
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Key Points |
Abnormal fetal lie or presentation may occur due to fetal size, fetal anomalies, uterine structural abnormalities, multiple gestation, or other factors. Diagnosis is by examination or ultrasonography. Management is with physical maneuvers to reposition the fetus, operative vaginal delivery , or cesarean delivery .
Terms that describe the fetus in relation to the uterus, cervix, and maternal pelvis are
Fetal presentation: Fetal part that overlies the maternal pelvic inlet; vertex (cephalic), face, brow, breech, shoulder, funic (umbilical cord), or compound (more than one part, eg, shoulder and hand)
Fetal position: Relation of the presenting part to an anatomic axis; for transverse presentation, occiput anterior, occiput posterior, occiput transverse
Fetal lie: Relation of the fetus to the long axis of the uterus; longitudinal, oblique, or transverse
Normal fetal lie is longitudinal, normal presentation is vertex, and occiput anterior is the most common position.
Abnormal fetal lie, presentation, or position may occur with
Fetopelvic disproportion (fetus too large for the pelvic inlet)
Fetal congenital anomalies
Uterine structural abnormalities (eg, fibroids, synechiae)
Multiple gestation
Several common types of abnormal lie or presentation are discussed here.

Transverse lie
Fetal position is transverse, with the fetal long axis oblique or perpendicular rather than parallel to the maternal long axis. Transverse lie is often accompanied by shoulder presentation, which requires cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation
There are several types of breech presentation.
Frank breech: The fetal hips are flexed, and the knees extended (pike position).
Complete breech: The fetus seems to be sitting with hips and knees flexed.
Single or double footling presentation: One or both legs are completely extended and present before the buttocks.
Types of breech presentations
Breech presentation makes delivery difficult ,primarily because the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge. Having a poor dilating wedge can lead to incomplete cervical dilation, because the presenting part is narrower than the head that follows. The head, which is the part with the largest diameter, can then be trapped during delivery.
Additionally, the trapped fetal head can compress the umbilical cord if the fetal umbilicus is visible at the introitus, particularly in primiparas whose pelvic tissues have not been dilated by previous deliveries. Umbilical cord compression may cause fetal hypoxemia.

Predisposing factors for breech presentation include
Preterm labor
Uterine abnormalities
Fetal anomalies
If delivery is vaginal, breech presentation may increase risk of
Umbilical cord prolapse
Birth trauma
Perinatal death

Face or brow presentation
In face presentation, the head is hyperextended, and position is designated by the position of the chin (mentum). When the chin is posterior, the head is less likely to rotate and less likely to deliver vaginally, necessitating cesarean delivery.
Brow presentation usually converts spontaneously to vertex or face presentation.
Occiput posterior position
The most common abnormal position is occiput posterior.
The fetal neck is usually somewhat deflexed; thus, a larger diameter of the head must pass through the pelvis.
Progress may arrest in the second phase of labor. Operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
Position and Presentation of the Fetus
If a fetus is in the occiput posterior position, operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
In breech presentation, the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge, which can cause the head to be trapped during delivery, often compressing the umbilical cord.
For breech presentation, usually do cesarean delivery at 39 weeks or during labor, but external cephalic version is sometimes successful before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.

