Dividing Decimals
How do we divide when there are decimal points involved?
Well, it is easier to divide by a whole number ... so multiply by 10 until it is!

Example: 15 divided by 0.2
When we multiply the 0.2 by 10 we get a whole number:
0.2 × 10 = 2
But we must also do it to the 15:
15 × 10 = 150
So 15 ÷ 0.2 has become 150 ÷ 2 ( both numbers are 10 times larger):
150 ÷ 2 = 75
And so the answer is:
15 ÷ 0.2 = 75
To divide decimal numbers:
Multiply the divisor by as many 10's as we need, until it is a whole number. Remember to multiply the dividend by the same number of 10's.
Multiplying by 10 is easy, we just shift one space over like this:
Example: Divide 6.4 by 0.4
Let us move one space for both :
6.4 0.4 is exactly the same as 64 4 as we did the move for both numbers .
Now we can calculate:
So the answer is:
6.4 0.4 = 16
Are there really 16 lots of 0.4 in 6.4 ? Let's see:
For harder questions we may need to use Long Division :
Example: Divide 0.539 by 0.11
First we need to make the move twice to make 0.11 into a whole number:
0.539 0.11 is exactly the same as 53.9 11
But what about 53.9? It still has a decimal point.
Well, we can ignore the decimal point in the dividend so long as we remember to put it back later .
First we do the calculation without the decimal point:
Now put the decimal point in the answer directly above the decimal point in the dividend:
The answer is 4.9
Another example:
Example: Divide 9.1 by 7
The divisor (7) is already a whole number, so no need for any moves.
Now, ignore the decimal point in the dividend and use Long Division:
Put the decimal point in the answer directly above the decimal point in the dividend:
The answer is 1.3
Have a look at these Decimal Division Animations for further help.
As a final check we can put our "common sense" hat on and think "is that the right size?", because we don't want to pay ten times too much for anything, nor do we want to get only one-tenth of what we need!
- Home |
- About |
- Contact Us |
- Privacy |
- Newsletter |
- Shop |
- 🔍 Search Site
- Easter Color By Number Sheets
- Printable Easter Dot to Dot
- Easter Worksheets for kids
- Kindergarten
- All Generated Sheets
- Place Value Generated Sheets
- Addition Generated Sheets
- Subtraction Generated Sheets
- Multiplication Generated Sheets
- Division Generated Sheets
- Money Generated Sheets
- Negative Numbers Generated Sheets
- Fraction Generated Sheets
- Place Value Zones
- Number Bonds
- Addition & Subtraction
- Times Tables
- Fraction & Percent Zones
- All Calculators
- Fraction Calculators
- Percent calculators
- Area & Volume Calculators
- Age Calculator
- Height Calculator
- Roman Numeral Calculator
- Coloring Pages
- Fun Math Sheets
- Math Puzzles
- Mental Math Sheets
- Online Times Tables
- Online Addition & Subtraction
- Math Grab Packs
- All Math Quizzes
- 1st Grade Quizzes
- 2nd Grade Quizzes
- 3rd Grade Quizzes
- 4th Grade Quizzes
- 5th Grade Quizzes
- 6th Grade Math Quizzes
- Place Value
- Rounding Numbers
- Comparing Numbers
- Number Lines
- Prime Numbers
- Negative Numbers
- Roman Numerals
- Subtraction
- Add & Subtract
- Multiplication
- Fraction Worksheets
- Learning Fractions
- Fraction Printables
- Percent Worksheets & Help
- All Geometry
- 2d Shapes Worksheets
- 3d Shapes Worksheets
- Shape Properties
- Geometry Cheat Sheets
- Printable Shapes
- Coordinates
- Measurement
- Math Conversion
- Statistics Worksheets
- Bar Graph Worksheets
- Venn Diagrams
- All Word Problems
- Finding all possibilities
- Logic Problems
- Ratio Word Problems
- All UK Maths Sheets
- Year 1 Maths Worksheets
- Year 2 Maths Worksheets
- Year 3 Maths Worksheets
- Year 4 Maths Worksheets
- Year 5 Maths Worksheets
- Year 6 Maths Worksheets
- All AU Maths Sheets
- Kindergarten Maths Australia
- Year 1 Maths Australia
- Year 2 Maths Australia
- Year 3 Maths Australia
- Year 4 Maths Australia
- Year 5 Maths Australia
- Meet the Sallies
- Certificates
Decimal Division Worksheets Related Facts to 1dp
Welcome to our Decimal Division Worksheets.
Here you will find our selection of division fact worksheets with decimals to 1dp.
The decimal problems on these pages are linked to the multiplication table and involve using related facts to work out division problems.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript.
Here are the instructions how to enable JavaScript in your web browser .
Decimal Division Worksheets
Using related facts with decimals to 1dp.
Here you will find a selection of Division sheets designed to help your child learn to use their Division facts up to 10x10 to answer related questions involving decimals to 1dp.
For example, if you know that 42 ÷ 6 = 7, then you should be able to use the fact to answer questions like 4.2 ÷ 6 = 0.7 or 42 ÷ 0.6 = 70.
The sheets are graded so that the related division facts start off easier, then get gradually harder.
The first sheet provides support to help kids grasp this concept.
Using these decimal division worksheets will help your child to:
- understand how division and multiplication are related;
- apply their division facts up to 10x10 to answer related questions involving decimals to 1dp.
These sheets are aimed at students working at 5th and 6th grade.
Multiplication & Division Sheets - Related Facts Decimals
The first two sheets involve using both multiplication and division facts to complete the missing equations.
They help to show the link between multiplication and division, and also that a fact sentence can be written in lots of different ways.
- Multiplication Division Related Facts to 1dp Sheet 1
- PDF version
- Multiplication Division Related Facts to 1dp Sheet 2
- Multiplication Division Related Facts to 1dp Sheet 3
Division Sheets - Related Facts Decimals
- Division Related Facts Decimals Sheet 1
- Division Related Facts Decimals Sheet 2
- Division Related Facts Decimals Sheet 3
- Division Related Facts Decimals Sheet 4
- Division Related Facts Decimals Sheet 5
Division Related Facts Walkthrough Video
This short video walkthrough shows several problems from our Division Related Facts Decimals Sheet 2 being solved and has been produced by the West Explains Best math channel.
If you would like some support in solving the problems on these sheets, please check out the video below!
Looking for some easier division sheets?
We also have some 4th Grade Division related facts worksheets.
This page focuses on working out division facts related to the multiplication table.
We also have long division worksheets both with and without remainders.
- Multiply and Divide by 10 100 (decimals)
- Divding by Multiples of 10 and 100 Worksheets
- 4th Grade Long Division Worksheets
More Recommended Math Worksheets
Take a look at some more of our worksheets similar to these.
More Fifth Grade Division Worksheets
Here you will find a range of Free Printable 5th Grade Division Worksheets.
The following worksheets involve using the 5th Grade Math skills of dividing, and solving division problems.
Using these sheets will help your child learn to:
- divide any whole number up to 10000 by a two digit number;
- express any division with a remainder in the form of a mixed number (a number with a fraction part).
- Long Division Worksheets (whole numbers)
- Long Division of Decimal Numbers
- Division Facts Worksheets (randomly generated)
Fifth Grade Fraction Worksheets
Here you will find a range of free printable 5th Grade Fraction Worksheets.
At 5th Grade level, children are introduced to adding and subtracting fractions with different denominators. They know and can use equivalent fractions, and can multiply a fraction by whole numbers, as well as adding mixed numbers.
Using these sheets will help your child to:
- add and subtract fractions and mixed numbers;
- understand how to multiply fractions by a whole number;
- understand how to multiply two fractions together, including mixed fractions;
- understand the relationship between fractions and division;
- know how to divide fractions and mixed fractions;
- convert decimals to fractions.
All the Math Worksheets in this section are informed by the Elementary Math Benchmarks for 5th Grade.
- Adding Subtracting Fractions Worksheets

- Convert Improper Fractions
- Multiplying Fractions Worksheets
- Multiplying Mixed Fractions
- How to Divide Fractions
- Dividing Fractions by Whole numbers
- How to Divide Mixed Numbers
- Free Printable Fraction Riddles (harder)
- Math Division Games
Here you will find a range of Free Printable Division Games to help kids learn their division facts.
Using these games will help your child to learn their division facts, and also to develop their memory and strategic thinking skills.
How to Print or Save these sheets 🖶
Need help with printing or saving? Follow these 3 steps to get your worksheets printed perfectly!
- How to Print support
Subscribe to Math Salamanders News
Sign up for our newsletter and get free math support delivered to your inbox each month. Free seasonal math grab pack included.

