW Repair Spring, TX for the best service.
Transit & transportation
Transit and transportation services are quite impressive in most of the urban cities; therefore people were getting better benefits from suitable transportation service. Urban cities like Moscow, Washington, New York and Tokyo; we have found high margin of transportation system that helps to build a better communication network in these cities. I hope through the help of modern transportation system we are able to bring revolutionary change in automobile industries; in this above article we have also found the same concepts to develop transportation system. Mercedes repair in Torrance
Moscow is bursting Noblesse
Moscow is bursting Noblesse at the seams. The core city covers more than 420 square miles (1,090 kilometers), and has a population of approximately 11.5 million people. With 27,300 residents per square mile (10,500 per square kilometer), Moscow is one percent more dense than the bleach anime watch city of New York, though Moscow covers 30 percent more land. The 23 ward area of Tokyo (see Note) is at least a third more dense, though Moscow's land area is at least half again as large as Tokyo. All three core areas rely
Belgravia Villas is a new
Belgravia Villas is a new and upcoming cluster housing located in the Ang Mo Kio area, nested right in the Ang Mo Kio landed area. It is within a short drive to Little India, Orchard and city area. With expected completion in mid 2016, it comprises of 118 units in total with 100 units of terrace and 18 units of Semi-D. belgravia villas
Russians seeing the light while Western elites are bickering?
What an extremely interesting analysis - well done, Wendell.
It is also extremely interesting that the Russian leadership is reasonably pragmatic about urban form, in contrast to the "planners" of the post-rational West.
An acquaintance recently sent me an article from "The New Yorker", re Moscow's traffic problems.
The article "abstract" is HERE (but access to the full article requires subscription)
http://www.newyorker.com/reporting/2010/08/02/100802fa_fact_gessen
One classic quote worth taking from it, is: "People will endure all manner of humiliation to keep driving".
I do find it odd that the "New Yorker" article author says nothing at all about the rail transit system Moscow had, on which everyone was obliged to travel, under Communism. It can't surely have vaporised into thin air?
Moscow is a classic illustration of just how outmoded rails are, and how important "automobility" is, when the auto supplants rails so rapidly than even when everybody did travel on rails up to a certain date, and the road network dates to that era, when nobody was allowed to own a car; an article written just 2 decades later does not even mention the rail transit system, other than to criticise the mayor for "failing to invest in a transit system".......!!!!!!!!
This is also a give-away of "The New Yorker's" inability to shake off the modern PC ideology on rails vs cars.
Subscribe to NG Articles
Get new posts by email:, connect with us:.

NewGeography.com is a joint venture of Joel Kotkin and Praxis Strategy Group
Featured Content

The Coming of Neo-Feudalism

Infinite Suburbia

Recent blog posts
- The Truth About Being Jewish and in College
- Feudal Future: The Impact of Third-Party Candidates in Tipping the Election Scale
- Multiple More Jobs Accessible by Automobile Than by Transit
- Large Majority of Minorities Live in Suburbs
- Feudal Future: Addressing the Housing Affordability Crisis & Protecting the Middle Class Dream
- Shift of Net Domestic Migration to Smaller MSAs and Outside CBSAs
- Feudal Future Podcast: Navigating the Global Politics That May Shape America's 2024 Elections
- YIMBY Can Populate Conference Halls (at Least)
- Feudal Future Podcast: Exploring the Impact of Catholic Schools on Underserved Communities
- Feudal Future Podcast: Exploring the Paradox of Peace and Economics in Taiwan-China Relations

Recent popular content
- Beyond the Two State Solution
- Sustaining Prosperity: A Long Term Vision for the New Orleans Region
- In One Chart: Achieving the Demographic Dividend
- XpressWest Las Vegas Train: Where are the Venture Capitalists?
- Planners Push Transit, But It's a Hard Sell in Western Cities
- The Future Of America's Working Class
- The Dispersing of Urbanism
- Race, Ancestry, and Genetic Composition of the U.S.
More from this author
- Largest World Cities: 2014
- Largest Cities in the World: 2016
- World Urban Areas Population and Density: A 2012 Update
- Largest 1,000 Cities on Earth: World Urban Areas: 2015 Edition
- The Evolving Urban Form: Rio de Janeiro
Recommended Books
Blogroll and partner sites.
- Burgh Diaspora
- Center for Economic Research and Forecasting
- China Urban Development Blog
- Chris Bradford - Austin Contrarian
- Houston Strategies
- LA Observed
- Multiplier Effect: Levy Economics Institute
- The Rural Blog
- The Urbanophile
- Request new password
- © 2024 New Geography
- CONTRIBUTORS :
- PRIVACY POLICY
- Stay up to date:


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The American education system is set up to create a clear division between the social classes. The quality of the education that children receive depends on whether they attend an elite school or urban schools. Elite schools are located in upper class neighborhoods. Students who attend elite schools receive high quality education.
Home-schooling is on the rise, private schools have gained students, and an unknown number have dropped out altogether; Los Angeles said up to 50,000 students were absent on the first day of class ...
The answer to solving the American education crisis is simple. We need to put education back in the hands of the teachers. The politicians and the government needs to step back and let the people ...
For inspiration, read Erin Aubrey Kaplan's op-ed essay, "School Choice Is the Enemy of Justice," which links a contemporary debate with the author's personal experience of school segregation.
Understanding the American Education System. Nov 7, 2021. The American education system offers a rich field of choices for international students. There is such an array of schools, programs and locations that the choices may overwhelm students, even those from the U.S. As you begin your school search, it's important to familiarize yourself ...
Learning Loss, AI and the Future of Education: Our 24 Most-Read Essays of 2023 - The 74. Learning Loss, AI and the Future of Education: Our 24 Most-Read Essays of 2023. From rethinking the American high school to the fiscal cliff, tutoring and special ed, what our most incisive opinion contributors had to say. By Bev Weintraub. December 7, 2023.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
US College Essay Tips for International Students. Published on September 21, 2021 by Kirsten Courault.Revised on December 8, 2023. Beyond your test scores and grades, the college essay is your opportunity to express your academic and personal character, writing skills, and ability to self-reflect.. You should use your unique culture and individual perspective to write a compelling essay with ...
1. Hook the readers with a relevant fact, quote, or question for the first sentence. An attention getter draws readers into your essay. Use a shocking statistic or a hypothetical question to get the reader thinking on your subject. Make sure not to use an attention getter unrelated to the topic of your essay.
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
2023 National High School Essay Contest. The American Foreign Service Association's national high school essay contest completed its twenty-third year with over 400 submissions from 44 states. Three randomized rounds of judging produced this year's winner, Justin Ahn, a junior from Deerfield Academy in Deerfield, Massachusetts.
American School The idea of the culture wars is introduced here, and these culture wars begin to illustrate just how our continued dependence on the dominant Protestant Anglo-American culture has formed and influenced America's schools throughout out history. The chapter also introduces the concepts of racism and democracy, and demonstrates how these two opposite ideals often live together in ...
How to Write the American University Essays 2023-2024. American University has one optional prompt for all applicants about why you want to attend AU. Additionally, the school has prompts for each of its special programs. There are three prompts for Honors Program applicants, two prompts for Global Scholars Program applicants, three prompts for ...
The following ideas work well for compare-contrast essays. ( Find 80+ compare-contrast essay topics for all ages here.) Public and private schools. Capitalism vs. communism. Monarchy or democracy. Dogs vs. cats as pets. WeAreTeachers. Paper books or e-books. Two political candidates in a current race.
American Films and School Life Essay. However, school life is the best time in human life. During this time, we experience physical development, emotions, friendships, relationships, and especially knowledge but I was beyond those expectations in school life. Sometimes we never really learn from the first mistake or the second or third.
Summary of The American Scholar by Ralph Waldo Emerson: "The American Scholar" is an essay by Ralph Waldo Emerson that was first delivered as a lecture in 1837. In this work, Emerson reflects on the role and responsibilities of the American scholar in society. He argues that the American scholar should strive to be independent, self-reliant ...
Patriots of the American Revolution High School Essay Contest. In preparation for the 250th anniversary of the nation's founding, the DAR has launched the "Patriots of the American Revolution DAR High School Essay Contest." This contest will focus on the men and women who figured in the events of the American Revolution (1773 - 1783), and ...
The Fund for American Diplomacy is AFSA's 501 (c) (3) charitable organization that supports AFSA's outreach goals. AFSA National High School Essay contest is AFSA's main outreach initiative to high school students. We appreciate your willingness to contribute. Rest assured that your contribution will be put to good use.
The Americanism Essay Contest instills in our youth patriotism in our country while allowing students to reflect on what freedom means to them. This contest serves the ALA's mission, creating a nation of citizens inspired to protect our liberties and respect our country's flag for future generations. The deadline for departments to submit ...
Josephine Abbott, a Seton High School junior, wrote a descriptive essay about Cherokee Nation War Chief Dragging Canoe and his many efforts to lead his people during the American Revolution.
Ahenewa El-Amin leads a conversation with students during her AP African American Studies class at Henry Clay High School in Lexington, Ky., on March 19, 2024. Jaclyn Borowski/Education Week
School was low-stress in the Netherlands. Where we lived in the Netherlands, children as young as four years old often happily walked themselves to school. The school my son attended in the ...
Mr. Bruni is a contributing Opinion writer and the author of the forthcoming book "The Age of Grievance," from which this essay is adapted. I warn my students. At the start of every semester ...
A new report has been published by the American Association of Colleges and Universities (AAC&U) on Mentored Undergraduate Research in Global Contexts, or MUR-GC. The publication, co-edited by Maureen Vandermaas-Peeler, details the integration of the high-impact practices of mentoring, undergraduate research, and global and intercultural learning.
The History of Moscow City. Moscow is the capital and largest city of Russia as well as the. It is also the 4th largest city in the world, and is the first in size among all European cities. Moscow was founded in 1147 by Yuri Dolgoruki, a prince of the region. The town lay on important land and water trade routes, and it grew and prospered.
1: Off-kilter genius at Delicatessen: Brain pâté with kefir butter and young radishes served mezze-style, and the caviar and tartare pizza. Head for Food City. You might think that calling Food City (Фуд Сити), an agriculture depot on the outskirts of Moscow, a "city" would be some kind of hyperbole. It is not.
The Evolving Urban Form: Moscow's Auto-Oriented Expansion. by Wendell Cox 02/21/2012. Moscow is bursting at the seams. The core city covers more than 420 square miles (1,090 kilometers), and has a population of approximately 11.5 million people. With 27,300 residents per square mile (10,500 per square kilometer), Moscow is one percent more ...
Walking tour around Moscow-City.Thanks for watching!MY GEAR THAT I USEMinimalist Handheld SetupiPhone 11 128GB https://amzn.to/3zfqbboMic for Street https://...