- Mammary Glands
- Fallopian Tubes
- Supporting Ligaments
- Reproductive System
- Gametogenesis
- Placental Development
- Maternal Adaptations
- Menstrual Cycle
- Antenatal Care
- Small for Gestational Age
- Large for Gestational Age
- RBC Isoimmunisation
- Prematurity
- Prolonged Pregnancy
- Multiple Pregnancy
- Miscarriage
- Recurrent Miscarriage
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
- Breech Presentation
- Abnormal lie, Malpresentation and Malposition
- Oligohydramnios
- Polyhydramnios
- Placenta Praevia
- Placental Abruption
- Pre-Eclampsia
- Gestational Diabetes
- Headaches in Pregnancy
- Haematological
- Obstetric Cholestasis
- Thyroid Disease in Pregnancy
- Epilepsy in Pregnancy
- Induction of Labour
- Operative Vaginal Delivery
- Prelabour Rupture of Membranes
- Caesarean Section
- Shoulder Dystocia
- Cord Prolapse
- Uterine Rupture
- Amniotic Fluid Embolism
- Primary PPH
- Secondary PPH
- Psychiatric Disease
- Postpartum Contraception
- Breastfeeding Problems
- Primary Dysmenorrhoea
- Amenorrhoea and Oligomenorrhoea
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
- Endometriosis
- Endometrial Cancer
- Adenomyosis
- Cervical Polyps
- Cervical Ectropion
- Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia + Cervical Screening
- Cervical Cancer
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Ovarian Cysts & Tumours
- Urinary Incontinence
- Genitourinary Prolapses
- Bartholin's Cyst
- Lichen Sclerosus
- Vulval Carcinoma
- Introduction to Infertility
- Female Factor Infertility
- Male Factor Infertility
- Female Genital Mutilation
- Barrier Contraception
- Combined Hormonal
- Progesterone Only Hormonal
- Intrauterine System & Device
- Emergency Contraception
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- Genital Warts
- Genital Herpes
- Trichomonas Vaginalis
- Bacterial Vaginosis
- Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
- Obstetric History
- Gynaecological History
- Sexual History
- Obstetric Examination
- Speculum Examination
- Bimanual Examination
- Amniocentesis
- Chorionic Villus Sampling
- Hysterectomy
- Endometrial Ablation
- Tension-Free Vaginal Tape
- Contraceptive Implant
- Fitting an IUS or IUD
Abnormal Fetal lie, Malpresentation and Malposition
Original Author(s): Anna Mcclune Last updated: 1st December 2018 Revisions: 12
- 1 Definitions
- 2 Risk Factors
- 3.2 Presentation
- 3.3 Position
- 4 Investigations
- 5.1 Abnormal Fetal Lie
- 5.2 Malpresentation
- 5.3 Malposition
The lie, presentation and position of a fetus are important during labour and delivery.
In this article, we will look at the risk factors, examination and management of abnormal fetal lie, malpresentation and malposition.
Definitions
- Longitudinal, transverse or oblique
- Cephalic vertex presentation is the most common and is considered the safest
- Other presentations include breech, shoulder, face and brow
- Usually the fetal head engages in the occipito-anterior position (the fetal occiput facing anteriorly) – this is ideal for birth
- Other positions include occipito-posterior and occipito-transverse.
Note: Breech presentation is the most common malpresentation, and is covered in detail here .
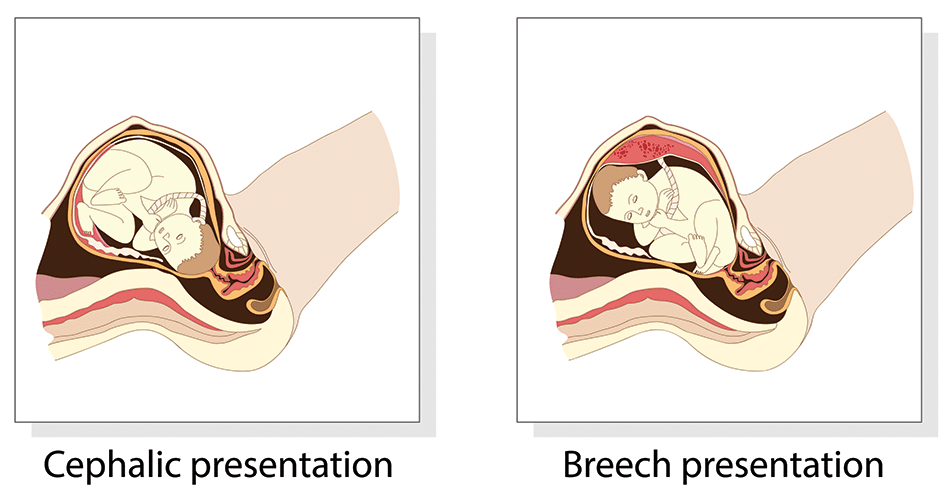
Fig 1 – The two most common fetal presentations: cephalic and breech.
Risk Factors
The risk factors for abnormal fetal lie, malpresentation and malposition include:
- Multiple pregnancy
- Uterine abnormalities (e.g fibroids, partial septate uterus)
- Fetal abnormalities
- Placenta praevia
- Primiparity
Identifying Fetal Lie, Presentation and Position
The fetal lie and presentation can usually be identified via abdominal examination. The fetal position is ascertained by vaginal examination.
For more information on the obstetric examination, see here .
- Face the patient’s head
- Place your hands on either side of the uterus and gently apply pressure; one side will feel fuller and firmer – this is the back, and fetal limbs may feel ‘knobbly’ on the opposite side
Presentation
- Palpate the lower uterus (above the symphysis pubis) with the fingers of both hands; the head feels hard and round (cephalic) and the bottom feels soft and triangular (breech)
- You may be able to gently push the fetal head from side to side
The fetal lie and presentation may not be possible to identify if the mother has a high BMI, if she has not emptied her bladder, if the fetus is small or if there is polyhydramnios .
During labour, vaginal examination is used to assess the position of the fetal head (in a cephalic vertex presentation). The landmarks of the fetal head, including the anterior and posterior fontanelles, indicate the position.
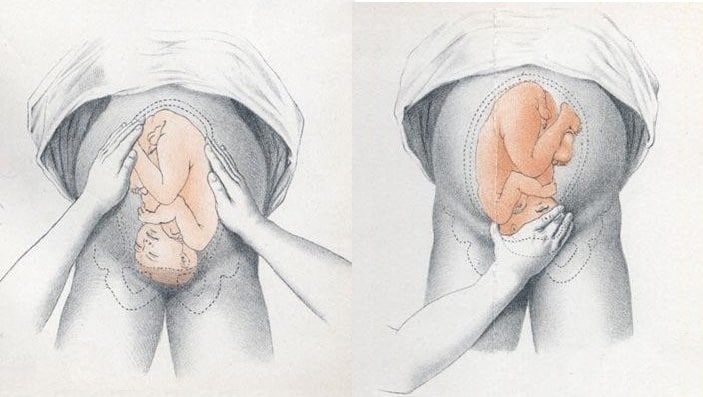
Fig 2 – Assessing fetal lie and presentation.
Investigations
Any suspected abnormal fetal lie or malpresentation should be confirmed by an ultrasound scan . This could also demonstrate predisposing uterine or fetal abnormalities.