- Newsletter Signup
Return to 5th Grade Math Worksheets
Return to Division Worksheets
Return from Printable Division Sheets to Math Salamanders Homepage
Math-Salamanders.com
The Math Salamanders hope you enjoy using these free printable Math worksheets and all our other Math games and resources.
We welcome any comments about our site or worksheets on the Facebook comments box at the bottom of every page.
New! Comments
TOP OF PAGE
© 2010-2024 Math Salamanders Limited. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
Decimals Worksheets
Thanks for visiting the Decimals Worksheets page at Math-Drills.Com where we make a POINT of helping students learn. On this page, you will find Decimals worksheets on a variety of topics including comparing and sorting decimals, adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing decimals, and converting decimals to other number formats. To start, you will find the general use printables to be helpful in teaching the concepts of decimals and place value. More information on them is included just under the sub-title.
Further down the page, rounding, comparing and ordering decimals worksheets allow students to gain more comfort with decimals before they move on to performing operations with decimals. There are many operations with decimals worksheets throughout the page. It would be a really good idea for students to have a strong knowledge of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division before attempting these questions.
Most Popular Decimals Worksheets this Week

Grids and Charts Useful for Learning Decimals
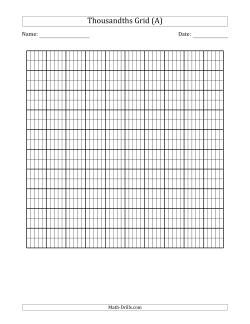
General use decimal printables are used in a variety of contexts and assist students in completing math questions related to decimals.
The thousandths grid is a useful tool in representing decimals. Each small rectangle represents a thousandth. Each square represents a hundredth. Each row or column represents a tenth. The entire grid represents one whole. The hundredths grid can be used to model percents or decimals. The decimal place value chart is a tool used with students who are first learning place value related to decimals or for those students who have difficulty with place value when working with decimals.
- Thousandths and Hundredths Grids Thousandths Grid Hundredths Grids ( 4 on a page) Hundredths Grids ( 9 on a page) Hundredths Grids ( 20 on a page)
- Decimal Place Value Charts Decimal Place Value Chart ( Ones to Hundredths ) Decimal Place Value Chart ( Ones to Thousandths ) Decimal Place Value Chart ( Hundreds to Hundredths ) Decimal Place Value Chart ( Thousands to Thousandths ) Decimal Place Value Chart ( Hundred Thousands to Thousandths ) Decimal Place Value Chart ( Hundred Millions to Millionths )
Decimals in Expanded Form

For students who have difficulty with expanded form, try familiarizing them with the decimal place value chart, and allow them to use it when converting standard form numbers to expanded form. There are actually five ways (two more than with integers) to write expanded form for decimals, and which one you use depends on your application or preference. Here is a quick summary of the various ways using the decimal number 1.23. 1. Expanded Form using decimals: 1 + 0.2 + 0.03 2. Expanded Form using fractions: 1 + 2 ⁄ 10 + 3 ⁄ 100 3. Expanded Factors Form using decimals: (1 × 1) + (2 × 0.1) + (3 × 0.01) 4. Expanded Factors Form using fractions: (1 × 1) + (2 × 1 ⁄ 10 ) + (3 × 1 ⁄ 100 ) 5. Expanded Exponential Form: (1 × 10 0 ) + (2 × 10 -1 ) + (3 × 10 -2 )
- Converting Decimals from Standard Form to Expanded Form Using Decimals Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Form Using Decimals ( 3 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Form Using Decimals ( 4 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Form Using Decimals ( 5 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Form Using Decimals ( 6 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Form Using Decimals ( 7 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Form Using Decimals ( 8 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Form Using Decimals ( 9 Decimal Places)
- Converting Decimals from Standard Form to Expanded Form Using Fractions Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Form Using Fractions ( 3 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Form Using Fractions ( 4 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Form Using Fractions ( 5 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Form Using Fractions ( 6 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Form Using Fractions ( 7 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Form Using Fractions ( 8 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Form Using Fractions ( 9 Decimal Places)
- Converting Decimals from Standard Form to Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals ( 3 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals ( 4 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals ( 5 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals ( 6 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals ( 7 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals ( 8 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals ( 9 Decimal Places)
- Converting Decimals from Standard Form to Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions ( 3 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions ( 4 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions ( 5 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions ( 6 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions ( 7 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions ( 8 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions ( 9 Decimal Places)
- Converting Decimals from Standard Form to Expanded Exponential Form Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Exponential Form ( 3 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Exponential Form ( 4 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Exponential Form ( 5 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Exponential Form ( 6 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Exponential Form ( 7 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Exponential Form ( 8 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Standard to Expanded Exponential Form ( 9 Decimal Places)
- Retro Converting Decimals from Standard Form to Expanded Form Retro Standard to Expanded Form (3 digits before decimal; 2 after) Retro Standard to Expanded Form (4 digits before decimal; 3 after) Retro Standard to Expanded Form (6 digits before decimal; 4 after) Retro Standard to Expanded Form (12 digits before decimal; 3 after)
- Retro European Format Converting Decimals from Standard Form to Expanded Form Standard to Expanded Form (3 digits before decimal; 2 after) Standard to Expanded Form (4 digits before decimal; 3 after) Standard to Expanded Form (6 digits before decimal; 4 after)
Of course, being able to convert numbers already in expanded form to standard form is also important. All five versions of decimal expanded form are included in these worksheets.
- Converting Decimals to Standard Form from Expanded Form Using Decimals Converting Decimals from Expanded Form Using Decimals to Standard Form ( 3 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Form Using Decimals to Standard Form ( 4 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Form Using Decimals to Standard Form ( 5 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Form Using Decimals to Standard Form ( 6 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Form Using Decimals to Standard Form ( 7 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Form Using Decimals to Standard Form ( 8 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Form Using Decimals to Standard Form ( 9 Decimal Places)
- Converting Decimals to Standard Form from Expanded Form Using Fractions Converting Decimals from Expanded Form Using Fractions to Standard Form ( 3 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Form Using Fractions to Standard Form ( 4 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Form Using Fractions to Standard Form ( 5 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Form Using Fractions to Standard Form ( 6 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Form Using Fractions to Standard Form ( 7 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Form Using Fractions to Standard Form ( 8 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Form Using Fractions to Standard Form ( 9 Decimal Places)
- Converting Decimals to Standard Form from Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals Converting Decimals from Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals to Standard Form ( 3 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals to Standard Form ( 4 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals to Standard Form ( 5 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals to Standard Form ( 6 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals to Standard Form ( 7 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals to Standard Form ( 8 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Factors Form Using Decimals to Standard Form ( 9 Decimal Places)
- Converting Decimals to Standard Form from Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions Converting Decimals from Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions to Standard Form ( 3 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions to Standard Form ( 4 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions to Standard Form ( 5 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions to Standard Form ( 6 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions to Standard Form ( 7 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions to Standard Form ( 8 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Factors Form Using Fractions to Standard Form ( 9 Decimal Places)
- Converting Decimals to Standard Form from Expanded Exponential Form Converting Decimals from Expanded Exponential Form to Standard Form ( 3 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Exponential Form to Standard Form ( 4 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Exponential Form to Standard Form ( 5 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Exponential Form to Standard Form ( 6 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Exponential Form to Standard Form ( 7 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Exponential Form to Standard Form ( 8 Decimal Places) Converting Decimals from Expanded Exponential Form to Standard Form ( 9 Decimal Places)
- Retro Converting Decimals to Standard Form from Expanded Form Retro Expanded to Standard Form (3 digits before decimal; 2 after) Retro Expanded to Standard Form (4 digits before decimal; 3 after) Retro Expanded to Standard Form (6 digits before decimal; 4 after) Retro Expanded to Standard Form (12 digits before decimal; 3 after)
- Retro European Format Converting Decimals to Standard Form from Expanded Form Retro European Format Expanded to Standard Form (3 digits before decimal; 2 after) Retro European Format Expanded to Standard Form (4 digits before decimal; 3 after) Retro European Format Expanded to Standard Form (6 digits before decimal; 4 after)