Abnormal Fetal Lie
If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted – ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation.
ECV is the manipulation of the fetus to a cephalic presentation through the maternal abdomen.
It has an approximate success rate of 50% in primiparous women and 60% in multiparous women. Only 8% of breech presentations will spontaneously revert to cephalic in primiparous women over 36 weeks gestation.
Complications of ECV are rare but include fetal distress , premature rupture of membranes, antepartum haemorrhage (APH) and placental abruption. The risk of an emergency caesarean section (C-section) within 24 hours is around 1 in 200.
ECV is contraindicated in women with a recent APH, ruptured membranes, uterine abnormalities or a previous C-section .
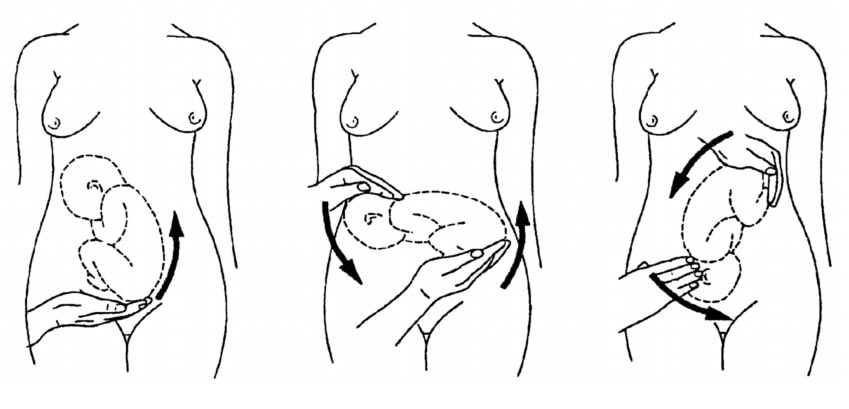
Fig 3 – External cephalic version.
Malpresentation
The management of malpresentation is dependent on the presentation.
- Breech – attempt ECV before labour, vaginal breech delivery or C-section
- Brow – a C-section is necessary
- If the chin is anterior (mento-anterior) a normal labour is possible; however, it is likely to be prolonged and there is an increased risk of a C-section being required
- If the chin is posterior (mento-posterior) then a C-section is necessary
- Shoulder – a C-section is necessary
Malposition
90% of malpositions spontaneously rotate to occipito-anterior as labour progresses. If the fetal head does not rotate, rotation and operative vaginal delivery can be attempted. Alternatively a C-section can be performed.
- Usually the fetal head engages in the occipito-anterior position (the fetal occiput facing anteriorly) - this is ideal for birth
If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted - ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation.
- Breech - attempt ECV before labour, vaginal breech delivery or C-section
Found an error? Is our article missing some key information? Make the changes yourself here!
Once you've finished editing, click 'Submit for Review', and your changes will be reviewed by our team before publishing on the site.
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising. To find out more, read our privacy policy .
Privacy Overview
- Getting Pregnant
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
- Birth Clubs
- See all in Community
- Ovulation Calculator
- How To Get Pregnant
- How To Get Pregnant Fast
- Ovulation Discharge
- Implantation Bleeding
- Ovulation Symptoms
- Pregnancy Symptoms
- Am I Pregnant?
- Pregnancy Tests
- See all in Getting Pregnant
- Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Week by Week
- Pregnant Sex
- Weight Gain Tracker
- Signs of Labor
- Morning Sickness
- COVID Vaccine and Pregnancy
- Fetal Weight Chart
- Fetal Development
- Pregnancy Discharge
- Find Out Baby Gender
- Chinese Gender Predictor
- See all in Pregnancy
- Baby Name Generator
- Top Baby Names 2023
- Top Baby Names 2024
- How to Pick a Baby Name
- Most Popular Baby Names
- Baby Names by Letter
- Gender Neutral Names
- Unique Boy Names
- Unique Girl Names
- Top baby names by year
- See all in Baby Names
- Baby Development
- Baby Feeding Guide
- Newborn Sleep
- When Babies Roll Over
- First-Year Baby Costs Calculator
- Postpartum Health
- Baby Poop Chart
- See all in Baby
- Average Weight & Height
- Autism Signs
- Child Growth Chart
- Night Terrors
- Moving from Crib to Bed
- Toddler Feeding Guide
- Potty Training
- Bathing and Grooming
- See all in Toddler
- Height Predictor
- Potty Training: Boys
- Potty training: Girls
- How Much Sleep? (Ages 3+)
- Ready for Preschool?
- Thumb-Sucking
- Gross Motor Skills
- Napping (Ages 2 to 3)
- See all in Child
- Photos: Rashes & Skin Conditions
- Symptom Checker
- Vaccine Scheduler
- Reducing a Fever
- Acetaminophen Dosage Chart
- Constipation in Babies
- Ear Infection Symptoms
- Head Lice 101
- See all in Health
- Second Pregnancy
- Daycare Costs
- Family Finance
- Stay-At-Home Parents
- Breastfeeding Positions
- See all in Family
- Baby Sleep Training
- Preparing For Baby
- My Custom Checklist
- My Registries
- Take the Quiz
- Best Baby Products
- Best Breast Pump
- Best Convertible Car Seat
- Best Infant Car Seat
- Best Baby Bottle
- Best Baby Monitor
- Best Stroller
- Best Diapers
- Best Baby Carrier
- Best Diaper Bag
- Best Highchair
- See all in Baby Products
- Why Pregnant Belly Feels Tight
- Early Signs of Twins
- Teas During Pregnancy
- Baby Head Circumference Chart
- How Many Months Pregnant Am I
- What is a Rainbow Baby
- Braxton Hicks Contractions
- HCG Levels By Week
- When to Take a Pregnancy Test
- Am I Pregnant
- Why is Poop Green
- Can Pregnant Women Eat Shrimp
- Insemination
- UTI During Pregnancy
- Vitamin D Drops
- Best Baby Forumla
- Postpartum Depression
- Low Progesterone During Pregnancy
- Baby Shower
- Baby Shower Games
Breech, posterior, transverse lie: What position is my baby in?

Fetal presentation, or how your baby is situated in your womb at birth, is determined by the body part that's positioned to come out first, and it can affect the way you deliver. At the time of delivery, 97 percent of babies are head-down (cephalic presentation). But there are several other possibilities, including feet or bottom first (breech) as well as sideways (transverse lie) and diagonal (oblique lie).
Fetal presentation and position
During the last trimester of your pregnancy, your provider will check your baby's presentation by feeling your belly to locate the head, bottom, and back. If it's unclear, your provider may do an ultrasound or an internal exam to feel what part of the baby is in your pelvis.
Fetal position refers to whether the baby is facing your spine (anterior position) or facing your belly (posterior position). Fetal position can change often: Your baby may be face up at the beginning of labor and face down at delivery.
Here are the many possibilities for fetal presentation and position in the womb.
Medical illustrations by Jonathan Dimes
Head down, facing down (anterior position)
A baby who is head down and facing your spine is in the anterior position. This is the most common fetal presentation and the easiest position for a vaginal delivery.
This position is also known as "occiput anterior" because the back of your baby's skull (occipital bone) is in the front (anterior) of your pelvis.
Head down, facing up (posterior position)
In the posterior position , your baby is head down and facing your belly. You may also hear it called "sunny-side up" because babies who stay in this position are born facing up. But many babies who are facing up during labor rotate to the easier face down (anterior) position before birth.
Posterior position is formally known as "occiput posterior" because the back of your baby's skull (occipital bone) is in the back (posterior) of your pelvis.
Frank breech
In the frank breech presentation, both the baby's legs are extended so that the feet are up near the face. This is the most common type of breech presentation. Breech babies are difficult to deliver vaginally, so most arrive by c-section .
Some providers will attempt to turn your baby manually to the head down position by applying pressure to your belly. This is called an external cephalic version , and it has a 58 percent success rate for turning breech babies. For more information, see our article on breech birth .
Complete breech
A complete breech is when your baby is bottom down with hips and knees bent in a tuck or cross-legged position. If your baby is in a complete breech, you may feel kicking in your lower abdomen.
Incomplete breech
In an incomplete breech, one of the baby's knees is bent so that the foot is tucked next to the bottom with the other leg extended, positioning that foot closer to the face.