Rounding Decimals Worksheets
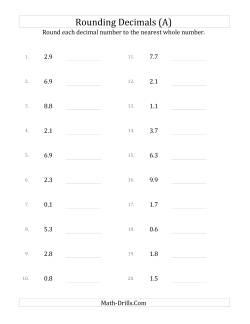
Rounding decimals is similar to rounding whole numbers; you have to know your place value! When learning about rounding, it is also useful to learn about truncating since it may help students to round properly. A simple strategy for rounding involves truncating, using the digits after the truncation to determine whether the new terminating digit remains the same or gets incremented, then taking action by incrementing if necessary and throwing away the rest. Here is a simple example: Round 4.567 to the nearest tenth. First, truncate the number after the tenths place 4.5|67. Next, look at the truncated part (67). Is it more than half way to 99 (i.e. 50 or more)? It is, so the decision will be to increment. Lastly, increment the tenths value by 1 to get 4.6. Of course, the situation gets a little more complicated if the terminating digit is a 9. In that case, some regrouping might be necessary. For example: Round 6.959 to the nearest tenth. Truncate: 6.9|59. Decide to increment since 59 is more than half way to 99. Incrementing results in the necessity to regroup the tenths into an extra one whole, so the result is 7.0. Watch that students do not write 6.10. You will want to correct them right away in that case. One last note: if there are three truncated digits then the question becomes is the number more than half way to 999. Likewise, for one digit; is the number more than half way to 9. And so on...
We should also mention that in some scientific and mathematical "circles," rounding is slightly different "on a 5". For example, most people would round up on a 5 such as: 6.5 --> 7; 3.555 --> 3.56; 0.60500 --> 0.61; etc. A different way to round on a 5, however, is to round to the nearest even number, so 5.5 would be rounded up to 6, but 8.5 would be rounded down to 8. The main reason for this is not to skew the results of a large number of rounding events. If you always round up on a 5, on average, you will have slightly higher results than you should. Because most pre-college students round up on a 5, that is what we have done in the worksheets that follow.
- Rounding Decimals to Whole Numbers Round Tenths to a Whole Number Round Hundredths to a Whole Number Round Thousandths to a Whole Number Round Ten Thousandths to a Whole Number Round Various Decimals to a Whole Number
- Rounding Decimals to Tenths Round Hundredths to Tenths Round Thousandths to Tenths Round Ten Thousandths to Tenths Round Various Decimals to Tenths
- Rounding Decimals to Hundredths Round Thousandths to Hundredths Round Ten Thousandths to Hundredths Round Various Decimals to Hundredths
- Rounding Decimals to Thousandths Round Ten Thousandths to Thousandths
- Rounding Decimals to Various Decimal Places Round Hundredths to Various Decimal Places Round Thousandths to Various Decimal Places Round Ten Thousandths to Various Decimal Places Round Various Decimals to Various Decimal Places
- European Format Rounding Decimals to Whole Numbers European Format Round Tenths to a Whole Number European Format Round Hundredths to a Whole Number European Format Round Thousandths to a Whole Number European Format Round Ten Thousandths to Whole Number
- European Format Rounding Decimals to Tenths European Format Round Hundredths to Tenths European Format Round Thousandths to Tenths European Format Round Ten Thousandths to Tenths
- European Format Rounding Decimals to Hundredths European Format Round Thousandths to Hundredths European Format Round Ten Thousandths to Hundredths
- European Format Rounding Decimals to Thousandths European Format Round Ten Thousandths to Thousandths
Comparing and Ordering/Sorting Decimals Worksheets.

The comparing decimals worksheets have students compare pairs of numbers and the ordering decimals worksheets have students compare a list of numbers by sorting them.
Students who have mastered comparing whole numbers should find comparing decimals to be fairly easy. The easiest strategy is to compare the numbers before the decimal (the whole number part) first and only compare the decimal parts if the whole number parts are equal. These sorts of questions allow teachers/parents to get a good idea of whether students have grasped the concept of decimals or not. For example, if a student thinks that 4.93 is greater than 8.7, then they might need a little more instruction in place value. Close numbers means that some care was taken to make the numbers look similar. For example, they could be close in value, e.g. 3.3. and 3.4 or one of the digits might be changed as in 5.86 and 6.86.
- Comparing Decimals up to Tenths Comparing Decimals up to Tenths ( Both Numbers Random ) Comparing Decimals up to Tenths ( One Digit Differs ) Comparing Decimals up to Tenths ( Both Numbers Close in Value ) Comparing Decimals up to Tenths ( Various Tricks )
- Comparing Decimals up to Hundredths Comparing Decimals up to Hundredths ( Both Numbers Random ) Comparing Decimals up to Hundredths ( One Digit Differs ) Comparing Decimals up to Hundredths ( Two Digits Swapped ) Comparing Decimals up to Hundredths ( Both Numbers Close in Value ) Comparing Decimals up to Hundredths ( One Number has an Extra Digit ) Comparing Decimals up to Hundredths ( Various Tricks )
- Comparing Decimals up to Thousandths Comparing Decimals up to Thousandths Comparing Decimals up to Thousandths ( One Digit Differs ) Comparing Decimals up to Thousandths ( Two Digits Swapped ) Comparing Decimals up to Thousandths ( Both Numbers Close in Value ) Comparing Decimals up to Thousandths ( One Number has an Extra Digit ) Comparing Decimals up to Thousandths ( Various Tricks )
- Comparing Decimals up to Ten Thousandths Comparing Decimals up to Ten Thousandths Comparing Decimals up to Ten Thousandths ( One Digit Differs ) Comparing Decimals up to Ten Thousandths ( Two Digits Swapped ) Comparing Decimals up to Ten Thousandths ( Both Numbers Close in Value ) Comparing Decimals up to Ten Thousandths ( One Number has an Extra Digit ) Comparing Decimals up to Ten Thousandths ( Various Tricks )
- Comparing Decimals up to Hundred Thousandths Comparing Decimals up to Hundred Thousandths Comparing Decimals up to Hundred Thousandths ( One Digit Differs ) Comparing Decimals up to Hundred Thousandths ( Two Digits Swapped ) Comparing Decimals up to Hundred Thousandths ( Both Numbers Close in Value ) Comparing Decimals up to Hundred Thousandths ( One Number has an Extra Digit ) Comparing Decimals up to Hundred Thousandths ( Various Tricks )
- European Format Comparing Decimals European Format Comparing Decimals up to Tenths European Format Comparing Decimals up to Tenths (tight) European Format Comparing Decimals up to Hundredths European Format Comparing Decimals up to Hundredths (tight) European Format Comparing Decimals up to Thousandths European Format Comparing Decimals up to Thousandths (tight)
Ordering decimals is very much like comparing decimals except there are more than two numbers. Generally, students determine the least (or greatest) decimal to start, cross it off the list then repeat the process to find the next lowest/greatest until they get to the last number. Checking the list at the end is always a good idea.
- Ordering/Sorting Decimals Ordering/Sorting Decimal Hundredths Ordering/Sorting Decimal Thousandths
- European Format Ordering/Sorting Decimals European Format Ordering/Sorting Decimal Tenths (8 per set) European Format Ordering/Sorting Decimal Hundredths (8 per set) European Format Ordering/Sorting Decimal Thousandths (8 per set) European Format Ordering/Sorting Decimal Ten Thousandths (8 per set) European Format Ordering/Sorting Decimals with Various Decimal Places(8 per set)
Converting Decimals to Fractions and Other Number Formats