Single footling breech
In the single footling breech presentation, one of the baby's feet is pointed toward your cervix.
Double footling breech
In the double footling breech presentation, both of the baby's feet are pointed toward your cervix.
Transverse lie
In a transverse lie, the baby is lying horizontally in your uterus and may be facing up toward your head or down toward your feet. Babies settle this way less than 1 percent of the time, but it happens more commonly if you're carrying multiples or deliver before your due date.
If your baby stays in a transverse lie until the end of your pregnancy, it can be dangerous for delivery. Your provider will likely schedule a c-section or attempt an external cephalic version , which is highly successful for turning babies in this position.
Oblique lie
In rare cases, your baby may lie diagonally in your uterus, with his rump facing the side of your body at an angle.
Like the transverse lie, this position is more common earlier in pregnancy, and it's likely your provider will intervene if your baby is still in the oblique lie at the end of your third trimester.
Was this article helpful?
What to know if your baby is breech

What's a sunny-side up baby?

What happens to your baby right after birth

How your twins’ fetal positions affect labor and delivery

BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies .
Ahmad A et al. 2014. Association of fetal position at onset of labor and mode of delivery: A prospective cohort study. Ultrasound in obstetrics & gynecology 43(2):176-182. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23929533 Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Gray CJ and Shanahan MM. 2019. Breech presentation. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448063/ Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Hankins GD. 1990. Transverse lie. American Journal of Perinatology 7(1):66-70. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2131781 Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Medline Plus. 2020. Your baby in the birth canal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002060.htm Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]

Where to go next

We have a new app!
Take the Access library with you wherever you go—easy access to books, videos, images, podcasts, personalized features, and more.
Download the Access App here: iOS and Android . Learn more here!
- Remote Access
- Save figures into PowerPoint
- Download tables as PDFs

CHAPTER 22: Normal Labor
- Download Chapter PDF
Disclaimer: These citations have been automatically generated based on the information we have and it may not be 100% accurate. Please consult the latest official manual style if you have any questions regarding the format accuracy.
Download citation file:
- Search Book
Jump to a Section
Fetal orientation.
- MECHANISMS OF LABOR
- NORMAL LABOR CHARACTERISTICS
- MANAGEMENT OF NORMAL LABOR
- LABOR MANAGEMENT PROTOCOLS
- Full Chapter
- Supplementary Content
Labor is the process that leads to childbirth. It begins with the onset of regular uterine contractions and ends with delivery of the newborn and expulsion of the placenta. Pregnancy and birth are physiological processes. Thus, labor and delivery should be considered normal for most women.
Fetal position within the birth canal is critical to labor progress and to the delivery route. It should be determined in early labor, and sonography can be implemented for unclear cases. Important relationships include fetal lie, presentation, attitude, and position.
Of these, fetal lie describes the relationship of the fetal long axis to that of the mother. In more than 99 percent of labors at term, the fetal lie is longitudinal . A transverse lie is less frequent. Occasionally, the fetal and maternal axes may cross at a 45-degree angle to form an oblique lie . This is unstable and becomes longitudinal or transverse during labor.
Fetal Presentation
The presenting part is the portion of the fetal body either within or in closest proximity to the birth canal. It usually can be felt through the cervix on vaginal examination. In longitudinal lies, the presenting part is either the fetal head or the breech, creating cephalic and breech presentations, respectively. When the fetus lies with the long axis transversely, the shoulder is considered the presenting part.
Cephalic presentations are subclassified according to the relationship between the head and body of the fetus ( Fig. 22-1 ). Ordinarily, the head is flexed sharply so that the chin contacts the thorax. The occipital fontanel is the presenting part, and this presentation is referred to as a vertex or occiput presentation . Much less often, the fetal neck may be sharply extended so that the occiput and back come into contact, and the face is foremost in the birth canal— face presentation . The fetal head may assume a position between these extremes. When the neck is only partly flexed, the anterior (large) fontanel may present— sinciput presentation . When the neck is only partially extended, the brow may emerge— brow presentation . These latter two are usually transient. As labor progresses, sinciput and brow presentations almost always convert into occiput or face presentations by neck flexion or extension, respectively. If not, dystocia can develop ( Chap. 23 , p. 441).
FIGURE 22-1
Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation. Differences in attitude of the fetal body in (A) occiput, (B) sinciput, (C) brow, and (D) face presentations. Note changes in fetal attitude as the fetal head becomes less flexed.

Pop-up div Successfully Displayed
This div only appears when the trigger link is hovered over. Otherwise it is hidden from view.
Please Wait

Cephalic presentation
October 14, 2016
A cephalic presentation or head presentation or head-first presentation is a situation at childbirth where the fetus is in a longitudinal lie and the head enters the pelvis first; the most common form of cephalic presentation is the vertex presentation where the occiput is the leading part (the part that first enters the birth canal). All other presentations are abnormal (malpresentations) which are either more difficult to deliver or not deliverable by natural means.
The movement of the fetus to cephalic presentation is called head engagement. It occurs in the third trimester. In head engagement, the fetal head descends into the pelvic cavity so that only a small part (or none) of it can be felt abdominally. The perineum and cervix are further flattened and the head may be felt vaginally. Head engagement is known colloquially as the baby drop, and in natural medicine as the lightening because of the release of pressure on the upper abdomen and renewed ease in breathing. However, it severely reduces bladder capacity, increases pressure on the pelvic floor and the rectum, and the mother may experience the perpetual sensation that the fetus will “fall out” at any moment.
The vertex is the area of the vault bounded anteriorly by the anterior fontanelle and the coronal suture, posteriorly by the posterior fontanelle and the lambdoid suture and laterally by 2 lines passing through the parietal eminences.
In the vertex presentation the occiput typically is anterior and thus in an optimal position to negotiate the pelvic curve by extending the head. In an occiput posterior position, labor becomes prolonged and more operative interventions are deemed necessary. The prevalence of the persistent occiput posterior is given as 4.7 %
The vertex presentations are further classified according to the position of the occiput, it being right, left, or transverse, and anterior or posterior:
Left Occipito-Anterior (LOA), Left Occipito-Posterior (LOP), Left Occipito-Transverse (LOT); Right Occipito-Anterior (ROA), Right Occipito-Posterior (ROP), Right Occipito-Transverse (ROT);
By Mikael Häggström – Own work, Public Domain
Cephalic presentation. (2016, September 17). In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia . Retrieved 05:18, September 17, 2016, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Cephalic_presentation&oldid=739815165
Insert/edit link
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content
- Find in topic
INTRODUCTION
● The curvature of the fetal spine is oriented downward (also called "back down" or dorsoinferior), and the fetal shoulder presents at the cervix ( figure 1 ).
● The curvature of the fetal spine is oriented upward (also called "back up" or dorsosuperior), and the fetal small parts and umbilical cord present at the cervix.
(Note: Lie refers to the long axis of the fetus relative to the longitudinal axis of the uterus; the long axis of the fetus can be transverse to, oblique to, or parallel to [longitudinal lie] the longitudinal axis of the uterus. Presentation refers to the fetal part that directly overlies the pelvic inlet; it is usually cephalic [head] or breech [buttocks] but can be a shoulder, compound [eg, head and hand], or funic [umbilical cord]. Position is the relationship of a nominated site of the presenting part to a denominating location on the maternal pelvis [eg, right occiput anterior].)
To continue reading this article, you must sign in . For more information or to purchase a personal subscription, click below on the option that best describes you:
- Medical Professional
- Resident, Fellow or Student
- Hospital or Institution
- Group Practice
- Patient or Caregiver
Print Options
- MSD careers
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Variations in Fetal Position and Presentation |
During pregnancy, the fetus can be positioned in many different ways inside the mother's uterus. The fetus may be head up or down or facing the mother's back or front. At first, the fetus can move around easily or shift position as the mother moves. Toward the end of the pregnancy the fetus is larger, has less room to move, and stays in one position. How the fetus is positioned has an important effect on delivery and, for certain positions, a cesarean delivery is necessary. There are medical terms that describe precisely how the fetus is positioned, and identifying the fetal position helps doctors to anticipate potential difficulties during labor and delivery.
Presentation refers to the part of the fetus’s body that leads the way out through the birth canal (called the presenting part). Usually, the head leads the way, but sometimes the buttocks (breech presentation), shoulder, or face leads the way.
Position refers to whether the fetus is facing backward (occiput anterior) or forward (occiput posterior). The occiput is a bone at the back of the baby's head. Therefore, facing backward is called occiput anterior (facing the mother’s back and facing down when the mother lies on her back). Facing forward is called occiput posterior (facing toward the mother's pubic bone and facing up when the mother lies on her back).
Lie refers to the angle of the fetus in relation to the mother and the uterus. Up-and-down (with the baby's spine parallel to mother's spine, called longitudinal) is normal, but sometimes the lie is sideways (transverse) or at an angle (oblique).
For these aspects of fetal positioning, the combination that is the most common, safest, and easiest for the mother to deliver is the following:
Head first (called vertex or cephalic presentation)
Facing backward (occiput anterior position)
Spine parallel to mother's spine (longitudinal lie)
Neck bent forward with chin tucked
Arms folded across the chest
If the fetus is in a different position, lie, or presentation, labor may be more difficult, and a normal vaginal delivery may not be possible.
Variations in fetal presentation, position, or lie may occur when
The fetus is too large for the mother's pelvis (fetopelvic disproportion).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains growths such as fibroids .
The fetus has a birth defect .
There is more than one fetus (multiple gestation).