There are many good reasons for converting decimals to other number formats. Dealing with a fraction in arithmetic is often easier than the equivalent decimal. Consider 0.333... which is equivalent to 1/3. Multiplying 300 by 0.333... is difficult, but multiplying 300 by 1/3 is super easy! Students should be familiar with some of the more common fraction/decimal conversions, so they can switch back and forth as needed.
- Converting Between Decimals and Fractions Converting Fractions to Terminating Decimals Converting Fractions to Terminating and Repeating Decimals Converting Terminating Decimals to Fractions Converting Terminating and Repeating Decimals to Fractions Converting Fractions to Hundredths
- Converting Between Decimals, Fraction, Percents and Ratios Converting Fractions to Decimals, Percents and Part-to-Part Ratios Converting Fractions to Decimals, Percents and Part-to-Whole Ratios Converting Decimals to Fractions, Percents and Part-to-Part Ratios Converting Decimals to Fractions, Percents and Part-to-Whole Ratios Converting Percents to Fractions, Decimals and Part-to-Part Ratios Converting Percents to Fractions, Decimals and Part-to-Whole Ratios Converting Part-to-Part Ratios to Fractions, Decimals and Percents Converting Part-to-Whole Ratios to Fractions, Decimals and Percents Converting Various Fractions, Decimals, Percents and Part-to-Part Ratios Converting Various Fractions, Decimals, Percents and Part-to-Whole Ratios Converting Various Fractions, Decimals, Percents and Part-to-Part Ratios with 7ths and 11ths Converting Various Fractions, Decimals, Percents and Part-to-Whole Ratios with 7ths and 11ths
Adding and Subtracting Decimals
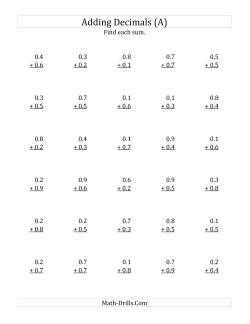
Try the following mental addition strategy for decimals. Begin by ignoring the decimals in the addition question. Add the numbers as if they were whole numbers. For example, 3.25 + 4.98 could be viewed as 325 + 498 = 823. Use an estimate to decide where to place the decimal. In the example, 3.25 + 4.98 is approximately 3 + 5 = 8, so the decimal in the sum must go between the 8 and the 2 (i.e. 8.23)
- Adding Tenths Adding Decimal Tenths with 0 Before the Decimal (range 0.1 to 0.9) Adding Decimal Tenths with 1 Digit Before the Decimal (range 1.1 to 9.9) Adding Decimal Tenths with 2 Digits Before the Decimal (range 10.1 to 99.9)
- Adding Hundredths Adding Decimal Hundredths with 0 Before the Decimal (range 0.01 to 0.99) Adding Decimal Hundredths with 1 Digit Before the Decimal (range 1.01 to 9.99) Adding Decimal Hundredths with 2 Digits Before the Decimal (range 10.01 to 99.99)
- Adding Thousandths Adding Decimal Thousandths with 0 Before the Decimal (range 0.001 to 0.999) Adding Decimal Thousandths with 1 Digit Before the Decimal (range 1.001 to 9.999) Adding Decimal Thousandths with 2 Digits Before the Decimal (range 10.001 to 99.999)
- Adding Ten Thousandths Adding Decimal Ten Thousandths with 0 Before the Decimal (range 0.0001 to 0.9999) Adding Decimal Ten Thousandths with 1 Digit Before the Decimal (range 1.0001 to 9.9999) Adding Decimal Ten Thousandths with 2 Digits Before the Decimal (range 10.0001 to 99.9999)
- Adding Various Decimal Places Adding Various Decimal Places with 0 Before the Decimal Adding Various Decimal Places with 1 Digit Before the Decimal Adding Various Decimal Places with 2 Digits Before the Decimal Adding Various Decimal Places with Various Numbers of Digits Before the Decimal
- European Format Adding Decimals European Format Adding decimal tenths with 0 before the decimal (range 0,1 to 0,9) European Format Adding decimal tenths with 1 digit before the decimal (range 1,1 to 9,9) European Format Adding decimal hundredths with 0 before the decimal (range 0,01 to 0,99) European Format Adding decimal hundredths with 1 digit before the decimal (range 1,01 to 9,99) European Format Adding decimal thousandths with 0 before the decimal (range 0,001 to 0,999) European Format Adding decimal thousandths with 1 digit before the decimal (range 1,001 to 9,999) European Format Adding decimal ten thousandths with 0 before the decimal (range 0,0001 to 0,9999) European Format Adding decimal ten thousandths with 1 digit before the decimal (range 1,0001 to 9,9999) European Format Adding mixed decimals with Various Decimal Places European Format Adding mixed decimals with Various Decimal Places (1 to 9 before decimal)
Base ten blocks can be used for decimal subtraction. Just redefine the blocks, so the big block is a one, the flat is a tenth, the rod is a hundredth and the little cube is a thousandth. Model and subtract decimals using base ten blocks, so students can "see" how decimals really work.
- Subtracting Tenths Subtracting Decimal Tenths with No Integer Part Subtracting Decimal Tenths with an Integer Part in the Minuend Subtracting Decimal Tenths with an Integer Part in the Minuend and Subtrahend
- Subtracting Hundredths Subtracting Decimal Hundredths with No Integer Part Subtracting Decimal Hundredths with an Integer Part in the Minuend and Subtrahend Subtracting Decimal Hundredths with a Larger Integer Part in the Minuend
- Subtracting Thousandths Subtracting Decimal Thousandths with No Integer Part Subtracting Decimal Thousandths with an Integer Part in the Minuend and Subtrahend
- Subtracting Ten Thousandths Subtracting Decimal Ten Thousandths with No Integer Part Subtracting Decimal Ten Thousandths with an Integer Part in the Minuend and Subtrahend
- Subtracting Various Decimal Places Subtracting Various Decimals to Hundredths Subtracting Various Decimals to Thousandths Subtracting Various Decimals to Ten Thousandths
- European Format Subtracting Decimals European Format Decimal subtraction (range 0,1 to 0,9) European Format Decimal subtraction (range 1,1 to 9,9) European Format Decimal subtraction (range 0,01 to 0,99) European Format Decimal subtraction (range 1,01 to 9,99) European Format Decimal subtraction (range 0,001 to 0,999) European Format Decimal subtraction (range 1,001 to 9,999) European Format Decimal subtraction (range 0,0001 to 0,9999) European Format Decimal subtraction (range 1,0001 to 9,9999) European Format Decimal subtraction with Various Decimal Places European Format Decimal subtraction with Various Decimal Places (1 to 9 before decimal)
Adding and subtracting decimals is fairly straightforward when all the decimals are lined up. With the questions arranged horizontally, students are challenged to understand place value as it relates to decimals. A wonderful strategy for placing the decimal is to use estimation. For example if the question is 49.2 + 20.1, the answer without the decimal is 693. Estimate by rounding 49.2 to 50 and 20.1 to 20. 50 + 20 = 70. The decimal in 693 must be placed between the 9 and the 3 as in 69.3 to make the number close to the estimate of 70.
The above strategy will go a long way in students understanding operations with decimals, but it is also important that they have a strong foundation in place value and a proficiency with efficient strategies to be completely successful with these questions. As with any math skill, it is not wise to present this to students until they have the necessary prerequisite skills and knowledge.
- Horizontally Arranged Adding Decimals Adding Decimals to Tenths Horizontally Adding Decimals to Hundredths Horizontally Adding Decimals to Thousandths Horizontally Adding Decimals to Ten Thousandths Horizontally Adding Decimals Horizontally With Up to Two Places Before and After the Decimal Adding Decimals Horizontally With Up to Three Places Before and After the Decimal Adding Decimals Horizontally With Up to Four Places Before and After the Decimal
- Horizontally Arranged Subtracting Decimals Subtracting Decimals to Tenths Horizontally Subtracting Decimals to Hundredths Horizontally Subtracting Decimals to Thousandths Horizontally Subtracting Decimals to Ten Thousandths Horizontally Subtracting Decimals Horizontally With Up to Two Places Before and After the Decimal Subtracting Decimals Horizontally With Up to Three Places Before and After the Decimal Subtracting Decimals Horizontally With Up to Four Places Before and After the Decimal
- Horizontally Arranged Mixed Adding and Subtracting Decimals Adding and Subtracting Decimals to Tenths Horizontally Adding and Subtracting Decimals to Hundredths Horizontally Adding and Subtracting Decimals to Thousandths Horizontally Adding and Subtracting Decimals to Ten Thousandths Horizontally Adding and Subtracting Decimals Horizontally With Up to Two Places Before and After the Decimal Adding and Subtracting Decimals Horizontally With Up to Three Places Before and After the Decimal Adding and Subtracting Decimals Horizontally With Up to Four Places Before and After the Decimal
Multiplying and Dividing Decimals