Position and Presentation of the Fetus
Variations in fetal position and presentation.
Some variations in position and presentation that make delivery difficult occur frequently.
Occiput posterior position
In occiput posterior position (sometimes called sunny-side up), the fetus is head first (vertex presentation) but is facing forward (toward the mother's pubic bone—that is, facing up when the mother lies on her back). This is a very common position that is not abnormal, but it makes delivery more difficult than when the fetus is in the occiput anterior position (facing toward the mother's spine—that is facing down when the mother lies on her back).
When a fetus faces up, the neck is often straightened rather than bent,which requires more room for the head to pass through the birth canal. Delivery assisted by a vacuum device or forceps or cesarean delivery may be necessary.
Breech presentation
In breech presentation, the baby's buttocks or sometimes the feet are positioned to deliver first (before the head).
When delivered vaginally, babies that present buttocks first are more at risk of injury or even death than those that present head first.
The reason for the risks to babies in breech presentation is that the baby's hips and buttocks are not as wide as the head. Therefore, when the hips and buttocks pass through the cervix first, the passageway may not be wide enough for the head to pass through. In addition, when the head follows the buttocks, the neck may be bent slightly backwards. The neck being bent backward increases the width required for delivery as compared to when the head is angled forward with the chin tucked, which is the position that is easiest for delivery. Thus, the baby’s body may be delivered and then the head may get caught and not be able to pass through the birth canal. When the baby’s head is caught, this puts pressure on the umbilical cord in the birth canal, so that very little oxygen can reach the baby. Brain damage due to lack of oxygen is more common among breech babies than among those presenting head first.
In a first delivery, these problems may occur more frequently because a woman’s tissues have not been stretched by previous deliveries. Because of risk of injury or even death to the baby, cesarean delivery is preferred when the fetus is in breech presentation, unless the doctor is very experienced with and skilled at delivering breech babies or there is not an adequate facility or equipment to safely perform a cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation is more likely to occur in the following circumstances:
Labor starts too soon (preterm labor).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains abnormal growths such as fibroids .
Other presentations
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.
In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.
Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor. If they do not, a cesarean delivery is usually recommended.
In transverse lie, the fetus lies horizontally across the birth canal and presents shoulder first. A cesarean delivery is done, unless the fetus is the second in a set of twins. In such a case, the fetus may be turned to be delivered through the vagina.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Longitudinal ultrasound assessment of fetal presentation: a review of 1010 consecutive cases
Affiliation.
- 1 University of New South Wales, New South Wales, Australia.
- PMID: 16866797
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1479-828X.2006.00603.x
Background: Abnormal presentation (detected in the early third trimester) causes concern for pregnant women and their carers. Definitive ultrasound-based data on the risk of persistence of abnormal presentation is lacking to allow appropriate counselling. Comparison of pregnancy outcome was made on the basis of maternal age at delivery.
Methods: Notes of 1010 women (426 primigravidae, 584 multigravidae), with singleton pregnancies, confined between 1997 and 2005 were reviewed to extract: (i) the gestation based on 18-20-week ultrasound in conjunction with the patient's recorded last menstrual period, and (ii) the presentation of each antenatal visit from 28+ weeks until delivery. Previous obstetric history, maternal age, mode of delivery, birthweight and outcomes were also documented.
Results: At 28-30 weeks, 216 babies presented abnormally. By 38+ weeks, 54 persisted as either a breech or a transverse lie. Thus, an abnormal presentation in the early trimester carries a 22.2% chance of persisting at term. Continuance of abnormal presentation at each subsequent week of the third trimester increased the risk of a Caesarean delivery at term. Conversely, in only six cases, a cephalic presentation at 28-30 weeks converted to a breech or other presentation during the third trimester-- a risk of 0.75%.
Conclusion: These statistics provide a useful tool in advising women of the chances of abnormal presentation at term based on the presentation at various stages of the third trimester, and prepare them for the potential requirement of a Caesarean section.
- Breech Presentation / diagnostic imaging*
- Breech Presentation / epidemiology*
- Cesarean Section
- Gestational Age
- Longitudinal Studies
- Maternal Age
- Medical Records
- New South Wales / epidemiology
- Pregnancy Outcome
- Pregnancy Trimester, Third
- Retrospective Studies
- Ultrasonography, Prenatal*