Multiplying decimals by whole numbers is very much like multiplying whole numbers except there is a decimal to deal with. Although students might initially have trouble with it, through the power of rounding and estimating, they can generally get it quite quickly. Many teachers will tell students to ignore the decimal and multiply the numbers just like they would whole numbers. This is a good strategy to use. Figuring out where the decimal goes at the end can be accomplished by counting how many decimal places were in the original question and giving the answer that many decimal places. To better understand this method, students can round the two factors and multiply in their head to get an estimate then place the decimal based on their estimate. For example, multiplying 9.84 × 91, students could first round the numbers to 10 and 91 (keep 91 since multiplying by 10 is easy) then get an estimate of 910. Actually multiplying (ignoring the decimal) gets you 89544. To get that number close to 910, the decimal needs to go between the 5 and the 4, thus 895.44. Note that there are two decimal places in the factors and two decimal places in the answer, but estimating made it more understandable rather than just a method.
- Multiplying Decimals by 1-Digit Whole Numbers Multiply 2-digit tenths by 1-digit whole numbers Multiply 2-digit hundredths by 1-digit whole numbers Multiply 2-digit thousandths by 1-digit whole numbers Multiply 3-digit tenths by 1-digit whole numbers Multiply 3-digit hundredths by 1-digit whole numbers Multiply 3-digit thousandths by 1-digit whole numbers Multiply various decimals by 1-digit whole numbers
- Multiplying Decimals by 2-Digit Whole Numbers Multiplying 2-digit tenths by 2-digit whole numbers Multiplying 2-digit hundredths by 2-digit whole numbers Multiplying 3-digit tenths by 2-digit whole numbers Multiplying 3-digit hundredths by 2-digit whole numbers Multiplying 3-digit thousandths by 2-digit whole numbers Multiplying various decimals by 2-digit whole numbers
- Multiplying Decimals by Tenths Multiplying 2-digit whole by 2-digit tenths Multiplying 2-digit tenths by 2-digit tenths Multiplying 2-digit hundredths by 2-digit tenths Multiplying 3-digit whole by 2-digit tenths Multiplying 3-digit tenths by 2-digit tenths Multiplying 3-digit hundredths by 2-digit tenths Multiplying 3-digit thousandths by 2-digit tenths Multiplying various decimals by 2-digit tenths
- Multiplying Decimals by Hundredths Multiplying 2-digit whole by 2-digit hundredths Multiplying 2-digit tenths by 2-digit hundredths Multiplying 2-digit hundredths by 2-digit hundredths Multiplying 3-digit whole by 2-digit hundredths Multiplying 3-digit tenths by 2-digit hundredths Multiplying 3-digit hundredths by 2-digit hundredths Multiplying 3-digit thousandths by 2-digit hundredths Multiplying various decimals by 2-digit hundredths
- Multiplying Decimals by Various Decimal Places Multiplying 2-digit by 2-digit numbers with various decimal places Multiplying 3-digit by 2-digit numbers with various decimal places
- Decimal Long Multiplication in Various Ranges Decimal Multiplication (range 0.1 to 0.9) Decimal Multiplication (range 1.1 to 9.9) Decimal Multiplication (range 10.1 to 99.9) Decimal Multiplication (range 0.01 to 0.99) Decimal Multiplication (range 1.01 to 9.99) Decimal Multiplication (range 10.01 to 99.99) Random # Digits Random # Places
- European Format Multiplying Decimals by 2-Digit Whole Numbers European Format 2-digit whole × 2-digit hundredths European Format 2-digit tenths × 2-digit whole European Format 2-digit hundredths × 2-digit whole European Format 3-digit tenths × 2-digit whole European Format 3-digit hundredths × 2-digit whole European Format 3-digit thousandths × 2-digit whole
- European Format Multiplying Decimals by 2-Digit Tenths European Format 2-digit whole × 2-digit tenths European Format 2-digit tenths × 2-digit tenths European Format 2-digit hundredths × 2-digit tenths European Format 3-digit whole × 2-digit tenths European Format 3-digit tenths × 2-digit tenths European Format 3-digit hundredths × 2-digit tenths European Format 3-digit thousandths × 2-digit tenths
- European Format Multiplying Decimals by 2-Digit Hundredths European Format 2-digit tenths × 2-digit hundredths European Format 2-digit hundredths × 2-digit hundredths European Format 3-digit whole × 2-digit hundredths European Format 3-digit tenths × 2-digit hundredths European Format 3-digit hundredths × 2-digit hundredths European Format 3-digit thousandths × 2-digit hundredths
- European Format Multiplying Decimals by Various Decimal Places European Format 2-digit × 2-digit with various decimal places European Format 3-digit × 2-digit with various decimal places
- Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Divide Tenths by a Whole Number Divide Hundredths by a Whole Number Divide Thousandths by a Whole Number Divide Ten Thousandths by a Whole Number Divide Various Decimals by a Whole Number
In case you aren't familiar with dividing with a decimal divisor, the general method for completing questions is by getting rid of the decimal in the divisor. This is done by multiplying the divisor and the dividend by the same amount, usually a power of ten such as 10, 100 or 1000. For example, if the division question is 5.32/5.6, you would multiply the divisor and dividend by 10 to get the equivalent division problem, 53.2/56. Completing this division will result in the exact same quotient as the original (try it on your calculator if you don't believe us). The main reason for completing decimal division in this way is to get the decimal in the correct location when using the U.S. long division algorithm.
A much simpler strategy, in our opinion, is to initially ignore the decimals all together and use estimation to place the decimal in the quotient. In the same example as above, you would complete 532/56 = 95. If you "flexibly" round the original, you will get about 5/5 which is about 1, so the decimal in 95 must be placed to make 95 close to 1. In this case, you would place it just before the 9 to get 0.95. Combining this strategy with the one above can also help a great deal with more difficult questions. For example, 4.584184 ÷ 0.461 can first be converted the to equivalent: 4584.184 ÷ 461 (you can estimate the quotient to be around 10). Complete the division question without decimals: 4584184 ÷ 461 = 9944 then place the decimal, so that 9944 is about 10. This results in 9.944.
Dividing decimal numbers doesn't have to be too difficult, especially with the worksheets below where the decimals work out nicely. To make these worksheets, we randomly generated a divisor and a quotient first, then multiplied them together to get the dividend. Of course, you will see the quotients only on the answer page, but generating questions in this way makes every decimal division problem work out nicely.
- Decimal Long Division with Quotients That Work Out Nicely Dividing Decimals by Various Decimals with Various Sizes of Quotients Dividing Decimals by 1-Digit Tenths (e.g. 0.72 ÷ 0.8 = 0.9) Dividing Decimals by 1-Digit Tenths with Larger Quotients (e.g. 3.2 ÷ 0.5 = 6.4) Dividing Decimals by 2-Digit Tenths (e.g. 10.75 ÷ 2.5 = 4.3) Dividing Decimals by 2-Digit Tenths with Larger Quotients (e.g. 387.75 ÷ 4.7 = 82.5) Dividing Decimals by 3-Digit Tenths (e.g. 1349.46 ÷ 23.8 = 56.7) Dividing Decimals by 2-Digit Hundredths (e.g. 0.4368 ÷ 0.56 = 0.78) Dividing Decimals by 2-Digit Hundredths with Larger Quotients (e.g. 1.7277 ÷ 0.39 = 4.43) Dividing Decimals by 3-Digit Hundredths (e.g. 31.4863 ÷ 4.61 = 6.83) Dividing Decimals by 4-Digit Hundredths (e.g. 7628.1285 ÷ 99.91 = 76.35) Dividing Decimals by 3-Digit Thousandths (e.g. 0.076504 ÷ 0.292 = 0.262) Dividing Decimals by 3-Digit Thousandths with Larger Quotients (e.g. 2.875669 ÷ 0.551 = 5.219)
These worksheets would probably be used for estimating and calculator work.
- Horizontally Arranged Decimal Division Random # Digits Random # Places
- European Format Dividing Decimals with Quotients That Work Out Nicely European Format Divide Tenths by a Whole Number European Format Divide Hundredths by a Whole Number European Format Divide Thousandths by a Whole Number European Format Divide Ten Thousandths by a Whole Number European Format Divide Various Decimals by a Whole Number
In the next set of questions, the quotient does not always work out well and may have repeating decimals. The answer key shows a rounded quotient in these cases.
- European Format Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers European Format Divide Tenths by a Whole Number European Format Divide Hundredths by a Whole Number European Format Divide Thousandths by a Whole Number European Format Divide Ten Thousandths by a Whole Number European Format Divide Various Decimals by a Whole Number
- European Format Dividing Decimals by Decimals European Format Decimal Tenth (0,1 to 9,9) Divided by Decimal Tenth (1,1 to 9,9) European Format Decimal Hundredth (0,01 to 9,99) Divided by Decimal Tenth (1,1 to 9,9) European Format Decimal Thousandth (0,001 to 9,999) Divided by Decimal Tenth (1,1 to 9,9) European Format Decimal Ten Thousandth (0,0001 to 9,9999) Divided by Decimal Tenth (1,1 to 9,9) European Format Various Decimal Places (0,1 to 9,9999) Divided by Decimal Tenth (1,1 to 9,9) European Format Various Decimal Places (0,1 to 9,9999) Divided by Various Decimal Places (1,1 to 9,9999)
Copyright © 2005-2024 Math-Drills.com You may use the math worksheets on this website according to our Terms of Use to help students learn math.
- Skills by Standard
- Skills by Grade
- Skills by Category
Go to profile
- Assignments
- Assessments
- Report Cards
- Our Teachers
Remove ads and gain access to the arcade and premium games!
Unlock harder levels by getting an average of 80% or higher.
Earn up to 5 stars for each level The more questions you answer correctly, the more stars you'll unlock!
Each game has 10 questions. Green box means correct. Yellow box means incorrect.
Need some help or instruction on how to do this skill?
Want a paper copy? Print a generated PDF for this skill.
Share MathGames with your students, and track their progress.
See how you scored compared to other students from around the world.
Learn Math Together.
Grade 7 - The Number System
Standard 7.NS.A.2c - Practice dividing decimals by whole numbers.
Included Skills:
Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide rational numbers.
If you notice any problems, please let us know .
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search
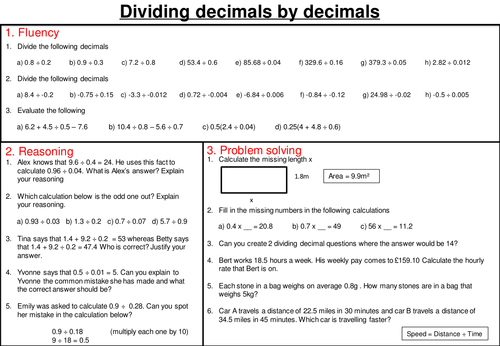
Dividing decimals - mastery worksheet
Subject: Mathematics
Age range: 11-14
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
24 September 2019
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest
Creative Commons "Sharealike"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Fantastic thought-provoking questions. Thank you for sharing.
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
tina_randle7
Differentiate tasks in dividing decimals, exactly what I wanted for my year 8. Thank you for sharing.
Moorerobs55
Fabulous worksheet - really well thought out. Thank you very much
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

Child Login
- Kindergarten
- Number charts
- Skip Counting
- Place Value
- Number Lines
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Word Problems
- Comparing Numbers
- Ordering Numbers
- Odd and Even
- Prime and Composite
- Roman Numerals
- Ordinal Numbers
- In and Out Boxes
- Number System Conversions
- More Number Sense Worksheets
- Size Comparison
- Measuring Length
- Metric Unit Conversion
- Customary Unit Conversion
- Temperature
- More Measurement Worksheets
- Writing Checks
- Profit and Loss
- Simple Interest
- Compound Interest
- Tally Marks
- Mean, Median, Mode, Range
- Mean Absolute Deviation
- Stem-and-leaf Plot
- Box-and-whisker Plot
- Permutation and Combination
- Probability
- Venn Diagram
- More Statistics Worksheets
- Shapes - 2D
- Shapes - 3D
- Lines, Rays and Line Segments
- Points, Lines and Planes
- Transformation
- Quadrilateral
- Ordered Pairs
- Midpoint Formula
- Distance Formula
- Parallel, Perpendicular and Intersecting Lines
- Scale Factor
- Surface Area
- Pythagorean Theorem
- More Geometry Worksheets
- Converting between Fractions and Decimals
- Significant Figures
- Convert between Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
- Proportions
- Direct and Inverse Variation
- Order of Operations
- Squaring Numbers
- Square Roots
- Scientific Notations
- Speed, Distance, and Time
- Absolute Value
- More Pre-Algebra Worksheets
- Translating Algebraic Phrases
- Evaluating Algebraic Expressions
- Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
- Algebraic Identities
- Quadratic Equations
- Systems of Equations
- Polynomials
- Inequalities
- Sequence and Series
- Complex Numbers
- More Algebra Worksheets
- Trigonometry
- Math Workbooks
- English Language Arts
- Summer Review Packets
- Social Studies
- Holidays and Events
- Worksheets >
- Pre-Algebra >
- Decimals >
Decimal Word Problem Worksheets
Extensive decimal word problems are presented in these sets of worksheets, which require the learner to perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division operations. This batch of printable decimal word problem worksheets is curated for students of grade 3 through grade 7. Free worksheets are included.

Adding Decimals Word Problems
Decimal word problems presented here help the children learn decimal addition based on money, measurement and other real-life units.
- Download the set

Subtracting Decimals Word Problems
These decimal word problem worksheets reinforce the real-life subtraction skills such as tender the exact change, compare the height, the difference between the quantities and more.

Decimals: Addition and Subtraction
It's review time for grade 4 and grade 5 students. Take these printable worksheets that help you reinforce the knowledge in adding and subtracting decimals. There are five word problems in each pdf worksheet.

Multiplying Decimals Whole Numbers
Reduce the chaos and improve clarity in your decimal multiplication skill using this collection of no-prep, printable worksheets. A must-have resource for young learners looking to ace their class!

Decimal Division Whole Numbers
Revive your decimal division skills with a host of interesting lifelike word problems involving whole numbers. Keep up with consistent practice and you’ll fly high in the topic in no time!

Multiplying Decimals Word Problems
Each decimal word problem involves multiplication of a whole number with a decimal number. 5th grade students are expected to find the product and check their answer using the answer key provided in the second page.