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Head first (called vertex or cephalic presentation) Facing backward (occiput anterior position) Spine parallel to mother's spine (longitudinal lie) Neck bent forward with chin tucked. Arms folded across the chest . If the fetus is in a different position, lie, or presentation, labor may be more difficult, and a normal vaginal delivery may not ...
Fetal lie: Relation of the fetus to the long axis of the uterus; longitudinal, oblique, or transverse. Normal fetal lie is longitudinal, normal presentation is vertex, and occiput anterior is the most common position. Abnormal fetal lie, presentation, or position may occur with. Fetopelvic disproportion (fetus too large for the pelvic inlet)
During routine prenatal care, clinicians assess fetal lie and presentation with physical examination in the late third trimester. Ultrasonography can also be done. If breech presentation is detected, external cephalic version can sometimes move the fetus to vertex presentation before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks.
Abnormal Fetal Lie. If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted - ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation. ECV is the manipulation of the fetus to a cephalic presentation through the maternal abdomen. It has an approximate success rate of 50% in primiparous women and 60% in multiparous women.
A cephalic presentation or head presentation or head-first presentation is a situation at childbirth where the fetus is in a longitudinal lie and the head enters the pelvis first; the most common form of cephalic presentation is the vertex presentation, where the occiput is the leading part (the part that first enters the birth canal). All other presentations are abnormal (malpresentations ...
Possible fetal positions can include: Occiput or cephalic anterior: This is the best fetal position for childbirth. It means the fetus is head down, facing the birth parent's spine (facing backward). Its chin is tucked towards its chest. The fetus will also be slightly off-center, with the back of its head facing the right or left.
The lie is longitudinal. The long axis of the fetus is parallel to the long axis of the mother. The head is at or in the pelvis. The back is on the left and anterior and is palpated easily except in obese women. The small parts are on the right and are not felt clearly. The breech is in the fundus of the uterus. The cephalic prominence (in this ...
Introduction. Cephalic presentation is the most physiologic and frequent fetal presentation and is associated with the highest rate of successful vaginal delivery as well as with the lowest frequency of complications 1.Studies on the frequency of breech presentation by gestational age (GA) were published more than 20 years ago 2, 3, and it has been known that the prevalence of breech ...
Cephalic presentation means head first. This is the normal presentation. Breech ... Whenever a fetal transverse lie is encountered near term or in labor, evaluate the patient carefully with ultrasound to determine if there are any predisposing factors, such as a placenta previa or pelvic kidney that could modify your management of the patient. ...
Fetal position refers to whether the baby is facing your spine (anterior position) or facing your belly (posterior position). Fetal position can change often: Your baby may be face up at the beginning of labor and face down at delivery. Here are the many possibilities for fetal presentation and position in the womb.
Cephalic presentations are subclassified according to the relationship between the head and body of the fetus ().Ordinarily, the head is flexed sharply so that the chin contacts the thorax. The occipital fontanel is the presenting part, and this presentation is referred to as a vertex or occiput presentation.Much less often, the fetal neck may be sharply extended so that the occiput and back ...
The term presentation refers to that part of the fetus presenting to the lower pole of the uterus. It can more precisely be defined by the presenting part, i.e., that part of the presentation that lies in close proximity to the internal os of the cervix. Thus the usual presentation is cephalic, and the presenting part is the vertex or occiput.
cephalic and breech Determining fetal lie, position, presentation and attitude Follow the 4 steps of the Leopold Maneuver for abdominal palpation to determine fetal lie and presentation. Diagnose Count for 60 seconds to have the fetal heart rate bpm (beats per minute) or count for 15 seconds and multiply by 4.
A cephalic presentation or head presentation or head-first presentation is a situation at childbirth where the fetus is in a longitudinal lie and the head enters the pelvis first; the most common form of cephalic presentation is the vertex presentation where the occiput is the leading part (the part that first enters the birth canal). All other presentations are abnormal (malpresentations ...
The use of intrapartum ultrasound to assess fetal position and presentation, in addi-tion to fetal attitude, to predict and aid in decision making regarding delivery can help in improving management decision making. Cephalic malpresentation and malposition is a unique subset of fetal orientation and can benefit from intrapartum ultrasound ...
The relative incidence of differing fetopelvic relations varies with diagnostic and clinical approaches to care. Among longitudinal lies, about 1 in 25 fetuses are not cephalic but breech at the onset of labor. 1 Of the differing lies a fetus may assume, about 1 in 100 is transverse or oblique, also referred to as nonaxial. As pregnancy proceeds to term, most fetuses assume a longitudinal lie ...
INTRODUCTION. Transverse lie refers to a fetal presentation in which the fetal longitudinal axis lies perpendicular to the long axis of the uterus. It can occur in either of two configurations: The curvature of the fetal spine is oriented downward (also called "back down" or dorsoinferior), and the fetal shoulder presents at the cervix ( figure ...
During pregnancy, the fetus can be positioned in many different ways inside the mother's uterus. The fetus may be head up or down or facing the mother's back or front. At first, the fetus can move around easily or shift position as the mother moves. Toward the end of the pregnancy the fetus is larger, has less room to move, and stays in one ...
A normal fetal lie is an ideal position for labor and baby delivery in which the baby is head-down with the chin tucked into its chest. The back of the head is positioned so that it is ready to enter the pelvis. The fetus faces the mother's back, called cephalic presentation, and the babies mostly settle in this position by 32 to 36 weeks of ...
Longitudinal ultrasound assessment of fetal presentation: a review of 1010 consecutive cases ... 54 persisted as either a breech or a transverse lie. Thus, an abnormal presentation in the early trimester carries a 22.2% chance of persisting at term. Continuance of abnormal presentation at each subsequent week of the third trimester increased ...
The vast majority of fetuses at term will be in longitudinal lie, with a well flexed cephalic presentation in the occipito-anterior position just prior to delivery. Longitudinal lie and cephalic presentation are encouraged in most instances by the shape of the uterus, maternal pelvis and the maternal abdominal musculature.