Dividing Decimals Word Problems
These division word problems require children to divide the decimals with the whole numbers. Ask the 6th graders to perform the division to find the quotient by applying long division method. Avoid calculator.

Decimals: Multiplication and Division
These decimal worksheets emphasize decimal multiplication and division. The perfect blend of word problems makes the grade 6 and grade 7 children stronger in performing the multiplication and division operation.
Related Worksheets
» Fraction Word Problems
» Ratio Word Problems
» Division Word Problems
Become a Member
Membership Information
Privacy Policy
What's New?
Printing Help
Testimonial
Copyright © 2024 - Math Worksheets 4 Kids
This is a members-only feature!


Or search by topic
Number and algebra
- The Number System and Place Value
- Calculations and Numerical Methods
- Fractions, Decimals, Percentages, Ratio and Proportion
- Properties of Numbers
- Patterns, Sequences and Structure
- Algebraic expressions, equations and formulae
- Coordinates, Functions and Graphs
Geometry and measure
- Angles, Polygons, and Geometrical Proof
- 3D Geometry, Shape and Space
- Measuring and calculating with units
- Transformations and constructions
- Pythagoras and Trigonometry
- Vectors and Matrices
Probability and statistics
- Handling, Processing and Representing Data
- Probability
Working mathematically
- Thinking mathematically
- Mathematical mindsets
- Cross-curricular contexts
- Physical and digital manipulatives
For younger learners
- Early Years Foundation Stage
Advanced mathematics
- Decision Mathematics and Combinatorics
- Advanced Probability and Statistics
Route Product
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
Which route or routes give the largest product?
Which route or routes give the smallest product?
Do you have any quick ways of working out the products each time?
[This problem is adapted from a SMILE Centre card. ]
Why do this problem?
Possible approach, key questions, possible extension, possible support.
Advertisement
Getting a Handle on Fraction-to-Decimal Conversions
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email
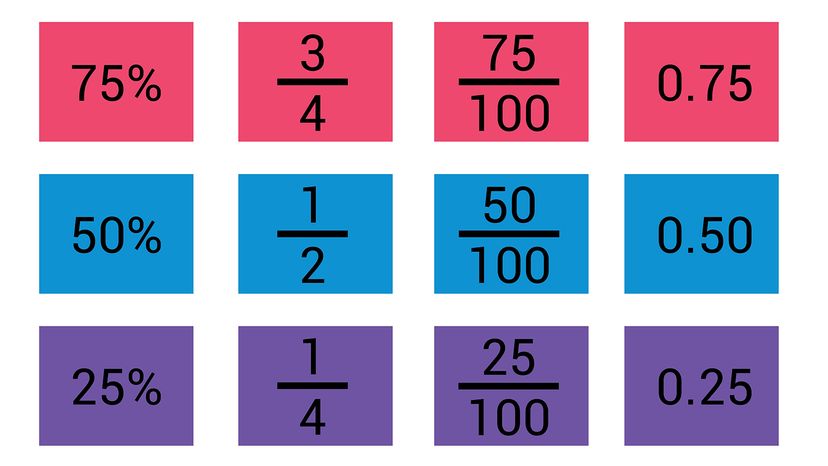
As you might recall from math class, fractions and decimals are two different ways of representing the same thing. A third option, percentages, is a close cousin of decimals. However, making use of this knowledge requires knowing how to convert one into the other.
Fraction to decimal conversion can be an opportunity to deepen your understanding of numbers and math. Sometimes the process will take more work, and sometimes less, but the operation is relatively straightforward.
What Are Fractions?
The case of improper fractions, what are decimals, going from fraction to decimal with a calculator, what is a repeating decimal, converting fractions to decimals using long division, how to convert a fraction to a percent, fraction-decimal conversion chart.
Fractions represent a division problem. If you look at the fraction 1/4, you can think of the line between the numbers (sometimes simply referred to as the "line," and sometimes as the "fraction bar") as a division sign.
That means that 1/4 is, in essence, saying "1 divided by 4."
That's all that fractions are. The top number, called the "numerator," is being divided by the bottom number, which is known as the "denominator." To calculate the decimal equivalent, you simply divide the numerator by the denominator, and you'll have your answer (which is 0.25, in this case).
If you're not a math maven, the sudden appearance of "improper" in the conversation might give you the heebie-jeebies. It may even trigger flashbacks of rational versus irrational numbers , as well as unpleasant memories of math exams.
Fear not! In this case, the phrase has a straightforward meaning: Whenever a fraction has a higher value numerator than denominator, you're looking at a so-called "improper fraction." This means that you're dealing with a number that is greater than 1.
This should make some intuitive sense, since the word "fraction" literally means "part of a whole." (In standard English, a "fraction" of something tends to connote a very small portion of that thing, but the essence is the same; it's a part, not the whole thing.)
Therefore, improper fractions are fractions that are more than a whole, such as 27/14 or 5/3.
A decimal is another way to represent a fraction — or, put differently, another way to write the part of a whole number. If we look back at the previous example of 1/4, we'll see that, if you divide 4 by 1, you'll get 0.25, which is the decimal equivalent of the fraction.
We haven't yet done the math problem that gives us the correct answer, but you're probably aware that 1/4, also known as a "quarter" or a "fourth," is 0.25. This is fairly easy to remember, since the coin we call the "quarter" has a value of 25 cents, and 4 of them together equal 1 dollar, or 100 cents.
You can also add them up:
Probably the easiest way to converting a fraction to decimal is to use a calculator. Chances are, you have a calculator app on your phone, and if you don't, you might still have a cheap calculator rattling around in a desk drawer.
Since you're now aware that a fraction is a straightforward division problem, once you've got your calculator at the ready, you can complete the necessary steps.
Let's start with 3/8. If you type "3 ÷ 8" into the calculator app, you'll get the decimal form: 0.375.
One nifty thing about calculators is their ability to handle some very big (or very small) numbers with ease. If you wanted to do the fraction to decimal conversion of 45/72, you would find your answer an instant.
Simply type 45 ÷ 72, and you'll get 0.625.
Not every fraction to decimal conversion yields a short string of numbers. Sometimes, you wind up with repeating decimals. Take the case of 2/3. If you type 2 ÷ 3 into your calculator, you'll get 0.66666666 and so on, for as many digits as your screen will allow.
This is a repeating decimal. Other fraction to decimal conversions that give you repeating digits are:
Here's the part that might require a refresher with grade-school mathematics. But don't stress: You'll find that once you get the basics of long division , you'll be every bit the decimal calculator that your phone now is. It will also require paper and a pencil, or anything to write with.
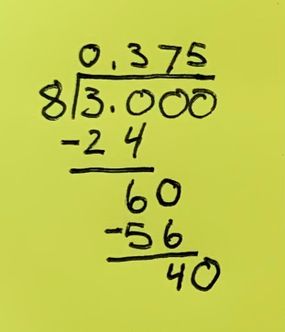
Let's dive into long division with a clear example. We'll use 3/8 to walk through this step-by-step process. Recall that 3/8 is equivalent to 3 ÷ 8.
- Set up the problem. Write the numerator (now called the dividend) 3 under the division bar and the divisor (formerly, the denominator) 8 outside the bar.
- Divide. But wait: 8 doesn't go into 3 evenly; 8 is a larger number than 3 (which is why we're getting fractions, not whole numbers, right?) .
- Add a 0. We get around this problem by adding a 0 after the 3. Now we're dealing with the more straightforward task of dividing 30 by 8.
- Divide again. How many times does 8 go into 30? Well, it goes in 3 times — not evenly (3 x 8 = 24), but that's okay. 24 is less than 30.
- Add a decimal. Put a decimal point before the 3 on top of the division bar. This is important, and it's what makes this fraction to decimal conversion work.
- Multiply. Multiplying the quotient (3) by the divisor (8) gives us an answer of 24: (3 x 8 = 24). Write 24 under the 30.
- Subtract. Subtract 24 from 30 to get 6. Draw a line under the 24, subtract, and write 6 below the line.
- Add another zero to the dividend. Now, bring down the 0, to sit next to the 6, making 60.
- Repeat the steps. 8 goes into 60 seven times (8 x 7 = 56), so write 7 above the bar next to the 3. Subtract 56 from 60 to get 4. Now, follow the same process you used in steps 1 through 8 and bring down the next zero. This gives you 40.
- Keep going until you have no remainder. Luckily for us, in this example, you're already there once you've reached that 40. 8 goes into 40 a clean 5 times. Put that 5 next to the 7, and you'll have your answer: 0.375.
Now you can say you know how to convert fractions to decimals using long division!
Luckily, adding percentages to the mix doesn't make things significantly more complex. In fact, once you become sufficiently comfortable with the fraction to decimal process, you really have only one more step to take.
In a sense, the decimal equivalent of a fraction is already a percent. All you have to do to make it official is to move the decimal point two positions to the right.
If you take the above example of 3/8, we know that the answer is .375. By shifting the decimal point two places to the right, you get 37.5. Now all that's left to do is throw a percentage sign (%) after the number.
Here are some common conversions in a handy-dandy reference chart.
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Figure 03: How to Divide Decimals: First, identify whether or not the divisor is a whole number. Lets start with the first step: Step One: Identify the dividend and the divisor and determine whether or not the divisor is a whole number (if it is, move onto Step Three). In the case of 1.5 ÷ 2. 2 is the divisor.
How to Divide decimal numbers. Step 1) Write out the long division in standard form. Step 2) Start the long division problem exactly as if it were a non-decimal problems. Step 3) Put the decimal point into the quotient (answer line) exactly above where it is in the dividend. Step 4) Bring the next digit down.
15 × 10 = 150. So 15 ÷ 0.2 has become 150 ÷ 2 ( both numbers are 10 times larger): 150 ÷ 2 = 75. And so the answer is: 15 ÷ 0.2 = 75. The number we divide by is called the divisor. To divide decimal numbers: Multiply the divisor by as many 10's as we need, until it is a whole number. Remember to multiply the dividend by the same number of ...
Multiply and divide by powers of 10. Write fractions as decimals (denominators of 10 & 100) Dividing whole numbers like 56÷35 to get a decimal. Dividing decimals 1. Dividing decimals 2. Dividing decimals: hundredths. Math>. 6th grade (WNCP)>.
One way to divide a whole number by a decimal is to first ignore the decimal point, divide the whole numbers, and in the end go as many places to the right as there are places in the decimal. Going to the right makes sense, because (for positive numbers) dividing by a smaller number gives a larger answer. Example: let's do 6 divided by 0.03.
The following worksheets involve using the 5th Grade Math skills of dividing, and solving division problems. Using these sheets will help your child learn to: divide any whole number up to 10000 by a two digit number; express any division with a remainder in the form of a mixed number (a number with a fraction part).
Divide Decimals by Integers 1. James is trying to solve a puzzle in an escape room. He has found several keys with different division calculations on each one. He says, What could this number be? Investigate which combination of keys James could use in order to solve the puzzle. Explore different possible solutions. 2.
Next: Multiplying Decimals Textbook Exercise GCSE Revision Cards. 5-a-day Workbooks
IXL plans. Virginia state standards. Textbooks. Test prep. Awards. Improve your math knowledge with free questions in "Divide decimals by whole numbers: word problems" and thousands of other math skills.
Welcome to Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers with Mr. J! Need help with how to divide a decimal by a whole number? You're in the right place!Whether you're ...
Ace your decimal-division tests and amp up practice with our pdf dividing decimals worksheets! Students of grade 5, grade 6, and grade 7 who are keen to enhance their practice of dividing decimals in tenths and hundredths, dividing multi-digit decimals, dividing decimals by adding zeros, and solving decimal division word problems will make a beeline for these printable tools.
When dividing a decimal by a whole number we can use a variety of methods. If we wanted to divide 1.64 by 4, one method which works well is to think about the component parts that go to make up your decimal number 1.64. 1.64 is made up of one whole, 6 tenths and 4 hundredths. If we were to reorganise these parts a little bit, we can see that we ...
Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Video 93 on www.corbettmaths.com Question 1: Four friends share £6.52 equally. How much do they each receive? Question 2: James has 3.65m of rope into 5 pieces of equal length. How long is equal piece of rope? Question 3: The perimeter of a square is 53.3cm. Work out the length of equal side.
Resources are designed to reflect and respond to students who might have: slower processing, cognitive ability, sensory overload and difficulties with rigid or over flexible thinking. Can easily be used for KS2, KS3 or KS4 intervention groups. Creative Commons "Sharealike". A lesson on Dividing decimals by whole numbers using short division.
For example, if the division question is 5.32/5.6, you would multiply the divisor and dividend by 10 to get the equivalent division problem, 53.2/56. Completing this division will result in the exact same quotient as the original (try it on your calculator if you don't believe us). The main reason for completing decimal division in this way is ...
Unlock harder levels by getting an average of 80% or higher. Earn up to 5 stars for each level The more questions you answer correctly, the more stars you'll unlock! Each game has 10 questions. Green box means correct. Yellow box means incorrect. Unlock harder levels by getting an average of 80% or higher.
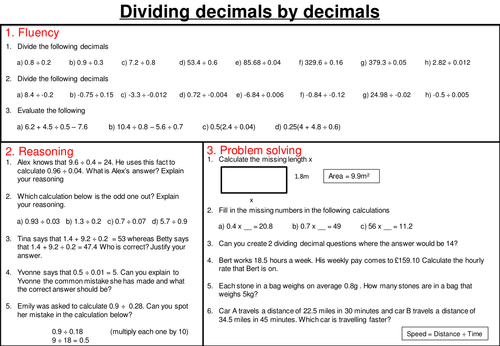
Dividing decimals - mastery worksheet. Subject: Mathematics. Age range: 11-14. Resource type: Worksheet/Activity. File previews. pptx, 89.37 KB. This is a mastery worksheet involving dividing 2 decimals. The worksheet is split into 3 sections, fluency, reasoning and problem solving so students can master the topic.
NRICH has several topics under the mathematical broad topic Fractions, decimals, percentages, ratio and proportion
Decimal Word Problem Worksheets. Extensive decimal word problems are presented in these sets of worksheets, which require the learner to perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division operations. This batch of printable decimal word problem worksheets is curated for students of grade 3 through grade 7. Free worksheets are included.
Parts of Division. For the division problem 471 divided by 32: 471 is the dividend; 32 is the divisor; 14.718 is the quotient calculated out to 3 decimal places; How to do Long Division with Decimals: Example. In this problem we divide 4.71 by 3.2 out to 3 decimal places in the quotient answer.
Multiplying decimals is perceived as a tricky task but this problem is written to encourage children to make the link between multiplying by a decimal and dividing by a whole number. This challenge also requires learners to work in a systematic way.
Reasoning and Problem Solving Multiply Decimals by Integers Reasoning and Problem Solving Multiply Decimals by Integers Developing 1a. 5.3 x 3 is the odd one out because this equals 15.9. The other calculations equal 13.6. 2a. 4.1 x 5 = 20.5. The cards 5.2, 21.5 and 4 are not needed. 3a. Mia has added the numbers instead of multiplying them.
As you might recall from math class, fractions and decimals are two different ways of representing the same thing. A third option, percentages, is a close cousin of decimals. ... Fractions represent a division problem. If you look at the fraction 1/4, you can think of the line between the numbers (sometimes simply referred to as the "line," and ...
Please be aware that the PowerPoint in this resource should be viewed in Slide Show mode in order to access the content. This well-planned pack of lesson resources is perfect for developing mastery when multiplying decimals by integers. This pack builds a mastery approach by providing varied opportunities to develop fluency, reasoning and problem-solving across both the PowerPoint presentation ...